News alert: UC Berkeley has announced its next university librarian

Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Conducting a literature review: why do a literature review, why do a literature review.
- How To Find "The Literature"
- Found it -- Now What?
Besides the obvious reason for students -- because it is assigned! -- a literature review helps you explore the research that has come before you, to see how your research question has (or has not) already been addressed.
You identify:
- core research in the field
- experts in the subject area
- methodology you may want to use (or avoid)
- gaps in knowledge -- or where your research would fit in
It Also Helps You:
- Publish and share your findings
- Justify requests for grants and other funding
- Identify best practices to inform practice
- Set wider context for a program evaluation
- Compile information to support community organizing
Great brief overview, from NCSU
Want To Know More?
- Next: How To Find "The Literature" >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 1:10 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/litreview

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 13 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
Libraries | Research Guides
Literature reviews, what is a literature review, learning more about how to do a literature review.
- Planning the Review
- The Research Question
- Choosing Where to Search
- Organizing the Review
- Writing the Review
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it relates to your research question. A literature review goes beyond a description or summary of the literature you have read.
- Sage Research Methods Core Collection This link opens in a new window SAGE Research Methods supports research at all levels by providing material to guide users through every step of the research process. SAGE Research Methods is the ultimate methods library with more than 1000 books, reference works, journal articles, and instructional videos by world-leading academics from across the social sciences, including the largest collection of qualitative methods books available online from any scholarly publisher. – Publisher
- Next: Planning the Review >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 10:39 AM
- URL: https://libguides.northwestern.edu/literaturereviews
Research Methods
- Getting Started
- Literature Review Research
- Research Design
- Research Design By Discipline
- SAGE Research Methods
- Teaching with SAGE Research Methods
Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- What is NOT a Literature Review?
- Purposes of a Literature Review
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Literature Reviews vs. Systematic Reviews
- Systematic vs. Meta-Analysis
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.
Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
- Summarizes and analyzes previous research relevant to a topic
- Includes scholarly books and articles published in academic journals
- Can be an specific scholarly paper or a section in a research paper
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic
- Help gather ideas or information
- Keep up to date in current trends and findings
- Help develop new questions
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Helps focus your own research questions or problems
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Suggests unexplored ideas or populations
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
- Identifies critical gaps, points of disagreement, or potentially flawed methodology or theoretical approaches.
- Indicates potential directions for future research.
All content in this section is from Literature Review Research from Old Dominion University
Keep in mind the following, a literature review is NOT:
Not an essay
Not an annotated bibliography in which you summarize each article that you have reviewed. A literature review goes beyond basic summarizing to focus on the critical analysis of the reviewed works and their relationship to your research question.
Not a research paper where you select resources to support one side of an issue versus another. A lit review should explain and consider all sides of an argument in order to avoid bias, and areas of agreement and disagreement should be highlighted.
A literature review serves several purposes. For example, it
- provides thorough knowledge of previous studies; introduces seminal works.
- helps focus one’s own research topic.
- identifies a conceptual framework for one’s own research questions or problems; indicates potential directions for future research.
- suggests previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, quantitative and qualitative strategies.
- identifies gaps in previous studies; identifies flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches; avoids replication of mistakes.
- helps the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research.
- suggests unexplored populations.
- determines whether past studies agree or disagree; identifies controversy in the literature.
- tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
As Kennedy (2007) notes*, it is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the original studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally that become part of the lore of field. In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews.
Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are several approaches to how they can be done, depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study. Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews:
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews.
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical reviews are focused on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [content], but how they said it [method of analysis]. This approach provides a framework of understanding at different levels (i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches and data collection and analysis techniques), enables researchers to draw on a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection and data analysis, and helps highlight many ethical issues which we should be aware of and consider as we go through our study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyse data from the studies that are included in the review. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?"
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to concretely examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review help establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
* Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147.
All content in this section is from The Literature Review created by Dr. Robert Larabee USC
Robinson, P. and Lowe, J. (2015), Literature reviews vs systematic reviews. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, 39: 103-103. doi: 10.1111/1753-6405.12393

What's in the name? The difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review, and why it matters . By Lynn Kysh from University of Southern California

Systematic review or meta-analysis?
A systematic review answers a defined research question by collecting and summarizing all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria.
A meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of these studies.
Systematic reviews, just like other research articles, can be of varying quality. They are a significant piece of work (the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination at York estimates that a team will take 9-24 months), and to be useful to other researchers and practitioners they should have:
- clearly stated objectives with pre-defined eligibility criteria for studies
- explicit, reproducible methodology
- a systematic search that attempts to identify all studies
- assessment of the validity of the findings of the included studies (e.g. risk of bias)
- systematic presentation, and synthesis, of the characteristics and findings of the included studies
Not all systematic reviews contain meta-analysis.
Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects of health care than those derived from the individual studies included within a review. More information on meta-analyses can be found in Cochrane Handbook, Chapter 9 .
A meta-analysis goes beyond critique and integration and conducts secondary statistical analysis on the outcomes of similar studies. It is a systematic review that uses quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.
An advantage of a meta-analysis is the ability to be completely objective in evaluating research findings. Not all topics, however, have sufficient research evidence to allow a meta-analysis to be conducted. In that case, an integrative review is an appropriate strategy.
Some of the content in this section is from Systematic reviews and meta-analyses: step by step guide created by Kate McAllister.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Research Design >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 4:07 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/researchmethods
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
What is the Purpose of a Literature Review?

4-minute read
- 23rd October 2023
If you’re writing a research paper or dissertation , then you’ll most likely need to include a comprehensive literature review . In this post, we’ll review the purpose of literature reviews, why they are so significant, and the specific elements to include in one. Literature reviews can:
1. Provide a foundation for current research.
2. Define key concepts and theories.
3. Demonstrate critical evaluation.
4. Show how research and methodologies have evolved.
5. Identify gaps in existing research.
6. Support your argument.
Keep reading to enter the exciting world of literature reviews!
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a critical summary and evaluation of the existing research (e.g., academic journal articles and books) on a specific topic. It is typically included as a separate section or chapter of a research paper or dissertation, serving as a contextual framework for a study. Literature reviews can vary in length depending on the subject and nature of the study, with most being about equal length to other sections or chapters included in the paper. Essentially, the literature review highlights previous studies in the context of your research and summarizes your insights in a structured, organized format. Next, let’s look at the overall purpose of a literature review.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Literature reviews are considered an integral part of research across most academic subjects and fields. The primary purpose of a literature review in your study is to:
Provide a Foundation for Current Research
Since the literature review provides a comprehensive evaluation of the existing research, it serves as a solid foundation for your current study. It’s a way to contextualize your work and show how your research fits into the broader landscape of your specific area of study.
Define Key Concepts and Theories
The literature review highlights the central theories and concepts that have arisen from previous research on your chosen topic. It gives your readers a more thorough understanding of the background of your study and why your research is particularly significant .
Demonstrate Critical Evaluation
A comprehensive literature review shows your ability to critically analyze and evaluate a broad range of source material. And since you’re considering and acknowledging the contribution of key scholars alongside your own, it establishes your own credibility and knowledge.
Show How Research and Methodologies Have Evolved
Another purpose of literature reviews is to provide a historical perspective and demonstrate how research and methodologies have changed over time, especially as data collection methods and technology have advanced. And studying past methodologies allows you, as the researcher, to understand what did and did not work and apply that knowledge to your own research.
Identify Gaps in Existing Research
Besides discussing current research and methodologies, the literature review should also address areas that are lacking in the existing literature. This helps further demonstrate the relevance of your own research by explaining why your study is necessary to fill the gaps.
Support Your Argument
A good literature review should provide evidence that supports your research questions and hypothesis. For example, your study may show that your research supports existing theories or builds on them in some way. Referencing previous related studies shows your work is grounded in established research and will ultimately be a contribution to the field.
Literature Review Editing Services
Ensure your literature review is polished and ready for submission by having it professionally proofread and edited by our expert team. Our literature review editing services will help your research stand out and make an impact. Not convinced yet? Send in your free sample today and see for yourself!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
9-minute read
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.

c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., how to write a successful book chapter for..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, what is academic writing: tips for students, why traditional editorial process needs an upgrade.

