- Accessories
- Entertainment
- PCs & Components
- Wi-Fi & Networks
- Newsletters
- Digital Magazine – Subscribe
- Digital Magazine – Info
- Smart Answers
- Best laptops
- Best antivirus
- Best monitors
- Laptop deals
- Desktop PC deals
When you purchase through links in our articles, we may earn a small commission. This doesn't affect our editorial independence .

Wi-Fi problems? Here’s how to diagnose your router issues

Whenever someone sends me a question about how to fix their Wi-Fi, I wince. It’s not that I dislike helping people with their router problems. In fact, there are few geeky endeavors I find more rewarding than fixing Wi-Fi connection issues at a friend or family member’s home.
But Wi-Fi has always felt more like a dark art than a science, and it’s an art that’s hard to conjure without being physically present. Potential points of failure are everywhere, and what works well in one home might not in another. Even the reviewers of networking gear can reach drastically different conclusions about the very same product.
Wi-Fi is fundamentally at odds, then, with my desire to answer questions with specific recommendations. The best I can do is walk your through how I diagnose Wi-Fi problems myself. That way, you can make better decisions on whether (and how) to upgrade your own gear.
Further reading: The best mesh Wi-Fi routers
Size up the Wi-Fi problem
The first step to solving Wi-Fi issues is to see if the slowdown is coming from your cable modem (which brings internet service into the home) or from the router (which distributes Wi-Fi connectivity throughout the home).
Start by plugging a computer directly into your modem with an ethernet cable and running a speed test. (The easiest way is to do a Google search for “speed test,” then hit the blue “Run Speed Test” button atop the search results.) A USB-to-Ethernet adapter will be necessary for testing on computers that don’t have an ethernet port, but if that’s too much trouble or you don’t have a proper computer at all, you can also try calling your internet provider and asking them to test your internet speed remotely.

Running speed tests throughout the house can help you figure out where the Wi-Fi trouble spots are.
Jared Newman / Foundry
If wired connection speeds are on par with your internet provider’s advertised speeds, the next step is to start running speed tests throughout the house. Measure speeds around the area where connectivity feels slow, then work your way back to where the router is located, running multiple tests in each area as you go.
The goal here is to figure out where your connection troubles are occurring. Consistently slow speeds throughout the house may be a sign of an outdated router, while dead zones or range issues may require a more powerful router or mesh Wi-Fi system. (More on that shortly.)
Find your Wi-Fi router’s 802.11 version
To figure out whether a router needs replacing, it helps to know how old it is. One way to do this to locate the router’s model number—it’s likely printed on the router itself—then search the web for info about which version of Wi-Fi it supports. Here are the major Wi-Fi versions to know about:
- 802.11a/b/g: Extremely old and almost certainly the source of all your Wi-Fi problems.
- 802.11a/b/g/n (or just 802.11n): Outdated at this point and a solid candidate for replacement. Many of these routers only support a single frequency band that’s slower and more congestion-prone, and “dual-band” variants have limited range on the faster 5 GHz frequency band.
- 802.11ac (also marketed as Wi-Fi 5): Not the latest standard, but still widely available even in some high-performance routers.
- 802.11ax (or Wi-Fi 6): Routers using this standard started shipping in late 2020, so your router is likely quite new.
- Wi-Fi 6E: Congrats, you probably just bought a new router .
Wi-Fi versions alone aren’t an indicator of quality—a cheap Wi-Fi 6 router can be worse than a high-end mesh system with Wi-Fi 5—but each successive version has introduced new features that improve connectivity, and we’ve generally seen a push toward better performance over time.
Try some smaller router fixes
Just to rehash a tip I discussed back in July , sometimes changing your router’s channel and bandwidth settings can work wonders for reducing Wi-Fi interference, especially if you’re seeing inconsistent speeds on devices that aren’t too far from the router. By digging into your router’s settings, you can bypass automatic channel selection and find a channel that might be less congested.
You can also try some other little tweaks, like getting your router off the ground and clearing some space around it—but I wouldn’t start rearranging your room for the router’s sake. Chances are the improvements will be minimal. Of course, moving your router to a more central location in the home can help, but that would likely require having the cable company rewire your home internet connection.
Wi-Fi extenders: a last resort

Because replacing a router is a pain, a lot of folks wonder if they can just solve their problems with a Wi-Fi extender or repeater , which take the wireless signal from a router and rebroadcast it farther away. (“Extender” sometimes refers to a device with a wired connection to the router, though I often see both terms used interchangeably.)
My experience with Wi-Fi extenders is hit or miss. Wireless repeaters will always degrade whatever signal they receive, so the benefits can cancel out if you’re trying to address a dead zone or interference from other nearby wireless devices. The same is true with powerline adapters , which send a wired ethernet connection from your router to another part of the house through your wall outlets. Depending on how your house is wired, this approach can give you a weak connection or not work at all.
I don’t tell people to avoid extenders outright, because they can work in some scenarios, but keep your expectations low and be prepared to return the device if it doesn’t help. Here’s how to set up a Wi-Fi extender if you decide to go that route.
Picking a new Wi-Fi router
Once you’ve concluded that it’s time to replace your router, then what?
our favorite mesh wi-fi system
Netgear orbi home wifi system (rbk50).

A mesh Wi-Fi system will be the surest way to solve your Wi-Fi problems, especially in larger homes or ones with lots of dead zones. These systems let you plug in multiple access points throughout the house, creating one big network. They’re better at managing connections than a router with an extender, and systems advertised as “Tri-Band” can connect each access point without congesting the rest of the network.
Such systems might not be necessary, though. If you haven’t replaced your router in a while, even a new standalone router might be enough to power through dead zones if they’re not too far away. Standalone routers are generally less expensive than mesh systems, and some have features that mesh systems lack, such as USB storage support or a large number of ethernet ports.
A supremely powerful gaming router
Tp-link gx90.

Ultimately, though, there’s no way to tell for sure if a new router will work without trying it yourself. You can read all sorts of reviews—PCWorld reviews both Wi-Fi mesh systems and the latest Wi-Fi 6E routers —but even the best advice isn’t one-size-fits-all. Buying a new router will always involve a leap of faith.
A note on modem/router combos
Finally, there’s one more complicating factor: Although cable companies used to distribute internet modems and routers separately—the former bringing in the internet from outside the house, and the latter to distributing Wi-Fi through the home—it’s increasingly common now to get both functions in one box. That makes installation easier for the cable company, but makes router replacement trickier for you.
If you have a combo box and are paying for it in rental fees, consider replacing it with two devices: A new router and a separate cable modem . But be aware that some companies—particularly fiber-optic internet providers such as AT&T and Verizon—make replacing the modem component difficult or impossible.
If replacing the modem isn’t possible or necessary, you can just disable its Wi-Fi features so they don’t interfere with your new router. The instructions for doing so can vary by provider, so expect to do some Googling of “modem mode” or “bridge mode” plus the name of your internet provider.
And if you’re still having Wi-Fi problems after all that, send me an email and I’ll do my best to help. You can also check out my Advisorator newsletter —where a version of this story first appeared—to get more practical tech advice every week.
Editor’s note: This article has been updated with up-to-date product recommendations.
Author: Jared Newman

Jared Newman has been helping folks make sense of technology for over a decade, writing for PCWorld, TechHive, and elsewhere. He also publishes two newsletters, Advisorator for straightforward tech advice and Cord Cutter Weekly for saving money on TV service.
Recent stories by Jared Newman:
- Wi-Fi 5 vs. Wi-Fi 6 vs. Wi-Fi 6E: Which router should you pick?
- Meta Quest 4
- Google Pixel 9
- Google Pixel 8a
- Apple Vision Pro 2
- Nintendo Switch 2
- Samsung Galaxy Ring
- Yellowstone Season 6
- Recall an Email in Outlook
- Stranger Things Season 5
Digital Trends may earn a commission when you buy through links on our site. Why trust us?
Wi-Fi not working? How to fix the most common problems

