

Problem-solving in Leadership: How to Master the 5 Key Skills
The role of problem-solving in enhancing team morale, the right approach to problem-solving in leadership, developing problem-solving skills in leadership, leadership problem-solving examples.
Other Related Blogs
What’s the Role of Problem-solving in Leadership?
- Getting to the root of the issue: First, Sarah starts by looking at the numbers for the past few months. She identifies the products for which sales are falling. She then attempts to correlate it with the seasonal nature of consumption or if there is any other cause hiding behind the numbers.
- Identifying the sources of the problem: In the next step, Sarah attempts to understand why sales are falling. Is it the entry of a new competitor in the next neighborhood, or have consumption preferences changed over time? She asks some of her present and past customers for feedback to get more ideas.
- Putting facts on the table: Next up, Sarah talks to her sales team to understand their issues. They could be lacking training or facing heavy workloads, impacting their productivity. Together, they come up with a few ideas to improve sales.
- Selection and application: Finally, Sarah and her team pick up a few ideas to work on after analyzing their costs and benefits. They ensure adequate resources, and Sarah provides support by guiding them wherever needed during the planning and execution stage.
- Identifying the root cause of the problem.
- Brainstorming possible solutions.
- Evaluating those solutions to select the best one.
- Implementing it.

- Analytical thinking: Analytical thinking skills refer to a leader’s abilities that help them analyze, study, and understand complex problems. It allows them to dive deeper into the issues impacting their teams and ensures that they can identify the causes accurately.
- Critical Thinking: Critical thinking skills ensure leaders can think beyond the obvious. They enable leaders to question assumptions, break free from biases, and analyze situations and facts for accuracy.
- Creativity: Problems are often not solved straightaway. Leaders need to think out of the box and traverse unconventional routes. Creativity lies at the center of this idea of thinking outside the box and creating pathways where none are apparent.
- Decision-making: Cool, you have three ways to go. But where to head? That’s where decision-making comes into play – fine-tuning analysis and making the choices after weighing the pros and cons well.
- Effective Communication: Last but not at the end lies effective communication that brings together multiple stakeholders to solve a problem. It is an essential skill to collaborate with all the parties in any issue. Leaders need communication skills to share their ideas and gain support for them.
How do Leaders Solve Problems?
Business turnaround, crisis management, team building.
Process improvement
Ace performance reviews with strong feedback skills..
Master the art of constructive feedback by reviewing your skills with a free assessment now.
Why is problem solving important?
What is problem-solving skills in management, how do you develop problem-solving skills.

Top 15 Tips for Effective Conflict Mediation at Work
Top 10 games for negotiation skills to make you a better leader, manager effectiveness: a complete guide for managers in 2024, 5 proven ways managers can build collaboration in a team.

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
Types of leadership styles to maximize your team's potential

Jump to section
What’s a leadership style?
18 types of leadership styles, 6 tips for identifying your leadership style, is it possible to change your leadership style, ready to become a better leader.
Every team makes mistakes, whether that’s missing deadlines or creating information silos . As a team leader, working with your team is how you make a difference. A good leader charts a course for their team, aligns members to a unified goal, and creates a culture of accountability in the workplace .
There’s no “correct” way to be a leader . It’s not about which leadership style is the best, it’s about the one that suits your team’s needs. And being a leader is different from being a manager . Managers might be responsible for leading teams, but leaders are people who inspire and motivate their team toward a shared vision, regardless of their seniority.
If you need some guidance to give your leadership more structure, choosing a style can help. Knowing what type of leadership style speaks to you can guide you toward a more consistent decision-making and team-building process. Here’s what the different types of leadership styles are and how to choose one to become a better leader.
A leadership style is how you lead and interact with your team based on your team’s needs, your personality, and company culture . Finding out what your leadership style is will help define your strengths and skills. It can help you find opportunities for growth or any areas for improvement to become an effective leader .
Finding your leadership style isn’t a short, one-time process, since you’ll need to adapt it to new situations. As well, your style may evolve over time as you learn new things and work with different teams. It depends on factors such as the size and composition of your team, the nature of the work you’re doing, and the stage of your team's development.
Everyone experiences leadership challenges , from delegating tasks to giving feedback . Identifying your leadership style can help you overcome any challenges you face.
Learn about 18 common ways to lead, and see if one style jumps out to you as one you’re already following or that could be effective for your team.
1. Transformational leadership
If you’re a transformational leader , you focus on inspiring and motivating your team to achieve a shared vision or goal. You emphasize creating a positive organizational culture that fosters creativity, innovation, and personal development . As its name suggests, transformational leadership is all about helping people and teams transform.
To be a great transformational leader, you should care deeply about the company and its employees. It requires a high degree of personal investment and emotional intelligence . That’s why this style is a good choice for fast-growing teams who love to innovate.
Steve Jobs is a great example: he inspired his team at Apple while taking his company from the brink of bankruptcy to one of the most valuable businesses in the world.
Here are some of the types of leadership skills you’ll need to be a transformational leader:
- Communication
- Active listening
- Empathetic leadership
- Strategic thinking
2. Delegative leadership
A delegative leadership style empowers team members to make decisions and take responsibility for their work. If you’re a delegative leader, you provide guidance and support but ultimately employ a hand-off approach. You trust your team to make the right choices.
The increased autonomy from this type of leadership fosters better accountability, teamwork, and trust. Sometimes, though, a delegative leadership style can create confusion within your team if you don’t communicate correctly. Team members may not know who to look to for direction or conflict resolution.
Key skills for delegative leaders include:
- Communication
- Transparency

3. Authoritative leadership
If you give clear direction with specific goals, you might have an authoritative leadership style. As an authoritative leader, sometimes known as an autocratic leader , you’re confident and assertive, and you provide guidance to help team members achieve results.
This eliminates confusion, leading to faster decision-making and improved performance. Unfortunately, offering one-sided authority can seem inflexible and extreme. A heavy hand that doesn’t let team members make their own choices might make them feel undervalued.
An authoritative leader should have:
- Communication
- Goal-setting
4. Transactional leadership
If you’re a transactional leader , you enforce the exchange of rewards (or consequences) to help your team achieve specific goals. You set clear expectations and provide incentives for achieving them.
This style lays out clear expectations and can lead to improved performance and productivity. It’s most useful in structured work environments. But a transactional leadership style can also restrict your team’s creativity and add unnecessary stress.
It’s not well-suited to complex or quickly-changing environments like tech startups because expectations can get lost in the hustle. Key skills you’ll need as a transactional leader include:
- Constructive feedback
- Negotiation
5. Visionary leadership
As a visionary or affiliative leader, you inspire teams to focus on the big picture and prioritize teamwork and collaboration . You create a positive work culture and emphasize the well-being of the team as a whole.
From this leadership style, team members feel like they’re part of something, and can be less likely to experience burnout at work . But this can result in a lack of direction or accountability and be overly reliant on consensus instead of individual voices.
If you want to be a visionary leader, you should strive to have these skills:
- Collaboration
6. Participative leadership
As a participative leader, you zero in on collaboration and involve team members in your decision-making process. You encourage open communication and feedback not just between coworkers, but between employees and managers.
Participative leadership is similar to a democratic leadership style because it acts as a democracy, fostering a safe space for everyone to pitch and implement new ideas.

This can also be a time-consuming leadership style because you need to give space to every person on the team. You could also develop a lack of clear direction if your team members aren’t self-motivated or creative thinkers. Use participative leadership styles on smaller teams and in less structured work environments.
Key skills for participative leaders include:
- Time management
- Conflict resolution
7. Democratic leadership
Democratic leadership , like participatory leadership, prioritizes collaboration. However, as a democratic leader, you take this one step further by promoting a democratic environment where all team members can contribute ideas, from planning to decision-making.
This style is ideal for teams in less-structured work environments that require creativity and innovation. Democratic leadership fosters diverse perspectives and approaches while ensuring everyone's voice is heard. But it can lead to slower decision-making processes as more people get involved.
The key skills for democratic leaders include:
- Flexibility
- Employee empowerment
- Trust-building
- Visionary thinking
8. Adaptive leadership
As an adaptive leader , you prioritize flexibility in response to changing circumstances, like the needs of your team or project hiccups. This leadership style requires a willingness to embrace change, take risks, and be innovative since you need to adjust quickly to new situations while staying on track for overall goals.
Adaptive leadership requires a combination of strategic thinking, practical problem-solving skills, and strong communication and collaboration. Use adaptive leadership in rapidly changing environments like startups, where traditional leadership approaches may be too slow or bureaucratic to be effective.
These are some key skills for adaptive leaders:
- Risk-taking
- Emotional intelligence
9. Authentic leadership
As an authentic leader, you prioritize transparency and honesty in your leadership style. You’re true to yourself and your values and encourage team members to be the same. By emphasizing everyone’s unique qualities, you empower your team to bring their own subject matter expertise to the table.
Authentic leadership requires self-awareness, strong communication skills, and the ability to build relationships based on trust and respect. As an authentic leader, you’ll clearly communicate your values and vision to inspire your team to work towards goals.
Authentic leaders have skills like:
- Self-awareness
10. Charismatic leadership
If you’re a charismatic leader , you motivate team members through your natural charisma. You articulate a clear vision and inspire your team and stakeholders to follow your lead.
Charismatic leadership can be highly effective in driving change and achieving results. But it can also be a double-edged sword. You may end up relying on your personal charm to get things done rather than nurturing your team's abilities.
Key skills for charismatic leaders include:
- Strong communication skills
- Self-confidence
- Ability to inspire and motivate others

11. Coaching leadership
If you employ a coaching leadership style , you prioritize developing your team members’ skills through personalized mentoring and one-on-one meetings . By promoting a culture of continuous learning and improvement, you help your team reach their full potential — both together and on an individual level.
Important skills for coaching leaders include:
- Constructive and positive feedback
12. Distributed leadership
As a distributed leader , you share leadership responsibilities and decision-making power with your team members. You rely on the expertise and skills of everyone involved, rather than just your own, to drive success.
To use distributed leadership effectively, you need to have a high level of trust and collaboration among your team members. You also need to let go of control , which can be difficult but worth it.
This leadership style has the potential to be highly effective in promoting innovation, creativity, and a culture of ownership within your team. Distributed leaders have skills like:
- Decision-making
13. Empathetic leadership
As an empathetic leader , you understand that your team isn’t just a means to an end. They’re people with their own lives, experiences, and emotions. That’s why you make a conscious effort to get to know them on a personal level, whether through regular check-ins, team-building exercises , or one-on-ones.
By demonstrating empathy, you create an environment where team members feel valued, supported, and motivated to do their best work.
To be an empathetic leader, you need to listen and respond to the needs of team members, which can sometimes be hard to do when people have different needs. You should also commit to building a culture of trust and mutual respect.
Key skills for empathetic leaders include:
- Supportiveness
14. Inclusive leadership
Inclusive leaders actively seek out diverse perspectives. If you’re inclusive, you’re open to feedback and ideas from team members with different backgrounds and experiences. You focus on creating a work environment that values and respects diversity in all its forms so that all your team members feel seen, heard, and valued.
Inclusive leadership requires a deep understanding of different perspectives and experiences to create a sense of psychological safety within the team. This helps people reach their full potential with creativity, innovation, and problem-solving . Inclusive leadership impacts the entire business , so it requires effort and commitment.
Key skills for inclusive leaders include:
- Open-mindedness
15. Servant leadership
Servant leaders prioritize team members’ needs above their own. If you’re a servant leader, you focus on empowering your team members through mentorship, guidance, and servitude.
By doing so, you build trust and respect within your team and encourage members to contribute their best work. This leadership style promotes teamwork, collaboration, and accountability.
Key skills for servant leaders include:
- Selflessness
- Coaching and mentoring
16. Situational leadership
Situational leadership is a flexible leadership style that focuses on adaptability. As a situational leader, you pivot and meet project developments based on the skillsets of your team members. This lets you promote growth and meet problematic situations head-on.
To be an effective situational leader, you need to have a deep understanding of your team members' strengths and weaknesses. You also need to provide the right level of support and guidance for each team member based on their individual needs.
Situational leaders are skilled at providing feedback, setting clear goals, and communicating expectations.
Key skills for situational leaders include:
- Flexibility and adaptability
- Problem-solving
17. Strategic leadership
As a strategic leader , you set a clear direction and develop a plan to achieve it. Effective strategic leadership requires a deep understanding of the organization's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) since these let you develop in-depth plans.
Use strategic leadership to promote growth and long-term success. Empower your team to take calculated risks, experiment with new ideas, and set big goals.
Key skills for strategic leaders include:
- Strategic planning and execution
- Analytical and critical thinking
- Effective communication
18. Organizational leadership
As an organizational leader , you manage people and resources with efficiency. You optimize the performance of your team, create a positive work culture, and align individuals toward company goals.
To be an effective organizational leader, you’ll need to delegate tasks and create systems that operate smoothly. Use this type of leadership in large, structured work environments where you need to standardize outputs and have streamlined work processes in place.
Key skills for organizational leaders include:
- Team management and delegation
- Process optimization
- Employee engagement and motivation
- Change management

No leadership style works for everyone. The key to effective leadership is figuring out which works best for you, your team, and your environment. And sometimes, that takes trial and error.
Here are six tips to help you identify your leadership style:
Identify your purpose: Understanding your purpose and what you want to accomplish can help you find which style works best for you and your team’s goals . For example, if you’re short on time and need to get things done, a delegative style might work best.
Make mistakes: Play around with different leadership styles to find the one that feels the most natural and effective. What may have worked for a previous group may not work for your current one. Some might appreciate transactional leadership, and others might dislike the pressure.
Be authentic: Your leadership values are part of what helps you succeed. Be true to yourself, and while it’s good to take cues from other leaders, don't focus on emulating someone else's leadership style. If an authoritative leadership style doesn’t feel right, try adjusting it in a way that works for you.
Ask for feedback: Ask your team members how they want to be led. This will help you understand how they’ll respond to your leadership style. They might prefer more direct instruction than participative leadership allows, or they might thrive under transformational leadership.
Brainstorm: Consider different scenarios and challenges you may face in your role, and think about which leadership style would be most effective in each situation. Then you can assess what style might work best for your roles and responsibilities . This is also known as situational leadership .
Find a coach to help you: If you’re feeling stuck, a second opinion about your leadership style can help. Getting input from a trusted mentor or career coach is a great way to identify your leadership style, improve your skills, and gain a better understanding of what works best for you and your team.
Anyone can change their leadership style. In fact, you should change it to adapt to different situations and workplaces. To be an effective leader, you need to empower your team members to reach their goals — and since every team is different, they need different leadership approaches.
But changing the way you lead is easier said than done. Leadership considers more than just your team. It’s about your personality, instincts, and tacit knowledge . Altering your leadership style takes effort and work.
Start by seeking out some leaders you admire. This can be a famous leader, a mentor, or someone on your team. You can also consult leadership books and resources to discover more about the mindsets and decisions of different leaders. Find out how they define and practice their leadership styles, and choose one to emulate.
Next, list the skills you should have to be that kind of leader. While effective communication and goal-setting are key to most leadership styles, each also has its own focus areas, like conflict resolution, team-building, or cognitive empathy . If you don’t already have these skills — or if they just aren’t your strengths — decide how to help them grow.
Remember: charting the course for a new style doesn’t mean that you’ll never change again. You may need to adjust your approach depending on the needs of your team or the circumstances of a particular project.
You might also discover that one leadership style doesn’t work for you, and that’s okay. Being a leader (and simply being a person) is a process of ongoing learning and growth.
Identify what type of leader you want to be and start paving the way to get there. Remember that your leadership style can, and will, change over time as you evolve, whether you’re working on a team of democratic leaders or prefer to take the authoritative route.
By identifying your strengths, weaknesses, and preferences, you can help lead your team to success. Finding a type of leadership style that works can help you become a better leader — and maybe even a great one.
Lead with confidence and authenticity
Develop your leadership and strategic management skills with the help of an expert Coach.
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
Refine your approach with these 7 leadership theories
7 key leadership behaviors you must have, what is servant leadership and how can it empower you team, are people born leaders debunking the trait theory of leadership, everything you need to know about strategic leadership, it depends. understanding the contingency theory of leadership, what is a leadership development program and why do you need one, the transactional leadership style still has a place, situational leadership®: what it is and how to build it, similar articles, parenting styles: learn how you influence your children’s future, coaching leadership style: examples and skills to get started, democratic leadership style: how to make it work as a team, 6 management styles: how to choose the right one for you, principles and examples of adaptive leadership, overcoming resistance to change within your organization, how to tap into heart and soul to lead with more charisma, learn what participative leadership is and how to practice it, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
- Choosing Workplace
- Customer Stories
- Workplace for Good
- Getting Started
- Why Workplace
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Future of Work
- How can Workplace help you?
- Business Communication
- Employee Engagement
- Strengthen Culture
- Getting Connected
- Frontline Workers
- Remote and Hybrid Working
- Integrations
- Interactive Demo
- Features at a Glance
- Connect to all your tools
- Workplace & Microsoft
- Integrations directory
- Knowledge Library
- Key Updates
- Auto-Translate
- Safety Center
- Access Codes
- Pricing Plans
- Forrester ROI Study
- Events & Webinars
- Ebooks & Guides
- Employee Experience
- Remote Working
- Team Collaboration
- Productivity
- Become A Partner
- Service & Reseller Partners
- Integrations Partners
- Start Using Workplace
- Mastering Workplace Features
- Workplace Use Cases
- Technical Resources
- Work Academy
- Help Center
- Customer Communities
- What's New in Workplace
- Set up Guides
- Domain Management
- Workplace Integrations
- Account Management
- Authentication
- IT Configuration
- Account Lifecycle
- Security and Governance
- Workplace API
- Getting started
- Using Workplace
- Managing Workplace
- IT and Developer Support
- Get in touch
Problem-solving skills in leadership
Do you find yourself fighting fires on a daily basis it’s time to sharpen your problem-solving skills to become a more effective leader..

What is problem solving in leadership?
To explain how problem solving relates to leadership, it’s best to begin with a basic definition. The Oxford English Dictionary describes problem solving as “the action of finding solutions to difficult or complex issues”.
The Chartered Management Institute (CMI) adds a little more color to this. It defines a problem as “the distance between how things currently are and the way they should be. Problem solving forms the ‘bridge’ between these two elements. In order to close the gap, you need to understand the way things are (problem) and the way they ought to be (solution).”
In the workplace, problem solving means dealing with issues or challenges that arise in the course of everyday operations. This could be anything from production delays and customer complaints to skills shortages and employee conflict .
For leaders, the objective is to bring clarity and purpose to problem solving in a way that makes sense for the organization. While the leader has the final say, finding solutions is a collaborative effort that should involve key stakeholders, including employees.
Untangle work with Workplace
From informing everyone about the return to the office to adopting a hybrid way of working, Workplace makes work more simple.

The process of fixing problems
Problem solving leadership should follow these four steps:
Identify the root cause of the problem – do this through fact-finding and getting feedback from those involved.
Brainstorm possible solutions – get ideas from as many people as you can to get a range of perspectives.
Evaluate solutions – draw up a shortlist of workable options and choose the best one.
Implement and evaluate your plan of action – communicate your solution with all stakeholders and explain your reasoning.
As businesses face increasingly complex challenges, some leaders are embracing what the MIT Sloan School of Management calls ‘problem-led leadership’. Instead of concentrating on managing their people, they inspire others through their enthusiasm to solve ‘cool’ problems. While this leadership style won’t be right for every situation, it can work well where innovation and entrepreneurship are needed.
Leaders who problem-solve effectively can improve efficiency , reduce costs, increase customer satisfaction and achieve their strategic goals. If left unresolved, however, problems can spiral and ultimately affect the overall health and performance of your business.
Why is problem solving important in leadership?
The importance of leadership problem-solving skills shouldn’t be underestimated. When you think about it, businesses are beset by processes and interactions that don’t work as well as they could. Having the knowhow – not to mention determination – to overcome such obstacles is vital to make workplaces better for everyone. In fact, a 2022 survey shows that problem solving is among the top five skills UK employees look for in a leader.
Learning how to solve problems proficiently can benefit your organization in many ways. It can help you:
Make better decisions
Being able to solve complex problems with clarity and a rational mindset helps with decision-making. It gives you the confidence to weigh up the pros and cons of each decision before making a final call, without jumping to the wrong conclusion. This ensures the choices you make are right for your team and organization as a whole.
Overcome challenges
No matter how tight a ship you run, you’re always going to come up against obstacles. Challenges are a way of life for businesses, however successful they are.
A leader with good problem-solving skills is able to anticipate issues and have measures in place to deal with them if and when they arise. But they also have the ability to think on their feet and adapt their strategies if needed.
Inspire creativity and innovation
Creativity is useful when trying to solve problems, particularly ones you haven’t experienced before. Leaders who think differently can be great innovators . But they also empower their teams to think outside the box too by creating a safe, non-judgmental environment where all ideas are welcome.
Encourage collaboration
A problem shared is a problem halved, so the saying goes. Successful leaders recognize that problem solving alone is less beneficial than problem solving with a team. This inspires a culture of collaboration , not just between leaders and their team members but between colleagues working together on projects.
Build trust
When your team members know they can rely on you to identify and resolve issues quickly and effectively, it builds trust. They’re also more likely to feel comfortable talking to you if they have a problem of their own that they’re struggling with.
If they’re worried about repercussions, they may avoid sharing it with you. Lack of trust is still an issue in many organizations, with 40% of frontline staff saying they don’t have faith in their leadership, according to Qualtrics .
Reduce risk
Being able to anticipate potential risks and put measures in place to mitigate them makes you better equipped to protect your organization from harm. Having good problem-solving skills in leadership allows you to make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes, even in times of uncertainty.
Boost morale
Leaders who approach problem solving with positivity and calmness are crucial to keeping team morale high . No one wants a leader who panics at the first sign of trouble. Workers want to feel reassured that they have someone capable in charge who can steer them through times of crisis.
What problems do leaders face?
As a leader, you’re likely to face all manner of setbacks and challenges. In fact, you probably find that hardly a day goes by without some kind of issue cropping up.
Common problems faced by leaders often involve communication barriers, team disagreements, production delays and missed financial targets. To give you an example, below are three common scenarios you might face in the workplace and how to tackle them.
Conflicts between team members
Problem: Cliques have developed and tensions are affecting communication so your team isn’t working as effectively as it could be.
Solution: Settle disputes by encouraging open and honest communication among all team members. Establish roles where each person’s responsibilities and expectations are clearly defined, and hold regular team building sessions to promote unity and togetherness.
Outdated technology hampering production
Problem: Hybrid and remote staff don’t have the right tools to do their job properly, and can’t keep track of who’s working on what, when and from where.
Solution: Evaluate your existing technology and upgrade to newer software and devices, getting feedback from your employees on what they need (52% of workers say the software related to their job is dated and difficult to use). Use a platform with apps that allow teams to collaborate and securely access work information from anywhere.
Customer service complaints
Problem: Customer response times are too slow – your team is taking too long to answer the phone and respond to emails, causing a rise in complaints.
Solution: Establish standard practice for what to do from the moment a customer query is received. Automate repetitive tasks and enable your customers to reach you via multiple channels including email, web chat, phone, social media and text.
What problem-solving skills do leaders need?
Problem solving is something we learn through experience, often by getting it wrong the first time. It requires continual learning, curiosity and agility so you develop a good instinct for what to do when things go wrong. Time is a great teacher, but leadership problem-solving skills can also be honed through workshops, mentoring and training programs.
Some of the key skills leaders need to solve problems include:
Effective communication
Problems can cause anxiety, but it’s vital to stay calm so you don’t transmit a feeling of panic to others. It’s important to establish the facts before clearly relaying the problem to key stakeholders. You’ll also need to inspire the people who are working on the solution to remain focused on the task in hand until it’s resolved. Sometimes, this may involve giving critical feedback and making team members more accountable.
Transparency is key here. When you don’t have open and honest communication across your organization, you develop silos – which can generate more issues than need fixing.
Analytical insight
Your objective should be to find the root cause of the problem. That way, you can find a permanent solution rather than simply papering over the cracks. You’ll need to assess to what extent the issue has affected the overall business by analyzing data, speaking to those involved and looking for distinct patterns of behavior.
Analytical thinking is also important when proposing solutions and taking what you believe to be the right course of action.
Promoting a culture of psychological safety
It’s a leader’s responsibility to create an environment conducive to problem solving. In a safe, open and inclusive workplace, all team members feel comfortable bringing their ideas to the table. No one feels judged or ridiculed for their contributions. Nor do they feel dismissed for questioning the effectiveness of long-established processes and systems.
Not playing the blame game
Mistakes happen.They’re a normal part of growth and development. Instead of pointing fingers when things go wrong, see it as a learning opportunity.
Although you need to identify the cause of an error or problem to solve it effectively – and give feedback where needed – it’s not the same as placing blame. Instead, work towards a solution that ensures the same mistakes don’t keep being repeated.
Emotional intelligence
One of the most important problem-solving skills for leaders is emotional intelligence – the ability to understand emotions and empathize with others. This is crucial when recognizing employees’ problems. An EY Consulting survey found that 90% of US workers believe empathetic leadership leads to greater job satisfaction.
If you approach a problem with anger and frustration, you might make a rash decision or overlook important information. If, on the other hand, you stay calm and measured, you’ll be more inclined to seek feedback to get a broader view of the issue.
A flexible mindset
Problem solving works best when you keep an open mind and aren’t afraid to change direction. Sometimes you’ll need to find a better or more innovative approach to overcoming challenges. A leader with a flexible mindset is always receptive to new ideas and other viewpoints.
It’s clear that problem solving is an essential skill for any leader to have in their armory. So, the next time you face a challenge, take a breath and embrace the opportunity to put your problem-solving leadership abilities to the test.
Keep reading
What is leadership and why is it so important.
- Why successful leadership depends on a growth mindset
- How to transition from manager to leader
Recent posts
Leadership | 11 minute read
What is a leader? Are leaders the same as managers? Can you learn to be a leader? We explore what makes a leader and why good leadership is business critical.
Leadership | 7 minute read
Collaborative leadership: what it is and how it can bring your teams together.
Collaborative leaders believe in bringing diverse teams together to achieve organizational goals, solve problems, make decisions and share information. But what does it really take to be a more collaborative leader? We take a look.
Leadership | 4 minute read
3 lessons leaders can take from life
It's the authentic experiences they have in real life that define who people are and can shape how they lead. Here are three of the best examples.