Why is it important to do a literature review in research?
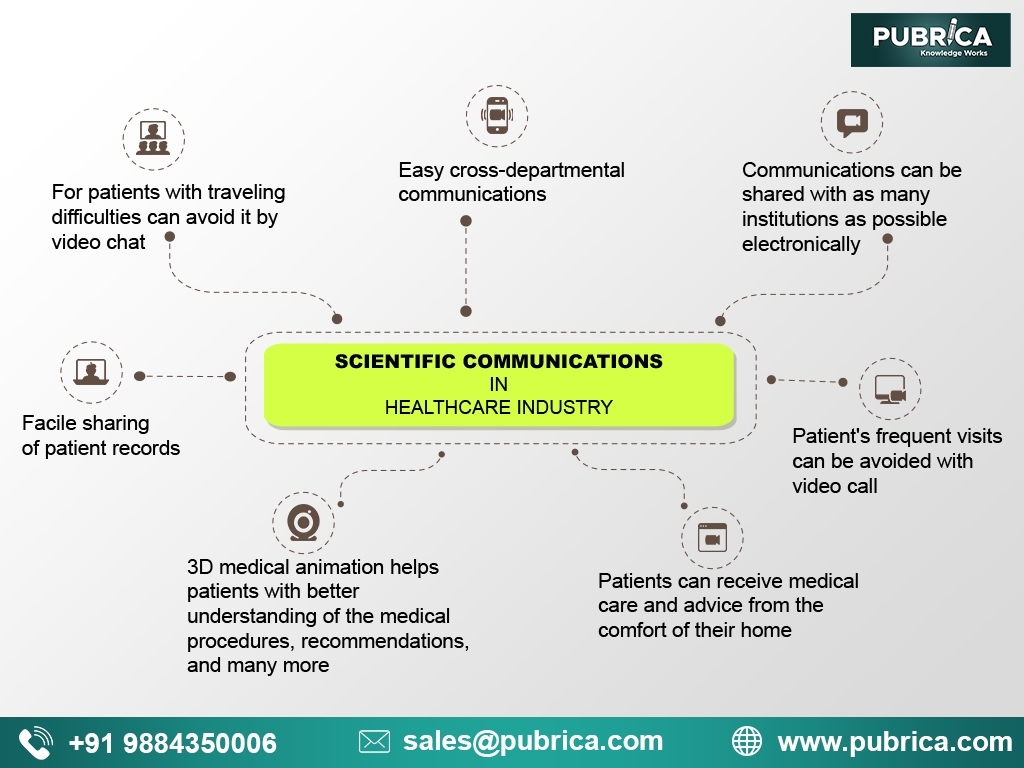
The importance of scientific communication in the healthcare industry
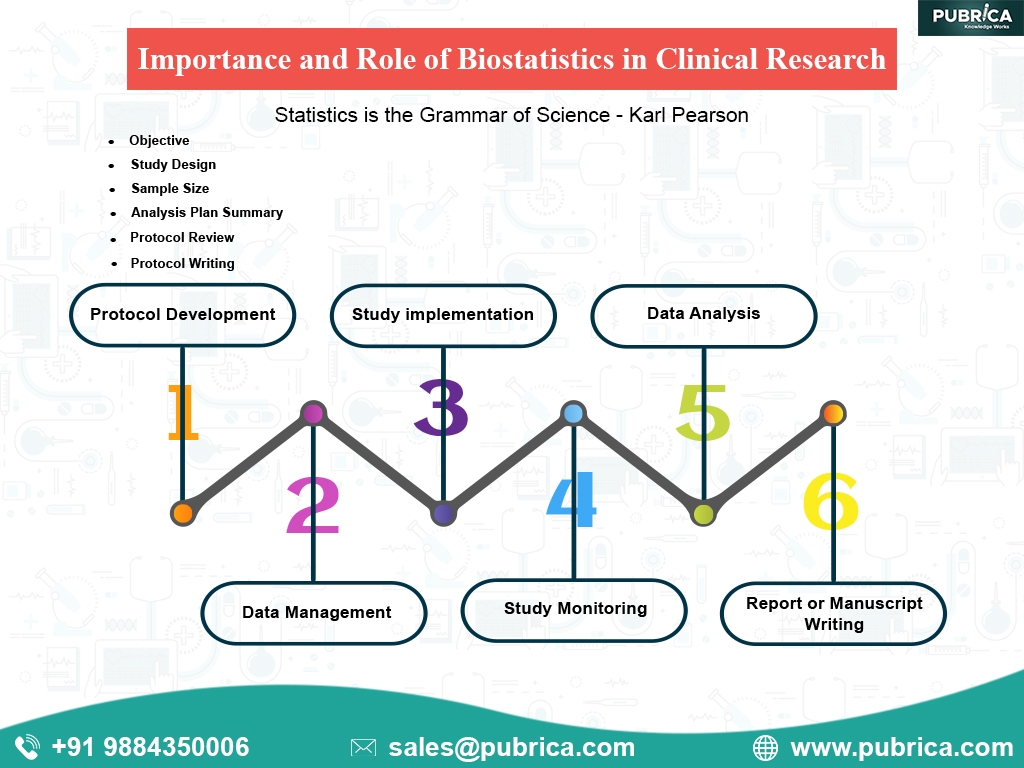
The Importance and Role of Biostatistics in Clinical Research
“A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated research”. Boote and Baile 2005
Authors of manuscripts treat writing a literature review as a routine work or a mere formality. But a seasoned one knows the purpose and importance of a well-written literature review. Since it is one of the basic needs for researches at any level, they have to be done vigilantly. Only then the reader will know that the basics of research have not been neglected.
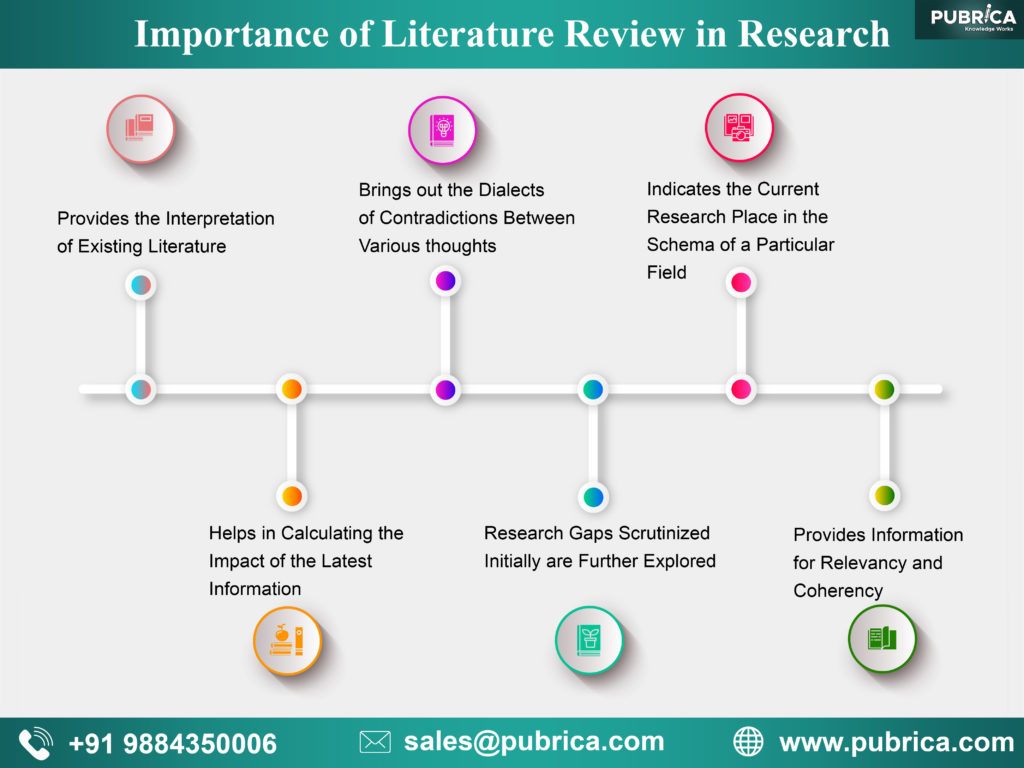
The aim of any literature review is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of existing knowledge in a particular field without adding any new contributions. Being built on existing knowledge they help the researcher to even turn the wheels of the topic of research. It is possible only with profound knowledge of what is wrong in the existing findings in detail to overpower them. For other researches, the literature review gives the direction to be headed for its success.
The common perception of literature review and reality:
As per the common belief, literature reviews are only a summary of the sources related to the research. And many authors of scientific manuscripts believe that they are only surveys of what are the researches are done on the chosen topic. But on the contrary, it uses published information from pertinent and relevant sources like
- Scholarly books
- Scientific papers
- Latest studies in the field
- Established school of thoughts
- Relevant articles from renowned scientific journals
and many more for a field of study or theory or a particular problem to do the following:
- Summarize into a brief account of all information
- Synthesize the information by restructuring and reorganizing
- Critical evaluation of a concept or a school of thought or ideas
- Familiarize the authors to the extent of knowledge in the particular field
- Encapsulate
- Compare & contrast
By doing the above on the relevant information, it provides the reader of the scientific manuscript with the following for a better understanding of it:
- It establishes the authors’ in-depth understanding and knowledge of their field subject
- It gives the background of the research
- Portrays the scientific manuscript plan of examining the research result
- Illuminates on how the knowledge has changed within the field
- Highlights what has already been done in a particular field
- Information of the generally accepted facts, emerging and current state of the topic of research
- Identifies the research gap that is still unexplored or under-researched fields
- Demonstrates how the research fits within a larger field of study
- Provides an overview of the sources explored during the research of a particular topic
Importance of literature review in research:
The importance of literature review in scientific manuscripts can be condensed into an analytical feature to enable the multifold reach of its significance. It adds value to the legitimacy of the research in many ways:
- Provides the interpretation of existing literature in light of updated developments in the field to help in establishing the consistency in knowledge and relevancy of existing materials
- It helps in calculating the impact of the latest information in the field by mapping their progress of knowledge.
- It brings out the dialects of contradictions between various thoughts within the field to establish facts
- The research gaps scrutinized initially are further explored to establish the latest facts of theories to add value to the field
- Indicates the current research place in the schema of a particular field
- Provides information for relevancy and coherency to check the research
- Apart from elucidating the continuance of knowledge, it also points out areas that require further investigation and thus aid as a starting point of any future research
- Justifies the research and sets up the research question
- Sets up a theoretical framework comprising the concepts and theories of the research upon which its success can be judged
- Helps to adopt a more appropriate methodology for the research by examining the strengths and weaknesses of existing research in the same field
- Increases the significance of the results by comparing it with the existing literature
- Provides a point of reference by writing the findings in the scientific manuscript
- Helps to get the due credit from the audience for having done the fact-finding and fact-checking mission in the scientific manuscripts
- The more the reference of relevant sources of it could increase more of its trustworthiness with the readers
- Helps to prevent plagiarism by tailoring and uniquely tweaking the scientific manuscript not to repeat other’s original idea
- By preventing plagiarism , it saves the scientific manuscript from rejection and thus also saves a lot of time and money
- Helps to evaluate, condense and synthesize gist in the author’s own words to sharpen the research focus
- Helps to compare and contrast to show the originality and uniqueness of the research than that of the existing other researches
- Rationalizes the need for conducting the particular research in a specified field
- Helps to collect data accurately for allowing any new methodology of research than the existing ones
- Enables the readers of the manuscript to answer the following questions of its readers for its better chances for publication
- What do the researchers know?
- What do they not know?
- Is the scientific manuscript reliable and trustworthy?
- What are the knowledge gaps of the researcher?
22. It helps the readers to identify the following for further reading of the scientific manuscript:
- What has been already established, discredited and accepted in the particular field of research
- Areas of controversy and conflicts among different schools of thought
- Unsolved problems and issues in the connected field of research
- The emerging trends and approaches
- How the research extends, builds upon and leaves behind from the previous research
A profound literature review with many relevant sources of reference will enhance the chances of the scientific manuscript publication in renowned and reputed scientific journals .
References:
http://www.math.montana.edu/jobo/phdprep/phd6.pdf
journal Publishing services | Scientific Editing Services | Medical Writing Services | scientific research writing service | Scientific communication services
Related Topics:
Meta Analysis
Scientific Research Paper Writing
Medical Research Paper Writing
Scientific Communication in healthcare
pubrica academy
Related posts.

