- Math Article
- Ratios And Proportion

Ratios and Proportion

Ratio and Proportion are explained majorly based on fractions. When a fraction is represented in the form of a:b, then it is a ratio whereas a proportion states that two ratios are equal. Here, a and b are any two integers. The ratio and proportion are the two important concepts, and it is the foundation to understand the various concepts in mathematics as well as in science.

In our daily life, we use the concept of ratio and proportion such as in business while dealing with money or while cooking any dish, etc. Sometimes, students get confused with the concept of ratio and proportion. In this article, the students get a clear vision of these two concepts with more solved examples and problems.
For example, ⅘ is a ratio and the proportion statement is 20/25 = ⅘. If we solve this proportional statement, we get:
20 x 5 = 25 x 4
Check: Ratio and Proportion PDF
Therefore, the ratio defines the relationship between two quantities such as a:b, where b is not equal to 0. Example: The ratio of 2 to 4 is represented as 2:4 = 1:2. And the statement is said to be in proportion here. The application of proportion can be seen in direct proportion .
What is Ratio and Proportion in Maths?
The definition of ratio and proportion is described here in this section. Both concepts are an important part of Mathematics. In real life also, you may find a lot of examples such as the rate of speed (distance/time) or price (rupees/meter) of a material, etc, where the concept of the ratio is highlighted.
Proportion is an equation that defines that the two given ratios are equivalent to each other. For example, the time taken by train to cover 100km per hour is equal to the time taken by it to cover the distance of 500km for 5 hours. Such as 100km/hr = 500km/5hrs.
Let us now learn Maths ratio and proportion concept one by one.
Ratio Meaning
In certain situations, the comparison of two quantities by the method of division is very efficient. We can say that the comparison or simplified form of two quantities of the same kind is referred to as a ratio. This relation gives us how many times one quantity is equal to the other quantity. In simple words, the ratio is the number that can be used to express one quantity as a fraction of the other ones.
The two numbers in a ratio can only be compared when they have the same unit. We make use of ratios to compare two things. The sign used to denote a ratio is ‘:’.
A ratio can be written as a fraction, say 2/5. We happen to see various comparisons or say ratios in our daily life.
Hence, the ratio can be represented in three different forms, such as:
Key Points to Remember:
- The ratio should exist between the quantities of the same kind
- While comparing two things, the units should be similar
- There should be significant order of terms
- The comparison of two ratios can be performed, if the ratios are equivalent like the fractions
Definition of Proportion
Proportion is an equation that defines that the two given ratios are equivalent to each other. In other words, the proportion states the equality of the two fractions or the ratios. In proportion, if two sets of given numbers are increasing or decreasing in the same ratio, then the ratios are said to be directly proportional to each other.
For example, the time taken by train to cover 100km per hour is equal to the time taken by it to cover the distance of 500km for 5 hours. Such as 100km/hr = 500km/5hrs.
Ratio and proportions are said to be faces of the same coin. When two ratios are equal in value, then they are said to be in proportion . In simple words, it compares two ratios. Proportions are denoted by the symbol ‘::’ or ‘=’.
The proportion can be classified into the following categories, such as:
Direct Proportion
Inverse proportion, continued proportion.
Now, let us discuss all these methods in brief:
The direct proportion describes the relationship between two quantities, in which the increases in one quantity, there is an increase in the other quantity also. Similarly, if one quantity decreases, the other quantity also decreases. Hence, if “a” and “b” are two quantities, then the direction proportion is written as a∝b.
The inverse proportion describes the relationship between two quantities in which an increase in one quantity leads to a decrease in the other quantity. Similarly, if there is a decrease in one quantity, there is an increase in the other quantity. Therefore, the inverse proportion of two quantities, say “a” and “b” is represented by a∝(1/b).
Consider two ratios to be a: b and c: d .
Then in order to find the continued proportion for the two given ratio terms, we convert the means to a single term/number. This would, in general, be the LCM of means.
For the given ratio, the LCM of b & c will be bc.
Thus, multiplying the first ratio by c and the second ratio by b, we have
First ratio- ca:bc
Second ratio- bc: bd
Thus, the continued proportion can be written in the form of ca: bc: bd
Ratio and Proportion Formula
Now, let us learn the Maths ratio and proportion formulas here.
Ratio Formula
Assume that, we have two quantities (or two numbers or two entities) and we have to find the ratio of these two, then the formula for ratio is defined as;
where a and b could be any two quantities .
Here, “a” is called the first term or antecedent , and “b” is called the second term or consequent .
Example: In ratio 4:9, is represented by 4/9, where 4 is antecedent and 9 is consequent.
If we multiply and divide each term of ratio by the same number (non-zero), it doesn’t affect the ratio.
Example: 4:9 = 8:18 = 12:27
Also, read: Ratio Formula
Proportion Formula
Now, let us assume that, in proportion, the two ratios are a:b & c:d. The two terms ‘b’ and ‘c’ are called ‘means or mean term,’ whereas the terms ‘a’ and ‘d’ are known as ‘ extremes or extreme terms.’
Example: Let us consider one more example of a number of students in a classroom. Our first ratio of the number of girls to boys is 3:5 and that of the other is 4:8, then the proportion can be written as:
3 : 5 :: 4 : 8 or 3/5 = 4/8
Here, 3 & 8 are the extremes, while 5 & 4 are the means.
Note: The ratio value does not affect when the same non-zero number is multiplied or divided on each term.
Important Properties of Proportion
The following are the important properties of proportion:
- Addendo – If a : b = c : d, then a + c : b + d
- Subtrahendo – If a : b = c : d, then a – c : b – d
- Dividendo – If a : b = c : d, then a – b : b = c – d : d
- Componendo – If a : b = c : d, then a + b : b = c+d : d
- Alternendo – If a : b = c : d, then a : c = b: d
- Invertendo – If a : b = c : d, then b : a = d : c
- Componendo and dividendo – If a : b = c : d, then a + b : a – b = c + d : c – d
Difference Between Ratio and Proportion
To understand the concept of ratio and proportion, go through the difference between ratio and proportion given here.
Fourth, Third and Mean Proportional
If a : b = c : d, then:
- d is called the fourth proportional to a, b, c.
- c is called the third proportion to a and b.
- Mean proportional between a and b is √(ab).
Comparison of Ratios
If (a:b)>(c:d) = (a/b>c/d)
The compounded ratio of the ratios: (a : b), (c : d), (e : f) is (ace : bdf).
Duplicate Ratios
If a:b is a ratio, then:
- a 2 :b 2 is a duplicate ratio
- √a:√b is the sub-duplicate ratio
- a 3 :b 3 is a triplicate ratio
Ratio and Proportion Tricks
Let us learn here some rules and tricks to solve problems based on ratio and proportion topics.
- If u/v = x/y, then uy = vx
- If u/v = x/y, then u/x = v/y
- If u/v = x/y, then v/u = y/x
- If u/v = x/y, then (u+v)/v = (x+y)/y
- If u/v = x/y, then (u-v)/v = (x-y)/y
- If u/v = x/y, then (u+v)/ (u-v) = (x+y)/(x-y), which is known as componendo -Dividendo Rule
- If a/(b+c) = b/(c+a) = c/(a+b) and a+b+ c ≠0, then a =b = c
Ratio and Proportion Summary
- Ratio defines the relationship between the quantities of two or more objects. It is used to compare the quantities of the same kind.
- If two or more ratios are equal, then it is said to be in proportion.
- The proportion can be represented in two different ways. Either it can be represented using an equal sign or by using a colon symbol. (i.e) a:b = c:d or a:b :: c:d
- If we multiply or divide each term of the ratio by the same number, it does not affect the ratio.
- For any three quantities, the quantities are said to be in continued proportion, if the ratio between the first and second quantity is equal to the ratio between the second and third quantity.
- For any four quantities, they are said to be in continued proportion, if the ratio between the first and second quantities is equal to the ratio between the third and fourth quantities
Ratio And Proportion Examples
Example 1:
Are the ratios 4:5 and 8:10 said to be in Proportion?
4:5= 4/5 = 0.8 and 8: 10= 8/10= 0.8
Since both the ratios are equal, they are said to be in proportion.
Are the two ratios 8:10 and 7:10 in proportion?
8:10= 8/10= 0.8 and 7:10= 7/10= 0.7
Since both the ratios are not equal, they are not in proportion.
Example 3:
Given ratio are-
Find a: b: c.
Multiplying the first ratio by 5, second by 3 and third by 6, we have
a:b = 10: 15
b:c = 15 : 6
c:d = 6 : 24
In the ratio’s above, all the mean terms are equal, thus
a:b:c:d = 10:15:6:24
Check whether the following statements are true or false.
a] 12 : 18 = 28 : 56
b] 25 people : 130 people = 15kg : 78kg
The given statement is false.
12 : 18 = 12 / 18 = 2 / 3 = 2 : 3
28 : 56 = 28 / 56 = 1 / 2 = 1 : 2
They are unequal.
b] 25 persons : 130 persons = 15kg : 78kg
The given statement is true.
25 people : 130 people = 5: 26
15kg : 78kg = 5: 26
They are equal.
The earnings of Rohan is 12000 rupees every month and Anish is 191520 per year. If the monthly expenses of every person are around 9960 rupees. Find the ratio of the savings.
Savings of Rohan per month = Rs (12000-9960) = Rs. 2040
Yearly income of Anish = Rs. 191520
Hence, the monthly income of Anish = Rs. 191520/12 = Rs. 15960.
So, the savings of Anish per month = Rs (15960 – 9960) = Rs. 6000
Thus, the ratio of savings of Rohan and Anish is Rs. 2040: Rs.6000 = 17: 50.
Twenty tons of iron is Rs. 600000 (six lakhs). What is the cost of 560 kilograms of iron?
1 ton = 1000 kg 20 tons = 20000 kg The cost of 20000 kg iron = Rs. 600000 The cost of 1 kg iron = Rs{600000}/ {20000} = Rs. 30 The cost of 560 kg iron = Rs 30 × 560 = Rs 16800
The dimensions of the rectangular field are given. The length and breadth of the rectangular field are 50 meters and 15 meters. What is the ratio of the length and breadth of the field?
Length of the rectangular field = 50 m
Breadth of the rectangular field = 15 m
Hence, the ratio of length to breadth = 50: 15
⇒ 50: 15 = 10: 3.
Thus, the ratio of length and breadth of the rectangular field is 10:3.
Obtain a ratio of 90 centimetres to 1.5 meters.
The given two quantities are not in the same units.
Convert them into the same units.
1.5 m = 1.5 × 100 = 150 cm
Hence, the required ratio is 90 cm: 150 cm
⇒ 90: 150 = 3: 5
Therefore, the ratio of 90 centimetres to 1.5 meters is 3: 5.
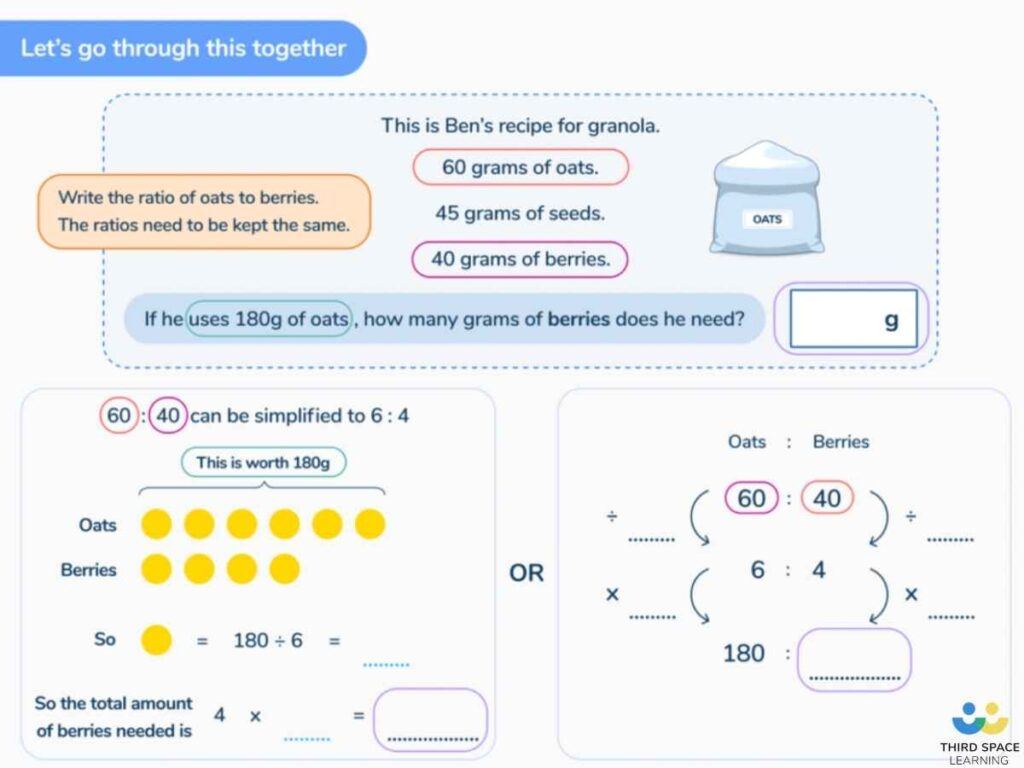
There exists 45 people in an office. Out of which female employees are 25 and the remaining are male employees. Find the ratio of
a] The count of females to males.
b] The count of males to females.
Count of females = 25
Total count of employees = 45
Count of males = 45 – 25 = 20
The ratio of the count of females to the count of males
The count of males to the count of females
Example 10:
Write two equivalent ratios of 6: 4.
Given Ratio : 6: 4, which is equal to 6/4.
Multiplying or dividing the same numbers on both numerator and denominator, we will get the equivalent ratio.
⇒(6×2)/(4×2) = 12/8 = 12: 8
⇒(6÷2)/(4÷2) = 3/2 = 3: 2
Therefore, the two equivalent ratios of 6: 4 are 3: 2 and 12: 8
Example 11 :
Out of the total students in a class, if the number of boys is 5 and the number of girls is 3, then find the ratio between girls and boys.
The ratio between girls and boys can be written as 3:5 (Girls: Boys). The ratio can also be written in the form of factor like 3/5.
Example 12:
Two numbers are in the ratio 2 : 3. If the sum of numbers is 60, find the numbers.
Given, 2/3 is the ratio of any two numbers.
Let the two numbers be 2x and 3x.
As per the given question, the sum of these two numbers = 60
So, 2x + 3x = 60
Hence, the two numbers are;
2x = 2 x 12 = 24
3x = 3 x 12 = 36
24 and 36 are the required numbers.
Maths ratio and proportion are used to solve many real-world problems. Register with BYJU’S – The Learning App and get solutions for many difficult questions in easy methodology and followed by the step-by-step procedure.
Frequently Asked Questions on Ratios and Proportion
What is the ratio give an example., what is a proportion give example, how to solve proportions with examples, what is the concept of ratios, what are the two different types of proportions.
The two different types of proportions are: Direct Proportion Inverse Proportion
Can we express ratio in terms of fractions?
Yes, we can express ratio in terms of fractions. For example, 3: 4 can be expressed as 3/4.
What is the formula for ratio and proportion?
The formula for ratio is: x:y ⇒ x/y, where x is the first term and y is the second term. The formula for proportion is: p: q :: r : s ⇒ p/q = r/s, Where p and r are the first term in the first and second ratio q and s are the second term and in the first and second ratio.
Find the means and extremes of the proportion 1: 2 :: 3: 4.
In the given proportion 1: 2 :: 3: 4, Means are 2 and 3 Extremes are 1 and 4.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Maths related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
Very helpful
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Proportions
Proportion says that two ratios (or fractions) are equal.
We see that 1-out-of-3 is equal to 2-out-of-6
The ratios are the same, so they are in proportion.
Example: Rope
A rope's length and weight are in proportion.
When 20m of rope weighs 1kg , then:
- 40m of that rope weighs 2kg
- 200m of that rope weighs 10kg
20 1 = 40 2
When shapes are "in proportion" their relative sizes are the same.
Example: International paper sizes (like A3, A4, A5, etc) all have the same proportions:
So any artwork or document can be resized to fit on any sheet. Very neat.
Working With Proportions
NOW, how do we use this?
Example: you want to draw the dog's head ... how long should it be?
Let us write the proportion with the help of the 10/20 ratio from above:
? 42 = 10 20
Now we solve it using a special method:
Multiply across the known corners, then divide by the third number
And we get this:
? = (42 × 10) / 20 = 420 / 20 = 21
So you should draw the head 21 long.
Using Proportions to Solve Percents
A percent is actually a ratio! Saying "25%" is actually saying "25 per 100":
25% = 25 100
We can use proportions to solve questions involving percents.
The trick is to put what we know into this form:
Part Whole = Percent 100
Example: what is 25% of 160 ?
The percent is 25, the whole is 160, and we want to find the "part":
Part 160 = 25 100
Multiply across the known corners, then divide by the third number:
Part = (160 × 25) / 100 = 4000 / 100 = 40
Answer: 25% of 160 is 40.
Note: we could have also solved this by doing the divide first, like this:
Part = 160 × (25 / 100) = 160 × 0.25 = 40
Either method works fine.
We can also find a Percent:
Example: what is $12 as a percent of $80 ?
Fill in what we know:
$12 $80 = Percent 100
Multiply across the known corners, then divide by the third number. This time the known corners are top left and bottom right:
Percent = ($12 × 100) / $80 = 1200 / 80 = 15%
Answer: $12 is 15% of $80
Or find the Whole:
Example: The sale price of a phone was $150, which was only 80% of normal price. What was the normal price?
$150 Whole = 80 100
Whole = ($150 × 100) / 80 = 15000 / 80 = 187.50
Answer: the phone's normal price was $187.50
Using Proportions to Solve Triangles
We can use proportions to solve similar triangles.
Example: How tall is the Tree?
Sam tried using a ladder, tape measure, ropes and various other things, but still couldn't work out how tall the tree was.

