

Narrative Writing: A Complete Guide for Teachers and Students
MASTERING THE CRAFT OF NARRATIVE WRITING
Narratives build on and encourage the development of the fundamentals of writing. They also require developing an additional skill set: the ability to tell a good yarn, and storytelling is as old as humanity.
We see and hear stories everywhere and daily, from having good gossip on the doorstep with a neighbor in the morning to the dramas that fill our screens in the evening.
Good narrative writing skills are hard-won by students even though it is an area of writing that most enjoy due to the creativity and freedom it offers.
Here we will explore some of the main elements of a good story: plot, setting, characters, conflict, climax, and resolution . And we will look too at how best we can help our students understand these elements, both in isolation and how they mesh together as a whole.

WHAT IS A NARRATIVE?

A narrative is a story that shares a sequence of events , characters, and themes. It expresses experiences, ideas, and perspectives that should aspire to engage and inspire an audience.
A narrative can spark emotion, encourage reflection, and convey meaning when done well.
Narratives are a popular genre for students and teachers as they allow the writer to share their imagination, creativity, skill, and understanding of nearly all elements of writing. We occasionally refer to a narrative as ‘creative writing’ or story writing.
The purpose of a narrative is simple, to tell the audience a story. It can be written to motivate, educate, or entertain and can be fact or fiction.
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING NARRATIVE WRITING

Teach your students to become skilled story writers with this HUGE NARRATIVE & CREATIVE STORY WRITING UNIT . Offering a COMPLETE SOLUTION to teaching students how to craft CREATIVE CHARACTERS, SUPERB SETTINGS, and PERFECT PLOTS .
Over 192 PAGES of materials, including:
TYPES OF NARRATIVE WRITING
There are many narrative writing genres and sub-genres such as these.
We have a complete guide to writing a personal narrative that differs from the traditional story-based narrative covered in this guide. It includes personal narrative writing prompts, resources, and examples and can be found here.

As we can see, narratives are an open-ended form of writing that allows you to showcase creativity in many directions. However, all narratives share a common set of features and structure known as “Story Elements”, which are briefly covered in this guide.
Don’t overlook the importance of understanding story elements and the value this adds to you as a writer who can dissect and create grand narratives. We also have an in-depth guide to understanding story elements here .
CHARACTERISTICS OF NARRATIVE WRITING
Narrative structure.
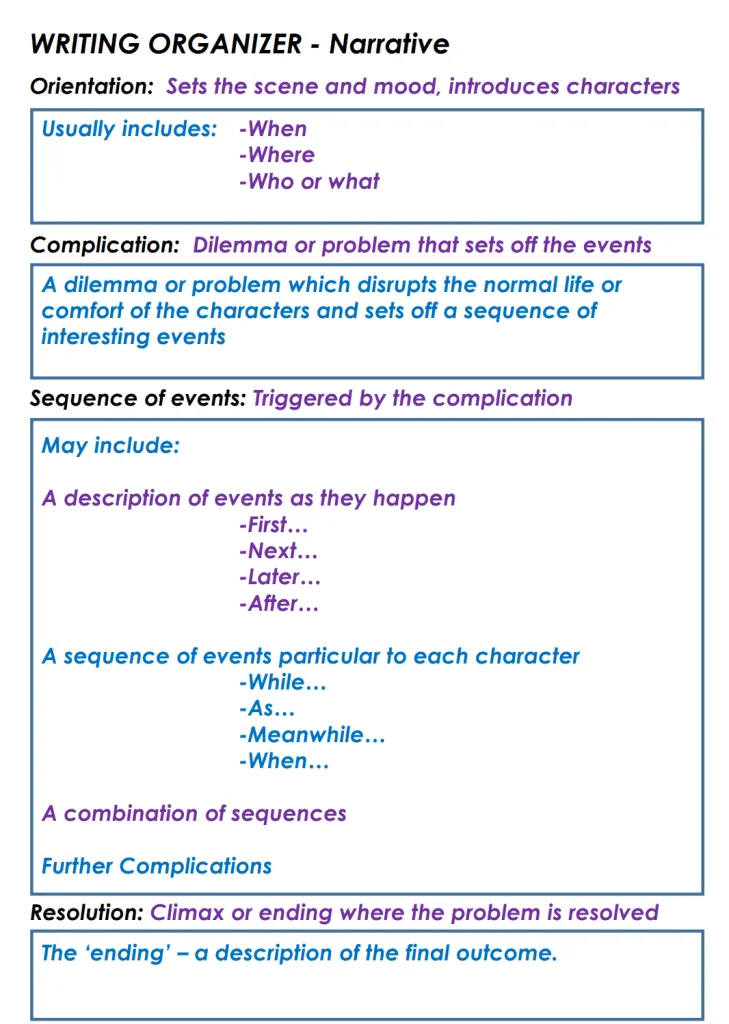
ORIENTATION (BEGINNING) Set the scene by introducing your characters, setting and time of the story. Establish your who, when and where in this part of your narrative
COMPLICATION AND EVENTS (MIDDLE) In this section activities and events involving your main characters are expanded upon. These events are written in a cohesive and fluent sequence.
RESOLUTION (ENDING) Your complication is resolved in this section. It does not have to be a happy outcome, however.
EXTRAS: Whilst orientation, complication and resolution are the agreed norms for a narrative, there are numerous examples of popular texts that did not explicitly follow this path exactly.
NARRATIVE FEATURES
LANGUAGE: Use descriptive and figurative language to paint images inside your audience’s minds as they read.
PERSPECTIVE Narratives can be written from any perspective but are most commonly written in first or third person.
DIALOGUE Narratives frequently switch from narrator to first-person dialogue. Always use speech marks when writing dialogue.
TENSE If you change tense, make it perfectly clear to your audience what is happening. Flashbacks might work well in your mind but make sure they translate to your audience.
THE PLOT MAP
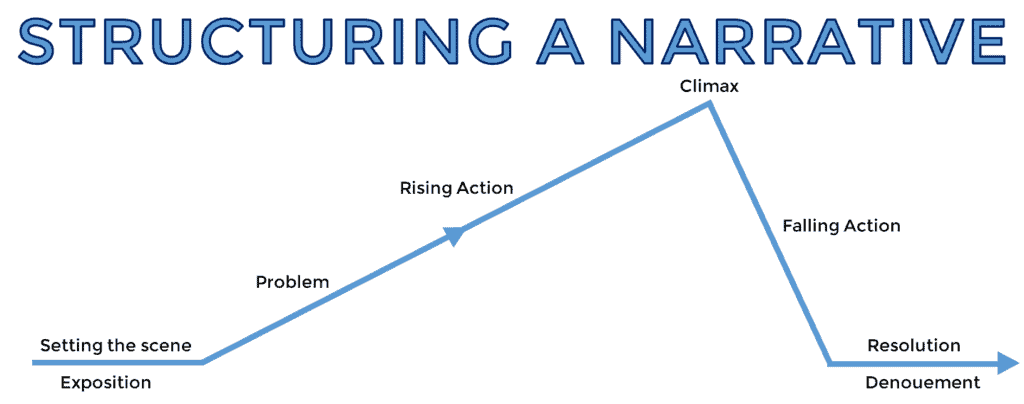
This graphic is known as a plot map, and nearly all narratives fit this structure in one way or another, whether romance novels, science fiction or otherwise.
It is a simple tool that helps you understand and organise a story’s events. Think of it as a roadmap that outlines the journey of your characters and the events that unfold. It outlines the different stops along the way, such as the introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution, that help you to see how the story builds and develops.
Using a plot map, you can see how each event fits into the larger picture and how the different parts of the story work together to create meaning. It’s a great way to visualize and analyze a story.
Be sure to refer to a plot map when planning a story, as it has all the essential elements of a great story.
THE 5 KEY STORY ELEMENTS OF A GREAT NARRATIVE (6-MINUTE TUTORIAL VIDEO)
This video we created provides an excellent overview of these elements and demonstrates them in action in stories we all know and love.

