Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Parts of Speech Overview

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A noun is a word that denotes a person, place, or thing. In a sentence, nouns answer the questions who and what.
In the sentence above, there are two nouns, dog and ball . A noun may be concrete (something you can touch, see, etc.), like the nouns in the example above, or a noun may be abstract, as in the sentences below.
The abstract concepts of integrity and love in the sentences above are both nouns. Nouns may also be proper.
Chicago , Thanksgiving , and November are all proper nouns, and they should be capitalized. (For more information on proper nouns and when to capitalize words, see our handout on Capital Letters .)
You may also visit our handout on Count and Noncount Nouns .
Learn how to spot verbs that act as nouns. Visit our handout on Verbals: Gerunds, Participles, and Infinitives .
A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun in a sentence.
In the sentence above, she is the pronoun. Like nouns, pronouns may be used either as subjects or as objects in a sentence.
In the example above, both she and him are pronouns; she is the subject of the sentence while him is the object. Every subject pronoun has a corresponding object form, as shown in the table below.
For more information on pronouns, go to our handout on Pronouns .
To find out what part of speech are that , which , and whom ? Visit our handout on Relative Pronouns .
Articles include a , an , and the . They precede a noun or a noun phrase in a sentence.
In example 1, the article a precedes the noun house , and a also precedes the noun phrase big porch , which consists of an adjective (big) and the noun it describes (porch). In example 2, the article the precedes the noun phrase blue sweater , in which sweater is the noun and blue, the adjective.
For more information, go to our handouts on Articles: A vs. An and How to Use Articles (a/an/the) .
An adjective is a word that modifies, or describes, a noun or pronoun. Adjectives may precede nouns, or they may appear after a form of the reflexive verb to be (am, are, is, was, etc.).
In example 1, two consecutive adjectives, red and brick , both describe the noun house. In example 2, the adjective tall appears after the reflexive verb is and describes the subject, she .
For more on adjectives, go to our handouts Adjective or Adverb and How to Use Adjectives and Adverbs .
A verb is a word that denotes action, or a state of being, in a sentence.
In example 1, rides is the verb; it describes what the subject, Beth, does. In example 2, was describes Paul’s state of being and is therefore the verb.
There may be multiple verbs in a sentence, or there may be a verb phrase consisting of a verb plus a helping verb.
In example 1, the subject she performs two actions in the sentence, turned and opened . In example 2, the verb phrase is was studying .
Some words in a sentence may look like verbs but act as something else, like a noun; these are called verbals. For more information on verbs that masquerade as other parts of speech, go to our handout on Verbals: Gerunds, Participles, and Infinitives .
To learn more about conjugating verbs, visit our handouts on Verb Tenses , Irregular Verbs , and Two-Part (Phrasal) Verbs (Idioms) .
Just as adjectives modify nouns, adverbs modify, or further describe, verbs. Adverbs may also modify adjectives. (Many, though not all, adverbs end in - ly .)
In the first example, the adverb wildly modifies the verb waved . In the second example, the adverb extremely modifies the adjective bright , which describes the noun shirt . While nouns answer the questions who and what , adverbs answer the questions how , when , why , and where .
For a more detailed discussion of adverbs, visit our handout Adjective or Adverb and become an expert.
Conjunctions
A conjunction is a word that joins two independent clauses, or sentences, together.
In the examples above, both but and so are conjunctions. They join two complete sentences with the help of a comma. And, but, for, or, nor, so, and yet can all act as conjunctions.
Prepositions
Prepositions work in combination with a noun or pronoun to create phrases that modify verbs, nouns/pronouns, or adjectives. Prepositional phrases convey a spatial, temporal, or directional meaning.
There are two prepositional phrases in the example above: up the brick wall and of the house . The first prepositional phrase is an adverbial phrase, since it modifies the verb by describing where the ivy climbed. The second phrase further modifies the noun wall (the object of the first prepositional phrase) and describes which wall the ivy climbs.
For a more detailed discussion on this part of speech and its functions, click on Prepositions .
Below is a list of prepositions in the English language:
Aboard, about, above, across, after, against, along, amid, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, into, like, near, of, off, on, onto, out, over, past, since, through, throughout, to, toward, under, underneath, until, unto, up, upon, with, within, without.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Grammar: Main Parts of Speech
Definitions and examples.
The name of something, like a person, animal, place, thing, or concept. Nouns are typically used as subjects, objects, objects of prepositions, and modifiers of other nouns.
- I = subject
- the dissertation = object
- in Chapter 4 = object of a preposition
- research = modifier
This expresses what the person, animal, place, thing, or concept does. In English, verbs follow the noun.
- It takes a good deal of dedication to complete a doctoral degree.
- She studied hard for the test.
- Writing a dissertation is difficult. (The "be" verb is also sometimes referred to as a copula or a linking verb. It links the subject, in this case "writing a dissertation," to the complement or the predicate of the sentence, in this case, "hard.")
This describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives typically come before a noun or after a stative verb, like the verb "to be."
- Diligent describes the student and appears before the noun student .
- Difficult is placed after the to be verb and describes what it is like to balance time.
Remember that adjectives in English have no plural form. The same form of the adjective is used for both singular and plural nouns.
- A different idea
- Some different ideas
- INCORRECT: some differents ideas
This gives more information about the verb and about how the action was done. Adverbs tells how, where, when, why, etc. Depending on the context, the adverb can come before or after the verb or at the beginning or end of a sentence.
- Enthusiastically describes how he completed the course and answers the how question.
- Recently modifies the verb enroll and answers the when question.
- Then describes and modifies the entire sentence. See this link on transitions for more examples of conjunctive adverbs (adverbs that join one idea to another to improve the cohesion of the writing).
This word substitutes for a noun or a noun phrase (e.g. it, she, he, they, that, those,…).
- they = applicants
- He = Smith; that = ideas; those = those ideas
This word makes the reference of the noun more specific (e.g. his, her, my, their, the, a, an, this, these, … ).
- Jones published her book in 2015.
- The book was very popular.
Preposition
This comes before a noun or a noun phrase and links it to other parts of the sentence. These are usually single words (e.g., on, at, by ,… ) but can be up to four words (e.g., as far as, in addition to, as a result of, …).
- I chose to interview teachers in the district closest to me.
- The recorder was placed next to the interviewee.
- I stopped the recording in the middle of the interview due to a low battery.
Conjunction
A word that joins two clauses. These can be coordinating (an easy way to remember this is memorizing FANBOYS = for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) or subordinating (e.g., because, although, when, …).
- The results were not significant, so the alternative hypothesis was accepted.
- Although the results seem promising, more research must be conducted in this area.
Auxiliary Verbs
Helping verbs. They are used to build up complete verbs.
- Primary auxiliary verbs (be, have, do) show the progressive, passive, perfect, and negative verb tenses .
- Modal auxiliary verbs (can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would) show a variety of meanings. They represent ability, permission, necessity, and degree of certainty. These are always followed by the simple form of the verb.
- Semimodal auxiliary verbs (e.g., be going to, ought to, have to, had better, used to, be able to,…). These are always followed by the simple form of the verb.
- primary: have investigated = present perfect tense; has not been determined = passive, perfect, negative form
- The modal could shows ability, and the verb conduct stays in its simple form; the modal may shows degree of certainty, and the verb lead stays in its simple form.
- These semimodals are followed by the simple form of the verb.
Common Endings
Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs often have unique word endings, called suffixes . Looking at the suffix can help to distinguish the word from other parts of speech and help identify the function of the word in the sentence. It is important to use the correct word form in written sentences so that readers can clearly follow the intended meaning.
Here are some common endings for the basic parts of speech. If ever in doubt, consult the dictionary for the correct word form.
Common Noun Endings
Common verb endings, common adjective endings, common adverb endings, placement and position of adjectives and adverbs, order of adjectives.
If more than one adjective is used in a sentence, they tend to occur in a certain order. In English, two or three adjectives modifying a noun tend to be the limit. However, when writing in APA, not many adjectives should be used (since APA is objective, scientific writing). If adjectives are used, the framework below can be used as guidance in adjective placement.
- Determiner (e.g., this, that, these, those, my, mine, your, yours, him, his, hers they, their, some, our, several,…) or article (a, an, the)
- Opinion, quality, or observation adjective (e.g., lovely, useful, cute, difficult, comfortable)
- Physical description
- (a) size (big, little, tall, short)
- (b) shape (circular, irregular, triangular)
- (c) age (old, new, young, adolescent)
- (d) color (red, green, yellow)
- Origin (e.g., English, Mexican, Japanese)
- Material (e.g., cotton, metal, plastic)
- Qualifier (noun used as an adjective to modify the noun that follows; i.e., campus activities, rocking chair, business suit)
- Head noun that the adjectives are describing (e.g., activities, chair, suit)
For example:
- This (1) lovely (2) new (3) wooden (4) Italian (5) rocking (6) chair (7) is in my office.
- Your (1) beautiful (2) green (3) French (4) silk (5) business (6) suit (7) has a hole in it.
Commas With Multiple Adjectives
A comma is used between two adjectives only if the adjectives belong to the same category (for example, if there are two adjectives describing color or two adjectives describing material). To test this, ask these two questions:
- Does the sentence make sense if the adjectives are written in reverse order?
- Does the sentence make sense if the word “and” is written between them?
If the answer is yes to the above questions, the adjectives are separated with a comma. Also keep in mind a comma is never used before the noun that it modifies.
- This useful big round old green English leather rocking chair is comfortable . (Note that there are no commas here because there is only one adjective from each category.)
- A lovely large yellow, red, and green oil painting was hung on the wall. (Note the commas between yellow, red, and green since these are all in the same category of color.)
Position of Adverbs
Adverbs can appear in different positions in a sentence.
- At the beginning of a sentence: Generally , teachers work more than 40 hours a week.
- After the subject, before the verb: Teachers generally work more than 40 hours a week.
- At the end of a sentence: Teachers work more than 40 hours a week, generally .
- However, an adverb is not placed between a verb and a direct object. INCORRECT: Teachers work generally more than 40 hours a week.
More Detailed Rules for the Position of Adverbs
- Adverbs that modify the whole sentence can move to different positions, such as certainly, recently, fortunately, actually, and obviously.
- Recently , I started a new job.
- I recently started a new job.
- I started a new job recently .
- Many adverbs of frequency modify the entire sentence and not just the verb, such as frequently, usually, always, sometimes, often , and seldom . These adverbs appear in the middle of the sentence, after the subject.
- INCORRECT: Frequently she gets time to herself.
- INCORRECT: She gets time to herself frequently .
- She has frequently exercised during her lunch hour. (The adverb appears after the first auxiliary verb.)
- She is frequently hanging out with old friends. (The adverb appears after the to be verb.)
- Adverbial phrases work best at the end of a sentence.
- He greeted us in a very friendly way .
- I collected data for 2 months .
Main Parts of Speech Video Playlist
Note that these videos were created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.
- Mastering the Mechanics: Nouns (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Introduction to Verbs (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Articles (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Introduction to Pronouns (video transcript)
- Mastering the Mechanics: Modifiers (video transcript)
Writing Tools: Dictionary and Thesaurus Refresher Video
Note that this video was created while APA 6 was the style guide edition in use. There may be some examples of writing that have not been updated to APA 7 guidelines.
- Writing Tools: Dictionary and Thesaurus Refresher (video transcript)
Related Resources
Knowledge Check: Main Parts of Speech
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Grammar
- Next Page: Sentence Structure and Types of Sentences
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Parts of Speech: The Ultimate Guide for Students and Teachers
This article is part of the ultimate guide to language for teachers and students. Click the buttons below to view these.
What are Parts of Speech ?
Just as a skilled bricklayer must get to grips with the trowel, brick hammer, tape measure, and spirit level, the student-writer must develop a thorough understanding of the tools of their trade too.
In English, words can be categorized according to their common syntactic function in a sentence, i.e. the job they perform.
We call these different categories Parts of Speech . Understanding the various parts of speech and how they work has several compelling benefits for our students.
Without first acquiring a firm grasp of the various parts of speech, students will struggle to fully comprehend how language works. This is essential not only for the development of their reading comprehension but their writing skills too.

Parts of speech are the core building blocks of grammar . To understand how a language works at a sentence and a whole-text level, we must first master parts of speech.
In English, we can identify eight of these individual parts of speech, and these will provide the focus for our Complete Guide to Parts of Speech .
THE EIGHT PARTS OF SPEECH (Click to jump to each section)
A complete unit on teaching figurative language.

FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE is like “SPECIAL EFFECTS FOR AUTHORS.” It is a powerful tool to create VIVID IMAGERY through words. This HUGE UNIT guides you through completely understanding FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE .
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (26 Reviews)

Often the first word a child speaks will be a noun, for example, Mum , Dad , cow , dog , etc.
Nouns are naming words, and, as most school kids can recite, they are the names of people, places, and things . But, what isn’t as widely understood by many of our students is that nouns can be further classified into more specific categories.
These categories are:
Common Nouns
Proper nouns, concrete nouns, abstract nouns, collective nouns, countable nouns, uncountable nouns.
All nouns can be classified as either common or proper .
Common nouns are the general names of people, places, and things. They are groups or classes on their own, rather than specific types of people, places, or things such as we find in proper nouns.
Common nouns can be further classified as abstract or concrete – more on this shortly!
Some examples of common nouns include:
People: teacher, author, engineer, artist, singer.
Places: country, city, town, house, garden.
Things: language, trophy, magazine, movie, book.
Proper nouns are the specific names for people, places, and things. Unlike common nouns, which are always lowercase, proper nouns are capitalized. This makes them easy to identify in a text.
Where possible, using proper nouns in place of common nouns helps bring precision to a student’s writing.
Some examples of proper nouns include:
People: Mrs Casey, J.K. Rowling, Nikola Tesla, Pablo Picasso, Billie Eilish.
Places: Australia, San Francisco, Llandovery, The White House, Gardens of Versailles.
Things: Bulgarian, The World Cup, Rolling Stone, The Lion King, The Hunger Games.
Nouns Teaching Activity: Common vs Proper Nouns
- Provide students with books suitable for their current reading level.
- Instruct students to go through a page or two and identify all the nouns.
- Ask students to sort these nouns into two lists according to whether they are common nouns or proper nouns.
As mentioned, all common and proper nouns can be further classified as either concrete or abstract .
A concrete noun is any noun that can be experienced through one of the five senses. In other words, if you can see, smell, hear, taste, or touch it, then it’s a concrete noun.
Some examples of concrete nouns include:
Abstract nouns refer to those things that can’t be experienced or identified through the five senses.
They are not physical things we can perceive but intangible concepts and ideas, qualities and states.
Some examples of abstract nouns include:
Nouns Teaching Activity: Concrete Vs. Abstract Nouns
- Provide students with a book suitable for their current reading level.
- Instruct students to go through a page or two and identify all the nouns (the lists from Practice Activity #1 may be suitable).
- This time, ask students to sort these nouns into two lists according to whether they are concrete or abstract nouns.
A collective noun is the name of a group of people or things. That is, a collective noun always refers to more than one of something.
Some examples of collective nouns include:
People: a board of directors, a team of football players, a cast of actors, a band of musicians, a class of students.
Places: a range of mountains, a suite of rooms, a union of states, a chain of islands.
Things: a bale of hay, a constellation of stars, a bag of sweets, a school of fish, a flock of seagulls.
Countable nouns are nouns that refer to things that can be counted. They come in two flavors: singular and plural .
In their singular form, countable nouns are often preceded by the article, e.g. a , an , or the .
In their plural form, countable nouns are often preceded by a number. They can also be used in conjunction with quantifiers such as a few and many .
Some examples of countable nouns include:
COUNTABLE NOUNS EXAMPLES
Also known as mass nouns, uncountable nouns are, as their name suggests, impossible to count. Abstract ideas such as bravery and compassion are uncountable, as are things like liquid and bread .
These types of nouns are always treated in the singular and usually do not have a plural form.
They can stand alone or be used in conjunction with words and phrases such as any , some , a little , a lot of , and much .
Some examples of uncountable nouns include:
UNCOUNTABLE NOUNS EXAMPLES
Nouns teaching activity: how many can you list .
- Organize students into small groups to work collaboratively.
- Challenge students to list as many countable and uncountable nouns as they can in ten minutes.
- To make things more challenging, stipulate that there must be an uncountable noun and a countable noun to gain a point.
- The winning group is the one that scores the most points.

