
- Peterborough


How to Write Academic Reviews
- What is a review?
- Common problems with academic reviews
- Getting started: approaches to reading and notetaking
- Understanding and analyzing the work
- Organizing and writing the review
What Is a Review?
A scholarly review describes, analyzes, and evaluates an article, book, film, or performance (through this guide we will use the term “work” to refer to the text or piece to be reviewed). A review also shows how a work fits into its disciplines and explains the value or contribution of the work to the field.
Reviews play an important role in scholarship. They give scholars the opportunity to respond to one another’s research, ideas and interpretations. They also provide an up-to-date view of a discipline. We recommend you seek out reviews in current scholarly journals to become familiar with recent scholarship on a topic and to understand the forms review writing takes in your discipline. Published scholarly reviews are helpful models for beginner review-writers. However, we remind you that you are to write your own assessment of the work, not rely on the assessment from a review you found in a journal or on a blog.
As a review-writer, your objective is to:
- understand a work on its own terms (analyze it)
- bring your own knowledge to bear on a work (respond to it)
- critique the work while considering validity, truth, and slant (evaluate it)
- place the work in context (compare it to other works).
Common Problems with Academic Reviews
A review is not a research paper.
Rather than a research paper on the subject of the work,an academic review is an evaluation about the work’s message, strengths, and value. For example, a review of Finis Dunaway’s Seeing Green would not include your own research about media coverage of the environmental movement; instead, your review would assess Dunaway’s argument and its significance to the field.
A review is not a summary
It is important to synthesize the contents and significance of the work you review, but the main purpose of a review is to evaluate, critically analyze, or comment on the text. Keep your summary of the work brief, and make specific references to its message and evidence in your assessment of the work.
A review is not an off-the-cuff, unfair personal response
An effective review must be fair and accurate. It is important to see what is actually in front of you when your first reaction to the tone, argument, or subject of what you are reviewing is extremely negative or positive.
You will present your personal views on the work, but they must be explained and supported with evidence. Rather than writing, “I thought the book was interesting,” you can explain why the book was interesting and how it might offer new insights or important ideas. Further, you can expand on a statement such as “The movie was boring,” by explaining how it failed to interest you and pointing toward specific disappointing moments.
Getting Started: Approaches to Reading and Notetaking
Pre-reading.
Pre-reading helps a reader to see a book as a whole. Often, the acknowledgments, preface, and table of contents of a book offer insights about the book’s purpose and direction. Take time before you begin chapter one to read the introduction and conclusion, examine chapter titles, and to explore the index or references pages.
Read more about strategies for critical and efficient reading
Reverse outline
A reverse outline helps a reader analyze the content and argument of a work of non-fiction. Read each section of a text carefully and write down two things: 1) the main point or idea, and 2) its function in the text. In other words, write down what each section says and what it does. This will help you to see how the author develops their argument and uses evidence for support.
Double-entry notebook
In its simplest form, the double-entry notebook separates a page into two columns. In one column, you make observations about the work. In the other, you note your responses to the work. This notetaking method has two advantages. It forces you to make both sorts of notes — notes about the work and notes about your reaction to the work — and it helps you to distinguish between the two.
Whatever method of notetaking you choose, do take notes, even if these are scribbles in the margin. If you don’t, you might rely too heavily on the words, argument, or order of what you are reviewing when you come to write your review.
Understand and Analyze the Work
It is extremely important to work toward seeing a clear and accurate picture of a work. One approach is to try to suspend your judgment for a while, focusing instead on describing or outlining a text. A student once described this as listening to the author’s voice rather than to their own.
Ask questions to support your understanding of the work.
Questions for Works of Non-Fiction
- What is the subject/topic of the work? What key ideas do you think you should describe in your review?
- What is the thesis, main theme, or main point?
- What major claims or conclusions does the author make? What issues does the work illuminate?
- What is the structure of the work? How does the author build their argument?
- What sources does the author consult? What evidence is used to support claims? Do these sources in any way “predetermine” certain conclusions?
- Is there any claim for which the evidence presented is insufficient or slight? Do any conclusions rest on evidence that may be atypical?
- How is the argument developed? How do the claims relate? What does the conclusion reveal?
Questions for Works of Fiction
- What is the main theme or message? What issues does the book illuminate?
- How does the work proceed? How does the author build their plot?
- What kind of language, descriptions, or sections of plot alert you to the themes and significance of the book?
- What does the conclusion reveal when compared with the beginning?
Read Critically
Being critical does not mean criticizing. It means asking questions and formulating answers. Critical reading is not reading with a “bad attitude.” Critical readers do not reject a text or take a negative approach to it; they inquire about a text, an author, themselves, and the context surrounding all three, and they attempt to understand how and why the author has made the particular choices they have.
Think about the Author
You can often tell a lot about an author by examining a text closely, but sometimes it helps to do a little extra research. Here are some questions about the author that would be useful to keep in mind when you are reading a text critically:
- Who is the author? What else has the author written?
- What does the author do? What experiences of the author’s might influence the writing of this book?
- What is the author’s main purpose or goal for the text? Why did they write it and what do they want to achieve?
- Does the author indicate what contribution the text makes to scholarship or literature? What does the author say about their point of view or method of approaching the subject? In other words, what position does the author take?
Think about Yourself
Because you are doing the interpreting and evaluating of a text, it is important to examine your own perspective, assumptions, and knowledge (positionality) in relation to the text. One way to do this is by writing a position statement that outlines your view of the subject of the work you are reviewing. What do you know, believe, or assume about this subject? What in your life might influence your approach to this text?
Here are some prompts that might help you generate a personal response to a book:
- I agree that ... because ...
- I disagree that ... because ...
- I don’t understand ...
- This reminds me of …
- I’m surprised by …
Another way to examine your thoughts in relation to a text is to note your initial response to the work. Consider your experience of the text – did you like it? Why or why not?
- What did I feel when I read this book? Why?
- How did I experience the style or tone of the author? How would I characterize each?
- What questions would I ask this author if I could?
- For me, what are the three best things about this book? The three worst things? Why?
Consider Context
A reviewer needs to examine the context of the book to arrive at a fair understanding and evaluation of its contents and importance. Context may include the scholarship to which this book responds or the author’s personal motive for writing. Or perhaps the context is simply contemporary society or today’s headlines. It is certainly important to consider how the work relates to the course that requires the review.
Here are some useful questions:
- What are the connections between this work and others on similar subjects? How does it relate to core concepts in my course or my discipline?
- What is the scholarly or social significance of this work? What contribution does it make to our understanding?
- What, of relevance, is missing from the work: certain kinds of evidence or methods of analysis/development? A particular theoretical approach? The experiences of certain groups?
- What other perspectives or conclusions are possible?
Once you have taken the time to thoroughly understand and analyze the work, you will have a clear perspective on its strengths and weaknesses and its value within the field. Take time to categorize your ideas and develop an outline; this will ensure your review is well organized and clear.
Organizing and Writing the Review
A review is organized around an assessment of the work or a focused message about its value to the field. Revisit your notes and consider your responses to your questions from critical reading to develop a clear statement that evaluates the work and provides an explanation for that evaluation.
For example:
X is an important work because it provides a new perspective on . . .
X’s argument is compelling because . . . ; however, it fails to address . . .
Although X claims to . . ., they make assumptions about . . . , which diminishes the impact . . .
This statement or evaluation is presented in the introduction. The body of the review works to support or explain your assessment; organize your key ideas or supporting arguments into paragraphs and use evidence from the book, article, or film to demonstrate how the work is (or is not) effective, compelling, provocative, novel, or informative.
As with all scholarly writing, a well-organized structure supports the clarity of your review. There is not a rigid formula for organization, but you may find the following guidelines to be helpful. Note that reviews do not typically include subheadings; the headings listed here serve to help you think about the main sections of your academic review.
Introduction
Introduce the work, the author (or director/producer), and the points you intend to make about this work. In addition, you should
- give relevant bibliographic information
- give the reader a clear idea of the nature, scope, and significance of the work
- indicate your evaluation of the work in a clear 1-2 sentence thesis statement
Provide background information to help your readers understand the importance of the work or the reasons for your appraisal. Background information could include:
- why the issue examined is of current interest
- other scholarship about this subject
- the author’s perspective, methodology, purpose
- the circumstances under which the book was created
Sample Introduction
Within educational research, much attention has been given to the importance of diversity and equity, and the literature is rife with studies detailing the best ways to create environments that are supportive of diverse students. In “Guidance Matters,” however, Carpenter and Diem (2015) examined these concepts in a less-studied source: policy documents related to leadership training. Using discourse analysis, they explored the ways in which government policies concerning the training of educational administrators discussed issues of diversity and equity. While their innovative methods allowed them to reveal the ways in which current policy promotes superficial platitudes to diversity rather than a deep commitment to promoting social justice, their data analysis left many of their identified themes vague and their discussion did not provide a clear explanation of the applications of their findings.
What works in this sample introduction:
- The nature of the larger issue, how best to create diversity and equity within educational environments, is clearly laid out.
- The paragraph clearly introduces the authors and study being reviewed and succinctly explains how they have addressed the larger issue of equity and diversity in a unique way.
- The paragraph ends with a clear thesis that outlines the strengths and weaknesses of the work.
Summary of the Work
Keep the summary of the work short! A paragraph or two should be sufficient. Summarize its contents very briefly and focus on:
- the purpose of the work
- the main points of the work
- the ideas, themes, or arguments that you will evaluate or discuss in the review
Analysis and Evaluation
Analyze and explain the significance of the main points of the work. Evaluate the work, answering questions such as the following:
- Does the work do what its author claimed it would?
- Is the work valid and accurate?
- How does the work fit into scholarship in the field?
- What are your reasons for agreeing, disagreeing, liking, disliking, believing, disbelieving?
Note that this section will take up the bulk of your review and should be organized into paragraphs. Because this form of writing typically does not use subheadings, strong paragraphing, particularly the use of clear topic sentences, is essential. Read more on paragraphing.
Reviews are informed by your critical reading or viewing of a work; therefore you need to include specific evidence from the work to support your claims about its message and its impact. Your writing and your assessment of the work will be most effective if you paraphrase or summarize the evidence you use, rather than relying on direct quotations. Be sure to follow the rules for citation in your discipline. Read more on paraphrasing and summarizing.
Sample Body Paragraph
One of the strengths of Carpenter and Diem’s (2015) study was innovative use of and nuanced explanation of discourse analysis. Critiquing much of the research on policy for its positivist promises of “value neutral and empirically objective” (p. 518) findings, Carpenter and Diem (2015) argued that discourse theory can provide an important lens through which to view policy and its relationship to educational outcomes. By interrogating the “inscribed discourses of policy making” (p. 518), they showed how policy language constructs particular social meanings of concepts such as diversity and equity. Significantly, this analysis was not simply about the language used within documents; instead, Carpenter and Diem (2015) argued that the language used was directly related to reality. Their “study examine[d] how dominant discourses related to equity, and their concretization within guiding policy documents, may shape the ways in which states, local school districts, and educational leaders are asked to consider these issues in their everyday practice” (Carpenter & Diem, 2015, p. 519). Thus, through the use of discourse theory, Carpenter and Diem (2015) framed policy language, which some might consider abstract or distant from daily life, as directly connected to the experience of educational leaders.
What works in this sample body paragraph:
- The paragraph begins with a clear topic sentence that connects directly to a strength mentioned in the thesis of the review.
- The paragraph provides specific details and examples to support how and why their methods are innovative.
- The direct quotations used are short and properly integrated into the sentences.
The paragraph concludes by explaining the significance of the innovative methods to the larger work.
Conclusion and Recommendation
Give your overall assessment of the work. Explain the larger significance of your assessment. Consider who would benefit from engaging with this work.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

Racing across the Atlantic: how we pulled together for ocean science
Career Feature 03 JUN 24

How I run a virtual lab group that’s collaborative, inclusive and productive
Career Column 31 MAY 24

Defying the stereotype of Black resilience
Career Q&A 30 MAY 24

Researcher parents are paying a high price for conference travel — here’s how to fix it
Career Column 27 MAY 24

How researchers in remote regions handle the isolation
Career Feature 24 MAY 24

Jaw-dropping views of the Milky Way and more — May’s best science images
News 04 JUN 24