20 Leadership
Content in this chapter comes from openstax.
After reading this chapter, you should be able to answer these questions:
- What is the nature of leadership and the leadership process?
- What are the processes associated with people coming to leadership positions?
- How do leaders influence and move their followers to action?
- What are the trait perspectives on leadership?
- What are the behavioral perspectives on leadership?
- What are the situational perspectives on leadership?
- What does the concept “substitute for leadership” mean?
- What are the characteristics of transactional, transformational, and charismatic leadership?
- How do different approaches and styles of leadership impact what is needed now?
EXPLORING MANAGERIAL CAREERS
John Arroyo: Springfield Sea Lions
John Arroyo is thrilled with his new position as general manager of the Springfield Sea Lions, a minor league baseball team in. Arroyo has been a baseball fan all of his life, and now his diligent work and his degree in sports management are paying off.
Arroyo knew he had a hard act to follow. The general manager whom John replaced, “T.J.” Grevin, was a much-loved old-timer who had been with the Sea Lions since their inception 14 years ago. John knew it would be difficult for whoever followed T.J., but he didn’t realize how ostracized and powerless he would feel. He tried a pep talk: “I’m the general manager—the CEO of this ball club! In time, the staff will respect me.” [Not a very good pep talk!]
After his first season ends, Arroyo is discouraged. Ticket and concession sales are down, and some long-time employees are rumored to be thinking about leaving. If John doesn’t turn things around, he knows his tenure with the Sea Lions will be short.
Questions: Is John correct in assuming that the staff will learn to respect him in time? What can John do to earn the loyalty of his staff and improve the ball club’s performance?
Outcomes: During the winter, John thinks long and hard about how he can earn the respect of the Sea Lions staff. Before the next season opener, John announces his plan: “So I can better understand what your day is like, I’m going to spend one day in each of your shoes. I’m trading places with each of you. I will be a ticket taker, a roving hot dog vendor, and a janitor. And I will be a marketer, and an accountant—for a day. You in turn will have the day off so you can enjoy the game from the general manager’s box.” The staff laughs and whistles appreciatively. Then the Springfield mascot, Sparky the Sea Lion, speaks up: “Hey Mr. Arroyo, are you going to spend a day in my flippers?” “You bet!” says John, laughing. The entire staff cheers.
John continues. “At the close of the season, we will honor a staff member with the T.J. Grevin Award for outstanding contributions to the Sea Lions organization. T.J. was such a great guy, it’s only right that we honor him.” The meeting ends, but John’s staff linger to tell him how excited they are about his ideas. Amidst the handshakes, he hopes that this year may be the best year yet for the Sea Lions.
Sarah Elizabeth Roisland is the manager of a district claims office for a large insurance company. Fourteen people work for her. The results of a recent attitude survey indicate that her employees have extremely high job satisfaction and motivation. Conflict is rare in Sarah’s office. Furthermore, productivity measures place her group among the most productive in the entire company. Her success has brought the company’s vice president of human resources to her office in an attempt to discover the secret to her success. Sarah’s peers, superiors, and workers all give the same answer: she is more than a good manager—she is an outstanding leader. She continually gets high performance from her employees and does so in such a way that they enjoy working for her.
There is no magic formula for becoming a good leader. There are, however, many identifiable reasons why some people are better and more effective leaders. Leaders, especially effective leaders, are not created by simply attending a one-day leadership workshop. Yet effective leadership skills are not something most people are born with. You can become an effective leader if you are willing to invest the time and energy to develop all of the “right stuff.”
According to Louise Axon, director of content strategy, and her colleagues at Harvard Business Publishing, in seeking management talent, leadership is an urgently needed quality in all managerial roles. 1 Good leaders and good leadership are rare. Harvard management professor John P. Kotter notes that “there is a leadership crisis in the U.S. today,” 2 and the late USC Professor Warren Bennis states that many of our organizations are overmanaged and underled. 3
The Nature of Leadership
The many definitions of leadership each have a different emphasis. Some definitions consider leadership an act or behavior, such as initiating structure so group members know how to complete a task. Others consider a leader to be the center or nucleus of group activity, an instrument of goal achievement who has a certain personality, a form of persuasion and power, and the art of inducing compliance. 4 Some look at leadership in terms of the management of group processes. In this view, a good leader develops a vision for the group, communicates that vision, 5 orchestrates the group’s energy and activity toward goal attainment, “[turns] a group of individuals into a team,” and “[transforms] good intentions into positive actions.” 6
Leadership is frequently defined as a social (interpersonal) influence relationship between two or more persons who depend on each other to attain certain mutual goals in a group situation. 7 Effective leadership helps individuals and groups achieve their goals by focusing on the group’s maintenance needs (the need for individuals to fit and work together by having, for example, shared norms) and task needs (the need for the group to make progress toward attaining the goal that brought them together).
Leader versus Manager
The two dual concepts, leader and manager, leadership and management, are not interchangeable, nor are they redundant. The differences between the two can, however, be confusing. In many instances, to be a good manager one needs to be an effective leader. Many CEOs have been hired in the hope that their leadership skills, their ability to formulate a vision and get others to “buy into” that vision, will propel the organization forward. In addition, effective leadership often necessitates the ability to manage—to set goals; plan, devise, and implement strategy; make decisions and solve problems; and organize and control. For our purposes, the two sets of concepts can be contrasted in several ways.
First, we define the two concepts differently. In Management and Organizational Behavior , we defined management as a process consisting of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling. Here we define leadership as a social (interpersonal) influence relationship between two or more people who are dependent on each another for goal attainment.
Second, managers and leaders are commonly differentiated in terms of the processes through which they initially come to their position. Managers are generally appointed to their role. Even though many organizations appoint people to positions of leadership, leadership per se is a relationship that revolves around the followers’ acceptance or rejection of the leader. 8 Thus, leaders often emerge out of events that unfold among members of a group.
Third, managers and leaders often differ in terms of the types and sources of the power they exercise. Managers commonly derive their power from the larger organization. Virtually all organizations legitimize the use of certain “carrots and sticks” (rewards and punishments) as ways of securing the compliance of their employees. In other words, by virtue of the position that a manager occupies (president, vice president, department head, supervisor), certain “rights to act” (schedule production, contract to sell a product, hire and fire) accompany the position and its place within the hierarchy of authority. Leaders can also secure power and the ability to exercise influence using carrots and sticks; however, it is much more common for leaders to derive power from followers’ perception of their knowledge (expertise), their personality and attractiveness, and the working relationship that has developed between leaders and followers.
From the perspective of those who are under the leader’s and manager’s influence, the motivation to comply often has a different base. The subordinate to a manager frequently complies because of the role authority of the manager, and because of the carrots and sticks that managers have at their disposal. The followers of a leader comply because they want to. Thus, leaders motivate primarily through intrinsic processes, while managers motivate primarily through extrinsic processes.
Finally, it is important to note that while managers may be successful in directing and supervising their subordinates, they often succeed or fail because of their ability or inability to lead. 9 As noted above, effective leadership often calls for the ability to manage, and effective management often requires leadership.
CONCEPT CHECK
The Leadership Process
Leadership is a process, a complex and dynamic exchange relationship built over time between leader and follower and between leader and the group of followers who depend on each other to attain a mutually desired goal. 10 There are several key components to this “working relationship”: the leader, the followers, the context (situation), the leadership process per se, and the consequences (outcomes) (see Figure 3 ). 11 Across time, each component interacts with and influences the other components, and whatever consequences (such as leader-follower trust) are created influence future interactions. As any one of the components changes, so too will leadership. 12
Leaders are people who take charge of or guide the activities of others. They are often seen as the focus or orchestrater of group activity, the people who set the tone of the group so that it can move forward to attain its goals. Leaders provide the group with what is required to fulfill its maintenance and task-related needs. (Later in the chapter, we will return to the “leader as a person” as part of our discussion of the trait approach to leadership.)
The Context
Situations make demands on a group and its members, and not all situations are the same. Context refers to the situation that surrounds the leader and the followers. Situations are multidimensional. We discuss the context as it pertains to leadership in greater detail later in this chapter, but for now let’s look at it in terms of the task and task environment that confront the group. Is the task structured or unstructured? Are the goals of the group clear or ambiguous? Is there agreement or disagreement about goals? Is there a body of knowledge that can guide task performance? Is the task boring? Frustrating? Intrinsically satisfying? Is the environment complex or simple, stable or unstable? These factors create different contexts within which leadership unfolds, and each factor places a different set of needs and demands on the leader and on the followers.
The Process
The process of leadership is separate and distinct from the leader (the person who occupies a central role in the group). The process is a complex, interactive, and dynamic working relationship between leader and followers. This working relationship, built over time, is directed toward fulfilling the group’s maintenance and task needs. Part of the process consists of an exchange relationship between the leader and follower. The leader provides a resource directed toward fulfilling the group’s needs, and the group gives compliance, recognition, and esteem to the leader. To the extent that leadership is the exercise of influence, part of the leadership process is captured by the surrender of power by the followers and the exercise of influence over the followers by the leader. 19 Thus, the leader influences the followers and the followers influence the leader, the context influences the leader and the followers, and both leader and followers influence the context.
The Consequences
A number of outcomes or consequences of the leadership process unfold between leader, follower, and situation. At the group level, two outcomes are important:
- Have the group’s maintenance needs been fulfilled? That is, do members of the group like and get along with one another, do they have a shared set of norms and values, and have they developed a good working relationship? Have individuals’ needs been fulfilled as reflected in attendance, motivation, performance, satisfaction, citizenship, trust, and maintenance of the group membership?
- Have the group’s task needs been met? That is, there are also important consequences of the leadership process for individuals: attendance, motivation, performance, satisfaction, citizenship, trust, and maintenance of their group membership.
The leader-member exchange (LMX) theory of the leadership process focuses attention on consequences associated with the leadership process. The theory views leadership as consisting of a number of dyadic relationships linking the leader with a follower. A leader-follower relationship tends to develop quickly and remains relatively stable over time. The quality of the relationship is reflected by the degree of mutual trust, loyalty, support, respect, and obligation. High- and low-quality relationships between a leader and each of his followers produce in and out groups among the followers. Members of the in group come to be key players, and high-quality exchange relationships tend to be associated with higher levels of performance, commitment, and satisfaction than are low-quality exchange relationships. 20 Attitudinal similarity and extroversion appear to be associated with a high-quality leader-member relationship. 21
The nature of the leadership process varies substantially depending on the leader, the followers, and the situation and context. Thus, leadership is the function of an interaction between the leader, the follower, and the context.
The leadership context for the leader of a group of assembly line production workers differs from the context for the leader of a self-managing production team and from the context confronted by the lead scientists in a research laboratory. The leadership tactics that work in the first context might fail miserably in the latter two.
CATCHING THE ENTREPRENEURIAL SPIRIT
How a Start-Up Finds the Right Leader
Start-ups, by their very nature, require innovation to bring new products and services to market. Along with establishing a new brand or product, the leader has to develop the relationships and processes that make a company succeed, or risk its early demise. While leading an established firm has its challenges, a start-up requires even more from a leader.
How critical is leadership to a start-up? Ask the four cofounders of the now-defunct PYP (Pretty Young Professionals), a website founded as a source of information for young professional women. What began as four young professional women working on a new start-up ended with hurt feelings and threats of legal action. In 2010, Kathryn Minshew, Amanda Pouchot, Caroline Ghosn, and Alex Cavoulacos decided to create the website and Minshew was named CEO (Cohan 2011a). Lines blurred about Minshew’s authority and the ultimate look, feel, and direction of the website. Ideals about shared leadership, where the company was going, and how it was going to get there ultimately got lost in the power shuffle. By June 2011, passwords were changed and legal actions began, and in August Minshew and Cavoulacos left altogether (Cohan 2011b).
When the legal haggling from PYP was over, Alex Cavoulacos and Kathryn Minshew, joined by Melissa McCreery, tried again. But this time, rather than hoping for the best, they put a leadership plan in place. Minshew was named CEO of the new start-up, The Daily Muse, with Cavoulacos as chief operating officer and McCreery as editor in chief. Rather than trusting to luck, the three cofounders based their team positions on strengths and personalities. Cavoulacos and McCreery agreed that Minshew’s outgoing personality and confidence made her the proper choice as CEO (Casserly 2013).
No single trait will guarantee that a person can lead a start-up from idea to greatness, but a survey of successful entrepreneurs does show some common traits. According to David Barbash, a partner at Boston-based law firm Posternak Blankstein & Lund LLP, personality is paramount: “You can have great technology but if you’re not a great communicator it may die in the lab” (Casserly 2013 n.p.). A start-up needs a leader who is confident and willing, if not eager, to face the future. According to Michelle Randall, a principal of Enriching Leadership International, start-up CEOs have to be willing to fundraise and not be too proud to beg (Casserly 2013). Peter Shankman, an entrepreneur and angel investor, says leaders have to be willing to make the hard decisions, even risking being the bad guy (Casserly 2013).
Gary Vaynerchuk credits his success to six factors. Angel investor, social media marketer, and early social media adopter, Vaynerchuk leveraged YouTube in its early years to market wine from the family’s liquor store, eventually increasing sales from $3 million to $60 million a year (Clifford 2017). Gary believes good leaders recognize that they don’t dictate to the market, but rather respond to where it is going. They have respect for and believe in other people, and have a strong work ethic, what Vaynerchuk called a “lunch pail work ethic”: they are willing to put in long hours because they love the work, not the perks. He also stresses that he loves technology and doesn’t fear it, is obsessed with the youth of today, and is optimistic about people and the future of humanity (Vaynerchuk 2017).
Leading a startup requires more than simple management. It requires the right leader for the right company at the right time, which means matching the right management skills with the proper flexibility and drive to keep it all together and moving in the right direction.
Why would start-up leaders need different leadership qualities than someone managing an established firm?
Leader Emergence
Leaders hold a unique position in their groups, exercising influence and providing direction. Leonard Bernstein was part of the symphony, but his role as the New York Philharmonic conductor differed dramatically from that of the other symphony members. Besides conducting the orchestra, he created a vision for the symphony. In this capacity, leadership can be seen as a differentiated role and the nucleus of group activity.
Organizations have two kinds of leaders: formal and informal. A formal leader is that individual who is recognized by those outside the group as the official leader of the group. Often, the formal leader is appointed by the organization to serve in a formal capacity as an agent of the organization. Jack Welch was the formal leader of General Electric, and Leonard Bernstein was the formal leader of the symphony. Practically all managers act as formal leaders as part of their assigned role. Organizations that use self-managed work teams allow members of the team to select the individual who will serve as their team leader. When this person’s role is sanctioned by the formal organization, these team leaders become formal leaders. Increasingly, leaders in organizations will be those who “best sell” their ideas on how to complete a project—persuasiveness and inspiration are important ingredients in the leadership equation, especially in high-involvement organizations. 22
Informal leaders, by contrast, are not assigned by the organization. The informal leader is that individual whom members of the group acknowledge as their leader. Athletic teams often have informal leaders, individuals who exert considerable influence on team members even though they hold no official, formal leadership position. In fact, most work groups contain at least one informal leader. Just like formal leaders, informal leaders can benefit or harm an organization depending on whether their influence encourages group members to behave consistently with organizational goals.
As we have noted, the terms leader and manager are not synonymous. Grace Hopper, retired U.S. Navy admiral, draws a distinction between leading and managing: “You don’t manage people, you manage things . You lead people .” 23 Informal leaders often have considerable leverage over their colleagues. Traditionally, the roles of informal leaders have not included the total set of management responsibilities because an informal leader does not always exercise the functions of planning, organizing, directing, and controlling. However, high-involvement organizations frequently encourage their formal and informal leaders to exercise the full set of management roles. Many consider such actions necessary for self-managing work teams to succeed. Informal leaders are acknowledged by the group, and the group willingly responds to their leadership.
Paths to Leadership
People come to leadership positions through two dynamics. In many instances, people are put into positions of leadership by forces outside the group. University-based ROTC programs and military academies (like West Point) formally groom people to be leaders. We refer to this person as the designated leader (in this instance the designated and formal leader are the same person). Emergent leaders , on the other hand, arise from the dynamics and processes that unfold within and among a group of individuals as they endeavor to achieve a collective goal.
A variety of processes help us understand how leaders emerge. Gerald Salancik and Jeffrey Pfeffer observe that power to influence others flows to those individuals who possess the critical and scarce resources (often knowledge and expertise) that a group needs to overcome a major problem. 24 They note that the dominant coalition and leadership in American corporations during the 1950s was among engineers, because organizations were engaged in competition based on product design. The power base in many organizations shifted to marketing as competition became a game of advertising aimed at differentiating products in the consumer’s mind. About 10–15 years ago, power and leadership once again shifted, this time to people with finance and legal backgrounds, because the critical contingencies facing many organizations were mergers, acquisitions, hostile takeovers, and creative financing. Thus, Salancik and Pfeffer reason that power and thus leadership flow to those individuals who have the ability to help an organization or group [overcome its critical contingencies]. As the challenges facing a group change, so too may the flow of power and leadership.
Many leaders emerge out of the needs of the situation. Different situations call for different configurations of knowledge, skills, and abilities. A group often turns to the member who possesses the knowledge, skills, and abilities that the group requires to achieve its goals. 25 People surrender their power to individuals whom they believe will make meaningful contributions to attaining group goals. 26 The individual to whom power is surrendered is often a member of the group who is in good standing. As a result of this member’s contributions to the group’s goals, he has accumulated idiosyncrasy credits (a form of competency-based status). These credits give the individual a status that allows him to influence the direction that the group takes as it works to achieve its goals. 27
It is important to recognize that the traits possessed by certain individuals contribute significantly to their emergence as leaders. Research indicates that people are unlikely to follow individuals who, for example, do not display drive, self-confidence, knowledge of the situation, honesty, and integrity.
Leadership as an Exercise of Influence
As we have noted, leadership is the exercise of influence over those who depend on one another for attaining a mutual goal in a group setting. But how do leaders effectively exercise this influence? Social or (interpersonal) influence is one’s ability to effect a change in the motivation, attitudes, and/or behaviors of others. Power , then, essentially answers the “how” question: How do leaders influence their followers? The answer often is that a leader’s social influence is the source of his power.
French and Raven provide us with a useful typology that identifies the sources and types of power. As a review those types of power are reward power, coercive power, referent power, expert power, and legitimate power. 28
As you know, not all forms of power are equally effective (see Figure 5 ), nor is a leader’s total power base the simple sum of the powers at his disposal. Different types of power elicit different forms of compliance: Leaders who rely on coercive power often alienate followers who resist their influence attempts. Leaders who rely on reward power develop followers who are very measured in their responses to [what?]; the use of rewards often leads people to think in terms of “How much am I getting?” or “How much should I give?” or “Am I breaking even?” The use of referent power produces identification with the leader and his cause. The use of rationality, expert power, and/or moralistic appeal generally elicits commitment and the internalization of the leader’s goals. 29
Leaders who use referent and expert power commonly experience a favorable response in terms of follower satisfaction and performance. Research suggests that rationality is the most effective influence tactic in terms of its impact on follower commitment, motivation, performance, satisfaction, and group effectiveness. 30
Reward and legitimate power (that is, relying on one’s position to influence others) produce inconsistent results. Sometimes these powers lead to follower performance and satisfaction, yet they also sometimes fail. Coercive power can result in favorable performance, yet follower and resistance dissatisfaction are not uncommon.
Good leaders, whether formal or informal, develop many sources of power. Leaders who rely solely on their legitimate power and authority seldom generate the influence necessary to help their organization and its members succeed. In the process of building their power base, effective leaders have discovered that the use of coercive power tends to dilute the effectiveness of other powers, while the development and use of referent power tends to magnify the effectiveness of other forms of power. A compliment or reward from a person we like generally has greater value than one from someone we dislike, and punishment from someone we love (such as “tough love” from a parent) is less offensive than the pain inflicted by someone we dislike. 31
In sum, one key to effective leadership, especially as it pertains to the exercise of social and interpersonal influence, relates to the type of power employed by the leader. Overall leader effectiveness will be higher when people follow because they want to follow. This is much more likely to happen when the leader’s influence flows out of intrinsic such as rationality, expertise, moralistic appeal, and/or referent power.
Leadership is also about having a vision and communicating that vision to others in such a way that it provides meaning for the follower. 32 Language, ritual, drama, myths, symbolic constructions, and stories are some of the tools leaders use to capture the attention of their “followers to be” to evoke emotion and to manage the meaning “of the task (challenges) facing the group.” 33 These tools help the leader influence the attitudes, motivation, and behavior of their followers.
Influence-Based Leadership Styles
Many writers and researchers have explored how leaders can use power to address the needs of various situations. One view holds that in traditional organizations members expect to be told what to do and are willing to follow highly structured directions. Individuals attracted to high-involvement organizations, however, want to make their own decisions, expect their leaders to allow them to do so, and are willing to accept and act on this responsibility. This suggests that a leader may use and employ power in a variety of ways.
The Tannenbaum and Schmidt Continuum
In the 1950s, Tannenbaum and Schmidt created a continuum (see Figure 6 ) along which leadership styles range from authoritarian to extremely high levels of worker freedom. 34 Subsequent to Tannenbaum and Schmidt’s work, researchers adapted the continuum by categorizing leader power styles as autocratic (boss-centered), participative (workers are consulted and involved), or free-rein (members are assigned the work and decide on their own how to do it; the leader relinquishes the active assumption of the role of leadership). 35
Theory X and Theory Y Leaders
McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y posits two different sets of attitudes about the individual as an organizational member. 36 Theory X and Y thinking gives rise to two different styles of leadership. The Theory X leader assumes that the average individual dislikes work and is incapable of exercising adequate self-direction and self-control. As a consequence, they exert a highly controlling leadership style. In contrast, Theory Y leaders believe that people have creative capacities, as well as both the ability and desire to exercise self-direction and self-control. They typically allow organizational members significant amounts of discretion in their jobs and encourage them to participate in departmental and organizational decision-making. Theory Y leaders are much more likely to adopt involvement-oriented approaches to leadership and organically designed organizations for their leadership group.
Theory X and Theory Y thinking and leadership are not strictly an American phenomenon. Evidence suggests that managers from different parts of the global community commonly hold the same view. A study of 3,600 managers from 14 countries reveals that most of them held assumptions about human nature that could best be classified as Theory X. 37 Even though managers might publicly endorse the merits of participatory management, most of them doubted their workers’ capacities to exercise self-direction and self-control and to contribute creatively. 38
Directive/Permissive Leadership Styles
Contemplating the central role of problem-solving in management and leadership, Jan P. Muczyk and Bernard C. Reimann of Cleveland State University offer an interesting perspective on four different leadership styles (see Figure 7 ) that revolve around decision-making and implementation processes. 39
A directive autocrat retains power, makes unilateral decisions, and closely supervises workers’ activities. This style of leadership is seen as appropriate when circumstances require quick decisions and organizational members are new, inexperienced, or underqualified. A doctor in charge of a hastily constructed shelter for victims of a tornado may use this style to command nonmedical volunteers.
The permissive autocrat mixes his or her use of power by retaining decision-making power but permitting organizational members to exercise discretion when executing those decisions. This leader behavior is recommended when decision-making time is limited, when tasks are routine, or when organizational members have sufficient expertise to determine appropriate role behaviors.
Also sharing power is the directive democrat, who encourages participative decision-making but retains the power to direct team members in the execution of their roles. This style is appropriate when followers have valuable opinions and ideas, but one person needs to coordinate the execution of the ideas. A surgeon might allow the entire surgical team to participate in developing a plan for a surgical procedure. Once surgery begins, however, the surgeon is completely in charge.
Finally, the permissive democrat shares power with group members, soliciting involvement in both decision-making and execution. This style is appropriate when participation has both informational and motivational value, when time permits group decision-making, when group members are capable of improving decision quality, and when followers are capable of exercising self-management in their performance of work.
The permissive democratic approach to leadership is characteristic of leadership in high-involvement organizations. Here, leaders act as facilitators, process consultants, network builders, conflict managers, inspirationalists, coaches, teachers/mentors, and cheerleaders. 40 Such is the role of Ralph Stayer, founder, owner, and CEO of Johnsonville Foods. He defines himself as his company’s philosopher. At Quad/Graphics, president Harry V. Quadracci is a permissive democrat because he encourages all Quad employees to play a major role in decision-making and execution as they manage their teams as independent profit centers.
- What is the role of the leader and follower in the leadership process?
- How do the theories of Tannenbaum and Schmidt’s leadership continuum and McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y attempt to define leadership?
The Trait Approach to Leadership
Ancient Greek, Roman, Egyptian, and Chinese scholars were keenly interested in leaders and leadership. Their writings portray leaders as heroes. Homer, in his poem The Odyssey , portrays Odysseus during and after the Trojan War as a great leader who had vision and self-confidence. His son Telemachus, under the tutelage of Mentor, developed his father’s courage and leadership skills. 41 Out of such stories there emerged the “great man” theory of leadership, and a starting point for the contemporary study of leadership.
The great man theory of leadership states that some people are born with the necessary attributes to be great leaders. Alexander the Great, Julius Caesar, Joan of Arc, Catherine the Great, Napoleon, and Mahatma Gandhi are cited as naturally great leaders, born with a set of personal qualities that made them effective leaders. Even today, the belief that truly great leaders are born is common. For example, Kenneth Labich, writer for Fortune magazine, commented that “the best leaders seem to possess a God-given spark.” 42
During the early 1900s, scholars endeavored to understand leaders and leadership. They wanted to know, from an organizational perspective, what characteristics leaders hold in common in the hope that people with these characteristics could be identified, recruited, and placed in key organizational positions. This gave rise to early research efforts and to what is referred to as the trait approach to leadership. Prompted by the great man theory of leadership and the emerging interest in understanding what leadership is, researchers focused on the leader—Who is a leader? What are the distinguishing characteristics of the great and effective leaders? The great man theory of leadership holds that some people are born with a set of personal qualities that make truly great leaders. Mahatma Gandhi is often cited as a naturally great leader.
Leader Trait Research
Ralph Stogdill, while on the faculty at The Ohio State University, pioneered our modern (late 20th century) study of leadership. 43 Scholars taking the trait approach attempted to identify physiological (appearance, height, and weight), demographic (age, education, and socioeconomic background), personality (dominance, self-confidence, and aggressiveness), intellective (intelligence, decisiveness, judgment, and knowledge), task-related (achievement drive, initiative, and persistence), and social characteristics (sociability and cooperativeness) with leader emergence and leader effectiveness. After reviewing several hundred studies of leader traits, Stogdill in 1974 described the successful leader this way:
The [successful] leader is characterized by a strong drive for responsibility and task completion, vigor and persistence in pursuit of goals, venturesomeness and originality in problem solving, drive to exercise initiative in social situations, self-confidence and sense of personal identity, willingness to accept consequences of decision and action, readiness to absorb interpersonal stress, willingness to tolerate frustration and delay, ability to influence other person’s behavior, and capacity to structure social interaction systems to the purpose at hand. 44
The last three decades of the 20th century witnessed continued exploration of the relationship between traits and both leader emergence and leader effectiveness. Edwin Locke from the University of Maryland and a number of his research associates, in their recent review of the trait research, observed that successful leaders possess a set of core characteristics that are different from those of other people. 45 Although these core traits do not solely determine whether a person will be a leader—or a successful leader—they are seen as preconditions that endow people with leadership potential. Among the core traits identified are:
- Drive —a high level of effort, including a strong desire for achievement as well as high levels of ambition, energy, tenacity, and initiative
- Leadership motivation —an intense desire to lead others
- Honesty and integrity —a commitment to the truth (nondeceit), where word and deed correspond
- Self-confidence —an assurance in one’s self, one’s ideas, and one’s ability
- Cognitive ability —conceptually skilled, capable of exercising good judgment, having strong analytical abilities, possessing the capacity to think strategically and multidimensionally
- Knowledge of the business —a high degree of understanding of the company, industry, and technical matters
- Other traits —charisma, creativity/originality, and flexibility/adaptiveness 46
While leaders may be “people with the right stuff,” effective leadership requires more than simply possessing the correct set of motives and traits. Knowledge, skills, ability, vision, strategy, and effective vision implementation are all necessary for the person who has the “right stuff” to realize their leadership potential. 47 According to Locke, people endowed with these traits engage in behaviors that are associated with leadership. As followers, people are attracted to and inclined to follow individuals who display, for example, honesty and integrity, self-confidence, and the motivation to lead.
Personality psychologists remind us that behavior is a result of an interaction between the person and the situation—that is, Behavior = f [(Person) (Situation)]. To this, psychologist Walter Mischel adds the important observation that personality tends to get expressed through an individual’s behavior in “weak” situations and to be suppressed in “strong” situations. 48 A strong situation is one with strong behavioral norms and rules, strong incentives, clear expectations, and rewards for a particular behavior. Our characterization of the mechanistic organization with its well-defined hierarchy of authority, jobs, and standard operating procedures exemplifies a strong situation. The organic social system exemplifies a weak situation. From a leadership perspective, a person’s traits play a stronger role in their leader behavior and ultimately leader effectiveness when the situation permits the expression of their disposition. Thus, personality traits prominently shape leader behavior in weak situations.
Finally, about the validity of the “great person approach to leadership”: Evidence accumulated to date does not provide a strong base of support for the notion that leaders are born. Yet, the study of twins at the University of Minnesota leaves open the possibility that part of the answer might be found in our genes. Many personality traits and vocational interests (which might be related to one’s interest in assuming responsibility for others and the motivation to lead) have been found to be related to our “genetic dispositions” as well as to our life experiences. 49 Each core trait recently identified by Locke and his associates traces a significant part of its existence to life experiences. Thus, a person is not born with self-confidence. Self-confidence is developed, honesty and integrity are a matter of personal choice, motivation to lead comes from within the individual and is within his control, and knowledge of the business can be acquired. While cognitive ability does in part find its origin in the genes, it still needs to be developed. Finally, drive, as a dispositional trait, may also have a genetic component, but it too can be self- and other-encouraged. It goes without saying that none of these ingredients are acquired overnight.
Behavioral Approaches to Leadership
The nearly four decades of research that focused on identifying the personal traits associated with the emergence of leaders and leader effectiveness resulted in two observations. First, leader traits are important—people who are endowed with the “right stuff” (drive, self-confidence, honesty, and integrity) are more likely to emerge as leaders and to be effective leaders than individuals who do not possess these characteristics. Second, traits are only a part of the story. Traits only account for part of why someone becomes a leader and why they are (or are not) effective leaders.
Still under the influence of the great man theory of leadership, researchers continued to focus on the leader in an effort to understand leadership—who emerges and what constitutes effective leadership. Researchers then began to reason that maybe the rest of the story could be understood by looking at what it is that leaders do . Thus, we now turn our attention to leader behaviors and the behavioral approaches to leadership.
It is now common to think of effective leadership in terms of what leaders do. CEOs and management consultants agree that effective leaders display trust in their employees, develop a vision, keep their cool, encourage risk, bring expertise into the work setting, invite dissent, and focus everyone’s attention on that which is important. 59 William Arruda, in a Fortune article, noted that “organizations with strong coaching cultures report their revenue to be above average, compared to their peer group.” Sixty-five percent of employees “from strong coaching cultures rated themselves as highly engaged,” compared to 13 percent of employees worldwide.” 60 Jonathan Anthony calls himself an intrapreneur and corporate disorganizer, because same-old, same-old comms practices are dying in front of our eyes. 61 Apple founder Steve Jobs believed that the best leaders are coaches and team cheerleaders. Similar views have been frequently echoed by management consultant Tom Peters.
During the late 1940s, two major research programs—The Ohio State University and the University of Michigan leadership studies—were launched to explore leadership from a behavioral perspective.
The Ohio State University Studies
A group of Ohio State University researchers, under the direction of Ralph Stogdill, began an extensive and systematic series of studies to identify leader behaviors associated with effective group performance. Their results identified two major sets of leader behaviors: consideration and initiating structure.
Consideration is the “relationship-oriented” behavior of a leader. It is instrumental in creating and maintaining good relationships (that is, addressing the group’s maintenance needs) with organizational members. Consideration behaviors include being supportive and friendly, representing people’s interests, communicating openly with group members, recognizing them, respecting their ideas, and sharing concern for their feelings.
Initiating structure involves “task-oriented” leader behaviors. It is instrumental in the efficient use of resources to attain organizational goals, thereby addressing the group’s task needs. Initiating structure behaviors include scheduling work, deciding what is to be done (and how and when to do it), providing direction to organizational members, planning, coordinating, problem-solving, maintaining standards of performance, and encouraging the use of uniform procedures.
After consideration and initiating structure behaviors were first identified, many leaders believed that they had to behave one way or the other. If they initiated structure, they could not be considerate, and vice versa. It did not take long, however, to recognize that leaders can simultaneously display any combination of both behaviors.
The Ohio State studies are important because they identified two critical categories of behavior that distinguish one leader from another. Both consideration and initiating structure behavior can significantly impact work attitudes and behaviors. Unfortunately, the effects of consideration and initiating structure are not consistent from situation to situation. 62 In some of the organizations studied, for example, high levels of initiating structure increased performance. In other organizations, the amount of initiating structure seemed to make little difference. Although most organizational members reported greater satisfaction when leaders acted considerately, consideration behavior appeared to have no clear effect on performance.
Initially, these mixed findings were disappointing to researchers and managers alike. It had been hoped that a profile of the most effective leader behaviors could be identified so that leaders could be trained in the best ways to behave. Research made clear, however, that there is no one best style of leader behavior for all situations.
The University of Michigan Studies
At about the same time that the Ohio State studies were underway, researchers at the University of Michigan also began to investigate leader behaviors. As at Ohio State, the Michigan researchers attempted to identify behavioral elements that differentiated effective from ineffective leaders. 63
The two types of leader behavior that stand out in these studies are job centered and organizational member centered. Job-centered behaviors are devoted to supervisory functions, such as planning, scheduling, coordinating work activities, and providing the resources needed for task performance. Employee-member-centered behaviors include consideration and support for organizational members. These dimensions of behavior, of course, correspond closely to the dimensions of initiating structure and consideration identified at Ohio State. The similarity of the findings from two independent groups of researchers added to their credibility. As the Ohio State researchers had done, the Michigan researchers also found that any combination of the two behaviors was possible.
The studies at Michigan are significant because they reinforce the importance of leader behavior. They also provide the basis for later theories that identify specific, effective matches of work situations and leader behaviors. Subsequent research at Michigan and elsewhere has found additional behaviors associated with effective leadership: support, work facilitation, goal emphasis, and interaction facilitation. 64
These four behaviors are important to the successful functioning of the group in that support and interaction facilitation contribute to the group’s maintenance needs, and goal emphasis and work facilitation contribute to the group’s task needs. The Michigan researchers also found that these four behaviors do not need to be brought to the group by the leader. In essence, the leader’s real job is to set the tone and create the climate that ensure these critical behaviors are present. 65
