How to Write a Case Study: Bookmarkable Guide & Template
Published: November 30, 2023
Earning the trust of prospective customers can be a struggle. Before you can even begin to expect to earn their business, you need to demonstrate your ability to deliver on what your product or service promises.

Sure, you could say that you're great at X or that you're way ahead of the competition when it comes to Y. But at the end of the day, what you really need to win new business is cold, hard proof.
One of the best ways to prove your worth is through a compelling case study. In fact, HubSpot’s 2020 State of Marketing report found that case studies are so compelling that they are the fifth most commonly used type of content used by marketers.

Below, I'll walk you through what a case study is, how to prepare for writing one, what you need to include in it, and how it can be an effective tactic. To jump to different areas of this post, click on the links below to automatically scroll.

Case Study Definition
Case study templates, how to write a case study.
- How to Format a Case Study
Business Case Study Examples
A case study is a specific challenge a business has faced, and the solution they've chosen to solve it. Case studies can vary greatly in length and focus on several details related to the initial challenge and applied solution, and can be presented in various forms like a video, white paper, blog post, etc.
In professional settings, it's common for a case study to tell the story of a successful business partnership between a vendor and a client. Perhaps the success you're highlighting is in the number of leads your client generated, customers closed, or revenue gained. Any one of these key performance indicators (KPIs) are examples of your company's services in action.
When done correctly, these examples of your work can chronicle the positive impact your business has on existing or previous customers and help you attract new clients.

Free Case Study Templates
Showcase your company's success using these three free case study templates.
- Data-Driven Case Study Template
- Product-Specific Case Study Template
- General Case Study Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Why write a case study?
I know, you’re thinking “ Okay, but why do I need to write one of these? ” The truth is that while case studies are a huge undertaking, they are powerful marketing tools that allow you to demonstrate the value of your product to potential customers using real-world examples. Here are a few reasons why you should write case studies.
1. Explain Complex Topics or Concepts
Case studies give you the space to break down complex concepts, ideas, and strategies and show how they can be applied in a practical way. You can use real-world examples, like an existing client, and use their story to create a compelling narrative that shows how your product solved their issue and how those strategies can be repeated to help other customers get similar successful results.
2. Show Expertise
Case studies are a great way to demonstrate your knowledge and expertise on a given topic or industry. This is where you get the opportunity to show off your problem-solving skills and how you’ve generated successful outcomes for clients you’ve worked with.
3. Build Trust and Credibility
In addition to showing off the attributes above, case studies are an excellent way to build credibility. They’re often filled with data and thoroughly researched, which shows readers you’ve done your homework. They can have confidence in the solutions you’ve presented because they’ve read through as you’ve explained the problem and outlined step-by-step what it took to solve it. All of these elements working together enable you to build trust with potential customers.
4. Create Social Proof
Using existing clients that have seen success working with your brand builds social proof . People are more likely to choose your brand if they know that others have found success working with you. Case studies do just that — putting your success on display for potential customers to see.
All of these attributes work together to help you gain more clients. Plus you can even use quotes from customers featured in these studies and repurpose them in other marketing content. Now that you know more about the benefits of producing a case study, let’s check out how long these documents should be.
How long should a case study be?
The length of a case study will vary depending on the complexity of the project or topic discussed. However, as a general guideline, case studies typically range from 500 to 1,500 words.
Whatever length you choose, it should provide a clear understanding of the challenge, the solution you implemented, and the results achieved. This may be easier said than done, but it's important to strike a balance between providing enough detail to make the case study informative and concise enough to keep the reader's interest.
The primary goal here is to effectively communicate the key points and takeaways of the case study. It’s worth noting that this shouldn’t be a wall of text. Use headings, subheadings, bullet points, charts, and other graphics to break up the content and make it more scannable for readers. We’ve also seen brands incorporate video elements into case studies listed on their site for a more engaging experience.
Ultimately, the length of your case study should be determined by the amount of information necessary to convey the story and its impact without becoming too long. Next, let’s look at some templates to take the guesswork out of creating one.
To help you arm your prospects with information they can trust, we've put together a step-by-step guide on how to create effective case studies for your business with free case study templates for creating your own.
Tell us a little about yourself below to gain access today:
And to give you more options, we’ll highlight some useful templates that serve different needs. But remember, there are endless possibilities when it comes to demonstrating the work your business has done.
1. General Case Study Template

Do you have a specific product or service that you’re trying to sell, but not enough reviews or success stories? This Product Specific case study template will help.
This template relies less on metrics, and more on highlighting the customer’s experience and satisfaction. As you follow the template instructions, you’ll be prompted to speak more about the benefits of the specific product, rather than your team’s process for working with the customer.
4. Bold Social Media Business Case Study Template

You can find templates that represent different niches, industries, or strategies that your business has found success in — like a bold social media business case study template.
In this template, you can tell the story of how your social media marketing strategy has helped you or your client through collaboration or sale of your service. Customize it to reflect the different marketing channels used in your business and show off how well your business has been able to boost traffic, engagement, follows, and more.
5. Lead Generation Business Case Study Template

It’s important to note that not every case study has to be the product of a sale or customer story, sometimes they can be informative lessons that your own business has experienced. A great example of this is the Lead Generation Business case study template.
If you’re looking to share operational successes regarding how your team has improved processes or content, you should include the stories of different team members involved, how the solution was found, and how it has made a difference in the work your business does.
Now that we’ve discussed different templates and ideas for how to use them, let’s break down how to create your own case study with one.
- Get started with case study templates.
- Determine the case study's objective.
- Establish a case study medium.
- Find the right case study candidate.
- Contact your candidate for permission to write about them.
- Ensure you have all the resources you need to proceed once you get a response.
- Download a case study email template.
- Define the process you want to follow with the client.
- Ensure you're asking the right questions.
- Layout your case study format.
- Publish and promote your case study.
1. Get started with case study templates.
Telling your customer's story is a delicate process — you need to highlight their success while naturally incorporating your business into their story.
If you're just getting started with case studies, we recommend you download HubSpot's Case Study Templates we mentioned before to kickstart the process.
2. Determine the case study's objective.
All business case studies are designed to demonstrate the value of your services, but they can focus on several different client objectives.
Your first step when writing a case study is to determine the objective or goal of the subject you're featuring. In other words, what will the client have succeeded in doing by the end of the piece?
The client objective you focus on will depend on what you want to prove to your future customers as a result of publishing this case study.
Your case study can focus on one of the following client objectives:
- Complying with government regulation
- Lowering business costs
- Becoming profitable
- Generating more leads
- Closing on more customers
- Generating more revenue
- Expanding into a new market
- Becoming more sustainable or energy-efficient
3. Establish a case study medium.
Next, you'll determine the medium in which you'll create the case study. In other words, how will you tell this story?
Case studies don't have to be simple, written one-pagers. Using different media in your case study can allow you to promote your final piece on different channels. For example, while a written case study might just live on your website and get featured in a Facebook post, you can post an infographic case study on Pinterest and a video case study on your YouTube channel.
Here are some different case study mediums to consider:
Written Case Study
Consider writing this case study in the form of an ebook and converting it to a downloadable PDF. Then, gate the PDF behind a landing page and form for readers to fill out before downloading the piece, allowing this case study to generate leads for your business.
Video Case Study
Plan on meeting with the client and shooting an interview. Seeing the subject, in person, talk about the service you provided them can go a long way in the eyes of your potential customers.
Infographic Case Study
Use the long, vertical format of an infographic to tell your success story from top to bottom. As you progress down the infographic, emphasize major KPIs using bigger text and charts that show the successes your client has had since working with you.
Podcast Case Study
Podcasts are a platform for you to have a candid conversation with your client. This type of case study can sound more real and human to your audience — they'll know the partnership between you and your client was a genuine success.
4. Find the right case study candidate.
Writing about your previous projects requires more than picking a client and telling a story. You need permission, quotes, and a plan. To start, here are a few things to look for in potential candidates.
Product Knowledge
It helps to select a customer who's well-versed in the logistics of your product or service. That way, he or she can better speak to the value of what you offer in a way that makes sense for future customers.
Remarkable Results
Clients that have seen the best results are going to make the strongest case studies. If their own businesses have seen an exemplary ROI from your product or service, they're more likely to convey the enthusiasm that you want prospects to feel, too.
One part of this step is to choose clients who have experienced unexpected success from your product or service. When you've provided non-traditional customers — in industries that you don't usually work with, for example — with positive results, it can help to remove doubts from prospects.
Recognizable Names
While small companies can have powerful stories, bigger or more notable brands tend to lend credibility to your own. In fact, 89% of consumers say they'll buy from a brand they already recognize over a competitor, especially if they already follow them on social media.
Customers that came to you after working with a competitor help highlight your competitive advantage and might even sway decisions in your favor.
5. Contact your candidate for permission to write about them.
To get the case study candidate involved, you have to set the stage for clear and open communication. That means outlining expectations and a timeline right away — not having those is one of the biggest culprits in delayed case study creation.
Most importantly at this point, however, is getting your subject's approval. When first reaching out to your case study candidate, provide them with the case study's objective and format — both of which you will have come up with in the first two steps above.
To get this initial permission from your subject, put yourself in their shoes — what would they want out of this case study? Although you're writing this for your own company's benefit, your subject is far more interested in the benefit it has for them.
Benefits to Offer Your Case Study Candidate
Here are four potential benefits you can promise your case study candidate to gain their approval.
Brand Exposure
Explain to your subject to whom this case study will be exposed, and how this exposure can help increase their brand awareness both in and beyond their own industry. In the B2B sector, brand awareness can be hard to collect outside one's own market, making case studies particularly useful to a client looking to expand their name's reach.
Employee Exposure
Allow your subject to provide quotes with credits back to specific employees. When this is an option for them, their brand isn't the only thing expanding its reach — their employees can get their name out there, too. This presents your subject with networking and career development opportunities they might not have otherwise.
Product Discount
This is a more tangible incentive you can offer your case study candidate, especially if they're a current customer of yours. If they agree to be your subject, offer them a product discount — or a free trial of another product — as a thank-you for their help creating your case study.
Backlinks and Website Traffic
Here's a benefit that is sure to resonate with your subject's marketing team: If you publish your case study on your website, and your study links back to your subject's website — known as a "backlink" — this small gesture can give them website traffic from visitors who click through to your subject's website.
Additionally, a backlink from you increases your subject's page authority in the eyes of Google. This helps them rank more highly in search engine results and collect traffic from readers who are already looking for information about their industry.
6. Ensure you have all the resources you need to proceed once you get a response.
So you know what you’re going to offer your candidate, it’s time that you prepare the resources needed for if and when they agree to participate, like a case study release form and success story letter.
Let's break those two down.
Case Study Release Form
This document can vary, depending on factors like the size of your business, the nature of your work, and what you intend to do with the case studies once they are completed. That said, you should typically aim to include the following in the Case Study Release Form:
- A clear explanation of why you are creating this case study and how it will be used.
- A statement defining the information and potentially trademarked information you expect to include about the company — things like names, logos, job titles, and pictures.
- An explanation of what you expect from the participant, beyond the completion of the case study. For example, is this customer willing to act as a reference or share feedback, and do you have permission to pass contact information along for these purposes?
- A note about compensation.
Success Story Letter
As noted in the sample email, this document serves as an outline for the entire case study process. Other than a brief explanation of how the customer will benefit from case study participation, you'll want to be sure to define the following steps in the Success Story Letter.
7. Download a case study email template.
While you gathered your resources, your candidate has gotten time to read over the proposal. When your candidate approves of your case study, it's time to send them a release form.
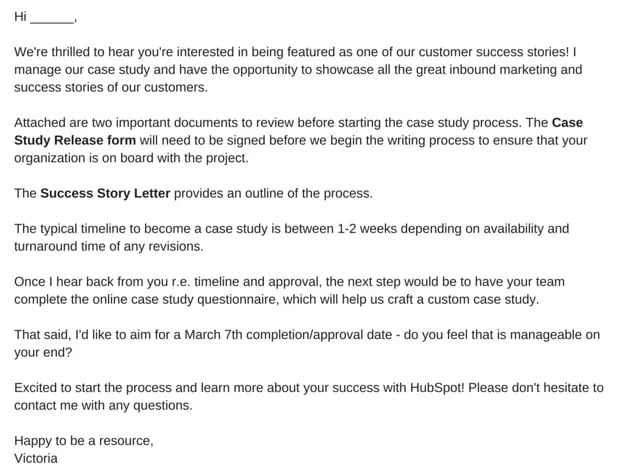
A case study release form tells you what you'll need from your chosen subject, like permission to use any brand names and share the project information publicly. Kick-off this process with an email that runs through exactly what they can expect from you, as well as what you need from them. To give you an idea of what that might look like, check out this sample email:
8. Define the process you want to follow with the client.
Before you can begin the case study, you have to have a clear outline of the case study process with your client. An example of an effective outline would include the following information.
The Acceptance
First, you'll need to receive internal approval from the company's marketing team. Once approved, the Release Form should be signed and returned to you. It's also a good time to determine a timeline that meets the needs and capabilities of both teams.
The Questionnaire
To ensure that you have a productive interview — which is one of the best ways to collect information for the case study — you'll want to ask the participant to complete a questionnaire before this conversation. That will provide your team with the necessary foundation to organize the interview, and get the most out of it.
The Interview
Once the questionnaire is completed, someone on your team should reach out to the participant to schedule a 30- to 60-minute interview, which should include a series of custom questions related to the customer's experience with your product or service.
The Draft Review
After the case study is composed, you'll want to send a draft to the customer, allowing an opportunity to give you feedback and edits.
The Final Approval
Once any necessary edits are completed, send a revised copy of the case study to the customer for final approval.
Once the case study goes live — on your website or elsewhere — it's best to contact the customer with a link to the page where the case study lives. Don't be afraid to ask your participants to share these links with their own networks, as it not only demonstrates your ability to deliver positive results and impressive growth, as well.
9. Ensure you're asking the right questions.
Before you execute the questionnaire and actual interview, make sure you're setting yourself up for success. A strong case study results from being prepared to ask the right questions. What do those look like? Here are a few examples to get you started:
- What are your goals?
- What challenges were you experiencing before purchasing our product or service?
- What made our product or service stand out against our competitors?
- What did your decision-making process look like?
- How have you benefited from using our product or service? (Where applicable, always ask for data.)
Keep in mind that the questionnaire is designed to help you gain insights into what sort of strong, success-focused questions to ask during the actual interview. And once you get to that stage, we recommend that you follow the "Golden Rule of Interviewing." Sounds fancy, right? It's actually quite simple — ask open-ended questions.
If you're looking to craft a compelling story, "yes" or "no" answers won't provide the details you need. Focus on questions that invite elaboration, such as, "Can you describe ...?" or, "Tell me about ..."
In terms of the interview structure, we recommend categorizing the questions and flowing them into six specific sections that will mirror a successful case study format. Combined, they'll allow you to gather enough information to put together a rich, comprehensive study.
Open with the customer's business.
The goal of this section is to generate a better understanding of the company's current challenges and goals, and how they fit into the landscape of their industry. Sample questions might include:
- How long have you been in business?
- How many employees do you have?
- What are some of the objectives of your department at this time?
Cite a problem or pain point.
To tell a compelling story, you need context. That helps match the customer's need with your solution. Sample questions might include:
- What challenges and objectives led you to look for a solution?
- What might have happened if you did not identify a solution?
- Did you explore other solutions before this that did not work out? If so, what happened?
Discuss the decision process.
Exploring how the customer decided to work with you helps to guide potential customers through their own decision-making processes. Sample questions might include:
- How did you hear about our product or service?
- Who was involved in the selection process?
- What was most important to you when evaluating your options?
Explain how a solution was implemented.
The focus here should be placed on the customer's experience during the onboarding process. Sample questions might include:
- How long did it take to get up and running?
- Did that meet your expectations?
- Who was involved in the process?
Explain how the solution works.
The goal of this section is to better understand how the customer is using your product or service. Sample questions might include:
- Is there a particular aspect of the product or service that you rely on most?
- Who is using the product or service?
End with the results.
In this section, you want to uncover impressive measurable outcomes — the more numbers, the better. Sample questions might include:
- How is the product or service helping you save time and increase productivity?
- In what ways does that enhance your competitive advantage?
- How much have you increased metrics X, Y, and Z?
10. Lay out your case study format.
When it comes time to take all of the information you've collected and actually turn it into something, it's easy to feel overwhelmed. Where should you start? What should you include? What's the best way to structure it?
To help you get a handle on this step, it's important to first understand that there is no one-size-fits-all when it comes to the ways you can present a case study. They can be very visual, which you'll see in some of the examples we've included below, and can sometimes be communicated mostly through video or photos, with a bit of accompanying text.
Here are the sections we suggest, which we'll cover in more detail down below:
- Title: Keep it short. Develop a succinct but interesting project name you can give the work you did with your subject.
- Subtitle: Use this copy to briefly elaborate on the accomplishment. What was done? The case study itself will explain how you got there.
- Executive Summary : A 2-4 sentence summary of the entire story. You'll want to follow it with 2-3 bullet points that display metrics showcasing success.
- About the Subject: An introduction to the person or company you served, which can be pulled from a LinkedIn Business profile or client website.
- Challenges and Objectives: A 2-3 paragraph description of the customer's challenges, before using your product or service. This section should also include the goals or objectives the customer set out to achieve.
- How Product/Service Helped: A 2-3 paragraph section that describes how your product or service provided a solution to their problem.
- Results: A 2-3 paragraph testimonial that proves how your product or service specifically benefited the person or company and helped achieve its goals. Include numbers to quantify your contributions.
- Supporting Visuals or Quotes: Pick one or two powerful quotes that you would feature at the bottom of the sections above, as well as a visual that supports the story you are telling.
- Future Plans: Everyone likes an epilogue. Comment on what's ahead for your case study subject, whether or not those plans involve you.
- Call to Action (CTA): Not every case study needs a CTA, but putting a passive one at the end of your case study can encourage your readers to take an action on your website after learning about the work you've done.
When laying out your case study, focus on conveying the information you've gathered in the most clear and concise way possible. Make it easy to scan and comprehend, and be sure to provide an attractive call-to-action at the bottom — that should provide readers an opportunity to learn more about your product or service.
11. Publish and promote your case study.
Once you've completed your case study, it's time to publish and promote it. Some case study formats have pretty obvious promotional outlets — a video case study can go on YouTube, just as an infographic case study can go on Pinterest.
But there are still other ways to publish and promote your case study. Here are a couple of ideas:
Lead Gen in a Blog Post
As stated earlier in this article, written case studies make terrific lead-generators if you convert them into a downloadable format, like a PDF. To generate leads from your case study, consider writing a blog post that tells an abbreviated story of your client's success and asking readers to fill out a form with their name and email address if they'd like to read the rest in your PDF.
Then, promote this blog post on social media, through a Facebook post or a tweet.
Published as a Page on Your Website
As a growing business, you might need to display your case study out in the open to gain the trust of your target audience.
Rather than gating it behind a landing page, publish your case study to its own page on your website, and direct people here from your homepage with a "Case Studies" or "Testimonials" button along your homepage's top navigation bar.
Format for a Case Study
The traditional case study format includes the following parts: a title and subtitle, a client profile, a summary of the customer’s challenges and objectives, an account of how your solution helped, and a description of the results. You might also want to include supporting visuals and quotes, future plans, and calls-to-action.

Image Source
The title is one of the most important parts of your case study. It should draw readers in while succinctly describing the potential benefits of working with your company. To that end, your title should:
- State the name of your custome r. Right away, the reader must learn which company used your products and services. This is especially important if your customer has a recognizable brand. If you work with individuals and not companies, you may omit the name and go with professional titles: “A Marketer…”, “A CFO…”, and so forth.
- State which product your customer used . Even if you only offer one product or service, or if your company name is the same as your product name, you should still include the name of your solution. That way, readers who are not familiar with your business can become aware of what you sell.
- Allude to the results achieved . You don’t necessarily need to provide hard numbers, but the title needs to represent the benefits, quickly. That way, if a reader doesn’t stay to read, they can walk away with the most essential information: Your product works.
The example above, “Crunch Fitness Increases Leads and Signups With HubSpot,” achieves all three — without being wordy. Keeping your title short and sweet is also essential.
2. Subtitle

Your subtitle is another essential part of your case study — don’t skip it, even if you think you’ve done the work with the title. In this section, include a brief summary of the challenges your customer was facing before they began to use your products and services. Then, drive the point home by reiterating the benefits your customer experienced by working with you.
The above example reads:
“Crunch Fitness was franchising rapidly when COVID-19 forced fitness clubs around the world to close their doors. But the company stayed agile by using HubSpot to increase leads and free trial signups.”
We like that the case study team expressed the urgency of the problem — opening more locations in the midst of a pandemic — and placed the focus on the customer’s ability to stay agile.
3. Executive Summary

The executive summary should provide a snapshot of your customer, their challenges, and the benefits they enjoyed from working with you. Think it’s too much? Think again — the purpose of the case study is to emphasize, again and again, how well your product works.
The good news is that depending on your design, the executive summary can be mixed with the subtitle or with the “About the Company” section. Many times, this section doesn’t need an explicit “Executive Summary” subheading. You do need, however, to provide a convenient snapshot for readers to scan.
In the above example, ADP included information about its customer in a scannable bullet-point format, then provided two sections: “Business Challenge” and “How ADP Helped.” We love how simple and easy the format is to follow for those who are unfamiliar with ADP or its typical customer.
4. About the Company

Readers need to know and understand who your customer is. This is important for several reasons: It helps your reader potentially relate to your customer, it defines your ideal client profile (which is essential to deter poor-fit prospects who might have reached out without knowing they were a poor fit), and it gives your customer an indirect boon by subtly promoting their products and services.
Feel free to keep this section as simple as possible. You can simply copy and paste information from the company’s LinkedIn, use a quote directly from your customer, or take a more creative storytelling approach.
In the above example, HubSpot included one paragraph of description for Crunch Fitness and a few bullet points. Below, ADP tells the story of its customer using an engaging, personable technique that effectively draws readers in.

5. Challenges and Objectives

The challenges and objectives section of your case study is the place to lay out, in detail, the difficulties your customer faced prior to working with you — and what they hoped to achieve when they enlisted your help.
In this section, you can be as brief or as descriptive as you’d like, but remember: Stress the urgency of the situation. Don’t understate how much your customer needed your solution (but don’t exaggerate and lie, either). Provide contextual information as necessary. For instance, the pandemic and societal factors may have contributed to the urgency of the need.
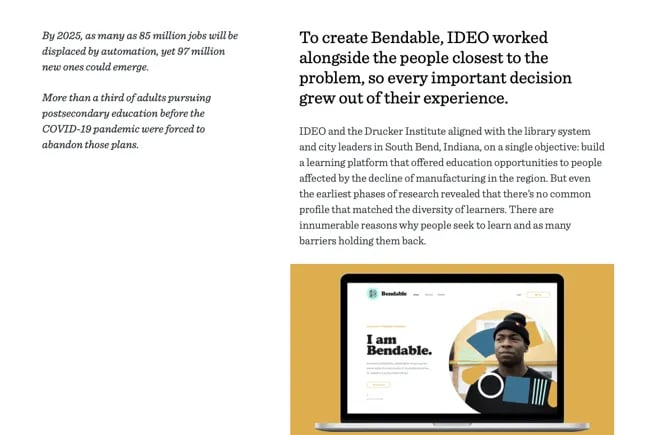
Take the above example from design consultancy IDEO:
“Educational opportunities for adults have become difficult to access in the United States, just when they’re needed most. To counter this trend, IDEO helped the city of South Bend and the Drucker Institute launch Bendable, a community-powered platform that connects people with opportunities to learn with and from each other.”
We love how IDEO mentions the difficulties the United States faces at large, the efforts its customer is taking to address these issues, and the steps IDEO took to help.
6. How Product/Service Helped
This is where you get your product or service to shine. Cover the specific benefits that your customer enjoyed and the features they gleaned the most use out of. You can also go into detail about how you worked with and for your customer. Maybe you met several times before choosing the right solution, or you consulted with external agencies to create the best package for them.
Whatever the case may be, try to illustrate how easy and pain-free it is to work with the representatives at your company. After all, potential customers aren’t looking to just purchase a product. They’re looking for a dependable provider that will strive to exceed their expectations.
In the above example, IDEO describes how it partnered with research institutes and spoke with learners to create Bendable, a free educational platform. We love how it shows its proactivity and thoroughness. It makes potential customers feel that IDEO might do something similar for them.

