How to Write a Systematic Review of the Literature
Affiliations.
- 1 1 Texas Tech University, Lubbock, TX, USA.
- 2 2 University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, USA.
- PMID: 29283007
- DOI: 10.1177/1937586717747384
This article provides a step-by-step approach to conducting and reporting systematic literature reviews (SLRs) in the domain of healthcare design and discusses some of the key quality issues associated with SLRs. SLR, as the name implies, is a systematic way of collecting, critically evaluating, integrating, and presenting findings from across multiple research studies on a research question or topic of interest. SLR provides a way to assess the quality level and magnitude of existing evidence on a question or topic of interest. It offers a broader and more accurate level of understanding than a traditional literature review. A systematic review adheres to standardized methodologies/guidelines in systematic searching, filtering, reviewing, critiquing, interpreting, synthesizing, and reporting of findings from multiple publications on a topic/domain of interest. The Cochrane Collaboration is the most well-known and widely respected global organization producing SLRs within the healthcare field and a standard to follow for any researcher seeking to write a transparent and methodologically sound SLR. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA), like the Cochrane Collaboration, was created by an international network of health-based collaborators and provides the framework for SLR to ensure methodological rigor and quality. The PRISMA statement is an evidence-based guide consisting of a checklist and flowchart intended to be used as tools for authors seeking to write SLR and meta-analyses.
Keywords: evidence based design; healthcare design; systematic literature review.
- Evidence-Based Medicine* / organization & administration
- Research Design*
- Systematic Reviews as Topic*
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution


Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- The PRISMA 2020...
The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews
PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews
- Related content
- Peer review
- Matthew J Page , senior research fellow 1 ,
- Joanne E McKenzie , associate professor 1 ,
- Patrick M Bossuyt , professor 2 ,
- Isabelle Boutron , professor 3 ,
- Tammy C Hoffmann , professor 4 ,
- Cynthia D Mulrow , professor 5 ,
- Larissa Shamseer , doctoral student 6 ,
- Jennifer M Tetzlaff , research product specialist 7 ,
- Elie A Akl , professor 8 ,
- Sue E Brennan , senior research fellow 1 ,
- Roger Chou , professor 9 ,
- Julie Glanville , associate director 10 ,
- Jeremy M Grimshaw , professor 11 ,
- Asbjørn Hróbjartsson , professor 12 ,
- Manoj M Lalu , associate scientist and assistant professor 13 ,
- Tianjing Li , associate professor 14 ,
- Elizabeth W Loder , professor 15 ,
- Evan Mayo-Wilson , associate professor 16 ,
- Steve McDonald , senior research fellow 1 ,
- Luke A McGuinness , research associate 17 ,
- Lesley A Stewart , professor and director 18 ,
- James Thomas , professor 19 ,
- Andrea C Tricco , scientist and associate professor 20 ,
- Vivian A Welch , associate professor 21 ,
- Penny Whiting , associate professor 17 ,
- David Moher , director and professor 22
- 1 School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia
- 2 Department of Clinical Epidemiology, Biostatistics and Bioinformatics, Amsterdam University Medical Centres, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, Netherlands
- 3 Université de Paris, Centre of Epidemiology and Statistics (CRESS), Inserm, F 75004 Paris, France
- 4 Institute for Evidence-Based Healthcare, Faculty of Health Sciences and Medicine, Bond University, Gold Coast, Australia
- 5 University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, San Antonio, Texas, USA; Annals of Internal Medicine
- 6 Knowledge Translation Program, Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute, Toronto, Canada; School of Epidemiology and Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada
- 7 Evidence Partners, Ottawa, Canada
- 8 Clinical Research Institute, American University of Beirut, Beirut, Lebanon; Department of Health Research Methods, Evidence, and Impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada
- 9 Department of Medical Informatics and Clinical Epidemiology, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, Oregon, USA
- 10 York Health Economics Consortium (YHEC Ltd), University of York, York, UK
- 11 Clinical Epidemiology Program, Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, Ottawa, Canada; School of Epidemiology and Public Health, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada; Department of Medicine, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada
- 12 Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine Odense (CEBMO) and Cochrane Denmark, Department of Clinical Research, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, Denmark; Open Patient data Exploratory Network (OPEN), Odense University Hospital, Odense, Denmark
- 13 Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, The Ottawa Hospital, Ottawa, Canada; Clinical Epidemiology Program, Blueprint Translational Research Group, Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, Ottawa, Canada; Regenerative Medicine Program, Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, Ottawa, Canada
- 14 Department of Ophthalmology, School of Medicine, University of Colorado Denver, Denver, Colorado, United States; Department of Epidemiology, Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, Maryland, USA
- 15 Division of Headache, Department of Neurology, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA; Head of Research, The BMJ , London, UK
- 16 Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Indiana University School of Public Health-Bloomington, Bloomington, Indiana, USA
- 17 Population Health Sciences, Bristol Medical School, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK
- 18 Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York, York, UK
- 19 EPPI-Centre, UCL Social Research Institute, University College London, London, UK
- 20 Li Ka Shing Knowledge Institute of St. Michael's Hospital, Unity Health Toronto, Toronto, Canada; Epidemiology Division of the Dalla Lana School of Public Health and the Institute of Health Management, Policy, and Evaluation, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada; Queen's Collaboration for Health Care Quality Joanna Briggs Institute Centre of Excellence, Queen's University, Kingston, Canada
- 21 Methods Centre, Bruyère Research Institute, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada; School of Epidemiology and Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada
- 22 Centre for Journalology, Clinical Epidemiology Program, Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, Ottawa, Canada; School of Epidemiology and Public Health, Faculty of Medicine, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, Canada
- Correspondence to: M J Page matthew.page{at}monash.edu
- Accepted 4 January 2021
The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement, published in 2009, was designed to help systematic reviewers transparently report why the review was done, what the authors did, and what they found. Over the past decade, advances in systematic review methodology and terminology have necessitated an update to the guideline. The PRISMA 2020 statement replaces the 2009 statement and includes new reporting guidance that reflects advances in methods to identify, select, appraise, and synthesise studies. The structure and presentation of the items have been modified to facilitate implementation. In this article, we present the PRISMA 2020 27-item checklist, an expanded checklist that details reporting recommendations for each item, the PRISMA 2020 abstract checklist, and the revised flow diagrams for original and updated reviews.
