- 0 Shopping Cart


Mumbai Case Study
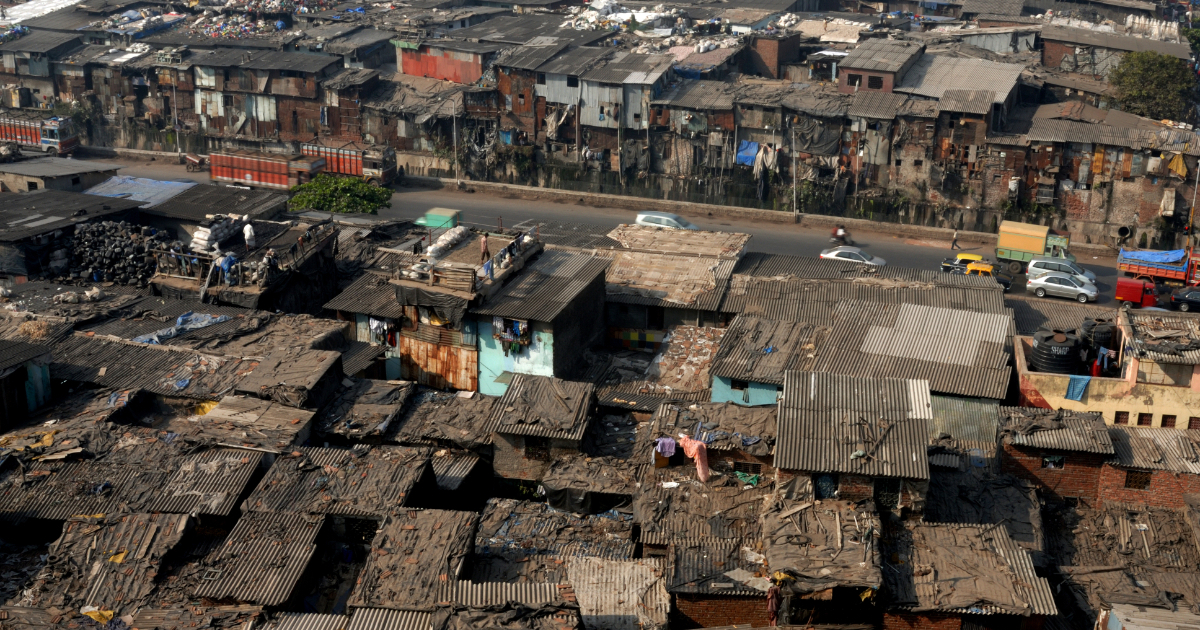

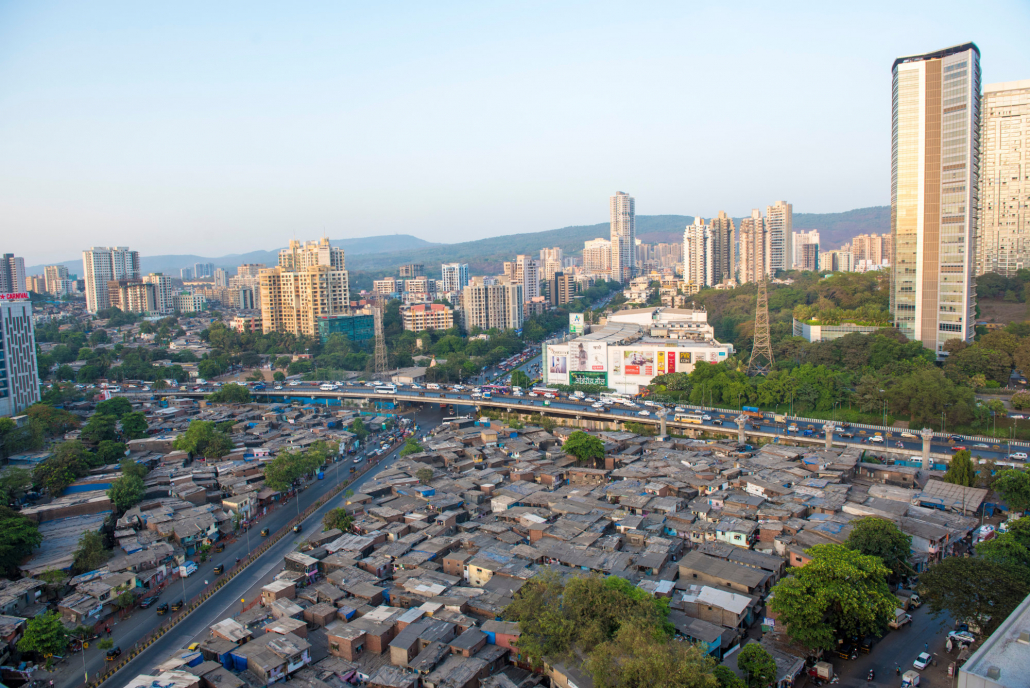
What is the location and importance of Mumbai?

Why is Mumbai growing?
What are Mumbai’s social and economic opportunities?
What challenges have been caused by urban growth in Mumbai?
How is urban planning improving the quality of life for the urban poor in Mumbai?
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Please Support Internet Geography
If you've found the resources on this site useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Search Internet Geography
Top posts and pages.
Latest Blog Entries
Pin It on Pinterest
- Click to share
- Print Friendly
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
40 Important Judgments that Transformed India
Last updated on September 23, 2022 by Alex Andrews George