Wi-Fi problems can strike anyone at any time, no matter how much networking experience you may have. But if you’ve not come across a particular Wi-Fi issue before, there’s no need to worry if you don’t know how to fix it. All you need are the right tools and a few tips, and you’ll be able to solve your Wi-Fi problem in no time.
Basic Wi-Fi troubleshooting checklist
Quick fixes for common problems, slow or no wi-fi or internet access in certain rooms, slow internet everywhere.
- One device can’t connect to the Wi-Fi
Nothing can connect to Wi-Fi
Connections drop at random times, wi-fi network disappears entirely, unknown devices on my wi-fi network, a recent update broke wi-fi.
- The satellite routers on my mesh network aren’t connecting
- My smart device isn’t connecting to Wi-Fi
- My console can’t connect to Wi-Fi
- Can’t connect to wireless printer
- Can’t connect to a guest Wi-Fi network that I set up
- Wi-Fi 6 or 6E isn’t working, even with a Wi-Fi 6 router
- Can’t find a router with Wi-Fi 7
Whether you’re experiencing problems with slow internet, Wi-Fi signal dropping, or you just can’t connect to Wi-Fi at all, here are some of the quickest and easiest fixes you can try. We’ll also cover some advanced advice on more troubling issues that would definitely result in your Wi-Fi not working at all, or at slower speeds.
If you have a non-specific problem with your Wi-Fi or don’t consider the problem serious enough to investigate more in-depth problems, consider the items on this list as a great way to start fixing your problem.
- Make sure your device’s Wi-Fi is on — Most laptops have a shortcut key that will turn off their Wi-Fi and it can be easy to press accidentally. Similarly, there is a quick toggle on most phones that will turn off the phone’s Wi-Fi capabilities.
- Restart your router — A quick restart of your router (achieved by unplugging it, waiting 30 seconds to 1 minute, and plugging it back in again) can fix many Wi-Fi difficulties.
- Check for an outage — Most ISP’s will have an outage map available on their website. Try using your phone’s data to check and see if an outage is reported in your area.
Forgot the Wi-Fi password
If you really can’t remember your Wi-Fi password, and there are no notes or cards with it written down somewhere, you’ll have to reset your router . Use a paperclip to press the hidden switch in the pinhole on the back of your router for 30 seconds. It should then default to factory settings.
- Best router deals: Save on mesh networks and Wi-Fi 6 routers
- The most common Windows 11 problems and how to fix them
- The most common GoTo Meeting problems and how to solve them
Use our guide to setting up a wireless router to get everything properly configured.
Wi-Fi connection lost when logging back into the computer
This problem can crop up on Windows 10 due to an issue with Fast Startup. Fast Startup keeps certain processes running so you can log back in very quickly. However, this can sometimes cause a bug with the wireless driver that prevents it from reconnecting to Wi-Fi properly. In the short term, you can turn off Fast Startup to prevent this problem . Search for Power Option s in your Windows 10 or Windows 11 search bar and go to this section of the Control Panel. Select Choose What the Power Button Does on the left-side menu, and then look at the new section Shutdown Settings . Find the option to Turn On Fast Startup and make sure it is deselected.
In the long term, you may need to update the driver for your wireless network adapter to fix any bugs causing this issue. You can follow our guide on how to update Windows 10 drivers for more information.
The network connects, but there’s no internet access
It might sound like a tired tip, but try resetting your modem by unplugging it and plugging it back in. If that’s no good, you can connect a laptop or desktop to your router with an Ethernet cable ( these are the best ones ) to see if it’s the router or your Wi-Fi that’s not working. If this works, then your best bet to get Wi-Fi working again is to reset your router . If there’s still no internet, though, you may have an outage. Contact your ISP.
Router crashes regularly and only restarting it helps
If your router needs to be restarted regularly, you should give your router a full reset . On most routers, you’ll find a Reset button that you can hold down with a paperclip. Do so for 30 seconds, and the router should default from factory settings. Use our guide to setting up a wireless router to get everything properly configured.
If that doesn’t work, your router may be on its way out. Your only real option is to return it if it is within its warranty period or to buy a new one.
Wi-Fi is made up of radio waves, meaning your Wi-Fi router broadcasts in all directions from a central location. If your router is in a far corner of your house, then you’re covering a great deal of the outside world unnecessarily. If you can, move your router to a more centralized location. The closer you can put your router to the center of your coverage area, the better reception will be throughout your home.
If you have external antennas, you can try adjusting those, too. Alternating between fully vertical and fully horizontal positions can help it reach in multiple directions.
If you live in an apartment building, other routers might be interfering with yours. Free software, like NetSpot on Mac, Windows, and Android, or Wi-Fi Analyzer for Android, can show you every wireless network nearby and what channel they’re using. If your router overlaps with nearby networks in particular rooms, consider switching to a less congested channel. If you need help switching, here’s our guide on how to change your Wi-Fi channel .
If none of that helps, your home might be too much for one router to handle. Consider purchasing a wireless repeater or setting up an old router to serve as one to extend the range of your main router. Upgrading to a whole-home mesh wireless system can also help with dead spots in certain areas of your home. Either way, it might be time to go and buy a new router .
If your Wi-Fi speed is slow no matter where you are, try plugging a laptop into your router directly and test your internet speed using one of the best internet speed tests . If speeds are still down, the problem is likely with your internet connection, not your router. Try some of these ways to improve your internet speed and contact your ISP.
If that’s not the issue, it could be that your current wireless channel is overcrowded by your devices or by those of other nearby networks. Consider changing the channel on your router in your router settings, by accessing the admin settings .
If that doesn’t help, performing a factory reset on your router and setting it up again may help. On most routers, there’s a Reset button that you can hold down with a paperclip. Do so for 30 seconds, and the router should default to factory settings. Use our guide to setting up a wireless router to get everything properly configured, and see if that helps.
If none of that works and your internet is fine on a wired connection, your router might be dying. Consider buying a new one: Here are the best routers we’ve reviewed and why they’re great picks. If the router seems fine, then it might instead be your modem, which could suffer connectivity issues if it’s on its way out, too. If you’re looking to upgrade your modem as a fix, we also have a guide on some of the top modem-router combos . Upgrading to a Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E router can also help ease issues with congestion and support faster speeds, provided that your broadband plan is capable of these boosted speeds.
One device can’t connect to the Wi-Fi
Sometimes you run into a Wi-Fi issue with one particular device. It’s probably just a momentary network issue, which is an easy fix. Try turning off the Wi-Fi on your device, then re-enabling it — or unplugging and replugging your Wi-Fi dongle. If that doesn’t work, restart the device and try again. Then try restarting the router itself.
If that doesn’t help, or if the problem reoccurs, consider deleting your current network from the list of saved networks on your device, then reconnect again.
If you’re running Windows 10 or 11, search for “wifi troubleshooting” and open the result, which should be Identify and Repair Network Issues . That will go through a series of diagnostics that may restore connectivity. On MacOS, you can run Wireless Diagnostics . Hold the Options key and click the AirPort (Wi-Fi) icon on the menu bar. Find Open Wireless Diagnostics , and then follow the on-screen instructions.
If you can’t connect to your Wi-Fi at all, plug your laptop into the router directly using an Ethernet cable, and see if you can connect that way. The particular type of Ethernet cable doesn’t matter, but there are some Ethernet cables that are better than others . If that works, your Wi-Fi is the problem and you should try some of the other fixes listed here. If it doesn’t work, then your internet may be down altogether. Check your ISP’s webpage and social accounts, or give them a call to see if they are reporting problems. Sometimes providers can be a little slow to note issues, so you can also check with a monitoring site like Downdetector and see if other users in your region are reporting problems.
Resetting your router can fix a myriad of issues, too, and an inability to connect is one of them. Press the Reset button on the back of the router with a paperclip for 30 seconds, and the router should default to factory settings. Use our guide to setting up a wireless router to get everything properly configured.
If that’s no use, you may need to consider buying a new router.
Is there some sort of pattern? Do connections drop whenever you use the microwave? Have you just installed a fish tank? It may sound weird, but some routers have trouble with these and other home hardware. The 2.5GHz band is readily interfered with by other devices, and 5GHz and 6GHz are notorious for being interrupted by physical objects. It could also be that you’re experiencing interference from other networks or devices. If your neighbors are heavy Wi-Fi users at a particular time each day, this could be slowing you down.
Changing your router’s channel might help. You can use NetSpot on Mac and Windows and Wi-Fi Analyzer for Android to show you every wireless network nearby. If yours overlaps with nearby networks, switching to a less congested channel in your router settings can help. We have a guide that will walk you through changing the channel on your router .
You can also try moving your router to a more accessible location so that there’s less distance (and interfering devices) between you and the router.
If that doesn’t work, try performing a factory reset on your router by pressing a paperclip into the miniature hole on it and following the reset steps as outlined in your manual.
If you lose track of your Wi-Fi network on any device, it’s possible that your router reset itself. Do you see an unprotected network named after your brand of router? That might be yours. Connect a laptop or desktop to it via an Ethernet cable, then use our guide to setting up a wireless router to get everything properly configured again.
If you don’t see such a network, plug your laptop into the router with an Ethernet cable, and see if you get a connection. Use our guide to finding your router’s IP address and login information for more help. Also, if you don’t have a cable, check out our guide on how to choose the right Ethernet cable .
Log into your Wi-Fi app or administrator settings (which you can find by searching your IP address on your browser ). Look for a list of currently connected devices and pinpoint the ones you don’t recognize.
First, make sure these don’t represent connections you didn’t realize you had — each smart device will have its own connection, for example, and they can have some strange titles if you didn’t name them. Game consoles and TVs may also be connected, and if you’ve had friends and family over recently they may have connected with unfamiliar devices.
If you’ve ruled out all familiar devices and there’s still a connection or two you don’t recognize, it’s possible someone else is hijacking your Wi-Fi network. In this case, look in your settings for an option to block these devices on your Wi-Fi and ban their MAC addresses, if possible. Then change your Wi-Fi password, and reboot your router. This may not stop especially determined hackers, but it’s usually enough to kick unwanted guests off your network.
If you want to take more drastic action, here are some steps for how to deal with someone stealing your Wi-Fi .
This can happen with some operating system updates. Windows 10 updates in mid-2020 had bugs that stopped some users from connecting to their Wi-Fi networks or even seeing a Wi-Fi connection at all. Similar updates to iOS, Android, and other platforms also have created bugs in the past that disrupt Wi-Fi connections.
When something like this happens, it’s best to wait for a patch that fixes the problem. In the meantime, remove the update and roll back your system to an earlier version to help get your online connectivity back.
While routers can last for years without needing a replacement, keep in mind that some problems can develop with age — a router may start lacking support for new device updates and similar issues that prevent it from working properly (as seen when Apple discontinued the AirPort Extreme, for example). That’s a sign that it’s time to look for a new router.
The satellite routers on my mesh network aren’t connecting
Make sure that your satellite devices are powered up and turned on. If they are, try unplugging and replugging the problematic device and see if it will connect to your network then. If your router app allows you to restart a Wi-Fi point (Google’s Home app, for example, allows this), then reboot that point and see if this helps, too.
Google also allows you to run a test to make sure the network is set up properly. You can find Wifi points on the Home app, under Test mesh . If the test comes back with a weak or failed connection, you should try repositioning your satellite routers to be closer to your primary router. This also is a good tactic for any mesh system that keeps dropping its satellite points — they could be too far away from the primary point.
You can also double-check to make sure that your satellite router devices have a different SSID than your primary router. If they were accidentally all assigned the same SSID, then the mesh network may not be able to coordinate properly.
If your router still seems unable to connect, then make sure that nothing significant has changed for your network settings. For example, if your ISP WAN (wide-area network) type changed for some reason, you may have to go back into the settings for the router and make sure that the right WAN setting is chosen.
There are additional special cases where certain Wi-Fi technology can interfere with mesh networks, so it’s also a good idea to contact router support directly and explain your situation if nothing is working.
My smart device isn’t connecting to Wi-Fi
First, make sure that your smart device and your router are both updated. Then try resetting your router and rebooting your smart device. You can either unplug and plug in the smart device or check its app for a reboot option — the Google Home app, for example, has a Reboot tool under each device section that you can use.
If the device still isn’t connecting properly, try moving it next to the router and seeing if it connects then — distance and interference can make a difference, especially for smaller smart devices. You should also double-check to make sure that your smart device doesn’t need a Zigbee hub to operate , which is more common among older smart devices but a problem that still occasionally crops up.
If your smart device keeps dropping a Wi-Fi signal, especially during busy times of the day, check to see if your router supports automatic band switching for devices. If it does, try turning this feature off. Sometimes a router will try to switch a smart device to a different band, but the device isn’t ready for that, causing it to lose a connection. There may also be issues with connecting to a mesh router, and you may have to be very specific about your network connection to make smart devices work.
It’s also a good idea to check if your particular device is suffering from temporary bugs that make connecting to Wi-Fi difficult or impossible. Nest minis and HomePod minis have both encountered such errors in the past. In these cases, a fix is usually patched in before too long, so keep making sure that your device is updated. Sometimes operating system updates, like a new iOS patch , also can affect smart device performance.
There are a number of other router settings that may block smart devices, but they are manufacturer dependent. If you can’t find what’s wrong, contact your router manufacturer’s support and explain that you think your router is having trouble connecting.
My console can’t connect to Wi-Fi
Check social media and Downdetector to make sure nothing is wrong with your gaming platform — sometimes your Xbox or PlayStation can get online just fine, but Xbox Live or Playstation Network is down for any number of reasons, but they’re typically back up again after a short period.
If everything looks all right there, reboot both your router and your game console and see if they can successfully connect. This is also a good time to test your internet connection. Major systems like Xbox and PlayStation have an option in their Settings menu to test your internet connection. On PlayStation, head to Settings , then Network , then select Test Internet Connection . On Xbox, go to Profile & System , select Settings , and in the General section, select Network Settings , where you will find an option to Test Network Speed & Statistics . This can provide more information about what’s going wrong and even tips on what you may need to change.
If your console and router seem to be acting properly but Wi-Fi keeps dropping, you may want to try moving the two devices closer to each other to see if the Wi-Fi signal improves. Try to remove any material or objects between the console and router: Placing both in a high, clear location often brings the best results. You can also try reducing the number of other devices on the network, especially if they’re streaming.
Can’t connect to wireless printer
First, make sure you are trying to connect to your Wi-Fi and not via Wi-Fi Direct — they are two different technologies. We also highly suggest the traditional routine of turning everything off and back on again, especially if your printer has connected to Wi-Fi successfully in the past. If your printer is far away from your router and keeps running into Wi-Fi errors, try moving it to a closer position.
If it looks like your printer is connected to Wi-Fi but you can’t get it to work, head into your printer settings on your computer and make sure the correct default printer is selected. Microsoft also has some troubleshooters you can run to see if they pick up on anything obviously awry.
It’s also a good idea to check your router security, firewalls, and VPN security to see if any of them are identifying the printer as a strange device and refusing a wireless connection. You may need to disable certain firewalls or reconfigure security protocols to use your printer successfully. When all else fails, uninstall your printer drivers and reinstall the more recent versions to see if this makes a difference.
And if your printer isn’t wirelessly enabled, consider upgrading to one that is. We have some recommendations for the best printers , laser printers , and multifunction printers that can be used wirelessly and connect to your home network.
Can’t connect to a guest Wi-Fi network that I set up
Guest Wi-Fi networks allow you to share your Wi-Fi with others in a secure way that helps prevent security issues. You’ve probably seen it on business routers, but it can be set up on home routers, too. If someone is having trouble connecting to the guest network but otherwise the Wi-Fi seems to be working, there are a few things you can try.
First, if you just set up your guest network, wait a few minutes. It may take a little time for the network to show up. If the guest network is visible, take a minute to head into your router app and check settings. Settings like Public Wi-Fi Active and Allow Guests to Access My Local Network should always be enabled. If it’s still not working, reset your router and try again.
Keep in mind, some guest networks have a stricter limit on how many devices can use them. If you have over a dozen people already on the guest network, others may not be able to log on.
Wi-Fi 6 or 6E isn’t working, even with a Wi-Fi 6 router
Wi-Fi 6 offers a host of improvements from older Wi-Fi standards, including improved performance, less latency, and better security. But if you don’t think you’re getting Wi-Fi 6 features from a router that supports it, something could be wrong with your setup.
Do you have any extenders on your network? If those aren’t compatible with Wi-Fi 6, you won’t be able to enjoy Wi-Fi 6 speed and features. If your device has picked up the signal from an extender, Wi-Fi 6 benefits may not be making the trip.
Additionally, most devices will need at least partial support for Wi-Fi 6 features to be able to use them. Devices that are several years old may not be compatible with any Wi-Fi 6 changes. That includes your phone and laptop, as well as smart devices that you might be using.
Even desktop computers may struggle with this. Internal Wi-Fi adapters may struggle to pick up on Wi-Fi 6 benefits when you switch to a new router, even if they are technically compatible. You should update your Wi-Fi drivers to fix any potential issues.
Can’t find a router with Wi-Fi 7
Wi-Fi 7 is the next generation of wireless technology, and it’s technical name is 802.11be. It’s the successor to existing Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E routers, and will offer much greater performance, with up to 36 Gbps data transfer rates — that’s more than three times faster than Wi-Fi 6 speeds. It also lets devices use multiple frequencies simultaneously to better utilize available network bandwidth.
The only downside to this is that Wi-Fi 7 routers aren’t yet available at competitive prices. There are some Wi-Fi 7 routers, like the impressive TP-Link Deco BE85 , but that’s a $1,500 mesh router system and complete overkill for just about anyone.
You can expect to see more Wi-Fi 7 routers with more approachable price tags in the coming months.
Editors' Recommendations
- ChatGPT not working? The most common problems and fixes
- The most common Skype problems and how to fix them
- The most common Microsoft Teams problems and how to fix them
- The most common Zoom problems and how to fix them
- How to change your router’s Wi-Fi password
- Work From Home

Whether you're designing it yourself or getting a pre-built PC, it can be easy to get a computer and realize that it doesn't have a native Wi-Fi adapter. Or, maybe it does, but you're internet speeds are getting faster, game downloads are getting bigger, you've already upgraded your router and need an adapter to match your newfound power requirements. No matter the situation, an external Wi-Fi adapter that you can add to your PC setup or even laptop setup will be worth your time. Here, we investigate the best Wi-Fi adapters for PC use. Most are incredibly affordable and just snap into a free USB port and start working. The best Wi-Fi adapter for PC in 2024
Buy the for the overall best Wi-Fi adapter for most people. Buy the as a good runner-up. Buy the for a convenient USB stick adapter on the affordable side. Buy the if you're having trouble with reception. Buy the for a miniature USB Wi-Fi adapter plug on the cheap. (Great for laptops!)
If you use a desktop PC or laptop for long enough, chances are you're going to come across one of the common GPU problems that have plagued gamers and workers since the humble graphics card debuted for the first time. The question is, do you know how to fix them? If not, never fear. We're here to help.
Whether you're encountering poor performance, overheating, visual artifacts, or a dreaded black screen, we're going to help you diagnose and fix these common GPU problems.
Your computer’s motherboard is one of the most vital components in your PC’s chain of command. Think of it as the brain of your entire system, handling everything from processors and graphics cards to power distribution and local memory. If your computer’s been running slower than normal, and you’ve done everything you can to clear your cache, cookies, and other digital debris, then there’s a good chance your motherboard may be the culprit.
Fortunately, there’s a couple of methods you can use for getting your motherboard back in working order, and we’re going to walk you through each part of the process.
Sign up for our daily newsletter
- Privacy Policy
- Advertise with Us
How to Troubleshoot a Router
If you’re having issues connecting to the Internet, your router may be to blame. Regardless of whether you’re trying to communicate with local devices or the wider Web, your router is the center of all your Internet activity. By working your way through the suggestions in this list, you can test whether your router really is the cause of your connection-related woes, troubleshoot if it is the cause, and get back online as quickly as possible.
Also read: Band Steering: Should 2.4GHz and 5GHz Be One Network or Two?
The Obvious Stuff
Before progressing to more complicated techniques, let’s try a few easy fixes. When you troubleshoot a Wi-Fi router, sometimes the simplest techniques will be enough to resolve your issues and restore your Internet connection:
- Switch off your router and switch it back on again . Then wait a few minutes and see whether your Internet connection is back up and running.
- Check whether there are any issues with your service provider . Most providers have a status page where you can access this information. If you’re unsure, try googling the name of your service provider, followed by a phrase such as “service status” or “outage map.”

- Try connecting with a different device . If you’re experiencing issues with a single device, there’s always the possibility the problem may lie with your device and not the Internet connection. Wherever possible, it’s a good idea to test your connection using at least one other Internet-enabled device. If this device manages to connect without any issues, then chances are the router isn’t at fault.
- Switch to an Ethernet cable . If you’re struggling to connect to Wi-Fi, you may get positive results by connecting your device to the router directly using an Ethernet cable. There are many factors that can interfere with a Wi-Fi connection, including physical barriers, such as walls. By physically connecting your device to the router, you can check whether the issue lies with the router itself or the quality of your Wi-Fi signal.
- Try a different Ethernet cable . Alternatively, if you’re already physically connected to the router, check that the cable is firmly attached. It may also help to remove and then reattach the Ethernet cable to see whether this kickstarts the connection. If you have access to a second Ethernet cable, you may want to try switching the cables.
- Pay attention to the router’s lights . One of the easiest ways to troubleshoot a router is to look at the lights themselves. Depending on the router, different light colors and flashing patterns indicate specific problems. Check the user manual to see if your router has error light indicators.
Also read: What Do Router AC Ratings Like AC1200 and AC3200 Mean?
Change Router Wi-Fi Channel
Perhaps you’re managing to connect to the network over Wi-Fi, but the network’s performance is slow or unreliable. In this scenario, it’s possible your Wi-Fi channel may be busy with traffic from other Wi-Fi users in your local area.

You can manually change your Wi-Fi channel through your router’s settings. To get to your router’s settings, you’ll need to know the router’s IP address. This is usually 192.168.1.1, 192.168.0.1, 192.168.1.254 or similar (check out the cheatsheet here ) and needs to be entered into your browser. Here’s how to find your router’s IP address on any platform .
Also read: 9 of the Best Dynamic DNS Providers You Can Use for Free
Once you’ve retrieved this information, enter your router’s IP address into your web browser. It should prompt you for your router username and login. This information varies by ISP, but is typically printed on the router itself.
If you haven’t manually changed the default username and password, you can often retrieve this information by using your favorite search engine and entering your router’s model number, followed by a phrase such as “default username and password” or “default login.” Your router’s model number should be printed in the manual or on the router itself.
Once you’re in your router’s Wi-Fi channel settings, how do you know which channel to pick? There’s quite a lot to it, so read our guide on how to find the best Wi-Fi channel for your network .
Some ISPs require you to download a separate app to manage your settings and perform any Wi-Fi troubleshooting. If so, you’ll see a prompt on how to download the required app. Also, for ISP-owned routers/modems, some settings/options in this post may not be available to you.
Also read: How to Find the Best Wi-Fi Channel for 5GHz Frequency
Reset Your Router
The more radical step up from simply restarting or rebooting your router is to reset it, which will restore the router to its default settings.

These steps can vary depending on your router, but it usually involves either pressing a physical button on the router itself or opening your router’s settings and searching for a reset option.
Upgrade Router Firmware
Another solution to troubleshoot your router that you can find right there in your router’s settings is a firmware upgrade. This can also be found through your router’s settings and will obviously require that your router is connected to the Internet to work (so that it can solve router-to-device connection issues but not Internet-to-router issues).

If you’re having router not working issues, you might not be able to connect to the Internet to update the firmware. In some cases, you can download the firmware directly from the router’s manufacturer, connect directly to your computer via an Ethernet cable, and update that way. However, that doesn’t work with all routers.
Also, every router brand has a different method for updating the firmware. Some update the firmware automatically, leaving you without the option to do so yourself. Others require a desktop tool or an app, and others offer the setting in the Web-based interface.
Also read: DD-WRT vs. Tomato vs. OpenWRT: Which Router Firmware Is the Best?
Diagnostic Tools
In addition to the tips above to troubleshoot your router, you may have to dig deeper to fix the problems you have with the Wi-Fi router not working. Network diagnostic tools can help you discover possible issues, including finding dead spots.
Many router brands offer their own tools to troubleshoot issues. These might be a separate download from their websites or included in your router’s settings. While they might not offer as comprehensive of a solution as you’d like, they do offer a starting point.
Third-party diagnostic tools are designed mainly to help you create a stronger home network. This includes detailing where to place your router and any access points or extenders. These tools won’t necessarily tell you what’s wrong with your router outside of letting you know that it is indeed the router that’s causing the problem.
A few third-party tools to try include:
- NetSpot – Get detailed Wi-Fi troubleshooting and analysis for macOS and Windows.
- NirSoft – While only for Windows, NirSoft provides a variety of network diagnostics tools. Even when you’re not having router issues, some of these are ideal to have for monitoring traffic and general network health.
- Windows network connection command prompts – Test your connection and help pinpoint issues with Windows built-in tools.