The results are essential, and the best part is that you don’t need to write the entirety of the case study before sharing them. Like HubSpot, IDEO, and ADP, you can include the results right below the subtitle or executive summary. Use data and numbers to substantiate the success of your efforts, but if you don’t have numbers, you can provide quotes from your customers.
We can’t overstate the importance of the results. In fact, if you wanted to create a short case study, you could include your title, challenge, solution (how your product helped), and result.
8. Supporting Visuals or Quotes

Let your customer speak for themselves by including quotes from the representatives who directly interfaced with your company.
Visuals can also help, even if they’re stock images. On one side, they can help you convey your customer’s industry, and on the other, they can indirectly convey your successes. For instance, a picture of a happy professional — even if they’re not your customer — will communicate that your product can lead to a happy client.
In this example from IDEO, we see a man standing in a boat. IDEO’s customer is neither the man pictured nor the manufacturer of the boat, but rather Conservation International, an environmental organization. This imagery provides a visually pleasing pattern interrupt to the page, while still conveying what the case study is about.
9. Future Plans
This is optional, but including future plans can help you close on a more positive, personable note than if you were to simply include a quote or the results. In this space, you can show that your product will remain in your customer’s tech stack for years to come, or that your services will continue to be instrumental to your customer’s success.
Alternatively, if you work only on time-bound projects, you can allude to the positive impact your customer will continue to see, even after years of the end of the contract.
10. Call to Action (CTA)
Not every case study needs a CTA, but we’d still encourage it. Putting one at the end of your case study will encourage your readers to take an action on your website after learning about the work you've done.
It will also make it easier for them to reach out, if they’re ready to start immediately. You don’t want to lose business just because they have to scroll all the way back up to reach out to your team.
To help you visualize this case study outline, check out the case study template below, which can also be downloaded here .
You drove the results, made the connection, set the expectations, used the questionnaire to conduct a successful interview, and boiled down your findings into a compelling story. And after all of that, you're left with a little piece of sales enabling gold — a case study.
To show you what a well-executed final product looks like, have a look at some of these marketing case study examples.
1. "Shopify Uses HubSpot CRM to Transform High Volume Sales Organization," by HubSpot
What's interesting about this case study is the way it leads with the customer. This reflects a major HubSpot value, which is to always solve for the customer first. The copy leads with a brief description of why Shopify uses HubSpot and is accompanied by a short video and some basic statistics on the company.
Notice that this case study uses mixed media. Yes, there is a short video, but it's elaborated upon in the additional text on the page. So, while case studies can use one or the other, don't be afraid to combine written copy with visuals to emphasize the project's success.
2. "New England Journal of Medicine," by Corey McPherson Nash
When branding and design studio Corey McPherson Nash showcases its work, it makes sense for it to be visual — after all, that's what they do. So in building the case study for the studio's work on the New England Journal of Medicine's integrated advertising campaign — a project that included the goal of promoting the client's digital presence — Corey McPherson Nash showed its audience what it did, rather than purely telling it.
Notice that the case study does include some light written copy — which includes the major points we've suggested — but lets the visuals do the talking, allowing users to really absorb the studio's services.
3. "Designing the Future of Urban Farming," by IDEO
Here's a design company that knows how to lead with simplicity in its case studies. As soon as the visitor arrives at the page, he or she is greeted with a big, bold photo, and two very simple columns of text — "The Challenge" and "The Outcome."
Immediately, IDEO has communicated two of the case study's major pillars. And while that's great — the company created a solution for vertical farming startup INFARM's challenge — it doesn't stop there. As the user scrolls down, those pillars are elaborated upon with comprehensive (but not overwhelming) copy that outlines what that process looked like, replete with quotes and additional visuals.
4. "Secure Wi-Fi Wins Big for Tournament," by WatchGuard
Then, there are the cases when visuals can tell almost the entire story — when executed correctly. Network security provider WatchGuard can do that through this video, which tells the story of how its services enhanced the attendee and vendor experience at the Windmill Ultimate Frisbee tournament.
5. Rock and Roll Hall of Fame Boosts Social Media Engagement and Brand Awareness with HubSpot
In the case study above , HubSpot uses photos, videos, screenshots, and helpful stats to tell the story of how the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame used the bot, CRM, and social media tools to gain brand awareness.
6. Small Desk Plant Business Ups Sales by 30% With Trello
This case study from Trello is straightforward and easy to understand. It begins by explaining the background of the company that decided to use it, what its goals were, and how it planned to use Trello to help them.
It then goes on to discuss how the software was implemented and what tasks and teams benefited from it. Towards the end, it explains the sales results that came from implementing the software and includes quotes from decision-makers at the company that implemented it.
7. Facebook's Mercedes Benz Success Story
Facebook's Success Stories page hosts a number of well-designed and easy-to-understand case studies that visually and editorially get to the bottom line quickly.
Each study begins with key stats that draw the reader in. Then it's organized by highlighting a problem or goal in the introduction, the process the company took to reach its goals, and the results. Then, in the end, Facebook notes the tools used in the case study.
Showcasing Your Work
You work hard at what you do. Now, it's time to show it to the world — and, perhaps more important, to potential customers. Before you show off the projects that make you the proudest, we hope you follow these important steps that will help you effectively communicate that work and leave all parties feeling good about it.
Editor's Note: This blog post was originally published in February 2017 but was updated for comprehensiveness and freshness in July 2021.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

How to Market an Ebook: 21 Ways to Promote Your Content Offers
![short case study planning 7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/most%20popular%20types%20of%20content.jpg)
7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]
![short case study planning How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/listicle-1.jpg)
How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]

28 Case Study Examples Every Marketer Should See
![short case study planning What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/business%20whitepaper.jpg)
What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]

What is an Advertorial? 8 Examples to Help You Write One

How to Create Marketing Offers That Don't Fall Flat

20 Creative Ways To Repurpose Content

16 Important Ways to Use Case Studies in Your Marketing

11 Ways to Make Your Blog Post Interactive
Showcase your company's success using these free case study templates.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
How to write a case study — examples, templates, and tools

It’s a marketer’s job to communicate the effectiveness of a product or service to potential and current customers to convince them to buy and keep business moving. One of the best methods for doing this is to share success stories that are relatable to prospects and customers based on their pain points, experiences, and overall needs.
That’s where case studies come in. Case studies are an essential part of a content marketing plan. These in-depth stories of customer experiences are some of the most effective at demonstrating the value of a product or service. Yet many marketers don’t use them, whether because of their regimented formats or the process of customer involvement and approval.
A case study is a powerful tool for showcasing your hard work and the success your customer achieved. But writing a great case study can be difficult if you’ve never done it before or if it’s been a while. This guide will show you how to write an effective case study and provide real-world examples and templates that will keep readers engaged and support your business.
In this article, you’ll learn:
What is a case study?
How to write a case study, case study templates, case study examples, case study tools.
A case study is the detailed story of a customer’s experience with a product or service that demonstrates their success and often includes measurable outcomes. Case studies are used in a range of fields and for various reasons, from business to academic research. They’re especially impactful in marketing as brands work to convince and convert consumers with relatable, real-world stories of actual customer experiences.
The best case studies tell the story of a customer’s success, including the steps they took, the results they achieved, and the support they received from a brand along the way. To write a great case study, you need to:
- Celebrate the customer and make them — not a product or service — the star of the story.
- Craft the story with specific audiences or target segments in mind so that the story of one customer will be viewed as relatable and actionable for another customer.
- Write copy that is easy to read and engaging so that readers will gain the insights and messages intended.
- Follow a standardized format that includes all of the essentials a potential customer would find interesting and useful.
- Support all of the claims for success made in the story with data in the forms of hard numbers and customer statements.
Case studies are a type of review but more in depth, aiming to show — rather than just tell — the positive experiences that customers have with a brand. Notably, 89% of consumers read reviews before deciding to buy, and 79% view case study content as part of their purchasing process. When it comes to B2B sales, 52% of buyers rank case studies as an important part of their evaluation process.
Telling a brand story through the experience of a tried-and-true customer matters. The story is relatable to potential new customers as they imagine themselves in the shoes of the company or individual featured in the case study. Showcasing previous customers can help new ones see themselves engaging with your brand in the ways that are most meaningful to them.
Besides sharing the perspective of another customer, case studies stand out from other content marketing forms because they are based on evidence. Whether pulling from client testimonials or data-driven results, case studies tend to have more impact on new business because the story contains information that is both objective (data) and subjective (customer experience) — and the brand doesn’t sound too self-promotional.

Case studies are unique in that there’s a fairly standardized format for telling a customer’s story. But that doesn’t mean there isn’t room for creativity. It’s all about making sure that teams are clear on the goals for the case study — along with strategies for supporting content and channels — and understanding how the story fits within the framework of the company’s overall marketing goals.
Here are the basic steps to writing a good case study.
1. Identify your goal
Start by defining exactly who your case study will be designed to help. Case studies are about specific instances where a company works with a customer to achieve a goal. Identify which customers are likely to have these goals, as well as other needs the story should cover to appeal to them.
The answer is often found in one of the buyer personas that have been constructed as part of your larger marketing strategy. This can include anything from new leads generated by the marketing team to long-term customers that are being pressed for cross-sell opportunities. In all of these cases, demonstrating value through a relatable customer success story can be part of the solution to conversion.
2. Choose your client or subject
Who you highlight matters. Case studies tie brands together that might otherwise not cross paths. A writer will want to ensure that the highlighted customer aligns with their own company’s brand identity and offerings. Look for a customer with positive name recognition who has had great success with a product or service and is willing to be an advocate.
The client should also match up with the identified target audience. Whichever company or individual is selected should be a reflection of other potential customers who can see themselves in similar circumstances, having the same problems and possible solutions.
Some of the most compelling case studies feature customers who:
- Switch from one product or service to another while naming competitors that missed the mark.
- Experience measurable results that are relatable to others in a specific industry.
- Represent well-known brands and recognizable names that are likely to compel action.
- Advocate for a product or service as a champion and are well-versed in its advantages.
Whoever or whatever customer is selected, marketers must ensure they have the permission of the company involved before getting started. Some brands have strict review and approval procedures for any official marketing or promotional materials that include their name. Acquiring those approvals in advance will prevent any miscommunication or wasted effort if there is an issue with their legal or compliance teams.
3. Conduct research and compile data
Substantiating the claims made in a case study — either by the marketing team or customers themselves — adds validity to the story. To do this, include data and feedback from the client that defines what success looks like. This can be anything from demonstrating return on investment (ROI) to a specific metric the customer was striving to improve. Case studies should prove how an outcome was achieved and show tangible results that indicate to the customer that your solution is the right one.
This step could also include customer interviews. Make sure that the people being interviewed are key stakeholders in the purchase decision or deployment and use of the product or service that is being highlighted. Content writers should work off a set list of questions prepared in advance. It can be helpful to share these with the interviewees beforehand so they have time to consider and craft their responses. One of the best interview tactics to keep in mind is to ask questions where yes and no are not natural answers. This way, your subject will provide more open-ended responses that produce more meaningful content.
4. Choose the right format
There are a number of different ways to format a case study. Depending on what you hope to achieve, one style will be better than another. However, there are some common elements to include, such as:
- An engaging headline
- A subject and customer introduction
- The unique challenge or challenges the customer faced
- The solution the customer used to solve the problem
- The results achieved
- Data and statistics to back up claims of success
- A strong call to action (CTA) to engage with the vendor
It’s also important to note that while case studies are traditionally written as stories, they don’t have to be in a written format. Some companies choose to get more creative with their case studies and produce multimedia content, depending on their audience and objectives. Case study formats can include traditional print stories, interactive web or social content, data-heavy infographics, professionally shot videos, podcasts, and more.
5. Write your case study
We’ll go into more detail later about how exactly to write a case study, including templates and examples. Generally speaking, though, there are a few things to keep in mind when writing your case study.
- Be clear and concise. Readers want to get to the point of the story quickly and easily, and they’ll be looking to see themselves reflected in the story right from the start.
- Provide a big picture. Always make sure to explain who the client is, their goals, and how they achieved success in a short introduction to engage the reader.
- Construct a clear narrative. Stick to the story from the perspective of the customer and what they needed to solve instead of just listing product features or benefits.
- Leverage graphics. Incorporating infographics, charts, and sidebars can be a more engaging and eye-catching way to share key statistics and data in readable ways.
- Offer the right amount of detail. Most case studies are one or two pages with clear sections that a reader can skim to find the information most important to them.
- Include data to support claims. Show real results — both facts and figures and customer quotes — to demonstrate credibility and prove the solution works.
6. Promote your story
Marketers have a number of options for distribution of a freshly minted case study. Many brands choose to publish case studies on their website and post them on social media. This can help support SEO and organic content strategies while also boosting company credibility and trust as visitors see that other businesses have used the product or service.
Marketers are always looking for quality content they can use for lead generation. Consider offering a case study as gated content behind a form on a landing page or as an offer in an email message. One great way to do this is to summarize the content and tease the full story available for download after the user takes an action.
Sales teams can also leverage case studies, so be sure they are aware that the assets exist once they’re published. Especially when it comes to larger B2B sales, companies often ask for examples of similar customer challenges that have been solved.
Now that you’ve learned a bit about case studies and what they should include, you may be wondering how to start creating great customer story content. Here are a couple of templates you can use to structure your case study.
Template 1 — Challenge-solution-result format
- Start with an engaging title. This should be fewer than 70 characters long for SEO best practices. One of the best ways to approach the title is to include the customer’s name and a hint at the challenge they overcame in the end.
- Create an introduction. Lead with an explanation as to who the customer is, the need they had, and the opportunity they found with a specific product or solution. Writers can also suggest the success the customer experienced with the solution they chose.
- Present the challenge. This should be several paragraphs long and explain the problem the customer faced and the issues they were trying to solve. Details should tie into the company’s products and services naturally. This section needs to be the most relatable to the reader so they can picture themselves in a similar situation.
- Share the solution. Explain which product or service offered was the ideal fit for the customer and why. Feel free to delve into their experience setting up, purchasing, and onboarding the solution.
- Explain the results. Demonstrate the impact of the solution they chose by backing up their positive experience with data. Fill in with customer quotes and tangible, measurable results that show the effect of their choice.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that invites readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to nurture them further in the marketing pipeline. What you ask of the reader should tie directly into the goals that were established for the case study in the first place.
Template 2 — Data-driven format
- Start with an engaging title. Be sure to include a statistic or data point in the first 70 characters. Again, it’s best to include the customer’s name as part of the title.
- Create an overview. Share the customer’s background and a short version of the challenge they faced. Present the reason a particular product or service was chosen, and feel free to include quotes from the customer about their selection process.
- Present data point 1. Isolate the first metric that the customer used to define success and explain how the product or solution helped to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 2. Isolate the second metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 3. Isolate the final metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Summarize the results. Reiterate the fact that the customer was able to achieve success thanks to a specific product or service. Include quotes and statements that reflect customer satisfaction and suggest they plan to continue using the solution.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that asks readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to further nurture them in the marketing pipeline. Again, remember that this is where marketers can look to convert their content into action with the customer.
While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success.
Juniper Networks
One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study , which puts the reader in the customer’s shoes. The beginning of the story quickly orients the reader so that they know exactly who the article is about and what they were trying to achieve. Solutions are outlined in a way that shows Adobe Experience Manager is the best choice and a natural fit for the customer. Along the way, quotes from the client are incorporated to help add validity to the statements. The results in the case study are conveyed with clear evidence of scale and volume using tangible data.

The story of Lenovo’s journey with Adobe is one that spans years of planning, implementation, and rollout. The Lenovo case study does a great job of consolidating all of this into a relatable journey that other enterprise organizations can see themselves taking, despite the project size. This case study also features descriptive headers and compelling visual elements that engage the reader and strengthen the content.
Tata Consulting
When it comes to using data to show customer results, this case study does an excellent job of conveying details and numbers in an easy-to-digest manner. Bullet points at the start break up the content while also helping the reader understand exactly what the case study will be about. Tata Consulting used Adobe to deliver elevated, engaging content experiences for a large telecommunications client of its own — an objective that’s relatable for a lot of companies.
Case studies are a vital tool for any marketing team as they enable you to demonstrate the value of your company’s products and services to others. They help marketers do their job and add credibility to a brand trying to promote its solutions by using the experiences and stories of real customers.
When you’re ready to get started with a case study:
- Think about a few goals you’d like to accomplish with your content.
- Make a list of successful clients that would be strong candidates for a case study.
- Reach out to the client to get their approval and conduct an interview.
- Gather the data to present an engaging and effective customer story.
Adobe can help
There are several Adobe products that can help you craft compelling case studies. Adobe Experience Platform helps you collect data and deliver great customer experiences across every channel. Once you’ve created your case studies, Experience Platform will help you deliver the right information to the right customer at the right time for maximum impact.
To learn more, watch the Adobe Experience Platform story .
Keep in mind that the best case studies are backed by data. That’s where Adobe Real-Time Customer Data Platform and Adobe Analytics come into play. With Real-Time CDP, you can gather the data you need to build a great case study and target specific customers to deliver the content to the right audience at the perfect moment.
Watch the Real-Time CDP overview video to learn more.
Finally, Adobe Analytics turns real-time data into real-time insights. It helps your business collect and synthesize data from multiple platforms to make more informed decisions and create the best case study possible.
Request a demo to learn more about Adobe Analytics.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/b2b-ecommerce-10-case-studies-inspire-you
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/business-case
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-real-time-analytics

Business growth
Marketing tips
16 case study examples (+ 3 templates to make your own)
I like to think of case studies as a business's version of a resume. It highlights what the business can do, lends credibility to its offer, and contains only the positive bullet points that paint it in the best light possible.
Imagine if the guy running your favorite taco truck followed you home so that he could "really dig into how that burrito changed your life." I see the value in the practice. People naturally prefer a tried-and-true burrito just as they prefer tried-and-true products or services.
To help you showcase your success and flesh out your burrito questionnaire, I've put together some case study examples and key takeaways.
What is a case study?
A case study is an in-depth analysis of how your business, product, or service has helped past clients. It can be a document, a webpage, or a slide deck that showcases measurable, real-life results.
For example, if you're a SaaS company, you can analyze your customers' results after a few months of using your product to measure its effectiveness. You can then turn this analysis into a case study that further proves to potential customers what your product can do and how it can help them overcome their challenges.
It changes the narrative from "I promise that we can do X and Y for you" to "Here's what we've done for businesses like yours, and we can do it for you, too."
16 case study examples
While most case studies follow the same structure, quite a few try to break the mold and create something unique. Some businesses lean heavily on design and presentation, while others pursue a detailed, stat-oriented approach. Some businesses try to mix both.
There's no set formula to follow, but I've found that the best case studies utilize impactful design to engage readers and leverage statistics and case details to drive the point home. A case study typically highlights the companies, the challenges, the solution, and the results. The examples below will help inspire you to do it, too.
1. .css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class]{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;cursor:pointer;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class]{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Volcanica Coffee and AdRoll

People love a good farm-to-table coffee story, and boy am I one of them. But I've shared this case study with you for more reasons than my love of coffee. I enjoyed this study because it was written as though it was a letter.
In this case study, the founder of Volcanica Coffee talks about the journey from founding the company to personally struggling with learning and applying digital marketing to finding and enlisting AdRoll's services.
It felt more authentic, less about AdRoll showcasing their worth and more like a testimonial from a grateful and appreciative client. After the story, the case study wraps up with successes, milestones, and achievements. Note that quite a few percentages are prominently displayed at the top, providing supporting evidence that backs up an inspiring story.
Takeaway: Highlight your goals and measurable results to draw the reader in and provide concise, easily digestible information.
2. Taylor Guitars and Airtable

This Airtable case study on Taylor Guitars comes as close as one can to an optimal structure. It features a video that represents the artistic nature of the client, highlighting key achievements and dissecting each element of Airtable's influence.
It also supplements each section with a testimonial or quote from the client, using their insights as a catalyst for the case study's narrative. For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail.
Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail.
3. EndeavourX and Figma

My favorite part of Figma's case study is highlighting why EndeavourX chose its solution. You'll notice an entire section on what Figma does for teams and then specifically for EndeavourX.
It also places a heavy emphasis on numbers and stats. The study, as brief as it is, still manages to pack in a lot of compelling statistics about what's possible with Figma.
Takeaway: Showcase the "how" and "why" of your product's differentiators and how they benefit your customers.
4. ActiveCampaign and Zapier

Zapier's case study leans heavily on design, using graphics to present statistics and goals in a manner that not only remains consistent with the branding but also actively pushes it forward, drawing users' eyes to the information most important to them.
The graphics, emphasis on branding elements, and cause/effect style tell the story without requiring long, drawn-out copy that risks boring readers. Instead, the cause and effect are concisely portrayed alongside the client company's information for a brief and easily scannable case study.
Takeaway: Lean on design to call attention to the most important elements of your case study, and make sure it stays consistent with your branding.
5. Ironclad and OpenAI
In true OpenAI fashion, this case study is a block of text. There's a distinct lack of imagery, but the study features a narrated video walking readers through the product.
The lack of imagery and color may not be the most inviting, but utilizing video format is commendable. It helps thoroughly communicate how OpenAI supported Ironclad in a way that allows the user to sit back, relax, listen, and be impressed.
Takeaway: Get creative with the media you implement in your case study. Videos can be a very powerful addition when a case study requires more detailed storytelling.
6. Shopify and GitHub

GitHub's case study on Shopify is a light read. It addresses client pain points and discusses the different aspects its product considers and improves for clients. It touches on workflow issues, internal systems, automation, and security. It does a great job of representing what one company can do with GitHub.
To drive the point home, the case study features colorful quote callouts from the Shopify team, sharing their insights and perspectives on the partnership, the key issues, and how they were addressed.
Takeaway: Leverage quotes to boost the authoritativeness and trustworthiness of your case study.
7 . Audible and Contentful

Contentful's case study on Audible features almost every element a case study should. It includes not one but two videos and clearly outlines the challenge, solution, and outcome before diving deeper into what Contentful did for Audible. The language is simple, and the writing is heavy with quotes and personal insights.
This case study is a uniquely original experience. The fact that the companies in question are perhaps two of the most creative brands out there may be the reason. I expected nothing short of a detailed analysis, a compelling story, and video content.
Takeaway: Inject some brand voice into the case study, and create assets that tell the story for you.
8 . Zoom and Asana
Asana's case study on Zoom is longer than the average piece and features detailed data on Zoom's growth since 2020. Instead of relying on imagery and graphics, it features several quotes and testimonials.
It's designed to be direct, informative, and promotional. At some point, the case study reads more like a feature list. There were a few sections that felt a tad too promotional for my liking, but to each their own burrito.
Takeaway: Maintain a balance between promotional and informative. You want to showcase the high-level goals your product helped achieve without losing the reader.
9 . Hickies and Mailchimp

