
- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam

CBSE Class 9th Maths 2023 : 30 Most Important Case Study Questions with Answers; Download PDF

SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.
CBSE Class 9 Maths exam 2022-23 will have a set of questions based on case studies in the form of MCQs. CBSE Class 9 Maths Question Bank on Case Studies given in this article can be very helpful in understanding the new format of questions.
Each question has five sub-questions, each followed by four options and one correct answer. Students can easily download these questions in PDF format and refer to them for exam preparation.
CBSE Class 9 All Students can also Download here Class 9 Other Study Materials in PDF Format.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences
- CBSE Class 9th 2023-24 : Science Practical Syllabus; Download PDF 19 April, 2023, 4:52 pm
- CBSE Class 9 Maths Practice Book 2023 (Released By CBSE) 23 March, 2023, 6:16 pm
- CBSE Class 9 Science Practice Book 2023 (Released By CBSE) 23 March, 2023, 5:56 pm
- CBSE Class 9th Maths 2023 : 30 Most Important Case Study Questions with Answers; Download PDF 10 February, 2023, 6:20 pm
- CBSE Class 9th Maths 2023 : Important Assertion Reason Question with Solution Download Pdf 9 February, 2023, 12:16 pm
- CBSE Class 9th Exam 2023 : Social Science Most Important Short Notes; Download PDF 16 January, 2023, 4:29 pm
- CBSE Class 9th Mathematics 2023 : Most Important Short Notes with Solutions 27 December, 2022, 6:05 pm
- CBSE Class 9th English 2023 : Chapter-wise Competency-Based Test Items with Answer; Download PDF 21 December, 2022, 5:16 pm
- CBSE Class 9th Science 2023 : Chapter-wise Competency-Based Test Items with Answers; Download PDF 20 December, 2022, 5:37 pm

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

CBSE Expert
CBSE Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions PDF Download
Download Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 9 Exams 2023-24. These Case Study and Passage Based questions are published by the experts of CBSE Experts for the students of CBSE Class 9 so that they can score 100% in Exams.

Case study questions play a pivotal role in enhancing students’ problem-solving skills. By presenting real-life scenarios, these questions encourage students to think beyond textbook formulas and apply mathematical concepts to practical situations. This approach not only strengthens their understanding of mathematical concepts but also develops their analytical thinking abilities.
Table of Contents
CBSE Class 9th MATHS: Chapterwise Case Study Questions
Inboard exams, students will find the questions based on assertion and reasoning. Also, there will be a few questions based on case studies. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. For Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions, there would be 5 case-based sub-part questions, wherein a student has to attempt 4 sub-part questions.

Chapterwise Case Study Questions of Class 9 Maths
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 1 Number System
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 2 Polynomials
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 3 Coordinate Geometry
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 5 Introduction to Euclid’s Geometry
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 6 Lines and Angles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 7 Triangles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 8 Quadrilaterals
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 9 Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 10 Circles
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 11 Constructions
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 12 Heron’s Formula
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 13 Surface Area and Volumes
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 14 Statistics
- Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Probability
Checkout: Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
And for mathematical calculations, tap Math Calculators which are freely proposed to make use of by calculator-online.net
The above Class 9 Maths Case Study Question s will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions have been developed by experienced teachers of cbseexpert.com for the benefit of Class 10 students.
Class 9 Maths Syllabus 2023-24
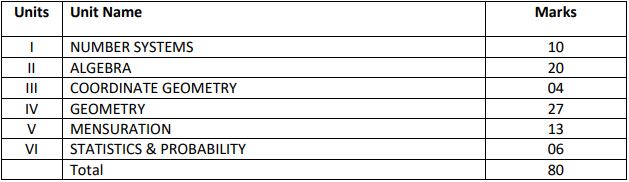
UNIT I: NUMBER SYSTEMS
1. REAL NUMBERS (18 Periods)
1. Review of representation of natural numbers, integers, and rational numbers on the number line. Rational numbers as recurring/ terminating decimals. Operations on real numbers.
2. Examples of non-recurring/non-terminating decimals. Existence of non-rational numbers (irrational numbers) such as √2, √3 and their representation on the number line. Explaining that every real number is represented by a unique point on the number line and conversely, viz. every point on the number line represents a unique real number.
3. Definition of nth root of a real number.
4. Rationalization (with precise meaning) of real numbers of the type

(and their combinations) where x and y are natural number and a and b are integers.
5. Recall of laws of exponents with integral powers. Rational exponents with positive real bases (to be done by particular cases, allowing learner to arrive at the general laws.)
UNIT II: ALGEBRA
1. POLYNOMIALS (26 Periods)
Definition of a polynomial in one variable, with examples and counter examples. Coefficients of a polynomial, terms of a polynomial and zero polynomial. Degree of a polynomial. Constant, linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials. Monomials, binomials, trinomials. Factors and multiples. Zeros of a polynomial. Motivate and State the Remainder Theorem with examples. Statement and proof of the Factor Theorem. Factorization of ax2 + bx + c, a ≠ 0 where a, b and c are real numbers, and of cubic polynomials using the Factor Theorem. Recall of algebraic expressions and identities. Verification of identities:
RELATED STORIES
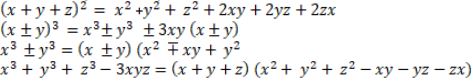
and their use in factorization of polynomials.
2. LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES (16 Periods)
Recall of linear equations in one variable. Introduction to the equation in two variables. Focus on linear equations of the type ax + by + c=0.Explain that a linear equation in two variables has infinitely many solutions and justify their being written as ordered pairs of real numbers, plotting them and showing that they lie on a line.
UNIT III: COORDINATE GEOMETRY COORDINATE GEOMETRY (7 Periods)
The Cartesian plane, coordinates of a point, names and terms associated with the coordinate plane, notations.
UNIT IV: GEOMETRY
1. INTRODUCTION TO EUCLID’S GEOMETRY (7 Periods)
History – Geometry in India and Euclid’s geometry. Euclid’s method of formalizing observed phenomenon into rigorous Mathematics with definitions, common/obvious notions, axioms/postulates and theorems. The five postulates of Euclid. Showing the relationship between axiom and theorem, for example: (Axiom)
1. Given two distinct points, there exists one and only one line through them. (Theorem)
2. (Prove) Two distinct lines cannot have more than one point in common.
2. LINES AND ANGLES (15 Periods)
1. (Motivate) If a ray stands on a line, then the sum of the two adjacent angles so formed is 180O and the converse.
2. (Prove) If two lines intersect, vertically opposite angles are equal.
3. (Motivate) Lines which are parallel to a given line are parallel.
3. TRIANGLES (22 Periods)
1. (Motivate) Two triangles are congruent if any two sides and the included angle of one triangle is equal to any two sides and the included angle of the other triangle (SAS Congruence).
2. (Prove) Two triangles are congruent if any two angles and the included side of one triangle is equal to any two angles and the included side of the other triangle (ASA Congruence).
3. (Motivate) Two triangles are congruent if the three sides of one triangle are equal to three sides of the other triangle (SSS Congruence).
4. (Motivate) Two right triangles are congruent if the hypotenuse and a side of one triangle are equal (respectively) to the hypotenuse and a side of the other triangle. (RHS Congruence)
5. (Prove) The angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal.
6. (Motivate) The sides opposite to equal angles of a triangle are equal.
4. QUADRILATERALS (13 Periods)
1. (Prove) The diagonal divides a parallelogram into two congruent triangles.
2. (Motivate) In a parallelogram opposite sides are equal, and conversely.
3. (Motivate) In a parallelogram opposite angles are equal, and conversely.
4. (Motivate) A quadrilateral is a parallelogram if a pair of its opposite sides is parallel and equal.
5. (Motivate) In a parallelogram, the diagonals bisect each other and conversely.
6. (Motivate) In a triangle, the line segment joining the mid points of any two sides is parallel to the third side and in half of it and (motivate) its converse.
5. CIRCLES (17 Periods)
1. (Prove) Equal chords of a circle subtend equal angles at the center and (motivate) its converse.
2. (Motivate) The perpendicular from the center of a circle to a chord bisects the chord and conversely, the line drawn through the center of a circle to bisect a chord is perpendicular to the chord.
3. (Motivate) Equal chords of a circle (or of congruent circles) are equidistant from the center (or their respective centers) and conversely.
4. (Prove) The angle subtended by an arc at the center is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle.
5. (Motivate) Angles in the same segment of a circle are equal.
6. (Motivate) If a line segment joining two points subtends equal angle at two other points lying on the same side of the line containing the segment, the four points lie on a circle.
7. (Motivate) The sum of either of the pair of the opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180° and its converse.
UNIT V: MENSURATION 1.
1. AREAS (5 Periods)
Area of a triangle using Heron’s formula (without proof)
2. SURFACE AREAS AND VOLUMES (17 Periods)
Surface areas and volumes of spheres (including hemispheres) and right circular cones.
UNIT VI: STATISTICS & PROBABILITY
STATISTICS (15 Periods)
Bar graphs, histograms (with varying base lengths), and frequency polygons.
To crack case study questions, Class 9 Mathematics students need to apply their mathematical knowledge to real-life situations. They should first read the question carefully and identify the key information. They should then identify the relevant mathematical concepts that can be applied to solve the question. Once they have done this, they can start solving the Class 9 Mathematics case study question.
Benefits of Practicing CBSE Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions
Regular practice of CBSE Class 9 Maths case study questions offers several benefits to students. Some of the key advantages include:
- Deeper Understanding : Case study questions foster a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts by connecting them to real-world scenarios. This improves retention and comprehension.
- Practical Application : Students learn to apply mathematical concepts to practical situations, preparing them for real-life problem-solving beyond the classroom.
- Critical Thinking : Case study questions require students to think critically, analyze data, and devise appropriate solutions. This nurtures their critical thinking abilities, which are valuable in various academic and professional domains.
- Exam Readiness : By practicing case study questions, students become familiar with the question format and gain confidence in their problem-solving abilities. This enhances their readiness for CBSE Class 9 Maths exams.
- Holistic Development: Solving case study questions cultivates not only mathematical skills but also essential life skills like analytical thinking, decision-making, and effective communication.
Tips to Solve CBSE Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions Effectively
Solving case study questions can be challenging, but with the right approach, you can excel. Here are some tips to enhance your problem-solving skills:
- Read the case study thoroughly and understand the problem statement before attempting to solve it.
- Identify the relevant data and extract the necessary information for your solution.
- Break down complex problems into smaller, manageable parts to simplify the solution process.
- Apply the appropriate mathematical concepts and formulas, ensuring a solid understanding of their principles.
- Clearly communicate your solution approach, including the steps followed, calculations made, and reasoning behind your choices.
- Practice regularly to familiarize yourself with different types of case study questions and enhance your problem-solving speed.Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions
Remember, solving case study questions is not just about finding the correct answer but also about demonstrating a logical and systematic approach. Now, let’s explore some resources that can aid your preparation for CBSE Class 9 Maths case study questions.
Q1. Are case study questions included in the Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions syllabus?
Yes, case study questions are an integral part of the CBSE Class 9 Maths syllabus. They are designed to enhance problem-solving skills and encourage the application of mathematical concepts to real-life scenarios.
Q2. How can solving case study questions benefit students ?
Solving case study questions enhances students’ problem-solving skills, analytical thinking, and decision-making abilities. It also bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, making mathematics more relevant and engaging.
Q3. How do case study questions help in exam preparation?
Case study questions help in exam preparation by familiarizing students with the question format, improving analytical thinking skills, and developing a systematic approach to problem-solving. Regular practice of case study questions enhances exam readiness and boosts confidence in solving such questions.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Number Systems
NCERT solutions for class 9 maths chapter 1 number systems consists of an introduction about the number system and the different kinds of numbers in it. The number system has been classified into different types of numbers like natural numbers, whole numbers , integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers , etc. The NCERT solutions class 9 maths chapter 1 covers all the basics of the number system which will be helpful in forming the basic foundation of mathematics.
Class 9 maths chapter 1 number systems will help the students in differentiating between rational and irrational numbers, wherein irrational numbers cannot be expressed in the form of a ratio, and also about real numbers. Class 9 maths NCERT solutions chapter 1 number systems sample exercises can be downloaded from the links below and also you can find some of these in the exercises given below.
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.1
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.2
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.3
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.4
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.5
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.6
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 PDF
These NCERT solutions for class 9 maths involving the important concepts of real numbers , rational and irrational numbers, are available for free pdf download. The questions involving real numbers and their decimal form, the law of exponents are given below:
☛ Download Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 Number Systems
NCERT Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Download PDF