Biomedical paper retractions have quadrupled in 20 years — why?
News 31 MAY 24

What is science? Tech heavyweights brawl over definition
Post-Doctoral Fellow in Chemistry and Chemical Biology
We are seeking a highly motivated, interdisciplinary scientist to investigate the host-gut microbiota interactions that are associated with driving...
Cambridge, Massachusetts
Harvard University - Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology
Postdoc Position (f/m/d) in “Building Healthcare Resilience Against Cyber-Attacks"
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) – The Research University in the Helmholtz Association creates and imparts knowledge for the society and th...
76344, Eggenstein-Leopoldshafen (DE)
Karlsruher Institut für Technologie (KIT) Campus Nord
Research assistant (Praedoc) (m/f/d) - Department of Biology, Chemistry, Pharmacy
Department of Biology, Chemistry, Pharmacy - Institute of Chemistry and Biochemistry AG Absmeier Research assistant (Praedoc) (m/f/d) with 65%-pa...
14195, Berlin (DE)
Freie Universität Berlin
Professor, Associate Professor, Postdoctoral Fellow Recruitment
Candidate shall have an international academic vision, and have a high academic level and strong scientific research ability.
Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Shenzhen University of Advanced Technology
Open Faculty Position in Mathematical and Information Security
We are now seeking outstanding candidates in all areas of mathematics and information security.
Dongguan, Guangdong, China
GREAT BAY INSTITUTE FOR ADVANCED STUDY: Institute of Mathematical and Information Security
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as you go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface with the option to save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.
- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, how to ace grant writing for research funding..., powerful academic phrases to improve your essay writing , how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., how to write a successful book chapter for..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai.
How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
3 straightforward steps (with examples) + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

38 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very timely.
I appreciate.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Organizing Research for Arts and Humanities Papers and Theses
- General Guide Information
- Developing a Topic
- What are Primary and Secondary Sources
- What are Scholarly and Non-Scholarly Sources
- Writing an Abstract
- Writing Academic Book Reviews
- Writing A Literature Review
- Using Images and other Media
Purpose of a Book Review
Note: This information is geared toward researchers in the arts and humanities. For a detailed guide on writing book reviews in the social sciences, please check the USC Libraries guide to Writing and Organizing Research in the Social Sciences , authored by Dr. Robert Labaree.
When writing an academic book review, start with a bibliographic citation of the book you are reviewing [e.g., author, title, publication information, length]. Adhere to a particular citation style, such as Chicago, MLA, or APA. Put your name at the very end of the book review text.
The basic purpose of a book review is to convey and evaluate the following:
a. what the book is about;
b. the expertise of the author(s);
c. how well the book covers its topic(s) and whether it breaks new ground;
d. the author’s viewpoint, methodology, or perspective;
e. the appropriateness of the evidence to the topical scope of the book;
f. the intended audience;
g. the arrangement of the book (chapters, illustrations) and the quality of the scholarly apparatus, such as notes and bibliographies.
Point "c. how well the book covers its topics and whether it breaks new ground" requires your engagement with the book, and can be approached in a variety of ways. The question of whether the book breaks new ground does not necessarily refer to some radical or overarching notion of originality in the author’s argument. A lot of contemporary scholarship in the arts or humanities is not about completely reorienting the discipline, nor is it usually about arguing a thesis that has never been argued before. If an author does that, that's wonderful, and you, as a book reviewer, must look at the validity of the methods that contextualize the author's new argument.
It is more likely that the author of a scholarly book will look at the existing evidence with a finer eye for detail, and use that detail to amplify and add to existing scholarship. The author may present new evidence or a new "reading" of the existing evidence, in order to refine scholarship and to contribute to current debate. Or the author may approach existing scholarship, events, and prevailing ideas from a more nuanced perspective, thus re-framing the debate within the discipline.
The task of the book reviewer is to “tease out” the book’s themes, explain them in the review, and apply a well-argued judgment on the appropriateness of the book’s argument(s) to the existing scholarship in the field.
For example, you are reviewing a book on the history of the development of public libraries in nineteenth century America. The book includes a chapter on the role of patronage by affluent women in endowing public libraries in the mid-to-late-1800s. In this chapter, the author argues that the role of women was overlooked in previous scholarship because most of them were widows who made their financial bequests to libraries in the names of their husbands. The author argues that the history of public library patronage, and moreover, of cultural patronage, should be re-read and possibly re-framed given the evidence presented in this chapter. As a book reviewer you will be expected to evaluate this argument and the underlying scholarship.
There are two common types of academic book reviews: short summary reviews, which are descriptive, and essay-length critical reviews. Both types are described further down.
[Parenthetically, writing an academic/scholarly book review may present an opportunity to get published.]
Short summary book reviews
For a short, descriptive review, include at least the following elements:
a. the bibliographic citation for the book;
b. the purpose of the book;
c. a summary of main theme(s) or key points;
d. if there is space, a brief description of the book’s relationship to other books on the same topic or to pertinent scholarship in the field.
e. note the author's affiliation and authority, as well as the physical content of the book, such as visual materials (photographs, illustrations, graphs) and the presence of scholarly apparatus (table of contents, index, bibliography, footnotes, endnotes, credit for visual materials);
f. your name and affiliation.
Critical or essay-length book reviews
For a critical, essay-length book review consider including the following elements, depending on their relevance to your assignment:
b. an opening statement that ought to peak the reader’s interest in the book under review
c. a section that points to the author’s main intentions;
d. a section that discusses the author’s ideas and the book’s thesis within a scholarly perspective. This should be a critical assessment of the book within the larger scholarly discourse;
e. if you found errors in the book, point the major ones and explain their significance. Explain whether they detract from the thesis and the arguments made in the book;
f. state the book's place within a strand of scholarship and summarize its importance to the discipline;
g. include information about the author's affiliation and authority, as well as the physical content of the book, such as visual materials (photographs, illustrations, graphs) and the presence of scholarly apparatus (table of contents, index, bibliography, footnotes, endnotes, credit for visual materials);
h. indicate the intended readership of the book and whether the author succeeds in engaging the audience on the appropriate level;
i. your name and affiliation.
Good examples of essay-length reviews may be found in the scholarly journals included in the JSTOR collection, in the New York Review of Books , and similar types of publications, and in cultural publications like the New Yorker magazine.
Remember to keep track of your sources, regardless of the stage of your research. The USC Libraries have an excellent guide to citation styles and to citation management software .
- << Previous: Writing an Abstract
- Next: Writing A Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Jan 19, 2023 3:12 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/ah_writing
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
How to Write a Peer Review

When you write a peer review for a manuscript, what should you include in your comments? What should you leave out? And how should the review be formatted?
This guide provides quick tips for writing and organizing your reviewer report.
Review Outline
Use an outline for your reviewer report so it’s easy for the editors and author to follow. This will also help you keep your comments organized.
Think about structuring your review like an inverted pyramid. Put the most important information at the top, followed by details and examples in the center, and any additional points at the very bottom.
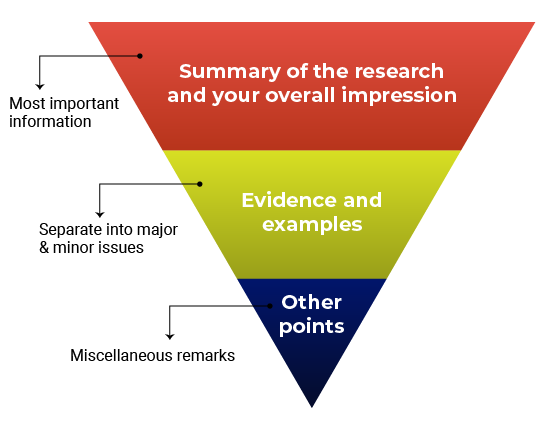
Here’s how your outline might look:
1. Summary of the research and your overall impression
In your own words, summarize what the manuscript claims to report. This shows the editor how you interpreted the manuscript and will highlight any major differences in perspective between you and the other reviewers. Give an overview of the manuscript’s strengths and weaknesses. Think about this as your “take-home” message for the editors. End this section with your recommended course of action.
2. Discussion of specific areas for improvement
It’s helpful to divide this section into two parts: one for major issues and one for minor issues. Within each section, you can talk about the biggest issues first or go systematically figure-by-figure or claim-by-claim. Number each item so that your points are easy to follow (this will also make it easier for the authors to respond to each point). Refer to specific lines, pages, sections, or figure and table numbers so the authors (and editors) know exactly what you’re talking about.
Major vs. minor issues
What’s the difference between a major and minor issue? Major issues should consist of the essential points the authors need to address before the manuscript can proceed. Make sure you focus on what is fundamental for the current study . In other words, it’s not helpful to recommend additional work that would be considered the “next step” in the study. Minor issues are still important but typically will not affect the overall conclusions of the manuscript. Here are some examples of what would might go in the “minor” category:
- Missing references (but depending on what is missing, this could also be a major issue)
- Technical clarifications (e.g., the authors should clarify how a reagent works)
- Data presentation (e.g., the authors should present p-values differently)
- Typos, spelling, grammar, and phrasing issues
3. Any other points
Confidential comments for the editors.
Some journals have a space for reviewers to enter confidential comments about the manuscript. Use this space to mention concerns about the submission that you’d want the editors to consider before sharing your feedback with the authors, such as concerns about ethical guidelines or language quality. Any serious issues should be raised directly and immediately with the journal as well.
This section is also where you will disclose any potentially competing interests, and mention whether you’re willing to look at a revised version of the manuscript.
Do not use this space to critique the manuscript, since comments entered here will not be passed along to the authors. If you’re not sure what should go in the confidential comments, read the reviewer instructions or check with the journal first before submitting your review. If you are reviewing for a journal that does not offer a space for confidential comments, consider writing to the editorial office directly with your concerns.
Get this outline in a template
Giving Feedback
Giving feedback is hard. Giving effective feedback can be even more challenging. Remember that your ultimate goal is to discuss what the authors would need to do in order to qualify for publication. The point is not to nitpick every piece of the manuscript. Your focus should be on providing constructive and critical feedback that the authors can use to improve their study.
If you’ve ever had your own work reviewed, you already know that it’s not always easy to receive feedback. Follow the golden rule: Write the type of review you’d want to receive if you were the author. Even if you decide not to identify yourself in the review, you should write comments that you would be comfortable signing your name to.
In your comments, use phrases like “ the authors’ discussion of X” instead of “ your discussion of X .” This will depersonalize the feedback and keep the focus on the manuscript instead of the authors.
General guidelines for effective feedback

- Justify your recommendation with concrete evidence and specific examples.
- Be specific so the authors know what they need to do to improve.
- Be thorough. This might be the only time you read the manuscript.
- Be professional and respectful. The authors will be reading these comments too.
- Remember to say what you liked about the manuscript!