Systematic reviews serve many critical roles. They can provide syntheses of the state of knowledge in a field, from which future research priorities can be identified; they can address questions that otherwise could not be answered by individual studies; they can identify problems in primary research that should be rectified in future studies; and they can generate or evaluate theories about how or why phenomena occur. Systematic reviews therefore generate various types of knowledge for different users of reviews (such as patients, healthcare providers, researchers, and policy makers). 1 2 To ensure a systematic review is valuable to users, authors should prepare a transparent, complete, and accurate account of why the review was done, what they did (such as how studies were identified and selected) and what they found (such as characteristics of contributing studies and results of meta-analyses). Up-to-date reporting guidance facilitates authors achieving this. 3
The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement published in 2009 (hereafter referred to as PRISMA 2009) 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 is a reporting guideline designed to address poor reporting of systematic reviews. 11 The PRISMA 2009 statement comprised a checklist of 27 items recommended for reporting in systematic reviews and an “explanation and elaboration” paper 12 13 14 15 16 providing additional reporting guidance for each item, along with exemplars of reporting. The recommendations have been widely endorsed and adopted, as evidenced by its co-publication in multiple journals, citation in over 60 000 reports (Scopus, August 2020), endorsement from almost 200 journals and systematic review organisations, and adoption in various disciplines. Evidence from observational studies suggests that use of the PRISMA 2009 statement is associated with more complete reporting of systematic reviews, 17 18 19 20 although more could be done to improve adherence to the guideline. 21
Many innovations in the conduct of systematic reviews have occurred since publication of the PRISMA 2009 statement. For example, technological advances have enabled the use of natural language processing and machine learning to identify relevant evidence, 22 23 24 methods have been proposed to synthesise and present findings when meta-analysis is not possible or appropriate, 25 26 27 and new methods have been developed to assess the risk of bias in results of included studies. 28 29 Evidence on sources of bias in systematic reviews has accrued, culminating in the development of new tools to appraise the conduct of systematic reviews. 30 31 Terminology used to describe particular review processes has also evolved, as in the shift from assessing “quality” to assessing “certainty” in the body of evidence. 32 In addition, the publishing landscape has transformed, with multiple avenues now available for registering and disseminating systematic review protocols, 33 34 disseminating reports of systematic reviews, and sharing data and materials, such as preprint servers and publicly accessible repositories. To capture these advances in the reporting of systematic reviews necessitated an update to the PRISMA 2009 statement.
Summary points
To ensure a systematic review is valuable to users, authors should prepare a transparent, complete, and accurate account of why the review was done, what they did, and what they found
The PRISMA 2020 statement provides updated reporting guidance for systematic reviews that reflects advances in methods to identify, select, appraise, and synthesise studies
The PRISMA 2020 statement consists of a 27-item checklist, an expanded checklist that details reporting recommendations for each item, the PRISMA 2020 abstract checklist, and revised flow diagrams for original and updated reviews
We anticipate that the PRISMA 2020 statement will benefit authors, editors, and peer reviewers of systematic reviews, and different users of reviews, including guideline developers, policy makers, healthcare providers, patients, and other stakeholders
Development of PRISMA 2020
A complete description of the methods used to develop PRISMA 2020 is available elsewhere. 35 We identified PRISMA 2009 items that were often reported incompletely by examining the results of studies investigating the transparency of reporting of published reviews. 17 21 36 37 We identified possible modifications to the PRISMA 2009 statement by reviewing 60 documents providing reporting guidance for systematic reviews (including reporting guidelines, handbooks, tools, and meta-research studies). 38 These reviews of the literature were used to inform the content of a survey with suggested possible modifications to the 27 items in PRISMA 2009 and possible additional items. Respondents were asked whether they believed we should keep each PRISMA 2009 item as is, modify it, or remove it, and whether we should add each additional item. Systematic review methodologists and journal editors were invited to complete the online survey (110 of 220 invited responded). We discussed proposed content and wording of the PRISMA 2020 statement, as informed by the review and survey results, at a 21-member, two-day, in-person meeting in September 2018 in Edinburgh, Scotland. Throughout 2019 and 2020, we circulated an initial draft and five revisions of the checklist and explanation and elaboration paper to co-authors for feedback. In April 2020, we invited 22 systematic reviewers who had expressed interest in providing feedback on the PRISMA 2020 checklist to share their views (via an online survey) on the layout and terminology used in a preliminary version of the checklist. Feedback was received from 15 individuals and considered by the first author, and any revisions deemed necessary were incorporated before the final version was approved and endorsed by all co-authors.
The PRISMA 2020 statement
Scope of the guideline.
The PRISMA 2020 statement has been designed primarily for systematic reviews of studies that evaluate the effects of health interventions, irrespective of the design of the included studies. However, the checklist items are applicable to reports of systematic reviews evaluating other interventions (such as social or educational interventions), and many items are applicable to systematic reviews with objectives other than evaluating interventions (such as evaluating aetiology, prevalence, or prognosis). PRISMA 2020 is intended for use in systematic reviews that include synthesis (such as pairwise meta-analysis or other statistical synthesis methods) or do not include synthesis (for example, because only one eligible study is identified). The PRISMA 2020 items are relevant for mixed-methods systematic reviews (which include quantitative and qualitative studies), but reporting guidelines addressing the presentation and synthesis of qualitative data should also be consulted. 39 40 PRISMA 2020 can be used for original systematic reviews, updated systematic reviews, or continually updated (“living”) systematic reviews. However, for updated and living systematic reviews, there may be some additional considerations that need to be addressed. Where there is relevant content from other reporting guidelines, we reference these guidelines within the items in the explanation and elaboration paper 41 (such as PRISMA-Search 42 in items 6 and 7, Synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) reporting guideline 27 in item 13d). Box 1 includes a glossary of terms used throughout the PRISMA 2020 statement.
Glossary of terms
Systematic review —A review that uses explicit, systematic methods to collate and synthesise findings of studies that address a clearly formulated question 43
Statistical synthesis —The combination of quantitative results of two or more studies. This encompasses meta-analysis of effect estimates (described below) and other methods, such as combining P values, calculating the range and distribution of observed effects, and vote counting based on the direction of effect (see McKenzie and Brennan 25 for a description of each method)
Meta-analysis of effect estimates —A statistical technique used to synthesise results when study effect estimates and their variances are available, yielding a quantitative summary of results 25
Outcome —An event or measurement collected for participants in a study (such as quality of life, mortality)
Result —The combination of a point estimate (such as a mean difference, risk ratio, or proportion) and a measure of its precision (such as a confidence/credible interval) for a particular outcome
Report —A document (paper or electronic) supplying information about a particular study. It could be a journal article, preprint, conference abstract, study register entry, clinical study report, dissertation, unpublished manuscript, government report, or any other document providing relevant information
Record —The title or abstract (or both) of a report indexed in a database or website (such as a title or abstract for an article indexed in Medline). Records that refer to the same report (such as the same journal article) are “duplicates”; however, records that refer to reports that are merely similar (such as a similar abstract submitted to two different conferences) should be considered unique.
