How to Write a Business Report: A Step By Step Guide with Examples


Table of contents

Enjoy reading this blog post written by our experts or partners.
If you want to see what Databox can do for you, click here .
With so much experience under your belt, you already know a lot about business reporting.
So, we don’t want to waste your time pointing out the obvious because we know what you need.
Secrets. Tricks. Best practices.sales rep drilldown business report
The answer to how to write a mind-blowing business report that you don’t need to spend hours and days writing.
A business report that will immediately allow you to identify your strengths and weaknesses.
A report that’ll help you learn more about your business and do more accurate forecasting and planning for the future.
We believe we have just that right here.
With this comprehensive guide, you’ll create effective sales, analytical, and informative business reports (and business dashboards ) that will help you improve your strategies, achieve your goals, and grow your business.
So, let’s dive in.
What Is a Business Report?
Importance of creating business reports, types of business reports, what should be included in a business report, how to write a business report: an 11-step guide.
- Business Report Examples
Although there’s a variety of business reports that differ in many aspects, in short, a business report definition would be the following:
A business report is an informative document that contains important data such as facts, analyses, research findings, and statistics about a business with the goal to make this information accessible to people within a company.
Their main purpose is to facilitate the decision-making process related to the future of the business, as well as to maintain effective communication between people who create the reports and those they report to.
A good business report is concise and well-organized, looks professional, and displays the relevant data you can act on. The point is to reflect upon what you’ve achieved so far (typically, over the past month, quarter or year) and to use the data to create a new strategy or adjust the current one to reach even more business goals.
Business reports should be objective and based on the data. When stating the facts, people rely on numbers rather than giving descriptions. For instance, instead of saying “our conversion rate skyrocketed”, you would display the exact percentages that back up that claim.
Business reporting matters for several reasons, among which the most important ones are:
Recognizing Opportunities to Grow
Detecting issues and solving them quickly, evaluating a potential partner, having a paper trail, keeping things transparent for the stakeholders, setting new company goals.
In fact, over half of the companies that contributed to Databox’s state of business reporting research confirmed that regular monitoring and reporting brought them significant concrete benefits.
If you never look back at what you’ve achieved, you can’t figure out what you’ve done well and what you can leverage in the future for even better results.
When you analyze a specific aspect of your business over a specific time period and present the data you gathered in a report, you can detect an opportunity to grow more easily because you have all the information in one place and organized neatly.
Is it time to introduce new products or services? Is there a way to enhance your marketing strategy? Prepare a report. Can you optimize your finances? Write a financial business report . Whatever decision you need to make, it’s easier when you base it on a report.
Reports are essential for crisis management because they can introduce a sense of calmness into your team. Putting everything on paper makes it easier to encompass all the relevant information and when you know all the facts, you can make a more accurate and effective decision about what to do next.
Writing business reports regularly will also help you identify potential issues or risks and act timely to prevent damage and stop it from escalating. That’s why monthly reporting is better than doing it only once a year.
Having an insight into your finances , operations and other business aspects more regularly allows you to have better control over them and mitigate potential risks more effectively.
Different types of business reports may be accessible to the general public. And if they’re not, specific situations may require a company to send them over to the person requesting them. That may happen if you’re considering a partnership with another company. Before making the final decision, you should learn about their financial health as every partnership poses a certain risk for your finances and/or reputation. Will this decision be profitable?
Having an insight into a company’s business report helps you establish vital business relationships. And it goes the other way around – any potential partner can request that you pull a business report for them to see, so writing business reports can help you prove you’re a suitable business partner.
In business, and especially in large companies, it’s easy to misplace information when it’s communicated verbally. Having a written report about any aspect of your business doesn’t only prevent you from losing important data, but it also helps you keep records so you can return to them at any given moment and use them in the future.
That’s why it’s always good to have a paper trail of anything important you want to share with colleagues, managers, clients, or investors. Nowadays, of course, it doesn’t have to literally be a paper trail, since we keep the data in electronic form.
Writing business reports helps you keep things transparent for the stakeholders, which is the foundation of efficient communication between these two sides.
You typically need to report to different people – sometimes they’re your managers, sometimes they’re a client. But your company’s stakeholders will also require an insight into the performance of your business, and relying on reports will help you maintain favorable business relationships. A business report shows you clearly how your company is performing and there isn’t room for manipulation.
Once you set business goals and the KPIs that help you track your progress towards them, you should remember they’re not set in stone. From time to time, you’ll need to revisit your goals and critical metrics and determine whether they’re still relevant.
When you write a business report and go through it with your team members or managers, you have a chance to do just that and determine if you’re efficient in reaching your goals. Sometimes, new insights will come up while writing these reports and help you identify new objectives that may have emerged.
Depending on your goals and needs, you’ll be writing different types of business reports. Here are five basic types of business reports .
Informational Report
Analytical report, research report, explanatory report, progress report.
Informational reports provide you with strictly objective data without getting into the details, such as explaining why something happened or what the result may be – just pure facts.
An example of this type of business report is a statement where you describe a department within your company: the report contains the list of people working in this department, what their titles are, and what they’re responsible for.
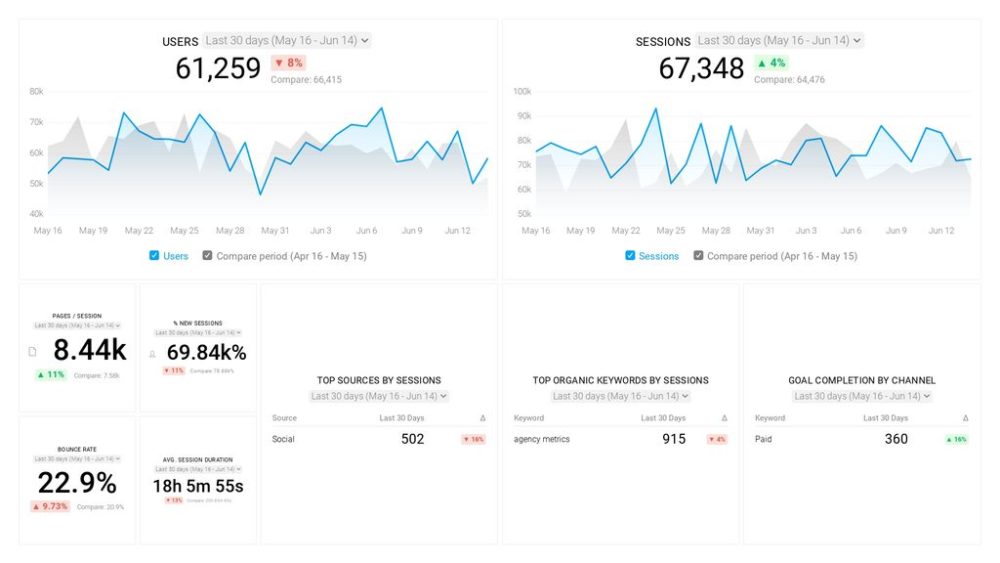
Another example related to a company’s website could look like this Google Analytics website traffic engagement report . As we explained above, this report shows objective data without getting too much into the details, so in this case, just the most important website engagement metrics such as average session duration, bounce rate, sessions, sessions by channel, and so on. Overall, you can use this report to monitor your website traffic, see which keywords are most successful, or how many returning users you have, but without further, in-depth analysis.
Analytical reports help you understand the data you’ve collected and plan for the future based on these insights. You can’t make business decisions based on facts only, so analytical reports are crucial for the decision-making process.
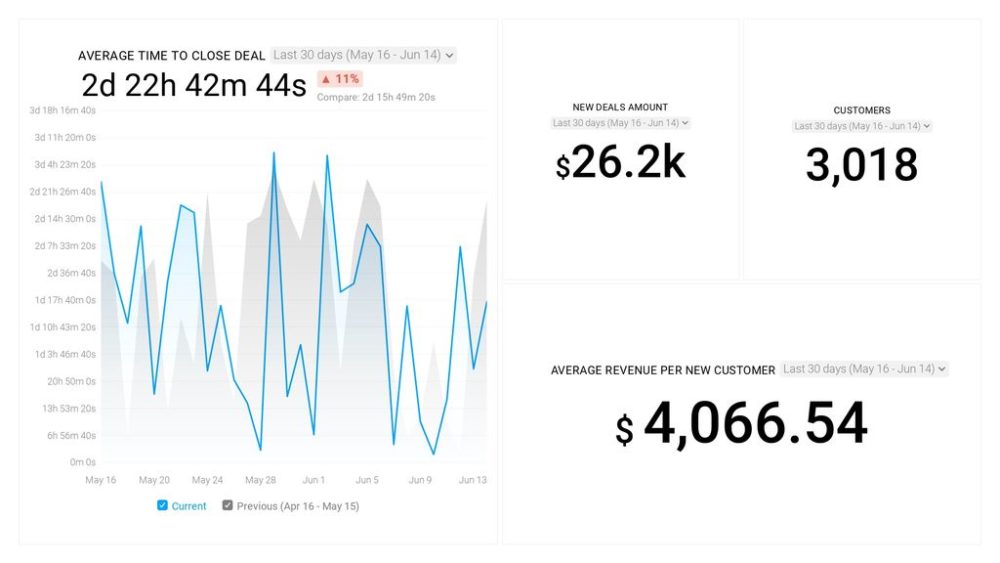
This type of business report is commonly used for sales forecasting. For instance, if you write a report where you identify a drop or an increase in sales, you’ll want to find out why it happened. This HubSpot’s sales analytics report is a good example of what metrics should be included in such a report, like average revenue per new client or average time to close the deal. You can find more web analytics dashboard examples here.
From these business reports, you can find out if you will reach your goals by implementing your current strategy or if you need to make adjustments.
Research is critical when you’re about to introduce a change to your business. Whether it’s a new strategy or a new partner, you need an extensive report to have an overview of all important details. These reports usually analyze new target markets and competition, and contain a lot of statistical data.
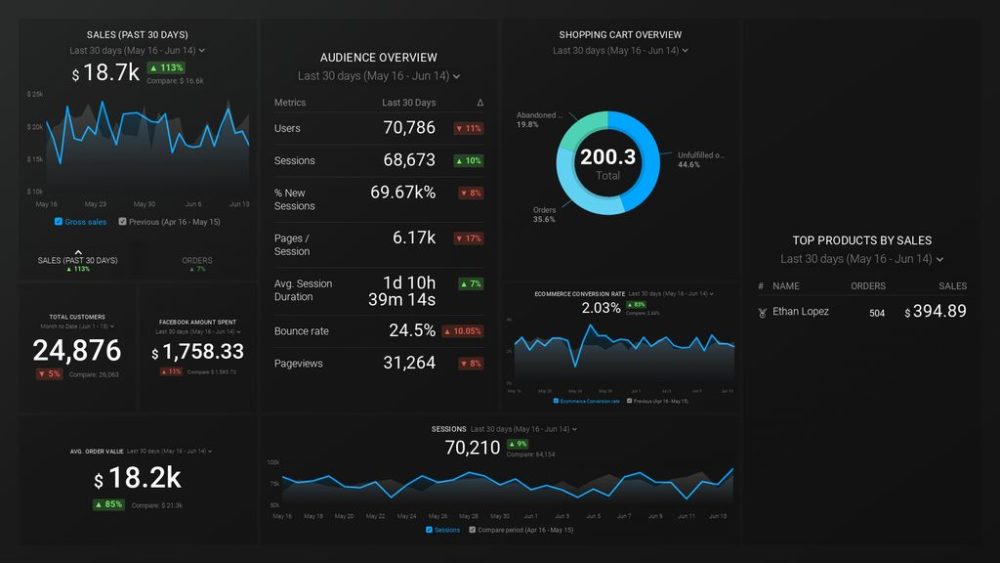
While not the same, here is an example of an ecommerce dashboard that could help track each part of a campaign in detail, no matter whether you are launching a new product, testing a new strategy, and similar. Similar to a research report, it contains key data on your audience (target market), shows your top-selling products, conversion rate and more. If you are an online store owner who is using paid ads, you can rely on this report to monitor key online sales stats in line with Facebook Ads and Google Analytics. See more ecommerce dashboards here.
As you might guess from its name, you write the explanatory report when it’s necessary for you to explain a specific situation or a project you’ve done to your team members. It’s important to write this report in a way that everyone will be able to understand.
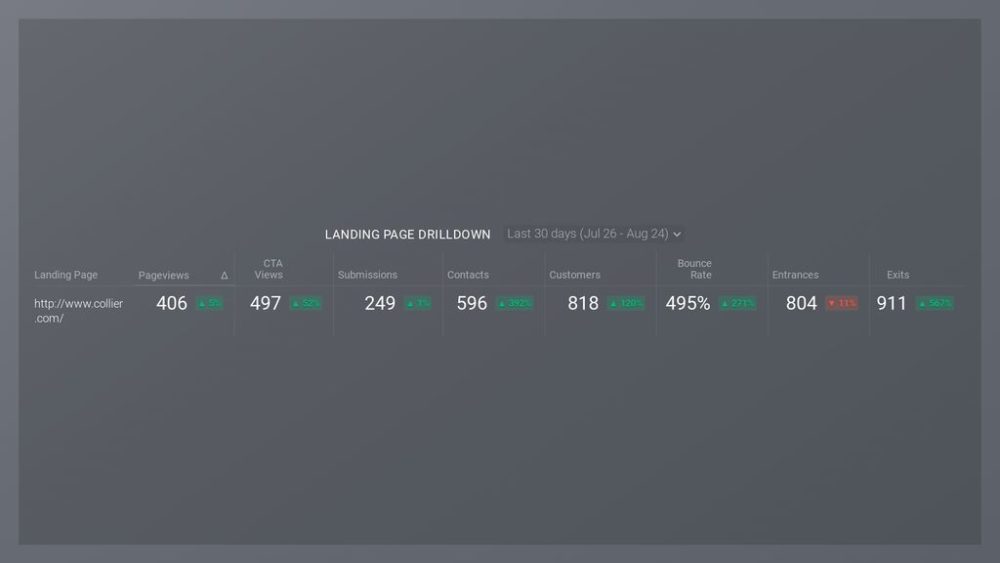
Explanatory reports include elements like research results, reasons and goals of the research, facts, methodology, and more. While not exactly an explanatory report, this example of a HubSpot marketing drilldown report is the closest thing to it, as it helps marketers drill into an individual landing page performance, and identify how good their best landing pages are at converting, or which ones have the best performance.
A progress report is actually an update for your manager or client – it informs them about where you stand at the moment and how things are going. It’s like a checkpoint on your way towards your goal.
These reports may be the least demanding to write since you don’t need to do comprehensive research before submitting them. You just need to sum up your progress up to the point when the report was requested. This business report may include your current results, the strategy you’re implementing, the obstacles you’ve come across, etc. If this is a marketing progress report you can use marketing report templates to provide a more comprehensive overview.
In many companies, progress reports are done on a weekly or even daily basis. Here is an example of a daily sales report from Databox. HubSpot users can rely on this sales rep drilldown business report to see how individual each sales rep is performing and measure performance against goals. Browse through all our KPI dashboards here.
What does a great business report look like? If you’re not sure what sections your report should have, you’ll learn what to include in the following lines.
Business Report Formatting
Different types of reports require different lengths and structures, so your business report format may depend on what elements your report needs to have. For example, progress reports are typically pretty simple, while analytical or explanatory reports are a different story.
However, most reports will start with a title and a table of contents, so the person reading the report knows what to expect. Then, add a summary and move on to the introduction. After you’ve written the body and the conclusion, don’t forget to include suggestions based on your findings that will help your team create an actionable plan as you move forward.
After that, list the references you used while creating the report, and attach any additional documents or images that can help the person reading the report understand it better.
This outline may vary depending on what kind of report you’re writing. Short business reports may not need a table of contents, and informative reports won’t contain any analyses. Also, less formal reports don’t need to follow a strict structure in every situation.
Business Report Contents
When it comes to the contents of your report, keep in mind the person who’s going to read it and try to balance between including all the relevant information, but not overwhelming the reader with too many details.
- The introduction to the report should state the reason why you’re writing it, and what its main goal is. Also, mention what methodology and reporting software you’ve used, if applicable.
- The body of the report is where you’ll expose all your key findings, explain your methodology, share the important data and statistics, and present your results and conclusion.
- The conclusion , similarly to the summary you’ll add at the beginning of the report, briefly singles out the most important points and findings of the report.
If you decide to include more sections like recommendations, this is where you’ll suggest the next steps your team or the company may want to take to improve the results or take advantage of them if they’re favorable.
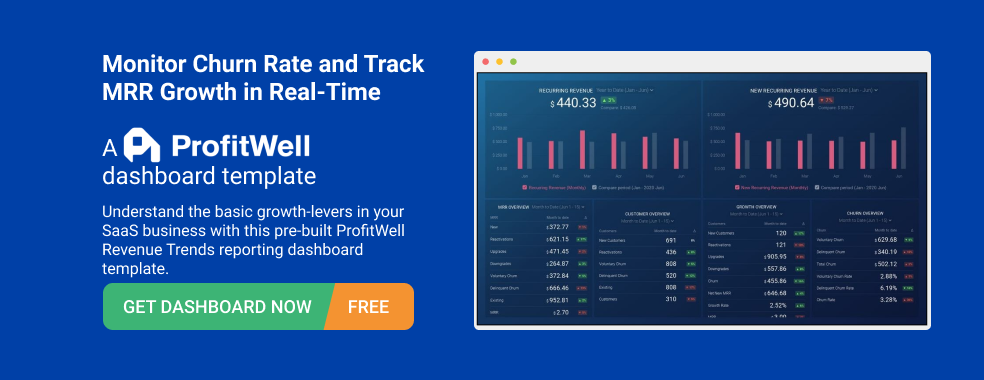
PRO TIP: Are You Tracking the Right Metrics for Your SaaS Company?
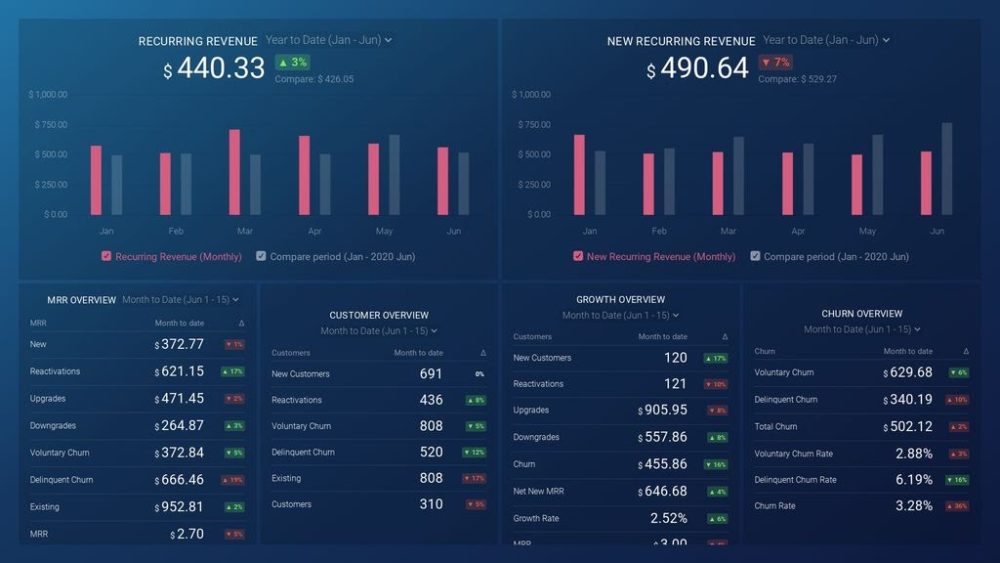
As a SaaS business leader, there’s no shortage of metrics you could be monitoring, but the real question is, which metrics should you be paying most attention to? To monitor the health of your SaaS business, you want to identify any obstacles to growth and determine which elements of your growth strategy require improvements. To do that, you can track the following key metrics in a convenient dashboard with data from Profitwell:
- Recurring Revenue. See the portion of your company’s revenue that is expected to grow month-over-month.
- MRR overview. View the different contributions to and losses from MRR from different kinds of customer engagements.
- Customer overview . View the total number of clients your company has at any given point in time and the gains and losses from different customer transactions.
- Growth Overview . Summarize all of the different kinds of customer transactions and their impact on revenue growth.
- Churn overview. Measure the number and percentage of customers or subscribers you lost during a given time period.
If you want to track these in ProfitWell, you can do it easily by building a plug-and-play dashboard that takes your customer data from ProfitWell and automatically visualizes the right metrics to allow you to monitor your SaaS revenue performance at a glance.
You can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set up the dashboard, follow these 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your Profitwell account with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.
Note : Other than text, make sure you include images, graphs, charts, and tables. These elements will make your report more readable and illustrate your points.
Whether you’re writing a specific type of business report for the first time or you simply want to improve the quality of your reports, make sure you follow this comprehensive guide to writing an effective business report.
- Do Your Research
- Create an Outline
- Determine Formatting Guidelines
- Think of an Engaging Title
- Write the Introduction
- Divide the Body of the Report into Sections
- Choose Illustrations
- Conclude Effectively
- Gather Additional Documentation
- Add a Summary
- Proofread Your Work
Step 1: Do Your Research
A well-planned report is a job half done. That means you need to do research before you start writing: you need to know who you’re writing for and how much they know about the topic of your report. You need to explore the best business dashboard software and templates you can use for your report.
Also, if you believe you will need additional resources and documents to add in the appendix, you should do it during this phase of report writing.
Step 2: Create an Outline
Once you’ve gathered the resources, it’s time to plan the report. Before you start writing, create an outline that will help you stick to the right structure. A business report is complex writing in which you can get lost very easily if you don’t have a clear plan.
Moreover, the report shouldn’t be complicated to read, so sticking to a plan will allow you to keep it concise and clear, without straying from the topic.
Step 3: Determine Formatting Guidelines
Most companies have their in-house formatting that every official document has to follow. If you’re not sure if such rules exist in your company, it’s time you checked with your managers.
If there arent’ any guidelines regarding formatting, make sure you set your own rules to make the report look professional. Choose a simple and readable format and make sure it supports all the symbols you may need to use in the report. Set up proper headings, spacing, and all the other elements you may need in Word or Google Docs.
Pro tip: Google Docs may be easier to share with people who are supposed to read your business report.
Step 4: Think of an Engaging Title
Even if you’re writing a formal business report, the title should be clear and engaging. Reports are typically considered dull as they’re a part of official business documentation, but there’s no reason why you can’t make them interesting to read. Your title should suit the report topic and be in different font size so the reader can recognize it’s a title. Underneath the title, you should add the name of the author of the report.
Step 5: Write the Introduction
A good introductory paragraph for a business report should explain to the reader why you’ve written the report. Use the introduction to provide a bit of background on the report’s topic and mention the past results if there’s been a significant improvement since your last report.
Step 6: Divide the Body of the Report into Sections
As this will be the most comprehensive part of your report, make sure you separate the data into logical sections. Your report is supposed to tell a story about your business, and these sections (such as methodology, hypothesis, survey, findings, and more) will help the data look well-organized and easy to read.
Step 7: Choose Illustrations
Of course, each of these sections should be followed with charts, graphs, tables, or other illustrations that help you make a point. Survey results are typically best displayed in pie charts and graphs, and these enable the reader to visualize the data better. From the formatting point of view, breaking the long text sections with illustrations makes the report more readable.
Pro tip: Using centralized dashboard solutions like Databox can bring your reporting game to the next level. Sign up for a forever-free trial now to see how you can use Databox to track and visualize performance easier than ever before .
Step 8: Conclude Effectively
Finish your report with a to-the-point conclusion that will highlight all the main data from the report. Make sure it’s not too long, as it’s supposed to be a summary of the body of the report. In case you don’t want to add a specific section for recommendations, this is where you can include them, along with your assessments.
Step 9: Gather Additional Documentation
If you’ve determined what additional documents, images, surveys, or other attachments you may need for your report, now is the time to collect them. Request access to those you may not be able to get on time, so you have everything you need by the deadline. Copy the documents you can use in the original form, and scan the documents you need in electronic format.
Step 10: Add a Summary
The summary is usually at the top of the report, but it’s actually something you should write after your report is completed. Only then will you know exactly what your most relevant information and findings are, so you can include them in this brief paragraph that summarizes your report’s main points.
The summary should tell the reader about the objective of the report, the methodology used, and even mention some of the key findings and conclusions.
Step 11: Proofread Your Work
It may seem like common sense, but this final step of the process is often overlooked. Proofreading your work is how you make sure your report will look professional because errors can ruin the overall impression the reader will form about your work, no matter how great the report is.
Look for any spelling or grammatical mistakes you can fix, and if you’re not sure about specific expressions or terminology, use Google to double-check it. Make sure your writing is to-the-point and clear, especially if you’re writing for people who may not know the industry so well. Also, double-check the facts and numbers you’ve included in the report before you send it out or start your reporting meeting.
Business Report Examples (with Ready-to-Use Templates)
Here, we’re sharing a few business reporting examples that you can copy, along with ready-to-use and free-to-download templates. If you don’t know where to start and what to include in different types of business reports, these business report examples are a great way to get started or at least get some inspiration to create yours.
Activity Report Example
Annual report example, project status report example, financial report example, sales report example, marketing report example.
Note : Each of the business report templates shared below can be customized to fit your individual needs with our DIY Dashboard Designer . No coding or design skills are necessary.
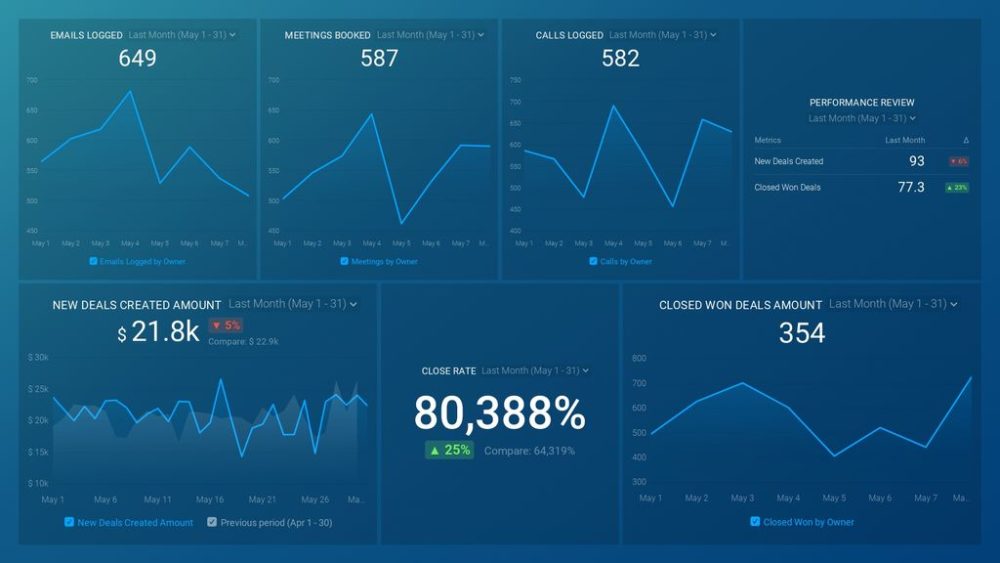
For reporting on sales activity, HubSpot users can rely this streamlined sales activity report that includes key sales metrics, such as calls, meetings, or emails logged by owner. This way, you can easily track the number of calls, meetings, and emails for each sales rep and identify potential leaks in your sales funnel. Check all our sales team activity dashboards here. Or if you are looking for dashboards that track general sales performance, browse through all Databox sales dashboards here.

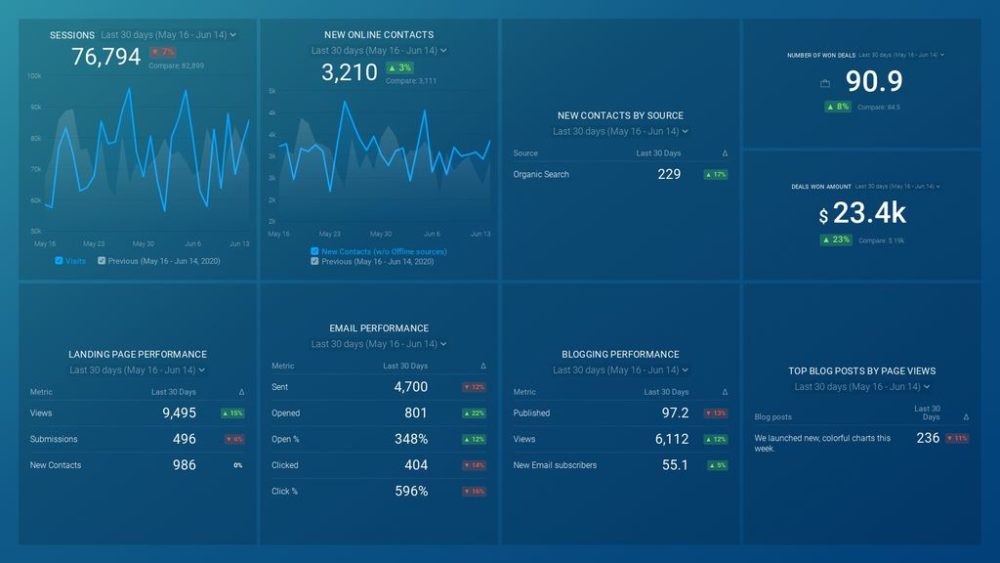
If you’re preparing for annual reporting, you will benefit from choosing this HubSpot annual performance report . It contains all the relevant metrics, such as email and landing page performance, new contacts, top blog posts by page views, and more. See all our performance dashboard templates here.
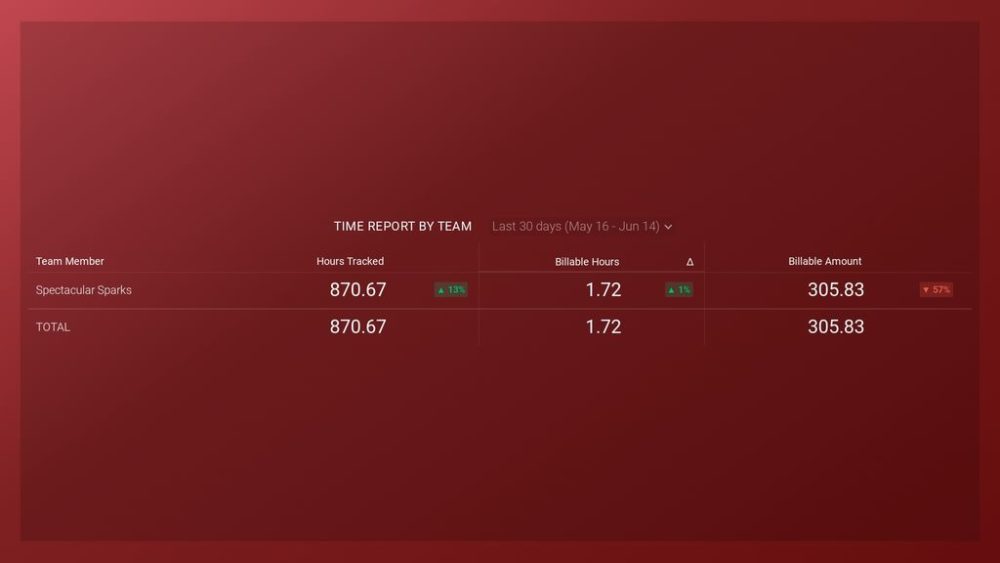
Project status reports can be very similar to progress reports. If you’re in need of one of those, here’s an example of a Project overview dashboard from Harvest that shows that can help you create simple, but well-organized report based on metrics that matter: hours tracked, billable hours, billable amount split by team members., and more. Check out more project management dashboard templates we offer here.
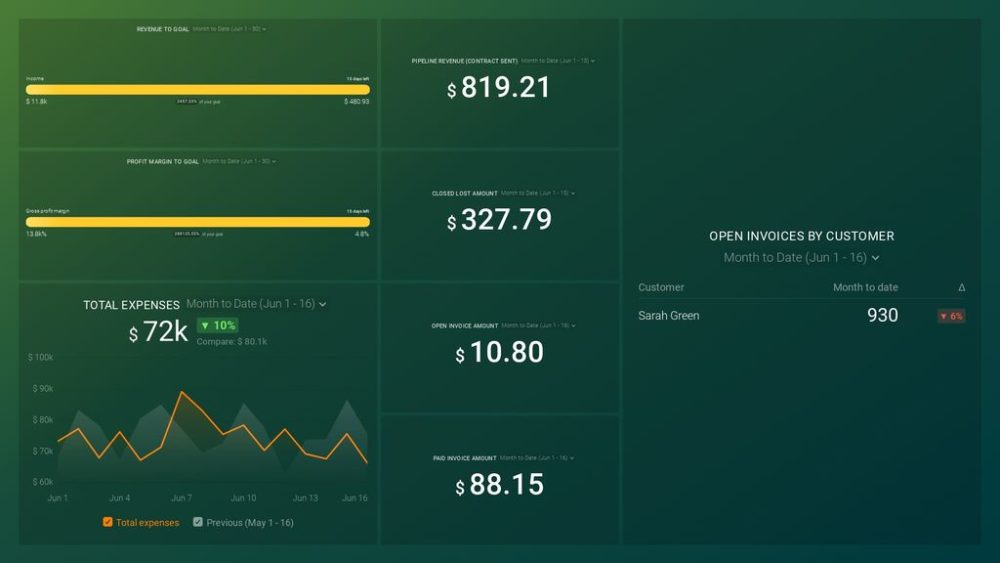
Are you creating a financial report? You will find this QuickBooks + HubSpot integration a great choice for a financial performance dashboard that makes creating a report simple. This dashboard focuses on the essential financial report
ting metrics and answers all your revenue-related questions. See all Databox financial dashboards here.
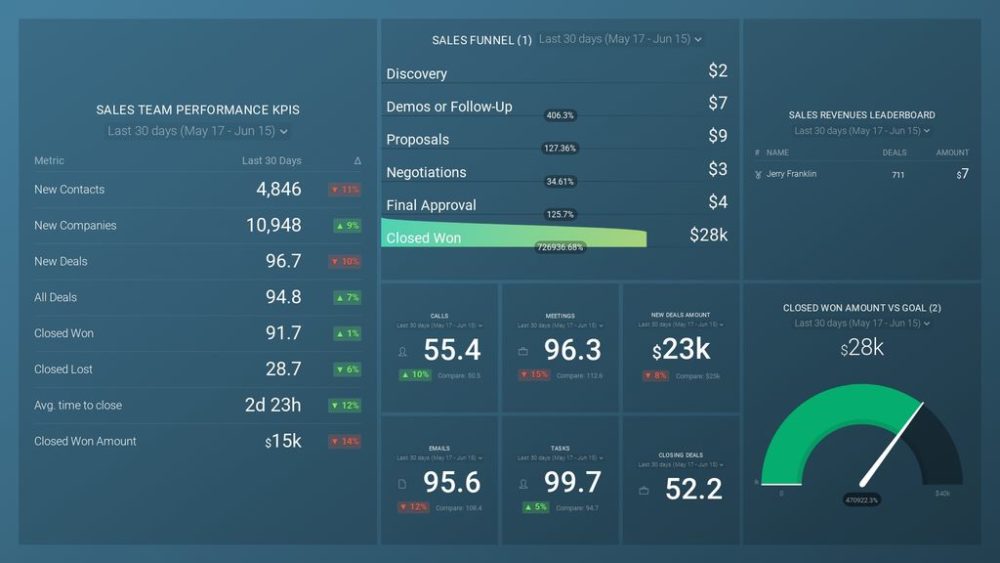
If you’re tracking your sales team’s monthly performance, this sales report template will help you prepare an outstanding report. Check out all the vital productivity KPIs, track your progress towards your goals, and understand well how your current sales pipeline is performing. See all sales performance dashboards we have available here.
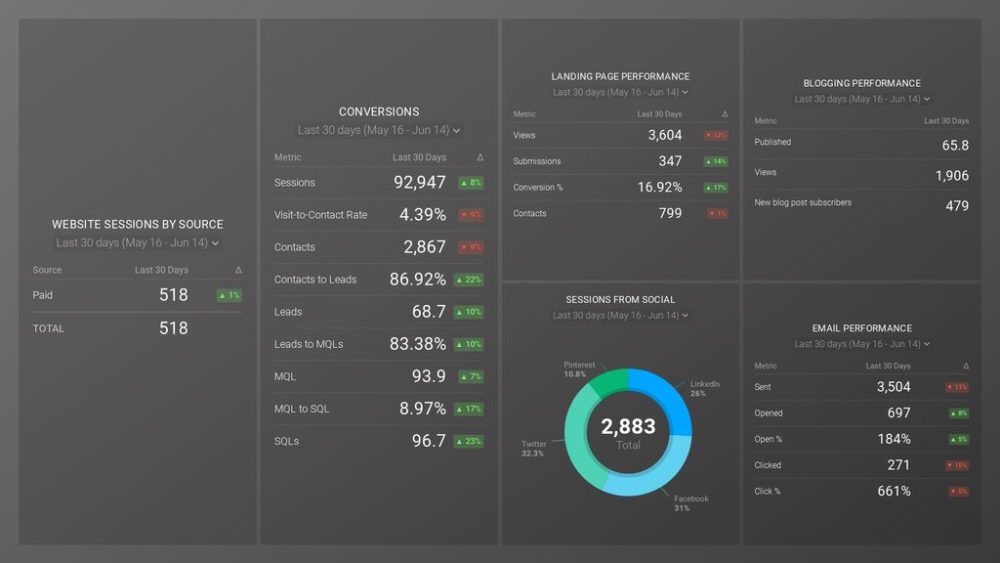
Marketing reports can be easily prepared by using this monthly marketing report template . With HubSpot’s reporting, you can determine where your website traffic is coming from, how your landing pages and specific blog posts are performing, and how successful your email campaigns are. Browse all Databox marketing dashboards or marketing report examples here.
Create a Professional Business Report in No Time with Databox
Does creating a business report still sound like a daunting task? It doesn’t have to be with Databox.
In times when we’re all trying to save our time and energy for things that matter rather than scattering valuable resources on tedious, repetitive tasks, it’s critical to optimize your business process. And we want to help you do just that.
Using a business reporting dashboard enables you to track data from all the different tools you’re using – but in one place. With Databox, you can monitor and report on performance in a single dashboard that is optimized for all your favorite devices and you can create streamlined and beautiful dashboards even if you are not that tech-savvy. (no coding or design skills are required).
Automating business reporting has never been easier. And with Databox, you can do exactly that in just a few clicks. Sign up now and get your first 3 business dashboards for free.
Do you want an All-in-One Analytics Platform?
Hey, we’re Databox. Our mission is to help businesses save time and grow faster. Click here to see our platform in action.
- Databox Benchmarks
- Future Value Calculator
- ROI Calculator
- Return On Ads Calculator
- Percentage Growth Rate Calculator
- Report Automation
- Client Reporting
- What is a KPI?
- Google Sheets KPIs
- Sales Analysis Report
- Shopify Reports
- Data Analysis Report
- Google Sheets Dashboard
- Best Dashboard Examples
- Analysing Data
- Marketing Agency KPIs
- Automate Agency Google Ads Report
- Marketing Research Report
- Social Media Dashboard Examples
- Ecom Dashboard Examples

Does Your Performance Stack Up?
Are you maximizing your business potential? Stop guessing and start comparing with companies like yours.

