How to Prepare an Annotated Bibliography: The Annotated Bibliography
- The Annotated Bibliography
- Fair Use of this Guide

Explanation, Process, Directions, and Examples
What is an annotated bibliography.
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations to books, articles, and documents. Each citation is followed by a brief (usually about 150 words) descriptive and evaluative paragraph, the annotation. The purpose of the annotation is to inform the reader of the relevance, accuracy, and quality of the sources cited.
Annotations vs. Abstracts
Abstracts are the purely descriptive summaries often found at the beginning of scholarly journal articles or in periodical indexes. Annotations are descriptive and critical; they may describe the author's point of view, authority, or clarity and appropriateness of expression.
The Process
Creating an annotated bibliography calls for the application of a variety of intellectual skills: concise exposition, succinct analysis, and informed library research.
First, locate and record citations to books, periodicals, and documents that may contain useful information and ideas on your topic. Briefly examine and review the actual items. Then choose those works that provide a variety of perspectives on your topic.
Cite the book, article, or document using the appropriate style.
Write a concise annotation that summarizes the central theme and scope of the book or article. Include one or more sentences that (a) evaluate the authority or background of the author, (b) comment on the intended audience, (c) compare or contrast this work with another you have cited, or (d) explain how this work illuminates your bibliography topic.
Critically Appraising the Book, Article, or Document
For guidance in critically appraising and analyzing the sources for your bibliography, see How to Critically Analyze Information Sources . For information on the author's background and views, ask at the reference desk for help finding appropriate biographical reference materials and book review sources.
Choosing the Correct Citation Style
Check with your instructor to find out which style is preferred for your class. Online citation guides for both the Modern Language Association (MLA) and the American Psychological Association (APA) styles are linked from the Library's Citation Management page .
Sample Annotated Bibliography Entries
The following example uses APA style ( Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 7th edition, 2019) for the journal citation:
Waite, L., Goldschneider, F., & Witsberger, C. (1986). Nonfamily living and the erosion of traditional family orientations among young adults. American Sociological Review, 51 (4), 541-554. The authors, researchers at the Rand Corporation and Brown University, use data from the National Longitudinal Surveys of Young Women and Young Men to test their hypothesis that nonfamily living by young adults alters their attitudes, values, plans, and expectations, moving them away from their belief in traditional sex roles. They find their hypothesis strongly supported in young females, while the effects were fewer in studies of young males. Increasing the time away from parents before marrying increased individualism, self-sufficiency, and changes in attitudes about families. In contrast, an earlier study by Williams cited below shows no significant gender differences in sex role attitudes as a result of nonfamily living.
This example uses MLA style ( MLA Handbook , 9th edition, 2021) for the journal citation. For additional annotation guidance from MLA, see 5.132: Annotated Bibliographies .
Waite, Linda J., et al. "Nonfamily Living and the Erosion of Traditional Family Orientations Among Young Adults." American Sociological Review, vol. 51, no. 4, 1986, pp. 541-554. The authors, researchers at the Rand Corporation and Brown University, use data from the National Longitudinal Surveys of Young Women and Young Men to test their hypothesis that nonfamily living by young adults alters their attitudes, values, plans, and expectations, moving them away from their belief in traditional sex roles. They find their hypothesis strongly supported in young females, while the effects were fewer in studies of young males. Increasing the time away from parents before marrying increased individualism, self-sufficiency, and changes in attitudes about families. In contrast, an earlier study by Williams cited below shows no significant gender differences in sex role attitudes as a result of nonfamily living.
Versión española
Tambíen disponible en español: Cómo Preparar una Bibliografía Anotada
Content Permissions
If you wish to use any or all of the content of this Guide please visit our Research Guides Use Conditions page for details on our Terms of Use and our Creative Commons license.
Reference Help

- Next: Fair Use of this Guide >>
- Last Updated: Sep 29, 2022 11:09 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.cornell.edu/annotatedbibliography
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / Citation Basics / Annotated Bibliography Format & Examples
Annotated Bibliography Format & Examples
A complete guide to the mla & apa annotated bibliography.
If you’ve just received an assignment that requires an MLA or APA annotated bibliography, you may be wondering where to start. This guide will help answer all of your questions and includes step-by-step instructions on how to do an annotated bibliography in MLA style, as well as an APA annotated bibliography. You will also find sample annotated bibliographies, real-life examples, and opportunities to practice what you have learned.
The MLA ( Modern Language Association ) and APA (American Psychological Association) are not associated with this guide. All of the information provided here, however, offers direction for students and researchers who use these citation styles in their work.
The structures and annotated bibliography templates on this page were created by the in-house librarians at EasyBib.com.
If you’re simply looking for an example of an annotated bibliography (both in MLA format and APA format), scroll down toward the bottom of the page. We’ve included links to visuals for those of you who need help with the structure and styling of an annotated bibliography. If you’re looking for a variety of annotated bibliography topics, and you’re truly searching for the answer to, “What is an annotated bibliography?” then continue reading!
Here’s a run-through of everything this page includes:
Table of contents
What is an annotated bibliography, annotations vs. abstract, why include annotations.
- Step 1: Analyze your sources
Step 2: Write the descriptions
- Step 3a: Formatting an MLA style annotated bibliography
- Step 3b: Formatting an APA style annotated bibliography
Annotated Bibliography Templates
Using the easybib annotation tool.
A bibliography is a complete list of the sources that were used to complete a research paper or project.
Depending on the style guide you follow, you may also see this called a Works Cited (also called an MLA bibliography) or Reference List (APA format). Each listed source, or citation , shares information about the author, title, publishing year, and other details that serve to credit the original authors whose work informed your research. These details also help other students and researchers find and read the source materials.
When your research is related to a scholastic assignment, you should always verify your instructor’s requirements for the types and number of sources to include, as well as the style you should adhere to when formatting your paper and bibliography.
An MLA annotated bibliography and an APA format annotated bibliography are bibliographies that include a concise explanation, or annotation , of each listed source. Depending on the assignment, this annotation may be solely descriptive, or analytical.
An abstract and annotation should not be confused; they differ in both their substance as well as their placement in a paper.
Annotations:
- Usually found in bibliographies at the end of a paper
- Are subjective
- Purpose is to summarize and evaluate . It should briefly communicate the work’s main point, but also discuss the background of the author or study, and the strengths/weaknesses of the work.
Abstracts:
- Usually found in journal databases or the beginning of a paper
- Are objective
- Purpose is to summarize . It should provide a short overview of the article and communicate the main points and themes.
If you would like to learn more , this link further explores the difference between an abstract and an annotation.
This resource provides additional information on how to write a bibliography with annotations in other formats. You can also take advantage of the plagiarism checker and bibliography tools that come with EasyBib Plus to help you create your reference lists.
Before you learn how to make an annotated bibliography, you may be wondering why you need to.
Sometimes instructors want you to create and include annotations in your bibliography, either as part of an assignment or as an assignment unto itself. Understanding the purpose of this approach to your reference list can help to ensure that you gain all of the benefits that the annotated bibliography process provides.
As a student, this method will help you develop or hone your research skills, providing you with practice not only in locating sources but also in analyzing and evaluating them for relevance and quality.
Your instructor will gain insight into your research abilities, as well, allowing them to assess your work more thoroughly. If you plan to publish your research, this comprehensive approach to detailing your sources will provide readers and other researchers with a substantial directory of resources to evaluate for their own work.
Whether you’re publishing or submitting your annotated bibliography, make sure your spelling and wording is correct! If you need to brush up on any parts of speech topics, check out our interjection , determiner , and adverb pages!
Step 1: Analyze your sources
Each annotation should be a summarization or analysis of your source. If you have been tasked with writing annotations as part of a research paper or project, begin to create both the citation and notes on the source while you identify and analyze your sources.
Not only will this approach help you to hone your research skills and identify sources that are relevant and useful for your topic, but you will also save time. When done in this manner, both your citations and annotations will be nearly complete before you begin to write the body of your paper.
Analyzing your potential sources requires a two-pronged approach that first evaluates the author, publication, and date, and then examines the content.
When conducting your initial assessment of the source, consider some of the following questions to guide your appraisal:
- What qualifies the author to write on this subject?
- Is the author affiliated with a reputable institution in this field?
- Is the author credentialed or otherwise considered an expert in this field?
- Is this source current?
- Is this the most recent edition?
- Is the publisher reputable?
- Is the journal reputable?
Once your primary evaluation is complete, you will move on the assessing the content itself. Consider some of these elements as you review each source:
- Who is the intended audience?
- Is the author presenting her opinion or interpretation as the truth, or stating facts?
- What supporting evidence does the author provide?
- Did the author perform the research, or curate and present the research of others?
- If the author used the research of others, are the sources the author cites credible?
- Are there errors or omissions of fact?
- Is the author writing objectively and without bias?
Also, consider the value each source provides to you:
- Is the information helpful for your particular assignment?
- Does it help answer your research question(s)?
- Is this source different from your other sources, or does it repeat information you already have?
- Is the source providing you with a different perspective on your topic, or changing your beliefs or thinking about your subject?
To make it easier for you to create your reference page, write your notes in the format you will be using when you construct this part of the assignment (for instance, as short phrases or complete sentences). Once you have identified all of the sources you wish to include, you will merely need to insert what you have already written on the page and write your citation, which is explained in the next section.
Click here for additional information and a supplementary annotated bibliography sample. For an MLA bibliography example (with annotations), check out our visual example of an MLA annotated bibliography .
An annotated bibliography entry may be written either as short phrases or complete sentences. Your instructor will advise you of which approach you are required to take.
Annotations should include either:
- The main points from the source, as well as the topics covered, the approach used, and any findings.
- Or your critical evaluation.
- A standard annotation is approximately one paragraph.
- Take care not to include any unnecessary details, as the goal is to summarize each source as succinctly as possible and, in some cases, evaluate them.
- Your field of study or instructor will determine what format your annotated bibliography will use. In this guide, you’ll find examples of an MLA and an APA annotated bibliography.
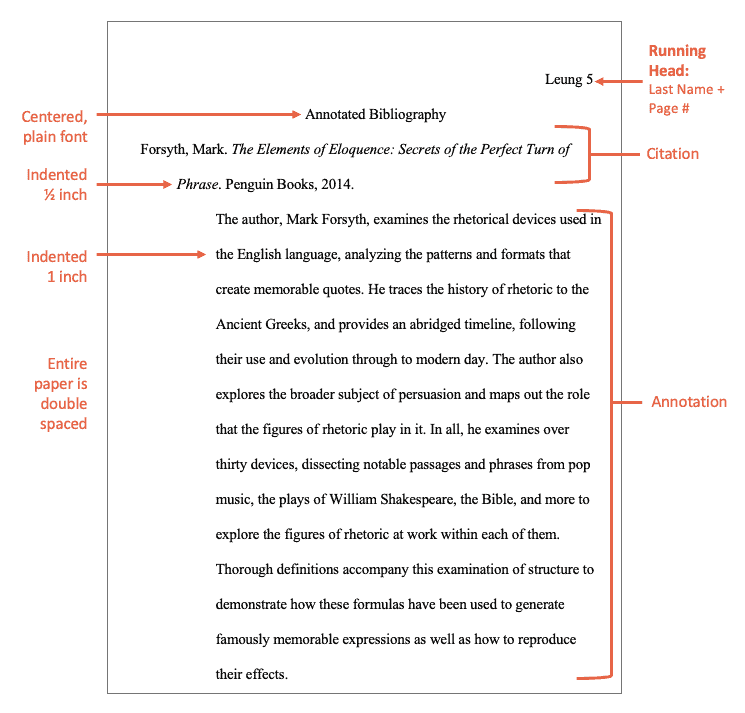
Here is an annotated bibliography example MLA annotation for the book The Elements of Eloquence: Secrets of the Perfect Turn of Phrase by UK author and blogger Mark Forsyth:
The author, Mark Forsyth, examines the rhetorical devices used in the English language, analyzing the patterns and formats that create memorable quotes. He traces the history of rhetoric to the Ancient Greeks, and provides an abridged timeline, following their use and evolution through to modern day. The author also explores the broader subject of persuasion and maps out the role that the figures of rhetoric play in it. In all, he examines over thirty devices, dissecting notable passages and phrases from pop music, the plays of William Shakespeare, the Bible, and more to explore the figures of rhetoric at work within each of them. Thorough definitions accompany this examination of structure to demonstrate how these formulas have been used to generate famously memorable expressions as well as how to reproduce their effects.
Notice how the annotated bibliography MLA entry above is descriptive enough so the reader has an idea of what the source is about with just a single paragraph. For more information on annotations, check out this informative site . If you’re looking to strengthen your writing in general, reading these grammar guides could be a good start.
For guidance on creating entries in MLA format , APA format , and more styles , check out the EasyBib library of resources or try the EasyBib annotation tool—we talk about it below!
Step 3a: MLA annotated bibliography format
The MLA Style Center and the current edition of the MLA Handbook provide the following guidance for formatting an MLA annotated bibliography:
- Title your reference page as “Annotated Bibliography” or “Annotated List of Works Cited.”
- Place each annotation after its reference.
- Annotations should typically not exceed a single paragraph.
- Annotations should be indented one inch from the start of your citation.
- Double-space all text on the page.
- 1-inch margins around the page.
Sources in an annotated bibliography can be organized alphabetically by the first word in each reference (as with a normal Works Cited page), by publication date, or by subject.
For a visual example of an annotated bibliography, as well as specific annotation examples, visit the MLA annotated bibliography guide .
If you are required to share your references in a manner other than in MLA bibliography format, the EasyBib style guides can help you with many common styles. While you’re at it, check out their conjunction , preposition , and pronoun pages to help keep your paper in mint condition!
Step 3b: APA annotated bibliography format
The American Psychological Association states that your instructor should set the guidelines for your annotated bibliography, but asks that the bibliography be formatted according to their standard reference page rules (see Section 9.51 of the Publication Manual ). If your teacher has requested an APA formatted annotated bibliography, first ask them for guidelines. Otherwise, here are some quick rules for you to follow:
- Double space all text on the page.
- Title your page “Annotated Bibliogra phy”. Bold and center the title.
- Organize references alphabetically by the first word of each reference.
- Only the first line of a ref erence is flush with the left margin. Any other lines after the first line should be indented ½ inch from the left.
- Add annotations on the next line after their paired reference.
- Fully indent annotations by a ½ inch from the left.
- Keep annotations short. No more than one paragraph.
For examples of a properly formatted APA annotation, visit this guide on APA annotated bibliographies .
In comparison to the sample annotated bibliography MLA, the APA sample formats its page elements and references differently.