Without a verb, there is no sentence! Verbs are the words we use to represent both internal and external actions or states of being. Without a verb, nothing happens.

There are many different types of verbs. Here, we will look at five important verb forms organised according to the jobs they perform:
Dynamic Verbs
Stative verbs, transitive verbs, intransitive verbs, auxiliary verbs.
Each verb can be classified as being either an action or a stative verb.
Dynamic or action verbs describe the physical activity performed by the subject of a sentence. This type of verb is usually the first we learn as children.
For example, run , hit , throw , hide , eat , sleep , watch , write , etc. are all dynamic verbs, as is any action performed by the body.
Let’s see a few examples in sentences:
- I jogged around the track three times.
- She will dance as if her life depends on it.
- She took a candy from the bag, unwrapped it, and popped it into her mouth.
If a verb doesn’t describe a physical activity, then it is a stative verb.
Stative verbs refer to states of being, conditions, or mental processes. Generally, we can classify stative verbs into four types:
- Emotions/Thoughts
Some examples of stative verbs include:
Senses: hurt, see, smell, taste, hear, etc.
Emotions: love, doubt, desire, remember, believe, etc.
Being: be, have, require, involve, contain, etc.
Possession: want, include, own, have, belong, etc.
Here are some stative verbs at work in sentences:
- That is one thing we can agree on.
- I remember my first day at school like it was yesterday.
- The university requires students to score at least 80%.
- She has only three remaining.
Sometimes verbs can fit into more than one category, e.g., be , have , look , see , e.g.,
- She looks beautiful. (Stative)
- I look through the telescope. (Dynamic)
Each action or stative verb can also be further classified as transitive or intransitive .
A transitive verb takes a direct object after it. The object is the noun, noun phrase, or pronoun that has something done to it by the subject of the sentence.
We see this in the most straightforward English sentences, i.e., the Subject-Verb-Object or SVO sentence.
Here are two examples to illustrate. Note: the subject of each sentence is underlined, and the transitive verbs are in bold.
- The teacher answered the student’s questions.
- She studies languages at university.
- My friend loves cabbage.
Most sentences in English employ transitive verbs.
An intransitive verb does not take a direct object after it. It is important to note that only nouns, noun phrases, and pronouns can be classed as direct objects.
Here are some examples of intransitive verbs – notice how none of these sentences has direct objects after their verbs.
- Jane’s health improved .
- The car ran smoothly.
- The school opens at 9 o’clock.
Auxiliary verbs, also known as ‘helping’ verbs, work with other verbs to affect the meaning of a sentence. They do this by combining with a main verb to alter the sentence’s tense, mood, or voice.
Auxiliary verbs will frequently use not in the negative.
There are relatively few auxiliary verbs in English. Here is a list of the main ones:
- be (am, are, is, was, were, being)
- do (did, does, doing)
- have (had, has, having)
Here are some examples of auxiliary verbs (in bold) in action alongside a main verb (underlined).
She is working as hard as she can.
- You must not eat dinner until after five o’clock.
- The parents may come to the graduation ceremony.
The Subject-Auxiliary Inversion Test
To test whether or not a verb is an auxiliary verb, you can use the Subject-Auxiliary Inversion Test .
- Take the sentence, e.g:
- Now, invert the subject and the suspected auxiliary verb to see if it creates a question.
Is she working as hard as she can?
- Can it take ‘not’ in the negative form?
She is not working as hard as she can.
- If the answer to both of these questions is yes, you have an auxiliary verb. If not, you have a full verb.
Verbs Teaching Activity: Identify the Verbs
- Instruct students to go through an appropriate text length (e.g., paragraph, page, etc.) and compile a list of verbs.
- In groups, students should then discuss and categorize each verb according to whether they think they are dynamic or stative, transitive or intransitive, and/or auxiliary verbs.
The job of an adjective is to modify a noun or a pronoun. It does this by describing, quantifying, or identifying the noun or pronoun. Adjectives help to make writing more interesting and specific. Usually, the adjective is placed before the word it modifies.

As with other parts of speech, not all adjectives are the same. There are many different types of adjectives and, in this article, we will look at:
Descriptive Adjectives
- Degrees of Adjectives
Quantitative Adjectives
Demonstrative adjectives, possessive adjectives, interrogative adjectives, proper adjectives.
Descriptive adjectives are what most students think of first when asked what an adjective is. Descriptive adjectives tell us something about the quality of the noun or pronoun in question. For this reason, they are sometimes referred to as qualitative adjectives .
Some examples of this type of adjective include:
- hard-working
In sentences, they look like this:
- The pumpkin was enormous .
- It was an impressive feat of athleticism I ever saw.
- Undoubtedly, this was an exquisite vase.
- She faced some tough competition.
Degrees of Adjectives
Descriptive adjectives have three degrees to express varying degrees of intensity and to compare one thing to another. These degrees are referred to as positive , comparative , and superlative .
The positive degree is the regular form of the descriptive adjective when no comparison is being made, e.g., strong .
The comparative degree is used to compare two people, places, or things, e.g., stronger .
There are several ways to form the comparative, methods include:
- Adding more or less before the adjective
- Adding -er to the end of one syllable adjectives
- For two-syllable adjectives ending in y , change the y to an i and add -er to the end.
The superlative degree is typically used when comparing three or more things to denote the upper or lowermost limit of a quality, e.g., strongest .
There are several ways to form the superlative, including:
- Adding most or least before the adjective
- Adding -est to the end of one syllable adjectives
- For two-syllable adjectives ending in y , change the y to an i and add -est to the end.
There are also some irregular adjectives of degree that follow no discernible pattern that must be learned off by students, e.g., good – better – best .
Let’s take a look at these degrees of adjectives in their different forms.
Let’s take a quick look at some sample sentences:
- It was a beautiful example of kindness.
Comparative
- The red is nice, but the green is prettier .
Superlative
- This mango is the most delicious fruit I have ever tastiest.
Quantitive adjectives provide information about how many or how much of the noun or pronoun.
Some quantitive adjectives include:
- She only ate half of her sandwich.
- This is my first time here.
- I would like three slices, please.
- There isn’t a single good reason to go.
- There aren’t many places like it.
- It’s too much of a good thing.
- I gave her a whole box of them.
A demonstrative adjective identifies or emphasizes a noun’s place in time or space. The most common demonstrative adjectives are this , that , these , and those .
Here are some examples of demonstrative adjectives in use:
- This boat is mine.
- That car belongs to her.
- These shoes clash with my dress.
- Those people are from Canada.
Possessive adjectives show ownership, and they are sometimes confused with possessive pronouns.
The most common possessive adjectives are my , your , his , her , our , and their .
Students need to be careful not to confuse these with possessive pronouns such as mine , yours , his (same in both contexts), hers , ours , and theirs .
Here are some examples of possessive adjectives in sentences:
- My favorite food is sushi.
- I would like to read your book when you have finished it.
- I believe her car is the red one.
- This is their way of doing things.
- Our work here is done.
Interrogative adjectives ask questions, and, in common with many types of adjectives, they are always followed by a noun. Basically, these are the question words we use to start questions. Be careful however, interrogative adjectives modify nouns. If the word after the question word is a verb, then you have an interrogative adverb on hand.
Some examples of interrogative adjectives include what , which , and whose .
Let’s take a look at these in action:
- What drink would you like?
- Which car should we take?
- Whose shoes are these?
Please note: Whose can also fit into the possessive adjective category too.
We can think of proper adjectives as the adjective form of proper nouns – remember those? They were the specific names of people, places, and things and need to be capitalized.
Let’s take the proper noun for the place America . If we wanted to make an adjective out of this proper noun to describe something, say, a car we would get ‘ American car’.
Let’s take a look at another few examples:
- Joe enjoyed his cup of Ethiopian coffee.
- My favorite plays are Shakespearean tragedies.
- No doubt about it, Fender guitars are some of the best in the world.
- The Mona Lisa is a fine example of Renaissance art.
Though it may come as a surprise to some, articles are also adjectives as, like all adjectives, they modify nouns. Articles help us determine a noun’s specification.
For example, ‘a’ and ‘an’ are used in front of an unspecific noun, while ‘the’ is used when referring to a specific noun.
Let’s see some articles as adjectives in action!
- You will find an apple inside the cupboard.
- This is a car.
- The recipe is a family secret.
Adjectives Teaching Activity: Types of Adjective Tally
- Choose a suitable book and assign an appropriate number of pages or length of a chapter for students to work with.
- Students work their way through each page, tallying up the number of each type of adjective they can identify using a table like the one below:
- Note how degrees of adjective has been split into comparative and superlative. The positive forms will take care of in the descriptive category.
- You may wish to adapt this table to exclude the easier categories to identify, such as articles and demonstrative, for example.

Traditionally, adverbs are defined as those words that modify verbs, but they do so much more than that. They can be used not only to describe how verbs are performed but also to modify adjectives, other adverbs, clauses, prepositions, or entire sentences.
With such a broad range of tasks at the feet of the humble adverb, it would be impossible to cover every possibility in this article alone. However, there are five main types of adverbs our students should familiarize themselves with. These are:
Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of time, adverbs of frequency, adverbs of place, adverbs of degree.
Adverbs of manner describe how or the way in which something happens or is done. This type of adverb is often the first type taught to students. Many of these end with -ly . Some common examples include happily , quickly , sadly , slowly , and fast .
Here are a few taster sentences employing adverbs of manner:
- She cooks Chinese food well .
- The children played happily together.
- The students worked diligently on their projects.
- Her mother taught her to cross the road carefully .
- The date went badly .
Adverbs of time indicate when something happens. Common adverbs of time include before , now , then , after , already , immediately , and soon .
Here are some sentences employing adverbs of time:
- I go to school early on Wednesdays.
- She would like to finish her studies eventually .
- Recently , Sarah moved to Bulgaria.
- I have already finished my homework.
- They have been missing training lately .
While adverbs of time deal with when something happens, adverbs of frequency are concerned with how often something happens. Common adverbs of frequency include always , frequently , sometimes , seldom , and never .
Here’s what they look like in sentences:
- Harry usually goes to bed around ten.
- Rachel rarely eats breakfast in the morning.
- Often , I’ll go home straight after school.
- I occasionally have ketchup on my pizza.
- She seldom goes out with her friends.
Adverbs of place, as the name suggests, describe where something happens or where it is. They can refer to position, distance, or direction. Some common adverbs of place include above , below , beside , inside , and anywhere .
Check out some examples in the sentences below:
- Underneath the bridge, there lived a troll.
- There were pizzerias everywhere in the city.
- We walked around the park in the pouring rain.
- If the door is open, then go inside .
- When I am older, I would like to live nearby .
Adverbs of degree express the degree to which or how much of something is done. They can also be used to describe levels of intensity. Some common adverbs of degree include barely , little , lots , completely , and entirely .
Here are some adverbs of degree at work in sentences:
- I hardly noticed her when she walked into the room.
- The little girl had almost finished her homework.
- The job was completely finished.
- I was so delighted to hear the good news.
- Jack was totally delighted to see Diane after all these years.
Adverb Teaching Activity: The Adverb Generator
- Give students a worksheet containing a table divided into five columns. Each column bears a heading of one of the different types of adverbs ( manner , time , frequency , place , degree ).
- Challenge each group to generate as many different examples of each adverb type and record these in the table.
- The winning group is the one with the most adverbs. As a bonus, or tiebreaker, task the students to make sentences with some of the adverbs.

Pronouns are used in place of a specific noun used earlier in a sentence. They are helpful when the writer wants to avoid repetitive use of a particular noun such as a name. For example, in the following sentences, the pronoun she is used to stand for the girl’s name Mary after it is used in the first sentence.
Mary loved traveling. She had been to France, Thailand, and Taiwan already, but her favorite place in the world was Australia. She had never seen an animal quite as curious-looking as the duck-billed platypus.
We also see her used in place of Mary’s in the above passage. There are many different pronouns and, in this article, we’ll take a look at:
Subject Pronouns
Object pronouns, possessive pronouns, reflexive pronouns, intensive pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, interrogative pronouns.
Subject pronouns are the type of pronoun most of us think of when we hear the term pronoun . They operate as the subject of a verb in a sentence. They are also known as personal pronouns.
The subject pronouns are:
Here are a few examples of subject pronouns doing what they do best:
- Sarah and I went to the movies last Thursday night.
- That is my pet dog. It is an Irish Wolfhound.
- My friends are coming over tonight, they will be here at seven.
- We won’t all fit into the same car.
- You have done a fantastic job with your grammar homework!
Object pronouns operate as the object of a verb, or a preposition, in a sentence. They act in the same way as object nouns but are used when it is clear what the object is.
The object pronouns are:
Here are a few examples of object pronouns in sentences:
- I told you , this is a great opportunity for you .
- Give her some more time, please.
- I told her I did not want to do it .
- That is for us .
- Catherine is the girl whom I mentioned in my letter.
Possessive pronouns indicate ownership of a noun. For example, in the sentence:
These books are mine .
The word mine stands for my books . It’s important to note that while possessive pronouns look similar to possessive adjectives, their function in a sentence is different.
The possessive pronouns are:
Let’s take a look at how these are used in sentences:
- Yours is the yellow jacket.
- I hope this ticket is mine .
- The train that leaves at midnight is theirs .
- Ours is the first house on the right.
- She is the person whose opinion I value most.
- I believe that is his .
Reflexive pronouns are used in instances where the object and the subject are the same. For example, in the sentence, she did it herself , the words she and herself refer to the same person.
The reflexive pronoun forms are:
Here are a few more examples of reflexive pronouns at work:
- I told myself that numerous times.
- He got himself a new computer with his wages.
- We will go there ourselves .
- You must do it yourself .
- The only thing to fear is fear itself .
This type of pronoun can be used to indicate emphasis. For example, when we write, I spoke to the manager herself , the point is made that we talked to the person in charge and not someone lower down the hierarchy.
Similar to the reflexive pronouns above, we can easily differentiate between reflexive and intensive pronouns by asking if the pronoun is essential to the sentence’s meaning. If it isn’t, then it is used solely for emphasis, and therefore, it’s an intensive rather than a reflexive pronoun.
Often confused with demonstrative adjectives, demonstrative pronouns can stand alone in a sentence.
When this , that , these , and those are used as demonstrative adjectives they come before the noun they modify. When these same words are used as demonstrative pronouns, they replace a noun rather than modify it.
Here are some examples of demonstrative pronouns in sentences:
- This is delicious.
- That is the most beautiful thing I have ever seen.
- These are not mine.
- Those belong to the driver.
Interrogative pronouns are used to form questions. They are the typical question words that come at the start of questions, with a question mark coming at the end. The interrogative pronouns are:
Putting them into sentences looks like this:
- What is the name of your best friend?
- Which of these is your favourite?
- Who goes to the market with you?
- Whom do you think will win?
- Whose is that?
Pronoun Teaching Activity: Pronoun Review Table
- Provide students with a review table like the one below to revise the various pronoun forms.
- They can use this table to help them produce independent sentences.
- Once students have had a chance to familiarize themselves thoroughly with each of the different types of pronouns, provide the students with the headings and ask them to complete a table from memory.
Prepositions