Statistical analyses of case-control studies

PUB - Selecting material (e.g. excipient, active pharmaceutical ingredient) for drug development
Selecting material (e.g. excipient, active pharmaceutical ingredient, packaging material) for drug development

PUB - Health Economics of Data Modeling
Health economics in clinical trials
Comments are closed.

Literature Review: Purpose of a Literature Review
- Literature Review
- Purpose of a Literature Review
- Work in Progress
- Compiling & Writing
- Books, Articles, & Web Pages
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Departmental Differences
- Citation Styles & Plagiarism
- Know the Difference! Systematic Review vs. Literature Review
The purpose of a literature review is to:
- Provide a foundation of knowledge on a topic
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication and give credit to other researchers
- Identify inconstancies: gaps in research, conflicts in previous studies, open questions left from other research
- Identify the need for additional research (justifying your research)
- Identify the relationship of works in the context of their contribution to the topic and other works
- Place your own research within the context of existing literature, making a case for why further study is needed.
Videos & Tutorials
VIDEO: What is the role of a literature review in research? What's it mean to "review" the literature? Get the big picture of what to expect as part of the process. This video is published under a Creative Commons 3.0 BY-NC-SA US license. License, credits, and contact information can be found here: https://www.lib.ncsu.edu/tutorials/litreview/
Elements in a Literature Review
- Elements in a Literature Review txt of infographic
- << Previous: Literature Review
- Next: Searching >>
- Last Updated: Oct 19, 2023 12:07 PM
- URL: https://uscupstate.libguides.com/Literature_Review
- Library Homepage
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide: Evaluating Sources & Literature Reviews
- Literature Reviews?
- Strategies to Finding Sources
- Keeping up with Research!
- Evaluating Sources & Literature Reviews
- Organizing for Writing
- Writing Literature Review
- Other Academic Writings
Evaluating Literature Reviews and Sources
- Tips for Evaluating Sources (Print vs. Internet Sources) Excellent page that will guide you on what to ask to determine if your source is a reliable one. Check the other topics in the guide: Evaluating Bibliographic Citations and Evaluation During Reading on the left side menu.
Criteria to evaluate sources:
- Authority : Who is the author? What are the author's credentials and areas of expertise? Is he or she affiliated with a university?
- Usefulness : How this source related to your topic? How current or relevant it is to your topic?
- Reliability : Does the information comes from a reliable, trusted source such as an academic journal?
- Critically Analyzing Information Sources: Critical Appraisal and Analysis (Cornell University Library) Ten things to look for when you evaluate an information source.
Reading Critically
Reading critically (summary from how to read academic texts critically).
- Who is the author? What is his/her standing in the field?
- What is the author’s purpose? To offer advice, make practical suggestions, solve a specific problem, critique or clarify?
- Note the experts in the field: are there specific names/labs that are frequently cited?
- Pay attention to methodology: is it sound? what testing procedures, subjects, materials were used?
- Note conflicting theories, methodologies, and results. Are there any assumptions being made by most/some researchers?
- Theories: have they evolved over time?
- Evaluate and synthesize the findings and conclusions. How does this study contribute to your project?
- How to Read Academic Texts Critically Excellent document about how best to read critically academic articles and other texts.
- How to Read an Academic Article This is an excellent paper that teach you how to read an academic paper, how to determine if it is something to set aside, or something to read deeply. Good advice to organize your literature for the Literature Review or just reading for classes.
- << Previous: Keeping up with Research!
- Next: Organizing for Writing >>
- Last Updated: Mar 5, 2024 11:44 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucsb.edu/litreview
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 16 May 2019
An analysis of current practices in undertaking literature reviews in nursing: findings from a focused mapping review and synthesis
- Helen Aveyard ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5133-3356 1 &
- Caroline Bradbury-Jones 2
BMC Medical Research Methodology volume 19 , Article number: 105 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
40k Accesses
25 Citations
10 Altmetric
Metrics details
In this paper we discuss the emergence of many different methods for doing a literature review. Referring back to the early days, when there were essentially two types of review; a Cochrane systematic review and a narrative review, we identify how the term systematic review is now widely used to describe a variety of review types and how the number of available methods for doing a literature review has increased dramatically. This led us to undertake a review of current practice of those doing a literature review and the terms used to describe them.
We undertook a focused mapping review and synthesis. Literature reviews; defined as papers with the terms review or synthesis in the title, published in five nursing journals between January 2017–June 2018 were identified. We recorded the type of review and how these were undertaken.
We identified more than 35 terms used to describe a literature review. Some terms reflected established methods for doing a review whilst others could not be traced to established methods and/or the description of method in the paper was limited. We also found inconsistency in how the terms were used.
We have identified a proliferation of terms used to describe doing a literature review; although it is not clear how many distinct methods are being used. Our review indicates a move from an era when the term narrative review was used to describe all ‘non Cochrane’ reviews; to a time of expansion when alternative systematic approaches were developed to enhance rigour of such narrative reviews; to the current situation in which these approaches have proliferated to the extent so that the academic discipline of doing a literature review has become muddled and confusing. We argue that an ‘era of consolidation’ is needed in which those undertaking reviews are explicit about the method used and ensure that their processes can be traced back to a well described, original primary source.
Peer Review reports
Over the past twenty years in nursing, literature reviews have become an increasingly popular form of synthesising evidence and information relevant to the profession. Along with this there has been a proliferation of publications regarding the processes and practicalities of reviewing [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ], This increase in activity and enthusiasm for undertaking literature reviews is paralleled by the foundation of the Cochrane Collaboration in 1993. Developed in response to the need for up-to-date reviews of evidence of the effectiveness of health care interventions, the Cochrane Collaboration introduced a rigorous method of searching, appraisal and analysis in the form of a ‘handbook’ for doing a systematic review [ 5 ] .Subsequently, similar procedural guidance has been produced, for example by the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (CRD) [ 6 ] and The Joanna Briggs Institute [ 7 ]. Further guidance has been published to assist researchers with clarity in the reporting of published reviews [ 8 ].
In the early days of the literature review era, the methodological toolkit for those undertaking a literature was polarised, in a way that mirrored the paradigm wars of the time within mixed-methods research [ 9 ]. We refer to this as the ‘dichotomy era’ (i.e. the 1990s), The prominent methods of literature reviewing fell into one of two camps: The highly rigorous and systematic, mostly quantitative ‘Cochrane style’ review on one hand and a ‘narrative style’ review on the other hand, whereby a body of literature was summarised qualitatively, but the methods were often not articulated. Narrative reviews were particularly popular in dissertations and other student work (and they continue to be so in many cases) but have been criticised for a lack of systematic approach and consequently significant potential for bias in the findings [ 10 , 11 ].
The latter 1990s and early 2000, saw the emergence of other forms of review, developed as a response to the Cochrane/Narrative dichotomy. These alternative approaches to the Cochrane review provided researchers with reference points for performing reviews that drew on different study types, not just randomised controlled trials. They promoted a systematic and robust approach for all reviews, not just those concerned with effectiveness of interventions and treatments. One of the first published description of methods was Noblet and Hare’s (1998) ‘Meta-ethnography’ [ 12 ]. This method, although its name suggests otherwise, could incorporate and synthesise all types of qualitative research, not just ethnographies. The potential confusion regarding the inclusion of studies that were not ethnographies within a meta-ethnography, promoted the description of other similar methods, for example, the meta-synthesis of Walsh and Downe (2005) [ 13 ] and the thematic synthesis of Thomas and Harden (2008) [ 14 ]. Also, to overcome the dichotomy of the quantitative/qualitative reviews, the integrative review was described according to Whitemore and Knafl (2005) [ 15 ]. These reviews can be considered to be literature reviews that have been done in a systematic way but not necessarily adhering to guidelines established by the Cochrane Collaboration. We conceptualise this as the ‘expansion era’. Some of the methods are summarised in Table 1 .
Over the past two decades there has been a proliferation of review types, with corresponding explosion of terms used to describe them. A review of evidence synthesis methodologies by Grant and Booth in 2009 [ 20 ] identified 14 different approaches to reviewing the literature and similarly, Booth and colleagues [ 21 ] detailed 19 different review types, highlighting the range of review types currently available. We might consider this the ‘proliferation era’. This is however, somewhat a double-edged sword, because although researchers now have far more review methods at their disposal, there is risk of confusion in the field. As Sabatino and colleagues (2014) [ 22 ] have argued, review methods are not always consistently applied by researchers.
Aware of such potential inconsistency and also our own confusion at times regarding the range of review methods available, we questioned what was happening within our own discipline of nursing. We undertook a snap-shot, contemporary analysis to explore the range of terms used to describe reviews, the methods currently described in nursing and the underlying trends and patterns in searching, appraisal and analysis adopted by those doing a literature review. The aim was to gain some clarity on what is happening within the field, in order to understand, explain and critique what is happening within the proliferation era.
In order to explore current practices in doing a literature review, we undertook a ‘Focused Mapping Review and Synthesis’ (FMRS) – an approach that has been described only recently. This form of review [ 19 ] is a method of investigating trends in academic publications and has been used in a range of issues relevant to nursing and healthcare, for example, theory in qualitative research [ 23 ] and vicarious trauma in child protection research [ 24 ].
A FMRS seeks to identify what is happening within a particular subject or field of inquiry; hence the search is restricted to a particular time period and to pre-identified journals. The review has four distinct features: It: 1) focuses on identifying trends in an area rather than a body of evidence; 2) creates a descriptive map or topography of key features of research within the field rather than a synthesis of findings; 3) comments on the overall approach to knowledge production rather than the state of the evidence; 4) examines this within a broader epistemological context. These are translated into three specific focused activities: 1) targeted journals; 2) a specific subject; 3) a defined time period. The FMRS therefore, is distinct from other forms of review because it responds to questions concerned with ‘what is happening in this field?’ It was thus an ideal method to investigate current practices in literature reviews in nursing.
Using the international Scopus (2016) SCImago Journal and Country Rank, we identified the five highest ranked journals in nursing at that time of undertaking the review. There was no defined method for determining the number of journals to include in a review; the aim was to identify a sample and we identified five journals in order to search from a range of high ranking journals. We discuss the limitations of this later. Journals had to have ‘nursing’ or ‘nurse’ in the title and we did not include journals with a specialist focus, such as nutrition, cancer etcetera. The included journals are shown in Table 2 and are in order according to their ranking. We recognise that our journal choice meant that only articles published in English made it into the review.
A key decision in a FMRS is the time-period within which to retrieve relevant articles. Like many other forms of review, we undertook an initial scoping to determine the feasibility and parameters of the project [ 19 ]. In our previous reviews, the timeframe has varied from three months [ 23 ] to 6 years [ 24 ]. The main criterion is the likelihood for the timespan to contain sufficient articles to answer the review questions. We set the time parameter from January 2017–June 2018. We each took responsibility for two and three journals each from which to retrieve articles. We reviewed the content page of each issue of each journal. For our purposes, in order to reflect the diverse range of terms for describing a literature review, as described earlier in this paper, any paper that contained the term ‘review’ or ‘synthesis’ in the title was included in the review. This was done by each author individually but to enhance rigour, we worked in pairs to check each other’s retrieval processes to confirm inter-rater consistency. This process allowed any areas of uncertainty to be discussed and agreed and we found this form of calibration crucial to the process. The inclusion and exclusion criteria are shown in Table 3 .
Articles meeting the inclusion criteria, papers were read in full and data was extracted and recorded as per the proforma developed for the study (Table 4 ). The proforma was piloted on two papers to check for usability prior to data extraction. Data extraction was done independently but we discussed a selection of papers to enhance rigour of the process. No computer software was used in the analysis of the data. We did not critically appraise the included studies for quality because our purpose was to profile what is happening in the field rather than to draw conclusions from the included studies’ findings.