HOW TO WRITE A NARRATIVE
Now that we understand the story elements and how they come together to form stories, it’s time to start planning and writing your narrative.
In many cases, the template and guide below will provide enough details on how to craft a great story. However, if you still need assistance with the fundamentals of writing, such as sentence structure, paragraphs and using correct grammar, we have some excellent guides on those here.
USE YOUR WRITING TIME EFFECTIVELY: Maximize your narrative writing sessions by spending approximately 20 per cent of your time planning and preparing. This ensures greater productivity during your writing time and keeps you focused and on task.
Use tools such as graphic organizers to logically sequence your narrative if you are not a confident story writer. If you are working with reluctant writers, try using narrative writing prompts to get their creative juices flowing.
Spend most of your writing hour on the task at hand, don’t get too side-tracked editing during this time and leave some time for editing. When editing a narrative, examine it for these three elements.
- Spelling and grammar ( Is it readable?)
- Story structure and continuity ( Does it make sense, and does it flow? )
- Character and plot analysis. (Are your characters engaging? Does your problem/resolution work? )
1. SETTING THE SCENE: THE WHERE AND THE WHEN

The story’s setting often answers two of the central questions in the story, namely, the where and the when. The answers to these two crucial questions will often be informed by the type of story the student is writing.
The story’s setting can be chosen to quickly orient the reader to the type of story they are reading. For example, a fictional narrative writing piece such as a horror story will often begin with a description of a haunted house on a hill or an abandoned asylum in the middle of the woods. If we start our story on a rocket ship hurtling through the cosmos on its space voyage to the Alpha Centauri star system, we can be reasonably sure that the story we are embarking on is a work of science fiction.
Such conventions are well-worn clichés true, but they can be helpful starting points for our novice novelists to make a start.
Having students choose an appropriate setting for the type of story they wish to write is an excellent exercise for our younger students. It leads naturally onto the next stage of story writing, which is creating suitable characters to populate this fictional world they have created. However, older or more advanced students may wish to play with the expectations of appropriate settings for their story. They may wish to do this for comic effect or in the interest of creating a more original story. For example, opening a story with a children’s birthday party does not usually set up the expectation of a horror story. Indeed, it may even lure the reader into a happy reverie as they remember their own happy birthday parties. This leaves them more vulnerable to the surprise element of the shocking action that lies ahead.
Once the students have chosen a setting for their story, they need to start writing. Little can be more terrifying to English students than the blank page and its bare whiteness stretching before them on the table like a merciless desert they must cross. Give them the kick-start they need by offering support through word banks or writing prompts. If the class is all writing a story based on the same theme, you may wish to compile a common word bank on the whiteboard as a prewriting activity. Write the central theme or genre in the middle of the board. Have students suggest words or phrases related to the theme and list them on the board.
You may wish to provide students with a copy of various writing prompts to get them started. While this may mean that many students’ stories will have the same beginning, they will most likely arrive at dramatically different endings via dramatically different routes.

A bargain is at the centre of the relationship between the writer and the reader. That bargain is that the reader promises to suspend their disbelief as long as the writer creates a consistent and convincing fictional reality. Creating a believable world for the fictional characters to inhabit requires the student to draw on convincing details. The best way of doing this is through writing that appeals to the senses. Have your student reflect deeply on the world that they are creating. What does it look like? Sound like? What does the food taste like there? How does it feel like to walk those imaginary streets, and what aromas beguile the nose as the main character winds their way through that conjured market?
Also, Consider the when; or the time period. Is it a future world where things are cleaner and more antiseptic? Or is it an overcrowded 16th-century London with human waste stinking up the streets? If students can create a multi-sensory installation in the reader’s mind, then they have done this part of their job well.
Popular Settings from Children’s Literature and Storytelling
- Fairytale Kingdom
- Magical Forest
- Village/town
- Underwater world
- Space/Alien planet
2. CASTING THE CHARACTERS: THE WHO
Now that your student has created a believable world, it is time to populate it with believable characters.
In short stories, these worlds mustn’t be overpopulated beyond what the student’s skill level can manage. Short stories usually only require one main character and a few secondary ones. Think of the short story more as a small-scale dramatic production in an intimate local theater than a Hollywood blockbuster on a grand scale. Too many characters will only confuse and become unwieldy with a canvas this size. Keep it simple!
Creating believable characters is often one of the most challenging aspects of narrative writing for students. Fortunately, we can do a few things to help students here. Sometimes it is helpful for students to model their characters on actual people they know. This can make things a little less daunting and taxing on the imagination. However, whether or not this is the case, writing brief background bios or descriptions of characters’ physical personality characteristics can be a beneficial prewriting activity. Students should give some in-depth consideration to the details of who their character is: How do they walk? What do they look like? Do they have any distinguishing features? A crooked nose? A limp? Bad breath? Small details such as these bring life and, therefore, believability to characters. Students can even cut pictures from magazines to put a face to their character and allow their imaginations to fill in the rest of the details.
Younger students will often dictate to the reader the nature of their characters. To improve their writing craft, students must know when to switch from story-telling mode to story-showing mode. This is particularly true when it comes to character. Encourage students to reveal their character’s personality through what they do rather than merely by lecturing the reader on the faults and virtues of the character’s personality. It might be a small relayed detail in the way they walk that reveals a core characteristic. For example, a character who walks with their head hanging low and shoulders hunched while avoiding eye contact has been revealed to be timid without the word once being mentioned. This is a much more artistic and well-crafted way of doing things and is less irritating for the reader. A character who sits down at the family dinner table immediately snatches up his fork and starts stuffing roast potatoes into his mouth before anyone else has even managed to sit down has revealed a tendency towards greed or gluttony.
Understanding Character Traits
Again, there is room here for some fun and profitable prewriting activities. Give students a list of character traits and have them describe a character doing something that reveals that trait without ever employing the word itself.
It is also essential to avoid adjective stuffing here. When looking at students’ early drafts, adjective stuffing is often apparent. To train the student out of this habit, choose an adjective and have the student rewrite the sentence to express this adjective through action rather than telling.
When writing a story, it is vital to consider the character’s traits and how they will impact the story’s events. For example, a character with a strong trait of determination may be more likely to overcome obstacles and persevere. In contrast, a character with a tendency towards laziness may struggle to achieve their goals. In short, character traits add realism, depth, and meaning to a story, making it more engaging and memorable for the reader.
Popular Character Traits in Children’s Stories
- Determination
- Imagination
- Perseverance
- Responsibility
We have an in-depth guide to creating great characters here , but most students should be fine to move on to planning their conflict and resolution.
3. NO PROBLEM? NO STORY! HOW CONFLICT DRIVES A NARRATIVE

