
- Library Catalogue

Academic writing: What is a literature review?
A review of the literature in a discipline is not the same as an annotated bibliography of sources, though an annotated bibliography can be a type of literature review. The purpose of a lit review is not only to tell your reader the state of scholarship about a given topic, but also to organize and evaluate the major points, parts, or arguments of each source. From the University of Toronto Writing Centre’s Tips on Conducting the Literature Review :
"A literature review is a piece of discursive prose , not a list describing or summarizing one piece of literature after another. It's usually a bad sign to see every paragraph beginning with the name of a researcher. Instead, organize the literature review into sections that present themes or identify trends, including relevant theory. You are not trying to list all the material published, but to synthesize and evaluate it according to the guiding concept of your thesis or research question."
A lit review may serve as a stand-alone piece or article. For example, see this published Stand-Alone Literature Review (content note: this literature review focuses on the topic of abuse against women with disabilities). However, more often a lit review is part of a larger research publication. For example, see this published research article that includes a Literature Review (content note: this article discusses depression among college students).
What should a literature review include?
Introduction: Explain why this research topic is important. Outline what direction your review will take: i.e., what aspects of the topic you’re focusing on.
Body : Present your summaries and evaluations of the sources in a clear, logical, and coherent manner. Some options for organizing your review include chronological, order of importance, two sides of a controversial problem, differences in perspective or viewpoint. Your review must “read” like a coherent paper, not a list.
Note: Most literature reviews describe only the main findings, relevant methodological issues, and/or major conclusions of other research.
Ensure your final list of references includes all sources you’ve discussed, and use the citation style required in your discipline.
Don’t provide a lot of detail about the procedures used in your sources. Don’t mention every study conducted on the topic. Include only the ones that are most relevant for the purpose and scope of your review.
Plan and organize your literature review
- Define your central problem, issue, or focus (create a research question or thesis statement)
- Consider audience expectations. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are.
- summarize the “gist” or main ideas of the source
- comment on the source’s usefulness, relevance, methodology, and/or findings in the context of your question or issue
- Do not use a “list-like” approach in drafting your lit review. Rather, organize your information logically to address your research question, thesis, or central issue. For more, see the Writeonline.ca guide to Literature Reviews and the Monash University Learn HQ mini-module on Literature Reviews (including sections on the process of writing a literature review, structuring a literature review, and the language of literature reviews).
Revise your literature review, keeping in mind these tips for effective writing
- Pay attention to sentence structure
- Use the active and passive voices appropriately
- Reduce or omit wordy, redundant phrases
- Proofread for common punctuation and expression errors
For more about literature reviews, including definitions, protocols and guidelines, search strategies, and managing citations, see the Library's Literature reviews for graduate students .