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Number Systems
It is advisable for the students to practice the questions in the above links as this will give them better clarity on the kind of numbers and their properties. An exercise-wise detailed analysis of NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 number systems is given below for reference.
- Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.1 - 4 Questions
- Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.2 - 4 Questions
- Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.3 - 9 Questions
- Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.4 - 2 Questions
- Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.5 - 5 Questions
- Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Ex 1.6 - 11 Questions
☛ Download Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 NCERT Book
Topics Covered: The important topics focussed upon are irrational numbers, real numbers, and real numbers when expanded in the decimal form. The class 9 maths NCERT solutions chapter 1 covers the representation of real numbers on a number line, methods to perform operations on real numbers, and laws of exponents when dealing with real numbers.
Total Questions: Class 9 maths chapter 1 Number Systems consists of total 35 questions of which 30 are easy, 2 are moderate and 3 are long answer-type questions.
List of Formulas in NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1
NCERT solutions class 9 maths chapter 1 covers important facts about the number systems which will help strengthen the math foundation. Like if a number ‘a’ is rational, and ‘b’ represents an irrational number, then ‘a+b’, and ‘a-b’ are irrational numbers, and ‘ab’ and ‘a/b’ are supposed to be irrational numbers, and ‘b’ is not equal to zero. For ‘a’ and ‘b’ positive real numbers the following formula or entities will be true:
- √ab = √a √b
- √(a/b) = √a / √b
Important Questions for Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 1
Video solutions for class 9 maths ncert chapter 1, faqs on ncert solutions class 9 maths chapter 1, do i need to practice all questions provided in ncert solutions class 9 maths number systems.
Practicing the NCERT solutions class 9 maths number systems and exercises on real numbers, rational numbers will help in exploring the number systems in a better way. The NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Number Systems will also provide a good insight into the solving of problems.
Why are Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 Important?
Since the number systems chapter deals with rational and irrational numbers, real numbers, and their expansion, their decimal form, also covering the law of exponents. Hence, this makes the NCERT solutions class 9 maths important for examinations.
What are the Important Formulas in NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1?
There are several formulas or entities for positive real numbers which will be helpful in learning mathematics even for higher grades. Like if one wants to rationalize the denominator of 1/ ( √a + b ), then we can multiply and divide by its algebraic conjugate which is √a - b
How Many Questions are there in NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers?
The questions in the NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 are a great way for learning real numbers. There are around 35 questions dealing with number systems with 25 of them being simple and have straightforward logic, 6 of them are with medium complexity and 4 are elaborative questions.
What are the Important Topics Covered in NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1?
The NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 deal with integers, real numbers, rational and irrational numbers. Apart from these the important topics covered are the real numbers, and what happens when they are expanded in decimal form, the law of exponents in the case of real numbers, how to differentiate between rational and irrational numbers etc.
How CBSE Students can utilize NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 effectively?
The students should first practice all the examples to understand the logic and problem solving technique and should try to solve all the exercise questions. The CBSE itself recommends the NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths for the board exam studies.
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
Case Based Questions
- MCQ Questions - 1 Mark
- Assertion Reasoning
- Picture Based Questions (MCQ)
- Match the following
- Fill in the blanks (MCQ)
- Complete the table
- Correct and rewrite the sentences
- NCERT Questions
- Past Year Questions - 2 Marks
- Past Year Questions - 3 Marks
- Past Year Questions - 5 Marks
Question 1 - Case Based Questions - Chapter 1 Class 9 Economics - The Story of Village Palampur - Economics
Last updated at April 16, 2024 by Teachoo
Read the text given below and answer the following questions:
Palampur is well-connected with neighbouring villages and towns. Raiganj, a big village, is 3 kms from Palampur. An all-weather road connects the village to Raiganj and further on to the nearest small town of Shahpur. This village has about 450 families belonging to several different castes. The 80 upper caste families own the majority of land in the village. Their houses, some of them quite large, are made of brick with cement plastering. The SCs (dalits) comprise one third of the population and live in one corner of the village and in much smaller houses some of which are of mud and straw. Most of the houses have electric connections. Electricity powers all the tube wells in the fields and is used in various types of small business. Palampur has two primary schools and one high school. There is a primary health centre run by the government and one private dispensary where the sick is treated. The story of Palampur, an imaginary village, will take us through the different types of production activities in the village. In villages across India, farming is the main production activity. The other production activities, referred to as non- farm activities include small manufacturing, transport, shop-keeping, etc. Every production is organised by combining land, labour, physical capital and human capital, which are known as factors of production.
Question (i)
Raiganj, a big village, is __________ kms from palampur. .
(a) 5
(b) 4
(c) 3
(d) 1
From the paragraph,
Palampur is well-connected with neighbouring villages and towns. Raiganj, a big village, is 3 kms from Palampur. An all-weather road connects the village to Raiganj and further on to the nearest small town of Shahpur. This village has about 450 families belonging to several different castes.
(c) Raiganj, a big village, is 3 kms from Palampur.
Question (ii)
Which of the following statement is true with respect to palampur: .
(a) Palampur has one primary school and two high schools.
(b) Palampur has two primary schools and one high school.
(c) Dairy is the main production activity.
(d) The village has about 600 families belonging to several different castes.
From the paragraph,
Electricity powers all the tube wells in the fields and is used in various types of small business . Palampur has two primary schools and one high school . There is a primary health centre run by the government and one private dispensary where the sick is treated. The story of Palampur, an imaginary village, will take us through the different types of production activities in the village.
Answer:
(b) Palampur has two primary schools and one high school.
Question (iii)
Raw materials and money in hand are called: .
(a) Working capital
(b) Fixed capital
(c) Human capital
(d) None of the above
Question (iv)
The variety of inputs required at every stage during production is known as_________. .
(a) Physical capital
(b) Labour
(d) None of the above
(a) Physical capital
Question (v)
How many primary schools and high schools do palampur has.
Electricity powers all the tube wells in the fields and is used in various types of small businesses. Palampur has two primary schools and one high school . There is a primary health center run by the government and one private dispensary where the sick are treated. The story of Palampur, an imaginary village, will take us through the different types of production activities in the village.
(a) Palampur has two primary schools and one high school.
Question (vi)
What are the factors of production.
In villages across India, farming is the main production activity. The other production activities, referred to as non-farm activities include small manufacturing, transport, shop-keeping, etc. Every production is organized by combining land, labor, physical capital, and human capital, which are known as factors of production.
Every production is organized by combining land, labor, physical capital, and human capital, which are known as factors of production.