This is often the area apprentice writers have the most difficulty with. Students must understand that without a problem or conflict, there is no story. The problem is the driving force of the action. Usually, in a short story, the problem will center around what the primary character wants to happen or, indeed, wants not to happen. It is the hurdle that must be overcome. It is in the struggle to overcome this hurdle that events happen.
Often when a student understands the need for a problem in a story, their completed work will still not be successful. This is because, often in life, problems remain unsolved. Hurdles are not always successfully overcome. Students pick up on this.
We often discuss problems with friends that will never be satisfactorily resolved one way or the other, and we accept this as a part of life. This is not usually the case with writing a story. Whether a character successfully overcomes his or her problem or is decidedly crushed in the process of trying is not as important as the fact that it will finally be resolved one way or the other.
A good practical exercise for students to get to grips with this is to provide copies of stories and have them identify the central problem or conflict in each through discussion. Familiar fables or fairy tales such as Three Little Pigs, The Boy Who Cried Wolf, Cinderella, etc., are great for this.
While it is true that stories often have more than one problem or that the hero or heroine is unsuccessful in their first attempt to solve a central problem, for beginning students and intermediate students, it is best to focus on a single problem, especially given the scope of story writing at this level. Over time students will develop their abilities to handle more complex plots and write accordingly.
Popular Conflicts found in Children’s Storytelling.
- Good vs evil
- Individual vs society
- Nature vs nurture
- Self vs others
- Man vs self
- Man vs nature
- Man vs technology
- Individual vs fate
- Self vs destiny
Conflict is the heart and soul of any good story. It’s what makes a story compelling and drives the plot forward. Without conflict, there is no story. Every great story has a struggle or a problem that needs to be solved, and that’s where conflict comes in. Conflict is what makes a story exciting and keeps the reader engaged. It creates tension and suspense and makes the reader care about the outcome.
Like in real life, conflict in a story is an opportunity for a character’s growth and transformation. It’s a chance for them to learn and evolve, making a story great. So next time stories are written in the classroom, remember that conflict is an essential ingredient, and without it, your story will lack the energy, excitement, and meaning that makes it truly memorable.
4. THE NARRATIVE CLIMAX: HOW THINGS COME TO A HEAD!

The climax of the story is the dramatic high point of the action. It is also when the struggles kicked off by the problem come to a head. The climax will ultimately decide whether the story will have a happy or tragic ending. In the climax, two opposing forces duke things out until the bitter (or sweet!) end. One force ultimately emerges triumphant. As the action builds throughout the story, suspense increases as the reader wonders which of these forces will win out. The climax is the release of this suspense.
Much of the success of the climax depends on how well the other elements of the story have been achieved. If the student has created a well-drawn and believable character that the reader can identify with and feel for, then the climax will be more powerful.
The nature of the problem is also essential as it determines what’s at stake in the climax. The problem must matter dearly to the main character if it matters at all to the reader.
Have students engage in discussions about their favorite movies and books. Have them think about the storyline and decide the most exciting parts. What was at stake at these moments? What happened in your body as you read or watched? Did you breathe faster? Or grip the cushion hard? Did your heart rate increase, or did you start to sweat? This is what a good climax does and what our students should strive to do in their stories.
The climax puts it all on the line and rolls the dice. Let the chips fall where the writer may…
Popular Climax themes in Children’s Stories
- A battle between good and evil
- The character’s bravery saves the day
- Character faces their fears and overcomes them
- The character solves a mystery or puzzle.
- The character stands up for what is right.
- Character reaches their goal or dream.
- The character learns a valuable lesson.
- The character makes a selfless sacrifice.
- The character makes a difficult decision.
- The character reunites with loved ones or finds true friendship.
5. RESOLUTION: TYING UP LOOSE ENDS
After the climactic action, a few questions will often remain unresolved for the reader, even if all the conflict has been resolved. The resolution is where those lingering questions will be answered. The resolution in a short story may only be a brief paragraph or two. But, in most cases, it will still be necessary to include an ending immediately after the climax can feel too abrupt and leave the reader feeling unfulfilled.
An easy way to explain resolution to students struggling to grasp the concept is to point to the traditional resolution of fairy tales, the “And they all lived happily ever after” ending. This weather forecast for the future allows the reader to take their leave. Have the student consider the emotions they want to leave the reader with when crafting their resolution.
While the action is usually complete by the end of the climax, it is in the resolution that if there is a twist to be found, it will appear – think of movies such as The Usual Suspects. Pulling this off convincingly usually requires considerable skill from a student writer. Still, it may well form a challenging extension exercise for those more gifted storytellers among your students.
Popular Resolutions in Children’s Stories
- Our hero achieves their goal
- The character learns a valuable lesson
- A character finds happiness or inner peace.
- The character reunites with loved ones.
- Character restores balance to the world.
- The character discovers their true identity.
- Character changes for the better.
- The character gains wisdom or understanding.
- Character makes amends with others.
- The character learns to appreciate what they have.
Once students have completed their story, they can edit for grammar, vocabulary choice, spelling, etc., but not before!
As mentioned, there is a craft to storytelling, as well as an art. When accurate grammar, perfect spelling, and immaculate sentence structures are pushed at the outset, they can cause storytelling paralysis. For this reason, it is essential that when we encourage the students to write a story, we give them license to make mechanical mistakes in their use of language that they can work on and fix later.
Good narrative writing is a very complex skill to develop and will take the student years to become competent. It challenges not only the student’s technical abilities with language but also her creative faculties. Writing frames, word banks, mind maps, and visual prompts can all give valuable support as students develop the wide-ranging and challenging skills required to produce a successful narrative writing piece. But, at the end of it all, as with any craft, practice and more practice is at the heart of the matter.
TIPS FOR WRITING A GREAT NARRATIVE
- Start your story with a clear purpose: If you can determine the theme or message you want to convey in your narrative before starting it will make the writing process so much simpler.
- Choose a compelling storyline and sell it through great characters, setting and plot: Consider a unique or interesting story that captures the reader’s attention, then build the world and characters around it.
- Develop vivid characters that are not all the same: Make your characters relatable and memorable by giving them distinct personalities and traits you can draw upon in the plot.
- Use descriptive language to hook your audience into your story: Use sensory language to paint vivid images and sequences in the reader’s mind.
- Show, don’t tell your audience: Use actions, thoughts, and dialogue to reveal character motivations and emotions through storytelling.
- Create a vivid setting that is clear to your audience before getting too far into the plot: Describe the time and place of your story to immerse the reader fully.
- Build tension: Refer to the story map earlier in this article and use conflict, obstacles, and suspense to keep the audience engaged and invested in your narrative.
- Use figurative language such as metaphors, similes, and other literary devices to add depth and meaning to your narrative.
- Edit, revise, and refine: Take the time to refine and polish your writing for clarity and impact.
- Stay true to your voice: Maintain your unique perspective and style in your writing to make it your own.
NARRATIVE WRITING EXAMPLES (Student Writing Samples)
Below are a collection of student writing samples of narratives. Click on the image to enlarge and explore them in greater detail. Please take a moment to read these creative stories in detail and the teacher and student guides which highlight some of the critical elements of narratives to consider before writing.
Please understand these student writing samples are not intended to be perfect examples for each age or grade level but a piece of writing for students and teachers to explore together to critically analyze to improve student writing skills and deepen their understanding of story writing.
We recommend reading the example either a year above or below, as well as the grade you are currently working with, to gain a broader appreciation of this text type.
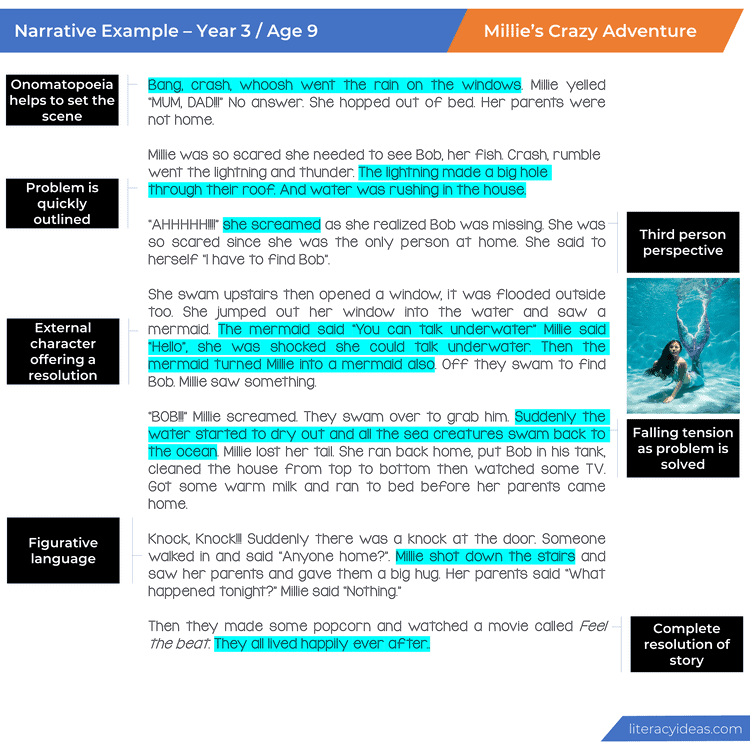
NARRATIVE WRITING PROMPTS (Journal Prompts)
When students have a great journal prompt, it can help them focus on the task at hand, so be sure to view our vast collection of visual writing prompts for various text types here or use some of these.
- On a recent European trip, you find your travel group booked into the stunning and mysterious Castle Frankenfurter for a single night… As night falls, the massive castle of over one hundred rooms seems to creak and groan as a series of unexplained events begin to make you wonder who or what else is spending the evening with you. Write a narrative that tells the story of your evening.
- You are a famous adventurer who has discovered new lands; keep a travel log over a period of time in which you encounter new and exciting adventures and challenges to overcome. Ensure your travel journal tells a story and has a definite introduction, conflict and resolution.
- You create an incredible piece of technology that has the capacity to change the world. As you sit back and marvel at your innovation and the endless possibilities ahead of you, it becomes apparent there are a few problems you didn’t really consider. You might not even be able to control them. Write a narrative in which you ride the highs and lows of your world-changing creation with a clear introduction, conflict and resolution.
- As the final door shuts on the Megamall, you realise you have done it… You and your best friend have managed to sneak into the largest shopping centre in town and have the entire place to yourselves until 7 am tomorrow. There is literally everything and anything a child would dream of entertaining themselves for the next 12 hours. What amazing adventures await you? What might go wrong? And how will you get out of there scot-free?
- A stranger walks into town… Whilst appearing similar to almost all those around you, you get a sense that this person is from another time, space or dimension… Are they friends or foes? What makes you sense something very strange is going on? Suddenly they stand up and walk toward you with purpose extending their hand… It’s almost as if they were reading your mind.
NARRATIVE WRITING VIDEO TUTORIAL

