
Discovery Play with Littles
2:01 pm ·

15 Powerful Problem Solving Activities for Toddlers and Preschoolers
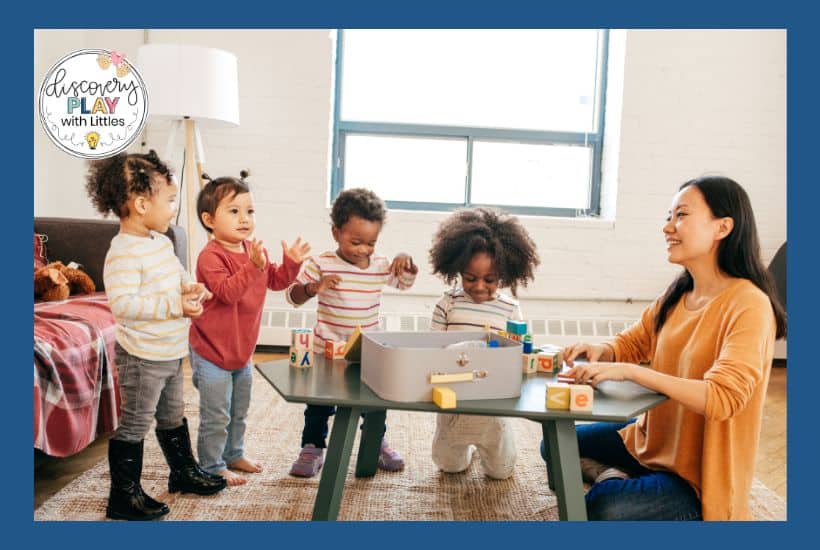
I looked over to her table and she’s crying. Again. While everyone else is happily working away, she sat there, unable to move, just crying.
Not asking for help.
Not trying to solve her problem.
Just crying.
I took a deep breath before heading over. We’ve already been at this for several months…isn’t it about time the problem-solving has kicked in yet?
One glance and I could tell what her problem was. She didn’t have her pencil.
Know how I knew?
It laid on the floor beside her. In plain sight.
As a kindergarten teacher, I don’t jump right in and solve problems for kids. It’s good for them to try to solve the problem themselves. This is something she struggled with.
I reminded myself of the need for patience and empathy as I walked up to her. “What’s wrong, Amanda?”
“I…can’t…find…my…pencil….” she sputtered out between sobs.
“Ok, that’s a problem we can solve. What have you tried?”
“I don’t know.”
After a long time trying to first, calm her down, and second, come up with some strategies she could try, she finally found her pencil. At that point, everyone else had finished the project.

What is Problem Solving?
Problem-solving is the process of finding a solution to your problem . This can be quite tricky for some young children, especially those with little experience in finding more than one way to solve a problem.
Why is Problem Solving Important?
Problem-solving skills are used throughout childhood into adulthood. As adults, we solve problems on a daily basis. Some problems we solve without thinking much- I wanted to make tacos for dinner but forgot to buy the ground beef. What are we going to have for dinner now?
Other problems are significantly more complicated.
Problems for kiddos can be problems with friendships, the inability to find something that’s needed, or even what to do when things don’t go your way.
Kids who lack problem-solving skills struggle to maintain friendships or even begin to attempt to solve their own problems.
Children who lack problem-solving skills are at a higher risk for depression as well.
What Are Problem-Solving Skills?
Problem-solving skills are:
- Breaking Down a Problem into Smaller Parts
- Communication
- Decision-making
- Logical Reasoning
- Perseverance
That’s a big list to teach toddlers and preschoolers. Where do you begin?
The Problem-Solving Steps
Sometimes kids are so overwhelmed with frustration that it affects their ability to solve problems.
Kids feel safe in routines, and routines help them learn and grow. After a few times of repeating this routine, you’ll find your kiddo starts to do this on their own.
It’s important not to skip straight to solving the problem , because your kiddo needs to be in a calm state of mind to solve the problem, and also they need to know their feelings are valid.
- The first thing to do when your kiddo is struggling with problem-solving is to validate their emotions.
In doing this, they will feel more understood and learn that their emotions are okay. There are no bad feelings, and we must learn how to manage our emotions.
This might sound something like “Oh, I can see you are really frustrated that the block won’t fit on there right. Let’s take some deep breaths to help us calm down before we think about what to do next.”
- Next, work through your calm-down process . This may be taking some deep breaths together, hugging a stuffie, or giving your kiddo some quiet time to calm down their heart and mind.
- Identify the problem . This sounds like something you may have already done (before the meltdown) but it’s important to be very clear on the problem you’re solving. Have the child tell you their problem out loud.
- Move on to solution-finding . When your kiddo is ready, talk about what the problem is and three possible solutions. When possible, let your kiddo do all of the talking. This allows him to practice his problem-solving skills. It’s important to remind him that the first thing he tries may not work, and that’s ok. There’s always another way to solve the problem. If he’s prepared for this, solutions that don’t work won’t be such a frustrating experience.
- After you’ve done that, test your solutions one by one. See what works. If you haven’t found a solution yet, go back and think of different ways you might be able to solve your problem and try again.

Are you tired of hearing “It’s TOO HARD!” followed by a meltdown?
Using this one simple phrase you’ll get in this powerful lesson, you’ll not only be able to help your kiddo not give up but you’ll:
>Activate their superpower of perseverance so that they can turn around a meltdown and keep trying
>Inspire them to use perseverance …even when it’s hard
>Teach them to recognize the warning signs of giving up , and how to turn it around by taking control of their choices.
Grab your powerful FREE video lesson to teach your kiddo one of the most powerful keys to perseverance.
Powerful Activities that Teach Problem-Solving Skills to Toddlers & Preschoolers
These activities below may look simple, but don’t let that deter you from trying them. A lot happens in little developing brains and these powerful activities help toddlers and preschoolers make connections and develop {many} essential skills-more than just problem-solving.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.
Puzzles are fun and a great way to encourage cognitive development in children. They are great for spacial reasoning and strengthening problem-solving skills. They also develop memory skills, critical thinking, and the ability to plan and execute the plan. Toddlers will enjoy the simple puzzles, and preschoolers will do great with floor puzzles with larger puzzle pieces.

Doing Simple Chores
Doing simple chores is a great way to teach children problem-solving skills, and it strengthens responsibility and perseverance as well.
During the toddler years , you may start with just picking up their toys, or helping you put their dirty clothes in the hamper.
Preschoolers can take their dirty dishes to the sink (or load them in the dishwasher), collect the trash, dust, wipe baseboards, and do their own personal care items like making their bed, taking care of their dirty clothes, and putting clean clothes away.
Stacking Rings
When watching a toddler play with stacking rings it doesn’t look like much is happening, but playing with these toys is full of ways to encourage development. It helps with visual and spacial perception and planning ahead, but it also with balance control, crossing the midline, creative play, and gross motor skills. Not to mention it’s a great opportunity to practice problem-solving.

Playing Hide-and-Seek
Hide and seek has many surprising benefits for kids. Playing hide and seek is like a treasure hunt that helps develop gross motor skills and encourages physical development, as well as problem-solving skills. It also helps young children develop visual tracking, working memory, and social-emotional skills.

Imaginative Play
Imaginative play (also called role-play) builds important skills. Through pretending to be in different situations, kids develop social skills, emotional skills, better communication, and problem-solving skills. Imaginative play is a great idea for young toddlers all the way to older children.
Free Play
Many young children don’t have {enough} time for free play. Free play is important for healthy brain development , not only developing imagination, cooperation, physical skills, and independence but also providing a great opportunity to strengthen problem-solving skills.
Playing with Wooden Blocks
Building blocks are a fun way for children to develop creative thinking, imagination, problem-solving, fine motor skills, and if working with others, cooperation, communication, and friendship.

Playing Memory
Memory games improve attention, focus, visual recognition, and concentration. It helps children recognize details and of course, strengthens problem-solving skills.

Ask Questions
When I see my son struggling with something, my first instinct is to give him choices or at least lead him in the right direction. The better thing to do is to ask very open-ended questions that lead his process, not his thoughts.
Questions like “What’s one way to solve your problem?” are much more effective in teaching problem-solving skills than “Well, where did you last see your stuffy?”
Read Books and Social Stories
Reading books is one of my favorite ways to teach any skill. It’s extremely effective at teaching, and it’s also an amazing bonding time with kids.
When we read stories, our brain reacts as if we’re living in the story. This is why reading books about skills such as problem-solving is so effective.
Kids of all ages learn from the people they love . (Yes, even those older kids who you don’t think are paying attention.) Often as adults, we’re too busy going through our daily routine to think about talking about the way we solved the problem at work that day.
Talking about how you use skills such as problem-solving, perseverance, and integrity is a great way to set an example, and an expectation that this is how we do things, and it will provide encouragement for your kiddo to do the same.
Scavenger Hunts
Scavenger hunts are a great group activity that can strengthen your child’s logical thinking and problem-solving skills.
When Your Kiddo is Ready, Add These Activities
Preschoolers would benefit from all of the fun activities on the list above and when they’re ready, feel free to add in the following activities.
Mazes are great for problem-solving and perseverance, but your kiddo will need to have decent fine motor skills to do these activities. Mazes are one of our favorite activities. We love to take our activity book of mazes in the car with us for road trips.

Board Games
Board games are a good way to strengthen problem-solving, teamwork, planning skills, patience, sportsmanship, and communication skills. They also strengthen family relationships by providing some intentional time of connection .
Any board game can also be turned into an academic game with just a deck of cards for whatever skill you’re working on. If you’re working on the alphabet, put one letter on each card. Before each player’s turn, they draw a letter card and say the letter’s name. (You may accidentally forget the name of a letter every now and then to see if your kiddo is really paying attention!)
Allow Opportunities for Hands-On Investigations
Kids are tactile. They love to touch and explore things with their hands. This is a good activity for toddlers also, as long as they are out of the putting everything in their mouth stage. Hands-on exploration is great for language development, sensory exploration, and problem-solving.
Allowing kids to investigate with their hands allows them to see how the world works up close. It also gives them time and space to try to make things work…and problem-solve when it doesn’t go as they think it should.
The Most Difficult Way (and Most Important Way) To Strengthen Problem-Solving Skills
Watching our kids struggle is hard ! We don’t want to see them having a hard time…and most of the time we don’t want to deal with the impending meltdown. Standing back and giving our kids time and space to work through even simple problems is hard to do. It’s also the most important way to strengthen problem-solving skills.
As parents, we’re like frogs in boiling water. When our kids are infants, they need us to recognize their needs and solve them immediately. As they get older, they can point to what they want, but we still have a lot of interpreting and problem-solving to do on our own. If we aren’t careful, we stay in this stage and don’t teach our kiddos the steps to problem-solving for themselves.
The next most difficult thing? Allowing natural consequences to happen. (As long as your child is safe of course.) If your child saves their money for a long time to buy a new toy, but walks down the toy aisle and picks up something you know they’ll be disappointed with, let it happen. It will teach a valuable lesson that will last for years to come.
Another Essential Part of Problem-Solving
Perseverance is a big part of problem-solving. We are rarely able to solve problems the first time, and it’s essential that kids can find more than one solution to a problem. Studies have found that perseverance is actually the biggest predictor of success, even more than aptitude or raw talent.
An entire module is dedicated to perseverance in our course for kids, Super Kid Adventures . Your kiddo will get 25 teacher-led lessons on character traits (perseverance, empathy, friendship, responsibility, and wellness) and activities that take their learning further.

Want a free preview? Grab a FREE Perseverance video lesson that teaches your kiddo one of the most important secrets that help them use perseverance.
Want More?
If you like this, you’ll love:
The Ultimate List of Books that Teach Perseverance
7 Simple Ways to Encourage Independence in Young Children
How to Help Your Child Develop Self-Help Skills
Your Turn
What are your favorite ways to teach problem-solving skills?
About Elizabeth
Elizabeth is a mama of two boys, a former teacher, and the founder of Discovery Play with Littles. Her mission is to make raising kids with character simple and fun. Join us for our best learning through play ideas, character growth activities, and family connection ideas so you can watch your child thrive.
Reader Interactions
As a SLP trying to guide parents as I work with their child. I would like to know what toys to recommend to my parents as I assist in guiding their child’s development in cognition and expressive language.

Perseverance is the biggest predictor of success, even more than raw talent or aptitude.
Grab a FREE lesson to teach your kiddo one of the keys to perseverance...which is how we talk to our brains.
They'll learn what to say when they encounter something difficult, and why it's so important.
PLAY is often talked about as if it were a relief from serious learning. But for children play is serious learning. Play is really the work of childhood. -Mr. Rogers
- How To Get Pregnant
- Infertility
- Pregnancy Week by Week
- Second Pregnancy
- Giving Birth
- Post Pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
- Development
- Browse Names
- Play & Activities
- Coloring Pages
- Food & Nutrition
- Health & Fitness
- Style & Beauty Care
- Collaborations
- New Parents
- Single Parenting
- Relationships
- Baby Eye Color Calculator
- Online Pregnancy Test
- Chinese Gender Predictor
- Implantation Calculator
- hCG Calculator
- Period Calculator
- ovulation calculator
- pregnancy due date calculator
- Child Height Predictor
- Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator
- Breast Milk Calculator
- Child Growth Percentile Calculator
- Baby Cost Calculator
- BMI Calculator For Kids & Teens
- Contraction Calculator
- Immunization Scheduler and Chart
- C-Section Checklist
- Online Twin Pregnancy Quiz
- Numerology calculator
- Child Blood Type Calculator
- Nakshatra Calculator
- Diaper Bag Checklist
- Baby Name Combiner
Home • Toddler • Play And Activities
13 Problem-Solving Activities For Toddlers And Preschoolers
Intriguing ideas to boost their analytical and rational thinking skills.
Elisabeth Daly is a state-certified high school English teacher. Over her two decade career, she has taught students in grades 9-12 at both public and private high schools, and worked as an adjunct professor at her local community college. ... read full bio
Kavita has a diverse background in finance, human resources, and teaching. She did her MBA in Finance and HR at Solapur University, and bachelor in Education at Pune University. After working for thre... read full bio
Rohit Garoo is a writer-turned-editor with over 9 years of experience in content writing, editing, and content marketing. He did his bachelors in Science at St. Xavier's College, Hyderabad, and master... read full bio
Vibha is a coder turned content writer. She holds a Masters degree in Computer Applications from Osmania University, Hyderabad and a certificate in 'Introduction To Child Psychology'. Her passion for ... read full bio
MomJunction believes in providing reliable, research-backed information to you. As per our strong editorial policy requirements, we base our health articles on references (citations) taken from authority sites, international journals, and research studies. However, if you find any incongruencies, feel free to write to us .
Image: Shutterstock
Problem-solving preschool activities are an essential part of learning, leading to the development of the most crucial skills for your child. Your child’s journey between realizing a problem and finding a solution involves effort, thinking, and patience. What comes in between realization and solution is important to understand, as it is the key to a lightning-fast intellect. The process is the most beautiful part, which is also the beginning of making a new genius for the world to witness. These little minds could one day become billionaires, philanthropists, or someone far more successful .
Read on to know some of the problem-solving activities for toddlers and preschoolers and how it helps them.
What Is Problem-Solving?
Image: IStock
Problem-solving is the art of realizing a problem and finding an apt solution by a series of interconnected thoughts in the cognitive area of the mind (1) . It requires identifying the problem and pondering over the causes and attempting to chalk out the reason. The next step would be to find a solution out of the many alternatives. Identifying the causes of a problem would involve some deep thinking, which can benefit a child’s growth and aid in their character development.
What Are Problem-Solving Skills?
Problem-solving skills are what every child needs to survive in this world. A few problem-solving skills are analytical thinking, logical reasoning, lateral thinking, creativity, initiative, persistence, negotiation, listening skills, cognitive skills, math skills, and decision-making. Good communication skills are also important as they improve the self-esteem of your child.
Why Is Problem-Solving Important In Preschool?
As parents, you may not want to fill your child’s minds with every problem-solving ability. But you must trust the process, as it is the most important phase of life, and they are learning new things every day.
- During preschool, they are constantly interacting with friends and surroundings. They come across various problems and learn from them. The best part is that it will be effortless for them to pick up these skills faster as they are in their learning stage.
- Also, the earlier they learn, the better it is (2)
- Children in preschool are introduced to the realm of creativity and imagination through storytelling and poems. It will be the perfect time to enhance their creative abilities.
- Children usually try to ignore things beyond their understanding. But problem-solving skills might help them see things differently.
- Developing problem-solving abilities can help them take new initiatives.
How To Teach Problem-Solving Skills To Preschoolers?
Making them listen with patience and willingness is a skill that will help them comprehend what you teach them. Here are some steps that you can follow:
- Teach them how to approach a problem in a practical way. Allow them to explore and find solutions by themselves. Problem-based learning will stick with them forever.
- Make them do simple household chores in their own way. And, there is no right or wrong style to it. Kitchen experiments are a great way to learn.
- Every kid is unique and has a different pace of learning. A teacher/ parent will have to be observing to analyze the best way to teach them.
- Usually, the first step would be to identify the problem.
- Once they find solutions, tell them to evaluate the pros and cons. And choose the best solution.
- Teach them to take failure positively.
- Encourage group activities as children tend to be active when their peers are along.
13 Problem-Solving Activities For Toddlers
You may try several problem-solving activities at home. We have listed some of the best activates here:
1. Simon Says
One of the children becomes Simon and gives commands. The rest have to follow the commands and enact only when they hear ’Simon says’ at the beginning of the command. If anyone acts when the words ‘Simon says’ is not told at the beginning, then that particular child is out. This game will improve listening skills and response time.
2. Tic–tac–toe
The game teaches decision-making and the cost of consequences. This game involves two players. One player has to mark X anywhere on the tic-tac-toe, followed by another player marking O. The idea is to make a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal line with either three X’s or O’s. Both players have to stop each other from winning. Sounds fun, right?
3. Treasure hunt
Divide the children into groups and give them clues to find hidden objects. Activities such as treasure hunt evidently improve their problem-solving skills and induce the idea of competition.
Puzzles can make a child think out of the box. They can develop a child’s logical reasoning. Arranging the crumbled pieces will surely improve their level of patience.
5. Hide and seek
Playing in a group can make them less shy and socialize with others. And, with hide and seek activity, children can learn devising strategies, escaping from a troublesome situation, and various other skills.
6. Sorting together
Give them various toys, pieces of clothing, or other random objects at home and some bins. Now ask your child to sort and place everything in the right bin. See how good they are at classifying the objects.
7. Spot the difference
Show them printouts of two similar pictures, with one picture having some differences. Ask them to spot the differences. This helps in actively improving their concentration and attention to detail.
8. Matching animals with sounds
Play sounds of various animals and let the children guess their names. You can also take them to an animal farm where they can observe their behavior. This activity may improve their sound recognition ability over time.
Give your child a blank canvas and some paints or coloring pencils. Let them get creative and produce a masterpiece.
10. Memory games
Memory games can improve a child’s retaining capacity. One such game is to sit in a circle and play “Chinese Whisper.” In this game, kids sit in a circle. Each of them has to whisper a word in their peer’s ear. The same word, along with a new one, is whispered into the next child’s ear. This should be continued till the last child in the circle announces it for all to hear.
11. Fort building
Building forts using toy material, Lego, pillows, or blankets can be fun. During the process of building a fort, children may have to face minor or major difficulties. Overcoming such issues and completing the target successfully helps in the improvement of logical and analytical abilities.
Solving mazes can also help a kid improve their approach towards dealing with problems and dead ends. It will enable lateral thinking and thinking out of the box.
13. Stacking rings
Stacking rings is an effective problem-solving activity for children as it enhances their cognitive skills, spatial awareness, and fine motor abilities. The task requires careful consideration of size, shape, and balance, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Children must strategize the order and orientation of the rings to successfully build a stable tower. This activity encourages creativity as they experiment with different stacking techniques. Give children a set of rings in varying sizes and materials for this activity. Ask the children to construct the tower and be watchful to prevent it from collapsing, as it offers them valuable insights into cause-and-effect relationships. Challenge them to create the tallest tower possible to promote teamwork and perseverance as they refine their approach through trial and error.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the stages of problem-solving?
Problem-solving is a cognitive skill that works through six stages – searching and determining the problem, generating alternative ideas or solutions, evaluating alternatives, selecting the best suitable solution, implementing the solution, and follow-up (3) .
2. At what age do toddlers begin problem-solving?
According to research, children begin problem-solving right after birth. Children learn problem-solving through exploration between zero to two years, whereas, by three years of age, they learn problem-solving through experimenting and trial and error. Four-year-olds learn problem-solving through cooperative activities with peers and friends. By five and six years, kids get enough experience to deal with problems that would need abstract thinking skills (4) .
3. How do toddlers develop critical thinking skills?
Critical thinking skills don’t develop in a day or week. Rather, it takes constant exposure to environments that hone a child’s critical thinking abilities. Indulging toddlers in critical thinking activities by asking open-ended questions or engaging in activities such as block constructing and puzzles and motivating them to think out of the box are simple ways to bolster your child’s critical thinking.
Problem-solving activities for toddlers enhance their thinking abilities and promote early brain development. You may introduce problem-solving activities such as tic-tac-toe, Simon says, hide and seek, treasure hunt, puzzles, etc., to enhance cognitive skills in toddlers. The problem-solving skills in preschoolers help them cope with various situations and mingle with other children. Problem-solving skills help children think differently and take the initiative in making decisions and solving problems. These activities help build the skills without any force or pressure.
Infographic: Hone Your Toddler’s Problem-Solving Skills
Illustration: Momjunction Design Team
Key Pointers
- Honing your child’s problem-solving skills during preschool can help them see things differently and enhance their creative abilities.
- Teach them to find the problem and use their analytical abilities to find a solution.
- Simon Says, treasure hunt, puzzles, and spot the difference are a few problem-solving activities a toddler can try.
Image: Stable Diffusion/MomJunction Design Team
- You Can Do It: Teaching Toddlers Problem-Solving Skills. https://va-itsnetwork.org/you-can-do-it-teaching-toddlers-problem-solving-skills/
- Developing Problem-Solving Skills At Early Age. https://kennedyglobalschool.edu.in/developing-problem-solving-skills-at-early-age-takes-kids-long-way-as-they-grow/#respond
- Problem solving. https://www.healthywa.wa.gov.au/Articles/N_R/Problem-solving
- Development: Ages & Stages–How Children Learn to Problem-Solve. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ738434
- Fact-checker
Elisabeth Daly MSEd
Kavita kankani mba, bed, rohit garoo bsc, mba, vibha navarathna mca, latest articles, best halloween songs, poems & quotes for kids to celebrate.
A journey that strengthens your bond with your child.
17 Best Thanksgiving Quotes And Poems For Kids
Thanksgiving is about spending time with family and making lots of memories together.
Top 10 Kids Birthday Party Places In India
Your search for the most desirable and fun party place in India ends here.
How To Draw Cartoons For Kids? A Step-By-Step Guide
Easy-to-understand drawing steps to make drawing a fun-learning experience for kids.
14 Best Speech Therapy Apps For Toddlers And Preschoolers
Best designed to improve their speech skill and boost spirits.
16 Colorful And Engaging Free Baby Game Apps
Use them for a short-time engagement for babies and pique their interest.
List Of 22 Best Rock Songs For Kids To Listen
These foot-tapping numbers can get your kids grooving. Join them and revel in.
17 Fun And Free Typing Games For Kids Of All Levels
Let the little fingers become more dextrous with these games.
How To Draw An Elephant For Kids: Step-By-Step Tutorial
Encourage your child to try creative ways of drawing an elephant.
32 Best TV Shows For Kids Of Age 3-12 Years
Informative and entertaining TV shows help children to learn while enjoying.
25 Best Ever Movies For Teens To Watch This Year
Time to spend your holidays by watching popular movies and munching on popcorn.
11 Best Theme Parks For Kids In USA
Create lasting memories with your little ones.
WELL BEINGS WITH ALYSIA
15 Brain Development Activities 2-Year-Olds Will Love
Parents and educators can provide 2-year-olds with fun activities that help them reach cognitive milestones. These activities are fantastic for 1-year-olds, 2-year-olds, and even 3-year-olds. I’m sharing fifteen favorite brain development activities you can do with your toddler at home or in the classroom.