The Leadership Grid ®
Much of the credit for disseminating knowledge about important leader behaviors must go to Robert R. Blake and Jane S. Mouton, who developed a method for classifying styles of leadership compatible with many of the ideas from the Ohio State and Michigan studies. 66 In their classification scheme, concern for results (production) emphasizes output, cost effectiveness, and (in for-profit organizations) a concern for profits. Concern for people involves promoting working relationships and paying attention to issues of importance to group members. As shown in Figure 9 , the Leadership Grid® demonstrates that any combination of these two leader concerns is possible, and five styles of leadership are highlighted here.
Blake and Mouton contend that the sound (contribute and commit) leader (a high concern for results and people, or 9,9) style is universally the most effective. 67 While the Leadership Grid® is appealing and well structured, research to date suggests that there is no universally effective style of leadership (9,9 or otherwise). 68 There are, however, well-identified situations in which a 9,9 style is unlikely to be effective. Organizational members of high-involvement organizations who have mastered their job duties require little production-oriented leader behavior. Likewise, there is little time for people-oriented behavior during an emergency. Finally, evidence suggests that the “high-high” style may be effective when the situation calls for high levels of initiating structure. Under these conditions, the initiation of structure is more acceptable, favorably affecting follower satisfaction and performance, when the leader is also experienced as warm, supportive, and considerate. 69
- What are the behavioral approaches to defining leadership?
- What roles do gender and the popular perceptions of gender roles have on views of leadership traits?
Situational (Contingency) Approaches to Leadership
As early as 1948, Ralph Stogdill stated that “the qualities, characteristics, and skills required in a leader are determined to a large extent by the demands of the situation in which he is to function as a leader.” 70 In addition, it had been observed that two major leader behaviors, initiating structure and consideration, didn’t always lead to equally positive outcomes. That is, there are times when initiating structure results in performance increases and follower satisfaction, and there are times when the results are just the opposite. Contradictory findings such as this lead researchers to ask “Under what conditions are the results positive in nature?” and “When and why are they negative at other times?” Obviously, situational differences and key contingencies are at work.
Several theories have been advanced to address this issue. These are Fiedler’s contingency theory of leadership, the path-goal theory of leader effectiveness, Hersey and Blanchard’s life cycle theory, cognitive resource theory, the decision tree, and the decision process theory. 71 We explore two of the better-known situational theories of leadership, Fred Fiedler’s contingency model and Robert J. House’s path-goal theory, here. Victor Vroom, Phillip Yetton, and Arthur Jago’s decision tree model also applies.
Fiedler’s Contingency Model
One of the earliest, best-known, and most controversial situation-contingent leadership theories was set forth by Fred E. Fiedler from the University of Washington. 72 This theory is known as the contingency theory of leadership. According to Fiedler, organizations attempting to achieve group effectiveness through leadership must assess the leader according to an underlying trait, assess the situation faced by the leader, and construct a proper match between the two.
The Leader’s Trait
Leaders are asked about their least-preferred coworker (LPC), the person with whom they least like to work. The most popular interpretation of the LPC score is that it reflects a leader’s underlying disposition toward others—for example: pleasant/unpleasant, cold/warm, friendly/unfriendly, and untrustworthy/trustworthy. (You can examine your own LPC score by completing the LPC self-assessment on the following page.)
Fiedler states that leaders with high LPC scores are relationship oriented —they need to develop and maintain close interpersonal relationships. They tend to evaluate their least-preferred coworkers in fairly favorable terms. Task accomplishment is a secondary need to this type of leader and becomes important only after the need for relationships is reasonably well satisfied. In contrast, leaders with low LPC scores tend to evaluate the individuals with whom they least like to work fairly negatively. They are task-oriented people, and only after tasks have been accomplished are low-LPC leaders likely to work on establishing good social and interpersonal relations.
The Situational Factor
Some situations favor leaders more than others do. To Fiedler, situational favorableness is the degree to which leaders have control and influence and therefore feel that they can determine the outcomes of a group interaction. 73 Several years later, Fiedler changed his situational factor from situational favorability to situational control—where situational control essentially refers to the degree to which a leader can influence the group process. 74 Three factors work together to determine how favorable a situation is to a leader. In order of importance, they are (1) leader-member relations —the degree of the group’s acceptance of the leader, their ability to work well together, and members’ level of loyalty to the leader; (2) task structure —the degree to which the task specifies a detailed, unambiguous goal and how to achieve it; and (3) position power —a leader’s direct ability to influence group members. The situation is most favorable for a leader when the relationship between the leader and group members is good, when the task is highly structured, and when the leader’s position power is strong (cell 1 in Figure 10 ). The least-favorable situation occurs under poor leader-member relations, an unstructured task, and weak position power (cell 8).
Leader-Situation Matches
Some combinations of leaders and situations work well; others do not. In search of the best combinations, Fiedler examined a large number of leadership situations. He argued that most leaders have a relatively unchangeable or dominant style, so organizations need to design job situations to fit the leader. 75
While the model has not been fully tested and tests have often produced mixed or contradictory findings, 76 Fiedler’s research indicates that relationship-oriented (high-LPC) leaders are much more effective under conditions of intermediate favorability than under either highly favorable or highly unfavorable situations. Fiedler attributes the success of relationship-oriented leaders in situations with intermediate favorability to the leader’s nondirective, permissive attitude; a more directive attitude could lead to anxiety in followers, conflict in the group, and a lack of cooperation.
For highly favorable and unfavorable situations, task-oriented leaders (those with a low LPC) are very effective. As tasks are accomplished, a task-oriented leader allows the group to perform its highly structured tasks without imposing more task-directed behavior. The job gets done without the need for the leader’s direction. Under unfavorable conditions, task-oriented behaviors, such as setting goals, detailing work methods, and guiding and controlling work behaviors, move the group toward task accomplishment.
As might be expected, leaders with mid-range LPC scores can be more effective in a wider range of situations than high- or low-LPC leaders. 77 Under conditions of low favorability, for example, a middle-LPC leader can be task oriented to achieve performance, but show consideration for and allow organizational members to proceed on their own under conditions of high situational favorability.
Controversy over the Theory
Although Fiedler’s theory often identifies appropriate leader-situation matches and has received broad support, it is not without critics. Some note that it characterizes leaders through reference to their attitudes or personality traits (LPC) while it explains the leader’s effectiveness through their behaviors—those with a particular trait will behave in a particular fashion. The theory fails to make the connection between the least-preferred coworker attitude and subsequent behaviors. In addition, some tests of the model have produced mixed or contradictory findings. 78 Finally, what is the true meaning of the LPC score—exactly what is being revealed by a person who sees their least-preferred coworker in positive or negative terms? Robert J. House and Ram N. Aditya recently noted that, in spite of the criticisms, there has been substantial support for Fiedler’s theory. 79
Path-Goal Theory
Robert J. House and Martin Evans, while on the faculty at the University of Toronto, developed a useful leadership theory. Like Fiedler’s, it asserts that the type of leadership needed to enhance organizational effectiveness depends on the situation in which the leader is placed. Unlike Fiedler, however, House and Evans focus on the leader’s observable behavior. Thus, managers can either match the situation to the leader or modify the leader’s behavior to fit the situation.
The model of leadership advanced by House and Evans is called the path-goal theory of leadership because it suggests that an effective leader provides organizational members with a path to a valued goal. According to House, the motivational function of the leader consists of increasing personal payoffs to organizational members for work-goal attainment, and making the path to these payoffs easier to travel by clarifying it, reducing roadblocks and pitfalls, and increasing the opportunities for personal satisfaction en route. 80
Effective leaders therefore provide rewards that are valued by organizational members. These rewards may be pay, recognition, promotions, or any other item that gives members an incentive to work hard to achieve goals. Effective leaders also give clear instructions so that ambiguities about work are reduced and followers understand how to do their jobs effectively. They provide coaching, guidance, and training so that followers can perform the task expected of them. They also remove barriers to task accomplishment, correcting shortages of materials, inoperative machinery, or interfering policies.
An Appropriate Match
According to the path-goal theory, the challenge facing leaders is basically twofold. First, they must analyze situations and identify the most appropriate leadership style. For example, experienced employees who work on a highly structured assembly line don’t need a leader to spend much time telling them how to do their jobs—they already know this. The leader of an archeological expedition, though, may need to spend a great deal of time telling inexperienced laborers how to excavate and care for the relics they uncover.
Second, leaders must be flexible enough to use different leadership styles as appropriate. To be effective, leaders must engage in a wide variety of behaviors. Without an extensive repertoire of behaviors at their disposal, a leader’s effectiveness is limited. 81 All team members will not, for example, have the same need for autonomy. The leadership style that motivates organizational members with strong needs for autonomy (participative leadership) is different from that which motivates and satisfies members with weaker autonomy needs (directive leadership). The degree to which leadership behavior matches situational factors will determine members’ motivation, satisfaction, and performance (see Figure 11 ). 82
Behavior Dimensions
According to path-goal theory, there are four important dimensions of leader behavior, each of which is suited to a particular set of situational demands. 83
- Supportive leadership —At times, effective leaders demonstrate concern for the well-being and personal needs of organizational members. Supportive leaders are friendly, approachable, and considerate to individuals in the workplace. Supportive leadership is especially effective when an organizational member is performing a boring, stressful, frustrating, tedious, or unpleasant task. If a task is difficult and a group member has low self-esteem, supportive leadership can reduce some of the person’s anxiety, increase his confidence, and increase satisfaction and determination as well.
- Directive leadership —At times, effective leaders set goals and performance expectations, let organizational members know what is expected, provide guidance, establish rules and procedures to guide work, and schedule and coordinate the activities of members. Directive leadership is called for when role ambiguity is high. Removing uncertainty and providing needed guidance can increase members’ effort, job satisfaction, and job performance.
- Participative leadership —At times, effective leaders consult with group members about job-related activities and consider their opinions and suggestions when making decisions. Participative leadership is effective when tasks are unstructured. Participative leadership is used to great effect when leaders need help in identifying work procedures and where followers have the expertise to provide this help.
- Achievement-oriented leadership —At times, effective leaders set challenging goals, seek improvement in performance, emphasize excellence, and demonstrate confidence in organizational members’ ability to attain high standards. Achievement-oriented leaders thus capitalize on members’ needs for achievement and use goal-setting theory to great advantage.
- Identify and describe the variables presented in Fiedler’s theory of leadership.
- What are the leadership behaviors in the path-goal theory of leadership?
- What role does culture have in how leadership is viewed?
- What are the differences between the trait, behavioral, and situational approaches to defining leadership?
Substitutes for and Neutralizers of Leadership
Several factors have been discovered that can substitute for or neutralize the effects of leader behavior (see Table 1 ). 89 Substitutes for leadership behavior can clarify role expectations, motivate organizational members, or satisfy members (making it unnecessary for the leader to attempt to do so). In some cases, these substitutes supplement the behavior of a leader. Sometimes it is a group member’s characteristics that make leadership less necessary, as when a master craftsperson or highly skilled worker performs up to his or her own high standards without needing outside prompting. Sometimes the task’s characteristics take over, as when the work itself—solving an interesting problem or working on a familiar job—is intrinsically satisfying. Sometimes the characteristics of the organization make leadership less necessary, as when work rules are so clear and specific that workers know exactly what they must do without help from the leader (see An Inside Look at flat management structure and the orchestra with no leader).
Neutralizers of leadership, on the other hand, are not helpful; they prevent leaders from acting as they wish. A computer-paced assembly line, for example, prevents a leader from using initiating structure behavior to pace the line. A union contract that specifies that workers be paid according to seniority prevents a leader from dispensing merit-based pay. Sometimes, of course, neutralizers can be beneficial. Union contracts, for example, clarify disciplinary proceedings and identify the responsibilities of both management and labor. Leaders must be aware of the presence of neutralizers and their effects so that they can eliminate troublesome neutralizers or take advantage of any potential benefits that accompany them (such as the clarity of responsibilities provided by a union contract). If a leader’s effectiveness is being neutralized by a poor communication system, for example, the leader might try to remove the neutralizer by developing (or convincing the organization to develop) a more effective system.
Followers differ considerably in their focus of attention while at work, thereby affecting the effectiveness of the act of leadership. Focus of attention is an employee’s cognitive orientation while at work. It reflects what and how strongly an individual thinks about various objects, events, or phenomena while physically present at work. Focus of attention reflects an individual difference in that not all individuals have the same cognitive orientation while at work—some think a great deal about their job, their coworkers, their leader, or off-the-job factors, while others daydream. 90 An employee’s focus of attention has both “trait” and “state” qualities. For example, there is a significant amount of minute-by-minute variation in an employee’s focus of attention (the “state” component), and there is reasonable consistency in the categories of events that employees think about while they are at work (the “trait” component).
Research suggests that the more followers focus on off-job (nonleader) factors, the less they will react to the leader’s behaviors. Thus, a strong focus on one’s life “away from work” (for example, time with family and friends) tends to neutralize the motivational, attitudinal, and/or behavioral effects associated with any particular leader behavior. It has also been observed, however, that a strong focus on the leader, either positive or negative, enhances the impact that the leader’s behaviors have on followers. 91
MANAGERIAL LEADERSHIP
You Are Now the Leader
Leading and managing are two very different things. Being a manager means something more than gaining authority or charge over former colleagues. With the title does come the power to affect company outcomes, but it also comes with something more: the power to shape the careers and personal growth of subordinates.
According to Steve Keating, a senior manager at the Toro Company, it is important not to assume that being made a manager automatically makes you a leader. Rather, being a manager means having the opportunity to lead. Enterprises need managers to guide processes, but the employees—the people—need a leader. Keating believes that leaders need a mindset that emphasizes people, and the leader’s job is to help the people in the organization to be successful. According to Keating, “If you don’t care for people, you can’t lead them” (Hakim 2017 n.p.).
For someone who has been promoted over his peers, ground rules are essential. “Promotion doesn’t mean the end of friendship but it does change it,” according to Keating. If a peer has been promoted, rather than grouse and give in to envy, it is important to step back and look at the new manager; take a hard look at why the peer was promoted and what skill or characteristic made you a less appealing fit for the position (Hakim 2017).
Carol Walker, president of Prepared to Lead, a management consulting firm, advises new managers to develop a job philosophy. She urges new managers to develop a core philosophy that provides a guide to the day-to-day job of leading. She urges managers to build up the people they are leading and work as a “servant leader.” The manager’s perspective should be on employee growth and success. Leaders must bear in mind that employees don’t work for the manager; they work for the organization—and for themselves. Managers coordinate this relationship; they are not the center of it. Work should not be assigned haphazardly, but with the employee’s skills and growth in mind. “An employee who understands why she has been asked to do something is far more likely to assume true ownership for the assignment,” Walker says (Yakowicz 2015 n.p.). A leader’s agenda should be on employee success, not personal glory. Employees are more receptive when they recognize that their leader is working not for their own success, but for the employee’s success.
A survey from HighGround revealed one important item that most new managers and even many seasoned managers overlook: asking for feedback. Everyone has room for growth, even managers. Traditional management dictates a top-down style in which managers review subordinates. But many companies have found it beneficial to turn things around and ask employees, “How can I be a better manager?” Of course, this upward review only works if employees believe that their opinion will be heard. Managers need to carefully cultivate a rapport where employees don’t fear reprisals for negative feedback. Listening to criticism from those you are leading builds trust and helps ensure that as a manager, you are providing the sort of leadership that employees need to be successful (Kauflin 2017). Showing respect and caring for employees by asking this simple question is inspiring —an important aspect of leadership itself. Whether asking for feedback or focusing on an employee’s fit with a particular job description, a leader helps guide employees through the day-to-day, builds a positive culture, and helps employees improve their skills.
- What do you think are the most important qualities in a leader? In a manager? Are your two lists mutually exclusive? Why?
- How do you think a leader can use feedback to model the growth process for employees?
- Identify and describe substitutes of leadership.
Transformational, Visionary, and Charismatic Leadership
Many organizations struggling with the need to manage chaos, to undergo a culture change, to empower organizational members, and to restructure have looked for answers in “hiring the right leader.” Many have come to believe that the transformational, visionary, and charismatic leader represents the style of leadership needed to move organizations through chaos.
The Transformational and Visionary Leader
Leaders who subscribe to the notion that “if it ain’t broke, don’t fix it” are often described as transactional leaders. They are extremely task oriented and instrumental in their approach, frequently looking for incentives that will induce their followers into a desired course of action. 92 These reciprocal exchanges take place in the context of a mutually interdependent relationship between the leader and the follower, frequently resulting in interpersonal bonding. 93 The transactional leader moves a group toward task accomplishment by initiating structure and by offering an incentive in exchange for desired behaviors. The transformational leader , on the other hand, moves and changes (fixes) things “in a big way”! Unlike transactional leaders, they don’t cause change by offering inducements. Instead, they inspire others to action through their personal values, vision, passion, and belief in and commitment to the mission. 94 Through charisma (idealized influence), individualized consideration (a focus on the development of the follower), intellectual stimulation (questioning assumptions and challenging the status quo), and/or inspirational motivation (articulating an appealing vision), transformational leaders move others to follow.
The transformational leader is also referred to as a visionary leader. Visionary leaders are those who influence others through an emotional and/or intellectual attraction to the leader’s dreams of what “can be.” Vision links a present and future state, energizes and generates commitment, provides meaning for action, and serves as a standard against which to assess performance. 95 Evidence indicates that vision is positively related to follower attitudes and performance. 96 As pointed out by Warren Bennis, a vision is effective only to the extent that the leader can communicate it in such a way that others come to internalize it as their own. 97
As people, transformational leaders are engaging. They are characterized by extroversion, agreeableness, and openness to experience. 98 They energize others. They increase followers’ awareness of the importance of the designated outcome. 99 They motivate individuals to transcend their own self-interest for the benefit of the team and inspire organizational members to self-manage (become self-leaders). 100 Transformational leaders move people to focus on higher-order needs (self-esteem and self-actualization). When organizations face a turbulent environment, intense competition, products that may die early, and the need to move fast, managers cannot rely solely on organizational structure to guide organizational activity. In these situations, transformational leadership can motivate followers to be fully engaged and inspired, to internalize the goals and values of the organization, and to move forward with dogged determination!
Transformational leadership is positively related to follower satisfaction, performance, and acts of citizenship. These effects result from the fact that transformational leader behaviors elicit trust and perceptions of procedural justice, which in turn favorably impact follower satisfaction and performance. 101 As R. Pillai, C. Schriesheim, and E. Williams note, “when followers perceive that they can influence the outcomes of decisions that are important to them and that they are participants in an equitable relationship with their leader, their perceptions of procedural justice [and trust] are likely to be enhanced.” 102 Trust and experiences of organizational justice promote leader effectiveness, follower satisfaction, motivation, performance, and citizenship behaviors.
Charismatic Leadership
Ronald Reagan, Jesse Jackson, and Queen Elizabeth I have something in common with Martin Luther King Jr., Indira Gandhi, and Winston Churchill. The effectiveness of these leaders originates in part in their charisma , a special magnetic charm and appeal that arouses loyalty and enthusiasm. Each exerted considerable personal influence to bring about major events.
It is difficult to differentiate the charismatic and the transformational leader. True transformational leaders may achieve their results through the magnetism of their personality. In this case, the two types of leaders are essentially one and the same, yet it is important to note that not all transformational leaders have a personal “aura.”
Sociologist Max Weber evidenced an interest in charismatic leadership in the 1920s, calling charismatic leaders people who possess legitimate power that arises from “exceptional sanctity, heroism, or exemplary character.” 103 Charismatic leaders “single-handedly” effect changes even in very large organizations. Their personality is a powerful force, and the relationship that they forge with their followers is extremely strong.
The charismatic leadership phenomenon involves a complex interplay between the attributes of the leader and followers’ needs, values, beliefs, and perceptions. 104 At its extreme, leader-follower relationships are characterized by followers’ unquestioning acceptance; trust in the leader’s beliefs; affection; willing obedience to, emulation of, and identification with the leader; emotional involvement with his mission; and feelings of self-efficacy directed toward the leader’s mission. 105 This can work to better the welfare of individuals, such as when Lee Iacocca saved thousands of jobs through his dramatic turnaround of a failing corporate giant, the Chrysler Corporation. It also can be disastrous, as when David Koresh led dozens and dozens of men, women, and children to their fiery death in Waco, Texas. Individuals working for charismatic leaders often have higher task performance, greater task satisfaction, and lower levels of role conflict than those working for leaders with considerate or structuring behaviors. 106 What are the characteristics of these people who can exert such a strong influence over their followers? Charismatic leaders have a strong need for power and the tendency to rely heavily on referent power as their primary power base. 107 Charismatic leaders also are extremely self-confident and convinced of the rightness of their own beliefs and ideals. This self-confidence and strength of conviction make people trust the charismatic leader’s judgment, unconditionally following the leader’s mission and directives for action. 108 The result is a strong bond between leader and followers, a bond built primarily around the leader’s personality.
Although there have been many effective charismatic leaders, those who succeed the most have coupled their charismatic capabilities with behaviors consistent with the same leadership principles followed by other effective leaders. Those who do not add these other dimensions still attract followers but do not meet organizational goals as effectively as they could. They are (at least for a time) the pied pipers of the business world, with lots of followers but no constructive direction.
ETHICS IN PRACTICE
Uber’s Need for an Ethical Leader
Almost since its initial founding in 2009 as a luxury car service for the San Francisco area, controversy has followed Uber. Many complaints are against the tactics employed by the company’s founder and former CEO, Travis Kalanick, but the effects are found throughout the business and its operations.
In 2009, UberBlack was a “black car” service, a high-end driving service that cost more than a taxi but less than hiring a private driver for the night. It wasn’t until 2012 that the company launched UberX, the taxi-esque service most people think of today when they say “Uber.” The UberX service contracted with private drivers who provided rides in their personal vehicles. A customer would use Uber’s smartphone app to request the ride, and a private driver would show up. Originally launched in San Francisco, the service spread quickly, and by 2017, Uber was in 633 cities. The service was hailed by many as innovative and the free market’s answer to high-priced and sometimes unreliable taxi services. But Uber has not been without its critics, both inside and outside of the company.
In 2013, as the UberX service spread, some UberBlack drivers protested at the company’s headquarters complaining about poor company benefits and pay. They also claimed that competition from the newly launched UberX service was cutting into their sales and undermining job security. Kalanick rebuffed the protests, basically calling the complaints sour grapes: most of the protestors had been laid off earlier for poor service (Lawler 2013). Controversy also arose over the use of contract drivers rather than full-time employees. Contractors complained about a lack of benefits and low wages. Competitors, especially taxi services, complained that they were being unfairly undercut because Uber didn’t have to abide by the same screening process and costs that traditional yellow taxi companies did. Some municipalities agreed, arguing further than Uber’s lack of or insufficient screening of drivers put passengers at risk.
Uber quickly generated a reputation as a bully and Kalanick as an unethical leader (Ann 2016). The company has been accused of covering up cases of sexual assault, and Kalanick himself has been quoted as calling the service “Boob-er,” a reference to using the service to pick up women (Ann 2016). Uber has been criticized for its recruiting practices; in particular, it has been accused of bribing drivers working for competitors to switch over and drive for Uber (Ann 2016).The company was also caught making false driver requests for competing companies and then canceling the order. The effect was to waste the other driver’s time and make it more difficult for customers to secure rides on the competing service (D’Orazio 2014). Susan J. Fowler, former site reliability engineer at Uber, went public with cases of outright sexual harassment within Uber (Fowler 2017). Former employees described Uber’s corporate culture as an “a**hole culture” and a “‘Hobbesian jungle’ where you can never get ahead unless someone else dies.” (Wong 2017) One employee described a leadership that encouraged a company practice of developing incomplete solutions for the purpose of beating the competitor to market. Fowler went so far as to compare the experience to Game of Thrones, and other former employees even consider “making it” at Uber a black mark on a resume (Wong 2017).
In terms of social acrimony and PR disasters, arguably caused or even encouraged by leadership, Uber’s rise to notoriety has arguably been more bad than good. In June 2017, Kalanick made one too many headlines and agreed to step down as the company’s CEO.
- In the summer of 2017, Transport of London (TfL) began proceedings to revoke Uber’s permit to operate in London. How do think Uber’s poor corporate reputation may have been a factor in TfL’s thinking?
- What steps do you think Uber’s new CEO, Dara Khosrowshahi, needs to take to repair Uber’s reputation?
- Despite Uber’s apparent success in launching in multiple markets, it continues to post quarterly losses in the millions and shareholders effectively subsidize 59 percent of every ride (https://www.reuters.com/article/us-uber-profitability/true-price-of-an-uber-ride-in-question-as-investors-assess-firms-value-idUSKCN1B3103). How is this an outworking of Uber’s overall corporate culture?
- What are the defining characteristics of transformational and charismatic leaders?
Leadership Needs in the 21st Century
Frequent headlines in popular business magazines like Fortune and Business Week call our attention to a major movement going on in the world of business. Organizations are being reengineered and restructured, and network, virtual, and modular corporations are emerging. People talk about the transnational organization, the boundaryless company, the post-hierarchical organization. By the end of the decade, the organizations that we will be living in, working with, and competing against are likely to be vastly different from what we know today.
The transition will not be easy; uncertainty tends to breed resistance. We are driven by linear and rational thinking, which leads us to believe that “we can get there from here” by making some incremental changes in who we are and what we are currently doing. Existing paradigms frame our perceptions and guide our thinking. Throwing away paradigms that have served us well in the past does not come easily.
A look back tells most observers that the past decade has been characterized by rapid change, intense competition, an explosion of new technologies, chaos, turbulence, and high levels of uncertainty. A quick scan of today’s business landscape suggests that this trend is not going away anytime soon. According to Professor Jay A. Conger from Canada’s McGill University, “In times of great transition, leadership becomes critically important. Leaders, in essence, offer us a pathway of confidence and direction as we move through seeming chaos. The magnitude of today’s changes will demand not only more leadership, but newer forms of leadership.” 109
According to Conger, two major forces are defining for us the genius of the next generation of leaders. The first force is the organization’s external environment. Global competitiveness is creating some unique leadership demands. The second force is the growing diversity in organizations’ internal environments. Diversity will significantly change the relationship between organizational members, work, and the organization in challenging, difficult, and also very positive ways.
What will the leaders of tomorrow be like? Professor Conger suggests that the effective leaders of the 21st century will have to be many things. 110 They will have to be strategic opportunists; only organizational visionaries will find strategic opportunities before competitors. They will have to be globally aware ; with 80 percent of today’s organizations facing significant foreign competition, knowledge of foreign markets, global economics, and geopolitics is crucial. They will have to be capable of managing a highly decentralized organization ; movement toward the high-involvement organization will accelerate as the environmental demands for organizational speed, flexibility, learning, and leanness increase. They will have be sensitive to diversity ; during the first few years of the 21st century, fewer than 10 percent of those entering the workforce in North America will be white, Anglo-Saxon males, and the incoming women, minorities, and immigrants will bring with them a very different set of needs and concerns. They will have to be interpersonally competent ; a highly diverse workforce will necessitate a leader who is extremely aware of and sensitive to multicultural expectations and needs. They will have to be builders of an organizational community ; work and organizations will serve as a major source of need fulfillment, and in the process leaders will be called on to help build this community in such a way that organizational members develop a sense of ownership for the organization and its mission.
Finally, it is important to note that leadership theory construction and empirical inquiry are an ongoing endeavor. While the study of traits, behavior, and contingency models of leadership provide us with a great deal of insight into leadership, the mosaic is far from complete. During the past 15 years, several new theories of leadership have emerged; among them are leader-member exchange theory, implicit leadership theory, neocharismatic theory, value-based theory of leadership, and visionary leadership, 111 each of which over time will add to our bank of knowledge about leaders and the leadership process.
Leaders of the 21st-century organization have a monumental challenge awaiting them and a wealth of self-enriching and fulfilling opportunities. The challenge and rewards awaiting effective leaders are awesome!
- What is the role of leadership in the 21st century?
A social (interpersonal) influence relationship between two or more persons who depend on each other to attain certain mutual goals in a group situation.
designated leader
The person placed in the leadership position by forces outside the group.
emergent leader
The person who becomes a group’s leader by virtue of processes and dynamics internal to the group.
formal leader
That individual who is recognized by those outside the group as the official leader of the group.
informal leader
That individual whom members of the group acknowledge as their leader.
great man theory of leadership
The belief that some people are born to be leaders and others are not.
consideration
A “relationship-oriented” leader behavior that is supportive, friendly, and focused on personal needs and interpersonal relationships.
initiating structure
A “task-oriented” leader behavior that is focused on goal attainment, organizing and scheduling work, solving problems, and maintaining work processes.
contingency theory of leadership
A theory advanced by Dr. Fred E. Fiedler that suggests that different leadership styles are effective as a function of the favorableness of the leadership situation least preferred.
Least-preferred coworker (LPC)
The person with whom the leader least likes to work.
path-goal theory of leadership
A theory that posits that leadership is path- and goal-oriented, suggesting that different leadership styles are effective as a function of the task confronting the group.
A special personal magnetic charm or appeal that arouses loyalty and enthusiasm in a leader-follower relationship.
charismatic leader
A person who possesses legitimate power that arises from “exceptional sanctity, heroism, or exemplary character.”
transformational leader
A leader who moves and changes things “in a big way” by inspiring others to perform the extraordinary.
visionary leader
A leader who influences others through an emotional and/or intellectual attraction to the leader’s dreams of what “can be.”
Summary of Learning Outcomes
13.1 The Nature of Leadership
Leadership is a primary vehicle for fulfilling the directing function of management. Because of its importance, theorists, researchers, and practitioners have devoted a tremendous amount of attention and energy to unlocking the secrets of effective leadership. They have kept at this search for perhaps a greater period of time than for any other single issue related to management.
13.2 The Leadership Process
Organizations typically have both formal and informal leaders. Their leadership is effective for virtually identical reasons. Leadership and management are not the same. Although effective leadership is a necessary part of effective management, the overall management role is much larger than leadership alone. Managers plan, organize, direct, and control. As leaders, they are engaged primarily in the directing function.
13.3 Leader Emergence
There are many diverse perspectives on leadership. Some managers treat leadership primarily as an exercise of power. Others believe that a particular belief and attitude structure makes for effective leaders. Still others believe it is possible to identify a collection of leader traits that produces a leader who should be universally effective in any leadership situation. Even today, many believe that a profile of behaviors can universally guarantee successful leadership. Unfortunately, such simple solutions fall short of the reality.
13.4 The Trait Approach to Leadership
13.5 Behavioral Approaches to Leadership
It is clear that effective leaders are endowed with the “right stuff,” yet this “stuff” is only a precondition to effective leadership. Leaders need to connect with their followers and bring the right configuration of knowledge, skills, ability, vision, and strategy to the situational demands confronting the group.
13.6 Situational (Contingency) Approaches to Leadership
We now know that there is no one best way to be an effective leader in all circumstances. Leaders need to recognize that how they choose to lead will affect the nature of their followers’ compliance with their influence tactics, and ultimately impacts motivation, satisfaction, performance, and group effectiveness. In addition, the nature of the situation—contextual demands and characteristics of the follower—dictates the type of leadership that is likely to be effective. Fiedler focuses on leader traits and argues that the favorableness of the leadership situation dictates the type of leadership approach needed. He recommends selecting leaders to match the situation or changing the situation to match the leader. Path-goal theory focuses on leader behavior that can be adapted to the demands of a particular work environment and organizational members’ characteristics. Path-goal theorists believe both that leaders can be matched with the situation and that the situation can be changed to match leaders. Together, these theories make clear that leadership is effective when the characteristics and behavior of the leader match the demands of the situation.
13.7 Substitutes for and Neutralizers of Leadership
- What does the concept of “substitute for leadership” mean?
Characteristics of followers, tasks, and organizations can substitute for or neutralize many leader behaviors. Leaders must remain aware of these factors, no matter which perspective on leadership they adopt. Such awareness allows managers to use substitutes for, and neutralizers of, leadership to their benefit, rather than be stymied by their presence.
13.8 Transformational, Visionary, and Charismatic Leadership
In recent years, there has been a renewed interest in key leader traits and behaviors. As organizations face increasing amounts of chaos in their external environments, searches for “the right leader” who can bring about major organizational transformations has intensified. This search once again focuses our attention on a set of “key” motives, knowledge, skills, and personality attributes. Emerging from this search has been the identification of the charismatic and transformational leader.
13.9 Leadership Needs in the 21st Century
Leadership in the high-involvement organization differs dramatically from that in the traditional and control-oriented organization. Leaders external to the team have as one of their primary roles empowering group members and the teams themselves to self-lead and self-manage. Leaders internal to the team are peers; they work alongside and simultaneously facilitate planning, organizing, directing, controlling, and the execution of the team’s work.
Although we know a great deal about the determinants of effective leadership, we have much to learn. Each theory presented in this chapter is put into practice by managers every day. None provides the complete answer to what makes leaders effective, but each has something important to offer.
Finally, our understanding of leadership has many shortcomings and limitations. The existing literature is largely based on observations from a Western industrialized context. The extent to which our theories of leadership are bound by our culture, limiting generalization to other cultures, is largely unknown. Cross-cultural leadership research will no doubt intensify as the global economy becomes an ever more dominant force in the world.
Chapter Review Questions
- Define leadership and distinguish between leadership and management.
- Discuss the processes associated with people coming to positions of leadership.
- Discuss the different forms of power available to leaders and the effects associated with each.
- It has been observed that effective leaders have the “right stuff.” What traits are commonly associated with leader emergence and effective leaders?
- Both the Ohio State University and University of Michigan leadership studies identified central leader behaviors. What are these behaviors, and how are they different from one another?
- Blake and Mouton’s work with the Leadership Grid® identified several leadership types. What are they, and how does this leadership model look from the perspective of situation theories of leadership?
- Identify and describe the three situational variables presented in Fiedler’s contingency theory of leadership.
- What are the four leadership behaviors in the path-goal theory of leadership?
- Discuss the differences between the internal and external leadership roles surrounding self-managed work teams.
- What are substitutes for leadership? What are neutralizers? Give an example of each.
- What are the distinguishing features of the transformational and the charismatic leader
Group Skills Application Exercises
- Identify a charismatic leader and a leader with little charisma. What are the traits and skills that allow them to succeed in their roles? How can you incorporate the traits that allow them to be successful in their roles into the skills you will need to have in a leadership position?
- You have just taken a leadership position where 40 percent of the workforce telecommutes. You want to encourage teamwork and want to ensure that telecommuting is not hurting teamwork. What is your plan to discover how things are working and how to communicate your desire to have effective teamwork?
- You are at a meeting, and during the meeting someone on the team addresses their manager and points out a crucial mistake that could doom the project. The person says that their manager should have caught it and because of that should resign. As a leader of the group, how would you deal with the subordinate, the manager, and communication with the entire team?
Problem Solving in Teams and Groups Copyright © 2021 by Cameron W. Piercy, Ph.D. is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- E-Statements & W-2’s
- Timecard – Bullhorn Log In
- Employment Verification