- macOS Wireless Diagnostics – Run a report to test network health on macOS.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. when should i replace my router.
As with all electronics, routers do wear out. If you can’t connect at all or multiple devices have trouble connecting simultaneously (assuming you have the data speeds to support your devices), it may be time to upgrade to a new router. As a general rule, some router brands recommend replacing every three to five years, though many brands have end-of-life lists for their routers .
2. Is it my router or my ISP?
If your router is newer, figuring out how to fix Internet connection issues may mean contacting your ISP. Even if outage maps don’t show an outage, regular connection issues could mean your ISP needs to upgrade their equipment. This may also include sending you a new router if your router was provided by them.
3. Is my router compatible with my modem?
An often overlooked router issue is compatibility with your modem. Some ISPs only allow specific brands and types of routers. Others may restrict you to just their routers and modems. Check with your ISP to ensure your router is compatible with their modem.
4. Is it my router or my devices?
If you’ve gotten a new Wi-Fi device, and it doesn’t work, you may not actually be experiencing any problems with your Wi-Fi router not working. It could be a simple case of your new device and router not being compatible.
For example, many smart home devices only work on 2.4 GHz bands, but if your router only uses 5 GHz or doesn’t let you switch bands, you’ll have trouble connecting, especially during the setup process. Or, a device may require a newer type of network than your older router provides. In this case, a new router is necessary.
Wrapping Up
The above are some of the main ways to troubleshoot a misbehaving router. If you have chosen to reset the router, you have to set it up again properly . If all else fails, consider contacting your ISP for a connection reset at their end. Beyond that, it may be worth looking at a new router (ideally provided for free by your ISP!) and learning how to put your old router to good use .
Also read: Modem vs. Router: What’s the Difference?
Our latest tutorials delivered straight to your inbox
Crystal Crowder has spent over 15 years working in the tech industry, first as an IT technician and then as a writer. She works to help teach others how to get the most from their devices, systems, and apps. She stays on top of the latest trends and is always finding solutions to common tech problems.

- Why Does My Internet Keep Going Out? How to Troubleshoot Home Internet Issues
Find out why your internet goes out and what you can do to fix it.

- There are a variety of things that can cause your internet to go down, from equipment and provider issues to bad weather and network congestion.
- Oftentimes, you can fix internet outages on your own with a few simple steps.
- Assessing your equipment and its placement, checking your internet speeds, and changing device settings can all help get you back online.
There’s nothing worse than curling up on the couch, ready to binge your favorite show (mine is “One Tree Hill”), only to see the buffering icon appear on your TV screen. I’ve encountered this situation more times than I can count, but luckily, the culprit — my Wi-Fi connection being down — is a temporary setback and not a permanent one.
Whether you’re in the middle of an online game, taking an important Zoom call, or working on a research paper, the internet always seems to go out at the most inopportune times. Luckily, you can diagnose and fix many internet problems without sitting on hold with your internet service provider for what feels like hours. Some of the most common reasons for internet outages include:
Issues With Your Modem or Router
Your speed or equipment isn’t cutting it, bad weather, issues with your internet service provider, network congestion, issues with network cables, your connection has been hacked.
In this guide, we’ll cover why these issues occur and how to fix them, along with some additional tips when all else fails.

Our routers and modems are plugged in and running all day long. Sometimes, they can get overworked, overheated, or even clogged with dust and dirt. These issues can lead to a slow or dropped internet connection.
Many times, restoring your internet connection back is as simple as unplugging your router or modem and plugging it back in. Here’s how:
- Unplug your router and modem from the power source.
- Wait for one minute.
- Plug your modem back in and wait 30 seconds.
- Plug your router back in.
- Wait five minutes and retry the connection. (Patience is a virtue here; I like to set a timer and go grab a snack.)
If you notice that your router looks a little worse for wear when you unplug it, give it a good cleaning. Wipe down your router with a duster or cleaning cloth. Then, use a vacuum attachment or condensed air duster to remove any trapped dust inside the device. I can’t remember if I’ve ever dusted or cleaned my router, but it probably would’ve helped in the long run!

If your internet is constantly lagging or buffering, it could be because you simply lack the speed to handle your online activities . Some things require a lot more speed and bandwidth than others. For instance, online gaming and streaming services take up a lot of bandwidth, while browsing the web and checking email use a lot less. If you live in a large household with multiple TVs, laptops, phones, and other devices connected to the internet, you’ll also need substantial speed.
Or you could have enough speed and your equipment is the culprit. Every router has a limit to how much speed it can support, which varies from one router to the next. One of my relatives has an internet plan that offers speeds up to 300 Mbps, but their router was designed to handle speeds up to 200 Mbps only. That means they never experienced speeds faster than 200 Mbps and they were missing out on the other 100 Mbps that they paid for (which I explained; they have since upgraded their router).
You can use our bandwidth calculator to assess the speed and bandwidth you need with your current internet usage. Then, take an internet speed test to see what speeds you’re actually getting. If you realize you need a faster speed than your current plan provides, consider upgrading your internet plan.
If you assess your needs and feel like your current plan should be fast enough to meet them, you might have an equipment issue. You can check to see how much speed your router is designed to handle by looking through the router’s product manual. Don’t have the manual? Just Google: “How much speed can [insert your router name here] handle?”
If you check the manual and realize your router should be able to handle your plan’s speeds, it could be a router placement issue. Try moving your router using the tips for optimal placement below:
- Choose a central location that is out in the open.
- Don’t place your router on the floor.
- Avoid putting it in the kitchen.
- Avoid placing it near mirrors or fish tanks.
- Avoid walls and place the router near an open space or doorway.
- Avoid other electronics that use radio signals, like baby monitors and cordless phones.
- Don’t place it in a cabinet or drawer.

Heavy rain, thunderstorms, snow, heavy cloud coverage, and other major weather events can cause your internet to go down or weaken the connection. All types of internet can be impacted, but satellite internet is more at risk of a weather-related outage than other kinds of internet.
This is because satellite internet transmits a signal from the satellite dish on your house to a satellite located in space thousands of miles away. Bad weather can scatter the signal, making it more difficult for it to travel the long distance between your dish and the satellite in space. A storm miles away from your home could even impact your connection if it gets in the way of the signal’s path.
I live in Tennessee, where it gets windy, but luckily, it hasn’t been so drastic that I’ve had my internet go out. Residents who live where there are more extreme weather conditions might not be so lucky, so they might have to wait out the bad weather for their internet to return. If you have satellite internet, you can also purchase a satellite dish heater or weather shield to help prevent weather-related outages.

While widespread internet outages are a lot less common than you might think, they still happen from time to time. There are several ways to confirm if your ISP is experiencing an outage.
You can do a quick Google search for “ [insert the name of your provider] outage” to see if there are any ongoing issues in your region. Also, check the provider’s social media pages and website for information. If that doesn’t generate any information, you can try signing in to your internet provider account to get an update. Calling customer support is a last resort, as you may experience long wait times. If the outage is impacting hundreds (or even thousands) of people, and many of them try to call at the same time, you’ll probably end up on hold for a while.
I have Spectrum, and with the My Spectrum App, as long as I turn on alerts for outages in my account settings, I’ll be notified if my area is affected. If there’s an outage, technicians can often resolve them in a matter of hours. In the meantime, you’ll have to wait it out. Outages and Hotspots: If you’re in an outage but need to connect to the internet, your smartphone may function as a mobile hotspot. You can turn on your mobile hotspot and hook up your connection to your computer (also known as tethering). It may not work at a high speed, but it’s the best alternative while you wait for the outage to end.

Just as we often sit in stop-and-go traffic during rush hour, our internet connection can experience network congestion during peak internet traffic times. During these peak times, you may experience slow speeds and a laggy connection. Fiber internet is the only type of internet that isn’t susceptible to this congestion, so if you have satellite, cable, or DSL internet, it may be an issue.
There isn’t much you can do about improving speeds until traffic on the metaphorical internet freeway clears up, but there are a few things that might help make the most of what you’ve got.
Wired connections will always be faster than wireless, so if possible, try plugging directly into your router with an Ethernet cable to see if that improves speeds. You can use a wired connection for devices that use the most bandwidth, including gaming consoles and smart TVs. Purchasing a Wi-Fi range extender can also help boost your signal in parts of the house that aren’t well covered by your initial internet signal. Here’s your reminder to make sure that your router is in an optimal place.
If these tips don’t help and the network congestion is a major headache, avoid using the internet during peak times whenever possible. I try to urge my kids to avoid using their devices during these times and set a limit on how long they can be online. You can also use your phone as a mobile hotspot or purchase a portable internet device for times when you really need to use the internet during rush hour.

If the physical network cables in your home are loose, damaged, or poorly configured, they can cause your internet to go down. There are a few things to look out for that could signify cable damage.
Here are a few signs to look for when it comes to your physical connection:
- Damaged cables: Check to see if there are kinks, tears, chew marks from pesky critters, or any other signs of damage on your coaxial cables. If you use a wired connection, check your Ethernet cable too.
- Loose cables: Ensure that the cables connected to your router, modem, and wall outlet are screwed in tightly. Loose cables can lead to a weak or spotty connection. Check that your Ethernet cables make an audible clicking sound when fully inserted and that you can’t pull out the cable without pressing down on the clip.
If you think there is an issue with your network cables, it’s time to call your internet provider and ask for a technician to take a look. Fixing cables requires specific tools and training, and you could cause more harm than good if you tinker with them yourself. A technician can also check to see if any active coaxial lines in your home aren’t in use. These unused lines can cause interference, and the technician can close them off using specialized equipment.

We all dread the day that we realize we’ve been hacked. While it’s one of the more unlikely causes of your internet issues, it’s still possible. Hackers can gain access to your home Wi-Fi network and control your ability to connect devices to the internet.
If you think that your connection has been hacked, it’s best to reset your Wi-Fi network with a new network name and password. Your new password should be strong and unique. Even if you’re not 100 percent sure you’ve been hacked, it’s better to be safe than sorry!
You can also install antivirus software to prevent future security breaches. Before purchasing new software, check to see if your ISP offers free malware protection, as it’s pretty common. If you already have antivirus software, make sure that it’s up to date. Outdated software could also cause network issues and leave you vulnerable to hackers. Ramping Up Your Security: Visit our guide to creating a secure home wireless network . It covers tips on everything from creating a strong network password to setting up encryption to keep your network safe and secure! Lastly, keeping your firmware up to date can help prevent hacking. Firmware is code that keeps your equipment running properly. Occasionally, this information needs updating. Below are links to detailed instructions for updates by brand and how to log in to each brand’s configuration area.
Still Having Issues? Here Are Some Other Ways to Fix Internet Problems
If you’ve tried all of the solutions above and your internet is still down, here are some additional tips and tricks.
Make Sure a New Device Isn’t Hogging Your Network Bandwidth
Did someone in your home recently get a new device, such as an Xbox Series X or a streaming media player, like an Apple TV 4K? If so, these additions to your network may cause performance degradation, especially when these new devices are in use.
If you suspect this is the issue, disconnect the new devices from the internet and recheck your connection. If it improves, the devices will eat up network bandwidth. You may need to consider upgrading your internet service to accommodate the number of devices in your household or decide if there are any devices you can reduce usage to free up bandwidth.
Reset Your Network Settings
Sometimes restoring the factory default state on your devices will solve your issue. Doing so may seem difficult, but for most routers, the process is relatively straightforward.
You’ll want to type in the name of your router on Google (which you can often find somewhere on the device itself), followed by “reset to factory.”
After you’ve reset your router, you’ll need to “forget” the network on your computer. Below are the steps to do this on a Mac and PC.
Restart your device and log back in to your Wi-Fi network. Ensure your connection is back up and running.
Call Your Internet Service Provider
While it’s a good idea to troubleshoot the problem on your own first, if nothing on this list gets you connected, it’s time to call your provider. If you experience long wait times on the phone, you can also try the company’s live chat feature if it has one.
In my experience, talking with someone over the phone will be the easiest solution. You can communicate the issues better and follow the steps outlined by the customer service representative in real time. You can find your provider’s customer service number by performing a Google search or locating it on the company website.
ENTER A ZIP CODE TO FIND PROVIDERS IN YOUR AREA
Broadband shopping guide.
- Determine what Internet speed you need
- Internet Bandwidth Calculator
- Compare Urban Internet Options: DSL vs Cable vs Fiber
- Compare Rural Internet Options: Satellite Internet vs DSL
- Decide Between a Bundle or Internet-Only
- Decide Whether to Buy or Rent Your Modem
- Internet Contracts and Fees 101
- Order and Install Internet Service
INTERNET TROUBLESHOOTING AND GUIDES
- How to Set Up A Home WiFi Network
- How to Extend Home WiFi
- WiFi Security Basics
- How to Optimize a Home Network for Gaming
- How to Fix Home WiFi and Router Issues
- How to Tell if You're Being Throttled
BROADBAND CONSUMER RESOURCES
- How to Switch or Cancel Internet Service
- Low and Fixed Income Internet Options
- FCC and FTC Internet Service Complaints
- How to Negotiate With Your Internet Provider
SATELLITE INTERNET RESOURCES
- What is Satellite Internet?
- Satellite Internet Pros & Cons
- Best Satellite Internet Providers of 2024
- Satellite Internet Data Caps Explained
- The Best Satellite Internet for Gaming
- Satellite Internet for Vans and RVs
- Satellite Internet for Boats
BUSINESS BROADBAND GUIDES
- Service Level Agreements
- How to Choose A Business Internet Service Provider
Offer Detail
Home » Internet Service
How to Restart Your Wi-Fi Router

