10 Best Problem-Solving Therapy Worksheets & Activities

Cognitive science tells us that we regularly face not only well-defined problems but, importantly, many that are ill defined (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
Sometimes, we find ourselves unable to overcome our daily problems or the inevitable (though hopefully infrequent) life traumas we face.
Problem-Solving Therapy aims to reduce the incidence and impact of mental health disorders and improve wellbeing by helping clients face life’s difficulties (Dobson, 2011).
This article introduces Problem-Solving Therapy and offers techniques, activities, and worksheets that mental health professionals can use with clients.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free . These science-based exercises explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology, including strengths, values, and self-compassion, and will give you the tools to enhance the wellbeing of your clients, students, or employees.

This Article Contains:
What is problem-solving therapy, 14 steps for problem-solving therapy, 3 best interventions and techniques, 7 activities and worksheets for your session, fascinating books on the topic, resources from positivepsychology.com, a take-home message.
Problem-Solving Therapy assumes that mental disorders arise in response to ineffective or maladaptive coping. By adopting a more realistic and optimistic view of coping, individuals can understand the role of emotions and develop actions to reduce distress and maintain mental wellbeing (Nezu & Nezu, 2009).
“Problem-solving therapy (PST) is a psychosocial intervention, generally considered to be under a cognitive-behavioral umbrella” (Nezu, Nezu, & D’Zurilla, 2013, p. ix). It aims to encourage the client to cope better with day-to-day problems and traumatic events and reduce their impact on mental and physical wellbeing.
Clinical research, counseling, and health psychology have shown PST to be highly effective in clients of all ages, ranging from children to the elderly, across multiple clinical settings, including schizophrenia, stress, and anxiety disorders (Dobson, 2011).
Can it help with depression?
PST appears particularly helpful in treating clients with depression. A recent analysis of 30 studies found that PST was an effective treatment with a similar degree of success as other successful therapies targeting depression (Cuijpers, Wit, Kleiboer, Karyotaki, & Ebert, 2020).
Other studies confirm the value of PST and its effectiveness at treating depression in multiple age groups and its capacity to combine with other therapies, including drug treatments (Dobson, 2011).
The major concepts
Effective coping varies depending on the situation, and treatment typically focuses on improving the environment and reducing emotional distress (Dobson, 2011).
PST is based on two overlapping models:
Social problem-solving model
This model focuses on solving the problem “as it occurs in the natural social environment,” combined with a general coping strategy and a method of self-control (Dobson, 2011, p. 198).
The model includes three central concepts:
- Social problem-solving
- The problem
- The solution
The model is a “self-directed cognitive-behavioral process by which an individual, couple, or group attempts to identify or discover effective solutions for specific problems encountered in everyday living” (Dobson, 2011, p. 199).
Relational problem-solving model
The theory of PST is underpinned by a relational problem-solving model, whereby stress is viewed in terms of the relationships between three factors:
- Stressful life events
- Emotional distress and wellbeing
- Problem-solving coping
Therefore, when a significant adverse life event occurs, it may require “sweeping readjustments in a person’s life” (Dobson, 2011, p. 202).

- Enhance positive problem orientation
- Decrease negative orientation
- Foster ability to apply rational problem-solving skills
- Reduce the tendency to avoid problem-solving
- Minimize the tendency to be careless and impulsive
D’Zurilla’s and Nezu’s model includes (modified from Dobson, 2011):
- Initial structuring Establish a positive therapeutic relationship that encourages optimism and explains the PST approach.
- Assessment Formally and informally assess areas of stress in the client’s life and their problem-solving strengths and weaknesses.
- Obstacles to effective problem-solving Explore typically human challenges to problem-solving, such as multitasking and the negative impact of stress. Introduce tools that can help, such as making lists, visualization, and breaking complex problems down.
- Problem orientation – fostering self-efficacy Introduce the importance of a positive problem orientation, adopting tools, such as visualization, to promote self-efficacy.
- Problem orientation – recognizing problems Help clients recognize issues as they occur and use problem checklists to ‘normalize’ the experience.
- Problem orientation – seeing problems as challenges Encourage clients to break free of harmful and restricted ways of thinking while learning how to argue from another point of view.
- Problem orientation – use and control emotions Help clients understand the role of emotions in problem-solving, including using feelings to inform the process and managing disruptive emotions (such as cognitive reframing and relaxation exercises).
- Problem orientation – stop and think Teach clients how to reduce impulsive and avoidance tendencies (visualizing a stop sign or traffic light).
- Problem definition and formulation Encourage an understanding of the nature of problems and set realistic goals and objectives.
- Generation of alternatives Work with clients to help them recognize the wide range of potential solutions to each problem (for example, brainstorming).
- Decision-making Encourage better decision-making through an improved understanding of the consequences of decisions and the value and likelihood of different outcomes.
- Solution implementation and verification Foster the client’s ability to carry out a solution plan, monitor its outcome, evaluate its effectiveness, and use self-reinforcement to increase the chance of success.
- Guided practice Encourage the application of problem-solving skills across multiple domains and future stressful problems.
- Rapid problem-solving Teach clients how to apply problem-solving questions and guidelines quickly in any given situation.
Success in PST depends on the effectiveness of its implementation; using the right approach is crucial (Dobson, 2011).
Problem-solving therapy – Baycrest
The following interventions and techniques are helpful when implementing more effective problem-solving approaches in client’s lives.
First, it is essential to consider if PST is the best approach for the client, based on the problems they present.
Is PPT appropriate?
It is vital to consider whether PST is appropriate for the client’s situation. Therapists new to the approach may require additional guidance (Nezu et al., 2013).
Therapists should consider the following questions before beginning PST with a client (modified from Nezu et al., 2013):
- Has PST proven effective in the past for the problem? For example, research has shown success with depression, generalized anxiety, back pain, Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, and supporting caregivers (Nezu et al., 2013).
- Is PST acceptable to the client?
- Is the individual experiencing a significant mental or physical health problem?
All affirmative answers suggest that PST would be a helpful technique to apply in this instance.
Five problem-solving steps
The following five steps are valuable when working with clients to help them cope with and manage their environment (modified from Dobson, 2011).
Ask the client to consider the following points (forming the acronym ADAPT) when confronted by a problem:
- Attitude Aim to adopt a positive, optimistic attitude to the problem and problem-solving process.
- Define Obtain all required facts and details of potential obstacles to define the problem.
- Alternatives Identify various alternative solutions and actions to overcome the obstacle and achieve the problem-solving goal.
- Predict Predict each alternative’s positive and negative outcomes and choose the one most likely to achieve the goal and maximize the benefits.
- Try out Once selected, try out the solution and monitor its effectiveness while engaging in self-reinforcement.
If the client is not satisfied with their solution, they can return to step ‘A’ and find a more appropriate solution.

Download 3 Free Positive Psychology Exercises (PDF)
Enhance wellbeing with these free, science-based exercises that draw on the latest insights from positive psychology.
Download 3 Free Positive Psychology Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
Positive self-statements
When dealing with clients facing negative self-beliefs, it can be helpful for them to use positive self-statements.
Use the following (or add new) self-statements to replace harmful, negative thinking (modified from Dobson, 2011):
- I can solve this problem; I’ve tackled similar ones before.
- I can cope with this.
- I just need to take a breath and relax.
- Once I start, it will be easier.
- It’s okay to look out for myself.
- I can get help if needed.
- Other people feel the same way I do.
- I’ll take one piece of the problem at a time.
- I can keep my fears in check.
- I don’t need to please everyone.

5 Worksheets and workbooks
Problem-solving self-monitoring form.
Answering the questions in the Problem-Solving Self-Monitoring Form provides the therapist with necessary information regarding the client’s overall and specific problem-solving approaches and reactions (Dobson, 2011).
Ask the client to complete the following:
- Describe the problem you are facing.
- What is your goal?
- What have you tried so far to solve the problem?
- What was the outcome?
Reactions to Stress
It can be helpful for the client to recognize their own experiences of stress. Do they react angrily, withdraw, or give up (Dobson, 2011)?
The Reactions to Stress worksheet can be given to the client as homework to capture stressful events and their reactions. By recording how they felt, behaved, and thought, they can recognize repeating patterns.
What Are Your Unique Triggers?
Helping clients capture triggers for their stressful reactions can encourage emotional regulation.
When clients can identify triggers that may lead to a negative response, they can stop the experience or slow down their emotional reaction (Dobson, 2011).
The What Are Your Unique Triggers ? worksheet helps the client identify their triggers (e.g., conflict, relationships, physical environment, etc.).
Problem-Solving worksheet
Imagining an existing or potential problem and working through how to resolve it can be a powerful exercise for the client.
Use the Problem-Solving worksheet to state a problem and goal and consider the obstacles in the way. Then explore options for achieving the goal, along with their pros and cons, to assess the best action plan.
Getting the Facts
Clients can become better equipped to tackle problems and choose the right course of action by recognizing facts versus assumptions and gathering all the necessary information (Dobson, 2011).
Use the Getting the Facts worksheet to answer the following questions clearly and unambiguously:
- Who is involved?
- What did or did not happen, and how did it bother you?
- Where did it happen?
- When did it happen?
- Why did it happen?
- How did you respond?
2 Helpful Group Activities
While therapists can use the worksheets above in group situations, the following two interventions work particularly well with more than one person.
Generating Alternative Solutions and Better Decision-Making
A group setting can provide an ideal opportunity to share a problem and identify potential solutions arising from multiple perspectives.
Use the Generating Alternative Solutions and Better Decision-Making worksheet and ask the client to explain the situation or problem to the group and the obstacles in the way.
Once the approaches are captured and reviewed, the individual can share their decision-making process with the group if they want further feedback.
Visualization
Visualization can be performed with individuals or in a group setting to help clients solve problems in multiple ways, including (Dobson, 2011):
- Clarifying the problem by looking at it from multiple perspectives
- Rehearsing a solution in the mind to improve and get more practice
- Visualizing a ‘safe place’ for relaxation, slowing down, and stress management
Guided imagery is particularly valuable for encouraging the group to take a ‘mental vacation’ and let go of stress.
Ask the group to begin with slow, deep breathing that fills the entire diaphragm. Then ask them to visualize a favorite scene (real or imagined) that makes them feel relaxed, perhaps beside a gently flowing river, a summer meadow, or at the beach.
The more the senses are engaged, the more real the experience. Ask the group to think about what they can hear, see, touch, smell, and even taste.
Encourage them to experience the situation as fully as possible, immersing themselves and enjoying their place of safety.
Such feelings of relaxation may be able to help clients fall asleep, relieve stress, and become more ready to solve problems.
We have included three of our favorite books on the subject of Problem-Solving Therapy below.
1. Problem-Solving Therapy: A Treatment Manual – Arthur Nezu, Christine Maguth Nezu, and Thomas D’Zurilla

This is an incredibly valuable book for anyone wishing to understand the principles and practice behind PST.
Written by the co-developers of PST, the manual provides powerful toolkits to overcome cognitive overload, emotional dysregulation, and the barriers to practical problem-solving.
Find the book on Amazon .
2. Emotion-Centered Problem-Solving Therapy: Treatment Guidelines – Arthur Nezu and Christine Maguth Nezu

Another, more recent, book from the creators of PST, this text includes important advances in neuroscience underpinning the role of emotion in behavioral treatment.
Along with clinical examples, the book also includes crucial toolkits that form part of a stepped model for the application of PST.
3. Handbook of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapies – Keith Dobson and David Dozois

This is the fourth edition of a hugely popular guide to Cognitive-Behavioral Therapies and includes a valuable and insightful section on Problem-Solving Therapy.
This is an important book for students and more experienced therapists wishing to form a high-level and in-depth understanding of the tools and techniques available to Cognitive-Behavioral Therapists.
For even more tools to help strengthen your clients’ problem-solving skills, check out the following free worksheets from our blog.
- Case Formulation Worksheet This worksheet presents a four-step framework to help therapists and their clients come to a shared understanding of the client’s presenting problem.
- Understanding Your Default Problem-Solving Approach This worksheet poses a series of questions helping clients reflect on their typical cognitive, emotional, and behavioral responses to problems.
- Social Problem Solving: Step by Step This worksheet presents a streamlined template to help clients define a problem, generate possible courses of action, and evaluate the effectiveness of an implemented solution.
If you’re looking for more science-based ways to help others enhance their wellbeing, check out this signature collection of 17 validated positive psychology tools for practitioners. Use them to help others flourish and thrive.

17 Top-Rated Positive Psychology Exercises for Practitioners
Expand your arsenal and impact with these 17 Positive Psychology Exercises [PDF] , scientifically designed to promote human flourishing, meaning, and wellbeing.
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
While we are born problem-solvers, facing an incredibly diverse set of challenges daily, we sometimes need support.
Problem-Solving Therapy aims to reduce stress and associated mental health disorders and improve wellbeing by improving our ability to cope. PST is valuable in diverse clinical settings, ranging from depression to schizophrenia, with research suggesting it as a highly effective treatment for teaching coping strategies and reducing emotional distress.
Many PST techniques are available to help improve clients’ positive outlook on obstacles while reducing avoidance of problem situations and the tendency to be careless and impulsive.
The PST model typically assesses the client’s strengths, weaknesses, and coping strategies when facing problems before encouraging a healthy experience of and relationship with problem-solving.
Why not use this article to explore the theory behind PST and try out some of our powerful tools and interventions with your clients to help them with their decision-making, coping, and problem-solving?
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free .
- Cuijpers, P., Wit, L., Kleiboer, A., Karyotaki, E., & Ebert, D. (2020). Problem-solving therapy for adult depression: An updated meta-analysis. European P sychiatry , 48 (1), 27–37.
- Dobson, K. S. (2011). Handbook of cognitive-behavioral therapies (3rd ed.). Guilford Press.
- Dobson, K. S., & Dozois, D. J. A. (2021). Handbook of cognitive-behavioral therapies (4th ed.). Guilford Press.
- Eysenck, M. W., & Keane, M. T. (2015). Cognitive psychology: A student’s handbook . Psychology Press.
- Nezu, A. M., & Nezu, C. M. (2009). Problem-solving therapy DVD . Retrieved September 13, 2021, from https://www.apa.org/pubs/videos/4310852
- Nezu, A. M., & Nezu, C. M. (2018). Emotion-centered problem-solving therapy: Treatment guidelines. Springer.
- Nezu, A. M., Nezu, C. M., & D’Zurilla, T. J. (2013). Problem-solving therapy: A treatment manual . Springer.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
Thanks for your information given, it was helpful for me something new I learned
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

The Empty Chair Technique: How It Can Help Your Clients
Resolving ‘unfinished business’ is often an essential part of counseling. If left unresolved, it can contribute to depression, anxiety, and mental ill-health while damaging existing [...]

29 Best Group Therapy Activities for Supporting Adults
As humans, we are social creatures with personal histories based on the various groups that make up our lives. Childhood begins with a family of [...]