Prepositions provide extra information showing the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another part of a sentence. These are usually short words that come directly before nouns or pronouns, e.g., in , at , on , etc.
There are, of course, many different types of prepositions, each relating to particular types of information. In this article, we will look at:
Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of place, prepositions of movement, prepositions of manner, prepositions of measure.
- Preposition of Agency
- Preposition of Possession
- Preposition of Source
Phrasal Prepositions
It’s worth noting that several prepositional words make an appearance in several different categories of prepositions.
Prepositions of time indicate when something happens. Common prepositions of time include after , at , before , during , in , on .
Let’s see some of these at work:
- I have been here since Thursday.
- My daughter was born on the first of September.
- He went overseas during the war.
- Before you go, can you pay the bill, please?
- We will go out after work.
Sometimes students have difficulty knowing when to use in , on , or at . These little words are often confused. The table below provides helpful guidance to help students use the right preposition in the right context.
The prepositions of place, in , at , on , will be instantly recognisable as they also double as prepositions of time. Again, students can sometimes struggle a little to select the correct one for the situation they are describing. Some guidelines can be helpful.
- If something is contained or confined inside, we use in .
- If something is placed upon a surface, we use on .
- If something is located at a specific point, we use at .
A few example sentences will assist in illustrating these:
- He is in the house.
- I saw it in a magazine.
- In France, we saw many great works of art.
- Put it on the table.
- We sailed on the river.
- Hang that picture on the wall, please.
- We arrived at the airport just after 1 pm.
- I saw her at university.
- The boy stood at the window.
Usually used with verbs of motion, prepositions of movement indicate movement from one place to another. The most commonly used preposition of movement is to .
Some other prepositions of movement include:
Here’s how they look in some sample sentences:
- The ball rolled across the table towards me.
- We looked up into the sky.
- The children ran past the shop on their way home.
- Jackie ran down the road to greet her friend.
- She walked confidently through the curtains and out onto the stage.
Preposition of manner shows us how something is done or how it happens. The most common of these are by , in , like , on , with .
Let’s take a look at how they work in sentences:
- We went to school by bus.
- During the holidays, they traveled across the Rockies on foot.
- Janet went to the airport in a taxi.
- She played soccer like a professional.
- I greeted her with a smile.
Prepositions of measure are used to indicate quantities and specific units of measurement. The two most common of these are by and of .
Check out these sample sentences:
- I’m afraid we only sell that fabric by the meter.
- I will pay you by the hour.
- She only ate half of the ice cream. I ate the other half.
- A kilogram of apples is the same weight as a kilogram of feathers.
Prepositions of Agency
These prepositions indicate the causal relationship between a noun or pronoun and an action. They show the cause of something happening. The most commonly used prepositions of agency are by and with .
Here are some examples of their use in sentences:
- The Harry Potter series was written by J.K. Rowling.
- This bowl was made by a skilled craftsman.
- His heart was filled with love.
- The glass was filled with water.
Prepositions of Possession
Prepositions of possessions indicate who or what something belongs to. The most common of these are of , to , and with .
Let’s take a look:
- He is the husband of my cousin.
- He is a friend of the mayor.
- This once belonged to my grandmother.
- All these lands belong to the Ministry.
- The man with the hat is waiting outside.
- The boy with the big feet tripped and fell.
Prepositions of Source
Prepositions of source indicate where something comes from or its origins. The two most common prepositions of source are from and by . There is some crossover here with prepositions of agency.
Here are some examples:
- He comes from New Zealand.
- These oranges are from our own orchard.
- I was warmed by the heat of the fire.
- She was hugged by her husband.
- The yoghurt is of Bulgarian origin.
Phrasal prepositions are also known as compound prepositions. These are phrases of two or more words that function in the same way as prepositions. That is, they join nouns or pronouns to the rest of the sentence.
Some common phrasal prepositions are:
- According to
- For a change
- In addition to
- In spite of
- Rather than
- With the exception of
Students should be careful of overusing phrasal prepositions as some of them can seem clichéd. Frequently, it’s best to say things in as few words as is necessary.
Preposition Teaching Activity: Pr eposition Sort
- Print out a selection of the different types of prepositions on pieces of paper.
- Organize students into smaller working groups and provide each group with a set of prepositions.
- Using the headings above as categories, challenge students to sort the prepositions into the correct groups. Note that some prepositions will comfortably fit into more than one group.
- The winning group is the one to sort all prepositions correctly first.
- As an extension exercise, students can select a preposition from each category and write a sample sentence for it.
ConjunctionS

Conjunctions are used to connect words, phrases, and clauses. There are three main types of conjunction that are used to join different parts of sentences. These are:
- Coordinating
- Subordinating
- Correlative
Coordinating Conjunctions
These conjunctions are used to join sentence components that are equal such as two words, two phrases, or two clauses. In English, there are seven of these that can be memorized using the mnemonic FANBOYS:
Here are a few example sentences employing coordinating conjunctions:
- As a writer, he needed only a pen and paper.
- I would describe him as strong but lazy.
- Either we go now or not at all.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions are used to introduce dependent clauses in sentences. Basically, dependent clauses are parts of sentences that cannot stand as complete sentences on their own.
Some of the most common subordinate conjunctions are:
Let’s take a look at some example sentences:
- I will complete it by Tuesday if I have time.
- Although she likes it, she won’t buy it.
- Jack will give it to you after he finds it.
Correlative Conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions are like shoes; they come in pairs. They work together to make sentences work. Some come correlative conjunctions are:
- either / or
- neither / nor
- Not only / but also
Let’s see how some of these work together:
- If I were you, I would get either the green one or the yellow one.
- John wants neither pity nor help.
- I don’t know whether you prefer horror or romantic movies.
Conjunction Teaching Activity: Conjunction Challenge
- Organize students into Talking Pairs .
- Partner A gives Partner B an example of a conjunction.
- Partner B must state which type of conjunction it is, e.g. coordinating, subordinating, or correlative.
- Partner B must then compose a sentence that uses the conjunction correctly and tell it to Partner A.
- Partners then swap roles.
InterjectionS

Interjections focus on feelings and are generally grammatically unrelated to the rest of the sentence or sentences around them. They convey thoughts and feelings and are common in our speech. They are often followed by exclamation marks in writing. Interjections include expressions such as:
- Eww! That is so gross!
- Oh , I don’t know. I’ve never used one before.
- That’s very… err …generous of you, I suppose.
- Wow! That is fantastic news!
- Uh-Oh! I don’t have any more left.
Interjection Teaching Activity: Create a scenario
- Once students clearly understand what interjections are, brainstorm as a class as many as possible.
- Write a master list of interjections on the whiteboard.
- Partner A suggests an interjection word or phrase to Partner B.
- Partner B must create a fictional scenario where this interjection would be used appropriately.
With a good grasp of the fundamentals of parts of speech, your students will now be equipped to do a deeper dive into the wild waters of English grammar.
To learn more about the twists and turns of English grammar, check out our comprehensive article on English grammar here.
DOWNLOAD THESE 9 FREE CLASSROOM PARTS OF SPEECH POSTERS

PARTS OF SPEECH TUTORIAL VIDEOS

MORE ARTICLES RELATED TO PARTS OF SPEECH
Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Parts of speech
The 8 Parts of Speech | Definition & Examples
A part of speech (also called a word class ) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyse how words function in a sentence and improve your writing.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and interjections . Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles .
Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on how they are used. For example, ‘laugh’ can be a noun (e.g., ‘I like your laugh’) or a verb (e.g., ‘don’t laugh’).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Prepositions, conjunctions, interjections, other parts of speech, frequently asked questions.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, concept, place, or thing. Nouns can act as the subject of a sentence (i.e., the person or thing performing the action) or as the object of a verb (i.e., the person or thing affected by the action).
There are numerous types of nouns, including common nouns (used to refer to nonspecific people, concepts, places, or things), proper nouns (used to refer to specific people, concepts, places, or things), and collective nouns (used to refer to a group of people or things).
Ella lives in France .
Other types of nouns include countable and uncountable nouns , concrete nouns , abstract nouns , and gerunds .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Pronouns typically refer back to an antecedent (a previously mentioned noun) and must demonstrate correct pronoun-antecedent agreement . Like nouns, pronouns can refer to people, places, concepts, and things.
There are numerous types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (used in place of the proper name of a person), demonstrative pronouns (used to refer to specific things and indicate their relative position), and interrogative pronouns (used to introduce questions about things, people, and ownership).
That is a horrible painting!
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., ‘jump’), occurrence (e.g., ‘become’), or state of being (e.g., ‘exist’). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
Verbs can change form depending on subject (e.g., first person singular), tense (e.g., past simple ), mood (e.g., interrogative), and voice (e.g., passive voice ).
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding’-ed’ to the end of the word (or ‘-d’ if the word already ends in ‘e’). Irregular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participles are formed in some other way.
‘I’ve already checked twice’.
‘I heard that you used to sing ‘.
Other types of verbs include auxiliary verbs , linking verbs , modal verbs , and phrasal verbs .
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive , appearing before a noun (e.g., ‘a red hat’), or predicative , appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like ‘to be’ (e.g., ‘the hat is red ‘).
Adjectives can also have a comparative function. Comparative adjectives compare two or more things. Superlative adjectives describe something as having the most or least of a specific characteristic.
Other types of adjectives include coordinate adjectives , participial adjectives , and denominal adjectives .
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding ‘-ly’ to the end of an adjective (e.g., ‘slow’ becomes ‘slowly’), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
There are numerous types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner (used to describe how something occurs), adverbs of degree (used to indicate extent or degree), and adverbs of place (used to describe the location of an action or event).
Talia writes quite quickly.
Other types of adverbs include adverbs of frequency , adverbs of purpose , focusing adverbs , and adverbial phrases .
A preposition is a word (e.g., ‘at’) or phrase (e.g., ‘on top of’) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time , place , and direction .
I left the cup on the kitchen counter.
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
The main types of conjunctions are coordinating conjunctions (used to connect items that are grammatically equal), subordinating conjunctions (used to introduce a dependent clause), and correlative conjunctions (used in pairs to join grammatically equal parts of a sentence).
You can choose what movie we watch because I chose the last time.
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of interjections include volitive interjections (used to make a demand or request), emotive interjections (used to express a feeling or reaction), cognitive interjections (used to indicate thoughts), and greetings and parting words (used at the beginning and end of a conversation).
Ouch ! I hurt my arm.
I’m, um , not sure.
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
Determiners
A determiner is a word that describes a noun by indicating quantity, possession, or relative position.
Common types of determiners include demonstrative determiners (used to indicate the relative position of a noun), possessive determiners (used to describe ownership), and quantifiers (used to indicate the quantity of a noun).
My brother is selling his old car.
Other types of determiners include distributive determiners , determiners of difference , and numbers .
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general.
- The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., ‘the door’, ‘the energy’, ‘the mountains’).
- The indefinite articles a and an refer to general or unspecific nouns. The indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns (e.g., ‘a poster’, ‘an engine’).
There’s a concert this weekend.
A is an indefinite article (along with an ). While articles can be classed as their own part of speech, they’re also considered a type of determiner .
The indefinite articles are used to introduce nonspecific countable nouns (e.g., ‘a dog’, ‘an island’).
In is primarily classed as a preposition, but it can be classed as various other parts of speech, depending on how it is used:
- Preposition (e.g., ‘ in the field’)
- Noun (e.g., ‘I have an in with that company’)
- Adjective (e.g., ‘Tim is part of the in crowd’)
- Adverb (e.g., ‘Will you be in this evening?’)
As a part of speech, and is classed as a conjunction . Specifically, it’s a coordinating conjunction .
And can be used to connect grammatically equal parts of a sentence, such as two nouns (e.g., ‘a cup and plate’), or two adjectives (e.g., ‘strong and smart’). And can also be used to connect phrases and clauses.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, what is a collective noun | examples & definition.
- What Is an Adjective? | Definition, Types & Examples
More interesting articles
- Definite and Indefinite Articles | When to Use 'The', 'A' or 'An'
- Ending a Sentence with a Preposition | Examples & Tips
- Using Conjunctions | Definition, Rules & Examples
- What Are Prepositions? | List, Examples & How to Use
- What Is a Determiner? | Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Interjection? | Examples, Definition & Types

paper-free learning
- conjunctions
- determiners
- interjections
- prepositions
- affect vs effect
- its vs it's
- your vs you're
- which vs that
- who vs whom
- who's vs whose
- averse vs adverse
- 250+ more...
- apostrophes
- quotation marks
- lots more...
- common writing errors
- FAQs by writers
- awkward plurals
- ESL vocabulary lists
- all our grammar videos
- idioms and proverbs
- Latin terms
- collective nouns for animals
- tattoo fails
- vocabulary categories
- most common verbs
- top 10 irregular verbs
- top 10 regular verbs
- top 10 spelling rules
- improve spelling
- common misspellings
- role-play scenarios
- favo(u)rite word lists
- multiple-choice test
- Tetris game
- grammar-themed memory game
- 100s more...
Parts of Speech
What are the parts of speech, a formal definition.
Table of Contents
The Part of Speech Is Determined by the Word's Function
Are there 8 or 9 parts of speech, the nine parts of speech, (1) adjective, (3) conjunction, (4) determiner, (5) interjection, (7) preposition, (8) pronoun, why the parts of speech are important, video lesson.

- You need to dig a well . (noun)
- You look well . (adjective)
- You dance well . (adverb)
- Well , I agree. (interjection)
- My eyes will well up. (verb)
- red, happy, enormous
- Ask the boy in the red jumper.
- I live in a happy place.
- I caught a fish this morning! I mean an enormous one.
- happily, loosely, often
- They skipped happily to the counter.
- Tie the knot loosely so they can escape.
- I often walk to work.
- It is an intriguingly magic setting.
- He plays the piano extremely well.
- and, or, but
- it is a large and important city.
- Shall we run to the hills or hide in the bushes?
- I know you are lying, but I cannot prove it.
- my, those, two, many
- My dog is fine with those cats.
- There are two dogs but many cats.
- ouch, oops, eek
- Ouch , that hurt.
- Oops , it's broken.
- Eek! A mouse just ran past my foot!
- leader, town, apple
- Take me to your leader .
- I will see you in town later.
- An apple fell on his head .
- in, near, on, with
- Sarah is hiding in the box.
- I live near the train station.
- Put your hands on your head.
- She yelled with enthusiasm.
- she, we, they, that
- Joanne is smart. She is also funny.
- Our team has studied the evidence. We know the truth.
- Jack and Jill went up the hill, but they never returned.
- That is clever!
- work, be, write, exist
- Tony works down the pit now. He was unemployed.
- I will write a song for you.
- I think aliens exist .
Are you a visual learner? Do you prefer video to text? Here is a list of all our grammar videos .
Video for Each Part of Speech
The Most Important Writing Issues
The top issue related to adjectives, the top issue related to adverbs.
- Extremely annoyed, she stared menacingly at her rival.
- Infuriated, she glared at her rival.
The Top Issue Related to Conjunctions
- Burger, Fries, and a shake
- Fish, chips and peas
The Top Issue Related to Determiners
The Top Issue Related to Interjections
The top issue related to nouns, the top issue related to prepositions, the top issue related to pronouns, the top issue related to verbs.
- Crack the parts of speech to help with learning a foreign language or to take your writing to the next level.