The way democracy now functions in India owes a lot to many Supreme Court judgments .
It is quite interesting to learn how the Supreme Court judgments protected the essence of the Indian Constitution, strengthened democracy, and transformed the lives of ordinary citizens of India.
The book “ Important Judgments that transformed India ” presents an easy understanding of the landmark court cases that everyone needs to know about.
Table of Contents
40 Important Judgments that Transformed India: List of Cases
- Romesh Thappar v. State of Madras (1950)
- State of Madras v. Smt. Champakam Dorairajan (1951)
- K. M. Nanavati v. State of Maharashtra (1959)
- Berubari Union v. Unknown (1960)
- Kedarnath Singh v. State of Bihar (1962)
- I. C. Golaknath and Others v. State of Punjab and Another (1967)
- Keshavananda Bharati Sripadagalvaru v. State of Kerala (1973)
- ADM, Jabalpur v. Shivkant Shukla (1976)
- Maneka Gandhi v. Union of India (1978)
- Bachan Singh v. State of Punjab (1980)
- Minerva Mills Ltd v. Union of India (1980)
- Mohd. Ahmad Khan v. Shah Bano Begum and others (1985)
- Dr. D. C. Wadhwa and others v. State of Bihar and others (1986)
- M. C. Mehta v. Union of India and others (1986)
- Mohini Jain v. State of Karnataka (1989)
- Indira Sawhney and others v. Union of India (1992)
- S. R. Bommai v. Union of India (1994)
- L. Chandra Kumar v. Union of India (1997)
- Vishakha and others v. State of Rajasthan (1997)
- Vineet Narain and others v. Union of India (1997)
- Three Judges Cases (1981, 1993, 1998)
- Prakash Singh and others v. Union of India and others (2006)
- M. Nagaraj and others v. Union of India (2006)
- Lily Thomas v. Union of India and others (2013)
- T. S. R. Subramanian and others v. Union of India and others (2013)
- National Legal Services Authority v. Union of India (2014)
- Shreya Singhal v. Union of India (2015)
- Shayara Bano v. Union of India and others (2016)
- Justice K. S. Puttaswamy (Retd.) and another v. Union of India and others (2017)
- Indian Young Lawyers Association v. the State of Kerala (2018)
- Joseph Shine v. Union of India (2018)
- Navtej Singh Johar and others v. Union of India (2018)
- Anuradha Bhasin v. Union of India and others (2020)
- Rambabu Singh Thakur v. Sunil Arora and others (2020)
- Internet and Mobile Association of India v. Reserve Bank of India (2020)
- Laxmibai Chandaragi and another v. State of Karnataka and others (2021)
- Mohammad Salimullah and another v. Union of India and others (2021)
- Farzana Batool v. Union of India and others (2021)
- Kerala Union of Working Journalists v. Union of India and others (2021)
- Barun Chandra Thakur v. Master Bholu and another (2022)
100+ Landmark Supreme Court Judgments in Brief
This book includes a lot of additional judgments. The summary of 100+ landmark Supreme Court judgments is given in table format for quick learning and revision.
Some of the other cases included in this book include:
- AK Gopalan Vs State of Madras (1950)
- State of Madras Vs Smt. Champakam Dorairajan (1951)
- Shankari Prasad Vs Union of India (1951)
- M. P. Sharma And Others Vs Satish Chandra (1954)
- Kharak Singh Vs The State Of U.P. & Others (1962)
- Sajjan Singh Vs State of Rajasthan (1965)
- Hussainara Khatoon & Ors Vs Home Secretary, State Of Bihar (1979)
- S.P. Gupta vs. President of India and others (1981)
- Indian Express Newspapers Vs Union Of India & Ors (1984)
- T.M.A. Pai Foundation & Ors Vs State Of Karnataka & Ors (2002)
- Jaya Bachchan Vs Union of India And Ors (2006)
- Independent Thought Vs Union Of India (2017)
- Common Cause (A Regd. Society) Vs Union of India (2018)
- Shakti Vahini Vs Union Of India (2018)
Famous Cases that made news headlines
The book also covers the summary of many famous cases that were constantly in news. Some of these include:
Add IAS, IPS, or IFS to Your Name!
Your Effort. Our Expertise.
Join ClearIAS
- Union Carbide Corporation vs Union of India: The Bhopal Gas Tragedy Case (1989)
- I.R.Coelho vs the State of Tamil Nadu and Others: The I. R. Coelho Case (2007)
- People’s Union for Civil Liberties (PUCL) vs Union of India: The Nota Case (2013):
- Manoharl Lal Sharma vs Narendra Damodardas Modi: The Rafale Case (2018)
- M Siddiq vs Mahant Suresh Das: The Ayodhya Case (2019)
Cases Laws: Conflict Areas vs Judgments
In exams, reverse thinking is also tested. That means with respect to a particular topic, you may need to mention all related case laws.
For example, in UPSC CSE Mains 2022 , the Commission had asked to mention case laws connected with Environment. In another question, UPSC asked to write case laws connected with the Representation of People’s Act.
The Important Judgments that transformed India (IJTTI) book includes special tables which compile such case laws. This will be extremely useful in UPSC/Law exams.
Appendices in the book Important Judgments that Transformed India 2nd Edition
- Appendix-1: 100+ Landmark Supreme Court Judgments in Brief
- Appendix-2: Famous Cases that made news headlines
- Appendix-3: Conflict Areas v. Judgments
- Appendix-4: Mindmaps Which Help You Understand the Indian Polity
- Appendix-5: Indian Judicial Doctrines – Principles of Constitutional Law Explained
- Appendix-6: Common Legal Terms
- Appendix-7: Previous Years’ Solved UPSC CSE (Prelims) Questions
- Appendix-8: Previous Years’ Solved UPSC CSE (Mains) Questions
Salient Features of the Important Judgments that Transformed India 2 Edition
- A detailed overview of 40 landmark Supreme Court judgments.
- An additional compilation of 100+ Supreme Court judgments with respect to the main area of conflict.
- The complicated legal context behind various Supreme Court cases is made simple and easy to understand.
- Each chapter is divided into introduction, background, arguments, judgment, importance and impact.
Special Attractions of the 2nd Edition of IJTTI
- A lot of value-added content to make your answers stand out.
- Each chapter starts with thought-provoking questions to understand the case’s significance.
- Learn from easy-to-understand tables and mindmaps.
- Master Judicial Doctrines and Judicial Terms.
- Revise UPSC Civil Services Preliminary and Main Examination Previous Year Questions and Answers from the topic.
Book Details
- Author: Alex Andrews George
- Publisher: McGraw Hill
- Language: English
- Paperback: 320 pages
- ISBN-10: 9355321295
- ISBN-13: 9789355321299
Buy Important Judgments that Transformed India – 2nd Edition
- Buy on Amazon
- Buy on Flipkart
- Buy on Snapdeal

Aim IAS, IPS, or IFS?

Prelims cum Mains (PCM) GS Course: Target UPSC CSE 2025 (Online)
₹95000 ₹59000

Prelims cum Mains (PCM) GS Course: Target UPSC CSE 2026 (Online)
₹115000 ₹69000

Prelims cum Mains (PCM) GS Course: Target UPSC CSE 2027 (Online)
₹125000 ₹79000
About Alex Andrews George
Alex Andrews George is a mentor, author, and social entrepreneur. Alex is the founder of ClearIAS and one of the expert Civil Service Exam Trainers in India.
He is the author of many best-seller books like 'Important Judgments that transformed India' and 'Important Acts that transformed India'.
A trusted mentor and pioneer in online training , Alex's guidance, strategies, study-materials, and mock-exams have helped many aspirants to become IAS, IPS, and IFS officers.
Reader Interactions
September 14, 2023 at 12:41 pm
Thank you sharing an Amazing Content.
March 9, 2024 at 11:43 am
sir hindi me milegi kya ye book
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
IAS/IPS/IFS Online Coaching: Target CSE 2025
Are you struggling to finish the upsc cse syllabus without proper guidance, take clearias mock exams: analyse your progress.
Analyse Your Performance and Track Your All-India Ranking

Constitutional Law - Notes, Case Laws And Study Material
Explore constitutional law resources: notes, case laws, and study material at legal bites..