Davneet Singh
Davneet Singh has done his B.Tech from Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. He has been teaching from the past 14 years. He provides courses for Maths, Science, Social Science, Physics, Chemistry, Computer Science at Teachoo.
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 9 Science Matter in our Surroundings
Case study questions class 9 science chapter 1 matter in our surroundings.
CBSE Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Matter in our Surroundings. Important Case Study Questions for Class 9 Exam. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Matter in our Surroundings.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks or 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science – Matter in our Surroundings
Case study 1:.
1.) A matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. Pen, paper, clips, sand, air, ice, etc. are different forms of matter. Every matter is made up of small particles. These particles are so tiny that they can’t be seen with naked eyes. Let’s see about the different characteristics of particles of matter.
- All matter is made up of very small particles.
- .Particles of matter has spaces between them.
- Particles of matter are continuously moving.
- Particles of matter attract each other.
Answer the following questions by referring above paragraph.
i.) Which of following is not matter?
c.) smell of perfume
d.) None of these
ii.) Thoughts coming in our mind are example of matter. True or false
c.) None of these
iii.) Which of the following is true about particles of matter?
a.) Particles of matter has spaces between them
b.) Particles of matter are continuously moving
c.) Particles of matter attract each other
d.) All of these
iv.) Give 5 examples of matter in our surroundings
v.) Enlist all properties of particles of matter
Answer key-1
iv.) pen, pencil, notebook, ice and water
v.) Different characteristics of particles of matter are
Case Study 2:
2.) There are three states of matter – solid, liquid and gas.
Solids have a definite shape, distinct boundaries and fixed volumes, that is, have negligible compressibility. Solids have a tendency to maintain their shape when subjected to outside force. Solids may break under force but it is difficult to change their shape, so they are rigid.
Liquids have no fixed shape but have a fixed volume. They take up the shape of the container in which they are kept. Liquids flow and change shape, so they are not rigid but can be called fluid.
Gas as has indefinite shape, no fixed volume. Gas gets the shape and volume of container.
Gas has very low density hence are light. Gas can flow easily and hence are called fluid.
i.) Which of the following state of matter takes shape of container in which it is filled?
d.) Both b and c
ii.) Distance between particles of matter least in
iii.) Compressibility is least in case of
iv.) Give properties of solids.
v.) Give properties of Gases.
Answer key-2
iv.) properties of solid are given below
- Solid has fixed volume.
- Solid has fixed shape.
- Solid has high density.
- Solids are heavy.
- Solid does not flow.
v.) Properties of gases are
- Gas has indefinite shape
- Gas has no fixed volume.
- Gas gets the shape and volume of container.
- Gas fills the container completely.
- Gas has very low density.
- Because of low density gas are light.
- Gas can flow easily and hence are called fluid.
Case Study 3:
3.) What happens inside the matter during change of state? On increasing the temperature of solids, the kinetic energy of the particles increases. Due to the increase in kinetic energy, the
Particles start vibrating with greater speed. The energy supplied by heat overcomes the forces of attraction between the particles. The particles leave their fixed positions and start moving more freely. A stage is reached when the solid melts and is converted to a liquid. The minimum temperature at which a solid melts to become a liquid at the atmospheric pressure is called its melting point.
The temperature of the system does not change after the melting point is reached, till all the ice melts. This happens even though we continue to heat the beaker, that is, we continue to supply heat. This heat gets used up in changing the state by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles. The amount of heat energy that is required to change 1 kg of a solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure at its melting point is known as the latent heat of fusion. So, particles in water at 0 0 C (273 K) have more energy as compared to particles in ice at the same temperature.
The temperature at which a liquid starts boiling at the atmospheric pressure is known as its boiling point. Boiling is a bulk phenomenon. Particles from the bulk of the liquid gain enough energy to change into the vapour state. A change of state directly from solid to gas without changing into liquid state is called sublimation and the direct change of gas to solid without changing into liquid is called deposition.
i.) A change of state directly from solid to gas without changing into liquid state is called
a.) Sublimation
b.) Deposition
c.) Boiling point
ii.) The direct change of gas to solid without changing into liquid is called
iii.) The energy supplied by heat to solid is used to overcome the forces of attraction between the particles. True or false
iv.) Define melting point and boiling point
v.) Define latent heat of fusion
Answer key-3
iv.) The minimum temperature at which a solid melts to become a liquid at the atmospheric pressure is called its melting point.
The temperature at which a liquid starts boiling at the atmospheric pressure is known as its boiling point.
v.) The amount of heat energy that is required to change 1 kg of a solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure at its melting point is known as the latent heat of fusion.
Case Study 4:
4 .) Do we always need to heat or change pressure for changing the state of matter? Can you quote some examples from everyday life where change of state from liquid to vapour takes place without the liquid reaching the boiling point? In the case of liquids, a small fraction of particles at the surface, having higher kinetic energy, is able to break away from the forces of attraction of other particles and gets converted into vapour. This phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapors at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.
i.) Evaporation of liquid takes place at
a.) Boiling point
b.) Above boiling point
c.) Below boiling point
ii.) Evaporation takes place at surface of liquid because
a.) They are heavy as compare to other particles
b.) They have sufficient kinetic energy to break the force
c.) They are light weight as compare to other particles
iii.) During evaporation particles of liquid change into vapour
a.) From the surface
b.) From the bottom
c.) From all over the liquid
iv.) Define evaporation.
v.) Explain process of evaporation
Answer key-4
iv.) The phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapors at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.
v.) In the case of liquids, a small fraction of particles at the surface, having higher kinetic energy, is able to break away from the forces of attraction of other particles and gets converted into vapour. This phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapors at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.
Case Study 5:
5.) You must have observed that the rate of evaporation increases with–
- an increase of surface area:
- We know that evaporation is a surface phenomenon. If the surface area is increased, the rate of evaporation increases. For example, while putting clothes for drying up we spread them out.
- an increase of temperature:
With the increase of temperature, more number of particles get enough kinetic energy to go into the vapour state.
In an open vessel, the liquid keeps on evaporating. The particles of liquid absorb energy from the surrounding to regain the energy lost during evaporation. This absorption of energy from the surroundings makes the surroundings cold. What happens when you pour some acetone (nail polish remover) on your palm? The particles gain energy from your palm or surroundings and evaporate causing the palm to feel cool. After a hot sunny day, people sprinkle water on the roof or open ground because the large latent heat of vaporization of water helps to cool the hot surface.
i.) Evaporation is surface phenomenon. True or false
ii.) As temperature increases the rate of evaporation is
a.) increases
b.) decreases
c.) remains constant
iii.) The rate of evaporation increases with
a.) Increase in wind speed
b.) Decrease in wind speed
c.) Does not have any effect from wind speed
iv.) What happens when you pour some acetone (nail polish remover) on your palm?
v.) We are able to sip hot tea from saucer than from cup. Why?
Answer key-5
iv.) The particles gain energy from your palm or surroundings and evaporate causing the palm to feel cool.
v.) We are able to sip hot tea from saucer than from cup. This is because saucer has large surface area, due to large surface area as compare to cut area tea evaporates at faster rate.
Thank you It helped me a lot
Why smell of Perfume is not a matter?
Because there is no particle
Because their are perfume particles suspended in air
These all case study questions are really helpful . Thanks
This is my first I was so nervous but these questions help me alot thank you
Smell of perfume is a matter because it have gas particles means perfume particles
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Case study questions class 6 maths factors and multiples, assertion and reason questions class 6 maths factors and multiples, case study questions class 6 maths number system, sikkim scert class 5 evs chapter 10 experiments with water solution.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
CBSE Case Based Questions for Class 9 Social Science - Pdf PDF Download
Cbse case study questions for class 9 social science.
Case based questions are a type of exam question designed to assess the student’s ability to apply information from the Social Science syllabus in a practical situation. These questions typically involve the student being given a brief scenario or case study and then asked to answer questions based on the data provided.
The purpose of case based questions is to test the student's analytical and problem solving skills, as well as their knowledge of the Social Science syllabus. In addition, they allow teachers to assess the student’s ability to think critically and creatively in order to come up with effective solutions. Case based questions also help to ensure that students have a better understanding of how their knowledge can be applied in real-world situations.