Is your Netflix show constantly buffering? Are you tired of that dreaded “ No internet connection ” error when you’re trying to work from home? Whatever the case, we feel you.
Before you rage at your internet service provider (ISP), try restarting your wireless router to see if a refresh fixes your issue. This simple fix could mean you don’t have to call customer support! That’s a win if we ever heard one.
Ready to give it a go? Let’s fix that internet and get you back online, pronto!
Guide to restarting your router:
- Unplug your router and modem
- Plug your modem back in
- Plug your router back in
- Update your firmware
- Look for a new provider
1. Unplug your router and modem
First, unplug your router and modem from the power outlet in the wall. Next, unplug any connections between your modem and wireless router.
Oh, also—look for power buttons on your router and modem. Some have ‘em—most don’t. If you do have them, try pressing those instead of unplugging everything. But don’t mix up the power buttons with the factory reset buttons! You do not want to press those.
Once the equipment is unplugged or powered down, it’s time to step away. You want your router and modem to rest for a bit so the equipment’s memory has time to refresh. This will take about a minute or two—but letting your equipment sit longer won’t hurt it.
Go make a cup of coffee, chat with a family member, or take your dog out for a walk while you wait.
2. Plug your modem back into the wall
After you’ve let your modem and router clear out their memory, plug your modem into the wall first.
We repeat, plug your modem’s power cord in first !
Don’t plug your router in yet, and don’t hook up any other connections.
Give your modem about a minute to power up. You’ll see the lights on the front blink or turn on and off, which is normal.
Once most or all of your modem’s lights steadily glow green, you’re ready for the next step.
3. Plug your router back in
Now it’s time for your router to start broadcasting that Wi-Fi signal. Go ahead and plug it back into the wall and reconnect it to your modem.
See that little reset button on your router? Don’t touch it! Chances are it will set your router back to factory settings. That means wiping your Wi-Fi password and that awesome Wi-Fi network name you set up. (We see you, Pretty Fly for a Wi-Fi.)
Once you’ve plugged your router back in, give it a minute to power back up.
Again, you’ll probably see lots of flashing lights at first—this is still normal as the router starts all of its processes back up again.
4. Update your firmware and apps
Once your modem and router power back up, it’s time to do your due diligence and update your firmware and any apps your equipment uses.
Why should you update the firmware? Firmware contains updates for your router and modem that keep them running smoothly. These firmware updates could squash performance problems and even boost your internet speed.
Make sure to download firmware only from official sites! Never download anything from a site you don’t know. Cybercriminals are always looking for ways to sneak malware onto your computer, so only download firmware for your router and modem straight from the manufacturer’s website.
5. Look for a new internet provider
You don't need to do this every time you reset your router, but if you're always headed to the basement or closet where the router's stored, you should consider switching internet service providers.
If your internet is constantly disconnecting or maybe just slow, look at our picks for the best internet service providers nationwide. One might offer you a better (and faster !) deal.
Recap: How do you restart your Wi-Fi router and fix your internet?
Restarting your modem and router is as easy as unplugging all your equipment, waiting a couple of minutes, then plugging in first your modem and then router after your modem powers back up
We also recommend updating your equipment’s firmware and apps to get the latest technical issue fixes and optimizations. Updated firmware can help increase your internet speeds, and who could say no to that?
Is it time for a new router? Here's what to look for.
We've got more easy ways to speed up your internet—without paying a dime.
Do you still have questions about restarting your router? We can help.
The first step is to be a computer guru—you’ll need to know your router’s IP address. According to Lifehacker, you can enter the address into a browser , which should lead you to the option to maintain your router (including restarting it).
But here’s a better way, as suggested by Lifewire—simply plug your router into a smart plug, and you can turn the plug on and off from anywhere .
No, restarting is not the same as resetting your router.
While restarting and resetting your router sound the same, they actually mean two very different things.
Resetting your router will completely wipe any configurations you’ve saved and restore it to factory default router settings. That means you’ll have to set up your Wi-Fi password, network name (SSID), and more all over again.
Restarting your router , which we cover in this guide, lets your equipment flush out any issues stored in the memory and cool off. All your configurations are still saved after a restart.
And what about rebooting? What does that mean?
Rebooting your router is the same thing as restarting it.
Move to FAQ
Restart your router at least once a month. This allows it to mend issues, take a breather, and fix internet connection problems.
Also, if your internet is moseying along at a snail's pace, go ahead and restart your router even if it hasn't been a month yet.
Similarly, if it’s been a month and your Wi-Fi’s clipping along without any connectivity issues, restart the router anyway. Just in case.
Manufacturers recommend checking for router firmware updates every three to four years. Some router companies may also contact you if they have a critical firmware update.
If your router seems to slow down your internet, it's worth checking for a firmware update on the official manufacturer's site.
Internet company reps love to tell you to "power cycle" your modem, but what the heck does that mean? Basically, power cycling your router and modem is unplugging your equipment from the wall, letting it rest for a few minutes, and then plugging everything back in.
Power cycling, like restarting your router, should help your equipment refresh itself and clean up any errors in its internal memory that could cause your internet to slow down.
The Wi-Fi router you use may depend on your ISP! Not all routers work with all providers.
But in some cases, you can choose your own router . If that happens, you should see our best wireless routers for streaming !
You can get internet by plugging a device directly into a modem, no router required. But you cannot get Wi-Fi without a router—Wi-Fi is, by its nature, a wireless connection.
Related Articles

Our Methodology
Go to Reviews.org AU edition
Internet in your area
Internet in Los Angeles
Internet in New York City
Internet in Atlanta
Internet in Houston
Stay updated on the latest products and services anytime, anywhere.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
All content © 2024 Reviews.org. All rights reserved. Disclaimer
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Computers and Electronics
- Computer Networking
- Wireless Networking
How to Fix Your Internet Connection: Troubleshoot Common Issues
Methods for improving and repairing your connection
Last Updated: September 27, 2023 Fact Checked
Slow or Inconsistent Wi-Fi Connections
Simple fixes for connection issues, advanced fixes for connection issues.
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Kyle Smith . Kyle Smith is a wikiHow Technology Writer, learning and sharing information about the latest technology. He has presented his research at multiple engineering conferences and is the writer and editor of hundreds of online electronics repair guides. Kyle received a BS in Industrial Engineering from Cal Poly, San Luis Obispo. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 818,346 times. Learn more...
While some network issues can only be addressed from your Internet Service Provider's (ISP's) side, there are plenty of simple steps that you can take to resolve minor to moderate network issues at home! From repositioning your router to resetting the network, there are a few things you can try to get things working. This wikiHow will show you how to fix your internet connection, from handling slow Wi-Fi networks to troubleshooting problems on your PC or Mac.
Things You Should Know
- For slow internet, move your router so there are as few obstacles as possible between it and your device.
- Restart your router and modem to resolve common internet connection issues.
- If your problem persists, try updating your router firmware by navigating to its router login page.

- If you’re having connection issues on a different floor of your home, try different antenna angles for better coverage.

- The best way to ensure a consistent Internet connection is by minimizing the number of obstacles between your Internet device and the router.

- Make sure to check what speed your router is rated for. This is typically labeled AC####, where the four numbers represent the speed in megabits per second (mbps). Get a router that matches or exceeds your internet plan’s mbps.

- If your computer is able to connect to the Internet while connected directly to the router, your computer's wireless reception is most likely the problem.
- If your computer is able to connect to the Internet while connected directly to the modem, then the issue is likely cause by your router.
- If you cannot connect to the internet while connected directly to your modem, there is something wrong with the modem or with your internet service in general. You'll need to get in touch with your internet service provider's technical support line to fix modem-related issues.

- To stay relatively up-to-date, consider clearing your browser's cache once per month.

- Internet Explorer

- Restarting your computer will often also turn back on your Internet adapter if it was off.

- You may have to hold the Fn button in order to be able to press the Wi-Fi button.
- The Wi-Fi button usually looks like three curved lines increasing in size.
- Skip this step on a desktop computer.

- Many modems can also be soft-reset in this manner.
- In some cases, you can soft-reset your network by opening your router's page and clicking a Reset button in the "Advanced" or "Power" options.

- In most cases, the "reset" button is a recessed button on the back of the modem and router, meaning that you'll need to use a pen or a paperclip (or similar tool) to press the button.

- Clearing the DNS cache will resolve issues such as websites failing to load, especially if you can view the website in one browser but not another.
- To clear the DNS cache on a mobile item such as a smartphone or a tablet, simply restart the item.

- Windows - Press ⊞ Win + R > type in ncpa.cpl > click OK > right-click your network adapter > click Diagnose > follow any on-screen prompts.

- Add a second router to extend the range .
- Increase your computer's Wi-Fi reception .
- Make your own directional "cantenna" for your wireless adapter .

- Remember to be as calm and polite as possible, and do not take out your frustration on the company.
Community Q&A
- Most ISPs will perform network diagnoses and fixes for free if you're renting a modem/router from them. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1

- Resetting your network should be a last-ditch attempt to fix the network. While it will fix most of your potential network problems, it's very inconvenient to have to set back up all of your Internet-connected items. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 5
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://osxdaily.com/2016/09/22/fix-wi-fi-problems-macos-sierra/
About This Article

1. Restart your computer. 2. Make sure your wireless adapter is enabled. 3. Restart your modem and router. 4. Try a hard network reset. 5. Move closer to the router. 6. Try using Ethernet. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Feb 15, 2017
Is this article up to date?

Jul 7, 2017
Bobert Jones
Jul 18, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
- I Tried Both: Apple Watch 9 vs Fitbit Charge 6
- Best Places to Print Photos Online
Why Is My Modem Not Working?
Troubleshooting tips and fixes for common issues
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/jonfishersquare-93eb80e77a004035887f56816d3623c5.jpg)
- Wichita Technical Institute
- The Wireless Connection
- Routers & Firewalls
- Network Hubs
- Installing & Upgrading
- Wi-Fi & Wireless
Before asking, “Why is my modem not working?” you should make sure your modem, not your router , is the underlying cause of your Wi-Fi problems. Once you've done that, you're ready to fix a modem that won't connect to the internet.
Causes of Modem Not Connecting to Internet
There could be several reasons why you can't connect to the internet , but here are some common issues relating to the modem:
- Loose power or coax connections
- Damaged Ethernet cable connections
- Miscommunication with the router
- Overheating
- Outdated firmware or equipment
Before you start troubleshooting the modem, try connecting to your Wi-Fi network on another device. If you can, then the problem lies with your device. If you can't connect to your Wi-Fi network at all, then the problem likely lies with your router, not your modem . In such cases, your focus should be on fixing your Wi-Fi network .
If you can connect to your network, but you still don't have internet access, then there's likely something wrong with your modem.
How to Fix a Modem That Won't Connect to the Internet
Try these fixes in order, checking along the way to see if the problem is solved before moving on to the next step.
Check the lights on your modem. The lights on the side of your modem can tell you whether or not your modem is connected to your router and the internet. If none of the lights on your modem are glowing, then your modem isn't turn on, so you should check the power cable.
Check the power supply and coax cables. Examine all of the cables on your modem to make sure there are no loose or frayed connections. If the lights on the modem flicker when you move the power cable, it's probably time for a new power adapter. Likewise, if the connection pin for the coax cable (the large, round cable that connects to the wall) is bent, you need to replace it.
Reboot your router and modem . Refreshing the device can clear out temporary technical hiccups that inevitably happen from time to time. If you're going to reboot the modem, you should reboot the router as well.
Rebooting is different than resetting . Rebooting just shuts down the modem and turns it back on.
Check your Ethernet cables . An Ethernet cable connects your modem and router. If you have a spare, switch them out to make sure there's not a problem with the physical connection.
Disconnect all connected devices. If you have many devices connected to your network (smart home devices, multiple computers, etc.), your modem could be overwhelmed. Disconnect all devices, reboot the modem, then reconnect your devices. If the internet starts working but then stops at a certain point, the modem might be at its limit, so you should talk to your ISP about an upgrade.
Plug your computer into your modem. If your PC has an Ethernet port , you can directly connect it to the modem. If you can use the internet, then the modem is fine, and the problem lies with your device or router.
Keep your modem cool. If your modem keeps resetting , it could be overheating. Keep it 6 inches away from other devices, and make sure the air vents are clear of dust. Don't keep it near a heater or in a humid environment.
Update your modem and router's firmware . Your ISP usually handles software upgrades for your modem, but if you use a router-modem combo, check for router firmware updates to ensure you have the latest security patches and bug fixes.
Change the Wi-Fi channel . If you have a router/modem combo unit, it could be assigning too many devices to one Wi-Fi channel. If possible, manually divide your devices between the two channels, choosing the best wireless channel for each device (not all devices can connect to 5 GHz).
Reset your router/modem to default settings . Look for a small hole on your modem's underside and use a straightened paperclip to press the small reset button inside. Restoring the router to its factory defaults will clear any problems with your router's settings, but it will also remove all passwords, custom DNS settings, and firewalls you've configured.
Contact your internet service provider (ISP) . Your ISP can tell you if there's an outage in your area and check for problems on their end. If they can't resolve the issue, they can point you in the right direction.
Buy a new modem. If you're not renting a modem from your ISP, the modem you're using might not support the latest wireless standards . Or, you could have more devices connected than your modem can handle. Check with your ISP for the recommended modem specs for your internet plan.
A modem is used to directly access the internet. A router is used to connect multiple devices to a Wi-Fi network. Unlike a modem, a router can't directly connect to the internet.
The lights on your modem can have different meanings depending on the model being used or your internet service provider. But, generally, green can mean an active internet connection; blue can mean a firmware update in progress; orange can mean your modem is in the process of establishing a connection; red can mean your device is overheating or there's no connection; white can mean your device is on or it's pairing with another device.
Find your default gateway IP address and navigate to it in a web browser. If you've never accessed your modem's settings before, there's a default username and password you can use to log in, depending on your device's manufacturer.
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
- How to Fix a Red Light on a Modem
- What to Do When Windows 11 Can't Connect to a Network
- What Do the Lights on My Modem Mean?
- How to Fix Amazon Error Code 1060
- How to Fix It When There's No Internet Connection
- How to Fix it When a Chromebook Won't Connect to Wi-Fi
- How to Fix a Vizio TV That Won't Connect to Wi-Fi
- How to Connect Two Routers on a Home Network
- How to Set up a Home Wi-Fi Network
- How to Set Up a Router
- How to Fix Netflix Error Code NW-2-5 on Any Device
- The Best Cable Modems of 2024
- How to Fix It When YouTube TV Isn't Working
- How to Fix a Netgear Router That's Not Working
- How to Connect to Your Home Router as an Administrator
- Why Does My Modem Keep Resetting?
- Home Internet
The most common Wi-Fi problems and how to fix them
We my not have to disconnect from the Internet to make a phone call anymore, but Wi-Fi problems persist. Here are some of the common issues you will run into and how to fix them.

Internet speeds and Wi-Fi have both improved significantly over the last several years. Data speeds are faster across the board and wireless connections are more reliable than ever.
However, Wi-Fi isn't without issue. Hang out at a Starbucks long enough and you can experience it firsthand.
Once you've set up your home network , here are some very common issues you may run into with Wi-Fi and how to correct them.
Locating local internet providers
Slow connection
Despite faster speeds reaching most homes around the globe, wireless (and often wired) networks can get bogged down. If your Internet connection is still working but the speeds are slower than normal, there is usually a logical explanation that can usually be fixed.
Cause: The most obvious problem with Wi-Fi speeds slowing down is being too far from the router. The further you are from the router, the more unreliable the connection and its throughput will become.
Fix: To fix this, just get a little closer. If the router is located in a different room, try going into the room where the router is located and see if that fixes the issue. If this is a consistent issue, try to position your router higher (up on a shelf), away from other devices, which can interfere with it, and in a central location in your home.
If that doesn't work, consider purchasing a second router and a set of powerline network adapters to extend your network.
Cause: Another cause for slowdowns is a lack of bandwidth. If everyone is home and using their computers, phones and televisions for data-hungry applications, your typically speedy Internet is being spread thin and shared across multiple devices.
Fix: Disconnect any devices that you aren't actively using. If multiple people are trying to stream videos from, say, YouTube and Netflix, while someone else is trying to game online, you can try connecting one or more of the devices directly to the router using a Cat-5 ethernet cable to free up some of the wireless bandwidth. But the problem may be that you just don't have fast enough Internet speeds to support everything at once.
There is also the possibility that someone nearby is leeching off your Internet. To prevent this from happening, be sure to setup security for your network and give out the password sparingly.