Students and researchers who type their research notes can save time by using an annotated bibliography template in MLA format while reviewing and analyzing sources. By adding the relevant information into a pre-formatted template, you’ll create a resource that helps you when you begin writing your paper in addition to saving time by completing your references and summaries alongside your research.
Students who prefer to take notes by hand can employ a modified version of this approach, with an additional step required to transfer your handwritten and formatted references from your notebook to populate your reference page.
Bibliography Template for MLA
To create an annotated bibliography MLA template, copy the following details into the program in which you will take notes or hand write it on the top margin of a page in your notebook. For each source, use this template to guide you as you identify the necessary details and insert them into your notes:
- Author (Last name, First name).
- Title of source.
- Title of the container ,
- Other contributors (names and roles),
- Publication Date,
- Location of the source (such as URL or page range).
- Summary or Analysis.
The MLA 9 model for MLA works cited entries offers a single format for all source type, and a great deal of flexibility to include the information most relevant to your topic and omit that which isn’t.
Hopefully our visual annotated bibliography example in MLA above has helped. If you still have lingering questions, visit the MLA Style Center online ( linked here ). Also, here’s a guide if you’re looking for more on the related topic of MLA in-text & parenthetical citations .
Bibliography Template for APA
Students and researchers who are still asking themselves how to piece together an annotated bibliography, or still questioning what is an annotated bibliography, could probably benefit from a template, similar to the one above. This one, however, is for those of you who are tasked with creating an annotated bibliography in the style created by the American Psychological Association.
The tricky thing about this specific style though, is that every reference is styled differently. Books, websites, journal articles, newspaper articles, and many others each have their own reference structure.
For most sources though, you should look for the following, basic information:
- Type of source
- Author (last name, first name)
- Title of source/article/web page, etc.
- Title of where source was found (e.g., database name, website name, etc.)
- Other contributors (names and roles)
- Location of the source (such as URL, DOI, or page range)
- Summary or Analysis
We understand it can get tricky, and it’s very different from the Modern Language Association’s structure for references. Take a moment to either use the other handy guides on EasyBib.com or use our automatic generator to form your references in just a few clicks. Our tools help take the pain away from having to rack your brain to form references properly. Capitals, lowercase letters, italics, quotation marks, punctuation in the appropriate places, it can all be quite overwhelming. Do yourself a favor, and use the EasyBib automatic citation generator.
Even though there are a lot of different variations, here’s a commonly used structure for sources:
Author’s Last Name, First initial, Middle initial. (Year the source was published). Title of the source . Retrieved from (insert the website address here)
Underneath the reference, include your summary or analysis paragraph.
Hopefully, this page helped answer all of your “What is an annotated bibliography?” questions. If you’re seeking out an annotated bibliography generator, follow the steps above the annotated bibliography examples.
Looking for additional help with other related topics? Don’t forget about the various beneficial guides on EasyBib.com! Our APA in-text citation guide and our APA parenthetical citation guide are two of our most popular pages. Learn the ins and outs of referencing your work in the body of your paper with our thorough, complete, and reader-friendly guides.
If you are creating a bibliography in MLA format, the EasyBib MLA bibliography generator can help save you time formatting your citations and annotations correctly. You can create entries for websites, books, videos, databases, dictionary articles, and many other types of sources.
In addition to forming the citations, you can also enter your annotation text to produce the complete entry for each source. The process for this is simple. You can follow along below to practice creating one:
- First, select your source type from among the 50+ available options. For this example, we will use the acting career of Keanu Reeves as our research topic and use the movie Point Break from 1991 as our first source. To cite this film, you would select the option for “Film/Online Video.” As you follow along, pick the option that is suitable for your source if you are using a different example.
- Enter the title of your source or, if you are citing a website, you may enter the URL. (Now would be a great time to peek at how to cite websites in MLA ). After you enter the title or URL for your reference, the EasyBib citation tool will scan for titles that match it and provide you with a list of results. Select “Cite this” next to the listing that matches your source.
- You will see a citation form. This gives you the option to add additional relevant or necessary information. For our sample topic, we will specifically cite Keanu Reeves as the performer and Kathryn Bigelow as the director.
- After entering any additional details, you have the option to expand your entry and include an annotation. To do so, select “Add annotation” at the bottom of the page, and a text box will open up.
Then, type your summary or analysis into the text box. If you took notes during the research stage using the format of your paper, this might be as simple as copying and pasting your already written summary or critique. Once you have entered all of the necessary information, select “Create citation” to generate the complete entry. You can then copy and paste this into your MLA bibliography.
Here’s what it’ll look like:
Point Break . Directed by Kathryn Bigelow, performance by Keanu Reeves, 20th Century Fox, 1991.
Reeves’ role as rookie FBI Agent Johnny Utah in Point Break marks the turning point in his Hollywood film career. While he’d risen to fame due to the success of the Bill and Ted franchise, his status today as an action star began when Point Break provided him with the material to establish himself as capable of portraying more than the lovable but unserious characters of his previous starring roles. In a parallel arc, director Kathryn Bigelow’s career also sees a shift beginning with Point Break , establishing her within the traditional action genre as a serious director capable of creating high-action and visually memorable films. While Point Break leaves plenty to be desired in terms of dialogue, it afforded Bigelow and Reeves the opportunities to showcase themselves and their talent in new ways that still echo in their work today.
- Works Cited
Harner, James L. On Compiling an Annotated Bibliography . 2nd ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2000.
MLA Handbook . 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . 7th ed., American Psychological Association, 2020.
“What Guidance Should I Give My Students for Preparing an Annotated Bibliography?” The MLA Style Center , The Modern Language Association, 4 Nov. 2016, style.mla.org/annotated-bibliographies/.
Visit our EasyBib Twitter feed to discover more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
Published October 18, 2015. Updated July 25, 2021.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and is the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
Citation Guides
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- Citation Examples
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Page Numbers
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
- Bibliography
- MLA 8 Updates
- View MLA Guide
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
An annotated bibliography is a list containing complete information of sources, such as journals, books, and reports, cited in the text. In addition, it provides a brief description of each source in about 100–150 words. The annotation can explain the topics covered in the source or evaluate the source. The main objective of giving the annotation is to provide the reader the importance, accuracy, and value of the source.
An example of an annotated bibliography in APA style is given below.
Lim, L. (2014). Ideology, rationality and reproduction in education: A critical discourse analysis. Discourse: Studies in the Cultural Politics of Education, 35 (1), 61–76. https://doi:10.1080/01596306.2012.739467
Lim (2014) focuses on issues of power and ideology dominant in curricular discourses of rationality to study a discourse analysis of the goals of one of the most important curricula in the teaching of thinking. He proves that political and class commitments are reproduced in the forms of thinking that are valued in societies. Through his research, Lim asserts that such curricula engage in making our understanding of what thinking and rationality are. It must facilitate the social reproduction of a specific proportion of the middle class.
If you want to evaluate or provide a description of a source you are citing, you can create an annotated bibliography. Write your annotation in 100–150 words and add it below the source for which you are providing your annotation. Remember, your annotation should provide the reader the importance, accuracy, and value of the source. Below are the guidelines and rules to be followed while writing an annotated bibliography for APA style:
Order your reference entries in alphabetical order, similar to how you would order entries in the reference list.
If you want to add an annotation to an entry, add it as a fresh paragraph below the reference entry. The annotation is indented 0.5 inches from the left margin. However, the first line of the annotation is not indented.
To format the annotated bibliography, follow the recommendations given below:
Set the left, right, top, and bottom margins to 1 inch.
Give double-line spacing.
Title the page “Annotated Bibliography.” Set it in bold.
The title should be aligned to the center of the page.
As you format reference entries, left-align all references in the annotated bibliography section. If any entry runs over more than a line, indent the subsequent lines 0.5 inch from the left margin.
Arrange all reference entries alphabetically according to the surname of the authors.
Provide your annotations below the reference entry for which you want to give your annotation. Indent annotations 0.5 inches from the left margin.
Citation Basics
Harvard Referencing
Plagiarism Basics
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