A 2-year-old is developing the following cognitive skills, according to the HSELOF :
- Exploration and discovery
- Reasoning and problem-solving
- Emergent mathematical thinking
- Imitation and symbolic representation
Brain Activities for 2-Year-Olds
Puzzles help 2-year-olds develop problem-solving, reasoning, exploration, and spatial awareness skills.
Jigsaw puzzles are too advanced for most toddlers. Instead, look for chunky puzzles, puzzles with easy-to-hold knobs, and frame puzzles. Toddlers can advance to big floor puzzles or inset puzzles (similar to jigsaw puzzles, but the pieces don’t interlock).
Obstacle Courses
Design an at-home obstacle course to challenge and entertain your two-year-old. Remember, the brain connects to the rest of the body through the nervous system. So encourage your 2-year-old to test their agility, balance, and coordination!
Here are some toddler-approved obstacle course ideas:
- A line of pillows or cushions
- Table or chair to crawl under
- Low stepstool to jump off
- Pop-up tunnel to crawl through
- Small slide
- Yarn “laser maze”
- Hula hoop hop
- Low balance beam
- Tape line “balance beams”
- Balance stepping stones
Shape Sorters
Shape sorters are the perfect activity for toddlers learning about different shapes. Shape-sorting activities help toddler brain development by improving emergent math, problem-solving, and exploration skills.
Show your 2-year-old how the toy works (if needed), then let them try to match the shapes themselves. Shape sorters are hard work, so praise your toddler’s effort. Even without successfully sorting, toddlers can build problem-solving skills and learn shape names.
Magnet Toys
Magnet toys are an incredible way to introduce science and engineering to 2-year-olds. Toddlers develop exploration and discovery skills while experimenting with how magnets attract and repel. Magnet toys promote skills in emergent math, reasoning, problem-solving, and symbolic representation.
Using magnet blocks to sort, stack, and build structures. Here are some of my favorite magnet play materials:
- Magnetic wooden blocks
- Ball & rod magnet toys
- Magnet boards
- Refrigerator magnets
Always inspect magnet toys and supervise your 2-year-old around magnets.
Block play provides toddlers with hands-on experience in problem-solving, spatial awareness, and symbolic representation. If possible, toddlers should have opportunities to play with regular blocks (wooden unit blocks) and interlocking blocks (Duplos, Mega-Bloks, etc.).
Blocks are also an opportunity for toddlers to explore stacking, dumping, falling, lining up, and more. Some 2-year-olds may be ready to construct buildings or use blocks in imaginary play.
Musical Instruments
Parents and caregivers can foster their creativity and promote their cognitive development by introducing 2-year-olds to musical play.
Exploring musical instruments to build toddler imitation and discovery skills. Playing musical instruments is a lifelong practice; toddlers can develop musical memory and problem-solving skills early.
If you don’t have access to toy musical instruments, you can create your rattles from bottles, drums from buckets, or a whole band from kitchen pots and utensils.
Search & Find
When toddlers search for objects, they use problem-solving, spatial awareness, reasoning, and memory skills. Search-and-find activities also encourage 2-year-olds to explore and learn about their environment.
Try some of these fun and easy search-and-find activities:
- Find the toy
- Hide and seek
- Scavenger hunts
- Find the picture in books

I have already reviewed the benefits of playing with play dough . But play dough activities are fantastic for supporting 2-year-olds’ brain development.
Younger toddlers will develop cognitive skills in exploration, discovery, and imitation. Older toddlers can use play dough for creative play, which develops problem-solving and symbolic representation skills.
Check out some of our favorite play dough ideas for toddlers .
Matching Games
Toddlers improve emergent mathematical thinking skills by matching objects and understanding similarities and differences. While playing, your 2-year-olds will also develop memory and attention skills while focusing on the details. Matching skills are closely related to sorting and classifying play .
Matching activities for 2-year-olds can be super easy. While playing together, point out when toys match in shape, color, texture, or pattern. Talk about matching during meals, while getting dressed, or at storytime.
You can purchase toddler sorting toys or collect household items to match and sort. Get more ideas on the loose parts material list .
Color Mixing
Toddlers are still learning colors, so color-mixing activities are perfect for hands-on learning. During color mixing activities, 2-year-olds build the cognitive skills of exploration, discovery, matching, and reasoning.
Try these fun color-mixing activities:
- Melting different colored ice cubes
- Mixing fingerpaint colors (on paper or in a ziploc bag)
- Combining play dough colors
- Securing colored cellophane paper over a flashlight
- Mixing dyed water (using food dye or liquid watercolor) in a water table
Nature Walk
Along with many other benefits, time outside helps children develop spatial awareness, memory, discovery, and exploration skills.
While on a nature walk, you and your 2-year-old can complete a nature scavenger hunt , collect loose parts, or talk about what you see, smell, hear, and feel.
Contact Paper Collage
All open-ended art activities are great for toddler brain development. A sticky contact paper collage adds a sensory-rich experience.
Tape a sheet of contact paper to the table, sticky side up. Then offer your 2-year-old pieces of ribbon, yarn, and scrap paper to stick and peel. Then you can seal the collage by placing another sheet of contact paper on top.
This activity helps toddlers develop problem-solving and spatial awareness skills while exploring new materials.
Stacking & Nesting Cups
A set of stacking/nesting cups is a pretty simple toy, but it creates many opportunities for brain-boosting play. These toys target cognitive skills such as exploration and discovery, problem-solving, and emergent mathematical thinking.
While playing with stacking/nesting cups, 2-year-olds explore graduating sizes and different ways to stack or combine cups. Use the cups for a pretend meal to build imitation and symbolic representation skills!
Tip : Measuring cups are low-cost substitutes for stacking/nesting cups!

Reading to your 2-year-old daily will support their brain development. Storytime together promotes your toddler’s literacy, memory, and symbolic representation skills.
Sound books and sensory books are perfect for targeting your curious 2-year-old’s exploration and discovery skills too!
Sink & Float
Your toddler can do a sink and float activity during bathtime, in a kiddie pool , or in a water table (or water-filled plastic tote!).
Start by collecting about a dozen objects, some that sink and some that float. Encourage your 2-year-old to drop these items into the water one at a time. Discuss how each item sinks to the bottom or floats on the water’s surface.
This activity targets the brain development skills of reasoning, problem-solving, exploration, and discovery. Your toddler gets to actively explore the properties of each object alongside splashing in the water.
Popular Questions about Toddler Brain Development
All interactive activities will boost your toddler’s brain development. Find an activity your child is interested in, and that also makes them think and problem-solve.
Play-based and age-appropriate activities in nurturing environments will help your child’s brain get strong. Children must also have their physical needs met, including plenty of sleep, hydration, and regular, nutritious meals.
You can stimulate your 2-year-old’s brain by stimulating their senses. Sensory , language , nature , play dough , and vestibular and proprioceptive activities will all support your child’s brain development.
Explore the post above for activities designed to stimulate your 2-year-old’s brain and support cognitive skills.
Parents and educators should teach 2-year-olds about their world through play. Teach your 2-year-old how to ask for help, explore the environment safely, and express themselves creatively.
Discover more play and learning activities for toddlers .
Around age two, children discover the toys and activities that interest them the most. Some typical activities a 2-year-old would do is look at books, stack blocks, scribble with crayons, sing nursery rhymes, fill and dump objects, climb and jump, and play with toy cars or toy figures.
You can learn more about this stage of play development here .
When 2-year-olds are playing and engaged, they are learning!
Limit screen time for your 2-year-old and focus on interactive activities such as, sensory play , backyard activities , and household loose parts .
More play ideas

The Magic of Container Play: Boost Baby & Toddler Learning

Literacy Ideas for Babies: Easy Activities from My Infant Classroom

The Best Block Play Activities & Environments for Young Children

My Ultimate Guide to Nature-Based Early Childhood Education
Developmental Therapist
Hello, I'm Alysia (uh-lee-shuh), a developmental therapist for infants and toddlers with a B.S. in Early Childhood Education and a minor in Special Education. As the founder of Well Beings with Alysia, I'm demystifying child development for parents and early educators. Learn how to introduce the play-based activities, books, nature materials, and toys I use in classrooms and early intervention. Contact me: [email protected]
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Some skills gained from the problem-solving activities include lateral thinking, analytical thinking, creativity, persistence, logical reasoning, communication skills, and decision-making skills.
The Importance of Problem-Solving Activities for Toddlers
In almost every stage of growth, children are likely to encounter some difficulties. How they handle these challenges depends on the skills they have built over time.
That’s why every parent should invest in quality problem-solving activities for their child. The skills mentioned above are critical for toddlers, and it can be challenging to develop them.

Early ages are the best time for children to learn how to solve different problems in a fun way.
In many cases, many young mothers are students who dream of spending as much time as possible with their children, but they are held up with advancing their knowledge in their areas of specialization.
To have more time for toddlers as young mothers, you can use the online essay writer service EduBirdie to have your research papers written by top writers. EduBirdie has great writers, and you will receive quality work at the right time. This automatically translates to excellent scores.
If you have more time with your child, you are likely to notice the challenges they are going through and choose the best problem-solving activities for them.
The more problem-solving activities they perform, the more likely the child will develop excellent skills that will enable them to navigate most of the challenges in their lifetime. Here are some simple problem-solving activities for toddlers:
1. Building a maze
Building a maze is fun outside and one of the best activities for 2-year-old toddlers. Since toddlers can’t yet do a maze in an activity book, this is a great way to use their problem solving and navigation skills.

Draw a big maze on the pavement with sidewalk chalk . Then, make passages, including a few that end in a dead-end. Teach your toddler how to walk through and find their way out.
Allow them to try it on their own. The more trials, the better the child gets at figuring out the best way out. If the child gets used to the simple maze, you can draw a more complex one, adding more dead-end passages to make finding their way out more complicated.
This way, you will enhance their cognitive skills, which are vital for success in their life.
Puzzles are some of the best sensory activities for toddlers. They help a lot in enhancing the thinking capabilities of toddlers.
A puzzle is a big set of muddled-up things that must be sorted out and put back together.
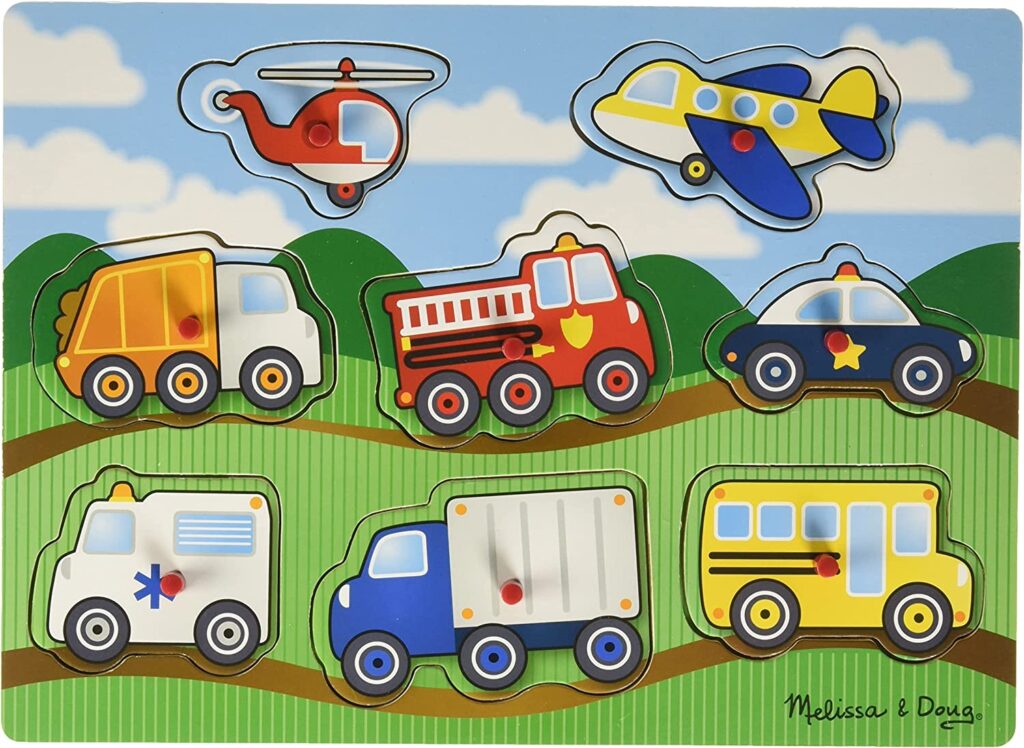

The best type of puzzle for children is wooden puzzles , as they last longer, and the frame provides a structure to guide the child while playing. Inset puzzles are perfect for toddlers, especially ones with familiar objects (transportation, animals, colors, and shapes).
So, make an effort to sit with your child and help them play different puzzles. It’s even better than leaving your toddler to play with fancy toys with flashing lights and music.
Solving puzzles is real learning and allows the students to build their skills at their own pace. It’s ok to let them get a little frustrated! The more you leave them to independently figure it out, the quicker they will gain the skill.
3. Following patterns
Following patterns is just a simple activity that can be played with colored blocks, counters, or shapes. In this case, the child should simply make a pattern with the blocks and vary it by changing the patterns’ colors, shapes, or sizes.

At first, you can demonstrate how to make simple patterns to your child and then make the patterns more complex as they get used to the simple ones. Following patterns train the toddler to analyze given information, make sense of it, recognize the pattern it should follow, and then recreate it.
For the complex patterns, carry out the first few steps and then ask your child to continue.
4. Board games

Playing board games is an excellent way to develop your problem-solving skills, and your child can quickly start with simple games. This could be CandyLand ( a huge hit with little ones) or Chutes and Ladders .
Board games teach toddlers the skill of following rules and moving logically.
With time, you can introduce games that require deeper thinking and planning, like Monopoly Junior. This game will require you to explain a lot, and sometimes you will have to play with the child.
You can also let your child play Go Fish to teach them how to think ahead and solve the problems they will encounter in the future.
Related Post: Perfect Board Games for 2 Year Olds
5. Storytime questions
Stories are a great way of teaching children moral values and the problem-solving skills they require for their lifetime. During storytelling, develop a habit of asking questions to help the child develop higher-order thinking skills like comprehension.