Study —An investigation, such as a clinical trial, that includes a defined group of participants and one or more interventions and outcomes. A “study” might have multiple reports. For example, reports could include the protocol, statistical analysis plan, baseline characteristics, results for the primary outcome, results for harms, results for secondary outcomes, and results for additional mediator and moderator analyses
PRISMA 2020 is not intended to guide systematic review conduct, for which comprehensive resources are available. 43 44 45 46 However, familiarity with PRISMA 2020 is useful when planning and conducting systematic reviews to ensure that all recommended information is captured. PRISMA 2020 should not be used to assess the conduct or methodological quality of systematic reviews; other tools exist for this purpose. 30 31 Furthermore, PRISMA 2020 is not intended to inform the reporting of systematic review protocols, for which a separate statement is available (PRISMA for Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement 47 48 ). Finally, extensions to the PRISMA 2009 statement have been developed to guide reporting of network meta-analyses, 49 meta-analyses of individual participant data, 50 systematic reviews of harms, 51 systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy studies, 52 and scoping reviews 53 ; for these types of reviews we recommend authors report their review in accordance with the recommendations in PRISMA 2020 along with the guidance specific to the extension.
How to use PRISMA 2020
The PRISMA 2020 statement (including the checklists, explanation and elaboration, and flow diagram) replaces the PRISMA 2009 statement, which should no longer be used. Box 2 summarises noteworthy changes from the PRISMA 2009 statement. The PRISMA 2020 checklist includes seven sections with 27 items, some of which include sub-items ( table 1 ). A checklist for journal and conference abstracts for systematic reviews is included in PRISMA 2020. This abstract checklist is an update of the 2013 PRISMA for Abstracts statement, 54 reflecting new and modified content in PRISMA 2020 ( table 2 ). A template PRISMA flow diagram is provided, which can be modified depending on whether the systematic review is original or updated ( fig 1 ).
Noteworthy changes to the PRISMA 2009 statement
Inclusion of the abstract reporting checklist within PRISMA 2020 (see item #2 and table 2 ).
Movement of the ‘Protocol and registration’ item from the start of the Methods section of the checklist to a new Other section, with addition of a sub-item recommending authors describe amendments to information provided at registration or in the protocol (see item #24a-24c).
Modification of the ‘Search’ item to recommend authors present full search strategies for all databases, registers and websites searched, not just at least one database (see item #7).
Modification of the ‘Study selection’ item in the Methods section to emphasise the reporting of how many reviewers screened each record and each report retrieved, whether they worked independently, and if applicable, details of automation tools used in the process (see item #8).
Addition of a sub-item to the ‘Data items’ item recommending authors report how outcomes were defined, which results were sought, and methods for selecting a subset of results from included studies (see item #10a).
Splitting of the ‘Synthesis of results’ item in the Methods section into six sub-items recommending authors describe: the processes used to decide which studies were eligible for each synthesis; any methods required to prepare the data for synthesis; any methods used to tabulate or visually display results of individual studies and syntheses; any methods used to synthesise results; any methods used to explore possible causes of heterogeneity among study results (such as subgroup analysis, meta-regression); and any sensitivity analyses used to assess robustness of the synthesised results (see item #13a-13f).
Addition of a sub-item to the ‘Study selection’ item in the Results section recommending authors cite studies that might appear to meet the inclusion criteria, but which were excluded, and explain why they were excluded (see item #16b).
Splitting of the ‘Synthesis of results’ item in the Results section into four sub-items recommending authors: briefly summarise the characteristics and risk of bias among studies contributing to the synthesis; present results of all statistical syntheses conducted; present results of any investigations of possible causes of heterogeneity among study results; and present results of any sensitivity analyses (see item #20a-20d).
Addition of new items recommending authors report methods for and results of an assessment of certainty (or confidence) in the body of evidence for an outcome (see items #15 and #22).
Addition of a new item recommending authors declare any competing interests (see item #26).
Addition of a new item recommending authors indicate whether data, analytic code and other materials used in the review are publicly available and if so, where they can be found (see item #27).
PRISMA 2020 item checklist
- View inline
PRISMA 2020 for Abstracts checklist*

PRISMA 2020 flow diagram template for systematic reviews. The new design is adapted from flow diagrams proposed by Boers, 55 Mayo-Wilson et al. 56 and Stovold et al. 57 The boxes in grey should only be completed if applicable; otherwise they should be removed from the flow diagram. Note that a “report” could be a journal article, preprint, conference abstract, study register entry, clinical study report, dissertation, unpublished manuscript, government report or any other document providing relevant information.
- Download figure
- Open in new tab
- Download powerpoint
We recommend authors refer to PRISMA 2020 early in the writing process, because prospective consideration of the items may help to ensure that all the items are addressed. To help keep track of which items have been reported, the PRISMA statement website ( http://www.prisma-statement.org/ ) includes fillable templates of the checklists to download and complete (also available in the data supplement on bmj.com). We have also created a web application that allows users to complete the checklist via a user-friendly interface 58 (available at https://prisma.shinyapps.io/checklist/ and adapted from the Transparency Checklist app 59 ). The completed checklist can be exported to Word or PDF. Editable templates of the flow diagram can also be downloaded from the PRISMA statement website.
We have prepared an updated explanation and elaboration paper, in which we explain why reporting of each item is recommended and present bullet points that detail the reporting recommendations (which we refer to as elements). 41 The bullet-point structure is new to PRISMA 2020 and has been adopted to facilitate implementation of the guidance. 60 61 An expanded checklist, which comprises an abridged version of the elements presented in the explanation and elaboration paper, with references and some examples removed, is available in the data supplement on bmj.com. Consulting the explanation and elaboration paper is recommended if further clarity or information is required.
Journals and publishers might impose word and section limits, and limits on the number of tables and figures allowed in the main report. In such cases, if the relevant information for some items already appears in a publicly accessible review protocol, referring to the protocol may suffice. Alternatively, placing detailed descriptions of the methods used or additional results (such as for less critical outcomes) in supplementary files is recommended. Ideally, supplementary files should be deposited to a general-purpose or institutional open-access repository that provides free and permanent access to the material (such as Open Science Framework, Dryad, figshare). A reference or link to the additional information should be included in the main report. Finally, although PRISMA 2020 provides a template for where information might be located, the suggested location should not be seen as prescriptive; the guiding principle is to ensure the information is reported.
Use of PRISMA 2020 has the potential to benefit many stakeholders. Complete reporting allows readers to assess the appropriateness of the methods, and therefore the trustworthiness of the findings. Presenting and summarising characteristics of studies contributing to a synthesis allows healthcare providers and policy makers to evaluate the applicability of the findings to their setting. Describing the certainty in the body of evidence for an outcome and the implications of findings should help policy makers, managers, and other decision makers formulate appropriate recommendations for practice or policy. Complete reporting of all PRISMA 2020 items also facilitates replication and review updates, as well as inclusion of systematic reviews in overviews (of systematic reviews) and guidelines, so teams can leverage work that is already done and decrease research waste. 36 62 63
We updated the PRISMA 2009 statement by adapting the EQUATOR Network’s guidance for developing health research reporting guidelines. 64 We evaluated the reporting completeness of published systematic reviews, 17 21 36 37 reviewed the items included in other documents providing guidance for systematic reviews, 38 surveyed systematic review methodologists and journal editors for their views on how to revise the original PRISMA statement, 35 discussed the findings at an in-person meeting, and prepared this document through an iterative process. Our recommendations are informed by the reviews and survey conducted before the in-person meeting, theoretical considerations about which items facilitate replication and help users assess the risk of bias and applicability of systematic reviews, and co-authors’ experience with authoring and using systematic reviews.