Annotated Bibliographies
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain why annotated bibliographies are useful for researchers, provide an explanation of what constitutes an annotation, describe various types of annotations and styles for writing them, and offer multiple examples of annotated bibliographies in the MLA, APA, and CBE/CSE styles of citation.
Introduction
Welcome to the wonderful world of annotated bibliographies! You’re probably already familiar with the need to provide bibliographies, reference pages, and works cited lists to credit your sources when you do a research paper. An annotated bibliography includes descriptions and explanations of your listed sources beyond the basic citation information you usually provide.
Why do an annotated bibliography?
One of the reasons behind citing sources and compiling a general bibliography is so that you can prove you have done some valid research to back up your argument and claims. Readers can refer to a citation in your bibliography and then go look up the material themselves. When inspired by your text or your argument, interested researchers can access your resources. They may wish to double check a claim or interpretation you’ve made, or they may simply wish to continue researching according to their interests. But think about it: even though a bibliography provides a list of research sources of all types that includes publishing information, how much does that really tell a researcher or reader about the sources themselves?
An annotated bibliography provides specific information about each source you have used. As a researcher, you have become an expert on your topic: you have the ability to explain the content of your sources, assess their usefulness, and share this information with others who may be less familiar with them. Think of your paper as part of a conversation with people interested in the same things you are; the annotated bibliography allows you to tell readers what to check out, what might be worth checking out in some situations, and what might not be worth spending the time on. It’s kind of like providing a list of good movies for your classmates to watch and then going over the list with them, telling them why this movie is better than that one or why one student in your class might like a particular movie better than another student would. You want to give your audience enough information to understand basically what the movies are about and to make an informed decision about where to spend their money based on their interests.
What does an annotated bibliography do?
A good annotated bibliography:
- encourages you to think critically about the content of the works you are using, their place within a field of study, and their relation to your own research and ideas.
- proves you have read and understand your sources.
- establishes your work as a valid source and you as a competent researcher.
- situates your study and topic in a continuing professional conversation.
- provides a way for others to decide whether a source will be helpful to their research if they read it.
- could help interested researchers determine whether they are interested in a topic by providing background information and an idea of the kind of work going on in a field.
What elements might an annotation include?
- Bibliography according to the appropriate citation style (MLA, APA, CBE/CSE, etc.).
- Explanation of main points and/or purpose of the work—basically, its thesis—which shows among other things that you have read and thoroughly understand the source.
- Verification or critique of the authority or qualifications of the author.
- Comments on the worth, effectiveness, and usefulness of the work in terms of both the topic being researched and/or your own research project.
- The point of view or perspective from which the work was written. For instance, you may note whether the author seemed to have particular biases or was trying to reach a particular audience.
- Relevant links to other work done in the area, like related sources, possibly including a comparison with some of those already on your list. You may want to establish connections to other aspects of the same argument or opposing views.
The first four elements above are usually a necessary part of the annotated bibliography. Points 5 and 6 may involve a little more analysis of the source, but you may include them in other kinds of annotations besides evaluative ones. Depending on the type of annotation you use, which this handout will address in the next section, there may be additional kinds of information that you will need to include.
For more extensive research papers (probably ten pages or more), you often see resource materials grouped into sub-headed sections based on content, but this probably will not be necessary for the kinds of assignments you’ll be working on. For longer papers, ask your instructor about their preferences concerning annotated bibliographies.
Did you know that annotations have categories and styles?
Decisions, decisions.
As you go through this handout, you’ll see that, before you start, you’ll need to make several decisions about your annotations: citation format, type of annotation, and writing style for the annotation.
First of all, you’ll need to decide which kind of citation format is appropriate to the paper and its sources, for instance, MLA or APA. This may influence the format of the annotations and bibliography. Typically, bibliographies should be double-spaced and use normal margins (you may want to check with your instructor, since they may have a different style they want you to follow).
MLA (Modern Language Association)
See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for basic MLA bibliography formatting and rules.
- MLA documentation is generally used for disciplines in the humanities, such as English, languages, film, and cultural studies or other theoretical studies. These annotations are often summary or analytical annotations.
- Title your annotated bibliography “Annotated Bibliography” or “Annotated List of Works Cited.”
- Following MLA format, use a hanging indent for your bibliographic information. This means the first line is not indented and all the other lines are indented four spaces (you may ask your instructor if it’s okay to tab over instead of using four spaces).
- Begin your annotation immediately after the bibliographic information of the source ends; don’t skip a line down unless you have been told to do so by your instructor.
APA (American Psychological Association)
See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for basic APA bibliography formatting and rules.
- Natural and social sciences, such as psychology, nursing, sociology, and social work, use APA documentation. It is also used in economics, business, and criminology. These annotations are often succinct summaries.
- Annotated bibliographies for APA format do not require a special title. Use the usual “References” designation.
- Like MLA, APA uses a hanging indent: the first line is set flush with the left margin, and all other lines are indented four spaces (you may ask your instructor if it’s okay to tab over instead of using four spaces).
- After the bibliographic citation, drop down to the next line to begin the annotation, but don’t skip an extra line.
- The entire annotation is indented an additional two spaces, so that means each of its lines will be six spaces from the margin (if your instructor has said that it’s okay to tab over instead of using the four spaces rule, indent the annotation two more spaces in from that point).
CBE (Council of Biology Editors)/CSE (Council of Science Editors)
See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for basic CBE/CSE bibliography formatting and rules.
- CBE/CSE documentation is used by the plant sciences, zoology, microbiology, and many of the medical sciences.
- Annotated bibliographies for CBE/CSE format do not require a special title. Use the usual “References,” “Cited References,” or “Literature Cited,” and set it flush with the left margin.
- Bibliographies for CSE in general are in a slightly smaller font than the rest of the paper.
- When using the name-year system, as in MLA and APA, the first line of each entry is set flush with the left margin, and all subsequent lines, including the annotation, are indented three or four spaces.
- When using the citation-sequence method, each entry begins two spaces after the number, and every line, including the annotation, will be indented to match the beginning of the entry, or may be slightly further indented, as in the case of journals.
- After the bibliographic citation, drop down to the next line to begin the annotation, but don’t skip an extra line. The entire annotation follows the indentation of the bibliographic entry, whether it’s N-Y or C-S format.
- Annotations in CBE/CSE are generally a smaller font size than the rest of the bibliographic information.
After choosing a documentation format, you’ll choose from a variety of annotation categories presented in the following section. Each type of annotation highlights a particular approach to presenting a source to a reader. For instance, an annotation could provide a summary of the source only, or it could also provide some additional evaluation of that material.
In addition to making choices related to the content of the annotation, you’ll also need to choose a style of writing—for instance, telescopic versus paragraph form. Your writing style isn’t dictated by the content of your annotation. Writing style simply refers to the way you’ve chosen to convey written information. A discussion of writing style follows the section on annotation types.
Types of annotations
As you now know, one annotation does not fit all purposes! There are different kinds of annotations, depending on what might be most important for your reader to learn about a source. Your assignments will usually make it clear which citation format you need to use, but they may not always specify which type of annotation to employ. In that case, you’ll either need to pick your instructor’s brain a little to see what they want or use clue words from the assignment itself to make a decision. For instance, the assignment may tell you that your annotative bibliography should give evidence proving an analytical understanding of the sources you’ve used. The word analytical clues you in to the idea that you must evaluate the sources you’re working with and provide some kind of critique.
Summary annotations
There are two kinds of summarizing annotations, informative and indicative.
Summarizing annotations in general have a couple of defining features:
- They sum up the content of the source, as a book report might.
- They give an overview of the arguments and proofs/evidence addressed in the work and note the resulting conclusion.
- They do not judge the work they are discussing. Leave that to the critical/evaluative annotations.
- When appropriate, they describe the author’s methodology or approach to material. For instance, you might mention if the source is an ethnography or if the author employs a particular kind of theory.
Informative annotation
Informative annotations sometimes read like straight summaries of the source material, but they often spend a little more time summarizing relevant information about the author or the work itself.
Indicative annotation
Indicative annotation is the second type of summary annotation, but it does not attempt to include actual information from the argument itself. Instead, it gives general information about what kinds of questions or issues are addressed by the work. This sometimes includes the use of chapter titles.
Critical/evaluative
Evaluative annotations don’t just summarize. In addition to tackling the points addressed in summary annotations, evaluative annotations:
- evaluate the source or author critically (biases, lack of evidence, objective, etc.).
- show how the work may or may not be useful for a particular field of study or audience.
- explain how researching this material assisted your own project.
Combination
An annotated bibliography may combine elements of all the types. In fact, most of them fall into this category: a little summarizing and describing, a little evaluation.
Writing style
Ok, next! So what does it mean to use different writing styles as opposed to different kinds of content? Content is what belongs in the annotation, and style is the way you write it up. First, choose which content type you need to compose, and then choose the style you’re going to use to write it
This kind of annotated bibliography is a study in succinctness. It uses a minimalist treatment of both information and sentence structure, without sacrificing clarity. Warning: this kind of writing can be harder than you might think.
Don’t skimp on this kind of annotated bibliography. If your instructor has asked for paragraph form, it likely means that you’ll need to include several elements in the annotation, or that they expect a more in-depth description or evaluation, for instance. Make sure to provide a full paragraph of discussion for each work.
As you can see now, bibliographies and annotations are really a series of organized steps. They require meticulous attention, but in the end, you’ve got an entire testimony to all the research and work you’ve done. At the end of this handout you’ll find examples of informative, indicative, evaluative, combination, telescopic, and paragraph annotated bibliography entries in MLA, APA, and CBE formats. Use these examples as your guide to creating an annotated bibliography that makes you look like the expert you are!
MLA Example
APA Example
CBE Example
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
American Psychological Association. 2010. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . 6th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Bell, I. F., and J. Gallup. 1971. A Reference Guide to English, American, and Canadian Literature . Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press.
Bizzell, Patricia, and Bruce Herzburg. 1991. Bedford Bibliography for Teachers of Writing , 3rd ed. Boston: Bedford Books.
Center for Information on Language Teaching, and The English Teaching Information Center of the British Council. 1968. Language-Teaching Bibliography . Cambridge: Cambridge University.
Engle, Michael, Amy Blumenthal, and Tony Cosgrave. 2012. “How to Prepare an Annotated Bibliography.” Olin & Uris Libraries. Cornell University. Last updated September 25, 2012. https://olinuris.library.cornell.edu/content/how-prepare-annotated-bibliography.
Gibaldi, Joseph. 2009. MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers , 7th ed. New York: The Modern Language Association of America.
Huth, Edward. 1994. Scientific Style and Format: The CBE Manual for Authors, Editors, and Publishers . New York: University of Cambridge.
Kilborn, Judith. 2004. “MLA Documentation.” LEO: Literacy Education Online. Last updated March 16, 2004. https://leo.stcloudstate.edu/research/mla.html.
Spatt, Brenda. 1991. Writing from Sources , 3rd ed. New York: St. Martin’s.
University of Kansas. 2018. “Bibliographies.” KU Writing Center. Last updated April 2018. http://writing.ku.edu/bibliographies .
University of Wisconsin-Madison. 2019. “Annotated Bibliography.” The Writing Center. Accessed June 14, 2019. https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/annotatedbibliography/ .
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
An annotated bibliography is a list of cited resources related to a particular topic or arranged thematically that include a brief descriptive or evaluative summary. The annotated bibliography can be arranged chronologically by date of publication or alphabetically by author, with citations to print and/or digital materials, such as, books, newspaper articles, journal articles, dissertations, government documents, pamphlets, web sites, etc., multimedia sources like films and audio recordings, or documents and materials preserved in archival collections.
Beatty, Luke and Cynthia Cochran. Writing the Annotated Bibliography: A Guide for Students and Researchers . New York: Routledge, 2020; Harner, James L. On Compiling an Annotated Bibliography . 2nd edition. New York: Modern Language Association, 2000.
Importance of a Good Annotated Bibliography
In lieu of writing a formal research paper or in preparation for a larger writing project, your professor may ask you to develop an annotated bibliography. An annotated bibliography may be assigned for a number of reasons, including :
- To show that you can identify and evaluate the literature underpinning a research problem;
- To demonstrate that you can identify and conduct an effective and thorough review of pertinent literature;
- To develop skills in discerning the most relevant research studies from those which have only superficial relevance to your topic;
- To explore how different types of sources contribute to understanding the research problem;
- To be thoroughly engaged with individual sources in order to strengthen your analytical skills; or,
- To share sources among your classmates so that, collectively, everyone in the class obtains a comprehensive understanding of research about a particular topic.
On a broader level, writing an annotated bibliography can lay the foundation for conducting a larger research project. It serves as a method to evaluate what research has been conducted and where your proposed study may fit within it. By critically analyzing and synthesizing the contents of a variety of sources, you can begin to evaluate what the key issues are in relation to the research problem and, by so doing, gain a better perspective about the deliberations taking place among scholars. As a result of this analysis, you are better prepared to develop your own point of view and contributions to the literature.
In summary, creating a good annotated bibliography...
- Encourages you to think critically about the content of the works you are using, their place within the broader field of study, and their relation to your own research, assumptions, and ideas;
- Gives you practical experience conducting a thorough review of the literature concerning a research problem;
- Provides evidence that you have read and understood your sources;
- Establishes validity for the research you have done and of you as a researcher;
- Gives you the opportunity to consider and include key digital, multimedia, or archival materials among your review of the literature;
- Situates your study and underlying research problem in a continuing conversation among scholars;
- Provides an opportunity for others to determine whether a source will be helpful for their research; and,
- Could help researchers determine whether they are interested in a topic by providing background information and an idea of the kind of scholarly investigations that have been conducted in a particular area of study.
In summary, writing an annotated bibliography helps you develop skills related to critically reading and identifying the key points of a research study and to effectively synthesize the content in a way that helps the reader determine its validity and usefulness in relation to the research problem or topic of investigation.
NOTE: Do not confuse annotating source materials in the social sciences with annotating source materials in the arts and humanities. Rather than encompassing forms of synopsis and critical analysis, an annotation assignment in arts and humanities courses refers to the systematic interpretation of literary texts, art works, musical scores, performances, and other forms of creative human communication for the purpose of clarifying and encouraging analytical thinking about what the author(s)/creator(s) have written or created. They are assigned to encourage students to actively engage with the text or creative object.
Annotated Bibliographies. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Annotated Bibliographies. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Annotated Bibliography. The Waldin Writing Center. Waldin University; Hartley, James. Academic Writing and Publishing: A Practical Guide . (New York: Routledge, 2008), p. 127-128; Writing an Annotated Bibliography. Assignment Structures and Samples Research and Learning Online, Monash University; Kalir, Remi H. and Antero Garcia. Annotation . Essential Knowledge Series. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2021.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Types
- Descriptive : This annotation describes the source without summarizing the actual argument, hypothesis, or message in the content. Like an abstract , it describes what the source addresses, what issues are being investigated, and any special features, such as appendices or bibliographies, that are used to supplement the main text. What it does not include is any evaluation or criticism of the content. This type of annotation seeks to answer the question: Does this source cover or address the topic I am researching? Collectively, this type of annotated bibliography synthesizes prior research about a topic or serves as a review of the literature before conducting a broader research study.
- Informative/Summative : This type of annotation summarizes what the content, message, or argument of the source is. It generally contains the hypothesis, methodology, and conclusion or findings, but like the descriptive type, you are not offering your own evaluative comments about such content. This type of annotation seeks to answer these types of questions: What are the author's main arguments? What are the key findings? What conclusions or recommended actions did the author state? Collectively, this type of annotated bibliography summarizes the way in which scholars have studied and documented outcomes about a topic.
- Evaluative/Critical/Analytical : This annotation includes your own evaluative statements about the content of a source. It is the most common type of annotation your professor will ask you to write. Your critique may focus on describing a study's strengths and weaknesses or it may describe the applicability of the conclusions to the research problem you are studying. This type of annotation seeks to answer these types of questions: Is the reasoning sound? Is the methodology sound? Does this source address all the relevant issues? How does this source compare to other sources on this topic? Collectively, this type of annotated bibliography offers a detailed analysis and critical assessment of the research literature about a topic.
NOTE: There are a variety of strategies you can use to critically evaluate a source based on its content, purpose, and format. A description of these strategies can be found here .
II. Choosing Sources for Your Bibliography
There are two good strategies to begin identifying possible sources for your bibliography--one that looks back into the literature and one that projects forward based on tracking sources cited by researchers.
- The first strategy is to identify several recently published [within the past few years] scholarly books using the USC Libraries catalog or journal articles found by searching a comprehensive, multidisciplinary database like ProQuest Multiple . Review the list of references to sources cited by the author(s). Review these citations to identify prior research published about your topic. For a complete list of scholarly databases GO HERE .
- The second strategy is to identify one or more books, book chapters, journal articles, or research reports on your topic and paste the title of the item into Google Scholar [e.g., from Negotiation Journal , entering the title of the article, " Civic Fusion: Moving from Certainty through Not Knowing to Curiosity " ]. If it is a short title or it uses a lot of common words, place quotation marks around the title so Google Scholar searches the source as a phrase rather than a combination of individual words. Below the citation may be a "Cited by" reference link followed by a number [e.g., Cited by 45]. This number refers to the number of times a source has subsequently been cited by other authors in other sources after the item you found was published.
Your method for selecting which sources to annotate depends on the purpose of the assignment and the research problem you are investigating . For example, if the course is on international social movements and the research problem you choose to study is to compare cultural factors that led to protests in Egypt with the factors that led to protests against the government of the Philippines in the 1980's, you should consider including non-U.S., historical, and, if possible, foreign language sources in your bibliography.
NOTE: Appropriate sources to include can be anything that you believe has value in understanding the research problem . Be creative in thinking about possible sources, including non-textual items, such as, films, maps, photographs, and audio recordings, or archival documents and primary source materials, such as, diaries, government documents, collections of personal correspondence, meeting minutes, or official memorandums. If you want to include these types of sources in your annotated bibliography, consult with a librarian if you're not sure where to locate them.
III. Strategies to Define the Scope of Your Bibliography
It is important that the scope of sources cited and summarized in your bibliography are well-defined and sufficiently narrow in coverage to ensure that you're not overwhelmed by the number of potential items to consider including. Many of the general strategies used to narrow a topic for a research paper are the same that be applied to framing the scope of sources to include in an annotated bibliography.
- Aspect -- choose one lens through which to view the research problem, or look at just one facet of your topic [e.g., rather than annotating a bibliography of sources about the role of food in religious rituals, create a bibliography on the role of food in Hindu ceremonies].
- Time -- the shorter the time period to be covered, the more narrow the focus [e.g., rather than political scandals of the 20th century, cite literature on political scandals during the 1980s].
- Comparative -- a list of resources that focus on comparing two or more issues related to the broader research topic can be used to narrow the scope of your bibliography [e.g., rather than college student activism during the 20th century, cite literature that compares student activism in the 1930s and the 1960s]
- Geography -- the smaller the area of analysis, the fewer items there are to consider including in your bibliography [e.g., rather than cite sources about trade relations in West Africa, include only sources that examine, as a case study, trade relations between Niger and Cameroon].
- Type -- focus your bibliography on a specific type or class of people, places, or things [e.g., rather than health care provision in Japan, cite research on health care provided to the elderly in Japan].
- Source -- your bibliography includes specific types of materials [e.g., only books, only scholarly journal articles, only films, only archival materials, etc.]. However, be sure to describe why only one type of source is appropriate.
- Combination -- use two or more of the above strategies to focus your bibliography very narrowly or to broaden coverage of a very specific research problem [e.g., cite literature only about political scandals during the 1980s that took place in Great Britain].
IV. Assessing the Relevance and Value of Sources All the items included in your bibliography should reflect the source's contribution to understanding the research problem . In order to determine how you will use the source or define its contribution, you will need to critically evaluate the quality of the central argument within the source or, in the case of including non-textual items, determine how the source contributes to understanding the research problem [e.g., if the bibliography lists sources about outreach strategies to homeless populations, a non-textual source would be a film that profiles the life of a homeless person]. Specific elements to assess a research study include an item’s overall value in relation to other sources on the topic, its limitations, its effectiveness in defining the research problem, the methodology used, the quality of the evidence, and the strength of the author’s conclusions and/or recommendations. With this in mind, determining whether a source should be included in your bibliography depends on how you think about and answer the following questions related to its content:
- Are you interested in the way the author(s) frame the research questions or in the way the author goes about investigating the questions [the method]?
- Does the research findings make new connections or promote new ways of understanding the problem?
- Are you interested in the way the author(s) use a theoretical framework or a key concept?
- Does the source refer to and analyze a particular body of evidence that you want to highlight?
- How are the author's conclusions relevant to your overall investigation of the topic?
V. Format and Content
The format of an annotated bibliography can differ depending on its purpose and the nature of the assignment. Contents may be listed alphabetically by author, arranged chronologically by publication date, or arranged under headings that list different types of sources [i.e., books, articles, government documents, research reports, etc.]. If the bibliography includes a lot of sources, items may also be subdivided thematically, by time periods of coverage or publication, or by source type. If you are unsure, ask your professor for specific guidelines in terms of length, focus, and the type of annotation you are to write. Note that most professors assign annotated bibliographies that only need to be arranged alphabetically by author.
Introduction Your bibliography should include an introduction that describes the research problem or topic being covered, including any limits placed on items to be included [e.g., only material published in the last ten years], explains the method used to identify possible sources [such as databases you searched or methods used to identify sources], the rationale for selecting the sources, and, if appropriate, an explanation stating why specific types of some sources were deliberately excluded. The introduction's length depends, in general, on the complexity of the topic and the variety of sources included.
Citation This first part of your entry contains the bibliographic information written in a standard documentation style , such as, MLA, Chicago, or APA. Ask your professor what style is most appropriate, and be consistent! If your professor does not have a preferred citation style, choose the type you are most familiar with or that is used predominantly within your major or area of study.
Annotation The second part of your entry should summarize, in paragraph form, the content of the source. What you say about the source is dictated by the type of annotation you are asked to write [see above]. In most cases, however, your annotation should describe the content and provide critical commentary that evaluates the source and its relationship to the topic.
In general, the annotation should include one to three sentences about the item in the following order : (1) an introduction of the item; (2) a brief description of what the study was intended to achieve and the research methods used to gather information; ( 3) the scope of study [i.e., limits and boundaries of the research related to sample size, area of concern, targeted groups examined, or extent of focus on the problem]; (4) a statement about the study's usefulness in relation to your research and the topic; (5) a note concerning any limitations found in the study; (6) a summary of any recommendations or further research offered by the author(s); and, (7) a critical statement that elucidates how the source clarifies your topic or pertains to the research problem.
Things to think critically about when writing the annotation include:
- Does the source offer a good introduction on the issue?
- Does the source effectively address the issue?
- Would novices find the work accessible or is it intended for an audience already familiar with the topic?
- What limitations does the source have [reading level, timeliness, reliability, etc.]?
- Are any special features, such as, appendices or non-textual elements effectively presented?
- What is your overall reaction to the source?
- If it's a website or online resource, is it up-to-date, well-organized, and easy to read, use, and navigate?
Length An annotation can vary in length from a few sentences to more than a page, single-spaced. However, they are normally about 300 words--the length of a standard paragraph. The length also depends on the purpose of the annotated bibliography [critical assessments are generally lengthier than descriptive annotations] and the type of source [e.g., books generally require a more detailed annotation than a magazine article]. If you are just writing summaries of your sources, the annotations may not be very long. However, if you are writing an extensive analysis of each source, you'll need to devote more space.
Annotated Bibliographies. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Annotated Bibliographies. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Annotated Bibliography. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Annotated Bibliography. Writing Center. Walden University; Annotated Bibliography. Writing Skills, Student Support and Development, University of New South Wales; Engle, Michael et al. How to Prepare an Annotated Bibliography. Olin Reference, Research and Learning Services. Cornell University Library; Guidelines for Preparing an Annotated Bibliography. Writing Center at Campus Library. University of Washington, Bothell; Harner, James L. On Compiling an Annotated Bibliography . 2nd edition. New York: Modern Language Association, 2000; How to Write an Annotated Bibliography. Information and Library Services. University of Maryland; Knott, Deborah. Writing an Annotated Bibliography. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Norton, Donna. Top 32 Effective Tips for Writing an Annotated Bibliography Top-notch study tips for A+ students blog; Writing from Sources: Writing an Annotated Bibliography. The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 9:45 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