11 ways to make your Wi-Fi faster

Cause: Interference can be a real issue, especially in crowded areas. When most people first get their Internet set up, they leave settings unchanged, which means default wireless frequency channels -- like 1, 6 and 11 -- become very crowded.
Fix: Fortunately, many newer model routers are capable of automatically selecting the least crowded frequencies upon rebooting. Perform a power cycle on your router or, log in to the admin panel and manually select a different channel.
Additionally, if you have a dual-band router, try enabling both 2.4GHz and 5GHz. Keep the 5GHz channel open for your most important connections.
Cause: During peak hours, Internet speeds can slow for everyone, especially in crowded, urban areas.
Fix: All you can really do when this is the case, if possible, is try to schedule your usage outside peak hours to get the best speeds.
Cause: Wireless technology has changed quite a bit over the last 10 years. New wireless standards have been put in place, speeds are faster than ever, fiber is being offered in more areas and devices you never thought would require an Internet connection need Wi-Fi -- televisions, speakers, refrigerator, printers, lights and more. The problem could easily be an outdated router.
Fix: If you think the limitation lies with your router, it may be time to start saving up for a new one. Upgrading your router every two years or so is good practice and can help you avoid certain issues altogether.
No Internet connection
Cause: Periodically, something glitches and the router or modem (or combination) just stop communicating. There isn't always an explanation. It just happens.
Fix: The best place to start is pulling the plug. Disconnect the modem and router from power and wait at least 30 seconds before restoring power to both.
Cause: For me, one of the most common problems that occurs with my Internet is the connection dropping completely -- not due to a hardware issue on my end, but rather a massive service outage.
Fix: Not much you can do here. You can go to the nearest coffee shop or get on the phone with your Internet service provider (ISP) and let them know you're affected. Sadly, this usually won't do much to speed up the recovery time, but it can help the ISP know more about which areas are affected by an outage.
Home Internet Guides
- Best Internet Providers in Los Angeles
- Best Internet Providers in New York City
- Best Internet Providers in Chicago
- Best Internet Providers in San Francisco
- Best Internet Providers in Seattle
- Best Internet Providers in Houston
- Best Internet Providers in San Diego
- Best Internet Providers in Denver
- Best Internet Providers in Charlotte NC
- Google Fiber Internet Review
- Xfinity vs Verizon Fios
- Verizon 5G vs. T-Mobile Home Internet
- Verizon Internet Review
- Xfinity Internet Review
- Best Rural Internet
- Best Cheap Internet and TV Bundles
- Best Speed Tests
- AT&T Home Internet Review
- Best Satellite Internet
- Verizon 5G Home Internet Review
- T-Mobile Home Internet Review
- Best Internet Providers
- Frontier Internet Review
- Best Mesh Wi-Fi Routers
- Eero 6 Plus Review
- TP-Link Review
- Nest Wi-Fi vs. Google Wi-Fi
- Best Wi-Fi Extender
- Best Wi-Fi 6 Routers
- Best Wi-Fi Routers
- What is 5G Home Internet?
- Home Internet Cheat Sheet
- Your ISP May Be Throttling Your Internet Speed
- How to Switch ISPs
- Internet Connection Types
- Internet for Apartments
- Top 10 Tips for Wi-Fi Security
- How to Save Money on Your Monthly Internet Bill
- How Much Internet Speed Do You Need?
- Compare Providers
- Review Providers
Why is My Wi-Fi Not Working? How to Fix Your Internet
What to do when you have a Wi-Fi signal but no internet access.
These days, the little Wi-Fi symbol in the corner of your phone or laptop screen is so synonymous with internet connectivity that it’s easy to forget that Wi-Fi and internet aren’t the same thing. And it is possible to have one without the other. This guide will help you figure out why your Wi-Fi isn’t connected to the internet and what you can do to fix it.
The difference between Wi-Fi and internet signals
Wi-Fi is a radio broadcast signal transmitted by a router that allows devices like phones and laptops to connect to a network wirelessly. Internet signals are a connection to the world wide web. When both work properly, your Wi-Fi network is a wireless bridge that feeds your devices access to the internet.
Essentially, that little Wi-Fi icon on your device screen tells you that you’re connected to a router, not necessarily the internet. The wireless router needs to be connected to the internet for you to access the web via Wi-Fi. You can tell if you’re actually connected to the internet in your device’s Wi-Fi settings.
Reasons you’re connected to Wi-Fi but not internet
You’re on the wrong wi-fi network.
Go into your device’s Wi-Fi settings and make sure you’re connected to the right Wi-Fi network.
Since the Wi-Fi icons on devices don’t usually display a network name, you usually assume you’re on the right network. But there are a ton of Wi-Fi signals sharing the same space. You might be connected to a neighbor’s Wi-Fi, a Wi-Fi extender, or a hotspot.
Your modem or router needs a restart
Your networking equipment may not be connected to the internet, but it can still broadcast Wi-Fi signals. Oftentimes simply restarting your modem, router, or gateway (modem/router combo) clears up the issue.
Whether you have a separate modem and router or a gateway, the restart process is the same:
Step 1: Disconnect the power cable from the back of the equipment.
Step 2: Wait 60 seconds.
Step 3: Reconnect the power cable to the back of the equipment.
Step 4: Wait while the equipment reboots. This can take up to 20 minutes.
Restart your computer or device too
This is especially helpful with computers. A system restart is an easy cure-all that’s so effective it’s always worth a shot.
Give your internet connection a health check
Download our speed test app to see if your internet connection is running as it should.

Use our speed test to see if your internet connection is running as it should.

Try your PC’s Network troubleshooter (Windows only)
Windows PCs have a built-in network troubleshooter capable of repairing many internet issues on your computer. It’s really easy to run the Windows Network troubleshooter:
Step 1: Right-click the Wi-Fi icon in the lower-right corner of the screen.
Step 2: Click “Troubleshoot problems.”
Step 3: Select “All network adapters” and click Next.
Step 4: Wait while the troubleshooter searches for the problem.
Your ISP is down
Your internet service provider (ISP) may be experiencing an outage. Unfortunately, if that’s the case, there’s not much you can do about it besides waiting it out. It’s times like these when a mobile hotspot or smartphone tethering come in handy.
Most ISPs have mobile apps you can use to find out if there’s an outage in your area—some even give you an estimate of when service will be restored. You can also explore signing up for text alerts from your ISP to get notified of outages due to weather, construction, etc.
The website or service your attempting to use is down
Individual websites and services have outages too, and they can make it seem like your internet isn’t working. Try to access a different website or service on your device. If it works, you know your internet is fine, and the site’s down.
The sites downformeoreveryone.com and downdetector.com are useful for checking when your favorite sites and services are down.
Ready for a new internet provider?
Enter your zip code to see what internet providers are available in your area.
Your antivirus is blocking your internet connection
Antivirus software is designed to protect you against threats on the internet, but sometimes it can get in the way of your normal web activities. Try briefly disabling your antivirus software to see if doing so restores your internet access.
We don’t recommend using the internet without your security software turned on, so don’t spend any additional time on the web without it. But if your antivirus is blocking your connection, try updating it. Because web threats evolve so quickly, web security software requires frequent updates. It’s a good idea to switch on the auto-update feature of your software due to the frequency of essential updates.
You can also try adding an exception to your security software’s firewall for the program or service you’re attempting to use.
If your antivirus software is causing too much frustration, consider switching to a new one.
Third-party software is causing internet connectivity issues
You probably have a bunch of programs running in the background of your computer. Sometimes, one of these programs interferes with your internet connection. An easy way to rule out background program problems is to boot your computer in safe mode, which disables most third-party background software.
If you have a healthy internet connection after booting in safe mode, one of your programs is likely causing the issue.
Reboot in Safe Mode on Windows 10:
Step 1: Click the Start button, then the cog wheel icon to open the settings menu.
Step 2: Type “recovery options” into the settings search box at the top of the menu and press enter.
Step 3: Under the Advanced startup sections, click “Restart now.”
Step 4: Your PC will reboot and display an options menu. From the options menu, select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart.
Step 5: Your PC will reboot again, and you’ll see a list of options. To reboot with networking, press 5.
Step 6: Your PC will reboot into safe mode with networking. From here, test your internet connection. If it works, a background program may have been causing trouble with your internet connection.
Restart MacOS computers (with Apple processors) in Safe Mode:
Step 1: Shut down your computer.
Step 2: Hold down the power button until “Loading startup options” appears on the screen.
Step 3: Choose a volume.
Step 4: While holding the shift key, select “Continue in Safe Mode.”
Restart MacOS computers (with Intel processors) in Safe Mode:
Step 1: Restart your Mac and hold down the shift key as it boots up.
Step 2: Log in (you might have to log in twice).
Step 3: You should see a Safe Boot indicator in the menu bar.
Your networking cables are loose or damaged
The cables connecting your equipment to the internet can become loose over time, or they can be damaged after repeated stress. Look for tears, harsh twisting, kinking, pressure from furniture, and chew marks from pets.
First, check the line that connects to your modem or gateway (modem/router combo) from the wall outlet. For cable internet customers, look for a coaxial cable (the same kind used for cable TV). Other internet types use coaxial or Ethernet cables. Coaxial cable connections should be twisted hand tight to the back of the modem and the wall outlet. Ethernet cables should make an audible click when inserted in the socket on your equipment.
If you have a separate modem and router, check the Ethernet cable connecting them as well.
Still stumped?
If you’re still having trouble establishing an internet connection, try our other resources to get your internet running smoothly.
- No Internet Connection Troubleshooting Guide
- Why Does My Internet Keep Disconnecting?
- Improve Your Wi-Fi Speed in 10 Simple Steps
- Why is My Internet So Slow?
Author - Austin Aguirre
Austin worked as a broadband technician installing and troubleshooting countless home internet networks for some of the largest ISPs in the U.S. He became a freelance writer in 2020 specializing in software guides. After graduating with a BS in technical communication from Arizona State University, he joined the team at HighSpeedInternet.com where he focuses on home network improvement and troubleshooting.
Editor - Rebecca Lee Armstrong
Rebecca Lee Armstrong has more than six years of experience writing about tech and the internet, with a specialty in hands-on testing. She started writing tech product and service reviews while finishing her BFA in creative writing at the University of Evansville and has found her niche writing about home networking, routers, and internet access at HighSpeedInternet.com. Her work has also been featured on Top Ten Reviews, MacSources, Windows Central, Android Central, Best Company, TechnoFAQ, and iMore.
Related Posts


Fix Wi-Fi connection issues in Windows
Troubleshooting network problems in windows.
If you can’t get email, browse the web, or stream music, chances are you’re not connected to your network and can’t get onto the internet. To fix the problem, here are some things you can try.
Things to try first
Try these things first to help you fix or narrow down the connection problem.
Run Get Help to troubleshoot and fix common connection problems. Right click the network icon in the right side of the taskbar and select Diagnose network problems or open Get Help for Network & Internet
Make sure Wi‑Fi is turned on. Select the No internet icon on the right side of the taskbar, and make sure Wi-Fi is turned on. If it isn't, select it to turn it on. Also, make sure Airplane mode is turned off.
Select Manage Wi-Fi connections ( > ) on the Wi-Fi quick setting, see if a Wi-Fi network you recognize and trust appears in the list of networks. If it does, select the Wi-Fi network, and they try to connect to it. If it says Connected underneath the network name, select Disconnect , wait a moment, and then select Connect again.
Try connecting to a network on a different frequency band. Many consumer Wi-Fi routers broadcast at two different network frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. These will appear as separate networks in the list of available Wi-Fi networks. If your list of available Wi-Fi networks includes both a 2.4 GHz network and a 5 GHz network, try connecting to the other network. To learn more about the differences between 2.4 GHz networks and 5 GHz networks, check out Wi-Fi problems and your home layout .
Make sure the physical Wi‑Fi switch on your laptop is turned on. (An indicator light usually shows when it's on.)
Restart your modem and wireless router. This helps create a new connection to your internet service provider (ISP). When you do this, everyone that is connected to your Wi-Fi network will be temporarily disconnected. The steps you take to restart your modem and router can vary, but here are the general steps.
Note: If you have a cable modem/Wi-Fi router combo device, you only need to follow the steps for the single device.
Unplug the power cable for the router from the power source.
Unplug the power cable for the modem from the power source. Some modems have a backup battery. If you unplug the modem and lights stay on, remove the battery from the modem.
Wait at least 30 seconds or so. If you had to remove the battery from the modem, put it back in.
Plug the modem back into the power source. The lights on the modem will blink. Wait for them to stop blinking.
Plug your router back into the power source. Wait a few minutes for the modem and router to fully power on. You can usually tell when they’re ready by looking at the status lights on the two devices.
On your PC, try to connect again.
Narrow down the source of the problem
Connection problems can be due to a variety of reasons—problems with the website, your device, the Wi-Fi router, modem, or your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Try the following steps to help narrow down the source of the problem.
If the "Wi-Fi connected" icon appears on the right side of the taskbar, visit a different website. If the website opens, there might be a problem with the specific website. If you can't connect to another website, go to the next step.
On another laptop or phone, try to connect to the same network. If you can connect, the source of the problem is likely due to your device—go to the section Network troubleshooting on your device . If you can't connect to the network on any device, continue to the next step.
Check to see if there is a problem with the connection to your Wi-Fi router. Do this by using a ping test.
Select Search on the taskbar, and type command prompt . The Command Prompt button will appear. To the right of it, select Run as administrator > Yes .
At the command prompt, type ipconfig , and then select Enter . Look for the name of your Wi-Fi network within the results, and then find the IP address listed next to Default gateway for that Wi-Fi network. Write down that address if you need to. For example: 192.168.1.1
At the prompt, type ping <DefaultGateway> and then select Enter . For example, type ping 192.168.1.1 and select Enter . The results should be something like this:
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=64
Ping statistics for 192.168.1.1: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 4ms, Maximum = 5ms, Average = 4ms
If you see results like this and are getting a reply, then you have a connection to your Wi-Fi router, so there might be a problem with your modem or ISP. Contact your ISP or check online on another device (if you can) to see if there's a service outage.
If the results of the ping test indicate that you are not getting a reply from the router, try connecting your PC directly to your modem by using an Ethernet cable (if you can). If you can connect to the internet using an Ethernet cable, it confirms the connection problem is due to the Wi-Fi router. Make sure you've installed the latest firmware and see the documentation for your router.
Network troubleshooting on your device
Run network commands
Try running these network commands to manually reset the TCP/IP stack, release and renew the IP address, and flush and reset the DNS client resolver cache:
At the command prompt, run the following commands in the listed order, and then check to see if that fixes your connection problem:
Type netsh winsock reset and select Enter .
Type netsh int ip reset and select Enter .
Type ipconfig /release and select Enter .
Type ipconfig /renew and select Enter .
Type ipconfig /flushdns and select Enter .
Uninstall the network adapter driver and restart
If the previous steps didn’t work, try to uninstall the network adapter driver, and then restart your computer. Windows will automatically install the latest driver. Consider this approach if your network connection stopped working properly after a recent update.
Before uninstalling, make sure you have drivers available as a backup. Visit the PC manufacturer’s website and download the latest network adapter driver from there. If your PC can't connect to the internet, you'll need to download a driver on a different PC and save it to a USB flash drive so you can install the driver on your PC. You’ll need to know the PC manufacturer and model name or number.
Select Search on the taskbar, type device manager , and then select Device Manager from the list of results.
Expand Network adapters , and locate the network adapter for your device.
Select the network adapter, press and hold (or right-click), and then select Uninstall device > check the Attempt to remove the driver for this device check box > Uninstall .
After uninstalling the driver, select Start > Power > Restart .
After your PC restarts, Windows will automatically look for and install the network adapter driver. Check to see if that fixes your connection problem. If Windows doesn't automatically install a driver, try to install the backup driver you saved before uninstalling.
Check if your network adapter is compatible with the latest Windows Update
If you lost your network connection immediately after upgrading to or updating Windows 11, it's possible that the current driver for your network adapter was designed for a previous version of Windows. To check, try temporarily uninstalling the recent Windows Update:
Select Start > Settings > Windows Update > Update history > Uninstall updates .
Select the most recent update, then select Uninstall .
If uninstalling the most recent update restores your network connection, check to see if an updated driver is available:
Select the network adapter, press and hold (or right-click), then select Update driver > Search automatically for updated driver software , and then follow the instructions.
After installing the updated driver, select Start > Power > Restart if you're asked to restart, and see if that fixes the connection issue.
If Windows can’t find a new driver for your network adapter, visit the PC manufacturer’s website and download the latest network adapter driver from there. You’ll need to know the PC manufacturer and model name or number.
Do one of the following:
If you couldn’t download and install a newer network adapter driver, hide the update that’s causing you to lose your network connection. To learn how to hide updates, see Hide Windows Updates or driver updates .
If you could successfully install updated drivers for your network adapter, then reinstall the latest updates. To do this, select Start > Settings > Windows Update > Check for updates .
Use network reset
Using network reset should be the last step you try. Consider using it if the steps above don’t help to get you connected.
This can help solve connection problems you might have after upgrading from Windows 10 to Windows 11. It can also help to fix the problem where you can connect to the internet, but can't connect to shared network drives. Network reset removes any network adapters you have installed and the settings for them. After your PC restarts, any network adapters are reinstalled, and the settings for them are set to the defaults.
Select Start > Settings > Network & internet > Advanced network settings > Network reset . Open Network & Internet Status settings
On the Network reset screen, select Reset now > Yes to confirm.
Wait for your PC to restart, and see if that fixes the problem.
After using network reset, you might need to reinstall and set up other networking software you might be using, such as VPN client software or virtual switches from Hyper‑V (if you're using that or other network virtualization software).
Network reset might set each one of your known network connections to a public network profile. In a public network profile, your PC is not discoverable to other PCs and devices on the network, which can help make your PC more secure. However, if your PC is used for file or printer sharing, you’ll need to make your PC discoverable again by setting it to use a private network profile. To do this, select Start > Settings > Network & internet > Wi-Fi . On the Wi-Fi screen, select Manage known networks > the network connection you want to change. Under Network profile type , select Private .
Additional troubleshooting steps
Check your Wi-Fi settings
Wi-Fi adapter manufacturers might have different advanced settings you can change based on your network environment or connection preferences.
Check the Wireless Mode setting for your network adapter and make sure it matches the capabilities of the network you’re trying to connect to. If it doesn’t match, you won’t be able to connect, and the network might not appear in the list of available networks. The Wireless Mode will often be set to Auto or something similar by default, which enables connection for every kind of network that’s supported.
To find the wireless mode setting
In Device Manager, select Network adapters , and then double-click the network adapter name.
Select the Advanced tab and look for a Wireless Mode setting. Make sure it’s set to the mode your network is using.
Wi-Fi profile settings
Windows uses the Wi-Fi profile to save the settings that are needed to connect to a Wi-Fi network. These settings include the network security type, key, network name (SSID), and so on. If you can’t connect to a Wi-Fi network that you could connect to before, it’s possible that the network settings might have changed or the profile is corrupted.
To fix this, remove (or "forget") the network connection, then reconnect to the network. When you forget a network connection, it removes the Wi-Fi network profile from your PC.
To forget a network
Select Start > Settings > Network & internet .
Select Wi-Fi , then select Manage known networks .
Select the network you want to forget, then select Forget .
Afterwards, select the Wi-Fi icon on the taskbar and try to reconnect to the network to renew the network connection.
Check your home layout
Your Wi-Fi network might be affected by the network's frequency band, channel congestion, and/or signal strength. For more info, see Wi-Fi problems and your home layout .
Check for additional symptoms for the "No internet connection" icon.
There may be additional troubleshooting steps you can try, depending on which symptoms you're having. To view these steps, check out Wi-Fi connection icons and what they mean .
Related topics
Setting up a wireless network
How to find your wireless network password
Analyze the wireless network report
Wi-Fi tools and apps
Make a Wi-Fi network public or private in Windows