But then Sam has a clever idea ... similar triangles!
Sam measures a stick and its shadow (in meters), and also the shadow of the tree, and this is what he gets:
Now Sam makes a sketch of the triangles, and writes down the "Height to Length" ratio for both triangles:
Height: Shadow Length: h 2.9 m = 2.4 m 1.3 m
h = (2.9 × 2.4) / 1.3 = 6.96 / 1.3 = 5.4 m (to nearest 0.1)
Answer: the tree is 5.4 m tall.
And he didn't even need a ladder!
The "Height" could have been at the bottom, so long as it was on the bottom for BOTH ratios, like this:
Let us try the ratio of "Shadow Length to Height":
Shadow Length: Height: 2.9 m h = 1.3 m 2.4 m
It is the same calculation as before.
A "Concrete" Example
Ratios can have more than two numbers !
For example concrete is made by mixing cement, sand, stones and water.

A typical mix of cement, sand and stones is written as a ratio, such as 1:2:6 .
We can multiply all values by the same amount and still have the same ratio.
10:20:60 is the same as 1:2:6
So when we use 10 buckets of cement, we should use 20 of sand and 60 of stones.
Example: you have just put 12 buckets of stones into a mixer, how much cement and how much sand should you add to make a 1:2:6 mix?
Let us lay it out in a table to make it clearer:
You have 12 buckets of stones but the ratio says 6.
That is OK, you simply have twice as many stones as the number in the ratio ... so you need twice as much of everything to keep the ratio.
Here is the solution:
And the ratio 2:4:12 is the same as 1:2:6 (because they show the same relative sizes)
So the answer is: add 2 buckets of Cement and 4 buckets of Sand. (You will also need water and a lot of stirring....)
Why are they the same ratio? Well, the 1:2:6 ratio says to have :
- twice as much Sand as Cement ( 1 : 2 :6)
- 6 times as much Stones as Cement ( 1 :2: 6 )
In our mix we have:
- twice as much Sand as Cement ( 2 : 4 :12)
- 6 times as much Stones as Cement ( 2 :4: 12 )
So it should be just right!
That is the good thing about ratios. You can make the amounts bigger or smaller and so long as the relative sizes are the same then the ratio is the same.
Direct & Inverse Proportions/Variations
In these lessons, we will learn how to solve direct proportions (variations) and inverse proportions (inverse variations) problems. (Note: Some texts may refer to inverse proportions/variations as indirect proportions/variations.)
Related Pages: Direct Variations Proportion Word Problems More Algebra Lessons
The following diagram gives the steps to solve ratios and direct proportion word problems. Scroll down the page for examples and step-by-step solutions.
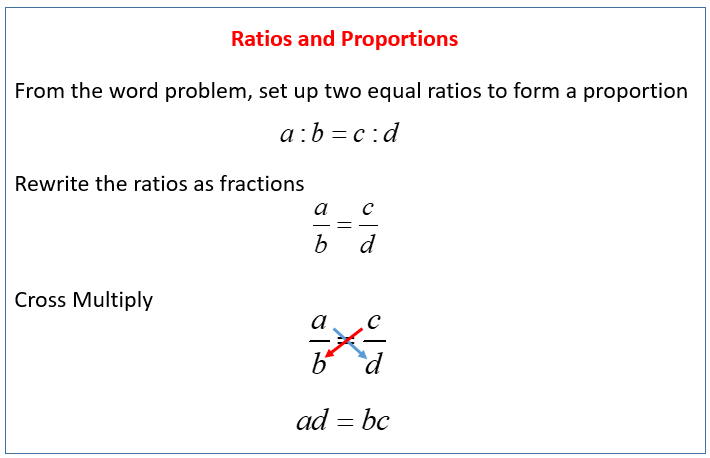
Direct Proportions/Variations
Knowing that the ratio does not change allows you to form an equation to find the value of an unknown variable.
Example : If two pencils cost $1.50, how many pencils can you buy with $9.00?
How To Solve Directly Proportional Questions?
Example 1: F is directly proportional to x. When F is 6, x is 4. Find the value of F when x is 5. Example 2: A is directly proportional to the square of B. When A is 10, B is 2. Find the value of A when B is 3.
How To Use Direct Proportion?
How To Solve Word Problems Using Proportions?
This video shows how to solve word problems by writing a proportion and solving 1. A recipe uses 5 cups of flour for every 2 cups of sugar. If I want to make a recipe using 8 cups of flour, how much sugar do I use? 2. A syrup is made by dissolving 2 cups of sugar in 2/3 cups of boiling water. How many cups of sugar should be used for 2 cups of boiling water? 3. A school buys 8 gallons of juice for 100 kids. how many gallons do they need for 175 kids?
Solving More Word Problems Using Proportions
1. On a map, two cities are 2 5/8 inches apart. If 3/8 inches on the map represents 25 miles, how far apart are the cities (in miles)? 2. Solve for the sides of similar triangles using proportions
Inverse Proportions/Variations Or Indirect Proportions
Two values x and y are inversely proportional to each other when their product xy is a constant (always remains the same). This means that when x increases y will decrease, and vice versa, by an amount such that xy remains the same.
Knowing that the product does not change also allows you to form an equation to find the value of an unknown variable
Example : It takes 4 men 6 hours to repair a road. How long will it take 8 men to do the job if they work at the same rate?
Solution : The number of men is inversely proportional to the time taken to do the job. Let t be the time taken for the 8 men to finish the job. 4 × 6 = 8 × t 24 = 8t t = 3 hours
Usually, you will be able to decide from the question whether the values are directly proportional or inversely proportional.
How To Solve Inverse Proportion Questions?
This video shows how to solve inverse proportion questions. It goes through a couple of examples and ends with some practice questions Example 1: A is inversely proportional to B. When A is 10, B is 2. Find the value of A when B is 8 Example 2: F is inversely proportional to the square of x. When A is 20, B is 3. Find the value of F when x is 5.
How To Use Inverse Proportion To Work Out Problems?
How to use a more advanced form of inverse proportion where the use of square numbers is involved.
More examples to explain direct proportions / variations and inverse proportions / variations
How to solve Inverse Proportion Math Problems on pressure and volume?
In math, an inverse proportion is when an increase in one quantity results in a decrease in another quantity. This video will show how to solve an inverse proportion math problem. Example : The pressure in a piston is 2.0 atm at 25°C and the volume is 4.0L. If the pressure is increased to 6.0 atm at the same temperature, what will be the volume?