Annotated Bibliography: How to Write...: Home
Phase 1: Understanding Your Needs
so, what is an annotation.
An annotation is more than just a brief summary of an article, book, Web site or other type of publication. An annotation should give enough information to make a reader decide whether to read the complete work. In other words, if the reader were exploring the same topic as you, is this material useful and if so, why?
How is an annotation different from an abstract?
While an abstract also summarizes an article, book, Web site or other type of publication, it is purely descriptive. Although annotations can be descriptive, they also include distinctive features about an item. Annotations can be evaluative and critical as we will see when we look at the two major types of annotations.
What is an annotated bibliography?
An annotated bibliography is an organized list of sources (like a reference list). It differs from a straightforward bibliography in that each reference is followed by a paragraph length annotation, usually 100–200 words in length.
Depending on the assignment, an annotated bibliography might have different purposes:
- Provide a literature review on a particular subject
- Help to formulate a thesis on a subject
- Demonstrate the research you have performed on a particular subject
- Provide examples of major sources of information available on a topic
- Describe items that other researchers may find of interest on a topic
Types of annotated bibliographies
There are two major types of annotated bibliographies:
- Descriptive or informative (see below)
- Analytical or critical (see below)
Phase 2: Getting Started
what's next.
Now that you have reviewed the information for Phase 1, you are ready to begin writing your own annotated bibliography.
- Choose your sources. Before writing your annotated bibliography, you must choose your sources. This involves doing research much like for any other project. Locate records to materials that may apply to your topic.
- Review the items. Then review the actual items and choose those that provide a wide variety of perspectives on your topic. Article abstracts are helpful in this process.
- Write the citation and annotation. When writing your annotation, the complete citation should always come first and the annotation follows. Depending on the type of annotated bibliography you are writing, you will want to include:
- The purpose of the work
- A summary of its content
- For what type of audience the work is written
- Its relevance to the topic
- Any special or unique features about the material
- The strengths, weaknesses or biases in the material
Annotated bibliographies may be arranged alphabetically or chronologically, check with your instructor to see what he or she prefers.
Guidelines for formatting the citations
Remember, the citations themselves must be formatted properly. Visit the Help Guides that Marshall University have prepared for you to help with your citation formatting:
- APA 7 Quick Guide (PDF)
- MLA 8 Quick Guide (PDF)
- Turabian Quick Guide (PDF)
- MU Libraries Citation Help (web)
Remember to check with your instructor if you are unsure which style to use.
The Two Types of Annotated Bibliographies
A descriptive or informative annotated bibliography describes or summarizes a source, similar to an abstract; it describes why the source is useful for researching a particular topic or question; and, it lists the article's distinctive features. In addition, it describes the author's main arguments and conclusions without evaluating what the author says or concludes.
For example:
Breeding evil. (2005, August 6). Economist , 376(8438), 9. Retrieved from http://www.economist.com
This editorial from the Economist describes the controversy surrounding video games and the effect they have on people who use them. The author points out that skepticism of new media have gone back to the time of the ancient Greeks, so this controversy surrounding video games is nothing new. The article also points out that most critics of gaming are people over 40 and it is an issue of generations not understanding one another, rather than of the games themselves. As the youth of today grow older, the controversy will die out, according to the author. The author of this article stresses the age factor over violence as the real reason for opposition to video games and stresses the good that gaming has done in most areas of human life. This article is distinctive in exploring the controversy surrounding video games from a generational standpoint and is written for a general audience.
Please pay attention to the last sentence . While it points out distinctive features about the item, it does not analyze the author's conclusions.
An analytical or critical annotation not only summarizes the material, it also analyzes what is being said. It examines the strengths and weaknesses of what is presented as well as describing the applicability of the author's conclusions to the research being conducted.
It is likely that, for most of your annotated bibliographies, you will be writing analytical or critical annotations.
This editorial from the Economist describes the controversy surrounding video games and the effect they have on people who use them. The article points out that most critics of gaming are people over 40 and it is an issue of age not of the games themselves. While the author briefly mentions studies done around the issue of violence and gaming, he does not go into enough depth for the reader to truly know the range of studies that have actually been done in this area, other than to take his word that the research is unsatisfactory. The author of this article stresses the age factor over violence as the real reason for opposition to video games and stresses the good gaming has done in most areas of human life. This article is a good resource for those wanting to begin to explore the controversy surrounding video games, however for anyone doing serious research, one should actually examine some of the research studies that have been done in this area rather than simply take the author's word that opposition to video games is simply due to an issue of generational divide.
Please pay attention to the last sentence . It criticizes the author's research.
Please note that in these samples, the citations follow the APA format. Your instructor may require you to use another citation format, such as MLA, so always check the assignment requirements first.
Visit our Ask a Librarian page to view all the ways you can ask a subject expert for help!
The content on this page was found online here , and used with permission from University of Maryland University College librarians.
- Last Updated: Sep 16, 2022 11:05 AM
- URL: https://libguides.marshall.edu/annotated-bib
How to Write an Annotated Bibliography - MLA Style
What is an annotation, how is an annotation different from an abstract, what is an annotated bibliography, types of annotated bibliographies, descriptive or informative, analytical or critical, to get started.
An annotation is more than just a brief summary of an article, book, website, or other type of publication. An annotation should give enough information to make a reader decide whether to read the complete work. In other words, if the reader were exploring the same topic as you, is this material useful and if so, why?
While an abstract also summarizes an article, book, website, or other type of publication, it is purely descriptive. Although annotations can be descriptive, they also include distinctive features about an item. Annotations can be evaluative and critical and the two major types of annotations included here demonstrate the difference.
An annotated bibliography is an organized list of sources (like a reference list). It differs from a straightforward bibliography in that each reference is followed by a paragraph length annotation, usually 100–200 words in length.
Depending on the assignment, an annotated bibliography might have different purposes:
- Provide a literature review on a particular subject
- Help to formulate a thesis on a subject
- Demonstrate the research you have performed on a particular subject
- Provide examples of major sources of information available on a topic
- Describe items that other researchers may find of interest on a topic
There are two major types of annotated bibliographies:
A descriptive or informative annotated bibliography describes or summarizes a source as does an abstract; it describes why the source is useful for researching a particular topic or question and its distinctive features. In addition, it describes the author's main arguments and conclusions without evaluating what the author says or concludes.
For example:
Gabbin, Joanne V. "Maya Angelou--The Peoples' Poet Laureate: An Introduction." Langston Hughes Review , vol. 19, Spring 2005, pp. 3-6. LION: Literature Online , gateway.proquest.com/openurl?ctx_ver=Z39.88-2003&xri:pqil:res_ver=0.2&res_id=xri:lion&rft_id=xri:lion:ft:criticism:R04012678:0&rft.accountid=14580. This scholarly article is a critical introduction to the works of Maya Angelou, and the criteria surrounding her success as a poet laureate. The author points out Angelou's literary influences, which include William Shakespeare, Edgar Allan Poe, Douglas Johnson, Langston Hughes, among others. This article also points out that her poetry lacks cultural boundaries, yet her trademark lies in the secular chants, songs, and games of the black vernacular tradition. The author discusses dialect and vernacular rhythms in several of Angelou's poems, and compares several of her works to the racy dialect of Sterling Brown and Langston Hughes. Also discussed is her political cultural voice and her deep understanding of emotion. This article is distinctive in its discussion of the need for a poet laureate to add to an audience's collective memory.
Please pay attention to the last sentence. While it points out distinctive features about the item it does not analyze the author's conclusions.
An analytical or critical annotation not only summarizes the material, it analyzes what is being said. It examines the strengths and weaknesses of what is presented as well as describing the applicability of the author's conclusions to the research being conducted.
Analytical or critical annotations will most likely be required when writing for a college-level course.
Gabbin, Joanne V. "Maya Angelou--The Peoples' Poet Laureate: An Introduction." Langston Hughes Review , vol. 19, Spring 2005, pp. 3-6. LION: Literature Online , gateway.proquest.com/openurl?ctx_ver=Z39.88-2003&xri:pqil:res_ver=0.2&res_id=xri:lion&rft_id=xri:lion:ft:criticism:R04012678:0&rft.accountid=14580. This scholarly article is a critical introduction to the works of Maya Angelou, and the criteria surrounding her success as a poet laureate. The author points out Angelou's literary influences, that include William Shakespeare, Edgar Allan Poe, Douglas Johnson, Langston Hughes, among others. This article also points out that her poetry lacks cultural boundaries, yet her trademark lies in the secular chants, songs, and games of the black vernacular tradition. The author discusses dialect and vernacular rhythms in several of Angelou's poems, and compares several of her works to the racy dialect of Sterling Brown and Langston Hughes. Also discussed is her political cultural voice and her deep understanding of emotion. This article is a good resource for those wanting to explore criteria related to the achievement of the award of poet laureate and how Angelou meets the criteria. This article begins to explore the poet's works and suggests her ability to add to an audience's collective memory. The author is a professor of English at James Madison University and has authored a book on Sterling Brown and numerous critical essays.
Please pay attention to the last three sentences. They give information about the author and critique the author's research.
To write an annotated bibliography here are the steps:
- Choose your sources - Before writing your annotated bibliography, you must choose your sources. This involves doing research much like for any other project. Locate records to materials that may apply to your topic.
- Review the items - Then review the actual items and choose those that provide a wide variety of perspectives on your topic. Article abstracts are helpful in this process.
- The purpose of the work
- A summary of its content
- Information about the author(s)
- For what type of audience the work is written
- Its relevance to the topic
- Any special or unique features about the material
- Research methodology
- The strengths, weaknesses or biases in the material
Annotated bibliographies are arranged alphabetically by the first author's last name.
Please see the MLA Examples Page for more information on citing in MLA style.
- Last Updated: Aug 8, 2023 1:53 PM
- URL: https://libguides.umgc.edu/annotated-bibliography-mla
Annotated Bibliography
An annotated bibliography is an organized list of sources, each of which is followed by a brief note or “annotation.”
These annotations do one or more of the following:
- describe the content and focus of the book or article
- suggest the source’s usefulness to your research
- evaluate its method, conclusions, or reliability
- record your reactions to the source.
How do I format the bibliographic citations?
Check with your instructor to determine which documentation style is required for your class: APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, CBE, Numbered References, APSA, etc.
Then, remember that the bibliography is an organized list of sources used. The annotation may immediately follow the bibliographic information on the same line, or it may begin on a new line, two lines below the publication information.
But, since style manuals differ, check with your instructor about which one to use concerning form, spacing, and consistency.
If you are using APA documentation, the Writing Center offers a short workshop called “APA Documentation”.
What goes into the content of the annotations?
Below are some of the most common forms of annotated bibliographies. Click on the links to see examples of each.
This form of annotation defines the scope of the source, lists the significant topics included, and tells what the source is about.
This type is different from the informative entry in that the informative entry gives actual information about its source.
In the indicative entry there is no attempt to give actual data such as hypotheses, proofs, etc. Generally, only topics or chapter titles are included.
Indicative (descriptive–tell us what is included in the source) Griffin, C. Williams, ed. (1982). Teaching writing in all disciplines. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. Ten essays on writing-across-the-curriculum programs, teaching writing in disciplines other than English, and teaching techniques for using writing as learning. Essays include Toby Fulwiler, “Writing: An Act of Cognition”; Barbara King, “Using Writing in the Mathematics Class: Theory and Pratice”; Dean Drenk, “Teaching Finance Through Writing”; Elaine P. Maimon, “Writing Across the Curriculum: Past, Present, and Future.” (Bizzell and Herzberg, 1991, p. 47)
Informative
Simply put, this form of annotation is a summary of the source.
To write it, begin by writing the thesis; then develop it with the argument or hypothesis, list the proofs, and state the conclusion.
Informative (summary–tell us what the main findings or arguments are in the source) Voeltz, L.M. (1980). Children’s attitudes toward handicapped peers. American Journal of Mental Deficiency, 84, 455-464. As services for severely handicapped children become increasingly available within neighborhood public schools, children’s attitudes toward handicapped peers in integrated settings warrant attention. Factor analysis of attitude survey responses of 2,392 children revealed four factors underlying attitudes toward handicapped peers: social-contact willingness, deviance consequation, and two actual contact dimensions. Upper elementary-age children, girls, and children in schools with most contact with severely handicapped peers expressed the most accepting attitudes. Results of this study suggest the modifiability of children’s attitudes and the need to develop interventions to facilitate social acceptance of individual differences in integrated school settings. (Sternlicht and Windholz, 1984, p. 79)
In this form of annotation you need to assess the source’s strengths and weaknesses.
You get to say why the source is interesting or helpful to you, or why it is not. In doing this you should list what kind of and how much information is given; in short, evaluate the source’s usefulness.
Evaluative (tell us what you think of the source) Gurko, Leo. (1968). Ernest Hemingway and the pursuit of heroism. New York: Crowell. This book is part of a series called “Twentieth Century American Writers”: a brief introduction to the man and his work. After fifty pages of straight biography, Gurko discussed Hemingway’s writing, novel by novel. There’s an index and a short bibliography, but no notes. The biographical part is clear and easy to read, but it sounds too much like a summary. (Spatt, 1991, p. 322) Hingley, Ronald. (1950). Chekhov: A biographical and critical study. London: George Allen & Unwin. A very good biography. A unique feature of this book is the appendix, which has a chronological listing of all English translations of Chekhov’s short stories. (Spatt, 1991, p. 411)