- Search Jobs
A Lesson in Leadership: 5 Effective Problem Solving Strategies Used by Great Leaders
- A Lesson in Leadership: 5…

No matter how well you run your organization, you are going to encounter problems along the way.
What makes or breaks an organization isn’t the problems they face, but how they handle these problems. This is why as a leader of an organization, it’s very important that you have the right problem solving strategies up your sleeve.
What do you need to know?
Check out this guide to discover the top problem-solving strategies used by great leaders.
1. Communicate Transparently
If you want to solve problems effectively, you need to be a transparent communicator .
This means that everyone needs to feel free to express their point of view and concerns. If people are afraid to speak up, then it can take a lot longer to get to the heart of the matter.
In order for transparent communication to happen, as a leader, you need to make sure you facilitate an environment that allows for open dialogue. Too many times, employees of organizations are afraid to speak up because they’re worried about losing their job or being exposed for doing something wrong.
Therefore, problem-solving effectively means creating an environment where everyone is comfortable discussing and tackling the problem in a collaborative manner .
2. Stop Finger Pointing
When a problem arises, it can be all too easy to play the blame game. But, doing this isn’t going to get you anywhere.
If your team is truly a team, then this means that everyone is working together toward one common goal. So, when one person messes up, this means that the whole team messes up.
When you point your finger at the one person who messes up, you’re just being a part of the problem. Instead, you want to be a part of the solution.
While you should teach everyone to take responsibility for their actions, when something happens, it’s important to work together to solve it.
3. Think Positive
In order to be an effective problem solver, you need to always think positively .
If an issue occurs and you come at it with a negative mindset, there’s no way you’re going to find a suitable solution. By having a positive perspective on things, you’ll be able to transfer that energy to your team members and motivate them to solve the problem.
4. Be Open-Minded
Don’t be that leader who locks themselves in their office when a problem occurs.
Problems often occur due to a break in communication. By locking yourself in your office to think about the problem, you’re only further straining your team’s communication.
The best thing to do is to discuss your ideas to solve the problem with your team members. And, you should encourage your team members to share their problem-solving ideas as well.
Problem Solving Strategies: Are You Ready to Start Solving?
Now that you have these problem solving strategies handy, you should be better equipped the next time a problem arises in your organization.
For more ways to improve your organization, be sure to check out this guide to learn how to engage your millennial candidates.
Related posts


Culture Development
Workplace problem-solving examples: real scenarios, practical solutions.
- March 11, 2024
In today’s fast-paced and ever-changing work environment, problems are inevitable. From conflicts among employees to high levels of stress, workplace problems can significantly impact productivity and overall well-being. However, by developing the art of problem-solving and implementing practical solutions, organizations can effectively tackle these challenges and foster a positive work culture. In this article, we will delve into various workplace problem scenarios and explore strategies for resolution. By understanding common workplace problems and acquiring essential problem-solving skills, individuals and organizations can navigate these challenges with confidence and success.

Understanding Workplace Problems
Before we can effectively solve workplace problems , it is essential to gain a clear understanding of the issues at hand. Identifying common workplace problems is the first step toward finding practical solutions. By recognizing these challenges, organizations can develop targeted strategies and initiatives to address them.
Identifying Common Workplace Problems
One of the most common workplace problems is conflict. Whether it stems from differences in opinions, miscommunication, or personality clashes, conflict can disrupt collaboration and hinder productivity. It is important to note that conflict is a natural part of any workplace, as individuals with different backgrounds and perspectives come together to work towards a common goal. However, when conflict is not managed effectively, it can escalate and create a toxic work environment.
In addition to conflict, workplace stress and burnout pose significant challenges. High workloads, tight deadlines, and a lack of work-life balance can all contribute to employee stress and dissatisfaction. When employees are overwhelmed and exhausted, their performance and overall well-being are compromised. This not only affects the individuals directly, but it also has a ripple effect on the entire organization.
Another common workplace problem is poor communication. Ineffective communication can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and errors. It can also create a sense of confusion and frustration among employees. Clear and open communication is vital for successful collaboration and the smooth functioning of any organization.
The Impact of Workplace Problems on Productivity
Workplace problems can have a detrimental effect on productivity levels. When conflicts are left unresolved, they can create a tense work environment, leading to decreased employee motivation and engagement. The negative energy generated by unresolved conflicts can spread throughout the organization, affecting team dynamics and overall performance.
Similarly, high levels of stress and burnout can result in decreased productivity, as individuals may struggle to focus and perform optimally. When employees are constantly under pressure and overwhelmed, their ability to think creatively and problem-solve diminishes. This can lead to a decline in the quality of work produced and an increase in errors and inefficiencies.
Poor communication also hampers productivity. When information is not effectively shared or understood, it can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and rework. This not only wastes time and resources but also creates frustration and demotivation among employees.
Furthermore, workplace problems can negatively impact employee morale and job satisfaction. When individuals are constantly dealing with conflicts, stress, and poor communication, their overall job satisfaction and engagement suffer. This can result in higher turnover rates, as employees seek a healthier and more supportive work environment.
In conclusion, workplace problems such as conflict, stress, burnout, and poor communication can significantly hinder productivity and employee well-being. Organizations must address these issues promptly and proactively to create a positive and productive work atmosphere. By fostering open communication, providing support for stress management, and promoting conflict resolution strategies, organizations can create a work environment that encourages collaboration, innovation, and employee satisfaction.

The Art of Problem Solving in the Workplace
Now that we have a clear understanding of workplace problems, let’s explore the essential skills necessary for effective problem-solving in the workplace. By developing these skills and adopting a proactive approach, individuals can tackle problems head-on and find practical solutions.
Problem-solving in the workplace is a complex and multifaceted skill that requires a combination of analytical thinking, creativity, and effective communication. It goes beyond simply identifying problems and extends to finding innovative solutions that address the root causes.
Essential Problem-Solving Skills for the Workplace
To effectively solve workplace problems, individuals should possess a range of skills. These include strong analytical and critical thinking abilities, excellent communication and interpersonal skills, the ability to collaborate and work well in a team, and the capacity to adapt to change. By honing these skills, individuals can approach workplace problems with confidence and creativity.
Analytical and critical thinking skills are essential for problem-solving in the workplace. They involve the ability to gather and analyze relevant information, identify patterns and trends, and make logical connections. These skills enable individuals to break down complex problems into manageable components and develop effective strategies to solve them.
Effective communication and interpersonal skills are also crucial for problem-solving in the workplace. These skills enable individuals to clearly articulate their thoughts and ideas, actively listen to others, and collaborate effectively with colleagues. By fostering open and honest communication channels, individuals can better understand the root causes of problems and work towards finding practical solutions.
Collaboration and teamwork are essential for problem-solving in the workplace. By working together, individuals can leverage their diverse skills, knowledge, and perspectives to generate innovative solutions. Collaboration fosters a supportive and inclusive environment where everyone’s ideas are valued, leading to more effective problem-solving outcomes.
The ability to adapt to change is another important skill for problem-solving in the workplace. In today’s fast-paced and dynamic work environment, problems often arise due to changes in technology, processes, or market conditions. Individuals who can embrace change and adapt quickly are better equipped to find solutions that address the evolving needs of the organization.
The Role of Communication in Problem Solving
Communication is a key component of effective problem-solving in the workplace. By fostering open and honest communication channels, individuals can better understand the root causes of problems and work towards finding practical solutions. Active listening, clear and concise articulation of thoughts and ideas, and the ability to empathize are all valuable communication skills that facilitate problem-solving.
Active listening involves fully engaging with the speaker, paying attention to both verbal and non-verbal cues, and seeking clarification when necessary. By actively listening, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the problem at hand and the perspectives of others involved. This understanding is crucial for developing comprehensive and effective solutions.
Clear and concise articulation of thoughts and ideas is essential for effective problem-solving communication. By expressing oneself clearly, individuals can ensure that their ideas are understood by others. This clarity helps to avoid misunderstandings and promotes effective collaboration.
Empathy is a valuable communication skill that plays a significant role in problem-solving. By putting oneself in the shoes of others and understanding their emotions and perspectives, individuals can build trust and rapport. This empathetic connection fosters a supportive and collaborative environment where everyone feels valued and motivated to contribute to finding solutions.
In conclusion, problem-solving in the workplace requires a combination of essential skills such as analytical thinking, effective communication, collaboration, and adaptability. By honing these skills and fostering open communication channels, individuals can approach workplace problems with confidence and creativity, leading to practical and innovative solutions.
Real Scenarios of Workplace Problems
Now, let’s explore some real scenarios of workplace problems and delve into strategies for resolution. By examining these practical examples, individuals can develop a deeper understanding of how to approach and solve workplace problems.
Conflict Resolution in the Workplace
Imagine a scenario where two team members have conflicting ideas on how to approach a project. The disagreement becomes heated, leading to a tense work environment. To resolve this conflict, it is crucial to encourage open dialogue between the team members. Facilitating a calm and respectful conversation can help uncover underlying concerns and find common ground. Collaboration and compromise are key in reaching a resolution that satisfies all parties involved.
In this particular scenario, let’s dive deeper into the dynamics between the team members. One team member, let’s call her Sarah, strongly believes that a more conservative and traditional approach is necessary for the project’s success. On the other hand, her colleague, John, advocates for a more innovative and out-of-the-box strategy. The clash between their perspectives arises from their different backgrounds and experiences.
As the conflict escalates, it is essential for a neutral party, such as a team leader or a mediator, to step in and facilitate the conversation. This person should create a safe space for both Sarah and John to express their ideas and concerns without fear of judgment or retribution. By actively listening to each other, they can gain a better understanding of the underlying motivations behind their respective approaches.
During the conversation, it may become apparent that Sarah’s conservative approach stems from a fear of taking risks and a desire for stability. On the other hand, John’s innovative mindset is driven by a passion for pushing boundaries and finding creative solutions. Recognizing these underlying motivations can help foster empathy and create a foundation for collaboration.
As the dialogue progresses, Sarah and John can begin to identify areas of overlap and potential compromise. They may realize that while Sarah’s conservative approach provides stability, John’s innovative ideas can inject fresh perspectives into the project. By combining their strengths and finding a middle ground, they can develop a hybrid strategy that incorporates both stability and innovation.
Ultimately, conflict resolution in the workplace requires effective communication, active listening, empathy, and a willingness to find common ground. By addressing conflicts head-on and fostering a collaborative environment, teams can overcome challenges and achieve their goals.
Dealing with Workplace Stress and Burnout
Workplace stress and burnout can be debilitating for individuals and organizations alike. In this scenario, an employee is consistently overwhelmed by their workload and experiencing signs of burnout. To address this issue, organizations should promote a healthy work-life balance and provide resources to manage stress effectively. Encouraging employees to take breaks, providing access to mental health support, and fostering a supportive work culture are all practical solutions to alleviate workplace stress.
In this particular scenario, let’s imagine that the employee facing stress and burnout is named Alex. Alex has been working long hours, often sacrificing personal time and rest to meet tight deadlines and demanding expectations. As a result, Alex is experiencing physical and mental exhaustion, reduced productivity, and a sense of detachment from work.
Recognizing the signs of burnout, Alex’s organization takes proactive measures to address the issue. They understand that employee well-being is crucial for maintaining a healthy and productive workforce. To promote a healthy work-life balance, the organization encourages employees to take regular breaks and prioritize self-care. They emphasize the importance of disconnecting from work during non-working hours and encourage employees to engage in activities that promote relaxation and rejuvenation.
Additionally, the organization provides access to mental health support services, such as counseling or therapy sessions. They recognize that stress and burnout can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental well-being and offer resources to help employees manage their stress effectively. By destigmatizing mental health and providing confidential support, the organization creates an environment where employees feel comfortable seeking help when needed.
Furthermore, the organization fosters a supportive work culture by promoting open communication and empathy. They encourage managers and colleagues to check in with each other regularly, offering support and understanding. Team members are encouraged to collaborate and share the workload, ensuring that no one person is overwhelmed with excessive responsibilities.
By implementing these strategies, Alex’s organization aims to alleviate workplace stress and prevent burnout. They understand that a healthy and balanced workforce is more likely to be engaged, productive, and satisfied. Through a combination of promoting work-life balance, providing mental health support, and fostering a supportive work culture, organizations can effectively address workplace stress and create an environment conducive to employee well-being.
Practical Solutions to Workplace Problems
Now that we have explored real scenarios, let’s discuss practical solutions that organizations can implement to address workplace problems. By adopting proactive strategies and establishing effective policies, organizations can create a positive work environment conducive to problem-solving and productivity.
Implementing Effective Policies for Problem Resolution
Organizations should have clear and well-defined policies in place to address workplace problems. These policies should outline procedures for conflict resolution, channels for reporting problems, and accountability measures. By ensuring that employees are aware of these policies and have easy access to them, organizations can facilitate problem-solving and prevent issues from escalating.
Promoting a Positive Workplace Culture
A positive workplace culture is vital for problem-solving. By fostering an environment of respect, collaboration, and open communication, organizations can create a space where individuals feel empowered to address and solve problems. Encouraging teamwork, recognizing and appreciating employees’ contributions, and promoting a healthy work-life balance are all ways to cultivate a positive workplace culture.
The Role of Leadership in Problem Solving
Leadership plays a crucial role in facilitating effective problem-solving within organizations. Different leadership styles can impact how problems are approached and resolved.
Leadership Styles and Their Impact on Problem-Solving
Leaders who adopt an autocratic leadership style may make decisions independently, potentially leaving their team members feeling excluded and undervalued. On the other hand, leaders who adopt a democratic leadership style involve their team members in the problem-solving process, fostering a sense of ownership and empowerment. By encouraging employee participation, organizations can leverage the diverse perspectives and expertise of their workforce to find innovative solutions to workplace problems.
Encouraging Employee Participation in Problem Solving
To harness the collective problem-solving abilities of an organization, it is crucial to encourage employee participation. Leaders can create opportunities for employees to contribute their ideas and perspectives through brainstorming sessions, team meetings, and collaborative projects. By valuing employee input and involving them in decision-making processes, organizations can foster a culture of inclusivity and drive innovative problem-solving efforts.
In today’s dynamic work environment, workplace problems are unavoidable. However, by understanding common workplace problems, developing essential problem-solving skills, and implementing practical solutions, individuals and organizations can navigate these challenges effectively. By fostering a positive work culture, implementing effective policies, and encouraging employee participation, organizations can create an environment conducive to problem-solving and productivity. With proactive problem-solving strategies in place, organizations can thrive and overcome obstacles, ensuring long-term success and growth.
Related Stories
- May 23, 2024
Software for Company Culture
Edgar schein models on organizational culture, best culture consulting firms, what can we help you find.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
8 Essential Leadership Communication Skills

- 14 Nov 2019
If you want to be an effective leader , you need to excel in communication. In fact, the success of your business relies on it.
According to a report from the Economist Intelligence Unit (pdf) , poor communication can lead to low morale, missed performance goals, and even lost sales. A separate study found that inadequate communication can cost large companies an average of $64.2 million per year, while smaller organizations are at risk of losing $420,000 annually.
But effective communication impacts more than just the bottom line. For leaders, it’s what enables them to rally their team around a shared vision, empower employees , build trust, and successfully navigate organizational change .
Why Is Communication Important in Leadership?
A leader is someone who inspires positive, incremental change by empowering those around them to work toward common objectives. A leader’s most powerful tool for doing so is communication.
Effective communication is vital to gain trust, align efforts in the pursuit of goals, and inspire positive change. When communication is lacking, important information can be misinterpreted, causing relationships to suffer and, ultimately, creating barriers that hinder progress.
If you’re interested in enhancing your leadership capabilities, here are eight communication skills you need to be more effective in your role.

Essential Communication Skills for Leaders
1. ability to adapt your communication style.
Different communication styles are the most frequently cited cause of poor communication, according to the Economist Intelligence Unit (pdf) , and can lead to more significant issues, such as unclear priorities and increased stress.
It’s essential to identify your leadership style , so that you can better understand how you’re interacting with, and perceived by, employees across the organization. For example, if you’re an authoritative leader , you likely have a clear vision for achieving success and align your team accordingly. While an effective approach for some, it might fall flat for others who seek more autonomy in their role.
Every employee’s motivations are different, so knowing how to tailor your communication is essential to influencing others and reaching organizational goals.
Related: 4 Tips for Developing Your Personal Leadership Style
2. Active Listening
Effective leaders know when they need to talk and, more importantly, when they need to listen. Show that you care by asking for employees’ opinions, ideas, and feedback. And when they do share, actively engage in the conversation—pose questions, invite them to elaborate, and take notes.
It’s important to stay in the moment and avoid interrupting. Keep your focus on the employee and what it is they’re saying. To achieve that, you also need to eliminate any distractions, including constant pings on your cell phone or checking incoming emails.
3. Transparency
In a survey by the American Management Association , more than a third of senior managers, executives, and employees said they “hardly ever” know what’s going on in their organizations. Transparency can go a long way in breaking down that communication barrier.
By speaking openly about the company’s goals, opportunities, and challenges, leaders can build trust amongst their team and foster an environment where employees feel empowered to share their ideas and collaborate. Just acknowledging mistakes can encourage experimentation and create a safe space for active problem-solving.
Every individual should understand the role they play in the company’s success. The more transparent leaders are, the easier it is for employees to make that connection.
When communicating with employees, speak in specifics. Define the desired result of a project or strategic initiative and be clear about what you want to see achieved by the end of each milestone. If goals aren’t being met, try simplifying your message further or ask how you can provide additional clarity or help.
The more clear you are, the less confusion there will be around priorities. Employees will know what they’re working toward and feel more engaged in the process.
5. Ability to Ask Open-Ended Questions
If you want to understand employees’ motivations, thoughts, and goals better, practice asking open-ended questions. Jennifer Currence, president of consulting firm The Currence Group, said to the Society of Human Resource Management to use the acronym TED, which stands for:
- “ T ell me more.”
- “ E xplain what you mean.”
- “ D efine that term or concept for me.”
By leveraging those phrases when speaking with your team, you can elicit more thoughtful, thorough responses and ensure you also have clarity around what they need from you to succeed.
There’s a reason empathy has been ranked the top leadership skill needed for success . The better you get at acknowledging and understanding employees’ feelings and experiences, the more heard and valued they’ll feel.
In a recent survey (pdf) , 96 percent of respondents said it was important for their employers to demonstrate empathy, yet 92 percent claimed it remains undervalued. If you want to improve your communication and build a stronger, more productive culture, practice responding with empathy.
Related: Emotional Intelligence Skills: What They Are & How to Develop Them
7. Open Body Language
Communication isn’t just what you say; it’s how you carry yourself. Ninety-three percent of communication’s impact comes from nonverbal cues, according to executive coach Darlene Price .
To ensure you’re conveying the right message, focus on your body language. If you’re trying to inspire someone, talking with clenched fists and a furrowed brow isn’t going to send the right message. Instead, make eye contact to establish interest and rapport and flash a genuine smile to convey warmth and trust.
8. Receiving and Implementing Feedback
Asking for feedback from your team can not only help you grow as a leader, but build trust among your colleagues. It’s critical, though, that you don’t just listen to the feedback. You also need to act on it.
If you continue to receive feedback from your team, but don’t implement any changes, they’re going to lose faith in your ability to follow through. It’s likely there will be comments you can’t immediately act on—be transparent about that. By letting your employees know they were heard and then apprising them of any progress you can, or do, make, they’ll feel as though you value their perspective and are serious about improving.
Related: How to Give Feedback Effectively

Improving Your Leadership Communication
Communication is at the core of effective leadership. If you want to influence and inspire your team, you need to practice empathy and transparency, and understand how others perceive you, through your verbal and non-verbal cues.
To improve your communication skills and become a better leader, begin by assessing your effectiveness so you can identify areas for improvement. Then, set goals and hold yourself accountable by creating a leadership development plan to guide and track your progress.
Do you want to enhance your leadership skills? Download our free leadership e-book and explore our online course Leadership Principles to discover how you can become a more effective leader and unleash the potential in yourself and others.
(This post was updated on June 16, 2020. It was originally published on November 14, 2019.)