We welcome your feedback, comments and questions about this site or page. Please submit your feedback or enquiries via our Feedback page.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2.6: Ratio and Proportion Applications
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 18338

\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Understand the difference between a ratio and a proportion.
- Solve proportions using cross multiplication.
- Solve applications involving proportions, including similar triangles.
Definitions
A ratio is a relationship between two numbers or quantities usually expressed as a quotient. Ratios are typically expressed using the following notation:
\(\frac{a}{b}\qquad a\:to\:b\qquad a:b\)
All of the above are equivalent forms used to express a ratio. However, the most familiar way to express a ratio is in the form of a fraction. When writing ratios, it is important to pay attention to the units. If the units are the same, then the ratio can be written without them.
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Express the ratio \(12\) feet to \(48\) feet in reduced form.
\(\begin{aligned} 12\text{ feet to }48\text{ feet} &=\frac{12\text{ feet}}{48\text{ feet}} \\ &=\color{black}{\frac{12\color{Cerulean}{\div 12}}{48\color{Cerulean}{\div 12}}} &\color{Cerulean}{Reduce.} \\ &=\frac{1}{4} \end{aligned}\)
\(1\) to \(4\)
If the units are different, then we must be sure to include them because the ratio represents a rate.
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Express the ratio \(220\) miles to \(4\) hours in reduced form.
\(\begin{aligned} 220\text{ miles to }4\text{ hours}&=\frac{220\text{ miles}}{4\text{ hours}} \\ &=\frac{55\text{miles}}{1\text{ hour}} \\ &=55\text{ miles\hour} \end{aligned}\)
\(55\) miles to \(1\) hours (or \(55\) miles per hour)
Rates are useful when determining unit cost, or the price of each unit. We use the unit cost to compare values when the quantities are not the same. To determine the unit cost, divide the cost by the number of units.
Example \(\PageIndex{3}\)
A local supermarket offers a pack of \(12\) sodas for $\(3.48\) on sale, and the local discount warehouse offers the soda in a \(36\)-can case for $\(11.52\). Which is the better value?
Divide the cost by the number of cans to obtain the unit price.
The supermarket sale price of $\(3.48\) for a \(12\)-pack is a better value at $\(0.29\) per can.
A proportion is a statement of equality of two ratios.
\[\frac{a}{b}=\frac{c}{d}\]
This proportion is often read “\(a\) is to \(b\) as \(c\) is to \(d\).” Here is an example of a simple proportion,
\(\frac{1}{2}=\frac{2}{4}\)
If we clear the fractions by multiplying both sides of the proportion by the product of the denominators, \(8\), then we obtain the following true statement:
\(\begin{aligned}\color{Cerulean}{8\cdot}\color{black}{\frac{1}{2}}&=\color{Cerulean}{8\cdot}\color{black}{\frac{2}{4}} \\ 4\cdot 1&=2\cdot 2\\ 4&=4 \end{aligned}\)
Given any nonzero real numbers \(a, b, c,\) and \(d\) that satisfy a proportion, multiply both sides by the product of the denominators to obtain the following:
\(\begin{aligned} \frac{a}{b}&=\frac{c}{d} \\ \color{Cerulean}{bd}\color{black}{\cdot \frac{a}{b}}&=\color{Cerulean}{bd}\color{black}{\cdot \frac{c}{d}} \\ ad&=bc \end{aligned}\)
This shows that cross products are equal, and is commonly referred to as cross multiplication.
\[\text{If }\frac{a}{b}=\frac{c}{d}\text{ then }ad=bc\]
Solving Proportions
Cross multiply to solve proportions where terms are unknown.
Example \(\PageIndex{4}\)
\(\frac{5}{8}=\frac{n}{4}\).
Cross multiply and then solve for \(n\).
.png?revision=1)
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)
\(\begin{aligned} 5\cdot 4&=8\cdot n &\color{Cerulean}{Cross\:multiply.} \\ 20&=8n \\ \frac{20}{\color{Cerulean}{8}} &=\frac{8n}{\color{Cerulean}{8}} &\color{Cerulean}{Divide\:by\:8.} \\ \color{black}{\frac{20\color{Cerulean}{\div 4}}{8\color{Cerulean}{\div 4}}} &=n &\color{Cerulean}{Reduce.} \\ \frac{5}{2}&=n \end{aligned}\)
\(n=\frac{5}{2}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{5}\)
\(\frac{15}{x}=\frac{5}{6}\).
Cross multiply then solve for \(x\).
\(\begin{aligned} \frac{15}{x}&=\frac{5}{6} \\ 15\cdot 6&=x\cdot 5 \\ 15\cdot 6&=5x \\ \frac{15\cdot 6}{\color{Cerulean}{5}}&=\frac{5x}{\color{Cerulean}{5}} \\ 3\cdot 6&=1x \\ 18&=x \end{aligned}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{6}\)
\(\frac{n+3}{5}=\frac{7}{2}\).
When cross multiplying, be sure to group \(n+3\). Apply the distributive property in the next step.
\(\begin{aligned} \frac{n+3}{5}&=\frac{7}{2} &\color{Cerulean}{Cross\:multiply.} \\ (n+3)\cdot 2&=5\cdot 7 &\color{Cerulean}{Distribute.} \\ 2n+6&=35 &\color{Cerulean}{Solve.} \\ 2n+6\color{Cerulean}{-6}&=35\color{Cerulean}{-6} \\ 2n&=29 \\ \frac{2n}{\color{Cerulean}{2}}&=\frac{29}{\color{Cerulean}{2}} \\ n&=\frac{29}{2} \end{aligned}\)
\(n=\frac{29}{2}\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
\(\frac{5}{3}=\frac{3n−1}{2}\).
\(n=\frac{13}{9}\)
Applications
When setting up proportions, consistency with the units of each ratio is critical. Units for the numerators should be the same and units for the denominators should also be the same.
Example \(\PageIndex{7}\)
It is claimed that \(2\) out of \(3\) dentists prefer a certain brand of toothpaste. If 600 dentists are surveyed, then how many will say they prefer that brand?
First, identify the unknown and assign it a variable.
Let \(n\) represent the number of dentists surveyed who prefer the brand name.
Since you are looking for the number of dentists who prefer the brand name out of a total of \(600\) surveyed, construct the ratios with the number of dentists who prefer the brand in the numerator and the total number surveyed in the denominator.
\(\begin{aligned} \underline{2}=\underline{n} &\quad\color{Cerulean}{\leftarrow\:number\:of\:dentists\:who\:prefer\:the\:brand} \\ 3\:\:600&\quad\color{Cerulean}{\leftarrow\:total\:number\:of\:dentists\:surveyed} \end{aligned}\)
Cross multiply and solve for \(n\),
\(\begin{aligned} 2\cdot 600&=3\cdot n \\ \frac{2\cdot 600}{\color{Cerulean}{3}}&=\frac{3\cdot n}{\color{Cerulean}{3}} \\ 2\cdot 200&=1n \\ 400&=n \end{aligned}\)
The claim suggests that \(400\) out of \(600\) dentists surveyed prefer the brand name.
Example \(\PageIndex{8}\)
In Tulare County, \(3\) out of every \(7\) voters said yes to Proposition 40. If \(42,000\) people voted, how many said no to Proposition 40?
The problem gives the ratio of voters who said yes, but it asks for the number who said no.
Let \(n\) represent the number of voters who said no.
If \(3\) out of \(7\) said yes, then we can assume \(4\) out of \(7\) said no. Set up the ratios with the number of voters who said no in the numerator and the total number of voters in the denominator.
\(\begin{aligned} &\underline{4}=\:\:\:\:\underline{n}&\color{Cerulean}{\leftarrow\:voters\:who\:voted\:no} \\ &7\:\:\:\:\:\:42,000&\color{Cerulean}{\leftarrow\:total\:number\:of\:voters} \end{aligned}\)
Cross multiply and solve for \(n\).
\(\begin{aligned} 4\cdot 42,000&=7\cdot n \\ \frac{4\cdot 42,000}{\color{Cerulean}{7}}&=\frac{7\cdot n}{\color{Cerulean}{7}} \\ 24,000&=n \end{aligned}\)
\(24,000\) voters out of \(42,000\) said no.
Example \(\PageIndex{9}\)
The sum of two integers in the ratio of \(4\) to \(5\) is \(27\). Find the integers.
The sum of two integers is \(27\); use this relationship to avoid two variables.
Let \(n\) represent one of the integers.
Let \(27-n\) represent the other integer.
The integers are given to be in the ratio of \(4\) to \(5\). Set up the following proportion:
\(\begin{aligned} \frac{4}{5}&=\frac{n}{27-n} \\ 4\cdot (27-n)&=5\cdot n \\ 108-4n&=5n \\ 108-4n\color{Cerulean}{+4n} &=5n\color{Cerulean}{+4n} \\ 108&=9n \\ \frac{108}{\color{Cerulean}{9}}&=\frac{9n}{\color{Cerulean}{9}} \\ 12&=n \end{aligned}\)
Use \(27 − n\) to determine the other integer.
\(27-n=27-\color{OliveGreen}{12}\color{black}{=15}\)
The integers are \(12\) and \(15\).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
A recipe calls for \(5\) tablespoons of sugar for every \(8\) cups of flour. How many tablespoons of sugar are required for \(32\) cups of flour?
\(20\) tablespoons of sugar
Similar Triangles
We will often encounter proportion problems in geometry and trigonometry. One application involves similar triangles, which have the same shape, but not necessarily the same size. The measures of the corresponding angles of similar triangles are equal, and the measures of the corresponding sides are proportional. Given similar triangles \(ABC\) and \(RST\),
.png?revision=1)
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)
We may write \(ABC ~ RST\) and conclude that all of the corresponding angles are equal. The notation indicates that angle \(A\) corresponds to angle \(R\) and that the measures of these angles are equal: \(A = R\).
.png?revision=1)
Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)
In addition, the measures of other pairs of corresponding angles are equal: \(B = S\) and \(C = T\).
.png?revision=1)
Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Use uppercase letters for angles and a lowercase letter to denote the side opposite of the given angle. Denote the proportionality of the sides as follows:
\(\frac{a}{r}=\frac{b}{s}=\frac{c}{t}\)
Example \(\PageIndex{10}\)
If triangle \(ABC\) is similar to \(RST\), where \(a=3, b=4, c=5,\) and \(r=9\), then find the remaining two sides.
Draw a picture and identify the variables pictorially. Represent the remaining unknown sides by \(s\) and \(t\). Set up proportions and solve for the missing sides.
.png?revision=1)
Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)
\(\begin{array}{c|c}{\underline{Find\:t}}&{\underline{Find\:s}}\\{\begin{aligned} \frac{5}{t}&=\frac{3}{9} \\ 5\cdot 9&=t\cdot 3 \\ \frac{5\cdot 9}{\color{Cerulean}{3}}&=\frac{t\cdot 3}{\color{Cerulean}{3}} \\ 5\cdot 3&=t \\ 15&=t \end{aligned}}&{\begin{aligned} \frac{4}{s}&=\frac{3}{9} \\ 4\cdot 9&=s\cdot 3 \\ \frac{4\cdot 9}{\color{Cerulean}{3}}&=\frac{s\cdot 3}{\color{Cerulean}{3}} \\ 4\cdot 3&=s \\ 12&=s \end{aligned}} \end{array}\)
The two remaining sides measure \(12\) units and \(15\) units.
The reduced ratio of any two corresponding sides of similar triangles is called the scale factor. In the previous example, the ratio of the two given sides \(a\) and \(r\) is
\(\frac{3}{9}=\frac{1}{3}\)
Therefore, triangle \(ABC\) is similar to triangle \(RST\) with a scale factor of \(\frac{1}{3}\). This means that each leg of triangle \(ABC\) is \(\frac{1}{3}\) of the measure of the corresponding legs of triangle \(RST\). Also, another interesting fact is that the perimeters of similar triangles are in the same proportion as their sides and share the same scale factor.
Example \(\PageIndex{11}\)
If a triangle \(ABC\) has a perimeter of \(12\) units and is similar to \(RST\) with a scale factor of \(\frac{1}{3}\), then find the perimeter of triangle \(RST\).
Let \(x\) represent the perimeter of triangle \(RST\).
Scale factor \(\frac{1}{3}\) implies that the perimeters are in proportion to this ratio. Set up a proportion as follows:
\(\begin{aligned} &\underline{1}=\underline{12} &\color{Cerulean}{\leftarrow\:perimeter\:of\:ABC} \\ &3\:\:\:\:\:\:x &\color{Cerulean}{\leftarrow\:perimeter\:of\:RST} \end{aligned}\)
Cross multiply and solve for \(x\).
\(\begin{aligned} 1\cdot x&=3\cdot 12 \\ x&=36 \end{aligned}\)
The perimeter of triangle \(RST\) is \(36\) units.
Key Takeaways
- Solve proportions by multiplying both sides of the equation by the product of the denominators, or cross multiply.
- When setting up a proportion, it is important to ensure consistent units in the numerators and denominators.
- The corresponding angles of similar triangles are equal and their corresponding sides are proportional. The ratio of any two corresponding sides determines the scale factor, which can be used to solve many applications involving similar triangles.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\) Ratios and Rates
Express each ratio in reduced form.
- \(100\) inches : \(250\) inches
- \(480\) pixels : \(320\) pixels