47 Free Therapy Resources to Help Kick-Start Your New Practice
Setting up a private practice in psychotherapy brings several challenges, including a considerable investment of time and money. You can reduce risks early on by [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (54)
- Coaching & Application (58)
- Compassion (26)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (23)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (27)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (44)
- Motivation & Goals (46)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (30)
- Positive Communication (22)
- Positive Education (48)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (19)
- Positive Parenting (16)
- Positive Psychology (34)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (18)
- Relationships (45)
- Resilience & Coping (39)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (38)
- Strengths & Virtues (32)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)
Mindfulness
Distress Tolerance
Emotion Regulation
Interpersonal Effectiveness
Miscellaneous
Problem Solving
Emotion Regulation is the Dialectical Behavioral Therapy module that teaches how emotions work. It provides skills to help manage emotions instead of being managed by them, reduce vulnerability to negative emotions, and build positive emotional experiences.
When you find yourself experiencing a challenging emotion, you are faced with the choice between changing the emotion or changing the situation. Often this decision depends on whether your emotion is justified or not, which you can determine by using the skill Check the Facts. If your emotion and its intensity are justified, consider changing the situation by Problem Solving. This skill will help you find a solution to the problem situation and put it into action. There is also a handy flow chart to help you figure out whether Problem Solving or Opposite Action is the right skill to use.
There are 7 steps to Problem Solving that can help you figure out what to do next.
1. What is the problem? Describe the situation
2. Use Check the Facts to ensure you’re describing it accurately
3. Figure out your goal in solving the problem
What needs to happen so you can feel okay?
Keep it simple and realistically attainable
4. Brainstorm as many solutions as you can
Ask for suggestions from people you trust
Practice willingness – don’t be critical of any ideas at first
5. Choose a solution that fits the goal and is likely to work
If you’re having trouble choosing one, pick two
Do a Pro-Con 4-Square to compare them, then pick the best to try first
6. Take it step by stepTry the solution
7. Did it work? If not, go back to step 5 and choose another solution to tryEvaluate the results
Check the Facts
Increasing positive emotions, opposite to emotion action, pleasant activities, sleep hygiene protocol, troubleshooting er skills, additional resources, mental health resources.
We aren't the only mental health resource out there. Check out these books, websites, social media accounts, and more for additional support. Read More
DBT Flashcards
Making DBT skills second nature takes practice. Use these flashcards on their page, download your own to print out, or purchase our pre-made set from our shop. Read More
DBT Encyclopedia
DBT has its own lingo which can be hard to understand for beginners. Visit our homemade DBT Encyclopedia to figure out what a term means. Read More
Mindfulness Exercises
Mindfulness practice is key to DBT. You don't have to meditate in silence everyday, though. Try these Mindfulness exercises to guide you. Read More
Diary Cards
Diary cards help track your emotions, urges, behaviors, and skill use. They help you see patterns. Learn how to use them and get samples. Read More
Problem solving
Worrying is a natural response to life's problems. But when it takes over and we can start to feel overwhelmed, it can really help to take a step back and break things down.
Learning new ways to work through your problems can make them feel more manageable, and improve your mental and physical wellbeing.
Video: Problem solving
The tips in this video can help you to find strategies and solutions for tackling the problems that can be solved, and learning how to manage and cope with those that cannot.
Steps and strategies to help you solve problems
1. focus on your values.
Feeling like you have lots of problems to solve in different areas of your life can make it difficult to know how and where to start.
A great way to focus is to write down a few areas of your life that are most important to you right now – for example, a relationship, finances or a long-term goal like studying or developing your career.
This can make it easier to prioritise which problems to tackle.
2. Tackle problems with possible solutions first
It's important to work out if your problem can be solved or is a "hypothetical worry" – things that are out of your control even though you might think about them often.
They might be based on something that happened in the past that cannot be changed or a worry about the future that starts with "what if…".
Ask yourself whether a problem can be dealt with by doing something practical. If the answer is no, it's a hypothetical worry.
Make a list of your problems, and work out which are solvable and which are hypothetical.
3. Set aside time to work through solvable problems
Set aside 5 or 10 minutes to think about possible solutions for one of your solvable problems.
Try to be as open-minded as you can, even if some ideas feel silly. Thinking broadly and creatively is often when the best solutions come to mind.
It may feel difficult at first but, over time, this approach can start to feel easier.
Once you have some ideas, think through or write down:
- the pros and cons of each solution
- whether it's likely to work
- if you have everything you need to try it
4. Make a plan
The next step is to choose a solution you want to try and make a plan for putting it into action. Try to be specific:
- What are you going to do?
- Do you need the support of anybody else?
- How much time do you need?
- When will you do it?
5. Try 'worry time'
Not all of our problems can be solved right away, but it can be difficult to switch off and stop ourselves from dwelling on them.
Using the "worry time" technique to stick to a short set time – say 10 to 15 minutes in the evening – for worrying can make this much easier to manage.
You can learn more about the worry time technique on tackling your worries .
6. Find time to relax
Worrying about our problems can make it harder to relax, but there are lots of things you can try to help you clear your mind and feel calmer.
The most important thing is to find what works for you. It might be getting active, spending time on an existing hobby or trying a new one, or techniques like mindfulness, meditation or our progressive muscle relaxation exercise.
Video: Progressive muscle relaxation
This video will guide you through an exercise to help you recognise when you're starting to get tense, and relax your body and mind.
7. Review and reflect
Once you start trying new approaches to solving and managing problems, consider setting aside time to review what went well with your solutions or anything else you noticed.
Make notes of the problems you face and any strategies you use to overcome them. This can come in handy later on and also be a good reminder of what works best for you.
Ticking off on a checklist any problems you manage to solve is a great way to recognise your achievements and boost your confidence.
8. Give journaling a go
Sometimes getting our thoughts out of our head – and down onto paper, our phones or anything else – is a great way to stop our worries and "what ifs" from spiralling out of control.
Expressing ourselves in this way can also make it easier to spot when our thoughts are unhelpful and we may benefit from a more balanced outlook. Give it a go to see if this works for you.
More self-help CBT techniques you can try
Bouncing back from life's challenges.
Taking steps to stay on top of your mental wellbeing and build resilience can really help you deal with problems when times are tougher. Learn more, and see tips and techniques you can use.

Tackling your worries

Facing your fears

Staying on top of things
Find more ideas to try in self-help CBT techniques
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Problem-Solving Strategies and Obstacles
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Sean is a fact-checker and researcher with experience in sociology, field research, and data analytics.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Sean-Blackburn-1000-a8b2229366944421bc4b2f2ba26a1003.jpg)
JGI / Jamie Grill / Getty Images
- Application
- Improvement
From deciding what to eat for dinner to considering whether it's the right time to buy a house, problem-solving is a large part of our daily lives. Learn some of the problem-solving strategies that exist and how to use them in real life, along with ways to overcome obstacles that are making it harder to resolve the issues you face.
What Is Problem-Solving?
In cognitive psychology , the term 'problem-solving' refers to the mental process that people go through to discover, analyze, and solve problems.
A problem exists when there is a goal that we want to achieve but the process by which we will achieve it is not obvious to us. Put another way, there is something that we want to occur in our life, yet we are not immediately certain how to make it happen.
Maybe you want a better relationship with your spouse or another family member but you're not sure how to improve it. Or you want to start a business but are unsure what steps to take. Problem-solving helps you figure out how to achieve these desires.
The problem-solving process involves:
- Discovery of the problem
- Deciding to tackle the issue
- Seeking to understand the problem more fully
- Researching available options or solutions
- Taking action to resolve the issue
Before problem-solving can occur, it is important to first understand the exact nature of the problem itself. If your understanding of the issue is faulty, your attempts to resolve it will also be incorrect or flawed.
Problem-Solving Mental Processes
Several mental processes are at work during problem-solving. Among them are:
- Perceptually recognizing the problem
- Representing the problem in memory
- Considering relevant information that applies to the problem
- Identifying different aspects of the problem
- Labeling and describing the problem
Problem-Solving Strategies
There are many ways to go about solving a problem. Some of these strategies might be used on their own, or you may decide to employ multiple approaches when working to figure out and fix a problem.
An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure that, by following certain "rules" produces a solution. Algorithms are commonly used in mathematics to solve division or multiplication problems. But they can be used in other fields as well.
In psychology, algorithms can be used to help identify individuals with a greater risk of mental health issues. For instance, research suggests that certain algorithms might help us recognize children with an elevated risk of suicide or self-harm.
One benefit of algorithms is that they guarantee an accurate answer. However, they aren't always the best approach to problem-solving, in part because detecting patterns can be incredibly time-consuming.
There are also concerns when machine learning is involved—also known as artificial intelligence (AI)—such as whether they can accurately predict human behaviors.
Heuristics are shortcut strategies that people can use to solve a problem at hand. These "rule of thumb" approaches allow you to simplify complex problems, reducing the total number of possible solutions to a more manageable set.
If you find yourself sitting in a traffic jam, for example, you may quickly consider other routes, taking one to get moving once again. When shopping for a new car, you might think back to a prior experience when negotiating got you a lower price, then employ the same tactics.
While heuristics may be helpful when facing smaller issues, major decisions shouldn't necessarily be made using a shortcut approach. Heuristics also don't guarantee an effective solution, such as when trying to drive around a traffic jam only to find yourself on an equally crowded route.
Trial and Error
A trial-and-error approach to problem-solving involves trying a number of potential solutions to a particular issue, then ruling out those that do not work. If you're not sure whether to buy a shirt in blue or green, for instance, you may try on each before deciding which one to purchase.
This can be a good strategy to use if you have a limited number of solutions available. But if there are many different choices available, narrowing down the possible options using another problem-solving technique can be helpful before attempting trial and error.
In some cases, the solution to a problem can appear as a sudden insight. You are facing an issue in a relationship or your career when, out of nowhere, the solution appears in your mind and you know exactly what to do.
Insight can occur when the problem in front of you is similar to an issue that you've dealt with in the past. Although, you may not recognize what is occurring since the underlying mental processes that lead to insight often happen outside of conscious awareness .
Research indicates that insight is most likely to occur during times when you are alone—such as when going on a walk by yourself, when you're in the shower, or when lying in bed after waking up.
How to Apply Problem-Solving Strategies in Real Life
If you're facing a problem, you can implement one or more of these strategies to find a potential solution. Here's how to use them in real life:
- Create a flow chart . If you have time, you can take advantage of the algorithm approach to problem-solving by sitting down and making a flow chart of each potential solution, its consequences, and what happens next.
- Recall your past experiences . When a problem needs to be solved fairly quickly, heuristics may be a better approach. Think back to when you faced a similar issue, then use your knowledge and experience to choose the best option possible.
- Start trying potential solutions . If your options are limited, start trying them one by one to see which solution is best for achieving your desired goal. If a particular solution doesn't work, move on to the next.
- Take some time alone . Since insight is often achieved when you're alone, carve out time to be by yourself for a while. The answer to your problem may come to you, seemingly out of the blue, if you spend some time away from others.
Obstacles to Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is not a flawless process as there are a number of obstacles that can interfere with our ability to solve a problem quickly and efficiently. These obstacles include:
- Assumptions: When dealing with a problem, people can make assumptions about the constraints and obstacles that prevent certain solutions. Thus, they may not even try some potential options.
- Functional fixedness : This term refers to the tendency to view problems only in their customary manner. Functional fixedness prevents people from fully seeing all of the different options that might be available to find a solution.
- Irrelevant or misleading information: When trying to solve a problem, it's important to distinguish between information that is relevant to the issue and irrelevant data that can lead to faulty solutions. The more complex the problem, the easier it is to focus on misleading or irrelevant information.
- Mental set: A mental set is a tendency to only use solutions that have worked in the past rather than looking for alternative ideas. A mental set can work as a heuristic, making it a useful problem-solving tool. However, mental sets can also lead to inflexibility, making it more difficult to find effective solutions.
How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills
In the end, if your goal is to become a better problem-solver, it's helpful to remember that this is a process. Thus, if you want to improve your problem-solving skills, following these steps can help lead you to your solution:
- Recognize that a problem exists . If you are facing a problem, there are generally signs. For instance, if you have a mental illness , you may experience excessive fear or sadness, mood changes, and changes in sleeping or eating habits. Recognizing these signs can help you realize that an issue exists.
- Decide to solve the problem . Make a conscious decision to solve the issue at hand. Commit to yourself that you will go through the steps necessary to find a solution.
- Seek to fully understand the issue . Analyze the problem you face, looking at it from all sides. If your problem is relationship-related, for instance, ask yourself how the other person may be interpreting the issue. You might also consider how your actions might be contributing to the situation.
- Research potential options . Using the problem-solving strategies mentioned, research potential solutions. Make a list of options, then consider each one individually. What are some pros and cons of taking the available routes? What would you need to do to make them happen?
- Take action . Select the best solution possible and take action. Action is one of the steps required for change . So, go through the motions needed to resolve the issue.
- Try another option, if needed . If the solution you chose didn't work, don't give up. Either go through the problem-solving process again or simply try another option.
You can find a way to solve your problems as long as you keep working toward this goal—even if the best solution is simply to let go because no other good solution exists.
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
Dunbar K. Problem solving . A Companion to Cognitive Science . 2017. doi:10.1002/9781405164535.ch20
Stewart SL, Celebre A, Hirdes JP, Poss JW. Risk of suicide and self-harm in kids: The development of an algorithm to identify high-risk individuals within the children's mental health system . Child Psychiat Human Develop . 2020;51:913-924. doi:10.1007/s10578-020-00968-9
Rosenbusch H, Soldner F, Evans AM, Zeelenberg M. Supervised machine learning methods in psychology: A practical introduction with annotated R code . Soc Personal Psychol Compass . 2021;15(2):e12579. doi:10.1111/spc3.12579
Mishra S. Decision-making under risk: Integrating perspectives from biology, economics, and psychology . Personal Soc Psychol Rev . 2014;18(3):280-307. doi:10.1177/1088868314530517
Csikszentmihalyi M, Sawyer K. Creative insight: The social dimension of a solitary moment . In: The Systems Model of Creativity . 2015:73-98. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-9085-7_7
Chrysikou EG, Motyka K, Nigro C, Yang SI, Thompson-Schill SL. Functional fixedness in creative thinking tasks depends on stimulus modality . Psychol Aesthet Creat Arts . 2016;10(4):425‐435. doi:10.1037/aca0000050
Huang F, Tang S, Hu Z. Unconditional perseveration of the short-term mental set in chunk decomposition . Front Psychol . 2018;9:2568. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02568
National Alliance on Mental Illness. Warning signs and symptoms .
Mayer RE. Thinking, problem solving, cognition, 2nd ed .
Schooler JW, Ohlsson S, Brooks K. Thoughts beyond words: When language overshadows insight. J Experiment Psychol: General . 1993;122:166-183. doi:10.1037/0096-3445.2.166
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Problem Solving

Download or send
Choose your language, professional version.
A PDF of the resource, theoretical background, suggested therapist questions and prompts.
Premium Feature
Client version.
A PDF of the resource plus client-friendly instructions where appropriate.
Fillable version (PDF)
A fillable version of the resource. This can be edited and saved in Adobe Acrobat, or other PDF editing software.
Editable version (PPT)
An editable Microsoft PowerPoint version of the resource.
Translation Template
Are you a qualified therapist who would like to help with our translation project?
Languages this resource is available in
- Chinese (Simplified)
- Chinese (Traditional)
- English (GB)
- English (US)
- Spanish (International)
Mechanisms associated with this resource
- Skills deficit
Introduction & Theoretical Background
Problem Solving is a helpful intervention whenever clients present with difficulties, dilemmas, and conundrums, or when they experience repetitive thought such as rumination or worry. Effective problem solving is an essential life skill and this Problem Solving worksheet is designed to guide adults through steps which will help them to generate solutions to ‘stuck’ situations in their lives. It follows the qualities of effective problem solving outlined by Nezu, Nezu & D’Zurilla (2013), namely: clearly defining a problem; generation of alternative solutions; deliberative decision making; and the implementation of the chosen solution.
The therapist’s stance during problem solving should be one of collaborative curiosity. It is not for the therapist to pass judgment or to impose their preferred solution. Instead it is the clinician’s role to sit alongside clients and to help them examine the advantages and disadvantages of their options and, if the client is ‘stuck’ in rumination or worry, to help motivate them to take action to become unstuck – constructive rumination asks “How can I…?” questions instead of “Why…?” questions.
In their description of problem solving therapy Nezu, Nezu & D’Zurilla (2013) describe how it is helpful to elicit a positive orientation towards the problem which involves: being willing to appraise problems as challenges; remain optimistic that problems are solvable; remember that successful problem solving involves time and effort.
Therapist Guidance
- What is the nature of the problem?
- What are my goals?
- What is getting the way of me reaching my goals?
- “Can you think of any ways that you could make this problem not be a problem any more?”
- “What’s keeping this problem as a problem? What could you do to target that part of the problem?”
- “If your friend was bothered by a problem like this what might be something that you recommend they try?”
- “What would be some of the worst ways of solving a problem like this? And the best?”
- “How would Batman solve a problem like this?”
- Consider short term and long-term implications of each strategy
- Implications may relate to: emotional well-being, choices & opportunities, relationships, self-growth
- The next step is to consider which of the available options is the best solution. If you do not feel positive about any solutions, the choice becomes “Which is the least-worst?”. Remember that “even not-making-a-choice is a form of choice”.
- The last step of problem solving is putting a plan into action. Rumination, worry, and being in the horns of a dilemma are ‘stuck’ states which require a behavioral ‘nudge’ to become unstuck. Once you have put your plan into action it is important to monitor the outcome and to evaluate whether the actual outcome was consistent with the anticipated outcome.
References And Further Reading
- Beck, A.T., Rush, A.J., Shaw, B.F., & Emery, G. (1979). Cognitive therapy of depression . New York: Guilford. Nezu, A. M., Nezu, C. M., D’Zurilla, T. J. (2013). Problem-solving therapy: a treatment manual . New York: Springer.
- For clinicians
- For students
- Resources at your fingertips
- Designed for effectiveness
- Resources by problem
- Translation Project
- Help center
- Try us for free
- Terms & conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
Your browser is outdated. To ensure the best experience, update to the latest version of your preferred browser. Update
Problem Solving Packet
Guide your clients and groups through the problem solving process with the help of the Problem Solving Packet . Each page covers one of five problem solving steps with a rationale, tips, and questions. The steps include defining the problem, generating solutions, choosing one solution, implementing the solution, and reviewing the process.
Be sure to talk to your clients about how the five problem solving steps can be useful in day-to-day life. Are there any steps that they usually skip? What questions or steps helped them work through their problem?
Download Fillable Worksheet
Instructions.
PDF reading software is required to use fillable worksheets. This software is pre-installed on many devices. However, if it is not on your device, it can be downloaded for free. We recommend Adobe Acrobat Reader or Foxit Reader .
Notice: Opening a fillable worksheet directly within an internet browser (e.g. Internet Explorer, Chrome, or Safari) may prevent work from being saved. Instead, the file should be saved to your device and opened with a PDF reader.
To learn more or share these instructions, visit the Fillable Worksheet Instructions .
Download Customizable Worksheet
Use custom worksheets for the purpose of education and treatment.
Download, print, and share unlimited copies of custom worksheets.
Do not remove or alter copyright information.
Do not redistribute on a website, or as a part of a database or library.
Do not sell or sublicense custom worksheets.
Read our complete Terms and Conditions of Use .
PREVIEW - Page of