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
Learning Resources
more actions:
This test is printable and sendable
Help Us Improve Grammar Monster
- Do you disagree with something on this page?
- Did you spot a typo?
Find Us Quicker!
- When using a search engine (e.g., Google, Bing), you will find Grammar Monster quicker if you add #gm to your search term.
You might also like...
Share This Page

If you like Grammar Monster (or this page in particular), please link to it or share it with others. If you do, please tell us . It helps us a lot!
Create a QR Code

Use our handy widget to create a QR code for this page...or any page.
< previous lesson
next lesson >
- Daytona State College
- DSC Library
Writing Strategies and Grammar
- Parts of Speech
- Writing Prompts
- Common Topics
- Writer's Block
- Brainstorming
- Prewriting/Outlining
- Paragraph Structure
- Thesis Statements
- Rhetoric Defined
- Understanding Citations
- Transitions
- Revision Process
- Improve Grammar
- Complete Sentences
- Punctuation
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Writing Center Homepage
- WC Blog This link opens in a new window
Definitions
MERRIAM-WEBSTER SIMPLE DEFINITIONS
What is a NOUN ?
a word that is the name of something (such as a person, animal, place, thing, quality, idea, or action) and is typically used in a sentence as subject or object of a verb or as object of a preposition
What is a VERB ?
a word (such as jump, think, happen, or exist ) that is usually one of the main parts of a sentence and that expresses an action, an occurrence, or a state of being
What is a PRONOUN ?
a word (such as I, he, she, you, it, we, or they ) that is used instead of a noun or noun phrase
What is a PROPER NOUN ?
a word or group of words (such as “Noah Webster,” “Kentucky,” or “U.S. Congress”) that is the name of a particular person, place, or thing and that usually begins with a capital letter
What is an ADJECTIVE ?
a word that describes a noun or a pronoun
What is an ADVERB ?
a word that describes a verb, an adjective, another adverb, or a sentence and that is often used to show time, manner, place, or degree
Subject-Noun
The Subject Noun
The SUBJECT NOUN is the primary element (or elements if plural) that performs the action in a sentence.
Example: The rattlesnake slithered in the grass.
- There are two nouns in this simple sentence: "rattlesnake" and "grass." However, there is only one subject noun. "Rattlesnake" is the subject noun because the rattlesnake is the noun doing the action. "The grass" isn't doing any action.
Example: Billy loves rattlesnakes.
- In this simple sentence, "Billy" is the subject noun because he is the one doing the loving, so to speak. The "rattlesnake" is simply the object of Billy’s love.
Example: Love is awesome.
- In this example, "Love" is the subject noun. Not all nouns are concrete, tangible things such as people, places, and objects. Concepts and actions can also function as nouns and as subject nouns. It depends on the construction of the sentence. As we've just seen, love can function as either a verb or a noun.
Example: Believing he was invincible, Billy caught the rattlesnake with his bare hands.
- In this example, Billy is the subject noun. The main clause is "Billy caught the rattlesnake with his bare hands." The introductory element ("Believing he was invincible") functions to set up that main clause with more meaning and context. When the subject noun doesn't start a sentence, it's often because there's an introductory element like this (often with a comma separating the introductory element from the main clause).
Example: Not surprisingly, the rattlesnake bit Billy’s hand and slithered away.
- Again, this sentence begins with an introductory element. The core sentence really begins after the comma. The subject noun is "rattlesnake" because the rattlesnake is the noun doing the action (it bit Billy and slithered away).
Example: Becky and Roger then took Billy to the hospital.
- In this example, "Becky and Roger" serve as the subject noun. More than one individual noun can serve as a subject noun. “They” is a pronoun that can be used to replace Becky and Roger as the subject noun.
Predicate Verb
The Predicate Verb
The PREDICATE is everything else in a sentence that’s not technically the subject or a part of a subject phrase. This includes the PREDICATE VERB and any other OBJECTS (such as the direct object receiving the action of the predicate verb). Of particular importance is the predicate verb. For a sentence to be complete, there must be both a subject noun and a predicate verb. Everything else is technically optional. Let’s focus on the predicate verb.
The PREDICATE VERB signifies what the SUBJECT is actually doing.
Example : The rattlesnake slithered in the grass.
- Because "rattlesnake" is the subject noun, "slithered" is the predicate verb. Slithered is what the rattlesnake did.
Example: Billy loves rattlesnakes.
- In this example, "loves" is clearly the predicate verb; that’s what Billy is doing.
Example: Love is awesome.
- Finally, because "love" is the subject noun, is is the predicate verb. Is, was, and have (and all their possible variations) are common predicate verbs.
For now, let’s focus again on our other three examples:
Example: Believing he was invincible, Billy caught the rattlesnake with his bare hands.
- As "Billy" is the subject noun, "caught" is the predicate verb because that’s what Billy did. Everything else is simply providing context and more information.
Example: Not surprisingly, the rattlesnake bit Billy’s hand and slithered away.
- What did the rattlesnake physically do? In this example, it actually did two things: bit Billy’s hand and slithered away. Thus, in this sentence, we actually have two predicate verbs following the single subject noun: "bit" and "slithered." This is, of course, totally permissible. Later, we’ll check out what happens when you have more than one subject noun and each subject noun has its own predicate verb (which makes a “compound sentence” possible).
Example: Becky and Roger then took Billy to the hospital.
- We already know that the subject noun is "Becky and Roger." In this example, however, the predicate verb is not the next word. The predicate verb is actually "took," not "then." In this example, then functions simply as an adverb giving more detail to the predicate verb, took.
Combinative Examples
COMBINATIVE EXAMPLES: As we’ve already seen, sentences can contain more than one subject noun and/or more than one predicate verb in a number of combinations. Let’s check out a number of examples. Subject nouns are in bold font, and predicate verbs are italicized:
- Billy catches rattlesnakes with his hands.
- He loves to catch venomous snakes.
- Becky and Roger think Billy is insane.
- They believe he’s going to get bit one day.
- Becky thinks Billy is an idiot and believes he’ll get what he deserves some day.
- One day, Billy caught a large rattlesnake.
- It bit him.
- Beck and Roger were not surprised.
- Billy died and was buried in his snakeskin boots.
- << Previous: Grammar and Mechanics
- Next: Improve Grammar >>
- Last Updated: Oct 27, 2023 2:23 PM
- URL: https://library.daytonastate.edu/Writing

Graduate Writing Center
Parts of speech - graduate writing center.
- Citations / Avoiding Plagiarism
- Critical Thinking
- Discipline-Specific Resources
- Generative AI
- Parts of speech
- Article usage
- Capitalization
- Conjunctive adverbs
- Coordinating conjunctions
- Dangling modifiers
- Phrases and clauses
- Prepositions
- Sentence subjects
- Subject–verb agreement
- Verbs and verb tense
- iThenticate FAQ
- Organization and Structure
- Punctuation
- Style: Clarity and Concision
- Writing Process
- Writing a Thesis
- Quick Clips & Tips
- Presentations and Graphics
Parts of Speech
The parts of speech —noun, pronoun, adjective, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction—are the building blocks of writing. We don't need to know every detail about these types of words to write—any more than we need to know exactly how each part of our car's engine works to drive. However, we do need to know enough to recognize when something needs repair!
Parts of Speech Lin ks
- Website: Parts of Speech
- Video series on many different parts of speech, Khan Academy
- Exercises on many different parts of speech, Khan Academy
Handout: " Qualifiers ," UNC Chapel Hill Writing Center
Writing Topics A–Z
This index makes findings topics easy and links to the most relevant page for each item. Please email us at [email protected] if we're missing something!
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z

How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
How to write a speech that your audience remembers
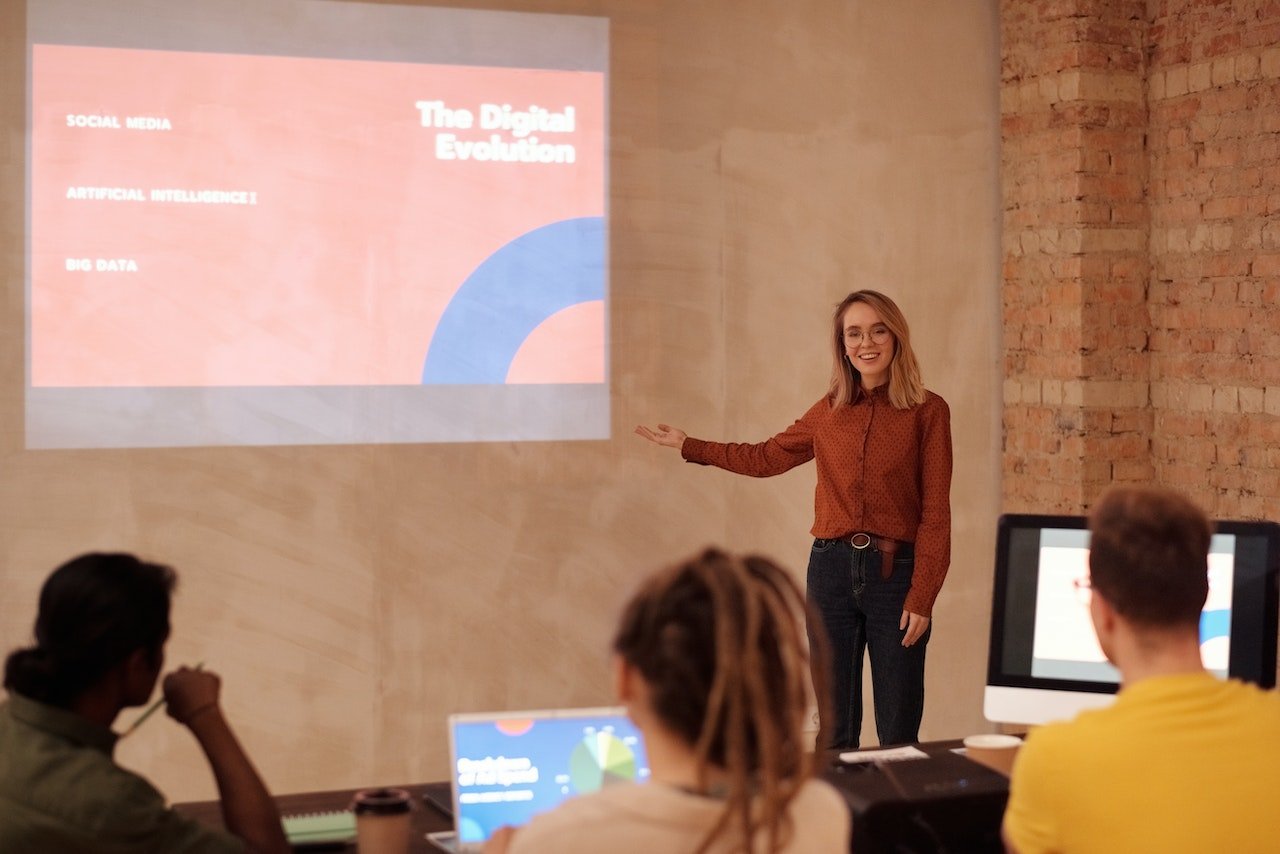

Whether in a work meeting or at an investor panel, you might give a speech at some point. And no matter how excited you are about the opportunity, the experience can be nerve-wracking .
But feeling butterflies doesn’t mean you can’t give a great speech. With the proper preparation and a clear outline, apprehensive public speakers and natural wordsmiths alike can write and present a compelling message. Here’s how to write a good speech you’ll be proud to deliver.
What is good speech writing?
Good speech writing is the art of crafting words and ideas into a compelling, coherent, and memorable message that resonates with the audience. Here are some key elements of great speech writing:
- It begins with clearly understanding the speech's purpose and the audience it seeks to engage.
- A well-written speech clearly conveys its central message, ensuring that the audience understands and retains the key points.
- It is structured thoughtfully, with a captivating opening, a well-organized body, and a conclusion that reinforces the main message.
- Good speech writing embraces the power of engaging content, weaving in stories, examples, and relatable anecdotes to connect with the audience on both intellectual and emotional levels.
Ultimately, it is the combination of these elements, along with the authenticity and delivery of the speaker , that transforms words on a page into a powerful and impactful spoken narrative.
What makes a good speech?
A great speech includes several key qualities, but three fundamental elements make a speech truly effective:
Clarity and purpose
Remembering the audience, cohesive structure.
While other important factors make a speech a home run, these three elements are essential for writing an effective speech.
The main elements of a good speech
The main elements of a speech typically include:
- Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your speech and grabs the audience's attention. It should include a hook or attention-grabbing opening, introduce the topic, and provide an overview of what will be covered.
- Opening/captivating statement: This is a strong statement that immediately engages the audience and creates curiosity about the speech topics.
- Thesis statement/central idea: The thesis statement or central idea is a concise statement that summarizes the main point or argument of your speech. It serves as a roadmap for the audience to understand what your speech is about.
- Body: The body of the speech is where you elaborate on your main points or arguments. Each point is typically supported by evidence, examples, statistics, or anecdotes. The body should be organized logically and coherently, with smooth transitions between the main points.
- Supporting evidence: This includes facts, data, research findings, expert opinions, or personal stories that support and strengthen your main points. Well-chosen and credible evidence enhances the persuasive power of your speech.
- Transitions: Transitions are phrases or statements that connect different parts of your speech, guiding the audience from one idea to the next. Effective transitions signal the shifts in topics or ideas and help maintain a smooth flow throughout the speech.
- Counterarguments and rebuttals (if applicable): If your speech involves addressing opposing viewpoints or counterarguments, you should acknowledge and address them. Presenting counterarguments makes your speech more persuasive and demonstrates critical thinking.
- Conclusion: The conclusion is the final part of your speech and should bring your message to a satisfying close. Summarize your main points, restate your thesis statement, and leave the audience with a memorable closing thought or call to action.
- Closing statement: This is the final statement that leaves a lasting impression and reinforces the main message of your speech. It can be a call to action, a thought-provoking question, a powerful quote, or a memorable anecdote.
- Delivery and presentation: How you deliver your speech is also an essential element to consider. Pay attention to your tone, body language, eye contact , voice modulation, and timing. Practice and rehearse your speech, and try using the 7-38-55 rule to ensure confident and effective delivery.
While the order and emphasis of these elements may vary depending on the type of speech and audience, these elements provide a framework for organizing and delivering a successful speech.

How to structure a good speech
You know what message you want to transmit, who you’re delivering it to, and even how you want to say it. But you need to know how to start, develop, and close a speech before writing it.
Think of a speech like an essay. It should have an introduction, conclusion, and body sections in between. This places ideas in a logical order that the audience can better understand and follow them. Learning how to make a speech with an outline gives your storytelling the scaffolding it needs to get its point across.
Here’s a general speech structure to guide your writing process:
- Explanation 1
- Explanation 2
- Explanation 3
How to write a compelling speech opener
Some research shows that engaged audiences pay attention for only 15 to 20 minutes at a time. Other estimates are even lower, citing that people stop listening intently in fewer than 10 minutes . If you make a good first impression at the beginning of your speech, you have a better chance of interesting your audience through the middle when attention spans fade.
Implementing the INTRO model can help grab and keep your audience’s attention as soon as you start speaking. This acronym stands for interest, need, timing, roadmap, and objectives, and it represents the key points you should hit in an opening.
Here’s what to include for each of these points:
- Interest : Introduce yourself or your topic concisely and speak with confidence . Write a compelling opening statement using relevant data or an anecdote that the audience can relate to.
- Needs : The audience is listening to you because they have something to learn. If you’re pitching a new app idea to a panel of investors, those potential partners want to discover more about your product and what they can earn from it. Read the room and gently remind them of the purpose of your speech.
- Timing : When appropriate, let your audience know how long you’ll speak. This lets listeners set expectations and keep tabs on their own attention span. If a weary audience member knows you’ll talk for 40 minutes, they can better manage their energy as that time goes on.
- Routemap : Give a brief overview of the three main points you’ll cover in your speech. If an audience member’s attention starts to drop off and they miss a few sentences, they can more easily get their bearings if they know the general outline of the presentation.
- Objectives : Tell the audience what you hope to achieve, encouraging them to listen to the end for the payout.
Writing the middle of a speech
The body of your speech is the most information-dense section. Facts, visual aids, PowerPoints — all this information meets an audience with a waning attention span. Sticking to the speech structure gives your message focus and keeps you from going off track, making everything you say as useful as possible.
Limit the middle of your speech to three points, and support them with no more than three explanations. Following this model organizes your thoughts and prevents you from offering more information than the audience can retain.
Using this section of the speech to make your presentation interactive can add interest and engage your audience. Try including a video or demonstration to break the monotony. A quick poll or survey also keeps the audience on their toes.
Wrapping the speech up
To you, restating your points at the end can feel repetitive and dull. You’ve practiced countless times and heard it all before. But repetition aids memory and learning , helping your audience retain what you’ve told them. Use your speech’s conclusion to summarize the main points with a few short sentences.
Try to end on a memorable note, like posing a motivational quote or a thoughtful question the audience can contemplate once they leave. In proposal or pitch-style speeches, consider landing on a call to action (CTA) that invites your audience to take the next step.