I've always been a fan of Mailchimp's comic-like branding, and this case study does an excellent job of sticking to their tradition of making information easy to understand, casual, and inviting.
It features a short video that briefly covers Hickies as a company and Mailchimp's efforts to serve its needs for customer relationships and education processes. Overall, this case study is a concise overview of the partnership that manages to convey success data and tell a story at the same time. What sets it apart is that it does so in a uniquely colorful and brand-consistent manner.
Takeaway: Be concise to provide as much value in as little text as possible.
10. NVIDIA and Workday
The gaming industry is notoriously difficult to recruit for, as it requires a very specific set of skills and experience. This case study focuses on how Workday was able to help fill that recruitment gap for NVIDIA, one of the biggest names in the gaming world.
Though it doesn't feature videos or graphics, this case study stood out to me in how it structures information like "key products used" to give readers insight into which tools helped achieve these results.
Takeaway: If your company offers multiple products or services, outline exactly which ones were involved in your case study, so readers can assess each tool.
11. KFC and Contentful
I'm personally not a big KFC fan, but that's only because I refuse to eat out of a bucket. My aversion to the bucket format aside, Contentful follows its consistent case study format in this one, outlining challenges, solutions, and outcomes before diving into the nitty-gritty details of the project.
Say what you will about KFC, but their primary product (chicken) does present a unique opportunity for wordplay like "Continuing to march to the beat of a digital-first drum(stick)" or "Delivering deep-fried goodness to every channel."
Takeaway: Inject humor into your case study if there's room for it and if it fits your brand.
12. Intuit and Twilio

Twilio does an excellent job of delivering achievements at the very beginning of the case study and going into detail in this two-minute read. While there aren't many graphics, the way quotes from the Intuit team are implemented adds a certain flair to the study and breaks up the sections nicely.
It's simple, concise, and manages to fit a lot of information in easily digestible sections.
Takeaway: Make sure each section is long enough to inform but brief enough to avoid boring readers. Break down information for each section, and don't go into so much detail that you lose the reader halfway through.
13. Spotify and Salesforce

Salesforce created a video that accurately summarizes the key points of the case study. Beyond that, the page itself is very light on content, and sections are as short as one paragraph.
I especially like how information is broken down into "What you need to know," "Why it matters," and "What the difference looks like." I'm not ashamed of being spoon-fed information. When it's structured so well and so simply, it makes for an entertaining read.
Takeaway: Invest in videos that capture and promote your partnership with your case study subject. Video content plays a promotional role that extends beyond the case study in social media and marketing initiatives .
14. Benchling and Airtable

Benchling is an impressive entity in its own right. Biotech R&D and health care nuances go right over my head. But the research and digging I've been doing in the name of these burritos (case studies) revealed that these products are immensely complex.
And that's precisely why this case study deserves a read—it succeeds at explaining a complex project that readers outside the industry wouldn't know much about.
Takeaway: Simplify complex information, and walk readers through the company's operations and how your business helped streamline them.
15. Chipotle and Hubble

The concision of this case study is refreshing. It features two sections—the challenge and the solution—all in 316 words. This goes to show that your case study doesn't necessarily need to be a four-figure investment with video shoots and studio time.
Sometimes, the message is simple and short enough to convey in a handful of paragraphs.
Takeaway: Consider what you should include instead of what you can include. Assess the time, resources, and effort you're able and willing to invest in a case study, and choose which elements you want to include from there.
16. Hudl and Zapier
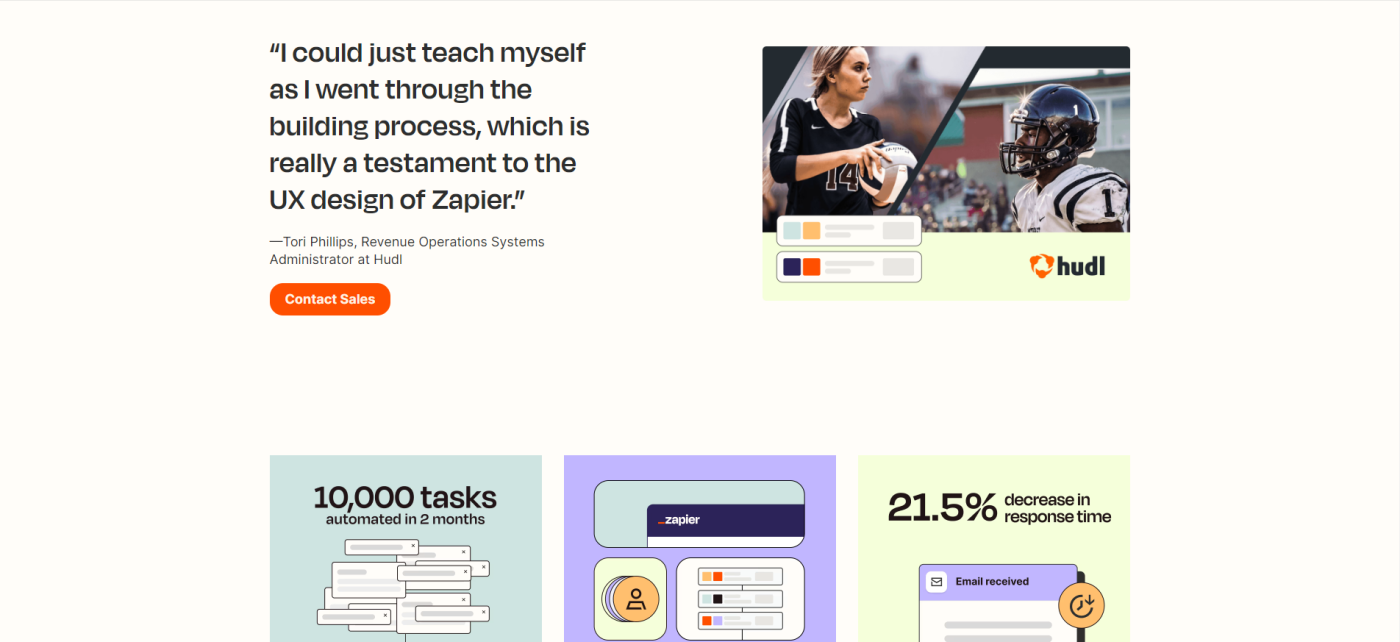
I may be biased, but I'm a big fan of seeing metrics and achievements represented in branded graphics. It can be a jarring experience to navigate a website, then visit a case study page and feel as though you've gone to a completely different website.
The Zapier format provides nuggets of high-level insights, milestones, and achievements, as well as the challenge, solution, and results. My favorite part of this case study is how it's supplemented with a blog post detailing how Hudl uses Zapier automation to build a seamless user experience.
The case study is essentially the summary, and the blog article is the detailed analysis that provides context beyond X achievement or Y goal.
Takeaway: Keep your case study concise and informative. Create other resources to provide context under your blog, media or press, and product pages.
3 case study templates
Now that you've had your fill of case studies (if that's possible), I've got just what you need: an infinite number of case studies, which you can create yourself with these case study templates.
Case study template 1

If you've got a quick hit of stats you want to show off, try this template. The opening section gives space for a short summary and three visually appealing stats you can highlight, followed by a headline and body where you can break the case study down more thoroughly. This one's pretty simple, with only sections for solutions and results, but you can easily continue the formatting to add more sections as needed.
Case study template 2

For a case study template with a little more detail, use this one. Opening with a striking cover page for a quick overview, this one goes on to include context, stakeholders, challenges, multiple quote callouts, and quick-hit stats.
Case study template 3

Whether you want a little structural variation or just like a nice dark green, this template has similar components to the last template but is designed to help tell a story. Move from the client overview through a description of your company before getting to the details of how you fixed said company's problems.
Tips for writing a case study
Examples are all well and good, but you don't learn how to make a burrito just by watching tutorials on YouTube without knowing what any of the ingredients are. You could , but it probably wouldn't be all that good.
Writing a good case study comes down to a mix of creativity, branding, and the capacity to invest in the project. With those details in mind, here are some case study tips to follow:
Have an objective: Define your objective by identifying the challenge, solution, and results. Assess your work with the client and focus on the most prominent wins. You're speaking to multiple businesses and industries through the case study, so make sure you know what you want to say to them.
Focus on persuasive data: Growth percentages and measurable results are your best friends. Extract your most compelling data and highlight it in your case study.
Use eye-grabbing graphics: Branded design goes a long way in accurately representing your brand and retaining readers as they review the study. Leverage unique and eye-catching graphics to keep readers engaged.
Simplify data presentation: Some industries are more complex than others, and sometimes, data can be difficult to understand at a glance. Make sure you present your data in the simplest way possible. Make it concise, informative, and easy to understand.
Use automation to drive results for your case study
A case study example is a source of inspiration you can leverage to determine how to best position your brand's work. Find your unique angle, and refine it over time to help your business stand out. Ask anyone: the best burrito in town doesn't just appear at the number one spot. They find their angle (usually the house sauce) and leverage it to stand out.
In fact, with the right technology, it can be refined to work better . Explore how Zapier's automation features can help drive results for your case study by making your case study a part of a developed workflow that creates a user journey through your website, your case studies, and into the pipeline.
Case study FAQ
Got your case study template? Great—it's time to gather the team for an awkward semi-vague data collection task. While you do that, here are some case study quick answers for you to skim through while you contemplate what to call your team meeting.
What is an example of a case study?
An example of a case study is when a software company analyzes its results from a client project and creates a webpage, presentation, or document that focuses on high-level results, challenges, and solutions in an attempt to showcase effectiveness and promote the software.
How do you write a case study?
To write a good case study, you should have an objective, identify persuasive and compelling data, leverage graphics, and simplify data. Case studies typically include an analysis of the challenge, solution, and results of the partnership.
What is the format of a case study?
While case studies don't have a set format, they're often portrayed as reports or essays that inform readers about the partnership and its results.
Related reading:
How Hudl uses automation to create a seamless user experience
How to make your case studies high-stakes—and why it matters
How experts write case studies that convert, not bore
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Hachem Ramki
Hachem is a writer and digital marketer from Montreal. After graduating with a degree in English, Hachem spent seven years traveling around the world before moving to Canada. When he's not writing, he enjoys Basketball, Dungeons and Dragons, and playing music for friends and family.
- Content marketing
Related articles

14 types of email marketing to experiment with
14 types of email marketing to experiment...
8 business anniversary marketing ideas and examples worth celebrating
8 business anniversary marketing ideas and...
A guide to verticalization: What it is, when to try it, and how to get started
A guide to verticalization: What it is, when...

12 Facebook ad copy examples to learn from
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.

We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Sep 07, 2023

Okay, let’s get real: case studies can be kinda snooze-worthy. But guess what? They don’t have to be!
In this article, I will cover every element that transforms a mere report into a compelling case study, from selecting the right metrics to using persuasive narrative techniques.
And if you’re feeling a little lost, don’t worry! There are cool tools like Venngage’s Case Study Creator to help you whip up something awesome, even if you’re short on time. Plus, the pre-designed case study templates are like instant polish because let’s be honest, everyone loves a shortcut.
Click to jump ahead:

What is a case study presentation?
What is the purpose of presenting a case study, how to structure a case study presentation, how long should a case study presentation be, 5 case study presentation examples with templates, 6 tips for delivering an effective case study presentation, 5 common mistakes to avoid in a case study presentation, how to present a case study faqs.
A case study presentation involves a comprehensive examination of a specific subject, which could range from an individual, group, location, event, organization or phenomenon.
They’re like puzzles you get to solve with the audience, all while making you think outside the box.
Unlike a basic report or whitepaper, the purpose of a case study presentation is to stimulate critical thinking among the viewers.
The primary objective of a case study is to provide an extensive and profound comprehension of the chosen topic. You don’t just throw numbers at your audience. You use examples and real-life cases to make you think and see things from different angles.

The primary purpose of presenting a case study is to offer a comprehensive, evidence-based argument that informs, persuades and engages your audience.
Here’s the juicy part: presenting that case study can be your secret weapon. Whether you’re pitching a groundbreaking idea to a room full of suits or trying to impress your professor with your A-game, a well-crafted case study can be the magic dust that sprinkles brilliance over your words.
Think of it like digging into a puzzle you can’t quite crack . A case study lets you explore every piece, turn it over and see how it fits together. This close-up look helps you understand the whole picture, not just a blurry snapshot.
It’s also your chance to showcase how you analyze things, step by step, until you reach a conclusion. It’s all about being open and honest about how you got there.
Besides, presenting a case study gives you an opportunity to connect data and real-world scenarios in a compelling narrative. It helps to make your argument more relatable and accessible, increasing its impact on your audience.
One of the contexts where case studies can be very helpful is during the job interview. In some job interviews, you as candidates may be asked to present a case study as part of the selection process.
Having a case study presentation prepared allows the candidate to demonstrate their ability to understand complex issues, formulate strategies and communicate their ideas effectively.
The way you present a case study can make all the difference in how it’s received. A well-structured presentation not only holds the attention of your audience but also ensures that your key points are communicated clearly and effectively.
In this section, let’s go through the key steps that’ll help you structure your case study presentation for maximum impact.
Let’s get into it.
Open with an introductory overview
Start by introducing the subject of your case study and its relevance. Explain why this case study is important and who would benefit from the insights gained. This is your opportunity to grab your audience’s attention.

Explain the problem in question
Dive into the problem or challenge that the case study focuses on. Provide enough background information for the audience to understand the issue. If possible, quantify the problem using data or metrics to show the magnitude or severity.

Detail the solutions to solve the problem
After outlining the problem, describe the steps taken to find a solution. This could include the methodology, any experiments or tests performed and the options that were considered. Make sure to elaborate on why the final solution was chosen over the others.

Key stakeholders Involved
Talk about the individuals, groups or organizations that were directly impacted by or involved in the problem and its solution.
Stakeholders may experience a range of outcomes—some may benefit, while others could face setbacks.
For example, in a business transformation case study, employees could face job relocations or changes in work culture, while shareholders might be looking at potential gains or losses.
Discuss the key results & outcomes
Discuss the results of implementing the solution. Use data and metrics to back up your statements. Did the solution meet its objectives? What impact did it have on the stakeholders? Be honest about any setbacks or areas for improvement as well.
Include visuals to support your analysis
Visual aids can be incredibly effective in helping your audience grasp complex issues. Utilize charts, graphs, images or video clips to supplement your points. Make sure to explain each visual and how it contributes to your overall argument.
Pie charts illustrate the proportion of different components within a whole, useful for visualizing market share, budget allocation or user demographics.
This is particularly useful especially if you’re displaying survey results in your case study presentation.
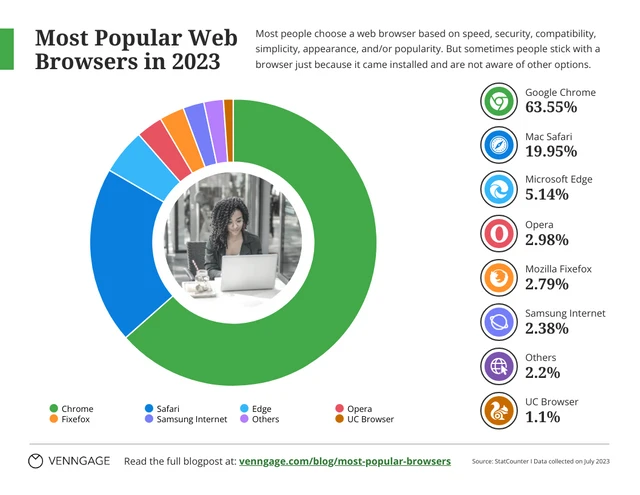
Stacked charts on the other hand are perfect for visualizing composition and trends. This is great for analyzing things like customer demographics, product breakdowns or budget allocation in your case study.
Consider this example of a stacked bar chart template. It provides a straightforward summary of the top-selling cake flavors across various locations, offering a quick and comprehensive view of the data.
Not the chart you’re looking for? Browse Venngage’s gallery of chart templates to find the perfect one that’ll captivate your audience and level up your data storytelling.
Recommendations and next steps
Wrap up by providing recommendations based on the case study findings. Outline the next steps that stakeholders should take to either expand on the success of the project or address any remaining challenges.
Acknowledgments and references
Thank the people who contributed to the case study and helped in the problem-solving process. Cite any external resources, reports or data sets that contributed to your analysis.
Feedback & Q&A session
Open the floor for questions and feedback from your audience. This allows for further discussion and can provide additional insights that may not have been considered previously.
Closing remarks
Conclude the presentation by summarizing the key points and emphasizing the takeaways. Thank your audience for their time and participation and express your willingness to engage in further discussions or collaborations on the subject.

Well, the length of a case study presentation can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the needs of your audience. However, a typical business or academic presentation often lasts between 15 to 30 minutes.
This time frame usually allows for a thorough explanation of the case while maintaining audience engagement. However, always consider leaving a few minutes at the end for a Q&A session to address any questions or clarify points made during the presentation.
When it comes to presenting a compelling case study, having a well-structured template can be a game-changer.
It helps you organize your thoughts, data and findings in a coherent and visually pleasing manner.
Not all case studies are created equal and different scenarios require distinct approaches for maximum impact.
To save you time and effort, I have curated a list of 5 versatile case study presentation templates, each designed for specific needs and audiences.
Here are some best case study presentation examples that showcase effective strategies for engaging your audience and conveying complex information clearly.
1 . Lab report case study template
Ever feel like your research gets lost in a world of endless numbers and jargon? Lab case studies are your way out!
Think of it as building a bridge between your cool experiment and everyone else. It’s more than just reporting results – it’s explaining the “why” and “how” in a way that grabs attention and makes sense.
This lap report template acts as a blueprint for your report, guiding you through each essential section (introduction, methods, results, etc.) in a logical order.

Want to present your research like a pro? Browse our research presentation template gallery for creative inspiration!
2. Product case study template
It’s time you ditch those boring slideshows and bullet points because I’ve got a better way to win over clients: product case study templates.
Instead of just listing features and benefits, you get to create a clear and concise story that shows potential clients exactly what your product can do for them. It’s like painting a picture they can easily visualize, helping them understand the value your product brings to the table.
Grab the template below, fill in the details, and watch as your product’s impact comes to life!

3. Content marketing case study template
In digital marketing, showcasing your accomplishments is as vital as achieving them.
A well-crafted case study not only acts as a testament to your successes but can also serve as an instructional tool for others.
With this coral content marketing case study template—a perfect blend of vibrant design and structured documentation, you can narrate your marketing triumphs effectively.

4. Case study psychology template
Understanding how people tick is one of psychology’s biggest quests and case studies are like magnifying glasses for the mind. They offer in-depth looks at real-life behaviors, emotions and thought processes, revealing fascinating insights into what makes us human.
Writing a top-notch case study, though, can be a challenge. It requires careful organization, clear presentation and meticulous attention to detail. That’s where a good case study psychology template comes in handy.
Think of it as a helpful guide, taking care of formatting and structure while you focus on the juicy content. No more wrestling with layouts or margins – just pour your research magic into crafting a compelling narrative.
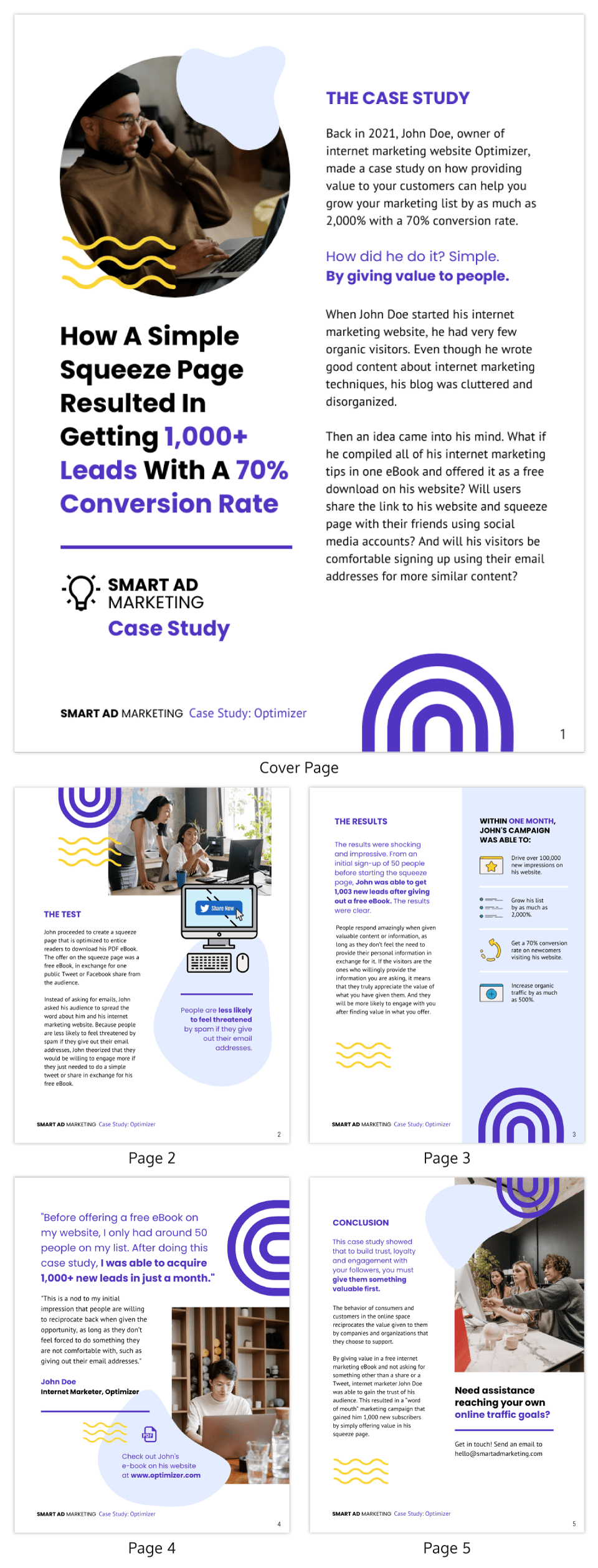
5. Lead generation case study template
Lead generation can be a real head-scratcher. But here’s a little help: a lead generation case study.
Think of it like a friendly handshake and a confident resume all rolled into one. It’s your chance to showcase your expertise, share real-world successes and offer valuable insights. Potential clients get to see your track record, understand your approach and decide if you’re the right fit.
No need to start from scratch, though. This lead generation case study template guides you step-by-step through crafting a clear, compelling narrative that highlights your wins and offers actionable tips for others. Fill in the gaps with your specific data and strategies, and voilà! You’ve got a powerful tool to attract new customers.
Related: 15+ Professional Case Study Examples [Design Tips + Templates]
So, you’ve spent hours crafting the perfect case study and are now tasked with presenting it. Crafting the case study is only half the battle; delivering it effectively is equally important.
Whether you’re facing a room of executives, academics or potential clients, how you present your findings can make a significant difference in how your work is received.
Forget boring reports and snooze-inducing presentations! Let’s make your case study sing. Here are some key pointers to turn information into an engaging and persuasive performance:
- Know your audience : Tailor your presentation to the knowledge level and interests of your audience. Remember to use language and examples that resonate with them.
- Rehearse : Rehearsing your case study presentation is the key to a smooth delivery and for ensuring that you stay within the allotted time. Practice helps you fine-tune your pacing, hone your speaking skills with good word pronunciations and become comfortable with the material, leading to a more confident, conversational and effective presentation.
- Start strong : Open with a compelling introduction that grabs your audience’s attention. You might want to use an interesting statistic, a provocative question or a brief story that sets the stage for your case study.
- Be clear and concise : Avoid jargon and overly complex sentences. Get to the point quickly and stay focused on your objectives.
- Use visual aids : Incorporate slides with graphics, charts or videos to supplement your verbal presentation. Make sure they are easy to read and understand.
- Tell a story : Use storytelling techniques to make the case study more engaging. A well-told narrative can help you make complex data more relatable and easier to digest.