Various strategies to increase the use of reporting guidelines and improve reporting have been proposed. They include educators introducing reporting guidelines into graduate curricula to promote good reporting habits of early career scientists 65 ; journal editors and regulators endorsing use of reporting guidelines 18 ; peer reviewers evaluating adherence to reporting guidelines 61 66 ; journals requiring authors to indicate where in their manuscript they have adhered to each reporting item 67 ; and authors using online writing tools that prompt complete reporting at the writing stage. 60 Multi-pronged interventions, where more than one of these strategies are combined, may be more effective (such as completion of checklists coupled with editorial checks). 68 However, of 31 interventions proposed to increase adherence to reporting guidelines, the effects of only 11 have been evaluated, mostly in observational studies at high risk of bias due to confounding. 69 It is therefore unclear which strategies should be used. Future research might explore barriers and facilitators to the use of PRISMA 2020 by authors, editors, and peer reviewers, designing interventions that address the identified barriers, and evaluating those interventions using randomised trials. To inform possible revisions to the guideline, it would also be valuable to conduct think-aloud studies 70 to understand how systematic reviewers interpret the items, and reliability studies to identify items where there is varied interpretation of the items.
We encourage readers to submit evidence that informs any of the recommendations in PRISMA 2020 (via the PRISMA statement website: http://www.prisma-statement.org/ ). To enhance accessibility of PRISMA 2020, several translations of the guideline are under way (see available translations at the PRISMA statement website). We encourage journal editors and publishers to raise awareness of PRISMA 2020 (for example, by referring to it in journal “Instructions to authors”), endorsing its use, advising editors and peer reviewers to evaluate submitted systematic reviews against the PRISMA 2020 checklists, and making changes to journal policies to accommodate the new reporting recommendations. We recommend existing PRISMA extensions 47 49 50 51 52 53 71 72 be updated to reflect PRISMA 2020 and advise developers of new PRISMA extensions to use PRISMA 2020 as the foundation document.
We anticipate that the PRISMA 2020 statement will benefit authors, editors, and peer reviewers of systematic reviews, and different users of reviews, including guideline developers, policy makers, healthcare providers, patients, and other stakeholders. Ultimately, we hope that uptake of the guideline will lead to more transparent, complete, and accurate reporting of systematic reviews, thus facilitating evidence based decision making.
Acknowledgments
We dedicate this paper to the late Douglas G Altman and Alessandro Liberati, whose contributions were fundamental to the development and implementation of the original PRISMA statement.
We thank the following contributors who completed the survey to inform discussions at the development meeting: Xavier Armoiry, Edoardo Aromataris, Ana Patricia Ayala, Ethan M Balk, Virginia Barbour, Elaine Beller, Jesse A Berlin, Lisa Bero, Zhao-Xiang Bian, Jean Joel Bigna, Ferrán Catalá-López, Anna Chaimani, Mike Clarke, Tammy Clifford, Ioana A Cristea, Miranda Cumpston, Sofia Dias, Corinna Dressler, Ivan D Florez, Joel J Gagnier, Chantelle Garritty, Long Ge, Davina Ghersi, Sean Grant, Gordon Guyatt, Neal R Haddaway, Julian PT Higgins, Sally Hopewell, Brian Hutton, Jamie J Kirkham, Jos Kleijnen, Julia Koricheva, Joey SW Kwong, Toby J Lasserson, Julia H Littell, Yoon K Loke, Malcolm R Macleod, Chris G Maher, Ana Marušic, Dimitris Mavridis, Jessie McGowan, Matthew DF McInnes, Philippa Middleton, Karel G Moons, Zachary Munn, Jane Noyes, Barbara Nußbaumer-Streit, Donald L Patrick, Tatiana Pereira-Cenci, Ba’ Pham, Bob Phillips, Dawid Pieper, Michelle Pollock, Daniel S Quintana, Drummond Rennie, Melissa L Rethlefsen, Hannah R Rothstein, Maroeska M Rovers, Rebecca Ryan, Georgia Salanti, Ian J Saldanha, Margaret Sampson, Nancy Santesso, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre, Jelena Savović, Christopher H Schmid, Kenneth F Schulz, Guido Schwarzer, Beverley J Shea, Paul G Shekelle, Farhad Shokraneh, Mark Simmonds, Nicole Skoetz, Sharon E Straus, Anneliese Synnot, Emily E Tanner-Smith, Brett D Thombs, Hilary Thomson, Alexander Tsertsvadze, Peter Tugwell, Tari Turner, Lesley Uttley, Jeffrey C Valentine, Matt Vassar, Areti Angeliki Veroniki, Meera Viswanathan, Cole Wayant, Paul Whaley, and Kehu Yang. We thank the following contributors who provided feedback on a preliminary version of the PRISMA 2020 checklist: Jo Abbott, Fionn Büttner, Patricia Correia-Santos, Victoria Freeman, Emily A Hennessy, Rakibul Islam, Amalia (Emily) Karahalios, Kasper Krommes, Andreas Lundh, Dafne Port Nascimento, Davina Robson, Catherine Schenck-Yglesias, Mary M Scott, Sarah Tanveer and Pavel Zhelnov. We thank Abigail H Goben, Melissa L Rethlefsen, Tanja Rombey, Anna Scott, and Farhad Shokraneh for their helpful comments on the preprints of the PRISMA 2020 papers. We thank Edoardo Aromataris, Stephanie Chang, Toby Lasserson and David Schriger for their helpful peer review comments on the PRISMA 2020 papers.
Contributors: JEM and DM are joint senior authors. MJP, JEM, PMB, IB, TCH, CDM, LS, and DM conceived this paper and designed the literature review and survey conducted to inform the guideline content. MJP conducted the literature review, administered the survey and analysed the data for both. MJP prepared all materials for the development meeting. MJP and JEM presented proposals at the development meeting. All authors except for TCH, JMT, EAA, SEB, and LAM attended the development meeting. MJP and JEM took and consolidated notes from the development meeting. MJP and JEM led the drafting and editing of the article. JEM, PMB, IB, TCH, LS, JMT, EAA, SEB, RC, JG, AH, TL, EMW, SM, LAM, LAS, JT, ACT, PW, and DM drafted particular sections of the article. All authors were involved in revising the article critically for important intellectual content. All authors approved the final version of the article. MJP is the guarantor of this work. The corresponding author attests that all listed authors meet authorship criteria and that no others meeting the criteria have been omitted.