Combination
Most annotated bibliographies are of this type.
They contain one or two sentences summarizing or describing content and one or two sentences providing an evaluation.
Combination Morris, Joyce M. (1959). Reading in the primary school: An investigation into standards of reading and their association with primary school characteristics. London: Newnes, for National Foundation for Educational Research. Report of a large-scale investigation into English children’s reading standards, and their relation to conditions such as size of classes, types of organisation and methods of teaching. Based on enquiries in sixty schools in Kent and covering 8,000 children learning to read English as their mother tongue. Notable for thoroughness of research techniques.
Which writing style should I use in the annotations?
The most important thing to understand is that entries should be brief.
Only directly significant details will be mentioned and any information apparent in the title can be omitted from the annotation.
In addition, background materials and references to previous work by the same author usually are not included.
Listed below are three writing styles used in annotated bibliographies. Click on a link to see examples of each.
Telegraphic
(phrases, non-sentences)
Get the information out, quickly and concisely. Be clear, but complete and grammatically correct sentences are unnecessary.
Telegraphic (phrases, non-sentences) Vowles, Richard B. (1962). Psychology and drama: A selected checklist. Wisconsin Studies in Contemporary Literature, 3,(1), 35-48. Divided by individual authors. Reviews the research between 1920 and 1961. (Bell and Gallup, 1971, p. 68)
Complete sentences
In this style you must always use complete sentences.
The length of the sentences varies. Subjects and conjunctions are not eliminated even though the tone may be terse. Avoid long and complex sentences.
Complete sentences Kinter, W. R., and R L. Pfaltzgraff. (1972). Assessing the Moscow SALT agreements. Orbis, 16, 34l-360. The authors hold the conservative view that SALT can not halt the slipping nuclear advantage of the United States. They conclude that the United States needs a national reassessment of defense policy. They further conclude that the only utility of SALT is in developing a dialogue with the Soviets. This is a good conservative critique of SALT I. (Strenski and Manfred, 1981, p. 165)
When using this form of annotation, you must write a full, coherent paragraph.
Sometimes this can be similar to the form of a bibliographic essay. It goes without saying that you need to use complete sentences.
Paragraph (a little more formal) Voeltz, L.M. (1980). Children’s attitudes toward handicapped peers. American Journal of Mental Deficiency, 84, 455-464. As services for severely handicapped children become increasingly available within neighborhood public schools, children’s attitudes toward handicapped peers in integrated settings warrant attention. Factor analysis of attitude survey responses of 2,392 children revealed four factors underlying attitudes toward handicapped peers: social- contact willingness, deviance consequation, and two actual contact dimensions. Upper elementary-age children, girls, and children in schools with most contact with severely handicapped peers expressed the most accepting attitudes. Results of this study suggest the modifiability of children’s attitudes and the need to develop interventions to facilitate social acceptance of individual differences in integrated school settings. (Sternlicht and Windholz, 1984, p. 79)
Additional information
If you have additional questions, ask your course instructor or consider scheduling an appointment with a Writing Center instructor.
The Writing Center also has information on different documentation systems, such as MLA, APA, Chicago/Turabian, CBE, Numbered References, and APSA styles of citation.
If you are using APA documentation, you are in luck! The Writing Center offers a short class called “The Basics of APA Documentation”!
References for examples used
Bell, Inglis F., and Jennifer Gallup. (1971). A reference guide to English, American, and Canadian literature . Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press.
Bizzell, Patricia, and Bruce Herzberg. (1991). Bedford bibliography for teachers of writing . 3rd ed. Boston: Bedford Books of St. Martin’s Press.
Center for Information on Language Teaching and The English Teaching Information Center of the British Council. (1968). A Language-teaching bibliography . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Spatt, Brenda. (1991). Writing from sources . 3rd ed. New York: St. Martin’s Press.
Sternlicht, Manny, and George Windholz. (1984). Social behavior of the mentally retarded. New York and London: Garland Press.
Strenski, Ellen, and Madge Manfred. (1981). The research paper workbook . 2nd ed. New York and London: Longman.

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
- Academic Skills
- Reading, writing and referencing
- Annotated bibliography
Writing an annotated bibliography
How to select resources and write an annotated bibliography.
What is an annotated bibliography?
An annotated bibliography reviews the research published on your problem of study. Unlike a literature review, articles are reviewed separately with a full citation, brief summary of their content and a statement on how or why they apply to your research. It is a list of citations, each followed by a short paragraph, of 150 – 200 words, reviewing each source. Depending on your assignment, in this paragraph you may reflect on, summarise, critique, evaluate or analyse the source.
An annotated bibliography may be a component of a larger assignment or it may be a standalone document.
Why write an annotated bibliography?
Depending on your specific assessment, you may be asked to create an annotated bibliography for the following reasons:
- To familiarise yourself with the material available on a particular topic
- To demonstrate the quality and depth of reading that you have done
- To identify range of sources available on your topic
- To highlight sources that may be of interest to other readers and researchers
- To explore and organise sources for further research, e.g. as the first step toward a literature review
What kind of resources should be studied?
Review recent academic materials such as academic books and peer reviewed journals. Textbooks and web pages are generally not appropriate as the content may be either too broad or unreliable.
The sources you choose will depend on your topic. Choose sources which most closely answer a clearly defined question or problem from a balanced range of approaches, not only those which confirm your current beliefs. Also, include any references which are considered central to your topic.
How to create an annotated bibliography
These are good places to start:
- Your lecture notes / references given in class
- The Library Guide for your subject
- The subject liaison librarian
First, read abstracts or academic book reviews to help you select studies most relevant to your problem, then select the most suitable from those to read in full. Take notes on your selected texts as you read. Pay attention to:
- the author’s theoretical approach.
- which parts of the topic are covered in this paper.
- main points or findings on the topic.
- the author’s position or argument.
Record evaluations in your notes; your bibliography should not merely be a catalogue but present your own informed position on the texts and the topic as a whole.
- How well does this text address your topic?
- Does it cover the topic thoroughly or only one aspect of it?
- Do the research methods seem appropriate and does the argument stand up to scrutiny?
- Does it agree with or contradict other studies?
- List texts in alphabetical order using citation conventions for a reference list.
- Create an annotation under each citation: a paragraph summarising each text and explaining how the text applies to your research question or problem. e.g. What aspect of your question/ problem does it address? How fully? Does it provide background information/ theory / useful results? How strong is the evidence? What are its limitations in answering your research question?
Find out what citation style you need to use, such as APA, Vancouver, MLA. Department style guides or detailed assignment briefs often provide information on this. Details of how to cite are explained in re:cite.
Write in complete sentences to create a cohesive ‘snapshot’ of the text and its contribution to your research. Be brief and selective; aim to outline the text in less than 200 words.
An annotation may contain all or part of the following elements depending on the word limit and the content of the sources you are examining:
You might include:
- the background of the author(s)
- the content or scope of the text
- the main argument
- the intended audience
- the research methods (if applicable)
- any conclusions made by the author/s
- comments on the reliability of the text
- any special features of the text that were helpful (charts, graphs etc.)
- the relevance or usefulness of the text for your research
- the strengths and limitations of the text
Below is a sample annotation (APA). The superscript numbers at the end of the sentence explain the features or elements covered.
Scoffer, J., Treet, M., Nibbell, A., Tayste, C., & Snacker, A. (2017). Visual priming for chocolate increases chocolate consumption–an attention bias modification study. Journal of Healthy Eating, 38(1), 176-183. 1
The study examines the effect of attention priming on subsequent chocolate consumption within a University context 2 . 120 subjects were primed with presentations of pictures either of shoes or chocolate, then participated in a chocolate search 3 . Findings indicated that the group primed with visual stimuli of chocolate showed significantly higher persistence in the chocolate searching task, consuming on average greater amounts of chocolate 4 . The authors contend that attention to food stimuli could increase risk of weight gain for many individuals 5 . By demonstrating the role of visual attention in subsequent food seeking behaviour and quantity consumed, this study provides evidence that such visual stimuli as web-based or billboard-based advertisements containing images of food may present a health risk to many individuals 6 . Limitations of the study include the lack of a true control since no non-primed condition was included. Another limitation is the use of a highly prized foodstuff, which limits the application of the findings to more everyday foods less closely related to reward 7 . However, the positive finding on the role of visual priming in food seeking and consumption provides useful support for the argument in my research that visual advertising contributes to weight problems, particularly in an obesogenic environment 8 .
1 Full citation
2 Aim and scope of the research
3 Brief summary of methods (where appropriate)
4 Summary of findings
5 Author’s main contention/ argument
6 Usefulness for your research
7 Limitations for your study
8 Reflection on how this work informs your research and how it will be applied.
As you research, keep in mind that annotated bibliographies are often preliminary research for a single, cohesive literature review about a situation or problem. Try to choose sources which together will present a comprehensive review of the issue under study.