How to write a good speech
If public speaking gives you the jitters, you’re not alone. Roughly 80% of the population feels nervous before giving a speech, and another 10% percent experiences intense anxiety and sometimes even panic.
The fear of failure can cause procrastination and can cause you to put off your speechwriting process until the last minute. Finding the right words takes time and preparation, and if you’re already feeling nervous, starting from a blank page might seem even harder.
But putting in the effort despite your stress is worth it. Presenting a speech you worked hard on fosters authenticity and connects you to the subject matter, which can help your audience understand your points better. Human connection is all about honesty and vulnerability, and if you want to connect to the people you’re speaking to, they should see that in you.
1. Identify your objectives and target audience
Before diving into the writing process, find healthy coping strategies to help you stop worrying . Then you can define your speech’s purpose, think about your target audience, and start identifying your objectives. Here are some questions to ask yourself and ground your thinking :
- What purpose do I want my speech to achieve?
- What would it mean to me if I achieved the speech’s purpose?
- What audience am I writing for?
- What do I know about my audience?
- What values do I want to transmit?
- If the audience remembers one take-home message, what should it be?
- What do I want my audience to feel, think, or do after I finish speaking?
- What parts of my message could be confusing and require further explanation?
2. Know your audience
Understanding your audience is crucial for tailoring your speech effectively. Consider the demographics of your audience, their interests, and their expectations. For instance, if you're addressing a group of healthcare professionals, you'll want to use medical terminology and data that resonate with them. Conversely, if your audience is a group of young students, you'd adjust your content to be more relatable to their experiences and interests.
3. Choose a clear message
Your message should be the central idea that you want your audience to take away from your speech. Let's say you're giving a speech on climate change. Your clear message might be something like, "Individual actions can make a significant impact on mitigating climate change." Throughout your speech, all your points and examples should support this central message, reinforcing it for your audience.

4. Structure your speech
Organizing your speech properly keeps your audience engaged and helps them follow your ideas. The introduction should grab your audience's attention and introduce the topic. For example, if you're discussing space exploration, you could start with a fascinating fact about a recent space mission. In the body, you'd present your main points logically, such as the history of space exploration, its scientific significance, and future prospects. Finally, in the conclusion, you'd summarize your key points and reiterate the importance of space exploration in advancing human knowledge.
5. Use engaging content for clarity
Engaging content includes stories, anecdotes, statistics, and examples that illustrate your main points. For instance, if you're giving a speech about the importance of reading, you might share a personal story about how a particular book changed your perspective. You could also include statistics on the benefits of reading, such as improved cognitive abilities and empathy.
6. Maintain clarity and simplicity
It's essential to communicate your ideas clearly. Avoid using overly technical jargon or complex language that might confuse your audience. For example, if you're discussing a medical breakthrough with a non-medical audience, explain complex terms in simple, understandable language.
7. Practice and rehearse
Practice is key to delivering a great speech. Rehearse multiple times to refine your delivery, timing, and tone. Consider using a mirror or recording yourself to observe your body language and gestures. For instance, if you're giving a motivational speech, practice your gestures and expressions to convey enthusiasm and confidence.
8. Consider nonverbal communication
Your body language, tone of voice, and gestures should align with your message . If you're delivering a speech on leadership, maintain strong eye contact to convey authority and connection with your audience. A steady pace and varied tone can also enhance your speech's impact.
9. Engage your audience
Engaging your audience keeps them interested and attentive. Encourage interaction by asking thought-provoking questions or sharing relatable anecdotes. If you're giving a speech on teamwork, ask the audience to recall a time when teamwork led to a successful outcome, fostering engagement and connection.
10. Prepare for Q&A
Anticipate potential questions or objections your audience might have and prepare concise, well-informed responses. If you're delivering a speech on a controversial topic, such as healthcare reform, be ready to address common concerns, like the impact on healthcare costs or access to services, during the Q&A session.
By following these steps and incorporating examples that align with your specific speech topic and purpose, you can craft and deliver a compelling and impactful speech that resonates with your audience.

Tools for writing a great speech
There are several helpful tools available for speechwriting, both technological and communication-related. Here are a few examples:
- Word processing software: Tools like Microsoft Word, Google Docs, or other word processors provide a user-friendly environment for writing and editing speeches. They offer features like spell-checking, grammar correction, formatting options, and easy revision tracking.
- Presentation software: Software such as Microsoft PowerPoint or Google Slides is useful when creating visual aids to accompany your speech. These tools allow you to create engaging slideshows with text, images, charts, and videos to enhance your presentation.
- Speechwriting Templates: Online platforms or software offer pre-designed templates specifically for speechwriting. These templates provide guidance on structuring your speech and may include prompts for different sections like introductions, main points, and conclusions.
- Rhetorical devices and figures of speech: Rhetorical tools such as metaphors, similes, alliteration, and parallelism can add impact and persuasion to your speech. Resources like books, websites, or academic papers detailing various rhetorical devices can help you incorporate them effectively.
- Speechwriting apps: Mobile apps designed specifically for speechwriting can be helpful in organizing your thoughts, creating outlines, and composing a speech. These apps often provide features like voice recording, note-taking, and virtual prompts to keep you on track.
- Grammar and style checkers: Online tools or plugins like Grammarly or Hemingway Editor help improve the clarity and readability of your speech by checking for grammar, spelling, and style errors. They provide suggestions for sentence structure, word choice, and overall tone.
- Thesaurus and dictionary: Online or offline resources such as thesauruses and dictionaries help expand your vocabulary and find alternative words or phrases to express your ideas more effectively. They can also clarify meanings or provide context for unfamiliar terms.
- Online speechwriting communities: Joining online forums or communities focused on speechwriting can be beneficial for getting feedback, sharing ideas, and learning from experienced speechwriters. It's an opportunity to connect with like-minded individuals and improve your public speaking skills through collaboration.
Remember, while these tools can assist in the speechwriting process, it's essential to use them thoughtfully and adapt them to your specific needs and style. The most important aspect of speechwriting remains the creativity, authenticity, and connection with your audience that you bring to your speech.

5 tips for writing a speech
Behind every great speech is an excellent idea and a speaker who refined it. But a successful speech is about more than the initial words on the page, and there are a few more things you can do to help it land.
Here are five more tips for writing and practicing your speech:
1. Structure first, write second
If you start the writing process before organizing your thoughts, you may have to re-order, cut, and scrap the sentences you worked hard on. Save yourself some time by using a speech structure, like the one above, to order your talking points first. This can also help you identify unclear points or moments that disrupt your flow.
2. Do your homework
Data strengthens your argument with a scientific edge. Research your topic with an eye for attention-grabbing statistics, or look for findings you can use to support each point. If you’re pitching a product or service, pull information from company metrics that demonstrate past or potential successes.
Audience members will likely have questions, so learn all talking points inside and out. If you tell investors that your product will provide 12% returns, for example, come prepared with projections that support that statement.
3. Sound like yourself
Memorable speakers have distinct voices. Think of Martin Luther King Jr’s urgent, inspiring timbre or Oprah’s empathetic, personal tone . Establish your voice — one that aligns with your personality and values — and stick with it. If you’re a motivational speaker, keep your tone upbeat to inspire your audience . If you’re the CEO of a startup, try sounding assured but approachable.
4. Practice
As you practice a speech, you become more confident , gain a better handle on the material, and learn the outline so well that unexpected questions are less likely to trip you up. Practice in front of a colleague or friend for honest feedback about what you could change, and speak in front of the mirror to tweak your nonverbal communication and body language .
5. Remember to breathe
When you’re stressed, you breathe more rapidly . It can be challenging to talk normally when you can’t regulate your breath. Before your presentation, try some mindful breathing exercises so that when the day comes, you already have strategies that will calm you down and remain present . This can also help you control your voice and avoid speaking too quickly.
How to ghostwrite a great speech for someone else
Ghostwriting a speech requires a unique set of skills, as you're essentially writing a piece that will be delivered by someone else. Here are some tips on how to effectively ghostwrite a speech:
- Understand the speaker's voice and style : Begin by thoroughly understanding the speaker's personality, speaking style, and preferences. This includes their tone, humor, and any personal anecdotes they may want to include.
- Interview the speaker : Have a detailed conversation with the speaker to gather information about their speech's purpose, target audience, key messages, and any specific points they want to emphasize. Ask for personal stories or examples they may want to include.
- Research thoroughly : Research the topic to ensure you have a strong foundation of knowledge. This helps you craft a well-informed and credible speech.
- Create an outline : Develop a clear outline that includes the introduction, main points, supporting evidence, and a conclusion. Share this outline with the speaker for their input and approval.
- Write in the speaker's voice : While crafting the speech, maintain the speaker's voice and style. Use language and phrasing that feel natural to them. If they have a particular way of expressing ideas, incorporate that into the speech.
- Craft a captivating opening : Begin the speech with a compelling opening that grabs the audience's attention. This could be a relevant quote, an interesting fact, a personal anecdote, or a thought-provoking question.
- Organize content logically : Ensure the speech flows logically, with each point building on the previous one. Use transitions to guide the audience from one idea to the next smoothly.
- Incorporate engaging stories and examples : Include anecdotes, stories, and real-life examples that illustrate key points and make the speech relatable and memorable.
- Edit and revise : Edit the speech carefully for clarity, grammar, and coherence. Ensure the speech is the right length and aligns with the speaker's time constraints.
- Seek feedback : Share drafts of the speech with the speaker for their feedback and revisions. They may have specific changes or additions they'd like to make.
- Practice delivery : If possible, work with the speaker on their delivery. Practice the speech together, allowing the speaker to become familiar with the content and your writing style.
- Maintain confidentiality : As a ghostwriter, it's essential to respect the confidentiality and anonymity of the work. Do not disclose that you wrote the speech unless you have the speaker's permission to do so.
- Be flexible : Be open to making changes and revisions as per the speaker's preferences. Your goal is to make them look good and effectively convey their message.
- Meet deadlines : Stick to agreed-upon deadlines for drafts and revisions. Punctuality and reliability are essential in ghostwriting.
- Provide support : Support the speaker during their preparation and rehearsal process. This can include helping with cue cards, speech notes, or any other materials they need.
Remember that successful ghostwriting is about capturing the essence of the speaker while delivering a well-structured and engaging speech. Collaboration, communication, and adaptability are key to achieving this.
Give your best speech yet
Learn how to make a speech that’ll hold an audience’s attention by structuring your thoughts and practicing frequently. Put the effort into writing and preparing your content, and aim to improve your breathing, eye contact , and body language as you practice. The more you work on your speech, the more confident you’ll become.
The energy you invest in writing an effective speech will help your audience remember and connect to every concept. Remember: some life-changing philosophies have come from good speeches, so give your words a chance to resonate with others. You might even change their thinking.
Boost your speech skills
Enhance your public speaking with personalized coaching tailored to your needs
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
How to write an impactful cover letter for a career change
6 presentation skills and how to improve them, how to be more persuasive: 6 tips for convincing others, the 11 tips that will improve your public speaking skills, what is a career statement, and should you write one, asking for a raise: tips to get what you’re worth, self-management skills for a messy world, a guide on how to find the right mentor for your career, want a leg up in your career master these 11 key listening skills, similar articles, how to write an executive summary in 10 steps, 18 effective strategies to improve your communication skills, how to pitch ideas: 8 tips to captivate any audience, your guide to what storytelling is and how to be a good storyteller, how to give a good presentation that captivates any audience, writing an elevator pitch about yourself: a how-to plus tips, how to make a presentation interactive and exciting, how to write a memo: 8 steps with examples, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Speech Writing

- Updated on
- Jan 16, 2024

The power of good, inspiring, motivating, and thought-provoking speeches can never be overlooked. If we retrospect, a good speech has not only won people’s hearts but also has been a verbal tool to conquer nations. For centuries, many leaders have used this instrument to charm audiences with their powerful speeches. Apart from vocalizing your speech perfectly, the words you choose in a speech carry immense weight, and practising speech writing begins with our school life. Speech writing is an important part of the English syllabus for Class 12th, Class 11th, and Class 8th to 10th. This blog brings you the Speech Writing format, samples, examples, tips, and tricks!
This Blog Includes:
What is speech writing, speech in english language writing, how do you begin an english-language speech, introduction, how to write a speech, speech writing samples, example of a great speech, english speech topics, practice time.
Must Read: Story Writing Format for Class 9 & 10
Speech writing is the art of using proper grammar and expression to convey a thought or message to a reader. Speech writing isn’t all that distinct from other types of narrative writing. However, students should be aware of certain distinct punctuation and writing style techniques. While writing the ideal speech might be challenging, sticking to the appropriate speech writing structure will ensure that you never fall short.
“There are three things to aim at in public speaking: first, to get into your subject, then to get your subject into yourself, and lastly, to get your subject into the heart of your audience.”- Alexander Gregg
The English language includes eight parts of speech i.e. nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives 410 , adverbs , prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
- Noun- A noun is a word that describes anything, such as an animal, a person, a place, or an emotion. Nouns are the building blocks for most sentences.
- Pronoun – Pronouns are words that can be used in place of nouns. They are used so that we don’t have to repeat words. This makes our writing and speaking much more natural.
- Verb – A verb is a term that implies activity or ‘doing.’ These are very vital for your children’s grammar studies, as a sentence cannot be complete without a verb.
- Adjective – An adjective is a term that describes something. An adjective is frequently used before a noun to add extra information or description.
- Prepositions- A preposition is a term that expresses the location or timing of something in relation to something else.
- Conjunction- Because every language has its own set of conjunctions, English conjunctions differ from those found in other languages. They’re typically used as a connecting word between two statements, concepts, or ideas.
- Interjections- Interjections are words that are used to describe a strong emotion or a sudden feeling.
Relevant Read: Speech on the Importance of English
The way you start your English speech can set the tone for the remainder of it. This semester, there are a variety of options for you to begin presentations in your classes. For example, try some of these engaging speech in English language starters.
- Rhetorical questions : A rhetorical question is a figure of speech that uses a question to convey a point rather than asking for a response. The answer to a rhetorical question may be clear, yet the questioner asks it to emphasize the point. Rhetorical questions may be a good method for students to start their English speeches. This method of introducing your material might be appealing to the viewers and encourage them to consider how they personally relate to your issue.
- Statistics: When making an instructive or persuasive speech in an English class, statistics can help to strengthen the speaker’s authority and understanding of the subject. To get your point over quickly and create an emotional response, try using an unexpected statistic or fact that will resonate with the audience.
- Set up an imaginary scene: Create an imaginary situation in your audience’s thoughts if you want to persuade them to agree with you with your speech. This method of starting your speech assists each member of the audience in visualizing a fantastic scenario that you wish to see come true.
Relevant Read: Reported Speech Rules With Exercises
Format of Speech Writing
Here is the format of Speech Writing:
- Introduction : Greet the audience, tell them about yourself and further introduce the topic.
- Body : Present the topic in an elaborate way, explaining its key features, pros and cons, if any and the like.
- Conclusion : Summary of your speech, wrap up the topic and leave your audience with a compelling reminder to think about!
Let’s further understand each element of the format of Speech Writing in further detail:
After the greetings, the Introduction has to be attention-getting. Quickly get people’s attention. The goal of a speech is to engage the audience and persuade them to think or act in your favour. The introduction must effectively include:
- A brief preview of your topic.
- Define the outlines of your speech. (For example, I’ll be talking about…First..Second…Third)
- Begin with a story, quote, fact, joke, or observation in the room. It shouldn’t be longer than 3-4 lines. (For Example: “Mahatma Gandhi said once…”, or “This topic reminds me of an incident/story…”)
This part is also important because that’s when your audience decides if the speech is worth their time. Keep your introduction factual, interesting, and convincing.
It is the most important part of any speech. You should provide a number of reasons and arguments to convince the audience to agree with you.
Handling objections is an important aspect of speech composition. There is no time for questions or concerns since a speech is a monologue. Any concerns that may occur during the speech will be addressed by a powerful speech. As a result, you’ll be able to respond to questions as they come in from the crowd. To make speech simpler you can prepare a flow chart of the details in a systematic way.
For example: If your speech is about waste management; distribute information and arrange it according to subparagraphs for your reference. It could include:
- What is Waste Management?
- Major techniques used to manage waste
- Advantages of Waste Management
- Importance of Waste Management
The conclusion should be something that the audience takes with them. It could be a reminder, a collective call to action, a summary of your speech, or a story. For example: “It is upon us to choose the fate of our home, the earth by choosing to begin waste management at our personal spaces.”
After concluding, add a few lines of gratitude to the audience for their time.
For example: “Thank you for being a wonderful audience and lending me your time. Hope this speech gave you something to take away.”