It’s simple: pause for a few minutes and pose questions about the story. Start with simple questions, like “What did the boy say?” or “Where did the family go?.”
Then move onto more abstract thinking, problem solving questions, like “what will the boy do now that his pet died?” or “what can the girl do to find her lost toy?”
You can also pose an unexpected question to make the child more attentive. Storytime questions teach toddlers to pay attention to details and concentrate on one activity at a time.
It also reinforces the message you were trying to pass to the toddler. As a result, the toddler will easily remember the story’s moral lessons and apply them when faced with challenges in their lifetime.
6. Building with construction toys
Construction toys could be engineering blocks, Legos, or a proper set of wooden blocks that can be used to construct simple structures.
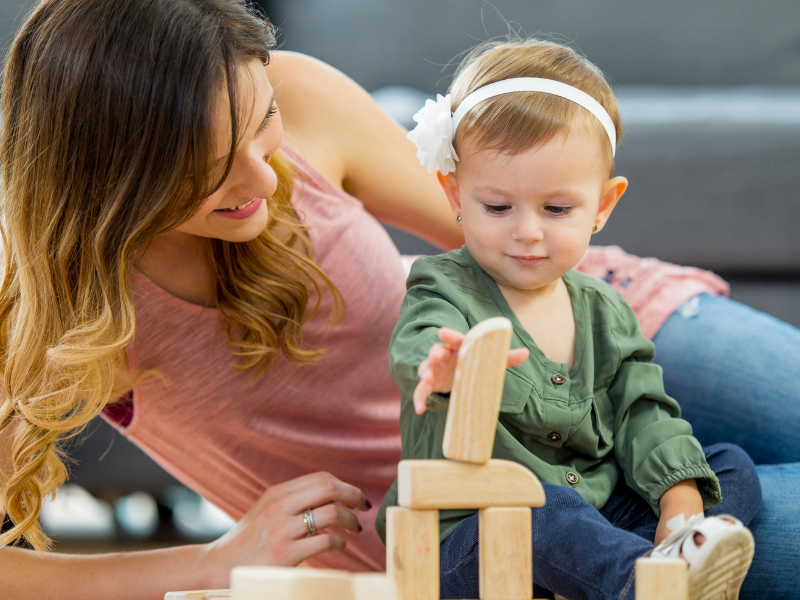

Everything the toddler will build is challenging as it requires critical thinking in brainstorming what to build and how to put the different pieces together.
The design built should be functional and work as expected. So, let the child construct freely and occasionally set for them a challenge to be completed within the set time with specific conditions.
This could be building two towers with a bridge joining them or building a creature with three arms standing on its own. Let the kids exercise their brains until they find a way to make the structure work.
7. Classifying and grouping activities

Classifying and grouping activities are among the best sensory activities for toddlers. You can easily do this with a tin of buttons or by unpacking the dishwasher. The idea behind classifying and grouping activities is to teach the skill of categorizing information.
There are several button activities for your kids that you can adopt, and they include a messy play tray, making a nameplate, sorting buttons, ordering buttons, or making a button necklace.
Each activity will teach the child an important skill they need to solve problems in the future.
When was the last time you engaged in any of the activities discussed above with your child? Start young with these problem-solving activities that help them navigate most of the challenges in their lifetime.
Take time and choose one of the activities discussed above for your toddler.
Author’s Bio
Helen Birk is a magnificent writer who creates beautiful stories that leave her readers asking for more. She’s been a wonderful storyteller and her years of experience help her do even better every time she takes up a new book to write. She’s currently planning a book that talks about the role of AI in the development of school education.
Related posts:
17 Learning Activities for 2-Year-Olds: Teaching Toddlers Through Play
Play-based learning is the best way for your toddler to learn about themselves and their world.

The world of your 2-year-old is full of exciting possibilities. They are developing quickly, and you will find them ready to dive into learning experiences. They are actively looking for ways to assert their independence and test their boundaries (and yours!).
Learning activities for 2-year-olds should look at their development holistically and engage them in new ways of thinking. Toddler learning activities are a fun way for you to connect with your child as you learn and grow together.
Play-Based Learning for Toddler Development
When your 2-year-old is playing, they are learning how the world works. Play ignites their curiosity and gets them to think creatively about simple tasks.
“Play is our brain’s favorite way of learning” – Diane Ackerman.
Here are some other ways that play is beneficial for development:
- Practice life skills
- Improves communication
- Develops empathy
- Encourages imagination
- Allows for independence and autonomy
- Fosters problem-solving skills
17 Learning Activities for Your 2-Year-Old
When it comes to educational activities for toddlers, you want to make them hands-on and fun. Learning should be joyful and creative. Fun activities can teach your child and keep them happily immersed in play.
Activities for Gross Motor Skills Development

1. Play Silks and Dancing
There is something magical about watching a child lost in their own world. Play silks are a great way to encourage imaginative movement in little kids.
Put on some music and let your little one move to the rhythm. This unstructured activity allows them to use any movements they want. The play silks help them move their bodies, become aware of themselves within a space, and embody different characters.
Fun Tip: Try music that evokes different moods. Watch as your child adjusts their movements to the music.
Benefits:
- Imagination
- Free movement
- Express emotion
2. Animal Imitation
What toddler doesn’t love pretend play?
You can use animal cards, toy animals, or even recorded animal sounds for this activity. Help your child think about how each animal moves and then watch as they try to imitate that movement. They can include the sound the animal makes to really get into character.
Fun Tip: Do this activity with your child. Yes, it may seem silly, but they will love it. Play is how our kids communicate with us, and something special happens when we join them in their world.
- Crossing the midline and gross motor skills
- Builds core strength
- Improves focus and attention
3. Mud Monster
Getting dirty is a great way to learn and a fun activity. Not only is mud a fantastic sensory experience, but it contains friendly bacteria that stimulate the release of serotonin .
To create your mud monster, draw one on a wall with mud or build one around a hula hoop placed on the ground. Your toddler will then make mud balls and have to throw them into the mud monster’s mouth. Your 2-year-old is learning to throw overhand at this stage, and this is a fun activity to practice.
Fun Tip: Let your toddler help you make the mud. The process of mixing sand and water is a valuable learning opportunity.
- Develops tactile skills
- Strengthens throwing motion
- It helps them identify their dominant arm
Activities that Develop Fine Motor Skills

4. Building Blocks
Building blocks are a classic toddler activity that has a multitude of benefits. Simply place a bag of blocks on the floor and watch as your little one begins to create. At this age, your 2-year-old will be able to build a tower of 4-7 blocks, opening up a world of possibilities for them.
Fun Tip: Add other elements such as cars, animals, and wood planks. This will help your toddler play with the blocks in new and imaginative ways.
- Problem-solving
- Early math skills
5. Simple Tracing
Your 2-year-old might not be holding a pencil confidently, but they will enjoy simple tracing activities. They will help them develop tensile strength in their fingers and work on their fine motor skills.
Use simple shapes and lines with an easy-to-follow dot-to-dot pattern. A chunky pencil or marker will work best for your child’s inexperienced fingers.
Fun Tip: Start with sidewalk chalk to encourage large, free-flowing movements. Before starting with a pencil, try a Q-tip and paint to follow a series of dot patterns.
- Hand-eye coordination
- Concentration
- Crossing the midline
6. Paper Washing Line
Reaching the washing line outside might be tricky, but you can create a mini version indoors. All you need is a cardboard box, some twine, and two pieces of dowel rod. You can cut out clothing from cardboard and let your 2-year-old peg them onto the line.
Fun Tip: You can use clothes pegs to hang up art, count, color sort, and paint with. They are a versatile option for 2-year-old development activities.
- Improve pincer grasp
- Motor accuracy
- Hand preference
7. Playdough Jars
Play dough is fantastic for sensory play and fine motor skills development. Put playdough and loose parts into different jars with the lids on. Then let your toddler open the jars and empty the contents. Opening the jars is good fine motor practice and your toddler is also at a stage where they love to empty containers.
Fun Tip: Ask your toddler to sort the items and place them back into the jars at the end of the activity.
- Strengthens fingers, hands, and wrists
- Improves concentration
Activities for Language Development

8. Picture Books
Picture books are essential in child development, particularly for emergent language. Reading picture books allows you to foster connection with your toddler while demonstrating a love of reading. Your 2-year-old will also learn to connect the words to the pictures. This will help them understand their meaning better.
Fun Tip: Play a game of ‘spot the x.’ You can help your child learn new words as they associate them with a picture.
- Listening skills
- Strengthen visual thinking skills
- Encourage conversations
9. Mystery Bag
This is a versatile game that you can play with almost any object. Put a selection of things into a bag. Ask your toddler to reach into the bag and try and name an object they feel before pulling it out. This is a fun way to introduce new words to your child’s vocabulary.
Fun Tip: For an interesting variation of this game, draw the outline of your toddler’s body on a large piece of paper. Then ask them to point to and name their different body parts.
- New vocabulary
- Improved tactile sense
10. Story Cubes
Story cubes have scenes/characters/objects depicted on them. Your toddler can choose the order of the cubes, and you can create a story together. This activity is excellent for teaching toddlers about creative thinking and future scenarios.
Fun Tip: Incorporate tower building into the process. Then start the story from the top of the tower and reverse it. This is a fun way to introduce the concepts of top and bottom while helping your toddler use their imagination.
- Imaginative play
11. Nursery Rhymes
Nursery rhymes are great for teaching 2-year-olds about phonics and help with language development. Keep your rhymes simple and choose ones with repetitive verses.
Some great nursery rhymes for 2-year-olds are Incy Wincy Spider, Old MacDonald, Twinkle Twinkle Little Star, Humpty Dumpty, and Hickory Dickory Dock.
Try to incorporate rhymes that have corresponding movements. The car is also great for practicing nursery rhymes with your toddler.
- Develop motor skills
- Teach grammar
- Introduce counting, colors, and shapes
Activities for Social/Emotional Development

12. Emotion Cards
2-year-olds are learning about themselves in relation to other children so talking about emotions is vital. Emotion cards work well as they show the picture that relates to a feeling. Start your day with the emotion cards and regularly bring them out.
Fun Tip: Take a ‘sportscasting’ approach to toddler behavior. That means you observe and repeat the facts of the situation. This allows your toddler to feel and deal with the emotion for themselves.
- Builds empathy
- It helps them learn self-regulation and self-control
- Emotional vocabulary development
13. Simon Says
2-year-olds are starting to copy the behavior they see around them. That makes Simon Says a fun and simple game to play. Your toddler is also becoming more aware of themselves, and Simon Says is a fun way to start teaching them about the parts of their body.
Fun Tip: Use the anatomical names for body parts. Children must know the real names as they become aware of themselves and their bodies.
- Developing body awareness
- Sequencing Skills
- Following instructions
14. Kitchen Time
Your 2-year-old is becoming more independent, and you may find them increasingly defiant. Spending time in the kitchen is a great way to help them feel empowered and capable.
Simple cookies, scrambled eggs, and banana muffins are easy recipes that your 2-year-old can make with you.
Fun Tip: Involve them in the whole process by allowing them to crack, mash, and scoop but also wash up.
- Basic math skills
- Builds independence
- Boosts confidence
Activities for Cognitive Development

15. Puppet Play
Puppet play is an amazing developmental tool for toddlers. Your 2-year-old is starting to engage in make-believe play and new language. Puppets encourage creativity, imagination, and new vocabulary. It also helps develop social skills.
Fun tip: You don’t need fancy puppets. Toddlers love craft activities, so why not make your own out of socks? You know, the ones that make it out of the dryer without a partner?
- Motor skills
- Builds self-confidence
16. Treasure Hunt
A treasure hunt is a versatile learning experience that you can use repeatedly. For example, you can have a color hunt where your toddler has to find items in the house that are a specific color. Or you can stick shapes around the house and ask them to find and sort them.
Fun Tip: Take this activity outside for a diverse sensory experience with different textures.
- Color identification
17. Sorting Basket
Sorting baskets are another fun matching game to help your toddler learn colors, numbers, shapes, and sizes. You can put almost anything in a sorting basket, from leaves and stones to blocks and fabric scraps.
Fun Tip: Mix up textures and color shades to challenge your toddler.
- Develops reasoning and thinking skills
- Encourage categorizing
- Early literacy and numeracy skills
Teaching Your Toddler Through Play
Play-based learning opportunities are the best activities to get your toddler engaged and excited. They allow you to introduce complex concepts through simple play that your 2-year-old can easily understand.
Watching your little one engage with the world around them is a magical time, so get on their level and get playing.

10 Simple Activities to Teach Your Preschooler Problem Solving
By: Author Tanja McIlroy
Posted on Last updated: 5 June 2024
Categories Activities for Preschoolers & Kindergarteners
During the first years of a child’s life, an important set of cognitive skills known as problem-solving abilities are developed. These skills are used throughout childhood and into adulthood.
Find out what problem solving is, why it’s important and how you can develop these skills with 10 problem-solving games and activities.
What is Problem Solving in Early Childhood?
So, what exactly is problem solving? Quite simply, it refers to the process of finding a solution to a problem .
A person uses their own knowledge and experience, as well as the information at hand to try and reach a solution. Problem solving is therefore about the thought processes involved in finding a solution.
This could be as complex as an adult working out how to get out of a financial crisis or as simple as a child working out how two blocks fit together.
Problem Solving Skills for Kids
Problem-solving skills refer to the specific thinking skills a person uses when faced with a challenge. Some problems require the use of many skills, while others are simple and may only require one or two skills.
These are some examples of problem-solving skills for preschoolers , as listed by kent.ac.uk .
- Lateral thinking
- Analytical thinking
- Decision-making skills
- Logical reasoning
- Persistence
- Communication skills
- Negotiation skills
The Importance of Developing Problem-Solving Skills in Early Childhood
Problem solving is a skill that would be difficult to suddenly develop as an adult. While you can still improve a skill at any age, the majority of learning occurs during the early years.

Preschool is the best time for a child to learn to problem solve in a fun way. The benefits of learning early will last a lifetime and the beauty of learning anything at a young age is that it is effortless .
It is like learning to play an instrument or picking up a new language – it’s just much easier and more natural at an early age.
Of all the many things preschoolers need to learn , what makes problem solving so important?
There aren’t many situations in life, at work or at school that don’t require some level of problem resolution.
Child’s play itself is filled with opportunity upon opportunity to solve all kinds of tricky situations and come up with solutions to challenges.
Problem Solving in Preschool
During the foundational years, children are constantly solving problems as they play .
Here are just a few examples of problem solving in early childhood :
- Resolving a fight over the same toy
- Reaching a ball that’s stuck in the tree
- Forming a circle while holding hands
- Making a bridge to connect two block towers
- Tying or untying a shoe
- Making up rules for a new game
- Trying to get the consistency of a mud cake right so it stops falling over
The more creative play opportunities and challenges children are given, the more they get to exercise their problem-solving muscles.
During free play , there are non-stop experiences for this, and parents and teachers can also encourage specific problem-solving skills through guided activities .
Problem Solving for Older Children
During the grades, children experience problems in many forms, some of which may be related to their academic, social and emotional well-being at school. Problems may come in the form of dealing with life issues, such as:
- Problems with friendships
- Struggling to understand something during a lesson
- Learning to balance the demands of sport and homework
- Finding the best way to study for a test
- Asking a teacher for help when needed
Problems will also form a large part of academic life as teachers will be actively developing this skill through various activities, for example:
- Solving a riddle or understanding a work of literature
- Working on projects with a friend
- Finding solutions during science experiments
- Solving mathematical problems
- Solving hypothetical problems during lessons
- Answering questions and completing exam papers
Children who have had practice during preschool will be a lot more capable when facing these challenges.
Solving Problems in Mathematics
Mathematics needs to be mentioned separately as although it is part of schooling, it is such a huge part and it depends heavily on a child’s ability to solve problems.
The entire subject of mathematics is based on solving problems. Whether you are adding 2 and 3, working out how many eggs will fit into each basket, or solving an algebraic expression, there is a problem in every question.
Mathematics is just a series of problems that need to be solved.
What we refer to as problem solving in Maths is usually answering word problems .
The reason many children find these so difficult to answer is that the question is presented as a problem through a story, rather than just numbers with symbols telling you what operation to use (addition, division, etc.)
This means a child is forced to think carefully, understand the problem and determine the best way to solve it.
These problems can involve various units (e.g. mass, capacity or currency) as well as fractions, decimals, equations and angles, to name a few. Problems tend to become more and more complex over the years.
My experience in the classroom has shown that many, many children struggle with solving word problems, from the early grades right into the senior years.
They struggle to analyze the question, understand it, determine what information they’ve been given, and what exactly they are required to solve.
The good news is that exposing a child to regular problem-solving activities and games in preschool can greatly help him to solve word problems later on in school.
If you need one good reason to do these kinds of activities, let it be for a smoother experience in mathematics – a subject so many children unnecessarily fear.
Problem Solving in the Workplace

Adults in the workplace seldom thrive without problem-solving skills. They are required to regularly solve problems .
As adults, employees are expected to independently deal with the frequent challenges, setbacks and problems that are a big part of every working environment.
Those who can face and solve their own problems will go further and cope better than those who seek constant help from others or cannot show initiative.
Some career websites even refer to problem solving as a universal job skill. They also mention that many employees are not good at it.
Again, although it may seem far removed, learning this skill at a young age will help a child cope right into adulthood and in the working world.
How to Teach Children Problem-Solving Skills
If early childhood is the best time to grow these skills in your young children, then how does one go about teaching them to toddlers, preschoolers and kindergarteners?