Looking for one-on-one advice?
Get tailored advice from an Academic Skills Adviser by booking an Individual appointment, or get quick feedback from one of our Academic Writing Mentors via email through our Writing advice service.
Go to Student appointments

- Research Guides
- CECH Library
How to Write an Annotated Bibliography
Writing annotations.
- Introduction
- New RefWorks
- Formatting Citations
- Sample Annotated Bibliographies
An annotation is a brief note following each citation listed on an annotated bibliography. The goal is to briefly summarize the source and/or explain why it is important for a topic. They are typically a single concise paragraph, but might be longer if you are summarizing and evaluating.
Annotations can be written in a variety of different ways and it’s important to consider the style you are going to use. Are you simply summarizing the sources, or evaluating them? How does the source influence your understanding of the topic? You can follow any style you want if you are writing for your own personal research process, but consult with your professor if this is an assignment for a class.
Annotation Styles
- Combined Informative/Evaluative Style - This style is recommended by the library as it combines all the styles to provide a more complete view of a source. The annotation should explain the value of the source for the overall research topic by providing a summary combined with an analysis of the source.
Aluedse, O. (2006). Bullying in schools: A form of child abuse in schools. Educational Research Quarterly , 30 (1), 37.
The author classifies bullying in schools as a “form of child abuse,” and goes well beyond the notion that schoolyard bullying is “just child’s play.” The article provides an in-depth definition of bullying, and explores the likelihood that school-aged bullies may also experience difficult lives as adults. The author discusses the modern prevalence of bullying in school systems, the effects of bullying, intervention strategies, and provides an extensive list of resources and references.
Statistics included provide an alarming realization that bullying is prevalent not only in the United States, but also worldwide. According to the author, “American schools harbor approximately 2.1 million bullies and 2.7 million victims.” The author references the National Association of School Psychologists and quotes, “Thus, one in seven children is a bully or a target of bullying.” A major point of emphasis centers around what has always been considered a “normal part of growing up” versus the levels of actual abuse reached in today’s society.
The author concludes with a section that addresses intervention strategies for school administrators, teachers, counselors, and school staff. The concept of school staff helping build students’ “social competence” is showcased as a prevalent means of preventing and reducing this growing social menace. Overall, the article is worthwhile for anyone interested in the subject matter, and provides a wealth of resources for researching this topic of growing concern.
(Renfrow & Teuton, 2008)
- Informative Style - Similar to an abstract, this style focuses on the summarizing the source. The annotation should identify the hypothesis, results, and conclusions presented by the source.
Plester, B., Wood, C, & Bell, V. (2008). Txt msg n school literacy: Does texting and knowledge of text abbreviations adversely affect children's literacy attainment? Literacy , 42(3), 137-144.
Reports on two studies that investigated the relationship between children's texting behavior, their knowledge of text abbreviations, and their school attainment in written language skills. In Study One, 11 to 12 year-old children reported their texting behavior and translated a standard English sentence into a text message and vice versa. In Study Two, children's performance on writing measures were examined more specifically, spelling proficiency was also assessed, and KS2 Writing scores were obtained. Positive correlations between spelling ability and performance on the translation exercise were found, and group-based comparisons based on the children's writing scores also showed that good writing attainment was associated with greater use of texting abbreviations (textisms), although the direction of this association is not clear. Overall, these findings suggest that children's knowledge of textisms is not associated with poor written language outcomes for children in this age range.
(Beach et al., 2009)
- Evaluative Style - This style analyzes and critically evaluates the source. The annotation should comment on the source's the strengths, weaknesses, and how it relates to the overall research topic.
Amott, T. (1993). Caught in the Crisis: Women in the U.S. Economy Today . New York: Monthly Review Press.
A very readable (140 pp) economic analysis and information book which I am currently considering as a required collateral assignment in Economics 201. Among its many strengths is a lucid connection of "The Crisis at Home" with the broader, macroeconomic crisis of the U.S. working class (which various other authors have described as the shrinking middle class or the crisis of de-industrialization).
(Papadantonakis, 1996)
- Indicative Style - This style of annotation identifies the main theme and lists the significant topics included in the source. Usually no specific details are given beyond the topic list .
Example:
Gambell, T.J., & Hunter, D. M. (1999). Rethinking gender differences in literacy. Canadian Journal of Education , 24(1) 1-16.
Five explanations are offered for recently assessed gender differences in the literacy achievement of male and female students in Canada and other countries. The explanations revolve around evaluative bias, home socialization, role and societal expectations, male psychology, and equity policy.
(Kerka & Imel, 2004)
Beach, R., Bigelow, M., Dillon, D., Dockter, J., Galda, L., Helman, L., . . . Janssen, T. (2009). Annotated Bibliography of Research in the Teaching of English. Research in the Teaching of English, 44 (2), 210-241. Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org/stable/27784357
Kerka, S., & Imel, S. (2004). Annotated bibliography: Women and literacy. Women's Studies Quarterly, 32 (1), 258-271. Retrieved from http://search.proquest.com/docview/233645656?accountid=2909
Papadantonakis, K. (1996). Selected Annotated Bibliography for Economists and Other Social Scientists. Women's Studies Quarterly, 24 (3/4), 233-238. Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org/stable/40004384
Renfrow, T.G., & Teuton, L.M. (2008). Schoolyard bullying: Peer victimization an annotated bibliography. Community & Junior College Libraries, 14(4), 251-275. doi:10.1080/02763910802336407
- << Previous: Formatting Citations
- Next: Sample Annotated Bibliographies >>
- Last Updated: Feb 27, 2023 10:50 AM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.uc.edu/annotated_bibliography
University of Cincinnati Libraries
PO Box 210033 Cincinnati, Ohio 45221-0033
Phone: 513-556-1424
Contact Us | Staff Directory
University of Cincinnati
Alerts | Clery and HEOA Notice | Notice of Non-Discrimination | eAccessibility Concern | Privacy Statement | Copyright Information
© 2021 University of Cincinnati
How to Write an Annotated Bibliography: .
How to write an annotated bibliography.
An annotation is a brief summary or description (usually 100 to 200 words) of a publication (article, book, web site, movie, etc.). Its purpose is to give the potential reader/viewer/listener an accurate idea of the contents of the publication so that the reader can judge whether the publication is appropriate to the reader’s interests. Note that the reader can be yourself: keeping an annotated list of sources you have consulted can help you later in your research when you are trying to remember what you read where.
An annotated bibliography is a list of publications on a topic with an annotation describing each item in the list. The list can be ordered alphabetically, or grouped thematically.
Annotations can be descriptive or evaluative:
- descriptive annotation: summarizes the content of the publication, pointing out key topics, significant features, intended audience, etc.
- evaluative annotation: in addition to a description, offers a brief critical assessment of the publication, assessing its relevance, accuracy, reliability, or usefulness for a particular audience or purpose.
In addition to the complete bibliographical information (author, title, publisher and date, etc), an entry in an annotated bibliography should include at least some of the following:
- Author: Authority, experience, or qualifications of the author.
- Purpose: Why did the author write this?
- Scope: Breadth or depth of coverage, topics included, etc.
- Audience: For whom was it written (general public, subject specialists, students…)?
- Viewpoint: What is the author’s perspective or approach (school of thought, etc.)? Do you detect an unacknowledged bias, or find any undefended assumptions?
- Sources: Does the author cite other sources, and if so, what types? Is it based on the author’s own research? Is it personal opinion? …
- Conclusion: What does the author conclude? Is the conclusion justified by the work?
- Features: Any significant extras, e.g. visual aids (charts, maps, etc.), reprints of source documents, an annotated bibliography?
- Comparison: How does it relate to other works on the topic: does it agree or disagree with another author or a particular school of thought; are there other works which would support or dispute it?
- A brief annotation, taken from From David Chalmers’ “Contemporary Philosophy of Mind: An Annotated Bibliography,” available online at http://hps.elte.hu/fulltext/chalmers.html :
Foss, J. E. 1989. On the logic of what it is like to be a conscious subject. Australasian Journal of Philosophy 67:305-320.
A Super Neuroscientist will know how we describe and think about experience, so will know as much as a Super Sympathist. One doesn't have to imagine to know what it's like. With remarks on bat experience.
[Note: this annotation presumes a familiarity with the subject. The terms "Super Neuroscientist" and "Super Sympathist" are unexplained, and it is assumed that the reader will know what they mean. And the note "With remarks on bat experience" is assumed to trigger a recognition of Thomas Nagel's famous article (well, famous in philosophy circles, anyway) "What is it like to be a bat?" That is fine if your readers are familiar with the subject. But if you cannot reasonably expect your intended audience to pick up on such things, you should explain what they mean.]
- A longer annotation, distilled and combined from a few annotations and reviews:
Searle, John R. Intentionality, an essay in the philosophy of mind. New York: Cambridge University Press, 1983.
In previous books ( Speech Acts [1969] and Expression and Meaning [1980]), Searle introduced the ideas behind speech acts and started to extend them to ‘intentionality’, by which he means the property of certain states of mind in virtue of which they are directed towards objects or states of affairs in the world. In this book, he extends that work to philosophy of mind. Searle rejects a simple physicalistic or linguistic picture of the mind. He locates intentional states within a network, and against a background of non-intentional states. In the course of expounding his general theory of their nature, he is led to give his own accounts of perception, action, causation, conventional linguistic meaning, indexicals and proper names. Searle thinks of himself as swimming against the current, and much of his argument is negative. Nevertheless the gist is everywhere positive: his book is full of novel suggestions in familiar areas, and all the commitments are clearly spelled out. This book will extend our ability to make sense of intentional states and will, it is to be hoped, render out-of-date some still-held theories about the mind. This very clearly written book can be read with profit by philosophers and their students, both undergraduate and graduate level.
[Note: in addition to outlining the content of the book itself and providing a general evaluation, it places the book in the context of Searle's other work and of the field in general. It does not, but could, include a more specific list and evaluation of Searle's conclusions in the book, though that would make it long for an annotated bibliography.]
- Last Updated: May 2, 2022 11:01 AM
- URL: https://libguides.wesleyan.edu/annotbib

- Finding Sources
- Writing the Annotations
- Formatting the Annotated Bibliography
- Citation This link opens in a new window
What is an Annotated Bibliography?
An annotated bibliography is a list of sources in proper citation format, each with a descriptive paragraph. The description may critique, analyze or just summarize the content of the item. For this assignment, you will write a critical/evaluative annotation for each source, critically appraising the evidence that addresses your practice problem.
A good annotated bibliography:
- Encourages you to think critically about the content of the works you are using, the importance of the works within the field of study, and the relation of the works to your own research and ideas
- Proves you have read and understand your sources
- Establishes your work as a valid source and you as a competent researcher
- Provides a way for others to decide whether a source will be helpful to their research if they read it
*Excerpted from The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill .
The Annotated Bibliography should be the final result after a thorough review of the literature on your topic. Different databases should be searched to get different perspectives. If 8-10 sources are required, you should be reviewing many more sources (20-25), in detail, before making final selections.
Steps to Writing an Annotated Bibliography
No matter which course or discipline you're researching in, the steps of writing an annotated bibliography should be similar:
- Research, identify, locate and read scholarly and professional articles, books, and documents for your bibliography
- Critically screen, analyze and evaluate the sources
- organize the sources in a logical order
- Create citations in proper APA format (see APA tab)
- Compose annotations
Resources on the Web
For more information on annotated bibliographies, visit these pages:
- Writing an Annotated Bibliography Dena Taylor, Health Sciences Writing Centre, University of Toronto
- Annotated Bibliographies The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Next: Finding Sources >>
- Last Updated: May 7, 2024 6:08 PM
- URL: https://stevenson.libguides.com/annotatedbib
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Annotated Bibliographies

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Definitions
A bibliography is a list of sources (books, journals, Web sites, periodicals, etc.) one has used for researching a topic. Bibliographies are sometimes called "References" or "Works Cited" depending on the style format you are using. A bibliography usually just includes the bibliographic information (i.e., the author, title, publisher, etc.).
An annotation is a summary and/or evaluation. Therefore, an annotated bibliography includes a summary and/or evaluation of each of the sources. Depending on your project or the assignment, your annotations may do one or more of the following.
For more help, see our handout on paraphrasing sources.
For more help, see our handouts on evaluating resources .
- Reflect : Once you've summarized and assessed a source, you need to ask how it fits into your research. Was this source helpful to you? How does it help you shape your argument? How can you use this source in your research project? Has it changed how you think about your topic?
Your annotated bibliography may include some of these, all of these, or even others. If you're doing this for a class, you should get specific guidelines from your instructor.
Why should I write an annotated bibliography?
To learn about your topic : Writing an annotated bibliography is excellent preparation for a research project. Just collecting sources for a bibliography is useful, but when you have to write annotations for each source, you're forced to read each source more carefully. You begin to read more critically instead of just collecting information. At the professional level, annotated bibliographies allow you to see what has been done in the literature and where your own research or scholarship can fit. To help you formulate a thesis: Every good research paper is an argument. The purpose of research is to state and support a thesis. So, a very important part of research is developing a thesis that is debatable, interesting, and current. Writing an annotated bibliography can help you gain a good perspective on what is being said about your topic. By reading and responding to a variety of sources on a topic, you'll start to see what the issues are, what people are arguing about, and you'll then be able to develop your own point of view.
To help other researchers : Extensive and scholarly annotated bibliographies are sometimes published. They provide a comprehensive overview of everything important that has been and is being said about that topic. You may not ever get your annotated bibliography published, but as a researcher, you might want to look for one that has been published about your topic.
The format of an annotated bibliography can vary, so if you're doing one for a class, it's important to ask for specific guidelines.
The bibliographic information : Generally, though, the bibliographic information of the source (the title, author, publisher, date, etc.) is written in either MLA or APA format. For more help with formatting, see our MLA handout . For APA, go here: APA handout .
The annotations: The annotations for each source are written in paragraph form. The lengths of the annotations can vary significantly from a couple of sentences to a couple of pages. The length will depend on the purpose. If you're just writing summaries of your sources, the annotations may not be very long. However, if you are writing an extensive analysis of each source, you'll need more space.
You can focus your annotations for your own needs. A few sentences of general summary followed by several sentences of how you can fit the work into your larger paper or project can serve you well when you go to draft.

How to Prepare an Annotated Bibliography
What is an annotated bibliography, types of annotations.
- Critical Appraisal & Analysis
- Sample Annotations
- Citation Styles
Need Help? Ask Us.