A basic understanding of the Constitutional Law is a must for every individual. The Constitution of India is the supreme law of the country. It includes the fundamental principles governing the Union and its territories; states and various rights; Executive, legislature and judiciary; Emergency provisions, etc. This subject also has ample weightage in every competitive exam related to law and order.
Legal Bites brings you the best study material on this subject with our brilliant up-to-date notes and case laws. The course is divided into fourteen modules to provide readers with a systematic study of constitutional laws. The modules have been specially designed to give students an in-depth insight into every aspect of constitutional law.
The well-researched miscellaneous articles and the 10-part series of important questions towards the end of this course give students an edge when participating in national-level competitions and exams. Our study material holds the key to success for aspiring lawyers.
Important articles and study material on Constitutional Law – Click on the links to Read:
Module i: historical overview and nature of the indian constitution.
- Introduction to concepts of the Constitution, Constitutional law and Constitutionalism
- Historical Background and Evolution of the Constitution
- Constitutional Law MCQs for Law Aspirants : Solved High-Quality MCQs for Judiciary Prelims
- Constituent Assembly – Journey and Challenges
- Indian Constituent Assembly: Features and its Committees
- Main Sources of the Indian Constitution
- Introduction to the Constitution of India
- Constitution of India – Full Text
Preamble: An Interpreter of the Constitution
- Preamble to the Constitution of India: Introduction, Features and Significance
- Features of the Constitution and a brief comparison with Various Constitutions
- Limited Government in India | Explained
Important Books and Practice Tests (Must Have)
- Constitutional Law of India by HM Seervai
- Constitution of India by V. N. Shukla
- The Constitution Of India Bare Act Along with Supreme Court Guidelines, Landmark Judgment, Important Tips, Legal Maxims, Words and phrases-Legally Defined
- 1000+ Detailed Questions MCQ Test Series for Competitions (Redirect to Law Aspirants)
Module II: Union and its Territory
- Formation of a state
- Concepts of Citizenship and Nationality
- Citizenship law in India | All you need to know
- A brief overview of the Citizenship Act, 1955
Module III: Concept of State and Various Fundamental Rights
- Concept of 'State' under Article 12
- Meaning of 'Law' under Article 13
- Article 13 and Power of Amendment under Article 368
- Right to Equality: Concept and Explanation | Article 14-18
- Case Analysis: Indra Sawhney v. Union of India (1993)
- Case Study: R.C. Poudyal v. Union of India [AIR 1993 SC 1804]
- Right to Freedom: Categories and Dimensions of Article 19
- The Golden Triangle in the Indian Constitution: Articles 14, 19, and 21
- Right to Life & Personal Liberty | Article 21 Explained
- Right to Privacy: Evolution
Module IV: Other Fundamental Rights
- Right to Education
- Right to Have a Clean and Healthy Environment: Analysing the Judicial Trends
- Right to Die with Dignity: A Constitutional Perspective
- Right Against Exploitation: A Comprehensive Analysis
- Right to Freedom of Religion (Articles 25-28)
- Cultural and Educational Rights (Art 29-30)
- Right to constitutional remedies (Art 32 and 226)
- Right to Property under the Indian Constitution Explained
- Martial Law in the Constitution of India
Module V: Interrelationship between Fundamental Rights and other parts of the Constitution
- Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy
- Parliamentary Privileges And Fundamental Rights
- Fundamental Rights and Emergency Provisions
- Freedom of Trade and Commerce: Explained
Module VI: Directive Principles Of State Policy And Fundamental Duties
- Directive Principles of State Policy: An Overview
- Fundamental Duties Enshrined in the Constitution of India
MODULE VII: Executive
- Constitutional provisions related to the President of India
- Constitutional provisions related to Governor
- Federalism in India: Unitary, Quasi, Cooperative, Competitive
MODULE VIII: Parliament and State Legislature
- The various forms of Government: A primary synopsis
- Indian Parliament: Composition, Functions, Privileges & Inter-relation
- State Legislature: Composition, Functions and Privileges
- Anti-Defection Law / Tenth Schedule
- Local Self Government In India | Panchayati Raj Institution & Urban Local self-governments
MODULE IX: Centre-State Relationship
- Distribution of Power: Legislative Relations between Centre and State
- Centre-State Financial relationship – Taxing powers of Union and State
- Administrative Relationship between the Centre and States
- Analysis of Provisions Related to Languages under the Indian Constitution
MODULE X: Union and State Judiciary
- Union Judiciary – Composition, Appointment, Condition of Services and Removal of Judges
- Jurisdiction of Supreme Court
- Special Leave Petition; Article 136 | Concept & Explanation
- State Judiciary – Composition, Appointment, Conditions of Services and Removal of Judges
- Jurisdiction of High Courts
- Judicial Review and Judicial Activism
MODULE XI: Emergency Provisions
- National Emergency Provisions Under the Indian Constitution
- Relationship between Fundamental Rights and Emergency Provisions
MODULE XII: Amendment of the Constitution
- The Doctrine of Basic Structure
- Judicial Review
- Constitutional Values of Landmark Amendments in India
- Important amendments in the Constitution of India
MODULE XIII: Other Miscellaneous Topics
- Schedules in the Indian Constitution | Explained
- Impact of Scrapping of Article 370 on the Fundamental Rights of the Citizens of J&K
- Public Service Commissions: Background, Establishment & Function
- Election Commission Of India: History, Composition, Powers and Functions
- Order of Precedence of the Government of India
Other Important articles and study material on Constitutional Law – Click on the links to Read:
8 Landmark Judgments on Article 15 of the Indian Constitution
- Conceptual Framework and Historical Evolution of the Right to Health
- Preventive Detention: Purpose and Implications
- Right to Privacy: Its Sanctity in India
- Important Judgments on Article 19: A Conceptual Analysis
- Genesis and Growth of Public Interest Litigation in India
- Salient Features of the Constitution of India
- Union and its Territories: As provided under Article 1-4 of the Indian Constitution
- Indian Constitution: Federal or Quasi-Federal
- Citizenship of India under the Indian Constitution
- Introduction to the Fundamental Rights of an Individual: As provided against the State
- Fundamental Rights – Nature, Scope and Importance
- Writ Jurisdiction of the Supreme Court
- Relationship between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policies (DPSPs)
- Fundamental Duties
- Governor's Role in the Context of Centre-State Relations
- Emergency Provisions
- Special Status of Jammu and Kashmir
- Freedom of Trade, Commerce And Intercourse
- Secularism in India – An Overview and Comparison with Saudi Arabia
- Pros and Cons of Constitutionalism
Concept of Eminent Domain
Significance of Studying Constitutional Law
Practice Prelims Test Series – Constitutional Law
Important Doctrines
Doctrine of Autrefois Acquit and Autrefois Convict: Double Jeopardy Protections in Law
- Doctrine of Territorial Nexus; Meaning, Explanation and Case Laws
Doctrine of Prospective Overruling
- Doctrine of Eclipse in Constitutional Law: Analysis with Related Case Laws
- Doctrine of Laches: Meaning and Elements
- Doctrine of Colourable Legislation
- Doctrine of Pith and Substance: Applicability in the Indian Constitution
- Doctrine of Incidental or Ancillary Powers: Explanation with Related Case Laws
Doctrine of Repugnancy
Important Case Laws
- Sajjan Singh v. State of Rajasthan (1965)
- Minerva Mills v. Union of India (1980)
- Bennett Coleman v. Union of India (1973)
- Indian Young Lawyers Association & Ors. v. The State of Kerala & Ors. (2018)
- Kuldip Nayar v. Union of India (2006)
- Lily Thomas v Union of India (2013)
- S.R. Bommai v. Union of India (1994)
- State of Haryana v. State of Punjab (2002)
Important Mains Questions Series for Judiciary, APO & University Exams
- Constitutional Law Mains Questions Series Part-I
- Constitutional Law Mains Questions Series Part-II
- Constitutional Law Mains Questions Series Part-III
- Constitutional Law Mains Questions Series Part-IV
- Constitutional Law Mains Questions Series Part-V
- Constitutional Law Mains Questions Series Part-VI
- Constitutional Law Mains Questions Series Part-VII
- Constitutional Law Mains Questions Series Part-VIII
- Constitutional Law Mains Questions Series Part-IX
- Constitutional Law Mains Questions Series Part-X
Your valuable feedback in the form of comments or any desired inputs are encouraged and always welcome. Every contribution toward a goal is valuable, regardless of how small it may be.
Admin Legal Bites
Legal Bites Study Materials correspond to what is taught in law schools and what is tested in competitive exams. It pledges to offer a competitive advantage, prepare for tests, and save a lot of money.
Related News


Case Study: Aid & Development in India
India's relationship with the world.

What are India's political relationships?
- India has historically had a bad relationship with Pakistan (which used to be part of India).
- India and China have historically had disputes over the border between the 2 countries. In 2020, during combat at the India-China border between Indian and Chinese soldiers, 20 people died.
- India is relatively isolated politically. However, its English speaking heritage and population have created economic ties - British Airways outsources its software development to India.
- India became a strategic partner of the EU in 2004. Initial negotiations over a free trade agreement started in 2007.

What are India's economic & trading relationships?
- The TAPI pipeline was funded by the Asian Development Bank and this flows from Turkmenistan to India, providing them all with Natural Gas.
- India is more open to foreign investment and US venture capitalists are investing in more Indian businesses like Byju's.
Types of Aid Received by India
India receives the following types of aid from the global community:

Short-term aid
- Short-term aid is meant to deal with emergencies.
- The 2005 Kashmir Earthquake led India to offer aid to its neighbours, Pakistan.
- In 2001, the UK sent aid to India after an earthquake.

Long-term aid
- Long-term aid is meant to help a country's development.
- Until 2012, India used to receive £280 million in aid, but now the UK gives its aid to poorer countries.
- In 2017, India received $3.1bn in foreign aid.

'Top-down' aid
- 'Top-down' aid usually comes from governments or NGOs. Governments decide how to spend the money and this is best spent on large projects or the development of infrastructure.

'Bottom-up' aid
- CDC Group is a government-owned finance institution that invests in India. Since 1988, it has invested $1.7bn in over 300 projects.
- Microfinance projects like KIVA allow individuals to invest in projects in India.
- 'Bottom-up' aid aims to help local people or individual projects, without requiring government support or direction.
What is the Impacts of Economic Development in India?

Higher quality of life
- In 2018, India's GNI per person was $2,020 and its HDI was 0.647.
- The adult literacy rate in India has increased to 74%, from 60%+ 10 years earlier.
- Access to clean water has improved, although before Narendra's Modi's Clean India campaign, only 39% of Indian households had access to toilets. Modi built 110 million toilets in India.