Download Options
Related Tools
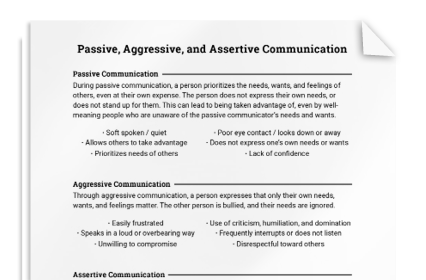
Passive, Aggressive, and Assertive Communication

Relationship Conflict Resolution
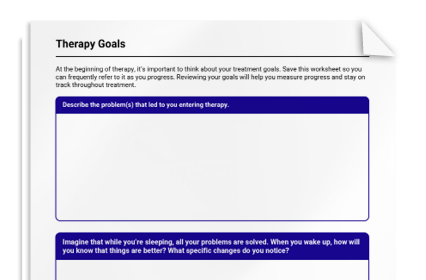
Therapy Goals
Become a Member!
- Customizable Worksheets
- Interactive Therapy Tools
- No More Ads
- Support Therapist Aid
Your account has been created.
Would you like to explore more features?
Recommended
Professional
Customizable and fillable worksheets.
Unlimited access to interactive therapy tools.
Support the creation of new tools for the entire mental health community.
Ad-free browsing.
Part of the Depression Grand Challenge:
Using the problem-solving framework
It’s normal to be worried. Worry can draw our attention and energy to urgent problems that need solving. But worry becomes an issue when it stops us from solving problems or when we spend time focusing on things we can’t control. Here, we share STAND skills for responding to worry over a solvable problem , reducing the time we spend worrying and how much those worries affect us.
First, when you notice your thoughts returning to negative outcomes, ask yourself two questions:
- What am I worried could happen? Be in touch with what is causing the worry.
- Do I have control over what could happen? In other words, is it solvable?
These two questions help us know which strategies might work better.
STAND Tip: Managing worry over a problem you can't solve
Problem-solving framework
Just because a problem can be solved doesn’t mean it’s easy to solve. We can even put off taking action because we aren’t sure what to do. This problem-solving framework created by Raphael Rose can help us decide what we should do:
- Write a clear, specific description of the problem. Identify the who, what, where, and when.
- Brainstorm solutions, as many as you can. All options should be considered.
- Rate the solutions. Consider pros and cons: time, effort, cost, possible negative consequences and the need to rely on others.
- Pick a solution. Choose one with the fewest cons and that can be done quickly.
- Make an action plan. Detail steps including the who, what, when, where, and how.
On your own: Walk through our problem-solving worksheet
Employ this problem-solving framework when you realize your worry concerns something solvable, as often as you need. Remember, worry over these kinds of problems is normal and able to be overcome with the help of this framework.
Downloadable resources to use on your own
Information Sheet
Managing Worry
Fillable Activity
Problem-Solving Worksheet
Need help now? Call the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline by dialing 988 .
© 2024 Regents of the University of California
- Accessibility
- Report Misconduct
- Privacy & Terms of Use
How to improve your problem solving skills and build effective problem solving strategies

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
54 great online tools for workshops and meetings, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, a step-by-step guide to planning a workshop.
- 18 Free Facilitation Resources We Think You’ll Love
Effective problem solving is all about using the right process and following a plan tailored to the issue at hand. Recognizing your team or organization has an issue isn’t enough to come up with effective problem solving strategies.
To truly understand a problem and develop appropriate solutions, you will want to follow a solid process, follow the necessary problem solving steps, and bring all of your problem solving skills to the table. We’ll forst look at what problem solving strategies you can employ with your team when looking for a way to approach the process. We’ll then discuss the problem solving skills you need to be more effective at solving problems, complete with an activity from the SessionLab library you can use to develop that skill in your team.
Let’s get to it!
Problem solving strategies
What skills do i need to be an effective problem solver, how can i improve my problem solving skills.
Problem solving strategies are methods of approaching and facilitating the process of problem-solving with a set of techniques , actions, and processes. Different strategies are more effective if you are trying to solve broad problems such as achieving higher growth versus more focused problems like, how do we improve our customer onboarding process?
Broadly, the problem solving steps outlined above should be included in any problem solving strategy though choosing where to focus your time and what approaches should be taken is where they begin to differ. You might find that some strategies ask for the problem identification to be done prior to the session or that everything happens in the course of a one day workshop.
The key similarity is that all good problem solving strategies are structured and designed. Four hours of open discussion is never going to be as productive as a four-hour workshop designed to lead a group through a problem solving process.
Good problem solving strategies are tailored to the team, organization and problem you will be attempting to solve. Here are some example problem solving strategies you can learn from or use to get started.
Use a workshop to lead a team through a group process
Often, the first step to solving problems or organizational challenges is bringing a group together effectively. Most teams have the tools, knowledge, and expertise necessary to solve their challenges – they just need some guidance in how to use leverage those skills and a structure and format that allows people to focus their energies.
Facilitated workshops are one of the most effective ways of solving problems of any scale. By designing and planning your workshop carefully, you can tailor the approach and scope to best fit the needs of your team and organization.
Problem solving workshop
- Creating a bespoke, tailored process
- Tackling problems of any size
- Building in-house workshop ability and encouraging their use
Workshops are an effective strategy for solving problems. By using tried and test facilitation techniques and methods, you can design and deliver a workshop that is perfectly suited to the unique variables of your organization. You may only have the capacity for a half-day workshop and so need a problem solving process to match.
By using our session planner tool and importing methods from our library of 700+ facilitation techniques, you can create the right problem solving workshop for your team. It might be that you want to encourage creative thinking or look at things from a new angle to unblock your groups approach to problem solving. By tailoring your workshop design to the purpose, you can help ensure great results.
One of the main benefits of a workshop is the structured approach to problem solving. Not only does this mean that the workshop itself will be successful, but many of the methods and techniques will help your team improve their working processes outside of the workshop.
We believe that workshops are one of the best tools you can use to improve the way your team works together. Start with a problem solving workshop and then see what team building, culture or design workshops can do for your organization!
Run a design sprint
Great for:
- aligning large, multi-discipline teams
- quickly designing and testing solutions
- tackling large, complex organizational challenges and breaking them down into smaller tasks
By using design thinking principles and methods, a design sprint is a great way of identifying, prioritizing and prototyping solutions to long term challenges that can help solve major organizational problems with quick action and measurable results.
Some familiarity with design thinking is useful, though not integral, and this strategy can really help a team align if there is some discussion around which problems should be approached first.
The stage-based structure of the design sprint is also very useful for teams new to design thinking. The inspiration phase, where you look to competitors that have solved your problem, and the rapid prototyping and testing phases are great for introducing new concepts that will benefit a team in all their future work.
It can be common for teams to look inward for solutions and so looking to the market for solutions you can iterate on can be very productive. Instilling an agile prototyping and testing mindset can also be great when helping teams move forwards – generating and testing solutions quickly can help save time in the long run and is also pretty exciting!
Break problems down into smaller issues
Organizational challenges and problems are often complicated and large scale in nature. Sometimes, trying to resolve such an issue in one swoop is simply unachievable or overwhelming. Try breaking down such problems into smaller issues that you can work on step by step. You may not be able to solve the problem of churning customers off the bat, but you can work with your team to identify smaller effort but high impact elements and work on those first.
This problem solving strategy can help a team generate momentum, prioritize and get some easy wins. It’s also a great strategy to employ with teams who are just beginning to learn how to approach the problem solving process. If you want some insight into a way to employ this strategy, we recommend looking at our design sprint template below!
Use guiding frameworks or try new methodologies
Some problems are best solved by introducing a major shift in perspective or by using new methodologies that encourage your team to think differently.
Props and tools such as Methodkit , which uses a card-based toolkit for facilitation, or Lego Serious Play can be great ways to engage your team and find an inclusive, democratic problem solving strategy. Remember that play and creativity are great tools for achieving change and whatever the challenge, engaging your participants can be very effective where other strategies may have failed.
LEGO Serious Play
- Improving core problem solving skills
- Thinking outside of the box
- Encouraging creative solutions
LEGO Serious Play is a problem solving methodology designed to get participants thinking differently by using 3D models and kinesthetic learning styles. By physically building LEGO models based on questions and exercises, participants are encouraged to think outside of the box and create their own responses.
Collaborate LEGO Serious Play exercises are also used to encourage communication and build problem solving skills in a group. By using this problem solving process, you can often help different kinds of learners and personality types contribute and unblock organizational problems with creative thinking.
Problem solving strategies like LEGO Serious Play are super effective at helping a team solve more skills-based problems such as communication between teams or a lack of creative thinking. Some problems are not suited to LEGO Serious Play and require a different problem solving strategy.
Card Decks and Method Kits
- New facilitators or non-facilitators
- Approaching difficult subjects with a simple, creative framework
- Engaging those with varied learning styles
Card decks and method kids are great tools for those new to facilitation or for whom facilitation is not the primary role. Card decks such as the emotional culture deck can be used for complete workshops and in many cases, can be used right out of the box. Methodkit has a variety of kits designed for scenarios ranging from personal development through to personas and global challenges so you can find the right deck for your particular needs.
Having an easy to use framework that encourages creativity or a new approach can take some of the friction or planning difficulties out of the workshop process and energize a team in any setting. Simplicity is the key with these methods. By ensuring everyone on your team can get involved and engage with the process as quickly as possible can really contribute to the success of your problem solving strategy.
Source external advice
Looking to peers, experts and external facilitators can be a great way of approaching the problem solving process. Your team may not have the necessary expertise, insights of experience to tackle some issues, or you might simply benefit from a fresh perspective. Some problems may require bringing together an entire team, and coaching managers or team members individually might be the right approach. Remember that not all problems are best resolved in the same manner.
If you’re a solo entrepreneur, peer groups, coaches and mentors can also be invaluable at not only solving specific business problems, but in providing a support network for resolving future challenges. One great approach is to join a Mastermind Group and link up with like-minded individuals and all grow together. Remember that however you approach the sourcing of external advice, do so thoughtfully, respectfully and honestly. Reciprocate where you can and prepare to be surprised by just how kind and helpful your peers can be!
Mastermind Group
- Solo entrepreneurs or small teams with low capacity
- Peer learning and gaining outside expertise
- Getting multiple external points of view quickly
Problem solving in large organizations with lots of skilled team members is one thing, but how about if you work for yourself or in a very small team without the capacity to get the most from a design sprint or LEGO Serious Play session?
A mastermind group – sometimes known as a peer advisory board – is where a group of people come together to support one another in their own goals, challenges, and businesses. Each participant comes to the group with their own purpose and the other members of the group will help them create solutions, brainstorm ideas, and support one another.
Mastermind groups are very effective in creating an energized, supportive atmosphere that can deliver meaningful results. Learning from peers from outside of your organization or industry can really help unlock new ways of thinking and drive growth. Access to the experience and skills of your peers can be invaluable in helping fill the gaps in your own ability, particularly in young companies.
A mastermind group is a great solution for solo entrepreneurs, small teams, or for organizations that feel that external expertise or fresh perspectives will be beneficial for them. It is worth noting that Mastermind groups are often only as good as the participants and what they can bring to the group. Participants need to be committed, engaged and understand how to work in this context.
Coaching and mentoring
- Focused learning and development
- Filling skills gaps
- Working on a range of challenges over time
Receiving advice from a business coach or building a mentor/mentee relationship can be an effective way of resolving certain challenges. The one-to-one format of most coaching and mentor relationships can really help solve the challenges those individuals are having and benefit the organization as a result.
A great mentor can be invaluable when it comes to spotting potential problems before they arise and coming to understand a mentee very well has a host of other business benefits. You might run an internal mentorship program to help develop your team’s problem solving skills and strategies or as part of a large learning and development program. External coaches can also be an important part of your problem solving strategy, filling skills gaps for your management team or helping with specific business issues.
Now we’ve explored the problem solving process and the steps you will want to go through in order to have an effective session, let’s look at the skills you and your team need to be more effective problem solvers.
Problem solving skills are highly sought after, whatever industry or team you work in. Organizations are keen to employ people who are able to approach problems thoughtfully and find strong, realistic solutions. Whether you are a facilitator , a team leader or a developer, being an effective problem solver is a skill you’ll want to develop.
Problem solving skills form a whole suite of techniques and approaches that an individual uses to not only identify problems but to discuss them productively before then developing appropriate solutions.
Here are some of the most important problem solving skills everyone from executives to junior staff members should learn. We’ve also included an activity or exercise from the SessionLab library that can help you and your team develop that skill.
If you’re running a workshop or training session to try and improve problem solving skills in your team, try using these methods to supercharge your process!
Active listening
Active listening is one of the most important skills anyone who works with people can possess. In short, active listening is a technique used to not only better understand what is being said by an individual, but also to be more aware of the underlying message the speaker is trying to convey. When it comes to problem solving, active listening is integral for understanding the position of every participant and to clarify the challenges, ideas and solutions they bring to the table.
Some active listening skills include:
- Paying complete attention to the speaker.
- Removing distractions.
- Avoid interruption.
- Taking the time to fully understand before preparing a rebuttal.
- Responding respectfully and appropriately.
- Demonstrate attentiveness and positivity with an open posture, making eye contact with the speaker, smiling and nodding if appropriate. Show that you are listening and encourage them to continue.
- Be aware of and respectful of feelings. Judge the situation and respond appropriately. You can disagree without being disrespectful.
- Observe body language.
- Paraphrase what was said in your own words, either mentally or verbally.
- Remain neutral.
- Reflect and take a moment before responding.
- Ask deeper questions based on what is said and clarify points where necessary.
Active Listening #hyperisland #skills #active listening #remote-friendly This activity supports participants to reflect on a question and generate their own solutions using simple principles of active listening and peer coaching. It’s an excellent introduction to active listening but can also be used with groups that are already familiar with it. Participants work in groups of three and take turns being: “the subject”, the listener, and the observer.
Analytical skills
All problem solving models require strong analytical skills, particularly during the beginning of the process and when it comes to analyzing how solutions have performed.
Analytical skills are primarily focused on performing an effective analysis by collecting, studying and parsing data related to a problem or opportunity.
It often involves spotting patterns, being able to see things from different perspectives and using observable facts and data to make suggestions or produce insight.
Analytical skills are also important at every stage of the problem solving process and by having these skills, you can ensure that any ideas or solutions you create or backed up analytically and have been sufficiently thought out.
Nine Whys #innovation #issue analysis #liberating structures With breathtaking simplicity, you can rapidly clarify for individuals and a group what is essentially important in their work. You can quickly reveal when a compelling purpose is missing in a gathering and avoid moving forward without clarity. When a group discovers an unambiguous shared purpose, more freedom and more responsibility are unleashed. You have laid the foundation for spreading and scaling innovations with fidelity.
Collaboration
Trying to solve problems on your own is difficult. Being able to collaborate effectively, with a free exchange of ideas, to delegate and be a productive member of a team is hugely important to all problem solving strategies.
Remember that whatever your role, collaboration is integral, and in a problem solving process, you are all working together to find the best solution for everyone.
Marshmallow challenge with debriefing #teamwork #team #leadership #collaboration In eighteen minutes, teams must build the tallest free-standing structure out of 20 sticks of spaghetti, one yard of tape, one yard of string, and one marshmallow. The marshmallow needs to be on top. The Marshmallow Challenge was developed by Tom Wujec, who has done the activity with hundreds of groups around the world. Visit the Marshmallow Challenge website for more information. This version has an extra debriefing question added with sample questions focusing on roles within the team.
Communication
Being an effective communicator means being empathetic, clear and succinct, asking the right questions, and demonstrating active listening skills throughout any discussion or meeting.
In a problem solving setting, you need to communicate well in order to progress through each stage of the process effectively. As a team leader, it may also fall to you to facilitate communication between parties who may not see eye to eye. Effective communication also means helping others to express themselves and be heard in a group.
Bus Trip #feedback #communication #appreciation #closing #thiagi #team This is one of my favourite feedback games. I use Bus Trip at the end of a training session or a meeting, and I use it all the time. The game creates a massive amount of energy with lots of smiles, laughs, and sometimes even a teardrop or two.
Creative problem solving skills can be some of the best tools in your arsenal. Thinking creatively, being able to generate lots of ideas and come up with out of the box solutions is useful at every step of the process.
The kinds of problems you will likely discuss in a problem solving workshop are often difficult to solve, and by approaching things in a fresh, creative manner, you can often create more innovative solutions.
Having practical creative skills is also a boon when it comes to problem solving. If you can help create quality design sketches and prototypes in record time, it can help bring a team to alignment more quickly or provide a base for further iteration.
The paper clip method #sharing #creativity #warm up #idea generation #brainstorming The power of brainstorming. A training for project leaders, creativity training, and to catalyse getting new solutions.
Critical thinking
Critical thinking is one of the fundamental problem solving skills you’ll want to develop when working on developing solutions. Critical thinking is the ability to analyze, rationalize and evaluate while being aware of personal bias, outlying factors and remaining open-minded.
Defining and analyzing problems without deploying critical thinking skills can mean you and your team go down the wrong path. Developing solutions to complex issues requires critical thinking too – ensuring your team considers all possibilities and rationally evaluating them.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Data analysis
Though it shares lots of space with general analytical skills, data analysis skills are something you want to cultivate in their own right in order to be an effective problem solver.
Being good at data analysis doesn’t just mean being able to find insights from data, but also selecting the appropriate data for a given issue, interpreting it effectively and knowing how to model and present that data. Depending on the problem at hand, it might also include a working knowledge of specific data analysis tools and procedures.
Having a solid grasp of data analysis techniques is useful if you’re leading a problem solving workshop but if you’re not an expert, don’t worry. Bring people into the group who has this skill set and help your team be more effective as a result.
Decision making
All problems need a solution and all solutions require that someone make the decision to implement them. Without strong decision making skills, teams can become bogged down in discussion and less effective as a result.
Making decisions is a key part of the problem solving process. It’s important to remember that decision making is not restricted to the leadership team. Every staff member makes decisions every day and developing these skills ensures that your team is able to solve problems at any scale. Remember that making decisions does not mean leaping to the first solution but weighing up the options and coming to an informed, well thought out solution to any given problem that works for the whole team.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
Dependability
Most complex organizational problems require multiple people to be involved in delivering the solution. Ensuring that the team and organization can depend on you to take the necessary actions and communicate where necessary is key to ensuring problems are solved effectively.
Being dependable also means working to deadlines and to brief. It is often a matter of creating trust in a team so that everyone can depend on one another to complete the agreed actions in the agreed time frame so that the team can move forward together. Being undependable can create problems of friction and can limit the effectiveness of your solutions so be sure to bear this in mind throughout a project.
Team Purpose & Culture #team #hyperisland #culture #remote-friendly This is an essential process designed to help teams define their purpose (why they exist) and their culture (how they work together to achieve that purpose). Defining these two things will help any team to be more focused and aligned. With support of tangible examples from other companies, the team members work as individuals and a group to codify the way they work together. The goal is a visual manifestation of both the purpose and culture that can be put up in the team’s work space.
Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligence is an important skill for any successful team member, whether communicating internally or with clients or users. In the problem solving process, emotional intelligence means being attuned to how people are feeling and thinking, communicating effectively and being self-aware of what you bring to a room.
There are often differences of opinion when working through problem solving processes, and it can be easy to let things become impassioned or combative. Developing your emotional intelligence means being empathetic to your colleagues and managing your own emotions throughout the problem and solution process. Be kind, be thoughtful and put your points across care and attention.
Being emotionally intelligent is a skill for life and by deploying it at work, you can not only work efficiently but empathetically. Check out the emotional culture workshop template for more!
Facilitation
As we’ve clarified in our facilitation skills post, facilitation is the art of leading people through processes towards agreed-upon objectives in a manner that encourages participation, ownership, and creativity by all those involved. While facilitation is a set of interrelated skills in itself, the broad definition of facilitation can be invaluable when it comes to problem solving. Leading a team through a problem solving process is made more effective if you improve and utilize facilitation skills – whether you’re a manager, team leader or external stakeholder.
The Six Thinking Hats #creative thinking #meeting facilitation #problem solving #issue resolution #idea generation #conflict resolution The Six Thinking Hats are used by individuals and groups to separate out conflicting styles of thinking. They enable and encourage a group of people to think constructively together in exploring and implementing change, rather than using argument to fight over who is right and who is wrong.
Flexibility
Being flexible is a vital skill when it comes to problem solving. This does not mean immediately bowing to pressure or changing your opinion quickly: instead, being flexible is all about seeing things from new perspectives, receiving new information and factoring it into your thought process.
Flexibility is also important when it comes to rolling out solutions. It might be that other organizational projects have greater priority or require the same resources as your chosen solution. Being flexible means understanding needs and challenges across the team and being open to shifting or arranging your own schedule as necessary. Again, this does not mean immediately making way for other projects. It’s about articulating your own needs, understanding the needs of others and being able to come to a meaningful compromise.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
Working in any group can lead to unconscious elements of groupthink or situations in which you may not wish to be entirely honest. Disagreeing with the opinions of the executive team or wishing to save the feelings of a coworker can be tricky to navigate, but being honest is absolutely vital when to comes to developing effective solutions and ensuring your voice is heard.
Remember that being honest does not mean being brutally candid. You can deliver your honest feedback and opinions thoughtfully and without creating friction by using other skills such as emotional intelligence.
Explore your Values #hyperisland #skills #values #remote-friendly Your Values is an exercise for participants to explore what their most important values are. It’s done in an intuitive and rapid way to encourage participants to follow their intuitive feeling rather than over-thinking and finding the “correct” values. It is a good exercise to use to initiate reflection and dialogue around personal values.
Initiative
The problem solving process is multi-faceted and requires different approaches at certain points of the process. Taking initiative to bring problems to the attention of the team, collect data or lead the solution creating process is always valuable. You might even roadtest your own small scale solutions or brainstorm before a session. Taking initiative is particularly effective if you have good deal of knowledge in that area or have ownership of a particular project and want to get things kickstarted.
That said, be sure to remember to honor the process and work in service of the team. If you are asked to own one part of the problem solving process and you don’t complete that task because your initiative leads you to work on something else, that’s not an effective method of solving business challenges.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.