Case based questions should be tailored to the specific grade level and topic under consideration. For example, a case-based question for Class 9 Social Science might involve the student analyzing a historical event or analyzing the impact of a government policy. The key is to provide the student with enough information to understand the scenario and formulate an appropriate response.
Case Based Questions For Class 9 History
Case-based questions for Class 9 History are a type of question that is based on a particular case study or event related to a historical event or period. These questions require students to apply their understanding of the historical context and analyze the case study to answer the questions. Case-based questions usually require students to identify the main issues or problems highlighted in the case study, evaluate the different perspectives or opinions presented, and make an informed judgment or conclusion based on the evidence presented. These questions test not only the student's knowledge of historical events but also their critical thinking and analytical skills.
Chapter Wise Case Based Questions for Class 9 History
Chapter-wise case-based questions for Class 9 History are a set of questions that are based on a specific chapter or topic in the history textbook. These questions are designed to help students apply their understanding of historical events and concepts to specific case studies or scenarios.
The CBSE Class 9 Case Based Questions can be accessed from Chapetrwise Links provided below:
Chapter 1: The French Revolution
- Case Based Questions: The French Revolution
Chapter 2: Socialism in Europe and the Russian Revolution
- Case Based Questions: Socialism in Europe and the Russian Revolution
Chapter 3: Nazism and the Rise of Hitler
- Case Based Questions: Nazism and the Rise of Hitler
Chapter 4: Forest Society and Colonialism
Chapter 5: Pastoralists in the Modern World
Case Based Questions For Class 9 Geography
Case-based questions for Class 9 Geography are a type of question that requires students to apply their understanding of geography concepts and analyze a particular case study related to a geographical phenomenon. These questions often require students to analyze a specific situation or scenario related to a geographical concept or phenomenon and answer the questions based on their understanding of the concept and the given situation.
Chapter Wise Case Based Questions for Class 9 Geography
Chapter-wise case-based questions for Class 9 Geography are a set of questions that are based on a specific chapter or topic in the geography textbook. These questions are designed to help students apply their understanding of geographical concepts and phenomena to specific case studies or scenarios. The CBSE Class 9 Case Based Questions can be accessed from Chapetrwise Links provided below:
Chapter 1: India – Size and Location
- Case Based Questions: India – Size and Location
Chapter 2: Physical Features of India
- Case Based Questions: Physical Features of India
Chapter 3: Drainage
- Case Based Questions: Drainage
Chapter 4: Climate
- Case Based Questions: Climate
Chapter 5: Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
- Case Based Questions: Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Chapter 6: Population
Case Based Questions For Class 9 Political Science
Case-based questions for Class 9 Political Science are a type of question that requires students to apply their understanding of political science concepts and analyze a particular case study related to a political phenomenon. These questions often require students to analyze a specific situation or scenario related to a political concept or phenomenon and answer the questions based on their understanding of the concept and the given situation.
Chapter Wise Case Based Questions for Class 9 Political Science
Chapter-wise case-based questions for Class 9 Political Science are a set of questions based on specific chapters or topics covered in the political science textbook. These questions are designed to help students apply their understanding of political science concepts to real-world situations and events.
Chapter 1: What is Democracy? Why Democracy?
- Case Based Questions: What is Democracy? Why Democracy?
Chapter 2: Constitutional Design
- Case Based Questions: Constitutional Design
Chapter 3: Electoral Politics
- Case Based Questions: Electoral Politics
Chapter 4: Working of Institutions
- Case Based Questions: Working of Institutions
Chapter 5: Democratic Rights
Case Based Questions For Class 9 Economics
Case-based questions for Class 9 Economics are a type of question that requires students to apply their understanding of economic concepts and analyze a particular case study related to an economic phenomenon. These questions often require students to analyze a specific situation or scenario related to an economic concept or phenomenon and answer the questions based on their understanding of the concept and the given situation.
Chapter Wise Case Based Questions for Class 9 Economics
Chapter-wise case-based questions for Class 9 Economics are a set of questions based on specific chapters or topics covered in the economics textbook. These questions are designed to help students apply their understanding of economic concepts to real-world situations and events.
Chapter 1: The Story of Village Palampur
- Case Based Questions: The Story of Village Palampur
Chapter 2: People as Resource
- Case Based Questions: People as Resource
Chapter 3: Poverty as a Challenge
- Case Based Questions: Poverty as a Challenge
Chapter 4: Food Security in India
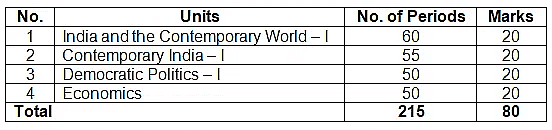
Weightage of Case Based Questions in Class 9 Social Science
Why are Case Study Questions important in Social Science Class 9?
- Enhance critical thinking: Case study questions require students to analyze a real-life scenario and think critically to identify the problem and come up with possible solutions. This enhances their critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Apply theoretical concepts: Case study questions allow students to apply theoretical concepts that they have learned in the classroom to real-life situations. This helps them to understand the practical application of the concepts and reinforces their learning.
- Develop decision-making skills: Case study questions challenge students to make decisions based on the information provided in the scenario. This helps them to develop their decision-making skills and learn how to make informed decisions.
- Improve communication skills: Case study questions often require students to present their findings and recommendations in written or oral form. This helps them to improve their communication skills and learn how to present their ideas effectively.
- Enhance teamwork skills: Case study questions can also be done in groups, which helps students to develop teamwork skills and learn how to work collaboratively to solve problems.
In summary, case study questions are important in Class 9 because they enhance critical thinking, apply theoretical concepts, develop decision-making skills, improve communication skills, and enhance teamwork skills. They provide a practical and engaging way for students to learn and apply their knowledge and skills to real-life situations.
Class 9 Social Science Curriculum at Glance
The Class 9 Social Science curriculum in India covers a wide range of topics and concepts. Here is a brief overview of the Social Science curriculum at a glance:
- History: The History section includes topics such as the French Revolution, Nazism and the rise of Hitler, socialism in Europe and the Russian Revolution, and the Indian National Movement.
- Geography: The Geography section includes topics such as India-Size and Location, Physical Features of India, Drainage, Climate, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife, Population, and Human Resource.
- Political Science: The Political Science section includes topics such as Democracy in the Contemporary World, Constitutional Design, Electoral Politics, Working of Institutions, and Democratic Rights.
- Economics: The Economics section includes topics such as The Story of Village Palampur, People as Resource, Poverty as a Challenge, Food Security in India, and Globalisation and the Indian Economy.
The Class 9 Social Science curriculum is designed to provide a strong foundation in social sciences and prepare students for higher education in the field. The curriculum is structured to develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills, and to promote the application of social science concepts in real-life situations. The curriculum is also designed to help students understand the socio-economic and political structures of India and the world and prepare them for active participation in society.
Students can also access Case Based Questions of all subjects of CBSE Class 9
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Maths
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Science
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 English
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Hindi
- Case Based Questions for Class 9 Sanskrit
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Case Based Questions for Class 9 Social Science
What are case-based questions in social science.
Case-based questions in social science are problem-solving tasks that require students to apply their knowledge and understanding of social science concepts and theories to real-world situations or scenarios.
How are case-based questions different from traditional social science questions?
Traditional social science questions typically focus on testing students' knowledge of specific facts, concepts, and theories. Case-based questions, on the other hand, require students to use their knowledge and understanding to analyze and interpret real-world situations and make informed decisions.
What are some common types of case-based questions in class 9 social science?
Common types of case-based questions in class 9 social science include analyzing historical events, interpreting data and statistics, and evaluating the impact of social policies and programs.
How can students prepare for case-based questions in social science?
To prepare for case-based questions in social science, students should practice analyzing real-world scenarios and interpreting data and statistics. They should also work on developing their critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Top Courses for Class 9
Faqs on cbse case based questions for class 9 social science - pdf, shortcuts and tricks, extra questions, semester notes, mock tests for examination, sample paper, past year papers, video lectures, important questions, previous year questions with solutions, practice quizzes, cbse case based questions for class 9 social science - pdf, viva questions, study material, objective type questions.