Ditching the dry reports and slide decks? Venngage’s case study templates let you wow customers with your solutions and gain insights to improve your business plan. Pre-built templates, visual magic and customer captivation – all just a click away. Go tell your story and watch them say “wow!”
Nailed your case study, but want to make your presentation even stronger? Avoid these common mistakes to ensure your audience gets the most out of it:
Overloading with information
A case study is not an encyclopedia. Overloading your presentation with excessive data, text or jargon can make it cumbersome and difficult for the audience to digest the key points. Stick to what’s essential and impactful. Need help making your data clear and impactful? Our data presentation templates can help! Find clear and engaging visuals to showcase your findings.
Lack of structure
Jumping haphazardly between points or topics can confuse your audience. A well-structured presentation, with a logical flow from introduction to conclusion, is crucial for effective communication.
Ignoring the audience
Different audiences have different needs and levels of understanding. Failing to adapt your presentation to your audience can result in a disconnect and a less impactful presentation.
Poor visual elements
While content is king, poor design or lack of visual elements can make your case study dull or hard to follow. Make sure you use high-quality images, graphs and other visual aids to support your narrative.
Not focusing on results
A case study aims to showcase a problem and its solution, but what most people care about are the results. Failing to highlight or adequately explain the outcomes can make your presentation fall flat.
How to start a case study presentation?
Starting a case study presentation effectively involves a few key steps:
- Grab attention : Open with a hook—an intriguing statistic, a provocative question or a compelling visual—to engage your audience from the get-go.
- Set the stage : Briefly introduce the subject, context and relevance of the case study to give your audience an idea of what to expect.
- Outline objectives : Clearly state what the case study aims to achieve. Are you solving a problem, proving a point or showcasing a success?
- Agenda : Give a quick outline of the key sections or topics you’ll cover to help the audience follow along.
- Set expectations : Let your audience know what you want them to take away from the presentation, whether it’s knowledge, inspiration or a call to action.
How to present a case study on PowerPoint and on Google Slides?
Presenting a case study on PowerPoint and Google Slides involves a structured approach for clarity and impact using presentation slides :
- Title slide : Start with a title slide that includes the name of the case study, your name and any relevant institutional affiliations.
- Introduction : Follow with a slide that outlines the problem or situation your case study addresses. Include a hook to engage the audience.
- Objectives : Clearly state the goals of the case study in a dedicated slide.
- Findings : Use charts, graphs and bullet points to present your findings succinctly.
- Analysis : Discuss what the findings mean, drawing on supporting data or secondary research as necessary.
- Conclusion : Summarize key takeaways and results.
- Q&A : End with a slide inviting questions from the audience.
What’s the role of analysis in a case study presentation?
The role of analysis in a case study presentation is to interpret the data and findings, providing context and meaning to them.
It helps your audience understand the implications of the case study, connects the dots between the problem and the solution and may offer recommendations for future action.
Is it important to include real data and results in the presentation?
Yes, including real data and results in a case study presentation is crucial to show experience, credibility and impact. Authentic data lends weight to your findings and conclusions, enabling the audience to trust your analysis and take your recommendations more seriously
How do I conclude a case study presentation effectively?
To conclude a case study presentation effectively, summarize the key findings, insights and recommendations in a clear and concise manner.
End with a strong call-to-action or a thought-provoking question to leave a lasting impression on your audience.
What’s the best way to showcase data in a case study presentation ?
The best way to showcase data in a case study presentation is through visual aids like charts, graphs and infographics which make complex information easily digestible, engaging and creative.
Don’t just report results, visualize them! This template for example lets you transform your social media case study into a captivating infographic that sparks conversation.

Choose the type of visual that best represents the data you’re showing; for example, use bar charts for comparisons or pie charts for parts of a whole.
Ensure that the visuals are high-quality and clearly labeled, so the audience can quickly grasp the key points.
Keep the design consistent and simple, avoiding clutter or overly complex visuals that could distract from the message.
Choose a template that perfectly suits your case study where you can utilize different visual aids for maximum impact.
Need more inspiration on how to turn numbers into impact with the help of infographics? Our ready-to-use infographic templates take the guesswork out of creating visual impact for your case studies with just a few clicks.
Related: 10+ Case Study Infographic Templates That Convert
Congrats on mastering the art of compelling case study presentations! This guide has equipped you with all the essentials, from structure and nuances to avoiding common pitfalls. You’re ready to impress any audience, whether in the boardroom, the classroom or beyond.
And remember, you’re not alone in this journey. Venngage’s Case Study Creator is your trusty companion, ready to elevate your presentations from ordinary to extraordinary. So, let your confidence shine, leverage your newly acquired skills and prepare to deliver presentations that truly resonate.
Go forth and make a lasting impact!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 9:45 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
Writing A Case Study
Case Study Examples
Brilliant Case Study Examples and Templates For Your Help
15 min read
People also read
A Complete Case Study Writing Guide With Examples
Simple Case Study Format for Students to Follow
Understand the Types of Case Study Here
It’s no surprise that writing a case study is one of the most challenging academic tasks for students. You’re definitely not alone here!
Most people don't realize that there are specific guidelines to follow when writing a case study. If you don't know where to start, it's easy to get overwhelmed and give up before you even begin.
Don't worry! Let us help you out!
We've collected over 25 free case study examples with solutions just for you. These samples with solutions will help you win over your panel and score high marks on your case studies.
So, what are you waiting for? Let's dive in and learn the secrets to writing a successful case study.
- 1. An Overview of Case Studies
- 2. Case Study Examples for Students
- 3. Business Case Study Examples
- 4. Medical Case Study Examples
- 5. Psychology Case Study Examples
- 6. Sales Case Study Examples
- 7. Interview Case Study Examples
- 8. Marketing Case Study Examples
- 9. Tips to Write a Good Case Study
An Overview of Case Studies
A case study is a research method used to study a particular individual, group, or situation in depth. It involves analyzing and interpreting data from a variety of sources to gain insight into the subject being studied.
Case studies are often used in psychology, business, and education to explore complicated problems and find solutions. They usually have detailed descriptions of the subject, background info, and an analysis of the main issues.
The goal of a case study is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject. Typically, case studies can be divided into three parts, challenges, solutions, and results.
Here is a case study sample PDF so you can have a clearer understanding of what a case study actually is:
Case Study Sample PDF
How to Write a Case Study Examples
Learn how to write a case study with the help of our comprehensive case study guide.
Case Study Examples for Students
Quite often, students are asked to present case studies in their academic journeys. The reason instructors assign case studies is for students to sharpen their critical analysis skills, understand how companies make profits, etc.
Below are some case study examples in research, suitable for students:
Case Study Example in Software Engineering
Qualitative Research Case Study Sample
Software Quality Assurance Case Study
Social Work Case Study Example
Ethical Case Study
Case Study Example PDF
These examples can guide you on how to structure and format your own case studies.
Struggling with formatting your case study? Check this case study format guide and perfect your document’s structure today.
Business Case Study Examples
A business case study examines a business’s specific challenge or goal and how it should be solved. Business case studies usually focus on several details related to the initial challenge and proposed solution.
To help you out, here are some samples so you can create case studies that are related to businesses:
Here are some more business case study examples:
Business Case Studies PDF
Business Case Studies Example
Typically, a business case study discovers one of your customer's stories and how you solved a problem for them. It allows your prospects to see how your solutions address their needs.
Medical Case Study Examples
Medical case studies are an essential part of medical education. They help students to understand how to diagnose and treat patients.
Here are some medical case study examples to help you.
Medical Case Study Example
Nursing Case Study Example
Want to understand the various types of case studies? Check out our types of case study blog to select the perfect type.
Psychology Case Study Examples
Case studies are a great way of investigating individuals with psychological abnormalities. This is why it is a very common assignment in psychology courses.
By examining all the aspects of your subject’s life, you discover the possible causes of exhibiting such behavior.
For your help, here are some interesting psychology case study examples:
Psychology Case Study Example
Mental Health Case Study Example
Sales Case Study Examples
Case studies are important tools for sales teams’ performance improvement. By examining sales successes, teams can gain insights into effective strategies and create action plans to employ similar tactics.
By researching case studies of successful sales campaigns, sales teams can more accurately identify challenges and develop solutions.
Sales Case Study Example
Interview Case Study Examples
Interview case studies provide businesses with invaluable information. This data allows them to make informed decisions related to certain markets or subjects.
Interview Case Study Example
Marketing Case Study Examples
Marketing case studies are real-life stories that showcase how a business solves a problem. They typically discuss how a business achieves a goal using a specific marketing strategy or tactic.
They typically describe a challenge faced by a business, the solution implemented, and the results achieved.
This is a short sample marketing case study for you to get an idea of what an actual marketing case study looks like.
Here are some more popular marketing studies that show how companies use case studies as a means of marketing and promotion:
“Chevrolet Discover the Unexpected” by Carol H. Williams
This case study explores Chevrolet's “ DTU Journalism Fellows ” program. The case study uses the initials “DTU” to generate interest and encourage readers to learn more.
Multiple types of media, such as images and videos, are used to explain the challenges faced. The case study concludes with an overview of the achievements that were met.
Key points from the case study include:
- Using a well-known brand name in the title can create interest.
- Combining different media types, such as headings, images, and videos, can help engage readers and make the content more memorable.
- Providing a summary of the key achievements at the end of the case study can help readers better understand the project's impact.
“The Met” by Fantasy
“ The Met ” by Fantasy is a fictional redesign of the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, created by the design studio Fantasy. The case study clearly and simply showcases the museum's website redesign.
The Met emphasizes the website’s features and interface by showcasing each section of the interface individually, allowing the readers to concentrate on the significant elements.
For those who prefer text, each feature includes an objective description. The case study also includes a “Contact Us” call-to-action at the bottom of the page, inviting visitors to contact the company.
Key points from this “The Met” include:
- Keeping the case study simple and clean can help readers focus on the most important aspects.
- Presenting the features and solutions with a visual showcase can be more effective than writing a lot of text.
- Including a clear call-to-action at the end of the case study can encourage visitors to contact the company for more information.
“Better Experiences for All” by Herman Miller
Herman Miller's minimalist approach to furniture design translates to their case study, “ Better Experiences for All ”, for a Dubai hospital. The page features a captivating video with closed-captioning and expandable text for accessibility.
The case study presents a wealth of information in a concise format, enabling users to grasp the complexities of the strategy with ease. It concludes with a client testimonial and a list of furniture items purchased from the brand.
Key points from the “Better Experiences” include:
- Make sure your case study is user-friendly by including accessibility features like closed captioning and expandable text.
- Include a list of products that were used in the project to guide potential customers.
“NetApp” by Evisort
Evisort's case study on “ NetApp ” stands out for its informative and compelling approach. The study begins with a client-centric overview of NetApp, strategically directing attention to the client rather than the company or team involved.
The case study incorporates client quotes and explores NetApp’s challenges during COVID-19. Evisort showcases its value as a client partner by showing how its services supported NetApp through difficult times.
- Provide an overview of the company in the client’s words, and put focus on the customer.
- Highlight how your services can help clients during challenging times.
- Make your case study accessible by providing it in various formats.
“Red Sox Season Campaign,” by CTP Boston
The “ Red Sox Season Campaign ” showcases a perfect blend of different media, such as video, text, and images. Upon visiting the page, the video plays automatically, there are videos of Red Sox players, their images, and print ads that can be enlarged with a click.
The page features an intuitive design and invites viewers to appreciate CTP's well-rounded campaign for Boston's beloved baseball team. There’s also a CTA that prompts viewers to learn how CTP can create a similar campaign for their brand.
Some key points to take away from the “Red Sox Season Campaign”:
- Including a variety of media such as video, images, and text can make your case study more engaging and compelling.
- Include a call-to-action at the end of your study that encourages viewers to take the next step towards becoming a customer or prospect.
“Airbnb + Zendesk” by Zendesk
The case study by Zendesk, titled “ Airbnb + Zendesk : Building a powerful solution together,” showcases a true partnership between Airbnb and Zendesk.
The article begins with an intriguing opening statement, “Halfway around the globe is a place to stay with your name on it. At least for a weekend,” and uses stunning images of beautiful Airbnb locations to captivate readers.
Instead of solely highlighting Zendesk's product, the case study is crafted to tell a good story and highlight Airbnb's service in detail. This strategy makes the case study more authentic and relatable.
Some key points to take away from this case study are:
- Use client's offerings' images rather than just screenshots of your own product or service.
- To begin the case study, it is recommended to include a distinct CTA. For instance, Zendesk presents two alternatives, namely to initiate a trial or seek a solution.
“Influencer Marketing” by Trend and WarbyParker
The case study "Influencer Marketing" by Trend and Warby Parker highlights the potential of influencer content marketing, even when working with a limited budget.
The “Wearing Warby” campaign involved influencers wearing Warby Parker glasses during their daily activities, providing a glimpse of the brand's products in use.
This strategy enhanced the brand's relatability with influencers' followers. While not detailing specific tactics, the case study effectively illustrates the impact of third-person case studies in showcasing campaign results.
Key points to take away from this case study are:
- Influencer marketing can be effective even with a limited budget.
- Showcasing products being used in everyday life can make a brand more approachable and relatable.
- Third-person case studies can be useful in highlighting the success of a campaign.
Marketing Case Study Example
Marketing Case Study Template
Now that you have read multiple case study examples, hop on to our tips.
Tips to Write a Good Case Study
Here are some note-worthy tips to craft a winning case study
- Define the purpose of the case study This will help you to focus on the most important aspects of the case. The case study objective helps to ensure that your finished product is concise and to the point.
- Choose a real-life example. One of the best ways to write a successful case study is to choose a real-life example. This will give your readers a chance to see how the concepts apply in a real-world setting.
- Keep it brief. This means that you should only include information that is directly relevant to your topic and avoid adding unnecessary details.
- Use strong evidence. To make your case study convincing, you will need to use strong evidence. This can include statistics, data from research studies, or quotes from experts in the field.
- Edit and proofread your work. Before you submit your case study, be sure to edit and proofread your work carefully. This will help to ensure that there are no errors and that your paper is clear and concise.
There you go!
We’re sure that now you have secrets to writing a great case study at your fingertips! This blog teaches the key guidelines of various case studies with samples. So grab your pen and start crafting a winning case study right away!
Having said that, we do understand that some of you might be having a hard time writing compelling case studies.
But worry not! Our expert case study writing service is here to take all your case-writing blues away!
With 100% thorough research guaranteed, our online essay service can craft an amazing case study within 24 hours!
So why delay? Let us help you shine in the eyes of your instructor!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
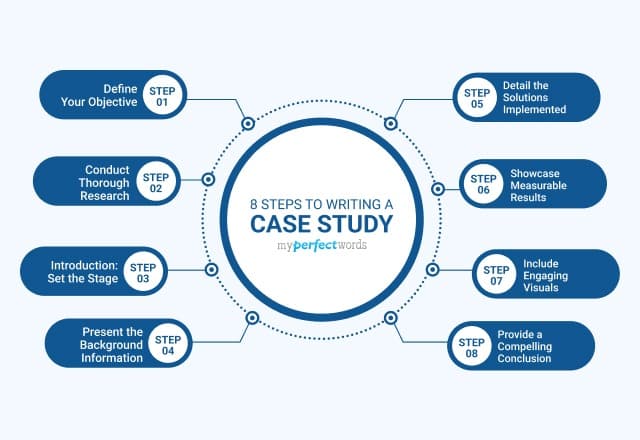
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up

- 12 Dec 2023
- Cold Call Podcast
Can Sustainability Drive Innovation at Ferrari?
When Ferrari, the Italian luxury sports car manufacturer, committed to achieving carbon neutrality and to electrifying a large part of its car fleet, investors and employees applauded the new strategy. But among the company’s suppliers, the reaction was mixed. Many were nervous about how this shift would affect their bottom lines. Professor Raffaella Sadun and Ferrari CEO Benedetto Vigna discuss how Ferrari collaborated with suppliers to work toward achieving the company’s goal. They also explore how sustainability can be a catalyst for innovation in the case, “Ferrari: Shifting to Carbon Neutrality.” This episode was recorded live December 4, 2023 in front of a remote studio audience in the Live Online Classroom at Harvard Business School.

- 12 Sep 2023
Can Remote Surgeries Digitally Transform Operating Rooms?
Launched in 2016, Proximie was a platform that enabled clinicians, proctors, and medical device company personnel to be virtually present in operating rooms, where they would use mixed reality and digital audio and visual tools to communicate with, mentor, assist, and observe those performing medical procedures. The goal was to improve patient outcomes. The company had grown quickly, and its technology had been used in tens of thousands of procedures in more than 50 countries and 500 hospitals. It had raised close to $50 million in equity financing and was now entering strategic partnerships to broaden its reach. Nadine Hachach-Haram, founder and CEO of Proximie, aspired for Proximie to become a platform that powered every operating room in the world, but she had to carefully consider the company’s partnership and data strategies in order to scale. What approach would position the company best for the next stage of growth? Harvard Business School associate professor Ariel Stern discusses creating value in health care through a digital transformation of operating rooms in her case, “Proximie: Using XR Technology to Create Borderless Operating Rooms.”

- 07 Jan 2019
- Research & Ideas
The Better Way to Forecast the Future
We can forecast hurricane paths with great certainty, yet many businesses can't predict a supply chain snafu just around the corner. Yael Grushka-Cockayne says crowdsourcing can help. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 30 Nov 2018
- What Do You Think?
What’s the Best Administrative Approach to Climate Change?
SUMMING UP: James Heskett's readers point to examples of complex environmental problems conquered through multinational cooperation. Can those serve as roadmaps for overcoming global warming? Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 04 May 2017
Leading a Team to the Top of Mount Everest
In a podcast, Amy Edmondson describes how students learn about team communication and decision making by making a simulated climb up Mount Everest. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 15 Mar 2017
- Lessons from the Classroom
More Than 900 Examples of How Climate Change Affects Business
MBA students participating in Harvard Business School’s Climate Change Challenge offer ideas on how companies can negate impacts from a changing environment. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 07 Apr 2014
Negotiation and All That Jazz
In his new book The Art of Negotiation, Michael Wheeler throws away the script to examine how master negotiators really get what they want. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 04 Sep 2013
How Relevant is Long-Range Strategic Planning?
Summing Up: Jim Heskett's readers argue that long-range planning, while necessary for organizational success, must be adaptable to the competitive environment. What do YOU think? Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 16 Jul 2012
Are You a Strategist?
Corporate strategy has become the bailiwick of consultants and business analysts, so much so that it is no longer a top-of-mind responsibility for many senior executives. Professor Cynthia A. Montgomery says it's time for CEOs to again become strategists. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 21 Dec 2011
The Most Common Strategy Mistakes
In the book, Understanding Michael Porter: The Essential Guide to Competition and Strategy, Joan Magretta distills Porter's core concepts and frameworks into a concise guide for business practitioners. In this excerpt, Porter discusses common strategy mistakes. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 09 May 2011
Moving From Bean Counter to Game Changer
New research by HBS professor Anette Mikes and colleagues looks into how accountants, finance professionals, internal auditors, and risk managers gain influence in their organizations to become strategic decision makers. Key concepts include: Many organizations have functional experts who have deep knowledge but lack influence. They can influence high-level strategic thinking in their organizations by going through a process that transforms them from "box-checkers" to "frame-makers." Frame-makers understand how important it is to attach the tools they create to C-level business goals, such as linking them to the quarterly business review. Frame-makers stay relevant by becoming personally involved in the analysis and interpretation of the tools they create. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 22 Nov 2010
Seven Strategy Questions: A Simple Approach for Better Execution
Successful business strategy lies not in having all the right answers, but rather in asking the right questions, says Harvard Business School professor Robert Simons. In an excerpt from his book Seven Strategy Questions, Simons explains how managers can make smarter choices. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 02 Jun 2010
How Do You Weigh Strategy, Execution, and Culture in an Organization’s Success?
Summing up: Respondents who ventured to place weights on the determinants of success gave the nod to culture by a wide margin, says HBS professor Jim Heskett. (Online forum now closed. Next forum opens July 2.) Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 22 Mar 2010
One Strategy: Aligning Planning and Execution
Strategy as it is written up in the corporate playbook often becomes lost or muddled when the team takes the field to execute. In their new book, Professor Marco Iansiti and Microsoft's Steven Sinofsky discuss a "One Strategy" approach to aligning plan and action. Key concepts include: The book combines practical experience at Microsoft with conceptual frameworks on how to develop strategies that are aligned with execution in a rapidly changing competitive environment. "Strategic integrity" occurs when the strategy executes with the full, aligned backing of the organization for maximum impact. The chief impediment to strategy execution is inertia. The One Strategy approach is less about formal reviews and more about one-on-one conversation. Blogs can be a powerful asset in managing an organization. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 11 Aug 2008
Strategy Execution and the Balanced Scorecard
Companies often manage strategy in fits and starts, with strategy execution lost along the way. A new book by Balanced Scorecard creators Robert S. Kaplan and David P. Norton aims to make strategy a continual process. Key concepts include: An excellent strategy often fades from memory as the organization tackles day-to-day operations issues. The operational plan and budget should be driven from the revenue targets in the strategic plan. The senior management team needs to have regular, probably monthly, meetings that focus only on strategy. The Office of Strategy Management is a small cadre of professionals that orchestrate strategy management processes for the executive team. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 11 Apr 2007
Adding Time to Activity-Based Costing
Determining a company's true costs and profitability has always been difficult, although advancements such as activity-based costing (ABC) have helped. In a new book, Professor Robert Kaplan and Acorn Systems' Steven Anderson offer a simplified system based on time-driven ABC that leverages existing enterprise resource planning systems. Key concepts include: The activity-based costing system developed in the 1980s fell out of favor for a number of reasons, including the need for lengthy employee interviews and surveys to collect data. The arrival of enterprise resource planning systems allows crucial data to be pumped automatically into a TDABC system. Managers must answer two questions to build an effective TDABC system: How much does it cost to supply resource capacity for each business process in our organization? How much resource capacity (time) is required to perform work for each of our company's transactions, products, and customers? Profit improvements of up to 2 percent of sales generally come in less than a year. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 24 Apr 2006
Managing Alignment as a Process
"Most organizations attempt to create synergy, but in a fragmented, uncoordinated way," say HBS professor Robert S. Kaplan and colleague David P. Norton. Their new book excerpted here, Alignment, tells how to see alignment as a management process. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 02 Feb 2004
Mapping Your Corporate Strategy
From the originators of the Balanced Scorecard system, Strategy Maps is a new book that explores how companies can best their competition. A Q&A with Robert S. Kaplan. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 12 Oct 1999
A Perfect Fit: Aligning Organization & Strategy
Is your company organizationally fit? HBS Professor Michael Beer believes business success is a function of the fit between key organizational variables such as strategy, values, culture, employees, systems, organizational design, and the behavior of the senior management team. Beer and colleague Russell A. Eisenstat have developed a process,termed Organizational Fitness Profiling, by which corporations can cultivate organizational capabilities that enhance their competitiveness. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.