A Message From Our CEO
At Databox, we’re obsessed with helping companies more easily monitor, analyze, and report their results. Whether it’s the resources we put into building and maintaining integrations with 100+ popular marketing tools, enabling customizability of charts, dashboards, and reports, or building functionality to make analysis, benchmarking, and forecasting easier, we’re constantly trying to find ways to help our customers save time and deliver better results.
Stefana Zarić is a freelance writer & content marketer. Other than writing for SaaS and fintech clients, she educates future writers who want to build a career in marketing. When not working, Stefana loves to read books, play with her kid, travel, and dance.
Get practical strategies that drive consistent growth
12 Tips for Developing a Successful Data Analytics Strategy

What Is Data Reporting and How to Create Data Reports for Your Business
What is kpi reporting kpi report examples, tips, and best practices.
Build your first dashboard in 5 minutes or less
Latest from our blog
- The State of B2B Content Creation: Navigating the Future of In-House Marketing Innovation May 9, 2024
- New in Databox: Analyze the Performance of Any Metric or KPI with Metric Insights April 22, 2024
- Metrics & KPIs
- vs. Tableau
- vs. Looker Studio
- vs. Klipfolio
- vs. Power BI
- vs. Whatagraph
- vs. AgencyAnalytics
- Product & Engineering
- Inside Databox
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Talent Resources
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- API Documentation

How to Write a Formal Business Report (Template and Examples)
Formal business reports are official documents that guide and inform stakeholders. These reports are valuable tools when solving company problems or making decisions.
You should be clear and include all relevant information to make your report useful in decision-making and problem-solving.
Here are five steps for writing a formal business report:
- Define the purpose and intended audience
- Gather and analyze data
- Create an outline
- Draft the business report
- Revise and format your report
Keep reading to get valuable details under every step and learn to segment your report.
But first, let’s delve deep into formal business reports, the different types, and what differentiates them. We’ll also discuss the elements of a business report and cover valuable tips to perfect your writing skills.
Let’s get started!
Understanding formal business reports
Business reports provide an analysis of the current performance of a business and offer recommended actions to improve operations. A formal business report should include detailed data, analysis, conclusions, and recommendations.
What is a formal and informal business report?
A formal business report is a detailed and organized document that provides information about a specific topic, like research findings, market trends, or a financial situation. It usually includes conclusions based on data collected during the research process.
Formal business reports can present complicated topics in an easy-to-understand format, allowing company executives to make informed decisions. A formal report typically includes an introduction, a body of information, and a conclusion. It should consist of accurate data and reliable sources and be written formally with proper grammar and spelling.
An informal business report does not follow traditional, formal reports’ formal structure and layout. Instead, it is written in an easy-to-understand language and typically includes summaries of key points, along with recommendations or suggestions for further action.
Unlike formal reports, informal business reports do not need to be approved by higher management and can be sent directly to the intended recipient. Businesses often use informal reports to quickly provide updates or summaries of projects, data, or other important information. They are also commonly used when sharing ideas, solutions, or findings that don’t necessarily require a formal response from the receiver.
While informal reports may need more depth and detail than formal reports, they can still communicate important information concisely and clearly.
Types of formal business reports
Formal business reports include different types that may be used to present data, analyze performance, or make recommendations. Examples of formal business reports include annual, research, feasibility, and marketing research reports.
Feasibility Reports
A feasibility report is an analytical document that outlines whether an activity or project has the potential to be successful. It includes cost estimates, expected outcomes, and other factors affecting the project’s success.
Business Plans
A business plan is a formal outline of a company’s objectives and strategies for achieving them. It is used to obtain financing, attract investors, and set goals for the company.
Business plans typically include sections on market analysis, organizational structure, competitive analysis, product or service description, financial projections, marketing strategies, and tactics.
Progress Reports
A progress report is a document that details the current status of a project or activity. It outlines the progress made, challenges encountered, and a timeline for when the project should be completed.
Financial Reports
Financial reports provide information about the company’s financial performance over some time. They include income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
A proposal is a document that outlines how an organization, company, or individual intends to complete a project. It usually includes information such as the purpose of the project, expected outcomes, methods, and associated costs. For example, businesses may use proposals to solicit funding from investors or government agencies.
Market Research Reports
A market research report is a document that provides information about customer needs and competitor activities to develop strategies for the organization. They typically include data on consumer preferences, product demand, market trends, and other relevant factors.
Risk Reports
A risk report is a document that details the potential risks associated with a specific activity or investment. It outlines possible losses and considers how they could affect an organization’s operations. Risk reports may also include measures the organization can take to mitigate losses and recommendations for further actions.
Technical Reports
Technical reports are documents that explain the results of a technical project or investigation in detail. They are used to document the findings of a project and provide a record that can be used as reference material.
Technical reports typically include sections on research methods, results, conclusions, recommendations, and implementation plans.
What are the key differences between writing a business report and writing an academic report?
Business reports inform a decision or provide direction in the form of recommendations. They may include factual data and analysis but are often practical and focus on the actionable steps needed to achieve a goal.
Academic reports take a more analytical approach, emphasizing research and thought-provoking discussions that examine different points of view.
Sources used
When writing business reports, only use real-world sources such as government reports. But when writing academic reports, you may cite theoretical works .
Conciseness
When writing business reports, use concise points with stakeholders in mind . As for academic reports, you may use technical terms and lengthy explanations to support a point.
Academic reports are often longer and more detailed than business reports and may also include recommendations but with a focus on developing new strategies or ideas.
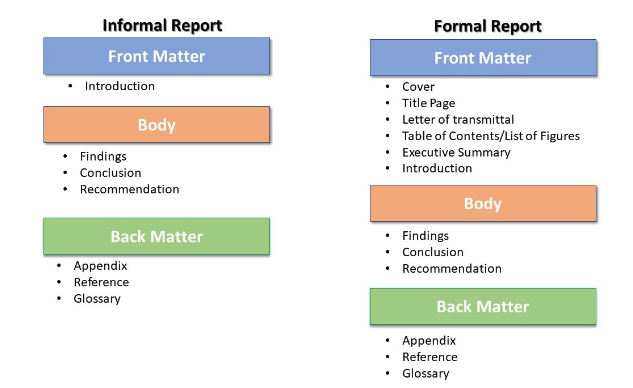
When writing a business report, adhere to the following structure: cover page, table of contents, list of figures, executive summary, introduction, body, conclusion, and recommendations.
But when writing an academic report, follow the structure: introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion.
The purpose of both types of reports is to provide information that is useful and relevant to the target audience. So keep the audience in mind when writing a report; what information do they need to know? How will it help them make decisions or understand a concept better?
Elements of a formal business report
An excellent formal business report organizes information into these sections:
- Table of contents
- List of Figures
- Executive summary
- Introduction
- Recommendation
1. Title page
The title page indicates the company name (and logo), the author’s and readers’ names and positions, and the date.
2. Table of contents
The table of contents lists the sections of a report with their page number and helps jump to a specific title.

3. List of Figures
The list mentions every chart or diagram included in the report and its page number for easy navigation.

4. Executive summary
The executive summary briefly overviews the report’s key points, findings, and conclusions. It helps readers to understand the report’s data without reading the entire document. Therefore, this section should be the last to write since the facts in the report will form the executive summary.

5. Introduction
The introduction outlines the research objectives and methods used to generate data for analysis. It sets the stage for what follows. Unlike the executive summary, it does not mention any conclusion or recommendation.

The body contains an in-depth review of the research results and their implications. It may include an analysis of trends, correlations, pictorial evidence, and other data supporting the report’s conclusions.
7. Conclusion
The conclusion summarizes the data discussed in the body . It is a brief sentence that takes around three to six sentences.
8. Recommendation
The recommendation suggests an action based on the facts presented in the report. It outlines steps or policy changes necessary to solve a problem.
9. Appendix
The appendix contains information that supports your report but would be distracting if you included it in the body. This information may consist of raw data, charts, transcripts, and surveys used for analysis or any additional resources used in the research process. You may also include acronyms used in the report.

10. References/Bibliography
This section consists of all references you used in your report. Citations protect you from plagiarism and give credit to your sources. You can write citations in APA, MLA, and Chicago styles , depending on the style of your formal report.
11. Glossary
The glossary is where you define all technical terms used in the report. Use an asterisk next to words you will describe in the glossary to indicate that the reader should check the glossary for a definition.