About the Author
Strategic Leadership
Senior level managers must tackle complex problems using creative problem-solving and a portfolio of skills and styles. Here’s a look at how being a strategic leader can move an organization—and your career—forward.
Pamela Reynolds
On any given day in a large organization, managers make dozens if not hundreds of decisions, both large and small. How many units are getting out the door? How well are employees performing? Are there supply chain issues or problems recruiting new hires? Is distribution functioning smoothly?
While some leaders spend their days immersed in these day-to-day, short-term operational issues, strategic leaders focus on the big picture — where the organization is going and how to best utilize talent to get there.
In this blog, we’ll look at exactly what it means to be a strategic leader. We’ll examine the top skills and qualities associated with senior-level leadership, as well as how you can become a strategic leader in your own right.
Defining Strategic Leadership
Strategic leadership is when managers use their creative problem-solving skills and strategic vision to help team members and an organization achieve long-term goals.
More specifically, according to Margaret Andrews, instructor of Strategic Leadership , a Professional & Executive Development program in the Harvard Division of Continuing Education, strategic leadership is not so much a clear-cut leadership style as a mindset — “that you want to be strategic about your leadership.”
“ Strategic leadership is about understanding yourself and your goals,” she says. “It’s about understanding the situation, considering options, and deciding. It’s also about getting the best out of people, the best out of the situation, so that the organization does well. Leaders who lead strategically have done the inner work necessary to lead with integrity, vision, and purpose.”
The concept of strategic leadership is not always straightforward . Leading strategically actually requires a manager to choose from among a variety of leadership styles depending on the situation and the people involved. Such leadership styles might include:
- Authoritarian leadership : when a leader imposes expectations and defines outcomes
- Participative leadership : when a leader involves team members in the decision-making process
- Delegative leadership : when a leader delegates tasks to other team members
- Transactional leadership : when a leader rewards or punishes team members in an effort to complete a task.
- Transformational leadership : when a leader uses a vision to inspire and motivate others
- Servant leadership : when a leader serves others by putting the needs of employees first, helping them develop to perform at higher levels
“It’s about using the leadership style that fits the situation at hand,” notes Andrews.
Browse Leadership and Management programs
What Are the Top Skills and Qualities of Strategic Leaders?
Adept strategic leaders have cultivated a special skill set beyond the obvious ones—being trustworthy, developing a strategic plan, and delegating—often cited in business textbooks and blogs.
Skills centered around emotional intelligence, the soft “people skills,” are the traits that allow strategic leaders to successfully adapt to an ever-changing economic and technological climate, remaining forward-looking and able to see industry trends and directions long before others in an organization do.
Passion, purpose, and conviction are what make strategic leaders “visionary.”
Some of the most important characteristics of someone who leads strategically include:
They Know Who They Are
“They really understand themselves, who they are and what matters,” says Andrews. “They know their values.”
They Are Interested in Others
Strategic leaders want to hear from team members, and they listen attentively as part of their leadership strategy. As a result, team members naturally feel more invested. Andrews references a famous quote of Theodore Roosevelt: “No one cares how much you know until they know how much you care.”
“There’s an element of truth in that,” she says. “People want direction. They want to be part of something bigger than themselves. They want to have their own ideas for how to achieve great things considered as well.”
They Are Good Communicators
It goes without saying that leaders who think strategically speak clearly in ways that others can easily understand. But there is an added dimension — good listening skills, the second trait in our list. Good communicators listen closely enough to hear the reservations of those wavering on the fence and are able to create buy-in by addressing those concerns.
In addition, they are aware how their words, actions, and moods affect their teammates, and can calibrate their words and actions accordingly.
Because they’re good listeners, with a good dose of empathy and compassion included in the mix, they can be very effective at motivating team members. Engaged employees are more likely to do good work, persist through problems, innovate, and contribute to the overall strategy.
They Are Open-Minded
Strategic leaders encourage and seek out diverse points of view.
“The easy problems are solved, and we’re left with the harder problems which need new ways of thinking, which often come from a diverse team,” says Andrews. “We need different points of view, which come from different vantage points, educational paths, and personal and professional experiences.”
Who Are Some Examples of Strategic Leaders?
Leaders who exemplify some of the qualities found in great strategic leadership abound. Below are four different types of leaders who demonstrate at least one of the traits of a strategic leader.
Oprah Winfrey @Oprah :The Great Communicator
Winfrey started off as the first black local news anchor at a Nashville television station, only to become one of the wealthiest businesswomen in the world as CEO of Harpo Inc. a multimedia production company. Although she has been hailed as the most powerful business woman in the world by Forbes thanks to her business acumen, she is best known in her more humble role as a day-time talk show host. In 25 seasons on the set of “Oprah,” she displayed a down-to-earth, relatable communication style that embodied attentive listening, empathy, compassion, and the ability to connect with people from radically different backgrounds.
Howard Schultz @HowardSchultz : Knowing His Purpose
Howard Schultz, CEO of Starbucks, made the radical decision to offer benefits for workers at the end of his first year as CEO of the coffee chain. At the time, it was virtually unheard of in the fast-food industry. Schultz, however, had grown up with a truck driving father who had no health insurance after breaking an ankle. Schultz was able to use his passion and sense of mission to persuade the Starbucks board to offer health insurance to baristas, even those working part-time.
Jacinda Ardern @jacindaardern : Interested in Others
Jacinda Ardern, Prime Minister of New Zealand, has been applauded around the world for her substantial leadership skills and steady hand during a crisis. She is often praised for her handling of the Covid-19 pandemic, in which she was able to keep levels of infection in the country relatively low. According to industry professionals, she “focuses on ‘we’ not ‘I,’” listens to expert advice and acts on what she hears, and acknowledges both her strengths and weaknesses, engendering trust.
Jeff Bezos @jeffbezos : Open to Big Ideas
Chairman and former CEO of Amazon, Jeff Bezos was able to transform his online bookstore into the world’s largest internet company by revenue, and the largest provider of virtual assistants and cloud infrastructure services. His vision was indeed of Amazonian proportions and has consequently changed the world. His innovation mindset and willingness to embrace bold new ideas means that his empire continues to grow, from moving Amazon into providing streaming movies to taking on sub-orbital spaceflight with his company Blue Origin.
How to Become a Strategic Leader
By now, it should be obvious that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to strategic leadership .
People who lead strategically come in all shapes and sizes and can be found in every arena, from politics, to entertainment, to business, and beyond.
But despite their variety of backgrounds, interests, and styles, there is one basic thing strategic leaders seem to know: “Leadership is the human side of business,” says Andrews. “That’s how we get things done, through other people, and that’s what leadership is about, since no two situations are alike.”
Ready to get started? Find the program that’s right for you.
Explore all Professional & Executive Development programs.
About the Author
Pamela Reynolds is a Boston-area feature writer and editor whose work appears in numerous publications. She is the author of “Revamp: A Memoir of Travel and Obsessive Renovation.”
How To Choose a Professional Development Program
Certificate programs and leadership courses can potentially advance your career. Here’s a guide to navigating the myriad choices.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

Becoming a great leader: effective leadership styles and behaviors
Jun 02, 2024
Posted by: Caitlin Burns
Leadership has long been a focal point of societal structures. In ancient times, autocratic rulers led empires as figures of authority, wielding power often granted to them through noble lineage. In the early days, societies largely based their understanding of leadership on an individual’s ability to command and control.
Today’s leadership is more democratic. It transcends the earlier focus on authority. Today’s leaders emphasize influence, inspiration and the ability to bring people together to work on a common goal. Leadership is more dynamic, with leaders striving to empower their followers. This has allowed a more cooperative society to form, driven by accountability and innovation.
This new form of leadership requires emotional intelligence, ethical behavior and a collaborative approach that didn’t really exist under leaders in the past.
Read on to learn more about leadership, the different types and how to become an effective leader.
What is leadership?
In the past, leaders were in charge of countries or armies. While those leaders still exist today, leadership has expanded into many other areas, particularly in the business world.
In modern organizations, leaders are often responsible for guiding and managing teams of employees to achieve specific goals and objectives. This contemporary context allows us to explore two distinct aspects that broadly define leadership: operational and strategic leadership.
Operational leadership
When we talk about operational leadership, we’re referring to the day-to-day management of an organization.
This aspect of leadership requires a more hands-on approach. It focuses on efficiency and problem-solving while striving to make the most of available resources.
Operational leadership primarily addresses an organization’s short-term needs. It also strives to ensure the organization meets its immediate goals and benchmarks.
Let’s look at what operational leadership looks like in different contexts:
- In the business world , operational leaders are responsible for overseeing the core activities that generate revenue. These include production, marketing and customer service.
- In the military , operational leaders make the tactical decisions that directly impact a mission’s immediate outcome.
- Non-profit leaders might guide the implementation of initiatives, build stakeholder engagement or work with community outreach efforts.
Strategic leadership
If operational leadership is about the short-term, strategic leadership is about the long-term. It’s this aspect of leadership that sets the vision for the organization.
Strategic leaders make high-level decisions. They try to position the organization for long-term success. This aspect of leadership requires:
- visionary thinking,
- a focus on innovation, and
- the ability to align internal objectives with external realities.
Strategic leaders also create the roadmap for the organization’s future. For businesses, this could be the long-term strategy of which products they will produce and when expansions will occur.
This element of leadership is significant within any organization. It requires:
- a clearly communicated strategic long-term vision, and
- stakeholder buy-in.
Without these two things, no organization will remain successful for very long.
Why is leadership important?
We’ve already seen how leaders impact an organization’s short-term and long-term goals. Both play a pivotal role in a business’s success, impacting sustainability and driving growth. Effective leaders inspire and motivate those who work for them, driving them to become better versions of themselves. This keeps people motivated, engaged and focused on achieving the organization’s goals.
This becomes even more important during times of crisis, which strain the emotions and capabilities of everyone involved. A leader who demonstrates resilience sets the tone for those who work for and with them.
Crises test the leader’s ability to make decisions under pressure and communicate them clearly. Leaders who handle this pressure gracefully can stabilize the organization, maintain morale and keep operations running as smoothly as possible.
While leadership is exceptionally important during crises, leaders also shape organizational culture at other times. For example, they set the tone for the workplace, establishing its values and ethical standards. Leaders who inspire a positive culture have happier, more productive and more loyal staff.
7 functions of leadership
The concept of operational versus strategic leadership is helpful in understanding the broad strokes of what a leader does. A leader’s role is multi-faceted and dynamic. However, they will need to fulfill several functions for their organization to thrive.
Let’s break down seven of the most common and important functions of leadership.
1. Providing direction
Whether for the short or long term, a primary function of leadership is providing direction. The leader, quite literally, guides the people who work under them. They chart the direction by establishing clear goals and expectations for team members and the organization as a whole.
To ensure everyone works toward a common purpose, leaders must effectively communicate the organization’s vision and direction. All team members need to understand and align with the established goals.
2. Influencing people
Influencing people is a critical function of leadership. It ensures that stakeholders agree on a chosen course of action and that team members are motivated to pursue goals and perform at their best.
Effective leaders use their emotional intelligence and collaborative skills to build consensus, inspire others and navigate complex interpersonal dynamics. They also understand the importance of managing public perception and maintaining a positive image of the organization among external stakeholders.
3. Fostering innovation
Competition is fierce, and today’s markets move fast. Leaders must foster an environment of creativity and innovation to keep their organization ahead of the curve.
To do this, they create a company culture that values curiosity, diversity and openness. When employees feel leadership values their ideas and encourages them to take risks, they feel empowered to speak up and share their thoughts. The quality of brainstorming that arises from such a culture is a major factor in a business staying ahead of the market.
4. Ensuring execution
While vision and strategy are important, they are meaningless without proper execution.
Meeting organizational goals requires careful planning, organization and oversight of the implementation. Good leaders monitor progress, making adjustments in real time when results drift off course. In doing so, leaders can ensure that their strategy plays out in reality.
Leaders must also hold team members accountable for their contributions to the execution process, providing guidance and support to ensure everyone works effectively toward the desired outcomes.
5. Mentoring and developing others
Effective leaders recognize that they cannot achieve success alone. This is why mentoring and developing others is a crucial aspect of good leadership.
By providing guidance, feedback and opportunities for growth, leaders prepare those working under them for success. When the people working for a leader succeed, so does the organization as a whole.
6. Building and sustaining a team
Mentoring individuals is only one part of building a successful organization. At some point, those individuals must work together as a team. This requires leaders to be effective at managing group dynamics.
Good leaders encourage collaboration and quickly resolve any conflicts. They do this by cultivating a sense of belonging and loyalty among team members.
7. Managing resources
There are very few areas of leadership where it isn’t beneficial to be able to do more with less. Budgets, time and human resources are limited. Without proper leadership managing these limitations effectively, an organization can become hamstrung, unable to achieve its goals with its available resources.
Effective leaders must be skilled at optimizing resource allocation. They should find innovative ways to maximize efficiency and make tough decisions when necessary to ensure the organization can achieve its goals within the given constraints.
Leadership vs. management
Leadership and management are distinct concepts, but they often overlap in practice.
However, not all managers excel at all aspects of leadership. This isn’t a problem in all organizations. If there’s sufficient leadership setting direction and ensuring everyone works toward shared goals, managers can focus on handling the more mundane tasks and day-to-day operations of running a business.
Managers typically excel with the logistical aspects of operations. These include overseeing employees, managing resources and keeping projects on track and on budget. These responsibilities are vital to running any organization. However, without effective leadership skills, managers may find it difficult to inspire or motivate their teams to perform at their best.
On the flip side, true leaders rise above administrative duties. They ignite passion in the workforce and instill a drive within their teams to perform at their best.
Leaders possess the foresight that allows them to see potential obstacles and create plans to work around them proactively. They excel at both the operational and strategic aspects of leadership. This is key, as it ensures organizations don’t just function but are well-positioned for future success.
Ultimately, the most successful organizations are those that foster a balance between strong leadership and effective management.
What are the different styles of leadership?
The ways in which leaders manage a team and create their long-term visions can vary dramatically. We call these leadership styles .
Leadership styles are sets of behaviors that drive a leader’s philosophy and approach to guiding and motivating their team. These behaviors influence how leaders manage their teams and create long-term visions.
Ideally, a leadership style must be compatible with the leader’s personality. However, effective and respected leaders understand that they must develop behaviors that positively impact their employees, their organization as a whole and the bottom line.
Unsurprisingly, there are many leadership styles out there. Each has its own set of behaviors and philosophies on how to lead.
Let’s review a few of the most recognizable leadership styles. Consider which style will help you build a strong, positive and engaged leadership practice.
Autocratic leadership
Autocrats are like the ancient leaders we discussed earlier. Here are some characteristics of autocratic leadership:
- Leaders assume power rather than building it through respect and influence.
- Leaders generally make decisions unilaterally.
- Teams have little to no input.
- Leaders assume strong control over all major decisions.
- Leaders tend to micromanage employees.
Although autocratic leadership is less common today than it once was, it can be effective in areas where quick decision-making is vital to a project’s success. Autocratic leaders often have a clear vision and are decisive in their actions, which can be beneficial in high-pressure situations or when time is of the essence.
However, this style often leads to decreased morale and creativity. The organization might experience high turnover among team members who feel their opinions and contributions are not valued.
Democratic/participative leadership
This is essentially the opposite of autocratic leadership. Democratic leaders actively encourage team members to speak up and contribute to the decision-making process. In doing so, they benefit from their team’s diverse knowledge and experiences. As they foster a more collaborative environment, they also benefit from stronger engagement and morale among team members.
However, the democratic approach can sometimes lead to slower decision-making processes. It may be unsuitable in some situations. Here are two examples:
- The situation requires swift, decisive action.
- Team members lack the necessary expertise to contribute effectively to decision-making.
Laissez-faire leadership
Laissez-faire leaders take a hands-off approach. Team members have a high degree of autonomy and minimal direct supervision. These leaders prefer to delegate decision-making responsibilities to their subordinates and trust them to complete tasks without much guidance.
This style can be effective when leading highly skilled, self-motivated individuals who thrive on independence and creativity. However, it’s unsuitable for most teams that usually require some degree of structure, guidance and coordination.
Here are some of the drawbacks of laissez-faire leadership:
- lack of direction
- decreased productivity
- potential confusion about roles and responsibilities within the team
Teams sometimes view laissez-faire leaders as “checked out” or ineffectual. As you’ll see, other styles are more suitable for high team empowerment.
Transformational leadership
Transformational leaders inspire and motivate their team members to achieve extraordinary results. They do so by appealing to their values, emotions and sense of purpose.
They create a compelling vision for the future and encourage their followers to work toward that vision with enthusiasm and commitment. They focus on nurturing each team member’s individual strengths and potential, helping them grow both personally and professionally.
This leadership style is particularly effective in driving innovation, navigating change and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. However, transformational leadership may not be suitable for all situations. It relies heavily on the leader’s charisma and ability to inspire others and may not provide the level of structure and direction some teams need.
Servant leadership
Servant leaders prioritize their team members’ needs, well-being and development above their own interests or the organization’s bottom line. They focus on empowering and nurturing their team, helping each individual reach their full potential.
Servant leaders build strong, engaged teams that consistently perform at a high level. They do this by creating a supportive environment that cultivates growth and collaboration.
Here are some of the advantages of servant leadership:
- increased employee morale
- employee loyalty
- job satisfaction
Bear in mind that servant leadership may not be ideal when:
- quick, top-down decision-making is critical, or
- the leader needs to prioritize the organization’s needs over individual team members’ preferences.
Situational leadership
Situational leaders adapt their leadership style based on their team members’ unique needs and specific challenges. They assess the development level of each individual and the demands of the situation. They then adjust their approach accordingly.
For example, they may provide more hands-on guidance and support to inexperienced team members and give more autonomy and responsibility to those with greater skills and expertise.
Situational leaders are flexible and responsive, recognizing that no single leadership style is optimal for every person or circumstance. This adaptability allows them to maximize their team’s performance and foster growth at all levels.
Leadership in different contexts
Leadership is vital in any area where people work or coexist together. Different sectors demand unique leadership strengths.
We’ll close this article by looking at a few specific sectors and the skills leaders need to excel in them.
Leadership in politics
Getting elected isn’t the be-all and end-all of being an effective political leader. Politicians who spend all their time preaching to the choir might get elected easily but fail to make positive changes.
Actual leadership in politics requires diplomacy, persuasive public speaking skills and a commitment to public service. Legislative environments can be complex and require dedication to navigate. The ability to forge alliances and effectively communicate a vision can shape national or even global landscapes.
Leadership in education
Educational leaders, such as principals and deans, have a chance to shape young minds. To do this, they need to effectively lead two groups of people: teachers and students.
They must inspire teachers to be passionate about teaching while creating an environment that’s conducive to student learning. The principal or dean’s vision in creating educational policies directly impacts educational outcomes.
Leadership in healthcare
In healthcare, leadership skills can make the difference between life and death. Hospitals and other healthcare facilities must be highly efficient.
This is especially important during emergencies when resources may be strained. Effective leaders must manage resources strategically and inspire and guide their teams to provide the best possible care under challenging and constantly evolving circumstances.
Here are some of the complex challenges healthcare leaders may face:
- coordinating large teams of healthcare professionals,
- adapting to changing regulatory requirements, and
- making critical decisions that directly impact patient outcomes.
Leadership in technology
Tech leaders are some of the most admired leaders in the modern world. Steve Jobs, Bill Gates, Elon Musk, Jeff Bezos and countless others have become household names.
In this industry, more than any other, a visionary mind is important for driving the products of the future.
Tech leaders must also be able to inspire others, anticipate future trends, identify opportunities for innovation and rally their teams to turn bold ideas into reality. They uphold a culture of creativity, experimentation and continuous learning, enabling their organizations to stay at the forefront of technological advancement.
Why is it important to understand your leadership style?
Becoming a great leader requires you to understand which philosophy you want to present to your team through your words and actions. But you don’t have to read all the theories to know this. Rather, you have to know what values you are expressing as a leader.
For example, are you an open, communicative leader who welcomes diverse opinions? Or are you a strategic leader who encourages collaboration to get things done?
Starting with this self-awareness enhances your effectiveness. Once you reflect on your various leader behaviors, see how they fit with the different styles we mentioned above. Try Googling the style and its behaviors to further define how they align with your current leadership practices.
Recognizing your leadership style gives you a better idea of how your behavior impacts others and can allow for stronger team dynamics. It also allows you to notice when you might need to adapt your style to fit different organizational needs.
You can use tools and assessments to identify your leadership style. Here are some suggestions:
- The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
- The Leadership Grid
- 360-degree feedback assessments

What are the qualities of a good leader?
Regardless of leadership style, all leaders must have a specific set of qualities. These are universally recognized values that help leaders inspire and guide others. Leaders who have these traits foster respect and loyalty among team members and make it much easier for leaders to achieve the goals they set for the organization.
Integrity and ethics
Strong ethical principles are a cornerstone of effective leadership. A leader who is unwavering in their integrity builds trust with their team. Without trust, team members are unlikely to follow the leader enthusiastically, limiting morale and reducing productivity.
Communication skills
A good leader must be able to clearly articulate the goals they have set and the broader vision they have for their company. The ability to make complex ideas understandable ensures that misunderstandings don’t sidetrack alignment with company goals.
Similarly, the ability to communicate criticism clearly and in a constructive and empathetic way increases the chance that team members improve where necessary.
Emotional intelligence
A strong leader has high emotional intelligence (EQ). High EQ enables them to understand and manage their own emotions and those of others.
A leader with high EQ is:
- self-aware,
- empathetic,
- able to regulate their emotional responses (particularly during high-stress situations),
- able to make sound decisions, and
- able to build strong relationships by addressing their team members’ emotional needs.
Emotionally intelligent leaders create a supportive environment that fosters trust, open communication and collaboration. In today’s complex work environments, leaders with strong EQ are better equipped to navigate challenges, inspire their teams and drive success.
Resilience and adaptability
Circumstances can change rapidly. When they do, the leader must remain resilient and adapt to the changes quickly.
Leaders set the tone for those who work under them. Crumbling under the pressure of setbacks and unexpected developments will bring down the whole team’s morale, which can hamper the organization’s ability to recover in a timely manner.
Visionary thinking
For the organization’s long-term health, a leader must be capable of visionary thinking. They need to have a clear sense of the direction they want to take and be able to inspire the type of innovation that will make it happen.
Visionary leaders look beyond the day-to-day, identifying and capitalizing on new opportunities that guide the organization toward success.
Leadership training and development
Not everyone is born with great leadership skills. While some individuals may possess natural leadership qualities, they can develop and refine their skills through learning and practice.
Effective leadership training programs help leaders enhance their ability to inspire people and effect change. They hone a leader’s existing skill set and introduce them to new skills that will help them improve. However, the learning journey doesn’t end there.
Leadership is like any other skill. The skills you need to be an effective leader change along with the times. Changing industry standards, technological advancements and evolving economic conditions are all examples of these changes.
A leader who is serious about staying on top of their game will find great value in continuously learning.
Leadership development programs
Leadership development programs exist in nearly every format imaginable. They include books, workshops, seminars, hands-on projects and more.
These programs often focus on developing a specific skill, like strategic thinking, team building, conflict resolution, decision-making and much more.
In addition to more formal training, current leadership may give an employee they think has high potential the opportunity to work under their mentorship.
Less formal tools, such as Pip Decks , are also available. Pip Decks is a set of card decks. Each deck focuses on a particular area of professional development, such as presenting , inspiring innovation , working with teams and much more. These step-by-step recipe cards help current and future leaders develop skills and get inspiration.
Evaluating the effectiveness of leadership training
Finding an effective leadership training program can be tricky. Outside of the workplace, you often have to rely on reviews from other participants or awards the program may have received. Tracking progress becomes more manageable when you develop an in-house leadership training program.
You can employ a combination of qualitative and quantitative measures to assess engagement, effectiveness and other crucial data. As with external programs, participant feedback can be very helpful in determining an in-house program’s effectiveness. However, a more tangible measure of the program’s impact comes from assessing leadership skills before and after the program.
Level up your career with Pip Club
Join 100,000+ leaders who get unique tips every week on storytelling, leadership and productivity - plus exclusive how-to guides, first-dibs on upcoming Pip Decks and our very best discounts.
Nearly there...
Check your inbox to confirm your email.

No spam, no email sharing - ever. Privacy Policy
One of the few newsletters I look forward to. — Dave Cunningham, Head of DesignOps @ NHS

You might find these articles useful

Active listening: meaning, techniques and examples

What is coaching leadership?
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
A New Model for Ethical Leadership
- Max H. Bazerman

Rather than try to follow a set of simple rules (“Don’t lie.” “Don’t cheat.”), leaders and managers seeking to be more ethical should focus on creating the most value for society. This utilitarian view, Bazerman argues, blends philosophical thought with business school pragmatism and can inform a wide variety of managerial decisions in areas including hiring, negotiations, and even time management. Creating value requires that managers confront and overcome the cognitive barriers that prevent them from being as ethical as they would like to be. Just as we rely on System 1 (intuitive) and System 2 (deliberative) thinking, he says, we have parallel systems for ethical decision-making. He proposes strategies for engaging the deliberative one in order to make more-ethical choices. Managers who care about the value they create can influence others throughout the organization by means of the norms and decision-making environment they create.
Create more value for society.
Idea in Brief
The challenge.
Systematic cognitive barriers can blind us to our own unethical behaviors and decisions, hampering our ability to maximize the value we create in the world.
The Solution
We have both an intuitive system for ethical decision-making and a more deliberative one; relying on the former leads to less-ethical choices. We need to consciously engage the latter.
In Practice
To make more-ethical decisions, compare options rather than evaluate them singly; disregard how decisions would affect you personally; make trade-offs that create more value for all parties in negotiations; and allocate time wisely.
Autonomous vehicles will soon take over the road. This new technology will save lives by reducing driver error, yet accidents will still happen. The cars’ computers will have to make difficult decisions: When a crash is unavoidable, should the car save its single occupant or five pedestrians? Should the car prioritize saving older people or younger people? What about a pregnant woman—should she count as two people? Automobile manufacturers need to reckon with such difficult questions in advance and program their cars to respond accordingly.
- MB Max H. Bazerman is the Jesse Isidor Straus Professor of Business Administration at Harvard Business School and the author (with Don A. Moore) of Decision Leadership: Empowering Others to Make Better Choices (Yale University Press, 2022) and Better, Not Perfect: A Realist’s Guide to Maximum Sustainable Goodness (Harper Business, 2020).
Partner Center
- View programs
- Take our program quiz
- Online BBA Degree Program
- > Specialization in Artificial Intelligence
- > Specialization in Business Analytics
- > Specialization in Digital Marketing
- > Specialization in Digital Transformation
- > Specialization in Entrepreneurship
- > Specialization in International Business
- > Specialization in Product Management
- > Specialization in Supply Chain Management
- Online BBA Top-Up Program
- Associate of Applied Science in Business (AAS)
- Online MS Degree Programs
- > MS in Data Analytics
- > MS in Digital Transformation
- > MS in Entrepreneurship
- Online MBA Degree Program
- > Specialization in Cybersecurity
- > Specialization in E-Commerce
- > Specialization in Fintech & Blockchain
- > Specialization in Sustainability
- Undergraduate certificates
- Graduate certificates
- Undergraduate courses
- Graduate courses
- Apply to Nexford
- Transfer to Nexford
- Explore Education Partners
- Scholarships
- For organizations
- Career Coalition
- Accreditation
- Our faculty
- Career services
- Academic model
- Learner stories
- Book consultation
- Careers - we're hiring!
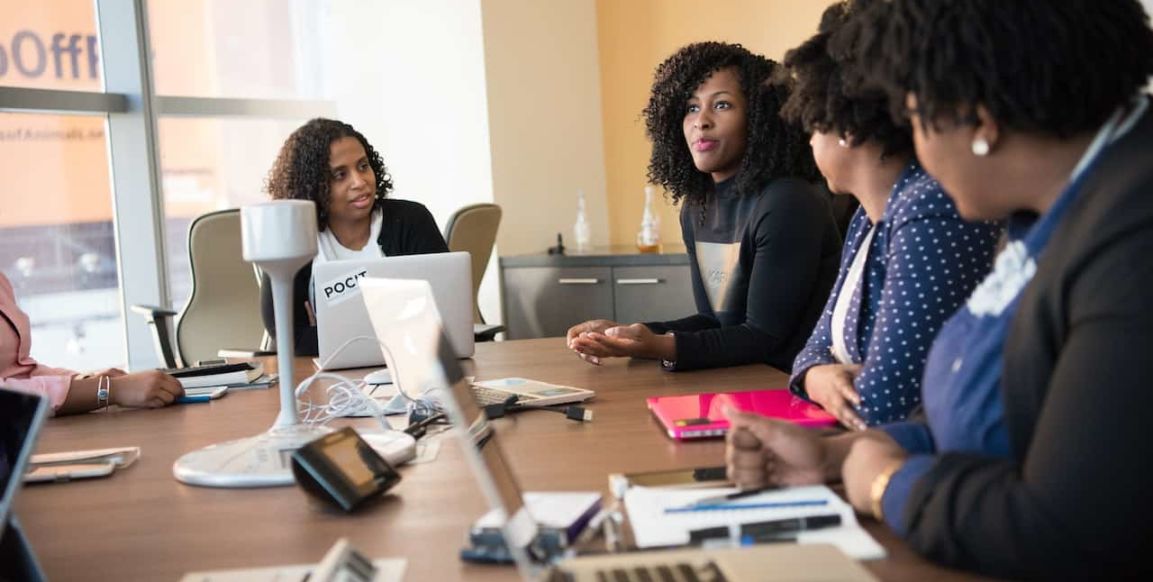

10 Leadership Conflict Management & Resolution Skills 2024
Being a leader in any organization is no easy task. Not only are leaders responsible for their actions, and the ramifications thereof, they are also responsible for the behavior and actions of their team members.
Running a team like a well-oiled machine is no easy task, as more often than not it doesn't run as well as a leader may like. There will be times that there will be conflict in the workplace, which could, if left unchecked, threaten to derail the productivity and profitability of the organization, and the morale of the team. This is where leadership conflict management and resolution skills for team leaders come to the fore.
They are qualities that set a good and a great leader apart. Success requires teamwork and clear communication. When leading a team, one of your primary responsibilities is making sure your team works well together and when it doesn't, you're able to resolve the conflict.
Often, individuals with varying personalities comprise these teams. The ability to recognize potential conflicts between individual team members and develop conflict resolution strategies to resolve them quickly is essential for projects to proceed successfully.
Leaders recognize that understanding conflict management can help them resolve issues before they occur or resolve existing conflicts in such a way that your team can still work together as a cohesive unit.