Afterwards, see if a Wi-Fi network you recognize and trust appears in the list of networks. If it does, select the Wi-Fi network, and they try to connect to it. If it says Connected underneath the network name, select Disconnect , wait a moment, and then select Connect again.
Try connecting to a network on a different frequency band. Many consumer Wi-Fi routers broadcast at two different network frequency bands: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. These will appear as separate networks in the list of available Wi-Fi networks. If your list of available Wi-Fi networks includes both a 2.4 GHz network and a 5 GHz network, try connecting to the other network. To learn more about the differences between 2.4 GHz networks and 5 GHz networks, check out Wi-Fi problems and your home layout .
Run the Network troubleshooter. The Network troubleshooter can help diagnose and fix common connection problems.
To run the Network troubleshooter
Select the Start button > Settings > Network & Internet > Status . Open Network & Internet Status settings
Under Change your network settings , select Network troubleshooter .
Follow the steps in the troubleshooter, and see if that fixes the problem.
Restart your modem and wireless router. This helps create a new connection to your internet service provider (ISP).
When you do this, everyone that is connected to your Wi-Fi network will be temporarily disconnected. The steps you take to restart your modem and router can vary, but here are the general steps. ( Note : If you have a cable modem/Wi-Fi router combo device, you only need to follow the steps for the single device.)
If the "Wi-Fi connected" icon appears on the right side of the taskbar, visit a different website. If the website opens, there might be a problem with the specific website. If you can't connect to another website, go to the next step.
On another laptop or phone, try to connect to the same network. If you can connect, the source of the problem is likely due to your device—go to the section Network troubleshooting on your device . If you can't connect to the network on any device, continue to the next step.
Check to see if there is a problem with the connection to your Wi-Fi router. Do this by using a ping test.
In the search box on the taskbar, type command prompt . The Command Prompt button will appear. To the right of it, select Run as administrator > Yes .
At the command prompt, type ipconfig , and then select Enter . Look for the name of your Wi-Fi network within the results, and then find the IP address listed next to Default gateway for that Wi-Fi network. Write down that address if you need to. For example: 192.168.1.1
At the prompt, type ping <DefaultGateway> and then select Enter . For example, type ping 192.168.1.1 and select Enter . The results should be something like this:
Type netsh winsock reset and select Enter .
Type netsh int ip reset and select Enter .
Type ipconfig /release and select Enter .
Type ipconfig /renew and select Enter .
Type ipconfig /flushdns and select Enter .
In the search box on the taskbar, type device manager , and then select Device Manager from the list of results.
Expand Network adapters , and locate the network adapter for your device.
Select the network adapter, press and hold (or right-click), and then select Uninstall device > check the Attempt to remove the driver software for this device check box > Uninstall .
After uninstalling the driver, select the Start button > Power > Restart .
If you lost your network connection immediately after upgrading or updating Windows 10, it's possible that the current driver for your network adapter was designed for a previous version of Windows. To check, try temporarily uninstalling the recent Windows Update:
Select the Start button, then select Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update > View update history > Uninstall updates .
Select the most recent update, then select Uninstall .
Select the network adapter, select Update driver > Search automatically for updated driver software , and then follow the instructions.
After installing the updated driver, select the Start button > Power > Restart if you're asked to restart, and see if that fixes the connection issue.
If you couldn’t download and install a newer network adapter driver, hide the update that’s causing you to lose your network connection. To learn how to hide updates, see Hide Windows Updates or driver updates .
If you could successfully install updated drivers for your network adapter, then reinstall the latest updates. To do this, select the Start button, then select Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update > Check for updates .
This can help solve connection problems you might have after upgrading from a previous version of Windows to Windows 10. It can also help to fix the problem where you can connect to the internet, but can't connect to shared network drives. Network reset removes any network adapters you have installed and the settings for them. After your PC restarts, any network adapters are reinstalled, and the settings for them are set to the defaults.
Note: To use network reset, your PC must be running Windows 10 Version 1607 or later. To see which version of Windows 10 your device is currently running, select the Start button, then select Settings > System > About .
Select the Start button, then select Settings > Network & Internet > Status > Network reset . Open Network & Internet Status settings
On the Network reset screen, select Reset now > Yes to confirm.
Network reset might set each one of your known network connections to a public network profile. In a public network profile, your PC is not discoverable to other PCs and devices on the network, which can help make your PC more secure. However, if your PC is used for file or printer sharing, you’ll need to make your PC discoverable again by setting it to use a private network profile. To do this, select the Start button, then select Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi . On the Wi-Fi screen, select Manage known networks > the network connection you want to change > Properties . Under Network profile , select Private .
In Device Manager, select Network adapters , and then double-click the network adapter name.
Select the Advanced tab and look for a Wireless Mode setting. Make sure it’s set to the mode your network is using.
Select the Wi-Fi network icon on the right side of the taskbar, then select Network & Internet settings .
Select Wi-Fi , then select Manage known networks .
Select the network you want to forget, then select Forget .
Afterwards, select the Wi-Fi icon on the taskbar and try to reconnect to the desired network to renew the network connection.
Your Wi-Fi network might be affected by the network's frequency band, channel congestion, and/or signal strength. For more info, see Wi-Fi problems and your home layout .
There may be additional troubleshooting steps you can try, depending on which symptoms you're having. To view these steps, check out Wi-Fi connection icons and what they mean .
Make a Wi-Fi network public or private in Windows 10
Check the basics on your PC
Make sure Wi-Fi is turned on.
Swipe in from the right edge of the screen, select Settings , then select the Network icon.
Turn on Wi-Fi .
Make sure your PC isn’t in airplane mode.
Turn off Airplane mode .
Move closer to the router or access point if you can.
If you don’t see the network name at all, the router or access point might not be set to broadcast the network name. In this case, you’ll need to connect to it manually.
Swipe in from the right edge of the screen, and then select Settings .
Select the Network icon, and then select Hidden network .
Type the network name and select Next .
Type the password and select Next .
Follow any additional instructions to get connected.
The network will be added to your list of networks and will be available to connect to when your computer is in range of the network. To connect to the network, follow these steps:
Open Connect to a Network by selecting the network icon in the notification area.
Select Unnamed Network , select Connect , and then type the network information. The network will be added to your list of networks and will be available to connect to in the future when your computer is in range of the network..
Use the Network Troubleshooter
Let Windows try to help you fix the problem. Try running the Network troubleshooter to see if it can diagnose and fix the problem.
Select the Start button, start typing Network problems , and then select Identify and repair network problems in the list.
Run network commands after using the Network Troubleshooter
The Network Troubleshooter (mentioned above) can help diagnose and fix common connection problems. After using that, try running the network commands below because the combination of doing these two things can help you get connected.
If your problem isn’t fixed after running the Network troubleshooter, try to:
Reset the TCP/IP stack.
Release the IP address.
Renew the IP address.
Flush and reset the DNS client resolver cache.
Here's how to run networking commands in a command prompt:
Select the Start button, start typing cmd , right-click Command Prompt in the list, select Run as Administrator , and then select Yes .
At the command prompt, run the following commands in the listed order and then check to see if that fixes your connection problem:
Type netsh winsock reset and press Enter.
Type netsh int ip reset and press Enter.
Type ipconfig /release and press Enter.
Type ipconfig /renew and press Enter.
Type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter.
Restart your modem and router
This helps create a new connection to your Internet service provider (ISP). When you do this, everyone that is connected to your Wi-Fi network will be temporarily disconnected.
The steps you take to restart your modem and router can vary, but here are the general steps:
Unplug the power cable for the modem from the power source. Some modems have a backup battery. So if you unplug the modem and lights stay on, remove the battery from the modem.
See if it's a problem with your modem or your ISP
Make sure it’s not a problem with your cable modem or Internet service provider (ISP). If it is, contact your ISP.
At the command prompt, type ipconfig . Look for the IP address listed next to Default gateway . Write down that address if you need to. For example, 192.168.1.1.
At the prompt, type ping <Default gateway> and press Enter . For example, type ping 192.168.1.1 and press Enter . The result should be something like this: Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=64 Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=64 Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=64 Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time=5ms TTL=64 Ping statistics for 192.168.1.1: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 4ms, Maximum = 5ms, Average = 4ms
If the ping is successful and you see results similar to the results above, but you can’t connect to the Internet on your PC, there may be a problem with your modem or Internet service provider (ISP).
Check your network adapter
If you’re still having trouble connecting to a network, it might be related to your network adapter.
Try using the Network Adapter troubleshooter to automatically find and fix some problems. This troubleshooter will disable and re-enable the adapter, and try some other common repairs. Select the Start button, start typing Troubleshooting , and then select Troubleshooting in the list. Select View all > Network Adapter .
Update the network adapter driver. An outdated or incompatible network adapter driver can cause connection problems. Check to see if an updated driver is available.
Select the Start button, start typing Device Manager , and then select it in the list.
In Device Manager, select Network adapters , right-click your adapter, and then select Properties .
Select the Driver tab, and then select Update Driver .
Select Search automatically for updated driver software .
If Windows can’t find a new driver for your network adapter, visit the PC manufacturer’s website and download the latest network adapter driver from there. If your PC can't connect to the Internet, you'll need to download a driver on a different PC and save it to a USB flash drive so you can install the driver on your PC. You’ll need to know the PC manufacturer and model name or number.
Other steps to try on your router
Here are some things to check and try with your router if you’re at home and having trouble getting connected.
If you don't see the network name, sign in to your router and check to see if it’s set to broadcast the network name.
Connect your PC to your router using an Ethernet cable.
Open your web browser and type the IP address for your wireless router. (For example, 192.168.1.1 or 172.16.0.0—check the documentation for your router to find the default IP address.)
Sign in with your user name and password, then make sure an option labeled Enable SSID Broadcast , Wireless SSID broadcast , or something similar is turned on. This setting is often on a Wireless Settings page.
Check to see if your Wi-Fi network uses Media Access Control (MAC) address filtering for security. If it does, you’ll need to add the MAC address for your PC to the access list on your router before you can connect.
Select the Start button. Start typing cmd and right-click Command Prompt in the list. Select Run as Administrator , and then select Yes .
At the command prompt, type ipconfig /all . Write down the address that appears next to Physical Address for your wireless network adapter. This is the address you’ll need to add to the access list on your router.
To add the MAC address to the access list on your router:
Sign in with your user name and password, then look for a setting that says MAC Address Filter or something similar.
Add the MAC address you wrote down for your PC to the access list and save your changes.
On your PC, try to connect to the Wi-Fi network again.

Look in the Wireless Network section. If Wi-Fi is on, the button should say Turn wireless off .
Check and make sure your PC isn’t in airplane mode.
Select Add , and then select Manually create a network profile .
Type the network information.
If you want Windows to automatically connect when the network is in range, select the Start this connection automatically check box.
Select the Connect even if the network is not broadcasting check box, select Next , and then select Close .
Open the Network troubleshooter by right-clicking the network icon in the notification area and then selecting Troubleshoot problems .

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Find solutions to common problems or get help from a support agent.

Online support
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
Ad-free. Influence-free. Powered by consumers.
The payment for your account couldn't be processed or you've canceled your account with us.
We don’t recognize that sign in. Your username maybe be your email address. Passwords are 6-20 characters with at least one number and letter.
We still don’t recognize that sign in. Retrieve your username. Reset your password.
Forgot your username or password ?
Don’t have an account?
- Account Settings
- My Benefits
- My Products
- Donate Donate
Save products you love, products you own and much more!
Other Membership Benefits:
Suggested Searches
- Become a Member
Car Ratings & Reviews
2024 Top Picks
Car Buying & Pricing
Which Car Brands Make the Best Vehicles?
Tires, Maintenance & Repair
Car Reliability Guide
Key Topics & News
Listen to the Talking Cars Podcast
Home & Garden
Bed & Bath
Top Picks From CR
Best Mattresses
Lawn & Garden
TOP PICKS FROM CR
Best Lawn Mowers and Tractors
Home Improvement
Home Improvement Essential
Best Wood Stains
Home Safety & Security
HOME SAFETY
Best DIY Home Security Systems
REPAIR OR REPLACE?
What to Do With a Broken Appliance
Small Appliances
Best Small Kitchen Appliances
Laundry & Cleaning
Best Washing Machines
Heating, Cooling & Air
Most Reliable Central Air-Conditioning Systems
Electronics
Home Entertainment
FIND YOUR NEW TV
Home Office
Cheapest Printers for Ink Costs
Smartphones & Wearables
BEST SMARTPHONES
Find the Right Phone for You
Digital Security & Privacy
MEMBER BENEFIT
CR Security Planner
Take Action
How to Get a Stronger WiFi Signal
Before you run out to buy a new router, try these tips for improving the signal throughout your home
When you shop through retailer links on our site, we may earn affiliate commissions. 100% of the fees we collect are used to support our nonprofit mission. Learn more .