Problem solving can be taught in such a way that you expose your child to various opportunities where they will be faced with challenges.
You would not necessarily sit your 3-year-old down and tell or “teach” him all about fixing problems. Instead, you want to create opportunities for your child to grow this skill .
Using the brain to think and find solutions is a bit like working a muscle over time. Eventually, your muscle gets stronger and can handle more “ weight. ” Your child will learn to problem solve in two ways:
- Incidentally – through free play
- Through guided opportunities provided by a parent or teacher
If you make a point of encouraging thinking through games and activities, your child will develop stronger skills than if you let it all happen incidentally.
Problem-Solving Strategies and Steps
If we take a look at the steps involved in solving a problem, we can see that there are many layers involved and different types of skills. Here are the problem-solving steps according to the University of Ken.
Step 1: Identify the problem
Step 2: Define the problem
Step 3: Examine the options
Step 4: Act on a plan
Step 5: Look at the consequences
Therefore, activities at a preschool level need not present complicated high-level problems.
- A simple activity such as identifying differences in a picture can work on the first skill needed – identifying a problem.
- Playing with construction toys can develop a child’s ability to try various solutions and examine the options when faced with a problem such as trying to find the best way to build something.
- Playing Tic-Tac-Toe would make a child predict the consequences of placing their mark in a particular square.
The most basic of activities can work on all these skills and make children competent solution finders.
How to Teach Problem Solving with Questions
The language you use around your child and your questioning technique will also greatly affect their understanding of a problem or challenge as merely something waiting for a solution to be found .
While your child is playing or when she comes to you with a problem, ask open-ended questions that will guide her in finding a potential answer independently. Use the steps listed above to formulate your questions.
Here are some examples of questions:
- What do you think made the tower of blocks fall down?
- If we build it again, how can we change the structure so that it won’t fall down next time?
- Is there a better way we can do it? If you think of a different way, we can both try it and see which works better.
- Did that work? The tower fell again so let’s try another solution.
Resist the temptation to fix every one of your child’s problems, including conflict with friends or siblings. These are important opportunities for children to learn how to resolve things by negotiating, thinking and reasoning.
With time, your child will get used to seeing a problem, understanding it, weighing up the options, taking action and evaluating the consequences.
Problems will be seen as challenges to be faced logically and not “problems.”
10 Problem-Solving Activities for Preschoolers
Here are 10 simple, easy games and problem solving activities for kids at home or at school. Many of them are the kinds of activities children should have daily exposure to.
Puzzles are one of the best thinking activities out there. Each puzzle is basically one big set of muddled-up things to be sorted out and put back together again. Find out why puzzles are important for development .
Children should have regular exposure to puzzles. They are great for developing thinking skills.
The best types to choose are sturdy, wooden puzzles with a board. They last longer and the frame provides a structure to guide children when building.
2. Memory games
Memory games will develop your child’s memory and attention to detail.
Use pairs of matching pictures and turn them all face down, shuffled, on a table. Take turns choosing any two cards and turning them face up on the table. If you turn over a matching pair you keep the cards and if the pair doesn’t match, turn the cards back over until it is your turn to try again.
Encourage your child to concentrate and pay attention to where the pictures are and try to find a matching pair on each turn.
(Get your own set of printable memory card games here!)
3. Building with Construction Toys
Construction toys such as engineering blocks, a proper set of wooden blocks or Legos (shown below) should be a daily staple in your home.
Everything your child builds is a challenge because it requires thinking about what to build and how to put the pieces together to get a design that works and is functional.
Leave your child to construct freely and occasionally set a challenge and ask him to build a specific structure, with conditions. For example:
- Make two towers with a bridge joining them together
- Build a creature that stands on its own and has 3 arms.
Then watch your child wracking his brain until he finds a way to make his structure work.
4. Activity Books
These activity books are really fun and develop a child’s ability to identify problems and search for information.
5. Following Patterns
This simple activity can be played with a set of coloured blocks, shapes or counters.
Simply make a pattern with the blocks and ask your child to continue it. Vary the pattern by changing the colours, shapes or sizes.
This activity will train your child to analyse the given information, make sense of it, recognise the pattern and re-create it.
6. Story Time Questions
Get into the habit of asking questions during your daily story time that develop higher-order thinking skills . Instead of just reading and your child passively listening, ask questions throughout, concentrating on solving problems.
Here are some examples:
- Why do you think the bear did that?
- Do you think his friend will be happy? Why?
- What would you do if you were the monkey?
- How do you think Peter can make things better with his friend?
- If the crocodile had decided not to eat the rabbit, how could the story have ended?
7. Board Games
Board games are an excellent way to develop problem-solving skills.
Start off with simple games like Ludo and Snakes and Ladders to teach the skill of following rules and moving in a logical sequence.
Card games like Go Fish are also great for teaching young children to think ahead and solve problems.
8. Tic-Tac-Toe
This is a perfect game to teach decision-making skills , thinking before acting and weighing up the possible consequences.
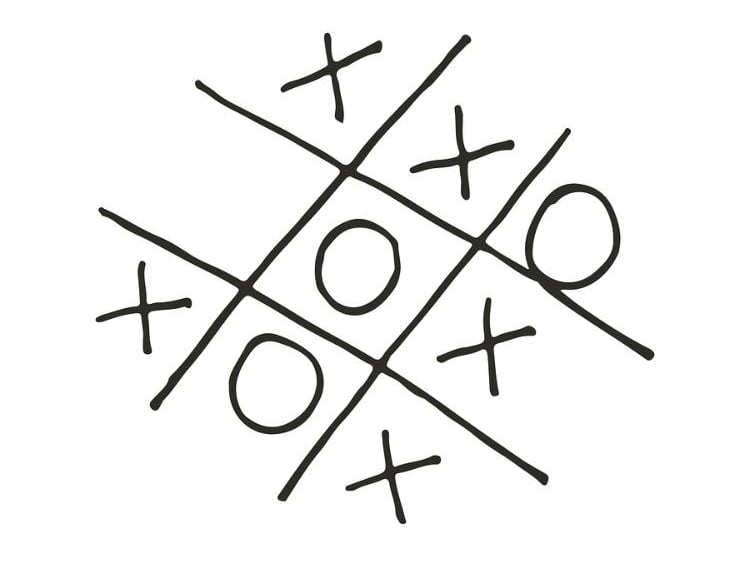
Use a Tic Tac Toe Board or d raw a simple table like the one above on paper or a chalkboard.
Take turns to add a nought or a cross to the table and see who can make a row of three first.
Your child will probably catch on in no time and start thinking carefully before placing their symbol. This game can also be played with coloured counters or different objects.
9. Classifying and Grouping Activities
This activity can be done with a tin of buttons or beads or even by unpacking the dishwasher. The idea is to teach the skill of classifying and categorizing information by learning with physical objects. Here are some other ideas for categorizing:
- Separate the washing – mom’s clothes, dad’s clothes, etc; or socks, tops, shorts, etc.
- Empty out the cutlery drawer for cleaning, mix all the utensils up and then sort into knives, tablespoons, teaspoons, etc.
- Classify and sort out the toys in your child’s bedroom together – all books, construction toys, soft toys, etc.
- Play category games .
Here are more button activities for kids .
10. Building a Maze
This activity is lots of fun and suitable for any age. It is also going to be way more fun than doing a maze in an activity book, especially for younger children.
Draw a big maze on the paving with sidewalk chalk . Make passages, including one or two that end in a dead-end. Teach your kids to find their way out .
As your child gets better at figuring out a route and finding the way out, make the maze more complex and add more dead-end passages.
Are you a preschool teacher or working in Early Childhood Education? Would you like to receive regular emails with useful tips and play-based activity ideas to try with your children? Sign up for the newsletter!

This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Friday 3rd of June 2022
hi maam , This Is Uma from India,Can i get this in pdf format or a book. Thank You
Tanja Mcilroy
Monday 6th of June 2022
Hi Uma, thanks for your message. These articles are not available in PDF, but you are welcome to copy and paste them from the website, as long as you add the reference: https://empoweredparents.co/problem-solving-activities-preschoolers/ Thanks for reading!
Wednesday 20th of May 2020
Very very useful content. Good work. Thank you.
Friday 22nd of May 2020
Thanks Ann.
Tuesday 19th of May 2020
Would like to download the free activity pack please.
Hi Kelly, Please download the activity pack on this page: www.empoweredparents.co
Official websites use .gov
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Important Milestones: Your Child By Two Years
CDC’s milestones and parent tips have been updated and new checklist ages have been added (15 and 30 months). For more information about the updates to CDC’s developmental milestones, please review the Pediatrics journal article and these important key points .
How your child plays, learns, speaks, acts, and moves offers important clues about your child’s development. Developmental milestones are things most children (75% or more) can do by a certain age.
Check the milestones your child has reached by 2 years by completing a checklist with CDC’s free Milestone Tracker mobile app, for iOS and Android devices, using the Digital Online Checklist , or by printing the checklist [1 MB, 2 Pages, Print Only] below.
“Learn the Signs. Act Early.” materials are not a substitute for standardized, validated developmental screening tools .
What most children do by this age:
Social/emotional milestones.

Language/Communication Milestones
Close this video
Cognitive Milestones (learning, thinking, problem-solving)
Movement/physical development milestones, notices when others are hurt or upset, like pausing or looking sad when someone is crying.

Tries to use switches, knobs, or buttons on a toy

Plays with more than one toy at the same time, like putting toy food on a toy plate

Kicks a ball

Walks (not climbs) up a few stairs with or without help

Eats with a spoon

Other important things to share with the doctor…
- What are some things you and your baby do together?
- What are some things your baby likes to do?
- Is there anything your baby does or does not do that concerns you?
- Has your baby lost any skills he/she once had?
- Does your baby have any special healthcare needs or was he/she born prematurely?
Concerned About Your Child’s Development? Act Early.
You know your child best. Don’t wait. If your child is not meeting one or more milestones, has lost skills he or she once had, or you have other concerns, act early. Talk with your child’s doctor, share your concerns, and ask about developmental screening. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children be screened for general development using standardized, validated tools at 9, 18, and 30 months and for autism at 18 and 24 months or whenever a parent or provider has a concern.
If you or the doctor are still concerned:
- Ask for a referral to a specialist who can evaluate your child more; and
- Call your state or territory’s early intervention program to find out if your child can get services to help. Learn more and find the number at cdc.gov/FindEI .
For more on how to help your child, visit cdc.gov/Concerned .

As your child’s first teacher, you can help his or her learning and brain development. Try these simple tips and activities in a safe way. Talk with your child’s doctor and teachers if you have questions or for more ideas on how to help your child’s development.
- Help your child learn how words sound, even if he can’t say them clearly yet. For example, if your child says, “or nana,” say “You want more banana.”
- Watch your child closely during playdates. Children this age play next to each other, but do not know how to share and solve problems. Show your child how to deal with conflicts by helping her share, take turns, and use words when possible.
- Have your child help you get ready for mealtime, by letting him carry things to the table, such as plastic cups or napkins. Thank your child for helping.
Click here for more tips and activities
- Give your child balls to kick, roll, and throw.
- Give toys that teach your child how to make things work and how to solve problems. For example, give her toys where she can push a button and something happens.
- Let your child play dress up with grown-up clothes, such as shoes, hats, and shirts. This helps him begin to pretend play.
- Allow your child to eat as much or as little as she wants at each meal. Toddlers don’t always eat the same amount or type of food each day. Your job is to offer her healthy foods and it’s your child’s job to decide if and how much she needs to eat.
- Have steady routines for sleeping and feeding. Create a calm, quiet bedtime for your child. Put on his pajamas, brush his teeth, and read 1 or 2 books to him. Children this age need 11 to 14 hours of sleep a day (including naps). Consistent sleep times make it easier.
- Ask your child’s doctor and/or teachers about toilet training to know if your child is ready to start. Most children are not able to toilet train until 2 to 3 years old. Starting too early can cause stress and setbacks, which can cause training to take longer.
- Use positive words when your child is being a good helper. Let him help with simple chores, such as putting toys or laundry in a basket.
- Play with your child outside, by playing “ready, set, go.” For example, pull your child back in a swing. Say “Ready, set….”, then wait and say “Go” when you push the swing.
- Let your child create simple art projects with you. Give your child crayons or put some finger paint on paper and let her explore by spreading it around and making dots. Hang it on the wall or refrigerator so your child can see it.
- Use positive words and give more attention to behaviors you want to see (“wanted behaviors”), than to those you don’t want to see. For example, say “Look how well you’re eating with your spoon.”
- Let your child play with sand toys or plastic containers, spoons, or a funnel in the tub or in a sandbox.
- Help your child do simple puzzles with shapes, colors, or animals. Name each piece when your child puts it in place.
- Encourage your child’s curiosity and help her learn and explore new things. Take her to the park, take walks, or go on a bus ride.
- Sing songs, such as “Head, Shoulders, Knees, and Toes,” to teach names of body parts. After singing it a few times, see if your child sings some of the words when you touch a body part and wait.
- Limit screen time (TV, tablets, phones, etc.) to no more than 1 hour a day of a children’s program with an adult present. Children learn by talking, playing, and interacting with others.
- Encourage your child to play with blocks. Take turns building towers and knocking them down.
- Ask your child to help you open the drawer when you put away clothes or open the door when you go outside.
Special acknowledgments to the subject matter experts and others who contributed to the review of data and selection of developmental milestones, especially Paul H. Lipkin, MD, Michelle M. Macias, MD, Julie F. Pajek, PhD, Judith S. Shaw, EdD, MPH, RN, Karnesha Slaughter, MPH, Jane K. Squires, PhD, Toni M. Whitaker, MD, Lisa D. Wiggins, PhD, and Jennifer M. Zubler, MD.
Sincere gratitude to Natalia Benza, MD and José O. Rodríguez, MD, MBA for their thoughtful review of the Spanish-language translation of these milestones.
- Developmental Disabilities
- Child Development
- Positive Parenting Tips
- National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities
- Foods and Drinks for 6 to 24 Month Olds
Print Milestone Checklist

English [1 MB, 2 Pages, Print Only] Spanish [1 MB, 2 Pages, Print Only]
Order free materials
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Stages of Play From 12–24 Months: Young Toddlers Are Problem Solvers
- February 26, 2015
Learn how infants and toddlers develop play skills from birth to 3, playing with toddlers, and what toys and activities are appropriate for their age.
What babies started to do and learn in their first 12 months really takes off during the next 12. Through their play experiences and interactions with you (remember, you are still their favorite toy!), they continue to figure out how the world around them works. Read on to learn more about playing with toddlers during this time—and what you can do to support your toddler’s development.
What Does It Do?
Toddlers are learning how objects are used together. This is why they enjoy filling-and-dumping water, sand, and blocks. Toddlers are also making connections between objects—the reason they like placing little people on a toy bus. Toddlers are learning about sizes as they stack rings. They’re noticing similarities when they line up two toy cars that look the same.
TOYS TO EXPLORE:
- Pop-beads or chunky interlocking plastic blocks
- Plastic spoon and cup
- Blocks and bucket
- Nesting cups/rings or shape-sorters
- Busy box with button to push, switch, and dial to turn
- Chunky wooden puzzles
HELPING YOUR TODDLER PLAY AND LEARN:
- Offer toys like these to your toddler and just watch to see what she does. Let her try to figure out how they work and discover what she can do with them.
- Then show your toddler how to use these toys in new ways. For example, you might put the spoon in the cup and stir. Then hand it to him and see what he does. Or pretend to give his stuffed bear a sip.
First Friends and Early Social Skills
Beginning at about 12 months, most young toddlers enjoy playing near peers. They may play games like “Ring Around the Rosie” or “chase” with another child, or join a peer in filling a bucket with mulch on the playground. These moments may not last long, but they give toddlers a sense of what it means to be a friend and have a friend.
- Musical instruments
- Sand/water play
- Art activities, such as painting or chalk
- Toy cars or trains, with one available for each child
- Create a toddler band by giving each child an instrument or scarf to shake along to the music. Or give each toddler a paint brush and unroll a long roll of paper so everyone has a place to paint. This helps little ones experience the joy of peers without the pressure of sharing!
- Model the words children should use when playing with others, including “Hi! I’m Logan,” “Can I play?”, “My turn?”, and “Thank you.” Toddlers will need to hear these words many, many times before they learn to use them. (This is one area where repetition is really important!)
Can You Hear Me Now? Building Communication Skills
Your 1-year-old is communicating with you using a combination of sounds, gestures, and facial expressions. She’ll likely begin using spoken language with one word, but her vocabulary will grow steadily as you continue to label, comment, and ask questions. She may not say much at first, but she understands almost everything you say!
- Toy telephone
- Child-safe mirror
- Dolls, stuffed animals, and puppets
- Use a toy telephone to help your child “talk” to you or other family members. Use dolls or puppets to “talk” with your child. Sit with your child in front of a mirror and say, “hello!” to each other.
- Ask your child to do a “one-step” request—this means asking him to do one thing, such as “please get your shoes” or “pick up the ball, please.” As your child approaches age 2, try adding a second step: “Please pick up the ball and give it to me.”

Playing with Toddlers: They’re Moving Now
Toddlers are learning to walk, run, climb, use stairs, and throw a ball. This means they need lots of active playtime to build strength, balance, and coordination. Because toddlers don’t understand rules yet, they benefit from free play when they can explore their own way.
- Balls of different sizes to roll, throw, and chase
- Toys that can be pulled while walking (a toy dog on a string; a wagon)
- Tunnel (purchased or homemade from a moving box)
- Child-size stool to climb onto and jump off of (with supervision)
- Create a toddler obstacle course where your child has a chance to crawl (through a moving box), climb (over a cushion), bounce (on a pile of blankets), and roll toward you for a kiss.
- Throw a soft playground ball and see if your child will run or crawl to get it. Or just roll the ball back-and-forth to one another—a game that builds social skills like turn-taking.
Related Resources
Striving for language equity: early intervention is key for language acquisition in deaf children, buzzwords explained: play-based learning, black educators and entrepreneurs inspiring the future, support zero to three.
We need your support now more than ever to ensure all babies have access to the quality care, services and support they need to thrive.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to after header navigation
- Skip to site footer

Preschool.org
The one-stop resource for preschool parents, teachers, directors, and owners!
Cognitive Milestones for 2-Year-Olds
At 2-years-old you will see many big changes in your toddler. They are constantly learning new things and mastering new skills. Their problem solving skills are developing as they begin to seek more independence and freedom. Providing your child with a variety of play experiences is the best way that you can support their overall development, including their cognitive development.

DEFINITION OF COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT
Cognitive development is not only about acquiring knowledge. It is also about learning to think, problem solve, and communicate. This also includes the development of a child’s executive functioning skills. Young children develop cognitively through experiencing and interacting with the world around them first-hand. At two-years-old your child is becoming more and more aware of their environment and how things work.
2-YEAR-OLD COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT MILESTONES
- Begins to sort objects by color, shape, or size
- Plays simple make-believe games
- Follows two-part directions
- Begins to understand simple time concepts like before and after
- Begins to understand the concept of numbers
- Completes simple puzzles
- Recognizes basic symbolism like nodding head for “yes”
- Finds objects even when hidden under covers
COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT ACTIVITIES
Young children learn best through play, and that is no different when it comes to developing their cognitive skills. Two-year-olds are beginning to understand the concept of numbers, so it is a great time to incorporate counting and number recognition into their play. Music is a great way to boost math skills and working memory, too.
PROCESS ART
Process art is a great way for young children to work on building their cognitive skills as well. When children have the freedom to choose what materials they use and how they use them to create works of art, they work on decision making skills, planning, and the ability to focus and follow through.
Let your child choose which materials they want to experiment with and how. Give them plenty of space and expect a mess. It is all about the process and allowing your child to take risks and feel successful.

BLOCKS & MANIPULATIVES
Provide your toddler with open-ended toys such as wooden blocks and other manipulatives that they can build with. This will give them an opportunity to work on developing critical thinking and spatial reasoning skills. You can also provide pictures of real life structures for your child to gain inspiration from and also to support their growing comprehension of structures.
PRETEND PLAY
Engaging in pretend play with your toddler will help them to learn how to think outside the box and make the connection between spoken and written language. You can set up a play restaurant or grocery store. Having them lead the play is always best, but toddlers often need some guidance as they begin to explore pretend play.
There are so many fun ways that you can support your child’s cognitive development. Most important of all though is to play and have fun with your child. You will be amazed at just how much your child learns through those play experiences.

Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Math for Kids
- Parenting Resources
- ELA for Kids
- Teaching Resources

How to Teach Long Division to Kids in 6 Easy Steps
15 Famous Mathematicians in History That Kids Should Know
11 Best Multiplication Apps for Kids
How to Teach Number Formation in 5 Easy Steps
13 Best Resources for Math Videos for Kids: Math Made Fun
6 Best Alternatives to Public Schooling: A Guide for Parents
How to Cope With Test Anxiety in 12 Easy Ways
Developmental Milestones for 4 Year Olds: The Ultimate Guide
Simple & Stress-Free After School Schedule for Kids of All Ages
When Do Kids Start Preschool: Age & Readiness Skills
How to Teach Letter Recognition in 6 Easy Steps
20 Fun Limericks for Kids
How to Improve Reading Comprehension: Strategies & Tips
40 Best Summer Writing Prompts for Kids of All Ages
12 Best Ways to Teach Rhyming Words to Kids
12 Best Tips for Substitute Teachers
30 Best Classroom Reward Ideas for Elementary Students
12 Best Websites for English Teachers
10 Best Game-Based Learning Platforms for Kids
60 Fun Animal Facts for Kids

20+ Best Fun Learning Activities for 2-Year-Olds

7 Educational Activities for 2 Year Olds
7 developmental activities for 2 year olds, 8 fun activities for 2 year olds with no prep, no mess, get started now.
We know that parenting a toddler can be both rewarding and challenging, so we’ve put together a list of activities to help your little one learn and grow while having lots of fun. Welcome to our guide of 20+ fun and learning activities for 2 year olds!
From simple crafts and games that help with fine motor skills to more active pursuits that will get your toddler moving, there’s something here for everyone. And the best part is that most of these activities can be done using things you already have around the house, so there is no need to go out and buy anything special.
We hope you enjoy trying out these activities with your toddler and that they help make your days a little bit brighter.
1. Color Sorting

What you’ll need: Construction paper in different colors, crayons, markers, or paint
What to do: Cut out different shapes from each color of construction paper. Talk about the different colors with your toddler as they sort the shapes. You can also have them trace the shapes with crayons, markers, or paint.
SplashLearn: Most Comprehensive Learning Program for PreK-5

SplashLearn inspires lifelong curiosity with its game-based PreK-5 learning program loved by over 40 million children. With over 4,000 fun games and activities, it’s the perfect balance of learning and play for your little one.
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting color recognition and fine motor skills. Toddlers also learn about shapes as they play.
2. Letter Matching
What you’ll need: Construction paper, scissors, crayons, markers, or paint
What to do: Cut out different letters from construction paper. Talk about the different letters with your toddler as they match them up. You can also have them trace the letters with crayons, markers, or paint.
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting letter recognition and fine motor skills. Learning letters early can also help your toddler with reading and writing later on.
3. Pattern Matching
What to do: Cut out different patterns from construction paper. Talk about the different patterns with your toddler as they match them up. You can also have them trace the patterns with crayons, markers, or paint.
Some patterns that toddlers can work with include stripes, polka dots, and zigzags.
What kids will learn: This activity promotes pattern recognition and fine motor skills. It also helps toddlers develop their problem-solving skills.
4. Play Math and Reading Games Online
What you’ll need: A computer with internet access
What to do: Many great math and reading games for toddlers are available online. Spend some time playing these games with your toddler to help them learn new skills. Ensure that children aren’t spending too much time looking at screens. For toddlers, 20–30 minutes is enough screen time.
What kids will learn: This activity encourages children to improve their math and reading skills. Toddlers also learn about computer use and basic game skills.
5. Put Together a Simple Toy Train Set

What you’ll need: A toy train set, such as the Thomas the Tank Engine Wooden Railway Starter Set.
What to do: Let your toddler help you put together a simple toy train set. They can connect the track pieces, place the trains on the tracks, and press the buttons to make them go.
What kids will learn: This activity promotes problem-solving, fine motor skills, and hand–eye coordination. Toddlers also learn about cause and effect as they play.
6. Paint With Watercolors
What you’ll need: Watercolors, paintbrushes, water, and paper.
What to do: This is a classic activity that toddlers will love! They can experiment with mixing the colors, painting different strokes, and adding water to create different effects.
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting art and creativity. Toddlers also learn about colors and mixing different shades.
7. Talk to Your Baby
What you’ll need: Nothing!
What to do: One of the best activities for 2 year olds, this is a great way to promote language development. Talk to your toddler about anything and everything. Describe what you’re doing, such as “I’m making lunch.” or “I’m putting on my shoes.” You can also ask them questions and encourage them to answer.
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting language development. Toddlers also learn about communication and conversation.

1. Trace the Body
W hat you’ll need: Paper, a pencil, and some crayons or markers
What to do: Help your toddler trace their body on a piece of paper. Then, they can decorate it however they like! This is a great way to encourage creativity and self-expression.
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting art and creativity. Toddlers also learn about their own bodies and how to use different art supplies.
2. Get Dressed
What you’ll need: Some clothes, shoes, and a mirror.
What to do: One of the most important activities for 2 year olds is to learn how to get dressed independently. You can start with simple clothing items, such as a shirt or pants. Show them how to wear clothing and then let them try it themselves. As they get better at dressing themselves, you can add more items, such as shoes, socks, and jackets.
This is a great activity to do when you are vacationing with the family as you can afford the time and patience it needs to help your kids learn how to button their shirts or tie their shoes correctly.
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting fine motor skills and independence. Toddlers also learn about different types of clothing and how to put them on.
3. Put Toys Away
What you’ll need: A toy box or bin and some toys.
What to do: Show them how to put the toys away in the toy box or bin. As they get better at this, you can add more toys or make it a game by timing them to see how fast they can put the toys away.
What kids will learn: This is a great activity for teaching toddlers about organization and responsibility. It is also a good way to promote problem-solving skills. Toddlers thus learn about cleaning up.
4. Clap to the Beat
What you’ll need: Some music or you can clap your hands yourself
What to do: Help your toddler clap their hands to the beat of the music. As they get better at this, you can add other body parts, such as their feet or head.
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting music and rhythm skills. Toddlers also learn about following directions.
5. Read to Your 2 Year Old
What you’ll need: Any good picture books, like The Very Hungry Caterpillar or The Cat in the Hat .
What to do: This activity is great for promoting literacy skills. Sit down with your toddler and read one of their favorite books . As they get better at this, you can start asking them questions about the story or having them point out different objects in the book.
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting literacy skills. Studies show that early exposure to reading is linked with higher reading achievement later in life. Toddlers also learn about communication and conversation.
6. Imitate Animal Sounds
What you’ll need: A video or audio recording of animal sounds, or you can make the sounds yourself.
What to do: This activity is great for promoting listening skills. Help your toddler identify different animal sounds. You can play a recording of the sounds or make them yourself. As they get better at this, you can start asking them questions about the animals, such as “Where does a lion live?” or “What does a cow eat?”
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting listening skills. Toddlers also learn about animals, their sounds, and maybe their habitats.
7. Play Kitchen Assistant
What you’ll need: A play kitchen, some pots and pans, and some plastic food
What to do: Show your toddler how to pretend to cook in the play kitchen. Let them help you stir the pots and pans or cut up the plastic food. As they get better at this, you can start asking them to make specific dishes.
Some 2 year old development activities that can be done in a real kitchen include; helping to pour ingredients into a bowl, using a child-safe knife to help cut soft foods, or helping to stir—all with adult supervision!
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting imaginative play. Toddlers also learn about cooking and following directions.

1. Pillow Roller Coasters
What you’ll need: Pillows, blankets, and a lot of space on the floor.
What to do: Create a pillow roller coaster for your toddler to ride. They will love going up and down the hill. As they get better at this, you can start asking them to go faster or slower.
You could create a smaller pillow road for their toy vehicles. Children can hold a race with their toy cars and make them go up and down the road.
Remote-controlled tanks or any other remote-controlled toy can also be used for this activity.
After your 2-year-old is done playing with the pillow roller coaster, you can just put the pillows, blankets, and toy cars away—no mess to clean up!
What kids will learn:
This activity is great for promoting gross motor skills. Toddlers will also learn about ramps and the energy needed to go up and down the slopes. This basic experiential learning can help them in their future physics classes.
2. Rescue Animals (from zip-lock bags)

What you’ll need: Clear zip-lock bags and small plastic animals.
What to do: Put their animals in clear zip-lock bags. Now ask them to help the animals get out by using their hands or opening the zip.
You can say, “I see the lion is roaring. It wants to come out. Can you help him?”
You can also put different kinds of objects in the zip-lock bags, like fruits, vegetables, leaves, etc. This will help your toddler learn about different textures and shapes.
After they are done playing with this activity, you can store animals and zip-lock bags separately or throw them in the toy box just as they are.
What kids will learn: Such games and 2 year old activities help kids learn about animal names, sounds, and textures. It also helps them develop their fine motor skills.
3. Balloon Pop
What you’ll need: Balloons and a sharp object (like a pin or a needle).
What to do: Help your toddler blow up the balloon and then let them pop it with the sharp object. Be sure to supervise them closely so that they don’t hurt themselves.
Your toddler will have a blast popping the balloons. The toddlers love the loud noise of the balloons popping and the feeling of popping them.
This activity can get a little messy since the balloon bits will be scattered around. But, it is easy to clean up—gather all the pieces and throw them away.
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting gross motor skills and hand–eye coordination. Toddlers will also learn about cause and effect as they see that their actions (popping the balloon) result in the desired outcome (the balloon makes a loud noise and pops).
4. Origami for Toddlers

What you’ll need: Square pieces of colored paper
What to do: Origami is the Japanese art of paper folding. There are many simple origami shapes that even toddlers can make.
You can start with something simple like a paper airplane or a boat. Just fold the paper in half and then in half again. Then, help your toddler make the folds to create the shape. Once they get the hang of it, they’ll be able to do it on their own.
We all know 2-year-olds love to display their creations, so be sure to have a spot ready to showcase their origami masterpieces.
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting fine motor skills and concentration. Toddlers will also learn about following instructions and different shapes.
5. Magnetic Letters

What you’ll need: Magnetic letters (you can find these at your local dollar store or online) and a metal surface
What to do: Stick the magnetic letters on the fridge or any other metal surface. Then, help your toddler spell out words with the letters. You can start with simple three-letter words and then move on to more difficult words.
You can even use these magnetic letters to offer clues to your toddler during a treasure hunt or pass on messages like a detective.
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting literacy skills and creativity. Toddlers will also learn about the alphabet, spelling, and simple words.
6. Decorating with Clothes Pegs

What you’ll need: Clothes pegs and containers or surfaces to decorate
What to do: Accept it: Painting with your baby can be a messy affair. Clothes pegs allow you to bring a pop of color and beautiful works of art together. And, with this method, you don’t have to worry about paint stains.
Just let your toddler put clothes pegs around the containers or surfaces. You can even use them to create patterns or shapes.
If you want, you can paint the clothes pegs before your toddler starts decorating or buy cheap plastic clothes pegs in different colors. This will add an extra layer of color and fun to the activity.
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting creativity and imagination early in children. They will learn that anything can be turned into a work of art with a little bit of creativity.
7. Transfer Books and Toys From One Box to Another
What you’ll need: Two cardboard boxes with lids and some toys or books
What to do: You will be surprised how much a toddler loves to help you do a chore and win compliments and hugs from you. It is a great way to keep them occupied while you’re busy with other things.
To set up, put some toys or books in one box and then close the lid. Then, have your toddler transfer the items into the other box. You can even make it a race to see who can transfer the most items in a minute.
You can easily make this a sorting and organizing activity, asking them to sort books, toys, or other objects by colors, shapes, or sizes.
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting fine motor skills and concentration in toddlers. It is also a good opportunity for parents to inculcate a sense of responsibility and ownership in their toddlers and build their confidence.
8. Play with Kinetic Sand
W hat you’ll need: Kinetic sand and some plastic toys
What to do: If you haven’t played with kinetic sand before, you’re in for a treat. It’s a type of sand that’s moldable and easy to shape. And it’s also very therapeutic to play with.
Let your toddler explore the sand and mold it into different shapes. You can even use the sand to make patterns or write words. If you want, you can add some plastic toys to the mix and see how your toddler plays with them.
And it does not create any mess! You can easily store the sand in a container when you’re done playing.
What kids will learn: This activity is great for promoting creativity and imagination in toddlers. They will also learn about different textures and how they can be manipulated.

Learning activities for 2 year olds must be creative, hands-on, and FUN! Parents must realize that a young child’s attention span can be short. So, the activities must be structured to maintain their interest, even outdoor activities for 2 year olds must be engaging and interesting. The key is to keep it short and sweet.
Do you need some “you” time? Engage your toddlers in one of the fun activities for 2 year olds mentioned above and take that five-minute break. These activities will not only occupy your toddler but also help their overall development.
Here are more online educational resources for kids that will help with their learning experience and make them smarter.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How to decide which activity is age-appropriate for 2 year olds.
Most two-year-olds can start with sorting shapes and colors, finding things hidden under objects, and doing simple puzzles. They may complete sentences in books they read regularly, follow two-step instructions, and love make-believe games. Activities built around developmental milestones for toddlers can help them progress to the next level.
What are some engaging indoor activities for two year olds that require few or no equipment?
Here are some indoor activities for 2 year olds that don’t require much equipment, if at all:
- transferring books and toys from one box to another
- sorting objects by colors, shapes, or sizes,
- playing with kinetic sand or clay,
- playing online learning games .
12 Best Social Skills Activities for Kids of All Ages
12 Best Pattern Activities for Preschoolers in 2024
15 Best Movement Activities for Preschoolers in 2024
- Pre-Kindergarten
- Kindergarten
Most Popular

15 Best Report Card Comments Samples

117 Best Riddles for Kids (With Answers)

40 Best Good Vibes Quotes to Brighten Your Day
Recent posts.

15 Best Fourth of July Crafts for Preschoolers

Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun., you see real learning outcomes..
Watch your kids fall in love with math & reading through our scientifically designed curriculum.
Parents, try for free Teachers, use for free

- Games for Kids
- Worksheets for Kids
- Math Worksheets
- ELA Worksheets
- Math Vocabulary
- Number Games
- Addition Games
- Subtraction Games
- Multiplication Games
- Division Games
- Addition Worksheets
- Subtraction Worksheets
- Multiplication Worksheets
- Division Worksheets
- Times Tables Worksheets
- Reading Games
- Writing Games
- Phonics Games
- Sight Words Games
- Letter Tracing Games
- Reading Worksheets
- Writing Worksheets
- Phonics Worksheets
- Sight Words Worksheets
- Letter Tracing Worksheets
- Prime Number
- Order of Operations
- Long multiplication
- Place value
- Parallelogram
- SplashLearn Success Stories
- SplashLearn Apps
- [email protected]
© Copyright - SplashLearn

Make study-time fun with 14,000+ games & activities, 450+ lesson plans, and more—free forever.
Parents, Try for Free Teachers, Use for Free
A password reset email has been sent to the email address on file for your account, but may take several minutes to show up in your inbox. Please wait at least 10 minutes before attempting another reset.
Email address *
Lost your password?
Lost your password? Please enter your email address. You will receive a link to create a new password via email.
Email address
Registering for this site allows you to access your order status and history. Just fill in the fields below, and we’ll get a new account set up for you in no time. We will only ask you for information necessary to make the purchase process faster and easier.
- Tweens & Teens
- GrowthMinded Login
- No products in the cart.
items in the cart: 0
How to Teach Problem-Solving Skills to Children and Preteens
- By Ashley Cullins
Whether it’s a toy-related conflict, a tough math equation, or negative peer pressure, kids of ALL ages face problems and challenges on a daily basis.
As parents or teachers, we can’t always be there to solve every problem for our children. In fact, this isn’t our job. Our job is to TEACH our children how to solve problems by themselves . This way, they can become confident , independent, and successful individuals.
Instead of giving up or getting frustrated when they encounter a challenge, kids with problem-solving skills manage their emotions, think creatively, and persist until they find a solution. Naturally, these abilities go hand-in-hand with a growth mindset .
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our FREE Your Words Matter Volume 2 Kit . With these 10 one-page parenting guides, you will know exactly how to speak to your child to help them stand up for themselves, be more confident, and develop a growth mindset.
So HOW do you teach problem-solving skills to kids?
Well, it depends on their age . As cognitive abilities and the size of the child’s challenges grow/evolve over time, so should your approach to teaching problem-solving skills.
Read on to learn key strategies for teaching problem-solving to kids, as well as some age-by-age ideas and activities.

3 General Strategies to Teach Problem-Solving at Any Age
1. model effective problem-solving .
When YOU encounter a challenge, do a “think-aloud” for the benefit of your child. MODEL how to apply the same problem-solving skills you’ve been working on together, giving the real-world examples that she can implement in her own life.
At the same time, show your child a willingness to make mistakes . Everyone encounters problems, and that’s okay. Sometimes the first solution you try won’t work, and that’s okay too!
When you model problem-solving, explain that there are some things that are out of our control. As we're solving a problem at hand we should focus on the things we CAN actually control.
You and your child can listen to Episode 35 of the Big Life Kids Podcast to learn about focusing on what you can control.
2. Ask for Advice
Ask your kids for advice when you have a problem. This teaches them that it’s common to make mistakes and face challenges. It also gives them the opportunity to practice problem-solving skills.
Plus, when you indicate that their ideas are valued , they’ll gain the confidence to attempt solving problems on their own.
3. Don’t Provide “The Answer”
As difficult as it may be, allow your child to struggle, sometimes fail , and ultimately LEARN from experiencing consequences.
Now, let’s take a look at some age-specific strategies and activities. The ages listed below are general guidelines, feel free to choose any strategies or activities that you feel will work for YOUR child.
Use Emotion Coaching
To step into a problem-solving mindset, young children need to first learn to manage their emotions . After all, it’s difficult for a small child to logically consider solutions to a problem if he’s mid-tantrum.
One way to accomplish this is by using the emotion coaching process outlined by John Gottman.
First, teach your kids that ALL emotions are acceptable. There are NO “bad” emotions. Even seemingly negative emotions like anger, sadness, and frustration can teach us valuable lessons. What matters is how we respond to these emotions.
Second, follow this process:
- Step One: Naming and validating emotions. When your child is upset, help her process the way she’s feeling. Say something like, “I understand that you’re upset because Jessica is playing with the toy you wanted.”
- Step Two: Processing emotions. Guide your child to her calming space. If she doesn't have one, it's a good idea to create one. Let her calm her body and process her emotions so she can problem-solve, learn, and grow.
- Step Three: Problem Solving. Brainstorm solutions with your child, doing more LISTENING than talking during the conversation. This allows your child to practice her problem-solving skills, and she’s more likely to actually implement the solutions she came up with herself.
Say, “Show Me the Hard Part”
When your child struggles or feels frustrated, try a technique suggested by mom and parenting blogger Lauren Tamm . Simply say, “Show me the hard part.”
This helps your child identify the ROOT of the problem, making it less intimidating and easier to solve.
Repeat back what your child says, “So you’re saying…”
Once you both understand the real problem, prompt your child to come up with solutions . “There must be some way you can fix that…” or “There must be something you can do…”
Now that your child has identified “the hard part,” she’ll likely be able to come up with a solution. If not, help her brainstorm some ideas. You may try asking the question, “If you DID know, what would you think?” and see what she comes up with.
Problem-Solve with Creative Play
Allow your child to choose activities and games based on her interests . Free play provides plenty of opportunities to navigate and creatively solve problems.
Children often learn best through play. Playing with items like blocks, simple puzzles, and dress-up clothes can teach your child the process of problem-solving.
Even while playing, your child thinks critically: Where does this puzzle piece fit? What does this do? I want to dress up as a queen. What should I wear? Where did I put my tiara? Is it under the couch?
Problem-Solve with Storybooks
Read age-appropriate stories featuring characters who experience problems, such as:
- Ladybug Girl and Bumblebee Boy by Jacky Davis: The story of two friends who want to play together but can’t find a game to agree on. After taking turns making suggestions, they arrive at a game they both want to play: Ladybug Girl and Bumblebee Boy.
- The Curious George Series by Margaret and H.E. Rey: A curious little monkey gets into and out of dilemmas, teaching kids to find solutions to problems of their own.
- Ira Sleeps Over by Bernard Waber: Ira’s thrilled to have a sleepover at his friend Reggie’s house. But there’s one problem: Should he or should he not bring his teddy bear? It may seem small, but this is the type of early social problem your child might relate to.
Connect these experiences to similar events in your child’s own life, and ASK your child HOW the characters in these stories could solve their problems. Encourage a variety of solutions, and discuss the possible outcomes of each.
This is a form of dialogue reading , or actively ENGAGING your child in the reading experience. Interacting with the text instead of passively listening can “turbocharge” the development of literacy skills such as comprehension in preschool-aged children.
By asking questions about the characters’ challenges, you can also give your child’s problem-solving abilities a boost.
You can even have your child role-play the problem and potential solutions to reinforce the lesson.
For book suggestions, refer to our Top 85 Growth Mindset Books for Children & Adults list.
Teach the Problem-Solving Steps
Come up with a simple problem-solving process for your child, one that you can consistently implement. For example, you might try the following five steps:
- Step 1: What am I feeling? Help your child understand what she’s feeling in the moment (frustration, anger, curiosity, disappointment, excitement, etc.) Noticing and naming emotions will diffuse their charge and give your child a chance to take a step back.
- Step 2: What’s the problem? Guide your child to identify the specific problem. In most cases, help her take responsibility for what happened rather than pointing fingers. For instance, instead of, “Joey got me in trouble at recess,” your child might say, “I got in trouble at recess for arguing with Joey.”
- Step 3: What are the solutions? Encourage your child to come up with as many solutions as possible. At this point, they don’t even need to be “good” solutions. They’re just brainstorming here, not yet evaluating the ideas they’ve generated.
- Step 4: What would happen if…? What would happen if your child attempted each of these solutions? Is the solution safe and fair? How will it make others feel? You can also try role-playing at this step. It’s important for your child to consider BOTH positive and negative consequences of her actions.
- Step 5: Which one will I try? Ask your child to pick one or more solutions to try. If the solution didn't work, discuss WHY and move on to another one. Encourage your child to keep trying until the problem is solved.
Consistently practice these steps so that they become second nature, and model solving problems of your own the same way. It's a good idea to reflect : What worked? What didn’t? What can you do differently next time?
Problem-Solve with Craft Materials
Crafting is another form of play that can teach kids to solve problems creatively.
Provide your child with markers, modeling clay, cardboard boxes, tape, paper, etc. They’ll come up with all sorts of interesting creations and inventive games with these simple materials.
These “open-ended toys” don’t have a “right way to play,” allowing your child to get creative and generate ideas independently .
Ask Open-Ended Questions
Asking open-ended questions improves a child’s ability to think critically and creatively, ultimately making them better problem-solvers. Examples of open-ended questions include:
- How could we work together to solve this?
- How did you work it out? or How do you know that?
- Tell me about what you built, made, or created.
- What do you think will happen next?
- What do you think would happen if…?
- What did you learn?
- What was easy? What was hard?
- What would you do differently next time?
Open-ended questions have no right answer and can’t be answered with a simple “Yes” or “No.”
You can ask open-ended questions even when your child isn’t currently solving a problem to help her practice her thinking skills, which will come in handy when she does have a problem to solve.
If you need some tips on how to encourage a growth mindset in your child, don't forget to download our FREE Your Words Matter Volume 2 Kit .