10 Leadership Conflict Management & Resolution Skills
1. communicate early and often .
To reduce misunderstandings and ambiguity, communicate your intentions and desires to not just one party, but rather every employee and as such all parties involved in the work environment. Ask what your colleagues need to work their best, and do your part to meet their needs or – at a minimum – avoid doing that which you know will cause harm. If you suspect conflict amongst team members, a leader must nip it in the bud quickly as problems will not just disappear, but rather linger if not. Failing to act as a leader when you spot a potential problem can create problems down the line.
2. Listen actively
Active listening is a proven leadership skill for conflict resolution, and involves developing a skill for listening to what is verbally and nonverbally communicated. Often, conflicts arise because two parties misunderstand or mishear what the other person is saying. Leaders know how to manage conflict and understand that active listening helps ensure that the sender and receiver understand one another and can more easily move towards a resolution. This is half the battle when it comes to being a mediator in resolving conflicts.
3. Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligence is the ability to perceive, manage, and control emotions not just in oneself, but also in others. Understanding, expressing, and effectively handling emotions are vital for conflict resolution. EI skills help improve communication and relationships and therefore is included in the vital skills for conflict resolution.
4. Problem solving
Problem-solving skills help leaders or parties in conflict recognize and address the root causes of conflicts by identifying the issues and exploring possible solutions. Leaders can apply the 5 problem-solving steps or 5 conflict management styles for conflict resolution: identify the problem, list possible solutions, evaluate the solutions, choose one solution, and implement it. People can find creative and equitable solutions to their conflicts by applying problem-solving skills.
5. Negotiation
Negotiation is trying to reach an agreement between two or more parties. It can be used to resolve disputes and every conflict and is integral to conflict resolution. Negotiation skills can be learned and practiced, and one can apply them in various situations. Therefore, it is vital to have effective negotiation skills to help achieve successful outcomes in any case. Negotiation is one of the powerful skills for conflict resolution, and it can help bring parties together to work toward a common goal.
Are you ready to take your career to the next level?
Nexford's Career Path Planner takes into account your experience and interests to provide you with a customized roadmap to success.
Receive personalized advice on the skills and qualifications you need to get ahead in areas like finance, marketing, management and entrepreneurship.
6. Observation
Observation is the key to effective conflict management. When a leader observes a conflict, one can understand it better and find solutions that work for both parties. You must also be able to keep track of your emotions and reactions to remain impartial. The skills required to be a practical observer will vary depending on the type of conflict you are dealing with.
7. Self-awareness
Self-awareness helps you understand your thoughts, feelings, and behavior, enabling you to identify the underlying causes of conflicts. Once you thoroughly understand the source of conflict, you can begin resolving it using other conflict management skills and techniques. This vital skill also helps you in identifying any biases you might have as a manager.
8. Team awareness
A conflict resolution team is especially important for effective conflict resolution, and must have the skills to work together effectively. One of the skills that are essential for conflict resolution is team awareness. This skill helps managers understand their team dynamics and how they interact with each other. In addition, it can help resolve conflict before it escalates into a severe issue. Conflict occurs through any disagreement and can cause rifts, so team awareness helps a manager to make their teams work through their differences and reach a consensus on a solution.
9. Patience
Conflict can mean different things to different people, but what is universal is that resolving conflict is a challenging but essential part of any relationship. It can be frustrating when an argument escalates quickly to the point of no return. But patience is critical to resolving conflict successfully. Effective leadership means that the best leaders need to take their time and not rush into a decision. When one is trying to resolve a conflict, it helps to circle back and understand the other person’s point of view to effectively manage things and develop a solution that works for both parties. By listening carefully and taking time to think about the situation, you can diffuse tense situations and build trust between you and the other person. All in all, patience can be one of the key skills for conflict resolution.
10. Impartiality
It is often difficult to stay impartial when you manage conflict, but in any conflict, a good manager should never take sides. Being impartial means that you can listen to both sides of the story and act accordingly. A problem at hand can't be resolved unless the historical issues are addressed. In this type of situation, it's best to separate the conflict from the people that are involved with it. Effective leaders understand that they shouldn't focus on people and their personal characteristics, instead, they should look at the problem and center their energy on finding a solution.
Looking To Further Develop Your Leadership Skills?
Leadership skills are extremely important to excel in a career. However, other soft and hard skills are also needed.
Discover how you can acquire the most in-demand skills with our free report, and open the doors to a successful career. Download the free report today!
Why not also check out our leadership and organization development course , which will give you skills need to be confident in leadership within an organization!
Conclusion
Heavy is the head that wears the crown. Being a true leader is no easy task, and nor too is managing interpersonal or interdepartmental conflict within an organization. When it comes to conflict, being cool, calm, collected, impartial and able to see the wood for the trees, are skills every leader/manager worth their salt must posses or face the consequences of lost productivity and other knock-on effects that may also affect the profitability of the company. Many leaders know that their role in solving workplace conflict is to help employees involved in the conflict to clarify their needs and guide them to a fair solution that both sides will accept. All conflict situations can lead to division, so as part of the conflict resolution, be sure to address all types of different conflict right away; however, don't rush when it comes to working out a resolution.
Whilst many say that leaders are born and not made, what is apparent is that modern leaders can be coached at a university like Nexford , that offers BBA and MBA programs, on how to spot conflict early and develop ways of managing conflict in the workplace before things spiral out of control. Nexford's Leadership Management and Teams course focuses on how to create a personal and shared vision and communicate effectively with teams, as a leader, a manager and a team member. On the course learners will develop a personal philosophy of leadership, management and membership in the global workplace through a personal inventory and assessment, as well as apply conflict management skills to a personal and organizational setting. Complimenting that, Nexford's Leadership and Organizational Development course examines individual and group interaction and helps learners gain a deeper understanding of how human behavior drives organizational behavior and development. On the course learners will apply various leadership styles, conflict management strategies, and change models to organizational situations to resolve conflict at hand.
Discover how you can acquire the most in-demand skills that can help with managing conflict within the workplace with our free report. Download the free report today!

What is conflict management?
Conflict management is an umbrella term for the way we identify and handle conflicts fairly and efficiently and is necessary for managing diverse teams. The goal is to minimize the potential negative impacts that are involved in a conflict and can arise from disagreements and increase the odds of a positive outcome.
What is a conflict management strategy?
Strategies for managing conflict are the ways a manager can engage with their employees productively when it seems like there is a risk of conflicts and arguments emerging. People naturally deal with conflicts in different ways, but some can be better than others when it comes to keeping everyone involved in the situation happy and productive. By combining your own natural conflict management style with any of the styles below, you can develop a range of responses to arguments and clashes in the workplace.
What types of conflict can occur in the workplace?
As no two days are ever the same, so too are the types of conflict that may occur in the office environment. Knowing how to spot them, and stop them early can help to resolve a conflict in double quick time. Experts maintain that there are 5 conflict types that occur in the workplace and they are leadership conflicts, work style conflicts, creative conflicts, personality conflicts, and task-based conflicts.
Learn how to develop the most in-demand skills for your future career!
Discover how you can acquire the most in-demand skills with our free report, and open the doors to a successful career.
Why is it crucial for a leader/employer to have conflict management skills?
Understanding conflict allows leaders to manage it more effectively and can provide a path to accomplishing positive outcomes. Conflict can lead to division, so every leader needs to understand that conflict management training can be an active force that will allow leaders grow healthy relationships within their organizations which can ultimately result in effective team work and productivity and make it easier to manage workplace disputes.
What does it take for a leader to resolve disputes in the workplace?
Depending on the situation, there are many skills and strategies leaders must look at for managing conflict and resolve disputes in the workplace. Leading from the front is just one and taking control of a situation before a molehill turns into a mountain. But if you had to put your finger on it, what exactly does it take for a leader to increase their resolution efforts and resolve disputes in the workplace? Experts would maintain that as a leader, even though you can initiate a constructive conversation, the effort always involves dialogue and discussion among the people involved. Conflict is inevitable, but by adopting a positive attitude toward the conflict, leaders find the best in people and in the situation, and maintain their sense of humor. Sounds easy enough, but more often than that it isn't necessarily so.
Looking to potentially take your career even further? Consider how an Online BBA or Online MBA can help you develop these skills and increase your earning potential.

Mark is a college graduate with Honours in Copywriting. He is the Content Marketing Manager at Nexford, creating engaging, thought-provoking, and action-oriented content.
Join our newsletter and be the first to receive news about our programs, events and articles.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
The Major Leadership Theories
The 8 Major Theories of Leadership
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Amy Morin, LCSW, is a psychotherapist and international bestselling author. Her books, including "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do," have been translated into more than 40 languages. Her TEDx talk, "The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong," is one of the most viewed talks of all time.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/VW-MIND-Amy-2b338105f1ee493f94d7e333e410fa76.jpg)
Karen Cilli is a fact-checker for Verywell Mind. She has an extensive background in research, with 33 years of experience as a reference librarian and educator.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_20180323_155727-dd779be58f484850bd9352fa78b81eb0.jpeg)
Verywell / Brianna Gilmartin
- "Great Man"
Contingency
- Situational
- Participative
- Relationship
What Kind of Leader Are You?
What is it that makes some people excel in leadership roles? Leadership theories seek to explain how and why certain people become leaders. Such theories often focus on the characteristics of leaders, but some attempt to identify the behaviors that people can adopt to improve their own leadership abilities in different situations.
Early debates on the psychology of leadership often suggested that such skills were simply abilities that people were born with. In other words, these theories proposed that certain people were simply "born leaders." Some more recent theories propose that possessing certain traits may help make people nature leaders, but that experience and situational variables also play a critical role.
A Closer Look at Leadership Theories
As interest in the psychology of leadership has increased over the last 100 years, a number of different leadership theories have been introduced to explain exactly how and why certain people become great leaders.
What exactly makes a great leader? Do certain personality traits make people better suited to leadership roles, or do characteristics of the situation make it more likely that certain people will take charge? When we look at the leaders around us—be it our employer or the President—we might find ourselves wondering exactly why these individuals excel in such positions.
People have long been interested in leadership throughout human history, but it has only been relatively recently that a number of formal leadership theories have emerged. Interest in leadership increased during the early part of the twentieth century.
Early leadership theories focused on what qualities distinguished between leaders and followers, while subsequent theories looked at other variables such as situational factors and skill levels. While many different leadership theories have emerged, most can be classified as one of eight major types.
"Great Man" Theories
Have you ever heard someone described as "born to lead?" According to this point of view, great leaders are simply born with the necessary internal characteristics such as charisma, confidence, intelligence, and social skills that make them natural-born leaders.
Great man theories assume that the capacity for leadership is inherent—that great leaders are born, not made. These theories often portray great leaders as heroic, mythic, and destined to rise to leadership when needed. The term "Great Man" was used because, at the time, leadership was thought of primarily as a male quality, especially in terms of military leadership.
Such theories suggest that people cannot really learn how to become strong leaders. It's either something you are born with or born without. It is very much a nature ( as opposed to nurture ) approach to explaining leadership.
Trait Theories
Similar in some ways to Great Man theories, trait theories assume that people inherit certain qualities and traits that make them better suited to leadership. Trait theories often identify a particular personality or behavioral characteristics shared by leaders. For example, traits like extroversion , self-confidence, and courage are all traits that could potentially be linked to great leaders.
If particular traits are key features of leadership, then how do we explain people who possess those qualities but are not leaders? This question is one of the difficulties in using trait theories to explain leadership.
There are plenty of people who possess the personality traits associated with leadership, yet many of these people never seek out positions of leadership. There are also people who lack some of the key traits often associated with effective leadership yet still excel at leading groups.
Contingency theories of leadership focus on particular variables related to the environment that might determine which particular style of leadership is best suited for the situation. According to this theory, no leadership style is best in all situations.
Leadership researchers White and Hodgson suggest that truly effective leadership is not just about the qualities of the leader, it is about striking the right balance between behaviors, needs, and context.
Good leaders are able to assess the needs of their followers, take stock of the situation, and then adjust their behaviors accordingly. Success depends on a number of variables including the leadership style, qualities of the followers, and aspects of the situation.
Situational Theories
Situational theories propose that leaders choose the best course of action based upon situational variables. Different styles of leadership may be more appropriate for certain types of decision-making.
For example, in a situation where the leader is the most knowledgeable and experienced member of a group, an authoritarian style might be most appropriate. In other instances where group members are skilled experts, a democratic style would be more effective.
Behavioral Theories
Behavioral theories of leadership are based upon the belief that great leaders are made, not born. Consider it the flip-side of the Great Man theories. Rooted in behaviorism , this leadership theory focuses on the actions of leaders, not on mental qualities or internal states. According to this theory, people can learn to become leaders through teaching and observation.
Participative Theories
Participative leadership theories suggest that the ideal leadership style is one that takes the input of others into account. These leaders encourage participation and contributions from group members and help group members feel more relevant and committed to the decision-making process. In participative theories, however, the leader retains the right to allow the input of others.
Management Theories
Management theories, also known as transactional theories , focus on the role of supervision, organization, and group performance. These theories base leadership on a system of rewards and punishments. Managerial theories are often used in business; when employees are successful, they are rewarded and when they fail, they are reprimanded or punished.
Relationship Theories
Relationship theories, also known as transformational theories, focus upon the connections formed between leaders and followers. Transformational leaders motivate and inspire people by helping group members see the importance and higher good of the task.
These leaders are focused on the performance of group members, but also want every person to fulfill their potential. Leaders with this style often have high ethical and moral standards.
Try our fast and free quiz to find out your usual leadership style.
There are many different ways of thinking about leadership, ranging from focusing on the personality traits of great leadership to emphasizing aspects of the situation that help determine how people lead.
Like most things, leadership is a highly multi-faceted subject and it is a mixture of many factors that help determine why some people become great leaders. Learn more about some of the things that make people strong leaders is one way of potentially improving your own skills.
Benmira S, Agboola M. Evolution of leadership theory . BMJ Leader . Published online January 8, 2021:leader-2020-000296. doi:10.1136/leader-2020-000296
Malakyan PG. Followership in leadership studies: A case of leader-follower trade approach . Journal of Leadership Studies . 2014;7(4):6-22. doi:10.1002/jls.21306
Mango E. Rethinking leadership theories . Open Journal of Leadership . 2018;07(01):57-88. doi:10.4236/ojl.2018.71005
Grant AM, Gino F, Hofmann DA. Reversing the extraverted leadership advantage: The role of employee proactivity . Academy of Management Journal. 2011;54(3):528-550. doi:10.5465/amj.2011.61968043
Khan ZA, Nawaz A, Khan IU. Leadership theories and styles: A literature review . Journal of Resources Development and Management . 2016;16:1-7.
Hodgson P, White R. Leadership, learning, ambiguity and uncertainty and their significance to dynamic organizations . In: Peterson R, Mannix E, eds. Leading and Managing People in the Dynamic Organization. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum; 2003.
Cote R. A comparison of leadership theories in an organizational environment . International Journal of Business Administration . 2017;8(5):28. doi:10.5430/ijba.v8n5p28
Amanchukwu R, Stanley G, Ololube N. A review of leadership theories, principles and styles and their relevance to educational management . Management . 2015;5(1)(2162-8416):6-14. doi:10.5923/j.mm.20150501.02
Groves KS, LaRocca MA. An empirical study of leader ethical values, transformational and transactional leadership, and follower attitudes toward corporate social responsibility . J Bus Ethics. 2011;103: 511. doi:10.1007/s10551-011-0877-y
- Gill, R. (2011). Theory and practice of leadership. London: SAGE Publications.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
83 Leadership Activities, Building Games, and Exercises

Leadership activities are associated with benefits to business, including increased performance and productivity.
However, perhaps the sign of a truly successful leader is a happy, healthy workplace. Interested in what leadership activities can do for your workplace or school? Read on.
With the activities below, there may be some overlap with activities found under certain headings – for example, activities suitable for adults may also be useful for groups, or with employees.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Leadership Exercises for free . These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or others adopt positive leadership practices and help organizations thrive.
This Article Contains:
What are leadership activities, what are they used for, 8 examples of leadership activities, 4 leadership workshop ideas, 2 activities that showcase different leadership styles, 3 situational leadership activities and scenarios, 8 games and activities for kids to learn leadership skills, 6 leadership development activities for teens and youth (pdf), 3 classroom leadership activities for students in elementary and middle school, 6 leadership activities and games for high school students, 3 activities and exercises for college students (pdf), 7 leadership games and activities for adults, 5 leadership group and team activities, 8 leadership training activities for employees, 5 leadership building exercises for managers, 11 leadership exercises for team building in the workplace, a take-home message.
Increasingly, people are assuming positions of leadership in the workplace (Cserti, 2018). However, the journey to becoming a leader is lengthy (Cserti, 2018). Leadership activities are valuable on the journey to becoming an effective leader , and also develop confidence in leadership teams (Cserti, 2018; Stepshift, 2016).
Leadership activities may be conducted on or off site, and be physical or sedentary (Stepshift, 2016). Leadership activities can either be performed by a leader in their own team, or with an external facilitator (Cserti, 2018). They may take the form of specially organized themed events, such as scavenger hunts (Stepshift, 2016). Or, they may be smaller, office-based tasks built into an ordinary workday.
For example, leadership activities could consist of meeting openers or conference break activities (Stepshift, 2016).
Leadership activities can be an effective way for individuals to practice and strengthen their leadership and team-building skills (Cserti, 2018). They can also be fun!
The structure of leadership activities is essential. It is important that the participants can relate the activity to the workplace setting (Stepshift, 2016).

The working style, principles, and values of a leader is a crucial aspect in determining the behavior within an organization (Cserti, 2018). Leadership training can help leaders become role-models (Cserti, 2018). The behavior of leaders and what they consider the “norm” determines which behaviors are enforced and those which are punished (Cserti, 2018).
Given the importance of a leader’s behavior, it is also essential that they learn skills, such as:
Communication
Leaders need to develop the ability to clearly, succinctly explain to employees everything from the goals of a company to the details of specific work-tasks (Doyle, 2019). Many components are important for effective communication , including active listening, reading body language and written communication such as emails (Doyle, 2019).
Leaders need to inspire employees. They may do this by increasing worker’s self-esteem , by recognizing effort and achievement, or by giving a worker new responsibilities to further their investment in the business (Doyle, 2019).
Leaders can achieve this by identifying the skills that workers have, and as such assign tasks to each worker based on the skills they have (Doyle, 2019).
Being positive helps develop a happy , healthy work environment, even when the workplace is busy or stressful (Doyle, 2019).
Trustworthiness
By demonstrating integrity , workers will feel at ease to approach their leader with questions or concerns (Doyle, 2019). Building trust is one of the most essential leadership skills.
Good leaders are willing to try novel solutions or to approach problems in a non-traditional way (Doyle, 2019).
Leaders are constantly on the lookout for opportunities to provide team members with information about their performance, without ‘micromanaging’ their work (Doyle, 2019).
Responsibility
A good leader accepts mistakes or failures and instead look for solutions for improvement of a situation (Doyle, 2019). This skill also includes being reflective and being open to feedback (Doyle, 2019).
A leader should strive to follow through with everything that they agree to do (Doyle, 2019). It also involves applying appropriate feedback and keeping promises (Doyle, 2019).
Flexibility
Leaders need to be able to accept changes and creatively problem-solve, as well as being open to suggestions and feedback (Doyle, 2019).
While these skills are explained in a workplace context, they can easily be applied to other leadership situations such as sports or community groups.
Now that you have more clarity as to what leadership activities are, and what they are used for, let us look at a wide selection of activities. While some of the activities and games may not immediately appear to be ‘leadership activities,’ the chosen activities might develop and promote the leadership skills outlined above.

Here are eight such activities:
- Sports Sports provide the experience of being a team member and developing leadership skills (Flavin, 2018).
- Cross-cultural experience Experiences with a different culture provide new, potentially uncomfortable situations and help develop communication skills that may not be learned elsewhere (Flavin, 2018). Overseas travel, or working with a different cultural group within your community can provide an opportunity to learn new skills, or may involve barriers that must be overcome – all teaching leadership (Flavin, 2018).
- Social groups Involvement in social activities helps potential leaders develop a well-rounded, confident personality which enhances their capacity to lead a team (Flavin, 2018).
- Internships Taking an internship position demonstrates initiative in finding opportunities to learn and seeking practical work – valuable skills in leadership (Flavin, 2018).
- Volunteering As well as showing ambition, volunteering shows that you are willing to commit yourself to something that you are passionate about (Flavin, 2018).
- Student government and organizations Specifically considering students, being involved in co-curricular organizations help individuals develop leadership (Flavin, 2018). Being involved in student government or organizations can provide opportunities to demonstrate leadership and have an impact on those around you (Flavin, 2018).
- ‘Passion projects’ Showing commitment to a passion for better communities; for example, mentoring shows that you are likely to focus on the greater good for a team (Flavin, 2018).
- ‘Teamwork’ This can be anything at all, from helping out with planning a family event or participating in a volunteer day, will demonstrate and develop leadership skills (Flavin, 2018).

Download 3 Free Positive Leadership Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or others to adopt positive leadership practices to help individuals, teams and organizations to thrive.
Download 3 Free Positive Leadership Exercises Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
- Email Address *
- Your Expertise * Your expertise Therapy Coaching Education Counseling Business Healthcare Other
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Effective leaders are aware that continuing professional and personal development is the key to ongoing success (Higgins, 2018). As such, they recognize that leadership workshops are important (Higgins, 2018). What activities can be used in such a workshop?
Here are four suggestions:
Idea 1: ‘Tallest Tower’ (from Stepshift, 2016)
Participants are provided with everyday items such as toothpicks, wooden blocks, uncooked pasta and so on. The task is to build the tallest possible free-standing structure from the materials provided. This activity is designed to encourage creative problem-solving and developing collaboration skills.
Idea 2: ‘Centre Stage’ (from Higgins, 2018)
Select four team members as volunteers. One team member plays the role of an employee who has missed meetings or been late to work in recent times. Each of the other three participants demonstrates a different style of leader (to save time, nominate the particular personality trait). Ask all participants to form a circle, and put two chairs in the middle of the circle.
After each demonstration of how to deal with the employee, ask the whole group to reflect on the different leadership approaches. For example, the group could consider what worked and what did not. Finally, to conclude this activity, ask the group to consider what the ‘ideal’ leader would do in the scenario.
Idea 3: ‘Minefield’ (from Stepshift, 2016)
This activity helps build trust and improve communication skills. It involves participants working in pairs, with one team member being blindfolded. Then, using only specified communication techniques, the pair negotiate their way around or over a ‘minefield’ of obstacles.
So, for example, the participants may be told they are only able to use commands such as the words ‘left’ or ‘right,’ ‘forwards’ or ‘backwards.’ The aim is to help the blindfolded team member to navigate the ‘minefield’.
Idea 4: ‘Magic Carpet’ (from Higgins, 2018)
Provide a small tarp or rug, which has enough room for all workshop participants to stand within its boundaries. Then, inform the group that their task is to work together to flip the rug or tarp over without any participant stepping off. If (or when) a participant steps off the teams have discussed all of the paragraphs or tarp, the team must begin again.

These are: autocratic (also known as authoritarian), delegative (also called ‘free reign)’ and democratic (which is also called participative) (Clark, 2015; Johnson-Gerard, 2017).
An autocratic leader makes decisions without first consulting others, while a delegative leader allows the staff to make the decisions (Johnson-Gerard, 2017). Finally, a democratic leader consults with the staff in making workplace decisions (Johnson-Gerard, 2017).
Here is an excellent resource for exploring different leadership styles.
The workbook also provides some helpful worksheets.
The following two activities help participants think more deeply about styles of leadership. The group should be divided into small groups of 3 – 4 participants. The participants work in groups for the first activity, and then they work individually on the second activity.
Activity One (Clark, 2015)
Provide a list of approximately 10 – 12 scenarios displaying the three different leadership styles. For example, “a new supervisor has just been put in charge of the production line. He immediately starts by telling the crew what change needs to be made. When some suggestions are made, he tells them he does not have time to consider them”.
The group then works together to figure out which leadership style is used in each scenario and to talk about whether it is effective, or if a different style could work better.
Encourage participants to think about themselves in a similar situation and their reaction to the particular leadership style.
Activity Two (Clark, 2015)
Provide participants with the statement ‘consider a time when you, or another leader, used the authoritarian (autocratic), participative (democratic) or delegative (free reign) style of leadership’.
Ask participants to reflect on the statement and make a few comments, such as: was it effective? Would a different leadership style have worked better? What were the employees’ experiences? Did they learn from the leadership style? What was it they learned? Which style is easiest to use (and why)? Alternatively, nominate the style which the participant prefers (and why).
To conclude these two activities, come together as a whole group and discuss what was learned about the three styles of leadership.
Leadership building activities – Project management training – ProjectManager
Situational leadership is when a leader is flexible in their approach and uses different leadership strategies depending on the situation (Johnson-Gerard, 2017). The following three games, from Johnson-Gerard (2017) provide an opportunity to explore situational leadership:
1. ‘Jumping Ship’
The aim of this game is for participants to reflect upon different leadership styles and come up with a list of actual workplace scenarios which would need a leader to abandon a natural leadership style for one that is more effective (i.e., to ‘jump ship’).
Each group is given three large pieces of paper. Ask the teams to write one style of leadership on each (i.e., autocratic, delegative, democratic). Then, allow the groups 45 minutes to come up with real work situations for which employing the particular leadership style would be disastrous.
Ask the groups to place the sheets of paper up on the wall, and to discuss the sheets as a team. As a whole group, review the posters.
2. ‘Who Ya Gonna Call’
Each participant begins by writing a one-paragraph description of a work situation that is not going well. Collect these, and at the top of each page, number them in consecutive order. Then, divide the participants into two teams.
Give each team half of the paragraphs. Then, ask the teams to choose the style of leadership that would be the least and the most effective in solving the problem. Have the teams note their answers on a piece of paper, being sure to identify the paragraph number on the top of each page, and their choices.
Then, ask the teams to swap paragraphs and repeat the activity.
When the teams have discussed all the paragraphs, discuss the scenarios and review the choices as a group. Where the team’s choices are different, discuss as a group.
3. ‘Ducks in a Row’
This particular activity enables participants to devise a 3-to-5 step decision-making process they can use when challenging leadership situations occur.
Ask participants to form pairs. Then, ask them to come up with the steps that an effective leader goes through in order to work out how to manage a difficult situation. After about 30 minutes, ask each pair to review the steps they have come up with for the group, and to write them on a large piece of paper.
Ask every pair to review their process, and after all the pairs have done so, have a group discussion that enables a consensus to be reached about the three to five most effective steps to take in a difficult leadership situation.