The impact of development on the environment
- Development has improved India's sewage system. Before Narendra's Modi's Clean India campaign, only 39% of Indian households had access to toilets. Modi built 110 million toilets in India.
- 51% of India's air pollution is caused by industry or manufacturing and people estimate that air pollution kills 2 million Indians prematurely each year.
- The city of Delhi is the most polluted city in the world.
- Forest habitats are destroyed to allow mining to happen.
- India's emissions of greenhouse gases have risen along with development.
1 The Challenge of Natural Hazards
1.1 Natural Hazards
1.1.1 Types of Natural Hazards
1.1.2 Hazard Risk
1.1.3 Consequences of Natural Hazards
1.1.4 End of Topic Test - Natural Hazards
1.1.5 Exam-Style Questions - Natural Hazards
1.2 Tectonic Hazards
1.2.1 Tectonic Plates
1.2.2 Tectonic Plates & Convection Currents
1.2.3 Plate Margins
1.2.4 Volcanoes
1.2.5 Effects of Volcanoes
1.2.6 Responses to Volcanic Eruptions
1.2.7 Earthquakes
1.2.8 Earthquakes 2
1.2.9 Responses to Earthquakes
1.2.10 Case Studies: The L'Aquila & Kashmir Earthquakes
1.2.11 Earthquake Case Study: Chile 2010
1.2.12 Earthquake Case Study: Nepal 2015
1.2.13 Living with Tectonic Hazards 1
1.2.14 Living with Tectonic Hazards 2
1.2.15 End of Topic Test - Tectonic Hazards
1.2.16 Exam-Style Questions - Tectonic Hazards
1.2.17 Tectonic Hazards - Statistical Skills
1.3 Weather Hazards
1.3.1 Global Atmospheric Circulation
1.3.2 Surface Winds
1.3.3 UK Weather Hazards
1.3.4 Tropical Storms
1.3.5 Features of Tropical Storms
1.3.6 Impact of Tropical Storms 1
1.3.7 Impact of Tropical Storms 2
1.3.8 Tropical Storms Case Study: Katrina
1.3.9 Tropical Storms Case Study: Haiyan
1.3.10 UK Weather Hazards Case Study: Somerset 2014
1.3.11 End of Topic Test - Weather Hazards
1.3.12 Exam-Style Questions - Weather Hazards
1.3.13 Weather Hazards - Statistical Skills
1.4 Climate Change
1.4.1 Evidence for Climate Change
1.4.2 Causes of Climate Change
1.4.3 Effects of Climate Change
1.4.4 Managing Climate Change
1.4.5 End of Topic Test - Climate Change
1.4.6 Exam-Style Questions - Climate Change
1.4.7 Climate Change - Statistical Skills
2 The Living World
2.1 Ecosystems
2.1.1 Ecosystems
2.1.2 Ecosystem Cascades & Global Ecosystems
2.1.3 Ecosystem Case Study: Freshwater Ponds
2.2 Tropical Rainforests
2.2.1 Tropical Rainforests - Intro & Interdependence
2.2.2 Adaptations
2.2.3 Biodiversity of Tropical Rainforests
2.2.4 Deforestation
2.2.5 Case Study: Deforestation in the Amazon Rainforest
2.2.6 Sustainable Management of Rainforests
2.2.7 Case Study: Malaysian Rainforest
2.2.8 End of Topic Test - Tropical Rainforests
2.2.9 Exam-Style Questions - Tropical Rainforests
2.2.10 Deforestation - Statistical Skills
2.3 Hot Deserts
2.3.1 Overview of Hot Deserts
2.3.2 Biodiversity & Adaptation to Hot Deserts
2.3.3 Case Study: Sahara Desert
2.3.4 Desertification
2.3.5 Case Study: Thar Desert
2.3.6 End of Topic Test - Hot Deserts
2.3.7 Exam-Style Questions - Hot Deserts
2.4 Tundra & Polar Environments
2.4.1 Overview of Cold Environments
2.4.2 Adaptations in Cold Environments
2.4.3 Biodiversity in Cold Environments
2.4.4 Case Study: Alaska
2.4.5 Sustainable Management
2.4.6 Case Study: Svalbard
2.4.7 End of Topic Test - Tundra & Polar Environments
2.4.8 Exam-Style Questions - Cold Environments
3 Physical Landscapes in the UK
3.1 The UK Physical Landscape
3.1.1 The UK Physical Landscape
3.2 Coastal Landscapes in the UK
3.2.1 Types of Wave
3.2.2 Weathering & Mass Movement
3.2.3 Processes of Erosion & Wave-Cut Platforms
3.2.4 Headlands, Bays, Caves, Arches & Stacks
3.2.5 Transportation
3.2.6 Deposition
3.2.7 Spits, Bars & Sand Dunes
3.2.8 Case Study: Landforms on the Dorset Coast
3.2.9 Types of Coastal Management 1
3.2.10 Types of Coastal Management 2
3.2.11 Coastal Management Case Study - Holderness
3.2.12 Coastal Management Case Study: Swanage
3.2.13 Coastal Management Case Study - Lyme Regis
3.2.14 End of Topic Test - Coastal Landscapes in the UK
3.2.15 Exam-Style Questions - Coasts
3.3 River Landscapes in the UK
3.3.1 The River Valley
3.3.2 River Valley Case Study - River Tees
3.3.3 Erosion
3.3.4 Transportation & Deposition
3.3.5 Waterfalls, Gorges & Interlocking Spurs
3.3.6 Meanders & Oxbow Lakes
3.3.7 Floodplains & Levees
3.3.8 Estuaries
3.3.9 Case Study: The River Clyde
3.3.10 River Management
3.3.11 Hard & Soft Flood Defences
3.3.12 River Management Case Study - Boscastle
3.3.13 River Management Case Study - Banbury
3.3.14 End of Topic Test - River Landscapes in the UK
3.3.15 Exam-Style Questions - Rivers
3.4 Glacial Landscapes in the UK
3.4.1 Erosion
3.4.2 Landforms Caused by Erosion
3.4.3 Landforms Caused by Transportation & Deposition
3.4.4 Snowdonia
3.4.5 Land Use in Glaciated Areas
3.4.6 Tourism in Glacial Landscapes
3.4.7 Case Study - Lake District
3.4.8 End of Topic Test - Glacial Landscapes in the UK
3.4.9 Exam-Style Questions - Glacial Landscapes
4 Urban Issues & Challenges
4.1 Urban Issues & Challenges
4.1.1 Urbanisation
4.1.2 Urbanisation Case Study: Lagos
4.1.3 Urbanisation Case Study: Rio de Janeiro
4.1.4 UK Cities
4.1.5 Case Study: Urban Regen Projects - Manchester
4.1.6 Case Study: Urban Change in Liverpool
4.1.7 Case Study: Urban Change in Bristol
4.1.8 Sustainable Urban Life
4.1.9 End of Topic Test - Urban Issues & Challenges
4.1.10 Exam-Style Questions - Urban Issues & Challenges
4.1.11 Urban Issues -Statistical Skills
5 The Changing Economic World
5.1 The Changing Economic World
5.1.1 Measuring Development
5.1.2 Classifying Countries Based on Wealth
5.1.3 The Demographic Transition Model
5.1.4 Physical & Historical Causes of Uneven Development
5.1.5 Economic Causes of Uneven Development
5.1.6 How Can We Reduce the Global Development Gap?
5.1.7 Case Study: Tourism in Kenya
5.1.8 Case Study: Tourism in Jamaica
5.1.9 Case Study: Economic Development in India
5.1.10 Case Study: Aid & Development in India
5.1.11 Case Study: Economic Development in Nigeria
5.1.12 Case Study: Aid & Development in Nigeria
5.1.13 Economic Development in the UK
5.1.14 Economic Development UK: Industry & Rural
5.1.15 Economic Development UK: Transport & North-South
5.1.16 Economic Development UK: Regional & Global
5.1.17 End of Topic Test - The Changing Economic World
5.1.18 Exam-Style Questions - The Changing Economic World
5.1.19 Changing Economic World - Statistical Skills
6 The Challenge of Resource Management
6.1 Resource Management
6.1.1 Global Distribution of Resources
6.1.2 Food in the UK
6.1.3 Water in the UK 1
6.1.4 Water in the UK 2
6.1.5 Energy in the UK
6.1.6 Resource Management - Statistical Skills
6.2.1 Areas of Food Surplus & Food Deficit
6.2.2 Food Supply & Food Insecurity
6.2.3 Increasing Food Supply
6.2.4 Case Study: Thanet Earth
6.2.5 Creating a Sustainable Food Supply
6.2.6 Case Study: Agroforestry in Mali
6.2.7 End of Topic Test - Food
6.2.8 Exam-Style Questions - Food
6.2.9 Food - Statistical Skills
6.3.1 The Global Demand for Water
6.3.2 What Affects the Availability of Water?
6.3.3 Increasing Water Supplies
6.3.4 Case Study: Water Transfer in China
6.3.5 Sustainable Water Supply
6.3.6 Case Study: Kenya's Sand Dams
6.3.7 Case Study: Lesotho Highland Water Project
6.3.8 Case Study: Wakel River Basin Project
6.3.9 Exam-Style Questions - Water
6.3.10 Water - Statistical Skills
6.4.1 Global Demand for Energy
6.4.2 Factors Affecting Energy Supply
6.4.3 Increasing Energy Supply: Renewables
6.4.4 Increasing Energy Supply: Non-Renewables
6.4.5 Carbon Footprints & Energy Conservation
6.4.6 Case Study: Rice Husks in Bihar
6.4.7 Exam-Style Questions - Energy
6.4.8 Energy - Statistical Skills
Jump to other topics