Break Down Problems into Chunks
This strategy is a more advanced version of “Show me the hard part.”
The bigger your child gets, the bigger her problems get too. When your child is facing a challenge that seems overwhelming or insurmountable, encourage her to break it into smaller, more manageable chunks.
For instance, let’s say your child has a poor grade in history class. Why is the grade so low? What are the causes of this problem?
As usual, LISTEN as your child brainstorms, asking open-ended questions to help if she gets stuck.
If the low grade is the result of missing assignments, perhaps your child can make a list of these assignments and tackle them one at a time. Or if tests are the issue, what’s causing your child to struggle on exams?
Perhaps she’s distracted by friends in the class, has trouble asking for help, and doesn’t spend enough time studying at home. Once you’ve identified these “chunks,” help your child tackle them one at a time until the problem is solved.
Show “ The Broken Escalator Video ”
Discuss the importance of embracing challenges and solving problems independently with the “broken escalator video.”
In the video, an escalator unexpectedly breaks. The people on the escalator are “stuck” and yelling for help. At this age, it’s likely that your child will find the video funny and immediately offer a solution: “Just walk! Get off the escalator!”
Tell your child that this is a simple example of how people sometimes act in difficult situations. Ask, “Why do you think they didn’t get off the escalator?” (they didn’t know how, they were waiting for help, etc.)
Sometimes, your child might feel “stuck” when facing problems. They may stop and ask for help before even attempting to find a solution. Encourage your child to embrace challenges and work through problems instead.
Problem-Solve with Prompts
Provide your child or a group of children with materials such as straws, cotton balls, yarn, clothespins, tape, paper clips, sticky notes, Popsicle sticks, etc.
With just these materials, challenge your kids to solve unusual problems like:
- Make a leprechaun trap
- Create a jump ramp for cars
- Design your own game with rules
- Make a device for two people to communicate with one another
This is a fun way to practice critical thinking and creative problem-solving. Most likely, it will take multiple attempts to find a solution that works, which can apply to just about any aspect of life.
Make Them Work for It
When your child asks for a new toy, technology, or clothes, have her make a plan to obtain the desired item herself. Not only will your child have to brainstorm and evaluate solutions, but she’ll also gain confidence .
Ask your child HOW she can earn the money for the item that she wants, and encourage her as she works toward her goal .
Put It on Paper
Have your child write out their problems on paper and brainstorm some potential solutions.
But now, she takes this process a step further: After attempting each solution, which succeeded? Which were unsuccessful? Why ?
This helps your child reflect on various outcomes, learning what works and what doesn’t. The lessons she learns here will be useful when she encounters similar problems in the future.
Play Chess Together
Learning to play chess is a great way for kids to learn problem-solving AND build their brains at the same time. It requires players to use critical thinking, creativity, analysis of the board, recognize patterns, and more. There are online versions of the game, books on how to play, videos, and other resources. Don’t know how to play? Learn with your teen to connect and problem solve together!
Have Them Learn To Code
Our teens and tweens are already tech-savvy and can use their skills to solve problems by learning to code. Coding promotes creativity, logic, planning, and persistence . There are many great tools and online or in-person programs that can boost your child’s coding skills.
Encourage to Start a Meaningful Project
This project has to be meaningful to your teen, for example starting a YouTube channel. Your teen will practice problem-solving skills as they’re figuring out how to grow their audience, how to have their videos discovered, and much more.
In the Big Life Journal - Teen Edition , there’s a section that guides them through planning their YouTube channel and beginning the problem-solving process.
Apply the SODAS Method
Looking for a game plan that your teen can employ when faced with a problem? The SODAS method can be used for big or small problems. Just remember this simple acronym and follow these ideas:
- D isadvantages
- A dvantages
Encourage to Join Problem-Solving Groups
Does your teen enjoy solving problems in a team? Have them join a group or club that helps them hone their skills in a variety of settings--from science and robotics to debating and international affairs. Some examples of groups include:
- Odyssey of the Mind
- Debate team
- Science Olympiad
Looking for additional resources? The Bestseller’s Bundle includes our three most popular printable kits packed with science-based activities, guides, and crafts for children. Our Growth Mindset Kit, Resilience Kit, and Challenges Kit work together as a comprehensive system designed specifically for children ages 5-11.
- Share this post:
25 thoughts on “ How to Teach Problem-Solving Skills to Children and Preteens ”
I love, love, love the point about emotional coaching. It’s so important to identify how children are feeling about a problem and then approach the solutions accordingly.
Thank you for putting this together. I wrote an article on problem-solving specifically from the point of view of developing a STEM aptitude in kids, if you like to check it out – https://kidpillar.com/how-to-teach-problem-solving-to-your-kids-5-8-years/
I feel that these techniques will work for my kid.. Worthy.. Thank you
I love you guys
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- New Printable
- Guide Printable
FOLLOW US ON INSTAGRAM
- Trying to Conceive
- Signs & Symptoms
- Pregnancy Tests
- Fertility Testing
- Fertility Treatment
- Weeks & Trimesters
- Staying Healthy
- Preparing for Baby
- Complications & Concerns
- Pregnancy Loss
- Breastfeeding
- School-Aged Kids
- Raising Kids
- Personal Stories
- Everyday Wellness
- Safety & First Aid
- Immunizations
- Food & Nutrition
- Active Play
- Pregnancy Products
- Nursery & Sleep Products
- Nursing & Feeding Products
- Clothing & Accessories
- Toys & Gifts
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- How to Talk About Postpartum Depression
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
How to Teach Kids Problem-Solving Skills
KidStock / Blend Images / Getty Images
- Steps to Follow
- Allow Consequences
Whether your child can't find their math homework or has forgotten their lunch, good problem-solving skills are the key to helping them manage their life.
A 2010 study published in Behaviour Research and Therapy found that kids who lack problem-solving skills may be at a higher risk of depression and suicidality. Additionally, the researchers found that teaching a child problem-solving skills can improve mental health .
You can begin teaching basic problem-solving skills during preschool and help your child sharpen their skills into high school and beyond.
Why Problem-Solving Skills Matter
Kids face a variety of problems every day, ranging from academic difficulties to problems on the sports field. Yet few of them have a formula for solving those problems.
Kids who lack problem-solving skills may avoid taking action when faced with a problem.
Rather than put their energy into solving the problem, they may invest their time in avoiding the issue. That's why many kids fall behind in school or struggle to maintain friendships .
Other kids who lack problem-solving skills spring into action without recognizing their choices. A child may hit a peer who cuts in front of them in line because they are not sure what else to do.
Or, they may walk out of class when they are being teased because they can't think of any other ways to make it stop. Those impulsive choices may create even bigger problems in the long run.
The 5 Steps of Problem-Solving
Kids who feel overwhelmed or hopeless often won't attempt to address a problem. But when you give them a clear formula for solving problems, they'll feel more confident in their ability to try. Here are the steps to problem-solving:
- Identify the problem . Just stating the problem out loud can make a big difference for kids who are feeling stuck. Help your child state the problem, such as, "You don't have anyone to play with at recess," or "You aren't sure if you should take the advanced math class."
- Develop at least five possible solutions . Brainstorm possible ways to solve the problem. Emphasize that all the solutions don't necessarily need to be good ideas (at least not at this point). Help your child develop solutions if they are struggling to come up with ideas. Even a silly answer or far-fetched idea is a possible solution. The key is to help them see that with a little creativity, they can find many different potential solutions.
- Identify the pros and cons of each solution . Help your child identify potential positive and negative consequences for each potential solution they identified.
- Pick a solution. Once your child has evaluated the possible positive and negative outcomes, encourage them to pick a solution.
- Test it out . Tell them to try a solution and see what happens. If it doesn't work out, they can always try another solution from the list that they developed in step two.
Practice Solving Problems
When problems arise, don’t rush to solve your child’s problems for them. Instead, help them walk through the problem-solving steps. Offer guidance when they need assistance, but encourage them to solve problems on their own. If they are unable to come up with a solution, step in and help them think of some. But don't automatically tell them what to do.
When you encounter behavioral issues, use a problem-solving approach. Sit down together and say, "You've been having difficulty getting your homework done lately. Let's problem-solve this together." You might still need to offer a consequence for misbehavior, but make it clear that you're invested in looking for a solution so they can do better next time.
Use a problem-solving approach to help your child become more independent.
If they forgot to pack their soccer cleats for practice, ask, "What can we do to make sure this doesn't happen again?" Let them try to develop some solutions on their own.
Kids often develop creative solutions. So they might say, "I'll write a note and stick it on my door so I'll remember to pack them before I leave," or "I'll pack my bag the night before and I'll keep a checklist to remind me what needs to go in my bag."
Provide plenty of praise when your child practices their problem-solving skills.
Allow for Natural Consequences
Natural consequences may also teach problem-solving skills. So when it's appropriate, allow your child to face the natural consequences of their action. Just make sure it's safe to do so.
For example, let your teenager spend all of their money during the first 10 minutes you're at an amusement park if that's what they want. Then, let them go for the rest of the day without any spending money.
This can lead to a discussion about problem-solving to help them make a better choice next time. Consider these natural consequences as a teachable moment to help work together on problem-solving.
Becker-Weidman EG, Jacobs RH, Reinecke MA, Silva SG, March JS. Social problem-solving among adolescents treated for depression . Behav Res Ther . 2010;48(1):11-18. doi:10.1016/j.brat.2009.08.006
Pakarinen E, Kiuru N, Lerkkanen M-K, Poikkeus A-M, Ahonen T, Nurmi J-E. Instructional support predicts childrens task avoidance in kindergarten . Early Child Res Q . 2011;26(3):376-386. doi:10.1016/j.ecresq.2010.11.003
Schell A, Albers L, von Kries R, Hillenbrand C, Hennemann T. Preventing behavioral disorders via supporting social and emotional competence at preschool age . Dtsch Arztebl Int . 2015;112(39):647–654. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2015.0647
Cheng SC, She HC, Huang LY. The impact of problem-solving instruction on middle school students’ physical science learning: Interplays of knowledge, reasoning, and problem solving . EJMSTE . 2018;14(3):731-743.
Vlachou A, Stavroussi P. Promoting social inclusion: A structured intervention for enhancing interpersonal problem‐solving skills in children with mild intellectual disabilities . Support Learn . 2016;31(1):27-45. doi:10.1111/1467-9604.12112
Öğülmüş S, Kargı E. The interpersonal cognitive problem solving approach for preschoolers . Turkish J Educ . 2015;4(17347):19-28. doi:10.19128/turje.181093
American Academy of Pediatrics. What's the best way to discipline my child? .
Kashani-Vahid L, Afrooz G, Shokoohi-Yekta M, Kharrazi K, Ghobari B. Can a creative interpersonal problem solving program improve creative thinking in gifted elementary students? . Think Skills Creat . 2017;24:175-185. doi:10.1016/j.tsc.2017.02.011
Shokoohi-Yekta M, Malayeri SA. Effects of advanced parenting training on children's behavioral problems and family problem solving . Procedia Soc Behav Sci . 2015;205:676-680. doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.09.106
By Amy Morin, LCSW Amy Morin, LCSW, is the Editor-in-Chief of Verywell Mind. She's also a psychotherapist, an international bestselling author of books on mental strength and host of The Verywell Mind Podcast. She delivered one of the most popular TEDx talks of all time.
Developing Problem-Solving Skills for Kids | Strategies & Tips

We've made teaching problem-solving skills for kids a whole lot easier! Keep reading and comment below with any other tips you have for your classroom!
Problem-Solving Skills for Kids: The Real Deal
Picture this: You've carefully created an assignment for your class. The step-by-step instructions are crystal clear. During class time, you walk through all the directions, and the response is awesome. Your students are ready! It's finally time for them to start working individually and then... 8 hands shoot up with questions. You hear one student mumble in the distance, "Wait, I don't get this" followed by the dreaded, "What are we supposed to be doing again?"
When I was a new computer science teacher, I would have this exact situation happen. As a result, I would end up scrambling to help each individual student with their problems until half the class period was eaten up. I assumed that in order for my students to learn best, I needed to be there to help answer questions immediately so they could move forward and complete the assignment.
Here's what I wish I had known when I started teaching coding to elementary students - the process of grappling with an assignment's content can be more important than completing the assignment's product. That said, not every student knows how to grapple, or struggle, in order to get to the "aha!" moment and solve a problem independently. The good news is, the ability to creatively solve problems is not a fixed skill. It can be learned by students, nurtured by teachers, and practiced by everyone!
Your students are absolutely capable of navigating and solving problems on their own. Here are some strategies, tips, and resources that can help:
Problem-Solving Skills for Kids: Student Strategies
These are strategies your students can use during independent work time to become creative problem solvers.
1. Go Step-By-Step Through The Problem-Solving Sequence
Post problem-solving anchor charts and references on your classroom wall or pin them to your Google Classroom - anything to make them accessible to students. When they ask for help, invite them to reference the charts first.

2. Revisit Past Problems
If a student gets stuck, they should ask themself, "Have I ever seen a problem like this before? If so, how did I solve it?" Chances are, your students have tackled something similar already and can recycle the same strategies they used before to solve the problem this time around.
3. Document What Doesn’t Work
Sometimes finding the answer to a problem requires the process of elimination. Have your students attempt to solve a problem at least two different ways before reaching out to you for help. Even better, encourage them write down their "Not-The-Answers" so you can see their thought process when you do step in to support. Cool thing is, you likely won't need to! By attempting to solve a problem in multiple different ways, students will often come across the answer on their own.
4. "3 Before Me"
Let's say your students have gone through the Problem Solving Process, revisited past problems, and documented what doesn't work. Now, they know it's time to ask someone for help. Great! But before you jump into save the day, practice "3 Before Me". This means students need to ask 3 other classmates their question before asking the teacher. By doing this, students practice helpful 21st century skills like collaboration and communication, and can usually find the info they're looking for on the way.
Problem-Solving Skills for Kids: Teacher Tips
These are tips that you, the teacher, can use to support students in developing creative problem-solving skills for kids.
1. Ask Open Ended Questions
When a student asks for help, it can be tempting to give them the answer they're looking for so you can both move on. But what this actually does is prevent the student from developing the skills needed to solve the problem on their own. Instead of giving answers, try using open-ended questions and prompts. Here are some examples:

2. Encourage Grappling
Grappling is everything a student might do when faced with a problem that does not have a clear solution. As explained in this article from Edutopia , this doesn't just mean perseverance! Grappling is more than that - it includes critical thinking, asking questions, observing evidence, asking more questions, forming hypotheses, and constructing a deep understanding of an issue.

There are lots of ways to provide opportunities for grappling. Anything that includes the Engineering Design Process is a good one! Examples include:
- Engineering or Art Projects
- Design-thinking challenges
- Computer science projects
- Science experiments
3. Emphasize Process Over Product
For elementary students, reflecting on the process of solving a problem helps them develop a growth mindset . Getting an answer "wrong" doesn't need to be a bad thing! What matters most are the steps they took to get there and how they might change their approach next time. As a teacher, you can support students in learning this reflection process.

4. Model The Strategies Yourself!
As creative problem-solving skills for kids are being learned, there will likely be moments where they are frustrated or unsure. Here are some easy ways you can model what creative problem-solving looks and sounds like.
- Ask clarifying questions if you don't understand something
- Admit when don't know the correct answer
- Talk through multiple possible outcomes for different situations
- Verbalize how you’re feeling when you find a problem
Practicing these strategies with your students will help create a learning environment where grappling, failing, and growing is celebrated!
Problem-Solving Skill for Kids
Did we miss any of your favorites? Comment and share them below!
Looking to add creative problem solving to your class?
Learn more about Kodable's free educator plan or create your free account today to get your students coding!
Kodable has everything you need to teach kids to code!
In just a few minutes a day, kids can learn all about the fundamentals of Computer Science - and so much more! With lessons ranging from zero to JavaScript, Kodable equips children for a digital future.