Impartiality
A particularly useful problem solving skill for product owners or managers is the ability to remain impartial throughout much of the process. In practice, this means treating all points of view and ideas brought forward in a meeting equally and ensuring that your own areas of interest or ownership are not favored over others.
There may be a stage in the process where a decision maker has to weigh the cost and ROI of possible solutions against the company roadmap though even then, ensuring that the decision made is based on merit and not personal opinion.
Empathy map #frame insights #create #design #issue analysis An empathy map is a tool to help a design team to empathize with the people they are designing for. You can make an empathy map for a group of people or for a persona. To be used after doing personas when more insights are needed.
Being a good leader means getting a team aligned, energized and focused around a common goal. In the problem solving process, strong leadership helps ensure that the process is efficient, that any conflicts are resolved and that a team is managed in the direction of success.
It’s common for managers or executives to assume this role in a problem solving workshop, though it’s important that the leader maintains impartiality and does not bulldoze the group in a particular direction. Remember that good leadership means working in service of the purpose and team and ensuring the workshop is a safe space for employees of any level to contribute. Take a look at our leadership games and activities post for more exercises and methods to help improve leadership in your organization.
Leadership Pizza #leadership #team #remote-friendly This leadership development activity offers a self-assessment framework for people to first identify what skills, attributes and attitudes they find important for effective leadership, and then assess their own development and initiate goal setting.
In the context of problem solving, mediation is important in keeping a team engaged, happy and free of conflict. When leading or facilitating a problem solving workshop, you are likely to run into differences of opinion. Depending on the nature of the problem, certain issues may be brought up that are emotive in nature.
Being an effective mediator means helping those people on either side of such a divide are heard, listen to one another and encouraged to find common ground and a resolution. Mediating skills are useful for leaders and managers in many situations and the problem solving process is no different.
Conflict Responses #hyperisland #team #issue resolution A workshop for a team to reflect on past conflicts, and use them to generate guidelines for effective conflict handling. The workshop uses the Thomas-Killman model of conflict responses to frame a reflective discussion. Use it to open up a discussion around conflict with a team.
Planning
Solving organizational problems is much more effective when following a process or problem solving model. Planning skills are vital in order to structure, deliver and follow-through on a problem solving workshop and ensure your solutions are intelligently deployed.
Planning skills include the ability to organize tasks and a team, plan and design the process and take into account any potential challenges. Taking the time to plan carefully can save time and frustration later in the process and is valuable for ensuring a team is positioned for success.
3 Action Steps #hyperisland #action #remote-friendly This is a small-scale strategic planning session that helps groups and individuals to take action toward a desired change. It is often used at the end of a workshop or programme. The group discusses and agrees on a vision, then creates some action steps that will lead them towards that vision. The scope of the challenge is also defined, through discussion of the helpful and harmful factors influencing the group.
Prioritization
As organisations grow, the scale and variation of problems they face multiplies. Your team or is likely to face numerous challenges in different areas and so having the skills to analyze and prioritize becomes very important, particularly for those in leadership roles.
A thorough problem solving process is likely to deliver multiple solutions and you may have several different problems you wish to solve simultaneously. Prioritization is the ability to measure the importance, value, and effectiveness of those possible solutions and choose which to enact and in what order. The process of prioritization is integral in ensuring the biggest challenges are addressed with the most impactful solutions.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
Project management
Some problem solving skills are utilized in a workshop or ideation phases, while others come in useful when it comes to decision making. Overseeing an entire problem solving process and ensuring its success requires strong project management skills.
While project management incorporates many of the other skills listed here, it is important to note the distinction of considering all of the factors of a project and managing them successfully. Being able to negotiate with stakeholders, manage tasks, time and people, consider costs and ROI, and tie everything together is massively helpful when going through the problem solving process.
Record keeping
Working out meaningful solutions to organizational challenges is only one part of the process. Thoughtfully documenting and keeping records of each problem solving step for future consultation is important in ensuring efficiency and meaningful change.
For example, some problems may be lower priority than others but can be revisited in the future. If the team has ideated on solutions and found some are not up to the task, record those so you can rule them out and avoiding repeating work. Keeping records of the process also helps you improve and refine your problem solving model next time around!
Personal Kanban #gamestorming #action #agile #project planning Personal Kanban is a tool for organizing your work to be more efficient and productive. It is based on agile methods and principles.
Research skills
Conducting research to support both the identification of problems and the development of appropriate solutions is important for an effective process. Knowing where to go to collect research, how to conduct research efficiently, and identifying pieces of research are relevant are all things a good researcher can do well.
In larger groups, not everyone has to demonstrate this ability in order for a problem solving workshop to be effective. That said, having people with research skills involved in the process, particularly if they have existing area knowledge, can help ensure the solutions that are developed with data that supports their intention. Remember that being able to deliver the results of research efficiently and in a way the team can easily understand is also important. The best data in the world is only as effective as how it is delivered and interpreted.
Customer experience map #ideation #concepts #research #design #issue analysis #remote-friendly Customer experience mapping is a method of documenting and visualizing the experience a customer has as they use the product or service. It also maps out their responses to their experiences. To be used when there is a solution (even in a conceptual stage) that can be analyzed.
Risk management
Managing risk is an often overlooked part of the problem solving process. Solutions are often developed with the intention of reducing exposure to risk or solving issues that create risk but sometimes, great solutions are more experimental in nature and as such, deploying them needs to be carefully considered.
Managing risk means acknowledging that there may be risks associated with more out of the box solutions or trying new things, but that this must be measured against the possible benefits and other organizational factors.
Be informed, get the right data and stakeholders in the room and you can appropriately factor risk into your decision making process.
Decisions, Decisions… #communication #decision making #thiagi #action #issue analysis When it comes to decision-making, why are some of us more prone to take risks while others are risk-averse? One explanation might be the way the decision and options were presented. This exercise, based on Kahneman and Tversky’s classic study , illustrates how the framing effect influences our judgement and our ability to make decisions . The participants are divided into two groups. Both groups are presented with the same problem and two alternative programs for solving them. The two programs both have the same consequences but are presented differently. The debriefing discussion examines how the framing of the program impacted the participant’s decision.
Team-building
No single person is as good at problem solving as a team. Building an effective team and helping them come together around a common purpose is one of the most important problem solving skills, doubly so for leaders. By bringing a team together and helping them work efficiently, you pave the way for team ownership of a problem and the development of effective solutions.
In a problem solving workshop, it can be tempting to jump right into the deep end, though taking the time to break the ice, energize the team and align them with a game or exercise will pay off over the course of the day.
Remember that you will likely go through the problem solving process multiple times over an organization’s lifespan and building a strong team culture will make future problem solving more effective. It’s also great to work with people you know, trust and have fun with. Working on team building in and out of the problem solving process is a hallmark of successful teams that can work together to solve business problems.
9 Dimensions Team Building Activity #ice breaker #teambuilding #team #remote-friendly 9 Dimensions is a powerful activity designed to build relationships and trust among team members. There are 2 variations of this icebreaker. The first version is for teams who want to get to know each other better. The second version is for teams who want to explore how they are working together as a team.
Time management
The problem solving process is designed to lead a team from identifying a problem through to delivering a solution and evaluating its effectiveness. Without effective time management skills or timeboxing of tasks, it can be easy for a team to get bogged down or be inefficient.
By using a problem solving model and carefully designing your workshop, you can allocate time efficiently and trust that the process will deliver the results you need in a good timeframe.
Time management also comes into play when it comes to rolling out solutions, particularly those that are experimental in nature. Having a clear timeframe for implementing and evaluating solutions is vital for ensuring their success and being able to pivot if necessary.
Improving your skills at problem solving is often a career-long pursuit though there are methods you can use to make the learning process more efficient and to supercharge your problem solving skillset.
Remember that the skills you need to be a great problem solver have a large overlap with those skills you need to be effective in any role. Investing time and effort to develop your active listening or critical thinking skills is valuable in any context. Here are 7 ways to improve your problem solving skills.
Share best practices
Remember that your team is an excellent source of skills, wisdom, and techniques and that you should all take advantage of one another where possible. Best practices that one team has for solving problems, conducting research or making decisions should be shared across the organization. If you have in-house staff that have done active listening training or are data analysis pros, have them lead a training session.
Your team is one of your best resources. Create space and internal processes for the sharing of skills so that you can all grow together.
Ask for help and attend training
Once you’ve figured out you have a skills gap, the next step is to take action to fill that skills gap. That might be by asking your superior for training or coaching, or liaising with team members with that skill set. You might even attend specialized training for certain skills – active listening or critical thinking, for example, are business-critical skills that are regularly offered as part of a training scheme.
Whatever method you choose, remember that taking action of some description is necessary for growth. Whether that means practicing, getting help, attending training or doing some background reading, taking active steps to improve your skills is the way to go.
Learn a process
Problem solving can be complicated, particularly when attempting to solve large problems for the first time. Using a problem solving process helps give structure to your problem solving efforts and focus on creating outcomes, rather than worrying about the format.
Tools such as the seven-step problem solving process above are effective because not only do they feature steps that will help a team solve problems, they also develop skills along the way. Each step asks for people to engage with the process using different skills and in doing so, helps the team learn and grow together. Group processes of varying complexity and purpose can also be found in the SessionLab library of facilitation techniques . Using a tried and tested process and really help ease the learning curve for both those leading such a process, as well as those undergoing the purpose.
Effective teams make decisions about where they should and shouldn’t expend additional effort. By using a problem solving process, you can focus on the things that matter, rather than stumbling towards a solution haphazardly.
Create a feedback loop
Some skills gaps are more obvious than others. It’s possible that your perception of your active listening skills differs from those of your colleagues.
It’s valuable to create a system where team members can provide feedback in an ordered and friendly manner so they can all learn from one another. Only by identifying areas of improvement can you then work to improve them.
Remember that feedback systems require oversight and consideration so that they don’t turn into a place to complain about colleagues. Design the system intelligently so that you encourage the creation of learning opportunities, rather than encouraging people to list their pet peeves.
While practice might not make perfect, it does make the problem solving process easier. If you are having trouble with critical thinking, don’t shy away from doing it. Get involved where you can and stretch those muscles as regularly as possible.
Problem solving skills come more naturally to some than to others and that’s okay. Take opportunities to get involved and see where you can practice your skills in situations outside of a workshop context. Try collaborating in other circumstances at work or conduct data analysis on your own projects. You can often develop those skills you need for problem solving simply by doing them. Get involved!
Use expert exercises and methods
Learn from the best. Our library of 700+ facilitation techniques is full of activities and methods that help develop the skills you need to be an effective problem solver. Check out our templates to see how to approach problem solving and other organizational challenges in a structured and intelligent manner.
There is no single approach to improving problem solving skills, but by using the techniques employed by others you can learn from their example and develop processes that have seen proven results.
Try new ways of thinking and change your mindset
Using tried and tested exercises that you know well can help deliver results, but you do run the risk of missing out on the learning opportunities offered by new approaches. As with the problem solving process, changing your mindset can remove blockages and be used to develop your problem solving skills.
Most teams have members with mixed skill sets and specialties. Mix people from different teams and share skills and different points of view. Teach your customer support team how to use design thinking methods or help your developers with conflict resolution techniques. Try switching perspectives with facilitation techniques like Flip It! or by using new problem solving methodologies or models. Give design thinking, liberating structures or lego serious play a try if you want to try a new approach. You will find that framing problems in new ways and using existing skills in new contexts can be hugely useful for personal development and improving your skillset. It’s also a lot of fun to try new things. Give it a go!
Encountering business challenges and needing to find appropriate solutions is not unique to your organization. Lots of very smart people have developed methods, theories and approaches to help develop problem solving skills and create effective solutions. Learn from them!
Books like The Art of Thinking Clearly , Think Smarter, or Thinking Fast, Thinking Slow are great places to start, though it’s also worth looking at blogs related to organizations facing similar problems to yours, or browsing for success stories. Seeing how Dropbox massively increased growth and working backward can help you see the skills or approach you might be lacking to solve that same problem. Learning from others by reading their stories or approaches can be time-consuming but ultimately rewarding.
A tired, distracted mind is not in the best position to learn new skills. It can be tempted to burn the candle at both ends and develop problem solving skills outside of work. Absolutely use your time effectively and take opportunities for self-improvement, though remember that rest is hugely important and that without letting your brain rest, you cannot be at your most effective.
Creating distance between yourself and the problem you might be facing can also be useful. By letting an idea sit, you can find that a better one presents itself or you can develop it further. Take regular breaks when working and create a space for downtime. Remember that working smarter is preferable to working harder and that self-care is important for any effective learning or improvement process.
Want to design better group processes?
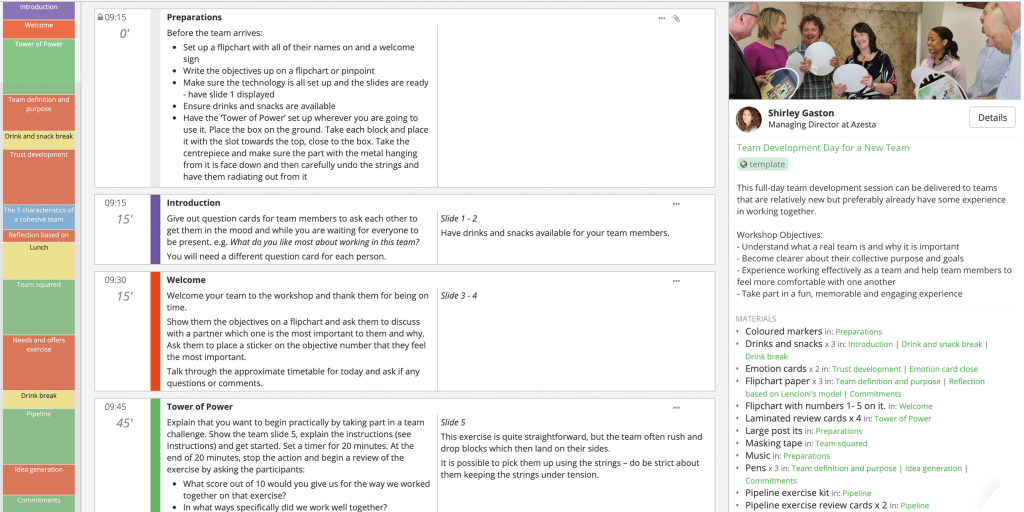
Over to you
Now we’ve explored some of the key problem solving skills and the problem solving steps necessary for an effective process, you’re ready to begin developing more effective solutions and leading problem solving workshops.
Need more inspiration? Check out our post on problem solving activities you can use when guiding a group towards a great solution in your next workshop or meeting. Have questions? Did you have a great problem solving technique you use with your team? Get in touch in the comments below. We’d love to chat!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of great workshop tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your life easier and run better workshops and meetings. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free