Unlock your full potential with GoStudent tutoring
Affordable 1:1 tutoring from the comfort of your home
Tutors are matched to your specific learning needs
30+ school subjects covered
Case Study: Economic Development in India
Case Study: Economic Development in Nigeria
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Edexcel B GCSE Geography Development - India Homework/Revision Booklet
Subject: Geography
Age range: 14-16
Resource type: Assessment and revision
Last updated
25 April 2024
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Whats Included
Exam-Targeted Content: This booklet is packed with exam-focused content, specifically catering to the Development in India section of the Edexcel B GCSE Geography curriculum. Every aspect is meticulously designed to align with the exam requirements, ensuring that students are fully prepared to tackle questions related to India’s development.
Expertly Crafted Revision Tasks: Featuring a series of meticulously structured revision tasks, this booklet ensures comprehensive coverage of the Development in India topic.
In-Depth Case Study Notes: Gain an in-depth understanding of India’s development through our comprehensive case study notes. These notes delve into the economic, social, and environmental aspects of India’s development, providing students with a solid foundation to tackle exam questions with confidence.
Diverse Range of Engaging Activities e.g. crossowrds, exam practise; multiple choice questions.
Mastery of Key Terminology: The booklet highlights and explains key terms and concepts essential for success in the Development in India topic. This aids students in becoming fluent in the language of geography, ensuring they’re equipped with the necessary vocabulary to excel in their exams.
Exemplary Model Answers: Sample model answers for select questions are included, showcasing top-scoring responses to guide students in understanding the depth and quality expected in their answers.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
Commerce Aspirant » Economics Class 12 » Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours Class 12 Notes
Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours Class 12 Notes
Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours Class 12 Notes are provided for the aid of students to assist them with fast learning. These notes ensure a simple and easy understanding of the text. The notes help students to compare, analyze and criticize the development path taken by India and its two neighbors i.e. Pakistan and China.
- Introduction
- The development path of China
- The development path of Pakistan
Similarities in the development path of all three countries India, China, and Pakistan
- Population size
- The growth rate of the population
- Density of population
- Fertility rate
- Urbanization
Comparison of GDP, the growth rate of GDP, and sectoral contribution
- Human development indicators
Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours Introduction
India , Pakistan and China have many similarities in their developmental strategies. Every country has been trying to adopt various means to strengthen their domestic economies;
- They are forming various regional and global economic grouping such as the EU (European Union), ASEAN Association of Southeast Asian Nations), BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa), GR and G-20, etc.
- They are also trying to understand know the development policies and strategies pursued by their neighboring countries to realize/ analyze their strengths and weakness because, in the process of globalization, they are facing competition not only from developed countries but also from other developing countries.
The development path of China – Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours Class 12 Notes
- China has one of the world’s oldest people and continuous civilizations. It is situated in eastern Asia, bounded by the Pacific in the east and the third-largest country in the world, next to Canada and Russia, with an area of 9.5 million square kilometers.
- It is the most populous country in the world with 134,76 crores people (as per 2011 estimates).
- After the establishment of the People’s Republic of China on 1 October 1949 under one-party rule, all the critical sectors of the economy, enterprises, and lands owned and operated by individuals were brought under government control
- Immediately after the revolution of 1949, the Chinese economy system was declared as a communist system, and the other economy became a command economy or centrally planned economy like that of the Soviet.
- The development path of the Chinese economy can broadly be divided into two periods:
- The Mao period or pre-reform period (1949-1976)
- The post-Mao period or the reform period (1976 onwards)
The Mao period or pre-reform period 1948-1976
The Mao period is characterized as a Soviet-style planned economy because it abolished/ removed the market system or price system and all critical sectors were brought under government control which was earlier operated and owned by individuals. China started planning development strategies and announced its first Five Year Plan in 1953.
Following policies pursued in the Mao period:
(a) great leap forward campaign.
The great leap forward campaign was initiated/ launched in 1958 by Mao to modernize China’s economy. Initially, China’s economy was agrarian and the basic aim of this campaign was to transform the agrarian economy into a modern economy through the process of rapid industrialization.
Under this program/ campaign, people were allowed/ encouraged to set up industries in their backyards to achieve the aim of industrialization at a massive scale.
Problems faced by GLF
- A severe drought caused havoc in China killing 30 million people.
- Withdrawal of Russian professionals by Russia due to conflict between China and Russia who had been helping China in its industrialization.
(B) Commune system
In order to increase agriculture production and productivity and modernize the agriculture sector, the commune system was launched/ started in 1958) in rural areas.
Commune means collective cultivation of lands, so under this system people collectively cultivated lands. In 1958, there were 26,000 communes, covering almost all the farm population.
(C) Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution
In 1966-67, Mao Tse Tung introduced the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, under which students and professionals were sent to work and learn in the countryside (different parts of the country).
Its basic aim was to weed out people opposed to the communist ideology. This revolution resulted in hardship for the people and a large number of people were also massacred.
Besides it, to support rapid industrialization, the central government undertook large-scale investment in physical and human capital during 1960. As the result, by 1978 nearly three-fourths of industrial production was
produced by centrally-controlled state-owned enterprises and private enterprises and foreign enterprises were nearly non-existent. The main goal was to make China’s economy relatively self-sufficient.
The post-Mao period or the reform period 1976 onwards
The present-day fast industrialization growth in China can be traced back to the reforms introduced in 1978.
The reforms were introduced in the followings phases;
(A) Initial/first phase
Reforms were initiated in agriculture, foreign trade, and investment sectors.
In the agriculture sector, commune lands were divided into small plots and allocated to the individual households for cultivation. They were allowed to keep all farm income after paying taxes to the government but they were not given ownership rights over these plots.
In the industrial sector, private sector firms and village enterprises were allowed to set up manufacturing units and produce goods that were earlier reserved for state-owned enterprises. The basic aim was to create a competitive environment and to achieve the objective, state-owned enterprises were made to face competition for enhancing efficiency and productivity.
To attract foreign investment, Special Economic Zones (SEZ) was set up.
(B) In the later phase
A dual pricing system was introduced. Under this system, farmers and industrial units were required to buy and sell fixed quantities of inputs (raw material) and outputs based on prices fixed by the government, and the rest were purchased and sold at market prices in the open market.
The development path of Pakistan – Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours Class 12 Notes
The development path of Pakistan has been described under the Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours Class 12 Notes as follows;
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, gained independence on 14 August 1947. In 1971, a civil war in East Pakistan resulted in the independence of Bangladesh. Pakistan is the sixth most populous country in the world with 17 crores people and has an area of 7, 96,095 square kilometers.
- After gaining independence in 1947, Pakistan also followed a mixed economy model with the co-existence of public and private sectors.
- In the late 1950s and 1960s, Pakistan introduced a variety of regulated policy framework for the growth of domestic industries. The policy combined tariff protection with direct import control.
- Pakistan started planning its development strategies and announced its first Five Year Plan in 1956.
- In the agriculture sector, the introduction of the green revolution and increase in public investment in infrastructure led to mechanization and a rise in food grain production. This changed the agrarian structure dramatically.
- In early 1970, capital goods industries were nationalized.