Don’t
- Recommend additional experiments or unnecessary elements that are out of scope for the study or for the journal criteria.
- Tell the authors exactly how to revise their manuscript—you don’t need to do their work for them.
- Use the review to promote your own research or hypotheses.
- Focus on typos and grammar. If the manuscript needs significant editing for language and writing quality, just mention this in your comments.
- Submit your review without proofreading it and checking everything one more time.
Before and After: Sample Reviewer Comments
Keeping in mind the guidelines above, how do you put your thoughts into words? Here are some sample “before” and “after” reviewer comments
✗ Before
“The authors appear to have no idea what they are talking about. I don’t think they have read any of the literature on this topic.”
✓ After
“The study fails to address how the findings relate to previous research in this area. The authors should rewrite their Introduction and Discussion to reference the related literature, especially recently published work such as Darwin et al.”
“The writing is so bad, it is practically unreadable. I could barely bring myself to finish it.”
“While the study appears to be sound, the language is unclear, making it difficult to follow. I advise the authors work with a writing coach or copyeditor to improve the flow and readability of the text.”
“It’s obvious that this type of experiment should have been included. I have no idea why the authors didn’t use it. This is a big mistake.”
“The authors are off to a good start, however, this study requires additional experiments, particularly [type of experiment]. Alternatively, the authors should include more information that clarifies and justifies their choice of methods.”
Suggested Language for Tricky Situations
You might find yourself in a situation where you’re not sure how to explain the problem or provide feedback in a constructive and respectful way. Here is some suggested language for common issues you might experience.
What you think : The manuscript is fatally flawed. What you could say: “The study does not appear to be sound” or “the authors have missed something crucial”.
What you think : You don’t completely understand the manuscript. What you could say : “The authors should clarify the following sections to avoid confusion…”
What you think : The technical details don’t make sense. What you could say : “The technical details should be expanded and clarified to ensure that readers understand exactly what the researchers studied.”
What you think: The writing is terrible. What you could say : “The authors should revise the language to improve readability.”
What you think : The authors have over-interpreted the findings. What you could say : “The authors aim to demonstrate [XYZ], however, the data does not fully support this conclusion. Specifically…”
What does a good review look like?
Check out the peer review examples at F1000 Research to see how other reviewers write up their reports and give constructive feedback to authors.
Time to Submit the Review!
Be sure you turn in your report on time. Need an extension? Tell the journal so that they know what to expect. If you need a lot of extra time, the journal might need to contact other reviewers or notify the author about the delay.
Tip: Building a relationship with an editor
You’ll be more likely to be asked to review again if you provide high-quality feedback and if you turn in the review on time. Especially if it’s your first review for a journal, it’s important to show that you are reliable. Prove yourself once and you’ll get asked to review again!
- Getting started as a reviewer
- Responding to an invitation
- Reading a manuscript
- Writing a peer review
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…

Book Reviews
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you write a book review, a report or essay that offers a critical perspective on a text. It offers a process and suggests some strategies for writing book reviews.
What is a review?
A review is a critical evaluation of a text, event, object, or phenomenon. Reviews can consider books, articles, entire genres or fields of literature, architecture, art, fashion, restaurants, policies, exhibitions, performances, and many other forms. This handout will focus on book reviews. For a similar assignment, see our handout on literature reviews .
Above all, a review makes an argument. The most important element of a review is that it is a commentary, not merely a summary. It allows you to enter into dialogue and discussion with the work’s creator and with other audiences. You can offer agreement or disagreement and identify where you find the work exemplary or deficient in its knowledge, judgments, or organization. You should clearly state your opinion of the work in question, and that statement will probably resemble other types of academic writing, with a thesis statement, supporting body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Typically, reviews are brief. In newspapers and academic journals, they rarely exceed 1000 words, although you may encounter lengthier assignments and extended commentaries. In either case, reviews need to be succinct. While they vary in tone, subject, and style, they share some common features:
- First, a review gives the reader a concise summary of the content. This includes a relevant description of the topic as well as its overall perspective, argument, or purpose.
- Second, and more importantly, a review offers a critical assessment of the content. This involves your reactions to the work under review: what strikes you as noteworthy, whether or not it was effective or persuasive, and how it enhanced your understanding of the issues at hand.
- Finally, in addition to analyzing the work, a review often suggests whether or not the audience would appreciate it.
Becoming an expert reviewer: three short examples
Reviewing can be a daunting task. Someone has asked for your opinion about something that you may feel unqualified to evaluate. Who are you to criticize Toni Morrison’s new book if you’ve never written a novel yourself, much less won a Nobel Prize? The point is that someone—a professor, a journal editor, peers in a study group—wants to know what you think about a particular work. You may not be (or feel like) an expert, but you need to pretend to be one for your particular audience. Nobody expects you to be the intellectual equal of the work’s creator, but your careful observations can provide you with the raw material to make reasoned judgments. Tactfully voicing agreement and disagreement, praise and criticism, is a valuable, challenging skill, and like many forms of writing, reviews require you to provide concrete evidence for your assertions.
Consider the following brief book review written for a history course on medieval Europe by a student who is fascinated with beer:
Judith Bennett’s Ale, Beer, and Brewsters in England: Women’s Work in a Changing World, 1300-1600, investigates how women used to brew and sell the majority of ale drunk in England. Historically, ale and beer (not milk, wine, or water) were important elements of the English diet. Ale brewing was low-skill and low status labor that was complimentary to women’s domestic responsibilities. In the early fifteenth century, brewers began to make ale with hops, and they called this new drink “beer.” This technique allowed brewers to produce their beverages at a lower cost and to sell it more easily, although women generally stopped brewing once the business became more profitable.
The student describes the subject of the book and provides an accurate summary of its contents. But the reader does not learn some key information expected from a review: the author’s argument, the student’s appraisal of the book and its argument, and whether or not the student would recommend the book. As a critical assessment, a book review should focus on opinions, not facts and details. Summary should be kept to a minimum, and specific details should serve to illustrate arguments.
Now consider a review of the same book written by a slightly more opinionated student:
Judith Bennett’s Ale, Beer, and Brewsters in England: Women’s Work in a Changing World, 1300-1600 was a colossal disappointment. I wanted to know about the rituals surrounding drinking in medieval England: the songs, the games, the parties. Bennett provided none of that information. I liked how the book showed ale and beer brewing as an economic activity, but the reader gets lost in the details of prices and wages. I was more interested in the private lives of the women brewsters. The book was divided into eight long chapters, and I can’t imagine why anyone would ever want to read it.
There’s no shortage of judgments in this review! But the student does not display a working knowledge of the book’s argument. The reader has a sense of what the student expected of the book, but no sense of what the author herself set out to prove. Although the student gives several reasons for the negative review, those examples do not clearly relate to each other as part of an overall evaluation—in other words, in support of a specific thesis. This review is indeed an assessment, but not a critical one.
Here is one final review of the same book:
One of feminism’s paradoxes—one that challenges many of its optimistic histories—is how patriarchy remains persistent over time. While Judith Bennett’s Ale, Beer, and Brewsters in England: Women’s Work in a Changing World, 1300-1600 recognizes medieval women as historical actors through their ale brewing, it also shows that female agency had its limits with the advent of beer. I had assumed that those limits were religious and political, but Bennett shows how a “patriarchal equilibrium” shut women out of economic life as well. Her analysis of women’s wages in ale and beer production proves that a change in women’s work does not equate to a change in working women’s status. Contemporary feminists and historians alike should read Bennett’s book and think twice when they crack open their next brewsky.
This student’s review avoids the problems of the previous two examples. It combines balanced opinion and concrete example, a critical assessment based on an explicitly stated rationale, and a recommendation to a potential audience. The reader gets a sense of what the book’s author intended to demonstrate. Moreover, the student refers to an argument about feminist history in general that places the book in a specific genre and that reaches out to a general audience. The example of analyzing wages illustrates an argument, the analysis engages significant intellectual debates, and the reasons for the overall positive review are plainly visible. The review offers criteria, opinions, and support with which the reader can agree or disagree.
Developing an assessment: before you write
There is no definitive method to writing a review, although some critical thinking about the work at hand is necessary before you actually begin writing. Thus, writing a review is a two-step process: developing an argument about the work under consideration, and making that argument as you write an organized and well-supported draft. See our handout on argument .
What follows is a series of questions to focus your thinking as you dig into the work at hand. While the questions specifically consider book reviews, you can easily transpose them to an analysis of performances, exhibitions, and other review subjects. Don’t feel obligated to address each of the questions; some will be more relevant than others to the book in question.
- What is the thesis—or main argument—of the book? If the author wanted you to get one idea from the book, what would it be? How does it compare or contrast to the world you know? What has the book accomplished?
- What exactly is the subject or topic of the book? Does the author cover the subject adequately? Does the author cover all aspects of the subject in a balanced fashion? What is the approach to the subject (topical, analytical, chronological, descriptive)?
- How does the author support their argument? What evidence do they use to prove their point? Do you find that evidence convincing? Why or why not? Does any of the author’s information (or conclusions) conflict with other books you’ve read, courses you’ve taken or just previous assumptions you had of the subject?
- How does the author structure their argument? What are the parts that make up the whole? Does the argument make sense? Does it persuade you? Why or why not?
- How has this book helped you understand the subject? Would you recommend the book to your reader?
Beyond the internal workings of the book, you may also consider some information about the author and the circumstances of the text’s production:
- Who is the author? Nationality, political persuasion, training, intellectual interests, personal history, and historical context may provide crucial details about how a work takes shape. Does it matter, for example, that the biographer was the subject’s best friend? What difference would it make if the author participated in the events they write about?
- What is the book’s genre? Out of what field does it emerge? Does it conform to or depart from the conventions of its genre? These questions can provide a historical or literary standard on which to base your evaluations. If you are reviewing the first book ever written on the subject, it will be important for your readers to know. Keep in mind, though, that naming “firsts”—alongside naming “bests” and “onlys”—can be a risky business unless you’re absolutely certain.
Writing the review
Once you have made your observations and assessments of the work under review, carefully survey your notes and attempt to unify your impressions into a statement that will describe the purpose or thesis of your review. Check out our handout on thesis statements . Then, outline the arguments that support your thesis.
Your arguments should develop the thesis in a logical manner. That logic, unlike more standard academic writing, may initially emphasize the author’s argument while you develop your own in the course of the review. The relative emphasis depends on the nature of the review: if readers may be more interested in the work itself, you may want to make the work and the author more prominent; if you want the review to be about your perspective and opinions, then you may structure the review to privilege your observations over (but never separate from) those of the work under review. What follows is just one of many ways to organize a review.
Introduction
Since most reviews are brief, many writers begin with a catchy quip or anecdote that succinctly delivers their argument. But you can introduce your review differently depending on the argument and audience. The Writing Center’s handout on introductions can help you find an approach that works. In general, you should include:
- The name of the author and the book title and the main theme.
- Relevant details about who the author is and where they stand in the genre or field of inquiry. You could also link the title to the subject to show how the title explains the subject matter.
- The context of the book and/or your review. Placing your review in a framework that makes sense to your audience alerts readers to your “take” on the book. Perhaps you want to situate a book about the Cuban revolution in the context of Cold War rivalries between the United States and the Soviet Union. Another reviewer might want to consider the book in the framework of Latin American social movements. Your choice of context informs your argument.
- The thesis of the book. If you are reviewing fiction, this may be difficult since novels, plays, and short stories rarely have explicit arguments. But identifying the book’s particular novelty, angle, or originality allows you to show what specific contribution the piece is trying to make.
- Your thesis about the book.
Summary of content
This should be brief, as analysis takes priority. In the course of making your assessment, you’ll hopefully be backing up your assertions with concrete evidence from the book, so some summary will be dispersed throughout other parts of the review.
The necessary amount of summary also depends on your audience. Graduate students, beware! If you are writing book reviews for colleagues—to prepare for comprehensive exams, for example—you may want to devote more attention to summarizing the book’s contents. If, on the other hand, your audience has already read the book—such as a class assignment on the same work—you may have more liberty to explore more subtle points and to emphasize your own argument. See our handout on summary for more tips.
Analysis and evaluation of the book
Your analysis and evaluation should be organized into paragraphs that deal with single aspects of your argument. This arrangement can be challenging when your purpose is to consider the book as a whole, but it can help you differentiate elements of your criticism and pair assertions with evidence more clearly. You do not necessarily need to work chronologically through the book as you discuss it. Given the argument you want to make, you can organize your paragraphs more usefully by themes, methods, or other elements of the book. If you find it useful to include comparisons to other books, keep them brief so that the book under review remains in the spotlight. Avoid excessive quotation and give a specific page reference in parentheses when you do quote. Remember that you can state many of the author’s points in your own words.
Sum up or restate your thesis or make the final judgment regarding the book. You should not introduce new evidence for your argument in the conclusion. You can, however, introduce new ideas that go beyond the book if they extend the logic of your own thesis. This paragraph needs to balance the book’s strengths and weaknesses in order to unify your evaluation. Did the body of your review have three negative paragraphs and one favorable one? What do they all add up to? The Writing Center’s handout on conclusions can help you make a final assessment.
Finally, a few general considerations:
- Review the book in front of you, not the book you wish the author had written. You can and should point out shortcomings or failures, but don’t criticize the book for not being something it was never intended to be.
- With any luck, the author of the book worked hard to find the right words to express her ideas. You should attempt to do the same. Precise language allows you to control the tone of your review.
- Never hesitate to challenge an assumption, approach, or argument. Be sure, however, to cite specific examples to back up your assertions carefully.
- Try to present a balanced argument about the value of the book for its audience. You’re entitled—and sometimes obligated—to voice strong agreement or disagreement. But keep in mind that a bad book takes as long to write as a good one, and every author deserves fair treatment. Harsh judgments are difficult to prove and can give readers the sense that you were unfair in your assessment.
- A great place to learn about book reviews is to look at examples. The New York Times Sunday Book Review and The New York Review of Books can show you how professional writers review books.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Drewry, John. 1974. Writing Book Reviews. Boston: Greenwood Press.
Hoge, James. 1987. Literary Reviewing. Charlottesville: University Virginia of Press.
Sova, Dawn, and Harry Teitelbaum. 2002. How to Write Book Reports , 4th ed. Lawrenceville, NY: Thomson/Arco.
Walford, A.J. 1986. Reviews and Reviewing: A Guide. Phoenix: Oryx Press.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.

Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Academic Book Review
4-minute read
- 13th September 2019
For researchers and postgraduates , writing a book review is a relatively easy way to get published. It’s also a good way to refine your academic writing skills and learn the publishing process. But how do you write a good academic book review? We have a few tips to share.
1. Finding a Book to Review
Before you can write a book review, you need a suitable book to review. Typically, there are two main ways to find one:
- Look to see which books journal publishers are seeking reviews for.
- Find a book that interests you and pitch it to publishers.
The first approach works by finding a journal in your field that is soliciting reviews. This information may be available on the journal’s website (e.g., on a page titled “Books for Review”). However, you can also email the editor to ask if there are book review opportunities available.
Alternatively, you can find a book you want to review and pitch it to journal editors. If you want to take this approach, pick a book that:
- Is about a topic or subject area that you know well.
- Has been published recently, or at least in the last 2–3 years.
- Was published by a reputable publisher (e.g., a university printing press).
You can then pitch the review to a journal that covers your chosen subject.
Some publishers will even give reviewers access to new books. Springer, for example, has a scheme where reviewers can access books online and receive a print copy once a review is published. So this is always worth checking.
2. Follow the Style Guide
Once you know the journal you want to write for, look for the publisher’s style guide. This might be called the “Author Instructions” or “Review Guidelines,” but it should be available somewhere on the publisher’s website. If it is not obviously available, consider checking with the editor.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
When you have found the style guide, follow its instructions carefully. It should provide information on everything from writing style and the word count to submitting your review, making the process much simpler.
3. Don’t Make It About You!
You’d be surprised how often people begin by summarizing the book they’re reviewing, but then abandon it in favor of explaining their own ideas about the subject matter. As such, one important tip when reviewing an academic book is to actually review the book , not just the subject matter.
This isn’t to say that you can’t offer your own thoughts on the issues discussed, especially if they’re relevant to what the author has argued. But remember that people read reviews to find out about the book being reviewed, so this should always be your focus.
4. Questions to Answer in a Book Review
Finally, while the content of a review will depend on the book, there are a few questions every good book review should answer. These include:
- What is the book about? Does it cover the topic adequately? What does the author argue? Ideally, you will summarize the argument early on.
- Who is the author/editor? What is their field of expertise? How does this book relate to their past work? You might also want to mention relevant biographical details about the author, if there are any.
- How does the author support their argument? Do they provide convincing evidence? Do they engage with counterarguments? Try to find at least one strength (i.e., something the book does well) and one weakness (i.e., something that could be stronger) to write about.
- As a whole, has the book helped you understand the subject? Who would you recommend it to? This will be the concluding section of your review.
If you can cover all these points, you should end up with a strong book review. All you need then is to have it proofread by the professionals .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Critical Reviews
How to Write an Article Review (With Examples)
Last Updated: April 24, 2024 Fact Checked
Preparing to Write Your Review
Writing the article review, sample article reviews, expert q&a.
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,109,759 times.
An article review is both a summary and an evaluation of another writer's article. Teachers often assign article reviews to introduce students to the work of experts in the field. Experts also are often asked to review the work of other professionals. Understanding the main points and arguments of the article is essential for an accurate summation. Logical evaluation of the article's main theme, supporting arguments, and implications for further research is an important element of a review . Here are a few guidelines for writing an article review.
Education specialist Alexander Peterman recommends: "In the case of a review, your objective should be to reflect on the effectiveness of what has already been written, rather than writing to inform your audience about a subject."
Article Review 101
- Read the article very closely, and then take time to reflect on your evaluation. Consider whether the article effectively achieves what it set out to.
- Write out a full article review by completing your intro, summary, evaluation, and conclusion. Don't forget to add a title, too!
- Proofread your review for mistakes (like grammar and usage), while also cutting down on needless information.

- Article reviews present more than just an opinion. You will engage with the text to create a response to the scholarly writer's ideas. You will respond to and use ideas, theories, and research from your studies. Your critique of the article will be based on proof and your own thoughtful reasoning.
- An article review only responds to the author's research. It typically does not provide any new research. However, if you are correcting misleading or otherwise incorrect points, some new data may be presented.
- An article review both summarizes and evaluates the article.

- Summarize the article. Focus on the important points, claims, and information.
- Discuss the positive aspects of the article. Think about what the author does well, good points she makes, and insightful observations.
- Identify contradictions, gaps, and inconsistencies in the text. Determine if there is enough data or research included to support the author's claims. Find any unanswered questions left in the article.

- Make note of words or issues you don't understand and questions you have.
- Look up terms or concepts you are unfamiliar with, so you can fully understand the article. Read about concepts in-depth to make sure you understand their full context.

- Pay careful attention to the meaning of the article. Make sure you fully understand the article. The only way to write a good article review is to understand the article.

- With either method, make an outline of the main points made in the article and the supporting research or arguments. It is strictly a restatement of the main points of the article and does not include your opinions.
- After putting the article in your own words, decide which parts of the article you want to discuss in your review. You can focus on the theoretical approach, the content, the presentation or interpretation of evidence, or the style. You will always discuss the main issues of the article, but you can sometimes also focus on certain aspects. This comes in handy if you want to focus the review towards the content of a course.
- Review the summary outline to eliminate unnecessary items. Erase or cross out the less important arguments or supplemental information. Your revised summary can serve as the basis for the summary you provide at the beginning of your review.

- What does the article set out to do?
- What is the theoretical framework or assumptions?
- Are the central concepts clearly defined?
- How adequate is the evidence?
- How does the article fit into the literature and field?
- Does it advance the knowledge of the subject?
- How clear is the author's writing? Don't: include superficial opinions or your personal reaction. Do: pay attention to your biases, so you can overcome them.

- For example, in MLA , a citation may look like: Duvall, John N. "The (Super)Marketplace of Images: Television as Unmediated Mediation in DeLillo's White Noise ." Arizona Quarterly 50.3 (1994): 127-53. Print. [9] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest.

- Your introduction should only be 10-25% of your review.
- End the introduction with your thesis. Your thesis should address the above issues. For example: Although the author has some good points, his article is biased and contains some misinterpretation of data from others’ analysis of the effectiveness of the condom.

- Use direct quotes from the author sparingly.
- Review the summary you have written. Read over your summary many times to ensure that your words are an accurate description of the author's article.

- Support your critique with evidence from the article or other texts.
- The summary portion is very important for your critique. You must make the author's argument clear in the summary section for your evaluation to make sense.
- Remember, this is not where you say if you liked the article or not. You are assessing the significance and relevance of the article.
- Use a topic sentence and supportive arguments for each opinion. For example, you might address a particular strength in the first sentence of the opinion section, followed by several sentences elaborating on the significance of the point.

- This should only be about 10% of your overall essay.
- For example: This critical review has evaluated the article "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS" by Anthony Zimmerman. The arguments in the article show the presence of bias, prejudice, argumentative writing without supporting details, and misinformation. These points weaken the author’s arguments and reduce his credibility.

- Make sure you have identified and discussed the 3-4 key issues in the article.

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libguides.cmich.edu/writinghelp/articlereview
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548566/
- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 24 July 2020.
- ↑ https://guides.library.queensu.ca/introduction-research/writing/critical
- ↑ https://www.iup.edu/writingcenter/writing-resources/organization-and-structure/creating-an-outline.html
- ↑ https://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/titles.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548565/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uconn.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/593/2014/06/How_to_Summarize_a_Research_Article1.pdf
- ↑ https://www.uis.edu/learning-hub/writing-resources/handouts/learning-hub/how-to-review-a-journal-article
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

If you have to write an article review, read through the original article closely, taking notes and highlighting important sections as you read. Next, rewrite the article in your own words, either in a long paragraph or as an outline. Open your article review by citing the article, then write an introduction which states the article’s thesis. Next, summarize the article, followed by your opinion about whether the article was clear, thorough, and useful. Finish with a paragraph that summarizes the main points of the article and your opinions. To learn more about what to include in your personal critique of the article, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Prince Asiedu-Gyan
Apr 22, 2022
Did this article help you?

Sammy James
Sep 12, 2017
Juabin Matey
Aug 30, 2017
Vanita Meghrajani
Jul 21, 2016
Nov 27, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Page Content
Overview of the review report format, the first read-through, first read considerations, spotting potential major flaws, concluding the first reading, rejection after the first reading, before starting the second read-through, doing the second read-through, the second read-through: section by section guidance, how to structure your report, on presentation and style, criticisms & confidential comments to editors, the recommendation, when recommending rejection, additional resources, step by step guide to reviewing a manuscript.
When you receive an invitation to peer review, you should be sent a copy of the paper's abstract to help you decide whether you wish to do the review. Try to respond to invitations promptly - it will prevent delays. It is also important at this stage to declare any potential Conflict of Interest.
The structure of the review report varies between journals. Some follow an informal structure, while others have a more formal approach.
" Number your comments!!! " (Jonathon Halbesleben, former Editor of Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology)
Informal Structure
Many journals don't provide criteria for reviews beyond asking for your 'analysis of merits'. In this case, you may wish to familiarize yourself with examples of other reviews done for the journal, which the editor should be able to provide or, as you gain experience, rely on your own evolving style.
Formal Structure
Other journals require a more formal approach. Sometimes they will ask you to address specific questions in your review via a questionnaire. Or they might want you to rate the manuscript on various attributes using a scorecard. Often you can't see these until you log in to submit your review. So when you agree to the work, it's worth checking for any journal-specific guidelines and requirements. If there are formal guidelines, let them direct the structure of your review.
In Both Cases
Whether specifically required by the reporting format or not, you should expect to compile comments to authors and possibly confidential ones to editors only.