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
When teaching narrative writing, it is essential that you have a range of tools, strategies and resources at your disposal to ensure you get the most out of your writing time. You can find some examples below, which are free and paid premium resources you can use instantly without any preparation.

FREE Narrative Graphic Organizer
THE STORY TELLERS BUNDLE OF TEACHING RESOURCES

A MASSIVE COLLECTION of resources for narratives and story writing in the classroom covering all elements of crafting amazing stories. MONTHS WORTH OF WRITING LESSONS AND RESOURCES, including:
NARRATIVE WRITING CHECKLIST BUNDLE

⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (92 Reviews)
OTHER GREAT ARTICLES ABOUT NARRATIVE WRITING

Narrative Writing for Kids: Essential Skills and Strategies

7 Great Narrative Lesson Plans Students and Teachers Love

Top 7 Narrative Writing Exercises for Students

How to Write a Scary Story
- Craft and Criticism
- Fiction and Poetry
- News and Culture
- Lit Hub Radio
- Reading Lists

- Literary Criticism
- Craft and Advice
- In Conversation
- On Translation
- Short Story
- From the Novel
- Bookstores and Libraries
- Film and TV
- Art and Photography
- Freeman’s
- The Virtual Book Channel
- Behind the Mic
- Beyond the Page
- The Cosmic Library
- The Critic and Her Publics
- Emergence Magazine
- Fiction/Non/Fiction
- First Draft: A Dialogue on Writing
- The History of Literature
- I’m a Writer But
- Lit Century
- Tor Presents: Voyage Into Genre
- Windham-Campbell Prizes Podcast
- Write-minded
- The Best of the Decade
- Best Reviewed Books
- BookMarks Daily Giveaway
- The Daily Thrill
- CrimeReads Daily Giveaway