Once the details from all the papers had been extracted onto the tables, we undertook an analysis to identify common themes in the included articles. Because our aim was to produce a snap-shot profile, our analysis was thematic and conceptual. Although we undertook some tabulation and numerical analysis, our primary focus was on capturing patterns and trends characterised by the proliferation era. In line with the FMRS method, in the findings section we have used illustrative examples from the included articles that reflect and demonstrate the point or claim being made. These serve as useful sources of information and reference for readers seeking concrete examples.
Between January 2017 and June 2018 in the five journals we surveyed, a total of 222 papers with either ‘review’ or ‘synthesis’ in the title were retrieved and included in our analysis. We identified three primary themes: 1) Proliferation in names for doing a review; 2) Allegiance to an established review method; 3) Clarity about review processes. The results section is organised around these themes.
Proliferation in names for doing a review
We identified more than 35 terms used by authors to describe a literature review. Because we amalgamated terms such as ‘qualitative literature review’ and ‘qualitative review’ the exact number is actually slightly higher. It was clear from reading the reviews that many different terms were used to describe the same processes. For example qualitative systematic review, qualitative review and meta-synthesis, qualitative meta-synthesis, meta-ethnography all refer to a systematic review of qualitative studies. We have therefore grouped together the review types that refer to a particular type of review as described by the authors of the publications used in this study (Table 5 ).
In many reviews, the specific type of review was indicated in the title as seen for example in Table 5 . A striking feature was that all but two of the systematic reviews that contained a meta-analysis were labelled as such in the title; providing clarity and ease of retrieval. Where a literature review did not contain a meta-analysis, the title of the paper was typically referred to a ‘systematic review’; the implication being that a systematic review is not necessarily synonymous with a meta-analysis. However as discussed in the following section, this introduced some muddying of water, with different interpretations of what systematic review means and how broadly this term is applied. Some authors used the methodological type of included papers to describe their review. For example, a Cochrane-style systematic review was undertaken [ 25 ] but the reviewers did not undertake a meta-analysis and thus referred to their review as a ‘quantitative systematic review’.
Allegiance to an established literature review method
Many literature reviews demonstrated allegiance to a defined method and this was clearly and consistently described by the authors. For example, one team of reviewers [ 26 ] articulately described the process of a ‘meta-ethnography’ and gave a detailed description of their study and reference to the origins of the method by Noblet and Hare (1988) [ 12 ]. Another popular method was the ‘integrative review’ where most authors referred to the work of one or two seminal papers where the method was originally described (for example, Whitemore & Knafl 2005 [ 15 ]).
For many authors the term systematic review was used to mean a review of quantitative research, but some authors [ 27 , 28 , 29 ],used the term systematic review to describe reviews containing both qualitative and quantitative data.
However in many reviews, commitment to a method for doing a literature review appeared superficial, undeveloped and at times muddled. For example, three reviews [ 30 , 31 , 32 ] , indicate an integrative review in the title of their review, but this is the only reference to the method; there is no further reference to how the components of an integrative review are addressed within the paper. Other authors do not state allegiance to any particular method except to state a ‘literature review’ [ 33 ] but without an outline of a particular method for doing so. Anther review [ 34 ] reports a ‘narrative review’ but does not give further information about how this was done, possibly indicative of the lack of methods associated with the traditional narrative review. Three other reviewers documented how they searched, appraised and analysed their literature but do not reference an over-riding approach for their review [ 35 , 36 , 37 ]. In these examples, the review can be assumed to be a literature review, but the exact approach is not clear.
In other reviews, the methods for doing a literature review appear to be used interchangeably. For example in one review [ 38 ] the term narrative review was used in the title but in the main text an integrative review was described. In another review [ 39 ] two different and distinct methods were combined in a ‘meta-ethnographic meta-synthesis’.
Some authors [ 40 , 41 ] referred to a method used to undertake their review, for example a systematic review, but did not reference the primary source from where the method originated. Instead a secondary source, such as a textbook is used to reference the approach taken [ 20 , 42 ].
Clarity about review processes
Under this theme we discerned two principal issues: searching and appraisal. The majority of literature reviews contain three components- searching, appraisal and analysis, details of which are usually reported in the methods section of the papers. However, this is not always the case and for example, one review [ 43 ] provides only a search strategy with no information about the overall method or how critical appraisal or analysis were undertaken. Despite the importance of the process of analysis, we found little discussion of this in the papers reviewed.
The overwhelming trend for those doing a literature review was to describe a comprehensive search; although for many in our sample, a comprehensive search appeared to be limited to a database search; authors did not describe additional search strategies that would enable them to find studies that might be missed through electronic searching. Furthermore, authors did not define what a comprehensive search entailed, for example whether this included grey literature. We identified a very small number of studies where authors had undertaken a purposive sample [ 26 , 44 ]; in these reviews authors clearly stated that their search was for ‘seminal papers’ rather than all papers.
We reviewed the approaches to critical appraisal described in the papers and there were varying interpretations of what this means and which aspect of the included articles were to be subject to appraisal. Some authors [ 36 , 45 , 46 ] used the term ‘critical appraisal’ to refer to relevance of the paper to the review, rather than quality criteria. In that sense critical appraisal was used more as an inclusion criterion regarding relevance, rather than quality in the methods used. Mostly though, the term was used to describe the process of critical analysis of the methodological quality of included papers included in a review. When the term was used in this way to refer to quality criteria, appraisal tools were often used; for example, one review [ 47 ] provides a helpful example when they explain how a particular critical appraisal tool was used to asses the quality of papers in their review. Formal critical appraisal was undertaken by the vast majority reviewers, however the role of critical appraisal in the paper was often not explained [ 33 , 48 ]. It was common for a lot of detail to be provided about the approach to appraisal, including how papers were assessed and how disagreements between reviewers about the quality of individual papers were resolved, with no further mention of the subsequent role of the appraisal in the review. The reason for doing the critical appraisal in the review was often unclear and furthermore, in many cases, researchers included all papers within their review regardless of quality. For example, one team of reviewers [ 49 ] explained how the process, in their view, is not to exclude studies but to highlight the quality of evidence available. Another team of reviewers described how they did not exclude studies on the basis of quality because of the limited amount of research available on the topic [ 50 ].
Our review has identified a multiplicity of similar terms and approaches used by authors when doing a literature review, that we suggests marks the ‘proliferation era’. The expansion of terms used to describe a literature review has been observed previously [ 19 , 21 ]. We have identified an even wider range of terms, indicating that this trend may be increasing. This is likely to give the impression of an incoherent and potentially confusing approach to the scholarly undertaking of doing a literature review and is likely to be particularly problematic for novice researchers and students when attempting to grapple with the array of approaches available to them. The range of terms used in the title of papers to describe a literature review may cause both those new to research to wonder what the difference is between a qualitative evidence synthesis and a qualitative systematic review and which method is most suitable for their enquiry.
The clearest articles in our review were those that reported a systematic review with or without a meta-analysis. For example, one team of reviewers [ 25 ] undertook a Cochrane-style systematic review but did not undertake a meta-analysis and thus referred to their review as a ‘quantitative systematic review’. We found this form of labelling clear and helpful and is indeed in line with current recommendations [ 8 ]. While guidelines exist for the publication of systematic reviews [ 8 , 51 ], given the range of terms that are used by authors, some may be unclear when these guidelines should apply and this adds some confusion to the field. Of course, authors are at liberty to call their review processes whatever they deem appropriate, but our analysis has unearthed some inconsistencies that are confusing to the field of literature reviewing.
There is current debate about the status of literature reviews that are not ‘Cochrane’ style reviews [ 52 ]. Classification can be complex and whilst it might be tempting to refer to all non Cochrane-style reviews as ‘narrative reviews’ [ 52 ], literature reviews that conform to a recognised method would generally not be considered as such [ 53 ] and indeed the Cochrane Collaboration handbook refers to the principles of systematic review as applicable to different types of evidence, not just randomised controlled trials [ 5 ] .This raises the question as to whether the term systematic review should be an umbrella term referring to any review with an explicit method; which is implicit in the definition of a systematic review, but which raises the question as to how rigorous a method has to be to meet these standards, a thorny issue which we have identified in this study.
This review has identified a lack of detail in the reporting of the methods used by those doing a review. In 2017, Thorne raised the rhetorical question: ‘What kind of monster have we created?‘ [ 54 ]. Critiquing the growing investment in qualitative metasyntheses, she observed that many reviews were being undertaken that position themselves as qualitative metasyntheses, yet are theoretically and methodologically superficial. Thorne called for greater clarity and sense of purpose as the ‘trend in synthesis research marches forward’ [ 54 ]. Our review covered many review types, not just the qualitative meta-synthesis and its derivatives. However, we concur with Thorne’s conclusion that research methods are not extensively covered or debated in many of the published papers which might explain the confusion of terms and mixing of methods.
Despite the proliferation in terms for doing a literature review, and corresponding associated different methods and a lack of consistency in their application, our review has identified how the methods used (or indeed the reporting of the methods) appear to be remarkably similar in most publications. This may be due to limitations in the word count available to authors. However for example, the vast majority of papers describe a comprehensive search, critical appraisal and analysis. The approach to searching is of particular note; whilst comprehensive searching is the cornerstone of the Cochrane approach, other aproaches advocate that a sample of literature is sufficient [ 15 , 20 ]. Yet in our review we found only two examples where reviewers had used this approach, despite many other reviews claiming to be undertaking a meta-ethnography or meta-synthesis. This indicates that many of those doing a literature review have defaulted to the ‘comprehensive search’ irrespective of the approach to searching suggested in any particular method which is again indicative of confusion in the field.
Differences are reported in the approach to searching and critical appraisal and these appear not to be linked to different methods, but seem to be undertaken on the judgement and discretion of the reviewers without rationale or justification within the published paper. It is not for us to question researchers’ decisions as regards managing the flow of articles through their reviews, but when it comes to the issue of both searching and lack of clarity about the role of critical appraisal there is evidence of inconsistency by those doing a literature review. This reflects current observations in the literature where the lack of clarity about the role of critical appraisal within a literature review is debated . [ 55 , 56 ].
Our review indicates that many researchers follow a very similar process, regardless of their chosen method and the real differences that do exist between published methods are not apparent in many of the published reviews. This concurs with previously mentioned concerns [ 54 ] about the superficial manner in which methods are explored within literature reviews. The overriding tendency is to undertake a comprehensive review, critical appraisal and analysis, following the formula prescribed by Cochrane, even if this is not required by the literature review method stated in the paper. Other researchers [ 52 ] have questioned whether the dominance of the Cochrane review should be questioned. We argue that emergence of different methods for doing a literature review in a systematic way has indeed challenged the perceived dominance of the Cochrane approach that characterised the dichotomy era, where the only alternative was a less rigourous and often poorly described process of dealing with literature. It is positive that there is widespread acknowledgement of the validity of other approaches. But we argue that the expansion era, whereby robust processes were put forward as alternatives that filled the gap left by polarisation, has gone too far. The magnitude in the number of different approaches identified in this review has led to a confused field. Thorne [ 54 ] refers to a ‘meta-madness’; with the proliferation of methods leading to the oversimplification of complex literature and ideas. We would extend this to describe a ‘meta-muddle’ in which, not only are the methods and results oversimplified, but the existence of so many terms used to describe a literature review, many of them used interchangeably, has added a confusion to the field and prevented the in-depth exploration and development of specific methods. Table 6 shows the issues associated with the proliferation era and importantly, it also highlights the recommendations that might lead to a more coherent reviewing community in nursing.