- Alzheimer’s Disease: A Comprehensive Overview and Latest Research Insights
- Dementia Prevention: Effective Strategies for Brain Health
- Senior Cognitive Function: Exploring Strategies for Mental Sharpness
- Neuroprotection: Strategies and Practices for Optimal Brain Health
- Aging Brain Health: Expert Strategies for Maintaining Cognitive Function
- Screen Time and Children’s Brain Health: Key Insights for Parents
- Autism and Brain Health: Unraveling the Connection and Strategies
- Dopamine and Brain Health: Crucial Connections Explained
- Serotonin and Brain Health: Uncovering the Connection
- Cognitive Aging: Understanding Its Impact and Progression
- Brain Fitness: Enhancing Cognitive Abilities and Mental Health
- Brain Health Myths: Debunking Common Misconceptions
- Brain Waves: Unlocking the Secrets of the Mind’s Signals
- Brain Inflammation: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
- Neurotransmitters: Unlocking the Secrets of Brain Chemistry
- Neurogenesis: Unraveling the Secrets of Brain Regeneration
- Mental Fatigue: Understanding and Overcoming Its Effects
- Neuroplasticity: Unlocking Your Brain’s Potential
- Brain Health: Essential Tips for Boosting Cognitive Function
- Brain Health: A Comprehensive Overview of Brain Functions and Its Importance Across Lifespan
- An In-depth Scientific Overview of Hydranencephaly
- A Comprehensive Overview of Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome (PTHS)
- An Extensive Overview of Autism
- Navigating the Brain: An In-Depth Look at The Montreal Procedure
- Gray Matter and Sensory Perception: Unveiling the Nexus
- Decoding Degenerative Diseases: Exploring the Landscape of Brain Disorders
- Progressive Disorders: Unraveling the Complexity of Brain Health
- Introduction to Embryonic Stem Cells
- Memory Training: Enhance Your Cognitive Skills Fast
- Mental Exercises for Kids: Enhancing Brain Power and Focus
- Senior Mental Exercises: Top Techniques for a Sharp Mind
- Nutrition for Aging Brain: Essential Foods for Cognitive Health
- ADHD and Brain Health: Exploring the Connection and Strategies
- Pediatric Brain Disorders: A Concise Overview for Parents and Caregivers
Child Cognitive Development: Essential Milestones and Strategies
- Brain Development in Children: Essential Factors and Tips for Growth
- Brain Health and Aging: Essential Tips for Maintaining Cognitive Function
- Pediatric Neurology: Essential Insights for Parents and Caregivers
- Nootropics Forums: Top Online Communities for Brain-Boosting Discussion
- Brain Health Books: Top Picks for Boosting Cognitive Wellbeing
- Nootropics Podcasts: Enhance Your Brainpower Today
- Brain Health Webinars: Discover Essential Tips for Improved Cognitive Function
- Brain Health Quizzes: Uncovering Insights for a Sharper Mind
- Senior Brain Training Programs: Enhance Cognitive Abilities Today
- Brain Exercises: Boost Your Cognitive Abilities in Minutes
- Neurofeedback: A Comprehensive Guide to Brain Training
- Mood Boosters: Proven Methods for Instant Happiness
- Cognitive Decline: Understanding Causes and Prevention Strategies
- Brain Aging: Key Factors and Effective Prevention Strategies
- Alzheimer’s Prevention: Effective Strategies for Reducing Risk
- Gut-Brain Axis: Exploring the Connection Between Digestion and Mental Health
- Meditation for Brain Health: Boost Your Cognitive Performance
- Sleep and Cognition: Exploring the Connection for Optimal Brain Health
- Mindfulness and Brain Health: Unlocking the Connection for Better Wellness
- Brain Health Exercises: Effective Techniques for a Sharper Mind
- Brain Training: Boost Your Cognitive Performance Today
- Cognitive Enhancers: Unlocking Your Brain’s Full Potential
- Neuroenhancers: Unveiling the Power of Cognitive Boosters
- Mental Performance: Strategies for Optimal Focus and Clarity
- Memory Enhancement: Proven Strategies for Boosting Brainpower
- Cognitive Enhancement: Unlocking Your Brain’s Full Potential
- Children’s Brain Health Supplements: Enhancing Cognitive Development
- Brain Health Supplements for Seniors: Enhancing Cognitive Performance and Memory
- Oat Straw Benefits
- Nutrition for Children’s Brain Health: Essential Foods and Nutrients for Cognitive Development
- Nootropic Drug Interactions: Essential Insights and Precautions
- Personalized Nootropics: Enhance Cognitive Performance the Right Way
- Brain Fog Remedies: Effective Solutions for Mental Clarity
- Nootropics Dosage: A Comprehensive Guide to Optimal Use
- Nootropics Legality: A Comprehensive Guide to Smart Drugs Laws
- Nootropics Side Effects: Uncovering the Risks and Realities
- Nootropics Safety: Essential Tips for Smart and Responsible Use
- GABA and Brain Health: Unlocking the Secrets to Optimal Functioning
- Nootropics and Anxiety: Exploring the Connection and Potential Benefits
- Nootropics for Stress: Effective Relief & Cognitive Boost
- Nootropics for Seniors: Enhancing Cognitive Health and Well-Being
- Nootropics for Athletes: Enhancing Performance and Focus
- Nootropics for Students: Enhance Focus and Academic Performance
- Nootropic Stacks: Unlocking the Power of Cognitive Enhancers
- Nootropic Research: Unveiling the Science Behind Cognitive Enhancers
- Biohacking: Unleashing Human Potential Through Science
- Brain Nutrition: Essential Nutrients for Optimal Cognitive Function
- Synthetic Nootropics: Unraveling the Science Behind Brain Boosters
- Natural Nootropics: Unlocking Cognitive Enhancements through Nature
- Brain Boosting Supplements: Enhancing Cognitive Performance Naturally
- Smart Drugs: Enhancing Cognitive Performance and Focus
- Concentration Aids: Enhancing Focus and Productivity in Daily Life
- Nootropics: Unleashing Cognitive Potential and Enhancements
- Best Nootropics 2024
- Alpha Brain Review 2023
- Neuriva Review
- Neutonic Review
- Prevagen Review
- Nooceptin Review
- Nootropics Reviews: Unbiased Insights on Brain Boosters
- Phenylpiracetam: Unlocking Cognitive Enhancement and Brain Health
- Modafinil: Unveiling Its Benefits and Uses
- Racetams: Unlocking Cognitive Enhancement Secrets
- Adaptogens for Brain Health: Enhancing Cognitive Function Naturally
- Vitamin B for Brain Health: Unveiling the Essential Benefits
- Caffeine and Brain Health: Unveiling the Connection
- Antioxidants for Brain: Enhancing Cognitive Function and Health
- Omega-3 and Brain Health: Unlocking the Benefits for Cognitive Function
- Brain-Healthy Foods: Top Picks for Boosting Cognitive Function
- Focus Supplements: Enhance Concentration and Mental Clarity Today
Child cognitive development is a fascinating and complex process that entails the growth of a child’s mental abilities, including their ability to think, learn, and solve problems. This development occurs through a series of stages that can vary among individuals. As children progress through these stages, their cognitive abilities and skills are continuously shaped by a myriad of factors such as genetics, environment, and experiences. Understanding the nuances of child cognitive development is essential for parents, educators, and professionals alike, as it provides valuable insight into supporting the growth of the child’s intellect and overall well-being.
Throughout the developmental process, language and communication play a vital role in fostering a child’s cognitive abilities . As children acquire language skills, they also develop their capacity for abstract thought, reasoning, and problem-solving. It is crucial for parents and caregivers to be mindful of potential developmental delays, as early intervention can greatly benefit the child’s cognitive development. By providing stimulating environments, nurturing relationships, and embracing diverse learning opportunities, adults can actively foster healthy cognitive development in children.
Key Takeaways
- Child cognitive development involves the growth of mental abilities and occurs through various stages.
- Language and communication are significant factors in cognitive development , shaping a child’s ability for abstract thought and problem-solving.
- Early intervention and supportive environments can play a crucial role in fostering healthy cognitive development in children.
Child Cognitive Development Stages
Child cognitive development is a crucial aspect of a child’s growth and involves the progression of their thinking, learning, and problem-solving abilities. Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget developed a widely recognized theory that identifies four major stages of cognitive development in children.
Sensorimotor Stage
The Sensorimotor Stage occurs from birth to about 2 years old. During this stage, infants and newborns learn to coordinate their senses (sight, sound, touch, etc.) with their motor abilities. Their understanding of the world begins to develop through their physical interactions and experiences. Some key milestones in this stage include object permanence, which is the understanding that an object still exists even when it’s not visible, and the development of intentional actions.
Preoperational Stage
The Preoperational Stage takes place between the ages of 2 and 7 years old. In this stage, children start to think symbolically, and their language capabilities rapidly expand. They also develop the ability to use mental images, words, and gestures to represent the world around them. However, their thinking is largely egocentric, which means they struggle to see things from other people’s perspectives. During this stage, children start to engage in pretend play and begin to grasp the concept of conservation, recognizing that certain properties of objects (such as quantity or volume) remain the same even if their appearance changes.
Concrete Operational Stage
The Concrete Operational Stage occurs between the ages of 7 and 12 years old. At this stage, children’s cognitive development progresses to more logical and organized ways of thinking. They can now consider multiple aspects of a problem and better understand the relationship between cause and effect . Furthermore, children become more adept at understanding other people’s viewpoints, and they can perform basic mathematical operations and understand the principles of classification and seriation.
Formal Operational Stage
Lastly, the Formal Operational Stage typically begins around 12 years old and extends into adulthood. In this stage, children develop the capacity for abstract thinking and can consider hypothetical situations and complex reasoning. They can also perform advanced problem-solving and engage in systematic scientific inquiry. This stage allows individuals to think about abstract concepts, their own thought processes, and understand the world in deeper, more nuanced ways.
By understanding these stages of cognitive development, you can better appreciate the complex growth process that children undergo as their cognitive abilities transform and expand throughout their childhood.
Key Factors in Cognitive Development
Genetics and brain development.
Genetics play a crucial role in determining a child’s cognitive development. A child’s brain development is heavily influenced by genetic factors, which also determine their cognitive potential , abilities, and skills. It is important to understand that a child’s genes do not solely dictate their cognitive development – various environmental and experiential factors contribute to shaping their cognitive abilities as they grow and learn.
Environmental Influences
The environment in which a child grows up has a significant impact on their cognitive development. Exposure to various experiences is essential for a child to develop essential cognitive skills such as problem-solving, communication, and critical thinking. Factors that can have a negative impact on cognitive development include exposure to toxins, extreme stress, trauma, abuse, and addiction issues, such as alcoholism in the family.
Nutrition and Health
Maintaining good nutrition and health is vital for a child’s cognitive development. Adequate nutrition is essential for the proper growth and functioning of the brain . Key micronutrients that contribute to cognitive development include iron, zinc, and vitamins A, C, D, and B-complex vitamins. Additionally, a child’s overall health, including physical fitness and immunity, ensures they have the energy and resources to engage in learning activities and achieve cognitive milestones effectively .
Emotional and Social Factors
Emotional well-being and social relationships can also greatly impact a child’s cognitive development. A supportive, nurturing, and emotionally healthy environment allows children to focus on learning and building cognitive skills. Children’s emotions and stress levels can impact their ability to learn and process new information. Additionally, positive social interactions help children develop important cognitive skills such as empathy, communication, and collaboration.
In summary, cognitive development in children is influenced by various factors, including genetics, environmental influences, nutrition, health, and emotional and social factors. Considering these factors can help parents, educators, and policymakers create suitable environments and interventions for promoting optimal child development.
Language and Communication Development
Language skills and milestones.
Children’s language development is a crucial aspect of their cognitive growth. They begin to acquire language skills by listening and imitating sounds they hear from their environment. As they grow, they start to understand words and form simple sentences.
- Infants (0-12 months): Babbling, cooing, and imitating sounds are common during this stage. They can also identify their name by the end of their first year. Facial expressions play a vital role during this period, as babies learn to respond to emotions.
- Toddlers (1-3 years): They rapidly learn new words and form simple sentences. They engage more in spoken communication, constantly exploring their language environment.
- Preschoolers (3-5 years): Children expand their vocabulary, improve grammar, and begin participating in more complex conversations.
It’s essential to monitor children’s language development and inform their pediatrician if any delays or concerns arise.
Nonverbal Communication
Nonverbal communication contributes significantly to children’s cognitive development. They learn to interpret body language, facial expressions, and gestures long before they can speak. Examples of nonverbal communication in children include:
- Eye contact: Maintaining eye contact while interacting helps children understand emotions and enhances communication.
- Gestures: Pointing, waving goodbye, or using hand signs provide alternative ways for children to communicate their needs and feelings.
- Body language: Posture, body orientation, and movement give clues about a child’s emotions and intentions.
Teaching children to understand and use nonverbal communication supports their cognitive and social development.
Parent and Caregiver Interaction
Supportive interaction from parents and caregivers plays a crucial role in children’s language and communication development. These interactions can improve children’s language skills and overall cognitive abilities . Some ways parents and caregivers can foster language development are:
- Reading together: From an early age, reading books to children enhance their vocabulary and listening skills.
- Encouraging communication: Ask open-ended questions and engage them in conversations to build their speaking skills.
- Using rich vocabulary: Expose children to a variety of words and phrases, promoting language growth and understanding.
By actively engaging in children’s language and communication development, parents and caregivers can nurture cognitive, emotional, and social growth.
Cognitive Abilities and Skills
Cognitive abilities are the mental skills that children develop as they grow. These skills are essential for learning, adapting, and thriving in modern society. In this section, we will discuss various aspects of cognitive development, including reasoning and problem-solving, attention and memory, decision-making and executive function, as well as academic and cognitive milestones.
Reasoning and Problem Solving
Reasoning is the ability to think logically and make sense of the world around us. It’s essential for a child’s cognitive development, as it enables them to understand the concept of object permanence , recognize patterns, and classify objects. Problem-solving skills involve using these reasoning abilities to find solutions to challenges they encounter in daily life .
Children develop essential skills like:
- Logical reasoning : The ability to deduce conclusions from available information.
- Perception: Understanding how objects relate to one another in their environment.
- Schemes: Organizing thoughts and experiences into mental categories.
Attention and Memory
Attention refers to a child’s ability to focus on specific tasks, objects, or information, while memory involves retaining and recalling information. These cognitive abilities play a critical role in children’s learning and academic performance . Working memory is a vital component of learning, as it allows children to hold and manipulate information in their minds while solving problems and engaging with new tasks.
- Attention: Focuses on relevant tasks and information while ignoring distractions.
- Memory: Retains and retrieves information when needed.
Decision-Making and Executive Function
Decision-making is the process of making choices among various alternatives, while executive function refers to the higher-order cognitive processes that enable children to plan, organize, and adapt in complex situations. Executive function encompasses components such as:
- Inhibition: Self-control and the ability to resist impulses.
- Cognitive flexibility: Adapting to new information or changing circumstances.
- Planning: Setting goals and devising strategies to achieve them.
Academic and Cognitive Milestones
Children’s cognitive development is closely linked to their academic achievement. As they grow, they achieve milestones in various cognitive domains that form the foundation for their future learning. Some of these milestones include:
- Language skills: Developing vocabulary, grammar, and sentence structure.
- Reading and mathematics: Acquiring the ability to read and comprehend text, as well as understanding basic mathematical concepts and operations.
- Scientific thinking: Developing an understanding of cause-and-effect relationships and forming hypotheses.
Healthy cognitive development is essential for a child’s success in school and life. By understanding and supporting the development of their cognitive abilities, we can help children unlock their full potential and prepare them for a lifetime of learning and growth.
Developmental Delays and Early Intervention
Identifying developmental delays.
Developmental delays in children can be identified by monitoring their progress in reaching cognitive, linguistic, physical, and social milestones. Parents and caregivers should be aware of developmental milestones that are generally expected to be achieved by children at different ages, such as 2 months, 4 months, 6 months, 9 months, 18 months, 1 year, 2 years, 3 years, 4 years, and 5 years. Utilizing resources such as the “Learn the Signs. Act Early.” program can help parents and caregivers recognize signs of delay early in a child’s life.
Resources and Support for Parents
There are numerous resources available for parents and caregivers to find information on developmental milestones and to learn about potential developmental delays, including:
- Learn the Signs. Act Early : A CDC initiative that provides pdf checklists of milestones and resources for identifying delays.
- Parental support groups : Local and online communities dedicated to providing resources and fostering connections between families experiencing similar challenges.
Professional Evaluations and Intervention Strategies
If parents or caregivers suspect a developmental delay, it is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals or specialists who can conduct validated assessments of the child’s cognitive and developmental abilities. Early intervention strategies, such as the ones used in broad-based early intervention programs , have shown significant positive impacts on children with developmental delays to improve cognitive development and outcomes.
Professional evaluations may include:
- Pediatricians : Primary healthcare providers who can monitor a child’s development and recommend further assessments when needed.
- Speech and language therapists : Professionals who assist children with language and communication deficits.
- Occupational therapists : Experts in helping children develop or improve on physical and motor skills, as well as social and cognitive abilities.
Depending on the severity and nature of the delays, interventions may involve:
- Individualized support : Tailored programs or therapy sessions specifically developed for the child’s needs.
- Group sessions : Opportunities for children to learn from and interact with other children experiencing similar challenges.
- Family involvement : Parents and caregivers learning support strategies to help the child in their daily life.
Fostering Healthy Cognitive Development
Play and learning opportunities.
Encouraging play is crucial for fostering healthy cognitive development in children . Provide a variety of age-appropriate games, puzzles, and creative activities that engage their senses and stimulate curiosity. For example, introduce building blocks and math games for problem-solving skills, and crossword puzzles to improve vocabulary and reasoning abilities.
Playing with others also helps children develop social skills and better understand facial expressions and emotions. Provide opportunities for cooperative play, where kids can work together to achieve a common goal, and open-ended play with no specific rules to boost creativity.
Supportive Home Environment
A nurturing and secure home environment encourages healthy cognitive growth. Be responsive to your child’s needs and interests, involving them in everyday activities and providing positive reinforcement. Pay attention to their emotional well-being and create a space where they feel safe to ask questions and explore their surroundings.
Promoting Independence and Decision-Making
Support independence by allowing children to make decisions about their playtime, activities, and daily routines. Encourage them to take age-appropriate responsibilities and make choices that contribute to self-confidence and autonomy. Model problem-solving strategies and give them opportunities to practice these skills during play, while also guiding them when necessary.
Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Promote a well-rounded lifestyle, including:
- Sleep : Ensure children get adequate and quality sleep by establishing a consistent bedtime routine.
- Hydration : Teach the importance of staying hydrated by offering water frequently, especially during play and physical activities.
- Screen time : Limit exposure to electronic devices and promote alternative activities for toddlers and older kids.
- Physical activity : Encourage children to engage in active play and exercise to support neural development and overall health .
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key stages of child cognitive development.
Child cognitive development can be divided into several key stages based on Piaget’s theory of cognitive development . These stages include the sensorimotor stage (birth to 2 years), preoperational stage (2-7 years), concrete operational stage (7-11 years), and formal operational stage (11 years and beyond). Every stage represents a unique period of cognitive growth, marked by the development of new skills, thought processes, and understanding of the world.
What factors influence cognitive development in children?
Several factors contribute to individual differences in child cognitive development, such as genetic and environmental factors. Socioeconomic status, access to quality education, early home environment, and parental involvement all play a significant role in determining cognitive growth. In addition, children’s exposure to diverse learning experiences, adequate nutrition, and mental health also influence overall cognitive performance .
How do cognitive skills vary during early childhood?
Cognitive skills in early childhood evolve as children progress through various stages . During the sensorimotor stage, infants develop fundamental skills such as object permanence. The preoperational stage is characterized by the development of symbolic thought, language, and imaginative play. Children then enter the concrete operational stage, acquiring the ability to think logically and solve problems. Finally, in the formal operational stage, children develop abstract reasoning abilities, complex problem-solving skills and metacognitive awareness.
What are common examples of cognitive development?
Examples of cognitive development include the acquisition of language and vocabulary, the development of problem-solving skills, and the ability to engage in logical reasoning. Additionally, memory, attention, and spatial awareness are essential aspects of cognitive development. Children may demonstrate these skills through activities like puzzle-solving, reading, and mathematics.
How do cognitive development theories explain children’s learning?
Piaget’s cognitive development theory suggests that children learn through active exploration, constructing knowledge based on their experiences and interactions with the world. In contrast, Vygotsky’s sociocultural theory emphasizes the role of social interaction and cultural context in learning. Both theories imply that cognitive development is a dynamic and evolving process, influenced by various environmental and psychological factors.
Why is it essential to support cognitive development in early childhood?
Supporting cognitive development in early childhood is critical because it lays a strong foundation for future academic achievement, social-emotional development, and lifelong learning. By providing children with diverse and enriching experiences, caregivers and educators can optimize cognitive growth and prepare children to face the challenges of today’s complex world. Fostering cognitive development early on helps children develop resilience, adaptability, and critical thinking skills essential for personal and professional success.
Direct Your Visitors to a Clear Action at the Bottom of the Page
E-book title.
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.