- In late 1970, there was a shift in government policy when it adopted the policy of denationalization. The government encouraged the private sector and offered various incentives to create a conducive climate for new investment. Besides it, during this period, Pakistan received financial assistance from western countries and remittances from emigrants (Pakistani workers settled in the Middle East) to the Middle East. This all helped in accelerating economic growth and creating a favorable environment for new investment.
- In 1988, reforms were initiated in the country into various sectors.
Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours Class 12 Notes state the following similarities in the development Path of these three nations.
- All three started development paths at the same time. While India and Pakistan gained independence in 1947. The Republic of China was established in 1949.
- All three countries started planning their development strategies in similar ways. While India announced its first Five Year Plan in 1951, Pakistan announced its first Five Year Plan in 1956 and China announced its first Five Year Plan in 1953.
- All three economies introduced reforms. Reforms introduced in India in 1991, in China in 1978, and Pakistan in 1988,
- Initially, all three countries adopted similar strategies such as creating a large public sector and raising public expenditure on social development.
- Until the 1980s, all three countries had similar growth rates and per capita income.
Comparisons of Demographic Indicators
Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours Class 12 Notes use the following demographic indicators to compare the three countries.
1. Population size
China is the most populous country in the world with 134 crore population which is 19.4% of the total world population. India is the second most populated country with 121 crore which is about 17% of the total world population. population. The population of Pakistan is very small/ less i.e. about 17 crore which is 2.5% of the total world population and it accounts for roughly one-tenth of China or India.
Out of every six persons living in the world, one is an Indian and another Chinese.
2. Growth rate of population
In Spite of being the most populous country in the world, China’s population growth rate (0.47%) is lower than India’s (1.7%) and Pakistan’s (2.5%). The reason behind the lowest growth rate of population is the “One Child Policy” introduced by China in 1979. It has successfully reduced the rate of population growth from 1.33 % in 1979 to 0.64% in 2005 and further 0.47% in the recent past.
3. Density of Population
Density refers to the number of persons living per square kilometer of land area. The density of population in China is the lowest (146) as compared to India (441) and Pakistan (245)
Reasons behind lowest population density:-
(a) China is the third-largest country and also largest among three with 95, 61,000 square kilometers area, followed by India with land area 32, 68,090 square kilometers and Pakistan is the smallest country with land area 8, 03,944 sq km.
(b)Lowest growth rate of population.
4. Sex Ratio
Due to the preference of sons, the sex ratio is low and biased against females in all three countries. The sex ratio is the lowest in China with 926 females per 1000 males and corresponding figures in India and Pakistan, are 940 and 943 females per male. It points to social backwardness and female foeticide is the principal cause of the low sex ratio.
5. Fertility Rate
It is defined as several children borne by a woman in the reproductive age of 15-45 years on average. The fertility rate in Pakistan is highest with 5.1 in comparison to 3 in India and 1.8 in China. Due to introduction
6. Urbanization
It is closely linked with structural transformation in the country and is a consequence of a shift of the workforce from the agriculture sector to the industry and service sector. Both Pakistan and China have relatively higher rates of urbanization as compared to India. In India, 30% of the population is urbanized compared with 47% in China and 36% in Pakistan.
GDP refers to the total value of final goods and services produced in the domestic territory of a country during one year. China has the second-largest GDP (PPP) of 7.2 trillion dollars whereas India’s GDP (PPP) is 3,3 trillion dollars and Pakistan’s GDP is roughly about 10% of India’s GDP.
GDP growth rate
When many developed countries were finding it difficult to maintain a growth rate of even 5%, China was able to maintain near double-digit growth for more than two decades. Until 1980, the economies of India, China, and Pakistan were growing slowly about 4% per annum.
(A) There was a marginal rise in China’s growth rate from 10.3% to 10.9%
(B) Pakistan also experienced a marginal rise from 5.3% to 5.8%
(C) Indians experienced a substantial rise from 5.7% to 7.8 %.
Sectoral contribution
It refers to the contribution (percentage share) made by each sector of the economy i.e. primary, secondary, and tertiary.
The historical experience of developed countries shows that an economy develops first the industrial sector and later the service sector but the experience of India and Pakistan has been different. In both countries, there has been a direct shift from the primary to the services sector.
(A) In both India and Pakistan, the service sector is emerging as a major player in development. The service sector contributes the highest to their GDP, with a contribution of 55.6 % in the case of India and 53.4% for Pakistan. But the contribution of the service sector to the GDP in China is 43.6%.
(B) In China, the contribution of the secondary sector is highest to GDP at 46.8 % whereas, in India and Pakistan, it contributes. in India and Pakistan 26.3% and 25.4% respectively.
Reasons:- GLF campaign launched in 1958 and reforms in 1978.
(C) Contribution of agriculture/ primary sector in India is 18.1% and in Pakistan is 21.2% whereas its contribution in China is only 9.6%.
(D) China’s growth is led by the industrial sector whereas the service sector is playing a dominant role in the growth of Pakistan and India.
Human Development Indicators
The human development index is one of the most important indicators to study the human development of a country.
This index was introduced by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). The first Human development
The report was prepared under the guidance of Mahbub-ul-Haq and published in 1990. It is a composite index of such indicators as life expectancy, infant mortality rate, maternal mortality rate, per capita income (PPP), poverty, sanitation, drinking water, etc. which is used to measure the performance of a country in social and economic development.
Some Selected Indicators of Human Development, 2017-2019
Reasons for re-emergence of poverty and slow growth rate in pakistan..
- Growth in agricultural and food supplies is based on good harvests, not on an institutionalized process of technical change. As a result, agricultural performance remains unstable and highly vulnerable to climatic conditions.
- For its foreign exchange needs, Pakistan mainly relies on foreign remittances and volatile agricultural exports.
- Lack of political stability.
- Growing dependence on foreign loans and the increasing difficulty of paying back the loans with interest.
- Huge allocation of funds for non-development activities like defense and reduction in development expenditure.
Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours Class 12 Notes gives a detailed understanding and comparison of the text which deals with the development path followed by three nations i.e India, China, and Pakistan after independence. The chapter also analyses the developmental status of the three countries in the present world and compares them.
CBSE Class 12 Economics Notes Term II Syllabus
Part A: Introductory Macroeconomics
- Circular Flow of Income Class 12 Notes
- Basic Concepts of Macroeconomics Class 12 Notes
- National Income and Related Aggregates Class 12 Notes – 10 Mark
- National Income and Related Aggregates Class 12 Numericals
- Aggregate Demand and Its Related Concepts Class 12 Notes
- Excess Demand and Deficit Demand Class 12 Notes
- National Income Determination and Investment Multiplier Class 12 Notes
Part B: Indian Economic Development
Current challenges facing Indian Economy – 12 Marks
- Employment Class 12 Notes
- Infrastructure Class 12 Notes
- Sustainable Economic Development Class 12 Notes
Development Experience of India – A Comparison with Neighbours – 6 Marks
- Comparative Development Experience of India and its Neighbours Class 12 Notes
- Economics Class 12 Notes
- Business Studies Class 12 Notes
- Accountancy Class 12 Notes
- Economics Class 12 MCQs
- Business Studies Class 12 MCQs
- Accountancy Class 12 MCQs
Sandeep garg Class 12 Solutions
Unit Number 319, Vipul Trade Centre, Sohna Road, Gurgaon, Sector 49, Gurugram, Haryana-122028, India
- +91-9667714335
- [email protected]
Class 11 Notes
- Economics Class 11 Notes
- Accountancy Class 11 Notes
Class 11 MCQs
- Economics Class 11 MCQs
- Business Studies Class 11 MCQs
Class 12 Notes
Class 12 MCQs
Cracking Class 12: Notes on Comparative Development Experiences of India and Its Neighbours
Welcome to an exploration into the comprehensive notes on the comparative experiences of India and its neighbors: Pakistan and China. For the students of Class 12 Economics gearing up for the 2023-24 board exams, this journey into Chapter 8 – Indian Economic Development is indispensable.
The Class 12 syllabus for the academic year 2023-24 mandates a thorough grasp of the comparative development experiences of India, Pakistan, and China.
To gain a deeper understanding, we'll compare India's development to that of its neighbors, Pakistan and China. By analyzing their policies, societies, and histories, we can identify India's strengths and weaknesses.