The terms used for doing a literature review are often used both interchangeably and inconsistently, with minimal description of the methods undertaken. It is not surprising therefore that some journal editors do not index these consistently within the journal. For example, in one edition of one journal included in the review, there are two published integrative reviews. One is indexed in the section entitled as a ‘systematic review’, while the other is indexed in a separate section entitled ‘literature review’. In another edition of a journal, two systematic reviews with meta-analysis are published. One is listed as a research article and the other as a review and discussion paper. It seems to us then, that editors and publishers might sometimes also be confused and bewildered themselves.
Whilst guidance does exist for the publication of some types of systematic reviews in academic journals; for example the PRISMA statement [ 8 ] and Entreq guidelines [ 51 ], which are specific to particular qualitative synthesis, guidelines do not exist for each approach. As a result, for those doing an alternative approach to their literature review, for example an integrative review [ 15 ], there is only general publication guidance to assist. In the current reviewing environment, there are so many terms, that more specific guidance would be impractical anyway. However, greater clarity about the methods used and halting the introduction of different terms to mean the same thing will be helpful.
Limitations
This study provides a snapshot of the way in which literature reviews have been described within a short publication timeframe. We were limited for practical reasons to a small section of high impact journals. Including a wider range of journals would have enhanced the transferability of the findings. Our discussion is, of course, limited to the review types that were published in the timeframe, in the identified journals and which had the term ‘review’ or ‘synthesis’ in the title. This would have excluded papers that were entitled ‘meta-analysis’. However as we were interested in the range of reviews that fall outside the scope of a meta-analysis, we did not consider that this limited the scope of the paper. Our review is further limited by the lack of detail of the methods undertaken provided in many of the papers reviewed which, although providing evidence for our arguments, also meant that we had to assume meaning that was unclear from the text provided.
The development of rigorous methods for doing a literature review is to be welcomed; not all review questions can be answered by Cochrane style reviews and robust methods are needed to answer review questions of all types. Therefore whilst we welcome the expansion in methods for doing a literature review, the proliferation in the number of named approaches should be, in our view, a cause for reflection. The increase in methods could be indicative of an emerging variation in possible approaches; alternatively, the increase could be due to a lack of conceptual clarity where, on closer inspection, the methods do not differ greatly and could indeed be merged. Further scrutiny of the methods described within many papers support the latter situation but we would welcome further discussion about this. Meanwhile, we urge researchers to make careful consideration of the method they adopt for doing a literature review, to justify this approach carefully and to adhere closely to its method. Having witnessed an era of dichotomy, expansion and proliferation of methods for doing a literature review, we now seek a new era of consolidation.
Bettany-Saltikov J. How to do a systematic literature review in nursing: a step-by-step guide. Maidenhead: Open University Press; 2012.
Google Scholar
Coughlan M, Cronin P, Ryan F. Doing a literature review in nursing, Health and social care. London: Sage; 2013.
Aveyard H. Doing a literature review in health and social care. Maidenhead: Open University Press; 2018.
Davis D. A practical overview of how to conduct a systematic review. Nurs Stand. 2016;31(12):60–70.
Article Google Scholar
Higgins and Green. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0: Cochrane Collaboration; 2011.
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination. Systematic Reviews: CRD's guidance for undertaking reviews in health care. York: University of York; 2008.
Aromataris E, Munn Z, editors. Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer's Manual: The Joanna Briggs Institute; 2017. Available from https://reviewersmanual.joannabriggs.org/
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P, Stewart L. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols. Br Med J. 2015;2:349 (Jan 02).
Creswell JW, Plano-Clark VL. Designing and conducting mixed methods research. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications; 2011.
Greenhalgh T. How to read a paper. 4th ed: Wiley; 2010.
Booth A, Papaioannou D, Sutton A. Systematic appproaches to a successful literature review Sage London; 2012.
Noblit GW, Hare RD. Meta-ethnography, synthesising qualitative studies, qualitative research methods, volume 11. London: SAGE Publications; 1988.
Walsh D, Downe S. Meta-synthesis method for qualitative research: a literature review. J Adv Nurs. 2005;50(2):204–11.
Thomas J, Harden A. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2008;8:45.
Whittemore R, Knafl K. The integrative review: updated methodology. J Adv Nurs. 2005;52:546–53.
Scoping Peters MDJ, Godfrey CM, McInerney P, Soares CB, Khalil H, Parker D. Methodology for Joanna Briggs institute scoping review. Joanna Briggs institute reviewers manual: Australia; 2015.
Wong G, Greenhalgh T, Westhorp G, Buckingham J, Pawson R. RAMESES publication standards: realist synthesis BMC medicine, vol. 11; 2013. p. 21.
Plüddemann A, Aronson JK, Onakpoya I, Heneghan C, Mahtani KR. Redefining rapid reviews: a flexible framework for restricted systematic reviews. BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine Epub ahead of print: 27 June 2018. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjemb-2018-110990 .
Bradbury-Jones C, Breckenridge J, Clark MT, Herber OR, Jones C, Taylor J. Advancing the science of literature reviewing: the focused mapping review and synthesis as a novel approach. Int J Soc Res Methodol. https://doi.org/10.1080/13645579.2019.1576328 .
Grant MJ, Booth A. A typology of review- an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Info Libr J. 2009;26(2):91–108.
Booth, A., Noyes, J., Flemming, K., Gerhardus, A., Wahlster, P., van der Wilt G.J., Mozygemba K, Refolo P, Sacchini D, Tummers, M, Rehfuess, E. (2016) Guidance on choosing qualitative evidence synthesis methods for use in health technology assessments of complex interventions. Available: http://www.integrate-hta.eu/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/Guidance-on-choosing-qualitative-evidence-synthesis-methods-for-use-in-HTA-of-complex-interventions.pdf
Sabatino L, Stievano A, Rocco G, Kallio H, Pietila A, KAngasniemi M. The dignity of the nursing profession: a meta-synthesis of qualitative research. Nurs Ethics. 2014;2(6):659–72.
Bradbury-Jones C, Taylor J, Herber O. How theory is used and articulated in qualitative research: development of a new typology. Soc Sci Med. 2014;120:135–41.
Taylor J, Bradbury-Jones C, Breckenridge J, Jones C, Herber OR. Risk of vicarious trauma in nursing research: a focused mapping review and synthesis. J Clin Nurs. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.13235 .
Haggman Laitila A, Rompannen J. Outcomes of interventions for nurse leaders’ well being at work. A quantitative systematic review. J Adv Nurs. 2018;74:34–44.
Strandos M, Bondas T. The nurse patient relationship as a story of health enhancement in community care- a meta-ethnography. J Adv Nurs. 2018;74:11–8.
Gilissen J, Pivodic L, Smets T, Gastmans C, Stichels RV, Delieus L, Van den Black L. Preconditions for successful advanced care planning in nursing homes: a systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2017;66:47–59.
Walczak A, Mcdonald F, Patterson P, Dobinson K, Kimberley A. How does parental cancer affect adolescent and young adult offspring. A systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018;77:54–80.
Leyva-Moral JM, Palmoero PA, Feijoo-Cid M, Edwards JE. Reproductive decision making in women living with HIV: systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018;77:207–21.
Pires S, Monteiro S, Pereira A, Chaló D, Melo E, Rodriguese A. Non technical skills assessment for pre-licensure nursing students: an integrative literature review nurse education today, vol. 58; 2017. p. 19–24.
Wilkinson A, Meilkle N, Law P, Yong A, Butler P, Kim J, Mulligan H, Hale L. How older adults and their informal carers prevent falls: an integrative review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018;82:13–8.
Drewniak D, Krones T, Wild V. Do attitudes and behaviours of health care professionals exacerbate health care disparities among immigrant and ethnic minority groups? An integrative literature review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2017;70:89–98.
Garone A, Craen Van de P. The role of language skills abd internationalisation in nursing degree programmes: a literature review. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;49:140–4.
Casey M, O’Connor L, Cashin A (et al) An overview of the outcomes and impact of specialist and advanced nursing and midwifery practice on quality of care, cost and access to services: A narrative review. Nurse Educ Today 2017;56:35-40.
Adib-Hajbaghery M, Sharifi N. Effect of simulation training on the development of nurses and nursing students critical thinking: a systematic review. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;50:17–24.
Irwin C, Bliss J, Poole J. Does preceptorship improve confidence and competence in newly qualified nurses: a systematic literature review. Nurse educ Today. 2018;60:35–46.
Jefferies D, McNallya S, Roberts K, Wallace A, Stunden A, D'Souzaa S, Glew P. The importance of academic literacy for undergraduate nursing students and its relationship to future professional clinical practice: a systematic review. Nurse educ Today. 2018;60:84–91.
Lewis ML, Neville C, Ashkanasy NM. Emotional intelligence and affective events in nurse education- a narrative review. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;53:34–40.
Jensen D, Sorensen A. Nurses experiences of working in organisations undergoing restructuring: a meta-synthesis of qualitative research studies. Int J Nurs Stud. 2017;66:7–14.
Milligan F, Wareing M, Preston-Shoot M, Pappas Y, Randhawa G, Bhandol J. Supporting nursing, midwifery and allied health professional students to raise concerns with the quality of care: a review of the research literature. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;57:29–39.
Rozendo CA, Salas AS. A critical review of social and health inequalities in the nursing curriculum. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;50:62–71.
Kiteley R, Stogdon C. Literature reviews in social work. London: Sage; 2014.
Book Google Scholar
Rebeiro G, Evans A, Edward K, Chapman R. Registered nurse buddies. Educators by proxy? Nurse Educ Today. 2017;55:1–4.
Sinclair S, Raffin Bouchal S, Venturato L, Milsonic-Kondejewski J, Smith Macdonald L. Compassion fatigue: a meta-narrative review of the health care literature. Int J Nurs Stud. 2017;69:9–24.
Hovey S, Dyck MJ, Reese C, Myoung JK. Nursing students’ attitudes towards persons who are aged: an integrative review. J Adv Nurs. 2017;49:145–52.
Granheim B, Shaw J, Mansah M. Use of interprofessional learning and simulation in undergraduate nursing programmes to address interprofessional communication and collaboration- an integrative review. Nurse Educ Today. 2018;62:118–27.
Philips P, Lumley E, Duncan R, Aber A, Buckley Woods H, Jones GC. A systematic review of qualitative research into people’s experiences of living with venous leg ulcers. J Adv Nurs. 2018;74:550–63.
Slater CE, Cusick A. Factors relating to self directed learning readiness of students in health professional programmes a scoping review. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;52:22–33.
Vanderspank-Wright B, Efstathiou N, Vandjk A. Critical care nurses experience of withdrawing treatment: a systematic review of qualitative evidence. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018;77:15–26.
Kelly M, Wills J, Sykes S. Do nurses’ personal health behaviours impact their health promotion practice? A systematic review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2017;76:62–77.
Tong A, Flemming K, McInnes E, Oliver S, Craig J. Enhancing transparency in the reporting in the synthesis of qualitative research. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2012;12(1):181.
Greenhalgh T, Thorne S, Malterud K. Time to challenge the spurious hierarchy of systematic over narrative reviews? Eur J Clin Investig. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/eci12931 .
Aveyard H, Payne S, Preston N. A postgraduate’s guide to doing a literature review. Maidenhead: Open University Press; 2016.
Thorne S. Metasynthetic madness: what kind of monster have we created? Qual Health Res. 2017;27(1):3–12.
Sibeoni J, Orri M, Colin S, Valentin M, Pradere J, Revah-Levy A. The lived experience of anorexia nervosa in adolescence, comparison of parents’ view of adolescence, parents and professionals: a meta-synthesis. Int J Nurs Stud. 2017;65:25–34.
Nightingale S, Spiby H, Sheen K, Slade P. The impact of emotional intelligence in long term health care professionals on caring behaviours towards patients in clinical and long term settings. Integrative review. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018;80:106–17.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Availability of data and materials.
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Health and Life Sciences, Oxford Brookes University, Jack Straw’s Lane, Oxford, OX3 0FL, England, UK
Helen Aveyard
University of Birmingham, Birmingham, England, UK
Caroline Bradbury-Jones
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Both HA and CB-J contributed to the data collection and analysis. HA wrote the paper and CB-J commented on the drafts. HA revised the paper according to the reviewers’ comments and CB-J commented on these revisions 30/4/19. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Helen Aveyard .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests, publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Aveyard, H., Bradbury-Jones, C. An analysis of current practices in undertaking literature reviews in nursing: findings from a focused mapping review and synthesis. BMC Med Res Methodol 19 , 105 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-019-0751-7
Download citation
Received : 16 December 2018
Accepted : 07 May 2019
Published : 16 May 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-019-0751-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Evidence synthesis
- Literature review
- Meta-ethnography
- Systematic review
BMC Medical Research Methodology
ISSN: 1471-2288
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Literature Reviews
- What Is It?
- Finding Literature Reviews
A literature review is both a process and a product. As a process, it involves searching for information related to your topic, to familiarize yourself with the relevant research and to identify issues and gaps in the research. In most cases you're seeking to identify the key authors and key arguments that are relevant to your topic, not to exhaustively read everything written on the subject.
Types of Literature Reviews
A stand alone literature review can be a single work in its own right. Examples include:
- A class assignment
- A review article
Literature reviews can also be component parts of larger bodies of work. Examples include:
- A thesis / dissertation
- An academic journal article introduction