- Go To Slide 1
- Go To Slide 2
- Go To Slide 3
- Go To Slide 4
- Go To Slide 5
The LeapStart ™ learning system prepares kids for the 21st century with the school and life skills they'll need to get ahead.
With over 200 key skills preparing your child has never been easier—or more fun!
Think problem solving, STEM, creativity, and communication.

LeapStart™ Kindergarten & 1st Grade Interactive Learning System
Best for inquisitive 5-7 year olds
Includes Kindergarten & 1st Grade Sampler Book
Sleek stylus supports proper writing grip
Storage pocket for extra book (Sold separately)
WHERE TO BUY

25 of the Best Toys for 2-Year-Olds
W hen it comes to selecting toys for 2-year-olds, you might find yourself wondering what will keep a kiddo who is in the prime of their toddlerhood engaged and interested. Narrowing down the best of the best toys for ever-curious, constantly-growing tiny humans can be daunting. Especially when those little humans tend to be interested in anything and everything. To simplify your search, we’re sharing 25 of our favorite toys for 2-year-olds. We think these are some of the best toddler toys out there.
5 Montessori Toys for 2-Year-Olds
Montessori toys are designed with open-ended, independent play in mind. They’re an excellent tool for encouraging 2-year-olds to build real-life skills while promoting creative thinking and problem-solving. Here are our favorite Montessori toys for 2-year-olds.
1. Lovevery Block Set
This beautiful, high-quality block set has everything your 2-year-old could need to build, sort, and thread, among other possibilities. Featuring a solid wood design and vibrant rainbow colors, it comes with 70 blocks plus additional tools, a storage bag and storage box, and an activity guide. Perfect for building spatial, language, and problem-solving skills .
2. Melissa & Doug Let’s Play House Dust! Sweep! Mop! Toy Cleaning Set
There’s no doubt that 2-year-olds love to help and be involved in important tasks. This realistic pretend play cleaning set includes a wooden broom, mop, and duster, as well as a dustpan, brush, and organizing stand. It’ll build toddlers’ confidence and sense of responsibility as they practice coordination, fine motor skills, and everyday chores .
3. Wobble/Balance Board
A wobble balance board is an irresistible, multipurpose toy for 2-year-olds. It stimulates the vestibular system, promotes balance and coordination, and can be used for wobbling, lounging, climbing, etc. This one is made from heirloom quality wood and supports up to 480 pounds, making it possible for everyone in the family to enjoy the fun.
4. Ramp Race Track
A car ramp racer allows kiddos to explore motion, direction, and cause and effect while practicing focusing and enjoying imaginative play . This ramp racer features five levels and comes with four wooden cars and two balls in primary colors. It’s made from durable, child-friendly wood, so it’s practical and aesthetically pleasing.
5. Hape Counting Stacker
This counting stacker allows children to practice counting to 10, basic color recognition, and fine motor development through stacking. It includes red, yellow, orange, blue, and green wooden stacking blocks and a stacking stand — all made from child-safe, non-toxic materials. An excellent activity for your 2-year-old’s playroom or the kitchen table.
4 Climbing Toys for 2-Year-Olds
Toddlers are busy people. They’re constantly on the go, exploring their surroundings and testing physical limits and boundaries. If you have a 2-year-old at home, you’ll want to invest in safe, toddler-approved climbing toys made to support gross motor development and foster independence . Here are some of our favorites.
1. Lily & River Little Climber XL
This top-rated Pikler Triangle is built for ages 2-8. It’s perfect for strengthening your little climber’s self-confidence, balance, gross motor skills, muscle growth, and creative /strategy play. This climber is made from natural birch and premium bamboo, durable enough for years. For added climbing fun, you can choose to add on a reversible ladder/slide or reversible rockwall/slide.
2. Lily & River Little Dome
Another beautifully-made toy from Lily & River, this climbing dome allows kiddos to climb, hang, and play to their heart’s desire. With a bit of imagination , it can become a mountain, cave, or monkey bar set. Choose from natural, white-sealed, rainbow-sealed, or other bold color finishes. For additional peace of mind, you can add on beautiful safety mat sets.
3. Avenlur Magnolia Indoor Playground
If you really want to take your playroom up a notch for your 2-year-old, an indoor playground is the way to go. Avenlur’s Magnolia Indoor Playground is a seven-in-one jungle gym featuring a slide, a climbing wall, a rope wall climber, monkey bars, a swing, and ladder climbers. It will provide hours of fun while seamlessly supporting gross motor development.
4. The Original Nugget Play Couch
A fan favorite for many reasons! The Nugget consists of four foam pieces (a base, a cushion, and two triangles) and can be set up in many configurations. The options for play, climbing, crashing, and lounging are endless here. It comes in various appealing colors and fabrics, including microsuede, double-brushed, and corduroy, and it is Greenguard Gold Certified to ensure all materials are child-safe. We think it’s worth the investment over competing play couches.
5 Outdoor Toys for 2-Year-Olds
What 2-year-old doesn’t love being outside ? When given the choice, we’re willing to bet most toddlers would gladly choose the outdoors over being cooped up inside. Sometimes, you just need a toddler-approved outdoor toy or two to make backyard playtime favorable for everyone in the family. Here are some of our favorites.
1. Step2 Rain Showers Splash Pond Water Table
A little bit of water play can reset almost any toddler’s day. That’s why a water table is a must for every 2-year-old. This one boasts 13 fun accessories, including maze-like spinners, ramps, and buckets, as well as a waterfall tray for a fun rainfall effect. Age-appropriate STEM play has never been easier to come by.
2. Little Tikes Easy Score Soccer Set
Group sports like soccer are an excellent way to build social skills , cooperation, and focus. Not to mention gross motor skills. Whether or not your tiny tot is on a team, this soccer set will quickly become a family favorite. It includes an easy-to-assemble kid-sized net, ball, and air pump.
3. Little Tikes Easy Score Basketball Set
Another must-have Little Tikes outdoor (or indoor) toy, this basketball set includes an adjustable basketball hoop and stand and three small soft basketballs. It features an oversized rim for simpler scoring (and increased confidence). Plus, you can choose from six heights — so it’ll grow with your kiddo.
4. Little Tikes First Slide
A go-to beginner’s slide! This one is suitable for use inside or out, folds up for easy storage, and doesn’t require any tools for setup. It promotes balance, fitness, and coordination — not to mention fun for your 2-year-old (or any child up to 60 pounds).
5. Step2 Naturally Playful Sand Table
Digging in sand (and dirt) is a rite of passage for toddlers, right? With a solid sand table, your kiddo can enjoy hours of structured sensory play — without all the mess. This one is raised to a height just right for standing and can hold up to 80 pounds of sand, soil, or any other sensory material. It comes with five accessories. It also features molded-in roadways on the lid, which can be used as a race track when covered.
3 Ride-On Toys for 2-Year-Olds
Being a toddler means constantly being on the move. In particular, 2-year-olds never seem to slow down. Because of this, ride-on toys are a must at this age. Here are some we think your child will love to take a spin on.
1. Step2 Up and Down Roller Coaster Toy for Kids
This kid’s roller coaster will bring the action into your home (or yard) with its 9-foot track and ATV-inspired car. It features a high back, a handrail, and footrests for maximum comfort and easily comes apart for convenient storage. While the included steps are helpful for the youngest riders, the coaster holds children up to 50 pounds.
2. Disney My First Minnie Plane
This ride-on plane is for toddlers 1-3 years old, so it’s just right for 2-year-olds. It features rotating propellers with alternating light-up patterns, 360-degree steering ability, realistic lift-off and landing sounds, and a steering wheel and honking horn. It doesn’t get much more adorable.
3. Little Tikes Cozy Coupe Ice Cream Truck
A reimagined take on the iconic Little Tikes Cozy Coupe! Mom or Dad can push this ice cream truck ride-on car, or your toddler can do it themselves with its detachable floorboard. It comes loaded with fun accessories and specs, including play ice cream cones, a credit card reader, and even an ice cream cone speaker that plays modern ice cream truck music.
5 Educational Toys for 2-Year-Olds
Toddler toys come in all forms. When they’re intended to be equal parts fun and educational, you can’t lose. Check out our favorite learning-inspired toys for 2-year-olds.
1. Learning Resources Farmer’s Market Color Sorting Set
This 30-piece color sorting set aims to develop color recognition and sorting skills. It offers realistic-looking red, orange, yellow, purple, and green fruits and vegetables, as well as five sorting baskets with labels and an activity guide. It’s an excellent toy for pretend play, language development , and vocabulary acquisition .
2. VTech Alphabet Apple
This learning toy introduces not only the alphabet but phonics, words, time concepts, music, and more — so it’ll easily grow with your child as they develop new skills. Apart from featuring the obvious (all 26 letters and sounds), it boasts 29 songs and melodies. We also love this pick’s carry handle.
3. Melissa & Doug Shapes Wooden Chunky Puzzle
Melissa & Doug offers a wide choice of wooden puzzles for toddlers. When it comes to learning shapes, this one is a must. With its eight chunky, easy-to-manipulate pieces (circle, square, diamond, rectangle, triangle, heart, star, and oval) and bright colors, your kiddo won’t even realize they’re learning.
4. Melissa & Doug Rainbow Caterpillar Gear Toy
Color recognition is an important skill for children to work toward in toddlerhood. This gear toy offers plenty of opportunities for color learning and reinforcement. It also promotes hand-eye coordination and fine motor skills. It’s a simple pick to occupy and engage your 2-year-old.
5. Learning Resources Primary Science Sensory Tubes
These sensory tubes are highly versatile and made to encourage science exploration, curiosity, and development of the senses. The four durable tubes have dual openings with two solid lids for each, and you can fill and refill them with your choice of objects. The kit includes four vented lids for exploring smells.
3 Other Toys for 2-Year-Olds
Whether you’re shopping for toys for toddler boys or girls, we could go on and on with exceptional options for 2-year-olds. Here are a few more of our favorite picks for this age. You won’t want to miss out on any of them.
1. Turtle Balance Stepping Stones
Honing coordination and balance is an important everyday task for 2-year-olds. These bright-colored, non-slip stepping stones are an incredible tool for doing just that. They’re durable (supporting up to 265 pounds each), stackable for quick storage, and perfect for creating endless obstacle courses. Plus, your toddler can use them indoors or outside. These will be an instant hit for your kiddo.
2. Hape Play Kitchen
A play kitchen is a wonderful addition to any child’s room. This one will surely promote creative thinking , imagination , and real-life skills practice all at once. It features a realistic-looking sink, stove, oven, cabinet, and spice shelf, as well as clickable, turnable knobs.
3. Green Toys Construction Trucks
This set of three toddler-sized construction trucks is an excellent pick for any car-, truck-, or construction-loving 2-year-old. The trucks are made from 100% recycled plastic and meet all international safety standards. You can’t go wrong with anything from Green Toys, as these items are ideal for indoor or outdoor use and can help develop imagination, motor skills, pretend play, language, and cause-and-effect reasoning. They’re even dishwasher-safe.
Toddlers aren’t always picky with their toys, but that doesn’t mean you shouldn’t be. If you’re not selective, toddler toys can end up taking up a lot of space and sitting idle. Quality and longevity are essential when shopping for toys for a 2-year-old. We think you’ll love the items we’ve recommended here!
This article may contain affiliate links that Microsoft and/or the publisher may receive a commission from if you buy a product or service through those links.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Puzzles. Puzzles are fun and a great way to encourage cognitive development in children. They are great for spacial reasoning and strengthening problem-solving skills. They also develop memory skills, critical thinking, and the ability to plan and execute the plan. Toddlers will enjoy the simple puzzles, and preschoolers will do great with ...
20 Best Games for 4-Year-Olds; 15 Board Games Every 9-Year-Old Will Love; Indoor Problem-Solving Activities for Kids Complete Simple Tasks: ... When it comes to fostering problem-solving skills in children, both parents and educators play pivotal roles. It's less about giving the right answers and more about asking the right questions.
Activities such as treasure hunt evidently improve their problem-solving skills and induce the idea of competition. 4. Puzzles. Puzzles can make a child think out of the box. They can develop a child's logical reasoning. Arranging the crumbled pieces will surely improve their level of patience. 5. Hide and seek.
Puzzles help 2-year-olds develop problem-solving, reasoning, exploration, and spatial awareness skills. Jigsaw puzzles are too advanced for most toddlers. Instead, look for chunky puzzles, puzzles with easy-to-hold knobs, and frame puzzles. Toddlers can advance to big floor puzzles or inset puzzles (similar to jigsaw puzzles, but the pieces don ...
Problem Solving Activities For Children Age 2-3. Sort objects by color, size, and shape. Help your child "write" his own book by writing his words while he or she draws the pictures. Teach the words; on, under, behind, around by playing games like Simon Says. Provide a "dress-up" box for your child for imaginative play.
Here are some simple problem-solving activities for toddlers: 1. Building a maze. Building a maze is fun outside and one of the best activities for 2-year-old toddlers. Since toddlers can't yet do a maze in an activity book, this is a great way to use their problem solving and navigation skills. Draw a big maze on the pavement with sidewalk ...
Problem-solving; Imagination; Early math skills; 5. Simple Tracing. Your 2-year-old might not be holding a pencil confidently, but they will enjoy simple tracing activities. They will help them develop tensile strength in their fingers and work on their fine motor skills. Use simple shapes and lines with an easy-to-follow dot-to-dot pattern.
If we take a look at the steps involved in solving a problem, we can see that there are many layers involved and different types of skills. Here are the problem-solving steps according to the University of Ken. Step 1: Identify the problem. Step 2: Define the problem. Step 3: Examine the options.
Play with sand and water. Give your child objects he can take apart and investigate. By exploring objects during play, children figure out how things work and develop problem-solving skills. Use everyday routines to notice patterns. Using language to explain these patterns helps your child become a logical thinker and increases her vocabulary ...
This post shares close to 40 easy, hands-on, learning activities for keeping 2-3 year olds busy learning & playing! These activities include sensory play, fine motor & gross motor skill building, color sorting, shape recognition, problem-solving skills, & early numeracy & literacy ac.
The toddler years are in full swing for 2-year-olds, and it's a big time for growth. But you may not be sure what skills are typical for kids this age. ... Shows simple problem-solving skills, like standing on a small stool to reach something. Follows two-step instructions like "Put the toy down and close the door." ...
How your child plays, learns, speaks, acts, and moves offers important clues about your child's development. Developmental milestones are things most children (75% or more) can do by a certain age. Check the milestones your child has reached by 2 years by completing a checklist with CDC's free Milestone Tracker mobile app, for iOS and ...
First Friends and Early Social Skills. Beginning at about 12 months, most young toddlers enjoy playing near peers. They may play games like "Ring Around the Rosie" or "chase" with another child, or join a peer in filling a bucket with mulch on the playground. These moments may not last long, but they give toddlers a sense of what it ...
At 2-years-old you will see many big changes in your toddler. They are constantly learning new things and mastering new skills. Their problem solving skills are developing as they begin to seek more independence and freedom.
Hands-on learning. Touch off a lifetime of scientific exploration by engaging your child's senses. Logic and problem-solving are important life skills, and you can help your two-year-old develop these skills with these simple activities, discussions and tips.
Teaching kids proper problem solving skills helps boost their self-esteem and self-confidence, helps them become more independent, and has a positive impact on their mental health. 6 Problem Solving Strategies for Kids. 1) Take a deep breath. The first step in teaching problem solving skills to kids is to ensure they are calm.
Creative thinking is the heart of problem solving. It is the ability to see a different way to do something, generate new ideas, and use materials in new ways. Central to creative thinking is the willingness to take risks, to experiment, and even to make a mistake. Part of creative thinking is "fluent" thinking, which is the ability to generate ...
These fun activities for 2 year olds enable parents to play, learn and discover the world together with their toddlers. Keeps the kids engaged and curious! ... It also helps toddlers develop their problem-solving skills. 4. Play Math and Reading Games Online. What you'll need: A computer with internet access.
1. Model Effective Problem-Solving When YOU encounter a challenge, do a "think-aloud" for the benefit of your child. MODEL how to apply the same problem-solving skills you've been working on together, giving the real-world examples that she can implement in her own life.. At the same time, show your child a willingness to make mistakes.Everyone encounters problems, and that's okay.
Here are the steps to problem-solving: . Identify the problem. Just stating the problem out loud can make a big difference for kids who are feeling stuck. Help your child state the problem, such as, "You don't have anyone to play with at recess," or "You aren't sure if you should take the advanced math class."
Problem-Solving Skills for Kids: Student Strategies. These are strategies your students can use during independent work time to become creative problem solvers. 1. Go Step-By-Step Through The Problem-Solving Sequence. Post problem-solving anchor charts and references on your classroom wall or pin them to your Google Classroom - anything to make ...
The Sensorimotor Stage occurs from birth to about 2 years old. During this stage, infants and newborns learn to coordinate their senses (sight, sound, touch, etc.) with their motor abilities. ... For example, introduce building blocks and math games for problem-solving skills, and crossword puzzles to improve vocabulary and reasoning abilities.
1. Puzzles. Puzzles are great to develop your child's thinking skills. They come in different forms and shapes, whether it's a wooden jigsaw puzzle for your preschooler or a crossword or sudoku puzzle for your older child. This blog takes a look at puzzles and how they help problem solving for kids. 2.
Help build your child's problem solving, STEM, creativity skills and more to help them prepare for 21st century learning. Learn more about LeapStart today! Products. BROWSE ALL PRODUCTS; BROWSE LEARNING TOYS ... Best for curious 2-4 year olds. Includes Preschool & Pre-Kindergarten Sampler Book. Easy to hold stylus for little hands.
They're an excellent tool for encouraging 2-year-olds to build real-life skills while promoting creative thinking and problem-solving. Here are our favorite Montessori toys for 2-year-olds.