10 Short Stories with Great Dialogue That Aren’t “Hills Like White Elephants”
Do you believe in life after hemingway.
Before you get excited: I have no problem with “Hills Like White Elephants.” In this classic story, Ernest Hemingway demonstrates a masterful, subtle use of dialogue—so much so that it has become, if not a totally clichéd, then at least a ubiquitous text in creative writing classrooms. I myself encountered it at least four times by the time I got to grad school—where I proceeded to teach it to my own Introduction to Creative Writing class. It’s the circle of life. This is only to say that I’m not immune—but I also know there are plenty of other stories with strong dialogue out there, and as another school year (such as it is, in 2021) gets going, they’re probably worth a look too. Just for fun, you know?
So I asked the Literary Hub staff to suggest some of their other favorite short stories that do cool things with dialogue, and I’ve collected a few of them here. Obviously this list is not exhaustive—among other things, we also shied away from some other tried-and-true dialogue-heavy classics, like “The Dead” and “What We Talk About When We Talk About Love,” and “Steady Hands at Seattle General”—and of course these stories are mostly not doing the same thing as “Hills Like White Elephants,” but they’re all doing something interesting. Just in case you want to mix it up a little this year.
Sam Lipsyte, “ The Dungeon Master ,” from The Fun Parts
Sample Dialogue:
The Dungeon Master has detention. We wait at his house by the county road. The Dungeon Master’s little brother Marco puts out corn chips and orange soda.
Marco is a paladin. He fights for the glory of Christ. Marco has been many paladins since winter break. They are all named Valentine, and the Dungeon Master makes certain they die with the least possible amount of dignity.
It’s painful enough when he rolls the dice, announces that a drunken orc has unspooled some Valentine’s guts for sport. Worse are the silly accidents. One Valentine tripped on a floor plank and cracked his head on a mead bucket. He died of trauma in the stable.
“Take it!” the Dungeon Master said that time. Spit sprayed over the top of his laminated screen. “Eat your fate,” he said. “Your thread just got the snippo!”
The Dungeon Master has a secret language that we don’t quite understand. They say he’s been treated for it.
Whenever the Dungeon Master kills another Valentine, Marco runs off and cries to their father. Dr. Varelli nudges his son back into the study, sticks his bushy head in the door, says, “Play nice, my beautiful puppies.”
“Father,” the Dungeon Master will say, “stay the fuck out of my mind realm.”
“I honor your wish, my beauty.”
Dr. Varelli says things like that. It’s not a secret language, just an embarrassing one. Maybe that’s why his wife left him, left Marco and the Dungeon Master, too. It’s not a decent reason to leave, but as the Dungeon Master hopes to teach us, the world is not a decent place to live.
Danielle Evans, “ Virgins ,” from Before You Suffocate Your Own Fool Self
“Look what Eddie gave me,” said Cindy, all friendly. She pulled a pink teddy bear out of her purse and squeezed its belly. It sang “You Are My Sunshine” in a vibrating robot voice.
“That’s nice,” said Jasmine, her voice so high that she sounded almost like the teddy bear. Cindy smiled and walked off with Eddie, swinging her hips back and forth.
“I don’t have a teddy bear neither,” said Eddie’s friend Tre, putting an arm around Jasmine. She pushed him off. Tre was the kind of boy my mother would have said to stay away from, but she said to stay away from all men.
“C’mon, Jasmine,” Tre said. “I lost my teddy bear, can I sleep with you tonight?”
Jasmine looked at Tre like he was stupid. Michael put an arm around each of our shoulders and kissed us both on the cheek, me first, then Jasmine.
“You know these are my girls,” he said to Tre. “Leave ’em alone.”
His friends mostly left me alone anyway, because they knew I wasn’t good for anything but a little kissing. But I was glad he’d included me. Michael nodded good-bye as he and his friends walked toward their movie. Eddie and Cindy stayed there, kissing, like that’s what they had paid admission for. I grabbed Jasmine’s hand and pulled her toward the ticket counter.
“That’s nasty,” I said. “She looks nasty all up on him in public like that.”
“No one ever bought me a singing teddy bear,” said Jasmine. “Probably no one ever will buy me a singing teddy bear.”
“I’ll buy you a singing teddy bear, stupid,” I said.
“Shut up,” she said. She’d been sucking on her bottom lip so hard she’d sucked the lipstick off it, and her lips were two different colors. “Don’t you ever want to matter to somebody?”
“I matter to you. And Michael.”
Jasmine clicked her tongue. “Say Michael had to shoot either you or that Italian chick who’s letting him hit it right now. Who do you think he would save?”
“Why does he have to shoot somebody?” I said.
“He just does.”
“Well, he’d save me then. She’s just a girl who’s fucking him.”
“And you’re just a girl who isn’t,” Jasmine said. “That’s your problem, Erica. You don’t understand adult relationships.”
“Where are there adults?” I asked, turning in circles with my hand to my forehead like a sea captain looking for land.
“You’re right,” she said. “I’m tired of these little boys. Next weekend we’re going to the city. We’re gonna find some real niggas who know how to treat us.”
That was not the idea I meant for Jasmine to have.
Ottessa Moshfegh, “ The Beach Boy ,” from Homesick for Another World
The friends wanted to know what the prostitutes had looked like, how they’d dressed, what they’d said. They wanted details.
“They looked like normal people,” Marcia said, shrugging. “You know, just young, poor people, locals. But they were very complimentary. They kept saying, ‘Hello, nice people. Massage? Nice massage for nice people?’ ”
“Little did they know!” John joked, furrowing his eyebrows like a maniac. The friends laughed.
“We’d read about it in the guidebook,” Marcia said. “You’re not supposed to acknowledge them at all. You don’t even look them in the eye. If you do, they’ll never leave you alone. The beach boys. The male prostitutes, I mean. It’s sad,” she added. “Tragic. And, really, one wonders how anybody can starve in a place like that. There was food everywhere. Fruit on every tree. I just don’t understand it. And the city was rife with garbage. Rife! ” she proclaimed. She put down her fork. “Wouldn’t you say, hon?”
“I wouldn’t say ‘rife,’ ” John answered, wiping the corners of his mouth with his cloth napkin. “Fragrant, more like.”
The waiter collected the unfinished plates of pasta, then returned and took their orders of cheesecake and pie and decaffeinated coffee. John was quiet. He scrolled through photos on his cell phone, looking for a picture he’d taken of a monkey seated on the head of a Virgin Mary statue. The statue was painted in bright colors, and its nose was chipped, showing the white, chalky plaster under the paint. The monkey was black and skinny, with wide-spaced, neurotic eyes. Its tail curled under Mary’s chin. John turned the screen of his phone toward the table.
“This little guy,” he said.
“Aw!” the friends cried. They wanted to know, “Were the monkeys feral? Were they smelly? Are the people Catholic? Are they all very religious there?”
“Catholic,” Marcia said, nodding. “And the monkeys were everywhere. Cute but very sneaky. One of them stole John’s pen right out of his pocket.” She rattled off whatever facts she could remember from the nature tour they’d taken. “I think there are laws about eating the monkeys. I’m not so sure. They all spoke English,” she repeated, “but sometimes it was hard to understand them. The guides, I mean, not the monkeys.” She chuckled.
“The monkeys spoke Russian, naturally,” John said, and put away his phone.
Sarah Gerard, “ The Killer ,” from Guernica
They paid the bill and left, gathering on the sidewalk.
Nathan said to them, “We live down the beach. Come over.”
Amy tried to decline. Benjamin held her by the elbow. She allowed him to lead her, and by the time they reached the sand behind the Pelican, she’d managed to free herself, and catch up with Carol.