How to write a formal business report step-by-step
When writing a formal business report, start by defining the purpose of the report and the intended audience. You then gather data and analyze it before writing the report. Finally, write the report and revise it accordingly.
1. Define the purpose and intended audience
Why are you writing the report? Consider what information you need to include and who will read the report. This will help you structure your document correctly and provide relevant information.
Defining your target audience will help you tailor the language used and choose relevant information to include in the report.
2. Gather and analyze the data
Collect all data relevant to achieving the goal of your report. This should include quantitative and qualitative data, such as customer satisfaction surveys, case studies, performance metrics, or feedback from stakeholders.
Once you have collected all of your data, analyze it and identify any trends or patterns that may be useful in writing the report. You can use various tools and techniques like statistical analysis , gap analysis , or cause-and-effect diagrams .
3. Create an outline
An outline will help you organize your research data, stay on topic, and avoid including unrelated information under a particular title. Besides having a section of each formal business report element above, outline your key points, headings, and subheadings.
Use self-explanatory headings, for example, “ Impact of expanding market share. ”
3. Draft the report
Organize the data you collected during research into the draft report. Start by introducing the topic, providing background information, and the report’s objectives. Then include each of the main points you want to discuss, supported by evidence from the research data.
Have the relevant elements mentioned above and write adequate information under each section. The draft does not have to be perfect; you just need to organize the data roughly.
4. Revise and format your report
After completing your draft, proofread and edit it to remove irrelevant data or add forgotten information. Make sure everything looks good, including the formatting. It also helps to share the business report with someone who can review it and propose necessary changes. Once everything is settled, share the report with your intended audience.
Tips for writing a formal business report
When writing a formal report, use data and evidence to support your argument, add visuals, use consistent fonts and headings, and highlight important information. You should also use clear language that is easy to understand, considering the audience’s background knowledge.
1. Only use credible sources
Credible sources strengthen your report because they are factual, unbiased, and reliable. To identify a credible source, look out for the following markers.
- The source’s author should be an expert in their field.
- The information in the source should be up-to-date.
- The source should include evidence. The author should not have their opinions or speculations.
- A credible source is peer-reviewed by other experts in the field.
2. Use diagrams in formal business reports
Use diagrams like graphs and charts to illustrate relationships between ideas. They are more engaging, easier to understand, and they capture your audience’s attention.
Mind that you don’t clutter your diagrams with too much information. Excess detail will confuse your readers.
Achieve simplicity by:
- Removing backgrounds that cause distractions.
- Removing or lightening gridlines. Gridlines clutter diagrams.
- Reduce the number of colors you use. Only use color on crucial data in the diagram.
- Instead of adding every tiny detail, use symbols and have a key. The key explains what each symbol, figure, or line represents.
3. Use a consistent format
A consistent format makes it easy to follow your report. Keep the format headings and subheadings uniform throughout your report. And make your page margins and font styles consistent.
4. Use bold fonts to highlight
Bold fonts stand out against regular text to draw focus on essential data and make it easier to skim through the report. Use bolding sparingly; otherwise, the effect of highlighting will not work.
Formal business report template
A formal business report template will save both time and energy by providing a framework that simplifies the process of assembling data into a comprehensive document.
Check out this collection of editable business report templates to find one that works for you.
Final Thoughts: Formal Business Report
Formal business reports are essential tools for any business. An excellent report drives company decisions and recommends solutions to company problems. Writing one may be challenging, but this guide gives you a clear pathway to ease the process.
Remember to use visual aids and credible sources to fortify your report. Organize data into the above sections, and use the discussed tips to write your business report like a pro!
You may also like:
- How to Write a Resignation Letter for a Better Opportunity [Samples + Template Included]
- Bullet Form Examples: How to Use Bullet Points Effectively
- How to Write a Subject Line for Job Applications [+Samples]
Get started With 2000 Free Monthly Credit
Want to level up your content game? Get started today with 2000 monthly free credit.
Advanced AI writing tool trained to write better content faster.
- Sentence Rewriter Tool
- Instagram hashtag generator
- LinkedIn headline generator
- Paraphrasing tool
- Acronym generator
- Title generator
- Business name generator
- Slogan generator
- Blog ideas generator
- Job Description Generator
- Brand Style Guide
- Affiliate Program
- Social Media Marketing
- Email Marketing
- Random Generator
- Name Generator
- Summary Generator
- Character Counter
- Word Counter
- Word Finder
- AI Content Detector
Copyright © 2024 WriterBuddy. All rights reserved.
What Are Business Reports & Why They Are Important: Examples & Templates
Table of Contents
1) What Is A Business Report?
2) Types Of Business Reports
3) Business Reports Examples & Samples
4) Why Do You Need Business Reports?
5) How To Setup A Business Report?
6) Challenges Of Business Reports
In your daily operations, you likely notice your processes and ‘activities’ constantly changing – sales trends and volume, marketing performance metrics, warehouse operational shifts, or inventory management changes, among many others.
All these little alterations in your organizational activities are impacting the global well-being of your company, your warehouse, your restaurant, or even your healthcare facility. Whether you manage a big or small company, business reports must be incorporated to establish goals, track operations, and strategy to get an in-depth view of the overall company state.
But with so much information being collected daily from every department, static business reports created manually will not give your company the fresh insights it needs to stay competitive. Businesses that want to succeed in today’s crowded market need to leverage the power of their insights in an accessible and efficient way. This is where modern business reports created with interactive data visualizations come to the rescue.
Traditional means of reporting are tedious and time-consuming. Due to how the human brain processes information, presenting insights in charts or graphs to visualize significant amounts of complex information is more accessible and intuitive. Thanks to modern, user-friendly online data analysis tools armed with powerful visualizations, companies can benefit from interactive reports that are accessible and understandable for everyone without needing prior technical skills.
Here, we take the time to define a business report, explore visual report examples, and look at how to create them for various needs, goals, and objectives. In the process, we will use online data visualization software to interact with and drill deeper into bits and pieces of relevant data. Let's get started.
What Is A Business Report?
A business report is a tool that helps collect and analyze historical and current data from a company’s operations, production, and more. Through various types of business reports, organizations make critical decisions to ensure growth and operational efficiency.
To understand the best uses for these reports, it’s essential to properly define them. According to authors Lesikar and Pettit, “A corporate-style report is an orderly, objective communication of factual information that serves some organizational purpose”. It organizes information for a specific business purpose. While some reports will go into a more detailed approach to analyzing the functionality and strategies of a department, other examples of business reports will be more concentrated on the bigger picture of organizational management, for example, investor relations. That’s where the magic of these kinds of reports truly shines: no matter for which company goal you need, their usage can be various and, at the same time, practical.
Traditional business reports are often static and text reach (bullet points, headings, subheadings, etc.). Classically formatted in sections such as the summary, table of contents, introduction, body, and conclusion, this report format is no longer the most efficient when it comes to extracting the needed insights to succeed in this fast-paced world. On one hand, by the time these reports have been finished, the insights included within them might not be useful anymore. On the other hand, the fact that it is mostly text and numbers makes them hard to understand, making the analysis strategy segregated and inefficient.
The visual nature of modern business dashboards leaves all the aforementioned issues in the past. Thanks to interactive data visualizations and modern business intelligence solutions , the analysis sequence can be done fast and efficiently while empowering non-technical users to rely on digital insights for their decision-making process.
Your Chance: Want to test professional business reporting software? Explore our 14-day free trial. Benefit from great business reports today!
Types Of Business Reports?
Before creating your business outcome reports, it is important to consider your core goals and objectives. This way, you can pick the correct type of report for each situation. Here, we present you with five common types of visual reports that you can use for different analytical purposes.
1. Analytical reports
Analytical reports are reporting tools that use qualitative and quantitative data to analyze the performance of a business strategy or as support when a company needs to make important decisions. A modern analytical dashboard created with top reporting software can include statistics, historical data, as well as forecasts, and real-time information. Let’s look into it with a sales example.
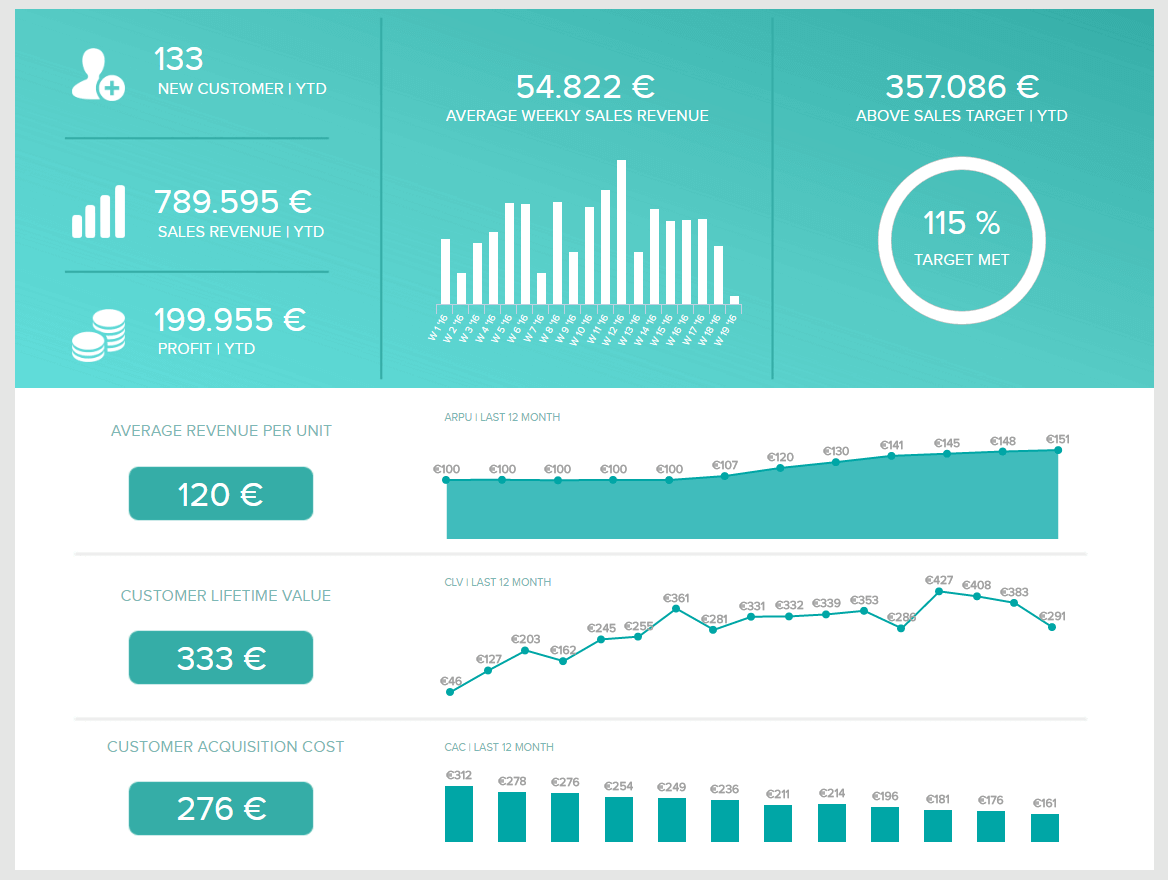
**click to enlarge**
This visually appealing business analysis report contains relevant sales KPIs to measure performance, such as the average revenue per unit, the customer lifetime value, acquisition costs, and some sales targets to be met. The value of this analytical report lies in the fact that you get a lot of relevant metrics in a single dashboard. The data can be filtered and explored on different time frames such as daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly, depending on the discussion that it needs to support.
With this kind of sample in hand, managers can quickly understand if they are meeting their targets, find improvement opportunities, get a bigger picture of their sales, and find efficient ways to proceed with new strategies.
2. Research reports
Next in our types of business reports that we will discuss is a research report. Companies often use these kinds of reports to test the viability of a new product, study a new geographical area to sell, or understand their customer’s perception of their brand image. To generate this type of report, managers often contact market research agencies to gather all the relevant information related to the studied topic. This brand analysis dashboard is a great example.
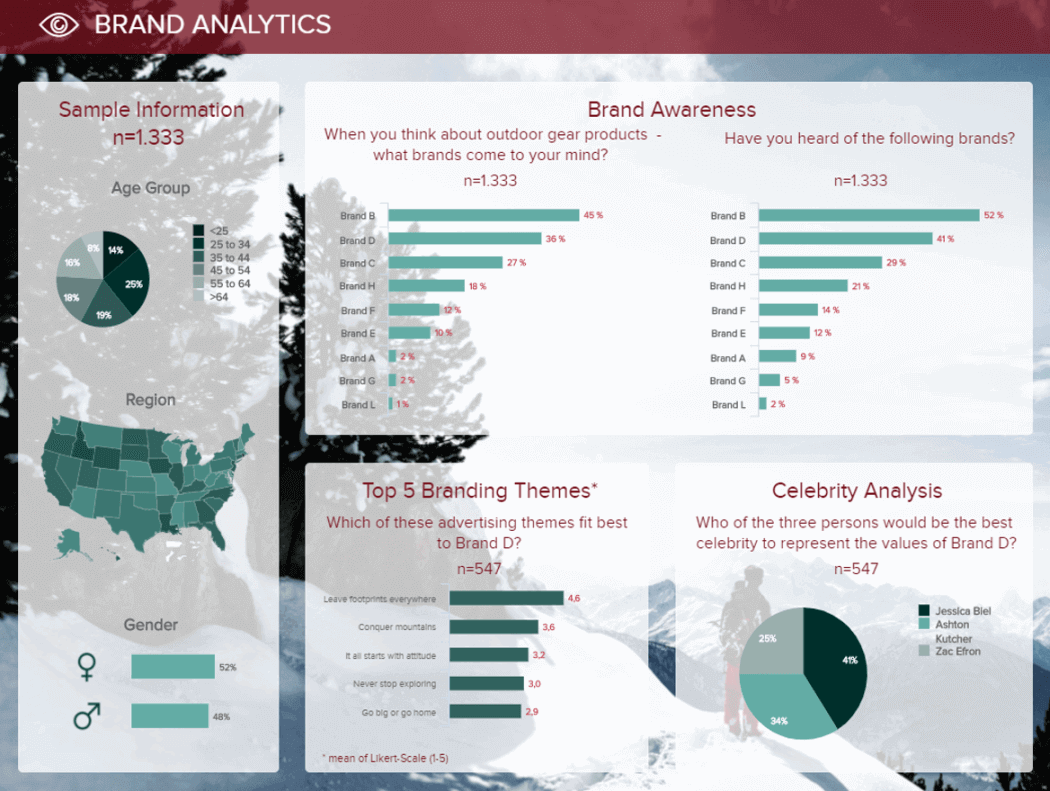
The image above is a business report template of a brand analysis. Here, we can see the results of a survey that was conducted to understand the brand’s public perception on different topics. The value of this market research dashboard lies in its interactivity. Often, research reports are depicted in long and static PowerPoint presentations. With a modern market research dashboard like this one, all the info can be filtered upon need, and the whole presentation of results can be done on one screen. For example, if you want to know the brand awareness of a particular region or age group, you just have to click on the graphs, and the entire dashboard will be filtered based on this information. Like this, the analysis sequence is fast, interactive, and efficient.
3. Industry reports
Following on from the research topic, our next type is an industry report. Benchmarks and targets are excellent ways to measure a company’s performance and success. But, these targets need to be based on realistic values, especially considering how crowded and competitive today’s markets are. For this purpose, companies perform industry reports. By getting a clear picture of the average industry numbers, such as the competitive landscape, industry size, economic indicators, and trends, they can plan smart strategies and create realistic targets for performance.
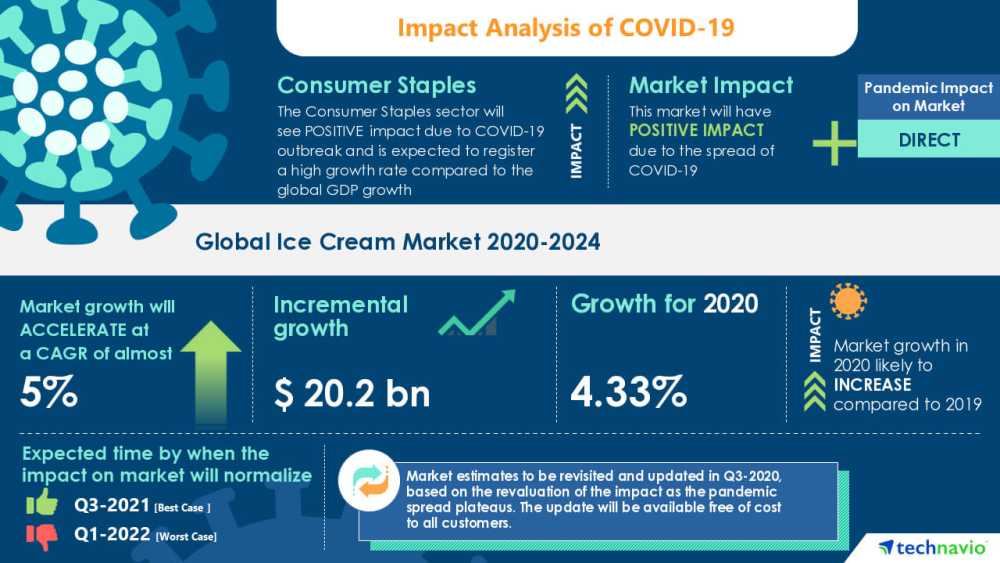
Let's take this industry report by Technavio about the Global Ice Cream Market as an example. Here, we can see relevant numbers concerning the ice cream market, how COVID-19 impacted it, and what is expected to happen between the years 2020-2024. For example, the business report sample shows that the pandemic has positively impacted the ice cream market and that it grew 4.33% during 2020. The report also shows that there is increasing popularity of plant-based ice cream and that this trend is driving market growth. This is invaluable information for an ice cream company as they can invest in new products with almost certain success.
4. Progress reports
Next, we have progress reports. Unlike our other examples, this type of business report is not necessarily based on deep research or advanced analytics but rather on delivering a clear picture of the performance of a particular area or business goal. Their visual nature makes them the perfect tool to support meetings or business discussions as they provide a glance into the status of different metrics. A common use of progress reports is with KPI scorecards . Let’s look at an example.
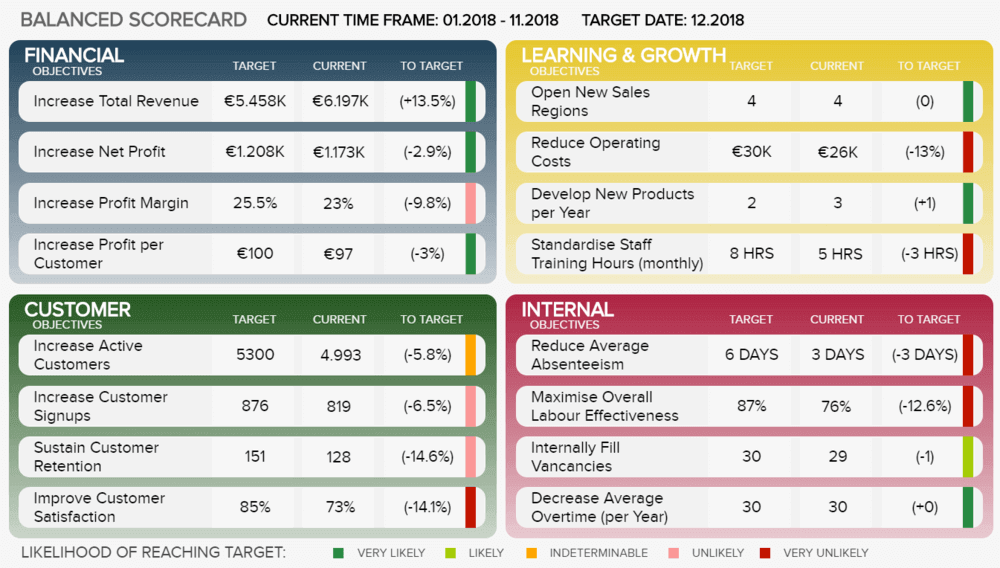
The image above is a business report example of a balanced scorecard. The goal here is to quickly understand the development of metrics related to 4 key business areas: financial, customers, learning and growth, and internal objectives. Each of these metrics is displayed in a current value and compared to a set target. Paired with this, the template has five colors for the performance status. This allows anyone who uses this report to quickly understand just by looking at the colors if the target is being met.
5. By business function
Getting a bigger picture of a company’s performance is a great benefit of the best business reports. But, apart from helping the company as a whole, the real value of these reports lies in the fact that they empower departments to leverage the power of data analysis for their decision-making process. Instead of the sales department, human resources, or logistics, your entire organization will be data-driven. Let’s look at it with a business report example by function on marketing.
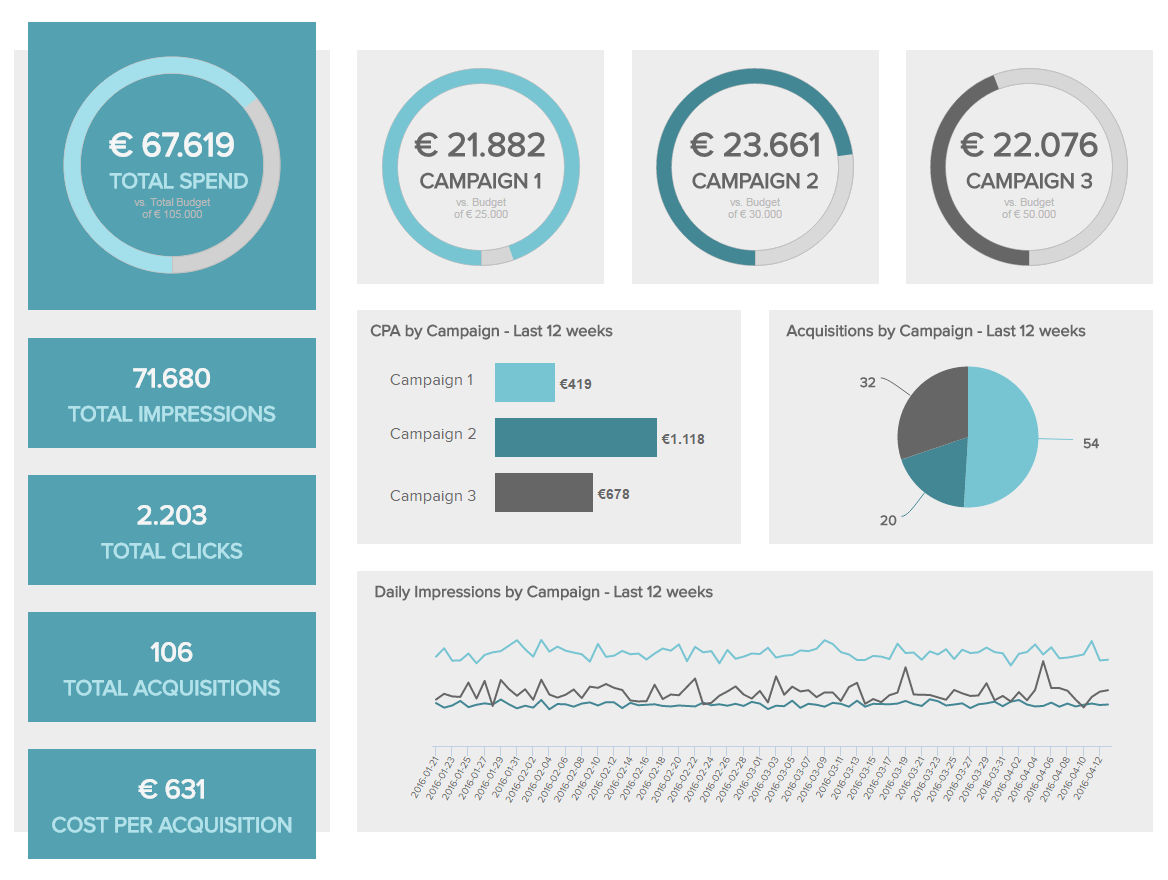
Created with modern marketing dashboard software , this example entirely focuses on the development of marketing campaigns. With metrics such as the total number of impressions, clicks, acquisitions, and cost per acquisition being depicted on intuitive gauge charts, you quickly get a clear understanding of the performance of your campaigns. Through this, you can spot any inefficiencies before they become bigger issues and find improvement opportunities to ensure your marketing efforts are paying off. If you want to dig even deeper, this interactive business report can be filtered for specific campaigns so you only see related insights, making this dashboard the perfect tool to support team meetings.
Business Report Examples And Templates
We’ve answered the question, ‘What is a business report?’ and now, it’s time to look at some real-world examples.
The examples of business reports that we included in this article can be utilized in many different industries; the data can be customized based on the factual information of the specific department, organization, company, or enterprise. Interdepartmental communication can then effectively utilize findings, and the content can be shared with key stakeholders.
Now that we know what they are, let's go over some concrete, real-world instances of visuals you will need to include in your reports.
1. Visual financial business report example
This first example focuses on one of the most vital and data-driven departments of any company: finance. It gathers the most essential financial KPIs a manager needs to have at his fingertips to make an informed decision: gross profit margin, operational expenses ratio (OPEX), both earning before interests (EBIT) and net profit margins, and the income statement. Next to these are the revenue evolution over a year compared to its target predefined, the annual evolution of operational expenses for various internal departments as well as the evolution of the EBIT compared to its target.
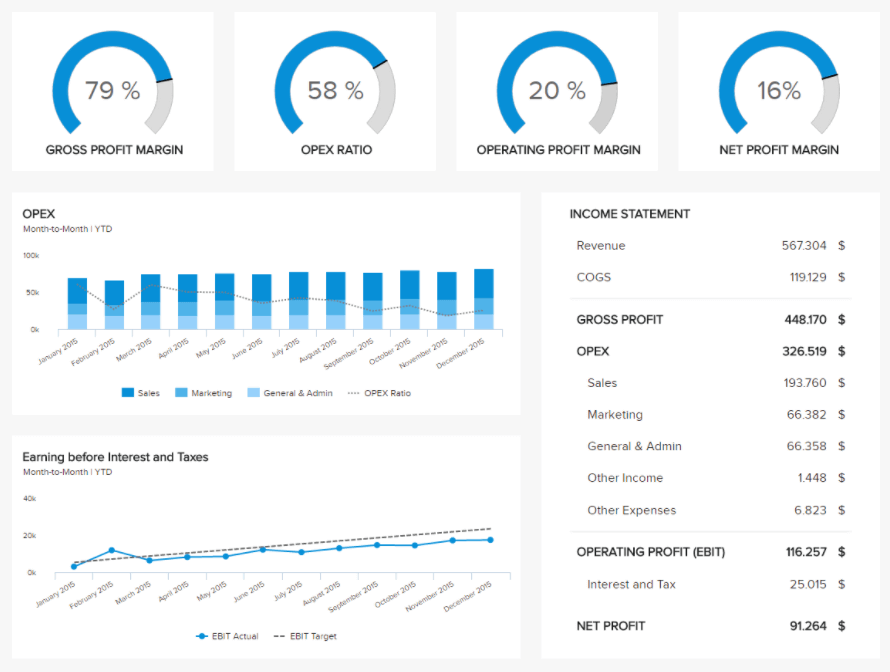
The different sets of visual representations of data can clearly point out particular trends or actions that need to be taken to stay on the financial track of a company. All your financial analysis can be integrated into a single visual. When the presentation becomes interactive, clicks will provide even deeper insights into your financial KPIs and the desired outcomes to make a company healthy in its financial operations. The importance of this finance dashboard lies in the fact that every finance manager can easily track and measure the whole financial overview of a specific company while gaining insights into the most valuable KPIs and metrics. Empowering a steadfast and operation-sensitive plan is among the most important goals a company can have, and finance is right in the middle of this process.
Thanks to all this information displayed on a single dashboard, your report is greatly enhanced and backed with accurate information for you to make sound decisions. It becomes easier to implement a solid and operation-sensitive management plan.
2. Visual investor's business report layout
As mentioned earlier, holding an account of your activity, performance, and organization’s assets is important for people outside of the company to understand how it works. When these people are investors, it is all the more critical to have a clean and up-to-date report for them to know how successful is the company they invest in and for you to increase your chances of having more funds. This example provides just that: an exact overview of the most important insights and specific values in a particular time frame.
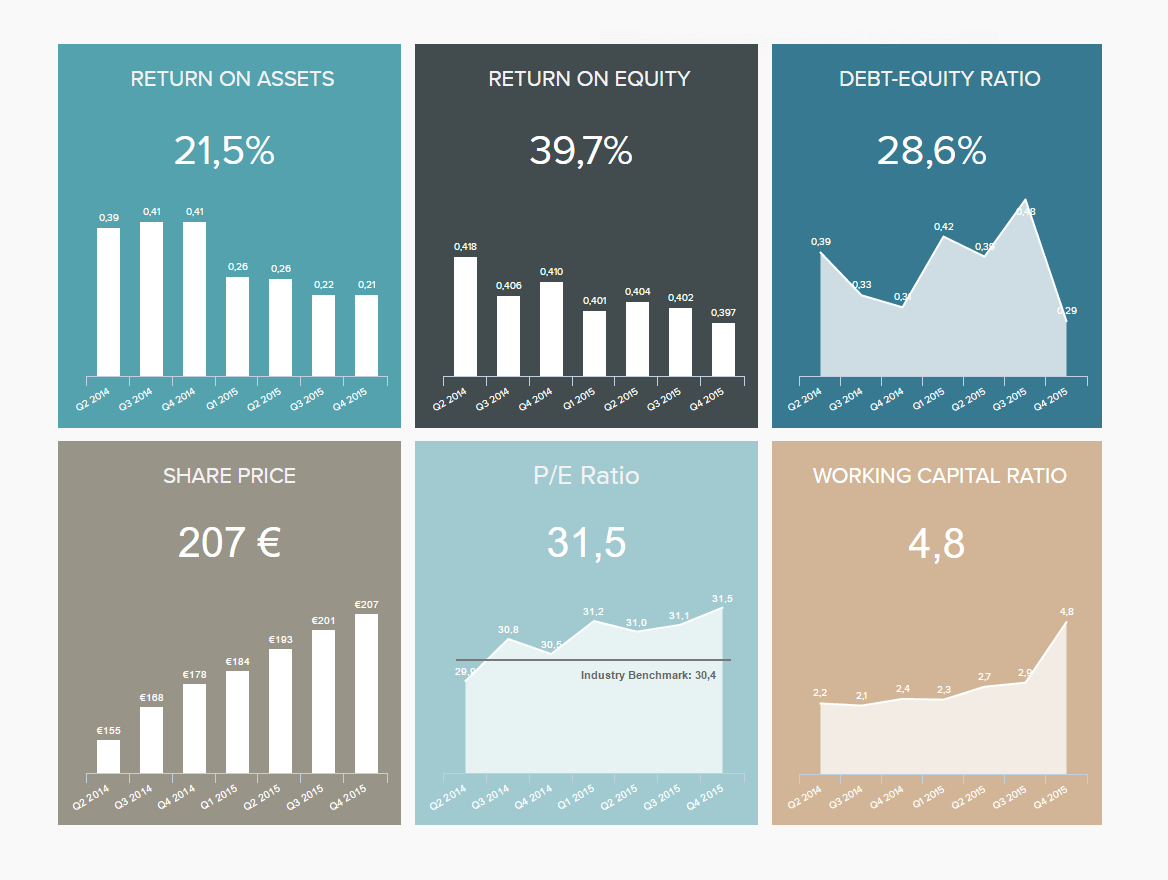
Calculating and communicating KPIs about the overall company situation is what this investors’ relationship dashboard tries to focus on. You learn about the return on equity and return on asset, the debt-equity ratio, and the working capital ratio, but also see the evolution of a share price over time. Each of these metrics is crucial for a potential shareholder, and if they are not monitored regularly and kept under control, it is easy to lose investors’ interest. Tracking them and visualizing them through a modern dashboard is a competitive advantage for your investors’ reports. You can even see on this visual a clear set of data, so you don’t have to dig through numerous amounts of spreadsheets, but clearly see the specific development over time, the percentage gained or lost, ratios, and returns on investments. Not to be limited just to these data, you can always customize and make sample business reports for your specific needs.
3. Visual management report example
The management KPIs presented below focus on the revenue and customer overview seen through a specified quarter of a year. With just a click, you can easily change your specific date range and make an overview of different months or years.
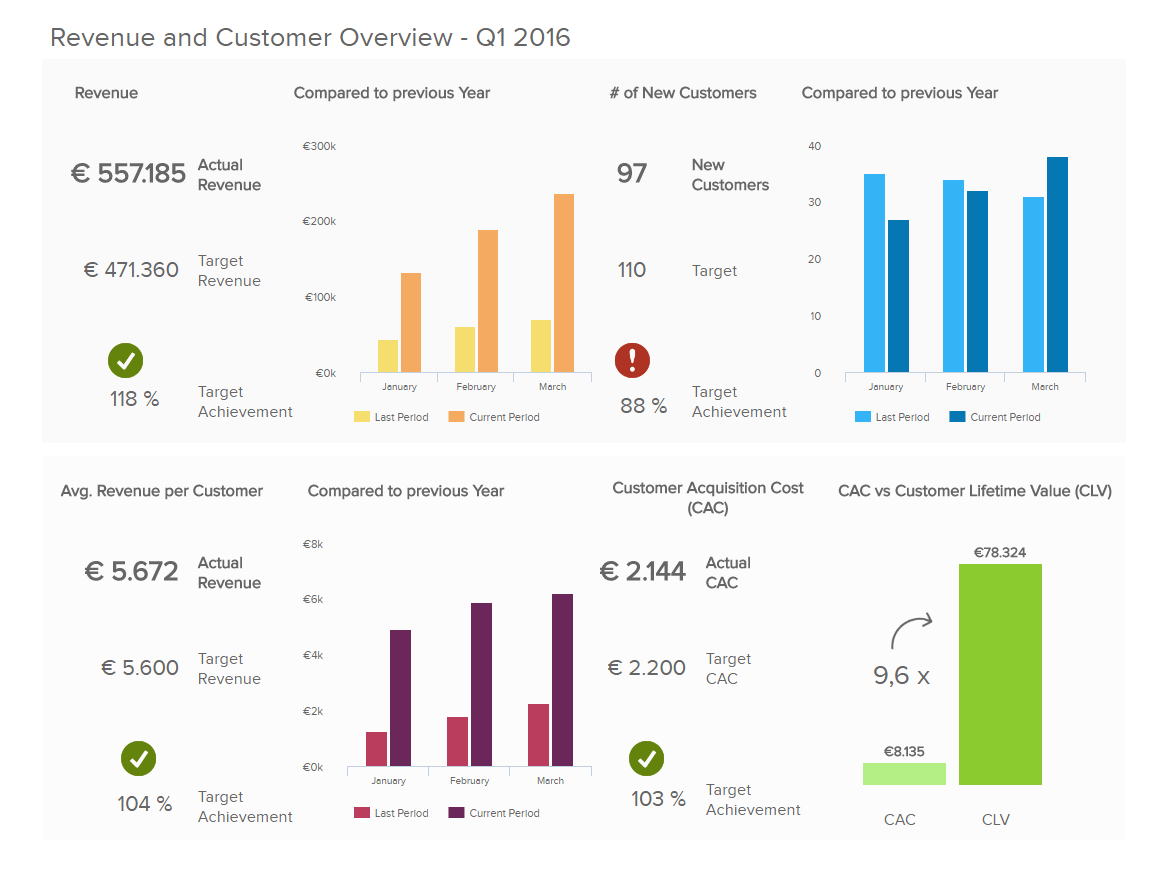
When analyzing insights on a more specific level, you can easily spot if the revenue is approaching your target value, compare it to the previous year, and see how much of the target you still need to work on. The average number of your revenue per customer compared to your targets can also identify on a more specific level how much you need to adjust your strategy based on your customers’ value. If you see your values have exceeded your goals, you can concentrate on KPIs that haven’t yet reached your target achievement. In this specific example, we have gained insights into how to present your management data, compare them, and evaluate your findings to make better decisions.
This clear overview of data can set apart the success of your management strategy since it is impossible to omit vital information. By gathering all your findings into a single CEO dashboard , the information presented is clear and specific to the management’s needs. The best part of this example report is seen through its interactivity: the more you click, the more data you can present, and the more specific conclusions you can look for.
These report templates that we have analyzed and presented in this article can be a roadmap to effectively create your own report or customize your data to tailor your needs and findings.
4. SaaS management dashboard
The next in our rundown of dynamic business report examples comes from our specialized SaaS metrics dashboard .
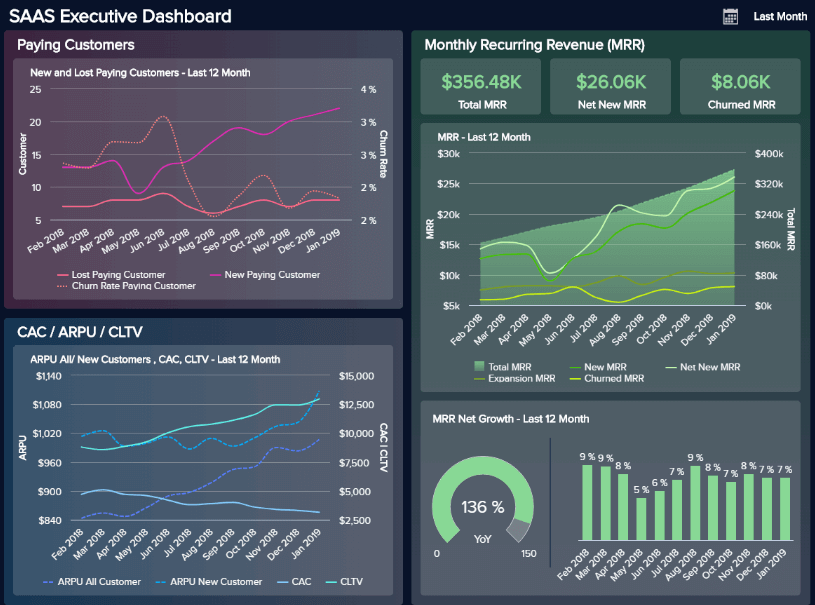
A SaaS company report example that packs a real informational punch, this particular report format offers a panoramic snapshot of the insights and information every ambitious software-as-a-service business needs to succeed.
With visual KPIs that include customer acquisition costs, customer lifetime value, MMR, and APRU, here, you will find everything you need to streamline your company’s initiatives at a glance. This is an essential tool for both short- and long-term evolution.
5. Sales KPI dashboard
Niche or sector aside, this most powerful of online business reports samples will empower your sales team to improve productivity while increasing revenue on a sustainable basis.
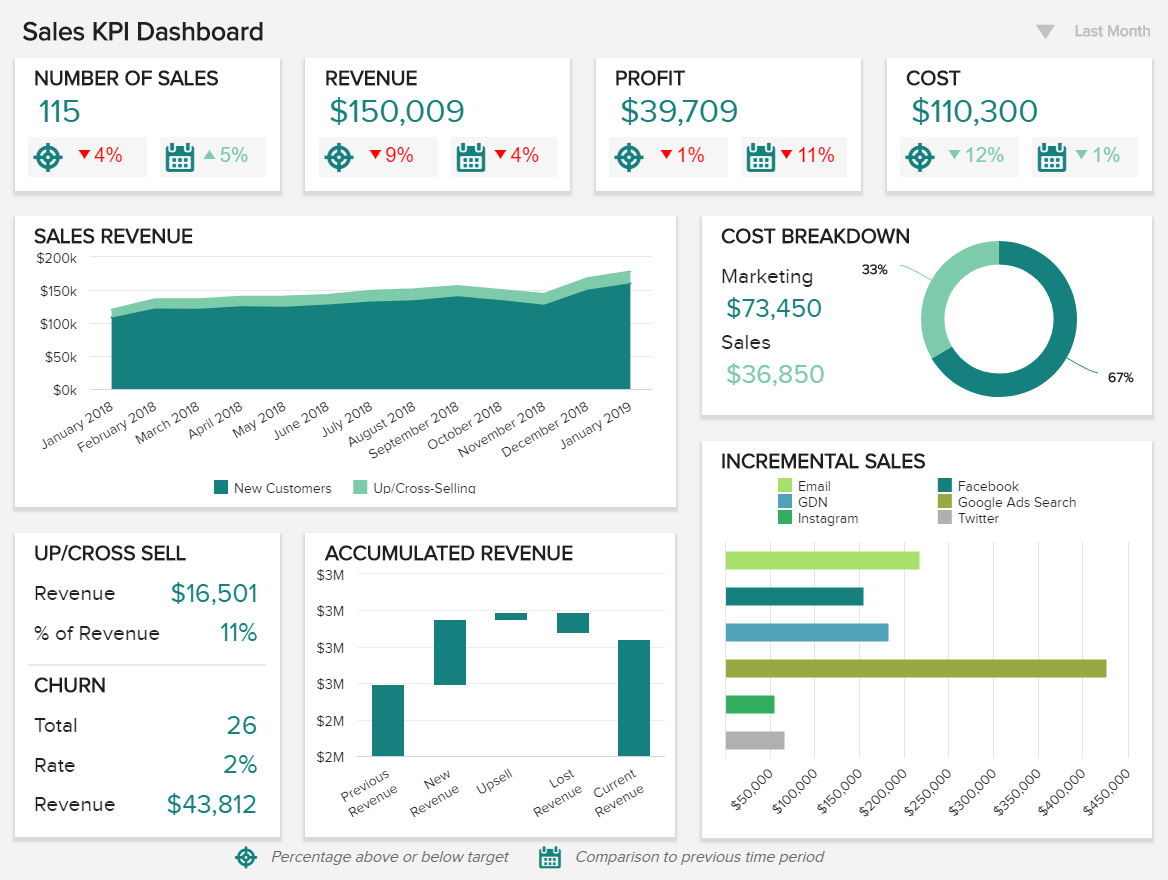
A powerful daily business activity report as well as a tool for long-term growth, our sales dashboard boasts a cohesive mix of visualizations built to boost your business's bottom line.
With centralized access to sales graphs and charts based on churn rates, revenue per sales rep, upselling & cross-selling, and more, this is a company report format that will help you push yourself ahead of the pack (and stay there). It’s a must-have tool for any modern sales team.
6. Retail store dashboard company report example
Retail is another sector that pays to utilize your data to its full advantage. Whatever branch of retail you work in, knowing how to generate a report is crucial, as is knowing which types of reports to work with.
Our interactive retail dashboard is one of our finest visual report examples, as it offers a digestible window of insight into the retail-centric unit as well as transaction-based information that can help you reduce costs while boosting your sales figures over time.
Ideal for target setting and benchmarking as well as strategy formulation, this is an unrivaled tool for any retailer navigating their activities in our fast-paced digital age. If you’re a retailer looking for steady, positive growth, squeezing every last drop of value from your retail metrics is essential—and this dashboard will get you there.
7. Customer service team dashboard
As a key aspect of any successful organizational strategy, optimizing your customer service communications across channels is essential. That’s where our customer service analytics report comes into play.
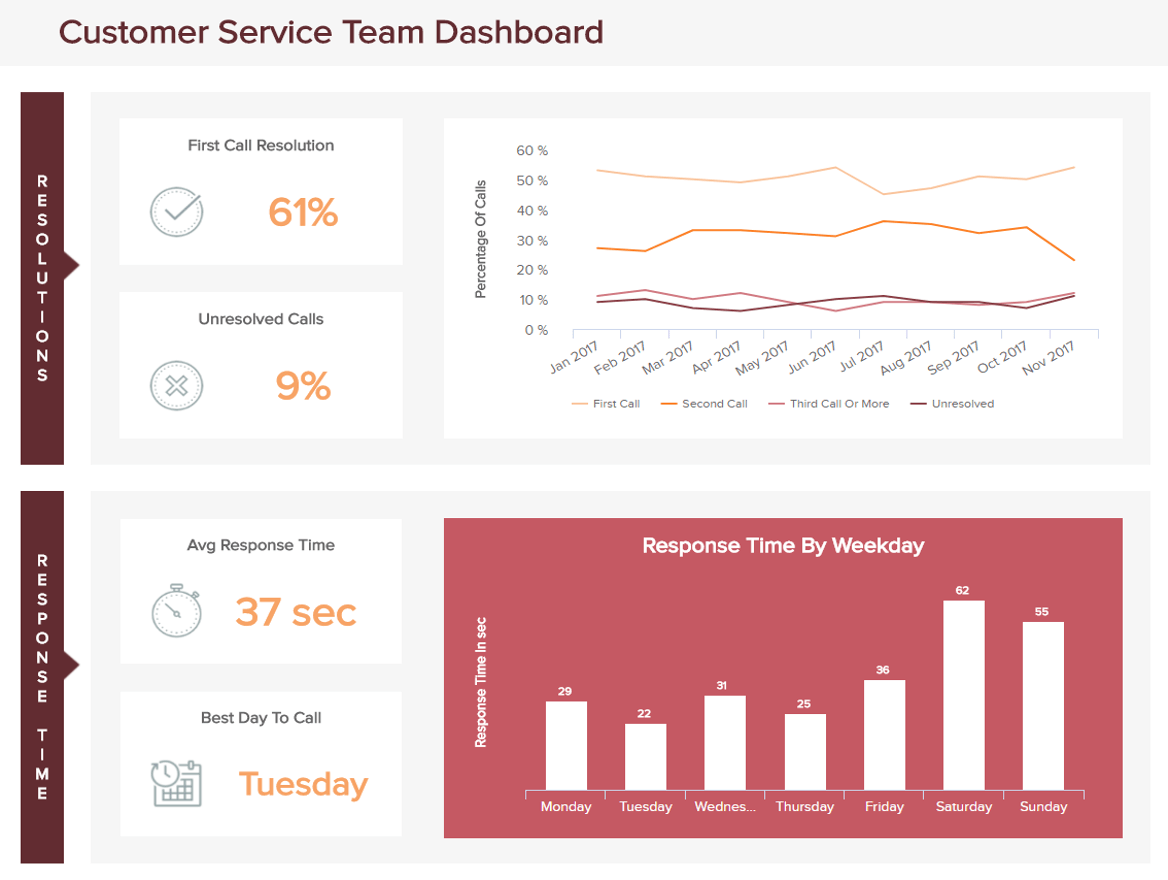
Making your customer service efforts more efficient, effective, and responsive will not only drastically improve your consumer loyalty rates but also set you apart from your competitors.
One of the best ways to achieve a mean, lean, well-oiled consumer-facing machine is by giving your customer service representatives the tools to perform to the best of their abilities at all times. Armed with a balanced mix of KPIs to track and enhance service performance, this most powerful of business report samples will help you drive down response times while improving your first call resolution rates. It’s a combination that will result in ongoing growth and success.
8. Employee performance dashboard
In addition to your customers, your employees are the beating heart of your organization. Our employee dashboard will give you the power to track the ongoing value and productivity of your internal talent.
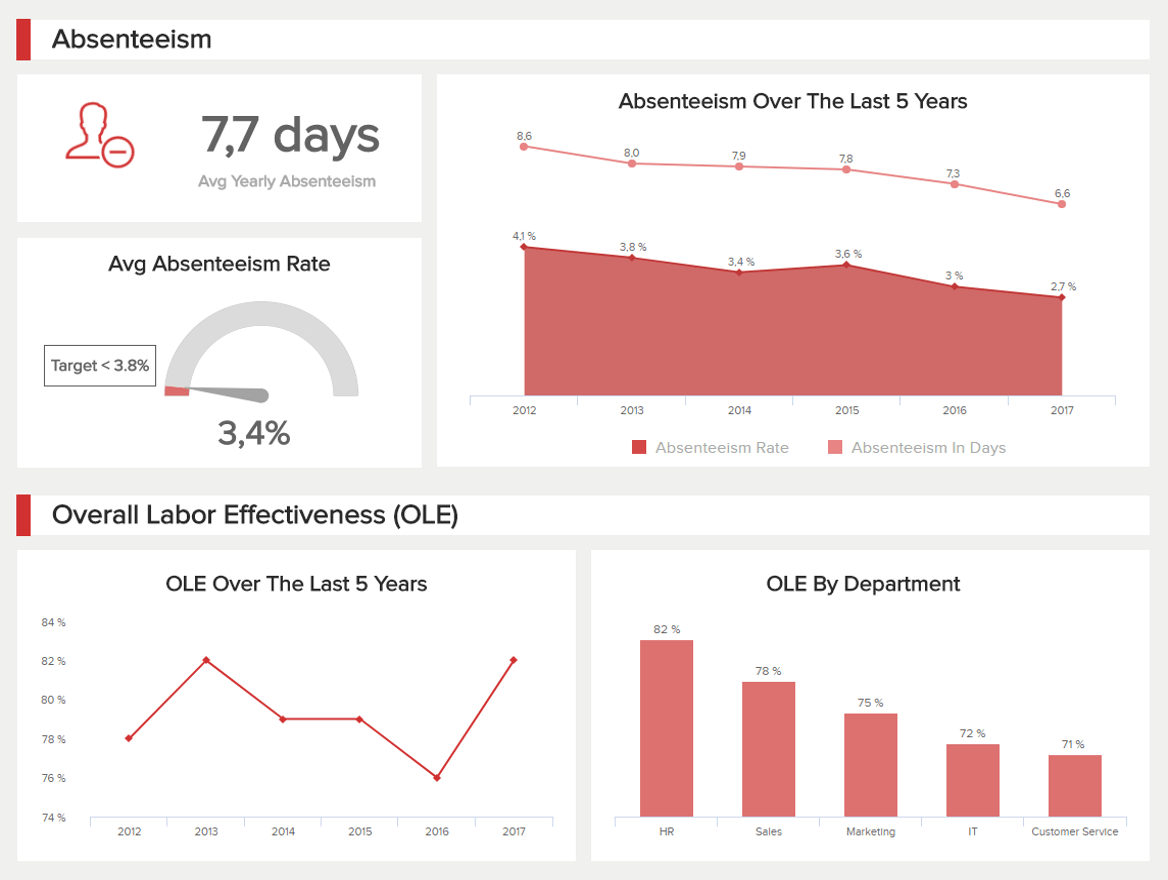
An ideal formal business report example for any modern HR department, this telling dashboard will give you deep insight into how your employees perform and behave over specific timeframes.
Here, you can examine trends in absenteeism rates, track overtime hours by age group, monitor your training costs, and explore peaks and troughs in productivity across the entire workforce. This melting pot of at-a-glance information will empower you to provide training exactly where it’s needed and get to the heart of any issue that’s affecting productivity or engagement levels.
Working with this business report format example consistently will ultimately ensure you get the very best return on investment (ROI) from your internal talent.
9. Marketing KPI dashboard
Without a solid multichannel marketing strategy, it’s unlikely that you’ll ever see a consistently healthy ROI from your promotional efforts. Shooting in the dark regarding marketing will also see you fall behind the competition. Enter our marketing dashboard .
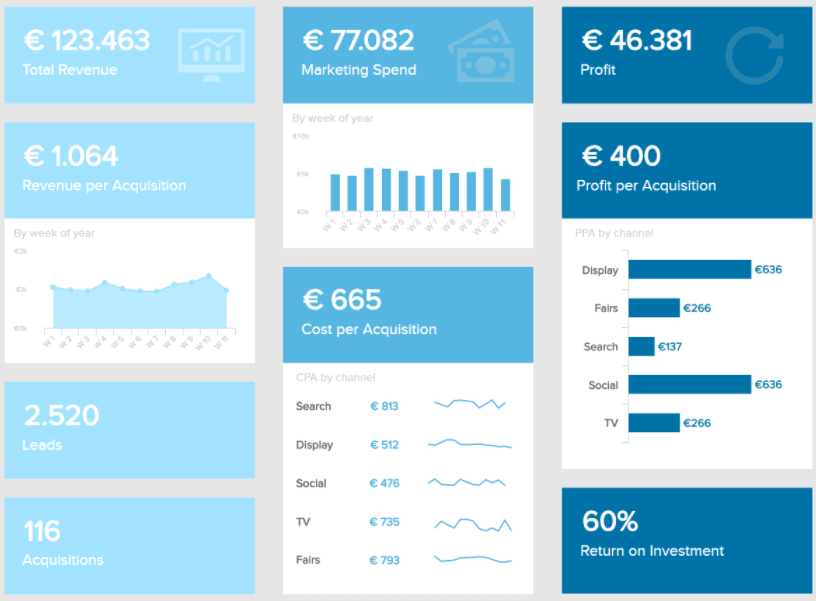
This business report format template brimming with insight, lets you set accurate performance benchmarks while uncovering a wealth of insight from one intuitive dashboard.
To optimize your promotional campaigns and activities, talking to specific audience segments and using the right touchpoints at precisely the right time is essential. Without a targeted approach, all you’re doing is throwing your time and money away.
This effective company report example offers a balanced overview of your campaigns’ performance by offering the tools to dig deep into vital metrics like cost per acquisition (CPA), customer lifetime value (CLTV), and ROI.
This perfect storm of metrics will show you where your communications or campaigns are failing to drive engagement and where they’re yielding positive results. Armed with this critical information, you can optimize all of your efforts to make the biggest possible impact across channels. An essential report design for any modern organization looking to scale swiftly and consistently.
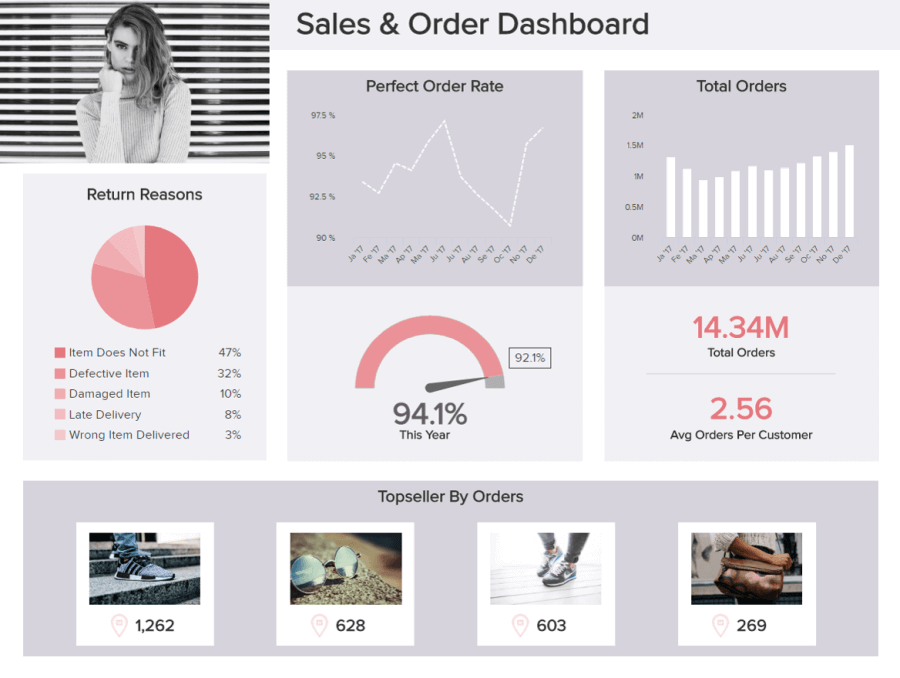
10. Warehouse KPI dashboard
Being a warehouse manager or decision-maker is a high-pressure job where every decision counts. To keep your fulfillment activities and initiatives fluid, functional, and primed for organizational growth, sweating your data correctly is a must.
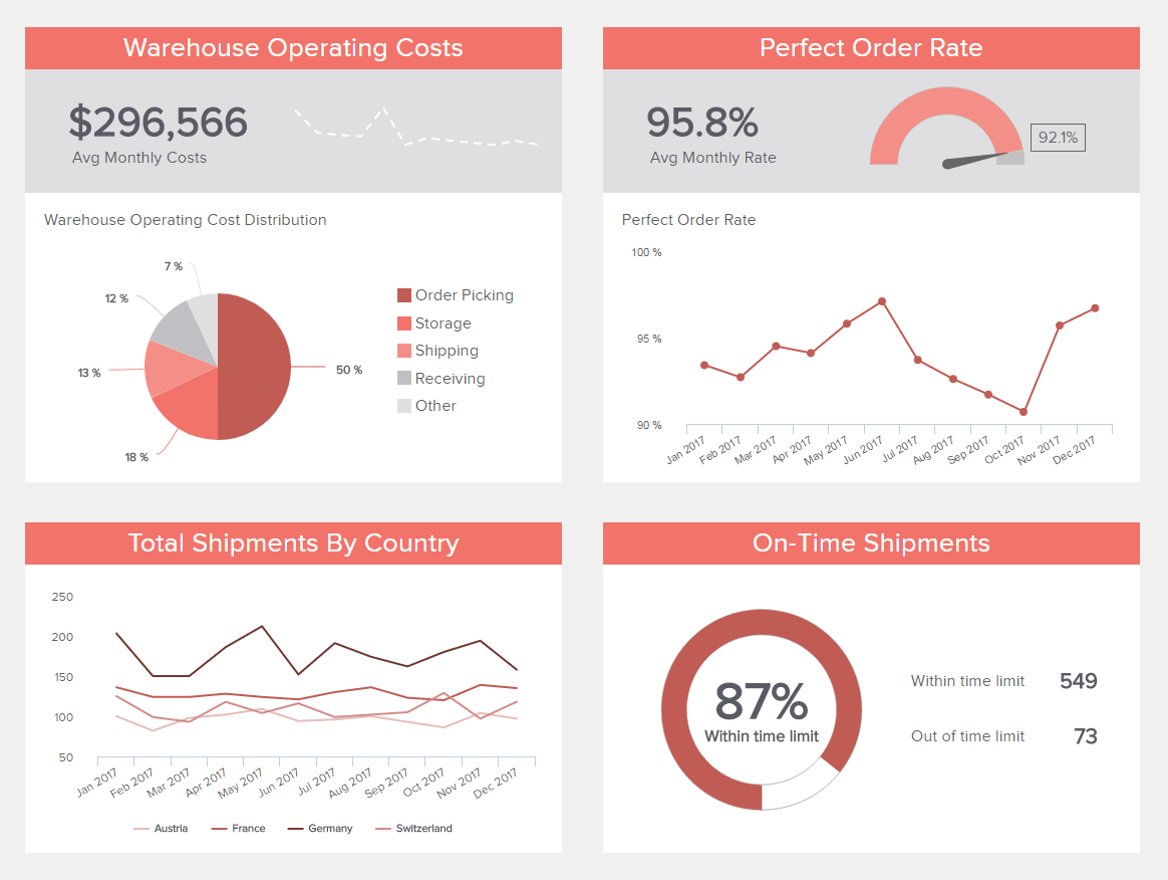
Our warehouse KPI dashboard is a business report sample that aids both real-time decision-making and longer-term strategic planning.
With a powerful selection of logistics-based KPIs, this highly visual business report structure features metrics based on on-time shipment rates, a breakdown of warehouse costs, the number of shipments made over a specified timeframe, and a perfect order rate.
By making this kind of business reports formats a core part of your daily operations, you can eliminate unnecessary costs or activities while boosting overall productivity and significantly improving the success, as well as accuracy, of your warehouse operations. It is an invaluable tool that will help consistently deliver on your fulfillment promises, improving your brand reputation in the process.
11. Cybersecurity dashboard
In our hyper-connected digital age, failing to invest in adequate cybersecurity solutions is the same as leaving your front door wide open when you’re on holiday.
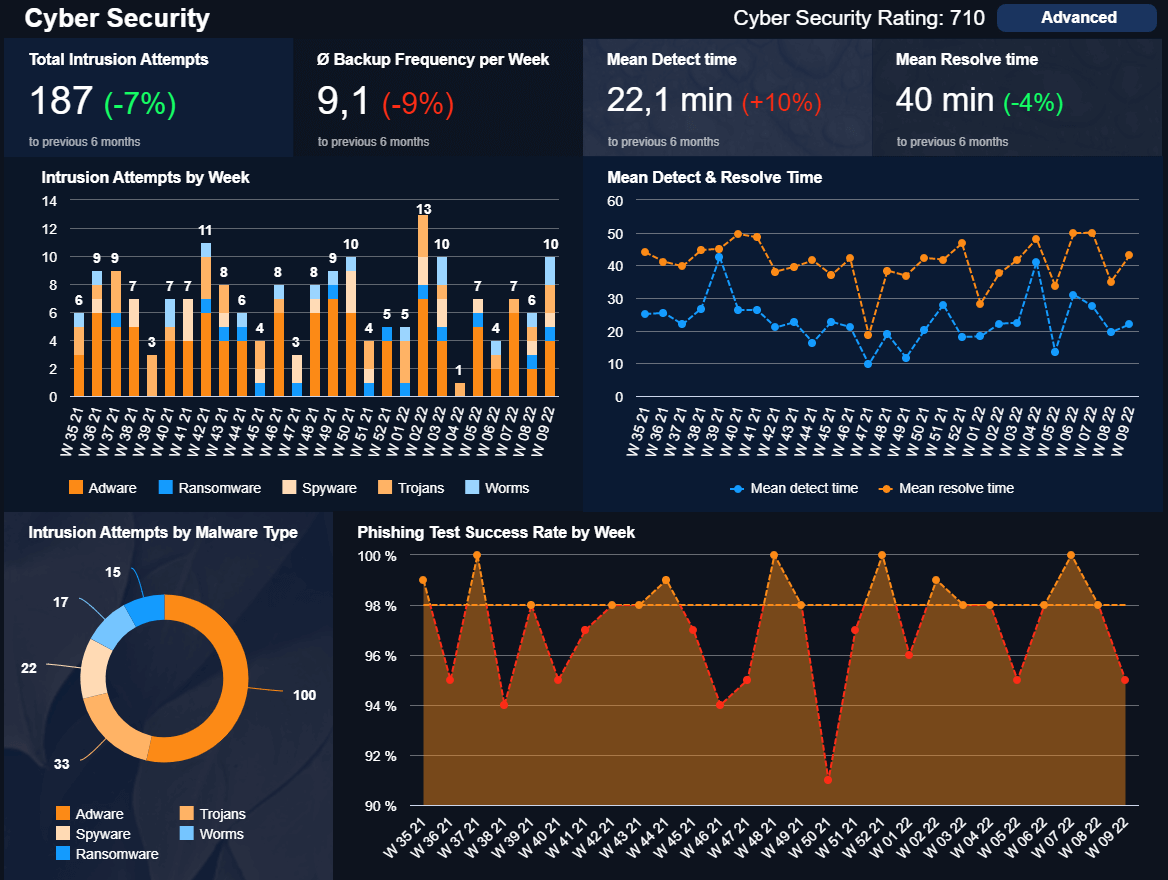
To avoid the devastating impact of organizational cyber attacks or informational breaches, our cyber security IT dashboard will ensure your company is fortified from every angle. This most vital of business report examples will help you fend off any prospective acts of cybercrime while monitoring for any attacks or abnormalities in real-time.
Here, you can keep on top of your cybersecurity rating, track your phishing test success rates, understand how long it takes you to identify an attack (and improve your responsivity), look at how often you backup your company's sensitive information, and discover the most common intrusion rates related to your company from a cohesive space. It’s an essential analysis tool designed to keep your company safe, secure, and happy.
12. CEO dashboard
The CEO is the highest leadership position in an organization. As such, they need to get a complete overview of the entire operations and performance to ensure everything is running smoothly and on track to meet expected goals. Our next example is a scorecard report tracking relevant metrics related to finances, marketing, customer service, and human resources.
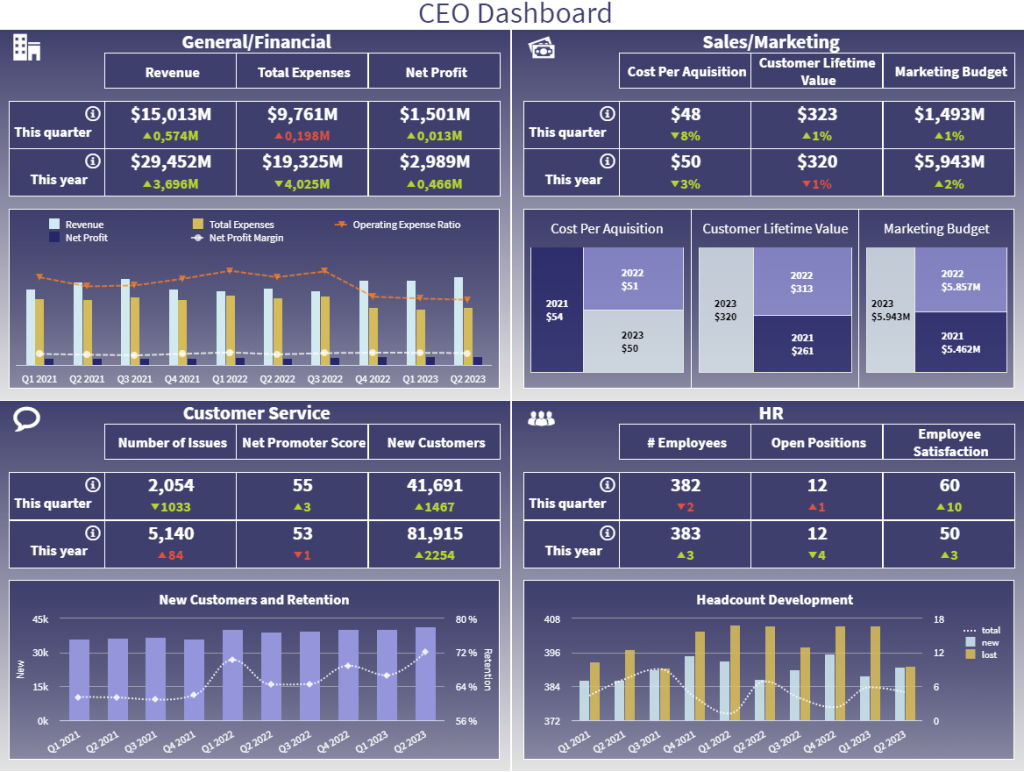
What makes this template so valuable for the CEO is the fact that it offers a long-term view with benchmarks for quarterly and annual performance. This way, leadership can evaluate the development of the different strategies and spot any inefficiencies at a glance by looking at the green or red colors depicted on each KPI. Plus, each section of the scorecard offers a detailed breakdown of additional information to help dive deeper into the reasons behind a specific result.
For instance, we can see that there is an increase in the total expenses in the current quarter. However, when taking a deeper look at the yearly breakdown, we can see that the operating expenses ratio has been decreasing for the past three months. Therefore, the quarterly increase is nothing to worry about.
13. Manufacturing production dashboard
As a production company, you must ensure every aspect of the process is efficiently carried out at its maximum capacity. This means, ensuring machines are working properly, the right amounts of products are being produced, and the least amount are being returned by customers. Our next template aims to help with that task by offering a 360-degree view into a company’s production processes.
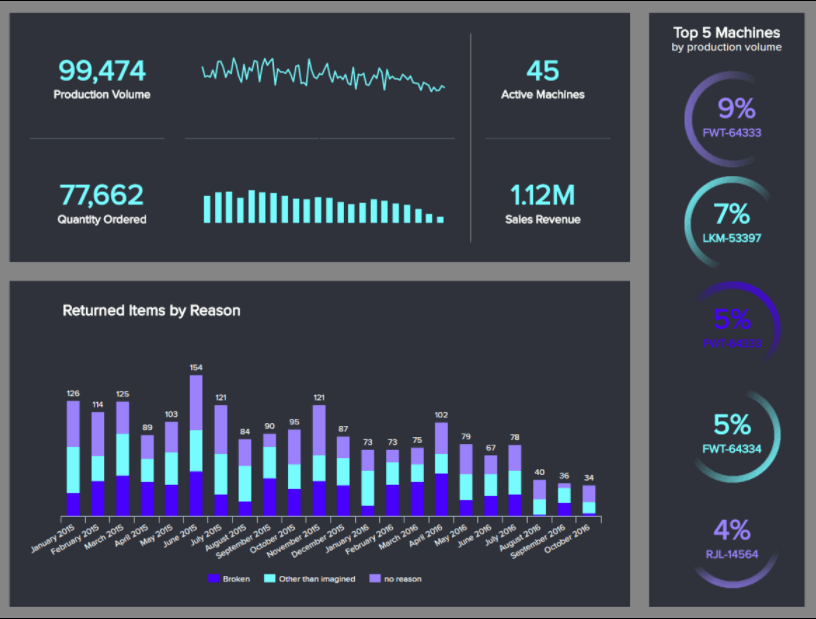
With insights into production volume vs. quantity ordered, top 5 machines by production volume, and return items by reason, the manufacturing manager can spot inefficiencies and identify trends to optimize production and ensure the highest possible ROI.
For example, looking at the top machines by production can help you spot the ones that might need some maintenance and plan that maintenance time without affecting production. On the other hand, analyzing the returned items by reason can also help improve customer experience and satisfaction. If you see a large amount of returns due to a broken product, it means you need to improve the quality of your materials or the packaging when they are sent to the customer to keep it safer.
14. IT project management dashboard
Completing a project successfully relies heavily on the team being connected to keep tasks moving at the expected speed. The issue is that it often involves multiple meetings that end up taking a lot of time that could be implemented actually completing the tasks. Our next sample aims to tackle that issue by providing a real-time overview of project development metrics.
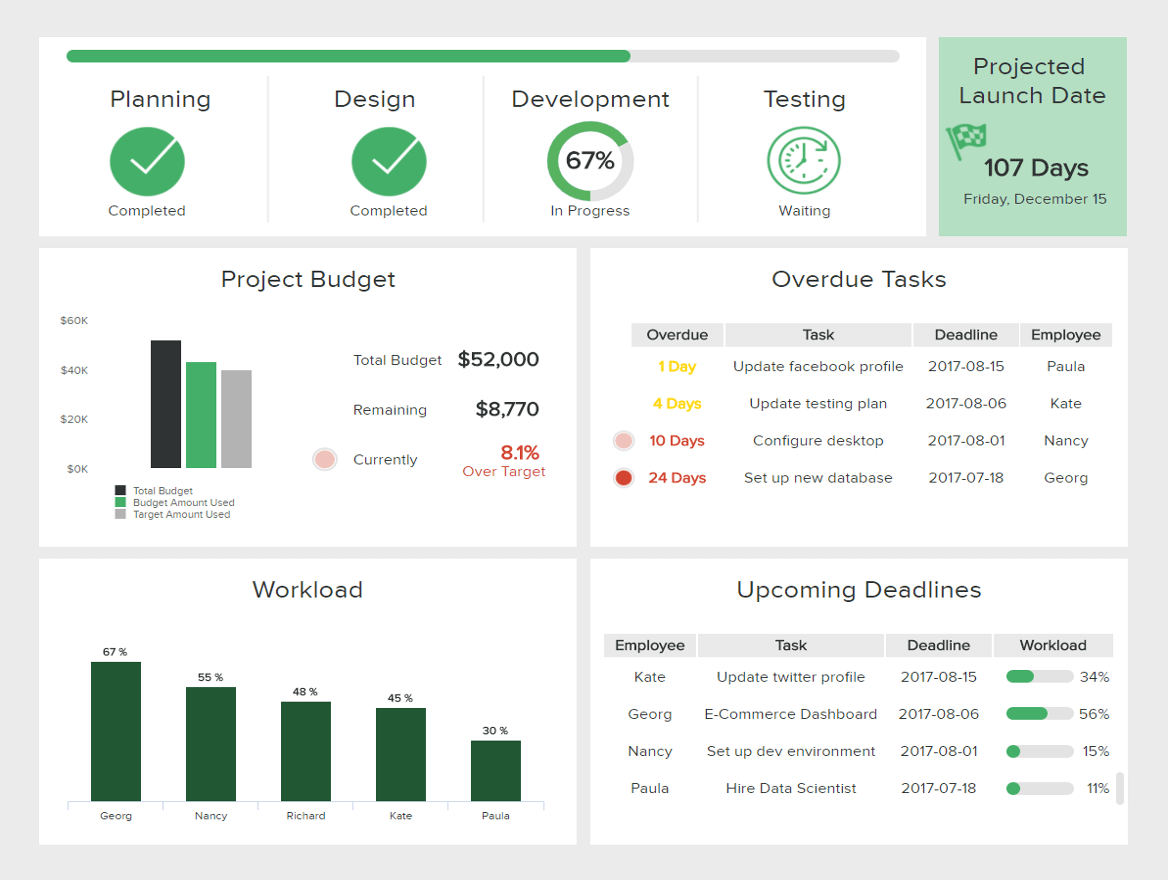
At the top of the report, we see a breakdown of the different stages of the project with a development percentage and a projected launch date. This is great information to have as it can inform the team about the status of the entire project and any external stakeholders as well.
We then get insights into the project budget, overdue tasks, upcoming deadlines, and employee workload. This is invaluable information that can help optimize any bottlenecks and increase overall efficiency. For instance, we can see that Georg and Nancy are 10+ days overdue with their tasks which is not good for the project. However, a deeper look shows us that these two employees are the ones with the biggest workload, which means they might need some help from other team members to speed up their tasks.
15. HR diversity dashboard
Diversity in the workplace has become a big priority for organizations and prospective talents. Each year, more and more businesses realize the value of having employees from different backgrounds and cultures as a way to boost their strategies and overall growth. That being said, to be considered a diverse company, you need to ensure your workforce feels comfortable and that the same opportunities are being given to all. Enters our last business report template.