Following the invitation to review, when you'll have received the article abstract, you should already understand the aims, key data and conclusions of the manuscript. If you don't, make a note now that you need to feedback on how to improve those sections.
The first read-through is a skim-read. It will help you form an initial impression of the paper and get a sense of whether your eventual recommendation will be to accept or reject the paper.
Keep a pen and paper handy when skim-reading.
Try to bear in mind the following questions - they'll help you form your overall impression:
- What is the main question addressed by the research? Is it relevant and interesting?
- How original is the topic? What does it add to the subject area compared with other published material?
- Is the paper well written? Is the text clear and easy to read?
- Are the conclusions consistent with the evidence and arguments presented? Do they address the main question posed?
- If the author is disagreeing significantly with the current academic consensus, do they have a substantial case? If not, what would be required to make their case credible?
- If the paper includes tables or figures, what do they add to the paper? Do they aid understanding or are they superfluous?
While you should read the whole paper, making the right choice of what to read first can save time by flagging major problems early on.
Editors say, " Specific recommendations for remedying flaws are VERY welcome ."
Examples of possibly major flaws include:
- Drawing a conclusion that is contradicted by the author's own statistical or qualitative evidence
- The use of a discredited method
- Ignoring a process that is known to have a strong influence on the area under study
If experimental design features prominently in the paper, first check that the methodology is sound - if not, this is likely to be a major flaw.
You might examine:
- The sampling in analytical papers
- The sufficient use of control experiments
- The precision of process data
- The regularity of sampling in time-dependent studies
- The validity of questions, the use of a detailed methodology and the data analysis being done systematically (in qualitative research)
- That qualitative research extends beyond the author's opinions, with sufficient descriptive elements and appropriate quotes from interviews or focus groups
Major Flaws in Information
If methodology is less of an issue, it's often a good idea to look at the data tables, figures or images first. Especially in science research, it's all about the information gathered. If there are critical flaws in this, it's very likely the manuscript will need to be rejected. Such issues include:
- Insufficient data
- Unclear data tables
- Contradictory data that either are not self-consistent or disagree with the conclusions
- Confirmatory data that adds little, if anything, to current understanding - unless strong arguments for such repetition are made
If you find a major problem, note your reasoning and clear supporting evidence (including citations).
After the initial read and using your notes, including those of any major flaws you found, draft the first two paragraphs of your review - the first summarizing the research question addressed and the second the contribution of the work. If the journal has a prescribed reporting format, this draft will still help you compose your thoughts.
The First Paragraph
This should state the main question addressed by the research and summarize the goals, approaches, and conclusions of the paper. It should:
- Help the editor properly contextualize the research and add weight to your judgement
- Show the author what key messages are conveyed to the reader, so they can be sure they are achieving what they set out to do
- Focus on successful aspects of the paper so the author gets a sense of what they've done well
The Second Paragraph
This should provide a conceptual overview of the contribution of the research. So consider:
- Is the paper's premise interesting and important?
- Are the methods used appropriate?
- Do the data support the conclusions?
After drafting these two paragraphs, you should be in a position to decide whether this manuscript is seriously flawed and should be rejected (see the next section). Or whether it is publishable in principle and merits a detailed, careful read through.
Even if you are coming to the opinion that an article has serious flaws, make sure you read the whole paper. This is very important because you may find some really positive aspects that can be communicated to the author. This could help them with future submissions.
A full read-through will also make sure that any initial concerns are indeed correct and fair. After all, you need the context of the whole paper before deciding to reject. If you still intend to recommend rejection, see the section "When recommending rejection."
Once the paper has passed your first read and you've decided the article is publishable in principle, one purpose of the second, detailed read-through is to help prepare the manuscript for publication. You may still decide to recommend rejection following a second reading.
" Offer clear suggestions for how the authors can address the concerns raised. In other words, if you're going to raise a problem, provide a solution ." (Jonathon Halbesleben, Editor of Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology)
Preparation
To save time and simplify the review:
- Don't rely solely upon inserting comments on the manuscript document - make separate notes
- Try to group similar concerns or praise together
- If using a review program to note directly onto the manuscript, still try grouping the concerns and praise in separate notes - it helps later
- Note line numbers of text upon which your notes are based - this helps you find items again and also aids those reading your review
Now that you have completed your preparations, you're ready to spend an hour or so reading carefully through the manuscript.
As you're reading through the manuscript for a second time, you'll need to keep in mind the argument's construction, the clarity of the language and content.
With regard to the argument’s construction, you should identify:
- Any places where the meaning is unclear or ambiguous
- Any factual errors
- Any invalid arguments
You may also wish to consider:
- Does the title properly reflect the subject of the paper?
- Does the abstract provide an accessible summary of the paper?
- Do the keywords accurately reflect the content?
- Is the paper an appropriate length?
- Are the key messages short, accurate and clear?
Not every submission is well written. Part of your role is to make sure that the text’s meaning is clear.
Editors say, " If a manuscript has many English language and editing issues, please do not try and fix it. If it is too bad, note that in your review and it should be up to the authors to have the manuscript edited ."
If the article is difficult to understand, you should have rejected it already. However, if the language is poor but you understand the core message, see if you can suggest improvements to fix the problem:
- Are there certain aspects that could be communicated better, such as parts of the discussion?
- Should the authors consider resubmitting to the same journal after language improvements?
- Would you consider looking at the paper again once these issues are dealt with?
On Grammar and Punctuation
Your primary role is judging the research content. Don't spend time polishing grammar or spelling. Editors will make sure that the text is at a high standard before publication. However, if you spot grammatical errors that affect clarity of meaning, then it's important to highlight these. Expect to suggest such amendments - it's rare for a manuscript to pass review with no corrections.
A 2010 study of nursing journals found that 79% of recommendations by reviewers were influenced by grammar and writing style (Shattel, et al., 2010).
1. The Introduction
A well-written introduction:
- Sets out the argument
- Summarizes recent research related to the topic
- Highlights gaps in current understanding or conflicts in current knowledge
- Establishes the originality of the research aims by demonstrating the need for investigations in the topic area
- Gives a clear idea of the target readership, why the research was carried out and the novelty and topicality of the manuscript
Originality and Topicality
Originality and topicality can only be established in the light of recent authoritative research. For example, it's impossible to argue that there is a conflict in current understanding by referencing articles that are 10 years old.
Authors may make the case that a topic hasn't been investigated in several years and that new research is required. This point is only valid if researchers can point to recent developments in data gathering techniques or to research in indirectly related fields that suggest the topic needs revisiting. Clearly, authors can only do this by referencing recent literature. Obviously, where older research is seminal or where aspects of the methodology rely upon it, then it is perfectly appropriate for authors to cite some older papers.
Editors say, "Is the report providing new information; is it novel or just confirmatory of well-known outcomes ?"
It's common for the introduction to end by stating the research aims. By this point you should already have a good impression of them - if the explicit aims come as a surprise, then the introduction needs improvement.
2. Materials and Methods
Academic research should be replicable, repeatable and robust - and follow best practice.
Replicable Research
This makes sufficient use of:
- Control experiments
- Repeated analyses
- Repeated experiments
These are used to make sure observed trends are not due to chance and that the same experiment could be repeated by other researchers - and result in the same outcome. Statistical analyses will not be sound if methods are not replicable. Where research is not replicable, the paper should be recommended for rejection.
Repeatable Methods
These give enough detail so that other researchers are able to carry out the same research. For example, equipment used or sampling methods should all be described in detail so that others could follow the same steps. Where methods are not detailed enough, it's usual to ask for the methods section to be revised.
Robust Research
This has enough data points to make sure the data are reliable. If there are insufficient data, it might be appropriate to recommend revision. You should also consider whether there is any in-built bias not nullified by the control experiments.
Best Practice
During these checks you should keep in mind best practice:
- Standard guidelines were followed (e.g. the CONSORT Statement for reporting randomized trials)
- The health and safety of all participants in the study was not compromised
- Ethical standards were maintained
If the research fails to reach relevant best practice standards, it's usual to recommend rejection. What's more, you don't then need to read any further.
3. Results and Discussion
This section should tell a coherent story - What happened? What was discovered or confirmed?
Certain patterns of good reporting need to be followed by the author:
- They should start by describing in simple terms what the data show
- They should make reference to statistical analyses, such as significance or goodness of fit
- Once described, they should evaluate the trends observed and explain the significance of the results to wider understanding. This can only be done by referencing published research
- The outcome should be a critical analysis of the data collected
Discussion should always, at some point, gather all the information together into a single whole. Authors should describe and discuss the overall story formed. If there are gaps or inconsistencies in the story, they should address these and suggest ways future research might confirm the findings or take the research forward.
4. Conclusions
This section is usually no more than a few paragraphs and may be presented as part of the results and discussion, or in a separate section. The conclusions should reflect upon the aims - whether they were achieved or not - and, just like the aims, should not be surprising. If the conclusions are not evidence-based, it's appropriate to ask for them to be re-written.
5. Information Gathered: Images, Graphs and Data Tables
If you find yourself looking at a piece of information from which you cannot discern a story, then you should ask for improvements in presentation. This could be an issue with titles, labels, statistical notation or image quality.
Where information is clear, you should check that:
- The results seem plausible, in case there is an error in data gathering
- The trends you can see support the paper's discussion and conclusions
- There are sufficient data. For example, in studies carried out over time are there sufficient data points to support the trends described by the author?
You should also check whether images have been edited or manipulated to emphasize the story they tell. This may be appropriate but only if authors report on how the image has been edited (e.g. by highlighting certain parts of an image). Where you feel that an image has been edited or manipulated without explanation, you should highlight this in a confidential comment to the editor in your report.
6. List of References
You will need to check referencing for accuracy, adequacy and balance.
Where a cited article is central to the author's argument, you should check the accuracy and format of the reference - and bear in mind different subject areas may use citations differently. Otherwise, it's the editor’s role to exhaustively check the reference section for accuracy and format.
You should consider if the referencing is adequate:
- Are important parts of the argument poorly supported?
- Are there published studies that show similar or dissimilar trends that should be discussed?
- If a manuscript only uses half the citations typical in its field, this may be an indicator that referencing should be improved - but don't be guided solely by quantity
- References should be relevant, recent and readily retrievable
Check for a well-balanced list of references that is:
- Helpful to the reader
- Fair to competing authors
- Not over-reliant on self-citation
- Gives due recognition to the initial discoveries and related work that led to the work under assessment
You should be able to evaluate whether the article meets the criteria for balanced referencing without looking up every reference.
7. Plagiarism
By now you will have a deep understanding of the paper's content - and you may have some concerns about plagiarism.
Identified Concern
If you find - or already knew of - a very similar paper, this may be because the author overlooked it in their own literature search. Or it may be because it is very recent or published in a journal slightly outside their usual field.
You may feel you can advise the author how to emphasize the novel aspects of their own study, so as to better differentiate it from similar research. If so, you may ask the author to discuss their aims and results, or modify their conclusions, in light of the similar article. Of course, the research similarities may be so great that they render the work unoriginal and you have no choice but to recommend rejection.
"It's very helpful when a reviewer can point out recent similar publications on the same topic by other groups, or that the authors have already published some data elsewhere ." (Editor feedback)
Suspected Concern
If you suspect plagiarism, including self-plagiarism, but cannot recall or locate exactly what is being plagiarized, notify the editor of your suspicion and ask for guidance.
Most editors have access to software that can check for plagiarism.
Editors are not out to police every paper, but when plagiarism is discovered during peer review it can be properly addressed ahead of publication. If plagiarism is discovered only after publication, the consequences are worse for both authors and readers, because a retraction may be necessary.
For detailed guidelines see COPE's Ethical guidelines for reviewers and Wiley's Best Practice Guidelines on Publishing Ethics .
8. Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
After the detailed read-through, you will be in a position to advise whether the title, abstract and key words are optimized for search purposes. In order to be effective, good SEO terms will reflect the aims of the research.
A clear title and abstract will improve the paper's search engine rankings and will influence whether the user finds and then decides to navigate to the main article. The title should contain the relevant SEO terms early on. This has a major effect on the impact of a paper, since it helps it appear in search results. A poor abstract can then lose the reader's interest and undo the benefit of an effective title - whilst the paper's abstract may appear in search results, the potential reader may go no further.
So ask yourself, while the abstract may have seemed adequate during earlier checks, does it:
- Do justice to the manuscript in this context?
- Highlight important findings sufficiently?
- Present the most interesting data?
Editors say, " Does the Abstract highlight the important findings of the study ?"
If there is a formal report format, remember to follow it. This will often comprise a range of questions followed by comment sections. Try to answer all the questions. They are there because the editor felt that they are important. If you're following an informal report format you could structure your report in three sections: summary, major issues, minor issues.
- Give positive feedback first. Authors are more likely to read your review if you do so. But don't overdo it if you will be recommending rejection
- Briefly summarize what the paper is about and what the findings are
- Try to put the findings of the paper into the context of the existing literature and current knowledge
- Indicate the significance of the work and if it is novel or mainly confirmatory
- Indicate the work's strengths, its quality and completeness
- State any major flaws or weaknesses and note any special considerations. For example, if previously held theories are being overlooked
Major Issues
- Are there any major flaws? State what they are and what the severity of their impact is on the paper
- Has similar work already been published without the authors acknowledging this?
- Are the authors presenting findings that challenge current thinking? Is the evidence they present strong enough to prove their case? Have they cited all the relevant work that would contradict their thinking and addressed it appropriately?
- If major revisions are required, try to indicate clearly what they are
- Are there any major presentational problems? Are figures & tables, language and manuscript structure all clear enough for you to accurately assess the work?
- Are there any ethical issues? If you are unsure it may be better to disclose these in the confidential comments section
Minor Issues
- Are there places where meaning is ambiguous? How can this be corrected?
- Are the correct references cited? If not, which should be cited instead/also? Are citations excessive, limited, or biased?
- Are there any factual, numerical or unit errors? If so, what are they?
- Are all tables and figures appropriate, sufficient, and correctly labelled? If not, say which are not
Your review should ultimately help the author improve their article. So be polite, honest and clear. You should also try to be objective and constructive, not subjective and destructive.
You should also:
- Write clearly and so you can be understood by people whose first language is not English
- Avoid complex or unusual words, especially ones that would even confuse native speakers
- Number your points and refer to page and line numbers in the manuscript when making specific comments
- If you have been asked to only comment on specific parts or aspects of the manuscript, you should indicate clearly which these are
- Treat the author's work the way you would like your own to be treated
Most journals give reviewers the option to provide some confidential comments to editors. Often this is where editors will want reviewers to state their recommendation - see the next section - but otherwise this area is best reserved for communicating malpractice such as suspected plagiarism, fraud, unattributed work, unethical procedures, duplicate publication, bias or other conflicts of interest.
However, this doesn't give reviewers permission to 'backstab' the author. Authors can't see this feedback and are unable to give their side of the story unless the editor asks them to. So in the spirit of fairness, write comments to editors as though authors might read them too.
Reviewers should check the preferences of individual journals as to where they want review decisions to be stated. In particular, bear in mind that some journals will not want the recommendation included in any comments to authors, as this can cause editors difficulty later - see Section 11 for more advice about working with editors.
You will normally be asked to indicate your recommendation (e.g. accept, reject, revise and resubmit, etc.) from a fixed-choice list and then to enter your comments into a separate text box.
Recommending Acceptance
If you're recommending acceptance, give details outlining why, and if there are any areas that could be improved. Don't just give a short, cursory remark such as 'great, accept'. See Improving the Manuscript
Recommending Revision
Where improvements are needed, a recommendation for major or minor revision is typical. You may also choose to state whether you opt in or out of the post-revision review too. If recommending revision, state specific changes you feel need to be made. The author can then reply to each point in turn.
Some journals offer the option to recommend rejection with the possibility of resubmission – this is most relevant where substantial, major revision is necessary.
What can reviewers do to help? " Be clear in their comments to the author (or editor) which points are absolutely critical if the paper is given an opportunity for revisio n." (Jonathon Halbesleben, Editor of Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology)
Recommending Rejection
If recommending rejection or major revision, state this clearly in your review (and see the next section, 'When recommending rejection').
Where manuscripts have serious flaws you should not spend any time polishing the review you've drafted or give detailed advice on presentation.
Editors say, " If a reviewer suggests a rejection, but her/his comments are not detailed or helpful, it does not help the editor in making a decision ."
In your recommendations for the author, you should:
- Give constructive feedback describing ways that they could improve the research
- Keep the focus on the research and not the author. This is an extremely important part of your job as a reviewer
- Avoid making critical confidential comments to the editor while being polite and encouraging to the author - the latter may not understand why their manuscript has been rejected. Also, they won't get feedback on how to improve their research and it could trigger an appeal
Remember to give constructive criticism even if recommending rejection. This helps developing researchers improve their work and explains to the editor why you felt the manuscript should not be published.
" When the comments seem really positive, but the recommendation is rejection…it puts the editor in a tough position of having to reject a paper when the comments make it sound like a great paper ." (Jonathon Halbesleben, Editor of Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology)
Visit our Wiley Author Learning and Training Channel for expert advice on peer review.
Watch the video, Ethical considerations of Peer Review