- \(96\) feet : \(72\) feet
- \(240\) miles \(4\) hours
- \(96\) feet \(3\) seconds
- \(6,000\) revolutions \(4\) minutes
- Google’s average 2008 stock price and earnings per share were $\(465.66\) and $\(14.89\), respectively. What was Google’s average price-to-earnings ratio in 2008? (Source: Wolfram Alpha)
- The F-22 Raptor has two engines that each produce \(35,000\) pounds of thrust. If the takeoff weight of this fighter jet is \(50,000\) pounds, calculate the plane’s thrust-to-weight ratio. (Source: USAF)
- A discount warehouse offers a box of \(55\) individual instant oatmeal servings for $\(11.10\). The supermarket offers smaller boxes of the same product containing \(12\) individual servings for $\(3.60\). Which store offers the better value?
- Joe and Mary wish to take a road trip together and need to decide whose car they will take. Joe calculated that his car is able to travel \(210\) miles on \(12\) gallons of gasoline. Mary calculates that her car travels \(300\) miles on \(19\) gallons. Which of their cars gets more miles to the gallon?
5. \(32\) feet per second
7. \(31.27\)
9. The discount warehouse
Exercise \(\PageIndex{4}\) Solving Proportions
- \(\frac{2}{3}=\frac{n}{150}\)
- \(\frac{7}{n}=\frac{2}{15}\)
- \(\frac{1}{3}=\frac{5}{n}\)
- \(\frac{1}{25}=\frac{6}{n}\)
- \(\frac{n}{8}=−\frac{3}{2}\)
- \(\frac{n}{3}=−\frac{5}{7}\)
- \(8=\frac{2n}{3}\)
- \(\frac{5}{n}=−30\)
- \(1=\frac{1}{n−1}\)
- \(−1=−\frac{1}{n+1}\)
- \(−\frac{40}{n}=−\frac{5}{3}\)
- \(\frac{2n+1}{3}=−\frac{3}{5}\)
- \(\frac{5}{3n+3}=\frac{2}{3}\)
- \(\frac{n+1}{2n−1}=\frac{1}{3}\)
- \(\frac{5n+7}{5}=\frac{n−1}{2}\)
- \(−\frac{2}{n+3}=\frac{n+7}{6}\)
- Find two numbers in the ratio of \(3\) to \(5\) whose sum is \(160\). (Hint: Use \(n\) and \(160 − n\) to represent the two numbers.)
- Find two numbers in the ratio of \(2\) to \(7\) whose sum is \(90\).
- Find two numbers in the ratio of \(−3\) to \(7\) whose sum is \(80\).
- Find two numbers in the ratio of \(−1\) to \(3\) whose sum is \(90\).
- A larger integer is \(5\) more than a smaller integer. If the two integers have a ratio of \(6\) to \(5\) find the integers.
- A larger integer is \(7\) less than twice a smaller integer. If the two integers have a ratio of \(2\) to \(3\) find the integers.
1. \(n=100\)
3. \(n=15\)
5. \(n=−12\)
7. \(n=12\)
11. \(n=24\)
13. \(n=\frac{3}{2}\)
15. \(n=−\frac{19}{5}\)
17. \(60, 100\)
19. \(−60, 140\)
21. \(25, 30\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{5}\) Solving Proportions
Given the following proportions, determine each ratio, \(x:y\).
- \(\frac{x}{3}=\frac{y}{4}\)
- \(\frac{x−2y}{3}=−\frac{3y}{5}\)
- \(\frac{2x+4y}{2x−4y}=\frac{3}{2}\)
- \(\frac{x+y}{x−y}=\frac{3}{5}\)
1. \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{6}\) Applications
Set up a proportion and then solve.
- If \(4\) out of every \(5\) voters support the governor, then how many of the \(1,200\) people surveyed support the governor?
- If \(1\) out of every \(3\) voters surveyed said they voted yes on Proposition 23, then how many of the \(600\) people surveyed voted yes?
- Out of \(460\) students surveyed, the ratio to support the student union remodel project was \(3\) to \(5\). How many students were in favor of the remodel?
- An estimated \(5\) out of \(7\) students carry credit card debt. Estimate the number of students that carry credit card debt out of a total of \(14,000\) students.
- If the ratio of female to male students at the college is \(6\) to \(5\), then determine the number of male students out of \(11,000\) total students.
- In the year 2009 it was estimated that there would be \(838\) deaths in the United States for every \(100,000\) people. If the total US population was estimated to be \(307,212,123\) people, then how many deaths in the United States were expected in 2009? (Source: CIA World Factbook)
- In the year 2009 it was estimated that there would be \(1,382\) births in the United States for every \(100,000\) people. If the total US population was estimated to be \(307,212,123\) people, then how many births in the United States were expected in 2009? (Source: CIA World Factbook)
- If \(2\) out of every \(7\) voters approve of a sales tax increase then determine the number of voters out of the \(588\) surveyed who do not support the increase.
- A recipe calls for \(1\) cup of lemon juice to make \(4\) cups of lemonade. How much lemon juice is needed to make \(2\) gallons of lemonade?
- The classic “Shirley Temple” cocktail requires \(1\) part cherry syrup to \(4\) parts lemon-lime soda. How much cherry syrup is needed to mix the cocktail given a \(12\)-ounce can of lemon-lime soda?
- A printer prints \(30\) pages in \(1\) minute. How long will it take to print a \(720\)-page booklet?
- A typist can type \(75\) words per minute. How long will it take to type \(72\) pages if there are approximately \(300\) words per page?
- On a particular map, every \(\frac{1}{16}\) inch represents \(1\) mile. How many miles does \(3\frac{1}{2}\) inches represent?
- On a graph every \(1\) centimeter represents \(100\) feet. What measurement on the map represents one mile?
- A candy store offers mixed candy at $\(3.75\) for every half-pound. How much will \(2.6\) pounds of candy cost?
- Mixed nuts are priced at $\(6.45\) per pound. How many pounds of mixed nuts can be purchased with $\(20.00\)?
- Corn at the farmers market is bundled and priced at $\(1.33\) for \(6\) ears. How many ears can be purchased with $\(15.00\)?
- If \(4\) pizzas cost $\(21.00\), then how much will \(16\) pizzas cost?
- A sweetened breakfast cereal contains \(110\) calories in one \(\frac{3}{4}\)-cup serving. How many calories are in a \(1\frac{7}{8}\)-cup serving?
- Chicken-flavored rice contains \(300\) calories in each \(2.5\)-ounce serving. How many calories are in a \(4\)-ounce scoop of chicken-flavored rice?
- A \(200\)-pound man would weigh about \(33.2\) pounds on the moon. How much will a \(150\)-pound man weigh on the moon?
- A \(200\)-pound man would weigh about \(75.4\) pounds on Mars. How much will a \(150\)-pound man weigh on Mars?
- There is a \(1\) out of \(6\) chance of rolling a \(1\) on a six-sided die. How many times can we expect a \(1\) to come up in \(360\) rolls of the die?
- There is a \(1\) out of \(6\) chance of rolling a \(7\) with two six-sided dice. How many times can we expect a \(7\) to come up in \(300\) rolls?
- The ratio of peanuts to all nuts in a certain brand of packaged mixed nuts is \(3\) to \(5\). If the package contains \(475\) nuts, then how many peanuts can we expect?
- A mixed bag of marbles is packaged with a ratio of \(6\) orange marbles for every \(5\) red marbles. If the package contains \(216\) orange marbles, then how many red marbles can we expect?
- A graphic designer wishes to create a \(720\)-pixel-wide screen capture. If the width to height ratio is to be \(3:2\), then to how many pixels should he set the height?
- If a video monitor is produced in the width to height ratio of \(16:9\) and the width of the monitor is \(40\) inches, then what is the height?
1. \(960\) people
3. \(276\) students
5. \(5,000\) male students
7. \(4,245,672\) births
9. \(8\) cups of lemon juice
11. \(24\) minutes
13. \(56\) miles
15. $\(19.50\)
17. \(66\) ears
19. \(275\) calories
21. \(24.9\) pounds
23. \(60\) times
25. \(285\) peanuts
27. \(480\) pixels
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7}\) Similar Triangles
If triangle \(ABC\) is similar to triangle \(RST\), find the remaining two sides given the information.
- \(a=6, b=8, c=10,\) and \(s=16\)
- \(b=36, c=48, r=20,\) and \(t=32\)
- \(b=2, c=4, r=6,\) and \(s=4\)
- \(b=3, c=2, r=10,\) and \(t=12\)
- \(a=40, c=50, s=3,\) and \(t=10\)
- \(c=2, r=7, s=9,\) and \(t=4\)
- At the same time of day, a tree casts a \(12\)-foot shadow while a \(6\)-foot man casts a \(3\)-foot shadow. Estimate the height of the tree.
- At the same time of day, a father and son, standing side by side, cast a \(4\)-foot and \(2\)-foot shadow, respectively. If the father is \(6\) feet tall, then how tall is his son?
- If the \(6-8-10\) right triangle \(ABC\) is similar to \(RST\) with a scale factor of \(\frac{2}{3}\), then find the perimeter of triangle \(RST\).
- If the \(3-4-5\) right triangle \(ABC\) is similar to \(RST\) with a scale factor of \(5\), then find the perimeter of triangle \(RST\).
- An equilateral triangle with sides measuring \(6\) units is similar to another with scale factor \(3:1\). Find the length of each side of the unknown triangle.
- The perimeter of an equilateral triangle \(ABC\) measures \(45\) units. If triangle \(ABC ~ RST\) and \(r=20\), then what is the scale factor?
- The perimeter of an isosceles triangle \(ABC\), where the two equal sides each measure twice that of the base, is \(60\) units. If the base of a similar triangle measures \(6\) units, then find its perimeter.
- The perimeter of an isosceles triangle ABC measures \(11\) units and its two equal sides measure \(4\) units. If triangle \(ABC\) is similar to triangle \(RST\) and triangle \(RST\) has a perimeter of \(22\) units, then find all the sides of triangle \(RST\).
- A \(6-8-10\) right triangle \(ABC\) is similar to a triangle \(RST\) with perimeter \(72\) units. Find the length of each leg of triangle \(RST\).
- The perimeter of triangle \(ABC\) is \(60\) units and \(b=20\) units. If \(ABC ~ RST\) and \(s=10\) units, then find the perimeter of triangle \(RST\).
1. \(t = 20, r = 12\)
3. \(a = 3, t = 8\)
5. \(r = 8, b = 15\)
7. \(24\) feet
9. \(36\) units
11. \(2\) units
13. \(30\) units
15. \(r = 18\) units, \(s = 24\) units, \(t = 30\) units
Exercise \(\PageIndex{8}\) Discussion Board Topics
- What is the golden ratio and where does it appear?
- Research and discuss the properties of similar triangles.
- Discuss the mathematics of perspective.
- Research and discuss the various aspect ratios that are available in modern media devices.
1. Answers may vary
3. Answers may vary
Aptitude - Ratio and Proportion
Why should i learn to solve aptitude questions and answers section on "ratio and proportion".
Learn and practise solving Aptitude questions and answers section on "Ratio and Proportion" to enhance your skills so that you can clear interviews, competitive examinations, and various entrance tests (CAT, GATE, GRE, MAT, bank exams, railway exams, etc.) with full confidence.
Where can I get the Aptitude questions and answers section on "Ratio and Proportion"?
IndiaBIX provides you with numerous Aptitude questions and answers based on "Ratio and Proportion" along with fully solved examples and detailed explanations that will be easy to understand.
Where can I get the Aptitude section on "Ratio and Proportion" MCQ-type interview questions and answers (objective type, multiple choice)?
Here you can find multiple-choice Aptitude questions and answers based on "Ratio and Proportion" for your placement interviews and competitive exams. Objective-type and true-or-false-type questions are given too.
How do I download the Aptitude questions and answers section on "Ratio and Proportion" in PDF format?
You can download the Aptitude quiz questions and answers section on "Ratio and Proportion" as PDF files or eBooks.
How do I solve Aptitude quiz problems based on "Ratio and Proportion"?
You can easily solve Aptitude quiz problems based on "Ratio and Proportion" by practising the given exercises, including shortcuts and tricks.
- Ratio and Proportion - Formulas
- Ratio and Proportion - General Questions
Let the third number be x .
Let the shares of A, B, C and D be Rs. 5 x , Rs. 2 x , Rs. 4 x and Rs. 3 x respectively.
Then, 4 x - 3 x = 1000
Originally, let the number of seats for Mathematics, Physics and Biology be 5 x , 7 x and 8 x respectively.
Number of increased seats are (140% of 5 x ), (150% of 7 x ) and (175% of 8 x ).
Quantity of water in it = (60- 40) litres = 20 litres.
New ratio = 1 : 2
Let quantity of water to be added further be x litres.
Current Affairs
Interview questions, group discussions.
- Data Interpretation
- Verbal Ability
- Verbal Test
- C Programming
- Technical Interview
- Placement Papers
- Submit Paper