More From Forbes
A psychologist tells you why you need to escape the toxic world of self-help.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Self-help sells. But it may not lead to self-improvement.
Many people come to therapy wondering why consuming self-help content isn’t helping them. They ask questions like:
- “I read more self-help books than anyone I know. It makes me feel inferior because other people don’t seem to need it as much as I do. What is wrong with me?”
- “My mindset changes with every self-help guru I come across. Because of this, I am unable to follow through on any of my self-improvement goals. What do I do about this?”
- “I spend a lot of money on self-help events. Sometimes I don’t even want to go, but I have a fear of missing out on valuable tips. How do I pick and choose?”
- “My Instagram feed is full of self-help influencers who claim their method is the best. How do I know who to trust?”
From how-to books to life coaching seminars, self-help is a multi-billion dollar market. While there’s nothing wrong with seeking out ways to improve yourself, self-help is not a cure-all solution. In fact, it may do more harm than good.
For example, a study showed that those who consumed self-help books had higher levels of cortisol (the stress hormone) and were more likely to have depressive symptoms compared to those who did not.
The problem may be that most self-help content available to the masses follows a one-size-fits-all approach to mental health.
Look at it this way. When you approach a mental health practitioner for help, they listen to you, understand you, and offer solutions that work for your unique situation.
On the contrary, when someone writes a self-help book, their goal is to sell to as many people as they can. So, self-help content is often oversimplified and sweetened with a false sense of hope and meaningless pats on the back. This is why so many people feel they can relate to these books and feel happy while reading them; it’s essentially toxic positivity .
Understand that, when it comes to self-help, it’s easy to get caught up in a cycle of books, seminars, and videos without really addressing the issues in your life. It can become an addiction of its own. Often, seeking out self-help content is a symptom rather than a solution.
Here are two ways to achieve self-improvement without being dragged into the toxic world of self-help.
#1. Understand that not all self-help is created equal
In general, the self-help industry loves to promise easy fixes for all your mental health problems. In fact, this is what keeps them selling in such large numbers.
But ask yourself this: if these promises were true, why do so many people rely on qualified mental health practitioners for help with their mental health issues? Although millions of self-help gurus peddle their magic solutions online, why is the demand for mental health practitioners consistently on the rise ?
This is because when it comes to helping people with a serious issue like mental health, legitimacy is paramount. Unfortunately, a good percentage of self-help gurus have no qualifications to discuss the topics they choose to discuss.
A classic study published in The American Psychologist has suggested that, because self-help is often laymen helping laymen, the solutions described in self-help books may not take into account an individual’s nuanced symptoms, which a psychotherapist is trained to interpret. The study, which reviewed over a 100 studies and case reports, also found that self-help treatment plans were often not easy to follow and were likely to be misinterpreted by the intended audience.
There are legitimate sources of self-help. These are the ones that don’t oversell their mission statements. Keep an eye out for such sources. Always run it by a qualified mental health professional before you commit to a do-it-yourself treatment plan.
#2. Understand the importance of setting goals and taking actionable steps
The business model of many self-help gurus is dependent on two connected ideas:
- Sell feel-good content to a wide audience
- Get repeat customers
This is why you often hear them talk about their exclusive newsletter, ebook, video, or seminar. They’ve built a customer base that is loyal to their framework of ‘solutions.’
To keep yourself on track, it is important that you think for yourself. Don’t be vague about your goals for self-improvement.
One study published in Current Directions in Psychological Science explained the importance of goal setting in improving motivation, self-esteem, autonomy, and self-confidence. And, as we know , you are more likely to achieve your goal if your goal is challenging and well-defined.
Once you know what you want to improve on, use legitimate self-help sources. Take the tips that you can implement in your everyday life, put them into practice, and don’t get hung up on the next problem to solve.
Understand that self-help content needs to stand on its own merit, not your loyalty to the guru who created it.
Self-help books can be a great resource for personal growth. However, it’s important to be aware of the dangers of unregulated advice, quick fixes, and one-size-fits-all solutions. When used with caution and critical thought, self-help materials can be a valuable tool on your journey to personal growth and development.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.

Cognitive Reappraisal
3 simple solutions to complex health challenges, ease suffering and improve well-being with these easy-to-use actions..
Posted June 28, 2024 | Reviewed by Ray Parker
- What Is Cognitive Reappraisal
- Find a therapist near me.
- People with complex mental health issues are more likely to seek help if the referral process is easy.
- Labels on toxic products raise awareness and reduce addictive behaviors.
- Simple reminders are an effective way to increase healthy behaviors.
Many health and mental health problems defy easy solutions. But some quick fixes are so simple and effective that they can lead to amazing progress. In fact, they make me want to slap my forehead and shout, “D'oh! Why didn’t I think of that?”
Here are three huge steps toward remedying complicated health challenges, starting with the most brilliant one of all.
1. Call 988 to get help and referrals for psychological problems. Who was the genius who realized there could be a three-digit phone number, parallel to 911, to call for mental health referrals and crises? Whoever you are, thank you! Before 988, a helping professional, a concerned friend, or a troubled person had to memorize or look up a random 10-digit number or fumble around for a crisis helpline business card. But now, people can just call 988 to reach the Suicide and Crisis Lifeline and speak with a trained crisis counselor. The website states, “The 988 Lifeline provides 24/7, free and confidential support for people in distress, prevention and crisis resources for you or your loved ones, and best practices for professionals in the United States."
Since 988 was rolled out in mid-2022, call volume has increased by 46%, texts by 1,135%, and chats by 141%, according to an April 2024 report by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA). On the darker side, many Americans are still unaware of the new number, and some states have not adequately funded the program. Still, the increased volume of calls and contacts indicates that the 988 system is working.
Remember: 988 is the 911 of mental health .
2. Stick a label on toxic substances and reduce addictive behaviors. Labeling harmful substances, such as cigarettes and other tobacco products, has been a surprisingly effective way to curb smoking —the one habit with the greatest potential to cause death, disability, and disease. Since 1965, labels on cigarette packets have displayed this warning or a variation of it: Warning: Cigarette Smoking Is Hazardous to Your Health. In the U.S., in 1965, approximately 42% of adults were smokers (52% of men and 34% of women); in 2021, only 11.5% of U.S. adults were smokers. Providing information and raising awareness via labels was one reason for the steady drop over time.
Labels are now being considered for other harmful substances, too. Most people are aware that smoking causes cancer, but did you know that alcohol increases the risk of cancer, too? Only about one in three Americans are aware that drinking alcoholic beverages can increase their risk of cancer, according to The New York Times . While some people do associate liver disease and liver cancer with alcohol, it is not widely known that alcohol has also been associated with other cancers, such as breast, colorectal, and esophageal cancers.
Since the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not regulate most alcohol products, but rather a bureau within the Treasury Department, the U.S. does not currently require warning labels, calorie information, or nutrition labels on alcohol. If they did, usage would likely fall. For example, in a study from the Yukon Territory, “Sales of products carrying the (warning) labels ... fell by around 7 percent during the intervention and several months that followed.”
Interestingly, labels can also work in the psychological domain. A series of studies by UCLA psychologist Matthew Lieberman showed the value of attaching labels to your own swirling thoughts and feelings. Study participants who inwardly named emotions like “ anger ” or “ fear ” had less activity in the amygdala, the fight-or-flight part of the brain, and more activity in the prefrontal cortex, the thinking part of the brain. In other words, labeling their feelings shifted them from an emotional state to a problem-solving state. (More here .)
3. Simple reminders can increase healthy behaviors. In this busy life, it’s easy for things you really want to do—like send a birthday card to your friend—to slide to the bottom of your to-do list, and then off of it altogether.
So it is with COVID vaccination boosters: Even people who want to get one might neglect to prioritize it. A recent study looked at whether offering free round-trip transportation to vaccination sites would increase the number of people getting boosters. Nope. The researchers discovered that offering a free ride had no effect on increasing vaccination rates.
What did work, however, were simple text reminders . As the research abstract puts it, “…behaviourally informed COVID-19 vaccination reminders…increased the 30-day COVID-19 booster uptake by 21% (1.05 percentage points) and spilled over to increase 30-day influenza vaccinations by 8% (0.34 percentage points) in our megastudy.” In other studies, simple reminders from healthcare providers also significantly raised booster rates.

What could be easier and more cost-effective than sending a text? Yet such a simple action can significantly reduce hospitalizations, disease, and deaths from COVID-19, flu, and other diseases.
A Simple Summary
- Make the right thing to do the easy thing to do.
- Labeling, whether products or thoughts, can raise awareness and reduce harmful and even addictive behaviors.
- Simple reminders are often the best way to help people increase healthy and socially valuable behaviors.
(c) Meg Selig, 2024. All rights reserved. For permissions, click here.
Milkman, K.L., et al. "Megastudy shows that reminders boost vaccination but adding free rides does not." Nature , 26 June 2024. Megastudy shows that reminders boost vaccination but adding free rides does not | Nature
https://www.nytimes.com/2024/04/09/health/alcohol-cancer-warning.html

Meg Selig is the author of Changepower! 37 Secrets to Habit Change Success .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that could derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face triggers with less reactivity and get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- Our Mission
7 Strategies to Activate Students’ SEL Skills
Social and emotional learning programs are most effective when students are given plenty of opportunities to practice those skills.

Even as more schools adopt curriculum programs related to social and emotional learning (SEL), we don’t always see corresponding improvement in youth mental health and achievement. That’s because SEL skills are learned most deeply when activated by adults in the learning environment. Let’s look at activating strategies that anyone can use—teachers, mental-health professionals, parents, or youth workers—to exercise students’ SEL muscles, regardless of whether they are being exposed to systematic SEL instruction.
Each strategy is followed by the Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) 5 skill to which it is most aligned.
7 SEL-Activating Strategies
1. Open-ended questions (social awareness). This strategy involves giving students multiple choices (“Do you think it might be a or b or c ? Why?”) or asking an open-ended question, starting with “How/Where/When might others see the situation differently?” This helps to foster consideration of other perspectives. One especially useful question is “What is positive/helpful/new in the comment your classmate just made?”
2. Flexible thinking (ethical decision-making). We want students to think outside of the box and not be satisfied that the first idea that comes to them is the best one . Key words to use are else and other and their variants, as in “What else can you think of?” or “How many other/different ways might that happen?”
Quick brainstorming is also useful (“Think of at least two other ideas after the first one you have”), as is alternative problem-solving, where you ask students to imagine various ways that other people might see/feel about a situation, in literature, history, current events, athletics, etc.
3. Self-calming and focusing (self-management). Two key elements help activate students’ self-calming strategies . First, remind or prompt them to use previously learned procedures (such as a breathing technique or visualizing a safe, calming place) in upcoming situations. It’s also helpful to have students engage in mindfulness activities at key points during the day.
Second, ask students as needed, “What should you be focusing on right now?” and “What exactly are your classmates/group/team members saying and expressing now?” Repeated prompting in this way fosters students’ asking themselves these questions and improving their own focus on themselves and those around them .
4. Goal setting (self-management). With all the distractions our students face, we need to activate their goal-setting skills. The best way to do that is through asking questions that help them articulate key outcomes (not unrelated to focusing). For example, prompts such as these all help with goal setting:
- “What do you/what do they/what did they want to have happen?”
- “What was/is the problem you are trying to solve?”
- “How would you like things to wind up at the end?”
It’s also valuable to periodically ask students to set personal and school-related goals (e.g., one or two areas in which they want to make themselves a better person, areas of character or academics they might want to improve, and/or ways they can make their class/group/team better.
5. Constructive feedback (relationship skills). Given how much work is now being done in teams and groups, constructive feedback prompts activate necessary relationship skills such as consideration for others and perspective taking.
Approaches like the “compliment sandwich” (one thing done well, one thing to improve, one thing done well) and helping students structure feedback in terms of “You said/did…; I think/feel these aspects were good/on target” and “I have some questions about… Do you think… could use some reconsideration?” tend to enable others to hear one’s feedback.
To help students pay attention to the impact of their comments and activate their improvement skills in this area, ask, “How will/did he/she take what you are saying?; What can you say to him/her that would be helpful/make his/her work better?”
6. Reflection (self-awareness). Reflection is the capacity to review one’s own actions and feedback from others, determine strengths and areas in need of improvement, and incorporate that information in a constructive spirit. It involves one’s thoughts, feelings, behaviors, goals, and purpose .
We reflect on what was learned (What is one takeaway from that experience?), what feelings arose (How are you feeling at this moment? How do you think X might be feeling at this moment/after Y or Z happened?), or how one’s ideas might have been changed (What questions have been raised for you? What new goals might you set?/How might your plans be adjusted?). Many students benefit from keeping a paper or electronic reflection journal.
7. Preparation for presentations (all skills). Presentation is the process of taking the results of one’s work and organizing it and communicating it for particular audiences. Students are “presenting” all the time, including deciding what and how to respond to a teacher’s question or classmate’s comment, how to craft an essay in response to an assignment, even how to read aloud. Help students make these presentation situations explicit by problem-solving the perspective of their audience and planning how to communicate information in ways that consider audiences’ emotions, motivations, or interests and specific requirements of the presentation context (e.g., length of time available, nature of the venue).
By using activating strategies consistently, we help students exercise their SEL muscles across varied school circumstances. This will improve their social and emotional competencies and character as well as their academic achievement and their contributions to school, classes, teams, clubs, and other relevant group contexts.