Funding: There was no direct funding for this research. MJP is supported by an Australian Research Council Discovery Early Career Researcher Award (DE200101618) and was previously supported by an Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Early Career Fellowship (1088535) during the conduct of this research. JEM is supported by an Australian NHMRC Career Development Fellowship (1143429). TCH is supported by an Australian NHMRC Senior Research Fellowship (1154607). JMT is supported by Evidence Partners Inc. JMG is supported by a Tier 1 Canada Research Chair in Health Knowledge Transfer and Uptake. MML is supported by The Ottawa Hospital Anaesthesia Alternate Funds Association and a Faculty of Medicine Junior Research Chair. TL is supported by funding from the National Eye Institute (UG1EY020522), National Institutes of Health, United States. LAM is supported by a National Institute for Health Research Doctoral Research Fellowship (DRF-2018-11-ST2-048). ACT is supported by a Tier 2 Canada Research Chair in Knowledge Synthesis. DM is supported in part by a University Research Chair, University of Ottawa. The funders had no role in considering the study design or in the collection, analysis, interpretation of data, writing of the report, or decision to submit the article for publication.
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at http://www.icmje.org/conflicts-of-interest/ and declare: EL is head of research for the BMJ ; MJP is an editorial board member for PLOS Medicine ; ACT is an associate editor and MJP, TL, EMW, and DM are editorial board members for the Journal of Clinical Epidemiology ; DM and LAS were editors in chief, LS, JMT, and ACT are associate editors, and JG is an editorial board member for Systematic Reviews . None of these authors were involved in the peer review process or decision to publish. TCH has received personal fees from Elsevier outside the submitted work. EMW has received personal fees from the American Journal for Public Health , for which he is the editor for systematic reviews. VW is editor in chief of the Campbell Collaboration, which produces systematic reviews, and co-convenor of the Campbell and Cochrane equity methods group. DM is chair of the EQUATOR Network, IB is adjunct director of the French EQUATOR Centre and TCH is co-director of the Australasian EQUATOR Centre, which advocates for the use of reporting guidelines to improve the quality of reporting in research articles. JMT received salary from Evidence Partners, creator of DistillerSR software for systematic reviews; Evidence Partners was not involved in the design or outcomes of the statement, and the views expressed solely represent those of the author.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Patient and public involvement: Patients and the public were not involved in this methodological research. We plan to disseminate the research widely, including to community participants in evidence synthesis organisations.
This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt and build upon this work, for commercial use, provided the original work is properly cited. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
- Gurevitch J ,
- Koricheva J ,
- Nakagawa S ,
- Liberati A ,
- Tetzlaff J ,
- Altman DG ,
- PRISMA Group
- Tricco AC ,
- Sampson M ,
- Shamseer L ,
- Leoncini E ,
- de Belvis G ,
- Ricciardi W ,
- Fowler AJ ,
- Leclercq V ,
- Beaudart C ,
- Ajamieh S ,
- Rabenda V ,
- Tirelli E ,
- O’Mara-Eves A ,
- McNaught J ,
- Ananiadou S
- Marshall IJ ,
- Noel-Storr A ,
- Higgins JPT ,
- Chandler J ,
- McKenzie JE ,
- López-López JA ,
- Becker BJ ,
- Campbell M ,
- Sterne JAC ,
- Savović J ,
- Sterne JA ,
- Hernán MA ,
- Reeves BC ,
- Whiting P ,
- Higgins JP ,
- ROBIS group
- Hultcrantz M ,
- Stewart L ,
- Bossuyt PM ,
- Flemming K ,
- McInnes E ,
- France EF ,
- Cunningham M ,
- Rethlefsen ML ,
- Kirtley S ,
- Waffenschmidt S ,
- PRISMA-S Group
- ↵ Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, et al, eds. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions : Version 6.0. Cochrane, 2019. Available from https://training.cochrane.org/handbook .
- Dekkers OM ,
- Vandenbroucke JP ,
- Cevallos M ,
- Renehan AG ,
- ↵ Cooper H, Hedges LV, Valentine JV, eds. The Handbook of Research Synthesis and Meta-Analysis. Russell Sage Foundation, 2019.
- IOM (Institute of Medicine)
- PRISMA-P Group
- Salanti G ,
- Caldwell DM ,
- Stewart LA ,
- PRISMA-IPD Development Group
- Zorzela L ,
- Ioannidis JP ,
- PRISMAHarms Group
- McInnes MDF ,
- Thombs BD ,
- and the PRISMA-DTA Group
- Beller EM ,
- Glasziou PP ,
- PRISMA for Abstracts Group
- Mayo-Wilson E ,
- Dickersin K ,
- MUDS investigators
- Stovold E ,
- Beecher D ,
- Noel-Storr A
- McGuinness LA
- Sarafoglou A ,
- Boutron I ,
- Giraudeau B ,
- Porcher R ,
- Chauvin A ,
- Schulz KF ,
- Schroter S ,
- Stevens A ,
- Weinstein E ,
- Macleod MR ,
- IICARus Collaboration
- Kirkham JJ ,
- Petticrew M ,
- Tugwell P ,
- PRISMA-Equity Bellagio group
Literature Review vs Systematic Review
- Literature Review vs. Systematic Review
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources
- Databases and Articles
- Specific Journal or Article
Subject Guide

Definitions
It’s common to confuse systematic and literature reviews because both are used to provide a summary of the existent literature or research on a specific topic. Regardless of this commonality, both types of review vary significantly. The following table provides a detailed explanation as well as the differences between systematic and literature reviews.
Kysh, Lynn (2013): Difference between a systematic review and a literature review. [figshare]. Available at: http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.766364
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Primary vs. Secondary Sources >>
- Last Updated: Dec 15, 2023 10:19 AM
- URL: https://libguides.sjsu.edu/LitRevVSSysRev
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Cryptography and Security
Title: large language models for cyber security: a systematic literature review.