“Don't be afraid to fail. Not failure, but low aim, is the greatest crime.” — Vince Lombardi
Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours Class 12 Notes
Table of contents, development path - a snapshot view.
All three countries had started planning their development strategies in similar ways.
- India announced its first Five Year Plan for 1951–56,
- Pakistan announced its first five-year plan, now called the Medium Term Development Plan, in 1956.
- China announced its First Five Year Plan in 1953.
- India and Pakistan adopted similar strategies, such as creating a large public sector and raising public expenditure on social development.
Till the 1980s, all three countries had similar growth rates and per capita incomes.
Great Leap Forward (GLF) campaign
- Initiated in 1958 aimed at industrializing the country on a massive scale.
- People were encouraged to set up industries in their backyards.
- In rural areas, communes were started. Under the Commune system , people collectively cultivated lands.
- A severe drought caused havoc in China killing about 30 million people.
- When Russia had conflicts with China, it withdrew its professionals who had earlier been sent to China to help in the industrialization process.
In 1965, Mao introduced the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution (1966–76) under which students and professionals were sent to work and learn from the countryside.
Reforms in China
- Reforms were introduced in China in 1978.
- In the initial phase, reforms were initiated in the agriculture, foreign trade, and investment sectors. In agriculture commune lands were divided into small plots, which were allocated (for use not ownership) to individual households.
- In the later phase, reforms were initiated in the industrial sector. Private sector firms were allowed to produce goods. At this stage, State Owned Enterprises—SOEs, were made to face competition.
- The reform process also involved dual pricing . This means fixing the prices in two ways; farmers and industrial units were required to buy and sell fixed quantities of inputs and outputs on the basis of prices fixed by the government and the rest were purchased and sold at market prices.
- In order to attract foreign investors, special economic zones were set up.
- Pakistan follows the mixed economy model.
- In the late 1950s and 1960s, Pakistan introduced a variety of regulated policy frameworks (for import substitution-based industrialization).
- The introduction of the Green Revolution led to mechanization and an increase in public investment in infrastructure in select areas
- In the late 1970s and 1980s, the major thrust areas were denationalization and encouragement of the private sector.
- During this period, Pakistan also received financial support from Western nations and remittances from the continuously increasing outflow of emigrants to the Middle East.
- In 1988, reforms were initiated in Pakistan
Note: Reforms were introduced in 1978 in China, in 1988 in Pakistan, and in 1991 in India.
Demographic Indicators
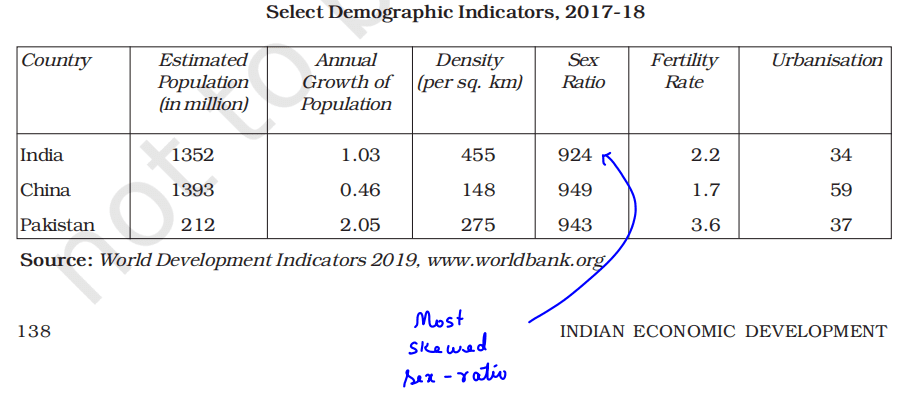
- The population of Pakistan is very small and accounts for roughly one-tenth of China or India.
- Though China is the largest nation and geographically occupies the largest area among the three nations, its density is the lowest.
- The population growth is the highest in Pakistan, followed by India and China.
- The one-child norm was introduced in China in the late 1970s.
- It is the major reason for low population growth.
- This led to a decline in the sex ratio.
- After a few decades, in China, there will be more elderly people in proportion to young people.
- India has the most skewed sex ratio.
- The fertility rate is low in China and very high in Pakistan.
- Urbanization is high in China with India having 34% of its people living in urban areas.
Gross Domestic Product and Sectors
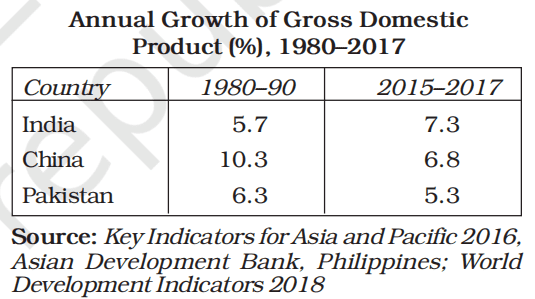
- When many developed countries were finding it difficult to maintain a growth rate of even 5%, China was able to maintain near double-digit growth during the 1980s.
- In the 1980s, Pakistan was ahead of India; China was having double-digit growth and India was at the bottom.
- In 2015–17, there was a decline in Pakistan and China’s growth rates, whereas, India met with a moderate increase in growth rates.
- Some scholars hold the reform processes introduced in Pakistan and political instability over a long period as reasons behind the declining growth rate in Pakistan.
Sectoral Share of Employment and GVA
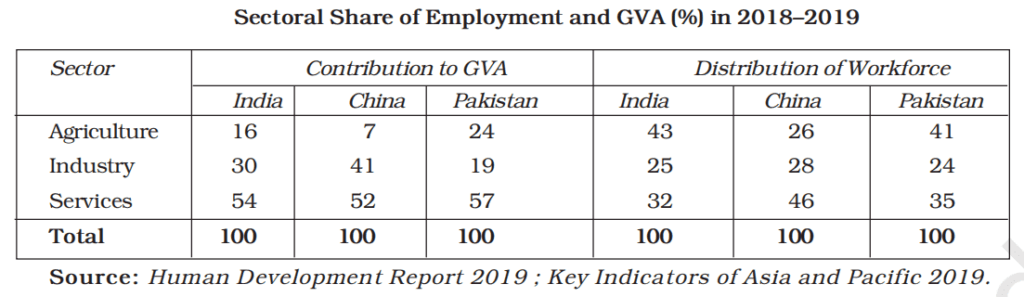
- Until the 1980s, more than 80% of the people in China were dependent on farming as their sole source of livelihood.
- In 2018-19, with 26% of its workforce engaged in agriculture, its contribution to the GVA in China was 7%
- In both India and Pakistan, the contribution of agriculture to GVA was 16 and 24 percent, respectively, but the proportion of the workforce that works in this sector is higher in India.
- In the normal course of development, countries first shift their employment and output from agriculture to Industry and then to services. This is happening in China.
- In all three countries, the service sector is emerging as a major player in development. It contributes more to GVA and, at the same time, emerges as a prospective employer.
- In the last five decades, the growth of the agriculture sector, which employs the largest proportion of the workforce in all three countries, has declined.
- China’s growth is contributed by the manufacturing and service sectors, and India’s growth by the service sector.
Indicators of Human Development
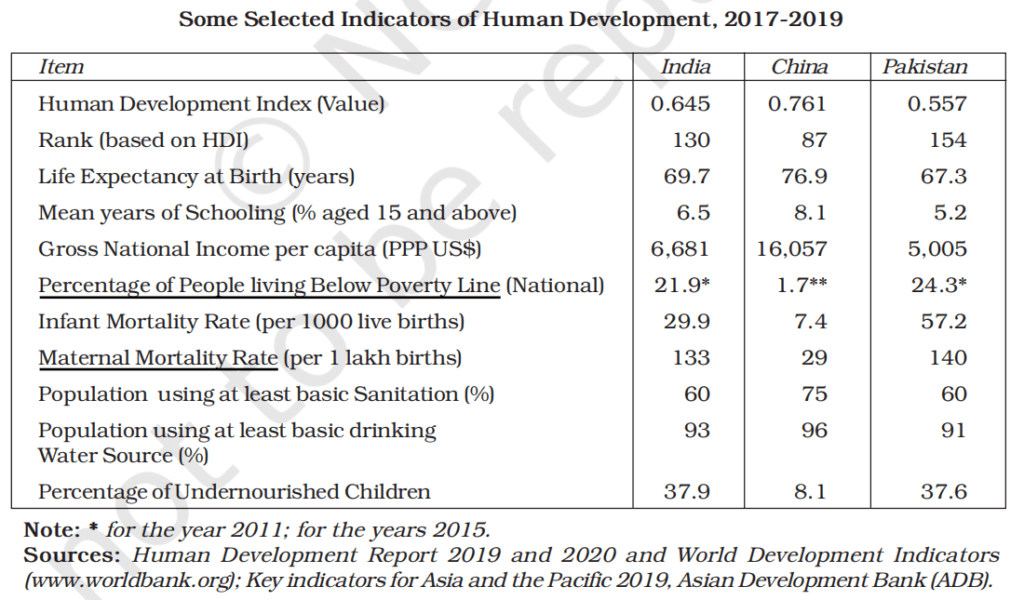
China is moving ahead of India and Pakistan. This is true for many indicators —
- income indicator such as GDP per capita
- proportion of the population below the poverty line
- health indicators such as mortality rates
- access to sanitation
- life expectancy
- malnourishment.
Liberty Indicators: Liberty indicators are measures or criteria used to evaluate the degree of freedom and individual rights within a society.
Here are some liberty indicators:
- Democratic Participation in Decision-Making
- Constitutional Protection of Citizens' Rights
- Independence of the Judiciary
- Rule of Law
Development Strategies - An Appraisal
- China did not have any compulsion to introduce reforms as dictated by the World Bank and International Monetary Fund to India and Pakistan.
- Before the introduction of reforms, there had already been a massive extension of basic health services in rural areas.
- Through the commune system, there was a more equitable distribution of food grains.
- Experts also point out that each reform measure was first implemented at a smaller level and then extended on a massive scale.
Scholars argue that in Pakistan the reform process led to the worsening of all the economic indicators.
The reasons for the slow-down of growth and re-emergence of poverty in Pakistan’s economy, are:
- political instability,
- over-dependence on remittances and foreign aid
- volatile performance of the agriculture sector
Hope you liked these Notes on Class 12 Economics Indian Economic Development Chapter 8 Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours. Please share this with your friends and do comment if you have any doubts/suggestions to share.
Related Posts
How to start class 11 preparation, cbse class 12 economics board exam 2023: paper analysis and answer key, indian economy on the eve of independence class 12 questions & answers, indian economy on the eve of independence: class 12 notes and study material, the last lesson class 12: top questions and answers for exam preparation, the third level class 12: important questions and answers, national income and related aggregates class 12 notes: a comprehensive guide, my mother at sixty-six class 12: important questions and answers, lost spring class 12: important questions and answers for your exam preparation, national income accounting class 12: important questions and answers, 1 thought on “cracking class 12: notes on comparative development experiences of india and its neighbours”.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Topic 1 – Economics India Case Study