30 Examples: Self Evaluation Comments for Problem Solving
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 19, 2023 — 9 minutes to read
Self-evaluation is an essential aspect of professional development. It helps you to identify areas of improvement and measure your progress towards achieving your goals. By evaluating your problem-solving skills, you can identify your strengths and weaknesses and take steps to improve your performance.
Problem Solving Self-Evaluation Comments Examples
- I was able to identify the root cause of the problem and develop a solution that addressed it effectively.
- I was able to think outside the box and come up with a creative solution to a complex problem.
- I was able to collaborate effectively with my team members to solve a challenging problem.
- I was able to prioritize tasks and allocate resources efficiently to solve a problem within a tight deadline.
- I was able to remain calm and composed under pressure while solving a critical problem.
- I was able to analyze data and information to identify patterns and trends that helped me solve a problem.
- I was able to communicate clearly and effectively with stakeholders to understand their needs and solve their problems.
- I was able to adapt to changing circumstances and adjust my problem-solving approach accordingly.
- I was able to learn from my mistakes and apply those lessons to future problem-solving situations.
- I was able to use critical thinking skills to evaluate multiple options and select the best solution to a problem.
- I was able to break down a complex problem into smaller, more manageable parts and solve each part individually.
- I was able to identify potential obstacles and develop contingency plans to overcome them while solving a problem.
- I was able to leverage my technical expertise to solve a problem that required specialized knowledge.
- I was able to use my creativity and innovation to develop a unique solution to a problem.
- I was able to gather and analyze feedback from stakeholders to continuously improve my problem-solving approach.
- I was able to use my leadership skills to motivate and guide my team members towards a successful problem-solving outcome.
- I was able to effectively manage competing priorities and still solve a problem within the given timeline.
- I was able to use my communication skills to explain complex technical solutions to non-technical stakeholders.
- I was able to use my analytical skills to identify patterns and trends that helped me solve a problem more efficiently.
- I was able to use my problem-solving skills to identify opportunities for process improvements and implement them successfully.
- I was able to use my research skills to gather information that helped me solve a problem more effectively.
- I was able to use my project management skills to break down a large-scale problem into smaller, more manageable tasks.
- I was able to use my negotiation skills to reach a mutually beneficial solution to a problem.
- I was able to remain objective and unbiased while evaluating potential solutions to a problem.
- I was able to use my attention to detail to identify small but critical issues that were contributing to a larger problem.
- I was able to use my interpersonal skills to build strong relationships with stakeholders and work collaboratively towards a solution.
- I was able to use my problem-solving skills to find a solution that balanced the needs of multiple stakeholders.
- I was able to use my persistence and determination to keep working towards a solution even when faced with obstacles.
- I was able to use my time management skills to prioritize tasks and allocate my time efficiently while solving a problem.
- I was able to use my empathy and understanding of others’ perspectives to develop a solution that met everyone’s needs.
Improving Problem Solving Skills
To become a better problem solver, you need to develop critical thinking skills, effective communication skills, prioritize tasks, and use brainstorming techniques. Here are some tips to help you improve your problem-solving skills:
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze a situation, identify problems, and come up with creative solutions. To develop critical thinking skills, you need to:
- Ask questions: Don’t be afraid to ask questions to clarify the problem or gather more information.
- Challenge assumptions: Don’t accept things at face value. Question assumptions and look for evidence to support them.
- Evaluate evidence: Look for evidence that supports or contradicts your assumptions. Evaluate the quality and reliability of the evidence.
- Consider alternative perspectives: Try to see the problem from different angles and consider alternative solutions.
Effective Communication Skills
Effective communication is essential for problem-solving because it helps you:
- Understand the problem: Good communication skills help you clarify the problem and understand what is expected of you.
- Collaborate with others: Effective communication skills help you work with others to find solutions.
- Express your ideas clearly: Clear communication helps you convey your ideas and solutions to others.
To improve your communication skills, you need to:
- Listen actively: Listen to others and try to understand their perspective.
- Speak clearly: Speak clearly and concisely to avoid confusion.
- Use nonverbal cues: Pay attention to body language and other nonverbal cues to understand what others are saying.
Prioritizing Tasks
Prioritizing tasks is essential for effective problem-solving because it helps you:
- Focus on the most important tasks: Prioritizing helps you focus on the tasks that will have the most significant impact.
- Manage your time: Prioritizing helps you manage your time more effectively.
- Avoid procrastination: Prioritizing helps you avoid procrastination by breaking down large tasks into smaller, more manageable ones.
To prioritize tasks effectively, you need to:
- Identify the most important tasks: Identify the tasks that will have the most significant impact.
- Break down large tasks: Break large tasks into smaller, more manageable ones.
- Set deadlines: Set deadlines for each task to help you stay on track.
Brainstorming Techniques
Brainstorming is a technique used to generate creative ideas and solutions. To brainstorm effectively, you need to:
- Generate a lot of ideas: Don’t be afraid to come up with as many ideas as possible, even if they seem silly or unrealistic.
- Encourage creativity: Encourage creative thinking by allowing everyone to contribute ideas.
- Avoid criticism: Don’t criticize or judge ideas during the brainstorming process.
To brainstorm effectively, you can use techniques like mind mapping, free writing, or group brainstorming sessions.
Time Management and Productivity
Managing time effectively.
One of the biggest challenges when it comes to problem-solving is managing your time effectively. It’s easy to get bogged down in the details and lose track of the big picture. To avoid this, set specific goals and deadlines for yourself. Make a to-do list and prioritize your tasks based on their importance and urgency. Use a timer or a stopwatch to keep track of how much time you spend on each task, and try to minimize distractions as much as possible.
For example, if you’re working on a project that requires a lot of research, set a goal to finish the research phase by the end of the day. Break the research down into smaller tasks, such as reading a certain number of articles or books, and set deadlines for each task. This will help you stay on track and ensure that you’re making progress towards your goal.
Overcoming Overwhelm
Feeling overwhelmed is a common problem when it comes to problem-solving. When you’re faced with a complex problem, it’s easy to feel like you don’t know where to start. To overcome this, break the problem down into smaller, more manageable parts. Identify the key issues or questions that need to be addressed, and focus on one at a time.
For example, if you’re trying to solve a problem with a product or service, start by identifying the key issues that are causing the problem. Once you’ve identified these issues, break them down into smaller, more manageable parts. Focus on one issue at a time, and come up with a plan to address it. Once you’ve addressed all of the key issues, you’ll have a better understanding of the problem as a whole, and you’ll be better equipped to come up with a solution.
Being Proactive
Being proactive is an important part of problem-solving. Instead of waiting for problems to arise, take a proactive approach and try to anticipate potential problems before they occur. This will help you stay ahead of the curve and avoid potential roadblocks.
For example, if you’re working on a project with a tight deadline, don’t wait until the last minute to start working on it. Instead, start working on it as soon as possible, and set specific goals and deadlines for yourself. This will help you stay on track and ensure that you’re making progress towards your goal. Additionally, be proactive in identifying potential roadblocks or issues that could arise, and come up with a plan to address them before they become a problem.
Performance Review and Goal Setting
Setting objectives.
When preparing for a performance review, it’s important to set specific objectives that will guide the conversation. Start by reflecting on your current role and responsibilities, and consider areas where you could improve or grow. These objectives should be measurable and achievable, and should align with your personal and professional goals.
For example, one objective might be to improve your communication skills by attending a workshop or taking an online course. Another objective might be to take on more leadership responsibilities within your team or department.
Measuring Performance
During the performance review, your manager will likely evaluate your progress towards meeting your objectives. It’s important to come prepared with concrete examples of how you’ve worked towards your goals, as well as any challenges or obstacles you’ve faced.
For example, if your objective was to improve your project management skills, you might share how you’ve successfully led a project from start to finish, or how you’ve implemented new tools or processes to streamline your workflow. If you’ve faced challenges, be honest about what went wrong and what you learned from the experience.
Creating an Action Plan
After reviewing your performance, you and your manager should work together to create an action plan for the next review period. This plan should include specific goals and objectives, as well as a timeline for achieving them. It’s also important to identify any resources or support you may need to reach your goals.
For example, if your objective is to improve your technical skills, you might discuss opportunities for additional training or mentorship. If your goal is to take on more leadership responsibilities, you might discuss ways to gain experience through shadowing or cross-functional projects.
Overall, the performance review and goal setting process is an important opportunity to reflect on your progress and set a course for future growth and development. By setting specific, measurable objectives and working collaboratively with your manager, you can ensure that you’re on track to achieve your personal and professional goals.
When writing self-evaluation comments, it is important to be honest and objective. Avoid making exaggerated or false claims about your abilities or achievements. Instead, focus on specific examples that demonstrate your skills and accomplishments.
- 30 Examples: Innovation and Creativity Self Evaluation Comments
- 45 Self Evaluation Sample Answers: Strengths and Weaknesses
- Authenticity: How to Be Your Authentic Self (Examples & Strategies)
- What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
- What is Self Compassion? (Exercises, Methods, Examples)
- How to Cultivate Self-Discipline: Essential Strategies

AI Generator

Self-help is a crucial aspect of personal development, empowering individuals to take control of their lives and improve their well-being. It encompasses a variety of practices, including self-care , which focuses on maintaining one’s physical and mental health. Self-efficacy , or the belief in one’s ability to achieve goals, plays a significant role in the effectiveness of self-help strategies. Engaging in self-introduction activities helps individuals build confidence and establish meaningful connections. By incorporating these elements, self-help fosters a holistic approach to personal growth and resilience.
What is Self Help?
Self-help is the practice of improving one’s life through individual efforts, focusing on personal growth and well-being. It involves adopting strategies for self-care, enhancing self-efficacy , and fostering positive behaviors and attitudes.
Examples of Self Help

- Reading Self-Help Books : Gaining insights and practical tips from experts.
- Practicing Mindfulness : Enhancing awareness and reducing stress.
- Setting Goals : Creating clear, achievable objectives for personal growth.
- Journaling : Reflecting on thoughts and experiences to gain clarity.
- Exercise : Engaging in physical activities to boost mental and physical health.
- Healthy Eating : Maintaining a balanced diet to support overall well-being.
- Meditation : Reducing anxiety and improving focus through mindful practice.
- Time Management : Organizing tasks to improve productivity and reduce stress.
- Positive Affirmations : Using positive statements to foster a healthy mindset.
- Learning New Skills : Expanding knowledge and capabilities for personal growth.
- Seeking Therapy : Getting professional help to work through personal issues.
- Volunteering : Helping others to gain a sense of purpose and fulfillment.
- Practicing Gratitude : Focusing on positive aspects of life to improve mood.
- Building a Support Network : Cultivating relationships that provide emotional support.
- Self-Introduction Activities : Enhancing social skills and confidence in new settings.
- Financial Planning : Managing finances to reduce stress and secure the future.
- Hobbies : Engaging in enjoyable activities to relax and rejuvenate.
- Listening to Podcasts : Learning from experts and gaining new perspectives.
- Limiting Screen Time : Reducing digital distractions to focus on personal goals.
- Practicing Self-Compassion : Being kind and understanding towards oneself in times of difficulty.
Mental Health Self Help Examples
- Volunteer Work : Helping others to gain a sense of purpose and fulfillment.
- Mindful Eating : Paying attention to the experience of eating to promote healthy habits.
- Developing Hobbies : Engaging in enjoyable activities to relax and rejuvenate.
- Limiting News Exposure : Reducing intake of negative news to decrease anxiety.
- Joining Support Groups : Connecting with others who share similar experiences.
- Learning Relaxation Techniques : Using methods like progressive muscle relaxation to reduce tension.
- Practicing Yoga : Combining physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation to enhance well-being.
- Establishing a Routine : Creating a daily schedule to provide structure and stability.
- Listening to Music : Using music to relax, uplift, or process emotions.
- Engaging in Physical Touch : Utilizing hugs, massages, or other forms of physical contact to boost mood.
- Seeking Educational Resources : Reading books, attending workshops, or taking courses to learn about mental health and self-care.
Self Help Examples for Students
- Setting Specific Goals : Defining clear academic and personal objectives.
- Time Management : Creating a study schedule to balance school and leisure.
- Organizational Skills : Keeping notes, assignments, and materials well-organized.
- Active Listening : Paying full attention during lectures and discussions.
- Mind Mapping : Using diagrams to visually organize information.
- Regular Exercise : Engaging in physical activities to boost energy and focus.
- Healthy Eating : Maintaining a balanced diet to support cognitive function.
- Adequate Sleep : Ensuring enough rest to improve concentration and memory.
- Study Groups : Collaborating with peers for mutual learning and support.
- Effective Note-Taking : Developing a method that works best for retaining information.
Physical Self-Help Examples
- Practicing Breathing Exercises : Doing deep breathing exercises to improve lung function and relaxation.
- Joining Fitness Classes : Participating in group fitness classes for guided exercise and motivation.
- Using Ergonomic Equipment : Setting up ergonomic workspaces to prevent physical strain.
- Cold Showers : Taking cold showers to boost circulation and invigorate the body.
- Foam Rolling : Using a foam roller to release muscle tightness and improve flexibility.
- Standing Desks : Using a standing desk to reduce sitting time.
- Massage Therapy : Getting professional massages to relieve stress and muscle tension.
- Avoiding Smoking : Not smoking to protect respiratory health.
- Limiting Alcohol : Reducing alcohol consumption for better overall health.
- Engaging in Active Hobbies : Pursuing hobbies that involve physical activity, such as dancing, gardening, or playing sports.
Personal Self Help Examples
- Hydration : Drinking plenty of water to maintain hydration and support bodily functions.
- Engaging in Active Hobbies : Pursuing hobbies that involve physical activity, such as dancing or playing sports.
- Practicing Self-Introduction : Enhancing social skills and confidence in new settings.
- Reading Inspirational Stories : Motivating oneself with stories of successful individuals.
Types of Self-Help
Personal Development : Personal Development focuses on improving self-awareness , self-knowledge, and skills. It often involves setting and achieving personal goals.
Mental Health and Emotional Well-Being ; This type of self-help is aimed at improving mental health and emotional resilience.
Physical Health and Wellness : Physical health self-help focuses on improving physical fitness and overall well-being.
Financial Self-Help : This type of self-help aims to improve financial literacy and management.
Relationship Improvement : Self-help in relationships focuses on building healthier and more fulfilling relationships.
Career Development : Career development self-help is geared towards advancing one’s professional life.
Spiritual Growth : This type of self-help involves practices that nurture spiritual beliefs and values.
Creativity and Hobbies : Engaging in creative activities and hobbies can significantly enhance personal satisfaction and mental well-being.
Habits and Behavioral Change : Self-help aimed at changing habits focuses on establishing positive behaviors and eliminating negative ones.
How to build a Self-Help action Plan
Identify Your Goals: Goals provide direction and motivation. Begin by identifying what you want to achieve. Your goals can be related to various aspects of your life, such as career, health, relationships, or personal development.
Break Down Goals into Smaller Tasks: Large goals can be overwhelming Breaking them down into smaller, manageable tasks makes them more achievable. For each goal, list the steps you need to take to accomplish it.
Prioritize Your Tasks : Not all tasks are equally important. Prioritize your tasks based on their impact and urgency.
Create a Timeline : A timeline helps you stay on track. Assign deadlines to your tasks. Be realistic about the time you need to complete each task. Use a calendar or a planner to map out your tasks and deadlines.
Develop Strategies : Strategies guide you towards your goals. Identify the resources and support you need to accomplish your tasks. Consider potential obstacles and plan how to overcome them.
Monitor Your Progress : Regular monitoring keeps you accountable. Track your progress regularly and adjust your plan as needed. Use tools like journals, apps, or spreadsheets to record your achievements and challenges.
Stay Motivated : Motivation is key to sticking with your plan. Celebrate your achievements, no matter how small. Reward yourself for reaching milestones.
Why is Self-Help Important?
Empowerment and Control : Self-help empowers individuals by giving them control over their lives. When you engage in self-help activities, you take responsibility for your own well-being.
Personal Growth : Engaging in self-help practices fosters personal growth. By continuously learning and improving, you can develop new skills, enhance your knowledge, and achieve your goals.
Mental Health Benefits : Self-help strategies, such as mindfulness, meditation, and positive thinking, can significantly improve mental health.
Physical Health Improvement : Self-help also encompasses physical health. Activities like regular exercise, proper nutrition, and adequate sleep are all forms of self-help that contribute to better physical health.
Improved Relationships : By working on yourself, you can improve your relationships with others. Self-help can teach you better communication skills, empathy, and understanding.
Enhanced Resilience : Self-help practices can build resilience, helping you to cope better with life’s challenges. Developing a positive mindset, learning from setbacks, and focusing on solutions rather than problems are all aspects of self-help that contribute to greater resilience.
Greater Productivity : When you engage in self-help, you often become more organized and focused. Techniques such as goal-setting, time management, and prioritizing tasks can lead to increased productivity and efficiency in both personal and professional settings.
Long-Term Success : Consistent self-help efforts can lead to long-term success. By continually improving yourself, you can achieve your personal and professional goals, leading to a more successful and satisfying life.
Self-Help Therapy
Accessibility and Convenience : Self-help therapy is accessible and convenient. It can be done at your own pace and in your own space, making it ideal for those with busy schedules or limited access to professional therapy.
Variety of Resources : There are numerous self-help resources available, including:
- Books : Self-help books cover a wide range of topics, from anxiety and depression to personal growth and productivity.
- Online Courses : Many platforms offer courses on mindfulness, cognitive-behavioral techniques, and other therapeutic methods.
- Apps : Mobile apps provide guided meditations, mood tracking, and mental health exercises.
Techniques and Strategies : Self-help therapy incorporates various techniques and strategies, such as:
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) : CBT techniques help individuals recognize and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Mindfulness and Meditation : These practices improve awareness and focus, reducing stress and anxiety.
- Journaling : Writing down thoughts and feelings can help process emotions and identify patterns.
- Positive Affirmations : Repeating positive statements can boost self-esteem and motivation.
Self-Help Therapy for Specific Issues : Self-help therapy can address a variety of specific issues, including:
- Anxiety : Techniques like deep breathing, mindfulness, and exposure therapy can help manage anxiety.
- Depression : Activities that promote positive thinking, physical exercise, and social connections can alleviate depressive symptoms.
- Stress Management : Strategies such as time management, relaxation exercises, and healthy lifestyle choices can reduce stress.
Benefits of Self-Help Therapy : The benefits of self-help therapy include:
- Empowerment : Taking charge of your mental health can boost your sense of control and self-efficacy.
- Cost-Effectiveness : Self-help resources are often more affordable than professional therapy.
- Privacy : Self-help therapy allows you to work on personal issues privately and at your own pace.
- Skill Development : Learning and applying therapeutic techniques can enhance your coping skills and resilience.
Combining Self-Help with Professional Therapy : While self-help therapy can be effective on its own, it can also complement professional therapy. Combining both approaches can provide a more comprehensive support system, especially for more severe or persistent issues.
List of Self-Help Topics
- Mental Health and Emotional Well-being
- Personal Development
- Relationships and Communication
- Health and Wellness
- Career and Professional Development
- Financial Well-being
- Personal Skills
- Spiritual Growth
Self Help Skills
- Time Management
- Stress Management
- Emotional Regulation
- Communication Skills
- Financial Management
- Problem-Solving
- Personal Hygiene and Self-Care
- Self-Motivation
- Conflict Resolution
- Learning and Self-Improvement
Self-Help Tips
- Practice Mindfulness : Spend a few minutes each day focusing on the present moment.
- Keep a Journal : Write down your thoughts, feelings, and experiences. Journaling can help you process emotions and gain clarity.
- Stay Connected : Maintain relationships with friends and family. Social connections are crucial for emotional support and well-being.
- Seek Professional Help : If you’re struggling with mental health issues, don’t hesitate to seek help from a therapist or counselor.
How can self-care improve my life?
Self-care practices, such as exercise and meditation, enhance mental and physical health, boosting self-awareness and overall well-being.
Why is self-awareness important in self-help?
Self-awareness helps you understand your strengths and weaknesses, enabling targeted personal development and effective self-appraisal .
How do I identify my personal strengths?
Reflect on your achievements and ask for feedback. Recognizing personal strengths builds confidence and informs your self-concept.
What are common self-help strategies?
Common strategies include practicing self-care, setting goals, and regularly assessing personal strengths and weaknesses through self-appraisal.
How can I work on my weaknesses?
Identify areas for improvement and develop a plan to address them. Self-awareness and self-appraisal guide effective strategies.
How does self-help improve self-concept?
Self-help enhances self-concept by promoting self-awareness, recognizing personal strengths, and addressing weaknesses.
What role does self-appraisal play in self-help?
Self-appraisal involves evaluating your actions and progress, helping to align efforts with goals and personal strength s.
Can self-help practices enhance professional growth?
Yes, self-help improves self-awareness, allowing better use of personal strengths and addressing weaknesses for career advancement.
How do I maintain a positive self-concept?
Engage in self-care and self-appraisal, focus on personal strengths, and work on weaknesses to maintain a healthy self-concept .
How can self-help boost confidence?
Identifying and leveraging personal strengths, along with addressing weaknesses, builds confidence and a positive self-concept.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Solving the 12 Most Common Customer Problems [Guide]
11 min read