They walked the waterline.
“There is another option if you don’t want to kill them yourself,” Carol told her. Then, turning to Nathan: “We can put them in touch with Chance.”
Nathan fell into step with them. He draped an arm around his wife’s waist.
“Is Chance an exterminator?” said Amy.
“I hesitate to tell you more about our relationship,” Nathan joked. “I don’t talk God or politics in mixed company.”
“I’m a registered Democrat,” said Benjamin.
“He comes out and shoots the iguanas, then disposes of the carcasses,” said Carol. “He charges a reasonable fee.”
Nathan smiled.
“He actually became somewhat notorious when he posted some pictures of one of his hunts on Facebook recently,” Carol continued. “He can guarantee up to one hundred iguanas in a single hunt. He had them all laid out in rows with their legs bound, and huge plastic bins of dead lizards, rooms and hallways full of them. Then these happy white men in t-shirts with the sleeves cut off, posing.”
“You can imagine,” said Nathan.
“Thousands of shares. People calling him a murderer.”
“He’s doing our community a service, really.”
They climbed a narrow path worn into the sea grass. It led to the screened-in pool of a stone lanai furnished in rattan. Nathan went behind the bar with his phone to his ear. He fixed their drinks out of earshot. Carol invited them to sit on a loveseat. She offered them each a cigarette. They declined.
“I suppose you know too much about the consequences of smoking.” She lit the cigarette and drew out the motion of removing it from her mouth. A slip of smoke hovered between her lips. “My father was a pack-a-day smoker until he died at ninety-two. I figure I’m immune.”
“I’m not sure that would stand up to peer review,” said Benjamin.
“You’re right. Too emotional.”
Kevin Barry, “ Fjord of Killary ,” from Dark Lies the Island
So I bought an old hotel on the fjord of Killary. It was set hard by the harbor wall, with Mweelrea Mountain across the water, and disgracefully gray skies above. It rained two hundred and eighty-seven days of the year, and the locals were given to magnificent mood swings. On the night in question, the rain was particularly violent—it came down like handfuls of nails flung hard and fast by a seriously riled sky god. I was at this point eight months in the place and about convinced that it would be the death of me.
“It’s end-of-the-fucking-world stuff out there,” I said.
The chorus of locals in the hotel’s lounge bar, as always, ignored me. I was a fretful blow-in, by their mark, and simply not cut out for tough, gnarly, West of Ireland living. They were listening, instead, to John Murphy, our alcoholic funeral director.
“I’ll bury anythin’ that fuckin’ moves,” he said.
“Bastards, suicides, tinkers,” he said.
“I couldn’t give a fuckin’ monkey’s,” he said.
Behind the bar: the Guinness tap, the Smithwicks tap, the lager taps, the line of optics, the neatly stacked rows of glasses, and a high stool that sat by a wee slit of window that had a view across the water toward Mweelrea. The iodine tang of kelp hung in the air always, and put me in mind of embalming fluid. Bill Knott looked vaguely from his Bushmills toward the water.
“Highish, all right,” he said. “But now what’d we be talkin’ about for Belmullet, would you say? Off a slow road?”
The primary interest of these people’s lives, it often seemed, was how far one place was from another, and how long it might take to complete the journey, given the state of the roads. Bill had been in haulage as a young man and considered himself expert.
“I don’t know, Bill,” I said.
“Would we say an hour twenty if you weren’t tailbacked out of Newport?”
“I said I really don’t fucking well know, Bill.”
“There are those’ll say you’d do it in an hour.” He sipped, delicately. “But you’d want to be grease fuckin’ lightnin’ coming up from Westport direction, wouldn’t you?”
“We could be swimming it yet, Bill.”
Toni Cade Bambara, “ The Lesson ,” from Gorilla, My Love
“Will you look at this sailboat, please,” say Flyboy, cuttin her off and pointin to the thing like it was his. So once again we tumble all over each other to gaze at this magnificent thing in the toy store which is just big enough to maybe sail two kittens across the pond if you strap them to the posts tight. We all start reciting the price tag like we in assembly. “Hand-crafted sailboat of fiberglass at one thousand one hundred ninety-five dollars.”
“Unbelievable,” I hear myself say and am really stunned. I read it again for myself just in case the group recitation put me in a trance. Same thing. For some reason this pisses me off. We look at Miss Moore and she lookin at us, waiting for I dunno what.
“Who’d pay all that when you can buy a sailboat set for a quarter at Pop’s, a tube of glue for a dime, and a ball of string for eight cents? It must have a motor and a whole lot else besides,” I say. “My sailboat cost me about fifty cents.”
“But will it take water?” say Mercedes with her smart ass.
“Took mine to Alley Pond Park once,” say Flyboy. “String broke. Lost it. Pity.”
“Sailed mine in Central Park and it keeled over and sank. Had to ask my father for another dollar.”
“And you got the strap,” laugh Big Butt. “The jerk didn’t even have a string on it. My old man wailed on his behind.”
Little Q.T. was staring hard at the sailboat and you could see he wanted it bad. But he too little and somebody’d just take it from him. So what the hell.
“This boat for kids, Miss Moore?”
“Parents silly to buy something like that just to get all broke up,” say Rosie Giraffe.
“That much money it should last forever,” I figure.
“My father’d buy it for me if I wanted it.”
“Your father, my ass,” say Rosie Giraffe getting a chance to finally push Mercedes.
“Must be rich people shop here,” say Q.T.
“You are a very bright boy,” say Flyboy. “What was your first clue?” And he rap him on the head with the back of his knuckles, since Q.T. the only one he could get away with. Though Q.T. liable to come up behind you years later and get his licks in when you half expect it.
Ali Smith, “ The Child ,” from The First Person and Other Stories
You’re a really rubbish driver, a voice said from the back of the car. I could do better than that, and I can’t even drive. Are you for instance representative of all women drivers, or is it just you among all women who’s so rubbish at driving?
It was the child speaking. But it spoke with so surprisingly charming a little voice that it made me want to laugh, a voice as young and clear as a series of ringing bells arranged into a pretty melody. It said the complicated words, representative and for instance, with an innocence that sounded ancient, centuries old, and at the same time as if it had only just discovered their meaning and was trying out their usage and I was privileged to be present when it did.
I slewed the car over to the side of the motorway, switched the engine off and leaned over the front seat into the back. The child still lay there helpless, rolled up in the tartan blanket, held in place by it inside the seatbelt. It didn’t look old enough to be able to speak. It looked barely a year old.
It’s terrible. Asylum seekers come here and take all our jobs and all our benefits, it said preternaturally, sweetly. They should all be sent back to where they come from.
There was a slight endearing lisp on the “s” sounds in the words asylum and seekers and jobs and benefits and sent.
What? I said.
Can’t you hear? Cloth in your ears? it said. The real terrorists are people who aren’t properly English. They will sneak into football stadiums and blow up innocent Christian people supporting innocent English teams.
The words slipped out of its ruby-red mouth. I could just see the glint of its little coming-through teeth.
It said: The pound is our rightful heritage. We deserve our heritage. Women shouldn’t work if they’re going to have babies. Women shouldn’t work at all. It’s not the natural order of things. And as for gay weddings. Don’t make me laugh.
Then it laughed, blondly, beautifully, as if only for me. Its big blue eyes were open and looking straight up at me as if I were the most delightful thing it had ever seen.
I was enchanted. I laughed back.
ZZ Packer, “The Ant of the Self,” from Drinking Coffee Elsewhere