- Our Approach
- Strategic Alignment
- Strategy Implementation Support
- Aligned Strategy Course
- Successful Strategy Implementation Course
- Strategy and Leadership Community
- Strategy and Leadership Podcast
- SME Strategy on Youtube
Strategic Plan Examples: Case Studies and Free Strategic Planning Template
By Anthony Taylor - May 29, 2023

As you prepare for your strategic planning process, it's important to explore relevant strategic plan examples for inspiration.
In today's competitive business landscape, a well-defined strategic plan holds immense significance. Whether you're a private company, municipal government, or nonprofit entity, strategic planning is essential for achieving goals and gaining a competitive edge. By understanding the strategic planning process, you can gain valuable insights to develop an effective growth roadmap for your organization.
In this blog, we will delve into real-life examples of strategic plans that have proven successful. These examples encompass a wide range of organizations, from Credit Unions that have implemented SME Strategy's Aligned Strategy process to the Largest Bank in Israel. By examining these cases, we can gain a deeper understanding of strategic planning and extract relevant insights that can be applied to your organization.
- Strategic Plan Example (Global Financial Services Firm)
- Strategic Plan Example (Joint Strategic Plan)
- Strategic Plan Example: (Government Agency)
- Strategic Plan Example (Multinational Corporation)
- Strategic Plan Example: (Public Company)
- Strategic Plan Example (Non Profit)
- Strategic Plan Example: (Small Nonprofit)
- Strategic Plan example: (Municipal Government)
- Strategic Plan Example: (Environmental Start-up)
When analyzing strategic plan examples, it is crucial to recognize that a strategic plan goes beyond being a mere document. It should encapsulate your organization's mission and vision comprehensively while also being actionable. Your strategic plan needs to be tailored to your organization's specific circumstances, including factors such as size, industry, budget, and personnel. Simply replicating someone else's plan will not suffice.
Have you ever invested significant time and resources into creating a plan, only to witness its failure during execution? We believe that a successful strategic plan extends beyond being a static document. It necessitates meticulous follow-through, execution, documentation, and continuous learning. It serves as the foundation upon which your future plans are built.
It is important to note that a company's success is not solely determined by the plan itself, but rather by how effectively it is executed. Our intention is to highlight the diverse roles that a company's mission, vision, and values play across different organizations, whether they are large corporations or smaller nonprofits.
Strategic plans can vary in terms of their review cycles, which can range from annual evaluations to multi-year periods. There is no one-size-fits-all example of a strategic plan, as each organization possesses unique needs and circumstances that must be taken into account.
Strategic planning is an essential process for organizations of all sizes and types. It assists in setting a clear direction, defining goals, and effectively allocating resources. To gain an understanding of how strategic plans are crafted, we will explore a range of examples, including those from private companies, nonprofit organizations, and government entities.
Throughout this exploration, we will highlight various frameworks and systems employed by profit-driven and nonprofit organizations alike, providing valuable insights to help you determine the most suitable approach for your own organization.
Watch: Examples of Strategic Plans from Real-Life Organizations
Strategic Plan Example - The Bank Hapoalim Vision: To be a leading global financial services firm, with its core in Israel, focused on its clients and working to enhance their financial freedom.
Bank Hapoalim, one of Israel's largest banks with 8,383 branches across 5 different countries as of 2022, has recently provided insights into its latest strategic plan. The plan highlights four distinct strategic priorities:
- Continued leadership in corporate banking and capital markets
- Adaptation of the retail banking operating model
- Resource optimization and greater productivity
- Differentiating and influential innovation
Check out their strategic plan here: Strategic Plan (2022-2026)
We talked to Tagil Green, the Chief Strategy Officer at Bank Hapoalim, where we delved into various aspects of their strategic planning process. We discussed the bank's strategic planning timeline, the collaborative work they engaged in with McKinsey, and the crucial steps taken to secure buy-in and ensure successful implementation of the strategy throughout the organization. In our conversation, Tagil Green emphasized the understanding that there is no universal template for strategic plans. While many companies typically allocate one, two, or three days for strategic planning meetings during an offsite, Bank Hapoalim recognized the significance of their size and complexity. As a result, their strategic plan took a comprehensive year-long effort to develop. How did a Large Global Organization like Bank Hapoalim decide on what strategic planning timeline to follow?
"How long do you want to plan? Some said, let's think a decade ahead. Some said it's irrelevant. Let's talk about two years ahead. And we kind of negotiated into the like, five years ahead for five years and said, Okay, that's good enough, because some of the complexity and the range depends on the field that you work for. So for banking in Israel, four or five years ahead, is good enough. " Tagil Green, Chief Strategy Officer, Bank Hapoalim
Another important aspect you need to consider when doing strategic planning is stakeholder engagement, We asked Tagil her thoughts and how they conducted stakeholder engagement with a large employee base.
Listen to the Full Conversation with Tagil:
Strategic Planning and Execution: Insights from the Chief Strategy Officer of Israel's Leading Bank
Strategic Plan Example: Region 16 and DEED (Joint Strategic Plan)
Mission Statement: We engage state, regional, tribal, school, and community partners to improve the quality and equity of education for each student by providing evidence-based services and supports.
In this strategic plan example, we'll explore how Region 16 and DEED, two government-operated Educational Centers with hundreds of employees, aligned their strategic plans using SME Strategy's approach . Despite facing the challenges brought on by the pandemic, these organizations sought to find common ground and ensure alignment on their mission, vision, and values, regardless of their circumstances.
Both teams adopted the Aligned Strategy method, which involved a three day onsite strategic planning session facilitated by a strategic planning facilitator . Together, they developed a comprehensive 29-page strategic plan outlining three distinct strategic priorities, each with its own objectives and strategic goals. Through critical conversations, they crafted a clear three year vision, defined their core customer group as part of their mission, refined their organizational values and behaviors, and prioritized their areas of focus.
After their offsite facilitation, they aligned around three key areas of focus:
- Effective Communication, both internally and externally.
- Streamlining Processes to enhance efficiency.
- Developing Effective Relationships and Partnerships for mutual success.
By accomplishing their goals within these strategic priorities, the teams from Region 16 and DEED aim to make progress towards their envisioned future.
To read the full review of the aligned strategy process click here
Download Now Starting your strategic planning process soon? Get our free Strategic Planning Template
Strategic Plan Example: (Government Agency) - The City of Duluth Workforce Development Board
What they do:
The Duluth Workforce Development Board identifies and aligns workforce development strategies to meet the needs of Duluth area employers and job seekers through comprehensive and coordinated systems.
An engaged and diverse workforce, where all individuals, regardless of background, have or are on a path to meaningful employment and a family sustaining wage, and all employers are able to fill jobs in demand.
The City of Duluth provides an insightful example of a strategic plan focused on regional coordination to address workforce needs in various industry sectors and occupations. With multiple stakeholders involved, engaging and aligning them becomes crucial. This comprehensive plan, spanning 82 pages, tackles strategic priorities and initiatives at both the state and local levels.
What sets this plan apart is its thorough outline of the implementation process. It covers everything from high-level strategies to specific meetings between different boards and organizations. Emphasizing communication, coordination, and connectivity, the plan ensures the complete execution of its objectives. It promotes regular monthly partner meetings, committee gatherings, and collaboration among diverse groups. The plan also emphasizes the importance of proper documentation and accountability throughout the entire process.
By providing a clear roadmap, the City of Duluth's strategic plan effectively addresses workforce needs while fostering effective stakeholder engagement . It serves as a valuable example of how a comprehensive plan can guide actions, facilitate communication, and ensure accountability for successful implementation.
Read this strategic plan example here: Strategic Plan (2021-2024)
Strategic Plan Example: McDonald's (Multinational Corporation)
McDonald's provides a great strategic plan example specifically designed for private companies. Their "Velocity Growth Plan" covers a span of three years from 2017 to 2020, offering a high-level strategic direction. While the plan doesn't delve into specific implementation details, it focuses on delivering an overview that appeals to investors and aligns the staff. The plan underscores McDonald's commitment to long-term growth and addressing important environmental and societal challenges. It also highlights the CEO's leadership in revitalizing the company and the active oversight provided by the Board of Directors.
The Board of Directors plays a crucial role in actively overseeing McDonald's strategy. They engage in discussions about the Velocity Growth Plan during board meetings, hold annual strategy sessions, and maintain continuous monitoring of the company's operations in response to the ever-changing business landscape.
The McDonald's strategic plan revolved around three core pillars:
- Retention: Strengthening and expanding areas of strength, such as breakfast and family occasions.
- Regain: Focusing on food quality, convenience, and value to win back lost customers.
- Convert: Emphasizing coffee and other snack offerings to attract casual customers.
These pillars guide McDonald's through three initiatives, driving growth and maximizing benefits for customers in the shortest time possible.
Read the strategic plan example of Mcdonlald's Velocity growth plan (2017-2020)
Strategic Plan Example: Nike (Public Company)
Nike's mission statement is “ to bring inspiration and innovation to every athlete in the world .”
Nike, as a publicly traded company, has developed a robust global growth strategy outlined in its strategic plan. Spanning a five-year period from 2021 to 2025, this plan encompasses 29 strategic targets that reflect Nike's strong commitment to People, Planet, and Pay. Each priority is meticulously defined, accompanied by tangible actions and measurable metrics. This meticulous approach ensures transparency and alignment across the organization.
The strategic plan of Nike establishes clear objectives, including the promotion of pay equity, a focus on education and professional development, and the fostering of business diversity and inclusion. By prioritizing these areas, Nike aims to provide guidance and support to its diverse workforce, fostering an environment that values and empowers its employees.
Read Nike's strategic plan here
Related Content: Strategic Planning Process (What is it?)
The Cost of Developing a Strategic Plan (3 Tiers)
Strategic Plan Example (Non Profit) - Alternatives Federal Credit Union
Mission: To help build and protect wealth for people with diverse identities who have been historically marginalized by the financial industry, especially those with low wealth or identifying as Black, Indigenous, or people of color.
AFCU partnered with SME Strategy in 2021 to develop a three year strategic plan. As a non-profit organization, AFCU recognized the importance of strategic planning to align its team and operational components. The focus was on key elements such as Vision, Mission, Values, Priorities, Goals, and Actions, as well as effective communication, clear responsibilities, and progress tracking.
In line with the Aligned Strategy approach, AFCU developed three strategic priorities to unite its team and drive progress towards their vision for 2024. Alongside strategic planning, AFCU has implemented a comprehensive strategy implementation plan to ensure the effective execution of their strategies.
Here's an overview of AFCU's 2024 Team Vision and strategic priorities: Aligned Team Vision 2024:
To fulfill our mission, enhance efficiency, and establish sustainable community development approaches, our efforts will revolve around the following priorities: Strategic Priorities:
Improving internal communication: Enhancing communication channels and practices within AFCU to foster collaboration and information sharing among team members.
Improving organizational performance: Implementing strategies to enhance AFCU's overall performance, including processes, systems, and resource utilization.
Creating standard operating procedures: Developing standardized procedures and protocols to streamline operations, increase efficiency, and ensure consistency across AFCU's activities.
By focusing on these strategic priorities, AFCU aims to strengthen its capacity to effectively achieve its mission and bring about lasting change in its community. Watch the AFCU case study below:
Watch the Full Strategic Plan Example Case Study with the VP and Chief Strategy Officer of AFCU
Strategic Plan Example: (Small Nonprofit) - The Hunger Project
Mission: To end hunger and poverty by pioneering sustainable, grassroots, women-centered strategies and advocating for their widespread adoption in countries throughout the world.
The Hunger Project, a small nonprofit organization based in the Netherlands, offers a prime example of a concise and effective three-year strategic plan. This plan encompasses the organization's vision, mission, theory of change, and strategic priorities. Emphasizing simplicity and clarity, The Hunger Project's plan outlines crucial actions and measurements required to achieve its goals. Spanning 16 pages, this comprehensive document enables stakeholders to grasp the organization's direction and intended impact. It centers around three overarching strategic goals, each accompanied by its own set of objectives and indicators: deepening impact, mainstreaming impact, and scaling up operations.
Read their strategic plan here
Strategic Plan example: (Municipal Government)- New York City Economic Development Plan
The New York City Economic Development Plan is a comprehensive 5-year strategic plan tailored for a municipal government. Spanning 68 pages, this plan underwent an extensive planning process with input from multiple stakeholders.
This plan focuses on the unique challenges and opportunities present in the region. Through a SWOT analysis, this plan highlights the organization's problems, the city's strengths, and the opportunities and threats it has identified. These include New York's diverse population, significant wealth disparities, and high demand for public infrastructure and services.
The strategic plan was designed to provide a holistic overview that encompasses the interests of a diverse and large group of business, labor, and community leaders. It aimed to identify the shared values that united its five boroughs and define how local objectives align with the interests of greater New York State. The result was a unified vision for the future of New York City, accompanied by a clear set of actions required to achieve shared goals.
Because of its diverse stakeholder list including; council members, local government officials, and elected representatives, with significant input from the public, their strategic plan took 4 months to develop.
Read it's 5 year strategic plan example here
Strategic Plan Example: Silicon Valley Clean Energy
Silicon Valley Clean Energy provides a strategic plan that prioritizes visual appeal and simplicity. Despite being in its second year of operation, this strategic plan example effectively conveys the organization's mission and values to its Board of Directors. The company also conducts thorough analyses of the electric utility industry and anticipates major challenges in the coming years. Additionally, it highlights various social initiatives aimed at promoting community, environmental, and economic benefits that align with customer expectations.
"This plan recognizes the goals we intend to accomplish and highlights strategies and tactics we will employ to achieve these goals. The purpose of this plan is to ensure transparency in our operations and to provide a clear direction to staff about which strategies and tactics we will employ to achieve our goals. It is a living document that can guide our work with clarity and yet has the flexibility to respond to changing environments as we embark on this journey." Girish Balachandran CEO, Silicon Valley Clean Energy
This strategic plan example offers flexibility in terms of timeline. It lays out strategic initiatives for both a three-year and five-year period, extending all the way to 2030. The plan places emphasis on specific steps and targets to be accomplished between 2021 and 2025, followed by goals for the subsequent period of 2025 to 2030. While this plan doesn't go into exhaustive detail about implementation steps, meeting schedules, or monitoring mechanisms, it effectively communicates the organization's priorities and desired long term outcomes. Read its strategic plan example here
By studying these strategic plan examples, you can create a strategic plan that aligns with your organization's goals, communicates effectively, and guides decision-making and resource allocation. Strategic planning approaches differ among various types of organizations.
Private Companies: Private companies like McDonald's and Nike approach strategic planning differently from public companies due to competitive market dynamics. McDonald's provides a high-level overview of its strategic plan in its investor overview.
Nonprofit Organizations: Nonprofit organizations, like The Hunger Project, develop strategic plans tailored to their unique missions and stakeholders. The Hunger Project's plan presents a simple yet effective structure with a clear vision, mission, theory of change, strategic priorities, and action items with measurable outcomes.
Government Entities: Government entities, such as the New York City Development Board, often produce longer, comprehensive strategic plans to guide regional or state development. These plans include implementation plans, stakeholder engagement, performance measures, and priority projects.
When creating a strategic plan for your organization, consider the following key points:
Strategic Priorities: Define clear strategic priorities that are easy to communicate and understand.
Stakeholder Engagement: Ensure your plan addresses the needs and interests of your stakeholders.
Measurements: Include relevant measurements and KPIs, primarily for internal use, to track, monitor and report your progress effectively.
Conciseness vs. Thoroughness: Adapt the level of detail in your plan based on the size of your organization and the number of stakeholders involved.
By learning from these examples, you can see that developing a strategic plan should be a process that fits your organization, effectively communicates your goals, and provides guidance for decision-making and resource allocation. Remember that strategic planning is an ongoing process that requires regular review and adjustment to stay relevant and effective.
Need assistance in maximizing the impact of your strategic planning? Learn how our facilitators can lead you through a proven process, ensuring effectiveness, maintaining focus, and fostering team alignment.

Our readers' favourite posts
Subscribe to our bi-weekly newsletter: leaders digest, quick links.
- Podcast (Spotify)
- Speaker & Media
- Alignment Book
- Privacy Policy
Free Resources
- Strategic planning session agenda (Sample)
- Strategic plan template
- How to create a strategic plan (Start here)
- Weekly Strategy Tips
- Non profit program
Products and Services
- Strategic Planning Facilitator
- Strategy Implementation Consulting
- Strategic Planning Course
- 1-855-895-5446

Copyright © 2011-2023 SME Strategy Consulting | Strategic Planning Facilitator + Strategy Implementation Consulting. All rights reserved.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Case Study: Career Choices When Life Is Short
- Joshua D. Margolis
A young man diagnosed with a terminal illness decides on his next move.
The leaders of MedPath didn’t typically shed tears in their weekly meetings, but this was an exception. Gil Lehner, one of the start-up’s four founders, had just told the others about his diagnosis: He had small cell lung cancer, and while he planned to fight it with his trademark tenacity, his chance of surviving longer than five years was only about 18%.
- JM Joshua D. Margolis is the James Dinan and Elizabeth Miller Professor of Business Administration and the head of the Organizational Behavior unit at HBS.
Partner Center
- Question Papers
- Scholarships
HRM Case Studies With Solutions
Let’s study Human Resource Management Case Studies with solutions. HRM Case studies play a vital role in management education especially in subjects like Human Resource Management (HRM), Personnel Management, PAAP and related subjects.
It gives a clear picture of the concepts when you practise them through case studies. Here we have given some live HRM case studies that are short, useful & interesting. This will allow you to think beyond the theoretical part and make you capable to apply the concepts in real-time situations.
Table of Contents
We are also providing solutions which are free of cost. We welcome your feedback about these HRM case studies.
Below are short and simple Case Studies on HRM with Solutions, Questions, and Answers.
HRM Case Study 1
Harsha and Franklin both of them are postgraduates in management under different streams from the same B-School. Both of them are close to each other from the college days itself and the same friendship is continuing in the organization too as they are placed in the same company, Hy-tech technology solutions. Harsha placed in the HR department as employee counsellor and Franklin in the finance department as a key finance executive. As per the grade is concerned both are at the same level but when responsibility is concerned Franklin is holding more responsibility being in core finance.
By nature, Harsha is friendly in nature and ready to help the needy. Franklin is silent in nature ready to help if approached personally and always a bit egoistic in nature. They have successfully completed 4 years in the organization. And management is very much satisfied with both of them as they are equally talented and constant performers.
Harsha felt that now a day’s Franklin is not like as he uses to be in the past. She noticed some behavioural changes with him. During general conversations, she feels that Franklin is taunting her that she is famous among the employees in the organization, on the other hand, he is not even recognized by fellow employees.
One morning Mr. Mehta General Manager Hy-tech technology solutions shocked while going through the mail received from Franklin about his resignation. Mr. Mehta called Harsha immediately and discussed the same as she is close to Franklin. By hearing the news Harsha got stunned and said that she does not know this before she also revealed here current experience with him. Mr. Mehta who does not want to lose both of them promised her that he will handle this and he won’t allow Franklin to resign.
In the afternoon Mr. Metha took Franklin to Canteen to make him comfortable after some general discussion he starts on the issue. Franklin, after some hesitation, opened his thinking in front of Mr. Mehta. The problem of Franklin is
1) when he comes alone to canteen the people from others don’t even recognize him but if he accompanied by Harsha he gets well treated by others.
2) one day Both of them entered the company together the security in the gate wished them but the next day when he came alone the same security did not do so.
3) Even in meetings held in the office, the points raised by Harsha will get more value so many times he keeps silent in the meeting.
It happens to Franklin that he has to face such degradation in each day of work which totally disturbs him. Franklin also questioned that ” Harsha and myself have the same qualification, from the same institute, passed out in the same year both with first class. We have the same number of experiences in this organization. Moreover, the responsibilities with me are more valuable than those of Harsha. After all these things if I am been ignored or unrecognized by the fellow employees my ego does not allow me to continue here”.
By listening to this statement Mr.Metha felt that it is not going to be very difficult to stop his resignation. Mr. Mehta explained Franklin the reasons for such partial behaviour of the employees. After listening to Mr. Mehta Franklin said sorry for his reaction and ready to take back his resignation. And he called Harsha and spoke with like before.
Questions for HRM Case Studies: Case Study 1
Find the reason that Mr. Mehta would have given to Franklin.
Solution for HRM Case Study 1
Mr. Mehta listening to this case understood the situation and realized the reason behind the partial response given by the employees towards Franklin and Harsha. As Franklin said both Harsha and Franklin are passed out from the same college in the same year. Both of them joined the company together both have the same experience. Even in performance-wise, both stands in the same level i.e. both are constant performers and good performers.
Franklin analyzed all the above-said similarities between him and Harsha. He also stated that he holds more responsibility than that of Harsha. One thing Franklin did not notice or analyzed is the job profile of Harsha. It is true that Franklin holds more responsibility than that of Harsha but when it comes to direct interaction with employees Harsha wins the employees’ attention in this aspect. Harsha being a counsellor in HR she faces the employees every day. She developed good rapport among the employees due to her friendly nature. She is always remembered by the employees whenever they face any problem as she gives good counselling and most of the time she suggests the best solutions for such issues.
Franklin though holding a key position in finance his profile does not allow him to interact with the employees. Though he has a helping tendency he does only when someone approached him personally. As the employees of other departments do not have any relation with him they never approach him for help. Mr. Mehta having a good experience understood these things when Franklin explained his problems one by one. Later he relates each situation, explained by Franklin with the above said reasons and made Franklin understood the reality.
Mr. Mehta said that the security in the gate or the employees in the canteen who recognized Harsha and not Franklin would have interacted with her during counselling or approached her for any issues. And as usual, she would have counselled well or solved the issues of them that is the reason why they treat her and wish her whenever where ever they meet her. When it comes to the case of Franklin they would have hardly met him or interacted with him.
When it comes to the point that even in-office meetings Harsha, points are valued so Franklin keeps mum. For this, Mr. Mehta replied that the points put forward by her would be related to employees or from the employees’ point of view which actually the management wants to know so they give value to her points. And as quoted Fraklin after, one or two such incidents keep silent in the meeting. He never made an attempt to raise some suggestions so management does not have any option to listen to that suggestion.
After listening to all the explanations given by Mr. Mehta Franklin realized his mistake and felt proud of the Rapport developed by Harsha among the employees. He said to Mr. Mehta that he will take back his resignation. And rushed to Harsha to make an apology and to meet her as a friend as like his college days.
HRM Case Studies Part 2:
HRM Case Study 2
Watson Public Ltd Company is well known for its welfare activities and employee-oriented schemes in the manufacturing industry for more than ten decades. The company employs more than 800 workers and 150 administrative staff and 80 management-level employees. The Top-level management views all the employees at the same level. This can be clearly understood by seeing the uniform of the company which is the Same for all starting from MD to floor level workers. The company has 2 different cafeterias at different places one near the plant for workers and others near the Administration building. Though the place is different the amenities, infrastructure and the food provided are of the same quality. In short, the company stands by the rule of Employee Equality.
The company has one registered trade union. The relationship between the union and the management is very cordial. The company has not lost a single man day due to strike. The company is not a paymaster in that industry. The compensation policy of that company, when compared to other similar companies, is very less still the employees don’t have many grievances due to the other benefits provided by the company. But the company is facing a countable number of problems in supplying the materials in the recent past days. Problems like quality issues, mismatch in packing materials (placing material A in the box of material B) incorrect labelling of material, not dispatching the material on time, etc…
The management views the case as there are loopholes in the system of various departments and hand over the responsibility to the HR department to solve the issue. When the HR manager goes through the issues he realized that the issues are not relating to the system but it relates to the employees. When investigated he come to know that the reason behind the casual approach by employees in work is
- The company hired new employees for a higher-level post without considering the potential internal candidates.
- The newly hired employees are placed with higher packages than that of existing employees in the same cadre.
- Narrate the case with a suitable title for the case. Justify your title.
Solution for HRM Case Case Study 2
Employee Equality is not the need for every hour. In the above-said case, Watson Ltd had provided all facilities to employees at each grade in an equal manner. But still, the employees started creating certain issues like materials are meeting the quality supply schedule is not met etc. And the HR manager said that the policy of hiring new employees for the higher post without considering old potential employees is the major problem.
“Employee recognition VS Employee equality ”. As the HR manager states that employees are not been recognized for the potential rather the company has gone for new recruitment. Because of which the company faces problems.
- The points rose by the HR manager as the reason for the latest issues in the organization is justifiable or not. Support your answer with Human resource related concepts.
Yes, the points raised by the HR manager is justifiable because “Human beings are social Animals as popularly” said by many Human resources Scholars. So human minds demand social recognition, self-respect, consideration, etc for their work and performance.
In the above-said case, even the company provides and stands by the concept of employee equality when it fails to recognize the potential talents of existing employee they felt dissatisfaction towards the organization and they showed in the way of quality issues and slow down production.
Related HR concept.
Slow down Production:
The concept of slow down production is a type of employee’s strike. The Industrial Relations sates that when the employee wants to show their dissatisfaction to the management but don’t want to go for strike they follow slow down strike. The impact of which will be understood after a particular time period.
Employee Recognition:
Human beings can be easily motivated by Rewards and recognition than that of money. In this case, also the employee is not satisfied even after all facilities just because of the reason that they are not recognized.
Hawthrone Experiment:
In the four types of test conducted by Elton Mayo, the remarkable hike in production is recognized in the stage when they consulted the employees for the management decisions regarding them. The same thing was missing in Watson Ltd. Before the new hires if the management consulted the employees both management and employees would have avoided this issue
Hygiene Factor:
The theory of hygiene factors states that there are certain factors related to employees the presence of which will not create a major impact but the absence of such things will lead to a de motivation to the employees. Employee Recognition is one such factor when the management fails to do so it will Detroit the employees to a great extent.
- Help the organization to come out from this critical issue. If you are in the role of HR manager what will be your immediate step to solve this case.
If I was in the post of the HR manager I will try to discuss the issue and ask for the reason from the management for new recruiting rather than considering available potential talents. I will personally analyse the reasons provided by management and if acceptable I will discuss the same with the employees. Everything is possible with a discussion. So I will discuss and convince the employee that this won’t happen again in the organization. I will also initiate the collective bargaining process for reasonable salary hike for the existing employees.
How to Download PDF of HRM Case Studies
You can copy and use this text for personal use.
This is all about HRM Case Studies with solutions. You can contact us for the PDF or PPT format.
You’ll also like Top 25 Human Resource Management MCQ With Answers (Updated)
Share with friends
Before you read the 3 Examples of Capacity Planning, you should read the first part of this article that broke down Capacity Planning in 10 Steps here: https://www.workclout.com/post/10-steps-to-create-apply-capacity-planning-for-manufacturing If you have read it already, read on! Capacity planning and techniques will function differently depending on production mode. Practical examples of models in capacity planning for different production modes include:
1. Make to Stock (MTS)
Make to Stock is common within discreet manufacturing and process manufacturing. As these operations often have complex multi-level BOMs, capacity planning must include planning for sub-processes required to produce components or assemblies for final construction. An example of this would be a production facility where single serve meal or snack kits are produced.
With each kit consisting of meat, cheese, bread and juice, a complex BOM is required to facilitate production of each. This would include the individual food types as well as tray formation and wrapping. It is also possible that these facilities would use a combination of in-house production for some parts of the kit and sub-contracted sourcing for others.
The complexity of the final product as well as the changing nature of the foods offered requires accurate BOMs, concise measurements of labor and machine capacity and the ability to changeover quickly and often. Companies with MRP systems in place could use Capacity Requirements Planning (CRP) that relies on MRP inputs and inventory to produce a capacity plan.
This type of operation could also use the rough-cut planning system of Capacity Planning Using Overall Factors, where production standards and the master schedule are used to develop a capacity plan. MTS production facilities would need to make full use of all ten steps above to develop accurate and actionable capacity plans.