Edsys (2016) provides eight suggested activities for children to learn leadership skills:
1. ‘Create a New You’
Provide children with materials such as textas, crayons, poster/construction paper, magazines, and scissors. Then, ask them to draw themselves, using things that clearly show that the picture is theirs – such as using cut-outs of their most favorite things to do, foods they like, pets, and whatever else makes them unique.
Once the children have finished their posters, they can show their completed work to the other children – helping kids to improve their confidence to lead.
2. ‘Same or Different’
The children sit in a circle. Ask the first child to point to another child in the circle who is similar to them, either in appearance, hair-style or clothing color. Then, when the child has chosen someone, ask them to note other differences and similarities they have with the child they have chosen.
3. ‘Move the Egg’
Ask children to form groups of four or five. Then, have the children select a leader for their team. Each participant is given a spoon and an egg. The leader has the task of finding an effective way to move the eggs from one point to another. For example, one option may be for children to form a line to pass each egg along.
Another leader may suggest forgetting about the spoons altogether and merely tell their group to make a run for it. The winner of the game is the group that can get their egg safely across the finish in the most creative way.
4. ‘Lead the Blindfolded’
This game requires a large indoor or outdoor area. Divide the children into two groups and give them enough blindfolds for everyone except one member to put on. The teams are placed at opposite sides of the space. The child who is not blindfolded is required to lead their team to the other side of the designated space, using clear commands.
Ensure that each member of the team has an opportunity to lead their team. The winner is the team that sees its members successfully cross the finish line.
5. ‘Charity Support’
Help children support a charity by organizing a fundraiser. Each child can have a different task. For example, one child may select the charity, another may find a suitable space to hold the fundraising activity, and another child can collect donations.
6. ‘Planning Strategies’
Teach children to divide a large task into smaller steps. Set the children a large task, such as holding a class function. Show the children a plan that enables them to achieve the task step by step. This activity can involve a number of children sharing tasks. Suggest to the children how they may be able to improve.
7. ‘Volunteer Roles’
Volunteering plays a role in leadership. Discuss with children how they would like to help someone in need. Older children may be interested in taking a role in an organization in their community. The children should be helped to select a volunteer opportunity that gives them a chance to practice leadership and work with other children.
8. ‘A Quick Quiz’
In this task, ask students to be prepared to evaluate an experience when it is over. Then, after the experience, ask the child questions. For example, inquire “Do you remember the name of the dog we saw?”, “What was it?”, “Did you touch the dog?”, “What is the owner’s name?” and so on.
This is an excellent introduction to leadership for kids in grades 4 – 6 (children aged approximately 9 – 12 years).
The following resources are appropriate for helping teens and youth to develop leadership:
1. “Leaders are, can, and think”
This looks at what a leader is, and what their role can and should be.
2. “Who do you admire and why?”
This worksheet examines leadership role models and the qualities we see in them that we want to develop in ourselves.
3. “4 Ways leaders approach tasks: Leaders Motivation”
This handout focuses on leadership attitude.
4. “Lesson Planet”
Links to 45+ reviewed resources for teen leadership which can be accessed free by registering your details.
5. The Women’s Learning Partnership
This partnership has created a comprehensive manual for promoting leadership for teens aged 13 – 17 years. The manual outlines a number of sessions which guide leadership development activities.
6. “I Care Values Activity”
This is a fun, engaging and introspective activity . It is suitable for students aged 13 and upwards, so it can be used with older students or adults too.

Examples of such activities are:
1. ‘Just Listen’ (Edsys, 2016)
Make an agreement that you and the student(s) will refrain from talking about yourselves for a whole day. Ask them, rather, to listen to others, and if they do talk to another person, it should be about the person whom they are talking to. This game helps children to learn how important it is to focus on other people rather than themselves, which forms the basis of ‘relational leadership’.
2. Silence Classroom Leadership Game (Stapleton, 2018).
To begin the activity, the teacher divides students into two teams, and the teams move to either side of the classroom. The desks may be pushed aside to create more space. The teacher instructs the students to, for example, ‘line up according to the first letter of your surname’ or ‘arrange yourselves into age order by the month your birthday is in’. The students then follow the directions without speaking a word to one another.
Students are permitted to use hand signals, or even write instructions down on paper. The teacher’s instruction to the students is that they are not allowed to talk. The winning team is the one that completes the task successfully.
3. ‘The Cup Game’ (Tony, 2018)
Divide students into pairs and select one student to be the leader. Each team should face each other standing up, with a plastic cup in the middle. The leader calls out simple directions, such as ‘touch your knee’, ‘close one eye’ and so on.
When the leader calls out “cup” the students should try and be the first to grab the cup. The player who successfully grabs the cup should pair up with another player who also got the cup. Those without a cup sit down and watch.
Once the new teams of two have formed, the cup is put in between the players and the game begins again. This process continues until only one person is left standing – and the resulting winner becomes the new leader… and play can begin all over again.
By high school, students are more sophisticated. Here are some interesting activities for high school students to develop leadership.
1. Brainstorming for change (Stapleton, 2018)
The teacher puts students into groups of 4 or 5. The goal is for students to come up with possible solutions to social, political or economic problems. Working together, students brainstorm both small- and large-scale solutions to a given problem topic.
Once the groups have finalized their list of detailed solutions, the teacher facilitates a discussion with the whole class, and together they examine which of the identified solutions could be a viable option and why.
2. Leadership characteristics (Stapleton, 2018)
The teacher puts students into pairs or groups of three. Then, each group member shares a story about someone whom they consider to be an influential leader. After each story has been shared, students discuss the characteristics that they think made the person in the story an effective leader.
Once each student has shared a story, students compile a list of all the characteristics of an influential leader they identified. Post these characteristics on the walls around the classroom.
3. Blindfold leader game (Stapleton, 2018)
The teacher arranges the students into a single line, and comes up with a starting point and finishing point. Then, the teacher places a blindfold on every student except for the student who is at the front of the line.
The teacher tells each student to put their left hand on the left shoulder of the person in front of them. Next, the teacher says “go”. The aim is for the leader (who is not blindfolded) to walk towards the finishing point, providing instructions to students behind, who are blindfolded.
An extra challenging game sees the teacher putting obstacles in the path – the leader must direct followers on how to avoid the obstacles and successfully reach the finish line. When this goal is achieved, a different student takes a turn of being the leader.
4. Buckets and balls (Cohen, 2017)
This game aims to move all the balls from one box to another. The catch is, team members cannot use their hands or arms. In equal-sized teams, players choose one ‘handler’ per team. This is the only person who can touch the balls with their hands.
The handler must remain behind the start line throughout the game. Team members attempt to get balls from their bucket at the finish line, and get them to the team’s handler without the ball touching their hands or arms.
The handler places the balls into the empty bucket at the start line. If a team member touches the ball, they are disqualified and can no longer participate. Give teams a 5-minute time limit. All teams play at the same time, and the team that has the most balls in the handler’s bucket at the end of the game wins.
5. Team jigsaw (Cohen, 2017)
Two teams have to complete a jigsaw puzzle within a 20 – 30-minute time limit. Give each team a box containing a puzzle. At first, A body will assume that their task is to complete the puzzle. As they work on it, however, teams will realize that the puzzle is missing some of its pieces and has some additional pieces that do not fit their puzzle.
Teams then have the task to communicate with one another, and they will eventually realize that they need to work together to complete the puzzle. Teams are only allowed to exchange pieces of the puzzle one at a time.
6. ‘Sneak-a-peak’ (Cohen, 2017)
Divide participants into two teams. Build a structure out of Lego. Make it complicated, but able to be replicated. Ensure that there is sufficient Lego left to build two similar copies of the structure.
Make sure that this structure is kept out of eyesight.
A player from each team is allowed to see the structure for 10 seconds. Then, the players will return to their respective teams and have 25 seconds in which to give his/her team instruction as to how to build the structure. Then, the teams have 1 minute to build the structure.
When that minute is up, another team member takes a look at the structure for 10 seconds and has a further 25 seconds to deliver their instructions to their team.
This process continues until all the team members have had a chance to examine the structure and provide instructions. The team that successfully built the structure is the winner.

- “ The Leadership Training Activity Book ” by Lois. B. Hart and Charlotte S. Waisman (2005) contains 50 handouts for leadership activities that would be suitable for college students. Find it on Amazon .
- This resource provides helpful leadership tip sheets that are suitable for college students. Examples of tip sheets are “ten keys to effective listening” and “basic confrontation guidelines”.
- Another valuable resource that can be used to develop team-building – an aspect of leadership.
A wide range of leadership activities are suitable for adults:
1. The Marshmallow Challenge
In this activity , teams use spaghetti sticks, tape and string to construct the tallest free-standing structure. They are given one marshmallow, which must be placed at the top of the structure. Devised by Tom Wujec.
2. ‘Stand up’ (Landau, 2018)
This game is convenient in that it requires no materials. It involves two people. They sit on the floor, facing one another. They hold hands, and the soles of their feet are placed together. Then, the task is for both people to stand up at the same time. This game builds trust and teamwork, and also develops skills in problem solving and collaboration.
3. Zoom (Stepshift, 2016)
A set of randomly provided sequential pictures are given to the participants. The task requires participants to put the pictures in the correct order to recreate the story, without knowing which pictures the other participants have. This activity can be an effective way to improve communication, patience, and tolerance.
4. ‘You’re a Poet’ (Landau, 2018)
To harness creativity and reflect on leadership concepts, one activity for adults is to write a poem. This activity can be done individually or in small groups. The aim is to consider leadership in creative ways to find new perspectives.
5. ‘Leadership Pizza’ (Cserti, 2018)
This activity can help adults develop leadership. It does so by providing a self-assessment tool. People begin by identifying the skills, attitudes, and attributes that they consider being important for successful leadership. The individual then rates their own development in the defined areas. The framework can also provide a helpful tool in assisting adults in identifying their leadership development goals in a coaching session.
6. Leadership advice from your role model (Cserti, 2018)
Each participant considers a role model who they admire. They then think about a young person they know. If the young person was to ask the role model for leadership advice, what kind of advice would the role model give?
In groups, discuss and share the sort of advice identified and talk about contradicting points and how they can be reconciled. This sharing discussion may be a practical introduction to the idea of situational leadership.
7. ‘Crocodile River’ (Cserti, 2018)
This outdoor activity challenges a group to physically provide support to the group members’ behavior move from one end of a designated space to the other.
Participants are told to pretend that the whole team must cross a wide river which contains dangerous crocodiles. Magic stones (which are represented by wooden planks) provide the only supports to be used to cross the river (which has ‘banks’ that are marked out by two ropes).
These ‘stones’ only float on the water if there is constant body contact. These ‘stones’ (i.e., the wooden planks) are placed next to the ‘river bank’ – there should be one less plank than the total number of participants. As part of the game, if a participant’s hand or foot touches the ‘water’, it will be bitten off (if this happens during the challenge, the participant must hold the hand behind their back).
The facilitator then pretends to be the ‘crocodile’, keeping a close eye on the group as they attempt to cross the river. When one of the stones (the planks) is not in body contact, it is removed. When participants mistakenly touch the ground with their hands or feet, tell them that the limb has therefore been bitten off and the player must continue without using it.
This activity continues until the group succeeds in getting all group members to the other side of the ‘river’. If anyone falls in, the group is deemed to have failed, and they must begin the river crossing attempt again.
1. ‘Feedback: Start, Stop, Continue’ (Cserti, 2018)

Openness creates trust, which then promotes further openness. This activity is designed to be used by a group that has spent sufficient time together in order to have a range of shared experiences they can draw from when they are providing feedback.
Each participant takes a post-it and writes the name of the person who they are addressing on it. Then, they write on the post-it:
“To…. Something I would like you to START doing is…. something I would like you to STOP doing is…. something I would like you to CONTINUE doing is……Signed: ___________”
In groups of around 4 to 6 people, participants complete these sentences on one post-it for the other participants in their group.
If they cannot think of relevant feedback for one of the prompts (i.e., start, stop, continue), they do not need to include it. Once the group has finished writing, they provide the feedback verbally, one at a time, and afterward hand the post-it to the relevant person.
2. Round Tables (Stepshift, 2016)
Four tables are set up with different tasks. Each task has separate steps that participants can be responsible for carrying out. The group select a team member, who is only allowed to communicate and delegate tasks but not take a part in the task. Each table is timed to record how long the task takes to be completed. Round Tables improves leadership and delegation skills.
3. ‘Pass the hoop’ (Landau, 2018)
This game requires participants to stand in a circle and hold hands. One person in the group has a hula hoop around their arm. The game aims to pass the hula hoop the whole way around the circle.
As well as promoting teamwork and problem-solving, this game develops communication skills. Being able to communicate effectively is a crucial skill for any successful leader to have.
4. ‘Improv night’ (Landau, 2018)
One key responsibility of the leader of a team is to encourage team bonding. One way to facilitate bonding is improvisation. ‘Improv’ develops skills in communication – helping teams to listen and pay attention. It also builds self-awareness, self-confidence, and creativity.
Arrange the group into ‘audience’ and ‘performers’. Then, members of the audience take turns in calling out the specified location, profession, and scenario (e.g., coffeehouse, cop, and purchasing a donut). Chosen suggestions are fun and should promote creativity.
5. ‘Shape-Shifting’ (Landau, 2018)
This game requires a rope that is tied at both ends to form a loop. The loop needs to be big enough for all group members to hold onto with both hands as they stand in a circle. The group is instructed to make a chosen shape (e.g., circle, square, triangle). The group attempts to create the shape on the floor.
Progressively, ask the group to make more complex shapes – e.g., a dog, or a tree. To add another layer of difficulty, instruct the team to communicate without talking – i.e., to rely on hand gestures. Afterward, have the group reflect on their experience and discuss the importance of communication.
Leadership is an integral feature of any workplace. Here are some activities to promote leadership in employees:
1. Your favorite manager (Cserti, 2018)
To begin this activity, employees individually take the role of three different people and brainstorm the particular behaviors that each person’s most favorite and least favorite managers demonstrate, from the chosen person’s perspective. After the employees have had the chance to reflect, the participants compare their list of behaviors – in pairs, and then subsequently, in groups.
The teams then prepare a list of ‘dos and don’ts’ for developing better employee perceptions of the leader’s style.
2. Explore your values (Cserti, 2018)
The values of a leader are reflected in their organization. In this activity, each participant writes ten things that they value most in their lives, each one on a post-it. Then, ask the employees to spread the Post-its in a way in which they can see them all clearly. Then, explain to them that they will have 30 seconds to select the three Post-its that are of least importance to them.
It is essential to time strictly, so that the participants rely on their gut feelings.
Repeat the process, this time allowing participants to have 20 seconds to discard two more values. Finally, give the participants a further 20 seconds to throw another two away. Participants should have three Post-its in front of them, showing their top three important values.
Following the activity, have participants reflect individually for about 15 minutes about what was found, and then to discuss reflection questions in pairs or groups of three.
Because this activity is done quickly, participants are encouraged to follow their own intuition – rather than over-thinking and finding what they perceive to be the ‘right’ values.
3. ‘Leadership Coat of Arms’ (Cserti, 2018; Landau, 2018).
Each leader has their own values and the things that they consider valuable and important. These values guide the behavior of the leader and make up a person’s unique leadership philosophy.
This activity sees participants drawing their own ‘leadership coat of arms’ embodying their leadership philosophy.
Individuals have 10 – 15 minutes to draw their coat of arms. They can divide the coat of arms (or ‘crest’) into four sections. To fill each section, consider the categories of leadership skills, values that help influence others, recent achievements/accomplishments and what you like most about your current work.
They should be encouraged not to be overly concerned with how visually appealing their picture is but rather that it expressed what they personally believe to be important aspects of a leader.
Once the drawings are complete, the participants can show their drawings to the others in the group and explain their unique coat of arms. It is also helpful to reflect on the activity – consider which section was easiest to complete and whether your crest reflects your company’s values.
4. Communication: Coach the Builder (Goyette, 2016)
Divide employees into groups of four to seven people. Each group should be given two sets of blocks (such as Lego). Each set should have a minimum of 10 blocks.
Beforehand, you should construct a sample object (e.g., a house) from one of the sets of blocks. In each group, select a leader, a delegator, a builder and a note-taker. The note-taker watches and records the group’s behavior during the task. They take note of what appeared to be done well and how employees could improve.
The leader is given the item that you built – however, they are the only group member to see the object. Set a timer for ten minutes. To begin with, the leader describes to the delegator how the builder should build a replica of the item. However, the delegator does not see the object, and at this stage of the activity, the builder should not hear the instructions.
The delegator can speak with the leader as often as necessary during the 10 minutes. The builder attempts to build the same item that the leader can see. However, they are only relying on the delegator’s instructions. At this stage, the delegator should not see the object that the builder is constructing.
When the time is up, reveal both objects to all participants and see how closely they match. Finally, to wrap up the activity, employees can discuss what was either frustrating or easy about the process and discuss how they may do things differently in order to achieve better results.
5. Accountability (Goyette, 2016)
Begin a meeting by saying to the group – “the seating arrangement is totally wrong for today’s meeting. You have 60 seconds to improve it”. If the employees ask further questions, only repeat the instructions. While some employees may continue asking questions, others may start moving the furniture around straight away. Observe the team and what they do without giving any further information, feedback, or instructions.
After 1 minute, let the employees know to stop. Then, ask them whether the objective was achieved, and how. Discuss with employees how and why a lack of clarity makes it challenging to complete a task.
Then, discuss who asked for clarification and how they felt when the leader refused to give further details. Use this opportunity to highlight to employees how if they fail to ask questions, and when the person in charge of a project doesn’t provide the necessary clarification, the whole team is at risk of making mistakes or even not completing a task.
Finally, ask how the time pressure affected behavior. Discuss how employees may be more likely to respond to pressure, or stress, by taking action without first confirming a plan and the significant problems this approach can lead to.
6. The “what if” game (Deputy, 2018)
Present different hypothetical problematic scenarios to employees. Either individually or by providing a document that requires written answers, present situations such as “you didn’t follow the rules, and subsequently lost an important client. You have lost a lot of money for the company. How do you justify this? What is your solution?”.
The questions only need to be rough, and employees should only receive a short time with which to think of their responses. If there is a particularly challenging question, provide a time limit of five minutes.
7. ‘Silver Lining’ (Cohen, 2017)
Employees form teams of at least two people who have shared a work experience – e.g., working on a project together. One person shares an experience from working together that was negative for them.
Then, the second person reflects on the same experience but instead reflects on the positive aspects of the experience (i.e., the ‘ silver lining ’). Then this same person shares their own negative experience, and this time it is up to the other person to focus on the positive aspects of it.
Often, when people reflect on an experience, they do so with a particular perspective . By looking at the positive aspects of a ‘negative’ experience, this helps individuals shift perspectives. Furthermore, by sharing experiences, employees develop deeper relationships, and team bonding is promoted.
8. My favorite brand (Training Course Material, n.d.).
Ask employees to bring three or four printed logos/brands that they use regularly or admire most. Then, form groups of 3 – 4 people. Teams have a period of ten minutes to share and discuss their chosen logos.
Their task is to agree upon the team’s top 2 logos or brands which is their team’s choice. The team also selects a team spokesperson who will report to the bigger group about why the team chose the specific brands/logos.
Participants are encouraged to share personal experiences or stories that they had with their chosen brand. After the ten minutes elapses, each spokesperson presents the logos that the team began with as well as their two top chosen logos/brands. It is their role to explain to the group why the team voted on their top brand/logo.
1. Manager or leader? (Training Course Material, n.d.)

Small groups of managers work together to create two tables, one titled ‘leader’ and one titled ‘manager’. In each table, the group writes statements describing either management behavior or leadership behavior.
For example, the ‘manager’ table may contain statements such as “schedules work to be done” or “delegates tasks”. On the other hand, statements in the ‘leader’ table could be “motivating staff” and “creating culture”.
The purpose of this activity is to demonstrate to managers the difference between management versus leadership, and show that while ‘every leader can be a manager, not every manager can be a leader’. However, by brainstorming leadership behaviors, managers begin the process of becoming a successful leader.
2. The race of the leaders (Deputy, 2018)
This activity encourages leadership behaviors. To begin with, write a list of leadership qualities – approximately 10 – 20 statements – on a piece of paper. Describe the qualities – e.g., ‘I determine everything that happens to me’, and ‘I will not blame others for my problems’.
Read these statements out loud, and participants take a step forward if they believe a statement describes them. They must be prepared to give reasons as to why they think they possess each quality. Continue reading the statements until there is a definite ‘winner’.
3. The best team member (Training Course Material, n.d.).
Divide the group into teams of about 4 – 5 participants. Give each team a large, blank piece of paper and markers. Each group has the task to come up with as many characteristics of their ‘ideal’ team member as they can. Teams should consider what this ‘best team member ever’ would be like.
After ten minutes, the groups should examine the characteristics that they have written and work out the portion which are ‘technical’ skills and those which are ‘interpersonal’. The aim is to work out whether most of the traits can be classified as technical or interpersonal skills.
Teams usually come to realize that interpersonal skills in employees are especially critical and that these have a tremendous impact on the quality and quantity of workplace performance.
This activity can be adapted according to the setting. For example, if the focus is on leadership development, teams could discuss their ideal leader/supervisor.
4. The importance of feedback (Training Course Material, n.d.).
Divide the group into three teams. Provide each team with poster paper and markers or pens.
Team A is required to consider as many reasons as they can that would make them apprehensive to provide feedback to another person.
Team B is asked to consider what feedback can help them so, i.e., what feedback will help them accomplish.
Team C comes up with as many things as they can that would make a feedback session effective.
Each team has 15 minutes to brainstorm their ideas, then, each team can present their ideas.
Point out to Team A that the hurdles they suggested are self-imposed ideas that will lead to the manager fearing the worst. Instead, managers should be encouraged to share feedback on a more regular basis to gain the necessary experience in having such conversations. Furthermore, by having an awareness of the most effective way to prepare and deliver feedback can help a manager conquer the issues holding them back.
Point out to Team B that providing constructive feedback as needed is imperative for developing a productive work environment. A feedback discussion that is well-planned and thought out delivers an opportunity to share what you have noticed about another person’s job performance and bring about productive change.
Finally, after Team C has shared their ideas, point out that effective feedback is specific, honest, and backed up with evidence. The feedback will help others to come up with goals, make and reinforce positive changes, promote self-confidence and encourage action in the workplace.
Thank all the teams for their participation and input.
5. ‘Shark Tank’ (Deputy, 2018).
This activity is derived from a famous TV show that gives people a chance to show their entrepreneurial skills. Managers may work individually or in groups. The aim of this activity is for employees to come up with a business plan that outlines the steps of how to build a successful company from ‘startup’.
Once the managers have a plan, they can create a ‘pitch’, which should contain the brand’s name, its’ tagline (or slogan), a detailed business plan, a detailed marketing plan, financial predictions (sales, profits and market) and potential problems (competition, lack of resources).
In a role play, appoint a few chosen managers to be the ‘sharks’ (the ones who consider the projects’ merit and offer imaginary ‘investments’). The winning group, or individual, is the one who raised the most money from the ‘shark’.

World’s Largest Positive Psychology Resource
The Positive Psychology Toolkit© is a groundbreaking practitioner resource containing over 500 science-based exercises , activities, interventions, questionnaires, and assessments created by experts using the latest positive psychology research.
Updated monthly. 100% Science-based.
“The best positive psychology resource out there!” — Emiliya Zhivotovskaya , Flourishing Center CEO
1. The Human Icebreaker (Stepshift, 2016).
This is a simple activity that can alleviate tension and promote discussion and contribution. Participants devise a list of questions that relate to people generally – for example, “who is left-handed?”. Participants then discover which team members meet the question’s criteria. After 10 minutes, the participant who has the most answers wins. This activity promotes communication and helps team members build inter-personal skills.
2. ‘Office trivia’ (Cohen, 2017)
This quick activity can help as an ice-breaker and provides a flexible option for team building. Create a list of trivia questions that are related to the workplace. For example, “how many people named ‘John’ work in the accounting department?” or, “how many people work in the IT department?”. Read the questions out loud to the whole group. The employee with the most correct answers at the end is the winner.
3. Plane crash (Stepshift, 2016)
The participants imagine that they are on a plane which has crashed on a deserted island. They are allowed to select a specified number of items from around the workplace that would help the group to survive. Each chosen item is ranked in importance. The whole group must agree on their decision. This activity helps with creative problem solving and collaboration.
4. ‘Magazine story’ (Cohen, 2017)
Each team works together to come up with an imaginary cover story of a magazine, about a successful project or business achievement. The team designs the images, headlines, and come up with quotes.
5. The Human Knot (Stepshift, 2016)
Relying on cooperation, this is a good problem-solving and communication activity. Participants stand shoulder to shoulder in a circle. Then, they put their right hand in the hand of a person who stands across from them. They then put their left hand in the hand of another different person (but not someone standing directly next to them).
Participants are required to untangle the human knot without breaking the chain. If the chain is broken, the participants must start over.
6. Make your own movie (Cohen, 2017)
This is a fun activity that is suitable for both indoors and outdoors. Although it requires the necessary equipment (i.e., camera, tripod, and microphone), teams enjoy it. Employees should work in large groups (more than eight people) and divide responsibilities. Teams work together to come up with scripts for a 5 – 7-minute movie.
7. Radio Play (Cohen, 2017)
This activity can provide an alternative to making a movie. Employees work together, spending about one-hour planning and writing a play and taking a further 15 – 20 minutes to ‘perform’ it, keeping in mind that it is designed for radio.
Each participant places their chair, in no particular order, around the room. The room should be cleared of tables and other furniture. Each person should sit on their chair, pointing in a different direction. Then, request one manager to volunteer and come to the front of the room. Their task is to walk slowly back to their empty chair and sit down.
If their chair is occupied, they can move to the next empty chair available and sit on it. However, everyone else has the task of stopping the volunteer from sitting down.
Only one person at a time can stand and move. No one can make two consecutive moves. A person cannot sit on the chair that they have just left. Once the activity begins, the room is required to be silent. No one is allowed to touch the volunteer.
Give the managers 2 minutes to come up with their strategy. After every round, the participants should discuss what happened and select a new volunteer for the next round. The team is given 2 minutes preparation time each round. It is important that the volunteer’s movement is kept at a slow walk.
At the conclusion of the activity, it is beneficial for the team to discuss the activity. They may reflect upon whether they need a leader, what made planning difficult, whether everyone agreed on the plan, and what would make the task easier.
9. Back to back drawing (Cohen, 2017)
Provide vector shapes on separate pieces of paper (they can be shapes of signs, objects or merely abstract shapes). Participants sit in pairs, back-to-back. Employee A is given a sheet of paper and a pen, and employee B is provided with one of the printed shapes.
The aim of the activity is for employee A to draw the shape relying only on verbal instructions from employee B. Person B cannot only tell the other person what the shape is – he/she is only able to provide directions about how to draw it, or to describe its uses. Each team has two 2 minutes to draw the shape.
10. ‘All Aboard’ (Stepshift, 2016).
Teams use various materials, for example, pieces of wood or mats, to build a pretend ‘boat’. All the participants must stand on the ‘boat’ at once. Then, pieces of the ‘boat’ should be removed. The team should still strive to stand in the diminished space on the ‘boat’. All Aboard can promote communication, problem-solving and critical thinking.
11. Body of words (Cohen, 2017)
Participants are divided into teams of between four and eight people, and each team elects one leader. To prepare the activity, record words that have one less letter than the number of people in the team (i.e., if there are five people in the team, a suitable word could be ‘book’ which has four letters). Randomly select a word, and then the teams have the task of making the word using only their bodies.
Each team member moves and bends their body to form a letter. The team leader can direct their team.
What stands out to me from this article is the complexity of leadership. This article demonstrates that even if one is not a ‘natural’ leader, there are plenty of activities that can promote leadership skills. Even children can develop leadership, and what’s more, have fun with activities at the same time.
What do you think espouses leadership? Do you think that there are people who might tend to be leaders more than others? Perhaps you have a story about a leadership activity you have participated in or delivered – I would dearly like to hear about your experiences.
Thank you for reading.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Positive Leadership Exercises for free .
- ‘tony’ (2018). Leadership games and activities for middle school students . Retrieved from https://www.kidsactivties.net/leadership-games-activities-for-middle-school-students/
- Clark, Donald (2015). Leadership Styles Activity . Retrieved from www.nwlink.com/~donclark/leader/styles.html
- Cohen, Esther (2017). 31 Team building activities your team will actually love . Retrieved from https://www.workamajig.com/blog/team-building-activities
- Cserti, Robert (2018). 12 Effective leadership activities and games . Retrieved from https://www.sessionlab.com/blog/leadership-activities/
- Deputy (2018). 6 Impactful leadership activities to try at work . Retrieved from https://www.deputy.com/blog/6-impactful-leadership-activities-to-try-at-work
- Doyle, A. (2019). Top 10 leadership skills employers look for . Retrieved from https://www.thebalancecareers.com/top-leadership-skills-2063782
- Edsys (2016). 1 0 Activities for teachers to grow leadership skills in children . Retrieved from https://www.edsys.in/10-activities-for-teachers-to-grow-leadership-skills-in-children/
- Flavin, B. (2018). 8 Leadership Experiences You Didn’t Know You Already Have . Retrieved from https://www.rasmussen.edu/student-experience/college-life/leadership-experience-you-didnt-know-you-already-have/
- Goyette, P.(2016). 3 Leadership activities that improve employee performance at all levels . Retrieved from https://www.eaglesflight.com/blog/3-leadership-activities-that-improve-employee-performance-at-all-levels
- Higgins, R. (2018). 5 Fun and Inspirational Leadership Workshop Ideas . Retrieved from https://www.eventbrite.com.au/blog/leadership-workshop-ideas-ds00
- Johnson-Gerard, M. (2017). Situational Leadership Games . Retrieved from https://bizfluent.com/list-6762581-situational-leadership-games.html
- Landau, P. (2018). The 9 best leadership games for skill development . Retrieved from https://www.projectmanager.com/blog/the-9-best-leadership-games
- Stapleton, S. (2018). Leadership activities for High School classrooms . Retrieved from https://classroom.synonym.com/leadership-activities-high-school-classrooms-7855904.html
- Stepshift (2016). Leadership Training Activities . Retrieved from https://www.stepshift.co.nz/blog/developing-team-performance-with-senior-leadership-teams/strategic-planning-with-an-independent-facilitator/leadership-training-activities.html
- The Pennsylvania State University (2012). I can be a leader! Leadership fun for children . Retrieved from https://extension.psu.edu/programs/betterkidcare/knowledge-areas/environment-curriculum/activities/all-activities/i-can-be-a-leader-leadership-fun-for-children
- Training Course Material (n.d.). Leadership and management activities . Retrieved from https://www.trainingcoursematerial.com/free-games-activities/leadership-and-management-activities
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
This great. Thank you
Great ideas, thank you!
Thank you so much for providing such a useful list of activities to demonstrate and for such a varied target population. Innovative and attention-seeking exercises yet practical.
Thank you for posting this informative blog. keep sharing.
Too interesting for me to try all.
Great article! Having group activities Melbourne helps the team to enhance working together. I love how it brings people together and motivates employees to learn from each other.
Great activities. Thank you.
This is an excellent article for every manager and leader tn build successful leadership. Thank you.
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Theory X and Theory Y (& Z): Employee Motivation Explained
Most leaders and managers are aware of the importance of motivating their employees and creating an environment for them to perform at their best (Sennewald [...]