26 Planning a Discursive Essay
Discursive essay – description.
A discursive essay is a form of critical essay that attempts to provide the reader with a balanced argument on a topic, supported by evidence. It requires critical thinking, as well as sound and valid arguments (see Chapter 25) that acknowledge and analyse arguments both for and against any given topic, plus discursive essay writing appeals to reason, not emotions or opinions. While it may draw some tentative conclusions, based on evidence, the main aim of a discursive essay is to inform the reader of the key arguments and allow them to arrive at their own conclusion.
The writer needs to research the topic thoroughly to present more than one perspective and should check their own biases and assumptions through critical reflection (see Chapter 30).
Unlike persuasive writing, the writer does not need to have knowledge of the audience, though should write using academic tone and language (see Chapter 20).
Choose Your Topic Carefully
A basic guide to choosing an assignment topic is available in Chapter 23, however choosing a topic for a discursive essay means considering more than one perspective. Not only do you need to find information about the topic via academic sources, you need to be able to construct a worthwhile discussion, moving from idea to idea. Therefore, more forward planning is required. The following are decisions that need to be considered when choosing a discursive essay topic:
- These will become the controlling ideas for your three body paragraphs (some essays may require more). Each controlling idea will need arguments both for and against.
- For example, if my topic is “renewable energy” and my three main (controlling) ideas are “cost”, “storage”, “environmental impact”, then I will need to consider arguments both for and against each of these three concepts. I will also need to have good academic sources with examples or evidence to support my claim and counter claim for each controlling idea (More about this in Chapter 27).
- Am I able to write a thesis statement about this topic based on the available research? In other words, do my own ideas align with the available research, or am I going to be struggling to support my own ideas due to a lack of academic sources or research? You need to be smart about your topic choice. Do not make it harder than it has to be. Writing a discursive essay is challenging enough without struggling to find appropriate sources.
- For example, perhaps I find a great academic journal article about the uptake of solar panel installation in suburban Australia and how this household decision is cost-effective long-term, locally stored, and has minimal, even beneficial environmental impact due to the lowering of carbon emissions. Seems too good to be true, yet it is perfect for my assignment. I would have to then find arguments AGAINST everything in the article that supports transitioning suburbs to solar power. I would have to challenge the cost-effectiveness, the storage, and the environmental impact study. Now, all of a sudden my task just became much more challenging.
- There may be vast numbers of journal articles written about your topic, but consider how relevant they may be to your tentative thesis statement. It takes a great deal of time to search for appropriate academic sources. Do you have a good internet connection at home or will you need to spend some quality time at the library? Setting time aside to complete your essay research is crucial for success.
It is only through complete forward planning about the shape and content of your essay that you may be able to choose the topic that best suits your interests, academic ability and time management. Consider how you will approach the overall project, not only the next step.
Research Your Topic
When completing a library search for online peer reviewed journal articles, do not forget to use Boolean Operators to refine or narrow your search field. Standard Boolean Operators are (capitalized) AND, OR and NOT. While using OR will expand your search, AND and NOT will reduce the scope of your search. For example, if I want information on ageism and care giving, but I only want it to relate to the elderly, I might use the following to search a database: ageism AND care NOT children. Remember to keep track of your search strings (like the one just used) and then you’ll know what worked and what didn’t as you come and go from your academic research.
The UQ Library provides an excellent step-by-step guide to searching databases:
Searching in databases – Library – University of Queensland (uq.edu.au)
Did you know that you can also link the UQ Library to Google Scholar? This link tells you how:
Google Scholar – Library – University of Queensland (uq.edu.au)
Write the Thesis Statement
The concept of a thesis statement was introduced in Chapter 21. The information below relates specifically to a discursive essay thesis statement.
As noted in the introduction to this chapter, the discursive essay should not take a stance and therefore the thesis statement must also impartially indicate more than one perspective. The goal is to present both sides of an argument equally and allow the reader to make an informed and well-reasoned choice after providing supporting evidence for each side of the argument.
Sample thesis statements: Solar energy is a cost -effective solution to burning fossil fuels for electricity , however lower income families cannot afford the installation costs .
Some studies indicate that teacher comments written in red may have no effect on students’ emotions , however other studies suggest that seeing red ink on papers could cause some students unnecessary stress. [1]
According to social justice principles, education should be available to all , yet historically, the intellectually and physically impaired may have been exempt from participation due to their supposed inability to learn. [2]
This is where your pros and cons list comes into play. For each pro, or positive statement you make, about your topic, create an equivalent con, or negative statement and this will enable you to arrive at two opposing assertions – the claim and counter claim.
While there may be multiple arguments or perspectives related to your essay topic, it is important that you match each claim with a counter-claim. This applies to the thesis statement and each supporting argument within the body paragraphs of the essay.
It is not just a matter of agreeing or disagreeing. A neutral tone is crucial. Do not include positive or negative leading statements, such as “It is undeniable that…” or “One should not accept the view that…”. You are NOT attempting to persuade the reader to choose one viewpoint over another.
Leading statements / language will be discussed further, in class, within term three of the Academic English course.
Thesis Structure:
- Note the two sides (indicated in green and orange)
- Note the use of tentative language: “Some studies”, “may have”, “could cause”, “some students”
- As the thesis is yet to be discussed in-depth, and you are not an expert in the field, do not use definitive language
- The statement is also one sentence, with a “pivot point” in the middle, with a comma and signposting to indicate a contradictory perspective (in black). Other examples include, nevertheless, though, although, regardless, yet, albeit. DO NOT use the word “but” as it lacks academic tone. Some signposts (e.g., although, though, while) may be placed at the start of the two clauses rather than in the middle – just remember the comma, for example, “While some studies suggest solar energy is cost-effective, other critical research questions its affordability.”
- Also note that it is based on preliminary research and not opinion: “some studies”, “other studies”, “according to social justice principles”, “critical research”.
Claims and Counter Claims
NOTE: Please do not confuse the words ‘claim’ and ‘counter-claim’ with moral or value judgements about right/wrong, good/bad, successful/unsuccessful, or the like. The term ‘claim’ simply refers to the first position or argument you put forward (whether for or against), and ‘counter-claim’ is the alternate position or argument.
In a discursive essay the goal is to present both sides equally and then draw some tentative conclusions based on the evidence presented.
- To formulate your claims and counter claims, write a list of pros and cons.
- For each pro there should be a corresponding con.
- Three sets of pros and cons will be required for your discursive essay. One set for each body paragraph. These become your claims and counter claims.
- For a longer essay, you would need further claims and counter claims.
- Some instructors prefer students to keep the pros and cons in the same order across the body paragraphs. Each paragraph would then have a pro followed by a con or else a con followed by a pro. The order should align with your thesis; if the thesis gives a pro view of the topic followed by a negative view (con) then the paragraphs should also start with the pro and follow with the con, or else vice versa. If not aligned and consistent, the reader may easily become confused as the argument proceeds. Ask your teacher if this is a requirement for your assessment.