CBSE Case Based Questions for Class 9 Social Science - Pdf Free PDF Download
Importance of cbse case based questions for class 9 social science - pdf, cbse case based questions for class 9 social science - pdf notes, cbse case based questions for class 9 social science - pdf class 9, study cbse case based questions for class 9 social science - pdf on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.

Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
myCBSEguide
- Class 9 Science Case...
Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you are wondering how to solve class 9 science case study questions, then myCBSEguide is the best platform to choose. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions.
You can find a wide range of solved case studies on myCBSEguide, covering various topics and concepts. Class 9 Science case studies are designed to help you understand the application of various concepts in real-life situations.
The rationale behind Science
Science is crucial for Class 9 students’ cognitive, emotional, and psychomotor development. It encourages curiosity, inventiveness, objectivity, and aesthetic sense.
In the upper primary stage, students should be given a variety of opportunities to engage with scientific processes such as observing, recording observations, drawing, tabulating, plotting graphs, and so on, whereas in the secondary stage, abstraction and quantitative reasoning should take a more prominent role in science teaching and learning. As a result, the concept of atoms and molecules as matter’s building units, as well as Newton’s law of gravitation, emerges.
Science is important because it allows Class 9 Science students to understand the world around us. It helps to find out how things work and to find solutions to problems at the Class 9 Science level. Science is also a source of enjoyment for many people. It can be a hobby, a career, or a source of intellectual stimulation.
Case study questions in Class 9 Science
The inclusion of case study questions in Class 9 science CBSE is a great way to engage students in critical thinking and problem-solving. By working through real-world scenarios, Class 9 Science students will be better prepared to tackle challenges they may face in their future studies and careers. Class 9 Science Case study questions also promote higher-order thinking skills, such as analysis and synthesis. In addition, case study questions can help to foster creativity and innovation in students. As per the recent pattern of the Class 9 Science examination, a few questions based on case studies/passages will be included in the CBSE Class 9 Science Paper. There will be a paragraph presented, followed by questions based on it.
Examples of Class 9 science class case study questions
Class 9 science case study questions have been prepared by myCBSEguide’s qualified teachers. Class 9 case study questions are meant to evaluate students’ knowledge and comprehension of the material. They are not intended to be difficult, but they will require you to think critically about the material. We hope you find Class 9 science case study questions beneficial and that they assist you in your exam preparation.
The following are a few examples of Class 9 science case study questions.
Class 9 science case study question 1
- due to its high compressibility
- large volumes of a gas can be compressed into a small cylinder
- transported easily
- all of these
- shape, volume
- volume, shape
- shape, size
- size, shape
- the presence of dissolved carbon dioxide in water
- the presence of dissolved oxygen in the water
- the presence of dissolved Nitrogen in the water
- liquid particles move freely
- liquid have greater space between each other
- both (a) and (b)
- none of these
- Only gases behave like fluids
- Gases and solids behave like fluids
- Gases and liquids behave like fluids
- Only liquids are fluids
Answer Key:
- (d) all of these
- (a) shape, volume
- (b) the presence of dissolved oxygen in the water
- (c) both (a) and (b)
- (c) Gases and liquids behave like fluids
Class 9 science case study question 2
- 12/32 times
- 18 g of O 2
- 18 g of CO 2
- 18 g of CH 4
- 1 g of CO 2
- 1 g of CH 4 CH 4
- 2 moles of H2O
- 20 moles of water
- 6.022 × 1023 molecules of water
- 1.2044 × 1025 molecules of water
- (I) and (IV)
- (II) and (III)
- (II) and (IV)
- Sulphate molecule
- Ozone molecule
- Phosphorus molecule
- Methane molecule
- (c) 8/3 times
- (d) 18g of CH 4
- (c) 1g of H 2
- (d) (II) and (IV)
- (c) phosphorus molecule
Class 9 science case study question 3
- collenchyma
- chlorenchyma
- It performs photosynthesis
- It helps the aquatic plant to float
- It provides mechanical support
- Sclerenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Epithelial tissue
- Parenchyma tissues have intercellular spaces.
- Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners.
- Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues.
- Meristematic tissues, in its early stage, lack vacuoles, muscles
- (I) and (II)
- (III) and (I)
- Transpiration
- Provides mechanical support
- Provides strength to the plant parts
- None of these
- (a) Collenchyma
- (b) help aquatic plant to float
- (b) Sclerenchyma
- (d) Only (III)
- (c) provide strength to plant parts
Cracking Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
There is no one definitive answer to Class 9 Science case study questions. Every case study is unique and will necessitate a unique strategy. There are, nevertheless, certain general guidelines to follow while answering case study questions.
- To begin, double-check that you understand the Class 9 science case study questions. Make sure you understand what is being asked by reading it carefully. If you’re unclear, seek clarification from your teacher or tutor.
- It’s critical to read the Class 9 Science case study material thoroughly once you’ve grasped the question. This will provide you with a thorough understanding of the problem as well as the various potential solutions.
- Brainstorming potential solutions with classmates or other students might also be beneficial. This might provide you with multiple viewpoints on the situation and assist you in determining the best solution.
- Finally, make sure your answer is presented simply and concisely. Make sure you clarify your rationale and back up your claim with evidence.
A look at the Class 9 Science Syllabus
The CBSE class 9 science syllabus provides a strong foundation for students who want to pursue a career in science. The topics are chosen in such a way that they build on the concepts learned in the previous classes and provide a strong foundation for further studies in science. The table below lists the topics covered in the Class 9 Science syllabus of the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). As can be seen, the Class 9 science syllabus is divided into three sections: Physics, Chemistry and Biology. Each section contains a number of topics that Class 9 science students must study during the course.
CBSE Class 9 Science (Code No. 086)
Theme: Materials Unit I: Matter-Nature and Behaviour Definition of matter; solid, liquid and gas; characteristics – shape, volume, density; change of state-melting (absorption of heat), freezing, evaporation (cooling by evaporation), condensation, sublimation. Nature of matter: Elements, compounds and mixtures. Heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures, colloids and suspensions. Particle nature and their basic units: Atoms and molecules, Law of constant proportions, Atomic and molecular masses. Mole concept: Relationship of mole to mass of the particles and numbers. Structure of atoms: Electrons, protons and neutrons, valency, the chemical formula of common compounds. Isotopes and Isobars.
Theme: The World of the Living Unit II: Organization in the Living World Cell – Basic Unit of life: Cell as a basic unit of life; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, multicellular organisms; cell membrane and cell wall, cell organelles and cell inclusions; chloroplast, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus; nucleus, chromosomes – basic structure, number. Tissues, Organs, Organ System, Organism: Structure and functions of animal and plant tissues (only four types of tissues in animals; Meristematic and Permanent tissues in plants).
Theme: Moving Things, People and Ideas Unit III: Motion, Force and Work Motion: Distance and displacement, velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion along a straight line; acceleration, distance-time and velocity-time graphs for uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion, derivation of equations of motion by graphical method; elementary idea of uniform circular motion. Force and Newton’s laws: Force and Motion, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Action and Reaction forces, Inertia of a body, Inertia and mass, Momentum, Force and Acceleration. Elementary idea of conservation of Momentum. Gravitation: Gravitation; Universal Law of Gravitation, Force of Gravitation of the earth (gravity), Acceleration due to Gravity; Mass and Weight; Free fall. Floatation: Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes’ Principle; Buoyancy. Work, energy and power: Work done by a Force, Energy, power; Kinetic and Potential energy; Law of conservation of energy. Sound: Nature of sound and its propagation in various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in humans; ultrasound; reflection of sound; echo.
Theme: Food Unit IV: Food Production Plant and animal breeding and selection for quality improvement and management; Use of fertilizers and manures; Protection from pests and diseases; Organic farming.
PRESCRIBED BOOKS:
- Science-Textbook for class IX-NCERT Publication
- Assessment of Practical Skills in Science-Class IX – CBSE Publication
- Laboratory Manual-Science-Class IX, NCERT Publication
- Exemplar Problems Class IX – NCERT Publication
myCBSEguide: A true helper
There are numerous advantages to using myCBSEguide to achieve the highest results in Class 9 Science.
- myCBSEguide offers high-quality study materials that cover all of the topics in the Class 9 Science curriculum.
- myCBSEguide provides practice questions and mock examinations to assist students in the best possible preparation for their exams.
- On our myCBSEguide app, you’ll find a variety of solved Class 9 Science case study questions covering a variety of topics and concepts. These case studies are intended to help you understand how certain principles are applied in real-world settings
- myCBSEguide is that the study material and practice problems are developed by a team of specialists who are always accessible to assist students with any questions they may have. As a result, students may be confident that they will receive the finest possible assistance and support when studying for their exams.
So, if you’re seeking the most effective strategy to study for your Class 9 Science examinations, myCBSEguide is the place to go!
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
NCERT Solutions for Social Science Economics Class 9 Chapter 1 - The Story Of Village Palampur
- NCERT Solutions
- Social Science Economics
- Chapter 1 The Story Of Village Palampur