Abstract: The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has opened up new opportunities for leveraging artificial intelligence in various domains, including cybersecurity. As the volume and sophistication of cyber threats continue to grow, there is an increasing need for intelligent systems that can automatically detect vulnerabilities, analyze malware, and respond to attacks. In this survey, we conduct a comprehensive review of the literature on the application of LLMs in cybersecurity (LLM4Security). By comprehensively collecting over 30K relevant papers and systematically analyzing 127 papers from top security and software engineering venues, we aim to provide a holistic view of how LLMs are being used to solve diverse problems across the cybersecurity domain. Through our analysis, we identify several key findings. First, we observe that LLMs are being applied to a wide range of cybersecurity tasks, including vulnerability detection, malware analysis, network intrusion detection, and phishing detection. Second, we find that the datasets used for training and evaluating LLMs in these tasks are often limited in size and diversity, highlighting the need for more comprehensive and representative datasets. Third, we identify several promising techniques for adapting LLMs to specific cybersecurity domains, such as fine-tuning, transfer learning, and domain-specific pre-training. Finally, we discuss the main challenges and opportunities for future research in LLM4Security, including the need for more interpretable and explainable models, the importance of addressing data privacy and security concerns, and the potential for leveraging LLMs for proactive defense and threat hunting. Overall, our survey provides a comprehensive overview of the current state-of-the-art in LLM4Security and identifies several promising directions for future research.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation

Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Bridging the gap: a systematic analysis of circular economy, supply chain management, and digitization for sustainability and resilience
- Published: 13 May 2024
Cite this article

- Bhawna ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3032-0104 1 , 2 ,
- Parminder Singh Kang 2 , 3 &
- Sanjeev Kumar Sharma 1
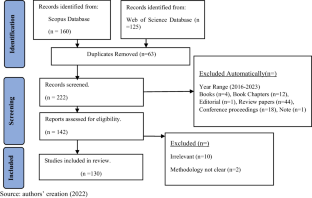
The primary objective of this research paper is to conduct a comprehensive and systematic literature review (SLR) focusing on Sustainable Supply Chain Management (SSCM) practices that promote Circular Economy (CE), sustainability, and resilience through adopting emerging digital technologies. A SLR of 130 research articles published between 1991 and 2023 was used to analyze emerging trends in CE, supply chain management (SCM), and digitalization. This study meticulously examined research publication patterns, the intricate themes explored, influential scholars, leading countries, and substantial scientific contributions that have shaped this multifaceted domain. This paper contributed to the collective understanding of how SSCM practices, driven by the principles of CE and empowered by the adoption of digital technologies, foster sustainability, resilience, and innovation within contemporary SCs. The research findings presented herein are primarily based on an analysis of the current literature from only Scopus and Web of Science (WoS) databases, which may restrict the generalizability of implementing these results. Based on this study, organizations and practitioners can assess the maturity of their SCM practices, gauge the resilience and digitalization levels of their SCs, and align them with academic literature trends. This enables practitioners to bridge the gap between scholarly advancements and real-world SCM implementation. Through its systematic review, the study provides a structured literature review that offers a collective understanding of SSCM practices driven by CE principles and empowered by digital technologies. This understanding enables sustainability, resilience, and innovation within contemporary SCs, benefiting academicians and practitioners.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Data availability
Data can be provided upon request.
Alamelu R, Jayanthi M, Dinesh S, Nalini R, Shobhana N, Amudha R (2023) Sustainable supply chain and circular economy ingenuities in small manufacturing firms-a stimulus for sustainable development. Mater Today: Proc 92:17–23
Google Scholar
Bag S, Pretorius JHC (2022) Relationships between industry 4.0, sustainable manufacturing and circular economy: proposal of a research framework. Int J Organ Anal 30(4):864–898. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOA-04-2020-2120
Article Google Scholar
Bag S, Wood LC, Xu L, Dhamija P, Kayikci Y (2020) Big data analytics as an operational excellence approach to enhance sustainable supply chain performance. Resour Conserv Recycl 153:104559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104559
Birkel H, Hohenstein N-O, Hähner S (2023) How have digital technologies facilitated supply chain resilience in the COVID-19 pandemic? An exploratory case study. Comput Ind Eng 183:109538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2023.109538
Branke J, Farid SS, Shah N (2016) Industry 4.0: a vision for personalized medicine supply chains? Cell Gene Therapy Insights 2(2):263–270. https://doi.org/10.18609/cgti.2016.027
Carter CR, Rogers DS (2008) A framework of sustainable supply chain management: moving toward new theory. Int J Phys Distribution Logistics Manage 38(5):360–387
Centobelli P, Cerchione R, Esposito E, Passaro R, Shashi (2021) Determinants of the transition towards circular economy in SMEs: a sustainable supply chain management perspective. Int J Prod Econ 242:108297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2021.108297
Cerqueira-Streit J, Endo G, Guarnieri P, Batista L (2021) Sustainable supply Chain Management in the Route for a circular economy: an integrative literature review. Logistics 5(4):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics5040081
Chadegani AA, Salehi H, Yunus MM, Farhadi H, Fooladi M, Farhadi M, Ebrahim NA (2013) A comparison between two Main Academic Literature collections: web of Science and Scopus databases. https://doi.org/10.48550/ARXIV.1305.0377
Chari A, Niedenzu D, Despeisse M, Machado CG, Azevedo JD, Boavida-Dias R, Johansson B (2022) Dynamic capabilities for circular manufacturing supply chains—exploring the role of industry 4.0 and resilience. Bus Strategy Environ 31(5):2500–2517. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.3040
Chauhan C, Singh A (2019) A review of industry 4.0 in supply chain management studies. J Manuf Technol Manage 31(5):863–886
Dentoni D, Pinkse J, Lubberink R (2021) Linking Sustainable Business models to Socio-Ecological Resilience through Cross-sector partnerships: a Complex Adaptive systems View. Bus Soc 60(5):1216–1252. https://doi.org/10.1177/0007650320935015
Donthu N, Kumar S, Pattnaik D (2020) Forty-five years of Journal of Business Research: a bibliometric analysis. J Bus Res 109:1–14
Edwin Cheng TC, Kamble SS, Belhadi A, Ndubisi NO, Lai K, Kharat MG (2022) Linkages between big data analytics, circular economy, sustainable supply chain flexibility, and sustainable performance in manufacturing firms. Int J Prod Res 60(22):6908–6922. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2021.1906971
El Baz J, Tiwari S, Akenroye T, Cherrafi A, Derrouiche R (2022) A framework of sustainability drivers and externalities for industry 4.0 technologies using the best-worst method. J Clean Prod 344:130909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130909
Esmaeilian B, Sarkis J, Lewis K, Behdad S (2020) Blockchain for the future of sustainable supply chain management in industry 4.0. Resour Conserv Recycl 163:105064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105064
Ferasso M, Beliaeva T, Kraus S, Clauss T, Ribeiro-Soriano D (2020) Circular economy business models: the state of research and avenues ahead. Bus Strategy Environ 29(8):3006–3024. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2554
Fisher O, Watson N, Porcu L, Bacon D, Rigley M, Gomes RL (2018) Cloud manufacturing as a sustainable process manufacturing route. J Manuf Syst 47:53–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2018.03.005
Gaur V, Gaiha A (2020) Building a transparent supply chain blockchain can enhance trust, efficiency, and speed. Harvard Business Rev 98(3):94–103
Ghisellini P, Cialani C, Ulgiati S (2016) A review on circular economy: the expected transition to a balanced interplay of environmental and economic systems. J Clean Prod 114:11–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.09.007