What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is the writing process of summarizing, synthesizing and/or critiquing the literature found as a result of a literature search. It may be used as background or context for a primary research project.
There are several reasons to review the literature :
- Identify the developments in the field of study
- Learn about the information sources and the research methodologies
- Find gaps in the literature that can become research questions
- Validate the originality of a research project
- Evaluate the methods
- Identify errors to avoid
- Highlight the strengths, weaknesses and controversies in the field of study
- Identify the subject experts
When writing your review, there are objectives you should keep in mind :
- Inform the audience of the developments in the field
- Establish your credibility
- Discuss the relevance and significance of your question(s)
- Provide the context for your methodological approach
- Discuss the relevance and appropriateness of your approach.
The level of detail or comprehensiveness of your literature review may depend on many things, but especially the purpose and audience of your review. For example, if you're writing a literature review that will aid you in writing a thesis or dissertation, you may want to have a very comprehensive lit review that reviews all relevant literature on a topic, as well as relevant sources beyond what is immediately and freely available (e.g. foundational scholarly articles not available through library collections).
Purpose of a Literature Review
Watch this YouTube video to understand the purpose of a literature review.
- Next: Finding Literature Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Dec 12, 2023 3:07 PM
- URL: https://library.knox.edu/literature-review

What is Literature Review? Importance, Functions, Process,
- Post last modified: 13 August 2023
- Reading time: 12 mins read
- Post category: Research Methodology