Ratio Practice Questions
Click here for questions, click here for answers, gcse revision cards.

5-a-day Workbooks

Primary Study Cards

Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Corbettmaths © 2012 – 2024
- Shortcuts, Tips & Tricks
- Shortcut, tips, and tricks
- Successive Discount 1
- Successive Discount 2
- Finding remainder of large powers
PREPINSTA PRIME
- Prime Video
Get Hiring Updates right in your inbox from PrepInsta
How To Solve Ratio And Proportion Questions Quickly
July 8, 2023
Solve Ratio and Proportion Questions Quickly
In some situations, the comparison by a division process makes good sense when compared to performing their difference. On this page you’ll learn How to Solve Ratio And Proportion Question Quickly.

How to Solve Ratio And Proportion Quickly – Compound Ratio Based On Individual Ratios
Question 1..
Find the compound ratio of (9 : 10), (11 : 13), (15 : 19).
A. 156:157 B. 297:494 C. 221:431 D. 1:5

Correct answer B
If we compound two or more ratio, then, a : b and c : d will become ac:bd.
Therefore, (9 : 10), (11 : 13), (15 : 19) = 9/10 * 11/13 * 15/19 = 1485/2470
Question 2.
Find the composite ratio of 2 : 3, 3 : 5, 5 : 7.
A. 11 : 24 B. 2 : 7 C. 14 : 23 D. 24 : 97
The composite ratio is intended by 2/3 * 3/5 * 5/7 = 30/105
Question 3.
Find the compounded ratio of (3 : 7), (9:5), and (11:21) A. 99:245 B. 13:17 C. 114:221 D. 305:711
Correct answer A
Therefore, (3 : 7), (9:5), and (11:21)= 3/7 * 9/5 * 11/21 = 297/735 = 99/245
Distributing Any Quantity Based On Ratios
Question 4..
Rs. 27440 is divided among 5 females, 3 men, and 1 child. The ratio of each woman, man, and kid, are 9 : 3 : 2. What is the child’s share?
A. 550 B. 760 C. 980 D. 952
Correct answer C
Given, the ratio of females, males, and toddlers = 9 : 3 : 2
No. of females, men, and child are 5, 3, 1 Thus actual ratio of females, men, and child = 9 * 5 : 3 * 3 : 2 * 1 = 45 : 9 : 2 Therefore, part of child = (2/56) * 27440 = Rs. 980
Question 5.
An amount of Rs. 58666 is divided among three employees in the ratio of 1/17, 1/19, and 1/21. Find the smallest share.
A. 17561.7 B. 17200.49 C. 17000 D. 11760.50
Given, three shares = 1/17, 1/19, 1/21.
Therefore, the ratio will be 399/6783, 357/6783, 323/6783
Thus, the ratio is 399 : 357 : 323
The smallest share = 58666*323/1079
Coins Based Ratio Problems
Question 6..
Sahil got old currencies from his cupboard worth Rs. 450 in the denomination of 2 paisa, 5 paisa, and 50 paisa in ratio 5 : 4 : 3. How many 2 paisa coins he got.
A. 1200 B. 1250 C. 1100 D. 1220
Let the number of 2 paisa coins be 5x
Let the number of 5 paisa coins be 4x
Let the number of 50 paisa coins be 3x
Then, 2*5x/100 + 5*4x/100 + 50*3x/100 = 180x/100
Given, 180x/100 = 450
Therefore, 450*100/180 = x
Hence, 2paisa coins = 5 * 250 = 1250
Question 7.
A person has 180 rupees in the denomination of 5paisa, 10paisa, and 25paisa in ratio 5 : 3 : 1. Calculate how many 25 paisa coins he has.
A. 225 B. 200 C. 350 D. 300
Let the number of 5 paisa coins be 5x
Let the number of 10 paisa coins be 3x
Let the number of 25 paisa coins be x
Then, 5*5x/100 + 10*3x/100 + 25x/100 = 80x/100
Given, 80x/100 = 180
Therefore, 180*100/80 = x
Hence, 25 paisa coins = 1*225 = 225 coins
Question 8.
Harish has 1500 rupees in the denomination of 5 paisa, 25 paisa, and 50 paisa in ratio 5 : 3 : 2. Calculate how many 25 paisa coins he has.
A.2800 B.2000 C.2500 D.2250
Correct answer D
Let the number of 25 paisa coins be 3x
Let the number of 1 rupee coins be 2x
Then, 5*5x/100 + 25*3x/100 + 50 * 2x/100 = 200x/100
Given, 200x/100 = 1500
Therefore, 1500*100/200 = x
Hence, 25 paisa coins = 3*750 = 2250
How to Solve Ratio And Proportion Quickly – Mixtures & Addition Based Ratio Problems
Question 9..
Chetan and Shaheen’s salaries are in the ratio 5 : 9. If both of their salaries are raised by Rs. 4200, then the proportion changes to 22 : 27. Find Shaheen’s salary.
A. 9250.95 B. 8058.32 C. 7199.97 D. 13580.45
Let Chetan and Shaheen’s salaries be 5x and 9x
Given, 5x + 4200 / 9x + 4200 = 22/27
135x + 113400 = 198x + 92400
63x = 21000
Therefore, Shaheen’s salary = 333.33 * 9 + 4200 = 7199.97
Question 10.
Salaries of Preeti and Bina are in the ratio 14 : 15. If both get an increment of Rs. 5300, the new ratio becomes 33 : 35. What is Preeti’s salary?
A. 24000 B. 34980 C. 30100 D. 10200
Let Preeti’s salary be 14x, and Bina’s salary be 15x
Given, 14x + 5300 = 33
Given, 15x + 5300 = 35
= 14x + 5300/15x + 5300 = 33/35
= 490x + 185500 = 495x + 174900
Therefore, Preeti’s salary = 14 * 2120 + 5300 = 34980
Question 11.
400 g of 25% sugar syrup was added to 600 g of 40% sugar syrup. Find the percentage of the syrup in the mixture.
A. 22% B. 34% C. 31% D. 38%
Amount of sugar syrup in mixture 1 = 25/100*400= 100
Amount of sugar syrup in mixture 2 = 40/100*600 = 240
The total amount of sugar syrup = 340
Percentage of sugar syrup in the mixture = 340 * 100/ 1000 = 34%
Prime Course Trailer
Related banners.
Get PrepInsta Prime & get Access to all 200+ courses offered by PrepInsta in One Subscription
Also Check Out

Get over 200+ course One Subscription
Courses like AI/ML, Cloud Computing, Ethical Hacking, C, C++, Java, Python, DSA (All Languages), Competitive Coding (All Languages), TCS, Infosys, Wipro, Amazon, DBMS, SQL and others
Checkout list of all the video courses in PrepInsta Prime Subscription
- Averages – Questions | Formulas | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Allegations and Mixtures – Questions | Formulas | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Simple & Compound Interest – Questions | Formulas | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Simple Interest – Questions | Formulas | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Compound Interest – Questions | Formulas | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Percentages – Questions | Formulas | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Profit & Loss – Questions | Formulas | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
- Profit & Loss – Questions | Formulas | How to Solve Quickly | Tricks & Shortcuts
Login/Signup to comment