2. Make to Order (MTO)
By nature, make to order production modes will require less WIP and fewer processes. However, they still rely on repeatable BOM structures to produce units higher in cost, or that are not commodified or consumable goods. An example of this type of manufacturing would be a facility that produces coffee makers. With a specific product line with less BOM levels, production can be triggered by the actual order itself rather than producing to maintain a stock level for consumables. In this mode, a factory may choose to utilize to use a rough-cut capacity planning method such as capacity bills or resource profiles. In capacity bills, the BOM and routing sheet is used to show the sequence or work center required for production along with the setup and run time. For an MTO utilizing resource bills, the same variables are used as in capacity bills but with lead time for product included in so workloads can be planned on a time scale.
MTO environments may contain sub-process production for key components and assemblies, but in the case of the example of the coffee maker manufacturer, they would also require a high degree of assembly for the final product. An MTO manufacturer would need to have tight control of its process routing and a deep understanding of resource capacity and resource utilization.

3. Engineer to Order (ETO)
In an engineer to order production system, each unit is a unique iteration of a product. And while a BOM may be developed to guide the construction and assembly, it is usually a single level BOM or one with fewer levels. As the calculations for workloads, work centers and resource capacity must be calculated at each order, a rough-cut method such as capacity bills would be most effective in capacity planning. An example of this type of manufacturing would be a factory that produces luxury limousines. As each finished unit is a unique iteration, the factors for each unit would need to be added together to develop a capacity plan.
Using the ten steps above, key considerations for an ETO would be in the establishment of a workload and in the document of equipment capabilities. In the case of the limo manufacturer, while standards cannot be developed for common products as each unit is a one-off, an accurate understanding of welder capacity, paint booth dwell time and other key functions along the line may be more important to an ETO than would some other steps in determining capacity.

If you want a free consultation on how to approach capacity planning at your factory, feel free to book a time with a capacity planning expert here: https://meetings.hubspot.com/workclout/free-30-min-supply-chain-consultation

- Become A Partner
- How It Works
- Template Marketplace
- Enterprise Download
- Schedule an Appointment

- Undergraduate Students in AS&E and SMFA
- Graduate Students in AS&E and SMFA
- Faculty & Staff
- Parents and Families
- What is a Career Community?
- Reflect, Discover & Explore Multiple Interests
- Arts, Communications & Media
- Education, Nonprofit & Social Impact
- Engineering, Technology & Physical Sciences
- Finance, Consulting, Entrepreneurship & Business
- Government, International Affairs & Law
- Healthcare, Life Sciences & the Environment
- Exploring Your Interests, Careers & Majors
- Writing Resumes & Cover Letters
- Finding an Internship
- Finding Jobs & Fellowships
- Preparing for Interviews
- Applying to Graduate & Professional School
- First Generation
- International Students
- Black, Indigenous & People of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Students with Undocumented Status
- Women & Gender
- For Employers
- Contact & Location
- Career Fellows
- Career Services by School
Case Interview: Complete Prep Guide
- Share This: Share Case Interview: Complete Prep Guide on Facebook Share Case Interview: Complete Prep Guide on LinkedIn Share Case Interview: Complete Prep Guide on X
Welcome to our preparation tips for case interviews! Whether you are just curious about case interviews or are planning to apply for consulting internships or full-time jobs, these tips and resources will help you feel more prepared and confident.

A case interview is a role playing exercise in which an employer assesses how logically and persuasively you can present a case. Rather than seeing if you get the “correct” answer, the objective is to evaluate your thought process. ( Adapted with permission from Case In Point: Complete Case Interview Preparation by Marc Cosentino).
Case interviews are very commonly used in the interview process for consulting firms and companies in similar industries. In the case interview, you will typically be given a business problem and then asked to solve it in a structured way. Learning this structure takes preparation and practice. You can learn more and practice using the resources listed below.
Why are Case Interviews Used?
Case interviews allow employers to test and evaluate the following skills:
- Analytical skills and logical ability to solve problems
- Structure and thought process
- Ability to ask for relevant data/information
- Tolerance for ambiguity and data overload
- Poise and communication skills under pressure and in front of a client
How can I prepare for Case Interviews?
1.) Read Management Consulted’s “Case Interview: Complete Prep Guide (2024)”
Management Consulted is a FREE resource for Tufts students : case and consulting resources such as 500 sample cases, Case Interview Bootcamp, Market Sizing Drills, Math Drills, case videos, consulting firm directory, and more
2.) Review additional resources:
- Case in Point – This book, by Marc Cosentino, is a comprehensive guide that walks you through the case interview process from beginning to end. This guide has helped many students over the years and can serve as an excellent foundation for how to approach business problems
- Casequestions.com – The companion website to Marc Cosentino’s book listed above offers preparation for case interviews, along with links to top 50 consulting firms
- Management Consulting Case Interviews: Cracking The Case – tips for case interviews from the other side of the table, from Argopoint, a Boston management consulting firm specializing in legal department consulting for Fortune 500 companies
- Preplounge.com – Free case preparation access for to up to 6 practice interviews with peers, selected cases, and video case solutions
- RocketBlocks – Features consulting preparation such as drills and coaching
- Practice sample online cases on consulting firm websites such as McKinsey , BCG , Bain , Deloitte and more!
3.) Schedule a mock case interview appointment with Karen Dankers or Kathy Spillane , our advisors for the Finance, Consulting, Entrepreneurship, and Business Career Community.
4.) PRACTICE PRACTICE PRACTICE cases out loud on your own (yes, that can feel odd) or preferably, with another person. See #2 and #3 above for resources and ideas to find partners to practice live cases
5.) Enjoy and have fun solving business problems!

Stuart Weitzman School of Design 102 Meyerson Hall 210 South 34th Street Philadelphia, PA 19104
215.898.3425
Get Directions
Get the latest Weitzman news in your Inbox:
Case studies in design: open call to study projects designed in community.
Receive Weitzman Press Announcements
Case Studies in Design is a new effort to create opportunities for community and design leaders to think together about ways to catalyze transformational design, planning, and place-keeping from the ground up. The goals are to learn from ambitious projects designed in community, to share knowledge and experience through dialogue and a public library of case studies, and to train ourselves for new practices of creative, collective action. We hope to build conversation among thinkers and doers in community organizations, movements, public agencies, schools, and the architecture, landscape, planning, heritage and art fields.
Projects designed in community Case Studies in Design will support the development of 5 case studies per year, over 3 years (15 case studies prepared by 15 people in total). The aim is to study projects where design and planning helped build community power, and where community-led processes produced new forms of design agency through:
1. Deep conversation to shape the nature and time horizon of the project 2. Openness and deference to rooted leadership 3. Reciprocal (not extractive) processes, creatively designed 4. Collaboration and resource-sharing 5. New alliances to achieve leverage.
Collective writing and thinking project Case Studies in Design is coordinated by PennPraxis , a center at Weitzman School of Design at the University of Pennsylvania that is dedicated to the translation of theory into praxis (or action). Our aspiration is to bring together people from a wide geography and set of perspectives on diverse change efforts. Case study projects could range from outstanding examples of community- engaged design practice to more radical roles and results of design, planning or place-keeping. To propel this collective writing and thinking project, we are seeking applications from people who would like to research and author a case study.
We will support 5 case study writers in 2024 with a fee and expense allowance of $50,000 per author to research, write, and curate or create illustrations for a case study over a period of 8 months. Fees for community members participating in interviews, travel and other expenses will be managed by authors within the resources of the $50,000 lump sum for fee and expense. (Two people may apply to work together on a case project, sharing the fee.)
Public library and action—oriented summit PennPraxis will publish the case studies and create an online public library to disseminate them. We will organize a variety of forums from the classroom to gatherings with policymakers and funders to propagate strategies that increase community conversation and influence in the built environment. In the third year of the effort, with 15 case studies in print, we will organize a summit for community leaders, policymakers, students, practitioners, and thinkers to probe more deeply into methods and to shape lessons learned for key audiences. The aim of the summit is to create culture-shifting dialogue between disciplines, spheres of action, governments, funders and community leaders, practice and theory.
Case study method of conversation and analysis Most design “case studies” are project descriptions and images that focus on the what, not the how—the built project and perhaps its reception and performance. Designers are skilled at presenting the thesis, appearance and materials of their projects; so much so, that it can be difficult to understand whether the project outcomes and process measure up to the image for those who will live with them. The statement of the designer rarely conveys how the project was made, or the perspectives of community leaders, policymakers, scientists and other participants in the process.
Our case studies will place focus on the process—the many collaborators and contingencies—and offer insight into how communities and interdisciplinary teams have attempted to traverse the “valley of death” between ideas and implementation.
We aim to create a case study method that invites analysis and requires participants to shape their own values and strategies—active learning for would-be activist designers and community leaders interested taking on complex challenges. Similar to teaching case studies developed in policy and business schools, we are interested in supporting the creation of case studies that are intentionally open-ended presentations of a compelling situation that carries some conflict and uncertainty, with many different viewpoints included in the reporting, rather than critical essays that offer the authors’ conclusions or a how-to guide. The purpose is to cultivate the users capacity for critical analysis, bias recognition, collaboration, leadership, decision-making and action on challenging issues and projects. We believe that, done well, case research and discussion can help us develop theory from practice, and apply new theory to practice.
Applying to study and document a project Individuals (or pairs) can apply to develop a case for a fee of $50,000 by submitting the following material via this webform in a single pdf file of no more than 20MB:
1) a writing sample—past work that demonstrates capacity for narrative and analytical writing 2) CV or résumé with current contact information 3 a) 2,000 to 3,000-word description of a project that you think would make an interesting case study in community-engaged design, planning or place-keeping, and why (project images are optional) AND / OR 3 b) 500 to 2,000-word response to our outline of the intent of the case study program, including any critique that you think would make it stronger.
An applicant who does not apply with an interest in a particular project (outlined in response to 3a above) may be invited to document a project suggested by someone else. The length of your résumé is less important than your perspective on projects designed in community and capacity to enrich the knowledge base through the medium of case study writing and illistration.
Suggesting a project if you are not applying to write a case study We also welcome suggestions of exemplary projects worthy of deep analysis from colleagues in community and indigenous organizations, movements, public agencies, design and planning practices, and foundations. You can submit a project suggestion (with or without images) via this webform . Recommendations can be of any length, even just a project name and location or link. We can accept file sizes up to 20MB. Please include your contact information in case we would like to reach out to learn more.
Send any questions to [email protected] .
Timeline Applications will be reviewed as they come in until the deadline at 12pm on June 30, 2024. We aim to award all contracts by July 28, 2024, and may award some contracts for early applicants prior to that date. Authors will have 8 months to submit a completed case study (April 1, 2025), with an interim review at roughly 4 months.
Documentation
Download a PDF version of the Call for Applications
A new sample-size planning approach for person-specific VAR(1) studies: Predictive accuracy analysis
- Original Manuscript
- Published: 08 May 2024
Cite this article

- Jordan Revol ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5511-3617 1 ,
- Ginette Lafit ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8227-128X 2 &
- Eva Ceulemans ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7611-4683 1
22 Accesses
6 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Researchers increasingly study short-term dynamic processes that evolve within single individuals using N = 1 studies. The processes of interest are typically captured by fitting a VAR(1) model to the resulting data. A crucial question is how to perform sample-size planning and thus decide on the number of measurement occasions that are needed. The most popular approach is to perform a power analysis, which focuses on detecting the effects of interest. We argue that performing sample-size planning based on out-of-sample predictive accuracy yields additional important information regarding potential overfitting of the model. Predictive accuracy quantifies how well the estimated VAR(1) model will allow predicting unseen data from the same individual. We propose a new simulation-based sample-size planning method called predictive accuracy analysis (PAA), and an associated Shiny app. This approach makes use of a novel predictive accuracy metric that accounts for the multivariate nature of the prediction problem. We showcase how the values of the different VAR(1) model parameters impact power and predictive accuracy-based sample-size recommendations using simulated data sets and real data applications. The range of recommended sample sizes is smaller for predictive accuracy analysis than for power analysis.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Reporting reliability, convergent and discriminant validity with structural equation modeling: A review and best-practice recommendations

Sampling Techniques for Quantitative Research

Estimating power in (generalized) linear mixed models: An open introduction and tutorial in R
We used the following packages: DataFrames (version 1.6.1), DataTables (version 0.1.0), DataAPI (version 1.1.0), CSV (version 0.10.12) to handle the data; LinearAlgebra (version 0.5.1), GLM (version 1.9.0), HypothesisTests (version 0.11.0), StatsBase (version 0.34.2) to estimate the model and extract the estimated parameters; Distributions (version 0.25.107) and Distances (version 0.10.11) to handle statistical distributions.
When generating (V)AR(1) time series, we have to use starting values, that is, the variable scores at the first time point. To remove the influence of these starting values, we removed the first 1000 time points (known as the burn-in phase).
Adolf, J. K., Voelkle, M. C., Brose, A., & Schmiedek, F. (2017). Capturing context-related change in emotional dynamics via fixed moderated time series analysis. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 52 (4), 499–531.
Ariens, S., Ceulemans, E., & Adolf, J. K. (2020). Time series analysis of intensive longitudinal data in psychosomatic research: A methodological overview. Journal of Psycho-somatic Research, 137 , 110191.
Article Google Scholar
Babyak, M. A. (2004). What you see may not be what you get: A brief, nontechnical introduction to overfitting in regression-type models. Psychosomatic Medicine, 66 (3), 411–421.
Bezanson, J., Karpinski, S., Shah, V., & Edelman, A. (2012). Julia: A fast dynamic language for technical computing.
Borsboom, D., & Cramer, A. O. (2013). Network analysis: An integrative approach to the structure of psychopathology. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 9 (1), 91–121.
Bulteel, K., Mestdagh, M., Tuerlinckx, F., & Ceulemans, E. (2018). VAR(1) based models do not always outpredict AR(1) models in typical psychological applications. Psychological Methods, 23 , 740–756.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Bulteel, K., Tuerlinckx, F., Brose, A., & Ceulemans, E. (2018). Improved insight into and prediction of network dynamics by combining VAR and dimension reduction. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 53 (6), 853–875.
Button, K. S., Ioannidis, J. P. A., Mokrysz, C., Nosek, B. A., Flint, J., Robinson, E. S. J., & Munafó, M. R. (2013). Power failure: Why small sample size undermines the reliability of neuroscience. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 14 (5), 365–376.
Chang, W., Cheng, J., Allaire, JJ., Sievert, C., Schloerke, B., Xie, Y., Allen, J., McPherson, J., Dipert, A., & Borges, B. (2023). Shiny: Web application framework for R.
Cohen, J. (1992). Statistical power analysis. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 1 (3), 98–101.
De Haan-Rietdijk, S., Voelkle, M. C., Keijsers, L., & Hamaker, E. L. (2017). Discretevs. continuous-time modeling of unequally spaced experience sampling method data. Frontiers in Psychology, 8 , 1849.
Dejonckheere, E., Kalokerinos, E. K., Bastian, B., & Kuppens, P. (2019). Poor emotion regulation ability mediates the link between depressive symptoms and affective bipolarity. Cognition and Emotion, 33 (5), 1076–1083.
Dejonckheere, E., Mestdagh, M., Houben, M., Rutten, I., Sels, L., Kuppens, P., & Tuerlinckx, F. (2019). Complex affect dynamics add limited information to the prediction of psychological well-being. Nature Human Behaviour, 3 (5), 478–491.
Epskamp, S., van Borkulo, C. D., van der Veen, D. C., Servaas, M. N., Isvoranu, A.-M., Riese, H., & Cramer, A. O. J. (2018). Personalized network modeling in psychopathology: The importance of contemporaneous and temporal connections. Clinical Psycho-logical Science, 6 (3), 416–427.
Fisher, A. J., Reeves, J. W., Lawyer, G., Medaglia, J. D., & Rubel, J. A. (2017). Exploring the idiographic dynamics of mood and anxiety via network analysis. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 126 (8), 1044–1056.
Green, P., & MacLeod, C. J. (2016). SIMR : An R package for power analysis of generalized linear mixed models by simulation. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 7 (4), 493–498.
Hamaker, E. L., Asparouhov, T., Brose, A., Schmiedek, F., & Muthén, B. (2018). At the frontiers of modeling intensive longitudinal data: Dynamic structural equation models for the affective measurements from the COGITO study. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 53 (6), 820–841.
Hamaker, E. L., Ceulemans, E., Grasman, R. P. P. P., & Tuerlinckx, F. (2015). Modeling affect dynamics: State of the art and future challenges. Emotion Review, 7 (4), 316–322.
Hamaker, E. L., & Wichers, M. (2017). No time like the present: Discovering the hidden dynamics in intensive longitudinal data. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 26 (1), 10–15.
Hamaker, E. L., Zhang, Z., & Van Der Maas, H. L. J. (2009). Using threshold autoregressive models to study dyadic interactions. Psychometrika, 74 (4), 727.
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., & Friedman, J. (2013). The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction . New York, NY: Springer.
Google Scholar
Heininga, V. E., Dejonckheere, E., Houben, M., Obbels, J., Sienaert, P., Leroy, B., van Roy, J., & Kuppens, P. (2019). The dynamical signature of anhedonia in major depressive disorder: Positive emotion dynamics, reactivity, and recovery. BMC Psychiatry, 19 (1), 59.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Jongerling, J., Laurenceau, J.-P., & Hamaker, E. L. (2015). A multilevel AR(1) model: Allowing for inter-individual differences in trait-scores, inertia, and innovation variance. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 50 (3), 334–349.
Kirtley, O. J. (2022). Advancing credibility in longitudinal research by implementing open science practices: Opportunities, practical examples, and challenges. Infant and Child Development, 31 (1).
Krone, T., Albers, C. J., Kuppens, P., & Timmerman, M. E. (2018). A multivariate statistical model for emotion dynamics. Emotion, 18 , 739–754.
Kuppens, P. (2015). It’s about time: A special section on affect dynamics. Emotion Review, 7 (4), 297–300.
Kuppens, P., Allen, N. B., & Sheeber, L. B. (2010). Emotional inertia and psychological maladjustment. Psychological Science, 21 (7), 984–991.
Kuppens, P., Champagne, D., & Tuerlinckx, F. (2012). The dynamic interplay between appraisal and core affect in daily life. Frontiers in Psychology, 3 .
Kuppens, P., & Verduyn, P. (2017). Emotion dynamics. Current Opinion in Psychology, 17 , 22–26.
Lafit, G., Adolf, J. K., Dejonckheere, E., Myin-Germeys, I., Viechtbauer, W., & Ceulemans, E. (2021). Selection of the number of participants in intensive longitudinal studies: A user-friendly shiny app and tutorial for performing power analysis in multilevel regression models that account for temporal dependencies. Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science, 4 (1), 251524592097873.
Lafit, G., Meers, K., & Ceulemans, E. (2022). A systematic study into the factors that affect the predictive accuracy of multilevel VAR(1) models. Psychometrika, 87 (2), 432–476.
Lafit, G., Revol, J., Cloos, L., Kuppens, P., & Ceulemans, E. (2023). The effect of different operationalizations of affect and preprocessing choices on power-based sample size recommendations in intensive longitudinal research .
Lafit, G., Sels, L., Adolf, J. K., Loeys, T., & Ceulemans, E. (2022b). PowerLAPIM: An application to conduct power analysis for linear and quadratic longitudinal actor–partner interdependence models in intensive longitudinal dyadic designs. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships , page 02654075221080128.
Lakens, D. (2022). Sample size justification. Collabra. Psychology, 8 (1), 33267.
Lane, S. P., & Hennes, E. P. (2018). Power struggles: Estimating sample size for multilevel relationships research. Journal of Social and Personal Relationships, 35 (1), 7–31.
Larson, R. & Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2014). The Experience Sampling Method, pages 21–34. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht.
Liu, S. & Zhou, D. J. (2023). Using cross-validation methods to select time series models: Promises and pitfalls. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology , page bmsp.12330.
Loossens, T., Dejonckheere, E., Tuerlinckx, F., & Verdonck, S. (2021). Informing VAR(1) with qualitative dynamical features improves predictive accuracy. Psychological Methods, 26 (6), 635–659.
Lütkepohl, H. (2005). New Introduction to Multiple Time Series Analysis . Berlin Heidelberg: Springer.
Mansueto, A. C., Wiers, R. W., van Weert, J. C. M., Schouten, B. C., & Epskamp, S. (2022). Investigating the feasibility of idiographic network models. Psychological Methods .
Marriott, F. H. C., & Pope, J. A. (1954). Bias in the estimation of autocorrelations. Biometrika, 41 (3/4), 390.
Munafó, M. R., Nosek, B. A., Bishop, D. V. M., Button, K. S., Chambers, C. D., Percie du Sert, N., Simonsohn, U., Wagenmakers, E.-J., Ware, J. J., & Ioannidis, J. P. A. (2017). A manifesto for reproducible science. Nature Human Behaviour, 1 (1), 0021.
Myin-Germeys, I., & Kuppens, P. (Eds.). (2021). The Open Handbook of Experience Sampling Methodology: A Step-by-Step Guide to Designing, Conducting, and Analyzing ESM Studies . Leuven: Center for Research on Experience Sampling and Ambulatory Methods.
Pe, M. L., Brose, A., Gotlib, I. H., & Kuppens, P. (2016). Affective updating ability and stressful events interact to prospectively predict increases in depressive symptoms over time. Emotion, 16 (1), 73–82.
Pe, M. L., Kircanski, K., Thompson, R. J., Bringmann, L. F., Tuerlinckx, F., Mestdagh, M., Mata, J., Jaeggi, S. M., Buschkuehl, M., Jonides, J., Kuppens, P., & Gotlib, I. H. (2015). Emotion-network density in major depressive disorder. Clinical Psychological Science, 3 (2), 292–300.
Phillips, P. C. B. (1995). Fully modified least squares and vector autoregression. Econo-metrica, 63 (5), 1023.
Provenzano, J., Fossati, P., Dejonckheere, E., Verduyn, P., & Kuppens, P. (2021). In exibly sustained negative affect and rumination independently link default mode network efficiency to subclinical depressive symptoms. Journal of Affective Disorders, 293 , 347–354.
Rosseel, Y. (2012). lavaan: An R package for structural equation modeling. Journal of Statistical Software, 48 (2), 1–36.
Schuurman, N. K., & Hamaker, E. L. (2019). Measurement error and person-specific reliability in multilevel autoregressive modeling. Psychological Methods, 24 (1), 70–91.
Sels, L., Ceulemans, E., & Kuppens, P. (2017). Partner-expected affect: How you feel now is predicted by how your partner thought you felt before. Emotion, 17 (7), 1066–1077.
Tong, H., & Lim, K. S. (1980). Threshold autoregression, limit cycles and cyclical data. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological), 42 (3), 245–268.
Trafimow, D. (2022). Generalizing across auxiliary, statistical, and inferential assumptions. Journal for the Theory of Social Behaviour, 52 (1), 37–48.
Trull, T. J., & Ebner-Priemer, U. W. (2020). Ambulatory assessment in psychopathology research: A review of recommended reporting guidelines and current practices. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 129 (1), 56–63.
Vanhasbroeck, N., Ariens, S., Tuerlinckx, F., & Loossens, T. (2021). Computational Models for Affect Dynamics. In C. E. Waugh & P. Kuppens (Eds.), Affect Dynamics (pp. 213–260). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Chapter Google Scholar
Vanhasbroeck, N., Loossens, T., Anarat, N., Ariens, S., Vanpaemel, W., Moors, A., & Tuerlinckx, F. (2022). Stimulus-driven affective change: Evaluating computational models of affect dynamics in conjunction with input. Affective Science, 3 (3), 559–576.
Yarkoni, T., & Westfall, J. (2017). Choosing prediction over explanation in psychology: Lessons from machine learning. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 12 (6), 1100–1122.
Zhang, Y., Revol, J., Lafit, G., Ernst, A., Razum, J., Ceulemans, E., & Bringmann, L. (2023). Sample size optimization for person-specific temporal networks using power analysis and predictive accuracy analysis. Manuscript in preparation.
Download references
The research presented in this article was supported by research grants from the Fund for Scientific Research-Flanders (FWO; Project No. G0C9821N) and from the Research Council of KU Leuven (C14/23/062; iBOF/21/090) awarded to E. Ceulemans.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Research Group of Quantitative Psychology and Individual Differences, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
Jordan Revol & Eva Ceulemans
Methodology of Educational Sciences Research Group, KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
Ginette Lafit
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The authors made the following contributions. Jordan Revol: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Software, Writing - Original Draft Preparation, Review & Editing; Ginette Lafit: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing - Original Draft Preparation, Review & Editing. Eva Ceulemans: Conceptualization, Methodology, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing - Original Draft Preparation, Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jordan Revol .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship or the publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Revol, J., Lafit, G. & Ceulemans, E. A new sample-size planning approach for person-specific VAR(1) studies: Predictive accuracy analysis. Behav Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-024-02413-4
Download citation
Accepted : 28 March 2024
Published : 08 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-024-02413-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Predictive accuracy
- Sample-size planning method
- Power analysis
- Monte Carlo simulation
- Intensive longitudinal designs
- Autoregressive models
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Original research article, virtual surgical planning/3d printing assisted fibula osteoseptocutaneous flap combined with anterolateral thigh flaps for extensive composite oromandibular defects reconstruction: a retrospective study of case series.