Hesburgh Library First Floor University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, IN 46556
(574) 631-6258 [email protected]
Chat with us!
A bibliography is a list of works (books, articles, films, etc.) on a particular topic. An annotated bibliography includes a paragraph following each citation that summarizes the work. An annotation can help the reader determine the value of each work on the topic and the contribution it might make to his own research. Abstracts are the purely descriptive summaries often found at the beginning of scholarly journal articles or in periodical indexes. Annotations are descriptive and/or critical; they expose the author's point of view, clarity and appropriateness of expression, and authority.
Elements of an Annotation

Sample elements of a critical annotated bibliography
Check with your instructor to determine what he/she wants to be included in annotations. In general, an annotation should inform the reader of the quality and relevance of the source. Annotations are detailed but succinct, typically about 150 words, and include:
- a brief summary (2-4 sentences) of the article, including the author’s name and what you think is the author’s primary point or thought;
- a description of the intended audience;
- how the article illuminates your bibliography topic;
- an evaluation of the source’s usefulness, reliability, strengths and weaknesses and its value for your research;
- how this specific article relates to another article in your bibliography
For more information, see:
- Annotated Bibliographies UMKC Libraries
- Preparing an Annotated Bibliography OWL at Purdue
- Descriptive
- Informative
There are different kinds of annotations, depending on what might be most important for your reader to learn about a source. Three common types of annotated bibliographies are Descriptive , Informative , and Critical .

Three Types of Annotations: Critical, Descriptive, and Informative
A Descriptive annotation may summarize:
- The main purpose or idea of the work
- The contents of the work
- The author’s conclusions
- The intended audience
- The author’s research methods
- Special features of the work such as illustrations, maps, and tables
This type of annotation seeks to answer the question, Does this source cover or address the topic I am researching?
An Informative annotation:
- Summarizes what the content, message, or argument of the source is
- Generally contains the hypothesis, methodology, main points, and conclusion or results
- Does not include any editorial or evaluative comments about such content
This type of annotation seeks to answer these types of questions, What are the author's main arguments? What conclusions did the author draw?
A Critical annotation includes value judgments or comments on the effectiveness of the work. In this context, critical means evaluative and may include both positive and negative comments. A critical annotation may contain the information found in a descriptive annotation and discuss some of the following features:
- The importance of the work’s contribution to the literature of the subject
- The author’s bias or tone
- The author’s qualifications for writing the work
- The accuracy of the information in the source
- Limitations or significant omissions
- The work’s contribution to the literature of the subject
- Comparison with other works on the topic
This type of annotation seeks to answer these types of questions:
- Is the author's presentation of the facts objective?
- Is the methodology sound? Is this source useful for my audience?
- Are the conclusions still valid in light of new research?
- What contribution does this make to the field?
- Does this source address all the relevant issues?
- Next: Critical Appraisal & Analysis >>
- Last Updated: Jul 28, 2022 10:35 AM
- URL: https://libguides.library.nd.edu/annotated-bibliography
Need help? Ask us.
Report a problem


UNE Library Services
Research Help
Annotated bibliographies.
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations to books, articles, and documents used for researching a topic, followed by a brief synopsis, or annotation.
Formatting Citations
Format citations according to the writing style for your assignment . If you aren’t sure, check with your instructor. Citations should be listed in the same order as in a reference list or bibliography.
The Annotation
Each citation is followed by a brief summary or evaluative paragraph of about 150 words. The purpose of the annotation is to inform the reader of the relevance, accuracy, and quality of the source.
The annotation should summarize the central theme and scope of the resource and:
- Evaluate the authority or background of the author.
- Comment on the intended audience.
- Compare or contrast this work with another you have cited.
- Explain how this work applies to your topic or helps shape your argument.
The annotations you include in your bibliography should reflect your research project and/or the guidelines of your assignment.
Carney, D. R., Cuddy, A. J. C., & Yap, A. J. (2010). Power posing: Brief nonverbal displays affect neuroendocrine levels and risk tolerance. Psychological Science, 21 (10), 1363-1368.
The authors – researchers at Columbia University and Harvard University – study neuroendocrine and behavioral changes to (male and female) participants to confirm their prediction that posing in high-power poses results in elevations in testosterone, decreases in cortisol, and increased feelings of power and tolerance for risk. In short, posing in displays of power caused advantaged and adaptive psychological, physiological, and behavioral changes and these findings suggest that embodiment extends to physiology and subsequent behavioral choices. That a person can, by assuming two simple 1-min poses, embody power and instantly become more powerful has real-world, actionable implications. Previous studies had shown that power generates these displays (power poses), no previous research has investigated whether these poses generate power.
Bingham RA, Ranker TA. 2000. Genetic diversity in alpine and foothill populations of Campanula Rotundifolia (Campanulaceae). Int J Plant Sci 161(3):403-411.
Bingham, a biology professor at Western State College of Colorado, writes that, because of highly effective pollination by bumblebees, some trees do not experience a decrease in genetic variability even when they grow at high elevation. This idea is supported by better research here than in other articles that I found. The research is important to me as I investigate the degree to which hummingbirds migrate the negative effects of cold, high altitude, environments on the pollination of Apache Paintbrush flowers.
From the YouTube video tutorial How to Write an Annotated Bibliography
Questions & Help
If you have questions on this, or another, topic, contact a librarian for help!

Writing an Annotated Bibliography
- Finding Sources
How to Write an Annotated Bibliography
- How to Format Your Bibliography
- How to Avoid Plagiarism
Each citation is followed by a brief (usually about 150 words) descriptive and evaluative paragraph, the annotation. The purpose of the annotation is to inform the reader of the relevance, accuracy, and quality of the sources cited. Unlike abstracts which are purely descriptive summaries often found at the beginning of scholarly journal articles or in periodical indexes, annotations are descriptive and critical ; they expose the author's point of view, clarity and appropriateness of expression, and authority.
The Process
Creating an annotated bibliography calls for the application of a variety of intellectual skills: concise exposition, succinct analysis, and informed library research
- First, locate and record citations to books, periodicals, and documents that may contain useful information and ideas on your topic.
- Briefly examine and review the actual items. Then choose those works that provide a variety of perspectives on your topic.
- Cite the book, article, or document using the appropriate style.
- evaluate the authority or background of the author,
- comment on the intended audience,
- compare or contrast this work with another you have cited, or
- explain how this work illuminates your bibliography topic.
The annotation should include most, if not all, of the following:
- Explanation of the main purpose and scope of the cited work;
- Brief description of the work's format and content ;
- Author's intellectual/academic credentials ;
- Theoretical basis and currency of the author's argument ;
- Work's intended audience ;
- Value and significance of the work as a contribution to the subject under consideration;
- Possible shortcomings or bias in the work;
- Any significant special features of the work (e.g., glossary, appendices, particularly good index);
- Your own brief impression of the work .
An annotated bibliography is an original work created by you for a wider audience, usually faculty and colleagues. Copying any of the above elements is plagiarism and intellectual dishonesty.
Permissions
Text from this page has been adapted from:
Olin Library Reference Research & Learning Services Cornell University Library Ithaca, NY, USA
https://guides.library.cornell.edu/annotatedbibliography/home
Roger Williams University
https://rwu.libguides.com/annotatedbibliography
- << Previous: Finding Sources
- Next: How to Format Your Bibliography >>
- Last Updated: Mar 20, 2024 11:25 AM
- URL: https://libguides.butler.edu/annotatedbib