30+ Companies are Hiring
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 3: Ratios and rates
About this unit.
Learn all about proportional relationships. How are they connected to ratios and rates? What do their graphs look like? What types of word problems can we solve with proportions?
Intro to ratios
- Intro to ratios (Opens a modal)
- Basic ratios (Opens a modal)
- Part:whole ratios (Opens a modal)
- Ratio review (Opens a modal)
- Basic ratios Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
Visualize ratios
- Ratios with tape diagrams (Opens a modal)
- Equivalent ratio word problems (Opens a modal)
- Ratios and double number lines (Opens a modal)
- Ratios with tape diagrams Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Equivalent ratios with equal groups Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Create double number lines Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Ratios with double number lines Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Relate double number lines and ratio tables Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Equivalent ratios
- Ratio tables (Opens a modal)
- Solving ratio problems with tables (Opens a modal)
- Equivalent ratios (Opens a modal)
- Equivalent ratios: recipe (Opens a modal)
- Understanding equivalent ratios (Opens a modal)
- Ratio tables Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Equivalent ratios Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Equivalent ratio word problems Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Equivalent ratios in the real world Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Understand equivalent ratios in the real world Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Ratio application
- Ratios on coordinate plane (Opens a modal)
- Ratios and measurement (Opens a modal)
- Part to whole ratio word problem using tables (Opens a modal)
- Ratios on coordinate plane Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Ratios and units of measurement Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Part-part-whole ratios Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Intro to rates
- Intro to rates (Opens a modal)
- Solving unit rate problem (Opens a modal)
- Solving unit price problem (Opens a modal)
- Rate problems (Opens a modal)
- Comparing rates example (Opens a modal)
- Rate review (Opens a modal)
- Unit rates Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
- Rate problems Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Comparing rates Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- IBPS RRB Exam 2023 - Free Course
- Current Affairs
- General Knowledge
- SSC CGL Pre.Yrs.Papers
- SSC CGL Practice Papers
- SBI Clerk PYQ
- IBPS PO PYQ
- IBPS Clerk PYQ
- SBI PO Practice Paper
- SBI PO Quantitative Aptitude Syllabus 2024
Simplification and Approximation:
- Simplification and Approximation
- Approximation - Aptitude Question and Answers
Profit & Loss:
- Profit and Loss - Aptitude Questions and Answers
- Practice Set For Profit and Loss
Mixtures & Allegations:
- Mixtures and Alligation
- Mixture and Alligation | Set 2
- Tricks To Solve Mixture and Alligation
Permutation and Combination:
- Combinations Formula with Examples
- Mathematics | Probability
Probability:
- Time and Work - Aptitude Questions and Answers
- Sequences and Series
- Special Series - Sequences and Series | Class 11 Maths
Sequence & Series:
- Simple Interest - Aptitude Questions and Answers
- Compound Interest - Aptitude Questions and Answers
- Simple Interest
Simple Interest & Compound Interest:
- Advance Level of Simple Interest
- Mensuration Formulas
- Mensuration 2D
- Area of Polygons
- Practice Question On Area And Perimeter Of All Shapes
Mensuration _ Cylinder, Cone, Sphere:
- Speed, Time and Distance – Formulas & Aptitude Questions
- Time Speed Distance
- Speed Time Distance Formula
- Speed and Distance Advance Level
Time, Speed, & Distance:
- Data Interpretation
- Ratio and Proportion
Data Interpretation:
- What is a Number System?
- Basic Concept Of Number System
Ratio & Proportion:
- Percentages - Aptitude Questions and Answers
- Basic Concept of Percentage
- Percentages
Number Systems:
- Practice Set For Height & Distance
- Basic Concepts Of Whole Numbers
- Tricks To Solve Questions On Average
Percentage:
Miscellaneous:, tricks to solve ratio and proportion.
Ratio and Proportion is one of the most important chapters in quant. In each bank exam (preliminary and mains) around 1 to 2 questions has been seen. If you are aware about basic ideas, tricks and short cuts of ratio and proportion you can easily solve the problems within a few seconds.
Ratio, Proportion form an interesting part . The basic fundamentals of ratio and proportion are extensively used in solving many questions in chapters like time and work, time and distance ,DI etc. You are likely to get a few questions in the actual exams, based on these concepts.
Ratio is the comparison between two quantities of the same kind of units,different kinds can not be compared. The ratio of a and b is expressed as a : b or a/b.
Types of Ratios:- There are various types of ratios, which are explained below
1. Duplicate Ratio:- If two numbers are in ratio, then the ratio of these two numbers squares is called duplicate ratio. If a and b are such two numbers, then the duplicate ratio of a and b = a² : b²
For example Duplicate ratio of 5:4=5²:4² = 25:16
2. Sub-duplicate Ratio:- If two numbers are in ratio, then the ratio of these two numbers square roots is called sub-duplicate ratio. If a and b are the two numbers, then the sub-duplicate ratio of a and b = √a : √b
For example Sub-duplicate ratio of 5 : 3 is = √5:√3.
3. Triplicate Ratio:- If two numbers are in ratio, then the ratio of these two numbers cubes is called triplicate ratio. If a and b are the two numbers, then the triplicate ratio of a and b = a³ : b³.
For example Triplicate ratio of 2:5=2³:5³ = 8:125
4. Sub-triplicate Ratio:- If two numbers are in ratio, then the ratio of these two numbers cube roots is called sub-triplicate ratio. If a and b are the two numbers, then the sub-triplicate ratio of a and b = ³√a : ³√b
For example Sub-triplicate ratio of 8 :125 = ³√8:³√125 = 2 : 5
5. Inverse Ratio:- If two numbers are in ratio and their antecedent and consequent are interchanged, then it is called inverse ratio . If a and b are two numbers and their ratio is a:b then its inverse ratio will be b :a
For example Inverse ratio of 7:5 is 5:7.
Ratio and Proportion questions are asked in SBI Clerk Pre, IBPS Clerk Pre, IBPS RRB Pre, IBPS RRB Office Assistant Pre, IBPS RRB Scale 1 Pre, IBPS RRB Office Assistant Mains, IBPS RRB Scale 1 Mains, IBPS PO Pre, IBPS SO Pre, IBPS PO, SBI PO Pre, SBI SO Pre, SBI PO, LIC, NIACL, OICAL, SSC CGL,SSC CHSL, MAT, NIFT, CTET etc.
1. Question If A : B = 3 : 7 and B : C = 4 : 1 ,then find A : B : C . A) 9 : 28 : 5 B) 6 : 28 : 3 C) 12 : 28 : 7 D) 15 : 28 : 9 E) None of these Answer :- C Explanation :- A : B = 3 : 7 ——-(×4) = 12 : 28 B : C = 4 : 1 ——-(×7 ) = 28 : 7 A : B : C = 12 : 28 : 7
2.Question If A : B = 1 : 2 , B : C = 4 : 3 and C : D = 6 : 7 ,then find A : D. A) 4 : 7 B) 6 : 49 C) 2 : 7 D) 8 : 7 E) None of these Answer:- A Tricks :- A/D = A/B × B/C × C/D = 1/2 × 4/3 × 6/7 = 4 : 7
3. Question Calculate the third proportional to 72 and 48. A) 5 B) 32 C) 6 D) 9 E) 12 Answer :- B Explanation :- Let, Third proportional be = x 72 : 48 = 48 : x => 72/48 = 48/x => x = 48×48/72 => x = 32 Tricks :- x = (48×48)/72 = 32 ( If A : B = B : C ,then C = B²/C)
4.Question Calculate the fourth proportional to 85 , 17 and 25 . A) 5 B) 12 C) 6 D) 18 E) None of these Answer :- A Explanation :- Let,fourth proportional = x 85 : 17 = 25 : x => 85/17 = 25/ x => 85x = 25×17 => x = (25×17)/85 => x = 5
Tricks :- If , a : b = c : d ,then d = bc/a Here, x = (17×25)/85 = 5
5.Question Find out the mean proportional between 27 and 75 . A) 81 B) 3 C) 6 D) 45 E) None of these
Answer :- D Explanation :- Let, mean proportional = X Then, 27 : X = X : 75 => 27/X = X /75 => X² = 75 × 27 => X = √(75×27) X = 45
Tricks :- If a : X = X : b then mean proportional,X = √ab Here, X = √(75×27) X = 45
6. Question Find out the duplicate ratio of 9 : 11 . A) 81 : 121 B) 121 : 81 C) 18 : 22 D) 729 : 1331 E) None of these Answer :- A Explanation :- Duplicate ratio of 9 : 11 = 9² : 11² = 81 : 121
7. Question what will be the sub- duplicate ratio of 400 : 9 ? A) 800 : 18 B) 160000 : 81 C) 20 : 3 D) 3 : 20 E) None of these Answer :- C Explanation :- Sub – duplicate ratio of 400 : 9 = √ 400 : √ 9 = 20 : 3
8. Question What will be the triplicate ratio of 6 : 11 ? A) 216 : 1331 B) 1331 : 216 C) 36 : 121 D) 121 : 36 E) None of these Answer :-A Explanation :- Triplicate ratio of 6 : 11 = 6³ : 11³ = 216 : 1331
9.Question Find the subtriplicate ratio of 1331: 125 . A) 121 : 25 B) 11 : 5 C) 7 : 10 D) 5 : 11 E) None of these Answer :- B Explanation :- Sub – triplicate ratio of 1331 : 125
= ³√1331 : ³√125
= 11 : 5
10. Question If P : Q = Q : R ,then what will be the ratio of P⁴ : Q⁴ ? A) P² : R² B) PR : Q² C) Q² : PR D) R² : P² E) None of these
Answer :-A Explanation :- P : Q = Q : R => P/Q = Q/R => Q² = PR :. Q⁴ = P²R² Now, P⁴ : Q⁴ = P⁴ : P²R² = P² : R²
11. Question
The ratio of tin and copper in a metal is 13 : 7. How much tin will be there in 220 kg of such a metal? A) 120 kg B) 135 kg C) 155 kg D) 143 kg E) 160 kg Correct Option: D Tricks :- Amount of tin= (220 × 13/20 )kg = 143 kg.
Hence, option D is correct.
12.Question In a private school the ratio of number of boys and girls of 720 students is 11 : 7. How many more girls should be joined to the School to make the ratio 1 : 1? A) 160 B) 100 C) 120 D) 150 E) 170
Correct Option: A Explanation :- Number of boys = (720 × 11/18) = 440
Number of girls= (720 – 440) = 280
∴ Number of girls to be joined = (440 – 280) = 160.
Hence, option A is correct.
13.Question
In a factory, the ratio of boys to women is 7 : 5. If there are 240 workers in the factory, then how many women are there? A) 50 B) 70 C) 80 D) 100 E) 90
Correct Option: D Explanation :- Let the number of boys and women are 7x and 5x, respectively.
Given, total number of workers= 240
⇒ 7x + 5x = 240 ⇒ 12x = 240
∴ x = 20
∴ Required number of women = 5x = 5 × 20= 100.
Tricks :- (7 + 5) = 12 unit ——-> 240 1 unit ——–> 20 Thus, number of women = 5 × 20 = 100
14.Question Zinc and bronze are in the ratio 5 : 3 in 800 gm of an alloy. How much of zinc (in grams) should be added to make the ratio 7 : 3? A) 150 B) 60 C) 70 D) 200 E) 250
Answer :- D Explanation :- Zinc = 5/8 × 800 = 500 gm Bronze = 800 – 500 = 300 gm Let, zinc should be added x gm. (500 + x)/300 = 7/3 => 1500 + 3x = 2100 => 3x = 600 :. x = 200 gm Thus, the required zinc = 200 gm
Tricks :- 8 unit = 800 1 unit = 100 Zinc should be added (7-5) = 2 unit = 2 × 100 = 200 gm
15.Question 70 percent of a number is equal to 30 percent of another number. What is the respective ratio of these two numbers?
A) 3 : 7 B) 21 : 31 C) 7 : 10 D) 12 : 13 E) Can’t be determined
Correct Option: A Explanation :-
Let, the first number = x and the second number = y.
According to the question,
70% of x = 30% of y ⇒ 70/100 * x = 30/100 * y => x/y = 30/70 So, required ratio = x : y = 3 : 7
Tricks :- 70% * 1st number = 30% * 2nd number => 1st number : 2nd number = 30 : 70 = 3 : 7
16.Question
What must be added to each term of the ratio 3 : 5 so that it may equal to 5 : 7 ? A) 5 B) 8 C) 3 D) 2 E) 7
Correct Option: D Explanation :- Let’s the added number = x. Then,
(3 +x) /(5 + x) = 5/7 ⇒ 21 + 7x = 25 + 5x => 2x = 4 => x = 2 Required number = x = 2
17. Question Syrup is 15 times as heavy as water and alcohol is 7 times as heavy as water in what ratio should these be mixed to get an alloy 10 times as heavy as water? A) 2 : 5 B) 3 : 5 C) 1 : 3 D) 2 : 7 E) None of these
Correct Option: B Tricks:-
Syrup = 15 water Alcohol = 7 water By allegation –
15 7 \ / 10 / \ 3 5
Hence, option B is correct
18. Question
The ratio of the two numbers is 7 : 4 and their sum is 440. Find the greatest number.
Answer :- D Explanation :- Let, the numbers are 7x and 4x. According to the question, 7x + 4x = 440 => 11x = 440 => x = 40 Thus,the greatest number = 7×40 = 280
Tricks :- (7+4) =11 units —-> 440 1 ———–> 40 :. 7 ———–> 40×7 = 280
19.Question The ratio of the two numbers is 11 : 6 and their sum is 850. Find the smallest number.
(E) None of these
Answer :- D Explanation :- Let, the numbers are 11x and 6x. According to the question, 11x + 6x = 850 => 17x = 850 => x = 50 Thus,the smallest number = 6×50 = 300
Tricks :- (11+6) =17 units —-> 850 1 ———–> 50 :. 6 ———–> 50×6 = 300
20.Question Five books and four pens cost as much as three books and nine pens. Find the ratio of the cost of one book to that of one pen .
(E) None of these
Answer :- C Explanation :- Let, cost of one book = x Cost of one pen = y According to the question, 5x + 4y = 3x + 9y => 2x = 5y => x : y = 5 : 2 Thus ,the required ratio is = 5 : 2
21.Question The speeds of three bikes are in the ratio 6 : 4 : 5 . Find the ratio between the times taken by them to cover the same distance .
(A) 5 : 4 : 6
(B) 6 : 4 : 5
(C) 10 : 15 : 12
(D) 12 : 15 : 10
Answer:-C Explanation :- Speed ratio = 6 : 4 : 5 We know, speed and time are inversely proportional .
Time ratio = 1/6 : 1/4 : 1/5 (LCM of 6 , 4 & 5 = 60) = 60/6 : 60/4 : 60/5 = 10 : 15 : 12
22.Question
A and B two numbers are respectively 25% and 50% more than a third number C. Find the ratio of A and B.
A) 3 : 5 B) 2 : 5 C) 4 : 5 D) 5 : 6 E) 5 : 4
Answer: D Explanation:
Let the third number be x.
Then, A= 125% of x =125x/100 = 5x/4
B =150% of x = 150x/100 = 3x/2
A : B = 5x/4 : 3x/2 = 5x : 6x = 5 : 6
23.Question There are Rs 840 consisting of Rs 1, 50 paise, 25 paise and 10 paisa coins. The ratio of their numbers in that order is 5 : 4 :2 : 9. Find the number of 50 paisa coins.
(a) 200 (b) 115 (c) 400 (d) 500 (e) None of these
Answer :- C Explanation:-
Let the number of coins of Rs 1, 50 paise , 25 paise and 10 paisa be 5x, 4x 2x and 9x respectively.
According to the question, (1) (5x) + (0.50)(4x) + (0.25)(2x) + (.10)(9x)= 840 => 5x + 2x + x/2 + 9x/10 = 840 => 50x + 20x + 5x + 9x = 840 × 10 [ Multiplied both sides by 10] => 84x = 840 × 10 => x = 100
Therefore, number of coins of 50 paisa = 4x = 4 × 100 = 400 24. Question A thief took 5 leaps for every 4 leaps of a police but 3 leaps of the police were equal to 4 leaps of the thief. What is the ratio of the speeds of the thief to that of the police? A) 15 : 16 B) 16 : 15 C) 9 : 17 D) 12 : 13 E) None of these
Answer :-A Tricks:-
4 leaps of thief = 3 leaps of police => 1 leap of thief = 3/4 leaps of police Now, required ratio of speed = ( 5 × thief’s leap) : ( 4 × police’s leap) = (5 ×3/4 police’s leap) : ( 4 × police’s leap) = 15 : 16
25. Question In an IT company, the ratio of the numbers of employees of three types P, Q and R is 9:13:18 and their wages are in the ratio of 10: 7:4. If number of employees of type R is 54 and wages of every employee of type Q is 1400, then find the total wages of all the employees of type P.
(a) Rs 52000
(b) Rs 53000
(c) Rs 54000
(d) Rs 56000
(e) Rs 60000
Answer :-C Explanation :- Let, Number of P’s employees = 9x Q’s employees = 13x R’s employees = 18x Now, According to the question 18x = 54 => x = 3 the number of employees of type P = 9×3 = 27 the wages of every employees in P = 1400× 10/7 = 2000 Rs. Thus ,the required total wages = 27×2000 = 54000
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Banking Practice Paper
- Banking Quantitative Aptitude
- SSC Practice Paper
- SSC Quantitative Aptitude
- SSC/Banking
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
Free ready-to-use math resources
Hundreds of free math resources created by experienced math teachers to save time, build engagement and accelerate growth
Ratio Questions And Practice Problems: Differentiated Practice Questions Included
Beki Christian
Ratio questions appear throughout middle and high school, building on students’ knowledge year on year. Here we provide a range of ratio questions and practice problems of varying complexity to use with your own students in class or as inspiration for creating your own.
What is ratio?
Ratio is used to compare the size of different parts of a whole. For example, the total number of students in a class is 30. There are 10 girls and 20 boys. The ratio of girls:boys is 10:20 or 1:2. For every one girl there are two boys.