Practice Your Speech Writing with these English Speech topics for students !
A good speech is well-timed, informative, and thought-provoking. Here are the tips for writing a good school speech:
Speech Sandwich of Public Speaking
The introduction and conclusion must be crisp. People psychologically follow the primacy effect (tendency to remember the first part of the list/speech) and recency effect (tendency to recall the last part of the list/speech).
Use Concrete Facts
Make sure you thoroughly research your topic. Including facts appeals to the audience and makes your speech stronger. How much waste is managed? Give names of organisations and provide numerical data in one line.
Use Rhetorical Strategies and Humour
Include one or two open-ended or thought-provoking questions. For Example: “Would we want our future generation to face trouble due to global warming?” Also, make good use of humour and convenient jokes that engages your audience and keeps them listening.
Check Out: Message Writing
Know your Audience and Plan Accordingly
This is essential before writing your speech. To whom is it directed? The categorised audience on the basis of –
- Knowledge of the Topic (familiar or unfamiliar)
Use the information to formulate the speech accordingly, use information that they will understand, and a sentence that they can retain.
Timing Yourself is Important
An important aspect of your speech is to time yourself. Don’t write a speech that exceeds your word limit. Here’s how can decide the right timing for your speech writing:
- A one-minute speech roughly requires around 130-150 words
- A two-minute speech requires roughly around 250-300 words
Recommended Read: Letter Writing
Speech Writing Examples
Here are some examples to help you understand how to write a good speech. Read these to prepare for your next speech:
Write a speech to be delivered in the school assembly as Rahul/ Rubaina of Delhi Public School emphasises the importance of cleanliness, implying that the level of cleanliness represents the character of its residents. (150-200 words)
“Cleanliness is next to godliness,” said the great John Wesley. Hello, respected principal, instructors, and good friends. Today, I, Rahul/Rubaina, stand in front of you all to emphasise the significance of cleanliness.
Cleanliness is the condition or attribute of being or remaining clean. Everyone must learn about cleaning, hygiene, sanitation, and the different diseases that are produced by unsanitary circumstances. It is essential for physical well-being and the maintenance of a healthy atmosphere at home and at school. A filthy atmosphere invites a large number of mosquitos to grow and spread dangerous diseases. On the other side, poor personal cleanliness causes a variety of skin disorders as well as lowered immunity.
Habits formed at a young age become ingrained in one’s personality. Even if we teach our children to wash their hands before and after meals, brush their teeth and bathe on a regular basis, we are unconcerned about keeping public places clean. On October 2, 2014, the Indian Prime Minister began the “Swachh Bharat” programme to offer sanitation amenities to every family, including toilets, solid and liquid waste disposal systems, village cleanliness, and safe and appropriate drinking water supplies. Teachers and children in schools are actively participating in the ‘Clean India Campaign’ with zeal and excitement.
Good health ensures a healthy mind, which leads to better overall productivity, higher living standards, and economic development. It will improve India’s international standing. As a result, a clean environment is a green environment with fewer illnesses. Thus, cleanliness is defined as a symbol of mental purity.
Thank you very much.
Relevant Read: Speech on Corruption
You are Sahil/Sanya, the school’s Head Girl/Head Boy. You are greatly troubled by the increasing instances of aggressive behaviour among your students. You decide to speak about it during the morning assembly. Create a speech about “School Discipline.” (150 – 200 words)
INDISCIPLINE IN SCHOOLS,
It has been reported that the frequency of fights and incidences of bullying in our school has increased dramatically in the previous several months. Good morning to everyone present. Today, I, Sahil/Sanya, your head boy/girl, am here to shed light on the serious topic of “Increased Indiscipline in Schools.”
It has come to light that instructor disobedience, bullying, confrontations with students, truancy, and insults are becoming more widespread. Furthermore, there have been reports of parents noticing a shift in their children’s attitudes. As a result, many children are suffering emotionally, psychologically, and physically. The impact of this mindset on children at a young age is devastating and irreversible.
Not to mention the harm done to the school’s property. Theft of chalk, scribbling on desks, walls and lavatory doors, destruction of CCTV cameras and so forth. We are merely depriving ourselves of the comforts granted to us by doing so.
Following numerous meetings, it was determined that the main reasons for the problem were a lack of sufficient guidance, excessive use of social media, and peer pressure. The council is working to make things better. Everyone is required to take life skills classes. Counselling, motivating, and instilling friendly ideals will be part of the curriculum. Seminars for parents and students will be held on a regular basis.
A counsellor is being made available to help you all discuss your sentiments, grudges, and personal problems. We are doing everything we can and expect you to do the same.
So, let us work together to create an environment in which we encourage, motivate, assist, and be nice to one another because we are good and civilised humans capable of a great deal of love.
Relevant Read: How to Write a Speech on Discipline?
The current increase in incidences of violent student misbehaviour is cause for alarm for everyone. Students who learn how to manage their anger can help to alleviate the situation. Write a 150-200-word speech about the topic to be delivered at the school’s morning assembly. (10)
HOW TO CONTROL ANGER
Honourable Principal, Respected Teachers, and Dear Friends, I’d like to share a few “Ways to Manage Anger” with you today.
The growing intolerance among the younger generation, which is resulting in violence against teachers, is cause for severe concern. The guru-shishya parampara is losing its lustre. Aggressive behaviour in students can be provoked by a variety of factors, including self-defence, stressful circumstance, over-stimulation, or a lack of adult supervision.
It has become imperative to address the situation. Life skills workshops will be included in the curriculum. Teachers should be trained to deal with such stubborn and confrontational behaviours. Meditation and deep breathing are very beneficial and should be practised every morning. Students should be taught to count to ten before reacting angrily. Sessions on anger control and its importance must also be held.
Remember that Anger is one letter away from danger. It becomes much more crucial to be able to control one’s rage. It’s never too late to start, as a wise man once said.
“Every minute you stay angry, you lose sixty seconds of peace of mind.”
Relevant Read: English Speech Topics for Students
Martin Luther King Jr’s ‘I Have A Dream’ is one of his most famous speeches. Its impact has lasted through generations. The speech is written by utilising the techniques above. Here are some examples:
“still sadly crippled by the manacles of segregation and the chains of discrimination” – emotive Language
“In a sense, we’ve come to our nation’s capital to cash a check” – personalising the speech
“to stand up for freedom together” – a call to action.
Importantly, this is an example of how the listener comes first while drafting a speech. The language chosen appeals to a specific sort of audience and was widely utilised in 1963 when the speech was delivered.
- The Best Day of My Life
- Social Media: Bane or Boon?
- Pros and Cons of Online Learning
- Benefits of Yoga
- If I had a Superpower
- I wish I were ______
- Environment Conservation
- Women Should Rule the World!
- The Best Lesson I Have Learned
- Paperbacks vs E-books
- How to Tackle a Bad Habit?
- My Favorite Pastime/Hobby
- Understanding Feminism
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): Is it real or not?
- Importance of Reading
- Importance of Books in Our Life
- My Favorite Fictional Character
- Introverts vs Extroverts
- Lessons to Learn from Sports
- Beauty is in the eye of the beholder
Also Read: How to Ace IELTS Writing Section?
Ans. Speech writing is the process of communicating a notion or message to a reader by employing proper punctuation and expression. Speech writing is similar to other types of narrative writing. However, students should be aware of some different punctuation and writing structure techniques.
Ans. Before beginning with the speech, choose an important topic. Create an outline; rehearse your speech, and adjust the outline based on comments from the rehearsal. This five-step strategy for speech planning serves as the foundation for both lessons and learning activities.
Ans. Writing down a speech is vital since it helps you better comprehend the issue, organises your thoughts, prevents errors in your speech, allows you to get more comfortable with it, and improves its overall quality.
Speech writing and public speaking are effective and influential. Hope this blog helped you know the various tips for writing the speech people would want to hear. If you need help in making the right career choices at any phase of your academic and professional journey, our Leverage Edu experts are here to guide you. Sign up for a free session now!
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
14 comments
This site has been very helpful to me
Wow i have gained more knowledge
lt’s a nice One and l have loved it
Thank you for your feedback! Happy that you loved it.
Thank you for your feedback!
Very educating.
thanks for your valuable feedback
This is indeed very helpful
Thanks for your valuable feedback!
I have learned alot thank you
Hi, Thanks for your feedback!
Wow so reliable, thanks.

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Table of Contents
Ai, ethics & human agency, collaboration, information literacy, writing process, pronoun – guide to writing with pronouns.
- © 2023 by Jenifer Paquette - Hillsborough Community College , Barbara McLain - The Out-of-Door Academy , Joseph M. Moxley - University of South Florida
This Guide to Writing with Pronouns in 2022 provides everything you need to know about pronouns . The Guide defines the different types of pronouns in English, analyzes the function of pronouns in sentences , and explains how to identify and fix pronoun errors . Learn about correct pronoun usage so you can establish a professional tone in your communications and ensure your language is clear , concise , inclusive and gender-sensitive.

If these sentences seem ok , that may be because you may hear people say them in everyday discourse. Still, from the standard of British or American English, the first three sentences contain a pronoun error. The fourth sentence, which until recently would have been considered an error, is correct.
What Are Pronouns?
Pronouns are words that substitute for other nouns. For instance, in the example below Dr. Johansen is a noun and she and her are pronouns:
- Dr. Johansen would prefer that she be addressed using her title, rather than her first name.
Pronouns are also a way to communicate your gender preferences.
- Dr. Johansen would prefer that they be addressed using their title, rather than their first name.
This example uses the singular “they.” For more information, see our article on inclusive language.
Why Do Pronouns Matter?
Pronouns are one of the 9 parts of speech ; they are a critical building block for writing meaningful sentences . Writers, speakers, knowledge workers . . .
- use pronouns to introduce variety into their sentences, avoid awkward repetition, provide context and emphasis, and clarify relationships between ideas
- use pronouns to express their sense of identify, particular with regards to their gender preference (he/she/they) .
Take a look at the following sample from a student paper, with and without pronouns:
McMurphy’s amiability to all — “wheelers and walkers and vegetables, hands that he has to pick up out of laps—” (23) regardless of their condition, is symbolic of the way Jesus spent time meeting the rich, poor, filthy, sinful, innocent, and all who he encountered, despite their status or loyalty to him . Additionally, by referring to the ward’s group meetings as a “pecking party,” (100) making the men aware of the metaphorical castration they undergo as Nurse Ratched strips them of their individuality, and telling the men that they “can’t let [Nurse Ratched] take over completely—” (100) McMurphy opens the eyes of his inmates (for the first time) to the fact that they are not reaching their full potential, which motivates them to become the men that they truly are.
Now with pronouns removed and replaced with their antecedents:
McMurphy’s amiability to the patients— “wheelers and Walkers and Vegetables, hands that McMurphy has to pick up out of laps—” (23) regardless of the patient’s condition, is symbolic of the way Jesus spent time meeting the rich, poor, filthy, sinful, innocent, and the people Jesus encountered, despite the person’s status or loyalty to Jesus. Additionally, by referring to the ward’s group meetings as a “pecking party,” (100) making the men aware of the metaphorical castration the men undergo as Nurse Ratched strips the men of the men’s individuality, and telling the men that they “can’t let [Nurse Ratched] take over completely—” (100) McMurphy opens the eyes of inmates (for the first time) to the fact that the inmates are not reaching the inmates’ full potential. McMurphy’s actions motivate the inmates to become the men the inmates truly are.
The paragraph without pronouns is repetitive, awkward, and unclear.