The template above offers a view into different diversity management metrics from recruitment to talent management. Through this insightful report, HR managers can test the success of their diversity strategies and spot any areas of improvement to ensure the highest level of employee satisfaction. The template is highly interactive and offers insights into diversity by gender, ethnicity, and disabilities.
Analyzing the content of the report, we can see that black employees are the ones with the highest voluntary turnover rate. This is something that needs to be looked into to find the reasons why these employees are not feeling comfortable at the company. On the other hand, we can see that the organization is 1% above the 2% industry standard for hiring employees with disabilities. This is a great indicator, and it can translate into a low 7% of voluntary leaves by these workers.
Now that we’ve looked at report samples, let’s consider the clear-cut business-boosting benefits of these essential analytical tools. These perks will make your company stronger, more fluent, and more efficient on a sustainable basis.
Why Do You Need Business Reports?

These reports also enable data collection by documenting the progress you make. Through them, you have the means to compare different periods and activity, growth, etc. You can better see which products or services are more successful than others, which marketing campaign outperforms which other, and which markets or segments require more attention. Collecting all this data is indispensable – and by doing so, you build a paper trail of your past (or, namely, a data trail). They let people outside the company (like banks or investors) know about your activity and performance and enable stakeholders to understand your organization’s tangible and intangible assets.
- Risk assessment & opportunity: With a business report, you can increase the understanding of risks and opportunities within your company . Sample reports accentuate the link between financial and non-financial performance: they streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve overall cohesion in an informed, commercially ‘safe’ way.
- Trends & connections: Business report samples can help you compare your performance to other internal units or companies in the same sector. On a more specific level, a report template can help you dig thoroughly into operational metrics and details and discover correlations that would be otherwise overlooked. In today’s hyper-connected digital age, gaining a deeper insight into your data will empower you to formulate strategies that will accelerate key areas of your business growth through trend identification. This fact alone highlights the importance of a business analysis report.
- Business intelligence (BI): If used correctly, the best BI tools will answer a vital question: ‘Will I survive on the market?’ By creating a business report of a company built to improve your BI activities and answer essential organizational questions, you will gain the ability to tackle deeper specific insights that can bring operational value and control the overall expenditures. By knowing how to set up such a report with specific samples and templates, you can provide building blocks to establish a successful business intelligence strategy.
- Buy-in: While there are many different types of business reports for a company, they all have one common trait: gathering data and tracking the business activities related to something specific. By working with the right reports, users can perform in-depth visual analyses of many key areas or functions and provide informed recommendations that will ultimately improve efficiency and encourage innovation. Regardless of how good or beneficial an idea might be , getting buy-in from senior executives or external partners is often a major roadblock to progress. However, a good report template presents a level of depth and presentation that is both factual and convincing and will encourage buy-in from the people with the power to sign off on new strategies, initiatives, or ideas.
- Operational efficiency: The more factual the report is, the clearer the data. When your data is well organized and crystal clear, it’s possible to interpret your business activities cost-effectively, reducing the time required to analyze findings while saving countless working hours sifting through metrics for actionable insights. A good template presents an in-depth analysis where the writers show how they have interpreted their findings. For example, a marketing report can reduce the time needed to analyze a specific campaign, while an HR report can provide insights into the recruiting process and evaluate, for example, why the cost per hire increased?
- Specificity: When you create a business information report, you are giving yourself a key opportunity to address specific issues that are often used when decisions need to be made. As author Alan Thomson says, “A company report conveys information to assist in business decision-making. [It] is the medium in which to present this information.” They have several purposes: some record information to plan for the future, some record past information to understand a situation, and others present a solution to a pressing problem. Some executive dashboards are for daily usage, while a monthly business report template will help you pinpoint your activities on a more gradual, incremental basis. They are all essential to commercial success, as they bring clarity to complex analysis. As mentioned earlier, the clearer the data, the more cost-effective results will be, so keeping in mind the exact data to incorporate into this kind of report should be essential in deciding what kind of report to generate. You can find multiple key performance indicator examples in different industries, which should be considered when creating that kind of report. You can also generate an interdepartmental report or between businesses to compare industry values and see how your company stands in the market.
- Accuracy & consistency: In The Age of Information, data is a vast landscape, and if you want to use it to your advantage, aiming for consistency and accuracy is key. If your data is off or presents hit-and-miss findings, it could cost your company in the long run. Working with an online dashboard tool to produce your reports is an incredible advantage for the ease of use, the time saved, and, most importantly, the accuracy of the information you will use. As you work with real-time data, everything on your report will be up-to-date, and the decisions you will take will be backed with the latest info. Business report examples are significantly helpful when you need to explore your data and perform data analyses to extract actionable insights. They will deliver an important added value to your report thanks to the visualization of your findings, bringing more clarity and comprehension to the analyses, which is their primary purpose.
- Engagement: As intuitive, digestible, and visual tools, business-centric reporting tools are easier to understand and tell a story that is far more likely to resonate with your audience. While exploring your data, with deeper insights generated with just a few clicks, the report doesn’t have to be dull, boring, and lost in hundreds of pages or spreadsheets of data. If you create a report that is clean and customized, you will bring more value than by printing or searching through a spreadsheet. Achieving a design like this is simple with the right KPI dashboard software . Imagine yourself in a meeting with 200 pages of analysis from the last 5 years of business management. One participant asks you a specific question regarding your operational costs dating 3 years back. And you’re sitting there, trying to find that specific piece of information that can make or break your business meeting. With business dashboards , you cannot go wrong. All the information you need is generated with a click, within a click.
- Benchmarking: If you know how to set up a business-centric report with efficiency, you will gain the ability to set defined, accurate benchmarks. By frequently setting targets based on your most important organizational goals and working with visual reporting tools, you will keep your organization flowing while catalyzing your overall growth and productivity levels.
- Communication: One of the best uses of these tools is improving internal collaboration and communication. By gaining 24/7 access to your most essential business data while enhancing the way you analyze and present it, you will empower everyone in the business with better access to information, which, in turn, will enhance internal communication and collaboration.
- Innovation: The intuitive nature of these reports makes them the most efficient way to steer a progressive analytical strategy. As such, it’s easier (and quicker) to uncover hidden insights, spot trends, and hone in on critical information. It’s this speed, ease, and accuracy that frees creativity and improves innovation across the organization, accelerating growth as a result.
These reports can also be of many different types, but they all have one common trait: gathering data and tracking the organizational activities related to something specific. From there, their author(s) will often perform an analysis and provide recommendations to the organizations.
How To Generate A Business Report
The primary importance of a corporate-centric report lies in gaining confidence and clarity. Before starting to create it, it’s vital to establish the goals and the audience. Knowing who you want to direct it to is key in its elaboration, from the tone, vocabulary/jargon you choose to the data you will focus on. A report to external stakeholders, to the CEOs, or to the technical engineers’ team will be drastically different from one another.
Likewise, the scope varies according to the objective of the report. State beforehand the needs and goals to direct you on the right path. It should be impartial and objective, with a planned presentation or dashboard reporting tool , which enables an interactive flow of data and immediate access to every piece of information needed to generate clear findings.
To help you write your daily, weekly, or monthly business-centric report template with confidence, let’s go over some essential steps and tips you should focus on:
1. Consider your audience
First of all, if you want to understand how to do a business report the right way, you have to think of your audience from the outset. Your reporting efforts must make sense and offer direct value to the end viewer or user - otherwise, they’ll be meaningless. That said, it’s critical that you take the time to consider who will use the reporting tool most and which information or features will add the most value, helping improve the organization in the process. Take the time to understand your audience, and your reporting tools will not only meet expectations but exceed them - one well-placed visualization at a time.
2. Determine and state the purpose
As we stated in the previous paragraph, defining the needs of your audience is vital to reporting success. As we said, a report usually assists in decision-making and addresses certain issues. You can state them at the beginning of the report. The more clear and specific the goal, the better the content will be. You won’t lose time adjusting information when you present your purpose in a clear and well-defined manner.
3. Use a mix of real-time and historical data
Another key component of this report is making sure you’re free of any informational blind spots. So many companies work with one form of metric, stunting their organizational progress in the process. To drill down deep into detailed pockets of information and gain a panoramic view of specific trends or patterns, working with a balanced mix of historical and real-time data is key. Doing so will empower you to capitalize on potential strengths while learning from historical weaknesses. This balanced approach will also give you the tools to develop strategies that return the best possible ROI while making powerful decisions under pressure.
4. Set actionable targets and goals
Once you’ve curated your informational sources and defined your audience, you should set actionable goals. Setting the right benchmarks will help you track your ongoing success with pinpoint accuracy while defining goals or targets will give you the insight you need to work with the right KPIs while ensuring your company is moving in the right direction. Taking the time to set actionable goals and targets that align with your organizational strategy will ensure your reports offer a consistently healthy ROI.
5. Define your reporting frequency
Another key component of successful organizational reporting is deciding how often you will analyze your metrics and information. Depending on the function or the goals you’re looking to achieve, you should decide whether your dashboard will serve as a daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly reporting tool. Setting the right frequency will ensure your analytical strategy is fully streamlined while connecting you with the insights that count most at exactly the right time. The best modern reporting tools also offer automated functionality, helping to monitor insights and offer alerts without human intervention - the best way to save time while ensuring you never miss a critical piece of information again.
6. Gather and organize the information
Now that the purpose and scope are clearly defined, you can start gathering the data in any form that can address the issue. Thanks to that information, you will carry out data analysis to understand what lies beneath and to extract valuable insights. These findings need to be balanced and justifiable – what significance they have to the report's purpose. Identifying key performance indicators for a specific company, organizing, comparing, and evaluating them on the needed level, can be one of the most important parts of creating this kind of report. An example of a business report that shows how to extract and define your analysis can be found above in the article, where we presented our visuals.
7. Present your findings
Explain how you uncovered them and how you interpreted them that way. Answer the original issue by detailing the action to take to overcome it and provide recommendations leading to a better decision-making process. A best practice to present the insights you have drawn out is using dashboards that communicate data visually in a very efficient way. A dashboard software like datapine can precisely answer that need while helping you with data exploration at the same time, which is a crucial part. When you click on a specific part of the dashboard, you can easily access your data in a more in-depth approach.
Comparing your findings is also one of the features you can use if you are asking yourself what has changed in relation to a specific period. When you assess these datasets in just a few clicks on your monitor, the whole reporting process and measurement of your strategy can be done in minutes, not days. Evaluating findings in today’s digital world has become one of the main focuses of businesses wanting to stay competitive in the market. The faster you can do that, the more information you gain, and the more successful your actions will become.
8. Align your visualizations
Expanding on presenting your findings, it’s also important to get your design elements right when considering how to write a business report. As a rule of thumb, your most essential at-a-glance insights should be at the top of your dashboard, and you should aim to be as clean, concise, and minimal as possible with your presentation to avoid cluttering or confusion. To improve your visual storytelling and bring every key element of your report together cohesively, getting your dashboard design just right is vital. Our essential guide to data visualization methods will help to steer your efforts in the right direction.
9. Proofread your reports
When you’re looking at a polished example of a business report, you’ll notice that every element of design and content is immaculate and makes complete logical sense. That said, to get the best returns for your analytical efforts, proofreading your reports is vital. Work through your report with a fine-toothed comb and ask trusted colleagues in your organization to do the same. Once you’ve carefully proofread your entire report, you can collectively tighten up any sloppy design elements, typos, misleading copy, and bad visual placements. Doing so is vital because it will make your examples of business reports slick, actionable, accurate, and built for success.
10. Be responsive
While modern reporting dashboards are dynamic and interactive in equal measure, it’s important that you also remain robust and responsive when writing a business-based report. What does this mean, exactly? It means that in the digital age, the landscape is always changing. As such, if you want to get the most from your reports or dashboards, you must commit to editing and updating them according to the changes around you. In an informational context, what is relevant today may be redundant tomorrow, so to remain powerful and relevant, your reports must always be optimized for success. When you write a business-style report, you should understand that, to some extent, you will need to rewrite it repeatedly. Remember, commit to regularly assessing your reports, and success will be yours for the taking.
You can easily find a sample of a business report on the Internet, but not all of them fit your needs. Make sure, at any moment, that the report you want to create is accurate, objective, and complete. It should be well-written, in a way that holds the reader’s attention and meets their expectations, with a clear structure.
Common Challenges Of Business Reports
As we just learned from the previous section, generating a successful report requires carefully following some steps and considerations. This often comes with challenges and limitations that users face during the generation and analysis process. To help you be aware of those challenges and how to overcome them efficiently, we will list some of the most common ones below.
- Data quality
All the time and effort dedicated to the reporting process will be for nothing if you are not working with high-quality information. Believe it or not, according to recent reports , 41% of companies cite inconsistent data across technologies as their biggest challenge. With only 16% labeling the data they are using as “very good”.
This presents a huge challenge as the consequences of poor data quality can be quite expensive since organizations are basing their most important strategic decisions on unreliable insights.
To prevent this issue from affecting you, it is essential to invest time and money in implementing a thoughtful data quality management plan to ensure your information is constantly checked under specified guidelines. Putting extra attention to the cleaning and constant manipulation of the information is also a huge aspect of the process.
- Lack of data literacy
Another big challenge that businesses face when implementing reporting practices is the level of literacy of their employees. As mentioned earlier in the post, the success of the entire process relies heavily on the entire workforce being involved in it and collaborating with each other. The issue is that generating a report and analyzing the data can be very intimidating for non-technical employees who often don’t have the necessary skills or confidence to integrate data-driven activities into their daily work.
That is why carrying out a careful analysis of the literacy level across your workforce can help you understand the actual situation and offer training instances to anyone who needs it. Paired with that, investing in self-service BI tools that allow any user, regardless of their technical knowledge, to generate a business report with just a few clicks is a great way to approach this challenge.
- Long generation processes
It is not a secret that manually generating a business report can take a lot of time and effort. In fact, in some cases, when a report is finally completed, the information in it might not be entirely valuable anymore. Luckily, this challenge has been tackled a long time ago thanks to the power of automation.
Modern online reporting tools offer users the possibility to automatically generate a report in a matter of seconds, eliminating any form of manual work. All they need to do is connect their data sources, select the KPIs they want to display, and enjoy a visually appealing and fully functional report in just a few clicks. This enables organizations to focus on the important part, which is extracting powerful insights to inform their strategies.
- Static vs. interactive business reports
Traditionally, these reports generated with tools such as Excel or PowerPoint have been static and full of text and complex numbers. Making it impossible to extract deeper conclusions from them or act on fresh insights. This is not to say that they are completely unuseful, but their historical and static perspective makes them less effective, especially considering how agile decision-making can represent a huge competitive advantage for organizations today.
To help you make the most out of your data-driven efforts and tackle this common limitation, we recommend you invest in tools that offer dynamic reports. BI reporting tools , such as datapine, give you the ability to generate interactive real-time reports, like the ones we saw earlier, which can be easily filtered to explore different periods or lower levels of data. This will give you the power to extract deeper and fresh insights to boost your strategies and growth.
- Ensuring data security and privacy
In the digital age we live in, we need to be fully aware of the risks of using online tools to manage our business’s operations. Studies have shown an increasing trend in cyberattacks and data breaches that has left decision-makers concerned about how they manage their sensitive data. One of these attacks can significantly impact an organization’s reputation but also incur considerable costs that can be hard to come back from. According to recent research, these types of breaches cost businesses an average of $4.35 million in 2022.
All of this makes security and privacy a big challenge for businesses of all sizes. Especially regarding their report-related activities, as they contain sensitive information about the company and its clients. Luckily, modern SaaS BI tools offer high levels of security to help you keep your data secure at all times, from the moment it is generated to the time it is shared with different stakeholders. Therefore, it is important to consider this topic before investing in such a tool.
Key Takeaways Professional Business Reports
"Once we know something, we find it hard to imagine what it was like not to know it." - Chip & Dan Heath , Authors of Made to Stick, Switch.
We live in a data-driven world, and as a business, it’s up to you to move with the times. If you ignore the power of smart data analytics, you are only stunting your own commercial progress.
We’ve explored many shining business reports examples, and one thing is abundantly clear: if you embrace the power of digital reporting, your company will be bigger, better, and exponentially more informed. The more confident and informed you are as a business, the better you will be able to respond to constant change. In today’s digital world, it doesn’t matter what sector you work in. If you’re rigid in your approach to data, you will get left behind. Digital reporting dashboards are the only way forward.
So, you now know what business reports are, how to structure and write them , and how they can benefit your business. Committing to the right reporting and information delivery can have a significant impact on your organization and orientate its strategy better. For more ideas about business reporting in a more specific, function-related way, you can dig deeper into some of our popular articles on sales reports and marketing reports !
Don’t miss out on that opportunity and start now with datapine’s online reporting software , and benefit from a free 14-day trial ! You won’t regret it.