Ratio Worksheet
Download this quiz to check your students’ understanding of ratios. Features 10 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
Uses of ratio
You might see ratios written on maps to show the scale of the map or use ratios to determine the currency exchange rate if you are going on vacation to another country.
Ratio will be seen as a topic in its own right as well as appearing within other topics. An example of this might be the area of two shapes being in a given ratio or the angles of a shape being in a given ratio.
Ratio in Middle School and High School
In middle school, ratio questions will involve writing and simplifying ratios, using equivalent ratios, dividing quantities into a given ratio and will begin to look at solving problems involving ratio. At high school, these skills are recapped and the focus will be more on ratio word problems which will require you to conduct problem solving using your knowledge of ratio.
Proportion and ratio
Ratio often appears alongside proportion and the two topics are related. Whereas ratio compares the size of different parts of a whole, proportion compares the size of one part with the whole. Given a ratio, we can find a proportion and vice versa.
Take the example of a box containing 7 counters; 3 red counters and 4 blue counters:
The ratio of red counters:blue counters is 3:4.
For every 3 red counters there are four blue counters.
The proportion of red counters is \frac{3}{7} and the proportion of blue counters is \frac{4}{7}.
3 out of every 7 counters are red and 4 out of every 7 counters are blue.
Direct proportion and inverse proportion
From 7th grade onwards, students learn about direct proportion and inverse proportion. When two things are directly proportional to each other, one can be written as a multiple of the other and therefore they increase at a fixed ratio.
How to solve a ratio problem
When looking at a ratio problem, the key pieces of information that you need are what the ratio is, whether you have been given the whole amount or a part of the whole and what you are trying to work out.
If you have been given the whole amount you can follow these steps to answer the question:
- Add together the parts of the ratio to find the total number of shares.
- Divide the total amount by the total number of shares.
- Multiply by the number of shares required.
If you have been been given a part of the whole you can follow these steps:
- Identify which part you have been given and how many shares it is worth.
- Use equivalent ratios to find the other parts.
- Use the values you have to answer your problem.
How to solve a proportion problem
As we have seen, ratio and proportion are strongly linked. If we are asked to find what proportion something is of a total, we need to identify the amount in question and the total amount. We can then write this as a fraction:
Proportion problems can often be solved using scaling. To do this you can follow these steps:
- Identify the values that you have been given which are proportional to each other.
- Use division to find an equivalent relationship.
- Use multiplication to find the required relationship.
Real life ratio problems and proportion problems
Ratio is all around us. Let’s look at some examples of where we may see ratio and proportion:
Cooking ratio question
When making yogurt, the ratio of starter yogurt to milk should be 1:9. I want to make 1,000 ml of yogurt. How much milk should I use?
Here we know the full amount – 1,000 ml.
The ratio is 1:9 and we want to find the amount of milk.
- Total number of shares = 1 + 9 = 10
- Value of each share: 1,000 ÷ 10 = 100
- The milk is 9 shares so 9 × 100 = 900
I need to use 900ml of milk.
Maps ratio question
The scale on a map is 1:10,000. What distance would 3.5cm on the map represent in real life?
Here we know one part is 3.5. We can use equivalent ratios to find the other part.
The distance in real life would be 35,000cm or 350m.
Speed proportion question
I traveled 60 miles in 2 hours. Assuming my speed doesn’t change, how far will I travel in 3 hours?
This is a proportion question.
- I traveled 60 miles in 2 hours.
- Dividing by 2, I traveled 30 miles in one hour.
- Multiplying by 3, I would travel 90 miles in 3 hours.
Middle School ratio questions
Ratio is introduced in middle school. Writing and simplifying ratios is explored and the idea of dividing quantities in a given ratio is introduced using proportion word problems such as the question below, before being linked with the mathematical notation of ratio.
Example Middle School worded question
Richard has a bag of 30 sweets. Richard shares the sweets with a friend. For every 3 sweets Richard eats, he gives his friend 2 sweets. How many sweets do they each eat?
Practice ratio questions for middle school
At this level, ratio questions ask you to write and simplify a ratio, to divide quantities into a given ratio and to solve problems using equivalent ratios. See below the example questions to support test prep.
Ratio questions for 6th grade
1. In Lucy’s class there are 12 boys and 18 girls. Write the ratio of girls to boys in its simplest form.