- Studying at university
- Being organised
- Free study planner
- Searching for information
- Reading and evaluating information
- Referencing
- Laboratory reports and lab books
- Dissertations, projects and theses
- Reflective writing
Book reviews
- Notes and other writing tasks
- Strategies for writing
- Developing as a writer
- Assessment and feedback
People who can help
You might be asked to write a book review as a way to help you read actively and form an opinion on the author's views and the context in which the book was written. Book reviews are common ways for academics to evaluate each others' contributions to the field of research, especially in the arts and social sciences where publishing in books is more usual than publishing in journals.
A good review is more than just a summary of the contents. It should include your view on what the purpose of the book is and who it is intended for, and it should address the context (time and place) in which the book has been written, an evaluation of the author's arguments for strengths and weaknesses, and your identification of any bias in their perspective on the topic. Your lecturer will probably give you some guidance on what they expect, and it is likely to involve you asking yourself some or all of the following questions:
- Who is the author? What is their disciplinary background? What have they published before? Is this building on their previous research or entering a new field?
- When was the book written? How might that affect the perspective taken? Is there, for example, a political, social or economic context that would impact on the writing?
- What is the book about? What is the main topic area and scope? How does it fit with other books that have been published in this area?
- What is the main argument in the book? Is it well argued? Are the author's assumptions valid? Is there any obvious bias in the source of evidence they use?
- Is the writing style appropriate? Is the book well structured and does it flow comfortably?
- What is your view on the book's strengths and weaknesses? Do you think it's a valuable contribution to the literature in the discipline?
All of this should be supported by reference to particular passages or chapters that provide evidence to support your views.

Further reading
Reading and interpreting sources and data.
- Finding resources
Practical advice on managing writing
- Managing reading and writing a literature review
- Writing critically
more from Academic Support study resources
Talk to someone in your school or a specialist support service
Studying Effectively
Kings Meadow Campus Lenton Lane Nottingham, NG7 2NR
telephone: +44 (0) 115 951 5151 fax: +44 (0) 115 951 3666 Contact us
Legal information
- Terms and conditions
- Posting rules
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
- Charity gateway
- Cookie policy
Connect with the University of Nottingham through social media and our blogs .
Home → Academic Writing → How to Start a Literature Review (Like a Pro)
How to Start a Literature Review (Like a Pro)
Jordan Kruszynski
- June 26, 2023

Ah, how to start a literature review – those words will be all too familiar to battle-hardened researchers, but to the rest of us, they may be a bit of a mystery.
Are you a student trying to get ahead of the game with your first literature review? Or are you a professional looking to learn more about literature reviews? If so, then this post is for you.
In this article, we’ll discuss how to start a literature review, the types of sources used in literature reviews, and the benefits of writing them. We’ll also outline the steps for preparing and writing your own literature review.
Read on and let the magic begin!
Literature Reviews – The Researcher’s Friend
A literature review is an essential part of any research project. It is a compilation of all the literature and research related to a particular topic. It is used to provide context and background for a research project. Literature reviews are important for two primary reasons. First, they provide a comprehensive and objective review of the existing literature on a topic. Second, they provide support for any conclusions or hypotheses that may be drawn from the research.
Literature reviews are used in many different fields, including business, education, and the sciences. They are used to provide an overview of a topic and to support the conclusions and hypotheses of a research project.
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a critical appraisal of existing research on a particular topic . It is a systematic and comprehensive review of all the published work in a particular field. The purpose of a literature review is to provide an overview of the existing research on a topic, to identify gaps in the literature, and to propose new directions for future research.
The literature review is an important part of the research process and should be conducted thoroughly and objectively. It should include a critical analysis of the existing literature, an evaluation of the research methods used, and an assessment of the quality of the evidence.
Types of Literature Review
There are several different types of literature reviews. They include narrative reviews, systematic reviews, meta-analyses, and scoping reviews.
- Narrative reviews are the most common type of literature review. They provide an overview of the existing literature on a topic. Narrative reviews typically include an introduction, a review of the literature, and a conclusion.
- Systematic reviews are more rigorous and comprehensive than narrative reviews. They involve rigorous and systematic searches of the literature and include a critical appraisal of the evidence. Systematic reviews are typically used in clinical research.
- Meta-analyses are reviews that combine the results of multiple studies to evaluate the overall effect of a particular treatment or intervention. Meta-analyses are more rigorous and comprehensive than narrative reviews and systematic reviews.
- Scoping reviews are used to identify the range of research on a particular topic. They are typically used to identify gaps in the literature and to propose new directions for future research.
Sourcing Pieces for Your Review
When conducting a literature review, it is important to use a variety of sources. These sources include journal articles, books, conference proceedings, dissertations, and other academic sources. It is also important to use a variety of search strategies to identify the most relevant and up-to-date sources.
Research papers will probably form the bulk of your literature review, and this is where Audemic can help – simply load any papers you want to use into the app, and you can organise them intuitively to make sourcing a breeze.
It is important to note that not all sources are created equal. Some sources may be more reliable than others. When evaluating sources for your literature review, it is important to consider their credibility, relevance, accuracy, and objectivity.
Benefits of Literature Reviews
Literature reviews are an essential part of any research project. They provide an overview of the existing literature on a topic and can be used to identify gaps in the literature, as well as propose new directions for future research. They also provide support for any conclusions or hypotheses that may be drawn from the research.
Literature reviews can also help researchers save time and money. By conducting a thorough and comprehensive review of the existing literature, researchers can avoid redundant research and save time and money.
How to Start a Literature Review
Now that you understand the purpose and benefits of a literature review, it’s time to learn how to start one. The first step in starting a literature review is to identify a topic. Once you have identified a topic, you can start searching for sources.
When searching for sources, it is important to use a variety of search strategies, such as keyword searches, author searches, and database searches. It is also important to use a variety of sources, such as journal articles, books, conference proceedings, and dissertations.
Preparing for Your Literature Review
Once you have identified and located the sources for your literature review, it is time to start preparing. Before you begin writing, it is important to read and analyse each source. This will help you identify the key points of each source and understand how it contributes to the literature on your topic.
It is also important to organise your sources. This can be done by creating a spreadsheet or using a reference management software, such as Mendeley or Zotero. This will help you keep track of your sources and make it easier to cite them in your literature review.
Did somebody say Zotero? Audemic features Zotero integration, so you can not only organise your sources, but also listen to them when you need a change of pace. Nice, eh?
Searching for Sources for Your Review
Now that you have identified a topic and prepared your sources, it’s time to start searching for additional sources. When searching for sources, it is important to use a variety of search strategies. These search strategies include keyword searches, author searches, database searches, and library catalogue searches.
It is also important to use a variety of sources. These sources include journal articles, books, conference proceedings, dissertations, and other academic sources. It is also important to consider the credibility, relevance, accuracy, and objectivity of each source.
Writing and Structuring Your Literature Review
Once you have identified and located the sources for your literature review, it is time to start writing. When writing your literature review, it is important to keep the structure and organisation in mind. Your literature review should include an introduction, a review of the literature, and a conclusion.
- When writing your introduction , it is important to provide context for your topic. This should include an explanation of the purpose of the literature review and a description of the research question.
- The review of the literature should provide an overview of the existing literature on the topic. It should include a summary of each source and an analysis of the evidence. It should also include an evaluation of the research methods used and an assessment of the quality of the evidence.
- Finally, the conclusion should summarise the key points of the literature review and provide recommendations for future research.
Final Thoughts
A literature review is an essential part of any research project, so it pays to master this critical academic skill. And with the guidance in this post, you should be well on your way to knowing how to start a literature review for yourself. By putting it into practice, you can unlock your writing potential and produce a thorough, engaging and comprehensive literature review.
So what are you waiting for? Search for those sources and get started! And why not use Audemic to speed up the review process and boost it into the cosmos!
Keep striving, researchers! ✨
Table of Contents
Related articles.

How to Publish a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
You’re in academia. You’re going steady. Your research is going well and you begin to wonder: ‘How exactly do I get a

Behind the Scenes: What Does a Research Assistant Do?
Have you ever wondered what goes on behind the scenes in a research lab? Does it involve acting out the whims of

How to Write a Research Paper Introduction: Hook, Line, and Sinker
Want to know how to write a research paper introduction that dazzles? Struggling to hook your reader in with your opening sentences?

Blog Podcast
Privacy policy Terms of service
Subscribe to our newsletter!
Discover more from Audemic: Access any academic research via audio
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

Academic Report
Report generator.

As a way of evaluating a student’s logical capacity, comprehension level and writing skill , some professors require their students to write a document presenting their ideas, thoughts, analyses, etc. about a certain topic. Other than writing an essay , the students can also use a report in order effectively present their objective deductions and findings.