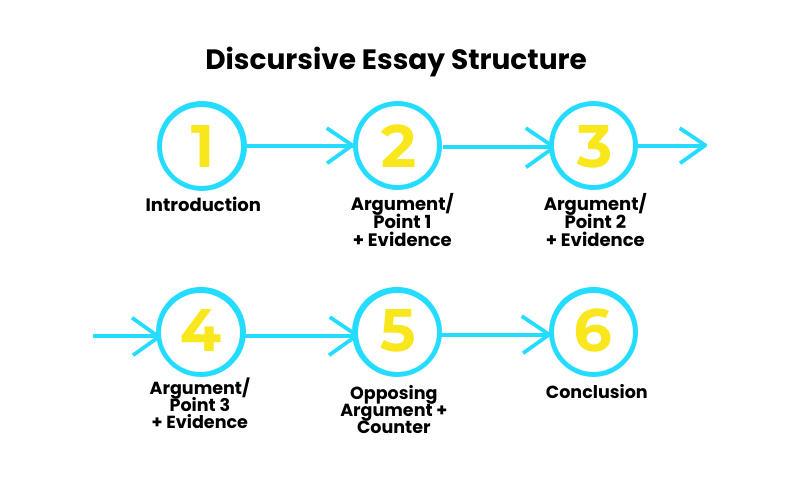
Use previous chapters to explore your chosen topic through concept mapping (Chapter 18) and essay outlining (Chapter 19), with one variance; you must include your proposed claims and counter claims in your proposed paragraph structures. What follows is a generic model for a discursive essay. The following Chapter 27 will examine this in further details.
Sample Discursive Essay Outline
The paragraphs are continuous; the dot-points are only meant to indicate content.
Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Essay outline (including 3 controlling ideas)
Body Paragraphs X 3 (Elaboration and evidence will be more than one sentence, though the topic, claim and counter claim should be succinct)
- T opic sentence, including 1/3 controlling ideas (the topic remains the same throughout the entire essay; it is the controlling idea that changes)
- A claim/assertion about the controlling idea
- E laboration – more information about the claim
- E vidence -academic research (Don’t forget to tell the reader how / why the evidence supports the claim. Be explicit in your E valuation rather than assuming the connection is obvious to the reader)
- A counter claim (remember it must be COUNTER to the claim you made, not about something different)
- E laboration – more information about the counter claim
- E vidence – academic research (Don’t forget to tell the reader how / why the evidence supports the claim. Be explicit in your E valuation rather than assuming the connection is obvious to the reader)
- Concluding sentence – L inks back to the topic and/or the next controlling idea in the following paragraph
Mirror the introduction. The essay outline should have stated the plan for the essay – “This essay will discuss…”, therefore the conclusion should identify that this has been fulfilled, “This essay has discussed…”, plus summarise the controlling ideas and key arguments. ONLY draw tentative conclusions BOTH for and against, allowing the reader to make up their own mind about the topic. Also remember to re-state the thesis in the conclusion. If it is part of the marking criteria, you should also include a recommendation or prediction about the future use or cost/benefit of the chosen topic/concept.
A word of warning, many students fall into the generic realm of stating that there should be further research on their topic or in the field of study. This is a gross statement of the obvious as all academia is ongoing. Try to be more practical with your recommendations and also think about who would instigate them and where the funding might come from.
This chapter gives an overview of what a discursive essay is and a few things to consider when choosing your topic. It also provides a generic outline for a discursive essay structure. The following chapter examines the structure in further detail.
- Inez, S. M. (2018, September 10). What is a discursive essay, and how do you write a good one? Kibin. ↵
- Hale, A., & Basides, H. (2013). The keys to academic English. Palgrave ↵
researched, reliable, written by academics and published by reputable publishers; often, but not always peer reviewed
assertion, maintain as fact
The term ‘claim’ simply refers to the first position or argument you put forward (whether for or against), and ‘counter-claim’ is the alternate position or argument.
Academic Writing Skills Copyright © 2021 by Patricia Williamson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Literary Devices
Literary devices, terms, and elements, definition of prose.
Prose is a communicative style that sounds natural and uses grammatical structure. Prose is the opposite of verse, or poetry, which employs a rhythmic structure that does not mimic ordinary speech. There is, however, some poetry called “prose poetry” that uses elements of prose while adding in poetic techniques such as heightened emotional content, high frequency of metaphors, and juxtaposition of contrasting images. Most forms of writing and speaking are done in prose, including short stories and novels, journalism, academic writing, and regular conversations.
The word “prose” comes from the Latin expression prosa oratio , which means straightforward or direct speech. Due to the definition of prose referring to straightforward communication, “prosaic” has come to mean dull and commonplace discourse. When used as a literary term, however, prose does not carry this connotation.
Common Examples of Prose
Everything that is not poetry is prose. Therefore, every utterance or written word that is not in the form of verse is an example of prose. Here are some different formats that prose comes in:
- Casual dialogue : “Hi, how are you?” “I’m fine, how are you?” “Fine, thanks.”
- Oration : I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character. –Martin Luther King, Jr.
- Dictionary definition : Prose (n)—the ordinary form of spoken or written language, without metrical structure, as distinguished from poetry or verse.
- Philosophical texts: Whoever fights monsters should see to it that in the process he does not become a monster. And if you gaze long enough into an abyss, the abyss will gaze back into you. –Friedrich Nietzsche
- Journalism: State and local officials were heavily criticized for their response to the January 2014 storm that created a traffic nightmare and left some motorists stranded for 18 hours or more.
Significance of Prose in Literature
Much of the world’s literature is written in a prose style. However, this was not always the case. Ancient Greek dramas, religious texts, and old epic poetry were all usually written in verse. Verse is much more highly stylized than prose. In literature, prose became popular as a way to express more realistic dialogues and present narration in a more straightforward style. With very few exceptions, all novels and short stories are written in prose.
Examples of Prose in Literature
I shall never be fool enough to turn knight-errant. For I see quite well that it’s not the fashion now to do as they did in the olden days when they say those famous knights roamed the world.
( Don Quixote by Miguel de Cervantes)
Don Quixote is often considered the forerunner of the modern novel, and here we can see Cervantes’s prose style as being very direct with some sarcasm.
The ledge, where I placed my candle, had a few mildewed books piled up in one corner; and it was covered with writing scratched on the paint. This writing, however, was nothing but a name repeated in all kinds of characters, large and small—Catherine Earnshaw, here and there varied to Catherine Heathcliff, and then again to Catherine Linton. In vapid listlessness I leant my head against the window, and continued spelling over Catherine Earnshaw—Heathcliff—Linton, till my eyes closed; but they had not rested five minutes when a glare of white letters started from the dark, as vivid as spectres—the air swarmed with Catherines; and rousing myself to dispel the obtrusive name, I discovered my candle wick reclining on one of the antique volumes, and perfuming the place with an odour of roasted calf-skin.
( Wuthering Heights by Emily Brontë)
In this prose example from Emily Brontë we hear from the narrator, who is focused on the character of Catherine and her fate. The prose style mimics his obsession in its long, winding sentences.
“I never know you was so brave, Jim,” she went on comfortingly. “You is just like big mans; you wait for him lift his head and then you go for him. Ain’t you feel scared a bit? Now we take that snake home and show everybody. Nobody ain’t seen in this kawn-tree so big snake like you kill.”
( My Antonia by Willa Cather)
In this excerpt from My Antonia , Willa Cather uses her prose to suggest the sound of Antonia’s English. She is a recent immigrant and as the book progresses her English improves, yet never loses the flavor of being a non-native speaker.
Robert Cohn was once middleweight boxing champion of Princeton. Do not think I am very much impressed by that as a boxing title, but it meant a lot to Cohn. He cared nothing for boxing, in fact he disliked it, but he learned it painfully and thoroughly to counteract the feeling of inferiority and shyness he had felt on being treated as a Jew at Princeton.
( The Sun also Rises by Ernest Hemingway)
Ernest Hemingway wrote his prose in a very direct and straightforward manner. This excerpt from The Sun Also Rises demonstrates the directness in which he wrote–there is no subtlety to the narrator’s remark “Do not think I am very much impressed by that as a boxing title.”
The Lighthouse was then a silvery, misty-looking tower with a yellow eye, that opened suddenly, and softly in the evening. Now— James looked at the Lighthouse. He could see the white-washed rocks; the tower, stark and straight; he could see that it was barred with black and white; he could see windows in it; he could even see washing spread on the rocks to dry. So that was the Lighthouse, was it? No, the other was also the Lighthouse. For nothing was simply one thing. The other Lighthouse was true too.
( To the Lighthouse by Virginia Woolf)
Virginia Woolf was noted for her stream-of-consciousness prose style. This excerpt from To the Lighthouse demonstrates her style of writing in the same way that thoughts occur to a normal person.
And if sometimes, on the steps of a palace or the green grass of a ditch, in the mournful solitude of your room, you wake again, drunkenness already diminishing or gone, ask the wind, the wave, the star, the bird, the clock, everything that is flying, everything that is groaning, everything that is rolling, everything that is singing, everything that is speaking. . .ask what time it is and wind, wave, star, bird, clock will answer you: “It is time to be drunk! So as not to be the martyred slaves of time, be drunk, be continually drunk! On wine, on poetry or on virtue as you wish.”
(“Be Drunk” by Charles Baudelaire)
Unlike the previous examples, this is an example of a prose poem. Note that it is written in a fluid way that uses regular grammar and rhythm, yet has an inarguably poetic sense to it.
Test Your Knowledge of Prose
1. Choose the best prose definition from the following statements: A. A form of communicating that uses ordinary grammar and flow. B. A piece of literature with a rhythmic structure. C. A synonym for verse. [spoiler title=”Answer to Question #1″] Answer: A is the correct answer.[/spoiler]
2. Why is the following quote from William Shakespeare’s “Sonnet 116” not an example of prose?
Let me not to the marriage of true minds Admit impediments. Love is not love Which alters when it alteration finds, Or bends with the remover to remove
A. It has a rhythmic structure. B. It contains rhymes. C. It does not use ordinary grammar. D. All of the above. [spoiler title=”Answer to Question #2″] Answer: D is the correct answer.[/spoiler]
3. Which of the following excerpts from works by Margaret Atwood is a prose example? A.
You’re sad because you’re sad. It’s psychic. It’s the age. It’s chemical. Go see a shrink or take a pill, or hug your sadness like an eyeless doll you need to sleep.
“A Sad Child” B.
I would like to believe this is a story I’m telling. I need to believe it. I must believe it. Those who can believe that such stories are only stories have a better chance. If it’s a story I’m telling, then I have control over the ending. Then there will be an ending, to the story, and real life will come after it. I can pick up where I left off.
The Handmaid’s Tale C.
No, they whisper. You own nothing. You were a visitor, time after time climbing the hill, planting the flag, proclaiming. We never belonged to you. You never found us. It was always the other way round.
“The Moment” [spoiler title=”Answer to Question #3″] Answer: B is the correct answer.[/spoiler]

- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- History of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- History of Art
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical Literature
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- History by Period
- Intellectual History
- Military History
- Political History
- Regional and National History
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Browse content in Literature
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Language
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Religious Studies
- Society and Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Company and Commercial Law
- Comparative Law
- Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Criminal Law
- History of Law
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Programming Languages
- Environmental Science
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business History
- Industry Studies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Browse content in Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Browse content in Education
- Higher and Further Education
- Browse content in Politics
- Asian Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Environmental Politics
- International Relations
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Political Economy
- Public Policy
- Security Studies
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Browse content in Social Work
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Browse content in Sociology
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Reviews and Awards
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic

- < Previous
- Next chapter >

1 Introducing the Prose Poem
- Published: October 2020
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This chapter traces prose poetry's development in nineteenth-century France and its early reception and subsequent critical views about the form. The prose poem in English is now established as an important literary form in many countries at a time when the composition and publication of poetry is thriving. However, while poetry generally continues to be recognized as a literary genre highly suited to expressing intense emotion, grappling with the ineffable and the intimate, and while lineated lyric poetry is widely admired for its rhythms and musicality, the main scholarship written about English-language prose poetry to date defines the form as problematic, paradoxical, ambiguous, unresolved, or contradictory. The common observation that the term “prose poetry” appears to contain a contradiction is not surprising given that poetry and prose are often understood to be fundamentally different kinds of writing. The chapter then defines the prose poem's main features and discusses the challenge prose poetry presents to established ideas of literary genre.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.

Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

Literature Review
1) select a topic, 2) search the literature, 3) write the literature review, 4) create a bibliography.
- Literature Review Samples
Research Help
Get started with the Library's Research Guides which provide access to the best books, articles, Internet sites, media, and statistics on a variety of topics.
Select a topic you can manage in the timeframe you have to complete your project. Narrow down the topic if it is too broad.
Establish your research questions and organize your literature into logical categories around the subject/topic areas of your questions.
Use a variety of resources - locate books, journals, and documents that contain useful information and ideas on your topic. Internet sites, theses, conference papers, eprints and government or industry reports can also be included. Do not rely solely on electronic full-text material which is more easily available. Reference sources such as dictionaries can assist in defining terminology, and encyclopedias may be useful in introducing topics and listing key references.
You will need to review literature and analyze the information presented in each source. The review process is ongoing - you may need to go back to locate additional materials as you identify new ideas to see if others have written on similar topics.
A literature review is a piece of discursive prose , not a list describing or summarizing one piece of literature after another.
You can organize the review in many ways; for example, you can center the review historically (how this topic has been dealt with over time); or center it on the theoretical positions surrounding your topic (those for a position vs. those against, for example); or you can focus on how each of your sources contributes to your understanding of your project.
Your literature review should include
- an introduction which explains how your review is organized.
- the body contains the evaluation or synthesize of the materials you want to include on your topic.
Create a bibliography of all the materials included in the literature review - books, articles, or documents using the appropriate style required by your instructor - APA, MLA, Chicago.
For citation examples see style manuals.
Or, you can visit the MU Tutoring & Writing Center's Resources for Writers .
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Literature Review Samples >>
- Last Updated: Apr 3, 2024 11:50 AM
- URL: https://guides.monmouth.edu/litreview
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Definition of discursive
Did you know.
The Latin verb discurrere meant "to run about", and from this word we get our word discursive , which often means rambling about over a wide range of topics. A discursive writing style generally isn't encouraged by writing teachers. But some of the great 19th-century writers, such as Charles Lamb and Thomas de Quincey, show that the discursive essay, especially when gracefully written and somewhat personal in tone, can be a pleasure to read. And the man often called the inventor of the essay, the great Michel de Montaigne, might touch on dozens of different topics in the course of a long discursive essay.
- digressional
- digressionary
Examples of discursive in a Sentence
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'discursive.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
borrowed from Medieval Latin discursīvus "showing reasoned thought, logical," from discursus, past participle of discurrere "to range over, discuss" (going back to Latin, "to run off in different directions, [of a mind or speaker] branch out, range") + Latin -īvus -ive — more at discourse entry 1
1595, in the meaning defined at sense 1b
Dictionary Entries Near discursive
discursive reason
Cite this Entry
“Discursive.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/discursive. Accessed 13 May. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of discursive, more from merriam-webster on discursive.
Nglish: Translation of discursive for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of discursive for Arabic Speakers
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
More commonly misspelled words, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, the words of the week - may 10, a great big list of bread words, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 8 uncommon words related to love, 9 superb owl words, games & quizzes.