What is a Business Report: How To Write it? (Examples & Format)
Table of Contents
This is a detailed guide to what is a business report, explained with examples, types, importance, and features, and how to write it with elements and a checklist.
Definition of business report
“A business report is an orderly, objective communication of factual information that serves some business purpose”. By Raymond Vincent Lesikar, and John D. Pettit
What is a Business Report?
A business report is a formal document that provides an analysis of a specific business issue or situation. It typically includes detailed information on the topic at hand such as data, research, and other relevant sources.
Business reports are used to make business decisions, identify problems or opportunities, or track progress toward goals. They are often written for an internal audience, such as managers or executives, but may also be shared with external stakeholders, such as investors or clients.
Business reports should be well-structured, concise, and objective, presenting findings and recommendations in a clear and easily understandable format. They may include charts, graphs, and other visual aids to help illustrate key points.
Difference between Market Report and Business Report
A business report typically focuses on a specific company’s performance, operations, and financial results. It can provide information on topics such as sales trends, revenue growth, expenses, and profitability.
In contrast, a market report focuses on the broader market landscape and provides information on the trends, opportunities, and challenges in a specific industry. Market reports can include information on market size, growth potential, competition, and consumer behavior.
While both reports aim to provide useful information for decision-making, their focus and scope are different, with business reports focusing on internal operations, and market reports focusing on external market factors.
Difference between a Business Report and a Business Plan
A business report is a document that provides detailed information on a specific aspect of a company’s operations, such as financial results, sales trends, customer feedback, or employee performance. It is used for decision-making, tracking progress, and communicating with stakeholders.
On the other hand, a business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, and tactics for achieving success. It typically includes an analysis of the market, a description of the company’s products or services, an overview of the management team, and a financial plan that details how the company will generate revenue and manage expenses over time.
How to Write a Business Report
Writing a business report can be a valuable tool for analyzing and presenting information related to a company’s performance or a specific business project. Here are some steps to follow when writing a business report:
1) Determining the purpose: Before writing the report, it’s important to define the purpose of the report. The writer must know what type of report they are writing and why it is being written. This helps in better research and writing.
2) Check target audience: After determining the purpose of the report, the writer must keep in mind who the report will be addressed. This can help in effectively conveying the message to the concerned persons.
3) Gather information: The writer must then gather data and conduct research. It is necessary to use credible sources such as industry reports, financial statements, or market research studies to collect relevant data.
4) Analysis of the supportive information: This is the main body of the report where the writer will present their findings. They must make sure to use data and statistics to support conclusions. This section can include charts, graphs, and tables to make the information easy to understand.
5) Findings and recommendations: Once the writer has presented their findings, they can draw conclusions and make recommendations based on the analysis. This is where they can suggest ways to improve the company’s performance or make recommendations for future business projects.
6) Determining report format: Before writing the report, the writer must determine what kind of business report it is. This is done so they can structure the report in a logical and easy-to-follow way. They can create outlines that include headings, subheadings, and sections to organize the information in a clear and concise manner.
Elements of a Business Report
A business report consists of three main elements – Front Matter, Body of the Report, and Back Matter.
The format of a business report is as follows:
(A)Front Matter: The front matter of a business report is the first section of the report and provides essential information about the report’s contents and purpose. It includes the following elements:
- Cover Page: This is the first page of the report, typically including the title, author or authors, date, and company logo.
- Title Page: It follows the cover page and provides more detailed information about the report.
- Table of Contents: It is also included in the front matter and provides an outline of the report’s contents, including headings and subheadings with page numbers.
- Executive Summary: It provides a brief overview of the report’s main findings, conclusions, and recommendations.
A portion of the executive summary in the business report: An executive summary is a brief overview of a business report that highlights the main points and conclusions of the report. It is usually the first section of the report that the reader sees and is often used as a standalone document for busy executives who need to quickly understand the report’s key findings. The purpose of an executive summary is to provide a concise and clear picture of the main purpose of the report, the methods used to gather data, the key findings and conclusions, and the recommendations based on those conclusions.
(B) Body of the Report: The body of a business report is the main section of the report where the writer presents the data, analysis, and interpretation of the findings in a clear and concise manner. It contains the following elements:
- Introduction: The introduction gives a background on the problem or issue being addressed in the report, the objectives of the report, and an explanation of the report’s scope.
- Methodology: It is a description of the research methods used to gather data and information for the report.
- Results: This section highlights the presentation of the findings or data gathered during the research phase, including tables, graphs, and other visual aids to support the information.
The importance of tables and graphs in a business report: Tables and graphs are important elements in a business report because they can help to communicate complex data and information in a visual and easy-to-understand way. They are useful for presenting large amounts of data in a clear and concise manner, making it easier for the reader to interpret and understand the information presented.
- Discussion: An analysis and interpretation of the results, including the significance of the findings and their implications.
- Conclusion: The conclusion contains a summary of the main points made in the report, including the conclusions drawn from the analysis and any recommendations for action.
- Recommendations: Finally, the recommendation section contains specific actions or strategies that are proposed to address the problem or issue being investigated in the report.
(C) Back Matter: The back matter of a business report is the section that comes after the main body of the report and includes any additional information that may be useful for the reader. This section may include
- Appendices: This contains additional materials such as charts, graphs, or data that support the report but are not included in the main body of the document.
- References: This contains all the citations and references used in the research and collection of data for the report.
- Glossary: A glossary lists the technical terms used in the report with their meanings and descriptions.
Must Read : What are the parts of a business report
How should headings be used in business reports?
Headings are an essential tool for organizing a business report and making it easy to read and navigate. Headings should be clear and descriptive, giving the reader a sense of what each section will cover.
They should also be formatted in a way that makes them stand out from the rest of the text, such as by using bold or larger font sizes. They should be used consistently throughout the report to guide the reader through the various sections and sub-sections.
When using headings in a business report, it is important to follow a logical and hierarchical structure. The main heading of the report should clearly state the purpose of the report and provide an overview of the main points that will be covered. Subheadings should be used to break down the report into smaller sections, each covering a specific topic related to the overall theme of the report.
Examples of business reports
Below we have listed business reports of some top companies along with the business performance metrics.

Topics for writing Business Reports Importance of the communication process ? Non-verbal aspect of business communication? Modes of the communication process? Changing patterns of business correspondence? Types of barriers in business communication ? How to overcome barriers of communication in an organization ?
Most common types of Business Reports
In business communication, there are many different types of business reports , with each type designed to provide specific information about a particular aspect of a company’s operations. Some common types of business reports include:
1) I nformational Report: This type of business report provides factual information on a particular topic or issue, without making any recommendations or drawing conclusions.
Further Reading : How to Write an informational report
2) Analytical Report: These reports use data and analysis to draw conclusions and make recommendations. It typically includes an executive summary, introduction, methods and results sections, and a conclusion with recommendations.
3) Routine Report: These reports are produced on a regular basis, such as weekly or monthly. It typically provides updates on specific activities or tasks, such as progress on a project or sales figures for a given period.
4) Informal Business Report: An informal business report is less structured and formal than other types of business reports. It may be used for internal communication between colleagues or departments and can include memos, emails, or short notes.
5) Short Report : This type of business report is concise and to the point, typically no more than five pages in length. It is often used to communicate a specific issue or recommendation quickly and may include only the most essential information.
Must Read : List of different types of business reports with classification
Importance of Business Reports
Business reports are an important tool for organizations to communicate and document important information related to the business. Some of the key reasons why business reports are important to include:
- Evaluation: Business reports can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of specific initiatives or programs by tracking progress toward goals and measuring outcomes.
- Communicating with stakeholders: Business reports can be used to communicate important information to a range of stakeholders, including investors, customers, suppliers, and employees.
- Supports decision-making: Business reports can provide the information and analysis needed to make informed decisions about business operations, investments, and strategies.
- Providing a record of performance: Business reports can provide a historical record of the organization’s performance, documenting trends and changes over time.
Must Read : What is the importance of a business report
Characteristics of Business Reports
A good business report should have the following characteristics:
1) Purpose: Business reports are written with a specific purpose in mind, such as informing a decision, presenting research findings, or providing updates on a project or initiative.
2) Audience: Reports are tailored to the needs and interests of the intended audience, which may include executives, managers, stakeholders, or external clients.
3) Structure: The report must have a clear and standardized structure, which typically includes an introduction, background information, results, analysis, recommendations, and conclusions.
4) Objectivity: Reports are expected to be objective and unbiased, and to present information and analysis in an accurate and factual manner.
Must Read : What are the characteristics of a good business report
Advantages and Disadvantages of Business Reports:
In this section, we will look at a few advantages and disadvantages of business reports .
Advantages:
- Business reports provide clear and concise information about various aspects of a business, such as financial performance, market trends, customer satisfaction, and employee productivity.
- Business reports can be used to share information among employees, departments, and stakeholders. This facilitates communication and collaboration, allowing everyone to stay informed and work together towards common goals.
Disadvantages:
- Business reports can be time-consuming to create, especially if they require extensive research and analysis. This can be a burden on employees who are already busy with their regular responsibilities.
- Depending on the length and complexity of the report, it can be overwhelming for readers to process and understand all of the information contained within it. This can be especially true if the report is full of technical jargon or financial data that may not be familiar to all readers.
Must Read : Advantages and disadvantages of business reports
What is a Small Business Report
A short business report is a concise document that provides a brief summary of key information related to a specific business topic. Short reports are typically between one and five pages in length and are often used to communicate information to a specific audience.
Short business reports typically include an introduction that highlights the context of the report, a summary of the key points or findings, and a conclusion or recommendation. They may also include supporting data, such as charts, graphs, or tables, to help illustrate key points.
Must Read : What is a small report and how to write a small report with examples
What is the Significance of Business Report Writing in Business Success?
Business report writing is a critical tool for achieving success in business. Reports provide valuable information to business owners and managers that can be used to make informed decisions, identify improvement areas, and create growth strategies.
They also facilitate communication within the organization, allowing employees and stakeholders to stay informed about the business’s progress and work together towards common goals. Business reports can be used to help plan for the future and set goals, and promote accountability by tracking and reporting on performance metrics.
Checklist for making your Business Report Reader-Friendly
Here is a checklist for making your business report reader-friendly:
- Use clear and concise language: Avoid using technical jargon and complex language that may be difficult for readers to understand. Use simple, clear language that is easy to read and comprehend.
- Organize your report effectively: Use headings, subheadings, and bullet points to break up your report into smaller, more digestible sections. This makes it easier for readers to navigate and find the information they are looking for.
- Use visual aids: Incorporate graphs, charts, and tables to help illustrate key points and make the information more engaging. This can help readers understand complex data more easily.
- Proofread your report: Ensure that your report is free of grammatical errors, typos, and other mistakes. This can help make your report appear more professional and increase the credibility of the information contained within it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) what is the purpose of a business report.
Ans: The purpose of a business report is to communicate relevant information about a company’s performance, activities, or other important data to various stakeholders, including executives, shareholders, employees, customers, or external partners. They also help in decision-making, evaluation, and keeping a record of business activities.
Q2) What are the important principles of a business report?
Ans: The important principles of the business report are the principle of objectivity, the principle of knowing your target audience, the principle of planning & framework, the principle of clarity, the principle of organizing your report, and the principle of evaluating information.
Q3) What are the 5 main parts of a business report?
Ans: The 5 main parts of a business report include a title page, executive summary, table of contents, findings, and discussion, and finally, the conclusion and recommendations.
Share Your Read Share this content
- Opens in a new window
Aditya Soni
You might also like.

10 Differences Between Formal & Informal Reports + Examples

11 Characteristics of a Good Business Report

24 Types of Business Reports With Samples & Writing Structure
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Marketing 50+ Essential Business Report Examples with Templates
50+ Essential Business Report Examples with Templates
Written by: Sara McGuire May 29, 2023

Reports may not be the most exciting communication format. But they’re important.
To make smart decisions about budgeting, marketing strategies, product development and growth strategies, you can’t rely on gut feeling alone.
And if you’re trying to sway stakeholders, creating a report with a simple, elegant design and creative data visualizations is guaranteed to impress.
This guide will deliver the most essential business report templates you can edit with Venngage, plus design tips and best practices.
Top business report templates (click to jump ahead):
What is a business report?
- Annual reports
- Project status reports
- Budget reports
- Sales reports
- Marketing reports
- Case studies
- White papers
- How to create a business report in 6 steps
- What are the types of business reports
- Business report template FAQs
A business report is a document that delivers important information about a company’s performance, financial health, a particular project, or other aspects that influence its decision-making process.
Business reports come in various formats, such as PowerPoint presentations and online dashboards, offering more than just traditional files and spreadsheets.
They are crucial for organizations as they provide vital details that guide decision-making for business owners and managers.
They act as GPS, highlighting essential aspects like customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and financial figures. Business reports serve different audiences and purposes, delivering information in a clear and engaging format for both internal and external stakeholders.
Want a quick rundown of some of the business report templates in this blog? Check out this video tutorial:
1. Annual Report Templates
An annual report is an all-encompassing document that allows you to reflect on your company’s past year, including:
- Your company’s mission statement
- Your company’s growth (financially, product-wise, culture-wise)
- Your statement of income and cash flow
- Your various business segments
- Information about the company’s directors and executive officers
- Information about your company’s stock and dividends
- Wins and success stories
A lot of that sounds pretty dry, doesn’t it?
There’s actually a lot to be excited about in that list. You’re talking about how your company has grown, your wins (and maybe a few losses), and what’s on the horizon for the coming year.
You can bring that story to life in your annual report design and we have business report samples to inspire you.
This annual business report example uses a variety of charts and unique sections like “program highlights” to tell the agency’s story:

Think about how you can represent your company visually:
- Are there photos you can include of your business in action?
- What fonts and colors reflect your business’s personality?
- Are there icons you can use to illustrate certain concepts?
The below annual report design uses an energizing orange and yellow color scheme and cute icons. The format is highly visual and modern. All this reflects a dynamic company that’s optimistic about the future.
This company annual report template uses a mountain motif to reflect the company’s ambitious goals. Take a look at how the different sections of the report (“Strategy”, “Finance” and “Performance”) are color-coded to make the report easier to scan:

In the business report example below, the sleek, modern design with bold color accents reflects design trends in the games industry, which would appeal to stakeholders.

The same design ideas can be applied to an annual report presentation.
Take this annual report presentation for a coffee shop company. The whole design reflects the coziness of a coffee shop, from the softly filtered photos to the old-fashioned font:

A few annual report best practices:
- Create an eye-catching cover for your report
- Tell your company’s story in your annual report design by using thematic visuals, like background images and icons
- Pick a decorative font for headers and pair it with a more minimalist font for body text
- Look for opportunities to visualize data using infographics , charts and pictograms
Related : Our blog post with 55+ annual report templates , plus design tips and best practices.
2. Project Status Report Templates
Communication is central in any project. Consultants, agencies and freelancers especially want to be as transparent as possible. That is why a project status report template is one of the business report examples we are sharing in the article.
A project status report is crucial for communicating updates on what you’ve accomplished and what’s still pending. It also helps you flag any issues, either current or on the horizon. This helps build trust with the client.
The project status report template below communicates key information in an easy-to-understand format.

The above template lets you alert the client if the project is:
- Suffering from budget or scope creep
- On track in terms of schedule
- Healthy or not i.e. milestones completed on schedule, issues resolved
You can add bullet points on the second page to quickly flag key issues that are impacting project success.
Related : Our post on how to write a project management plan .
Simple Project Status Report Templates
Avoid ad-hoc emails or meetings. Use a simple project status report template to present your latest work and keep everyone on the same page, without endless back and forth.

The project status report below would work well for weekly updates.
This template lets you quickly provide an overview to busy stakeholders, who’ll be able to spot key project issues and progress at a glance.

Project Status Report Template PPT
Big updates might require consultants to communicate the status of a project in person. The below presentation template uses charts and data visualization to get your key points across immediately.
Clients or other stakeholders can see what’s been accomplished and when, while the last slide leaves room for what’s still pending.

A few project status report best practices:
- Include a summary of all important tasks currently in progress. If you have a weekly meeting with the client, this section will probably serve as the jumping-off point for your conversation.
- Stakeholders should be able to tell at a glance if the project is way off schedule or there are too many unresolved issues.
- Document all outstanding problems and concerns. It’s important to have a record in case you run into issues with the client later on.
Related : Our post with 30+ project plan examples plus design tips.
3. Budget Report Templates
This is Business 101: on a quarterly or yearly basis, you should be analyzing your budget, expenses and revenue.
A budget report typically breaks down:
- The different categories of your budget
- The last year or quarter’s spending for each category of your budget
- Areas where you may need to cut or increase spending
- Forecasts for the coming year or quarter
Business Monthly Expenses Template
A full budget report is a bit too dense to pass around a room during a meeting.
But, a visually engaging presentation or one-page summary, like the business report example below, is perfect for keeping your team and stakeholders up to speed.

You can provide an overview of the last period’s spending by category, and highlight the amount you saved or exceeded the budget by.
For example, take a look at this summary budget report slide that uses a thematic background image to make it more engaging:
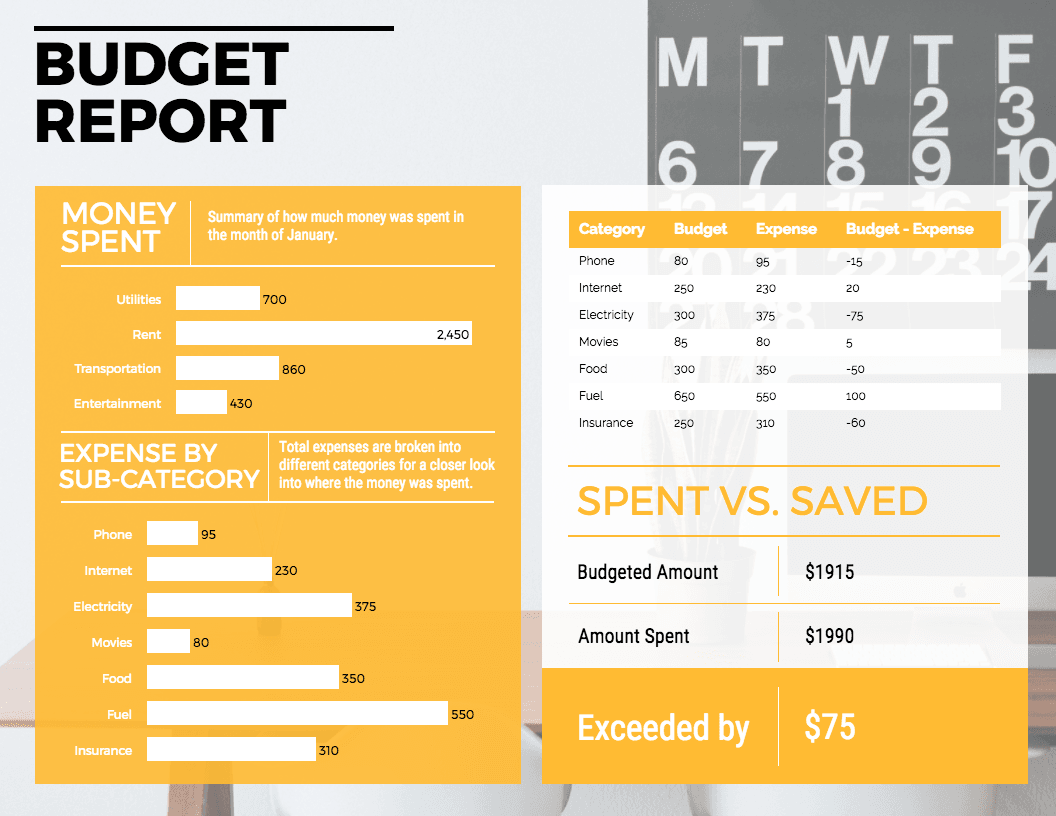
A quick summary page is also the perfect opportunity to creatively visualize data.
While tables are certainly efficient for comparing amounts spent, you could also use a more unusual visual like a bubble chart. This is because unique visuals make memorable business report examples.
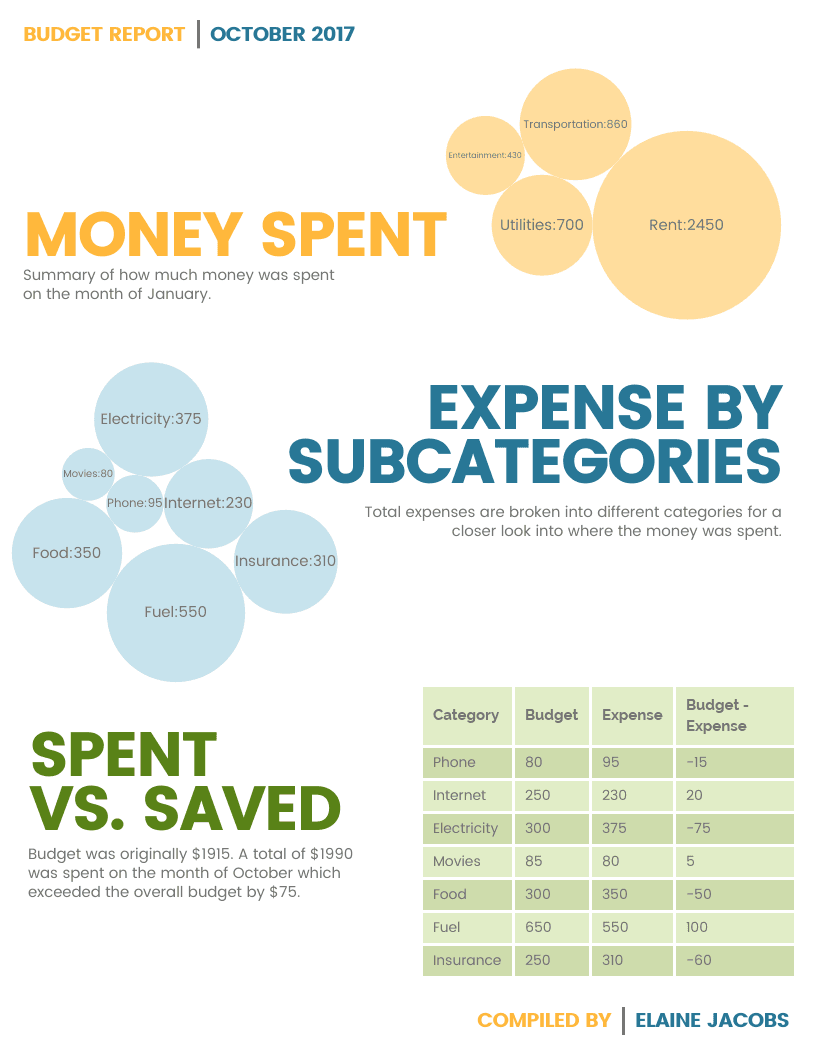
Forecast Budget Template
A forecast is an essential business report that shows where a business is headed financially. It’s not a plan for the future, but rather its current short-term direction .
Use this forecast template to project your businesses’ revenue, and take appropriate action.

A few budget report best practices:
- Clearly label the period the report covers (monthly, quarterly, yearly)
- Provide a brief description of each section of your report, to highlight important insights
- Use a table to compare amounts of money saved vs. spent
- Use bar charts, pie charts and bubble charts to visualize budget allotment
- Highlight important insights using contrasting colors, bold fonts and icons
4. Sales Report Templates
If you aren’t tracking your sales on a weekly, monthly, quarterly and yearly basis, it’s time to start.
Creating a sales report for different time periods can help you identify trends, as well as an opportunity for growth. Regularly reporting on your sales can also help your team stay focused on your goals.
What should be included in a sales report?
A sales report typically covers any of the following data:
- An overview of sales goals and whether or not those goals are being met
- Revenue and expenses
- Sales forecasts for the upcoming periods (month, quarter, year)
- Products and services that are selling the most and ones that are lagging
- Number of leads and conversion rates for a given period
- Any challenges or roadblocks
Weekly sales report template
Consider making sales reporting a segment of your weekly team meetings. You may want to provide a quick update for company-wide meetings and a more in-depth report for sales and marketing team meetings.
Here’s an example of what a quick weekly sales report could look like:

The slide simply covers the total sales for the week and compares them to previous weeks to highlight growth.
While this sales report presentation digs deeper into KPIs (key performance indicators) and conversions :
Monthly sales report template
For a monthly, quarterly or yearly sales report, you will probably want to go more in-depth into your metrics as you plan for upcoming periods.
That said, you don’t want to produce a 62-page text-heavy document no one will read. Surprise your client or boss with a fresh new way of doing things that are engaging and concise. You’ll differentiate yourself as an innovator.
For example, the following monthly sales report template uses a variety of charts and tables to keep the data fresh:

The below sales report template will help you visualize key sales metrics using pie charts, bar graphs and tables. The weighted text and icons help organize information in an easily digestible way.
Making your sales report easily accessible will help build your reputation as someone who’s transparent and trustworthy.
A few sales report best practices:
- Clearly identify the time period you are reporting on
- Use descriptive section headers and include descriptions for any charts or tables that need more clarification
- Provide context for readers, explain any major trends they should be aware of, any challenges your team encountered, and how the goals have been impacted
- Use line charts and bar graphs to show changes over time and highlight trends
- Emphasize key metrics in big, bold fonts (for example, the total sales for a given week)
- Use contrasting colors to emphasize keywords or one point on a graph
Related : 5 ways to host a more successful sales demo by using images.
5. Digital Marketing Report Templates
If you’re a SaaS or e-commerce business, I don’t have to tell you how important digital marketing is. It’s the thing that can make or break many small businesses.
In order to scale and grow your business , it’s important to make informed, deliberate digital marketing decisions.
That means always looking for ways to improve your search rankings, grow your social media engagement, and optimize your ad campaigns.
A ‘ digital marketing report ‘ is a pretty broad term for a report that could be an overview of all your digital marketing channels or one particular channel.
A digital marketing report that covers all your main marketing channels could include any (or all) of the following data:
- An overview of your current digital marketing strategy
- Your main marketing goals and whether or not they are being met
- An overview of your conversion metrics, including the number of leads, paid vs. organic leads, and your cost per conversion
- An overview of your traffic metrics, organized by channel
- An SEO overview , including any chhttps://growthbarseo.com/anges in rankings for target keywords
- An overview of PPC campaigns you’re running, including clickthrough rate, ROI and cost per click
- An overview of your social media channels, including engagement metrics and leads from specific channels
For example, take a look at this digital marketing report template that dedicates one page to each channel. Note how the company’s branding has also been incorporated into the design by using the brand’s colors and visuals that reflect the computer theme:

In a digital marketing report that focuses on one specific marketing channel, you will probably want to go more in-depth into each metric.
For example, in a social media report, you should cover:
- A comparison of your performance on specific social media channels like Facebook, Twitter and YouTube (you could try visualizing it with a comparison infographic )
- Specific engagement metrics like impressions, clicks, subscriber count, likes and comments
- An overview of your followers, including demographic information like age, gender and profession
- Conversion metrics from each specific social media channel
The below social media report visualizes some of these key metrics.
As a consultant, you may be gifted in social media marketing but totally flummoxed by all things design. Look better than you are by using the above template. It’ll help you present your findings in a way that’s effective and professional, while still managing to be playful and engaging.
If you’re concerned about organizing information by channel, here’s an example of a social media marketing report presentation that uses colored columns to make it easy to scan for a specific channel’s metrics:

A few digital marketing report best practices:
- Provide an overview of the performance of all your channels, or a particular channel
- Organize your report by channel (“Organic Search”, “Social Media”, “PPC”) or by specific campaigns/projects
- If your report is long enough, include a table of content to make it easier for readers to navigate your report
- Use bar charts and tables to compare your performance on different marketing channels
- Use icons to emphasize key information and visualize different channels (for example, different social media networks)
- Try to communicate your information concisely and focus on only one topic per page or slide
Related : Our post on what is a marketing plan and how to write and design one for maximum effectiveness.
6. Competitor Analysis Templates
Get the attention of marketers with a competitor analysis report. The best reports show exactly what a company must face off (and beat) to be successful.
A competitor analysis report usually has the following sections:
- Product summary
- Competitor strengths and weaknesses
- Competitor strategies and objectives
- Outlook: is the market growing? Flat? Splintering into niche segments?
The following competitor analysis template neatly organizes these categories into compact sections and highlights important stats. Stakeholders can quickly compare them with their own company’s numbers and get an immediate sense of how they measure up.

Using a pre-designed competitor analysis template is also a great idea for consultants who want to set themselves apart from big consulting firms or boutiques. Visualizing data is a way to set yourself apart as numbers-focused, unique and innovative, as in this business report example.

A few competitor analysis report best practices:
- If you’re listing all competitors, add those entering the market in the next year as well as indirect competitors who sell to the same customers as yours.
- Find customer satisfaction surveys for competitors (usually carried out by trade press) and include their findings.
- Talk to the sales department to get a sense of the competitor’s customers.
- Do informal research on the competitor’s strengths and weaknesses. Talk to journalists who cover this specific industry. Don’t just rely on online information.
Related : Our post on how to create a competitor analysis report (with templates).
7. Case Study Templates
One of the business report examples on our list is the business case study. Though not a report exactly, a case study analyzes a particular aspect of a company or a situation it faced. A consultant may need to write one as part of a corporate training program they’re developing.
Case studies usually focus on one of these situations:
- Startup or early-stage venture
- Merger, joint venture, acquisition
- Market entry or expansion
- New project or product
- Pricing optimization
- Profitability
- Industry landscape
- Growth strategy
What makes case studies unique is how they tell a story. They include background information on the company, a protagonist or key players, the situation and outcomes.
The below case study template has plenty of space for this narrative while using icons and numbers to highlight key details.

Make sure to include a conclusion that contains your key findings. Why did the protagonist make the decisions she made? What were the outcomes? What can we learn from this? Circle back to the key question the case study raises and answer it.
Business case study template
Business case studies are usually teaching tools to show how real companies approached a particular scenario or problem. The case study usually reflects a business theory and demonstrates its real-life application.
For example, the following business case study template shows how a crafts retailer uses earned media to drive engagement-heavy traffic.

This is another version of the above case study. Notice the changes in branding in this business report example that sets it apart from the previous template.

Marketing case study template
Case studies are a powerful form of marketing as they show a potential customer how existing customers are already using your product or service to meet their goals.
For example, this social media marketing case study illustrates how Toy Crates used content marketing to radically increase their sales:

A few case study best practices:
- Outline any constraints and challenges the protagonist of the case study faced that affected her decision (such as a tight deadline).
- Attach supporting documentation, such as financial statements.
- Include an original title, such as “Design Thinking and Innovation at Apple.” The title should mention the company and the subject of the case study.
Related : Our post on how to write and design a case study .
8. Growth Strategy Templates
Setting goals for your business might seem easy in theory… but setting ambitious yet realistic goals can actually be quite challenging.
At Venngage, we follow these 5 steps to set our goals:
- Identifying and set high-level goals.
- Understand which inputs and outputs impact those goals.
- Run experiments to impact those inputs.
- Validate those experiments.
- Foster accountability for the results within the team.
For a more in-depth look at this process read our growth strategy guide .
For example, if you’re a SaaS company, your high-level goals would probably be a specific number for revenue, a number of daily active users or employee count, like in the business report template below:

Once you’ve identified your high-level goals, the next step is to identify your OKRs (Objective Key Results), the metrics that impact your goals. Generally, you will probably want to break down your OKRs by channel.
So, if one of your goals is to hit a certain number of daily active users, your OKRs could be organized by:
- Acquisition OKRs, like organic traffic and paid traffic
- Conversion OKRs, like conversion rate
- Retention OKRs, like retention rate
Once you’ve identified your OKRs, you can come up with experiments to run that will impact those OKRs.
At Venngage, we use a weekly sprint to plan, execute and analyze our growth experiments. But I know other companies that use longer sprints, like two-week or month-long sprints.
Before you run an experiment, you should validate that it’s an experiment worth running. You can do that by identifying which goal it impacts, what resources the experiment will require, and how much effort you anticipate it will take to run the experiment.
This is the exact marketing sprint validator template that our marketing team uses when we schedule growth experiments:
After you’ve run a growth experiment, it’s extremely important to track your results.
At the end of every sprint, take a good chunk of time to analyze your experiments to see what learnings you can take from them. Then, classify an experiment as a “Winner” or “Loser” based on whether or not the results lined up with your hypothesis.
You can use your results from the sprint that just ended to inform your experiments in the upcoming print.
Here’s an example of a sprint release and results template that you could use. Note how each experiment is owned by a team member to foster accountability for the process and results:

A few growth strategy report best practices:
- Divide your growth strategy reports into color-coded columns based on goals, OKRs, or stages in a sprint
- Use icons like checkmarks and x’s to identify winning experiments and losing experiments
- Include brief descriptions on each template, to make it easy to understand
- Attribute each growth experiment to a team member, to foster accountability for the process and results
- Use your company colors, fonts and logo to maintain consistent branding across all of your communications
Related : Our complete guide to developing a growth strategy checklist.

9. Market Research Report Templates
Even after you’ve launched your business, it’s a good idea to do regular market research. You can use your research to plan and refine your marketing strategies, to identify new prospective customers and product plan.
Market research generally involves gathering information about the needs, problems and wants of your customers. This research can help you come up with your customer personas and specific problems you want to solve with your product or service.
You can conduct market research in two ways:
- Qualitative research (calls, focus groups)
- Survey research
For example, many consultants struggle to get buy-in from various stakeholders. The boss may be constantly changing the scope of the project based on a whim, such as the latest article he’s scoured from the internet! Employees may be set in their ways and resistant to incorporate consultants into their workflow.
One way to get clients on board and build trust is to provide stats and research that support your recommendations.
Here’s a market research business report example that lays out the industry landscape and gives clear guidance on the way forward, all backed up by facts.

This cheerful, icon-heavy market research report should help energize reluctant stakeholders. Packaging new (and sometimes daunting) information in fresh ways can help break through resistance.

You may also want to look at competitor statistics and industry trends. This template includes a competitor case study, including website analytics, and a SWOT analysis :

When it comes to creating your market research report, you may want to do an in-depth overview of all of your market research. Or you may want to focus on one area of your research, such as your survey results.
Survey Report Template
This survey report template helps visualize your findings; the pictogram and chart make the findings easy to understand.
The one-slide market research report identifies the demographics of the survey participants. The report categorizes participants by their jobs, locations, and the topics that they find most engaging. Note how each persona is visualized using an icon:

This business report example highlights how you can give your team and stakeholders a quick overview of your main market and what topics they’re interested in.
One of the purposes of a market research report is to present any conclusions that you came to after analyzing the data.
These could be conclusions about who your target customers are, areas where you can expand your business, and customer needs that aren’t currently being met. The below business report example visualizes this data and also provides space to draw your own conclusions.