- 1 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
- 2 School of Stomatology, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
- 3 Dental Digital Medicine and 3D Printing Engineering Laboratory of Qingdao, Qingdao, China
- 4 Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Digital Medicine and Computer-Assisted Surgery, Qingdao, China
Oromandibular tumors or osteoradionecrosis often lead to extensive composite defects encompassing intraoral, bone and extraoral tissues. A single flap cannot simultaneously offer sufficient bone and soft tissue. The combination of free flaps could be a prospective approach to overcome the challenge. The study aims to assess the efficacy of virtual surgical planning (VSP) and 3D printing assisted fibula osteoseptocutaneous flap (FOSCF) combined with anterolateral thigh flaps (ALT) in reconstructing extensive composite defects in the oromandibular region. A retrospective analysis was conducted on 8 patients who underwent reconstruction using FOSCFs combined with ALTs. Post-surgical excision of the lesions, we obtained mean values for the defects of intraoral soft tissue, bone, extraoral soft tissue, namely, being 42.7 cm 2 , 96 mm, and 68.9 cm 2 . The mean surgical procedures took 712.5 min. A total of 16 flaps were harvested and transplanted for the 8 patients, with all successfully surviving. Postoperatively, complications manifested as localized intraoral infections in 2 cases, intermuscular vein thrombosis in another 2 cases, and pulmonary infections in 2 patients. Two patients unfortunately experienced tumor recurrence, at 12 and 3 months post-operation respectively. For the surviving 6 patients, the average follow-up period was 12.2 months. Regarding patient satisfaction, one expressed dissatisfaction with the contour of the mandible, and two exhibited moderate trismus. Objective assessments identified 1 case of oral incontinence and 2 cases where external flap contractures were observed. All 8 patients experienced restoration of masticatory function and were able to consume a soft diet within a month post-surgery. VSP/3D printing assisted FOSCFs combined with ALTs can be performed safely to reconstruct the extensive composite tissue defects in our study, with desirable esthetic and functional results, and it is a reliable option in selecting patients with defects involving multiple tissue types. However, the benefits of this method needed more cases to validate.
1 Introduction
Extensive composite oromandibular defects are frequently caused by surgical resection of sizeable primary tumors in the head and neck region, or the result of osteoradionecrosis (ORN) post-radiotherapy. The reconstruction of such complex defects, encompassing multiple structures such as external skin, mandible, and oral mucosa presents a formidable challenge. Free flap reconstruction is the standard of care in these extensive defects, while there may not exist a single free flap capable of simultaneously offering sufficient bone stock and soft tissue. In these instances, the combination of multiple free flaps proves to be an efficacious treatment strategy ( Lee et al., 2010 ; Weitz et al., 2015 ).
Selecting suitable free flap is integral to the reconstructive success and overall outcome. In contrast to iliac or scapular osteocutaneous free flaps, the FOSCF can provide longer bone segments as well as ample skin paddle for intraoral lining ( Taylor et al., 2016 ; Liu et al., 2022 ). The ALT is the most useful workhorse flap employed for microsurgical reconstruction. Depending on requirements, the flap can be harvested as myocutaneous, fasciocutaneous, adipofascial, or in combination with the adjacent tissues or muscles as chimeric flaps. This versatility makes it particularly suited for the reconstruction of extensive extraoral skin defects ( Hsieh et al., 2021 ; Ranganath et al., 2022 ). The advent of VSP and 3D printing marks a significant milestone for the FOSCF. The utilization of these techniques enhances the safety, accuracy, and symmetry of this surgical procedure while considerably reducing the operating time ( Ritschl et al., 2021 ; Al-Sabahi et al., 2022 ; Idris et al., 2022 ).
Despite their advantages, multi-flap approaches for the reconstruction of composite oromandibular defects continue to be challenging and are a subject of ongoing debate. A few reports are available on the functional and aesthetic outcome of double free flap reconstructions in these defects ( Lee et al., 2010 ; Tharakan et al., 2023 ). The objective of this study is to evaluate the effect of the combination of VSP/3D printing-assisted FOSCF with ALT in composite tissue defects reconstruction which could not be solved by one single flap.
2 Patients and methods
This study received approval from the Ethics Committee at the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao (ethics number, QYFYWZLL 27958). A retrospective review was conducted of 8 patients who underwent extensive composite oromandibular defects repair using the combination of VSP/3D printing-assisted FOSCF with ALT between July 2019 and December 2022 at our department.
The cohort comprised seven males and one female. All patients had undergone lesion resection, with extensive defects variably involving oral mucosa, mandible, and perioral skin areas. All defects were reconstructed using a FOSCF in combination with ALT. A two-team approach was consistently employed throughout all stages of the operation.
2.1 Preparation of the FOSCF assisted by VSP and 3D printing
All patients underwent routine preoperative three-dimensional CT scan of the mandible and fibula (SOMATOM Force CT, slice thickness 0.625 mm), in addition to lower limb CT angiography (CTA). The acquired data were input into the Mimics 17.0 software (Materialise, Leuven, Belgium) in the DICOM format. The software was used to simulate tumor excision, fibula osteotomy, mandibular reconstruction, and the design of repositioning guides. In the process, the mandibular osteotomy guide and the fibula positioning guide share the same nail track to ensure the accuracy of mandibular reconstruction. For those mandibular defects not traversing the midline, mirror technology was employed to accomplish reconstruction. However, in cases where the defects did cross the midline, a synergistic approach combining mirror and surface reconstruction techniques was adopted. Following the completion of the virtual surgery, the designed guides were materialized using an 3D printer (UltraCraft A2D, HeyGears), and subsequently sterilized with plasma. The reconstruction-team prepared the FOSCF. The skin perforator was located and the skin paddle was incised in accordance with the magnitude of the intraoral soft tissue defect. The fibula osteotomy guide was positioned, leading to the fibula being cut to the length prescribed in the virtual surgery. The distal end of the fibular artery was ligated, preserving the proximal vascular pedicle. The fibula was then contoured using the shaping guide and secured in position with miniplates. Upon completing the FOSCF preparation, the same team proceeded to harvest the ALT.
2.2 Oral lesion excision
The resection-team was tasked with the excision of the tumor at its safe boundary. According to the preoperative virtual surgical design, the mandibular osteotomy guide was positioned, followed by the segmental resection of the mandible. After the complete excision of the tumor, two sets of recipient vessels were prepared. Subsequent to the surgical procedure, patients were admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU), and tracheostomy was not a routine intervention. Patients were typically transferred back to the general ward within a period of 3–5 days postoperatively, contingent upon their stabilized condition. All patients needed nasogastric feeding for 1 week post-surgery. Subsequently, a soft or normal diet was gradually adopted. All patients except No.5 and No.8 underwent postoperative radiation therapy.
Surgical and medical complications were documented. A patients satisfaction questionnaire was administered to make subjective evaluation on chewing, speech, dry mouth and facial appearance, which were divided into three grades: very satisfied, satisfied and dissatisfied. To determine objective evaluation, facial appearance, oral incontinence, speech problems, eating problems, xerostomia, and flap contracture were assessed. Each individual item was scored using a Likert scale (1 = extremely abnormal and 5 = completely normal).
Our study comprised 8 patients including 7 males and 1 female, aged from 45 to 68 years (mean, 60.5 years). Seven of these patients presented with oral malignant tumors, all diagnosed as squamous cell carcinoma, while one patient (No.5) had osteoradionecrosis as a consequence of radiation therapy. A total of 16 flaps were prepared for 8 patients, which consisted 8 FOSCFs and 8 ALTs. Post-excision of the lesions, the dimensions of the intraoral soft tissue defects ranged from 7.5 × 4 cm to 12 × 6.5 cm (mean, 42.7 cm 2 ). The length of the bone defects extended from 76 mm to 125 mm (mean, 96 mm), while the extraoral soft tissue defects varied from 8 × 5 cm to 14 × 9 cm (mean, 68.9 cm 2 ). The anastomosis involved recipient arteries that included the facial artery, superior thyroid artery, and lingual artery. Concurrently, the recipient veins involved were the facial vein, superior thyroid vein, internal jugular vein, and external jugular vein. One case required vascular grafting. The operative duration for these procedures ranged between 600 and 840 min, with an average of approximately 712.5 min ( Table 1 ).
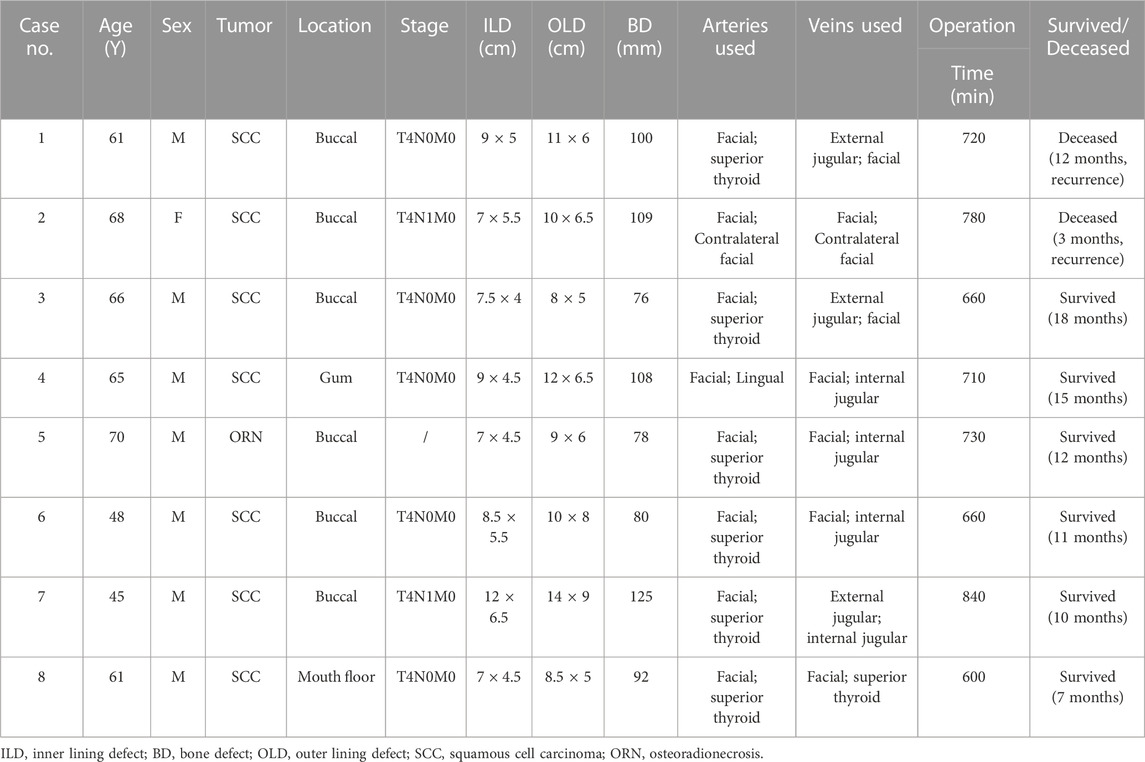
TABLE 1 . Patient data.
Remarkably, all of the flaps survived without any vascular crises or local flap necrosis. Two cases (No.3, No.4) developed local oral infections. Additionally, intermuscular vein thrombosis in the lower limbs was observed 2 patients (No.2, No.5). Pulmonary infection was found in 2 cases (No.2, No.4). Unfortunately, 2 of the 8 patients succumbed due to tumor recurrence at 12 months and 3 months post-surgery respectively. The mean follow-up time of the remaining 6 patients was 12.2 months (range, 7 months–18 months). Patient satisfaction assessments revealed one individual (No.3) was dissatisfied with their post-operative appearance, while two (No.2, No.4) reported moderate trismus. However, the remaining patients all reported satisfaction levels above average. Objective evaluations indicated oral incontinence in 1 case (No.4) and external flap contracture in 2 cases (No.2, No.4). Impressively, all 8 patients regained masticatory function and resumed a soft diet within a month post-operation.
3.1 Case presentation
A 45-year-old male patient diagnosed with a squamous cell carcinoma on his left cheek. The tumor demonstrated regression by radiation therapy (66 Gy) 7 months ago. However, the anterior part was ulcerated and gradually formed a penetrating defect after 1 month. Histopathological examination confirmed squamous cell carcinoma, staged clinically as T4N1M0. With the assistance of VSP and 3D printing technology, the reconstruction utilising both flaps was successfully performed ( Figures 1 , 2 ).
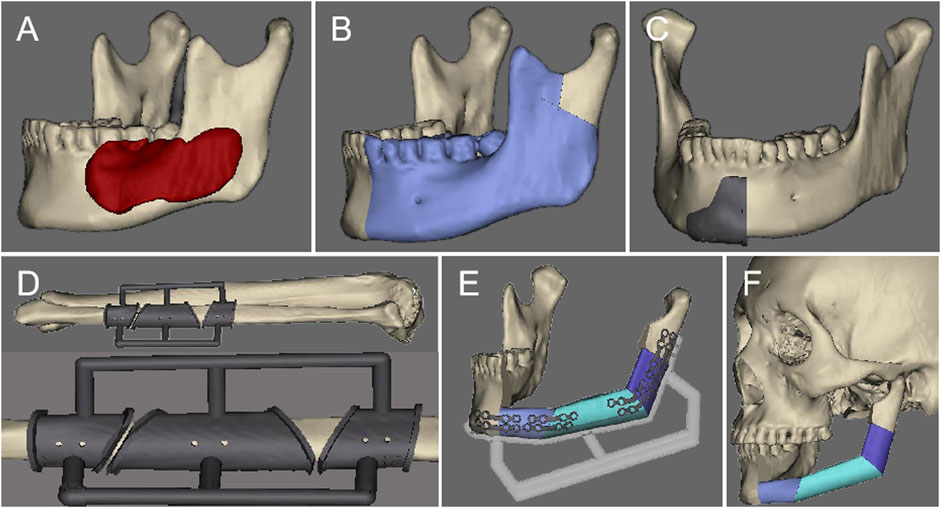
FIGURE 1 . The preoperative virtual surgical design: (A) . Determine the range of the lesion. (B) Simulate the range of bone cutting. (C) Design the bone cutting guide. (D) Design the fibula osteotomy guide. (E) Design the fibula repositioning guide. (F) Restore the mandibular contour.
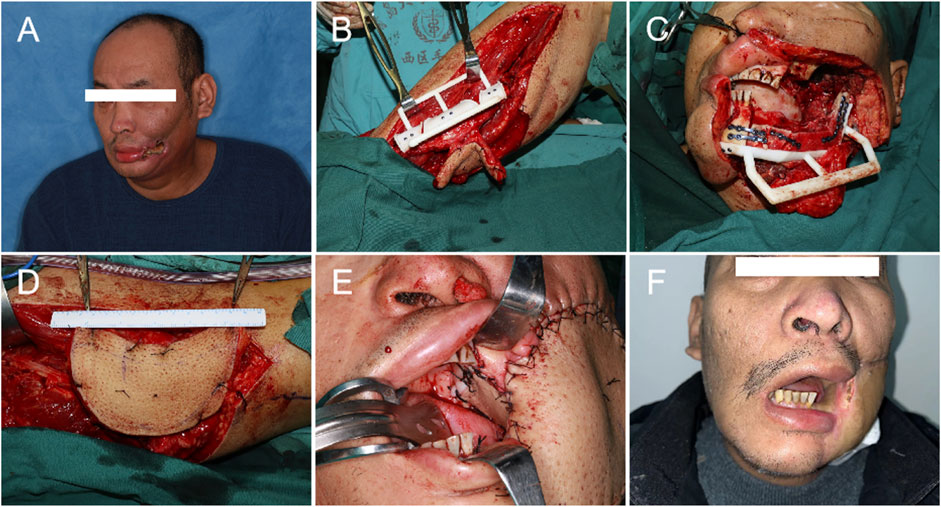
FIGURE 2 . Operational procedure: (A) . Preoperative photo. (B) Fibula shaping. (C) Fibula positioning. (D) Harvest of the ALT. (E) The fibula osteoseptocutaneous flap was used to repair the oral soft tissue and the mandible, and the ALT was used to repair the extraoral tissues. (F) 6 months post-operation.
4 Discussion
Surgical removal of oral tumors or osteoradionecrosis can result in substantial composite tissue defects, presenting formidable challenges for reconstructive repair. A single flap is often insufficient to adequately address these extensive defects. Consequently, the combination of multiple flaps has emerged as an innovative therapeutic approach ( Lee et al., 2010 ; Weitz et al., 2015 ; Hsieh and Bewley, 2019 ; Silva et al., 2019 ; Moratin et al., 2021 ; Raghuram et al., 2021 ; Santilli et al., 2021 ; Tharakan et al., 2023 ). The ALT can furnish sufficient tissue volume and can be fashioned into a chimeric flap with minimal impact on the donor site, rendering it an optimal choice for repair and reconstruction of large soft tissue defects in the oromandibular region ( Thomas et al., 2020 ). The FOSCF is exceptionally suitable for large bone tissue defects. Its accompanying skin paddle can repair tissues both inside or outside the oral cavity, and its associated muscle can effectively fill the surgical dead space ( Dowthwaite et al., 2013 ). Therefore, for large composite tissue defects in the oromandibular region, we opt for the ALT for the repair of extraoral soft tissue defects and the FOSCF for the repair of bone and intraoral soft tissue defects. Nevertheless, surgical alternatives should be carefully considered. The fibular flap can be substituted with a reconstruction plate, iliac bone muscle flap, or scapular bone muscle flap. Soft tissue flap can be replaced with a vascularized free flap or pedicled flap, such as the forearm flap, rectus abdominis flap, or pectoralis major myocutaneous flap. However, the radial forearm flap offers limited soft tissue volume, it is difficult to fill the dead cavity effectively. Its application is further limited by the severe scarring left on the forearm, tendon exposure, and forearm mobility disorders ( Ranganath et al., 2022 ). The rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap can deliver a satisfactory volume of soft tissue, yet it may trigger complications such as reduced abdominal wall strength and incisional hernia. While the pectoralis major flap supplies generous soft tissue, it’s typically considered a backup option. The free iliac flap has insufficient bone length to adequately repair the defects. Besides, the free scapular flap cannot effectively mimic the shape of the mandibula, and has limitations in deficient bone length ( Liu et al., 2022 ). Moreover, reconstruction plates are prone to complications like screw loosening, plate fracture, plate exposure and stress shielding.
A unique aspect of our study is the incorporation of VSP and 3D printing. VSP allows for tailoring surgical approaches, ensuring precise lesion delineation, osteotomy localization, and fibula harvest estimation. Preoperative mandibular modeling not only reduces surgical time but also ensures superior functional and aesthetic outcomes. 3D-printed guides, enhance surgical accuracy, fostering a closer match to the original mandibular structure. Shared screw tracks between the mandibular osteotomy and fibula positioning guides simplify the procedure, further minimizing trauma and operative time ( Seruya et al., 2013 ; Schepers et al., 2015 ; Wu et al., 2021 ). Using the osteotomy guide and positioning guide, the fibula is contoured and then affixed with mini titanium plates. Shaw et al. (2004) proved that there were no significant differences in complications between miniplates and reconstruction plates, but the author also highlighted the defects of reconstruction plates, including stress shielding, interference with the vascular pedicle, and problems of metal fatigue when bending plates in the sagittal plane. In comparison, miniplates which avoid the above drawbacks are a better choice. Intermaxillary fixation was performed after surgery for 1 week, encouraging oral exercises to prevent trismus.
The vascular pedicle is severed after the recipient vessels are prepared, markedly reducing ischemic time and overall duration of the surgery. Literature indicates that when the ALT donor site width is under 8.0 cm, primary closure is feasible; for wider defects, skin grafting becomes necessary ( Chen and Tang, 2003 ). Some reports suggest that direct suturing is feasible when the width is less than 10.0 cm ( Townley et al., 2011 ). Studies have proposed that the ratio of flap width to thigh circumference can serve as a reliable metric for direct wound closure, with a ratio less than 16% indicating direct closure ( Boca et al., 2010 ). In our study, we found that for one patient, the flap width was 9.0 cm, and direct suturing did not induce fascial compartment syndrome or other complications.
While the use of double flaps allows for the repair of large composite tissue defects in the oromandibular region, overcoming the limitations of a single flap or composite flap due to vascular pedicle restrictions, it demands higher provisions for neck vessels. This includes the preparation of two sets of anastomotic arteries and veins in the recipient area. In our study, it was found that arteries were relatively easier to prepare, with a total of 16 arteries prepared. The most frequently used anastomotic arteries were the facial artery and the superior thyroid artery, while the facial vein and internal jugular vein were the most commonly used anastomotic veins. Flow-through flaps, as reported in literature ( Qing et al., 2015 ; He et al., 2021 ), allow the usage of only one set of recipient area vessels. However, this approach carries a significant drawback: if a vascular crisis arises, both flaps are in danger of necrosis. Therefore, we advocate for the preparation of two sets of anastomotic arteries and veins in the recipient area to mitigate such circumstances. Literature suggests that the ligated internal jugular vein can be utilized for end-to-side anastomosis, offering a method for venous anastomosis ( Akazawa et al., 2019 ). Furthermore, it has been reported that the transverse cervical vein and superficial temporal vein can also serve as recipient area vessels ( Hansen et al., 2007 ; Tessler et al., 2017 ; Wang et al., 2021 ).
This method affords greater flexibility and autonomy, but it involves extended operation time, high costs, considerable trauma, and numerous potential complications. It mandates superior surgical skill, restricting its broader implementation. Inexperienced medical institutions and young physicians should first master single flap reconstruction before considering advanced techniques. Without this foundation, there’s a risk of increased surgical complications and irreversible outcomes. Additionally, the inclusion of 3D printing escalates treatment costs, making this approach unfeasible for institutions lacking this technology. In our study, though every flap transplantation was triumphant, five cases did confront complications. Two cases suffered from local oral infections and gradually recovered after conservative treatments. Two patients presented with intermuscular vein thrombosis in the lower limbs, which were successfully managed with oral medication, preventing the progression to potential organ embolisms such as cardiac, pulmonary, or cerebral embolism. Additionally, two cases demonstrated a pulmonary infection, which was effectively controlled with antibiotic therapy ( Tharakan et al., 2023 ). reported postoperative complications in multi-flap surgeries to range from 26% to 50%, aligning with our findings. Earlier research indicated a 5-year survival rate for advanced head and neck cancers between 25% and 56% ( Abdelmeguid et al., 2021 ; Mody et al., 2021 ). Our study, with 2 out of 8 patients succumbing to postoperative tumor recurrence, indicates a marginally superior survival rate, albeit potentially influenced by the relatively shorter follow-up duration. In summary, our study’s outcomes resonate with existing literature, suggesting that this approach doesn’t elevate complications or mortality rates.
It is crucial to acknowledge that patients who are candidates for this procedure are typically in the advanced stages of oral cancer. As such, it is of utmost importance to strictly adhere to the surgical indications:
1) The presence of extensive composite tissue defects, including intraoral, mandibula, and extraoral tissue defects that are too extensive to be repaired with a single flap;
2) The patient must be in good physical health, without obvious surgical contraindications such as congestive heart failure, pulmonary dysfunction, or neck vessel thrombosis;
3) The tumor can be completely resectable without systemic metastasis of lung and bone tissues;
4) The patient must possess a strong desire to combat the disease, as a positive attitude towards treatment is crucial.
However, this study does have limitations. Denture restoration is crucial for patients’ masticatory function ( Sozzi et al., 2017 ). Found that implant survival was high and implant-supported prostheses were a reliable rehabilitation option in patients whose jaws have been reconstruction with fibula-free flap. In our surgical method, fibula was used to prepare for implant repair in the future. However, due to postoperative adjuvant radiotherapy, patients paid more attention to tumor treatment and neglected denture repair. Both function and aesthetics are critically important, yet there is a potential gap in patients’ understanding of these aspects. Consequently, it’s our responsibility to educate them, promoting the benefits of implant restorations to restore masticatory function. Because of the rarity of such patients, we were unable to conduct controlled studies to objectively evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of this method compared to other treatment modalities. Nonetheless, we are confident that as the number of cases increases, the effectiveness of this treatment strategy will be confirmed. Moreover, the success of the double-flap surgery heavily relies on a precise preoperative surgical design and thorough considerations. The surgical approach offers limited flexibility, and the surgical procedure cannot be changed arbitrarily during the operation, as any deviations may result in a mismatch with the original design. Should unforeseen circumstances arise intraoperatively, we are prepared to implement alternative surgical strategies. Developing methodologies to anticipate, mitigate, and adeptly respond to such occurrences will constitute a primary objective in our ongoing research endeavors.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, VSP/3D printing assisted FOSCFs combined with ALTs offers a safe and effective avenue for reconstructing oromandibular massive composite tissue defects in the study. However, the broader benefits and efficacy of this technique necessitate further validation through an expanded patient cohort.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the ethical committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
YX: Investigation, Writing–original draft. YL: Investigation, Visualization, Writing–original draft. WX: Visualization, Writing–original draft. JY: Data curation, Writing–review and editing. LX: Validation, Writing–review and editing. LL: Data curation, Writing–review and editing. ZX: Formal Analysis, Writing–review and editing. JS: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Qingdao Medical and Health Research Program (grant number: 2021-WJZD193), the Qingdao University Affiliated Hospital Clinical Medicine + X Scientific Research Project (grant number: QDFY+X202101041), the Shandong Province Medical and Health Technology Development Plan Project (grant number: 202208020979), Qingdao Key Health Discipline Development Fund and Oral Medicine Climbing Discipline Project in Qingdao.
Acknowledgments
This study was approved by the ethical committee of the affiliated hospital of qingdao university (NO. QYFYWZLL 27958).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abdelmeguid, A. S., Silver, N. L., Boonsripitayanon, M., Glisson, B. S., Ferrarotto, R., Gunn, G. B., et al. (2021). Role of induction chemotherapy for oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 127, 3107–3112. doi:10.1002/cncr.33616
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Akazawa, T., Sekido, M., Adachi, K., Sasaki, K., Aihara, Y., Shibuya, Y., et al. (2019). End-to-Side venous anastomosis to a ligated vein stump for free flap transfer in head and neck reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 83, 180–182. doi:10.1097/sap.0000000000001905
Al-Sabahi, M. E., Jamali, O. M., Shindy, M. I., Moussa, B. G., Amin, A. A., and Zedan, M. H. (2022). Aesthetic reconstruction of onco-surgical mandibular defects using free fibular flap with and without CAD/CAM customized osteotomy guide: a randomized controlled clinical trial. BMC Cancer 22, 1252. doi:10.1186/s12885-022-10322-y
Boca, R., Kuo, Y. R., Hsieh, C. H., Huang, E. Y., and Jeng, S. F. (2010). A reliable parameter for primary closure of the free anterolateral thigh flap donor site. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 126, 1558–1562. doi:10.1097/prs.0b013e3181ef8cb7
Chen, H. C., and Tang, Y. B. (2003). Anterolateral thigh flap: an ideal soft tissue flap. Clin. Plast. Surg. 30, 383–401. doi:10.1016/s0094-1298(03)00040-3
Dowthwaite, S. A., Theurer, J., Belzile, M., Fung, K., Franklin, J., Nichols, A., et al. (2013). Comparison of fibular and scapular osseous free flaps for oromandibular reconstruction: a patient-centered approach to flap selection. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 139, 285–292. doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2013.1802
Hansen, S. L., Foster, R. D., Dosanjh, A. S., Mathes, S. J., Hoffman, W. Y., and Leon, P. (2007). Superficial temporal artery and vein as recipient vessels for facial and scalp microsurgical reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 120, 1879–1884. doi:10.1097/01.prs.0000287273.48145.bd
He, J., Qing, L., Wu, P., Zhou, Z., Yu, F., and Tang, J. (2021). Large wounds reconstruction of the lower extremity with combined latissimus dorsi musculocutaneous flap and flow-through anterolateral thigh perforator flap transfer. Microsurgery 41, 533–542. doi:10.1002/micr.30754
Hsieh, F., Leow, O. Q. Y., Cheong, C. F., Hung, S. Y., and Tsao, C. K. (2021). Musculoseptocutaneous perforator of anterolateral thigh flap: a clinical study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 147, 103e–110e. doi:10.1097/prs.0000000000007471
Hsieh, T. Y., and Bewley, A. (2019). Use of multiple free flaps in head and neck reconstruction. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 27, 392–400. doi:10.1097/moo.0000000000000574
Idris, S., Logan, H., Tabet, P., Osswald, M., Nayar, S., and Seikaly, H. (2022). The accuracy of 3D surgical design and simulation in prefabricated fibula free flaps for jaw reconstruction. J. Pers. Med. 12, 1766. doi:10.3390/jpm12111766
Lee, J. T., Hsu, H., Wang, C. H., Cheng, L. F., Sun, T. B., Huang, C. C., et al. (2010). Reconstruction of extensive composite oromandibular defects with simultaneous free anterolateral thigh fasciocutaneous and fibular osteocutaneous flaps. J. Reconstr. Microsurg 26, 145–151. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1242134
Liu, A. Q., Deane, E. C., Heffernan, A., Ji, Y., Durham, J. S., and Prisman, E. (2022). Patient-reported outcomes and morbidity after head and neck reconstructions: an evaluation of fibular and scapular free flaps. Oral Oncol. 132, 106019. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2022.106019
Mody, M. D., Rocco, J. W., Yom, S. S., Haddad, R. I., and Saba, N. F. (2021). Head and neck cancer. Lancet 398, 2289–2299. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(21)01550-6
Moratin, J., Horn, D., Heinemann, M., Metzger, K., Mrosek, J., Ristow, O., et al. (2021). Multiple sequential free flap reconstructions of the head and neck: a single-center experience. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 148, 791e–799e. doi:10.1097/prs.0000000000008432
Qing, L., Wu, P., Liang, J., Yu, F., Wang, C., and Tang, J. (2015). Use of flow-through anterolateral thigh perforator flaps in reconstruction of complex extremity defects. J. Reconstr. Microsurg 31, 571–578. doi:10.1055/s-0035-1555138
Raghuram, A. C., Manfro, G., Teixeira, G. V., Cernea, C. R., Dias, F. L., Marco, M., et al. (2021). Use of single chimeric free flaps or double free flaps for complex head and neck reconstruction. J. Reconstr. Microsurg 37, 791–798. doi:10.1055/s-0041-1727188
Ranganath, K., Jalisi, S. M., Naples, J. G., and Gomez, E. D. (2022). Comparing outcomes of radial forearm free flaps and anterolateral thigh free flaps in oral cavity reconstruction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 135, 106214. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2022.106214
Ritschl, L. M., Mucke, T., Hart, D., Unterhuber, T., Kehl, V., Wolff, K. D., et al. (2021). Retrospective analysis of complications in 190 mandibular resections and simultaneous reconstructions with free fibula flap, iliac crest flap or reconstruction plate: a comparative single centre study. Clin. Oral Investig. 25, 2905–2914. doi:10.1007/s00784-020-03607-8
Santilli, M., D'Addazio, G., Rexhepi, I., Sinjari, B., and Filippini, A. (2021). Multiple free flap reconstruction of a complex intraoral defect after squamous cell carcinoma excision: a case report. Med. Kaunas. 58, 54. doi:10.3390/medicina58010054
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Schepers, R. H., Raghoebar, G. M., Vissink, A., Stenekes, M. W., Kraeima, J., Roodenburg, J. L., et al. (2015). Accuracy of fibula reconstruction using patient-specific CAD/CAM reconstruction plates and dental implants: a new modality for functional reconstruction of mandibular defects. J. Craniomaxillofac Surg. 43, 649–657. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2015.03.015
Seruya, M., Fisher, M., and Rodriguez, E. D. (2013). Computer-assisted versus conventional free fibula flap technique for craniofacial reconstruction: an outcomes comparison. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 132, 1219–1228. doi:10.1097/prs.0b013e3182a3c0b1
Shaw, R. J., Kanatas, A. N., Lowe, D., Brown, J. S., Rogers, S. N., and Vaughan, E. D. (2004). Comparison of miniplates and reconstruction plates in mandibular reconstruction. Head. Neck 26, 456–463. doi:10.1002/hed.10343
Silva, A. K., Humphries, L. S., Maldonado, A. A., and Gottlieb, L. J. (2019). Chimeric vs composite flaps for mandible reconstruction. Head. Neck 41, 1597–1604. doi:10.1002/hed.25606
Sozzi, D., Novelli, G., Silva, R., Connelly, S. T., and Tartaglia, G. M. (2017). Implant rehabilitation in fibula-free flap reconstruction: a retrospective study of cases at 1-18 years following surgery. J. Craniomaxillofac Surg. 45, 1655–1661. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2017.06.021
Taylor, G. I., Corlett, R. J., and Ashton, M. W. (2016). The evolution of free vascularized bone transfer: a 40-year experience. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 137, 1292–1305. doi:10.1097/prs.0000000000002040
Tessler, O., Gilardino, M. S., Bartow, M. J., St Hilaire, H., Womac, D., Dionisopoulos, T., et al. (2017). Transverse cervical artery: consistent anatomical landmarks and clinical experience with its use as a recipient artery in complex head and neck reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 139, 745e–751e. doi:10.1097/prs.0000000000003085
Tharakan, T., Marfowaa, G., Akakpo, K., Jackson, R., Zenga, J., Puram, S. V., et al. (2023). Multiple simultaneous free flaps for head and neck reconstruction: a multi-institutional cohort. Oral Oncol. 136, 106269. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2022.106269
Thomas, W. W., Calcagno, H. E., Azzi, J., Petrisor, D., Cave, T., Barber, B., et al. (2020). Incidence of inadequate perforators and salvage options for the anterior lateral thigh free flap. Laryngoscope 130, 343–346. doi:10.1002/lary.28176
Townley, W. A., Royston, E. C., Karmiris, N., Crick, A., and Dunn, R. L. (2011). Critical assessment of the anterolateral thigh flap donor site. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 64, 1621–1626. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2011.07.015
Wang, L., Ma, C. Y., Shen, Y., Fang, J., Haugen, T. W., Guo, B., et al. (2021). Transverse cervical artery anterior perforator flap for head and neck oncological reconstruction: preliminary study. Head. Neck 43, 3598–3607. doi:10.1002/hed.26873
Weitz, J., Kreutzer, K., Bauer, F. J., Wolff, K. D., Nobis, C. P., and Kesting, M. R. (2015). Sandwich flaps as a feasible solution for the management of huge mandibular composite tissue defects. J. Craniomaxillofac Surg. 43, 1769–1775. doi:10.1016/j.jcms.2015.07.038
Wu, P., Hu, L., Li, H., Feng, L., Liu, Y., Zhang, S., et al. (2021). Clinical application and accuracy analysis of 3D printing guide plate based on polylactic acid in mandible reconstruction with fibula flap. Ann. Transl. Med. 9, 460. doi:10.21037/atm-20-6781
Keywords: flap transplantation, reconstructive surgery, virtual surgical planning, multipleflap, 3D printing
Citation: Xu Y, Li Y, Xiao W, Yue J, Xue L, Li L, Xu Z and Sun J (2023) Virtual surgical planning/3D printing assisted fibula osteoseptocutaneous flap combined with anterolateral thigh flaps for extensive composite oromandibular defects reconstruction: a retrospective study of case series. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11:1273318. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1273318
Received: 05 August 2023; Accepted: 23 October 2023; Published: 02 November 2023.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2023 Xu, Li, Xiao, Yue, Xue, Li, Xu and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jian Sun, [email protected]
This article is part of the Research Topic
Advanced Oral Disease Therapy: Approaches, Biotechnology, and Bioactive Materials, Volume II