How to Write a Discursive Essay: Tips to Succeed & Examples
So, you need to accomplish your discursive essay writing. The typical questions most students ask are: How do you write it? What is discursive essay?
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
A discursive essay is an academic paper that involves a discussion on a particular topic. It is usually assigned to college students. You may be required to write a paper wherein you have to do one of the following:
- argue for the issue or against it;
- present your points of view on both sides;
- provide your unprejudiced opinion on that matter.
Don’t panic!
Check out the tips from Custom-writing.org experts below. They will assist you in discursive writing and encourage you to examine essay examples. Moreover, in this article, you’ll also learn about different types of discursive essay, and its introduction, main body, and conclusion structure.
- ❓ What Is It?
- 🏁 Main Types
Introduction
- Basic Don’Ts
- ✏️ Frequent Questions
❓ What Is a Discursive Essay?
First of all, let’s figure out what the discursive essay is.
You may think it’s similar to the argumentative essay. Yes, but there’s a difference between them in the structure and purpose of these two types of assignments:
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
We will take a detailed look at how to structure a discursive essay later, and now let’s find out what are the types of this assignment.
Keep reading!
🏁 Discursive Essay: Main Types
You have to think more critically and more in-depth when reviewing all viewpoints and aspects of discursive writing. Check these three main types of essay writing:
- Opinion Essay requires the author’s opinion on an issue which is stated in the introductory paragraph. It should be clearly presented and followed by reasons and supporting examples. Also, this essay paper should contain an opposing argument that comes before the conclusion. The writer must explain to readers why the mentioned argument is considered to be unconvincing. The writer’s opinion should be restated/summarized in the conclusion.
- For and Against Essay provides readers with a thorough debate on the topic with the help of opposing points of view. Each point should be discussed objectively and described in details. The introductory paragraph puts the issue under consideration. The main body of this essay paper should present examples, reasons, and arguments supported by justifications. The author’s own opinion with balanced reflections on the topic should be stated only in conclusion.
- Essay Suggesting Solution to a Problem discusses problems and finds the main solutions. The introduction paragraph explicitly declares a problem and analyses its causes and consequences. The main body of the essay should offer some suggestions for a possible solution to the problem and potential state consequences or expected results. In conclusion, author’s opinion should be distinctly summarized.
📑 How to Write a Discursive Essay
Well, it’s time to talk about the structure of a discursive essay. Like most of the assignments, a discursive paper starts with an introduction and ends with a conclusion:
The first question you may ask is how to start a discursive essay introduction. Simple!
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 15% off your first order!
- Give your readers a hook – something that would sound interesting to them.
- Provide a short explanation of the problem. You may use quotations, as well as rhetorical questions.
- Show your readers both sides of the arguments and sum up.
You may be wondering…
Is there something I should avoid in my discursive essay introduction?
Yes. No stereotypes and generalizations, please!
The next step under formal essay writing you should take is to compose the body.
There are a few points you should remember:
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
- First and foremost: stay unprejudiced . Assess all of the aspects of an issue. Leave your feelings behind or for another essay type.
- Second: build your argumentation . If you have several arguments for your viewpoint—provide them in separate paragraphs. This will help you to keep your essay comprehensible and distinct. Don’t forget to submit supporting evidence.
- Third: write the body of an essay in an alternate manner. What does it mean? If your first paragraph supports the paper’s argument, then in the second paragraph you should write something in the opposite of it. Such a combination of supporting and opposite paragraphs will make your essay look apparent, and well researched. Besides, it will help you to remain neutral.
- Fourth: include topic sentences and evidence . Write a summary of the argument at the beginning of the paragraph. It will allow the reader to easier understand what the paragraph is about. Provide evidence to show that you’re not making the facts up.
Well, you’ve almost finished your writing. Now you should focus on the last section. Keep reading, and you will learn how to write a conclusion for a discursive essay.
- In the last section, you should summarize your article including the main points, specified in the body paragraphs.
- You may also logically express your opinion. Remember: it should resonate with your evidence stated in the body paragraphs.
- Don’t repeat findings, just summarize them.
Keep it short. Your conclusion length should not exceed one paragraph.
👍 Do’s and Don’ts
Do you want more discursive essay writing tips? Fine! Just check them below:
Basic Do’s of a Discursive Essay
- Write in formal, impersonal style.
- Introduce each point in a separate paragraph
- Use topic sentences for each paragraph
- Write well-developed paragraphs
- Give reasons and examples for each point
- Use sequencing
- Use linking words and phrases
- Make references to other sources and make sure that you follow proper citation style
- Identify used sources
Basic Don’Ts of a Discursive Essay
- Don’t use short forms, like I’ll, don’t, they’ve
- Don’t use informal/colloquial language, for example: old as the hills, ain’t, gonna, etc.
- Don’t use very emotional language, since it might make your discursive article look prejudiced
- Don’t use over-generalizations. Extending the features of some elements from a group more than it is reasonable will lead to generous and inaccurate conclusions.
- Don’t express your personal opinion too insistently
- Don’t refer to statistics without proper referencing (check our citation guides )
- Don’t use personal examples, leave it for a personal experience essay
Well, now you know what discursive essay means, what are its main types, and how to structure it.

Discursive Essay Topics
- Discussion of risk factors that impact human health.
- Discuss the necessity of understanding cultural heritage to provide efficient health care.
- Analyze different opinions on withdrawing patients’ treatment.
- Examine different views on the Civil War.
- Discuss what hostile emotional states are and how they impact human life.
- Discuss the meaning of metaphors used by Virgil in Aeneid .
- Describe different opinions on telehealth in nursing homes.
- The ethicality of stem cell technology.
- Explore the effectiveness of motivational interviewing .
- Discuss how people present themselves online .
- Discuss the reasons for Coca-Cola’s marketing success.
- Analyze the food safety issues and the ways to improve the situation.
- Examine the essential meaning of sleep for people’s physical and mental health.
- Explore various complications of working with groups.
- Discussion of the modern issues with virtue ethics .
- Describe different views on the definition of love .
- Give the for and against arguments considering food security technologies .
- Discuss how the concept of the American dream is presented in the film The Great Gatsby.
- Analyze the influence of family problems on children and suggest ways to improve the situation.
- Present the various points of view on the ethical concepts of Buddhism.
- Examine the attitudes towards the problem of homelessness and the suggested ways of its solution.
- Explore different opinions on the American revolution and its consequences.
- Discuss various policies and views around the globe on abortion .
- Discussion of the history of food foraging in different communities.
- Multiple thoughts on civility on the Internet .
- Analyze arguments on the effectiveness of hand sanitizers.
- Discuss the importance of visual aids in learning.
- Present and evaluate the theories of international development .
- Discuss how to prevent the spread of the West Nile Virus (WNV).
- Is embracing renewable energy sources beneficial for both environment and the global economy?
- Examine the correctness of the statement that the ideology of pleasure is the foundation of social activism.
- Discussion of the ethical dilemma of population control.
- Discuss the ethics of experimental studies .
- Analyze the topic of gun violence and gun control laws.
- Explore the reasons for opioid crises in the US.
- Give arguments for and against random drug testing.
- Discuss the problem of endangered species .
- Express your opinion on the necessity of parents to be included in children’s education .
- Present your attitude towards working in a bureaucratic organization.
- Discuss the issue of the nursing shortage and suggest a solution.
- Give different viewpoints on the definition of beauty .
- Analyze the problem of police misconduct .
- Discuss the description of violence of African people in literature.
- Examine the views on Gardner’s multiple intelligence theory .
- Describe the various opinions on mysticism and express your attitude towards it.
- Discuss the diverse standpoints on spirituality.
- Is nature protection an urgent problem?
- Analyze different ideas on physical privacy at work.
- Discussion on the Jewish heritage in nursing.
- Examine the views on the meaning of life .
Good luck with your discussions and discursive essays! Be sure to check out the articles on our blog for more academic wisdom. By the way, on the Custom-Writing website, you may find the best essay topics for your academic writing.
And don’t forget to share your opinion in the comments below.
You might also be interested in:
- Friendship Essay: Writing Guide & Topic Ideas about Friendship
- Teamwork Essay: Quick Guide on How to Write a Good Paper
- Compare and Contrast Essay Writing Tips and Examples
- Transportation Essay: Writing Tips and Brilliant Topics
✏️ Discursive Essay FAQ
There is no one definitely correct answer to this question. Like any other essay, the text should have a clear structure with an introduction, body, and conclusion. The most important thing is that the overall book needs to be cohesive, persuasive, and exciting to read.
An example of a step by step guide is:
1. Take a closer look at the topic, think about the points to cover.
2. Choose the most relevant points and compose the Body of the essay.
3. Add an appropriate Introduction and Conclusion.
To write a good conclusion, you need to have the rest of the essay finished. Does the body of your essay present well-structured points? Great, then see what you can conclude based on that. If possible, make a connection between the introduction and the conclusion.
To ensure that your essay has a perfect structure, start with creating an outline. Based on such a plan, you can present your points step by step. Your text should have a relevant introduction, several points in the main body (with examples), and a logical conclusion.
🔗 References
- Writing an Opinion Essay: Grace Fleming, ThoughtCo
- How to Write a Good Argumentative Essay: Easy Step-by-Step Guide: Master Class
- Ending the Essay: Conclusions: Harvard College Writing Center
- Academic Writing Style: University of Southern California
- Cite Your Sources: Library Guides at University of California, Santa Cruz
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