DOWNLOAD THE RESOURCE
Resource Description
Highly detailed case study into India’s economy for topic 1 economics. Received mark of 10/30
Report a problem
Popular HSC Resources
- Speech on George Orwell ‘1984’ – Human Experiences
- How To Survive the HSC
- One Night the Moon – Analysis (Video)
- 2020 – Physics – PHS (Trial Paper)
- Business Studies Influences on HR (Quiz)
- Sci Ext – Portfolio Pack
- 2020 – Science Ext – Exam Choice (Trial Paper)
- Domino’s Marketing Case Study
Become a Hero
Easily become a resource hero by simply helping out HSC students. Just by donating your resources to our library!
What are you waiting for, lets Ace the HSC together!
Join our Email List
No account needed.
Get the latest HSC updates.
All you need is an email address.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
India's Economy. Source: mgmresearch.com. India has the fifth largest economy in the world, with GDP (Gross Domestic Product) rising steadily for the last twenty years (GDP = the value of any goods, produce or services made or conducted in a country). This increased rate of economic growth is largely due to India's trade becoming more ...
GCSE; Edexcel; Case study - development in an emerging country - India - Edexcel A brief introduction to India. India is a new emerging economy (NEE) that is experiencing rapid economic development.
A case study of a sparsely populated area - Himalayan Mountains; A case study of a densely populated area - Greater London; What is a settlement? ... Population Case Study: Kerala, India; Population change in MEDCs; Resources. Types of Energy; Non-renewable Energy; Renewable Energy; Resource Management.
Catherine looks at a case study of development in India for your GCSE Geography exam. In this episode, she will look at the background to the country of Indi...
Union Carbide Corporation vs Union of India: The Bhopal Gas Tragedy Case (1989) I.R.Coelho vs the State of Tamil Nadu and Others: The I. R. Coelho Case (2007) People's Union for Civil Liberties (PUCL) vs Union of India: The Nota Case (2013): Manoharl Lal Sharma vs Narendra Damodardas Modi: The Rafale Case (2018) M Siddiq vs Mahant Suresh Das: The Ayodhya Case (2019)
Explore Constitutional Law resources: Notes, Case Laws, and Study Material at Legal Bites. ... Union of India (1993) Case Study: R.C. Poudyal v. Union of India [AIR 1993 SC 1804] Right to Freedom: Categories and Dimensions of Article 19; The Golden Triangle in the Indian Constitution: Articles 14, 19, and 21;
Provides 33% of India's entire tax revenue 40% of international flights to India land in Mumbai - tourism Mumbai is the home of Bollywood, the huge film hub which produces more lms than Hollywood each year. This is a huge part of the revenue that supports Mumbai, as well as attracting tourists from around the world.
Mumbai is a megacity in Western India, along the coast of the Arabian Sea. There are many reasons why Mumbai is a leading city economically: Mumbai has a population of 22 million and is the second largest city in India. Mumbai has a large deep-water port that is critical for international trade. Mumbai International Airport sees 32 million ...
In 2018, India's GNI per person was $2,020 and its HDI was 0.647. The adult literacy rate in India has increased to 74%, from 60%+ 10 years earlier. Access to clean water has improved, although before Narendra's Modi's Clean India campaign, only 39% of Indian households had access to toilets. Modi built 110 million toilets in India.
In-Depth Case Study Notes: Gain an in-depth understanding of India's development through our comprehensive case study notes. These notes delve into the economic, social, and environmental aspects of India's development, providing students with a solid foundation to tackle exam questions with confidence.
Case study - development in an emerging country - India - Edexcel Test questions India is a new emerging economy (NEE) that is experiencing rapid economic development. This is leading to social ...
India has 12 major ports and more than 20 international airports. 96% of children are now enrolled in a school. Life expectancy has increased from 58 in 1990 to 68 in 2014. Fertility decreased from 4.0 in 1990 to 2.4 in 2014. In 1990, only 26% of the population lived in urban areas. By 2015, this had risen to 33%.
1. Large fish stocks, 2. Huge potential for offshore wind, tidal and wave power. 3. 35% of coast ladened with minerals and heavy metal deposits. 4. Oil and natural gas offshore. 5. Tourism - beaches, wildlife sanctuaries, archeological sites.
Published in October 2021, this report reviews the ways in which the Covid-19 pandemic impacted India's education sector. It was written by the UNICEF regional offices for South Asia and East Asia and Pacific, in collaboration with UNESCO, Bangkok. Cambridge Education, a consultancy firm based in the United Kingdom, helped carry out the analysis. The report reviews relevant secondary data to ...
Odisha coast overview. Location: South east coast of India, boardering the Bay of Bengal. Size: 9th largest state by area and 11th by population. Physical challenges of Odisha. Geology: Mainly sandy beaches and sedimentary rock = weak. Erosional Processes: Cyclones and storms cause erosion, wave action on vulnerable coatlines.
Comparative Development Experiences of India and its Neighbours Class 12 Notes use the following demographic indicators to compare the three countries. 1. Population size. China is the most populous country in the world with 134 crore population which is 19.4% of the total world population. India is the second most populated country with 121 ...
Reach Us 12, Main AB Road, Bhawar Kuan, Indore, Madhya Pradesh, 452007 641, 1 st Floor, Mukherjee Nagar, Delhi-110009 ; 21, Pusa Rd, WEA, Karol Bagh, Delhi-110005
Welcome to an exploration into the comprehensive notes on the comparative experiences of India and its neighbors: Pakistan and China. For the students of Class 12 Economics gearing up for the 2023-24 board exams, this journey into Chapter 8 - Indian Economic Development is indispensable. The Class 12 syllabus for the academic year 2023-24 mandates […]
2020 International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank 1818 H Street NW Washington DC 20433 Telephone: 202-473-1000 Internet: www.worldbank.org. This work is a product of the staff of The World Bank with external contributions.
rape case. Case study: Why did Ford choose Gujarat over Chennai for its second car plant in India? This is a good example of the locational factors that may determine where a company builds a new plant. The Chief Minister of Gujarat, Narendra Modi, wanted to increase April 2013 no.690 India: A Case Study of a newly industrialising country
Midterm Case Study Abdelrahman Younes Eslsca University MKT521: Marketing Management Dr. Ann Adham November 29, 2023. This case study provides a comprehensive view of India's e-commerce market, primarily focusing on Flipkart and Amazon and their strategies to capture and retain market share. The study explores various aspects such as the growth ...
50K new study notes added every day, from the world's most active student communities. 35M. Study resources. ... HRM Harvard Case Study - Recruitment of a Star. Human Resource Management. 28. Java - Lecture notes 1. ... India. Company. About us; Ask AI; Studocu World University Ranking 2023; E-Learning Statistics; Doing Good;
DOWNLOAD THE RESOURCE. Resource Description. Highly detailed case study into India's economy for topic 1 economics. Received mark of 10/30. Report a problem. Subscribe. Download this Assessment Task document for HSC - Economics. Find free HSC resources like study notes, essays, past papers, assignment, case studies & ...
1 The medieval period in India began after the death of Harshavardhana . 2 The study of coins is calledNumismatics. 3 William Hawkins was an ambassador of king James I in the court of Jahangir. 4 Alberuni , a Persian traveller visited India with Mahmud of Ghazni. 5 Akbarnama was written by Abul Fazal. 6 Turks, Afghans and Mongols entered India