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case study examples. Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study: Amazon Web Services, Inc. provides companies with cloud computing platforms and APIs on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis.
Video Case Study. Plan on meeting with the client and shooting an interview. Seeing the subject, in person, talk about the service you provided them can go a long way in the eyes of your potential customers. ... In fact, if you wanted to create a short case study, you could include your title, challenge, solution (how your product helped), and ...
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
The five case studies listed below are well-written, well-designed, and incorporate a time-tested structure. 1. Lane Terralever and Pinnacle at Promontory. This case study example from Lane Terralever incorporates images to support the content and effectively uses subheadings to make the piece scannable. 2.
15 Real-Life Case Study Examples. Now that you understand what a case study is, let's look at real-life case study examples. In this section, we'll explore SaaS, marketing, sales, product and business case study examples with solutions. Take note of how these companies structured their case studies and included the key elements.
In this case study example, the short and long-term goals are clearly distinguished by light blue boxes and placed side by side so that they are easy to compare. ... Planning and Branding; Best Marketing Strategies for Consultants and Freelancers in 2019 [Study + Infographic]
A case study is a detailed analysis of a specific topic in a real-world context. It can pertain to a person, place, event, group, or phenomenon, among others. The purpose is to derive generalizations about the topic, as well as other insights. Case studies find application in academic, business, political, or scientific research.
For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail. Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail. 3. EndeavourX and Figma.
To save you time and effort, I have curated a list of 5 versatile case study presentation templates, each designed for specific needs and audiences. Here are some best case study presentation examples that showcase effective strategies for engaging your audience and conveying complex information clearly. 1. Lab report case study template.
Most resources tell you that a case study should be 500-1500 words. We also encourage you to have a prominent snapshot section of 100 words or less. The results and benefits section should take the bulk of the word count. Don't use more words than you need. Let your data, images, and customers quotes do the talking.
A case study is a document that focuses on a business problem and provides a clear solution. Marketers use case studies to tell a story about a customer's journey or how a product or service solves a specific issue. Case studies can be used in all levels of business and in many industries. A thorough case study often uses metrics, such as key ...
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity.
Identify the key problems and issues in the case study. Formulate and include a thesis statement, summarizing the outcome of your analysis in 1-2 sentences. Background. Set the scene: background information, relevant facts, and the most important issues. Demonstrate that you have researched the problems in this case study. Evaluation of the Case
This is a short sample marketing case study for you to get an idea of what an actual marketing case study looks like. Elevating Brands: A Data-Driven Content Marketing Case Study. ... A dynamic marketing team implemented a comprehensive content marketing plan, focusing on data-driven strategies for long-term success. Solutions:
One Strategy: Aligning Planning and Execution. Strategy as it is written up in the corporate playbook often becomes lost or muddled when the team takes the field to execute. In their new book, Professor Marco Iansiti and Microsoft's Steven Sinofsky discuss a "One Strategy" approach to aligning plan and action.
Strategic Plan Example - The Bank Hapoalim Vision: To be a leading global financial services firm, with its core in Israel, focused on its clients and working to enhance their financial freedom. Bank Hapoalim, one of Israel's largest banks with 8,383 branches across 5 different countries as of 2022, has recently provided insights into its latest strategic plan.
Case Study: Career Choices When Life Is Short. The leaders of MedPath didn't typically shed tears in their weekly meetings, but this was an exception. Gil Lehner, one of the start-up's four ...
Case study research is typically extensive; it draws on multiple methods of data collection and involves multiple data sources. The researcher begins by identifying a specific case or set of cases to be studied. Each case is an entity that is described within certain parameters, such as a specific time frame, place, event, and process.
Synopsis of Case Study. Learning case studies force students to make critical judgments based on the data presented and. provides them with problems and challenges based on actual life scenarios ...
the total context of the planning pro-cess. In this paper, we cite a case study of "planning"' at the Ahmedabad Branch of the Praja Bank.' This study underlines how creative aspects of the planning process can suffer if planning is reduced to mechanistic target-setting and budgeting exercise with or with-out formal use of environmental data.
HRM Case studies play a vital role in management education especially in subjects like Human Resource Management (HRM), Personnel Management, PAAP and related subjects. It gives a clear picture of the concepts when you practise them through case studies. Here we have given some live HRM case studies that are short, useful & interesting.
Practical examples of models in capacity planning for different production modes include: . 1. Make to Stock (MTS) Make to Stock is common within discreet manufacturing and process manufacturing. As these operations often have complex multi-level BOMs, capacity planning must include planning for sub-processes required to produce components ...
Planning focuses on achieving objectives. Objectives are set in planning and all the means, resources and courses of action to achieve these objectives are formulated in planning. Planning is the primary function of management. Planning is the base of (and guide to) all the remaining functions of management. Planning is pervasive.
Case interviews allow employers to test and evaluate the following skills: Analytical skills and logical ability to solve problems. Structure and thought process. Ability to ask for relevant data/information. Tolerance for ambiguity and data overload. Poise and communication skills under pressure and in front of a client.
Case Studies in Design is a new effort to create opportunities for community and design leaders to think together about ways to catalyze transformational design, planning, and place-keeping from the ground up. The goals are to learn from ambitious projects designed in community, to share knowledge and experience through dialogue and a public library of case studies, and to train ourselves for ...
Researchers increasingly study short-term dynamic processes that evolve within single individuals using N = 1 studies. The processes of interest are typically captured by fitting a VAR(1) model to the resulting data. A crucial question is how to perform sample-size planning and thus decide on the number of measurement occasions that are needed. The most popular approach is to perform a power ...
The COVID-19 pandemic emphasized the importance of public spaces. Accessing public spaces during the pandemic improves physical health, reduces feelings of loneliness, and lessens depression. However, not all public spaces can provide an effective response during the pandemic. The public spaces' ability to respond to the pandemic varies depending on their resilience level, which refers to the ...
The general objectives of this research are an understanding of strategic planning and to apply it in one of the aspects of regional development, to explain the steps and process of strategic planning, and also how to determine and prioritize strategies. This research is descriptive in nature and applied-developmental in terms of purpose.
Oromandibular tumors or osteoradionecrosis often lead to extensive composite defects encompassing intraoral, bone and extraoral tissues. A single flap cannot simultaneously offer sufficient bone and soft tissue. The combination of free flaps could be a prospective approach to overcome the challenge. The study aims to assess the efficacy of virtual surgical planning (VSP) and 3D printing ...