How to write a narrative essay? To do that, you need to know what a narrative essay is. It is an academic text usually written as a story and containing all the usual elements of a story. Narrative essays are often personal, experiential, and creative. Still, they should be made...
![discursive prose example College Essay Writing 101—the Comprehensive Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/student-girl-making-notes-in-a-copybook-with-a-pencil-e1565634333206-284x153.png)
So, you can’t wait to get into college and join a fraternity, sorority, or student union. Well, we have some incredibly useful tips and helpful information for college admission essay writing! Remember: getting into college takes more than money. And outstanding essays get you great college scholarships!
![discursive prose example Americanism Essay: Examples, Tips & Topics [2024 Update]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/american-flag-284x153.jpg)
It’s not hard to see why Americanism is one of the most popular essay topics. The concept of Americanism is in the center of the US identity. Writing an essay about it is an excellent way to find out more about this great country.

An art critique paper involves a comprehensive analysis and assessment of an artwork. Though this looks a bit complicated, the task doesn’t require a lot of time if you have sufficient critique writing skills. It’s an interesting assignment for students of art colleges as well as high schoolers. All you...

An article review is an academic assignment that invites you to study a piece of academic research closely. Then, you should present its summary and critically evaluate it using the knowledge you’ve gained in class and during your independent study. If you get such a task at college or university,...

Short essays answer a specific question on the subject. They usually are anywhere between 250 words and 750 words long. A paper with less than 250 words isn’t considered a finished text, so it doesn’t fall under the category of a short essay. Essays of such format are required for...

When you hear the phrase “spiritual leadership,” you probably think it’s only associated with religion. But did you know that this form of leadership can also be found in business? The book Spiritual Leadership: Moving People on to God’s Agenda by Henry and Richard Blackaby is a good starting point...

High school and college students often face challenges when crafting a compare-and-contrast essay. A well-written paper of this kind needs to be structured appropriately to earn you good grades. Knowing how to organize your ideas allows you to present your ideas in a coherent and logical manner This article by...

“If a tree falls in the forest, does it make a sound?” is one of the most debatable philosophical questions regarding observation and perception. Many tried to answer it, including the English philosopher John Locke. Do you need to explore Locke’s perspective on this question in your essay? You are on the right...

The long-standing debate surrounding abortion has many opponents and advocates. Groups known as Pro-Choice and Pro-Life argue which approach is better, with no easy solution in sight. This ethical complexity is what makes abortion a popular topic for argumentative writing. As a student, you need to tackle it appropriately. If...

What is the most important part of any essay or research paper? Of course, it’s the thesis statement—a sentence that expresses the paper’s main idea and guides the readers through your arguments. But where do you place the thesis? You’ve probably answered, “in the introduction.” However, that’s not all of...

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide...
It’s very helpful!
it’s a good site to learn from. However, it will be perfect if there is a small essay to clear the mess understanding from the advice
This was so helpful , thank you God bless you
Very good site,thank so much for your effort in writing the posts.
thank you my n word 👨🏿🦳
thank you so much!!!! is there any way to access an annotated example to help?
Thank you so much. That really helped me with writing my essay.
thanku so much for increasing my knowledge
Thank you. It was really helpful. It has answered all my questions.
The literature review: discursive prose
- PMID: 22441043
- DOI: 10.1097/01.ASW.0000413595.12814.04
Publication types
- Evidence-Based Medicine*
- Information Dissemination
- Review Literature as Topic*
- Skin Ulcer / therapy*
- Wounds and Injuries / therapy*
Video Series
How to Read the Bible Series
How to Read Biblical Prose Discourse
A quarter of the Bible is written in a style called prose discourse. Learn how this style is used to communicate key parts of Scripture.
How to Read the Bible Series Series • 3 Episodes