Here’s an example of a market research report template that emphasizes key findings in the larger text before providing supporting data:
A few market research report best practices:
- Use icons to illustrate your customer personas
- Use charts and graphs to compare demographic information like customer age, gender, location, and occupations
- Include the main conclusions you came from after analyzing your data
- If your market research report is long enough, include a table of contents
- Include a brief summary of your data collection methods , including the sample size
10. White Paper Templates
White papers are great tools to educate and persuade stakeholders. Consultants can also use them to improve their reputation vis-a-vis big consulting firms and boutique firms or use them as lead magnets in Facebook ads etc.
As always, a polished design is much more likely to engage senior leaders or potential clients.
A business report template or consulting report template is the fastest way to produce something that’s both attractive and easy to understand.
The below consulting report example has a full page dedicated to visuals. It’s the perfect way to break up the text and let it breathe. It also reinforces the information.

Browse our library of thousands of professional, free stock photos to swap in images that suit your topic best. Or upload your own.
Our editor makes it simple to adapt any of our business and consulting report templates to your needs. Change the text, fonts, photos, icons, colors, anything you want.
The next business report template is perfect for marketers and marketing consultants. It has an inviting and fun (but still professional) cover page that quickly communicates the content marketing process using icons.

Venngage has an extensive library of thousands of custom, modern and diverse icons you can swap into the above consulting report example. For instance, you could add the Twitter or Facebook logo or a “thumbs up” icon.
Then, click on the template’s chart or graph (pages four and five) to add your own data.
Struggling with organizing information in your reports? It’s important for consultants and marketers to find a way to communicate key takeaways, and not overwhelm your reader with data.
The below consulting report template uses filled text boxes and icons on the third page to highlight top findings.

Different-colored headers also help create a hierarchy of information and add more variety to the design.
A few white paper best practices:
- Create an eye-catching white paper cover page using a background in bold color, photos or icons.
- Add a key takeaways section, with a header and bullet points.
- Visualize data using charts and pictograms in order to highlight key data.
- Incorporate your branding into your white paper template (brand colors and logo).
Related : Our blog post with 20+ white paper examples for even more templates and design tips.
11. Project Plan Templates
A project plan is the best way to keep a project on track.
But, showcasing the steps towards completing a project and showing how each step is actionable and measurable can be tough.
This is especially difficult if you’re a consultant and you don’t have company templates to rely on.
The below project plan template is a simple way to visualize what needs to happen, and when.

The above highly organized project plan template uses bar graphs, icons and color-coding to present information in an accessible way. Once you enter the editor, click on the bar graph to customize the schedule.
The project timeline below also uses icons and color-coding to organize information, though in a slightly different way.
Projects suffer when there’s confusion about deadlines and what’s required at each step. This timeline from a business report sample makes it crystal clear what tasks belong to what step and how long each step should take.

A timeline is a perfect way for your team or client to refer back to the project schedule without having to read through tons of text.
You can also revise your timeline as the project progresses to reflect changes in the schedule.
The below consulting report template has a more traditional format for a project plan. Still, like the timelines, this business report sample relies heavily on visuals to create an easily scannable and understandable project overview.

Scope creep is the enemy of any project’s success (and the bane of many consultant’s existence). That’s why it’s so important to define the project from the very beginning. The consulting report template above has a section to do just that.
Of course, projects change and evolve. The project report below will help you raise any issues as soon as they happen and present solutions. That way, stakeholders can make a decision before the project schedule is seriously derailed.

Check out our blog post with 15+ project plan templates for even more examples and design tips.
A few project plan best practices:
- Plot your project schedule visually using a timeline.
- Use color to categorize tasks and milestones.
- Use icons to illustrate steps in a process.
- Insert charts to track the duration of each phase of a project.
- Pick a flexible template that you can update as the project progresses and things change.
Related : Our post on the four phases of the project life cycle .
12. Business Proposal Templates
A business proposal is a document that presents your product or service as the solution to a client’s problem. The goal of a business proposal is to persuade a prospective client to buy your product or service. These proposals can be either solicited or unsolicited.
The contents of a business proposal report will vary depending on the problem.
Typically, a business proposal will include these sections:
- Information about your company (mission, qualifications, competitive edge)
- A detailed description of your client’s problem
- The cost of your product/service
- The methodology of how you propose to solve the client’s problem
- A timeline of your approach to solving the problem
A few business report examples and design tips:
Create an engaging title page for your business proposal. Think of it as the cover of a book or a movie poster. This will be your prospective client’s first impression of your business.
Use a design that tells a story about your company’s mission and the people you serve. For example, the cover for this business proposal template shows a happy team working together:

Meanwhile, this simple business proposal example uses icons to illustrate what the company does. The motif is carried throughout the rest of the proposal design:

Use visuals to highlight the emotion behind the problem
Businesses are made up of people, and people are emotionally charged. When identifying the problem, use imagery to highlight the frustration, confusion, or dissatisfaction behind the problem. This will show empathy towards the people you’re proposing your solution to.
This business report sample page from a business proposal contrasts one image to illustrate the “problem” with a more cheerful image for the “solution”:

This marketing business proposal uses a variety of visuals like icons, bold typography and photos to tell a story:

Related : Our post on consulting proposal templates or our guide to creating a business proposal .
How to create a business report in 6 steps?
Creating a business report can seem daunting, especially if you’ve never done it before. don’t let the word “business” intimidate you – these steps can be used for writing a report in any field!
Step 1: Define the purpose and scope of your report
Know the purpose of your report. Are you aiming to share the results of a project? Analyze performance? Recommend specific actions? Whatever the goal, keep it in mind as you go through the process. Also, consider the scope of your report. Decide what information you’ll be including, as well as what you can leave out.
Example: Let’s say your boss wants a report on your team’s sales performance during the last quarter. Your purpose might be to analyze the numbers and identify trends, areas for improvement, or opportunities for growth.
Step 2: Gather relevant data and information
Now that you know what you’re aiming for, it’s time to gather the information you’ll need. This might involve pulling data from internal systems, interviewing colleagues, or even conducting your research. Remember, the quality of your report depends on the accuracy and relevance of the information you provide, so double-check your sources and make sure you’ve got everything you need.
Example: For our sales performance report, you’ll need to collect data on product sales, individual and team performance, and any factors that may have influenced sales during the quarter.
Step 3: Organize your content
Next up is organizing all that information into a logical and easy-to-follow structure. This will depend on the specific requirements of your report, but some common components are an introduction, executive summary, main body, conclusion, and recommendations. A clear and logical structure helps readers easily understand and follow your report.
Example: In a sales performance report, you might start with an executive summary highlighting sales growth (or declines), outline individual team member’s performance, and then delve into a more detailed analysis of factors and trends.
Step 4: Write the report
When writing your report, start by developing a clear and concise writing style, avoiding jargon and buzzwords. Keep your audience in mind – make sure your report is easily digestible for your intended readers.
Example: When writing about sales performance, share facts and figures in simple terms that everyone can understand. Instead of saying, “Our sales team demonstrated a 12.3% compound annual growth rate,” say, “Our sales team increased their sales by 12.3% each year.”
Step 5: Add visual aids
To make your report more engaging and easier to understand, consider adding visual aids like graphs, charts, or images. These can help break up large blocks of text and highlight key findings or trends.
Example: For your sales performance report, you might create a bar chart showing sales growth over time or a pie chart displaying individual team members’ contributions.
Step 6: Review and refine
Last but not least, review your report. Does it achieve the purpose you set at the beginning? Are there any gaps in the information? Are there areas that could be clearer or more concise? Address any issues you find and refine your report until it meets your goals and is easy to understand for your target audience.
Example: In your sales performance report, if you find that you haven’t adequately explored the impact of a new product launch on sales, go back and add that analysis to provide a more comprehensive view.
What are the types of business reports?
Different types of business reports cater to various purposes, including monitoring performance, making decisions, and more, offering a range of options beyond standard reports.
1. Informational reports
The primary purpose of informational reports is, well, to inform. These reports provide all the nitty-gritty details of specific aspects of your business without any conclusions or opinions.
Examples include daily sales reports, inventory levels, or even project updates. This is the essential “just the facts, ma’am” type of report you need to stay in the loop.
2. Analytical reports
Analytical reports give you a more in-depth look at the data to help you make decisions. These reports come with all the bells and whistles – charts, graphs, and recommendations based on thorough analysis. Analytical reports are what you whip out when you need to decide whether to invest in a new project, evaluate your marketing efforts, or diagnose challenges within the company. The goal of such a report is to help you make smarter decisions for the growth and development of your business.
3. Summaries & reviews:
If you’re a little short on time and need a quick overview of your business’s performance, summary reports are your best bet. These reports condense the crucial details from other reports at regular intervals (monthly, quarterly, or annually) and present them in a digestible format.
4. Research reports
As the name suggests, these in-depth reports dig into specific topics or issues relevant to your business. Research reports are great when exploring new markets, considering new product development, or requiring a detailed evaluation of business practices. These reports act as guides for making major decisions that could significantly impact your company’s direction and success.
5. Progress reports
Let’s say you’ve got a fantastic project idea underway. You’ll need to keep track of every stage of it to ensure it’s smooth sailing ahead. Enter progress reports. They track the achievements, setbacks, and future plans of ongoing projects. These are essential for keeping everyone – from employees to investors – in the loop.
Business report template FAQs
1. what are the best practices for creating a business report.
You could open up Google doc, record your metrics and make a few points of analysis, send it to your team and call it a day. But is that the most effective way to report on your findings?
Many people may not even read those types of reports. Not to mention, a plain old report probably won’t impress stakeholders.
It’s important to brand yourself (and stand out from your competition). And then there’s the ever-important need to create buy-in from stakeholders and convince them of your recommendations.
That’s why it pays to make your reports as engaging as possible. That means visualizing data , processes , and concepts to make them easier to understand and more fun to look at, as you’ve seen from the business report examples in this post.

You can do that easily by getting started with a business report template or consulting report template .
There are two big reasons why it’s a good idea to create a highly visual business report:
- You will be able to organize, analyze and summarize your findings .
- You will be able to communicate your reports more effectively with your team, stakeholders and customers.
For example, the below business report template shows four different ways you can visualize information. It’s much more captivating and easily digested than a block of text.
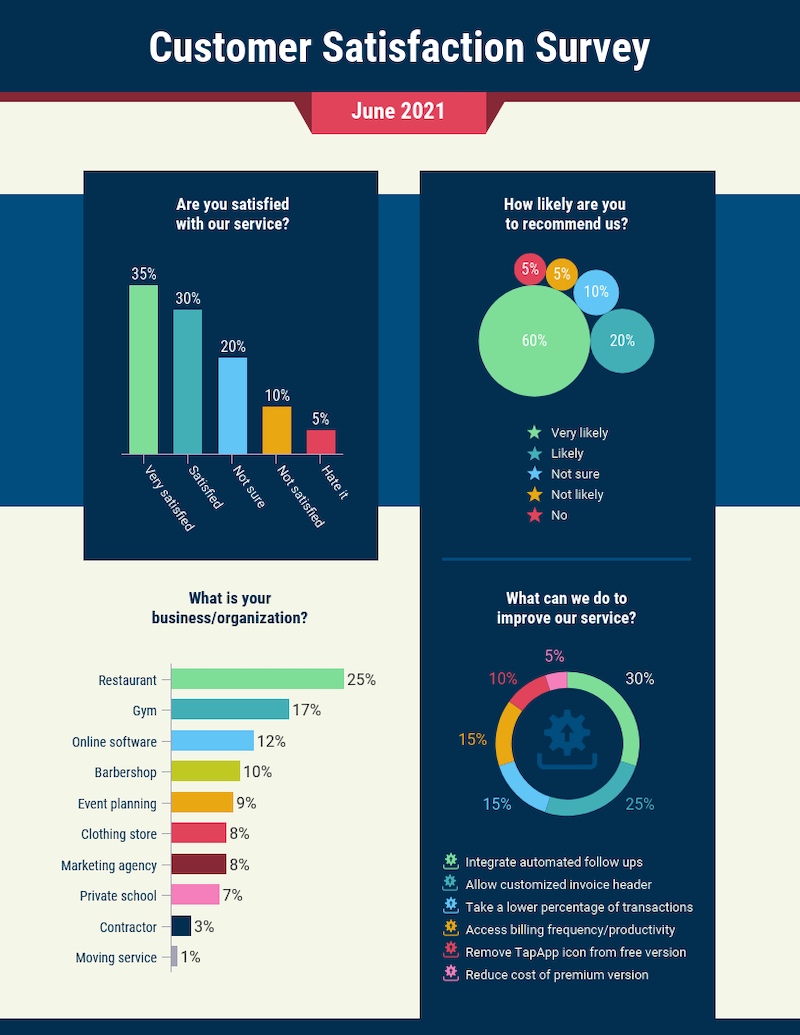
And don’t worry about how time-consuming designing a report might be. If you start with a solid business report template, you can repurpose that template over and over again.
Use the template as a framework, then customize your information and design to fit your specific needs. Then, use a chart tool to convert cumbersome data into clear visuals.
Just like in the above business report sample, you’ll have a succinct, powerful (and polished) report that stakeholders can understand at a glance.
2. How do you design a business report template?
Incorporate your branding into the design
Part of building a strong brand is using consistent branding across all of your content, both internal and public-facing. You can incorporate your branding into your business report design by importing your logo and using your brand colors and fonts.
Our My Brand Kit feature automatically imports company logos and fonts from any website. You can then apply them to your design with one click.
Stick to only one topic per page or slide
When creating a report, it’s easy to try and cram a bunch of text onto one page. But then you run the risk of creating an impenetrable wall of text.
Instead, focus on only one topic per page or slide. If you find that even that makes your page look too cramped, then try breaking up your information into two pages or looking for ways to better summarize your information .
Put functionality first
When you’re designing a business report, you should look for opportunities to visualize data and creatively present information. That being said, the primary goal of your business report should still be to communicate information clearly.
Use design elements such as icons or fonts in different sizes, weights and colors to highlight, emphasize and categorize information, not obscure it. If a page you’re working on looks cluttered or confusing, take another stab at it.
Remember that functionality comes first, and that includes using the right visuals for your information.
3. What is the best business report maker?
You can make a business report online using a number of tools. As we have mentioned, a great business report is visually appealing, includes icons, images, clear fonts, easy-to-understand charts and graphs, as well as being branded.
Venngage is the one-stop design solution when it comes to creating reports. The business report examples in this article highlight how easy it is to design a variety of reports for every type of organization and activity. Make design simple by using Venngage.
More business communication guides:
- The Ultimate Guide to Consulting Proposals (2024)
- 20+ White Paper Examples [Design Guide + White Paper Templates]
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

How to Write Business Reports That Make an Impact
Learn how to write a corporate report that stakeholders love from structure to final touches, from how to start to how to conclude, and build your authority.

Jackie Plaza
6 minute read

Short answer
How to write a business report.
- Understand the Purpose: Identify the report's objective and audience.
- Conduct Research: Gather relevant data and information.
- Create an Outline: Organize your thoughts and structure your report.
- Write the Report: Start with a draft, focusing on clarity and conciseness.
- Review and Revise: Proofread, edit for clarity, and ensure accuracy of data.
- Finalize: Prepare the final version, ensuring it's professionally presented.
Effective business reporting drive decision making
Business reports, or corporate reports, are more than just documents; they're tools that communicate vital information, drive decisions, and shape the future of your company.
They're your voice in the corporate world and they lay the foundations for your authority in the eyes of stakeholders, investors, and partners.
In this comprehensive guide on business report writing. We'll cover everything from the basics to specific report types, with actionable tips and examples.
This guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to write compelling corporate reports that move hearts and move the needle.
Let's dive in!
What is the role of business reports in corporate communication?
Business reports are the backbone of corporate communication. They provide a reliable, consistent source of information that drives strategic decisions. These reports communicate vital data to stakeholders, investors, partners, and customers.
corporate reports are a key communication tool that fosters transparency, promotes accountability, and guides decision-making within a business.
What is the accepted structure of business reports
Every great report follows a structure. Let's decode this blueprint. The basic structure of a corporate report typically includes the same sections as I cover below.
But the exact structure can vary depending on the type of corporate report and the specific requirements of the company.
1. Title Page: This is the first page of the report that includes the title of the report, the name of the company, the authors, and the date of the report.
2. Executive Summary : This is a brief overview of the report, summarizing the main points, findings, and recommendations. It should be concise and informative enough that a reader can understand the gist of the full report without reading it.
3. Table of Contents: This section lists the main headings and subheadings of the report along with their page numbers to help readers navigate through the document.
4. Introduction: The introduction provides background information, states the purpose of the report, and outlines what will be covered.
5. Body: This is the main part of the report, where the information is presented in detail. It's usually divided into sections and subsections with headings and subheadings. The body of a corporate report often includes information about the company's operations, financial performance, and strategic initiatives.
6. Conclusion: This section summarizes the findings or results discussed in the body of the report. It should tie together the main points and show how they support the report's purpose or objective.
7. Recommendations: Based on the findings in the report, this section provides suggestions for future actions. Not all corporate reports will include this section—it depends on the purpose of the report.
8. References/Bibliography: If any external sources were used in the report, they should be listed here.
9. Appendices: This section includes any additional information that is relevant but not necessary to include in the main body of the report, such as detailed financial tables, survey results, or interview transcripts.
How to begin a business report
Starting can be tough, but with the right approach, you'll be off to a great start.
Understanding Your Purpose and Audience: Before you start writing, identify your report's purpose and audience. It's like setting a GPS for your report—you need to know your destination and who's coming along for the ride.
Conducting Preliminary Research: Research is the fuel for your report. Gather all necessary data and information before you start writing. It's like stocking up for a long journey.
Drafting a Report Outline: An outline is your report's skeleton. It helps you organize your thoughts and ensures you cover all necessary points.
How to conclude a business report
Concluding your report is as important as starting it. Let's wrap things up effectively.
Summarizing Your Key Findings: Recap your report's key findings. It's like the highlight reel at the end of a sports game.
Discussing the Implications: Discuss what your findings mean for your company. This is where you interpret the data and explain its significance.
Providing Actionable Recommendations: Based on your findings, provide recommendations. This is your chance to suggest next steps and influence future decisions.
Tips for effective business report writing for external stakeholders
Crafting corporate reports for external stakeholders like investors, clients, and partners requires a strategic approach.
These audiences have different interests and needs compared to internal stakeholders, and your report should reflect that.
Here are some tips to help you create compelling business reports for external stakeholders:
1) Understand your audience
First and foremost, know who you're writing for. Investors might be interested in financial performance and growth prospects, clients may want to know about your products or services, and partners could be keen on collaborative achievements.
Tailor your content to meet their specific interests.
2) Be transparent and honest
External stakeholders value transparency. Be open about your successes and challenges. Honesty builds trust and shows that you're a reliable partner.
3) Use clear and concise language
Avoid jargon and complex language. Your report should be easy to understand, regardless of the reader's background. Remember, clarity is king in business communication.
4) Highlight key points
With the potential for numerous reports landing on their desk, external stakeholders appreciate brevity. Highlight key points and use summaries to help them quickly grasp the essence of your report.
5) Use visuals
Graphs, charts, and infographics can convey information more effectively than text alone. They can help stakeholders understand complex data at a glance.
6) Provide context
Don't just present data—interpret it. Explain what the numbers mean for your business and why they should matter to the stakeholder.
7) End with a strong conclusion
Summarize your main points and end with a strong conclusion. If appropriate, include a call to action, such as an invitation to a meeting or a request for feedback.
8) Proofread
Lastly, ensure your report is free of errors. Mistakes can undermine your credibility and distract from your message.
Great report content must be complemented by great design
Below you’ll find tried and tested interactive report design templates . These will bring your content to life and make it an engaging read for your audience.
These templates will save you time and expense on content production, but also make your reports much more memorable and share-worthy.
Grab a template!
Hi, I’m Jackie, Creative Marketing Specialist at Storydoc, I write on everything business presentations. I love to research and bring to light critical information that helps marketing, sales, and design teams get better results with their collateral.

Found this post useful?
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Get notified as more awesome content goes live.
(No spam, no ads, opt-out whenever)
You've just joined an elite group of people that make the top performing 1% of sales and marketing collateral.
Create your best report to date
Try Storydoc interactive presentation maker for 14 days free (keep any presentation you make forever!)

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Business Communication - How to Write a Powerful Business Report
Business communication -, how to write a powerful business report, business communication how to write a powerful business report.

Business Communication: How to Write a Powerful Business Report
Lesson 8: how to write a powerful business report.
/en/business-communication/how-to-write-a-formal-business-letter/content/
How to write a powerful business report

When a company needs to make an informed decision, it can create a business report to guide its leaders. Business reports use facts and research to study data, analyze performance, and provide recommendations on a company's future.
Watch the video below to learn how to write and format a business report.
The basics of a business report
Business reports are always formal , objective , and heavily researched . Every fact must be clear and verifiable, regardless of whether the report focuses on a single situation or examines the overall performance of an entire company.
Because objectivity is crucial in a business report, avoid subjective descriptions that tell the reader how to feel. For instance, if sales were down last quarter, don’t say “Sales were terrible last quarter,” but rather let the sales data speak for itself. There should also be no personal pronouns, such as “I think we should invest more capital.” A business report should remain impersonal and framed from the company’s perspective.
The structure of a business report
Although the size of a report can range from one page to 100, structure is always important because it allows readers to navigate the document easily. While this structure can vary due to report length or company standards, we’ve listed a common, reliable structure below:
- Front matter : List your name, job title, contact information, and the date of submission. You can also create a title for the report.
- Background : State the background of the topic you’ll be addressing, along with the purpose of the report itself.
- Key findings : Provide facts , data , and key findings that are relevant to the purpose stated in the background. Be clear and specific, especially because the entire report depends on the information in this section.
- Conclusion : Summarize and interpret the key findings, identify issues found within the data, and answer questions raised by the purpose.
- Recommendations : Recommend solutions to any problems mentioned in the conclusion, and summarize how these solutions would work. Although you’re providing your own opinion in this section, avoid using personal pronouns and keep everything framed through the company’s perspective.
- References : List the sources for all the data you've cited throughout the report. This allows people to see where you got your information and investigate these same sources.
Some companies may also require an executive summary after the front matter section, which is a complete summary that includes the report’s background, key findings, and recommendations. This section lets people learn the highlights quickly without having to read the entire document. The size of an executive summary can range from a paragraph to multiple pages, depending on the length of the report.
As mentioned in Business Writing Essentials , revision is key to producing an effective document. Review your writing to keep it focused and free of proofreading errors, and ensure your factual information is correct and presented objectively. We also recommend you get feedback from a colleague before submitting your work because they can spot errors you missed or find new opportunities for analysis or discussion.
Once you’ve revised your content, think about the report’s appearance . Consider turning your front matter section into a cover page to add some visual polish. You can also create a table of contents if the report is lengthy. If you’re printing it out, use quality paper and a folder or binder to hold the report together. To diversify the presentation of your data, try using bulleted lists, graphics, and charts.
Example of a business report
To demonstrate the principles of this lesson, we’ve created a brief business report for you to review.
Let's start by looking at the first page of this two-page report.

The layout of the front matter is simple and effective, while the background sets the stage in a quick, specific manner. The key findings provide the main takeaways that warrant further investigation, along with a chart to add emphasis and visual variety.
Now let's look at the following page.

The conclusion features a little of the writer's opinion on the key findings, although the writing is still centered around the company's perspective. The recommendations are clear and supported by the data, while the references are thorough.
While business reports may seem intimidating, you have the ability to create a thorough, informative document through practice and careful research. Collect the facts and present them in an organized, objective manner, and you’ll help your business make informed decisions.
/en/business-communication/how-to-write-an-effective-business-email/content/
👀 Turn any prompt into captivating visuals in seconds with our AI-powered visual tool ✨ Try Piktochart AI!
- Piktochart Visual
- Video Editor
- AI Design Generator
- Infographic Maker
- Banner Maker
- Brochure Maker
- Diagram Maker
- Flowchart Maker
- Flyer Maker
- Graph Maker
- Invitation Maker
- Pitch Deck Creator
- Poster Maker
- Presentation Maker
- Report Maker
- Resume Maker
- Social Media Graphic Maker
- Timeline Maker
- Venn Diagram Maker
- Screen Recorder
- Social Media Video Maker
- Video Cropper
- Video to Text Converter
- Video Views Calculator
- AI Brochure Maker
- AI Document Generator
- AI Flyer Generator
- AI Infographic
- AI Instagram Post Generator
- AI Newsletter Generator
- AI Report Generator
- AI Timeline Generator
- For Communications
- For Education
- For eLearning
- For Financial Services
- For Healthcare
- For Human Resources
- For Marketing
- For Nonprofits
- Brochure Templates
- Flyer Templates
- Infographic Templates
- Newsletter Templates
- Presentation Templates
- Resume Templates
- Business Infographics
- Business Proposals
- Education Templates
- Health Posters
- HR Templates
- Sales Presentations
- Community Template
- Explore all free templates on Piktochart
- Course: What is Visual Storytelling?
- The Business Storyteller Podcast
- User Stories
- Video Tutorials
- Need help? Check out our Help Center
- Earn money as a Piktochart Affiliate Partner
- Compare prices and features across Free, Pro, and Enterprise plans.
- For professionals and small teams looking for better brand management.
- For organizations seeking enterprise-grade onboarding, support, and SSO.
- Discounted plan for students, teachers, and education staff.
- Great causes deserve great pricing. Registered nonprofits pay less.
What is a Business Report? (Examples, Tips and How to Make One)

According to a recent survey by Zapier , 76% of respondents said they spend 1-3 hours a day simply moving data from one place to another. Additionally, 73% of workers spend 1-3 hours just trying to find relevant data or a particular document. Another survey by TrackVia found that 44% of workers spend more than one day per week on manual, administrative tasks such as generating reports .
Fortunately, there are tools available to automate the report creation process and produce high-quality reports efficiently. However, it’s essential to understand the key factors that make a report effective and distinguish your report from the rest, without relying on plain Excel/PowerPoint tools.
Are you ready to take your report writing skills to the next level?
A business report is a document that presents information in a structured format, typically written for a specific audience or purpose. Business reports are used to convey data, research findings, recommendations, and other types of information in a clear, concise, and organized manner.
Business reports may be written for a variety of contexts. They may vary in length and complexity, depending on the type of information being presented and the intended audience.
You can also jump right into creating business reports by selecting a template and following along this guide, or create a report using our AI-powered report maker for free today.
Table of Contents
General business reporting templates, specialized business reporting examples, other reports, what makes a great business report format, what are the five main parts of a business report, how to present the report in a more visual way, and now, over to you.
- Progress reports : These are reports used to easily track progress on a particular project or activity, and can be divided into daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly progress reports.

- Feasibility reports: These are reports that assess the feasibility of a particular project or initiative, such as a new product or service.

- Executive Summary Reports: These reports provide a brief summary of a larger report in business management. They are typically used to provide key decision-makers with a quick overview of the report topic.

- Financial reports : These are reports that present financial information, such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, which measure performance of the company.

- Annual reports : These are reports that provide an overview of an organization’s performance over the course of a year, including company goals, new insights, and average revenue.

- Sales and Marketing Reports : These reports provide relevant information on sales and marketing activities, such as sales forecasts, customer overview demographics, marketing report and market research, typically created by sales rep.

- Human Resources Reports : These reports provide information on employee-related matters, such as recruitment, training, and performance management.

- Incident Reports: These reports document workplace incidents, such as accidents, injuries, or security breaches. They may be used for legal or insurance purposes.
- Environmental Reports: These reports assess the environmental impact of a company’s operations. They may include information on energy consumption, waste management, and carbon emissions.

- Investigative reports : These are reports that investigate a particular issue, such as a workplace incident or accident.

- Academic reports: This is an analytical report used in academic settings to convey research findings, such as lab reports, research reports, and case studies.
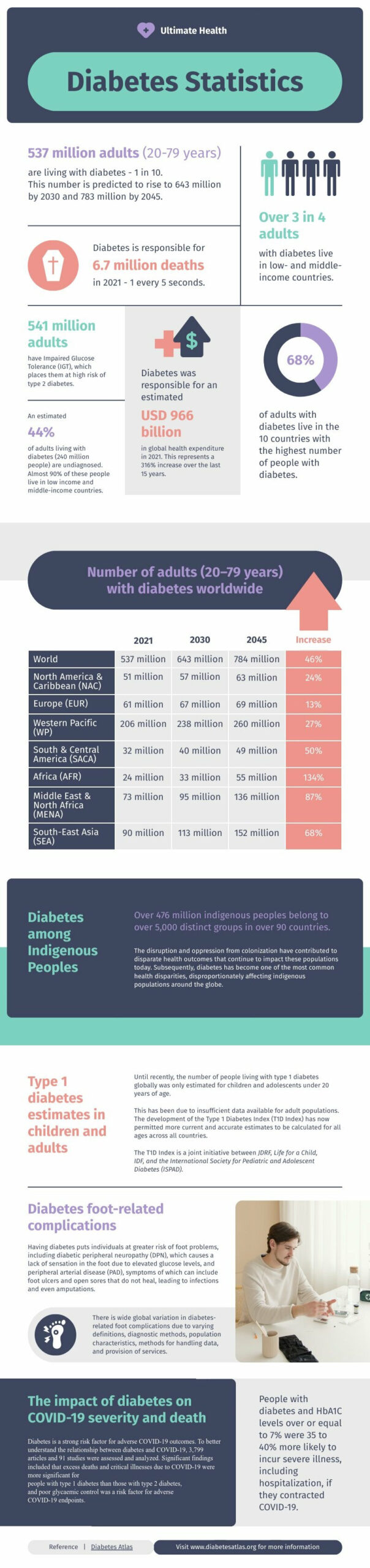
- Technical reports: These are reports that communicate technical information, such as engineering reports, scientific reports, and project reports. It may contain all the relevant explanatory reports and research methods.

There are several elements that make a great formal business report, including:
Clear purpose and scope
A report can contain a lot of information, it is important not to lose the bigger picture. It should be easy to access the report’s main points through a table of contents at the introduction.
Define the purpose and scope of the entire report : Determine the objectives of the report and the information that needs to be collected to achieve those objectives.
Accurate and relevant metrics/data
Identify the sources of information : Determine where the critical information can be found. Sources can include primary sources such as surveys, interviews, and experiments, or secondary sources such as books, articles, and online databases.
Collect the historical data: Gather the necessary data by conducting interviews, surveys, experiments, analytical reports, or other means. Be sure to record and organize the data in a systematic and organized manner.
The gathering of relevant data is often time consuming. It would be good to collaborate on this process and assign multiple stakeholders different portions of the report so that the information gathering isn’t spent on analytical reports by one individual only. Piktochart has the ability to help you collaborate in teams specifically for this purpose.
Comprehensive analysis
Analyze the data : Once the data has been collected, conduct an in depth analysis to identify patterns, trends, and relationships. Use statistical tools, software, or other analysis methods to make sense of the data.
Go from big picture to small details. It is good practice to create an outline of the report and what should be communicated in official document before going into the actuals of putting the report together.
Break the analysis down into multiple pages. Use a page to convey one main point instead of cramming in multiple charts and figures.
Clear and concise writing
Interpret and present the findings : Draw conclusions based on the data and present the findings in a clear and organized manner. Use charts, tables, graphs, and other visual aids to help convey the factual information.
For example, one may opt for the use of bullet points sparingly and opt to make the sentences shorter and without jargon. A visual layout of two columns may also help in some cases.
Effective communication in research report
A report can be consumed digitally or via print. If it’s consumed digitally e.g. in a single dashboard , you can provide a TLDR summary or explanatory report for the readers via email so that they would know what to expect.
Visual aids
The best option here is to go with diagrams, images, tables and charts that help to convey the main point of a particular page.
If the report is hosted online, it is also possible to include other videos or audio content to get the viewers interested.
Recommendations and conclusions
Revise and finalize the report: Review and revise the report to ensure that it is accurate, complete, and well-organized. Be sure to proofread for spelling errors, grammar mistakes, and punctuation.
It is important to address the concerns that the key decision maker has about the progress report and aid decision making process. The language and tone of the report should always be future-looking and positive. You can do this by balancing potential risks and key opportunity areas.
Professional formatting and presentation
Aim to use brand colors and fonts throughout the whole presentation. These “tiny” signals give the impression that the report has been professionally designed.
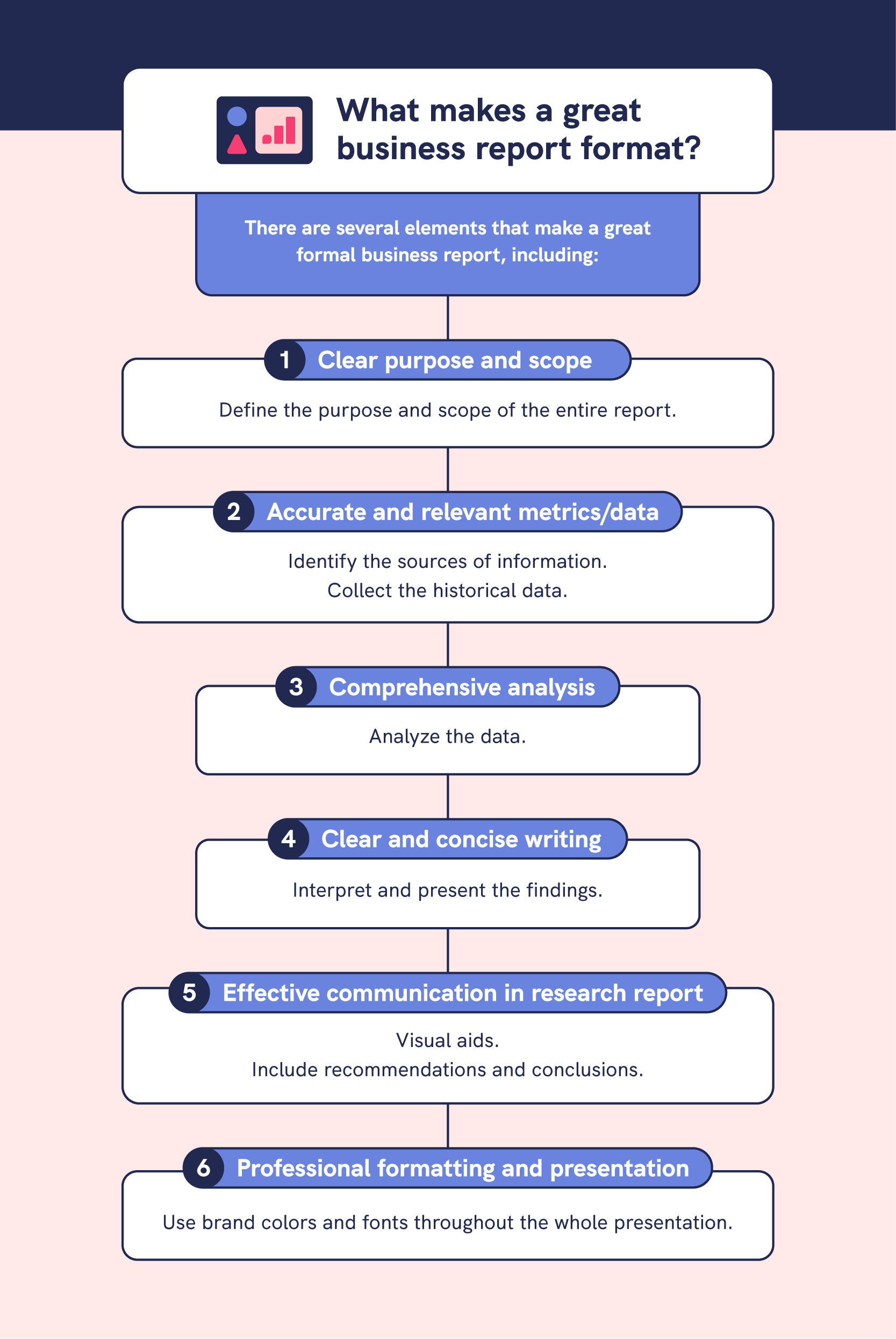
Business reporting typically includes:
- Introduction that provides background information. The title and table of contents can go here. Occasionally, it also includes some brief opening remarks from the leadership team.