Golicic SL, Smith CD (2013) A meta-analysis of environmentally sustainable supply chain management practices and firm performance. J Supply Chain Manage 49(2):78–95
Govindan K, Hasanagic M (2018) A systematic review on drivers, barriers, and practices towards circular economy: a supply chain perspective. Int J Prod Res 56(1–2):278–311. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2017.1402141
Graham G, Hardaker G (2000) Supply-chain management across the Internet. Int J Phys Distrib Logist Manag 30(3/4):286–295. https://doi.org/10.1108/09600030010326055
Hendry LC, Stevenson M, MacBryde J, Ball P, Sayed M, Liu L (2019) Local food supply chain resilience to constitutional change: the Brexit effect. Int J Oper Prod Manage 39(3):429–453. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOPM-03-2018-0184
Hofmann E, Rüsch M (2017) Industry 4.0 and the current status as well as future prospects on logistics. Comput Ind 89:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compind.2017.04.002
Ingemarsdotter E, Jamsin E, Kortuem G, Balkenende R (2019) Circular strategies enabled by the internet of things—A framework and analysis of current practice. Sustainability 11(20):5689
Jabbarzadeh A, Fahimnia B, Sabouhi F (2018) Resilient and sustainable supply chain design: sustainability analysis under disruption risks. Int J Prod Res 56(17):5945–5968. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2018.1461950
Lopes de Sousa Jabbour AB, Jabbour CJ, Godinho Filho M, Roubaud D (2018) Industry 4.0 and the circular economy: a proposed research agenda and original roadmap for sustainable operations. Ann Oper Res 270:273–286
Kähkönen A-K, Lintukangas K, Hallikas J (2018) Sustainable supply management practices: making a difference in a firm’s sustainability performance. Supply Chain Management: Int J 23(6):518–530
Karmaker CL, Aziz A, Ahmed R, Misbauddin T, Moktadir MA (2023) Impact of industry 4.0 technologies on sustainable supply chain performance: the mediating role of green supply chain management practices and circular economy. J Clean Prod 419:138249
Lu HE, Potter A, Sanchez Rodrigues V, Walker H (2018) Exploring sustainable supply chain management: a social network perspective. Supply Chain Management: Int J 23(4):257–277
Luthra S, Mangla SK (2018) Evaluating challenges to industry 4.0 initiatives for supply chain sustainability in emerging economies. Process Saf Environ Prot 117:168–179
MacArthur E (2013) Towards the circular economy. J Ind Ecol 2(1):23–44
MacArthur E (2017) A new textiles economy: redesigning fashion’s future. Ellen MacArthur Foundation 1–150
Merli R, Preziosi M, Acampora A (2018) How do scholars approach the circular economy? A systematic literature review. J Clean Prod 178:703–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.12.112
Morali O, Searcy C (2013) A review of sustainable supply Chain Management practices in Canada. J Bus Ethics 117(3):635–658. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-012-1539-4
Nandi S, Sarkis J, Hervani AA, Helms MM (2021) Redesigning Supply chains using blockchain-enabled circular economy and COVID-19 experiences. Sustainable Prod Consum 27:10–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2020.10.019
Obeidat SM, Abdalla S, Al Bakri AAK (2023) Integrating green human resource management and circular economy to enhance sustainable performance: an empirical study from the Qatari service sector. Empl Relations: Int J 45(2):535–563. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-01-2022-0041
Pagell M, Wu Z (2009) Building a more complete theory of sustainable supply chain management using case studies of 10 exemplars. J Supply Chain Manage 45(2):37–56
Pettit TJ, Fiksel J, Croxton KL (2010) Ensuring supply chain resilience: development of a conceptual framework. J Bus Logistics 31(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.2158-1592.2010.tb00125.x
Ren Y, Li R, Wu K-J, Tseng M-L (2023) Discovering the systematic interlinkages among the circular economy, supply chain, industry 4.0, and technology transfer: a bibliometric analysis. Clean Responsible Consum 9:100123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clrc.2023.100123
Schmidt CVH, Kindermann B, Behlau CF, Flatten TC (2021) Understanding the effect of market orientation on circular economy practices: the mediating role of closed-loop orientation in German SMEs. Bus Strategy Environ 30(8):4171–4187. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2863
Shin N, Park S (2021) Supply chain leadership driven strategic resilience capabilities management: a leader-member exchange perspective. J Bus Res 122:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.08.056
Singh G, Singh S, Daultani Y, Chouhan M (2023) Measuring the influence of digital twins on the sustainability of manufacturing supply chain: a mediating role of supply chain resilience and performance. Comput Ind Eng 186:109711
Stock T, Seliger G (2016) Opportunities of Sustainable Manufacturing in Industry 4.0. Procedia CIRP 40:536–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2016.01.129
Talla A, McIlwaine S (2022) Industry 4.0 and the circular economy: using design-stage digital technology to reduce construction waste. Smart Sustainable Built Environ. https://doi.org/10.1108/SASBE-03-2022-0050
Tavera Romero CA, Castro DF, Ortiz JH, Khalaf OI, Vargas MA (2021) Synergy between circular economy and industry 4.0: a literature review. Sustainability 13(8):4331. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13084331
Tortorella G, Fogliatto FS, Gao S, Chan T-K (2022) Contributions of industry 4.0 to supply chain resilience. Int J Logistics Manage 33(2):547–566
Yadav G, Luthra S, Jakhar SK, Mangla SK, Rai DP (2020) A framework to overcome sustainable supply chain challenges through solution measures of industry 4.0 and circular economy: an automotive case. J Clean Prod 254:120112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120112
Download references
This research paper is part of a funded research project under Mitacs, Canada (Funding Ref. FR106245).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University Institute of Applied Management Sciences (UIAMS), Panjab University, Chandigarh, India
Bhawna & Sanjeev Kumar Sharma
Department of Decision Sciences, School of Business, MacEwan University, Edmonton, AB, Canada
Bhawna & Parminder Singh Kang
School of Engineering and Sustainable Development, Faculty of Technology, De Montfort University, Leicester, UK
Parminder Singh Kang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Bhawna .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
There are no relevant financial or non-financial competing interests to report.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Bhawna, Kang, P.S. & Sharma, S.K. Bridging the gap: a systematic analysis of circular economy, supply chain management, and digitization for sustainability and resilience. Oper Manag Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-024-00490-4
Download citation
Received : 12 October 2023
Revised : 20 March 2024
Accepted : 16 April 2024
Published : 13 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-024-00490-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Sustainable supply chain management
- Circular economy
- Supply chain sustainability
- Supply chain digitalization
- Research trends
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Systematic Reviews in the Engineering Literature: A Scoping Review
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Literature reviews establish the foundation of academic inquires. However, in the planning field, we lack rigorous systematic reviews. In this article, through a systematic search on the methodology of literature review, we categorize a typology of literature reviews, discuss steps in conducting a systematic literature review, and provide suggestions on how to enhance rigor in literature ...
The systematic, transparent searching techniques outlined in this article can be adopted and adapted for use in other forms of literature review (Grant & Booth 2009), for example, while the critical appraisal tools highlighted are appropriate for use in other contexts in which the reliability and applicability of medical research require ...
The semi-systematic or narrative review approach is designed for topics that have been conceptualized differently and studied by various groups of researchers within diverse disciplines and that hinder a full systematic review process (Wong et al., 2013). That is, to review every single article that could be relevant to the topic is simply not ...