My father just got a DUI—again—though that didn’t stop him from asking for the keys. When I didn’t give them up, he sighed and shook his head as though I withheld keys from him daily. “C’mon, Spurge,” he’d said. “The pigs aren’t even looking.”
He’s the only person I know who still calls cops “pigs,” a holdover from what he refers to as his Black Panther days, when “the brothers” raked their globes of hair with black-fisted Afro picks, then left them stuck there like javelins. When, as he tells it, he and Huey P. Newton would meet in basements and wear leather jackets and stick it to whitey. Having given me investment advice, he now watches the world outside the Honda a little too jubilantly. I take the curve around the city, past the backsides of chain restaurants and malls, office parks and the shitty Louisville zoo.
“That’s your future,” he says winding down from his rant. “Sound investments.”
“Maybe you should ask the pigs for your bail money back,” I say. “We could invest that.”
“You keep getting money from debate, we could invest.”
When most people talk about investing, they mean stocks or bonds or mutual funds. What my father means is his friend Splo’s cockfighting arena, or some dude who goes door to door selling exercise equipment that does all the exercise for you. He’d invested in a woman who tried selling African cichlids to pet shops, but all she’d done was dye ordinary goldfish so they looked tropical. “Didn’t you just win some cash?” he asks. “From debate?”
“Bail,” I say. “I used it to pay your bail.”
He’s quiet for a while. I wait for him to stumble out a thanks. I wait for him to promise to pay me back with money he knows he’ll never have. Finally he sighs and says, “Most investors buy low and sell high. Know why they do that?” With my father there are not only trick questions, but trick answers. Before I can respond, I hear his voice, loud and naked. “I axed you, ‘Do you know why they do that?'” He’s shaking my arm as if trying to wake me. “You answer me when I ask you something.”
I twist my arm from his grasp to show I’m not afraid. We swerve out of our lane. Cars behind us swerve as well, then zoom around us and pull ahead as if we are a rock in a stream.
“Do you know who this is ?” he says. “Do you know who you’re talking to ?”
I haven’t been talking to anyone, but I keep this to myself.
Jhumpa Lahiri, “ A Temporary Matter ,” from Interpreter of Maladies
The microwave had just beeped when the lights went out, and the music disappeared.
“Perfect timing,” Shoba said.
“All I could find were birthday candles.” He lit up the ivy, keeping the rest of the candles and a book of matches by his plate.
“It doesn’t matter,” she said, running a finger along the stem of her wineglass. “It looks lovely.”
In the dimness, he knew how she sat, a bit forward in her chair, ankles crossed against the lowest rung, left elbow on the table. During his search for the candles, Shukumar had found a bottle of wine in a crate he had thought was empty. He clamped the bottle between his knees while he turned in the corkscrew. He worried about spilling, and so he picked up the glasses and held them close to his lap while he filled them. They served themselves, stirring the rice with their forks, squinting as they extracted bay leaves and cloves from the stew.
Every few minutes Shukumar lit a few more birthday candles and drove them into the soil of the pot.
“It’s like India,” Shoba said, watching him tend his makeshift candelabra. “Sometimes the current disappears for hours at a stretch. I once had to attend an entire rice ceremony in the dark. The baby just cried and cried. It must have been so hot.”
Their baby had never cried, Shukumar considered. Their baby would never have a rice ceremony, even though Shoba had already made the guest list, and decided on which of her three brothers she was going to ask to feed the child its first taste of solid food, at six months if it was a boy, seven if it was a girl.
“Are you hot?” he asked her. He pushed the blazing ivy pot to the other end of the table, closer to the piles of books and mail, making it even more difficult for them to see each other. He was suddenly irritated that he couldn’t go upstairs and sit in front of the computer.
“No. It’s delicious,” she said, tapping her plate with her fork. “It really is.”
He refilled the wine in her glass. She thanked him.
They weren’t like this before. Now he had to struggle to say something that interested her, something that made her look up from her plate, or from her proofreading files. Eventually he gave up trying to amuse her. He learned not to mind the silences.
“I remember during power failures at my grandmother’s house, we all had to say something,” Shoba continued. He could barely see her face, but from her tone he knew her eyes were narrowed, as if trying to focus on a distant object. It was a habit of hers.
“Like what?”
“I don’t know. A little poem. A joke. A fact about the world. For some reason my relatives always wanted me to tell them the names of my friends in America. I don’t know why the information was so interesting to them. The last time I saw my aunt she asked after four girls I went to elementary school with in Tucson. I barely remember them now.”
Shukumar hadn’t spent as much time in India as Shoba had. His parents, who settled in New Hampshire, used to go back without him. The first time he’d gone as an infant he’d nearly died of amoebic dysentery. His father, a nervous type, was afraid to take him again, in case something were to happen, and left him with his aunt and uncle in Concord. As a teenager he preferred sailing camp or scooping ice cream during the summers to going to Calcutta. It wasn’t until after his father died, in his last year of college, that the country began to interest him, and he studied its history from course books as if it were any other subject. He wished now that he had his own childhood story of India.
“Let’s do that,” she said suddenly.
“Say something to each other in the dark.”
“Like what? I don’t know any jokes.”
“No, no jokes.” She thought for a minute. “How about telling each other something we’ve never told before.”
Grace Paley, “ My Father Addresses Me on the Facts of Old Age ,” from Here and Somewhere Else
My father had decided to teach me how to grow old. I said O.K. My children didn’t think it was such a great idea. If I knew how, they thought, I might do so too easily. No, no, I said, it’s for later, years from now. And, besides, if I get it right it might be helpful to you kids in time to come.
They said, Really?
My father wanted to begin as soon as possible. For God’s sake, he said, you can talk to the kids later. Now, listen to me, send them out to play. You are so distractable.
We should probably begin at the beginning, he said. Change. First there is change, which nobody likes—even men. You’d be surprised. You can do little things—putting cream on the corners of your mouth, also the heels of your feet. But here is the main thing. Oh, I wish your mother was alive—not that she had time—
But Pa, I said, Mama never knew anything about cream. I did not say she was famous for not taking care.
Forget it, he said sadly. But I must mention squinting. don’t squint. Wear your glasses. Look at your aunt, so beautiful once. I know someone has said men don’t make passes at girls who wear glasses, but that’s an idea for a foolish person. There are many handsome women who are not exactly twenty-twenty.
Please sit down, he said. Be patient. The main thing is this—when you get up in the morning you must take your heart in your two hands. You must do this every morning.
That’s a metaphor, right?
Metaphor? No, no, you can do this. In the morning, do a few little exercises for the joints, not too much. Then put your hands like a cup over and under the heart. Under the breast. He said tactfully. It’s probably easier for a man. Then talk softly, don’t yell. Under your ribs, push a little. When you wake up, you must do this massage. I mean pat, stroke a little, don’t be ashamed. Very likely no one will be watching. Then you must talk to your heart.
- Share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Google+ (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)