- Main body that presents the data or findings. This can be broken down into several pages and it is best to present one salient piece of information per page. The aim is not to reduce the number of pages, but to go for concise writing so that there is a strong message per page.
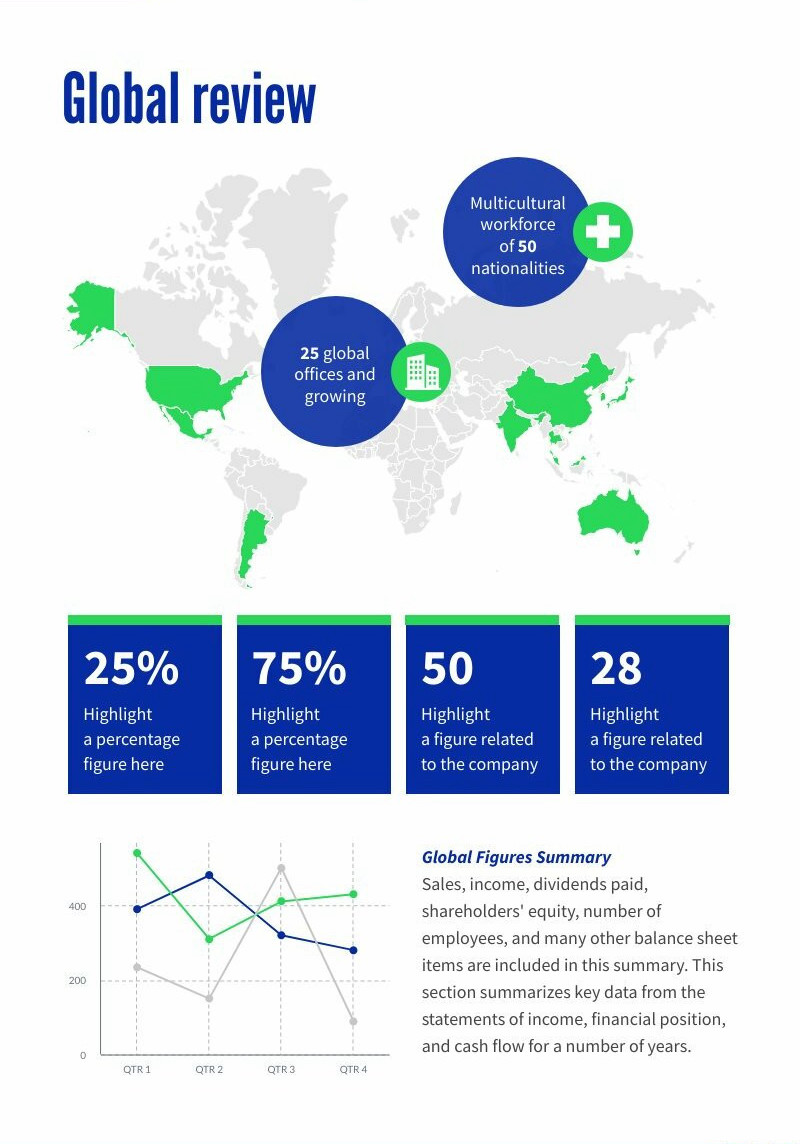
- Conclusion that summarizes the key points.

An important part of conclusion is recommendations for further action. A report would be incomplete if it does not bear any future-forward messages for the business/activity.

While there is no specific format that has to be followed, Piktochart has some great business report examples for you to get started. Sign up to access more professionally designed templates of presentations , infographics , social media graphics and more.
Use charts and diagrams
Visual aids such as pie charts, bar graphs, and line graphs can help to convey complex information in a clear and concise manner.
Choose the right type of chart or diagram
There are many different types of charts and diagrams available, including bar charts, pie charts, line graphs, scatter plots, flowcharts, and more. Choose the type of chart or diagram that best represents the data you are presenting and is most appropriate for your audience.


Keep it simple
While charts and diagrams can be useful for presenting complex information, it’s important to keep them simple and easy to understand. Avoid cluttering your chart or diagram with too much information, and use clear and concise labels and titles.
Use appropriate scaling
When creating a chart or diagram, it’s important to use appropriate scaling to ensure that the data is accurately represented. Make sure that the scale of the chart or diagram is appropriate for real value of the data you are presenting, and avoid distorting the data by using uneven scales.
Provide context
Charts and diagrams can be difficult to interpret without proper context. Make sure to provide context for your data by including clear and concise explanations of what the chart or diagram represents and how it relates to the rest of the report.
Use color strategically
Color can be a powerful tool for highlighting key data points or drawing attention to important information. However, it’s important to use color strategically and sparingly to avoid overwhelming your audience.
Use color sparingly
Color can help to highlight important information and make the report more visually appealing.
While color can be a powerful tool for emphasizing important information, using too much color can be overwhelming and distracting. Use color strategically to draw attention to key data points, headings, or other elements that you want to emphasize.

Choose colors carefully
When selecting colors, consider the target audience and purpose of the report.
Stick to a color scheme that is appropriate for the subject matter and aligns with the company’s branding. Avoid using too many bright or bold colors, which can be jarring to the reader.
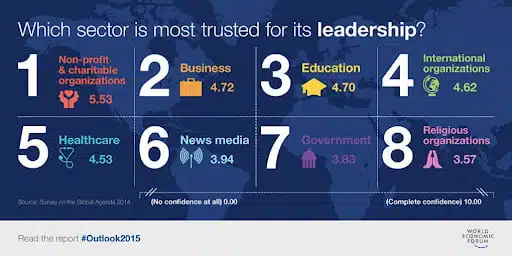
Use contrast
One of the most effective ways to use color in a business report is to create contrast between different elements. For example, use a bold color for headings or subheadings to make them stand out from the surrounding text.

Use color to organize information
Color can be a useful tool for organizing information and making it easier to scan. Consider using color to create sections or categories within the report, or to distinguish between different types of data.
Be consistent
To avoid confusion, it’s important to be consistent in your use of color throughout the report. Use the same colors for the same types of information, and make sure that the colors you use are consistent with the company’s in house format or branding guidelines.
Use a consistent layout
Using a consistent layout throughout the report broken down by headings and subheadings can help to make it more visually appealing and easier to follow.
A single-column format is often used because it is easier to read and allows for a more logical flow of information. It also allows for the use of larger fonts and more white space, which can help improve readability.
In some exceptions, some reports may use a multi-column layout, typically with two columns, if they contain a large amount of data or if the report is intended to be read on a digital device, such as a tablet or computer screen. A multi-column format can help improve the organization of the data and make it easier to compare information across different sections.
Choose an appropriate and concise length
Do not cram too much information within a single page. Here are some more helpful tips on the language that you can use for business reports.
Use active voice
Active voice makes your writing clearer and more concise, and it can help you communicate your ideas more effectively.
For example, instead of writing “The report was analyzed,” write “We analyzed such a report.”

Avoid overly technical language
While some technical language may be necessary, avoid using jargon or technical terms that your readers may not be familiar with. If you must use technical terms, provide clear definitions or explanations.
Use simple, clear sentences
Avoid long, convoluted sentences that are difficult to understand. Instead, use simple, straightforward sentences that clearly communicate your ideas.
Don’t use more words than necessary to convey your message. A sentence should not contain more than 20-30 words (unless you’re writing a technical or academic report).
The average length of an annual report is 10,000 words (50 pages) for a smaller company and 50,000 (150 pages+) words for an enterprise. Typically, not every page contains text, as some may have more charts/tables.

Use bullet points, tables, and graphs to help convey your ideas concisely.
Use appropriate tone
The tone of your report should be professional and objective. Avoid using emotional language or language that is overly informal.
For example, “I’m totally excited to announce that our new product is going to blow the competition out of the water! It’s absolutely amazing and customers are going to love it.”

This sentence uses informal language (“totally excited”) and emotionally charged language (“blow the competition out of the water,” “absolutely amazing,” “customers are going to love it”) that may not be appropriate for a business report.
Ultimately, the language you use in your business reports should be tailored to your audience and the purpose of the most professional business report itself. Consider who will be reading the formal business report and what information they need to know, and adjust your language accordingly.
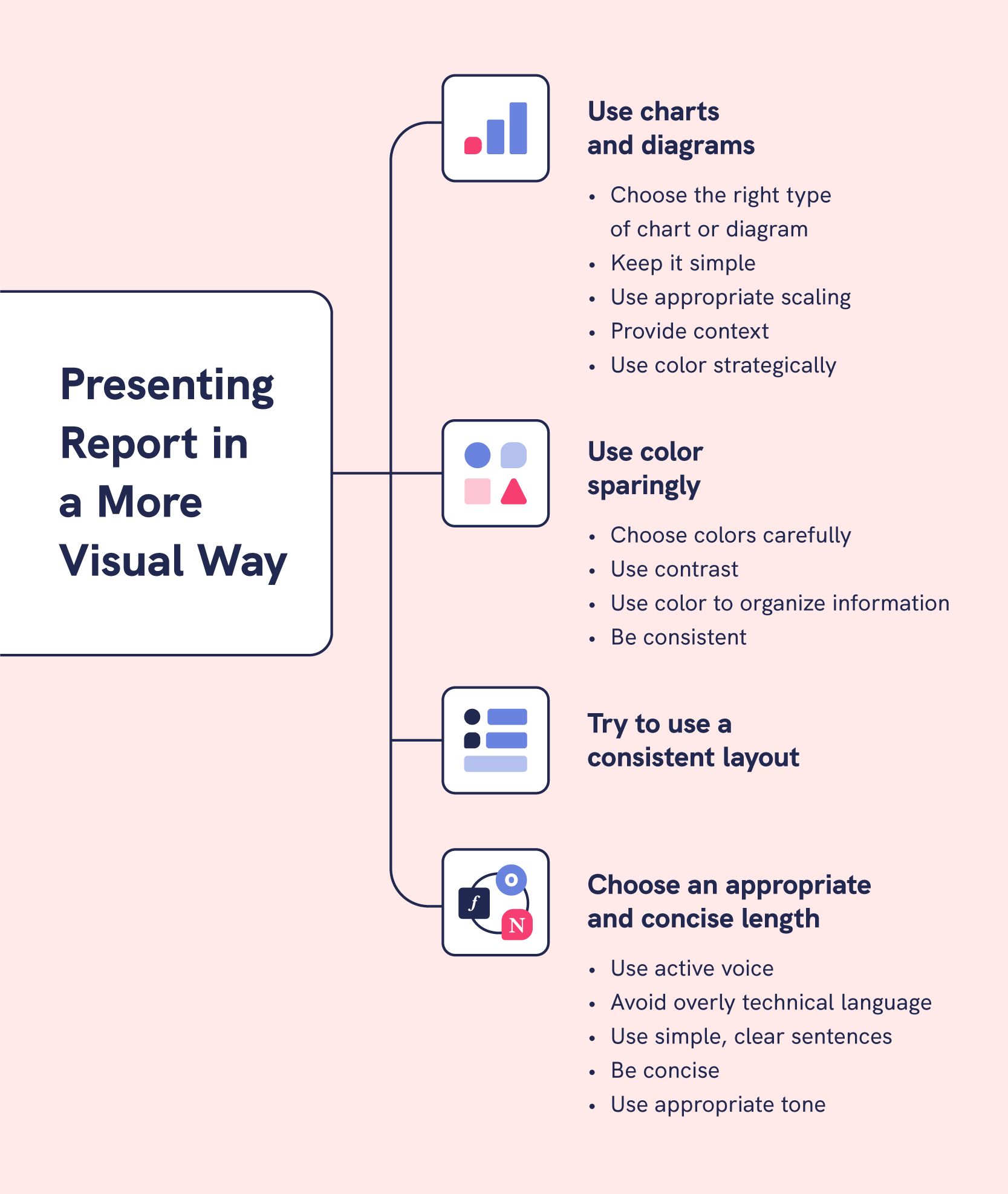
For more information, you can check out a step by step guide to create your business report sample. You can also browse our template gallery and select a template to get started.
CTA: Check out Piktochart’s business report template gallery to get you started! https://piktochart.com/templates/reports/

Other Posts
10 Best Sales Report Templates for Tracking Revenue, KPIs & Growth

10 Types of HR Reports (With Templates and Examples)

7 Captivating Report Design Ideas And Tips (With Templates and Examples)
How to Write a Business Report
A business report is a collection of data and analyses that helps make relevant information easily accessible to a company. There are many different types of business reports, but this guide will show you the basic outline.
Before You Begin:
- Think about your audience and their expectations, and plan your report accordingly. For example, are they expecting a formal or informal report? Do they have an understanding of the vocabulary/terms used? Do they require more background information? Do they need to be heavily persuaded?
- What is the purpose of the report? Make sure this is clear.
- Gather and organize your supporting information/data/visuals.
- Focus on the facts.
- Make sure to be clear and concise, so the report is easy for everyone to read and understand.
- Use a professional, standard font in a readable size.
Components of a Business Report
- Table of Contents: Depending on the length of the report, you might want to consider including a table of contents. This will make finding specific information easier for readers.
- Tip: Even though this is the first section, consider writing this section after you have finished the report. This will help you determine which points are the most important to address.
- Introduction: This section outlines what you will be going over in your report. It includes the main points, chosen report structure, and, most importantly, the objective of your report.
- Conclusion: In the conclusion, be sure to briefly summarize all of the main points in the order they were presented in the report.
- Recommendations: This section is where you provide your recommendations or suggestions based on the findings you noted in earlier sections. Indicate the potential benefits for the company to applying your suggestions.
- References: Be sure to cite all sources used in the report in this section.
- Appendices: In the Appendix, you can add relevant documents, surveys, graphs, etc. that you referenced in the report.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Structure a Business Report

- 4-minute read
- 4th November 2018
The content of a business report will depend on what you are writing about. Even the writing style may vary depending on who you are writing for (although clear, concise and formal is usually best).
However, there is a general structure that most business reports should follow. Read on below to find out what you need to include in your business report and how you should present it.
1. Title Page
Every business report should feature a title page . The title itself should clearly set out what the report is about. In addition, you would usually include your name and the date of the report on the title page.
Most reports begin with a summary of the key points within, including:
- An overview of what the report is about
- Data collection and analysis methods used
- The findings of the report
- Any conclusions or recommendations
In a short report, a paragraph or two should be enough. In a longer business report, though, you may want to include a full executive summary .
3. Table of Contents
Short reports may not need a table of contents, especially if you have included a summary. But any longer business report should set out the structure and what each section contains. Make sure that the headings here match the ones used in the report. You may also want to number the sections.
4. Introduction
This will set out the brief you were given when asked to write the report. Typically, this section should include:
- Background information (e.g. the business history or market information)
- The purpose of the report (i.e. what you hope to find out or achieve)
- Its scope (i.e. what the report will cover and what it will ignore)
Collectively, these are known as the ‘terms of reference’.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
5. Methods and Findings
If you are conducting original research, include a section about your methods. This may be as simple as setting out the sources you are using and why you chose them. After this, you will need to explain your findings. This section will present the results of your research clearly and concisely, making sure to cover all of the main points set out in the brief.
One tip here is to break the findings down into subsections, using headings to guide the reader through your data. Using charts and illustrations , meanwhile, can help get information across visually, but make sure to label these clearly so that the reader knows how they relate to the text.
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
The last main sections of your report will cover conclusions and recommendations. The conclusion section should summarise what you have learned from the report. If you have been asked to do so, you should also recommend potential courses of action based on your conclusions. If you are not sure what to suggest, think back to the objectives set out in your brief.
7. References
If you have used any third-party sources while writing your report, make sure to list them in a bibliography . This could include other business reports, academic articles or even news reports. The key is to show the reader what you have based your findings and conclusions upon.
8. Appendices (If Applicable)
Finally, you may have gathered extra documentation during your research, such as interview transcripts, marketing material or financial data. Including all of this in your main report will make it too long and unfocused, but you can add it to an appendix (or multiple appendices) at the end of the document. It will then be available should your reader need to see it.
Summary: How to Structure a Business Report
If you are writing a business report, aim to structure it as follows:
- Title Page – Include a clear, informative title, your name and the date.
- Summary – A summary of what the report is about, the data collection methods, the findings and any recommendations you want to make.
- Table of Contents – A list of the sections in the report.
- Introduction – A short section setting out the brief for the report.
- Methods and Findings – A description of any data collection and analysis methods used in the report, as well as the findings of your research.
- Conclusions and Recommendations – Any conclusions that you reached, plus recommendations for what to do next (if required).
- References – A list of any sources used in your report.
- Appendices – If you have used any supporting material (e.g. interview transcripts, raw data) while writing your report, you can include it in an appendix at the end of the document.
And don’t forget that a business report should be clear, concise and formal in tone. So if you would like help making sure that your business writing is easy to read and error free, just let us know .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Get help from a language expert. Try our proofreading services for free.
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
9-minute read
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Writing Formal Reports
While you may write much shorter, more casual reports, it’s helpful to go into a bit of detail about formal reports. Formal reports are modular, which means that they have many pieces. Most audience members will not read every piece, so these pieces should stand on their own. That means that you will often repeat yourself. That’s okay. Your audience should be able to find exactly what they need in a particular section, even if that information has been repeated elsewhere.
While it’s fine to copy and paste between sections, you will likely need to edit your work to ensure that the tone, level of detail and organization meet the needs of that section. For example, the Executive Summary is aimed at managers. It’s a short, persuasive overview of everything in the report. The Introduction may contain very similar information, but it focuses on giving a short, technical overview of everything in the report. Its goal is to inform, not to persuade.
Let’s take a look at some of the parts of the report in greater detail.
The title page provides the audience with the:
- This should appear 2 inches from the top margin in uppercase letters.
- Type “Prepared for” on one line, followed by two separate lines that provide the receiving organization’s name and then the city and state. Some reports may include an additional line that presents the name of a specific person.
- Type “prepared by” on one line, followed by the name(s) of the author(s) and their organization, all on separate lines.
- This date may differ from the date the report was written. It should appear 2 inches above the bottom margin.
The items on the title page should be equally spaced apart from each other.
A note on page numbers:
The title page should not include a page number, but this page is counted as page “i.” Use software features to create two sections for your report. You can then utilize two different types of numbering schemes. When numbering the pages (i.e., i, ii, iii, etc.) for a formal report, use lowercase roman numerals for all front matter components. Utilize arabic numbers for the other pages that follow. Additionally, if you intend to bind the report on the left, move the left margin and center 0.25 inches to the right.
Letter of Transmittal
A letter of transmittal announces the report topic to the recipient(s).
If applicable, the first paragraph should identify who authorized the report and why the report is significant. Provide the purpose of the report in the first paragraph as well. The next paragraph should briefly identify, categorize, and describe the primary and secondary research of the report. Use the concluding paragraph to offer to discuss the report; it is also customary to conclude by thanking the reader for their time and consideration.
The letter of transmittal should be formatted as a business letter . Some report writers prefer to send a memo of transmittal instead.
When considering your audience for the letter or memo of transmittal, make sure that you use a level of formality appropriate for your relationship with the reader. While all letters should contain professional and respectful language, a letter to someone you do not know should pay closer attention to the formality of the word choice and tone.
Table of Contents
The table of contents page features the headings and secondary headings of the report and their page numbers, enabling audience members to quickly locate specific parts of the report. Leaders (i.e. spaced or unspaced dots) are used to guide the reader’s eye from the headings to their page numbers.
The words “TABLE OF CONTENTS” should appear at the top of the page in all uppercase and bolded letters. Type the titles of major report parts in all uppercase letters as well, double spacing between them. Secondary headings should be indented and single spaced, using a combination of upper- and lowercase letters.
Executive Summary
An executive summary presents an overview of the report that can be used as a time-saving device by recipients who do not have time to read the entire report.
The executive summary should include a:
- Summary of purpose
- Overview of key findings
- Identification of conclusions
- Overview of recommendations
To begin, type “EXECUTIVE SUMMARY” in all uppercase letters and centered. Follow this functional head with paragraphs that include the above information, but do not use first-level headings to separate each item. Each paragraph of information should be single-spaced with double spacing between paragraphs. Everything except for the title should be left-aligned.
An executive summary is usually ten percent of the length of the report. For example, a ten-page report should offer a one-page summary. A 100-page report should feature a summary that is approximately ten pages.
The executive summary is usually seen as the most important part of the report, and it should be written last. When you’re writing the executive summary, imagine that you’re sitting across from your most important audience member. If you only have a few minutes to talk to them, what do you want them to know? What would be most persuasive?
Introduction
The body of a formal report begins with an introduction. The introduction sets the stage for the report, clarifies what need(s) motivated it, and helps the reader understand what structure the report will follow.
Most report introductions address the following elements: background information, problem or purpose, significance, scope, methods, organization, and sources. As you may have noticed, some parts of a formal report fulfill similar purposes. Information from the letter of transmittal and the executive summary may be repeated in the introduction. Reword the information in order to avoid sounding repetitive.
To begin this section, type “BACKGROUND” or “INTRODUCTION” in all uppercase letters. This functional head should be followed by the information specified above (i.e., background information, problem or purpose, etc.). You do not need to utilize any first-level headings in this section.Because this section includes background information, it would be the appropriate place to address the needs of audiences that may need additional knowledge about the topic. Provide definitions of technical terms and instruction about the overall project if necessary. If you are uncertain if your audience needs a particular piece of information, go ahead and include it; it’s better to give your reader a little bit too much background than not enough.
Discussion of Findings
The Discussion of Findings section presents the evidence for your conclusions.
This key section should be carefully organized to enhance readability.
Useful organizational patterns for report findings include but are not limited to:
- Best Case/Worst Case
- Compare/Contrast
- Journalism Pattern
Use a Best Case/Worst Case organizational pattern when you think that the audience may lack interest in the topic. When examining a topic with clear alternatives to your proposed solution, consider using a Compare/Contrast pattern. Geographical patterns work effectively for topics that are discussed by location.
When describing the organization of the report in the first paragraph, broadly identify how the material in the report is organized rather than state that the report uses a specific pattern (e.g. Chronology, Geography). For example, write, “The research findings address curriculum trends in three provinces: (a) British Columbia, (b) Alberta, and (c) Ontario,” not, “This report uses a geographical organizational pattern.”
Follow the first paragraph with a first-level heading. Use first-level headings for all other major parts of this section. First-level headings should appear in bold, uppercase letters. Center first-level headings, but align any second-level headings with the left margin. Type any second-level headings in bold, upper- and lowercase letters.
As you present, interpret, and analyze evidence, consider using both text and graphics. Take into account what will be easiest for your audience to understand.
Include citations for all quoted or paraphrased material from sources as well; check with your organization as to whether they prefer parenthetical citations or footnotes.
Integrating Graphics
Formal report authors use graphics to present data in different forms. Paragraphs of text and complex or numerical data tend to bog readers down, making graphics a beneficial enhancement. Graphics also make data easier to understand, so they sometimes make a stronger impact on the audience.
Knowing when—and how—to effectively employ graphics is the key to successfully integrating them. Keeping the audience in mind is also critical. You will learn more about creating charts and graphs in the chapter on Visual Communication Strategies .
Conclusions and Recommendations
The conclusions and recommendations section conveys the key results from the analysis in the discussion of findings section. Up to this point, readers have carefully reviewed the data in the report; they are now logically prepared to read the report’s conclusions and recommendations.
Type “CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS” in all uppercase letters. Follow this functional head with the conclusions of the report. The conclusions should answer any research questions that were posed earlier in the report. Present the conclusions in an enumerated or bulleted list to enhance readability.
Recommendations offer a course of action, and they should answer any problem or research questions as well. Think back to the expectations of your audience. Have all of their requirements been addressed?
Works Cited
All formal reports should include a works cited page; his page documents the sources cited within the report. The recipient(s) of the report can also refer to this page to locate sources for further research.
It is acceptable to follow MLA (Modern Language Association), CMS (Chicago Manual of Style), or APA (American Psychological Association) documentation style for entries on this page. Arrange all sources alphabetically. Refer to the latest edition of the appropriate style handbook for more information about how to format entries for print and electronic sources on the Works Cited page
While some of the formatting rules may seem tedious at first, they are necessary in order for your audience to better understand the report. Using a regulated format allows for a more universal organization that everyone will understand. Being aware of your audience’s needs and expectations will allow for a strong report that will satisfy your employee and demonstrate your competence in your field.
Test Your Knowledge
Understanding the parts of the report can be challenging, so test your knowledge by dragging the part of the report to its definition.
Image Description
Figure 11.1 image description: This is a diagram of a report title page. Leave 2 inches between the top and the title of the report (which should be in uppercase letters), then write in the middle of the page who the report was prepared for. 3/4 of the way down the page, say who the report was prepared for. Then write the date submitted. [Return to Figure 11.1]
Figure 11.2 image description: A sample table of contents and List of Figures. Use uppercase letters for major parts and use leaders to guide the reader’s eye to the page numbers. The list of figures should be separate from the table of contents. [Return to Figure 11.2]
Figure 11.3 image description: A sample body page of an introduction. This one is separated into ‘PROBLEM’ (all in uppercase letters, bold, and in the center) and BACKGROUND. Each paragraph is single spaced with double spacing between paragraphs. [Return to Figure 11.3]
Business Writing For Everyone Copyright © 2021 by Arley Cruthers is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Business Report: Objectives, Qualities, Steps