A formal report is another way of presenting facts and analysis you have gathered from your readings about a certain topic. In requires thorough research, readings, rationalizing, analyzing and making a point. It goes beyond that of an essay, it is more than just arguing a position and drawing conclusions, although a report can also do that, it must comprehensively present pertinent facts and information in order for the reader to see the subject in new light.
As you may know, report writing is a very useful skill not only academically but also in your future career. Not only does it hones your writing skills it also improves your analytical and critical thinking skills since it urges you to come up with objective findings based on facts. Therefore, it will surely help you be good at whatever job you wish to pursue in the future; no employer says no to a critically and analytically adept individual. You may also see marketing report examples.
Academic Research Report Template

- Google Docs
- Apple Pages
Size: 31 KB
Academic Report Format Guide Example

Size: 168 KB
Difference Between an Essay and Report
An essay and a report are both effective ways of presenting information and data. However, some professors may prefer one over the other. In order to know the difference between the two, a list of their differences are presented below:
- Essay are rarely used outside the academic realm.
- It focuses on analyzing or evaluating theory, past research by other people, and ideas.
- Rarely presents the findings of a newly conducted research.
- It only has four significant parts or elements.
- The flow of writing is continuous and does not have dividing sections.
- It usually does not include table, charts, and/or diagrams.
- It should not be used as the method in arriving at conclusions.
- Is usually not reflective about the process of researching and writing the essay itself.
- It does not include recommendations.
- It is argumentative and mostly based on ideas.
- Only offers conclusions on a question or on presented issues or problems.
You may also see business report examples.
- Originated from the professional world but is still used academically.
- Often presents data and findings that the researcher himself has gathered.
- Uses data gathering methods such as surveys, experiment or case study, or by applying theory.
- Commonly has at least 12 parts or sections and 14 parts or sections at most.
- Topics are divided into different sections or headings or sub-headings.
- It usually contains tables, graphs, charts and diagrams.
- Includes the method/s the researcher used.
- It includes recommendations on what actions to make.
- It is an informative and fact-based document.
- Follows specific style for each section.
- It is written with a specific purpose and reader in mind.
You may also like examples of short report .
Management Decisions and Control Academic Report Example

Size: 170 KB
Digital Storytelling Academic Report Example

Size: 309 KB
Flood Mitigation and Water Storage Engineering Academic Report Example

Size: 201 KB
Contents of an Academic Report
An effective academic report must have the contents and sections necessary to nit-pick and through explain a subject. Listed below are the contents of an academic report:
- Author Declaration
- Abstract or Executive Summary
- Acknowledgements
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Method or Methodology or Research Design
- Results or Findings
- Discussion of Results or Analysis or Interpretation
- Conclusions
- Recommendations
- References or Bibliography
How to Write an Academic Report
1. title page.
This means what it literally means. The title of the general report should be indicated on this page of the academic report. In some cases, the title page also includes your name as the author and student number, the name of the course and the course code. For example:
Communication Skills Relevant in International Business
John Smith (012345) Business 300
2. Author Declaration
In some universities or colleges, you will need to fill out a form from the department or faculty conforming that the report is in fact your own output. This form is attached to any assigned report or essay for your course.
3. Abstract or Executive Summary
An abstract is a short opening for your entire report. It is a basically a summary of the report as a whole and therefore should only be around 150 words in length. In order to effectively write it, a good techniques is writing it after all the sections, headings and sub-headings have been presented. Here’s a tip: write one or two sentences representing each section of the report in order to have a complete and comprehensive abstract.
4. Acknowledgements
Although acknowledgements are normally necessary in major reports, it can also be included in an academic report. This acknowledges the people who have supported you in your research and has contributed in the completion of the report. However, do not go overboard. This should only be short and direct to the point. You may also like consulting report examples.
6. Table of Contents
This is where the reader goes to look for specific sections or topics found in your report. This contains the actual titles of each section, heading and sub-headings along with their actual page numbers. A good way or organizing your table of contents is to list the contents in according to hierarchy numbers, from first to last. After the list of the contents comes a separate list for the tables, charts, diagrams, etc that is found in your report. You may also check out management report examples.
7. Introduction
The introduction must present the purpose or objective of the report and explain why the report is necessary or how it’s useful. It must immediately let the reader know that the report is useful in the field it is focused on and that it has a positive impact and recommendations on the subject at hand. In addition, you can define key terms you have repeatedly used in the report so that the reader has a clear idea on what you mean when you use the term. You might be interested in recruitment report examples.
Author’s Note : The following sections (8-11) are primarily used in major reports such as research, an experiment, survey or observation. If your report is based on reading, you can replace these sections with topic heading of your own choosing.
8. Literature Review
In this section, describe and report the previous and current thinking and research on the topic. You include a summary on what other have written about the topic you are reporting. This section will mostly consist of in-text citations from the books, articles, reports, etc. you have read about the topic. You may also see report examples in excel .
Simply, it is a review of all the literature you have read in order to form your own thinking about the topic. These literature are your basis for conducting your own report. The literature review should follow the format, MLA or APA format, you professor has required in citing your references.
9. Method or Methodology or Research Design
This section is all about the method or way you have gathered or collected your data. You present and tell your reader/s how were you able the data you have in your report. For example, you can describe the step-by-step process you did when you conducted an experiment or write a detailed description of a situation you have observed. In addition, in this section it is normal that you also have to explain why you collected the data through that method. An normally, the justification should also be quite detailed. You can include some in-text references to research methods references to help explain and justify your choice of method(s). You may also like monthly report examples & samples.
10. Results or Findings
Simply present the results or findings of your report in this section. There is no need for discussions, analysis and explanations of the results. Oftentimes, this section includes a table to comprehensively present the findings. Aside from that, this is also where you state whether you accept or reject the hypothesis or hypotheses you have made in you report. You may also check out sample activity reports .
11. Discussion of Results or Analysis or Interpretation
This is where you present what you think about the results you have formulated in your report. You can also include comment abut your results in this section. Here are other things the discussion section can include:
- Describing and suggesting reasons for any patterns in the results, possibly including anomalies (results that don’t ‘fit in with’ the rest).
- Explaining what you found (perhaps with reference to theory). You may also see performance report examples.
- Commenting on how much your findings agree or disagree with the literature.
- Considering the accuracy and reliability of your results (and how the methods you used might have affected that accuracy).
- Considering the implications of your results – what they might mean for your practice, for example. • Discussing what further research in this area might be useful in future. You may also like investigation report samples and examples.
12. Conclusions
In the conclusions, you should summarize the key findings of your report. Remember that all the information that you include in the conclusions should have been presented before and are new information. The conclusions should effectively summarize and present all the major points you have made so far in you report.
13. Recommendations
Recommendations are not necessarily needed in all academic reports, however, work-related and case studies should always present recommendations. These suggestions are for future actions in order to solve or improve issues or problems presented in the report. You may also check out free report examples & samples.
14. References or Bibliography
There should be a list on all the references you have used to cite and to back your claims. It should only contain all the literature you have cited in your report. Depending on the requirement, you can follow either an MLA or APA format for citation.
15. Appendices
Appendices contains all the supplementary information is ‘stored’. This could be table of data, copies of observation forms or notes, extracts from large documents, a transcript of a recording, etc. You might be interested in technical report examples & samples.
School Program Report Example

Size: 183 KB
New School Report Example
We hope you found our article on creating an academic report to be useful for your academic studies. We also included some examples which you can use as a reference/guide.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate a report on the impact of technology in the classroom on student learning outcomes
Prepare a report analyzing the trends in student participation in sports and arts programs over the last five years at your school.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an Academic Book Review
- 4-minute read
- 22nd January 2019
For researchers and postgraduates , writing a book review is a relatively easy way to get published. It’s also a good way to refine your academic writing skills and learn about the publishing process. But how do you write a good academic book review? We have a few tips to share.
1. Finding a Book to Review
Before you can write an academic book review, you need to find a suitable book . There are two main ways to do this:
- Look to see which books journal publishers are seeking reviews for.
- Find a book that interests you and pitch it to publishers.
The first approach works by finding a journal in your field that is soliciting reviews. This information may be available on their website (e.g. on a page titled ‘Books for Review’). However, you can also email the editor to ask if there are book review opportunities available.
Alternatively, you can find a book you want to review and pitch it to journal editors. If you want to take this approach, pick a book that:
- Is about a topic or subject area that you know well.
- Has been published recently, or at least in the last 2–3 years.
- Was published by a reputable publisher (e.g. a university printing press).
You can then pitch your review to a journal that covers the same subject as the book. Some publishers will even give reviewers access to new books. Springer, for example, has a scheme where reviewers can access books online and receive a print copy once a review is published.
2. Follow the Style Guide
Once you know the journal you’re hoping to write for, look for the publisher’s style guide. This might be called the ‘Author Instructions’ or ‘Review Guidelines’, but it should be available somewhere on the publisher’s website; if it is not obviously available, consider checking with the editor.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
And when you have found the style guide, follow its instructions carefully. It should provide information on everything from writing style and the word count to submitting your review.
3. Don’t Make It About You!
You’d be surprised how often academics begin a review by summarising the book in question, only to then abandon it in favour of explaining their own ideas about the subject matter. As such, one important tip when reviewing an academic book is to actually review the book .
This isn’t to say that you can’t offer your own thoughts on the subject matter, especially if they are relevant to what the author is arguing in the book. But remember that people read reviews to find out about the book being reviewed, so this should always be your focus.
4. Questions for an Academic Book Review
Finally, while the content of a review will depend on the book, there are a few questions every good book review should answer. These include:
- What is the book about? Does it cover the topic adequately? What does the author argue? Ideally, you will summarise the argument early on.
- Who is the author/editor? What is their field of expertise? How does this book relate to their past work? You might also want to mention relevant biographical details, if there are any.
- How does the author support their argument? Do they provide convincing evidence? Do they engage with counterarguments? Try to find at least one strength (i.e. something the book does well) and one weakness (i.e. something that could be stronger) to write about.
- As a whole, has the book helped you understand the subject? Who would you recommend it to? This will be the concluding section.
If you can cover these points, you should end up with a strong book review. All you need then is to have it proofread by the professionals .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Get help from a language expert. Try our proofreading services for free.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Entire Site
- Research & Funding
- Health Information
- About NIDDK
- Diabetes Overview
- Insulin, Medicines, & Other Diabetes Treatments
- Español
Insulin, Medicines, & Other Diabetes Treatments
On this page:
What medicines might I take for diabetes?
What type of diabetes do i have, what are the different types of insulin, what are the different ways to take insulin, what oral medicines treat type 2 diabetes, what other injectable medicines treat diabetes, what should i know about side effects of diabetes medicines.
- What questions should I ask about my diabetes medicines?
Do I have other treatment options for my diabetes?
Clinical trials for insulin, medicines, & other diabetes treatments.
Taking insulin or other diabetes medicines is often part of treating diabetes. In addition to making healthy food and beverage choices, getting physical activity, getting enough sleep, and managing stress, medicines can help you manage the disease. Some other treatment options are also available.
The medicine you take depends on the type of diabetes you have and how well the medicine controls your blood glucose levels, also called blood sugar levels. Other factors, such as any other health conditions you may have, medication costs, your insurance coverage and copays, access to care, and your lifestyle, may affect what diabetes medicine you take.
Type 1 diabetes
If you have type 1 diabetes , you must take insulin because your pancreas does not make it. You will need to take insulin several times during the day, including when you eat and drink, to control your blood glucose level.
There are different ways to take insulin . You can use a needle and syringe , an insulin pen , or an insulin pump . An artificial pancreas —also called an automated insulin delivery system—may be another option for some people.
Type 2 diabetes
Some people with type 2 diabetes can control their blood glucose level by making lifestyle changes. These lifestyle changes include consuming healthy meals and beverages, limiting calories if they have overweight or obesity , and getting physical activity.
Many people with type 2 diabetes need to take diabetes medicines as well. These medicines may include diabetes pills or medicines you inject, such as insulin. Over time, you may need more than one diabetes medicine to control your blood glucose level. Even if you do not take insulin, you may need it at special times, such as if you are pregnant or if you are in the hospital for treatment.
Gestational diabetes
If you have gestational diabetes , you can manage your blood glucose level by following a healthy eating plan and doing a moderate-intensity physical activity, such as brisk walking for 150 minutes, each week. If consuming healthy food and beverages and getting regular physical activity aren’t enough to keep your blood glucose level in your target range, a doctor will work with you and may recommend you take insulin. Insulin is safe to take while you are pregnant.
No matter what type of diabetes you have, taking diabetes medicines every day can feel like a burden sometimes. New medications and improved delivery systems can help make it easier to manage your blood glucose levels. Talk with your doctor to find out which medications and delivery systems will work best for you and fit into your lifestyle.
Several types of insulin are available. Each type starts to work at a different speed, known as “onset,” and its effects last a different length of time, known as “duration.” Most types of insulin reach a peak, which is when they have the strongest effect. After the peak, the effects of the insulin wear off over the next few hours or so. Table 1 lists the different types of insulin, how fast they start to work, when they peak, and how long they last.
Table 1. Types of insulin and how they work 1,2
Another type of insulin, called premixed insulin, is a combination of insulins listed in Table 1. Premixed insulin starts to work in 15 to 60 minutes and can last from 10 to 16 hours. The peak time varies depending on which insulins are mixed.
Your doctor will work with you to review your medication options. Talk with your doctor about your activity level, what you eat and drink, how well you manage your blood glucose levels, your age and lifestyle, and how long your body takes to absorb insulin.
Follow your doctor’s advice on when and how to take your insulin. If you're worried about the cost, talk with your doctor. Some types of insulin cost more than others. You can also find resources to get financial help for diabetes care .
The way you take insulin may depend on your lifestyle, insurance plan, and preferences. Talk with your doctor about the options and which one is best for you. Most people with diabetes take insulin using a needle and syringe, insulin pen, or insulin pump. Inhalers and insulin jet injectors are less common ways to take insulin. Artificial pancreas systems are now approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Talk with your doctor to see if an artificial pancreas is an option for you.
Needle and syringe
You can give yourself insulin shots using a needle and syringe . You draw up your dose of insulin from the vial—or bottle—through the needle into the syringe. Insulin works fastest when you inject it in your belly, but your doctor may recommend alternating the spot where you inject it. Injecting insulin in the same spot repeatedly could cause the tissue to harden, making it harder to take shots in that area over time. Other spots you can inject insulin include your thigh, buttocks, or upper arm, but it may take longer for the insulin to work from those areas. Some people with diabetes who take insulin need 2 to 4 shots a day to reach their blood glucose targets. Others can take a single shot. Injection aids can help you give yourself the shots.