There are few things quite as frustrating as a crummy WiFi connection.
Picture the scene: You’re at home relaxing after a hard day of work and you decide to stream the latest episode of “Masters of the Air” on Apple TV+ . With some snacks on the coffee table and a drink in hand, you hit the Play button on your remote control and wait for the program to begin.
- Is Your Router Slow?
Which Router Is Best for You?
- 5 Common WiFi Problems
- Recommended WiFi Routers
And wait and wait and wait.
When it works, your home WiFi connection is your gateway to all the internet has to offer: the latest hits on Apple TV+ and Netflix; white-knuckle competitive gaming in Call of Duty ; and sporting events available exclusively on Peacock or Prime Video.
Got an all-night dance party planned? A reliable WiFi connection ensures your Sonos can seamlessly stream Spotify without annoying skips in the music.
But when it fails you, your home WiFi connection can be a great big headache.
We’re here to help. We test dozens of WiFi routers a year in our labs just north of New York City, from high-end mesh router systems that can blanket a sprawling home layout in coverage to $20 extenders that eliminate dead spots in your home office. (The full results of these tests are available to CR members .) We’ve seen it all—which is how we know what steps you can take today to improve your WiFi signal.
Is Your Router a Slowpoke?
Understanding the basics of router operation can help you fix some hiccups.
“Think of a router as an electronic traffic cop,” says Richard Fisco, who oversees electronics testing for Consumer Reports.
Once it’s hooked up to the modem provided by your internet service provider (ISP), it directs the internet access throughout your home, making it wirelessly available to devices like your laptop , phone , and TV .
If your WiFi connection is noticeably sluggish, you may be tempted to write off your current router as a dud. But don’t be too hasty—there may be other factors at play.
First, take a look at a bill from your ISP to see what level of broadband you’re paying for. You’ll need a connection of at least 15 megabits per second to stream Netflix in 4K, for example. So, if you’re not paying for at least that, or don’t have access to that kind of speed where you live, a brand new router isn’t going to help you.
You can easily run a speed test using a service like fast.com to see what you’re really getting. You may want to run this test a few times. First, run it with your laptop plugged into your router to check your speed in the best-case scenario. You can then move around with your laptop to different areas of your home to see how fast WiFi is at different locations.
Next, you’ll want to assess the placement of your router. They tend to do best when set up in the center of a home, allowing the WiFi signal to reach out in every direction. A router tucked away in a corner may not have the range to travel to the other side of the house, or from the second floor to the basement, because the signal degrades the farther it gets from the source.
If your router is in a suboptimal spot (a closet, say, or perhaps the basement), try moving it. One way is to buy a long Ethernet cable (keep it under 300 feet), plug it into the modem and the router, and move the router yourself. Or you can ask your ISP to help you relocate the modem, though the company may charge you depending on the labor involved. If you’re planning to change providers, Fisco says, you may be able to get the job done free, so ask while you’re negotiating the switch.
If your router is already in a central location, the slow connection might be due to obstacles in the house that can impede a WiFi signal. You can try moving the router around a room to address such problems.
If those tweaks don’t help, it may be time to find a model better suited to your needs, especially if you’ve been using a single-unit router in a multi-story home.
There are two types of WiFi routers on the market: traditional models and mesh network models. There are also WiFi extenders, which we’ll explain in a bit.
You’re probably familiar with traditional WiFi routers. They’re single-unit devices that plug into a modem. They can be plenty fast, supporting even the data-hungry activities of families with dozens of internet-connected devices. But they don’t always have the range to effectively blanket a whole home in WiFi, especially if you have a large or obstacle-laden layout. (See WiFi Roadblocks below.)
Mesh routers are typically packaged in a set with multiple units—a hub and one or more satellites—that work together to steer WiFi around certain obstacles and spread it into the far-flung corners of a home. If you place the hub, which plugs into your modem, near the center of your home, you can shift around the satellites, which help relay the WiFi signal, until you find a configuration that helps you eliminate any dead spots.
So why doesn’t everyone simply choose a mesh router? They’re pricey, for one thing. The top-rated models in our ratings regularly cost several hundred dollars, with a few models even reaching $1,000. That’s a lot of money just to watch Seinfeld reruns on Netflix. But we do recommend some models that cost roughly $100 to $200.
There’s also an argument to be made for simplicity.
With a mesh system, you have several devices strewn about your home vs. just one with a traditional router. If you don’t actually need a mesh router, there’s no reason to invest in one.
As for WiFi extenders, these are devices that can extend the reach of your existing WiFi network by repeating the signal. They’re not as effective as mesh routers, but can cost as little as $20. And at that price, given our testing of several popular models , they may be useful for those merely trying to eliminate a single trouble spot in their homes, such as one WiFi dead zone in a spare bedroom or attic office.
Rodrigo Damati Rodrigo Damati
5 Common WiFi Roadblocks & How to Fix Them
Here are some common obstacles to think about as you search for the ideal place to put your router. In this diagram, we’ve arranged a three-piece mesh router network to help eliminate potential dead spots in a multilevel home.
For the best results, place the hub in the center of your home (1) and between the satellites (2 and 3), says CR’s Fisco. Note that satellite 3 sits on the kitchen counter away from the refrigerator (4). The WiFi signal from both the hub and satellites can also reach up and down to other floor levels, eliminating potential dead zones.
The Walls Thicker walls tend to absorb more of a WiFi signal than thinner walls. While you can’t easily change how thick your walls are, simply repositioning a mesh satellite closer to a room’s entrance may help boost the signal.
The Fridge A refrigerator and other appliances that contain a lot of metal can cause trouble, too. WiFi signals may bounce off them instead of passing through to the other side. Metal plumbing and rebar in your walls create similar problems.
The Neighbors If you live in an apartment building or a heavily populated neighborhood, you might be susceptible to wireless congestion created by nearby devices running on the 2.4GHz frequency band. Most routers released within the last 10 years support an additional frequency band, 5GHz, while routers released within the past four years may also support the 6GHz band. These two bands are faster than 2.4GHz. Depending on your exact router model, you may have to go into the device settings to select these faster bands.
The Microwave Microwaves also operate in the 2.4GHz frequency band, which can cause interference if, for example, you decide to make a second bag of popcorn while streaming a Netflix movie. To avoid the interruption on movie night, make sure your device is on either the 5GHz or 6GHz band.
The Fish Tank Water absorbs electromagnetic radiation like WiFi signals, so make sure your router isn’t parked next to your new 20-gallon fish tank.
Product Picks
Check out these wireless routers that impressed our product testers.
Editor's Note: This article also appeared in the March 2020 issue of Consumer Reports magazine.
Home WiFi Mesh Networks
Can’t get a decent wireless internet connection in your home? On the " Consumer 101 " TV show, Consumer Reports’ expert Nicholas De Leon explains to show host Jack Rico how mesh networks provide faster speeds and better coverage.
Nicholas De Leon
Nicholas De Leon is a senior reporter for Consumer Reports, covering laptops, wireless routers, tablets, and more. He has been at CR since 2017. He previously covered tech for Vice, News Corp, and TechCrunch. He lives in Tucson, Ariz. Follow him on Twitter for all things tech and soccer @nicholasadeleon .
Sharing is Nice
We respect your privacy . All email addresses you provide will be used just for sending this story.
Linksys MR55WH Classic Micro Pro 6
Linksys mr20wh (ln3111), netgear orbi 750 series ax5200 (3-pack), linksys velop micro ax3000 ln11011202 ( 2-pack), imicro atom audio mesh ax5400 (2-pack), tenda ax3000 ex12 mesh wifi 6 system (3-pack), tp-link be9300, tp-link deco we10800 (2-pack), d-link eagle pro ai ax1800, d-link covr ax1800 (2-pack), asus zenwifi ax3000 hybrid (2-pack), eero max 7 (2-pack).
See All Ratings
Trending in Wireless routers
Should You Buy a WiFi Extender?
Best Deals on Electronics
How Much Internet Speed Do You Need?
Set Your WiFi to Automatically Shut Off So Your Kids Will Go to Sleep
What to do if your broadband internet is slow
Slow broadband got you down? Stop tearing your hair out and fix it fast!

In a time where we use digital devices in many aspects of our daily lives, and in which we have a limitless supply of internet content at our disposal, having slow broadband can be a real inconvenience.
It’s not just the often agonising wait times we endure, it’s also how it can affect our productivity – especially when we rely on the internet on a professional basis.
However, what you might not appreciate here is that slow broadband isn’t always a technical issue, it can be related to several external factors. The positive is that there are steps we can take to get our broadband speeds back into the fast lane, ranging from upgrading your router to simply switching to one of the best broadband deals .
So be sure to read on as in this guide we’ve explained everything you need to know about this subject, and we’ve detailed all the approaches you can try when faced with a slow internet connection.
How is broadband speed measured?
Before we get started, it’s a good idea to get clued up on how exactly we measure broadband speed, so you can more easily identify when it’s being ‘slow’.
When we talk about ‘speed’ what we mean is how fast data is sent online between the internet server and your physical device. This is also split into two types of connections:
- Download speed - Typically what is referred to when mentioning broadband speeds, this is how fast information transfers from the internet to a device
- Upload speed - How fast information goes from a device to the internet (e.g. uploading an attachment to an email and sending it)
The rates of these connections are also determined in ‘megabits per second’ or ‘Mbps’ and in simple terms, the higher these numbers, the faster the data can be moved - therefore the faster your internet ‘speed’.

What can cause slow broadband?
Here are some common reasons why broadband speeds can slow down:
- There are multiple users with high online demands using your connection at the same time, essentially creating more traffic than it can manage.
- Your provider’s network is seeing high usage and a similar effect to the above point is happening.
- You have a weak WiFi signal, or it is being disrupted by external factors like the weather or even walls and furniture.
- Your router or your devices are older or malfunctioning.
- Your devices have spyware or viruses affecting them.
- The broadband connection supplying your property is broken, possibly due to wear and tear or accidental damage.
- You’re about to exceed any data limits you might have on your broadband package.
- The broadband package you have simply doesn’t offer fast broadband speeds.
It might also be the case that you’re suffering from a combination of some of the above if you do have slow internet, which as you can imagine can only compound the situation.
What is a 'slow broadband package'?
To pick up on that last bullet point above, a ‘slow’ broadband package by today’s standards would be an ADSL or basic fibre connection.
These are the legacy connections that still use old copper phone lines and are limited by the amount of data they can send. It’s also rare that you’ll even be able to get these now as they’re in the process of being phased out completely. They’re only really for those in remote areas who can’t access faster fibre and Full Fibre broadband.
Although, as we’ve also alluded to above, even ultrafast Full Fibre connections can be slowed down by some of these issues, the effect may not be as significant as it would be on an older broadband connection type, however.
How to identify if you have slow broadband
For those of you who suspect your internet is slow, but you’re not certain, it’s easy to find out.
Firstly, you should check your contract or speak directly with your provider to see what speeds or minimum speed guarantees you have in place. Then, using this as a benchmark, run a broadband speed test and see what the results show you.
It’s useful to run several tests in different rooms and on different devices, just to see where any particularly bad spots might be in your home or business.

Consumer rights for slow broadband
Speaking of ‘minimum speed guarantees’, you also might be entitled to compensation if you can prove your broadband supplier isn’t living up to the speeds it promises in your contract. You can learn more about this here with the ‘ Codes of practice ’ that the UK telecommunications regulator, Ofcom, has in place for all UK broadband providers.
How you can speed up your broadband
Before you do raise any issues with your broadband provider, there are some things you can do that might help speed up your broadband.
- Restart your router and refresh your devices (yes, “try turning them on and off again!”)
- Move your router to a more central and open location. Avoid blocking its signal with things like furniture or thick walls.
- Invest in some WiFi boosting technology (individual signal boosters or a mesh router system) and place these around your home.
- Invest in some antivirus software/protection - if you do have issues with malware.
- Disable the internet on devices you don’t tend to use that often to free up the bandwidth.
- Be smart with when you use your broadband - e.g. avoid things like browsing, streaming, and online gaming all at the same time.
If these don’t work then you need to contact your provider and get them to assess the situation from their side. They may be able to help identify the fault and offer advice and guidance on how to speed up your slow internet connection.
However, another thing you can of course do is look to move to a new broadband deal - be it with the same provider or a new one - especially if faster, unlimited and more dependable Full Fibre options are now available to you.

How to find a faster broadband deal
If the idea of a new broadband deal has piqued your interest, then we can help. Head over to our best broadband deals page and you’ll get an idea of what options are available to you.
Better still, if you enter your postcode into our widget below you’ll be able to see the broadband deals you can actually get right now in your specific location.
You can then either sign up for a new broadband deal - although you should check with your existing provider if you’re still under contract, as you could incur exit fees - or speak to your current supplier and haggle for a better tariff.
Get daily insight, inspiration and deals in your inbox
Sign up for breaking news, reviews, opinion, top tech deals, and more.

Rich is a freelance copywriter and content strategist with over 10 years' experience. His career has seen him work in-house and in various agencies, producing online and offline content marketing campaigns and copywriting for clients in the energy industry.
Do you dread trying to change your router settings? Login problems could soon be a thing of the past
Google’s Nest Wi-Fi routers have vanished from the Google Store - could a Wi-Fi 7 model be inbound?
Atalanta vs Bayer Leverkusen live stream: How to watch Europa League final game online for free
- 2 I tried Samsung’s best OLED TV with its flagship Dolby Atmos soundbar, and the audio combo is out of this world
- 3 Pilates instructor recommends these 5 moves to undo the damage of sitting at a desk all day
- 4 Scientists have created an ultra resistant storage solution that can resist temperatures of 1100°F — shame that it will only be available in megabyte capacities for a foreseeable future
- 5 30TB hard drives will finally become mainstream next year — Japanese rival to Seagate and Western Digital reveals plans to launch two 30TB+ HDDs in 2025 using two different technologies
- 2 Samsung Galaxy A35 review: a Samsung Galaxy S24 for the rest of us
- 3 Google is bringing back classic search, with no AI – and I couldn't be happier about that
- 4 Fujifilm's most affordable medium-format camera gets a whopping $1,000 reduction
- 5 Forget Intel and AMD - Nvidia's next big competitor might be a company you've never heard of

How to fix: Router doesn't connect to the internet after a reset
Resetting your router can be a quick way to solve some connectivity issues or to get a fresh start, but if your internet connection doesn’t come back on, it’s very frustrating. Your router is part of a large collection of devices that directs data from your connected devices to the right server online and back again, so there are a lot of things that can prevent your connection from working. If you’ve reset your router, and it won’t connect to the internet, there are some quick fixes you can try.
First things first, did you actually reset the router or simply restart it? If you didn’t hold the reset button long enough, the router may have just restarted instead of resetting. If you still see your SSID as available on your devices, you likely didn't do a full reset.
Check your connections
When you’re troubleshooting connection issues, one of the most important concepts to remember is signal flow. That is, to find an issue with a connection, start at the source and follow the signal to the destination. Check the lights on your router to make sure they’re lighting up properly, especially if you’ve got a light for your internet connection. If it’s blinking, you’ve got a signal, but if it’s off, then your connection may have loosened.
When you’re picking up and moving a router around to reset it, it’s possible that some connections got loose or came unplugged on the back. If your cable line or fiber line plugs directly into your router, make sure it’s all the way in and snug. Even if you’ve got a status light on, it’s worth checking the connections anyway.
Also, make sure all of the cables that you plugged in are correct for the equipment you’re using. While the power cable for a separate modem and router may look identical, they may have different power outputs and one device may not be getting the full power it needs.
If you’ve got 5G internet, you may need to talk to customer service at the provider to make sure all of your information is set up correctly to access the network.
Once you’ve made sure everything is plugged in, restart both the modem and router at the same time. If there was an IP address issue between the two, restarting both can help.
Troubleshoot your router-modem combo
If you’ve got a router-modem combo that both provides Wi-Fi and takes your cable ISP’s coaxial cable, you may need to request a refresh signal. Your modem needs to handshake with your ISP to get connected and if you didn’t get a refresh signal when you reset the router-modem combo, you may need to request one.
On a lot of ISPs, like Xfinity, you can see your modem on the devices section of your account page on the ISP’s website or in the app. If no modem is detected, you should check your connections, and check again after a few minutes. If it is detected, check if you can send a refresh signal from the website. Customer service should also be able to send a refresh signal.
If you can’t access the devices on your account page, the easiest way to get a refresh from your cable provider is by restarting your modem. While this should have happened in the initial reset, restarting the modem is an easy place to start with a high rate of success.
If you rent your equipment from your ISP, get in contact with customer support — it’s part of what you’re paying for, after all. Customer support will be able to see in just a couple of minutes if your modem is connecting properly and may be able to offer a quick solution if you’ve encountered a known problem.
Troubleshoot your standalone router
If you have a separate modem (or ONT) and router, it’s a good start to check the connection directly from the modem. There should be an Ethernet cable coming out of the modem and plugging into the WAN port on your router. That Ethernet cable can be plugged into a PC and if it connects to the internet, you know the problem is with the router, not the modem. If you’re not getting a connection directly from the modem, you know the problem likely lies with the modem or your ISP.
One thing to keep in mind before getting too far ahead of yourself is that it can take a few minutes for a router to come back on after a reset, so you may just need to give it ten or so minutes to get everything figured out. Even the best Wi-Fi routers need a minute or two to scan for signals and check for updates before they finish starting up. Routers often scan for other wireless signals before turning on Wi-Fi, so it can take a little longer than expected.
Finally, don’t forget that the router needs to be set up again. While many routers will start up with functioning default settings, your input may be needed to complete the setup. This can be especially important if you have DSL or satellite internet that needs you to sign in to get connected.
Check for ISP-specific settings
While it’s not very common with cable, some DSL, fiber, and satellite internet services require the customer to enter login information in their router to confirm the connection. When you’re setting up your router , you’ll typically be asked if you need to sign in to get online. If so, follow the steps to get signed in. If not, check the WAN settings for your router for the option. It’s often labeled as PPPoE in the router settings. Without this information, the ISP won’t be able to link your connection to your account.
If you need to sign in to your ISP from your router, you’ll need to contact customer service for the correct information, or you may have it written down with the rest of the paperwork from when you first set your connection up.
While you’re in your settings, check to see if you’re using IPV6 or IPV4. While most ISPs are moving to support IPV6, it’s possible that your ISP hasn’t implemented the change yet. Some regional ISPs with fewer customers, for example, may not have prioritized the switch.
I don’t like calling my ISP any more than the next person, but sometimes when it comes to internet connection issues, that’s your best path forward. Your ISP will be able to see if you’re equipment is showing up on their end and can help you find where exactly your issue is coming from. And, unlike a lot of troubleshooting tests, you don’t need a PC or internet connection to call support.
Check the logs
If you're heading to the forums for more specific help, you may be asked for your logs. Routers keep a record of errors they encounter, which would surely include failed attempts to connect to the internet. Log in to your router and navigate to the system settings to find your logs. You can save them to your PC or just give them a read to see if anything jumps out as being wrong.