The question asks for the ratio of girls to boys, so girls must be first and boys second. It also asks for the answer in its simplest form.
2. The ratio of cups of flour to cups of water in a pizza dough recipe is 9:4. A pizza restaurant makes a large quantity of dough, using 36 cups of flour. How much water should they use?
The ratio of cups of flour to cups of water is 9:4. We have been given one part so we can work this out using equivalent ratios.
Ratio questions 7th grade
3. The ratio of men to women working in a company is 3:5. What proportion of the employees are women?
In this company, the ratio of men to women is 3:5 so for every 3 men there are 5 women.
This means that for every 8 employees, 5 of them are women.
Therefore \frac{5}{8} of the employees are women.
4. Mac traveled 30 miles in \frac{3}{4} of an hour. Assuming his speed doesn’t change, how far will Mac travel in 1 hour?
We have been given a part so we can work this out using equivalent ratios.
The ratio of miles to hours is 30: \frac{3}{4} .
To create an equivalent ratio, divide each side by the same number. Since we are solving to find how far Mac will travel in 1 hour, divide both sides by \frac{3}{4} .
30: \frac{3}{4}
30 \div \frac{3}{4}: \frac{3}{4} \div \frac{3}{4}
Mac will travel 40 miles in 1 hour.
Ratio questions 8th grade
While the Common Core State Standards does not explicitly include ratio and proportional relationships in the 8th grade, it may pop up on your own curriculums and offers a good opportunity to revisit and extend their knowledge of ratio and proportion before they enter high school.
5. The angles in a triangle are in the ratio 3:4:5. Work out the size of each angle.
30^{\circ} , 40^{\circ} and 50^{\circ}
22.5^{\circ}, 30^{\circ} and 37.5^{\circ}
60^{\circ} , 60^{\circ} and 60^{\circ}
45^{\circ} , 60^{\circ} and 75^{\circ}
The angles in a triangle add up to 180 ^{\circ} . Therefore 180 ^{\circ} is the whole and we need to divide 180 ^{\circ} in the ratio 3:4:5.
The total number of shares is 3 + 4 + 5 = 12.
Each share is worth 180 ÷ 12 = 15 ^{\circ} .
3 shares is 3 x 15 = 45 ^{\circ} .
4 shares is 4 x 15 = 60 ^{\circ} .
5 shares is 5 x 15 = 75 ^{\circ} .
6. Paint Pro makes pink paint by mixing red paint and white paint in the ratio 3:4.
Colour Co makes pink paint by mixing red paint and white paint in the ratio 5:7.
Which company uses a higher proportion of red paint in their mixture?
They are the same
It is impossible to tell
The proportion of red paint for Paint Pro is \frac{3}{7}
The proportion of red paint for Colour Co is \frac{5}{12}
We can compare fractions by putting them over a common denominator using equivalent fractions
\frac{3}{7} = \frac{36}{84} \hspace{3cm} \frac{5}{12}=\frac{35}{84}
\frac{3}{7} is a bigger fraction so Paint Pro uses a higher proportion of red paint.
High school ratio questions
At high school, we apply the knowledge that we have of ratios to solve different problems. Ratio can be linked with many different topics, for example similar shapes and probability, as well as appearing as problems in their own right.
Ratio high school questions (low difficulty)
7. The students in Ellie’s class walk, cycle or drive to school in the ratio 2:1:4. If 8 students walk, how many students are there in Ellie’s class altogether?
We have been given one part so we can work this out using equivalent ratios.
The total number of students is 8 + 4 + 16 = 28
8. A bag contains counters. 40% of the counters are red and the rest are yellow.
Write down the ratio of red counters to yellow counters. Give your answer in the form 1:n.
If 40% of the counters are red, 60% must be yellow and therefore the ratio of red counters to yellow counters is 40:60. Dividing both sides by 40 to get one on the left gives us
Since the question has asked for the ratio in the form 1:n, it is fine to have decimals in the ratio.
9. Rosie and Jim share some sweets in the ratio 5:7. If Jim gets 12 sweets more than Rosie, work out the number of sweets that Rosie gets.
Jim receives 2 shares more than Rosie, so 2 shares is equal to 12.
Therefore 1 share is equal to 6. Rosie receives 5 shares: 5 × 6 = 30.
10. Rahim is saving for a new bike which will cost $480. Rahim earns $1,500 per month. Rahim spends his money on bills, food and extras in the ratio 8:3:4. Of the money he spends on extras, he spends 80% and puts 20% into his savings account.
How long will it take Rahim to save for his new bike?
Rahim’s earnings of $1,500 are divided in the ratio of 8:3:4.
The total number of shares is 8 + 3 + 4 = 15.
Each share is worth $ 1,500 ÷ 15 = £100 .
Rahim spends 4 shares on extras so 4 × $ 100 = $400 .
20% of $400 is $80.
The number of months it will take Rahim is $ 480 ÷ $ 80 = 6
Ratio GCSE exam questions higher
11. The ratio of milk chocolates to white chocolates in a box is 5:2. The ratio of milk chocolates to dark chocolates in the same box is 4:1.
If I choose one chocolate at random, what is the probability that that chocolate will be a milk chocolate?
To find the probability, we need to find the fraction of chocolates that are milk chocolates. We can look at this using equivalent ratios.
To make the ratios comparable, we need to make the number of shares of milk chocolate the same in both ratios. Since 20 is the LCM of 4 and 5 we will make them both into 20 parts.
We can now say that milk to white to dark is 20:8:5. The proportion of milk chocolates is \frac{20}{33} so the probability of choosing a milk chocolate is \frac{20}{33} .
12. In a school the ratio of girls to boys is 2:3.
25% of the girls have school dinners.
30% of the boys have school dinners.
What is the total percentage of students at the school who have school dinners?
In this question you are not given the number of students so it is best to think about it using percentages, starting with 100%.
100% in the ratio 2:3 is 40%:60% so 40% of the students are girls and 60% are boys.
25% of 40% is 10%.
30% of 60% is 18%.
The total percentage of students who have school dinners is 10 + 18 = 28%.
13. For the cuboid below, a:b = 3:1 and a:c = 1:2.
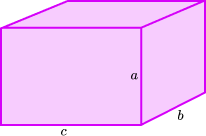
Find an expression for the volume of the cuboid in terms of a.
If a:b = 3:1 then b=\frac{1}{3}a
If a:c = 1:2 then c=2a.
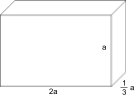
Ratio high school questions (average difficulty)
14. Bill and Ben win some money in their local lottery. They share the money in the ratio 3:4. Ben decides to give $40 to his sister. The amount that Bill and Ben have is now in the ratio 6:7.
Calculate the total amount of money won by Bill and Ben.
Initially the ratio was 3:4 so Bill got $3a and Ben got $4a. Ben then gave away $40 so he had $(4a-40).
The new ratio is 3a:4a-40 and this is equal to the ratio 6:7.
Since 3a:4a-40 is equivalent to 6:7, 7 lots of 3a must be equal to 6 lots of 4a-40.
The initial amounts were 3a:4a. a is 80 so Bill received $240 and Ben received $320.
The total amount won was $560.
15. On a farm the ratio of pigs to goats is 4:1. The ratio of pigs to piglets is 1:6 and the ratio of goats to kids is 1:2.
What fraction of the animals on the farm are babies?
The easiest way to solve this is to think about fractions.
\\ \frac{4}{5} of the animals are pigs, \frac{1}{5} of the animals are goats.
\frac{1}{7} of the pigs are adult pigs, so \frac{1}{7} of \frac{4}{5} is \frac{1}{7} \times \frac{4}{5} = \frac{4}{35}
\frac{6}{7} of the pigs are piglets, so \frac{6}{7} of \frac{4}{5} is \frac{6}{7} \times \frac{4}{5} = \frac{24}{35}
\frac{1}{3} of the goats are adult goats, so \frac{1}{3} of \frac{1}{5} is \frac{1}{3} \times \frac{1}{5} = \frac{1}{15}
\frac{2}{3} of the goats are kids, so \frac{2}{3} of \frac{1}{5} is \frac{2}{3} \times \frac{1}{5} = \frac{2}{15}
The total fraction of baby animals is \frac{24}{35} + \frac{2}{15} = \frac{72}{105} +\frac{14}{105} = \frac{86}{105}
Looking for more middle school and high school ratio math questions?
- Algebra questions
- Probability questions
- Trigonometry questions
- Venn diagram questions
- Long division questions
- Pythagorean theorem questions
Do you have students who need extra support in math? Give your students more opportunities to consolidate learning and practice skills through personalized math tutoring with their own dedicated online math tutor. Each student receives differentiated instruction designed to close their individual learning gaps, and scaffolded learning ensures every student learns at the right pace. Lessons are aligned with your state’s standards and assessments, plus you’ll receive regular reports every step of the way. Personalized one-on-one math tutoring programs are available for: – 2nd grade tutoring – 3rd grade tutoring – 4th grade tutoring – 5th grade tutoring – 6th grade tutoring – 7th grade tutoring – 8th grade tutoring Why not learn more about how it works ?
Related articles

15 Venn Diagram Questions And Practice Problems (Middle & High School): Exam Style Questions Included

15 Probability Questions And Practice Problems for Middle and High School: Harder Exam Style Questions Included

9 Algebra Questions And Practice Problems To Do With Your Middle Schoolers

15 Trigonometry Questions And Practice Problems To Do With High Schoolers
Solving Inequalities Questions [FREE]
Downloadable skills and applied questions about solving inequalities.
Includes 10 skills questions, 5 applied questions and an answer key. Print and share with your classes to support their learning.
Privacy Overview

COMMENTS
It compares the amount of one ingredient to the sum of all ingredients. part: whole = part: sum of all parts. To write a ratio: Determine whether the ratio is part to part or part to whole. Calculate the parts and the whole if needed. Plug values into the ratio. Simplify the ratio if needed.
Ratio problem solving is a collection of ratio and proportion word problems that link together aspects of ratio and proportion into more real life questions. This requires you to be able to take key information from a question and use your knowledge of ratios (and other areas of the curriculum) to solve the problem.
Proportion word problems. Sam used 6 loaves of elf bread on an 8 day hiking trip. He wants to know how many loaves of elf bread ( b) he should pack for a 12 day hiking trip if he eats the same amount of bread each day. How many loaves of elf bread should Sam pack for a 12 day trip? Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics ...
The video is a bit confusing, and I'm struggling to transfer this to solving the questions for "Solving Proportions". For example in the question: 4/z = 12/5 I understand that you begin by multiplying by z. z * 4/z = 12/5*z--> 4 = 12/5*z After this, the solution set asks you to multiply both sides by 5/12, the opposite fraction of the right side.
For example, If there are 10 10 boys in a class and 15 15 girls, the ratio of boys to girls is 10 : 15 10: 15 which is read as "10 "10 to 15." 15.". This is an example of a part to part ratio. You could also say the ratio of total students to girls is 15 : 25. 15: 25. This is an example of a part to whole ratio.
For example, ⅘ is a ratio and the proportion statement is 20/25 = ⅘. If we solve this proportional statement, we get: 20/25 = ⅘. 20 x 5 = 25 x 4. 100 = 100. Check: Ratio and Proportion PDF. Therefore, the ratio defines the relationship between two quantities such as a:b, where b is not equal to 0. Example: The ratio of 2 to 4 is ...
Ratio problem solving is a collection of word problems that link together aspects of ratio and proportion into more real life questions. This requires you to be able to take key information from a question and use your knowledge of ratios (and other areas of the curriculum) to solve the problem. A ratio is a relationship between two or more ...
The main things to be aware about for ratio problems are: Change the quantities to the same unit if necessary. Write the items in the ratio as a fraction. Make sure that you have the same items in the numerator and denominator. Ratio Problems: Two-Term Ratios. Example 1: In a bag of red and green sweets, the ratio of red sweets to green sweets ...
Proportion says that two ratios (or fractions) are equal. Example: We see that 1-out-of-3 is equal to 2-out-of-6. The ratios are the same, so they are in proportion. Example: Rope. A rope's length and weight are in proportion. When 20m of rope weighs 1kg , then: 40m of that rope weighs 2kg. 200m of that rope weighs 10kg.
Tips & Tricks To Solve Ratio & Proportion - Advance Level; Solved Questions on Ratios and Proportion Q 1. If a: b = 5: 9 and b: c = 7: 4, then find a: b: c. Solution: Here, we make the common term 'b' equal in both ratios. Therefore, we multiply the first ratio by 7 and the second ratio by 9.
How to write ratios. Ratios are used to compare two or more quantities and are usually written in the form a:b. Purple paint is made from \ (3\) parts blue paint and \ (2\) parts red paint. The ...
This video shows how to solve inverse proportion questions. It goes through a couple of examples and ends with some practice questions. Example 1: A is inversely proportional to B. When A is 10, B is 2. Find the value of A when B is 8. Example 2: F is inversely proportional to the square of x. When A is 20, B is 3. Find the value of F when x is 5.
Book a free Trial with Cuemath HERE:-https://bit.ly/34rKDr2Download Maths Gym App HERE:-https://bit.ly/34uKTW9Maths Puzzle (Part 1)https://youtu.be/si0gWd5PJ...
Solve ratio and proportion problems. Sometimes a proportion problem may also involve ratio. For example, A cafe sells apples and bananas in the ratio 2:3. They sell 35 pieces of fruit altogether. ... There may be several ways to get to the correct answer for proportion questions. Some ways are more efficient than others depending on the numbers ...
Understand the difference between a ratio and a proportion. Solve proportions using cross multiplication. Solve applications involving proportions, including similar triangles. Definitions. A ratio is a relationship between two numbers or quantities usually expressed as a quotient. Ratios are typically expressed using the following notation:
Why should I learn to solve Aptitude questions and answers section on "Ratio and Proportion"? Learn and practise solving Aptitude questions and answers section on "Ratio and Proportion" to enhance your skills so that you can clear interviews, competitive examinations, and various entrance tests (CAT, GATE, GRE, MAT, bank exams, railway exams, etc.) with full confidence.
Solve for y . 611=y3. y=. Your answer should be. an integer, like 6. a simplified properfraction, like 3/5. a simplified improperfraction, like 7/4. a mixed number, like 1 3/4. an exactdecimal, like 0.75.
Practice Questions. Previous: Percentages of an Amount (Non Calculator) Practice Questions. Next: Rotations Practice Questions. The Corbettmaths Practice Questions on Ratio.
What do their graphs look like? What types of word problems can we solve with proportions? Learn all about proportional relationships. How are they connected to ratios and rates? ... Solving proportions Get 5 of 7 questions to level up! ... Proportion word problems Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Equations of proportional relationships. Learn ...
How to Solve Ratio And Proportion Quickly - Mixtures & Addition Based Ratio Problems Question 9. Chetan and Shaheen's salaries are in the ratio 5 : 9. If both of their salaries are raised by Rs. 4200, then the proportion changes to 22 : 27. Find Shaheen's salary. A. 9250.95 B. 8058.32 C. 7199.97 D. 13580.45. Correct answer C Solution:
Practice. Ratios with tape diagrams Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Equivalent ratios with equal groups Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Create double number lines Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Ratios with double number lines Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Relate double number lines and ratio tables Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Ratio and Proportion is one of the most important chapters in quant. In each bank exam (preliminary and mains) around 1 to 2 questions has been seen. If you are aware about basic ideas, tricks and short cuts of ratio and proportion you can easily solve the problems within a few seconds. Ratio, Proportion form an interesting part .
Here we know the full amount - 1,000 ml. The ratio is 1:9 and we want to find the amount of milk. Add together the parts of the ratio to find the total number of shares. Divide the total amount by the total number of shares. Multiply by the number of shares required. Total number of shares = 1 + 9 = 10.