An insulin pen looks like a writing pen but has a needle for its point. Some insulin pens come filled with insulin and are disposable. Others have room for an insulin cartridge that you insert and replace after use. Many people find insulin pens easier to use, but they cost more than needles and syringes. You may want to consider using an insulin pen if you find it hard to fill the syringe while holding the vial or cannot read the markings on the syringe. Different pen types have features that can help with your injections. Some reusable pens have a memory function, which can recall dose amounts and timing. Other types of “connected” insulin pens can be programmed to calculate insulin doses and provide downloadable data reports, which can help you and your doctor adjust your insulin doses.

An insulin pump is a small machine that gives you steady doses of insulin throughout the day. You wear one type of pump outside your body on a belt or in a pocket or pouch. The insulin pump connects to a small plastic tube and a very small needle. You insert the plastic tube with a needle under your skin, then take out the needle. The plastic tube will stay inserted for several days while attached to the insulin pump. The machine pumps insulin through the tube into your body 24 hours a day and can be programmed to give you more or less insulin based on your needs. You can also give yourself doses of insulin through the pump at mealtimes.
Another type of pump has no tubes. This pump attaches directly to your skin with a self-adhesive pad and is controlled by a hand-held device. The plastic tube and pump device are changed every several days.

Another way to take insulin is by breathing powdered insulin into your mouth from an inhaler device. The insulin goes into your lungs and moves quickly into your blood. You may want to use an insulin inhaler to avoid using needles. Inhaled insulin is only for adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Taking insulin with an inhaler is less common than using a needle and syringe.
Jet injector
A jet injector is a device that sends a fine spray of insulin into the skin at high pressure instead of using a needle to deliver the insulin. It is used less commonly than a needle and syringe or a pen.
Artificial pancreas
An artificial pancreas is a system of three devices that work together to mimic how a healthy pancreas controls blood glucose in the body. A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) tracks blood glucose levels every few minutes using a small sensor inserted under the skin that is held in place with an adhesive pad. The CGM wirelessly sends the information to a program on a smartphone or an insulin infusion pump. The program calculates how much insulin you need. The insulin infusion pump will adjust how much insulin is given from minute to minute to help keep your blood glucose level in your target range. An artificial pancreas is mainly used to help people with type 1 diabetes.
You may need to take medicines to manage your type 2 diabetes, in addition to consuming healthy foods and beverages and being physically active. You can take many diabetes medicines by mouth. These medicines are called oral medicines.
Most people with type 2 diabetes start with metformin pills. Metformin also comes as a liquid. Metformin helps your liver make less glucose and helps your body use insulin better. This drug may help you lose a small amount of weight.
Other oral medicines act in different ways to lower blood glucose levels. Combining two or three kinds of diabetes medicines can lower blood glucose levels better than taking just one medicine.
Read about different kinds of diabetes medicines (PDF, 2.8 MB) from the FDA.
If you have type 1 diabetes, your doctor may recommend you take other medicines, in addition to insulin, to help control your blood glucose. Some of these medicines work to slow how fast food and beverages move through your stomach . These medicines also slow down how quickly and how high your blood glucose levels rise after eating. Other medicines work to block certain hormones in your digestive system that raise blood glucose levels after meals or help the kidneys to remove more glucose from your blood.
Besides insulin, other types of injected medicines (PDF, 2.8 MB) are available that will keep your blood glucose level from rising too high after you eat or drink. These medicines, known as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists, 3 may make you feel less hungry and help you lose some weight. GLP-1 medicines are not substitutes for insulin.
Side effects are problems that result from taking a medicine. Some diabetes medicines can cause hypoglycemia , also called low blood glucose, if you don’t balance your medicines with food and activity.
Ask your doctor whether your diabetes medicine can cause hypoglycemia or other side effects, such as upset stomach and weight gain. Aim to take your diabetes medicines as your doctor instructs you, to help prevent side effects and diabetes problems.
If medicines and lifestyle changes are not enough to manage your diabetes, there are other treatments that might help you. These treatments include weight-loss (bariatric) surgery for certain people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, or pancreatic islet transplantation for some people with type 1 diabetes.
Weight-loss surgery
Weight-loss surgery are operations that help you lose weight by making changes to your digestive system. Weight-loss surgery is also called bariatric or metabolic surgery.
This type of surgery may help some people who have obesity and type 2 diabetes lose a large amount of weight and bring their blood glucose levels back to a healthy range. How long the improved response lasts can vary by patient, type of weight-loss surgery, and the amount of weight the person lost. Other factors include how long a person had diabetes and whether the person used insulin. Some people with type 2 diabetes may no longer need to use diabetes medicines after weight-loss surgery . 4
Researchers are studying whether weight-loss surgery can help control blood glucose levels in people with type 1 diabetes who have obesity. 5
Pancreatic islet transplantation
Pancreatic islet transplantation is an experimental treatment for people with type 1 diabetes who have trouble controlling their blood glucose levels. Pancreatic islets are clusters of cells in the pancreas that make the hormone insulin. In type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system attacks these cells. A pancreatic islet transplantation replaces destroyed islets with new islets from organ donors. The new islets make and release insulin. Because researchers are still studying pancreatic islet transplantation , the procedure is only available to people enrolled in research studies.
The NIDDK conducts and supports clinical trials in many diseases and conditions, including diabetes. The trials look to find new ways to prevent, detect, or treat disease and improve quality of life.
What are clinical trials for insulin, medicines, and other diabetes treatments?
Clinical trials—and other types of clinical studies —are part of medical research and involve people like you. When you volunteer to take part in a clinical study, you help health care professionals and researchers learn more about disease and improve health care for people in the future.
Find out if clinical trials are right for you .
Researchers are studying many aspects of diabetes medicines, including
- new types of insulin
- the most effective times to take diabetes medicines
- new types of monitoring devices and delivery systems
Watch a video of NIDDK Director Dr. Griffin P. Rodgers explaining the importance of participating in clinical trials.
What clinical trials for insulin, medicines, and other diabetes treatments are looking for participants?
You can view a filtered list of clinical studies on insulin, medicines, and other diabetes treatments covered in this health topic that are federally funded, open, and recruiting at www.ClinicalTrials.gov . You can expand or narrow the list to include clinical studies from industry, universities, and individuals; however, the National Institutes of Health does not review these studies and cannot ensure they are safe. Always talk with your health care provider before you participate in a clinical study.
This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), part of the National Institutes of Health. NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
The NIDDK would like to thank Stuart A. Weinzimer, M.D., Yale University School of Medicine

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Read each section of a text carefully and write down two things: 1) the main point or idea, and 2) its function in the text. In other words, write down what each section says and what it does. This will help you to see how the author develops their argument and uses evidence for support.
Step 5 - Write your literature review. Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction, a main body, and a conclusion. What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review. Introduction. The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
An academic book review provides the main ideas, and since published book reviews typically have a limited word count, the summary should remain brief. Analysis and Significance. Compare the book and its argument with the other literature on the topic. Discuss its contribution to past and current research and literature.
Whatever stage you are at in your academic life, you will have to review the literature and write about it. You will be asked to do this as a student when you write essays, dissertations and theses. Later, whenever you write an academic paper, there will usually be some element of literature review in the introduction. And if you have to
Structure of a Scientific Review Article. Writing a high-quality scientific review article is "a balancing act between the scientific rigor needed to select and critically appraise original studies, and the art of telling a story by providing context, exploring the known and the unknown, and pointing the way forward" . The ideal scientific ...
0 comment 1. A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing ...
Okay - with the why out the way, let's move on to the how. As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter.
When writing an academic book review, start with a bibliographic citation of the book you are reviewing [e.g., author, title, publication information, length]. Adhere to a particular citation style, such as Chicago, MLA, or APA. ... Good examples of essay-length reviews may be found in the scholarly journals included in the JSTOR collection, ...
Think about structuring your review like an inverted pyramid. Put the most important information at the top, followed by details and examples in the center, and any additional points at the very bottom. Here's how your outline might look: 1. Summary of the research and your overall impression. In your own words, summarize what the manuscript ...
It usually takes me a few hours. Most of the time is spent closely reading the paper and taking notes. Once I have the notes, writing the review itself generally takes less than an hour. - Walsh. It can take me quite a long time to write a good review, sometimes a full day of work and sometimes even longer.
Structure the review like an essay with an introduction, body, and conclusion. A typical book review might look like this: Introduction—Possibly explain what attracted you to read the book, or discuss the problems or issues the book addresses and why it is a timely topic. Summary of the book's argument and main point—Be brief.
This handout will help you write a book review, a report or essay that offers a critical perspective on a text. ... and that statement will probably resemble other types of academic writing, with a thesis statement, supporting body paragraphs, and a conclusion. ... But keep in mind that a bad book takes as long to write as a good one, and every ...
A good review article provides readers with an in-depth understanding of a field and highlights key gaps and challenges to address with future research. Writing a review article also helps to expand the writer's knowledge of their specialist area and to develop their analytical and communication skills, amongst other benefits.
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels ...
It's also a good way to refine your academic writing skills and learn the publishing process. But how do you write a good academic book review? We have a few tips to share. 1. Finding a Book to Review. Before you can write a book review, you need a suitable book to review. Typically, there are two main ways to find one:
Include this information when writing up the method for your review. 5 Look for previous reviews on the topic. Use them as a springboard for your own review, critiquing the earlier reviews, adding more recently published material, and pos-sibly exploring a different perspective. Exploit their refer-ences as another entry point into the literature.
Start your review by referring to the title and author of the article, the title of the journal, and the year of publication in the first paragraph. For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest. 4. Write the introduction.
Briefly summarize what the paper is about and what the findings are. Try to put the findings of the paper into the context of the existing literature and current knowledge. Indicate the significance of the work and if it is novel or mainly confirmatory. Indicate the work's strengths, its quality and completeness.
Macaro's English Medium Instruction will no doubt become one of the quintessential authoritative sources for future EMI research. Name (with reasons) the book's possible readers (and non-readers). Mention a possible weakness in terms of potential readers. Counter that possible criticism.
Book reviews are common ways for academics to evaluate each others' contributions to the field of research, especially in the arts and social sciences where publishing in books is more usual than publishing in journals. A good review is more than just a summary of the contents. It should include your view on what the purpose of the book is and ...
Your literature review should include an introduction, a review of the literature, and a conclusion. When writing your introduction, it is important to provide context for your topic. This should include an explanation of the purpose of the literature review and a description of the research question. The review of the literature should provide ...
How to Write an Academic Report 1. Title Page. This means what it literally means. The title of the general report should be indicated on this page of the academic report. In some cases, the title page also includes your name as the author and student number, the name of the course and the course code.
We have a few tips to share. 1. Finding a Book to Review. Before you can write an academic book review, you need to find a suitable book. There are two main ways to do this: Look to see which books journal publishers are seeking reviews for. Find a book that interests you and pitch it to publishers. The first approach works by finding a journal ...
An insulin pen looks like a writing pen but has a needle for its point. Some insulin pens come filled with insulin and are disposable. Others have room for an insulin cartridge that you insert and replace after use. Many people find insulin pens easier to use, but they cost more than needles and syringes.
Write a message that goes with a kitten gif for a friend on a rough day (opens in a new window) Test my knowledge on ancient civilizations ... Help me pick an outfit that will look good on camera (opens in a new window) Write an email to request a quote from local plumbers (opens in a new window)