Contingency Theory: Mastering Leadership Flexibility
While most of us would recognize a great leader, few of us know what it takes to become one (Hill et al., 2022). And it’s [...]

Change Management: The Art of Positive Change
While change is a given for all modern organizations, it often fails due to its complexity and the resistance it faces (Dhiman & Marques, 2020). [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (49)
- Coaching & Application (58)
- Compassion (25)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (23)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (44)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (30)
- Positive Communication (22)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (19)
- Positive Parenting (16)
- Positive Psychology (34)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (18)
- Relationships (43)
- Resilience & Coping (38)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (38)
- Strengths & Virtues (32)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)

- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Smart. Open. Grounded. Inventive. Read our Ideas Made to Matter.
Which program is right for you?

Through intellectual rigor and experiential learning, this full-time, two-year MBA program develops leaders who make a difference in the world.
A rigorous, hands-on program that prepares adaptive problem solvers for premier finance careers.
A 12-month program focused on applying the tools of modern data science, optimization and machine learning to solve real-world business problems.
Earn your MBA and SM in engineering with this transformative two-year program.
Combine an international MBA with a deep dive into management science. A special opportunity for partner and affiliate schools only.
A doctoral program that produces outstanding scholars who are leading in their fields of research.
Bring a business perspective to your technical and quantitative expertise with a bachelor’s degree in management, business analytics, or finance.
A joint program for mid-career professionals that integrates engineering and systems thinking. Earn your master’s degree in engineering and management.
An interdisciplinary program that combines engineering, management, and design, leading to a master’s degree in engineering and management.
Executive Programs
A full-time MBA program for mid-career leaders eager to dedicate one year of discovery for a lifetime of impact.
This 20-month MBA program equips experienced executives to enhance their impact on their organizations and the world.
Non-degree programs for senior executives and high-potential managers.
A non-degree, customizable program for mid-career professionals.

Our method of teaching leadership stands apart.
At MIT, leadership is not a person or a position. It's a process of surfacing and solving problems. MIT students’ leadership journeys start with self-awareness and reflection. Students can then better recognize how to identify the right resources to solve complex problems at the individual, the team, and the organizational levels. They learn to seek diverse opinions, manage conflict, and reflect on their experiences.
And true to MIT’s ethos, they test and refine their personalized approach again and again. Our integrated approach combines science-based frameworks, personalized coaching, and practical application to develop highly effective leaders.
Support our work
MIT Leadership Center
Integrated Coaching for Students
Coaching is integrated into our leadership courses. Our coaches help students identify the gaps in their leadership development and set a plan to close those gaps during their time at Sloan.
The MIT Leadership Center helps students understand that their leadership development can't be found in a textbook. It's found by turning inward and learning about themselves.
MIT Sloan Students We Support
We design courses and programs that facilitate students’ leadership development during their time at Sloan, and into their future.
For MBA Students
Leadership courses and programming designed for MBA students.
For EMBA Students
Leadership courses and programming designed for EMBA students.
For MIT Sloan Fellows
Leadership courses and programming designed for SFMBA students.
MIT Sloan Executive Education Leadership Courses
Our non-degree executive courses are led by MIT Sloan faculty and provide a targeted and flexible means to futureproof your career.
explore leadership-centered Exec Ed Courses
What is decision making?

Decisions, decisions. When was the last time you struggled with a choice? Maybe it was this morning, when you decided to hit the snooze button—again. Perhaps it was at a restaurant, with a miles-long menu and the server standing over you. Or maybe it was when you left your closet in a shambles after trying on seven different outfits before a big presentation. Often, making a decision—even a seemingly simple one—can be difficult. And people will go to great lengths—and pay serious sums of money—to avoid having to make a choice. The expensive tasting menu at the restaurant, for example. Or limiting your closet choices to black turtlenecks, à la Steve Jobs.
Get to know and directly engage with senior McKinsey experts on decision making
Aaron De Smet is a senior partner in McKinsey’s New Jersey office, Eileen Kelly Rinaudo is McKinsey’s global director of advancing women executives and is based in the New York office, Frithjof Lund is a senior partner in the Oslo office, and Leigh Weiss is a senior adviser in the Boston office.
If you’ve ever wrestled with a decision at work, you’re definitely not alone. According to McKinsey research, executives spend a significant portion of their time— nearly 40 percent , on average—making decisions. Worse, they believe most of that time is poorly used. People struggle with decisions so much so that we actually get exhausted from having to decide too much, a phenomenon called decision fatigue.
But decision fatigue isn’t the only cost of ineffective decision making. According to a McKinsey survey of more than 1,200 global business leaders, inefficient decision making costs a typical Fortune 500 company 530,000 days of managers’ time each year, equivalent to about $250 million in annual wages. That’s a lot of turtlenecks.
How can business leaders ease the burden of decision making and put this time and money to better use? Read on to learn the ins and outs of smart decision making—and how to put it to work.
Learn more about our People & Organizational Performance Practice .
How can organizations untangle ineffective decision-making processes?
McKinsey research has shown that agile is the ultimate solution for many organizations looking to streamline their decision making . Agile organizations are more likely to put decision making in the right hands, are faster at reacting to (or anticipating) shifts in the business environment, and often attract top talent who prefer working at companies with greater empowerment and fewer layers of management.
For organizations looking to become more agile, it’s possible to quickly boost decision-making efficiency by categorizing the type of decision to be made and adjusting the approach accordingly. In the next section, we review three types of decision making and how to optimize the process for each.
What are three keys to faster, better decisions?
Business leaders today have access to more sophisticated data than ever before. But it hasn’t necessarily made decision making any easier. For one thing, organizational dynamics—such as unclear roles, overreliance on consensus, and death by committee—can get in the way of straightforward decision making. And more data often means more decisions to be taken, which can become too much for one person, team, or department. This can make it more difficult for leaders to cleanly delegate, which in turn can lead to a decline in productivity.
Leaders are growing increasingly frustrated with broken decision-making processes, slow deliberations, and uneven decision-making outcomes. Fewer than half of the 1,200 respondents of a McKinsey survey report that decisions are timely, and 61 percent say that at least half the time they spend making decisions is ineffective.
What’s the solution? According to McKinsey research, effective solutions center around categorizing decision types and organizing different processes to support each type. Further, each decision category should be assigned its own practice—stimulating debate, for example, or empowering employees—to yield improvements in effectiveness.
Here are the three decision categories that matter most to senior leaders, and the standout practice that makes the biggest difference for each type of decision.
- Big-bet decisions are infrequent but high risk, such as acquisitions. These decisions carry the potential to shape the future of the company, and as a result are generally made by top leaders and the board. Spurring productive debate by assigning someone to argue the case for and against a potential decision can improve big-bet decision making.
- Cross-cutting decisions, such as pricing, can be frequent and high risk. These are usually made by business unit heads, in cross-functional forums as part of a collaborative process. These types of decisions can be improved by doubling down on process refinement. The ideal process should be one that helps clarify objectives, measures, and targets.
- Delegated decisions are frequent but low risk and are handled by an individual or working team with some input from others. Delegated decision making can be improved by ensuring that the responsibility for the decision is firmly in the hands of those closest to the work. This approach also enhances engagement and accountability.
In addition, business leaders can take the following four actions to help sustain rapid decision making :
- Focus on the game-changing decisions, ones that will help an organization create value and serve its purpose.
- Convene only necessary meetings, and eliminate lengthy reports. Turn unnecessary meetings into emails, and watch productivity bloom. For necessary meetings, provide short, well-prepared prereads to aid in decision making.
- Clarify the roles of decision makers and other voices. Who has a vote, and who has a voice?
- Push decision-making authority to the front line—and tolerate mistakes.

Introducing McKinsey Explainers : Direct answers to complex questions
How can business leaders effectively delegate decision making.
Business is more complex and dynamic than ever, meaning business leaders are faced with needing to make more decisions in less time. Decision making takes up an inordinate amount of management’s time—up to 70 percent for some executives—which leads to inefficiencies and opportunity costs.
As discussed above, organizations should treat different types of decisions differently . Decisions should be classified according to their frequency, risk, and importance. Delegated decisions are the most mysterious for many organizations: they are the most frequent, and yet the least understood. Only about a quarter of survey respondents report that their organizations make high-quality and speedy delegated decisions. And yet delegated decisions, because they happen so often, can have a big impact on organizational culture.
The key to better delegated decisions is to empower employees by giving them the authority and confidence to act. That means not simply telling employees which decisions they can or can’t make; it means giving employees the tools they need to make high-quality decisions and the right level of guidance as they do so.
Here’s how to support delegation and employee empowerment:
- Ensure that your organization has a well-defined, universally understood strategy. When the strategic intent of an organization is clear, empowerment is much easier because it allows teams to pull in the same direction.
- Clearly define roles and responsibilities. At the foundation of all empowerment efforts is a clear understanding of who is responsible for what, including who has input and who doesn’t.
- Invest in capability building (and coaching) up front. To help managers spend meaningful coaching time, organizations should also invest in managers’ leadership skills.
- Build an empowerment-oriented culture. Leaders should role model mindsets that promote empowerment, and managers should build the coaching skills they want to see. Managers and employees, in particular, will need to get comfortable with failure as a necessary step to success.
- Decide when to get involved. Managers should spend effort up front to decide what is worth their focused attention. They should know when it’s appropriate to provide close guidance and when not to.
How can you guard against bias in decision making?
Cognitive bias is real. We all fall prey, no matter how we try to guard ourselves against it. And cognitive and organizational bias undermines good decision making, whether you’re choosing what to have for lunch or whether to put in a bid to acquire another company.
Here are some of the most common cognitive biases and strategies for how to avoid them:
- Confirmation bias. Often, when we already believe something, our minds seek out information to support that belief—whether or not it is actually true. Confirmation bias involves overweighting evidence that supports our belief, underweighting evidence against our belief, or even failing to search impartially for evidence in the first place. Confirmation bias is one of the most common traps organizational decision makers fall into. One famous—and painful—example of confirmation bias is when Blockbuster passed up the opportunity to buy a fledgling Netflix for $50 million in 2000. (Actually, that’s putting it politely. Netflix executives remember being “laughed out” of Blockbuster’s offices.) Fresh off the dot-com bubble burst of 2000, Blockbuster executives likely concluded that Netflix had approached them out of desperation—not that Netflix actually had a baby unicorn on its hands.
- Herd mentality. First observed by Charles Mackay in his 1841 study of crowd psychology, herd mentality happens when information that’s available to the group is determined to be more useful than privately held knowledge. Individuals buy into this bias because there’s safety in the herd. But ignoring competing viewpoints might ultimately be costly. To counter this, try a teardown exercise , wherein two teams use scenarios, advanced analytics, and role-playing to identify how a herd might react to a decision, and to ensure they can refute public perceptions.
- Sunk-cost fallacy. Executives frequently hold onto underperforming business units or projects because of emotional or legacy attachment . Equally, business leaders hate shutting projects down . This, researchers say, is due to the ingrained belief that if everyone works hard enough, anything can be turned into gold. McKinsey research indicates two techniques for understanding when to hold on and when to let go. First, change the burden of proof from why an asset should be cut to why it should be retained. Next, categorize business investments according to whether they should be grown, maintained, or disposed of—and follow clearly differentiated investment rules for each group.
- Ignoring unpleasant information. Researchers call this the “ostrich effect”—when people figuratively bury their heads in the sand , ignoring information that will make their lives more difficult. One study, for example, found that investors were more likely to check the value of their portfolios when the markets overall were rising, and less likely to do so when the markets were flat or falling. One way to help get around this is to engage in a readout process, where individuals or teams summarize discussions as they happen. This increases the likelihood that everyone leaves a meeting with the same understanding of what was said.
- Halo effect. Important personal and professional choices are frequently affected by people’s tendency to make specific judgments based on general impressions . Humans are tempted to use simple mental frames to understand complicated ideas, which means we frequently draw conclusions faster than we should. The halo effect is particularly common in hiring decisions. To avoid this bias, structured interviews can help mitigate the essentializing tendency. When candidates are measured against indicators, intuition is less likely to play a role.
For more common biases and how to beat them, check out McKinsey’s Bias Busters Collection .
Learn more about Strategy & Corporate Finance consulting at McKinsey—and check out job opportunities related to decision making if you’re interested in working at McKinsey.
Articles referenced include:
- “ Bias busters: When the crowd isn’t necessarily wise ,” McKinsey Quarterly , May 23, 2022, Eileen Kelly Rinaudo , Tim Koller , and Derek Schatz
- “ Boards and decision making ,” April 8, 2021, Aaron De Smet , Frithjof Lund , Suzanne Nimocks, and Leigh Weiss
- “ To unlock better decision making, plan better meetings ,” November 9, 2020, Aaron De Smet , Simon London, and Leigh Weiss
- “ Reimagine decision making to improve speed and quality ,” September 14, 2020, Julie Hughes , J. R. Maxwell , and Leigh Weiss
- “ For smarter decisions, empower your employees ,” September 9, 2020, Aaron De Smet , Caitlin Hewes, and Leigh Weiss
- “ Bias busters: Lifting your head from the sand ,” McKinsey Quarterly , August 18, 2020, Eileen Kelly Rinaudo
- “ Decision making in uncertain times ,” March 24, 2020, Andrea Alexander, Aaron De Smet , and Leigh Weiss
- “ Bias busters: Avoiding snap judgments ,” McKinsey Quarterly , November 6, 2019, Tim Koller , Dan Lovallo, and Phil Rosenzweig
- “ Three keys to faster, better decisions ,” McKinsey Quarterly , May 1, 2019, Aaron De Smet , Gregor Jost , and Leigh Weiss
- “ Decision making in the age of urgency ,” April 30, 2019, Iskandar Aminov, Aaron De Smet , Gregor Jost , and David Mendelsohn
- “ Bias busters: Pruning projects proactively ,” McKinsey Quarterly , February 6, 2019, Tim Koller , Dan Lovallo, and Zane Williams
- “ Decision making in your organization: Cutting through the clutter ,” McKinsey Quarterly , January 16, 2018, Aaron De Smet , Simon London, and Leigh Weiss
- “ Untangling your organization’s decision making ,” McKinsey Quarterly , June 21, 2017, Aaron De Smet , Gerald Lackey, and Leigh Weiss
- “ Are you ready to decide? ,” McKinsey Quarterly , April 1, 2015, Philip Meissner, Olivier Sibony, and Torsten Wulf.

Want to know more about decision making?
Related articles.

What is productivity?

What is the future of work?

What is leadership?
More From Forbes
The seven archetypes of leadership and how entrepreneurs become ceos.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Transitions ahead.
Ask any MBA and they’ll be able to trace the twists and turns of the corporate maturity curve with blindfolds on.
Ask them to describe the inflection points on their personal career trajectory from entrepreneurs to CEOs and you’ll be facing a fair share of blank stares.
In our efforts to raise future leaders who will carry our economy forward, we’re rightfully solving for the company and its wellbeing. In our emphasis on the analytical and transactional, we often overlook the importance of personal growth to the great detriment of those who will end up leading our corporations.
Based on what we know today, whole-person growth and self-reflection are among the most powerful drivers of success in leadership development.
The journey entrepreneurs take embodies ample opportunities for both, and all a leader that is motivated to grow needs is a North Star to navigate to.
One framework that provides just that is the Seven Archetypes of Leadership model that can help you in setting goals and self-reflecting as you grow with your company.
Leaders and Their Companies Are On A Shared Journey Of Growth
Leaders don’t simply grow; they co-evolve with their companies.
1 Dead And 26 Hurt In Overnight Shooting In Akron Ohio
Trump falsely claims he didn’t back ‘lock her up’ chants targeting clinton while warning of ‘breaking point’ if he’s jailed, suicide squad kill the justice league ends its weekly updates.
As the company grows in complexity, so does the list of desired skills it imposes on its leadership, requiring them to flex new skills and approaches at consistent intervals.
The process of reinventing oneself can be painful. No other role requires incumbents to so drastically change their behavior and competencies, often without any clear signposts or external support.
For most leaders who are nearing an inflection point, the only signal they get is a creeping feeling that the company needs something that they cannot provide.
Listening to this feeling instead of dismissing it is of paramount importance. Equally important is realizing that often the right way to address it is by becoming a kind of leader yourself.
McKinsey’s research found that CEOs taking on new roles often find success by dedicating the first six to 12 months on personal growth and organizational transitions. Listening intently to your organization, your staff as well as to your own emotions and reactions is key, and knowing which ‘ big question ’ to prioritize is essential.
Knowing what your company needs from you today is not enough, however. A leader’s task is to chart a path to the future, which necessitates knowing where the ship is heading.
While every journey of growth that a leader and their company shares is unique, there are seven archetypes that arise at key inflection points within the Seven Archetypes of Leadership model.
As you read through the below, reflect on what archetype you most strongly identify with today. Is that the leader your company most desperately needs?
If not, which archetype is your company calling for, and what do you need to do to embody it to its fullest?
The Seven Archetypes of Leadership
The bootstrapper.
At the inception of a company, most leaders take on the role of the Bootstrapper. This leader is resourceful to the point of scrappiness, willing to wear every hat required to make the company survive another week. The Bootstrapper either thrives in environments of uncertainty or quickly learns to tolerate them, and their main task is to manifest the company’s future by means of sheer determination and creativity. This is the playground of the entrepreneur and their teams filled with ninjas and rockstars.
“ At the beginning of the company you need scrappier processes and an entirely different mentality than later on ,” Mike and Aaron Hall, the co-founding brothers behind Anza Renewables noted during our discussion on the move from an entrepreneur to a CEO.
“ It’s not a binary switch that one turns on or off. There’s a leadership spectrum that starts with the bootstrapping entrepreneur and grows into different roles and requirements based on what the company needs ,” they added in retrospect of their tenure at the helm of the solar power and storage procurement facilitator.
The Salesperson
As the company begins to gain traction and the most critical life-sustaining logistics have been delegated to new hires, many leaders find themselves taking on aspects of the Salesperson archetype. This leader excels at building relationships, selling the vision, and driving revenue growth either by sheer tenacity or charismatic ability. Their main task is to connect with customers and stakeholders in order to establish a fully fleshed out product-market-fit and to carve out a decisive market presence.
The Problem Solver
The Problem Solver is a leader who is called into service at a time of great need for clarity and decisiveness. Over time, a company is bound to encounter several existential crises, each requiring strategic overhauls and on-demand pivots. Extraordinary times require extraordinary leadership, and the Problem Solver embraces their analytical, pragmatic and decisive nature to chart a path forward. For many entrepreneurs, this is the first archetype that truly pushes them to their limits. Maturity and past experiences help navigate the demands imposed on the Problem Solver, and many lean on support from their networks and external advisors.
For a growing number of leaders, this is the time when they get serious about their personal growth and mentorship. “ Being a CEO is one of toughest jobs one can have. Seeking help used to be a taboo, but thankfully we’re seeing a growing number of CEOs enter into mentorship and coaching relationships. Boards have had a big part to play in this, and we often see CEOs being encouraged to get external support for their leadership growth, particularly when being called into the role of a problem solver ,” Constantine Alexandrakis, CEO of Russell Reynolds Associates , noted during our recent discussion on the firm's new approach to leadership growth and executive mentoring.
The Stabilizer
A natural counterpart to the above is the Stabilizer. After each storm a moment of reprieve arises, which presents opportunities for triage, consolidation and compression. The Stabilizer focuses on efficiency, optimization and profitability in order to maintain what has been achieved and to set sustainable trajectories for future growth. Entrepreneurs who have nurtured their companies from Day One often find the role of the Stabilizer particularly difficult. Cutting costs, letting go of friends and rethinking runways are unsavory tasks, let alone for those who have built it all from the ground up themselves.
The Visionary
As companies mature and there are more hands on deck to weather small storms, an inflection point that calls for the Visionary opens up. This leader gazes boldly beyond the horizon and builds narratives and inroads to a long-term future. Visionaries live and die with inspiration, creativity and innovation, and they need to find ways to unshackle themselves from what moors the company down to its foundations today. Becoming a version of Steve Jobs on call isn’t easy, particularly when the day-to-day demands of the role keeps your mind fully occupied. Finding the time to detach is often harder than it seems.
The Great Facilitator
As the company continues to scale, they start calling for an archetype that is closer to a CEO than an entrepreneur. The Great Facilitator’s role is one of empowerment and efficiency, and the focus is less on personal impact and more on what your team can accomplish. These leaders focus on enablement and organizational cultures, and their main currencies are efficiency, collaboration and trust. Taking on the role of the Great Facilitator requires loosening the reins and handing over control to others, a task which many entrepreneurs might find difficult to do particularly if they are called to this role shortly after being the Bootstrapper.
“ Once the company grows to 200 people or more, the CEOs job becomes HR. You need to learn to accomplish more through others than on your own, and setting the right culture by example and leadership is the main task ,” Mike and Aaron Hall reflected.
The Change Agent
Finally, we arrive at the Change Agent. This leader is called to the helm when the other archetypes have exhausted their toolkits. Change Agents are summoned to shepherd the organization safely through large-scale transformations and processes of change that reposition and realign the company for the future. This role often entails letting go of one or more facets of the company, be it tangible departments or previous visions and operating models. As such, Change Agents benefit from the ability to focus on the company’s well being and culture instead of its mere continuity, calling for a human-centered approach and an ability to see beyond the status quo.
“ My career has been a series of S-curves ,” Debashis Chatterjee, CEO at LTIMindtree , reminisced about his career that has taken him from the helm of several large-scale companies to his current role leading a publicly listed global IT services company.
“ I’ve carried many roles and embodied the DNA of many types of leadership styles during my time. During periods of intense change I have always kept the human aspect of our work at the center. Ultimately, our clients and their experience is what matters the most. It’s my job to keep our organization poised to bring out the best of my staff so that they can focus on serving our clients .”
As with leadership overall, the Seven Archetypes of Leadership model is more art than it is science. However we categorize the different types of leadership, there is no avoiding the fact that each leader will face a series of inflection points that are as much challenges as they are invitations to grow.
Embracing these inflection points as an opportunity to evolve into a better version of yourself as a leader is what sets long-lasting successes apart from the rest.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Read more on Leadership styles or related topics Decision making and problem solving and Collaboration and teams Partner Center Latest Magazine Ascend Topics Podcasts Store The Big Idea Data ...
Whether you are a leader for a large corporation or a small business owner, here are the four most effective ways to solve problems. 1. Transparent Communication. Problem solving requires ...
Brainstorming possible solutions. Evaluating those solutions to select the best one. Implementing it. Sharpening problem-solving skills is crucial for taking the initiative, decision-making, and critical reflection. Social responsibility and personal brand are also enhanced through effective problem-solving.
Often leaders will think they are driving a problem-solving culture by insistent, or even just encouraging, team members to utilize the tools and templates of problem-solving. However, most ...
4 Problem-Solving Skills All Leaders Need. 1. Problem Framing. One key skill for any leader is framing problems in a way that makes sense for their organization. Problem framing is defined in Design Thinking and Innovation as determining the scope, context, and perspective of the problem you're trying to solve.
Much has been written about common leadership styles and how to identify the right style for you, whether it's transactional or transformational, bureaucratic or laissez-faire. But according to ...
This leadership style requires a willingness to embrace change, take risks, and be innovative since you need to adjust quickly to new situations while staying on track for overall goals. Adaptive leadership requires a combination of strategic thinking, practical problem-solving skills, and strong communication and collaboration.
Rather than dictating solutions, coaches empower leaders to discover their unique leadership style, overcome challenges, and achieve their professional and personal goals. They educate their coaches to help themselves and strengthen their own problem-solving capacities and resilience. Leadership coaching has the following positive effects: 1.
One of the most important problem-solving skills for leaders is emotional intelligence - the ability to understand emotions and empathize with others. This is crucial when recognizing employees' problems. An EY Consulting survey found that 90% of US workers believe empathetic leadership leads to greater job satisfaction.
In this episode, she outlines a five-step process for solving any problem and explains why starting with trust and ending with speed is so important for effective change leadership. As she says ...
Directive/Permissive Leadership Styles. Contemplating the central role of problem-solving in management and leadership, Jan P. Muczyk and Bernard C. Reimann of Cleveland State University offer an interesting perspective on four different leadership styles (see Figure 7) that revolve around decision-making and implementation processes.39
Therefore, problem-solving effectively means creating an environment where everyone is comfortable discussing and tackling the problem in a collaborative manner. 2. Stop Finger Pointing. When a problem arises, it can be all too easy to play the blame game. But, doing this isn't going to get you anywhere.
Once you have identified your problem-solving styles, you can use them to enhance your leadership skills and performance. To do so, it's important to recognize your strengths and weaknesses.
Leadership Styles and Their Impact on Problem-Solving. Leaders who adopt an autocratic leadership style may make decisions independently, potentially leaving their team members feeling excluded and undervalued. On the other hand, leaders who adopt a democratic leadership style involve their team members in the problem-solving process, fostering ...
2. Delegative Leadership. Often referred to as "laissez-faire," a delegative leadership style focuses on delegating initiative to team members. This is generally known as one of the least intrusive forms of leadership; this translates to "let them do.". This is therefore considered a very hand-off leadership style.
Essential Communication Skills for Leaders. 1. Ability to Adapt Your Communication Style. Different communication styles are the most frequently cited cause of poor communication, according to the Economist Intelligence Unit (pdf), and can lead to more significant issues, such as unclear priorities and increased stress.
Autocratic leaders are skilled at making decisions fast and moving forward, which is incredibly valuable when you don't have time to seek input and weigh options. 2. Democratic. A democratic ...
Here's how you can adjust your leadership style for various creative problem-solving scenarios. Powered by AI and the LinkedIn community. 1. Embrace Flexibility. Be the first to add your personal ...
Strategic leadership is when managers use their creative problem-solving skills and strategic vision to help team members and an organization achieve long-term goals. More specifically, according to Margaret Andrews, instructor of Strategic Leadership, a Professional & Executive Development program in the Harvard Division of Continuing ...
Leadership styles and problem solving - de Bono's 'Six Hats' ... While there is no agreed list of qualities that make a good leader And different leadership styles suit different situations It is widely agreed that leaders tend to have the following characteristics: Intelligence ð ...
This is why mentoring and developing others is a crucial aspect of good leadership. By providing guidance, feedback and opportunities for growth, leaders prepare those working under them for success. When the people working for a leader succeed, so does the organization as a whole. 6. Building and sustaining a team.
A New Model for Ethical Leadership. Create more value for society. Summary. Rather than try to follow a set of simple rules ("Don't lie." "Don't cheat."), leaders and managers seeking ...
Problem-solving skills help leaders or parties in conflict recognize and address the root causes of conflicts by identifying the issues and exploring possible solutions. Leaders can apply the 5 problem-solving steps or 5 conflict management styles for conflict resolution: identify the problem, list possible solutions, evaluate the solutions ...
Management Theories. Management theories, also known as transactional theories, focus on the role of supervision, organization, and group performance. These theories base leadership on a system of rewards and punishments. Managerial theories are often used in business; when employees are successful, they are rewarded and when they fail, they ...
This activity is designed to encourage creative problem-solving and developing collaboration skills. Idea 2: 'Centre Stage' (from Higgins, 2018) ... The aim of this game is for participants to reflect upon different leadership styles and come up with a list of actual workplace scenarios which would need a leader to abandon a natural ...
Problem-solving skills. Problem-solving skills are important for cross-functional teams. Effective cross-functional leaders quickly identify the source of problems and cultivate creative solutions to satisfy organisational goals. Creating a culture of problem-solving allows teams to tackle complications and drive the organisation toward success.
Integrated Coaching for Students. Coaching is integrated into our leadership courses. Our coaches help students identify the gaps in their leadership development and set a plan to close those gaps during their time at Sloan. The MIT Leadership Center helps students understand that their leadership development can't be found in a textbook.
But decision fatigue isn't the only cost of ineffective decision making. According to a McKinsey survey of more than 1,200 global business leaders, inefficient decision making costs a typical Fortune 500 company 530,000 days of managers' time each year, equivalent to about $250 million in annual wages. That's a lot of turtlenecks.
The CFO's guide to best practices in 2024. Her view of the rapidly changing role matches the findings of her company's current research report, " Secrets of Successful CFOs ," where 96% of those surveyed believe the role will change in the next three years, and 89% have seen their job evolve even from a year ago. Jacqui Cartin. Courtesy ...
Extraordinary times require extraordinary leadership, and the Problem Solver embraces their analytical, pragmatic and decisive nature to chart a path forward. For many entrepreneurs, this is the ...