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 - The Story of Village Palampur
NCERT Solutions for Economics Class 9 Chapter 1 explores the economic life of a fictional village called Palampur. Class 9 students studying Economics can find answers to exercises in Chapter 1 - The Story of Village Palampur in their NCERT book. These solutions are a great resource for improving writing skills and preparing for school exams. They are based on NCERT textbooks and are both easy to understand and accurate.
NCERT solutions are especially helpful for CBSE exams, aligning with the type of questions that may be asked. By practicing these NCERT Solutions , students can enhance their preparation and increase their chances of scoring well in exams. If students are struggling with questions from the Class 9 NCERT textbook, they can refer to our free and accessible NCERT Solutions for Class 9.
Students may also use our Economics Class 9 Chapter 1 Additional Questions and Worksheet to help them. Students who want to do well in their half-yearly exams can study from the Class 9th Economics Chapter 1 Notes offered here. When students study from NCERT Economics Class 9 Ch 1 Crucial Questions, they will have an advantage over their peers.
Below you will find Economic Class 9 Chapter 1 PDF for your convenience. If you are looking for the best curated NCERT solutions for class 9 maths you don't need to search anymore. Science Students who are looking for NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science will also find the Solutions curated by our Master Teachers really Helpful.

Access NCERT Solutions of Economics Class 9 Chapter 1 - The Story of Village Palampur
1. Every village in India is surveyed once in ten years during the Census and some of details are presented in the following format. Fill up the following based on information on Palampur.
(a) Location
Ans: Bulandshahr district, Western Uttar Pradesh
(b) Total Area of the Village
Ans: 226 hectares
(c) Land Use(in hectares)
Ans: Cultivated Land not available for cultivation (Area covering dwellings, roads, ponds, grazing ground)
200 hectares –26 hectares
(d) Facilities:
Educational: There are two primary schools and one high school in Palampur.
Medical: A primary health centre was run by the government, also there was a private dispensary to treat sick people.
Market: Raiganj and Shahpur
Communication: Well-connected with neighbouring villages and towns. 3 kms from Palampur.
Electricity Supply: Most of the houses had electric connections and it was also used to run the tube wells in fields.
Nearest Town: Raiganj, because many roads are connected to the Raiganj and to Shahpur.
2. Modern farming methods require more inputs which are manufactured in industry. Do you agree?
Ans: Yes, modern farming methods make use of a greater number of industrial outputs as compared to traditional farming methods. Modern farming methods make use of high-yielding seeds. These seeds require pesticides and chemical fertilisers, equipment of agriculture which are manufactured in industries like tractors, and advanced irrigation facilities like electric tube wells in order to produce the best results.
3. How did the spread of electricity help farmers in Palampur?
Ans: The spread of electricity has helped the farmers of Palampur:
Almost every household has an electric supply.
Electric supply was used for tube wells to run it in agricultural fields.
Electricity is also used in small business’s activities.
4. Is it important to increase the area under irrigation? Why?
Ans: In India, nearly two-thirds of the people are dependent on farming. From that total cultivated area in the country, less than 40% is irrigated. In the other areas, farming is dependent on rainfall which is not regular. Modern farming methods are really difficult to apply in the presence of inadequate water supplies. India cannot achieve self- sufficiency in food grains until land is increased for the use of irrigation.
5. Construct a table on the distribution of land among the 450 families of Palampur.
6. Why are the wages for farm labourers in Palampur less than minimum wages?
Ans: In Palampur farm workers used to get less wages than the minimum wages fixed by the government. The minimum wages for a farm labourer are fixed at Rs 115 per day, but the farm labourers only get Rs. 70 – 80, since there was heavy competition for work among the farm labourers.
7. In your region, talk to two labourers. Choose either farm labourers or labourers working at construction sites. What wages do they get? Are they paid in cash or kind? Do they get work regularly? Are they in debt?
Ans: The labourers working at construction sites, get daily wages Rs. 600 per day. They are paid in cash, for regular work. They don’t have any debt.
8. What are the different ways of increasing production on the same piece of land? Use examples to explain.
Ans: The different ways of increasing production on the same piece of land are:
Multiple Cropping: The most common method of growing the production on a given piece of land. Here, more than one crop is grown on the same piece of land. Indian farmers grow at least more than two main crops in a year.
Modern Farming Methods: Modern farming consists of cultivable areas where HYV seeds and irrigation are used there. The use of simple wooden plough is replaced by tractors and fertilizers or pesticides are used.
9. Describe the work of a farmer with 1 hectare of land.
Ans: A farmer with one hectare of land is in the category of small farmer. Most of the work is done by the farmer and his family members. The farmer will use a pair of bullocks to plough the field. His family members will assist him in sowing the seeds. During harvest time, he may need a few labourers.
10. How do the medium and large farmers obtain capital for farming? How is it different from the small farmers?
Ans: By selling farm produce medium and large farmers usually produce surplus cash. Because they have land and a house, getting a loan from banks is very easy. Small farmers may not be able to get bank loans. They have to depend on the moneylender and local merchant for a loan.
11. On what terms did Savita get a loan from Tajpal Singh? Would Savita’s condition be different if she could get a loan from the bank at a low rate of interest?
Ans: Savita needed money for buying pesticides, seeds and fertilisers, and water for irrigation. She required money for the repairing of her farm instruments. Hence, she decided to borrow money from Tejpal Singh, who was a large farmer in her village. Tejpal Singh convinced to give the loan of Rs. 3000 at an interest rate of 24% for four months. He agreed with Savita to work on his field during the harvest season for Rs. 35 a day.
If Savita would have borrowed the loan from the bank, then her condition would have been better. Banks provide loans at low interest rates. Moreover, Savita should have devoted more time to her own field instead of working for Tejpal Singh as farm labourer.
12. Talk to some old residents in your region and write a short report on the changes in irrigation and changes in production methods during the last 30 years.
Ans: In the past 30 years, there were many changes in terms of irrigation and production methods. For irrigation, instead of canals, tube wells are being used for water supply. Many electric pumps replaced other old systems. Instead of bullocks, now tractors are being used for larger farms.
13. What are the non-farm production activities taking place in your region? Make a short list.
Ans: The non-farm production activities taking place in our region are:
General Stores
Transportation
14. What can be done so that more non-farm production activities can be started in villages?
Ans: Three things that need to be done to encourage non-farm production activities in villages:
The government can bring new schemes to landless labourers and small farmers, who are able to get loans at cheaper rates to start small individual/community businesses.
From financial assistance, the government should set up rural workshops to enable the villagers to build on their skill levels.
The government needs to work towards improving the infrastructure of villages, this will help the rural parts of the country to get connected with urban parts.
Summary of NCERT Solutions Class 9th Economics Chapter 1 The Story of Village Palampur
Economincs Class 9 NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 The Story of Village Palampur is an interesting read for the students of Class 9. It is a unique effort to teach students how rural people undertake the production of crops and other non-farm activities in the villages like Palampur. The chapter further elaborates how the need for capital and human power for the production of various products is essential and beneficial for farming and production.
The story deals with a village Palampur whose primary activity is agriculture. 75 percent of the people belonging to Palampur depend on farming for their livelihood. These people comprise farmers or agricultural labourers. Moreover, other activities like small-scale manufacturing, dairy, transport, etc. are carried out by some of them at a limited level.
From this chapter, students will gain an understanding of the type of farming practised in Palampur, the various types of crops grown in the village, and the techniques employed to grow crops.
Class 9th Economics chapter 1, The Story of Village Palampur deals with three major topics. These are as follows.
A. Organisation of Production
I. Factors of production
II. Fixed and working capital
B. Factors affecting production, such as
I. Distribution of land
II. Distribution of labour
II. Land sustainability
IV. The capital needed
C. Non-farming activities
For a detailed understanding of the chapter, key concepts, topics, and themes, download the PDF for NCERT Solutions of Economics Ch 1 Class 9 The Story of Village Palampur, and give your preparation the right direction.
NCERT Solutions of Social Science Economics CLass 9 Chapter 1 Explanation
CBSE Class 9th Economics Chapter 1 introduces students to the organization of production, land distribution, capital for farming, and other production activities through an exciting story of village Palampur. The NCERT Solutions Class 9 Notes is helpful for students to prepare for their upcoming examinations. The fourth Unit of Social Studies includes Economics. CBSE has formulated a thematic village story of Palampur to build basics of Economic concepts.
Though students have learned about farming in the early stages, The Story of Village Palampur Notes brings Class 9 students closer to the production process and how it combines the various types of resources to produce the desired goods and services. The Economics Class 9 NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 PDF further tries to develop knowledge about various methods to produce more from the same piece of land. At the same time, students need to reflect on the Green Revolution. Students are asked to find out how to restore the overuse of land leading to loss of soil fertility.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 9th Economics Chapter 1 goes beyond teaching the subject and getting excellent marks. It is also about building awareness for villages and contributing to society. When students ponder over such issues, they are sensitized to care for their environment and come up with innovative ideas to ensure the future development of agricultural production.
Weightage Marks of Economics Class 9 Chapter 1 - The Story of Village Palampur
The Class IX question paper for the academic year 2024-25 marks distribution is as follows.
The entire Unit IV - Understanding Economic Development weighs 20 marks. Social Studies is for 100 marks. The break-ups of the total are as follows.
Teachers allocate compulsory project work to students to expose them to life skills. Project work marks are further distributed in three categories-
Benefits of NCERT Solutions Class 9th Economics Chapter 1
The students will benefit to a great extent if they go through the Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 notes.
Expert teachers in Economics have designed the story of village palampur NCERT Solutions PDF for easy comprehension.
Teachers with expertise in the field of Economics have prepared A-Level study materials in compliance with the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Chapter 1 with pictures.
The Economic Class 9 Chapter 1 Extra Questions and Answers are included here to assist students with their assignments.
Social Science Economics Class 9 Chapter 1: Important Points at a Glance
The following are the important points discussed in the story.
The essential prerequisites for the production of goods and services, often known as factors of production, are land, labour, and capital.
The land encompasses all of nature's free offerings, such as soil, water, forests, minerals, and so on.
Labour refers to human effort, which encompasses both physical and mental labour.
Following land and labour, capital is the third most important factor in production. Capital is required by all types of farmers.
Local producers borrow from richer farmers, local moneylenders, or traders who supply them with various agricultural materials.
The third criterion for development is physical capital.
Fixed capital and raw materials such as seeds for farmers and yarn for weavers are examples of physical capital.
Conclusion
The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Chapter 1 - "The Story of Village Palampur" offer a comprehensive understanding of the economic aspects and functioning of a village in India.
Through this chapter, students are introduced to the village of Palampur and its various economic activities, including farming, non-farming activities, and the use of modern technology. The solutions help students comprehend the factors of production, such as land, labour, capital, and entrepreneurship, and how these elements contribute to the village's economy.
Additionally, the solutions provide an overview of important concepts such as fixed capital, working capital, multiple cropping, and the significance of the farm and non-farm sectors in the village's overall economic development.
Chapter wise NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science - Economics
Chapter 2: People As Resource
Chapter 3: Poverty As A Challenge
Chapter 4: Food Security In India