A systematic review collects all possible studies related to a given topic and design, and reviews and analyzes their results [ 1 ]. During the systematic review process, the quality of studies is evaluated, and a statistical meta-analysis of the study results is conducted on the basis of their quality. A meta-analysis is a valid, objective ...
A Systematic Literature Review (SLR) is a research methodology to collect, identify, and critically analyze the available research studies (e.g., articles, conference proceedings, books, dissertations) through a systematic procedure [12]. An SLR updates the reader with current literature about a subject [6].
The systematic, transparent searching techniques outlined in this article can be adopted and adapted for use in other forms of literature review (Grant & Booth 2009), for example, while the critical appraisal tools highlighted are appropriate for use in other contexts in which the reliability and applicability of medical research require ...
A preliminary review, which can often result in a full systematic review, to understand the available research literature, is usually time or scope limited. Complies evidence from multiple reviews and does not search for primary studies. 3. Identifying a topic and developing inclusion/exclusion criteria.
Systematic reviews are characterized by a methodical and replicable methodology and presentation. They involve a comprehensive search to locate all relevant published and unpublished work on a subject; a systematic integration of search results; and a critique of the extent, nature, and quality of evidence in relation to a particular research question.
Cite this article: Lame, G. (2019) 'Systematic Literature Reviews: An Introduction', in Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Engineering Design (ICED19), Delft, The Netherlands, 5-8 August 2019. DOI:10.1017/ ... SRs treat the literature review process like a scientific process, and apply concepts of empirical ...
Cite this article: Lame, G. (2019) 'Systematic Literature Reviews: An Introduction', in Pr oceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Engineering Design (ICED19), Delft, The Netherlands ...
This article provides a step-by-step approach to conducting and reporting systematic literature reviews (SLRs) in the domain of healthcare design and discusses some of the key quality issues associated with SLRs. SLR, as the name implies, is a systematic way of collecting, critically evaluating, integrating, and presenting findings from across ...
This article also discusses bibliographic mapping approaches to visualise bibliometric information and findings from a systematic literature review. We hope that the insights provided in this article are useful for researchers at different stages of their careers - ranging from doctoral students who wish to assemble a broad overview of their ...
CONCLUSION. Siddaway 16 noted that, "The best reviews synthesize studies to draw broad theoretical conclusions about what the literature means, linking theory to evidence and evidence to theory" (p. 747). To that end, high quality systematic reviews are explicit, rigorous, and reproducible. It is these three criteria that should guide authors seeking to write a systematic review or editors ...
Systematic review vs. literature review. A literature review is a type of review that uses a less systematic and formal approach than a systematic review. Typically, an expert in a topic will qualitatively summarize and evaluate previous work, without using a formal, explicit method. ... The purpose of writing a systematic review article is to ...
The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement, published in 2009, was designed to help systematic reviewers transparently report why the review was done, what the authors did, and what they found. Over the past decade, advances in systematic review methodology and terminology have necessitated an update to the guideline. The PRISMA 2020 statement ...
Overview. A Systematic Literature Review (SLR) is a research methodology to collect, identify, and critically analyze the available research studies (e.g., articles, conference proceedings, books, dissertations) through a systematic procedure .An SLR updates the reader with current literature about a subject .The goal is to review critical points of current knowledge on a topic about research ...
A literature search is distinguished from, but integral to, a literature review. Literature reviews are conducted for the purpose of (a) locating information on a topic or identifying gaps in the literature for areas of future study, (b) synthesising conclusions in an area of ambiguity and (c) helping clinicians and researchers inform decision-making and practice guidelines.
Systematic reviews that summarize the available information on a topic are an important part of evidence-based health care. There are both research and non-research reasons for undertaking a literature review. It is important to systematically review the literature when one would like to justify the need for a study, to update personal ...
Systematic literature review articles are important for synthesizing knowledge in management and business research. However, to date, we lack clear guidelines how to review such articles. This editorial takes the perspective of the reviewer. It presents ten key questions and criteria that reviewers should ask when reviewing systematic literature reviews.
Regardless of this commonality, both types of review vary significantly. The following table provides a detailed explanation as well as the differences between systematic and literature reviews. Kysh, Lynn (2013): Difference between a systematic review and a literature review.
View a PDF of the paper titled Large Language Models for Cyber Security: A Systematic Literature Review, by HanXiang Xu and 7 other authors. View PDF Abstract: The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has opened up new opportunities for leveraging artificial intelligence in various domains, including cybersecurity. As the volume ...
In this paper, a systematic review is conducted to synthesize the extant literature and analyze the content to ascertain the value disposition of HIS in relation to healthcare delivery. Preceding this review, the used of search engines was employed to retrieve related research publications that fit the study scope and contexts.
The development of information and communication technologies has changed our way of working, emphasizing the need for individuals to develop collaborative skills. The aim of the present systematic review was to examine the extent to which these skills can be developed through the use of digital tools. A search of seven electronic databases ...
A systematic review can be distinguished from a narrative review because it will have explicitly stated objectives (the focused clinical question), materials (the relevant medical literature) and methods (the way in which studies are assessed and summarized).[1,2] A systematic review that incorporates quantitative pooling of similar studies to ...
A systematic review follows explicit methodology to answer a well-defined research question by searching the literature comprehensively, evaluating the quantity and quality of research evidence rigorously, and analyzing the evidence to synthesize an answer to the research question. The evidence gathered in systematic reviews can be qualitative ...
The primary objective of this research paper is to conduct a comprehensive and systematic literature review (SLR) focusing on Sustainable Supply Chain Management (SSCM) practices that promote Circular Economy (CE), sustainability, and resilience through adopting emerging digital technologies. A SLR of 130 research articles published between 1991 and 2023 was used to analyze emerging trends in ...
A systematic review is a specialized type of literature review used to collect and synthesize all the available evidence related to a research question. The methods for systematic reviews should be transparent and reproducible so that other researchers can use, replicate, and build upon the findings. Systematic reviews have been published for decades in medical literature where it is necessary ...
This allowed us to obtain a one-stop overview of the literature around the incubation process as guided by recent literature review works (Ferasso et al., 2020, Kraus et al., 2018). Secondly, we conducted a systematic literature review using the CIMO methodology as guided by Denyer et al. (2008). 3.2. Literature collection, synthesis and analysis
Background. A systematic review, as its name suggests, is a systematic way of collecting, evaluating, integrating, and presenting findings from several studies on a specific question or topic.[] A systematic review is a research that, by identifying and combining evidence, is tailored to and answers the research question, based on an assessment of all relevant studies.[2,3] To identify assess ...
Recognizing the pivotal role of information and communication technologies (ICTs) in generating economic benefits within the tourism and hospitality industry, this research aimed to develop a comprehensive understanding of the economic impacts of ICTs through a systematic review of the literature published on this topic since 2000.