QUICK LINKS
Library Hours Study Rooms My Library Account Library Website

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

13.9: Tracking Research with Annotated Bibliographies
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 250494
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Why create annotated bibliographies?
Research and critical reading strategies play an important role in the writing process. However, in research-intensive assignments, it’s easy to become overwhelmed by the information. Our brains can only hold so much information at one time (what psychologists call “cognitive load”); as a result, each new piece of information we read can erase or confuse previous research. To avoid the problem of being overwhelmed, academic researches often rely on annotated bibliographies . The phrase sounds fancy, but the strategy is fairly straightforward.
Components of an Annotated Bibliography: Citation + Annotation
Each course and its instructor may have slightly different expectations for what to include in your annotated bibliography, and what an annotation looks like may also vary. However, there are certain conventions that apply to nearly all of them:
Works Cited Reference
The first element of an annotated bibliography is the citation reference.
If you’re new to organizing academic research, the process generating a citation reference can seem daunting at first. The different citation styles, such as APA, MLA, etc., only compound the issue. Kurt Schick’s article for the Chronicle , “ Citation Obsession? Get Over It! ” discusses the problem with focusing too much on the demands of citation conventions. If students get too caught up in formatting things correctly, it distracting from the more important work of generating interesting and original ideas. However, he also suggests that the basics of citation play an important role in the writing process, and the most important information isn’t as complex as it first seems. [1] All citation styles expect a writer to include the following information:
- title of the work
- publication information, such as the website or journal, but also the date and url
The trickiest part is often the publication information, because it really contains a few sub-parts, such as the publisher/sponsor, the date it was published, and the stable url if it was published online. But it helps to know that all citation styles will expect you to include these three elements. Become comfortable with identifying them. The chapter in this textbook, “Creating a References Section,” offers more guidance for how to spot these elements.
Your paragraph about the source
The next element in an annotated bibliography is the actual annotation, which is the bulk of the writing. Some instructors might call this a “source summary.”
Annotations/source summaries are almost always a single paragraph that does the following things:
- Introduce the source : At the beginning, refer to the title, author, and main idea or argument of the piece. You can use signal phrases to help open this part: “In _______________, the author ______________ argues that _________________.”
- Briefly identify the key points of the text : If the source is argumentative, for example, some of the important points might be the evidence or reasoning. On the other hand, secondary ideas, such as counterarguments and rebuttals, are probably too tertiary and detailed that they should be left out. Stick with a broad outline, and try to put as most of the summary as you can in your own words. Quotes should be used sparingly, if at all, and they must be placed in quotes and be cited (e.g., the page number). When summarizing key information, maintain a neutral tone and use the third-person point of view and present tense (“Thomson argues” rather than “Thomson argued”).
- Discuss, analyze, or evaluate the source in terms of your assignment or essay project. Can the article be used as evidence for a certain claim? Does it serve as a strong counterargument? What about the quality of the source? Is it authoritative? Depending on the annotated bibliographic assignment, you instructor may have specific requirements for how to discuss the source.
This basic structure of an annotation reinforces the “M-E-A-L” strategy discussed in the chapter, “ The Basics of Integration .” Annotations/source summaries are excellent ways to practice integration at the most basic level.
The video, “What is an annotated bibliography?”, by Santiago Community College, offers a great visual overview:
The Annotated Bibliography Exercise
by Steven Krause
What is an Annotated Bibliography?
As you develop a working thesis for your research project and begin to collect different pieces of evidence, you will soon find yourself needing some sort of system for keeping track of everything. The system discussed in this chapter is an annotated bibliography, which is a list of sources on a particular topic that includes a brief summary of what each source is about. This writing exercise is a bit different from the others in this part of The Process of Research Writing in that isn’t an “essay” per se; rather it is an ongoing writing project that you will be “building” as you discover new pieces of evidence for your research project.
Here is an example of an entry from an annotated bibliography in MLA style:
Parsons, Matt. “Protecting Children on the Electronic Frontier: A Law Enforcement Challenge.” FBI Law Enforcement Bulletin 69.10 (2000): 22-26.
This article is about an educational program used by the U.S. Navy to educate people in the Navy and their families about some of the things that are potentially dangerous to children about the Internet. Parsons says that the educational program has been effective.Annotated bibliography entries have two parts. The top of the entry is the citation. It is the part that starts “Parsons, Matt’” and that lists information like the name of the writer, where the evidence appeared, the date of publication, and other publishing information.
The second part of the entry is the summary of the evidence being cited. A good annotated bibliography summary provides enough information in a sentence or two to help you and others understand what the research is about in a neutral and non-opinionated way.
The first two sentences of this annotation are an example of this sort of very brief, “just the facts” sort of summary. In the brief summaries of entries in an annotated bibliography, stay away from making evaluations about the source—“I didn’t like this article very much” or “I thought this article was great.” The most important goal of your brief summary is to help you, colleagues, and other potential readers get an idea about the subject of the particular piece of evidence.
Summaries can be challenging to write, especially when you are trying to write them about longer and more complicated sources of research. Keep these guidelines in mind as you write your own summaries.
- Keep your summary short. Good summaries for annotated bibliographies are not “complete” summaries; rather, they provide the highlights of the evidence in as brief and concise a manner as possible, no more than a sentence or two.
- Don’t quote from what you are summarizing. Summaries will be more useful to you and your colleagues if you write them in your own words. Instead of quoting directly what you think is the point of the piece of evidence, try to paraphrase it. (For more information on paraphrasing your evidence, see Chapter 3, “Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Avoiding Plagiarism”).
- Don’t “cut and paste” from database abstracts. Many of the periodical indexes that are available as part of your library’s computer system include abstracts of articles. Do no “cut” this abstract material and then “paste” it into your own annotated bibliography. For one thing, this is plagiarism. Second, “cutting and pasting” from the abstract defeats one of the purposes of writing summaries and creating an annotated bibliography in the first place, which is to help you understand and explain your research.
Different writers will inevitably write slightly different summaries of the same evidence. Some differences between different writers’ summaries of the same piece of evidence result from different interpretations of what it important in the research; there’s nothing wrong with that.
However, two summaries from different writers should both provide a similar summary. In other words, its not acceptable when the difference of interpretation is the result of a lack of understanding of the evidence.
Why Write Annotated Bibliographies?
An annotated bibliography is an excellent way to keep track of the research you gather for your project. Make no mistake about it— it is extremely important that you keep track of all of your evidence for your research project, and that you keep track of it from the beginning of the process of research writing.
There’s nothing more frustrating than finding an excellent article or book chapter you are excited about incorporating into your research project, only to realize you have forgotten where you found the article or book chapter in the first place. This is extremely frustrating, and it’s easily avoided by doing something like writing an annotated bibliography.
You could use other methods for keeping track of your research. For example, you could use note cards and write down the source information as a proper citation, then write down the information about the source that is important. If the material you know you want to use from a certain source is short enough, you might even write a direct quote, which is where you write down word for word what the source says exactly as it is written. At other times, you can write a paraphrase, which is where you write down what the source means using your own words.
While note cards and other methods have their advantages, annotated bibliographies are an extremely useful tool for keeping track of your research. An annotated bibliography:
- Centralizes your research into one document that you can keep track of both as a print-out of a word-processed file and as a file you save electronically.
- Allows you to “copy and paste” citation information into the works cited part of your research project.
An annotated bibliography also gives you the space to start writing and thinking a bit about how some of your research might fit into your project. Consider these two sample entries from an annotated bibliography from a research project on pharmaceutical advertising:
Siegel, Marc. “Fighting the Drug (ad) Wars.” The Nation 17 June 2002: 21.
Siegel, who is a doctor himself, writes about how drug advertising has undermined the communication between doctors and patients. He says that drug ads have driven up the costs of prescription drugs, particularly big selling drugs like those for cholesterol.
Wechsler, Jill. “Minority Docs See DTC Ads as Way to Address ‘Race Gap.’” Pharmaceutical Executive May 2002: 32, 34. WilsonSelect Database. Eastern Michigan University Halle Library. 20 October 2002. < http://www.emich.edu/halle >.
This article is about a study that said that African-American doctors saw advertising of prescription drugs as a way of educating their patients. The ads are useful because they talk about diseases that affect African-Americans.
Even from the limited amount of information available in these entries, it’s clear that a relationship between these articles exists. Both are similar articles about how the doctor/patient relationship is affected by drug advertising. But both are also different. The first article is from the newspaper The Nation, which is in many ways similar to an academic journal and which is also known for its liberal views. The second article is from a trade journal (also similar to academic journals in many ways) that obviously is an advocate for the pharmaceutical industry.
In other words, in the process of compiling an annotated bibliography, you are doing more than keeping track of your research. You are starting to make some comparisons and beginning to see some relationships between your evidence, a process that will become increasingly important as you gather more research and work your way through the different exercises that lead to the research project.
But remember: However you decide to keep track of your research as you progress through your project—annotated bibliography, note cards, or another method—the important thing is that you need to keep track of your research as you progress through your project!
How many sources do I need?
Inevitably, students in research writing classes always ask how many sources they need to include in their research projects. In one sense, “how many sources do I need?” is a utilitarian question, one usually attached to a student’s exploration of what it will take to get a particular grade. Considered more abstractly, this question is also an effort to explore the scope of a research project. Like a certain page or word count requirement, the question “how many sources do I need?” is an effort to get a handle on the scope of the research project assignment. In that sense, asking about the number of sources is probably a good idea, a little like asking how much something weighs before you attempt to pick it up.
But ultimately, there is no right or wrong answer to this question. Longer research projects tend to have evidence from more different sources than shorter projects, but there is no cut-and-dry formula where “X” number of pages will equal “X” number of sources.
However, an annotated bibliography should contain significantly more entries than you intend or expect to include in your research project. For example, if you think you will need or if your instructor requires you to have research from about seven different sources, you should probably have about 15 different entries on your annotated bibliography.
The reasons you need to find twice as many sources as you are likely to use is that you want to find and use the best research you can reasonably find, not the first pieces of research you can find. Usually, researchers have to look at a lot more information than they would ever include in a research writing project to begin making judgements about their research. And by far the worst thing you can do in your research is to stop right after you have found the number of sources required by the instructor for your project.
Using Computers to Write Annotated Bibliographies
Personal computers, word-processing software, and the Internet can make putting together an annotated bibliography more useful and a lot easier. If you use word-processing software to create your annotated bibliography, you can dramatically simplify the process of creating a “works cited” or “references” page, which is a list of the sources you quote in your research project. All you will have to do is “copy and paste” the citation from the annotated bibliography into your research project—that is, using the functions of your computer and word processing software, “copy” the full citation that you have completed on your annotated bibliography page and “paste” it into the works cited page of your research project.
This same sort of “copy and paste” function also comes in handy when doing research on the web. For example, you can usually copy and paste the citation information from your library’s online database for pieces of evidence you are interested in reading. In most cases, you should be able to “copy and paste” information you find in your library’s online database into a word processing file. Many library databases—both for books and for periodicals—also have a feature that will allow you to email yourself results from a search.
Keep two things in mind about using computers for your annotated bibliographies:
- You will have to reformat whatever information you get from the Internet or your library’s databases in order to meet MLA or APA style.
- Don’t use the copy and paste feature to plagiarize! Simply copying things like abstracts defeats one of the important purposes for writing an annotated bibliography in the first place, and it’s cheating.
Assignment: Writing an Annotated Bibliography
As you conduct your research for your research writing project, compile an annotated bibliography with 15-20 entries. Each entry in your annotated bibliography should contain a citation, a brief summary of the cited material. You will be completing the project in phases and a complete and revised version of it will be due when you have completed your research.
You should think of your annotated bibliography as having roughly twice as many sources as the number of sources you will need to include for the research project, but your instructor might have a different requirement regarding the number of sources required.
Also, you should work on this assignment in parts. Going to the library and trying to complete this assignment in one sitting could turn this into a dreadful writing experience. However, if you complete it in stages, you will have a much better understanding of how your resources relate to each other.
You will probably need to discuss with your instructor the style of citation you need to follow for your research project and your annotated bibliography. Following a citation style isn’t difficult to do, but you will want to be consistent and aware of the “rules” from the beginning. In other words, if you start off using MLA style, don’t switch to APA style halfway through your annotated bibliography or your research project.
Last, but not least, you will need to discuss with your instructor the sorts of materials you need to include in your research and your annotated bibliography. You may be required to include a balance of research from scholarly and non-scholarly sources, and from “traditional” print resources (books, magazines, journals, newspapers, and so forth) and the Internet.
Questions to ask while writing and researching
- Would you classify the material as a primary or a secondary source? Does the research seem to be difficult to categorize this way? (For more information on primary and secondary sources, see Chapter 1, “Thinking Critically About Research” and the section “Primary versus Secondary Research”).
- Is the research from a scholarly or a non-scholarly publication? Does the research seem difficult to categorize this way?
- Is the research from the Internet—a web page, a newsgroup, an email message, etc.? Remember: while Internet research is not necessarily “bad” research, you do need to be more careful in evaluating the credibility of Internet-based sources. (For more information on evaluating Internet research, see Chapter 1, “Thinking Critically About Research,” and the sections “The Internet: The Researcher’s Challenge” and “Evaluating the Quality and Credibility of Your Research.”
- Do you know who wrote the material you are including in your annotated bibliography? What qualifications does your source say the writer has?
- Why do you think the writer wrote it? Do they have a self-interest or a political viewpoint that might make them overly biased?
- Besides the differences between scholarly, non-scholarly, and Internet sources, what else do you know about where your research was published? Is it an academic book? An article in a respected journal? An article in a news magazine or newspaper?
- When was it published? Given your research topic, how important do you think the date of publication is?
- Are you keeping your summaries brief and to the point, focusing on the point your research source is trying to make?
- If it’s part of the assignment, are you including a sentence or two about how you see this piece of research fitting into your overall research project?
Revision and Review
Because of its ongoing nature, revising an annotated bibliography is a bit different than the typical revision process. Take opportunities as you compile your annotated bibliography to show your work in progress to your classmates, your instructor, and other readers you trust. If you are working collaboratively on your research projects, you will certainly want to share your annotated bibliography with classmates who are working on a similar topic. Working together like this can be a very useful way to get more ideas about where your research is going.
It is best to approach the annotated bibliography in smaller steps—five or six entries at a time. If that’s how you’re approaching this project, then you will always be in a process of revision and review with your classmates and your instructor. You and your readers (your instructor and your classmates) should think about these questions as you revise, review, and add entries:
- Are the summaries you are including brief and to the point? Do your readers understand what the cited articles are about?
- Are you following a particular style guide consistently?
- If you are including a sentence or two about each of your resources, how do these sentences fit with your working thesis? Are they clarifying parts of your working thesis that were previously unclear? Are they suggesting changes to the approach you took when you began the research process?
- Based on the research you have so far, what other types of research do
- you think you need to find?
The first half of this chapter is original content by the editors. The second half of the chapter is from Steven D. Krause’s The Process of Research Writing , “ The Annotated Bibliography Exercise ,” CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0.
- Meta comment: This paragraph is almost like an annotation of Schick's article! ↵

COMMENTS
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that includes a short descriptive text (an annotation) for each source. It may be assigned as part of the research process for a paper, or as an individual assignment to gather and read relevant sources on a topic. Scribbr's free Citation Generator allows you to easily create and manage ...
Write the citation and annotation - When writing your annotation, the complete citation should always come first and the annotation follows. Depending on the type of annotated bibliography you are writing, you will want to include some or all of the following: The purpose of the work; A summary of its content; Information about the author(s)
What Is an Annotated Bibliography? An annotated bibliography is a list of citations to books, articles, and documents. Each citation is followed by a brief (usually about 150 words) descriptive and evaluative paragraph, the annotation. The purpose of the annotation is to inform the reader of the relevance, accuracy, and quality of the sources ...
For an MLA bibliography example (with annotations), check out our visual example of an MLA annotated bibliography. Step 2: Write the descriptions. An annotated bibliography entry may be written either as short phrases or complete sentences. Your instructor will advise you of which approach you are required to take. Annotations should include ...
Select the source that matches the title you are looking for. Modify your source as needed and scroll down to the "Annotation" box. Add your annotation into the box and click "Cite.". Once your annotations are done, select "Copy All + Paste" or "Export.". Paste into a Microsoft Word document.
Bibliographies for CSE in general are in a slightly smaller font than the rest of the paper. When using the name-year system, as in MLA and APA, the first line of each entry is set flush with the left margin, and all subsequent lines, including the annotation, are indented three or four spaces.
MLA provides guidelines for writing and formatting your annotated bibliography. An example of a typical annotation is shown below. Kenny, Anthony. A New History of Western Philosophy: In Four Parts. Oxford UP, 2010. Broad history of Western philosophy from the ancient Greeks to the present day. Divided into four periods—ancient, medieval ...
An annotation is a short paragraph that summarizes a source and describes how it is relevant to your research. To annotate literally means "to make notes.". There is not an official format for annotated bibliographies, though usually the bibliographic citation is written in APA or MLA format. If this is being done for a class, ask the ...
An annotated bibliography is a list of sources on a single topic, with an annotation provided for each source. An annotation is a one or two paragraph summary and/or analysis of an article, book, or other source. Generally, the first paragraph of the annotation provides a summary of the source in direct, clear terms.
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations (references) to books, articles, and documents followed by a brief summary, analysis or evaluation, usually between 100-300 words, of the sources that are cited in the paper. ... Writing an annotated bibliography (EasyBib.com) Oct 22, 2020. 4:53 min. Creating an annotated bibliography (Laurier ...
In summary, writing an annotated bibliography helps you develop skills related to critically reading and identifying the key points of a research study and to effectively synthesize the content in a way that helps the reader determine its validity and usefulness in relation to the research problem or topic of investigation.
Article abstracts are helpful in this process. Write the citation and annotation. When writing your annotation, the complete citation should always come first and the annotation follows. Depending on the type of annotated bibliography you are writing, you will want to include: The purpose of the work. A summary of its content.
Write the citation and annotation - When writing your annotation, the complete citation should always come first and the annotation follows. Depending on the type of annotated bibliography you are writing, you will want to include some or all of the following: The purpose of the work; A summary of its content; Information about the author(s)
Annotated Bibliography. An annotated bibliography is an organized list of sources, each of which is followed by a brief note or "annotation.". These annotations do one or more of the following: describe the content and focus of the book or article. suggest the source's usefulness to your research. evaluate its method, conclusions, or ...
An annotated bibliography provides a brief account of the available research on a given topic. Find out how to select resources, what to include, and which writing style to use. ... Why write an annotated bibliography? Depending on your specific assessment, you may be asked to create an annotated bibliography for the following reasons: ...
An annotation is a brief note following each citation listed on an annotated bibliography. The goal is to briefly summarize the source and/or explain why it is important for a topic. They are typically a single concise paragraph, but might be longer if you are summarizing and evaluating.
An annotated bibliography is a list of publications on a topic with an annotation describing each item in the list. The list can be ordered alphabetically, or grouped thematically. Annotations can be descriptive or evaluative: evaluative annotation: in addition to a description, offers a brief critical assessment of the publication, assessing ...
An annotated bibliography is a list of sources in proper citation format, each with a descriptive paragraph. The description may critique, analyze or just summarize the content of the item. For this assignment, you will write a critical/evaluative annotation for each source, critically appraising the evidence that addresses your practice problem.
A bibliography is a list of sources (books, journals, Web sites, periodicals, etc.) one has used for researching a topic. Bibliographies are sometimes called "References" or "Works Cited" depending on the style format you are using. A bibliography usually just includes the bibliographic information (i.e., the author, title, publisher, etc.).
In general, an annotation should inform the reader of the quality and relevance of the source. Annotations are detailed but succinct, typically about 150 words, and include: a brief summary (2-4 sentences) of the article, including the author's name and what you think is the author's primary point or thought; a description of the intended ...
How to Write an Annotated Bibliography. Format citations according to the writing style for your assignment. If you aren't sure, check with your instructor. Citations should be listed in the same order as in a reference list or bibliography. The Annotation. Each citation is followed by a brief summary or evaluative paragraph of about 150 words.
Each citation is followed by a brief (usually about 150 words) descriptive and evaluative paragraph, the annotation.The purpose of the annotation is to inform the reader of the relevance, accuracy, and quality of the sources cited.Unlike abstracts which are purely descriptive summaries often found at the beginning of scholarly journal articles or in periodical indexes, annotations are ...
An annotated bibliography also gives you the space to start writing and thinking a bit about how some of your research might fit into your project. Consider these two sample entries from an annotated bibliography from a research project on pharmaceutical advertising: Siegel, Marc. "Fighting the Drug (ad) Wars." The Nation 17 June 2002: 21.
Structuring a literature review. In general, literature reviews are structured in a similar way to a standard essay, with an introduction, a body and a conclusion. These are key structural elements. Additionally, a stand-alone extended literature review has an abstract. Throughout, headings and subheadings are used to divide up the literature ...
Here's a step-by-step guide to help you write an annotated bibliography: Cite Your Sources: Begin by citing each source in the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Include all necessary bibliographic information such as author (s), title, publication date, publisher, and URL (if applicable). Format Your Annotations: Start with ...