Emily Temple
Previous article, next article, support lit hub..

Join our community of readers.
to the Lithub Daily
Popular posts.

Follow us on Twitter

On Finally Being Old Enough to Love Proust
- RSS - Posts
Literary Hub
Created by Grove Atlantic and Electric Literature
Sign Up For Our Newsletters
How to Pitch Lit Hub
Advertisers: Contact Us
Privacy Policy
Support Lit Hub - Become A Member
Become a Lit Hub Supporting Member : Because Books Matter
For the past decade, Literary Hub has brought you the best of the book world for free—no paywall. But our future relies on you. In return for a donation, you’ll get an ad-free reading experience , exclusive editors’ picks, book giveaways, and our coveted Joan Didion Lit Hub tote bag . Most importantly, you’ll keep independent book coverage alive and thriving on the internet.

Become a member for as low as $5/month
TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Guides • Perfecting your Craft
Posted on May 17, 2021
What is a Short Story? Definitions and Examples
A short story is a form of fiction writing defined by its brevity . A short story usually falls between 3,000 and 7,000 words — the average short story length is around the 5,000 mark. Short stories primarily work to encapsulate a mood, typically covering minimal incidents with a limited cast of characters — in some cases, they might even forgo a plot altogether.
Many early-career novelists have dabbled in the form and had their work featured in literary magazines and anthologies. Others, like Raymond Carver and Alice Munro, have made it their bread and butter. From “starter” short story writers to short story experts, there’s an incredible range of short stories out there.
In this series of guides, we'll be looking into short stories and showing you how any writer can write a powerful piece of short fiction — and even get it published. But before we get into the weeds, let's look at a few examples to demonstrate the range and flexibility of this form.
What short story should you read next?
Find out here! Takes 30 seconds
Broadly speaking, you could answer the question of "what is a short story" in a few ways, starting with the most obvious.
A classic short narrative
Though short stories must inherently be concise pieces of writing, they often incorporate elements of the novel to retain a similar impact. A ‘classic short narrative’ is the most story-telling-by-the-numbers that a short story can get — the plot will imitate long-form fiction by having a defined exposition, escalating rising action , a climax, and a resolution.
Short stories do differ from longer prose works in some respects: they’re unlikely to contain a huge cast of characters, multiple points of view , or successive climaxes like those found in novellas and novels. But despite these cuts, if the author does their job right, a ‘classic’ short story will be just as affecting and memorable as a novel — if not more so.
Example #1: “Speaking in Tongues” by ZZ Packer

Tia, disillusioned with her strict Pentecostal upbringing in a sleepy Southern town, escapes her great-aunt’s clutches to find her mother in Atlanta. This story starts with a classic expository beat — Tia at school, flicking through a religious textbook, dreaming of another life. This is followed by a crisis: Tia travels by bus to the big city, befriends a man on the street, and goes to stay with him, only to learn that he is a drug dealer and a pimp. Eventually, Tia returns home to her great-aunt. In all, it’s a sensitive story about the vulnerability of youth and the longing for family.
As short stories go, “Speaking In Tongues” has a pretty impressive narrative. You can see how the premise and plot could work as a longer piece of fiction, but they pack even more of a punch in this shorter form.
A vignette is a short story that presents a neatly packaged moment in time, usually in quite a technically accomplished fashion. ‘Vignette’ is French word more frequently used to signify a small portrait, but in a literary sense, it means “a brief evocative description, account, or episode”. This could be of a person, event or place.
Fleetingness is at the crux of a vignette short story. For that reason, it is likely to be heavy on description, light on plot. You might find a particularly embellished description of a character or setting, often with a strong dose of symbolism that corresponds with a central theme.
Example #2: “Viewfinder” by Raymond Carver
“Viewfinder” has a simple premise: a traveling photographer takes a photo of the narrator’s house, sells it to him on his doorstep, and is invited in for coffee. The story emphasizes feelings of loneliness that come to the fore in their interaction, captured brilliantly by Carver’s unadorned writing style. Tales like this that attribute importance to the mundane are arguably best served by a concise form as Carver's fascination with banal events could have become repetitive and rudderless in a longer piece of work.
Many critics agree that no one writes the American working classes quite like Carver. His stories chronicle the everyday experiences of Midwestern men and women eking out a living then fish, play cards, and shoot the breeze as life passes them by. It won Carver immense critical acclaim in his lifetime and is a great example of short-form writing that emphasizes mood rather than plot.

An anecdote
An anecdote recounted to friends is most successful when it’s pacey, humorous, and has a quick crescendo. The same can be said of short stories that capitalize on this storytelling device.
Anecdotal stories take on a more conversational tone and are more meandering in style, in contrast to the directness of other short stories and flash fiction . It can have a conventional story structure, like the classic short narrative, or it may focus on a particular stylistic recounting of an event. Basically, an anecdote allows a writer to have fun with the way a story is told — though exactly how it unfolds remains important too.
Example #3: “We Love You Crispina” by Jenny Zhang

Zhang’s 2017 short story collection Sour Heart chronicles the rough-and-tumble lives of recently immigrated Chinese-American living in downtown Manhattan. The stories in this collection are told from the perspectives of children, and the narrative takes full advantage of the impish, filterless way in which children relate their own experiences to themselves and others.
In “We Love You Crispina”, young Christina’s life in a crowded Washington Heights tenement block is refracted through her naive, contradictory understandings of the world. Her parents are struggling to get a leg up and are contemplating sending her back to Shanghai — but Christina is more concerned with how the bed bugs in their cramped apartment are making her itchy, and dissecting the interactions she has in the school playground. It’s a wonderfully nuanced exercise in contrast, as well as a reminder of what feels most important to us when we’re small, rendered potently through Christina’s 'anecdotal' voice.
An experiment with genre
Short stories, by nature, are more flexible pieces of fiction that aren’t wedded to the diktat of longer-form fiction. It means they can play around with and challenge the expectations of a genre’s expected conventions, in a relatively ‘low stakes’ way compared to a full-blown novel.
Oftentimes, an experiment won’t be a complete reinvention of the genre. Instead, one might find a refreshing twist on a classic trope — or, as in the example below, upping the ante and taking a genre to heights it has never been before.
Example #4: “A Good Man is Hard to Find” by Flannery O’Connor
This short story sent shock waves through the American literary establishment when it was first published in 1953. It follows a Southern family on a road trip to visit the children’s grandmother — who end up crashing their car and happening upon a mysterious group of men. I won’t spoil the rest for you, but one word of warning: don’t expect a happy ending.
“A Good Man Is Hard To Find” incorporates common themes of Southern gothic literature , like religious imagery, and — surprise surprise — characters meeting a gruesome demise, but its controversial final scene marks it out. The macabre detail was shocking to audiences at the time but is now held up as a stellar example of the genre (and also exemplifies how a well-executed bit of subversion can become the golden standard in literature!). You might want to sleep with one eye open after reading this, but that’s half the point, right?
An exercise in extreme brevity
How many words do you actually need to tell a great story? If you were to ask that to someone who writes flash fiction , they tell you "fewer than 1,000 words."
The defining element that sets flash fiction apart from the standard-issue short story — other than word count — is that much more needs to be implied, rather than said upfront. Flash fiction, and especially mega-short microfiction, perfectly embody this principle of inference, which itself derives from Ernest Hemingway ’s Iceberg Theory of story development.
Example #5 “Curriculum” by Sejal Shah
“ Curriculum ”, clocking in at exactly 500 words, is a great sampling of the emotional, personal language that appears frequently in flash fiction. A handkerchief, some cream cloth, and a pair of glasses become important symbols around which Shah contemplates identity and womanhood, in the form of a series of questions that follow her descriptions of the objects.
This kind of deliberate, highly considered structure ensures that Shah’s flash fiction makes a razor-sharp point, whilst also allowing for a contemplative tone that transcends the words on the page. When done well, this style of short fiction can be a greater-than-expected vehicle for thoughtful comments on a range of issues.
If you’re in the mood to read more around the form, check out our picks for the 31 best short stories .
As you can see, the short story is an art form on its own that requires deftness, clarity, and a strong grasp of how to make an economy of words compelling and innovative. If you’re feeling ready to write a short story of your own, proceed to the next post in this series.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.

Craft a satisfying story arc
Outline and write your short story with our step-by-step template.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:

IMAGES
VIDEO