A surefire way to improve engagement and retention is to focus on solving customer problems.
Think about it – what would you do if you needed help but all you got was an incredibly unhelpful customer service agent? Chances are, you would take your business elsewhere.
That is precisely why you need to focus on improving your customer service problem-solving and providing excellent support focused on reducing the number of dissatisfied customers.
Where to get started? That’s what this guide is for, outlining frequent customer service issues and their solutions.
- Customer service problem-solving is the process of identifying and efficiently resolving customer concerns in a timely manner.
- Focusing on solving customer problems is vital because it offers key benefits, like improved retention , satisfaction , and loyalty , along with reduced support costs.
- Common customer service issues include lengthy wait times, inaccessible human reps, slow resolution, inconsistent support quality , and poor communication skills of the support team.
- A few shared reasons, like insufficient training, limited staffing, complex customer issues, and no standardized procedures or centralized knowledge bases , cause these issues.
- Possible solutions for these complaints involve implementing callback systems, simplifying automated menus, establishing clear resolution timelines, and standardizing training.
- Some additional effective techniques for problem-solving include empathizing, active listening, sincerely apologizing, proactively communicating, and offering compensation where needed.
- Improving your self-service resources and ensuring consistent operating hours are also useful best practices.
- Ready to optimize your customer service problem-solving strategy? Schedule a Userpilot demo and see how you can get started.
Try Userpilot and Take Your Customer Experience to the Next Level
- 14 Day Trial
- No Credit Card Required

What is customer service problem-solving?
Customer service problem-solving is a discipline focused on optimally identifying, addressing, and resolving issues customers encounter with a product or service.
It is important to note that, contrary to its name, customer service problem-solving is not just about fixing customer complaints.
It’s much more complex than that.
It requires effective problem-solving skills along with other key capabilities like communication , empathy , and critical thinking. It’s also about creating a system where all customer issues are prevented or solved as fast and efficiently as possible.
If done right, customer service problem-solving offers great benefits, such as improved customer satisfaction and loyalty .
Why solving customer problems is so important
Providing excellent customer service is a whole art, one that requires you to develop a functional strategy to do it right. But once you perfect your customer service problem-solving and better train your customer service team, the benefits are endless. Here are just a few:
- Increases customer retention .
- Enhances customer experience .
- Builds customer loyalty.
- Encourages customer engagement .
- Reduces support costs.
- Facilitates customer feedback collection.
- Drives customer satisfaction.
12 most common customer service problems (and how to fix them)
Different companies run into several types of customer service issues. However, there are quite a few recurring customer queries and complaints almost all customer service agents face. So let’s deep dive into what these are and learn the golden rules needed to solve customer service problems.
1. Long wait times
When you look at customer feedback, a common problem that frequently comes up is how often customers have to wait for customer support . All these extended hold times and long queues just add to the customer’s annoyance and dissatisfaction .
Main reasons :
- High call volume.
- Insufficient staffing.
- Complex customer complaints.
- Inadequate training .
- Limited self-service options.
- Backlog of unresolved issues.
Implement a callback system so customers don’t have to wait hours to talk to a customer service rep. Next, focus on streamlining your processes and consider increasing staffing during peak hours. Lastly, introduce chatbots for instant support on low-priority issues.

2. Frustration with inaccessible human reps
Customers often get frustrated with complex automated customer service menus and the inability to reach a human representative.
- Cost-saving strategies.
- Fewer customer service representatives.
- Outdated technology .
- Poor menu design .
- Language limitations.
There are several ways to solve this customer service problem. Start by simplifying automated menus and adding a clear option to speak with a human customer service agent.
Additionally, create comprehensive self-service materials so customers can troubleshoot independently. Also, regularly test the system for ease of usability and accessibility.
3. Slow resolution times
The next common customer service problem is customers having to follow up multiple times to get their issues resolved. This need to constantly check up on the issue wastes more of the customer’s time and is a sign of poor customer service.
- High workload and ticket volume .
- Complicated customer issues.
- Poor internal communication .
- Incomplete issue documentation .
- Ineffective prioritization of tasks.
Establish a clear resolution timeline, improve internal communication, and ensure regular follow-ups with customers until the issues are resolved.
4. Inconsistent support across channels
Customers experience different levels of support quality depending on the contact channel they use. So, a chatbot might not offer much help but an email ends up providing effective customer service problem-solving. This inconsistency only leaves customers confused about which channel to trust .
Main Reasons :
- Varying levels of support training.
- Different support team structures .
- Inconsistent use of knowledge bases.
- Lack of standardized procedures.
- Limited integration between channels.
Start by providing consistent training and resources to service reps across all platforms. Next, ensure that all support channels are well-integrated so information and user data flow seamlessly between them.

A good example of such omnichannel communication is Bluehost, which offers the same quality of live chat and phone support.

5. Excessive transfers between departments
Instead of any issue resolution , customers are often transferred several times between departments without making any progress . In the end, all that’s left is an angry customer and their unresolved complaint.
- Poor initial issue categorization.
- High specialization within departments.
- Insufficient cross-department communication.
- Inconsistent problem-solving protocols.
- Miscommunication or misunderstandings.
Instead of having multiple departments handle specific issues, train all customer service agents to handle a wide range of problems . Also, establish clear protocols for when transfers are necessary and explain the procedure to customers as well.
6. Poor communication skills of customer service reps
Sometimes customers feel undervalued and misunderstood because the customer service representatives lack empathy , communication, or problem-solving skills.
- Insufficient training programs .
- Inadequate soft skills development.
- Lack of performance monitoring .
- Limited knowledge of products or services.
- Limited focus on customer empathy .
Invest in your customer support team, training them in skills like empathy, active listening, and clear communication. Introduce regular monitoring and evaluation of customer service interactions , via CES surveys for example, for quality control.

7. Insufficient knowledge among support staff
Oftentimes, support representatives fail at customer service problem-solving because they lack relevant knowledge . In some cases, they even recommend wrong solutions , which only worsen the customer complaint and potentially increase churn and losses.
- Lack of customer service training.
- Limited access to updated product information .
- Complex product or service offerings.
- Rapid changes in products or services.
- Poorly designed knowledge management systems .
Provide comprehensive training to your customer representatives, ensuring that they are well-versed with the product or service.
Next, try maintaining an up-to-date customer service knowledge base that is accessible to all. This way, representatives can refer to it whenever needed instead of suggesting flawed solutions.
8. Conflicting information from different reps
A common customer complaint is how often they receive conflicting information from different support representatives, leading to confusion and greater mistrust.
- Lack of clear documentation and standardized procedures.
- Inconsistent training across different departments.
- Outdated or inaccurate knowledge base .
- Insufficient supervision and monitoring .
- Varying levels of agent experience.
Make sure all customer service agents are on the same page, by standardizing important information and procedures. Moreover, ensure that each team member gets access to the same resources , training, and product information.
9. Perceived difficulty in contacting customer service
Sometimes, the customer service problem-solving quality itself isn’t the issue. Instead, the problem is that some companies avoid direct contact, making customers exert a lot of effort to get in touch with customer service.
- Cost reduction strategies.
- Overreliance on self-service options and automation .
- Limited staffing resources.
- Overwhelmed support infrastructure.
- Challenges in scaling customer support operations.
Make contact information easily accessible, mentioning it clearly at several touchpoints . Also, to cater to varying customer needs , provide multiple contact channels, and ensure prompt responses.
Hostinger does a good job at this, clearly outlining numerous support channels, along with links to other help center resources like tutorials :

10. Difficulty in resolving issues through self-service
Providing self-service options is great, but it shouldn’t be the only way customers can get help . Companies need to consider that not all customers find it easy to troubleshoot and resolve issues on their own.
- Complex or inaccessible UI design .
- Lack of sufficient information.
- Limited types of content (e.g. only blogs, no videos or tooltips ).
- Technical glitches or bugs .
- Inability to handle complex customer complaints.
- No human support options.
Simplify self-service interfaces and ensure easy access to human support as well for customers who prefer it.

Introduce various content types within the resource center , such as comprehensive and interactive guides , FAQs, blogs, case studies , checklists , etc.

11. Unresolved customer issues
Usually, the main reason behind decreasing customer satisfaction is simple: their problems and complaints aren’t getting resolved. When this happens, customers feel neglected and are more at risk of churning .
- Lack of technical skills and training.
- Inadequate knowledge management systems .
- Complexity of the product or service.
- High employee turnover affects resolution continuity.
- Poor integration between departments.
- Ineffective prioritization of customer issues.
To improve customer retention, implement a follow-up system to ensure all issues are resolved and offer timely updates to customers. In addition, provide personalized customer service to build trust and understand specific pain points so you can resolve issues better.
12. Inconsistent operating hours
Last but not least, a recurring customer service problem is when support is not available at consistent or convenient times. This just makes it harder for customers to seek help , causing them to ultimately give up on your business entirely.
- Limited resources for 24/7 support.
- Lack of sufficient staffing to cover all time zones.
- High cost associated with around-the-clock service reps.
- Difficulty in recruiting and retaining staff for non-traditional hours.
To avoid any confusion, standardize your operating hours and communicate them clearly to customers. If customer complaints about operating hours still continue, then consider providing extended hours as well.
Here’s an example by SiteGround that clearly advertises it’s 24-hour support:

Try Userpilot and Take Your Customer Service to the Next Level
The key customer service problem-solving techniques.
Now that you’ve gone over all the common customer complaints and queries, it’s time to focus on making sure they don’t happen again. To help with that, here are the top customer service problem-solving best practices guaranteed to delight customers.
Empathy, active listening, and personalization
One simple technique for providing the best customer support is to listen carefully. This requires that you solely focus on the customer without any distractions, show interest, and ask clarifying questions. Only through such active listening can you truly understand the customer’s needs .
Along with listening intently, you also need to be patient and reflect on the customer’s feelings. In other words, you must empathize with your customers’ experience before jumping to a solution. This helps build trust and rapport necessary for long-lasting relationships.
Lastly, it is important to acknowledge that all customers are unique, and therefore each customer’s problem should be treated individually. This allows for a more personalized solution , best-suited for the customer’s specific complaint.
Troubleshooting based on experience
It’s true – practice does make perfect. So if you want to improve your customer service problem-solving skills, the best way is through hands-on experience . The more practice you get working on and learning from previous cases, the more your ability to diagnose and fix issues will improve.
However, this doesn’t mean you don’t need any training at all. Instead, the two go hand-in-hand. Training provides the necessary foundational knowledge , while hands-on experience refines that knowledge through practical application .
Both these things also help ensure cross-department exchange of information and improved collaboration over time.
Providing sincere apologies
A golden rule of customer service: Never ever argue with the customer. When a customer is upset or in need of help, arguing with them will only make matters worse. Plus, arguing only further ruins the customer experience and could lead to negative word of mouth .
The right thing to do is to apologize sincerely. Often, a genuine apology is all customers need to feel validated, helping de-escalate the situation. Moreover, once you’ve apologized, customers are more open to trusting you, thereby making them receptive to any proposed solutions.
To ensure an apology is effective, it should be timely, specific to the customer’s issue, and accompanied by a clear plan for resolution. If done right, sincere apologies contribute greatly to customer satisfaction , loyalty, and a positive brand reputation.
Consistent follow-up and proactive communication
In order to provide effective customer support, simply resolving the problem is not enough. There are other elements you need to simultaneously take care of as well, to provide customers with a seamless experience throughout.
To start off, the service team must keep customers informed about the progress of their issues. This includes letting them know of any delays or necessary follow-up actions. Such transparency in the resolution process helps reassure the customer and highlights your commitment to customer service.
Even after providing a solution, you must follow up with the customer again to ensure the problem has been fully resolved.
Offer compensation
In certain cases, simply apologizing for the issue is not sufficient. Rather, it is important that you offer compensation for the negative experience.
This helps repair the relationship by demonstrating accountability on your part and showing how committed you are to customer satisfaction . It also provides a tangible gesture of goodwill , which can hopefully reduce any negative impact the issue may have caused.
Glovo (a food delivery app) is a good example to quote here. If your order is missing some parts or has other issues, Glovo often issues instant refunds.

Improving self-service resources
Finally, the last trick to perfecting your customer service problem-solving ability is to create comprehensive self-service options . These can include resource centers, knowledge bases , how-to videos, community forums, help center portals, user guides , and more.
Providing these resources empowers customers to quickly resolve issues on their own, reducing wait times and boosting satisfaction . Additionally, self-service portals also decrease the workload on customer service teams, enabling them to focus on more complex inquiries.

For example, here’s a look at the self-service options Zendesk offers:

Effectively and quickly solving customer problems is crucial for driving retention and enhancing satisfaction. But there are several other facets to customer service problem-solving to keep in mind too, such as empathy, active listening, and other soft skills.
To make things easier, try keeping a few tips and best practices in mind. For example, focus on training your customer service team, proactively communicating, offering multiple channels of contact, and enhancing self-service resources.
With all these techniques in hand, you’ll be able to reduce churn and create a positive customer experience in no time!
Want to get started solving customer problems? Get a Userpilot Demo and see how you can improve customer loyalty.
Try Userpilot and Take Your Customer Loyalty to the Next Level
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth,Management & Trends.
The coolest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends. Delivered fresh to your inbox, weekly.
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
You might also be interested in ...
10 great in-app tutorials that drive product adoption.
Aazar Ali Shad
15 Welcome Email Examples That Drive Engagement
The top 15 customer success webinars to watch in 2024.
If we’re all so busy, why isn’t anything getting done?
Have you ever asked why it’s so difficult to get things done in business today—despite seemingly endless meetings and emails? Why it takes so long to make decisions—and even then not necessarily the right ones? You’re not the first to think there must be a better way. Many organizations address these problems by redesigning boxes and lines: who does what and who reports to whom. This exercise tends to focus almost obsessively on vertical command relationships and rarely solves for what, in our experience, is the underlying disease: the poor design and execution of collaborative interactions.
About the authors
This article is a collaborative effort by Aaron De Smet , Caitlin Hewes, Mengwei Luo, J.R. Maxwell , and Patrick Simon , representing views from McKinsey’s People & Organizational Performance Practice.
In our efforts to connect across our organizations, we’re drowning in real-time virtual interaction technology, from Zoom to Slack to Teams, plus group texting, WeChat, WhatsApp, and everything in between. There’s seemingly no excuse to not collaborate. The problem? Interacting is easier than ever, but true, productive, value-creating collaboration is not. And what’s more, where engagement is occurring, its quality is deteriorating. This wastes valuable resources, because every minute spent on a low-value interaction eats into time that could be used for important, creative, and powerful activities.
It’s no wonder a recent McKinsey survey found 80 percent of executives were considering or already implementing changes in meeting structure and cadence in response to the evolution in how people work due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Indeed, most executives say they frequently find themselves spending way too much time on pointless interactions that drain their energy and produce information overload.
Most executives say they frequently find themselves spending way too much time on pointless interactions.
Three critical collaborative interactions
What can be done? We’ve found it’s possible to quickly improve collaborative interactions by categorizing them by type and making a few shifts accordingly. We’ve observed three broad categories of collaborative interactions (exhibit):
- Decision making, including complex or uncertain decisions (for example, investment decisions) and cross-cutting routine decisions (such as quarterly business reviews)
- Creative solutions and coordination, including innovation sessions (for example, developing new products) and routine working sessions (such as daily check-ins)
- Information sharing, including one-way communication (video, for instance) and two-way communication (such as town halls with Q&As)
Below we describe the key shifts required to improve each category of collaborative interaction, as well as tools you can use to pinpoint problems in the moment and take corrective action.
Decision making: Determining decision rights
When you’re told you’re “responsible” for a decision, does that mean you get to decide? What if you’re told you’re “accountable”? Do you cast the deciding vote, or does the person responsible? What about those who must be “consulted”? Sometimes they are told their input will be reflected in the final answer—can they veto a decision if they feel their input was not fully considered?
It’s no wonder one of the key factors for fast, high-quality decisions is to clarify exactly who makes them. Consider a success story at a renewable-energy company. To foster accountability and transparency, the company developed a 30-minute “role card” conversation for managers to have with their direct reports. As part of this conversation, managers explicitly laid out the decision rights and accountability metrics for each direct report. The result? Role clarity enabled easier navigation for employees, sped up decision making, and resulted in decisions that were much more customer focused.
How to define decision rights
We recommend a simple yet comprehensive approach for defining decision rights. We call it DARE, which stands for deciders, advisers, recommenders, and executors:
Deciders are the only ones with a vote (unlike the RACI model, which helps determine who is responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed). If the deciders get stuck, they should jointly agree on how to escalate the decision or figure out a way to move the process along, even if it means agreeing to “disagree and commit.”
Advisers have input and help shape the decision. They have an outsize voice in setting the context of the decision and have a big stake in its outcome—for example, it may affect their profit-and-loss statements—but they don’t get a vote.
Recommenders conduct the analyses, explore the alternatives, illuminate the pros and cons, and ultimately recommend a course of action to advisers and deciders. They see the day-to-day implications of the decision but also have no vote. Best-in-class recommenders offer multiple options and sometimes invite others to suggest more if doing so may lead to better outcomes. A common mistake of recommenders, though, is coming in with only one recommendation (often the status quo) and trying to convince everyone it’s the best path forward. In general, the more recommenders, the better the process—but not in the decision meeting itself.
Executers don’t give input but are deeply involved in implementing the decision. For speed, clarity, and alignment, executers need to be in the room when the decision is made so they can ask clarifying questions and spot flaws that might hinder implementation. Notably, the number of executers doesn’t necessarily depend on the importance of the decision. An M&A decision, for example, might have just two executors: the CFO and a business-unit head.
To make this shift, ensure everyone is crystal clear about who has a voice but no vote or veto. Our research indicates while it is often helpful to involve more people in decision making, not all of them should be deciders—in many cases, just one individual should be the decider (see sidebar “How to define decision rights”). Don’t underestimate the difficulty of implementing this. It often goes against our risk-averse instinct to ensure everyone is “happy” with a decision, particularly our superiors and major stakeholders. Executing and sustaining this change takes real courage and leadership.
Creative solutions and coordination: Open innovation
Routine working sessions are fairly straightforward. What many organizations struggle with is finding innovative ways to identify and drive toward solutions. How often do you tell your teams what to do versus empowering them to come up with solutions? While they may solve the immediate need to “get stuff done,” bureaucracies and micromanagement are a recipe for disaster. They slow down the organizational response to the market and customers, prevent leaders from focusing on strategic priorities, and harm employee engagement. Our research suggests key success factors in winning organizations are empowering employees and spending more time on high-quality coaching interactions.
How microenterprises empower employees to drive innovative solutions
Haier, a Chinese appliance maker, created more than 4,000 microenterprises (MEs) that share common approaches but operate independently. Haier has three types of microenterprises:
- Market-facing MEs have roots in Haier’s legacy appliance business, reinvented for today’s customer-centric, web-enabled world. They are expected to grow revenue and profit ten times faster than the industry average.
- Incubating MEs focus on emerging markets such as e-gaming or wrapping new business models around familiar products. They currently account for more than 10 percent of Haier’s market capitalization.
- “Node” MEs sell market-facing ME products and services such as design, manufacturing, and human-resources support.
Take Haier. The Chinese appliance maker divided itself into more than 4,000 microenterprises with ten to 15 employees each, organized in an open ecosystem of users, inventors, and partners (see sidebar “How microenterprises empower employees to drive innovative solutions”). This shift turned employees into energetic entrepreneurs who were directly accountable for customers. Haier’s microenterprises are free to form and evolve with little central direction, but they share the same approach to target setting, internal contracting, and cross-unit coordination. Empowering employees to drive innovative solutions has taken the company from innovation-phobic to entrepreneurial at scale. Since 2015, revenue from Haier Smart Home, the company’s listed home-appliance business, has grown by more than 18 percent a year, topping 209 billion renminbi ($32 billion) in 2020. The company has also made a string of acquisitions, including the 2016 purchase of GE Appliances, with new ventures creating more than $2 billion in market value.
Empowering others doesn’t mean leaving them alone. Successful empowerment, counterintuitively, doesn’t mean leaving employees alone. Empowerment requires leaders to give employees both the tools and the right level of guidance and involvement. Leaders should play what we call the coach role: coaches don’t tell people what to do but instead provide guidance and guardrails and ensure accountability, while stepping back and allowing others to come up with solutions.
Haier was able to use a variety of tools—including objectives and key results (OKRs) and common problem statements—to foster an agile way of working across the enterprise that focuses innovative organizational energy on the most important topics. Not all companies can do this, and some will never be ready for enterprise agility. But every organization can take steps to improve the speed and quality of decisions made by empowered individuals.
Managers who are great coaches, for example, have typically benefited from years of investment by mentors, sponsors, and organizations. We think all organizations should do more to improve the coaching skills of managers and help them to create the space and time to coach teams, as opposed to filling out reports, presenting in meetings, and other activities that take time away from driving impact through the work of their teams.
But while great coaches take time to develop, something as simple as a daily stand-up or check-in can drive horizontal connectivity, creating the space for teams to understand what others are doing and where they need help to drive work forward without having to specifically task anyone in a hierarchical way. You may also consider how you are driving a focus on outcomes over activities on a near-term and long-term basis. Whether it’s OKRs or something else, how is your organization proactively communicating a focus on impact and results over tasks and activities? What do you measure? How is it tracked? How is the performance of your people and your teams managed against it? Over what time horizons?
The importance of psychological safety. As you start this journey, be sure to take a close look at psychological safety. If employees don’t feel psychologically safe, it will be nearly impossible for leaders and managers to break through disempowering behaviors like constant escalation, hiding problems or risks, and being afraid to ask questions—no matter how skilled they are as coaches.
Employers should be on the lookout for common problems indicating that significant challenges to psychological safety lurk underneath the surface. Consider asking yourself and your teams questions to test the degree of psychological safety you have cultivated: Do employees have space to bring up concerns or dissent? Do they feel that if they make a mistake it will be held against them? Do they feel they can take risks or ask for help? Do they feel others may undermine them? Do employees feel valued for their unique skills and talents? If the answer to any of these is not a clear-cut “yes,” the organization likely has room for improvement on psychological safety and relatedness as a foundation to high-quality interactions within and between teams.
Information sharing: Fit-for-purpose interactions
Do any of these scenarios sound familiar? You spend a significant amount of time in meetings every day but feel like nothing has been accomplished. You jump from one meeting to another and don’t get to think on your own until 7 p.m. You wonder why you need to attend a series of meetings where the same materials are presented over and over again. You’re exhausted.
An increasing number of organizations have begun to realize the urgency of driving ruthless meeting efficiency and of questioning whether meetings are truly required at all to share information. Live interactions can be useful for information sharing, particularly when there is an interpretive lens required to understand the information, when that information is particularly sensitive, or when leaders want to ensure there’s ample time to process it and ask questions. That said, most of us would say that most meetings are not particularly useful and often don’t accomplish their intended objective.
We have observed that many companies are moving to shorter meetings (15 to 30 minutes) rather than the standard default of one-hour meetings in an effort to drive focus and productivity. For example, Netflix launched a redesign effort to drastically improve meeting efficiency, resulting in a tightly controlled meeting protocol. Meetings cannot go beyond 30 minutes. Meetings for one-way information sharing must be canceled in favor of other mechanisms such as a memo, podcast, or vlog. Two-way information sharing during meetings is limited by having attendees review materials in advance, replacing presentations with Q&As. Early data show Netflix has been able to reduce the number of meetings by more than 65 percent, and more than 85 percent of employees favor the approach.
Making meeting time a scarce resource is another strategy organizations are using to improve the quality of information sharing and other types of interactions occurring in a meeting setting. Some companies have implemented no-meeting days. In Japan, Microsoft’s “Work Life Choice Challenge” adopted a four-day workweek, reduced the time employees spend in meetings—and boosted productivity by 40 percent. 1 Bill Chappell, “4-day workweek boosted workers’ productivity by 40%, Microsoft Japan says,” NPR, November 4, 2019, npr.org. Similarly, Shopify uses “No Meeting Wednesdays” to enable employees to devote time to projects they are passionate about and to promote creative thinking. 2 Amy Elisa Jackson, “Feedback & meeting-free Wednesdays: How Shopify beats the competition,” Glassdoor, December 5, 2018, glassdoor.com. And Moveline’s product team dedicates every Tuesday to “Maker Day,” an opportunity to create and solve complex problems without the distraction of meetings. 3 Rebecca Greenfield, “Why your office needs a maker day,” Fast Company , April 17, 2014, fastcompany.com.
Finally, no meeting could be considered well scoped without considering who should participate, as there are real financial and transaction costs to meeting participation. Leaders should treat time spent in meetings as seriously as companies treat financial capital. Every leader in every organization should ask the following questions before attending any meeting: What’s this meeting for? What’s my role? Can I shorten this meeting by limiting live information sharing and focusing on discussion and decision making? We encourage you to excuse yourself from meetings if you don’t have a role in influencing the outcome and to instead get a quick update over email. If you are not essential, the meeting will still be successful (possibly more so!) without your presence. Try it and see what happens.
High-quality, focused interactions can improve productivity, speed, and innovation within any organization—and drive better business performance. We hope the above insights have inspired you to try some new techniques to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of collaboration within your organization.
Aaron De Smet is a senior partner in McKinsey’s New Jersey office; Caitlin Hewes is a consultant in the Atlanta office; Mengwei Luo is an associate partner in the New York office; J.R. Maxwell is a partner in the Washington, DC, office; and Patrick Simon is a partner in the Munich office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Author Talks: Beyond collaboration overload

Battling burnout: A conversation with resiliency expert Dr. Amit Sood

Author Talks: Why burnout is an epidemic—and what to do about it

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This self-help guide is intended for people with mild-to-moderate mental health issues. If you're feeling distressed, in a state of despair, suicidal or in need of emotional support you can phone NHS 24 on 111. For an emergency ambulance phone 999. It's easy to feel overwhelmed by problems, particularly if you're experiencing mental health ...
In insight problem-solving, the cognitive processes that help you solve a problem happen outside your conscious awareness. 4. Working backward. Working backward is a problem-solving approach often ...
Answering the questions in the Problem-Solving Self-Monitoring Form provides the therapist with necessary information regarding the client's overall and specific problem-solving approaches and ... Visualization can be performed with individuals or in a group setting to help clients solve problems in multiple ways, including (Dobson, 2011):
Problem Solving. Step 1. Identify the Problem. Break it down into smaller steps and decide what you need to action first. Step 2. Brainstorm and write down as many ideas as you can that might help solve the problem, no matter how silly they seem - don't dismiss any possible solutions. Step 3.
2. Use Check the Facts to ensure you're describing it accurately. 3. Figure out your goal in solving the problem. What needs to happen so you can feel okay? Keep it simple and realistically attainable. 4. Brainstorm as many solutions as you can. Ask for suggestions from people you trust.
Problem solving. Worrying is a natural response to life's problems. But when it takes over and we can start to feel overwhelmed, it can really help to take a step back and break things down. Learning new ways to work through your problems can make them feel more manageable, and improve your mental and physical wellbeing.
You can set project goals (e.g. do this task and then this task, etc.) or time goals (work on this task for 4 hours). Taking manageable steps is important, because trying to tackle the problem all ...
Problem-solving therapy is a short-term treatment used to help people who are experiencing depression, stress, PTSD, self-harm, suicidal ideation, and other mental health problems develop the tools they need to deal with challenges. This approach teaches people to identify problems, generate solutions, and implement those solutions.
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
Problem-solving is a vital skill for coping with various challenges in life. This webpage explains the different strategies and obstacles that can affect how you solve problems, and offers tips on how to improve your problem-solving skills. Learn how to identify, analyze, and overcome problems with Verywell Mind.
Problem Solving is a helpful intervention whenever clients present with difficulties, dilemmas, and conundrums, or when they experience repetitive thought such as rumination or worry. Effective problem solving is an essential life skill and this Problem Solving worksheet is designed to guide adults through steps which will help them to generate ...
Step 1. Identify the Problem Break it down into smaller steps and decide what you need to action first. Step 2. Brainstorm and write down as many ideas as you can that might help solve the problem, no matter how silly they seem - don't dismiss any possible solutions. Step 3. Consider the pros and cons of each possible solution, using a ...
Block out time in your calendar to get curious, either in isolation or with others. Ponder and expose yourself to how people from an opposing viewpoint see a topic. Ask others their opinion or ...
worksheet. Guide your clients and groups through the problem solving process with the help of the Problem Solving Packet. Each page covers one of five problem solving steps with a rationale, tips, and questions. The steps include defining the problem, generating solutions, choosing one solution, implementing the solution, and reviewing the process.
Effective problem solving can help ensure that your team or organization is well positioned to overcome challenges, be resilient to change and create innovation. In my experience, problem solving is a combination of skillset, mindset and process, and it's especially vital for leaders to cultivate this skill. ... Participants then self ...
Teaches Effective and Authentic Communication. Teaches Sales and Persuasion. Teaches Buying and Selling Real Estate. Teaches Designing Your Career. Teaches Leading Winning Teams. Teaches Purposeful Communication. On the Power of Personal Branding. Teaches Disruptive Entrepreneurship. Teaches Relational Intelligence.
This self-help guide is intended for people with mild-to-moderate symptoms of anxiety. If you're feeling distressed, in a state of despair, suicidal or in need of emotional support you can phone NHS 24 on 111. For an emergency ambulance phone 999. This guide aims to help you to: There are a number of conditions that have anxiety as a symptom ...
Problem Solving and Actions Plans are cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) emotion regulation skills. When changing our ...
On your own: Walk through our problem-solving worksheet. Employ this problem-solving framework when you realize your worry concerns something solvable, as often as you need. Remember, worry over these kinds of problems is normal and able to be overcome with the help of this framework. Downloadable resources to use on your own. Information Sheet
By using this problem solving process, you can often help different kinds of learners and personality types contribute and unblock organizational problems with creative thinking. Problem solving strategies like LEGO Serious Play are super effective at helping a team solve more skills-based problems such as communication between teams or a lack ...
Problem solving is an exceptionally important workplace skill. Being a competent and confident problem solver will create many opportunities for you. By using a well-developed model like Simplexity Thinking for solving problems, you can approach the process systematically, and be comfortable that the decisions you make are solid.
FACE: Problem Solving Overcome problems by using FACE: Find and identify your target problem - what you need to face and solve Action - decide on the steps you need to take Coping - identify your coping strategies and resources Evaluate - how did it go? FIND Identify what problem you would like to be able to FACE and solve, rather than ...
Here are two ways to achieve self-improvement without being dragged into the toxic world of self-help. #1. Understand that not all self-help is created equal. In general, the self-help industry ...
Since 988 was rolled out in mid-2022, call volume has increased by 46%, texts by 1,135%, and chats by 141%, according to this April 2024 report by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services ...
Self-calming and focusing (self-management). Two key elements help activate students' self-calming strategies. First, ... Help students make these presentation situations explicit by problem-solving the perspective of their audience and planning how to communicate information in ways that consider audiences' emotions, motivations, or ...
Self-evaluation is an essential aspect of professional development. It helps you to identify areas of improvement and measure your progress towards achieving your goals. By evaluating your problem-solving skills, you can identify your strengths and weaknesses and take steps to improve your performance. Problem Solving Self-Evaluation Comments Examples I was able to identify the root...
Rome offers six suggestions for parents who want to help their teen build resilience. 1. Teach your teen to tackle problems in bite-size pieces. Think back to the biggest problems in your life at ...
Self-help is a crucial aspect of personal development, empowering individuals to take control of their lives and improve their well-being. It encompasses a variety of practices, including self-care, which focuses on maintaining one's physical and mental health. Self-efficacy, or the belief in one's ability to achieve goals, plays a significant role in the effectiveness of self-help strategies.
The key customer service problem-solving techniques. Now that you've gone over all the common customer complaints and queries, it's time to focus on making sure they don't happen again. To help with that, here are the top customer service problem-solving best practices guaranteed to delight customers. Empathy, active listening, and ...
Advisers have input and help shape the decision. They have an outsize voice in setting the context of the decision and have a big stake in its outcome—for example, it may affect their profit-and-loss statements—but they don't get a vote. ... And Moveline's product team dedicates every Tuesday to "Maker Day," an opportunity to create ...