What Are the Different Types of Pronouns?
Personal Pronouns
- Personal Pronouns refer to specific individuals or group.
- Examples: I, me, you, they, them, she, her, he, him, it, we, us
- In a sentence: I am going to get coffee. Would you like some?
Indefinite Pronouns
- Indefinite Pronouns refer to nouns that have not been specifically identified.
- Examples: another, anyone, anybody, anything, each, either, enough, everyone, everything, everybody, other, one, something, much, nobody, few
- In a sentence: Does anyone need anything from the store when I go?
Possessive Pronouns
- Possessive pronouns show possession or ownership
- Examples: my, mine, ours, your, yours, his, her, hers, their, theirs
- In a sentence: The last slice of pizza is mine .
Demonstrative Pronouns
- Demonstrative pronouns reference or point to nouns or noun phrases that have already been mentioned.
- Examples: this, that, these, those
- In a sentence: You never listen. That is why I’m always nagging!
Reflexive Pronouns
- Reflexive pronouns refer back to the subject of the sentence. You use these pronouns when the subject and the object are the same.
- Examples: myself, yourself, himself, herself, oneself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves
- In a sentence: I built this house myself .
Reciprocal Pronouns
- Reciprocal pronouns refer to a reciprocal or mutual relationship.
- Examples: each other, one another
- In a sentence: We need to be kinder to each other.
Relative Pronouns
- Relative pronouns connect relative clauses to independent clauses
- Examples: which that what who whom
- In a sentence: The man who refused to acknowledge his own errors was soon promoted. (In this sentence, “who refused to acknowledge his own errors” is the relative clause—that is, a clause that tells us more about people and things).
Interrogative Pronouns
- Interrogative pronouns are used in questions
- Examples: who, whom (refer to people); what and which (refer to inanimate objects and animals); who (functions as a subject); whom (functions as an object of preposition or verb); whose (shows possession)
- In a sentence: Which shoes do you prefer?
How Do Pronouns Function in Sentences?
Subject and object pronouns.
Because pronouns replace nouns, they can function in sentences in the same way. This means that the pronouns listed above can act as both the subject and the object of a sentence.
Subject Pronouns
Subject pronouns act as the subject of a sentence, which means that they
1) are what is doing the action
2) usually appear at the beginning of the sentence.
Some subject pronouns are I, you, he, she, we, they, and who. In the sentence “Gene went to the movies,” Gene is the subject of the sentence and could be replaced with a subject pronoun: “ He went to the movies.”
Object Pronouns
Object pronouns act as the object of the sentence, which means that they
1) are what is receiving the action
2) usually appear at the END of the sentence.
Some object pronouns are: me, you, him, her, us, them, and whom. In the sentence “Gene went to the movies with Xavier,” Xavier is the object of this sentence and could be replaced with an object pronoun: “Gene went to the movies with him .”
Note: Who and whom work the same way—who is always the subject of a sentence and whom is always the object. You can rephrase a question and replace “who” and “whom” with “he” and “him” to help you determine which to use. For example, “Who is going to the movies with whom?” becomes “He is going to the movies with him.”
How Do I Correct Errors in Pronoun Usage?
The three most common errors with pronoun use are
- Mixing up subject and object pronouns
- Unclear pronoun placement (ambiguous antecedent)
- Pronouns that don’t agree with their antecedents
How Do I Correct Errors with Subject and Object Pronouns?
In many cases, it’s easy to choose the correct pronoun because the wrong choice sounds wrong.
Example: Her went to the movies with him.
Most English speakers would recognize that sentence as wrong even without being able to articulate why. But when sentences contain multiple subject and objects, it can be a little trickier to make sure you’re using the right pronoun because the wrong pronoun won’t necessarily sound wrong.
Example: She and Jim went to the movies with Bob and I.
The above example doesn’t sound wrong, but it is. It has a subject pronoun (“I”) acting as an object. A simple solution for determining whether you’ve subject and object pronouns correctly is to read the sentence without the other nouns, and see how the pronouns sound on their own.
Original: She and Jim went to the movies with Bob and I.
With nouns removed: She went to the movies with I.
See? It sounds wrong (because it is!).
How Do I Correct Ambiguous Pronouns?
When using pronouns, it is important to make sure it’s clear what the pronoun is referring to. Pronouns whose antecedents are unclear are often referred to as ambiguous pronouns.
- Example: Drake’s brother wondered whether he had passed his driver’s test.
Who is “he”? It isn’t clear to readers whether this pronoun refers to Drake or Drake’s brother.
- Example: While trying to balance both her computer and notebook, Shelly felt it slip from her hand.
What is “it”? It isn’t clear to readers whether Shelly dropped her computer or her notebook.
- Example: Mr. Ball told his student he was needed in the office.
Who is “he”? It isn’t clear to readers whether Mr. Ball or his student are needed in the office.
Demonstrative pronouns like this, that, and those are also frequently used ambiguously.
- Example: In the digital age, consumers are forced to give away privacy and security in exchange for the ability to participate in digital marketplaces. This is something most of us have learned to accept.
It isn’t clear in this example exactly what “this” refers to. Is it the loss of privacy? The loss of security? The fact that it is a requirement of participation? When using a demonstrative pronoun, especially when it follows a sentence where you’ve introduced complicated information, it’s best to pair that pronoun with a specific reference to the antecedent.
- Example: In the digital age, consumers are forced to give away privacy and security in exchange for the ability to participate in digital marketplaces. This loss of privacy is something most of us have learned to accept.
How Do I Correct Errors in Pronoun-Antecedent Agreement?
An antecedent is the word that a pronoun is replacing. Pronouns should agree with their antecedents in number, gender, and person. For example, if the antecedent is a singular noun, the pronoun should be singular. If the noun is a gendered noun referring to females, the pronoun also should be gendered appropriately. If a sentence is written in the second person, it should remain in that person.
Number Agreement
Pronouns should agree in number with their antecedents. Singular pronouns should follow singular antecedents, and plural pronouns should follow plural antecedents.
Common Singular Pronouns
I, me, mine, myself
she, her, hers, herself
he, him, his, himself
it, its, itself
they, them, theirs, themselves
Common Plural Pronouns
we, us, ours
Singular examples:
- Shelly wished that she was more outgoing.
- The mailman his final package that day. He was tired and ready to go home.
As you can see, a pronoun and its antecedent won’t necessarily appear in the same sentence.
Plural examples:
- The teachers decided to strike. They conferred with the union to draft a list of demands.
- As if waiting for this precise moment, the neighborhood dogs began to bark the moment he closed his eyes and no amount of shouting convinced them to stop.
Ensuring that your pronouns agree in number with their antecedents is usually pretty straightforward; however, it can be harder to spot errors in complex sentences where the pronoun and antecedent are far removed from each other.
- Example: Mr. Brown has long argued that facilitating students’ access to non-academic resources like food and personal grooming products can improve (his/their) ability to perform well on tests.
It can help to look at an example and ask yourself who the phrase in question must be referring to. In this case, you would ask: Who in this sentence would have the ability to perform well on tests? The answer in this case is the students, and so the correct answer is “their.”
Person Agreement
Pronouns also use “persons” as in the first, second, or third person. The first person assumes the writer or speaker is included in the pronoun (I, we, us, ours, we, etc.). The second person assumes the stance of you (you, your, yours). The third person assumes a more objective, distanced stance because the writer or speaker is not present in the pronoun (she, he, it, they, their, them, etc.). It’s important to maintain consistency in your writing. If you begin an essay writing in the third-person, you need to stay there.
Gender Agreement
Similar to number and person agreement, pronouns must also correspond to the gender of the antecedent.
- Example: Mr. Green decided it was best to hide his evidence in the pantry.
- Example: Lady Germaine was a bear to deal with in the morning. She was much more tolerable after a little coffee.
Using “They” As a Gender-Neutral Singular Pronoun
A problem arises when a sentence begins with a singular gender-neutral common noun (like student, official, customer) because English does not have a singular gender-neutral pronoun to pair with these words.
- Example: If a student wishes to be excused from physical education, ________ must submit an appeal to the school board.
The solution is certainly not to bypass the pronoun and repeat the noun (e.g. If a student wishes to be excused from physical education, a student must submit an appeal to the school board).
At one time, students were instructed to default to male singular pronouns in these cases.
- Example: If a student wishes to be excused from physical education, he must submit an appeal to the school board.
Eventually, this evolved to the more inclusive but much clunkier “he or she.”
- Example: If a student wishes to be excused from physical education, he or she must submit an appeal to the school board.
Another option is to change the structure of the sentence to avoid the problem.
- Example: If students wish to be excused from physical education, they must submit an appeal to the school board.
However, making gender neutral singular nouns plural is not always possible. The fact is that the lack of an ungendered singular pronoun is a failure of the English language, and the question of how to deal with it continues to be polarizing. However, more and more English speakers and writers agree that it is acceptable to use “they” as a gender-neutral singular pronoun in addition to its traditional use as a gender-neutral plural pronoun.
- Example: If a student wishes to be excused from physical education, they must submit an appeal to the school board.
The same applies when writing about Individuals who identify as non-binary.
- Example: Florence wants to have another look at the house before they make a decision.
An adherence to the rules of grammar shouldn’t ever supersede our humanity. There is no circumstance in which it is appropriate to refer to an individual by a pronoun that doesn’t correspond to their gender identity. In this case, however, the solution is wonderfully simple: Use whichever pronouns the individual has requested.
Indefinite pronouns present a host of thorny agreement issues. Because indefinite pronouns do not refer to a specific noun, when they act as the antecedent it can be tricky to determine which pronouns should correspond.
Singular Indefinite Pronouns
Many indefinite pronouns are always treated as singular. Here are some: each, either, anybody, everybody, everyone, no one, nothing, something. In these cases, the corresponding pronoun will always be singular.
But because these pronouns are all gender-neutral, this raises the same issue addressed above: there is no gender-neutral singular personal pronoun to pair with them. Again, the use of “they” as a singular gender-neutral pronoun has become a widely accepted solution.
- Example: Everyone deserves access to clean water to quench their thirst.
The Chicago Manual of Style and the AP allow for the singular “they,” but recommend trying to write around the agreement issue first:
- Example: All people deserve access to clean water to quench their thirst.
Plural Indefinite Pronouns
Some indefinite pronouns are always plural. These are generally easier to spot because in other contexts, they are words that can also serve as adjectives or adverbs that mean more than one. Here are some: both, few/fewer, many, others, several. In these cases, the corresponding pronoun should always be plural.
- Example: Both of my parents decided to cancel their gym memberships.
Indefinite Pronouns That Can Be Singular or Plural
Some indefinite pronouns can be treated as singular OR plural. Here is a complete list of those pronouns:
In the case of these indefinite pronouns, look at the object of the preposition to determine whether its use is singular or plural.
- Footwear = singular object of the preposition
- Shoes = plural object of the preposition
Agreement with indefinite pronouns that can be singular or plural is particularly challenging because we typically ignore the object of the preposition when making choices about agreement. The treatment of all, any, none, most, more, and some represents an exception to that rule.
Note: This exception also applies when choosing a verb that agrees in number to all, any, most more and some:
All of your work is excellent.
Work= singular
All of the farmers are planting winter wheat.
Farmers= Plural.
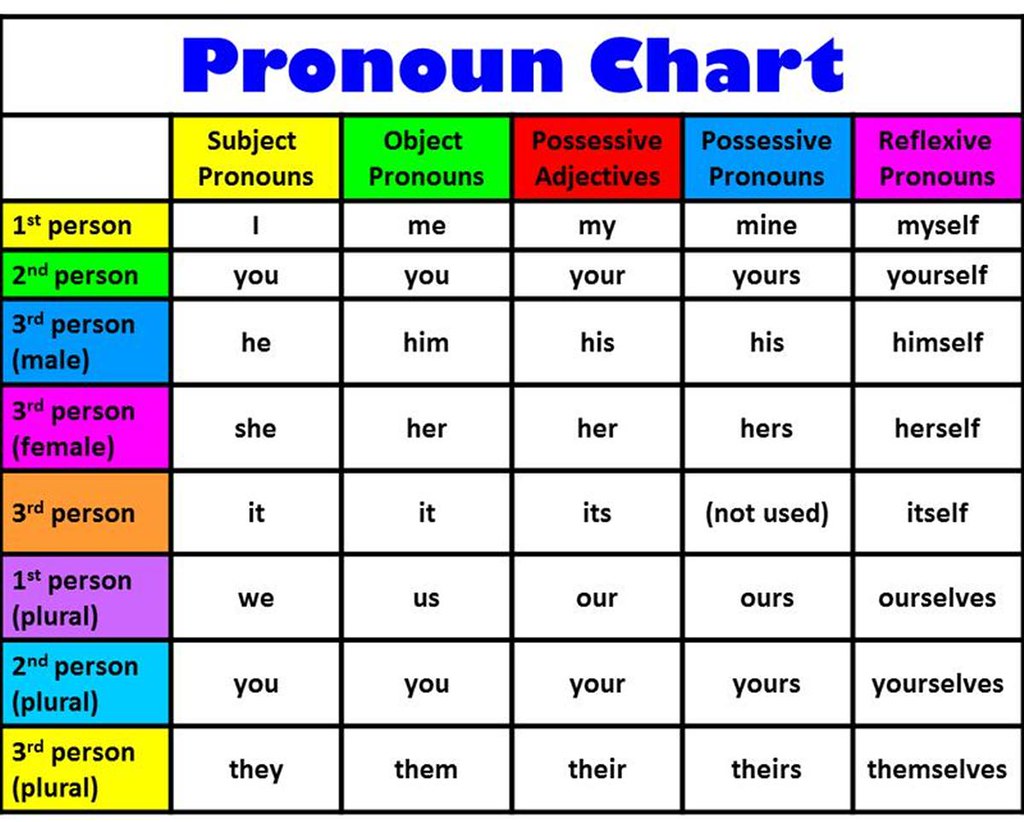
Collective Nouns
Collective nouns (nouns that identify a group like class , team , and committee ) also get special treatment when it comes to agreement.
Collective nouns are treated as plural when each member of the group is acting independently.
- Example: Before the match began, the team took their places on the field.
Each team member is acting independently and going to a different place. There are many actions taking place, so the pronoun is plural .
Collective nouns are treated as singular when the group is acting in unison.
- Example: The committee agreed to spend its surplus budget on yo-yos.
The committee is completing a single action as a group, so the pronoun is singular .
Named businesses, schools, and organizations are always treated as singular.
- Example: Southwest High School takes great pride in the service projects of its students.
- Neither the teachers nor the principal neglected (his/their) duties.
- Skydivers are taught that (you/they) should check their parachutes before even getting on a plane.
- The school board will present (its/their) proposed budget at the next meeting.
- Both Cheryl and Denise will bring (her/their) supplies.
- Some of the participants declined to sign (his or her/their) waivers.
Related Articles:

Pronouns and Inclusivity - How Are Pronouns Tied to Inclusive Language?
Suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