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Social Science Economics Class 9 Chapter 1 - The Story Of Village Palampur
1. Did the Spread of Electricity Help the Farmers in Palampur in Their Agricultural Activities?
The flow of electric current in villages succumbed by darkness helped the farmers in Palampur extensively in their agricultural activities. It has bestowed power to the powerless farmers. Here is the list of benefits the farmers derived from the spread of electricity.
Powered tube wells efficiently irrigate extensive farmland. Earlier farmers found it difficult to water their large area of the agricultural field with the complex Persian wheel.
Electricity is pivotal in increasing production in villages.
Electricity in houses could provide a comfortable life for farmers.
Electricity facilitated small-scale industries in processing.
2. Farm Labourer’s Wages are Less than Minimum Wages. Explain.
Farmers put forth a lot of effort to develop crops, yet they are not adequately paid. Agricultural labourers are considered impoverished. Their daily minimum salary for working under severe conditions is Rs-60, far less than the mandated minimum wage. A large population is to blame for this. The hamlet of Palampur has more labourers but less job prospects. The intense rivalry among labourers for a single position drives down pay. As a result, farm labourers in Palampur village are willing to work for cheap rates.
3. What are the important topics discussed in Chapter 1 of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics?
Following are the important topics discussed in Chapter 1 of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics:
Organisation of production
Fixed capital and working capital
Factors of production
The types of farming in Palampur
Non-farming activities in Palampur
Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 9 include answers to every question of the Class 9 NCERT Economics book in an easy way. These solutions will help the students to write answers in exams in an efficient manner.
4. Where can I get the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 PDF online?
By clicking on the download link, you can get the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 PDF for free from Vedantu's official website. The solutions are written by subject-matter specialists who construct the answers to achieve high exam scores. The solutions efficiently explain every topic of the Class 9 Economics syllabus so that students may readily comprehend them.
5. What is Economics according to class 9?
In CBSE Class 9, Economics is a branch of Social Science that is the fundamental step to understand how an economy functions. It is essential to refer to reliable study resources for your understanding and exam preparation. Vedantu’s NCERT Class 9 Economics Solutions are prepared by subject experts who follow the CBSE curriculum and provide every answer to the questions in the NCERT Economics book in a simple way.
6. What type of village is Palampur?
Palampur is a made-up town where farming is the primary source of revenue. The town is involved in activities such as dairy and transportation. The story emphasises fundamental agricultural and production concepts including crop production, capital, work, creation, and transportation. These concepts are presented properly in Vedantu's NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 so that students may understand them. Students may also access the resources using Vedantu's app. All resources are free to use.
7. What is the area of Palampur?
The total area of Palampur is 226 hectares. The hypothetical village is located in the Bulandshahar district of Uttar Pradesh. This chapter explains the different economic aspects of farming that provide the majority of occupation for people in India. You need to prefer reliable resources to study the chapter. Vedantu’s NCERT Class 9 Economics Solutions explain every concept comprehensively and efficiently for students to understand.
8. What is the theme of the story of village Palampur?
The theme of the story of village Palampur revolves around understanding the basics of production and economic activities in a rural Indian setting. It introduces concepts like:
Farming and crop cultivation
Land and labor
Capital and infrastructure
Production process
Market and exchange
9. What are the five features of village Palampur?
The five features of Village Palampur are:
Agriculture-based economy: Farming is the primary occupation in Palampur, with a majority of the population involved in cultivating crops and raising livestock.
Diverse occupations: While farming is dominant, other activities like dairy, small-scale manufacturing, and transport contribute to the village economy.
Social diversity: The story mentions Palampur has around 450 families belonging to different castes and creeds, reflecting a mix of social groups.
Developing infrastructure: The village has basic infrastructure like electricity, transportation (roads, bullock carts, tractors), a primary health center, and schools.
Market connectivity: Palampur is connected to nearby towns, suggesting it participates in buying and selling goods, essential for any economy.
NCERT Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter wise Solutions
Ncert solutions for class 9 social science, cbse study materials.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science History Chapter 1 The French Revolution
- Last modified on: 10 months ago
- Reading Time: 4 Minutes
[Download] Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science History Chapter 1 The French Revolution
Case Study Question
Question 1:
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows:
The society of estates was part of the feudal system that dated back to the Middle Ages. The term Old Regime is usually used to describe the society and institutions of France before 1789. French society was organised in system of estates. Peasants made up about 90 per cent of the population. However, only a small number of them owned the land they cultivated. About 60 per cent of the land was owned by nobles, the Church and other richer members of the third estate. The members of the first two estates, that is, the clergy and the nobility, enjoyed certain privileges by birth. The most important of these was exemption from paying taxes to the state. The nobles further enjoyed feudal privileges. These included feudal dues, which they extracted from the peasants. Peasants were obliged to render services to the lord – to work in his house and fields – to serve in the army or to participate in building roads.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option:
(i) The term Old Regime describes the Society and Institutions of France before _______ (A) 1879 (B) 1789 (C) 1987 (D) 1798
(ii) What was the ratio of the Peasants? (A) 80% (B) 50% (C) 60% (D) 90%
(iii) About ________percent of the land was owned by nobles, the church and other richer members of the third estate. (A) 50 (B) 80 (C) 60 (D) 70
(iv) The feudal dues were extracted from: (A) Businessmen (B) Peasants (C) Artisans (D) Merchants
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- School Guide
- Class 9 Syllabus
- Maths Notes Class 9
- Science Notes Class 9
- History Notes Class 9
- Geography Notes Class 9
- Political Science Notes Class 9
- NCERT Soln. Class 9 Maths
- RD Sharma Soln. Class 9
- Math Formulas Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Economics Chapter 1 The Story of Village Palampur
- The Story of Village Palampur - CBSE Class 9 Economics
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Economics Chapter 2 : Sectors of the Indian Economy
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Economics Social Science Chapter 2: People as Resource
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 English Moments Chapter 3 Iswaran The Storyteller
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 English Beehive Chapter 1 The Road Not Taken (Poem)
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Economics Chapter 3: Poverty as a Challenge
- NCERT Solution for Supplementary English Class 9 Chapter 9 The Beggar
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Economics Social Science Chapter 1 : Development
- NCERT Notes for Class 9 Science Chapter 12: Improvement in Food Resources
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 History: Chapter 3 – Ruling the Countryside
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Economics Social Science Chapter 2 : Sectors of the Indian Economy
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Economics Chapter 4: Food Security in India
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 History: Chapter 2 – From Trade to Territory: The Company Establishes Power
- NCERT Geography Class-9 Chapter-Wise Solutions
- CBSE Class 8 Geography Chapter-Wise Revision Notes
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 English Beehive Chapter 5 A Legend of the Northland (Poem)
- Globalisation and the Indian Economy : CBSE Class 10 Economics Notes Chapter 4
NCERT Revision Notes Class-9 Economics Chapter-1: The Story of Village Palampur
NCERT Notes Class 9 Economics: Chapter 1: The Story of Village Palampur: The Story of Village Palampur is a chapter from NCERT Class 9 Economics. It is a fictional story about a village called Palampur and its inhabitants. The story is used to introduce students to the basic concepts of economics, such as production, distribution, and consumption. The story begins by describing the village of Palampur and its people. Palampur is a small village with about 450 families. The majority of the people in Palampur are farmers. The story then goes on to describe the different types of production that take place in Palampur.
Table of Content
Organization of Production
Farming in palampur, non-farm activities in palampur.
The story introduces production concepts through a hypothetical village called Palampur, where farming is the main activity. Other activities include small-scale manufacturing, dairy, and transport. The story demonstrates how resources combine to produce desired goods and services.
Introduction
Palampur is a well-connected village with 450 families, mostly belonging to the upper-caste families. The village has a well-developed system of roads, transport, electricity, irrigation, schools, and a health center. The village has two primary schools one high school, and a primary health centre run by the government. The story of Palampur focuses on different types of production activities, including farming, small manufacturing, transport, and shop-keeping. The village has a well-developed infrastructure, with electricity powering tubewells in fields and used in various small businesses.
Production aims to produce desired goods and services by meeting four requirements: land, labor, physical capital, and human capital. Land is essential for natural resources like water, forests, and minerals. Labor is necessary for certain activities, including highly educated and manual workers. Physical capital includes tools, machines, and buildings, which can be fixed or used over time. Raw materials and money in hand are used in production, while human capital requires knowledge and enterprise to combine land, labor, and physical capital. Production is organized by combining these factors, known as factors of production.
1. Land is Fixed
Palampur’s main production activity is farming, with 75% of working people relying on it for livelihood. However, since 1960, land area under cultivation has remained fixed, limiting the potential for growth. This has led to some wastelands being converted into cultivable land.
2. Is there a way one can grow more from the same Land?
Palampur, a village in western Uttar Pradesh, is a major agricultural hub, with all land cultivated. Farmers grow jowar, bajra, potato, wheat, and sugarcane during the rainy season, and sell surplus wheat at the Raiganj market. The well-developed irrigation system in Palampur allows for three different crops per year. Electricity arrived early, transforming irrigation systems. Electric-run tubewells were installed by the government, but private tubewells were set up, leading to the entire cultivated area of 200 hectares being irrigated by mid-1970s. Multiple cropping is the most common way to increase production on a given piece of land. Modern farming methods, such as using high-yielding varieties (HYVs) of seeds, have also contributed to higher yields. Farmers in Punjab, Haryana, and Western Uttar Pradesh were the first to try modern farming methods, setting up tubewells for irrigation, using HYV seeds, chemical fertilizers, and pesticides. This led to a significant increase in wheat production and surplus wheat for market sale.
3. Will the Land Sustain?
Modern farming methods have overused natural resources, leading to soil fertility loss and groundwater depletion. Environmental resources like soil and groundwater are built up over years, making it difficult to restore them. Careful use of land is crucial for future agriculture development.
4. How is land distributed between the farmers of Palampur?
Land is crucial for agriculture, but not all farmers have sufficient land. In Palampur, one-third of 450 families are landless, with 150 families, mostly dalits, lacking land. Only 240 families cultivate small plots, not providing adequate income. Over half of the village is covered by large plots, with 60 medium and large farmers cultivating over 2 hectares.
5. Who will provide the Labour?
Farming requires labor, with small farmers cultivating their fields and medium and large farmers hiring farm labourers. Wages vary from region to region, crop to crop, and duration of employment. Dala, a landless farm labourer in Palampur, works on daily wages, despite the government’s minimum wage of Rs 300 per day. He faces heavy competition among workers, leading to lower wages. Dala and Ramkali, both poorer individuals, complain about their situation.
6. The capital needed in Farming
Modern farming methods demand significant capital, causing farmers to borrow from large farmers, village moneylenders, or traders. These loans are often high in interest, causing distress for small farmers. However, medium and large farmers have their own savings, enabling them to secure the necessary capital.
7. Sale of Surplus Farm Products
Farmers produce wheat using three factors: harvest, harvest, and completion. They retain a portion for family consumption and sell surplus wheat. Small farmers have little surplus wheat, while medium and large farmers supply it to the market. Tejpal Singh, a large farmer, has a surplus of 350 quintals and sells it at the Raiganj market. He uses his earnings to lend to other farmers and buy additional equipment. Other large and medium farmers also sell surplus farm products, save some for future capital, and use the savings for non-farm activities.
Palampur’s main production activity is farming, with only 25% of its workforce engaged in non-farm activities.
1. Dairy — the other Common Activity
Palampur families engage in dairy production, feeding buffalos grass and rainy jowar and bajra. Milk is sold in Raiganj village, with traders from Shahpur town setting up cum chilling centers.
2. An example of small-scale manufacturing in Palampur
Palampur’s manufacturing employs less than fifty people, primarily using simple, small-scale methods at home or in fields, with minimal hiring of laborers.
3. The Shopkeepers of Palampur
Palampur’s trade is primarily driven by shopkeepers who buy goods from wholesale markets and sell them in the village. Small general stores sell a variety of items, while some families near bus stands open small shops selling eatables.
4. Transport: a Fast-Developing Sector
The road connecting Palampur to Raiganj features various vehicles including Rickshawallahs, tongawallahs, jeeps, tractor drivers, truck drivers, and traditional bullock carts, with the number of transport service providers increasing in recent years.
Conclusion – NCERT Notes Class 9 Economics: Chapter 1: The Story of Village Palampur
The Story of Village Palampur is a valuable resource for students of Class 9 Economics. The story provides a concrete example of how the concepts of economics are applied in the real world. The story also helps students to understand the importance of agriculture and non-farm activities in the Indian economy. The story begins by describing the village of Palampur and its people. Palampur is a small village with about 450 families. The majority of the people in Palampur are farmers. The story then goes on to describe the different types of production that take place in Palampur. The main type of production in Palampur is agriculture. The farmers in Palampur grow a variety of crops, including rice, wheat, and vegetables. They also raise livestock, such as cows, buffaloes, and goats.
Also Check:
- CBSE Class 10 Notes Economics Chapter 1: Development
- CBSE Notes Class 10 Economics Chapter 3: Money and Credit
FAQs on NCERT Notes Class 9 Economics: Chapter 1: The Story of Village Palampur
What is the main focus of ncert notes class 9 economics chapter 1: the story of village palampur.
The chapter focuses on understanding the economic activities, production, and livelihoods in the fictional village of Palampur.
What are the primary sources of livelihood in Palampur?
Agriculture is the main source of livelihood, supplemented by other activities like dairy, small-scale manufacturing, and services.
How does Palampur illustrate the concept of multiple cropping?
Palampur practices multiple cropping, where farmers grow more than one crop on the same piece of land in a year to maximize productivity and income.
What are the challenges faced by farmers in Palampur?
Farmers in Palampur face challenges like small landholdings, lack of modern technology, inadequate irrigation facilities, and seasonal unemployment.
How is transportation connected to economic activities in Palampur?
Transportation plays a crucial role in linking Palampur to markets, facilitating the movement of goods and people, and supporting economic development.
What role do non-farm activities play in Palampur’s economy?
Non-farm activities like dairy, small-scale industries, and services provide employment diversification and additional income sources in Palampur.
How does the government support agriculture in Palampur?
The government provides support through subsidies, irrigation facilities, rural infrastructure development, and agricultural extension services to improve productivity and livelihoods in Palampur.

Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- School Economics
- Social Science
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions of Chapter 2 Polynomials PDF Download
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 2 Comments
Case study Questions in Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 2 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions Chapter 2 Polynomials
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

These case study questions challenge students to apply their knowledge of polynomials in real-life scenarios, enhancing their problem-solving abilities. This article provides for the Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions of Chapter 2: Polynomials , enabling students to practice and excel in their examinations.
Polynomials Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
Case Study/Passage Based Questions
Ankur and Ranjan start a new business together. The amount invested by both partners together is given by the polynomial p(x) = 4x 2 + 12x + 5, which is the product of their individual shares.
Coefficient of x 2 in the given polynomial is (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 12
Answer: (c) 4
Total amount invested by both, if x = 1000 is (a) 301506 (b)370561 (c) 4012005 (d)490621
Answer: (c) 4012005
The shares of Ankur and Ranjan invested individually are (a) (2x + 1),(2x + 5)(b) (2x + 3),(x + 1) (c) (x + 1),(x + 3) (d) None of these
Answer: (a) (2x + 1),(2x + 5)
Name the polynomial of amounts invested by each partner. (a) Cubic (b) Quadratic (c) Linear (d) None of these
Answer: (c) Linear
Find the value of x, if the total amount invested is equal to 0. (a) –1/2 (b) –5/2 (c) Both (a) and (b) (d) None of these
Answer: (c) Both (a) and (b)
One day, the principal of a particular school visited the classroom. The class teacher was teaching the concept of a polynomial to students. He was very much impressed by her way of teaching. To check, whether the students also understand the concept taught by her or not, he asked various questions to students. Some of them are given below. Answer them
Which one of the following is not a polynomial? (a) 4x 2 + 2x – 1 (b) y+3/y (c) x 3 – 1 (d) y 2 + 5y + 1
Answer: (b) y+3/y
The polynomial of the type ax 2 + bx + c, a = 0 is called (a) Linear polynomial (b) Quadratic polynomial (c) Cubic polynomial (d) Biquadratic polynomial
Answer: (a) Linear polynomial
The value of k, if (x – 1) is a factor of 4x 3 + 3x 2 – 4x + k, is (a) 1 (b) –2 (c) –3 (d) 3
Answer: (c) –3
If x + 2 is the factor of x 3 – 2ax 2 + 16, then value of a is (a) –7 (b) 1 (c) –1 (d) 7
Answer: (b) 1
The number of zeroes of the polynomial x 2 + 4x + 2 is (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4
Answer: (b) 2
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 3. Amit and Rahul are friends who love collecting stamps. They decide to start a stamp collection club and contribute funds to purchase new stamps. They both invest a certain amount of money in the club. Let’s represent Amit’s investment by the polynomial A(x) = 3x^2 + 2x + 1 and Rahul’s investment by the polynomial R(x) = 2x^2 – 5x + 3. The sum of their investments is represented by the polynomial S(x), which is the sum of A(x) and R(x).
Q1. What is the coefficient of x^2 in Amit’s investment polynomial A(x)? (a) 3 (b) 2 (c) 1 (d) 0
Answer: (a) 3
Q2. What is the constant term in Rahul’s investment polynomial R(x)? (a) 2 (b) -5 (c) 3 (d) 0
Answer: (c) 6
Q3. What is the degree of the polynomial S(x), representing the sum of their investments? (a) 4 (b) 3 (c) 2 (d) 1
Answer: (c) 2
Q4. What is the coefficient of x in the polynomial S(x)? (a) 7 (b) -3 (c) 0 (d) 5
Answer: (b) -3
Q5. What is the sum of their investments, represented by the polynomial S(x)? (a) 5x^2 + 7x + 4 (b) 5x^2 – 3x + 4 (c) 5x^2 – 3x + 5 (d) 5x^2 + 7x + 5
Answer: (b) 5x^2 – 3x + 4
Case Study 4. A school is organizing a fundraising event to support a local charity. The students are divided into three groups: Group A, Group B, and Group C. Each group is responsible for collecting donations from different areas of the town.
Group A consists of 30 students and each student is expected to collect ‘x’ amount of money. The polynomial representing the total amount collected by Group A is given as A(x) = 2x^2 + 5x + 10.
Group B consists of 20 students and each student is expected to collect ‘y’ amount of money. The polynomial representing the total amount collected by Group B is given as B(y) = 3y^2 – 4y + 7.
Group C consists of 40 students and each student is expected to collect ‘z’ amount of money. The polynomial representing the total amount collected by Group C is given as C(z) = 4z^2 + 3z – 2.
Q1. What is the coefficient of x in the polynomial A(x)? (a) 2 (b) 5 (c) 10 (d) 0
Answer: (b) 5
Q2. What is the degree of the polynomial B(y)? (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 1
Answer: (b) 3
Q3. What is the constant term in the polynomial C(z)? (a) 4 (b) 3 (c) -2 (d) 0
Answer: (c) -2
Q4. What is the sum of the coefficients of the polynomial A(x)? (a) 2 (b) 5 (c) 10 (d) 17
Answer: (c) 10
Q5. What is the total number of students in all three groups combined? (a) 30 (b) 20 (c) 40 (d) 90
Answer: (c) 40
The Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions of Chapter 2: Polynomials serve as a valuable resource for students seeking to enhance their understanding of polynomial concepts and problem-solving skills. By practicing these case studies, students can strengthen their grasp of polynomials and their applications in real-life scenarios. Embrace the opportunity to engage with practical problems and excel in your mathematical journey.
By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Class 9 science mcq questions for chapter 15 improvement in food resources with answers, class 9 science case study questions chapter 8 motion, class 9 science case study questions chapter 15 improvement in food resources, this post has 2 comments.
I didnt understand last question
The number of zeroes of the polynomial x2 + 4x + 2 is The answer is too easy, i.e. 2
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
5. The prime factorization of 13915 is. a) 5 × 11 3 × 13 2. b) 5 × 11 3 × 23 2. c) 5 × 11 2 × 23. d) 5 × 11 2 × 13 2. Show Answer. Case Study 2: Srikanth has made a project on real numbers, where he finely explained the applicability of exponential laws and divisibility conditions on real numbers. He also included some assessment ...
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers Case Study Questions: Question 1: Himanshu has made a project on real numbers, where he finely explained the applicability of exponential laws and divisibility conditions on real numbers. He also included some assessment questions at the end of his project as listed below. Answer … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 9 ...
CBSE Class 9 Maths Question Bank on Case Studies given in this article can be very helpful in understanding the new format of questions. Each question has five sub-questions, each followed by four options and one correct answer. Students can easily download these questions in PDF format and refer to them for exam preparation. Case Study Questions.
Download Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions to prepare for the upcoming CBSE Class 9 Exams 2023-24. These Case Study and Passage Based questions are published by the experts of CBSE Experts for the students of CBSE Class 9 so that they can score 100% in Exams. Case study questions play a pivotal role in enhancing students' problem-solving skills.
b) Dissolution, combustion, sublimation, and oxidation. c) Fermentation, photosynthesis, respiration, and digestion. d) Oxidation, reduction, precipitation, and ionization. Answer: a) Evaporation, condensation, melting, and freezing. Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 ...
Class 9 Mathematics Case study question 2. Read the Source/Text given below and answer any four questions: Maths teacher draws a straight line AB shown on the blackboard as per the following figure. Now he told Raju to draw another line CD as in the figure. The teacher told Ajay to mark ∠ AOD as 2z.
Introduction of CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths - Pdf in English is available as part of our Class 9 preparation & CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths - Pdf in Hindi for Class 9 courses. Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Case Study Based Questions | NUMBER SYSTEM | CLASS 9 MATHS CHAPTER 1 | NCERT Solutions | Math Infinity. This is a Super Amazing Session with Our Master Teach...
Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 Probability. The above Case studies for Class 9 Mathematics will help you to boost your scores as Case Study questions have been coming in your examinations. These CBSE Class 9 Maths Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of schools.studyrate.in for benefit of Class 10 students.
The class 9 maths NCERT solutions chapter 1 covers the representation of real numbers on a number line, methods to perform operations on real numbers, and laws of exponents when dealing with real numbers. Total Questions: Class 9 maths chapter 1 Number Systems consists of total 35 questions of which 30 are easy, 2 are moderate and 3 are long ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 1 Number System - Free PDF 2024-25. Chapter 1 number system class 9 delves into the principles covered under the topic of the number system. Vedantu offers an expert-curated NCERT answer for CBSE Class 9 Chapter 1. To ace your preparations, get the NCERT solution supplied by our professionals.
Palampur is well-connected with neighbouring villages and towns. Raiganj, a big village, is 3 kms from Palampur. An all-weather road connects the village to Raiganj and further on to the nearest small town of Shahpur. This village has about 450 families belonging to several different castes. The 80 upper caste families own the majority of land ...
Class 9 Social Science Case Study Question 1. Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow: On the morning of 14 July 1789, the city of Paris was in a state of alarm. The king had commanded troops to move into the city. Rumours spread that he would soon order the army to open fire upon the citizens.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks or 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science - Matter in our Surroundings Case Study 1: 1.) A matter is anything that has mass and occupies ...
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings. Here we are providing case study questions for class 9 science chapter 12 sound. Students are suggested to go through each and every case study questions for better understanding of the chapter. Case Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1:
Maths Case-Study Qs. Maths Case-Study Qs. VIEW ALL. TopperLearning offers an online platform to access case studies for CBSE Class 9 students. Explore your analytical and problem-solving skills by solving case studies with our expert guidance. Get started today!
These questions are designed to help students apply their understanding of historical events and concepts to specific case studies or scenarios. The CBSE Class 9 Case Based Questions can be accessed from Chapetrwise Links provided below: Chapter 1: The French Revolution. Case Based Questions: The French Revolution.
Class 9 science case study question 1. Gases are highly compressible as compared to solids and liquids. The liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) cylinder that we get in our home for cooking or the oxygen supplied to hospitals in cylinders is compressed gas. Compressed natural gas (CNG) is used as fuel these days in vehicles.
NCERT Solutions for Economics Class 9 Chapter 1 explores the economic life of a fictional village called Palampur. Class 9 students studying Economics can find answers to exercises in Chapter 1 - The Story of Village Palampur in their NCERT book. These solutions are a great resource for improving writing skills and preparing for school exams.
Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 India - Size and Location Case Study Questions Question 1: Read the following source and answer the questions that follows: India's contacts with the World have continued through ages but her relationships through the land routes are much older than her maritime contacts. The … Continue reading Case Study Questions for ...
[Download] Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science History Chapter 1 The French Revolution Case Study Question Question 1: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follows: The society of estates was part of the feudal system that dated back to the Middle Ages. The term Old Regime is usually used … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science ...
Number System Case Study Questions (CSQ's) Practice Tests. Timed Tests. Select the number of questions for the test: Select the number of questions for the test: TopperLearning provides a complete collection of case studies for CBSE Class 9 Maths Number System chapter. Improve your understanding of biological concepts and develop problem ...
NCERT Notes Class 9 Economics: Chapter 1: The Story of Village Palampur: The Story of Village Palampur is a chapter from NCERT Class 9 Economics. It is a fictional story about a village called Palampur and its inhabitants. The story is used to introduce students to the basic concepts of economics, such as production, distribution, and consumption.
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials. Case Study/Passage Based Questions. Ankur and Ranjan start a new business together. The amount invested by both partners together is given by the polynomial p (x) = 4x 2 + 12x + 5, which is the product of their individual shares.