What is Literature Review?
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing research, studies, articles, books, and other relevant sources on a specific topic or subject. It serves as a foundational step in the research process, helping researchers understand the current state of knowledge, identify gaps in the literature, and establish a context for their own study.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Literature Review?
- 2 Importance of a Literature Review
- 3 Functions of a Literature Review
- 4.1 Search the Existing Literature in Your Field of Interest
- 4.2 Review the Literature Obtained
- 4.3 Develop a Theoretical Framework
- 4.4 Write the Literature Review
- 5 How to Write a Literature Review
- 6 Types of Sources for Review
In most research reports or research papers, you will see that literature review is an essential element and it forms the basis for advancing knowledge, facilitates theory development, discovers new research areas and closes old ones. When researchers want to understand the management dilemma, they study various books, articles and all other available sources.
In the research reports, the researchers present a summary of their search, study and evaluation of the literature that is already available related to the research topic. When the researcher presents a summary of their study of present literature in addition to their analysis of how this literature is related to or essential for the current research report; then, this process is known as literature review.
For example, in a research paper titled ‘Attrition Analysis in a Leading Sales Organisation in India’, authored by Mamta Mohapatra (International Management Institute, New Delhi, India), Amisha Gupta (Birlasoft, New Delhi, India) and Nikita Lamba (Genpact, New Delhi, India), literature review is presented as follows:
Organisations and researchers usually conduct literature review in order to establish how their own research fits within the context of existing literature.
Apart from these, some other objectives of carrying out literature review are:
- Develop an understanding of how each source of literature helps in understanding the research problem
- Examine the interrelationships among different variables
- Find out ways to interpret earlier similar researches on the topic under study
- Rectify the conflicts that exist among previously conducted studies
- Get an idea regarding the required sample size
- Get an estimate of how much variance is there in the variables of interest
- Understand the type of relationship that exists among variables
- Determine the research method that can be used in the research
Importance of a Literature Review
There are various reasons for carrying out literature review. Majorly, literature review helps in:
- Assessing the current state and level of research on a given topic
- Identifying experts related to particular research
- Identifying questions that need further research and exploration
- Identifying what methodologies have been used in the related past studies and what methodology should be used in current research
- Justifying a proposed research methodology
- Indicating the originality and relevance of the given research problem
- Demonstrating the preparedness of a researcher to complete the research
Functions of a Literature Review
Some of the major functions of literature review are:
- Establishing a context for the research
- Demonstrating that the researcher has actually read related literature extensively and is aware of most theory and methodology related to the given research topic
- Providing a shape for the research under consideration
- Establishing a connection between what the researcher is proposing and what he has already read
- Demonstrating how the findings of researcher can be integrated with the already existing research findings.
- Revealing the differences or areas of gap between present and earlier research findings
- Improving researcher’s research methodology
- Expanding researcher’s knowledge base
- Ensuring that the researcher is carrying out new research that has not been carried out earlier
Process of a Literature Review
The second step in the research process is to carry out the review of already existing literature. Before engaging in literature review, the researcher must be clear as to what is the area and topic of research. There are four steps involved in the literature review process as shown in Figure:
Search the Existing Literature in Your Field of Interest
In the literature review process, the first step is to find out what research has already been done in the area that the researcher has chosen. This step involves preparing a list or bibliography of existing sources of relevant literature such as books, journals, abstracts of articles on your research topic, citation indices and digital libraries.
Review the Literature Obtained
After the researcher has identified related literature including journals, books, research papers, etc.; the next step is to study, evaluate and analyse the literature critically. This study of literature helps a researcher identify themes and issues related to the research topic.
An evaluation of literature helps in:
- Identifying the different theories and their criticism
- Identifying different methodologies used in different studies including their sample size, data used, measurement methods
- Assessing if the researcher’s theory is confirmed beyond doubt
- Preparing a list of different opinions of different researchers and researcher should also add his/her opinion about the validity of these different opinions
Develop a Theoretical Framework
Since carrying out literature review is a time-consuming activity but the researcher has to do it within a limited time. In order to do so, the researcher usually establishes a boundary and parameters for the research work. Also, the researcher must sort information obtained from all the sources of literature. For a researcher, the theoretical framework acts as a base on which he can further or extend his research. At times, the researchers may modify their research framework after analysing the available literature.
Write the Literature Review
The last step in literature review is to make a summary of all the literature that the researcher has studied and reviewed. Usually, writing a literature review starts with a write-up on the main theme of research followed by the important ideas on which the research would focus. After this, the all the major themes and sub-themes to be discussed are organised and related. This will help the researcher in structuring the literature review. The researcher should also identify and describe the theories and studies that are relevant for the study under consideration. The researcher should then list and describe all the gaps that are present in the current body of knowledge. In addition, the researcher may also explain the recent advances and trends in the given research field. To conclude, the researcher should compare and evaluate his findings on the basis of research assumptions, related research theories, hypotheses, applied research designs, variables selected and potential future work speculated by the researchers. Finally, the researcher must acknowledge, cite and quote all the sources that he/she has used in his research. One specific characteristic of literature review is that the researcher must ensure that he gives due credit to all people who have contributed in the research work.
How to Write a Literature Review
While writing the literature review, the researcher must adopt or adhere to certain strategies as follows:
- Establish a focus around the central theme and ideas of the research
- Describe what a reader can expect from the given research study
- Organise the literature research to include basic elements such as introduction, body and conclusions
Types of Sources for Review
A researcher usually uses secondary data for literature review. Some of the major and widely used sources for literature reviews include articles in professional journals, statistical data from government websites and website material from professional organisations.
Apart from the previously mentioned sources, certain other sources of data can also be used by researchers that provide them first-hand information that is important for the study. These sources include reports, theses, emails, letters, conference proceedings, company reports, autobiographies, official reports, research articles, etc.
Apart from these, the researcher may also refer to other such as review articles, academic journals, books, newspapers, documentaries, encyclopaedias, dictionaries, bibliographies and citation indexes.
Business Ethics
( Click on Topic to Read )
- What is Ethics?
- What is Business Ethics?
- Values, Norms, Beliefs and Standards in Business Ethics
- Indian Ethos in Management
- Ethical Issues in Marketing
- Ethical Issues in HRM
- Ethical Issues in IT
- Ethical Issues in Production and Operations Management
- Ethical Issues in Finance and Accounting
- What is Corporate Governance?
- What is Ownership Concentration?
- What is Ownership Composition?
- Types of Companies in India
- Internal Corporate Governance
- External Corporate Governance
- Corporate Governance in India
- What is Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)?
- What is Assessment of Risk?
- What is Risk Register?
- Risk Management Committee
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
- Theories of CSR
- Arguments Against CSR
- Business Case for CSR
- Importance of CSR in India
- Drivers of Corporate Social Responsibility
- Developing a CSR Strategy
- Implement CSR Commitments
- CSR Marketplace
- CSR at Workplace
- Environmental CSR
- CSR with Communities and in Supply Chain
- Community Interventions
- CSR Monitoring
- CSR Reporting
- Voluntary Codes in CSR
- What is Corporate Ethics?
Lean Six Sigma
- What is Six Sigma?
- What is Lean Six Sigma?
- Value and Waste in Lean Six Sigma
- Six Sigma Team
- MAIC Six Sigma
- Six Sigma in Supply Chains
- What is Binomial, Poisson, Normal Distribution?
- What is Sigma Level?
- What is DMAIC in Six Sigma?
- What is DMADV in Six Sigma?
- Six Sigma Project Charter
- Project Decomposition in Six Sigma
- Critical to Quality (CTQ) Six Sigma
- Process Mapping Six Sigma
- Flowchart and SIPOC
- Gage Repeatability and Reproducibility
- Statistical Diagram
- Lean Techniques for Optimisation Flow
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- What is Process Audits?
- Six Sigma Implementation at Ford
- IBM Uses Six Sigma to Drive Behaviour Change
- Research Methodology
- What is Research?
What is Hypothesis?
- Sampling Method
- Research Methods
- Data Collection in Research
- Methods of Collecting Data
- Application of Business Research
- Levels of Measurement
- What is Sampling?
- Hypothesis Testing
- Research Report
- What is Management?
- Planning in Management
- Decision Making in Management
- What is Controlling?
- What is Coordination?
- What is Staffing?
- Organization Structure
- What is Departmentation?
- Span of Control
- What is Authority?
- Centralization vs Decentralization
- Organizing in Management
- Schools of Management Thought
- Classical Management Approach
- Is Management an Art or Science?
- Who is a Manager?
Operations Research
- What is Operations Research?
- Operation Research Models
- Linear Programming
- Linear Programming Graphic Solution
- Linear Programming Simplex Method
- Linear Programming Artificial Variable Technique
- Duality in Linear Programming
- Transportation Problem Initial Basic Feasible Solution
- Transportation Problem Finding Optimal Solution
- Project Network Analysis with Critical Path Method
- Project Network Analysis Methods
- Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
- Simulation in Operation Research
- Replacement Models in Operation Research
Operation Management
- What is Strategy?
- What is Operations Strategy?
- Operations Competitive Dimensions
- Operations Strategy Formulation Process
- What is Strategic Fit?
- Strategic Design Process
- Focused Operations Strategy
- Corporate Level Strategy
- Expansion Strategies
- Stability Strategies
- Retrenchment Strategies
- Competitive Advantage
- Strategic Choice and Strategic Alternatives
- What is Production Process?
- What is Process Technology?
- What is Process Improvement?
- Strategic Capacity Management
- Production and Logistics Strategy
- Taxonomy of Supply Chain Strategies
- Factors Considered in Supply Chain Planning
- Operational and Strategic Issues in Global Logistics
- Logistics Outsourcing Strategy
- What is Supply Chain Mapping?
- Supply Chain Process Restructuring
- Points of Differentiation
- Re-engineering Improvement in SCM
- What is Supply Chain Drivers?
- Supply Chain Operations Reference (SCOR) Model
- Customer Service and Cost Trade Off
- Internal and External Performance Measures
- Linking Supply Chain and Business Performance
- Netflix’s Niche Focused Strategy
- Disney and Pixar Merger
- Process Planning at Mcdonald’s
Service Operations Management
- What is Service?
- What is Service Operations Management?
- What is Service Design?
- Service Design Process
- Service Delivery
- What is Service Quality?
- Gap Model of Service Quality
- Juran Trilogy
- Service Performance Measurement
- Service Decoupling
- IT Service Operation
- Service Operations Management in Different Sector
Procurement Management
- What is Procurement Management?
- Procurement Negotiation
- Types of Requisition
- RFX in Procurement
- What is Purchasing Cycle?
- Vendor Managed Inventory
- Internal Conflict During Purchasing Operation
- Spend Analysis in Procurement
- Sourcing in Procurement
- Supplier Evaluation and Selection in Procurement
- Blacklisting of Suppliers in Procurement
- Total Cost of Ownership in Procurement
- Incoterms in Procurement
- Documents Used in International Procurement
- Transportation and Logistics Strategy
- What is Capital Equipment?
- Procurement Process of Capital Equipment
- Acquisition of Technology in Procurement
- What is E-Procurement?
- E-marketplace and Online Catalogues
- Fixed Price and Cost Reimbursement Contracts
- Contract Cancellation in Procurement
- Ethics in Procurement
- Legal Aspects of Procurement
- Global Sourcing in Procurement
- Intermediaries and Countertrade in Procurement
Strategic Management
- What is Strategic Management?
- What is Value Chain Analysis?
- Mission Statement
- Business Level Strategy
- What is SWOT Analysis?
- What is Competitive Advantage?
- What is Vision?
- What is Ansoff Matrix?
- Prahalad and Gary Hammel
- Strategic Management In Global Environment
- Competitor Analysis Framework
- Competitive Rivalry Analysis
- Competitive Dynamics
- What is Competitive Rivalry?
- Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy
- What is PESTLE Analysis?
- Fragmentation and Consolidation Of Industries
- What is Technology Life Cycle?
- What is Diversification Strategy?
- What is Corporate Restructuring Strategy?
- Resources and Capabilities of Organization
- Role of Leaders In Functional-Level Strategic Management
- Functional Structure In Functional Level Strategy Formulation
- Information And Control System
- What is Strategy Gap Analysis?
- Issues In Strategy Implementation
- Matrix Organizational Structure
- What is Strategic Management Process?
Supply Chain
- What is Supply Chain Management?
- Supply Chain Planning and Measuring Strategy Performance
- What is Warehousing?
- What is Packaging?
- What is Inventory Management?
- What is Material Handling?
- What is Order Picking?
- Receiving and Dispatch, Processes
- What is Warehouse Design?
- What is Warehousing Costs?
You Might Also Like
What is research methodology, what is measurement scales, types, criteria and developing measurement tools, primary data and secondary data, data processing in research, what is scaling techniques types, classifications, techniques, what is measure of skewness, what is hypothesis definition, meaning, characteristics, sources, types of charts used in data analysis, research process | types, what is causal research advantages, disadvantages, how to perform, what is measure of dispersion, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
World's Best Online Courses at One Place
We’ve spent the time in finding, so you can spend your time in learning
Digital Marketing
Personal growth.