- Barbara McLain
Gender-neutral pronouns have been the subject of debate for hundreds of years. Find out how the debate began and where the writing community stands on inclusive pronoun use today.
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Speech & Writing
- May 26, 2024
What is the Writing Process? A 5-Step Guide for Success
Julia mccoy.
Creator and Co-founder
You’ve got a brilliant idea for a piece of writing, but you’re not sure where to start. The writing process can feel overwhelming, especially if you’re new to the game.
But here’s the thing: even the most seasoned writers struggle with getting their thoughts down on paper. The key is to break it down into manageable steps.
In this post, I’ll walk you through the five essential stages of the writing process. From brainstorming to publishing, you’ll learn how to create compelling content that your audience will love.
Let’s get started!
Table Of Contents:
What is the writing process, the 5-step writing process, step 1: prewriting, step 2: drafting, step 3: revising, step 4: editing, step 5: publishing, great content starts with following the writing process.
Writing is a 5-step process that includes a prewriting stage, writing the first draft, revising and editing, and finally publishing.
Each step has its own set of activities and strategies to help you move your writing project forward.
However, the writing process is not always linear. You might find yourself jumping back and forth between stages as you refine your ideas and improve your work. That’s totally normal and part of the creative process.
Now, you might be wondering, “Why can’t I just sit down and start writing?”
Well, you could, but the result might be a disorganized mess.
Following these writing steps helps ensure that your final product is well-structured, coherent, and effective in communicating your message.
Plus, following a process can reduce stress and writer’s block. When you know what steps to take next, it’s easier to keep moving forward, even when the words aren’t flowing as easily as you’d like.
Here’s a breakdown of the five key steps of the writing process:
This is the brainstorming phase, where you generate ideas, research, and organize your thoughts.
Prewriting strategies like mind mapping, freewriting, and outlining can help you get the creative juices flowing.
Time to start putting your ideas into writing.
In the drafting stage, you take the ideas from your prewriting and start fleshing them out into full sentences and body paragraphs.
Don’t worry about perfection just yet – the goal is to get your thoughts down on paper.
Once you have a rough draft, it’s time to start making improvements.
Revising involves evaluating your content, organization, and word choice to make sure your writing is clear, coherent, and effective.
This is also a good time to get feedback from others.
After revising, it’s time to polish your writing at the sentence level.
Editing involves checking for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors, as well as ensuring consistency in your formatting and citations.
A thorough edit can take your writing from good to great.
Finally, it’s time to share your work with the world.
Publishing can take many forms, from submitting a paper to a professor to posting on a blog or submitting to a literary journal.
Whatever the format, the key is to get your writing in front of your intended audience.
Now let’s dive into the nitty-gritty of the writing process.
Prewriting is the first stage of the writing process, and it’s all about getting those creative juices flowing. This is where you brainstorm ideas, do some research, and start organizing your thoughts.
One of my favorite prewriting strategies is mind mapping . Mind maps are a great way to visually organize your ideas and see connections between different concepts. To create a mind map, start with your main topic in the center, then branch out with subtopics and supporting details.
Another technique is asking journalistic questions about your topic – who, what, where, when, why, and how. This can help you generate ideas and identify areas where you need to do more research.
Speaking of research, it’s an important part of the prewriting process, especially if you’re writing about a complex or unfamiliar topic.
Start by gathering information from reputable sources like books, articles, and websites. As you read, take notes and jot down ideas for how you can incorporate the information into your writing.
But don’t just regurgitate facts and figures – think critically about the information you’re gathering. Consider the credibility and biases of your sources, and look for ways to synthesize and analyze the information to support your own ideas.
Once you’ve generated some ideas and done your research, it’s time to start organizing your thoughts into an outline.
An outline is like a roadmap for your writing – it helps you see the overall structure and flow of your piece.
Start by identifying your main points or arguments, then add supporting details and examples under each one. You can also use your outline to identify areas where you need to do more research or development.
Remember, your outline doesn’t have to be set in stone – it’s a flexible tool that you can adjust as you write and revise. But having that initial structure can make the writing process feel much more manageable.
Alright, you’ve done your prewriting and you’re ready to start drafting. It’s time to start putting your ideas into full sentences and paragraphs.
Drafting can feel intimidating, but remember – it’s just a first attempt. The goal is to get your thoughts down on paper, not to create a perfect final product. Give yourself permission to write freely and without judgment.
Create a Thesis Statement
One key element of drafting is creating a strong thesis statement. This is a sentence or two that summarizes the main point or argument of your piece. It’s like a signpost for your readers, telling them what to expect in the rest of your writing.
Your thesis statement should be specific, arguable, and clearly stated. It’s okay if it takes a few tries to get it just right – you can always revise it later.
Write Topic Sentences
Once you have your thesis statement, it’s time to start fleshing out your ideas in the body of your piece.
One helpful strategy is to write clear topic sentences for each paragraph. A topic sentence introduces the main idea of the paragraph and connects it back to your thesis.
Think of your topic sentences as mini-thesis statements for each paragraph. They should be specific, relevant, and engaging, and they should give your readers a clear sense of what to expect in the rest of the paragraph.
Develop Your Paragraphs
With your topic sentences in place, it’s time to develop your paragraphs with supporting details and examples. Each paragraph should focus on one main idea that supports your thesis statement.
As you draft, try to use concrete, specific language to illustrate your points. Avoid vague or general statements – instead, use vivid descriptions and examples to bring your ideas to life.
Use Supporting Evidence
To make your writing more persuasive and credible, it’s important to use supporting evidence to back up your claims. This can include facts, statistics, examples, and expert opinions.
As you incorporate evidence into your writing, be sure to use proper citation and attribution. This shows that you’ve done your research and helps you avoid plagiarism.
When you’re drafting, just get those thoughts flowing onto paper. Don’t stress about making it super polished yet—you’ll have your tune-up time later for all the tweaks and edit magic.
You’ve got a draft – congratulations. Now it’s time to take a step back and evaluate your work with a critical eye.
Revising is all about making improvements to your content and structure to make your writing as clear, coherent, and effective as possible.
Evaluate Content
Start by reading through your draft and asking yourself some key questions:
- Does my writing have a clear purpose and audience?
- Does each paragraph support my main point?
- Is my evidence convincing and relevant?
As you evaluate your content, look for areas where you can cut irrelevant or redundant information, and add more detail or explanation where needed.
Remember, every sentence should serve a purpose and contribute to your overall message.
Improve Organization
Next, take a look at the overall organization and flow of your piece.
Does it have a clear beginning, middle, and end? Do your ideas logically build on each other? Are there any gaps or jumps in your reasoning?
If needed, don’t be afraid to move paragraphs around, add transitions, or restructure your piece to create a more logical and coherent flow.
A reverse outline can be a helpful tool for evaluating and improving your organization.
Enhance Word Choice
As you revise your draft, pay attention to your word choice and tone.
Are you using clear, concise language that your audience will understand? Can you replace any vague or overused words with more specific or descriptive language?
Think about the connotations and emotional impact of your words, and choose language that supports your purpose and engages your readers.
Refine Sentence Structure
Finally, take a close look at your sentence structure and variety.
Are your sentences clear and easy to follow? Do you have a good mix of simple, compound, and complex sentences?
Look for opportunities to vary your sentence beginnings, lengths, and structures to create a more engaging and dynamic writing style. But be careful not to overdo it – too much variety can be just as distracting as too little.
Remember, revising is an ongoing process. You may need to go through multiple rounds of revision to get your writing where you want it to be. But each revision brings you one step closer to a polished, effective final product.
You’ve revised your content and structure – now it’s time to polish your writing at the sentence level.
Editing involves carefully reviewing your work for errors in grammar, punctuation, spelling, and formatting.
Proofreading for Grammar and Punctuation
One key aspect of editing is proofreading for grammar and punctuation mistakes. This includes things like subject-verb agreement, pronoun usage, comma placement, and more.
Reading your work out loud can be a helpful technique for catching awkward or incorrect phrasing. You can also try reading your work backward, sentence by sentence, to help you focus on each sentence without getting caught up in the overall flow.
Checking for Consistency
Another important aspect of editing is checking for consistency in your writing. This includes things like verb tense, point of view, and formatting.
For example, if you start your piece in the present tense, make sure you stay in the present tense throughout.
If you’re using MLA formatting, make sure you follow MLA guidelines consistently throughout your piece.
Formatting and Citations
Speaking of formatting, it’s important to make sure your work follows the appropriate style guide for your discipline or publication. This includes things like font choice, margin size, and citation style.
If you’re using sources in your writing, make sure to properly cite them both in-text and in your works cited or reference list. Proper citation not only gives credit to your sources but also helps you avoid plagiarism.
Editing can be a tedious process, but it’s an important step in creating a polished, professional piece of writing.
Don’t be afraid to ask for help from a friend, tutor, or colleague – a fresh set of eyes can catch mistakes that you might miss on your own.
You’ve brainstormed, drafted, revised, and edited – now it’s time to share your work with the world.
Choosing a Publishing Platform
The first step in publishing is choosing the right platform for your work. Consider your audience, purpose, and genre when making this decision.
For example, if you’re writing a research paper for a class, you’ll likely submit it directly to your professor.
If you’re writing a personal essay, you might consider submitting it to a literary journal or magazine.
If you’re writing a blog post, you’ll need to choose a blogging platform and domain name.
Formatting for Publication
Once you’ve chosen your publishing platform, it’s important to format your work according to their guidelines.
Pay close attention to submission rules and follow them carefully. A poorly formatted submission can hurt your chances of acceptance, even if your writing is strong.
Promoting Your Work
Finally, don’t be afraid to promote your published work. Share it on social media, send it to friends and family, and include it in your writing portfolio.
If you’re submitting to a literary journal or magazine, you can also promote your work by attending readings or events hosted by the publication.
Building relationships with other writers and editors can help you grow your audience and find new opportunities for your work.
Remember, publishing is not the end of the writing process – it’s just the beginning. Use the feedback and experience you gain from publishing to continue growing and improving as a writer.
The writing process is a journey, not a destination. By breaking it down into these five essential steps, you can approach your writing with confidence and clarity.
Remember, the key is to stay focused on your message and your audience. Whether you’re brainstorming ideas, drafting your piece, or polishing your final draft, keep your reader in mind every step of the way.
With practice and persistence, you’ll develop your own unique writing process that works for you. So don’t be afraid to experiment, take risks, and let your creativity shine through.
It’s time to build your blog empire.
Want to be a real Content Hacker along with us, but not sure where to start?
We’ve got custom-created resources just for you, friend.
Get inside the Content Hacker Community ❤️ – at just $20/month, it’s a no-brainer. On-call, expert support, live calls, and so much more.
Want to go deeper? Check out our AIO Blogger course – an immersive one-week course teaching you everything you need to know to build a money-making online blog.
Can’t WAIT to welcome you inside.
with gratitude,
Become a Content Hacker
Collaborate with other growth-minded, savvy Content Hackers – plus a host of experts. The price of two coffees/month gets you in.
- Cancel Anytime
- For the Price of 2 Coffees a Month
- 100% Risk Free
Where marketers and founders get the content strategy, skills, and systems to grow exponentially online.
Join thousands of Content Hackers learning smarter content and business strategies.
© 2024 Contenthacker.com

Speech planning: How our brains prepare to speak
I n a fascinating exploration of speech planning, research led by the NYU Grossman School of Medicine reveals how our brains prepare to speak before we actually verbalize our thoughts.
The study, conducted among individuals undergoing surgery for epilepsy treatment, is pivotal for advancing our understanding of speech production . It unveils significant insights into the brain's mechanisms behind speech planning.
The brain's blueprint for speech
The study delves into the roles of the inferior frontal gyrus and motor cortex - two regions situated in the outer layers of the cerebral cortex. These areas are pivotal for controlling the muscles involved in speech production, influencing our selection of words and sounds.
The researchers examined brain-mapping recordings from 16 patients, aged 14 to 43, at NYU Langone Health over the period from 2018 to 2021. These individuals were undergoing pre-surgical evaluations for epilepsy.
The process involved stimulating brain regions to pinpoint and conserve areas critical to speech while targeting seizure-inducing tissue for removal.
Importantly, a key innovation of this research lies in measuring the brief time intervals, less than two seconds, between brain stimulation and its impact on speech. This approach offers fresh perspectives on the cortex's role in speech planning.
Exploring speech production
The researchers have unveiled new insights into the organization of speech within the brain. They found that the delays before speech disruption, known as latencies, vary across different brain regions. This discovery highlights the brain's complex role in speech production and its elaborate mechanisms.
"Our study adds evidence for the role of the brain's motor cortex and inferior frontal gyrus in planning speech and determining what people are preparing to say, not just voicing words using the vocal cords or mouthing the words by moving the tongue and lips," stated Dr. Heather Kabakoff, a speech pathologist at NYU Langone.
Furthermore, Dr. Adeen Flinker, the study's senior investigator and a neuroscientist, explained: "Our results show that mapping out the millisecond time intervals, or latencies, between electrical stimulation in parts of the brain to the disruption or slurring of words and eventual inability to speak can be used to better understand how the human brain works and the roles played by different brain regions in human speech."
Dr. Flinker emphasized the clinical implications of these findings. Additionally, he suggested that this research could pave the way for improved surgical techniques to protect speech functions during brain surgeries.
The next frontier in speech and brain research
The team is now expanding their focus, setting their sights on broader horizons. Consequently, they aim to unravel the roles of other brain parts in speech and auditory processing.
The researchers are studying real-time brain corrections of speech errors to enhance our understanding of speech control and modification. This endeavor marks another step forward in decoding the complexities of human communication.
The process of speech planning
The process of speech planning in the brain is a complex, multi-step process involving various brain regions working in coordination. It includes several key stages:
Conceptualization
This is the initial stage where the intent or idea of what one wants to communicate is formed. It involves abstract thinking and decision-making processes in the prefrontal cortex, where the brain decides on the message it wants to convey.
Lexical selection
Once the concept is formed, the brain selects the appropriate words to express the idea. This involves the temporal lobe, particularly the left temporal lobe for most people, where language comprehension and vocabulary are managed.
Syntactic processing
After selecting the words, the brain organizes them into a grammatically correct structure. This involves Broca's area, located in the left frontal lobe, which is responsible for speech production and the grammatical aspects of language .
Phonological processing
This stage involves planning the sounds that need to be produced to articulate the words. This involves the interaction between Wernicke's area, which is involved in language comprehension and the processing of phonological (sound) information, and Broca's area for the motor aspects of speech production.
Motor planning
Before speech occurs, the brain must plan and coordinate the specific movements of the mouth, tongue, vocal cords, and lungs that produce speech.
This involves the motor cortex, which controls voluntary muscle movements, and the cerebellum, which coordinates the timing and precision of these movements.
Finally, the motor cortex sends signals through the nervous system to the speech organs, executing the planned movements and producing speech. This involves intricate coordination of muscles and breathing to articulate words and modulate voice.
Throughout this speech planning process, the brain also relies on feedback mechanisms involving auditory and somatosensory systems to monitor and adjust speech production in real-time. This ensures accuracy in articulation and intonation.
The exact neural pathways and interactions between these areas are still a subject of ongoing research, as the brain's processes for managing speech are incredibly complex and vary from person to person.
The study is published in the journal Brain .
Like what you read? Subscribe to our newsletter for engaging articles, exclusive content, and the latest updates.
Check us out on EarthSnap , a free app brought to you by Eric Ralls and Earth.com.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A part of speech (also called a word class) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence.Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing. The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs ...
Prepositional phrases convey a spatial, temporal, or directional meaning. Example 1: Ivy climbed up the brick wall of the house. There are two prepositional phrases in the example above: up the brick wall and of the house. The first prepositional phrase is an adverbial phrase, since it modifies the verb by describing where the ivy climbed.
Table of contents. Step 1: Prewriting. Step 2: Planning and outlining. Step 3: Writing a first draft. Step 4: Redrafting and revising. Step 5: Editing and proofreading. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the writing process.
The parts of speech refer to categories to which a word belongs. In English, there are eight of them : verbs , nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Many English words fall into more than one part of speech category. Take the word light as an example.
This comes before a noun or a noun phrase and links it to other parts of the sentence. These are usually single words (e.g., on, at, by ,…) but can be up to four words (e.g., as far as, in addition to, as a result of, …). I chose to interview teachers in the district closest to me. The recorder was placed next to the interviewee.
Parts of Speech refers to the different ways words can function in a sentence. There are 9 Parts of Speech in English: Parts of Speech Grammatical Function 1. Articles 2. Adjectives modifies noun 3. Adverbs a word used to modify verbs and verb phrases 4.
Parts of Speech: The Ultimate Guide for Students and Teachers. By Shane Mac Donnchaidh September 11, 2021March 5, 2024 March 5, 2024. This article is part of the ultimate guide to language for teachers and students. Click the buttons below to view these.
Parts of Speech. You're probably quite familiar with the "grammar police"—those people who find it necessary to correct any grammar mistake you make. You, in fact, may be a member of the "grammar police" squad yourself, but if you're not, you probably get a little tired of the corrections. After all, this person understood what ...
Parts of Speech refers to the different ways words can function in a sentence. There are 9 Parts of Speech in English: Parts of Speech. Grammatical Function. 1. Articles. 2. Adjectives. modifies noun.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles. Many words can function as different parts of ...
The 9 parts of speech are adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, determiners, interjections, nouns, prepositions, pronouns, and verbs. (These are also known as "word classes.") A Formal Definition. A "part of speech" is a category to which a word is assigned in accordance with its syntactic functions. In English, the main parts of speech are noun ...
This article provides a comprehensive, research-based introduction to the major steps, or strategies, that writers work through as they endeavor to communicate with audiences.. Since the 1960s, the writing process has been defined to be a series of steps, stages, or strategies. Most simply, the writing process is conceptualized as four major steps: prewriting, drafting, revising, editing.
The College of Saint Rose Writing Center, 2008 Parts of Speech What are parts of speech? They are eight categories of words defined in terms of their purpose, place, meaning, and use within sentences. The categories are: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Part of Speech Definition Examples
The Predicate Verb. The PREDICATE is everything else in a sentence that's not technically the subject or a part of a subject phrase. This includes the PREDICATE VERB and any other OBJECTS (such as the direct object receiving the action of the predicate verb). Of particular importance is the predicate verb. For a sentence to be complete, there ...
Writing the Speech. After you have analyzed your audience, selected the topic, collected supporting materials, and written an outline, it is time to write the speech with an introduction, body and conclusion. These major parts follow the broadcaster's maxim: (1) Tell them what you are going to tell them. (2) Tell them.
The parts of speech—noun, pronoun, adjective, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction—are the building blocks of writing. We don't need to know every detail about these types of words to write—any more than we need to know exactly how each part of our car's engine works to drive. However, we do need to know enough to recognize when something needs repair!
Your speech is a journey. Your audience needs to know your key premise and understand where you intend to bring them along the path to your conclusion. This is most successfully accomplished in the writing phase with a proper outline. An outline allows you to organize your thoughts before you go any further in the writing process and keep ...
Here are five more tips for writing and practicing your speech: 1. Structure first, write second. If you start the writing process before organizing your thoughts, you may have to re-order, cut, and scrap the sentences you worked hard on. Save yourself some time by using a speech structure, like the one above, to order your talking points first.
Speech writing is an important part of the English syllabus for Class 12th, Class 11th, and Class 8th to 10th. This blog brings you the Speech Writing format, samples, examples, tips, and tricks! ... What is speech writing? Ans. Speech writing is the process of communicating a notion or message to a reader by employing proper punctuation and ...
1) are what is doing the action. 2) usually appear at the beginning of the sentence. Some subject pronouns are I, you, he, she, we, they, and who. In the sentence "Gene went to the movies," Gene is the subject of the sentence and could be replaced with a subject pronoun: " He went to the movies.".
Step 1: Prewriting. Prewriting is the first stage of the writing process, and it's all about getting those creative juices flowing. This is where you brainstorm ideas, do some research, and start organizing your thoughts. One of my favorite prewriting strategies is mind mapping.
The process of speech planning in the brain is a complex, multi-step process involving various brain regions working in coordination. It includes several key stages: This is the initial stage ...