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This month, our featured continuing education article is an excellent example of a well-constructed literature review. Discursive Prose. A literature review should be a good piece of discursive prose (proceeding by argument or reasoning rather than by intuition). It should not be a list describing or summarizing one piece of literature after ...
English literature - Discursive Prose: The French Revolution prompted a fierce debate about social and political principles, a debate conducted in impassioned and often eloquent polemical prose. Richard Price's Discourse on the Love of Our Country (1789) was answered by Edmund Burke's conservative Reflections on the Revolution in France (1790) and by Wollstonecraft's A Vindication of the ...
"A literature review is a piece of discursive prose, not a list describing or summarizing one piece of literature after another. It's usually a bad sign to see every paragraph beginning with the name of a researcher. ... For example, see this published research article that includes a Literature Review (content note: this article discusses ...
A discursive essay is a form of critical essay that attempts to provide the reader with a balanced argument on a topic, supported by evidence. It requires critical thinking, as well as sound and valid arguments (see Chapter 25) that acknowledge and analyse arguments both for and against any given topic, plus discursive essay writing appeals to ...
Definition of Prose. Prose is a communicative style that sounds natural and uses grammatical structure. Prose is the opposite of verse, or poetry, which employs a rhythmic structure that does not mimic ordinary speech. There is, however, some poetry called "prose poetry" that uses elements of prose while adding in poetic techniques such as ...
Organising a discursive essay. There are two basic types of discursive essay. Firstly there are persuasive essays in which you can argue strongly either in favour of or against a given discussion ...
This is an example of discursive prose rather than of prose poetry, but it uses some of the devices often associated with poetry, most conspicuously, vivid image-making and insistent repetition, along with some noticeably iambic rhythms. ... For example, many prose poets emphasize that their works are prose poems by presenting them on the page ...
A lit review is a piece of discursive (fluid, expansive) prose, not a list describing or summarizing one piece of literature after another. Organize your lit review into logical sections that present themes or identify trends, including relevant theory. The purpose of the review is not to present a bibliography of all the works published on the ...
A literature review is a piece of discursive prose, not a list describing or summarizing one piece of literature after another.. You can organize the review in many ways; for example, you can center the review historically (how this topic has been dealt with over time); or center it on the theoretical positions surrounding your topic (those for a position vs. those against, for example); or ...
Example literature review. What is a literature review? A literature review is not research, it is a review of the research that has been done on your topic. ... A literature review is a piece of discursive prose, not a list describing or summarizing one piece of literature after another. It's usually a bad sign to see every paragraph beginning ...
A literature review is a piece of discursive prose, not a list describing or summarizing one piece of literature after another. When do Researchers Conduct ... An Outline of the Previous Example • Forecasts of increasing rate of AR/RS introduction (1) • Storage assignment/interleaving policies (Hausman, Schwartz, Graves
discursive: [adjective] moving from topic to topic without order : rambling. proceeding coherently from topic to topic.
This month, our featured continuing education article is an excellent example of a well-constructed literature review. Discursive Prose. A literature review should be a good piece of discursive prose (proceeding by argument or reasoning rather than by intuition). It should not be a list describing or summarizing one piece of literature after ...
quality in poetry which I mean by "discursive" is to say that it is primarily neither ironic nor ecstatic. It is speech, organized by its meaning, avoiding the distances and complications of irony on one side and the ecstatic fusion of speaker, meaning and subject on the other. The idea is to have all of the virtues of prose, in
discursive /dɪ ˈ skɚsɪv/ adjective. Britannica Dictionary definition of DISCURSIVE. [more discursive; most discursive] formal. : talking or writing about many different things in a way that is not highly organized. The instructor gave a discursive [= rambling] lecture that wandered from one topic to another. discursive prose.
Start with an introduction to the topic. Discuss each essay question in a single paragraph. Begin each paragraph with a powerful issue sentence. Paragraphs with one point usually followed by a counterpoint paragraph. Its style is general for essays as the reader should understand what you stand for.
discursive prose, Josephine Miles. provides a background to the discussion. of. Christensen, Rodgers, and Becker. (BN) TE 500 134. 9. ci G.1.1. ci. ... There are paragraphs ( for example, my. D ) in which coor&nate subtopics are. developed some by additions to the sub-topic sentence and others by added sen-tences. Such interchangeability.
How To Write A Band 6 Module C Discursive Essay (New Syllabus) Don't know what a discursive essay is? Do you know what the differences between a discursive and persuasive essay are? Don't worry. In this article, we explain what discursive writing for Year 12 Module C: The Craft of Writing is and give you a step-by-step process for writing a ...
discursive: 1 adj proceeding to a conclusion by reason or argument rather than intuition Synonyms: dianoetic logical capable of or reflecting the capability for correct and valid reasoning adj (of e.g. speech and writing) tending to depart from the main point or cover a wide range of subjects "a rambling discursive book" Synonyms: digressive , ...
Adv Skin Wound Care. 2012 Apr;25(4):150. doi: 10.1097/01.ASW.0000413595.12814.04.
How to Read Biblical Prose Discourse. A quarter of the Bible is written in a style called prose discourse. Learn how this style is used to communicate key parts of Scripture. How to Read the Bible Series Series • 3 Episodes.
1. In this sense the discursive or ideational is only ever relatively autonomous of the material. 2. 1. Advertisement. It is a fundamentally discursive environment which takes the asynchronous discussion board as its central tool. 1. 0. Power was once largely discursive, But it now is largely informational.