While a report is generally understood as an oral or written description of events, a business report specifically pertains to business-related matters. A report provides a spoken or written account of something heard, seen, done, studied, etc., especially one that is published or broadcast.
Learn Business Report and its Features, Characters, Objectives, and Importance.
What is a report.
Reports are crucial in the business world, serving as a fundamental mode of communication used on a global scale. The larger an organization, the greater its reliance on reports for the efficient and effective coordination of activities.
Reports become even more essential when organizations engage in technical and complex work. The English term “report” is derived from the French word “Rapportes,” which means the assembly of homogeneous facts into a coherent whole.
What is a Business Report?
Various definitions shed light on the concept of a business report:
- Betty R. Rick and Kay F. Gow (1989) define it as “A report is a written or oral message presenting information that will help a decision-maker solve a business problem.”
- Littlefield and others define it as “A report is a statement prepared to present facts relating to planning, coordinating, performance, and the general state of business in an organization.”
- Raymond V. Lesikar and John D. Pettit (2002:400) state, “A business report is an orderly, objective communication of factual information that serves some business purpose.”
- Thill and Bovee (1999:265) describe a business report as “the written, factual account that objectively communicates information about some aspect of the business.”
These definitions collectively emphasize that a business report is a purpose-driven form of communication that assists management in understanding and addressing specific problems or situations.
It presents facts and figures related to a particular scenario, enabling management to make effective decisions and achieve favorable outcomes for the business.
Therefore, a business report is a systematically prepared, written or oral statement of facts about an event designed to aid management in resolving business problems effectively.
12 Characteristics of Business Report
A business report possesses distinct features or characteristics that differentiate it from other types of reports. The following is a detailed description of these features:
Orderly Communication
Business communication is meticulously prepared with a well-defined format. It presents facts sequentially in a chronological manner. This sets it apart from casual, routine information exchanges that commonly occur in business.
Objective Communication
Business reports maintain an objective and unbiased approach to the presented facts. They seek the truth, regardless of potential consequences. Objectivity in reports encompasses fundamental ethical aspects.
Approaching facts impartially, deriving logical meaning from them, and presenting ideas clearly and fairly to others reflect a highly sophisticated form of ethical thinking. Consequently, a business report objectively presents facts with the utmost neutrality.
Communication
A business report is, in every respect, a form of communication. It employs various means to convey meaning to the intended recipient, who requires the report to make decisions about a specific event.
Factual Information
A business report primarily presents factual information, such as events, records, and various forms of data relevant to conducting business.
Serves a Business Purpose
Not all reports are considered business reports. Only reports that serve a business purpose qualify as business reports.
This means that a business report is prepared to address a business problem or enhance business operations. It must contribute to resolving business-related issues to be classified as a business report.
Handles Large Quantities of Data
Business reports deal with complex business situations involving substantial facts, figures, interpretations, and inferences. Business problems often comprise a complicated set of interrelated and/or interdependent issues.
Consequently, every business report necessitates managing a large volume of data to gain an accurate understanding of a business problem and effectively communicate the facts.
Chronological Description of Facts
Business reports encompass a multitude of facts related to the specific problem under investigation. They present these facts chronologically, allowing managers to comprehensively understand the events contributing to the problem.
Assigned Job
Business communication is not a spontaneously initiated task.
A superior individual or body typically assigns it to a subordinate person or body responsible for conducting the investigation and reporting back to the superior authority.
Upward Communication
Business reports consistently constitute upward communication. They are prepared by subordinate individuals or bodies and submitted to superiors.
Signed and Dated
Business reports are specifically assigned responsibilities entrusted to particular individuals or groups. These assigned individuals prepare the report, incorporating their comments and opinions. Consequently, the responsibility for the report lies with them, necessitating the inclusion of signatures and dates to authenticate the report.
Use of Past Tense and First Person
Business reports focus on specific events that have occurred within or outside the organization but have an impact on business operations. They are prepared by designated individuals or groups, leading to the use of past tense and first-person writing.
Business reports adhere to a predefined format with specific structural and writing conventions. Reports may vary in length, but they must follow one of the established formats. This format has been standardized through the practices of business professionals and communication experts worldwide.
11 Objectives of Business Report
A business report is prepared for a specific business purpose. It is initiated to uncover facts about a business situation and use them for decision-making to resolve problems. A report is a fundamental management tool used for decision-making.
However, the following are the specific objectives of a business report:
The primary objective of a business report is to inform the management about a particular event or issue that management needs to be aware of.
A business report presents the information discovered through an investigation into a situation that impacts the business’s welfare and profitability.
To Recommend Action
Business reports aim to recommend courses of action to effectively address a specific problem. The person conducting the investigation gains insights into the nature of the issues involved and can suggest the appropriate actions to resolve the problem. A business report provides recommendations for efficient problem-solving.
To Analyze Facts and Situations
Another objective of a business report is to analyze facts and situations related to a specific business scenario. The goal is to delve into the problem and uncover its underlying elements. This analysis provides management with insights into the complexities of the problem, making problem-solving more manageable.
To Present a Detailed Account of an Event
Business reports are investigative in nature and provide a comprehensive account of an event subject to investigation.
Therefore, a business report offers a detailed statement of the issues involved in an event, allowing management to understand the event completely.
To Provide Documentation of an Event
A critical objective of the business report is to offer documentary evidence of the investigated event. This enables management to take effective action on any matter. The evidence can also be preserved for future reference.
To Measure Performance
Measuring the performance of individuals requires field information. Managers base their assessments of performance on performance reports. Business reports are prepared to measure the actual performance of the organization’s human resources.
To Help Navigate Changes
One of the objectives of a business report is to assist management in navigating changes favorably. Business reports provide information about potential changes, their nature, and consequences.
This information helps management design strategies to mitigate negative consequences and turn them into opportunities for the organization.
To Assist in Coordinating Organizational Work
Another objective of the business report is to aid in coordinating organizational tasks. This is achieved by providing information about work progress in various organization departments. These progress reports serve as fundamental documents for task coordination.
To Facilitate Inter-Firm Comparison
The inter-firm comparison allows a business to evaluate its performance and determine the desirability of its results. Business reports are oriented to provide management with essential data about other competing firms in the economy. This enables management to compare the firm’s performance with that of others and take improvement measures.
To Aid in Strategy Development
Business reports help management formulate various strategies to thrive in a competitive environment. These strategies are used to develop information about past, present, and future trends in the macro and micro environments.
To Comply with Regulatory Requirements
Business reports are prepared to comply with legal or regulatory requirements of the business, such as audit reports, director’s reports, annual reports, etc. These types of reports are submitted on a recurring basis.
12 Importance of Business report
A business report is a vital document for management. Large organizations rely on business reports to maintain continued and coordinated operations.
Business reports are virtually indispensable documents for all organizations, regardless of their size and operations. The following points highlight the importance of business reports:
Facilitating Decision Making
Business reports assist management in making decisions on various complex matters by providing timely and relevant information.
They collect facts about the problems or issues management must address effectively. Accurate and timely information is crucial for informed decision-making, and business reports are key in providing this information.
Providing Detailed Insights
Business reports serve as investigative documents that delve into specific events or issues. They gather inside information about these events and present it to management organizationally. This enables management to gain comprehensive insights into the matters under consideration.
Supporting Critical Analysis
Business reports explore all the facets of a particular event or issue, systematically organizing the information for management. This structured presentation allows management to critically analyze the event and clearly understand all the relevant factors.
Objective Presentation
Business reports present information neutrally, without bias or distortion. They assemble and present facts objectively, providing management with an unbiased view of the subject matter, which leads to fair and impartial decision-making.
Aiding in Planning, Coordination, and Control
Business reports offer information about the past, present, and future. They cover current ongoing activities in various functional departments, historical data, and anticipated future events relevant to the business. This information supports management in planning, coordinating, and controlling the organization’s activities.
Integrating Past and Present Events
Business reports provide investigative information about events, integrating historical data with current issues. Management uses this information to make decisions that consider past and present business events.
Reducing Administrative Costs
By providing comprehensive and accurate information, business reports help management make effective decisions that can significantly reduce administrative costs.
Assessing Stakeholder Opinions
Business reports are prepared with the facts and opinions of concerned parties. They enable management to assess the opinions of individuals or parties involved in a particular issue, aiding in the decision-making process.
Publishing Facts
Business reports serve as documents of facts and figures related to a matter. They enable management to publish facts for external stakeholders and maintain them as permanent records.
Providing Legal Documentation
Business reports offer documented evidence of facts related to a specific business event, and these documents are legally valid and admissible.
Attracting New Business or Funding
External parties use business reports to assess a firm’s financial and managerial capabilities. Reports such as feasibility reports, audit reports, and technical reports help interested parties evaluate the viability of a project and make investment decisions. Market reports assist in expanding market strategies.
Meeting Legal Obligations
Business reports assist management in fulfilling legal obligations. Statutory reports like audit reports and annual reports are prepared to comply with mandatory legal requirements.
21 Qualities of a Good Business Report
A good business report is a fundamental management tool for decision-making and other managerial purposes. Hence, it is of utmost importance for every business concern. Therefore, it must be prepared with extra care and caution.
The report must be reliable, dependable, and trustworthy. Thus, a good business report, like all types of reports, must have certain qualities that will make it distinct and acceptable to all. The following is a description of such qualities:
Accuracy of facts is a fundamental requirement for a good business report. Since reports invariably lead to decision-making, inaccurate facts may lead to disastrous decisions. Therefore, all information presented in the business report must be true and correct.
Precision provides a sense of unity and coherence to the business report and makes it a valuable document. In a good business report, the writer should be very clear about the exact purpose of the report. The central purpose should direct everything presented in the report.
Good Judgment
A business report should demonstrate good judgment in presenting facts and opinions. Managers make decisions and conclusions based on it. So, the writer of the business report should exercise utmost intelligence and wisdom while presenting and interpreting facts.
Responsive Format, Style, and Organization
A business report should adhere to a specific format, style, and organization of facts. This format ensures that the report is presented systematically and meaningfully.
Objectivity
A business report is a purposeful document. Therefore, all facts and other issues should be collected and arranged in such a manner that they lead to the successful attainment of the objectives of the report and the organization.
A business report should be simple, written in clear, unambiguous language, with short and simple sentences. Facts should be presented in a straightforward manner to ensure easy understanding.
Clarity is a fundamental virtue of a business report. A good report is absolutely clear, with a systematic arrangement of facts, a clear purpose, source identification, findings, and recommendations. It should be divided into short paragraphs with headings for greater clarity.
A business report should be analytical and interpretative. Its purpose is to present facts and interpretations of those facts to facilitate decision-making.
A business report should be concise, as executives do not have time for lengthy reports. It should be as brief as possible while still conveying all necessary information.
Proper Terms of Reference and Title
A business report should have appropriate terms of reference and a clear title to help management quickly grasp the key facts and information.
A business report should maintain neutrality in presenting facts and figures. An unbiased and objective explanation of events makes a business report reliable.
Transitional Words and Sentences
The report should use transitional words and sentences to ensure a synchronized flow of thoughts and maintain reading consistency.
Use of Correct Grammatical Form
Grammatical accuracy is essential in a good business report. Proper sentence construction ensures clarity and understanding.
The report should minimize the use of technical jargon to ensure understanding by all readers.
A business report should be realistic and adaptive to the current environment, using contemporary terms, styles, and formats.
Business reports should be prepared promptly to avoid changes in the factual context. Timely presentation to management is crucial for its usefulness.
A business report should include only relevant facts related to the central purpose of the report. Irrelevant facts can confuse, while excluding relevant facts renders the report incomplete.
The report should present viewpoints from all concerned parties in a reliable manner, providing management with a comprehensive understanding of the event.
Reader-Oriented
A good business report is reader-oriented and tailored to the needs of the intended audience, whether technical or general readers.
Completeness
A business report should be complete in all aspects, leaving no relevant elements of the situation under investigation untouched. Management should have a comprehensive understanding of the event to make informed decisions.
Recommendation
Business reports should contain recommendations to address problems or complexities. These recommendations should be logical conclusions drawn from the investigation and analysis, impartial, and objective.
5 Steps for Writing a Business Report
Business report writing is a technical skill. One has to have a thorough knowledge of the process of writing a business report. The acceptability and attractiveness of the report will depend on the art of writing and assembling facts synchronized.
However, the following steps are required to write an effective business report:
Step 1: Determining the purpose of the report
The work of writing a business report begins with a problem. Someone or some group requires information for a business purpose. They may need information only, or they may need both information and analysis, or they may need information, analysis, and recommendations.
Whatever the case, individuals with this need will authorize you to do the work. Usually, they will do so orally, but they may also use a letter or memorandum.
After you have been assigned the task of writing a report, your first step is to establish the problem clearly in your mind. This is a basic and elementary task in every report-writing effort, but it is often done haphazardly.
Frequently, it is the reason for the failure of a report to reach its goals. How will you start the work and get your mind set on the right nature of the problem? The following guidelines will help you determine the purpose of the business report in its correct shape:
Conduct a preliminary investigation.
In order to gather all the information needed to understand the problem, conduct a preliminary investigation into the matter. Gathering the right information involves many things, depending on the nature of the problem.
It may mean collecting material from organizational files, discussing the problem with experts, searching through printed sources, and discussing the problem with those authorizing it. You should continue the preliminary investigation until you have the information necessary to understand the problem.
Clearly state the problem.
Now, state the problem clearly. You should state it, preferably in writing. A written statement of the problem will help preserve it permanently. You can refer to it time and again without the danger of it being changed. In addition, other people can review, approve, and evaluate it for improvement.
Most importantly, putting it in writing forces you to understand the problem clearly. In this way, this practice serves as a valuable form of self-discipline. The problem statement normally takes one of three forms: infinitive, question, and declarative.
For example:
- Infinitive phrase: The purpose of the report is “to determine the cause of decreasing sales in Khulna territory.”
- Question form: “What are the causes for decreasing sales in Khulna territory?”
- Declarative Statement: “The sales in Khulna territory are decreasing, and management wants to know why.”
Determine the factors of the problem.
It is time to determine the subject areas you must investigate to satisfy the overall objectives. Within the framework of your logical imagination, you should look for the factors of the problem. Factors can be of three types:
1. They may be subtopics of the broader topics the report is concerned about.
This is a breakdown of the main areas about which information is needed. A study of the problems of operation may have the following subtopics:
- Production,
- Human resource management,
- Product development, etc.
2. They may be hypotheses to be tested.
Hypotheses are the possible explanations or solutions that the researcher takes about a problem. Once determined, hypotheses are tested and then related to the problem. The following are the hypotheses of your previous problem: “What are the causes for decreasing sales in Khulna territory?”
Hypotheses:
- Competitors’ activities have caused the decline of sales.
- Merchandising deficiencies have caused the decline of sales.
- Sales force inefficiency has caused the decline of sales.
- Price increases have caused the decline of sales.
You should test each hypothesis. You may find one, two, or all apply, or maybe none do. Then you have to develop additional hypotheses for further evaluation. You would continue this process of generating hypotheses until you determine answers to your problem statement.
3. They may be bases on which the comparisons are made.
In case of evaluative research, you need to determine the characteristics to be evaluated. It may include the criteria to be used in evaluating each characteristic. For example: “Comparative study of the performances of the Khulna and Dhaka sales territories.”
- Sales in amount and in units,
- Gross profit margin,
- Inventory turnover, etc.
Break down the factors into sub-factors.
Sometimes, the factors may have factors of their own. In that case, they may be broken down into sub-factors. Breaking factors into other factors gives the problem order and serves as a guide to the investigation that follows.
Step 2: Gathering The Needed Information
This logical step involves gathering needed information from the field. How you obtain the information depends on the nature of your problem. The source of information may be primary or secondary.
The primary sources are your company files, managerial personnel, employees, or customers, etc. You may need to conduct a survey or experiment to collect information from primary sources. Whatever the source or sources are, it requires a systematic method to collect information.
You may apply an interview question schedule or questionnaire method to collect field information from the primary sources. Any printed materials published in any form would be your secondary source. You may need to collect information from either one or both sources.
However, you will take all possible measures to collect complete information so that you can have a comprehensive understanding of the problem issue.
Step 3: Applying the Findings to the problem
Now, you will apply the gathered facts selectively to the problem or hypotheses. After completing your research, You will find a lot of information on your subject.
Thus, you must go through what you have collected and apply each item of information to the problem’s needs. If the information helps answer a need, you keep it. If it does not, you discard it.
This is an interpretation of facts. The whole process is a mental one- a process of judgment. Your interpretation will continue until you have completed the report project.
Fundamentals of Interpretation
Interpretation is a mental activity that improves with experience and knowledge. After you have arranged your findings in a logical order, you are ready to finish your interpretation of them in terms of how they apply to the problem.
You apply certain fundamentals of interpretation to have a correct interpretation of facts. These fundamentals are logically grouped into five areas (Lesikar and Pettit, 2002:418):
1. Human frailties that lead to interpretation errors.
Interpretation is the product of the mind and thus is affected by the limitations of the mind. Our minds are subject to quirks of peculiarity, irrationality, and inconsistency. These frailties limit our ability to interpret. You can take the following care to guard against them:
Do not exaggerate the meaning of facts
This happens due to the desire for the spectacular, our love for the unusual. It often results in the feeling that the facts uncovered are too dull and common and must be made more interesting. This view may lead to exaggeration in interpretation. You must continuously be aware of this possibility and consciously work to avoid it.
Do not think your facts are the final answer
This comes out of the belief that conclusions are essential. It is a wrong assumption that absolute finality and certainty are needed in all cases. A few areas of information can be interpreted definitively. Lack of adequate information or the possibility of many interpretations may cause such a situation. So, modified or no interpretation is better than unjustified interpretations.
Support every conclusion with facts
Those that cannot be supported by facts cannot be made. You must have evidence to support your interpretations.
2. Fallacious procedures in interpretation.
Fallacies have no place in a business report. A fallacy is an error in thinking. When a writer does not think correctly, facts and their meanings become distorted, and the report becomes suspect. Fallacious thinking can stem from many causes. In any case, it has no place in interpretation.
Five errors are the most frequently committed errors. You can make your report more accurate and believable by avoiding these errors:
Bias in interpretation
Bias results from viewpoints that the analyst developed before interpreting facts in a report. Bias may be deliberate or unconscious. Deliberate bias is unethical, and unconscious bias shows superficial thinking. Eliminate these biases by constantly guarding against them. Keep in mind that bias is not excusable.
Comparison of Non-comparable data
The data that are used to compare may not be truly comparable. Therefore, you should work hard to include only valid comparisons as the basis for conclusions. So, compare only those facts that are logical.
Cause-effect confusion
This error confuses association among data with causation. It results from the mistaken assumption that a cause-effect relationship among sets of data exists. So, do not equate association and causation. Keep in mind that (i) data are related; (ii) there is evidence of cause and effect relations; and (iii) there is evidence to rule out other factors that may have caused the relationship among the sets of data.
Unreliable and unrepresentative data
Interpretation depends on the data that support it. Mistaken data would be fallacious. So, be sure to use reliable data and use representative data—facts that match the whole.
Neglect of important factors
Oversimplification of report problems causes this error. If you consider a few factors and neglect others that are equally or more important, your analysis will be incomplete. So, look for all factors that affect the problem and include those in your problem description.
3. Attitudes and practices conducive to sound interpretation.
Good interpretation requires clear thinking. Unfortunately, not all of us are equally good at interpreting. You can clarify and improve your thinking with the following attitudes and practices:
Cultivate a critical point of view
Criticize your work as much as you support it. You should look at the opposite side of the interpretation with equal vigor.
Maintain a judicial attitude
Take the role of a judge. Judges decide without emotion, without prejudice, and with open minds. So, look at your work as a judge and uncover the truth.
Consult with others
You do not know everything. So, talk over report problems with others, especially ardent critics. You will be in a better position to interpret with their opinions.
Test interpretations
Deliberately test your interpretations to make them more correct and realistic. You can do it in two ways:
- Apply the test of reason. Ask questions—Is each interpretation logically based on your knowledge or experience? If the answer is right, your interpretation will be right.
- Apply the negative test. Make an opposite interpretation and build a case for it. You compare the two opposite interpretations and retain the one with stronger support.
4. Statistical aids to interpretation.
Statistics permit one to examine a set of facts. Statistical techniques provide many methods for analyzing data. By knowing them, you can improve your ability to interpret. Descriptive statistics should help the most.
The measures of central tendency—mean, median, and mode—will help you find a common value. The measures of dispersion—ranges, variances, and standard deviations—should help you describe the spread of a series. Probabilities, ratios, inferential, and other statistical approaches are also helpful.
But do not allow statistics to confuse the reader; they should help in interpretation.
5. Techniques in interpreting for the reader.
Put your interpretation into words and symbols that the reader will understand. Adapt to the reader’s filter, which is the reader’s knowledge, viewpoints, and emotions.
You must explain and justify your interpretations so that the reader will benefit from your exhaustive analysis. Your interpretation must present a fair, accurate picture to your reader.
Interpretation Procedures
There is no magic panacea or mechanical formula for interpreting data. Each report problem is unique. Still, there are common elements to the interpretation procedure that can help you.
You can alter the plan to fit the unique requirements of a special situation. The steps involved in the interpretation procedure are stated below:
1. Relate information to the problem
Look for ways to combine the facts with parts of the reported problem.
There are many ways to do so.
- You may relate one part to the problem and find that the relationship plays a paramount role in the entire report.
- You may combine large amounts of information to highlight a single, minor point.
- You may develop a maze of comparisons and cross-comparisons.
2. Make all credible interpretations
You should not ignore any interpretation with merit. Make all plausible interpretations. You should emphasize the quantity of interpretations; later on, you can prune for quality.
3. Reevaluate interpretations
Review carefully all the interpretations you have formulated. You should thoroughly evaluate each interpretation in the light of the facts that support it.
4. Select the interpretations with the most merits
Retain those interpretations that have the most support. You should drop those interpretations that have less support.
5. Derive conclusions from the interpretations
Conclusions are answers to your report problem. It is the interpretation of previous interpretations in a report. In such a process, there may be facts, interpretations of facts, interpretations of facts interpretations, and possibly recommendations.
Therefore, draw conclusions from your interpretations. Recommendations are lines of action to which conclusions logically lead. Thus, they are interpretations drawn from conclusions.
All parts of the interpretation process are linked together in a hierarchy; facts support interpretations, interpretations support conclusions, and conclusions support recommendations.
Step 4: Organizing the Report Information
Now, you must organize the facts. Give the gathered information the order in which it will appear. Research findings are often in some form of disorder – Note cards, Questionnaires, Sheets of recordings, etc. They should be arranged in order for better understanding. Then, apply it to the problem. The nature of the research will determine the style of the order.
Guidelines for arranging report information
Write an outline.
An outline is simply a plan for the writing task. It forms the table of contents and headings of the report. It will guide your efforts and compel you to think before you write.
Choose an appropriate Pattern of Report Organization
There are three Possible Outline Patterns. You should decide on the sequence or pattern you will use in your report. The patterns are:
- Logical Pattern: This pattern teaches that you present the findings in inductive or indirect order – moving from the known to the unknown. The logical sequence follows the order: Introduction > Facts > Summary > Conclusions > Recommendations.
- Direct Pattern: The direct pattern presents the subject matter in a deductive fashion. It presents the parts of the report in the following way: Summaries > Conclusions > Recommendations > Introduction > Facts.
- Chronological Pattern: The chronological pattern presents the findings in the order in which they happened. It follows the order of time. The chronological plan may be combined with either of the two preceding orders. A problem of historical nature takes this course:
- From Present to Past
- From Past to Present
- From present to future
- From Future to present
Select the type of headings
There are four types of headings – topic, complete sentence, imperative sentence, and variant. You can select any one of them, but headings are the most commonly used.
- Topic Captions/Headings: These are short constructions, frequently one/two words in length, that do nothing more than identify the topic of discussion. This heading only gives the subject of discussion and is constituted with nouns or short phrases. Examples: History or History of the Problem, Background or Background of the Study, Determinants or Determinants of commitment, or Root reasons, Sources of Conflict, etc.
- Complete Sentence Captions/Headings: These identify the subject and tell what is being said about it. They are written in a complete sentence that carries the sense of content in a nutshell and include a subject and a verb. Example: “Problems and Prospects of E-commerce in Bangladesh.” Or “Corrective Measures For Improvement.”
- Imperative sentence heading: It begins with a verb, and the subject is omitted. It is written in a decapitated sentence. Example: “Make promotion effective” or “Take time to outline.”
- Variant heading: Variant heading begins with a particle and is used to make the heading attractive and catchy. Example: “Granting aid to the Tsunami victims.”
Choose a system of Outline symbols
Outline symbols are needed to show the importance of each part and exhibit the degrees of importance of your ideas. Three options are available:
Numeral-letter Combination
This method uses numbers as the first degree of division and then uses letters for the second degree of division. Example:
- First degree of division.
- Second degree of division
- Third degree of division
- Fourth degree of division
Numerical Form
This is also known as the Decimal system of outlining symbols. It uses whole numbers to designate the major sections of a report, with whole numbers followed by decimals and additional digits indicating subsections of the major sections. Example:
- First degree of division
Letter-numeral Combination
This system uses letters before main headings and then uses numbers to indicate additional topics. Example:
- First degree of heading
- Second degree of heading
- Third degree of heading
- Fourth degree of heading
Follow the heading writing pattern
There are formalized systems of headings and subheadings to identify their sections, subsections, and paragraphs, along with specific styles for writing them systematically.
Check 5 cautions regarding headings and subheadings:
- Place the most important ideas in the highest degree of headings.
- Try to balance the sections regarding the number of headings.
- Have at least two subheadings if you divide any topic.
- Use about three to seven main points in a report.
- Avoid using the report title as a section heading.
Maintain a reasonable extent of Outlining
The outline should contain Introduction > Body > Recommendation > Conclusion.
Keep parallelism of construction.
Captions that make up a level of division should be grammatically parallel. In other words, all headings at the same level should be of the same grammatical construction.
Step 5: Preparing Business Report
Now, the intended report will be prepared in a systematic format. It is better to create a draft of the report first. Then, necessary proofreading and revising of the initial draft are done to produce an impressive and effective final draft.
There are many variations in the makeup of a business report. A business report typically consists of three parts: prefatory, report proper, and appended parts.
A long formal report will contain all these parts, but a short or informal report may omit some elements.
The prefatory parts include the title fly, title page, letter of transmittal and authorization, table of contents, and executive summary. These prefatory parts appear before the report text.
The report’s proper parts include the introduction, findings and summaries, conclusions, or recommendations. This section contains the main story and proposed courses of action to address the problem situation.
The appended parts consist of the bibliography, appendix, and index. These contain supplementary materials that are not essential to the report but may be helpful to some readers.
The format of the report will follow the pattern below:
10 FAQs About Business Report
What is the primary purpose of a business report.
The primary purpose of a business report is to inform management about a particular event or issue that they need to be aware of. It presents information discovered through an investigation into a situation that impacts the welfare and profitability of the business.
What characteristics differentiate a business report from other types of reports?
A business report is characterized by orderly communication, objective presentation of facts, serving a specific business purpose, handling large quantities of data, chronological description of facts, being an assigned job, constituting upward communication , and being signed and dated. It also uses past tense and first person and adheres to a set format.
Why is objectivity important in a business report?
Objectivity is crucial in a business report as it maintains an unbiased approach to presenting facts. This unbiased presentation gives management a truthful view of the subject matter, leading to fair and impartial decision-making. It reflects a sophisticated form of ethical thinking.
How does a business report assist in organizational work?
A business report aids in coordinating organizational tasks by providing information about work progress in various departments: these progress reports serve as fundamental documents for task coordination, helping navigate changes, and designing strategies to turn potential consequences into opportunities.
What are the steps involved in writing an effective business report?
Writing an effective business report involves determining the report’s purpose, gathering the needed information, applying the findings to the problem, organizing the information systematically, and finally, writing the report. Each step requires careful consideration and a systematic approach to ensure the report is comprehensive and serves its intended purpose.
What role do business reports play in decision-making within an organization?
Business reports facilitate decision-making by providing timely, relevant, factual information about complex matters. They help management address problems or issues effectively, thereby contributing to informed and strategic decision-making.
How does a business report contribute to reducing administrative costs?
By offering comprehensive and accurate information, business reports enable management to make effective decisions, which can optimize processes and resources, ultimately reducing administrative costs.
Why is it important for a business report to be neutral and unbiased?
Neutrality and unbiasedness in a business report ensure the reliability and credibility of the information presented. It allows for an objective assessment of the situation or issue, which is essential for fair and impartial decision-making.
What is the significance of having a set format in a business report?
Having a set format in a business report ensures consistency, clarity, and systematic presentation of information. It aids in better understanding and interpretation of the report, making it a valuable document for management.
Can you explain the importance of timeliness in preparing a business report?
Timeliness is crucial in preparing a business report as it ensures the relevance and accuracy of the information presented. Promptly prepared reports allow management to make informed decisions based on the most current data, thereby enhancing the report’s usefulness.
Business reports are indispensable in organizational decision-making, providing comprehensive, accurate, and timely information on various aspects of business operations.
The primary purpose of these reports is to inform management about specific events or issues, thereby aiding in formulating strategic responses. The characteristics that set business reports apart include orderly and objective communication, adherence to a set format, and the ability to handle large quantities of data.
The importance of neutrality and unbiasedness in business reports cannot be overstated, as these qualities ensure the reliability and credibility of the information presented, leading to fair and impartial decision-making. Furthermore, the adherence to a set format contributes to the clarity and systematic presentation of information, enhancing the report’s value to management.
Timeliness in report preparation is equally crucial, ensuring the relevance and currentness of the data, which is vital for informed decision-making.
The meticulous process of writing a business report, involving determining the purpose, gathering information, applying findings, and systematic organization, underscores its significance in reducing administrative costs and facilitating strategic planning within an organization.

- 309-452-2831
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
- Mailing Address: PO Box 341, Normal, IL 61761
Business Report Writing
Report Writing
Save 10% off each course when you enroll in two or more courses. See suggested combinations below for our most popular combinations.
Save 10% off each course when you enroll in two or more courses. See suggested combinations in the right column for our most popular combinations.
The best practices for writing business reports in a high-quality course.
The style and form vary from company to company, but the core principles and best practices of business report writing are the same. We teach you how to write business reports that will be useful in any business.
Course Highlights
- Learn the best practices for writing business reports
- Learn how to plan and organize clear, concise reports
- Learn how to guide readers so they praise the report for clarity
- Receive extensive, helpful comments on the reports you write
- Learn how to get down to writing and write efficiently
- Learn the best practices for writing informative, readable reports
- Learn to choose the correct business vocabulary
Course Description
The Business Report Writing course teaches the skills required for writing business reports that are clear and explicit. We focus on the structure critical to all business report writing, providing the fundamental knowledge you can use in any business context.
We work on five samples of your own writing. Your instructor will evaluate your work and coach you through the skills you need to learn.
When You Complete This Course...
- You will know how to identify your readers and tailor your work to their expectations and work goals.
- You will understand the basic principles of report writing and how to put them to use to create impressive and easy-to-read reports.
- You will be able to write clear, well-organized, professional business reports.
How It Works
Work online.
When you enroll, we give you access to all the online lessons and training materials. Each lesson builds on the lessons that precede it. We offer clear explanations for every part of our training and plenty of real-world examples of how to apply the skills you are learning.
Set Your Own Pace
You go at your own pace and submit assignments when you are ready. You don’t have to be online with other students or perform activities at specific times.
Instructor Feedback
Your instructor evaluates all your work, coaches you through learning the skills, and gives you personalized feedback on what you are doing well and what still needs polish. You can contact your instructor at any time if you have questions about your training, business writing , or the English language.
Certificate
When you finish the course within four months, you receive a graduation certificate.
Course Outline
Know your readers., choose strategies based on the goals and readers., write a clear, complete introduction., state the contents of the report., state conclusions and recommendations in the introduction., write the report in blocks., keep explanations of a subject together in one block., check each block for focus., check each block for completeness., open each block with a statement of the contents., use headings to open blocks., bold field or data names to identify them as blocks., create lists., open list blocks., mark the list items clearly., keep list items in a single list., keep list items in the same format., present information in tables when possible., have an organizational pattern in mind., use special organizational patterns for some reports., write to build conclusions in the reader's mind., write clear, complete, relevant explanations., use key words consistently., fully explain every new concept word or phrase., use full phrases to define words clearly., write a conclusion that achieves your goals., use paragraphs to organize information., write concisely., combine sentences to show relationships; separate sentences to make them clearer., write clear, simple, straightforward sentences., write strong, direct sentences., use words the reader will understand., write clearly and simply for non-technical readers, write synopses or executive summaries to help readers., use your spell checker and grammar checker., start learning today, suggested combinations, this course and business research report writing skills.
Organize your research findings into easy-to-read, informative, actionable reports.
Add both to cart $711.00 Save $79.00
This course and Basic Grammar Skills Tutorial
One-on-one grammar training customized just for you, without wasting time on skills you don’t need.
Add both to cart $801.00 Save $89.00
This course and Business Writing Skills
Our fundamental writing course for clear, effective, professional business documents.
This course and Individualized Writing for Nonnative Speakers of English
A customized tutorial that starts with an evaluation of your writing and then coaches you through personalized training.

Writing Coaching by Dr. Robert Hogan
Dr. Hogan has been training writers for 40 years in universities, colleges of business, consulting companies, and professional writing companies.
Course Features
Course Materials: Online
Certificate upon Completion: Yes
Instructor Feedback: Yes
Letter of Recommendation: Yes
Lesson Count: 37
Practice Activities: 0

45 Business Writing Courses

7,000+ Clients Worldwide

- Awards and Recognition

Corporate & Government Training

The Business Writing Center’s highly trained instructors with backgrounds in higher education teach the latest best practices that we know enable business writers to write documents that are clear and have impact.
"> "> Contact Us
- +1 309 452-2831
- PO Box 341, Normal, IL 61761
"> "> About Us
- Testimonials
- Clients Served
- About the Instructors
- Corporate and Government Training
Privacy Overview
Functional cookies help to perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collect feedbacks, and other third-party features.
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
Course Syllabus

Course Description
Mastering the Art of Business Reporting: Transcend Traditional Report Writing
In today's fast-paced business world, effective communication is the linchpin of success. Reports, central to this communication framework, hold the power to drive change, shape strategies, and foster informed decisions. But far too often, the intricacies of report writing stymie professionals, turning what should be a powerful tool into a cumbersome obligation.
Enter our comprehensive course: a beacon for professionals navigating the complex seas of business reporting.
Reports—more than just documentation—are strategic narratives. They illuminate issues, elucidate solutions, and empower businesses to seize new opportunities. Whether it's charting expenses, justifying budget increments, shedding light on incidents, or architecting lucrative proposals that woo stakeholders, reports play a pivotal role in bridging understandings, both within and outside an enterprise.
Yet, the formidable challenge remains: How does one craft a compelling report without being a seasoned writer? How do you transition from the daunting emptiness of a blank page to a cohesive, impactful narrative?
Course Highlights
This course, segmented into twelve meticulously designed lessons, deciphers the essence of report writing for the contemporary business professional. Moving beyond conventional teachings, we usher in an era where report writing is not just a task but a valuable skill.
You will unveil:
- Streamlined strategies to structure and draft reports, eliminating the labyrinth of complexity.
- Techniques to pinpoint pivotal information, ensuring your reports resonate and command attention.
- Refined presentation skills that amplify persuasion, paving the way for actionable insights.
- A blueprint to craft reports that not only convey but convince, aligning with your strategic objectives.
Each lesson unfolds a facet of report crafting, complemented by interactive exercises and assignments. These exercises, mandatory for course completion, are meticulously curated to reinforce learning. Meanwhile, the optional assignments are golden opportunities, allowing for deeper immersion into the course materials.
Section reviews punctuate lessons, presenting multiple-choice questions tied to distinct report segments. These reviews are instrumental in honing your skills, aiding you in mastering the organization and articulation of diverse report sections. Like the exercises, these reviews are essential milestones on your learning journey.
Redefine Your Report Writing Paradigm
This course challenges preconceived notions. If you've been tethered to templates, it's time to liberate yourself. If dread and apprehension have been your companions in report writing, prepare for an empowering paradigm shift. Believe this: you don't need to be a writer to produce impactful reports. Often, breaking free from restrictive templates ignites creativity and clarity.
Join us, as we unravel the magic of report writing. Whether you're a novice grappling with the basics or a professional seeking to elevate your reporting game, this course is your gateway to mastering the art of business reporting. Let us guide you in transforming this "necessary evil" into your most potent business tool.
- Completely Online
- Printable Lessons
- 6 Months to Complete
- 24/7 Availability
- Start Anytime
- PC & Mac Compatible
- Android & iOS Friendly
- Accredited CEUs

Learning Outcomes
- Describe what report writing actually entails.
- Describe perfecting your writing style.
- Summarize using correct and consistent spelling and abbreviations.
- Demonstrate writing the report.
- Describe informal reports.
- Describe semi-formal reports.
- Describe formal reports.
- Demonstrate mastery of lesson content at levels of 70% or higher.
Assessment Guide

- Course Catalog
- Group Discounts
- Gift Certificates
- For Libraries
- CEU Verification
- Medical Terminology
- Accounting Course
- Writing Basics
- QuickBooks Training
- Proofreading Class
- Sensitivity Training
- Excel Certificate
- Teach Online
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 2: Create an Outline. Once you've gathered the resources, it's time to plan the report. Before you start writing, create an outline that will help you stick to the right structure. A business report is complex writing in which you can get lost very easily if you don't have a clear plan.
Every business report should feature a title page. The title itself should clearly set out what the report is about. Typically, you should also include your name and the date of the report. 2. Summary. Most business reports begin with a summary of its key points. Try to include: A brief description of what the report is about
When writing a formal report, use data and evidence to support your argument, add visuals, use consistent fonts and headings, and highlight important information. You should also use clear language that is easy to understand, considering the audience's background knowledge. 1. Only use credible sources.
Armed with a balanced mix of KPIs to track and enhance service performance, this most powerful of business report samples will help you drive down response times while improving your first call resolution rates. It's a combination that will result in ongoing growth and success. 8. Employee performance dashboard.
A business report is a formal document that provides an analysis of a specific business issue or situation. It typically includes detailed information on the topic at hand such as data, research, and other relevant sources. Business reports are used to make business decisions, identify problems or opportunities, or track progress toward goals.
Give your report a title. Depending on the brief, you may receive the title of the report or you may write it yourself. At the beginning of the report, make sure the title is clear and visible. The report should also include your name, the names of others who worked on it, and the date it was written.
These reports provide all the nitty-gritty details of specific aspects of your business without any conclusions or opinions. Examples include daily sales reports, inventory levels, or even project updates. This is the essential "just the facts, ma'am" type of report you need to stay in the loop. 2. Analytical reports.
Explain what the numbers mean for your business and why they should matter to the stakeholder. 7) End with a strong conclusion. Summarize your main points and end with a strong conclusion. If appropriate, include a call to action, such as an invitation to a meeting or a request for feedback.
Front matter: List your name, job title, contact information, and the date of submission. You can also create a title for the report. Background: State the background of the topic you'll be addressing, along with the purpose of the report itself. Key findings: Provide facts, data, and key findings that are relevant to the purpose stated in ...
A business report is a document that presents information in a structured format, typically written for a specific audience or purpose. Business reports are used to convey data, research findings, recommendations, and other types of information in a clear, concise, and organized manner. Business reports may be written for a variety of contexts.
Tip: Even though this is the first section, consider writing this section after you have finished the report. This will help you determine which points are the most important to address. Introduction: This section outlines what you will be going over in your report. It includes the main points, chosen report structure, and, most importantly ...
Add your name, the names of the other people who worked on it and the date under the title. Write an index or table of contents: A table of contents or index is essential in any business report, especially if the document is long and complex. Add a list of each section of the document under the title and ensure the page numbers accurately match ...
3.1 Use effective headings and subheadings. Headings and subheadings are useful tools in business writing. Ensure they are descriptive of the content to follow. In other words, rather than labelling a section Section 2.5, it would be better to describe it as 2.5 Justification for the high risk scenario.
The following is the format of a business report: Step 1: Create a plan before writing. Before commencing the report, identify the purpose of the report. Find out the objective to accomplish with ...
3. Add a title. You might get the title of the report with the brief or you may write it yourself. Make sure the title is clear and visible at the beginning of the report. You should also add your name and the names of others who have worked on the report and the date you wrote it. 4.
If you are writing a business report, aim to structure it as follows: Title Page - Include a clear, informative title, your name and the date. Summary - A summary of what the report is about, the data collection methods, the findings and any recommendations you want to make. Table of Contents - A list of the sections in the report.
2. Follow the Right Report Writing Format: Adhere to a structured format, including a clear title, table of contents, summary, introduction, body, conclusion, recommendations, and appendices. This ensures clarity and coherence. Follow the format suggestions in this article to start off on the right foot. 3.
Business acumen. A business report is a document in which the author analyses a business issue and gives recommendations based on that analysis. It may also be referred to as writing a business case or a manager's briefing. HR practitioners are likely to write business reports to summarise their investigations into a particular situation (for ...
Figure 11.1 image description: This is a diagram of a report title page. Leave 2 inches between the top and the title of the report (which should be in uppercase letters), then write in the middle of the page who the report was prepared for. 3/4 of the way down the page, say who the report was prepared for. Then write the date submitted.
5 Steps for Writing a Business Report. Business report writing is a technical skill. One has to have a thorough knowledge of the process of writing a business report. The acceptability and attractiveness of the report will depend on the art of writing and assembling facts synchronized. However, the following steps are required to write an ...
This course teaches the best practices of business report writing that will enable you to write business reports that are well organized. 309-452-2831; [email protected]; ... Course Description. The Business Report Writing course teaches the skills required for writing business reports that are clear and explicit. We focus on the ...
Here's how to write one that works for your business. 1. Start with your basics. The goal of a business description is to introduce any reader to your company—-and to do that quickly. So when you're getting started writing this description, it's a good idea to list out the basic information that you'll need to include.
Course Description. Mastering the Art of Business Reporting: Transcend Traditional Report Writing. In today's fast-paced business world, effective communication is the linchpin of success. Reports, central to this communication framework, hold the power to drive change, shape strategies, and foster informed decisions. ...