Development

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for ...
This is why the literature review as a research method is more relevant than ever. Traditional literature reviews often lack thoroughness and rigor and are conducted ad hoc, rather than following a specific methodology. Therefore, questions can be raised about the quality and trustworthiness of these types of reviews.
Purpose and Importance of the Literature Review. An understanding of the current literature is critical for all phases of a research study. Lingard 9 recently invoked the "journal-as-conversation" metaphor as a way of understanding how one's research fits into the larger medical education conversation. As she described it: "Imagine yourself joining a conversation at a social event.
Literature review is approached as a process of engaging with the discourse of scholarly communities that will help graduate researchers refine, define, and express their own scholarly vision and voice. This orientation on research as an exploratory practice, rather than merely a series of predetermined steps in a systematic method, allows the ...
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply: be thorough, use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and. look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
A literature review is a review and synthesis of existing research on a topic or research question. A literature review is meant to analyze the scholarly literature, make connections across writings and identify strengths, weaknesses, trends, and missing conversations. A literature review should address different aspects of a topic as it ...
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic. A literature review is important because it: Explains the background of research on a topic. Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area. Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
The importance of the literature review is directly related to its aims and purpose. Nursing and allied health disciplines contain a vast amount of ever increasing lit-erature and research that is important to the ongoing development of practice. The literature review is an aid to gathering and synthesising that information. The pur-
A literature review is a critical summary and evaluation of the existing research (e.g., academic journal articles and books) on a specific topic. It is typically included as a separate section or chapter of a research paper or dissertation, serving as a contextual framework for a study. ... This helps further demonstrate the relevance of your ...
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing ...
A literature review is essential to any scientific research study, which entails an in-depth analysis and synthesis of the existing literature and studies related to the research topic. The ...
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
"A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated research". Boote and Baile 2005 . Authors of manuscripts treat writing a literature review as a routine work or a mere formality. But a seasoned one knows the purpose and importance of a well-written literature review.
The purpose of a literature review is to: Provide a foundation of knowledge on a topic; Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication and give credit to other researchers; Identify inconstancies: gaps in research, conflicts in previous studies, open questions left from other research;
A good literature review evaluates a wide variety of sources (academic articles, scholarly books, government/NGO reports). It also evaluates literature reviews that study similar topics. This page offers you a list of resources and tips on how to evaluate the sources that you may use to write your review.
No matter what the reason for the literature review or the paradigm within which the researcher is working, many aspects of the literature review process are the same. A general outline for conducting a literature review is provided in Box 3.1. Some of the differences in the process that emanate from paradigm choice include the following: 1.
A literature review is a piece of academic writing demonstrating knowledge and understanding of the academic literature on a specific topic placed in context. A literature review also includes a critical evaluation of the material; this is why it is called a literature review rather than a literature report. ... the researcher analyzes relevant ...
A key decision in a FMRS is the time-period within which to retrieve relevant articles. Like many other forms of review, we undertook an initial scoping to determine the feasibility and parameters of the project [].In our previous reviews, the timeframe has varied from three months [] to 6 years [].The main criterion is the likelihood for the timespan to contain sufficient articles to answer ...
A literature review is the writing process of summarizing, synthesizing and/or critiquing the literature found as a result of a literature search. It may be used as background or context for a primary research project. There are several reasons to review the literature: Identify the developments in the field of study.
Some Issues in Liter ature R eview. 1. A continuous and time consuming process runs. through out r esearch work (more whil e selecting. a resear ch problem and writing 'r eview of. liter ature ...
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing research, studies, articles, books, and other relevant sources on a specific topic or subject. It serves as a foundational step in the research process, helping researchers understand the current state of knowledge, identify gaps in the literature, and establish a context ...
Cancer immunotherapy is a rapidly developing field of medicine that aims to use the host's immune mechanisms to inhibit and eliminate cancer cells. Antibodies targeting CTLA-4, PD-1, and its ligand PD-L1 are used in various cancer therapies. However, the most thoroughly researched pathway targeting PD-1/PD-L1 has many limitations, and multiple malignancies resist its effects. Human ...
Moreover, it remains unclear whether anthropogenic OPs affect the CH 4 cycle, a concern of significant importance in the context of the increasing rate of global warming. The literature examined in this review also calls for additional research into the date of OPs in waste and sewage and in their impact on environmental microbiomes.