How-To Geek
Internet problems here's how to tell if it's your isp's fault.
Do your own investigation to find out if it's really your fault.
Quick Links
If it's not you, it's them, ruling out user-side problems, diagnose your cable signal quality, prepare your list of findings and demand a line inspection.
No one likes internet downtime. It can make you feel completely crippled in your ability to work or communicate, control your home, or monitor your security system. But in those situations, how do you tell who's to blame?
As remote work and smart home setups become more prevalent, our tolerance for connection failure is shrinking fast. Connection loss is a common intermittent occurrence, but what do you do when the problem becomes incessant and unmanageable? If your issues become persistent, it is possible that the root of the problem has nothing to do with your equipment or settings, but rather is due to a problem on the side of your Internet Service Provider (ISP) and may require a special line technician to intervene.
That may be easier said than done.
Home technician appointments almost never occur on the day you call in a complaint. In fact, chances are that appointments are booked as far as a month out, and getting a line technician to make an appearance is particularly tricky. Line technicians are different than the home technicians that typically answer house calls. Line techs address problems stemming from the main connection to the cable line outside your home.
In cities, these main connections, or "drops" usually terminate near high voltage power lines and transformers, not to mention the seemingly endless intersecting tangles of cables, lines, and wires. The height, danger, and complexity of line servicing mean that line techs require special licensure and are very costly. Your ISP won't be too keen on sending out the big guns for any old internet problem.
Related: How to Make Your Phone Useful When There's No Internet
Before you start down the path of pursuing a line repair, it is important you take a calculated approach to ensure that the problem is, in fact, a problem that needs addressing by your provider and not something on your end. ISP customer support agents and home technicians will try and say most anything to avoid taking on the blame if you aren't prepared with an exhaustive list of user-side troubleshooting steps you have already checked. We will start from square one.
You may have tried several, or all these already, but the checklist below will make sure you've examined your issues from all angles before tackling the task of getting a line tech to come out. Document your findings as you progress through this list.
Check Connectivity on Another Device
If you're experiencing a connection problem, try connecting and testing your connection on another device of the same kind. To get fine-tuned results, use SpeedTest.net to get a gauge of your download and upload speeds.
Try Power Cycling the Problem Device
You will be able to quickly tell if the whole network is down, but if the issue is isolated to one device, shut it down completely, unplug it from power, and remove any batteries if possible. Wait at least 30 seconds and power the device back on. If the issue persists, move on to the next step.
Power Cycle Your Router
Unplug the router from power, wait at least 30 seconds, and power it back on. If that doesn't fix the issue, move to the next step.
If you have any local file sharing or network storage devices, you should still be able to use them normally even if there is no internet connection to the outside world. If these protocols work fine, it further points to an issue with cabling, modem, or main line connection.
Power Cycle Your Modem
Follow the same routine as power cycling the router. Unplug for 30 seconds and power back on.
If you rent your equipment from your ISP, your modem and router are likely combined into one device.
Check the Modem Lights
Your modem will likely have at least four lights on the front that flash during the powering-on process. These lights indicate the status of four important parameters: Power, Downlink, Uplink, and Internet connection. They indicate success by lighting solid. If one of these lights doesn't light solid and remains blinking, it may indicate to you the source of your incoming signal.
- Power: Indicates that the modem is connected to power and turned on.
- Downlink: This light is typically symbolized as an arrow pointing downward and indicates that the modem has established a connection to a downstream channel . This channel(s) brings data from the internet into your home/business.
- Uplink: This light is typically an upward pointing arrow and indicates attempted/successful connection to an upstream channel . This carries data from your home/business out to the web.
- Internet: This light is typically stylized as a globe and indicates that the internet is available. This light will not go solid if there is a failure of any of the previous three light confirmation.
If the previous steps yielded no improvement, you can assess its cable connection quality via the modem's graphic user interface (GUI). This interface is accessed using a normal web browser. It is here where you can find information about signal quality and power levels.
If you have a device with an ethernet port, use that to connect directly into one of the available ports on your modem. If you don't have an ethernet-capable device, try using your WiFi connection. The following instructions are for a standalone modem. If you are using a router/modem combo rented from your ISP, you may be redirected to a web page prompting you to input your account login info.
Depending on your network configuration, accessing the modem GUI via WiFi may not be possible. Contact your ISP for more information.
Now open any web browser. Type your modem's IP address into the address bar. This address varies between manufacturers, but the most common addresses are
. Once you've entered the correct IP, you will be greeted with a web page displaying the logo of your modem's manufacturer. Use the page to navigate to the status page. Once there, you can analyze your power levels.
Ideal power levels can vary based on your router's DOCSIS specifications. However, the modem used for this example is the Arris Surfboard 8200 . It is one of the most popular modems in the world, and its firmware is used in the majority of ISP-leased modem/router combos. So, chances are that these target values apply to you
- Downstream power levels should be between -7 to +7 dBmV.
- Upstream power levels should be between 38-48 dBmV.
Interpreting Your Level Readings
Any power levels outside of the above ranges should be noted, particularly excessive upstream power values. Contrary to what instinct might tell you, high upstream power values indicate low power levels. Once your upstream power value increases past 48 dBmV, it means that your modem is having to work harder to output adequate upstream power. Once this value reaches 53 dBmV, the modem will automatically power cycle and retry the connection. This often results in a boot loop that leaves the modem unable to connect for hours or even days.
This is the most common cause of repeated modem connection failure due to power issues.
To learn more, check out how to read modem diagnostics.
Whether or not your power level investigation yielded any significant findings, you will still want to assess your environment to look for any last-ditch fixes. First, check for outages. Visit your ISP's Twitter and check for any posts concerning service interruptions or system maintenance.
If that turns up nothing, sites like Downdetector can provide more info. These sites are online communities where service users can report disruptions. If your issues pertain to a larger local outage, you may just need to wait it out. If there is not a larger outage, continue by checking your modem and cabling environment.
Rule Out Overheating Issues
Your modem should be stationed in a cool, dry place with access to open air. Like any electronic device, your modem can be prone to overheating if placed on carpet or in small, enclosed spaces. Ensure that your modem is not placed directly in the sun.
Environmental Signal Interference
Your modem and the cable that provides your broadband should be positioned a safe distance from any possible sources of radio interference. This includes microwaves, air conditioners, refrigerators, and other large appliances. Take note if your connection seems to be affected when using a certain appliance.
Inspect Your Cable Run
Lastly, you will want to trace and inspect the placement and physical quality of the cable line itself. This may not be possible if your cabling is hidden in your walls. However, if your cable runs along the outside of your building as mine does, trace back along its entire length as far as you safely can.
Keep a sharp eye out for things that may indicate a damaged cable. Physical deformities like cracked insulation, chew marks from animals, or sharp bends may be the source of your internet problems. In this case, you would likely need a new cable run.
Connection points should be dry and free of corrosion. Along with physical deformities, keep an eye out for any unnecessary splitters along your cable run. Splitters are small metal devices used to create two cable outputs from one input. They are commonly used to provide cable TV to multiple televisions in the home. Their usefulness is fading as the world moves toward more internet-based entertainment access.
While splitters are fine for multiplying incoming television signal, they can produce unstable broadband signal. Remove any splitters from your cable run if possible. To do this, simply unscrew the connectors just like you would on a modem or cable television. You will be left with two male coaxial connectors. To bridge them together, be prepared with a coaxial coupler .
With this checklist at the ready, you are equipped with some knowledge and terminology to force your ISP to take further action in rectifying your connectivity issues and compensating you for prior downtime. This can be a lengthy and trying effort. Be persistent, and good luck!
[Fix] iPhone 15 Pro Max Wi-Fi and Cellular Data Not Working
The iPhone 15 Pro Max boasts lightning-fast internet speeds as it has 5G cellular connectivity and Wi-Fi 6 compatibility. For the most part, these features work fine. However, a surprising number of users have recently been complaining about their Wi-Fi and cellular data not working properly. Their connection keeps dropping.
These problems are unacceptable on new devices. But before you call Apple for repairs, I suggest going through these solutions—they could save you a trip to the Apple Store.
How To Fix Wi-Fi and Cellular Data Not Working on iPhone 15 Pro Max
1. enable and disable airplane mode.
Time needed: 3 minutes
Turn Airplane Mode on and off again. It resets your iPhone’s network connection, clearing up minor glitches and bugs.
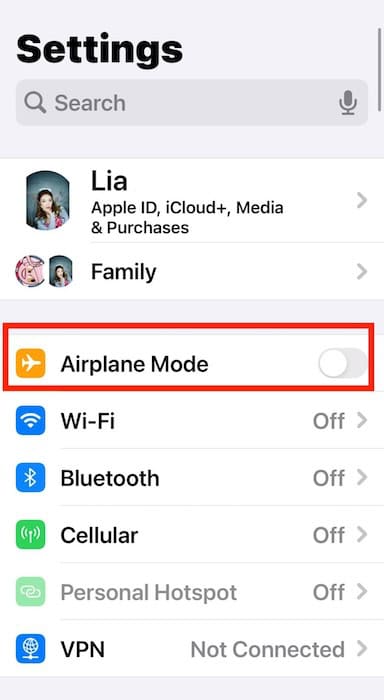
2. Restart Your Router
Don’t underestimate the power of restarting your router. It’s a quick, simple way to resolve a lot of network issues. Just unplug it from the power source, wait two minutes, and then plug it back into the outlet.
3. Test Your Wi-Fi and Cellular Data on Another Device
Try using your Wi-Fi and cellular data on another device. If either network runs properly, it’s safe to assume that the issue is with your iPhone.
For cellular data, I suggest turning on your Personal Hotspot.
- Go to Settings > Cellular and toggle Cellular Data .
4. Update Your iPhone to the Latest iOS
These network issues may stem from software update bugs, in which case you can install the latest stable iOS update . If it isn’t out yet, you can opt for Public Beta versions .
- Open Settings > General > Software Update .
5. Reset Network Settings
Try resetting your network settings to their factory defaults. It removes network-related data involving your mobile carrier, Wi-Fi preferences, and Bluetooth. Unfortunately, you’ll have to configure them manually afterward, which is honestly quite a hassle, so save this step for last.
- Open Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone .

Call your carrier and ISP should network issues persist. Only reach out to Apple Support if both Wi-Fi and cellular data are not working on your iPhone 15 Pro Max. Likewise, now’s a good time to troubleshoot your other Apple devices. You can also reset your network settings if your Mac isn’t connecting to the internet .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Jose Luansing Jr.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Size up the Wi-Fi problem. The first step to solving Wi-Fi issues is to see if the slowdown is coming from your cable modem (which brings internet service into the home) or from the router (which ...
Whatever the problem -- from a flaky connection to Wi-Fi troubles or even no access to the Internet at all -- some router troubleshooting could fix things. Quick Links. Reboot the Router. Check for Overheating. Verify Cables Are Securely Connected. Reposition the Router. Change the Wireless Channel. Reset Your Router to Factory Default Settings.
Here's the process: Unplug or power off your router. Wait five more minutes and retry the connection. In most cases, this should fix your issue and allow you to get back online. If you go through these steps and something still isn't working, you may need to contact your internet service provider for assistance.
Loose or damaged cables can cause a wide range of internet issues. Sometimes the fix is as simple as tightening a connection, other times you may need to replace a cable or require the help of a broadband technician. See instructions. 3. Move your router to a better spot If you're using the internet over Wi-Fi, router placement is crucial.
Try turning off the Wi-Fi on your device, then re-enabling it — or unplugging and replugging your Wi-Fi dongle. If that doesn't work, restart the device and try again. Then try restarting the ...
Cause of Wi-Fi Router Issues . Quite a few things can cause issues with your Wi-Fi router. The most common scenario is a wireless channel overcrowded by too many devices using too much bandwidth. The least likely scenario is a hardware failure with the router itself. There are also issues like malware on your device, a hacked router, and more.
To get to your router's settings, you'll need to know the router's IP address. This is usually 192.168.1.1, 192.168..1, 192.168.1.254 or similar (check out the cheatsheet here) and needs to be entered into your browser. Here's how to find your router's IP address on any platform.
And clear your browser's cache and cookies. 2. Check the Wi-Fi Settings. (Credit: PCMag / Apple) Check the Wi-Fi settings on your device and make sure you are connected to the proper SSID. If not ...
Step 1: In the Windows search bar, type "device manager," and press enter. Step 2: Click "Network adapters" in the list of the devices. Step 3: In the expanded dropdown menu, right-click your network adapter and select "Update Driver Software.".
The Fix. Many times, restoring your internet connection back is as simple as unplugging your router or modem and plugging it back in. Here's how: Unplug your router and modem from the power source. Wait for one minute. Plug your modem back in and wait 30 seconds. Plug your router back in. Wait five minutes and retry the connection.
Enter your zip code below to check out other internet providers in your area. 1. Unplug your router and modem. First, unplug your router and modem from the power outlet in the wall. Next, unplug any connections between your modem and wireless router. Oh, also—look for power buttons on your router and modem.
Step 1: Unplug the power cable from the back of the router or gateway. Step 2: Wait 60 seconds. This cooldown allows all the power to completely drain from the device and ensures a full restart. Step 3: Reconnect the power cable to the back of the router or gateway. Step 4: Wait while the device reboots.
When troubleshooting a router, first check the cords running into the back of the device. If one of the cords isn't plugged in or came halfway undone from its port, the solution to your internet woes might be as simple as pushing it back in. If it seems like one of your cables is consistently coming loose, consider buying a new one.
Restart your modem and router. The easiest way to do this is by unplugging both your modem and your router from their respective power sources, waiting for a few seconds, and plugging them back in. Like restarting your computer, this can solve the bulk of minor Internet issues. 6. Perform a soft reset on your network.
Try Restarting the Problem Device. Ensure That Network Hardware Is Working. Reboot Your Router. Check the Connection Status on Your Router/Modem. Try Another Device to Isolate the Issue. Finally: Contact Your Service Provider. It's useful to have a checklist of things to try when your internet is not working.
1. Move a connected device closer to your wireless router, and/or remove any obstructions or obstacles between the wireless router and the device. If this speeds the Internet connection on your testing device, you have a WiFi signal fidelity issue. Leave the wireless router as unobstructed as possible.
Ultimately, most connection problems you'll run into are probably someone else's problem -- you can't necessarily solve them yourself. Often, the only thing you can do is wait for your Internet service provider or a specific website to fix the problem you're experiencing. (However, restarting a flaky router can solve lots of problems.)
Causes of Modem Not Connecting to Internet. There could be several reasons why you can't connect to the internet, but here are some common issues relating to the modem: Loose power or coax connections. Damaged Ethernet cable connections. Miscommunication with the router. Overheating.
Fix: To fix this, just get a little closer. If the router is located in a different room, try going into the room where the router is located and see if that fixes the issue. If this is a ...
https://broadbandnow.comIs your WiFi not working? Has it slowed down, or has the network disappeared entirely? Having trouble connecting your devices to WiFi...
Step 1: Right-click the Wi-Fi icon in the lower-right corner of the screen. Step 2: Click "Troubleshoot problems.". Step 3: Select "All network adapters" and click Next. Step 4: Wait while the troubleshooter searches for the problem.
Right click the network icon in the right side of the taskbar and select Diagnose network problems or open Get Help for Network & Internet. Make sure Wi‑Fi is turned on. Select the No internet icon on the right side of the taskbar, and make sure Wi-Fi is turned on. If it isn't, select it to turn it on. Also, make sure Airplane mode is turned off.
First, run it with your laptop plugged into your router to check your speed in the best-case scenario. You can then move around with your laptop to different areas of your home to see how fast ...
How you can speed up your broadband. Before you do raise any issues with your broadband provider, there are some things you can do that might help speed up your broadband. Restart your router and ...
Routers keep a record of errors they encounter, which would surely include failed attempts to connect to the internet. Log in to your router. and navigate to the system settings to find your logs ...
Now open any web browser. Type your modem's IP address into the address bar. This address varies between manufacturers, but the most common addresses are. 192 .168.100.1. and. 192 .168.0.1. Once you've entered the correct IP, you will be greeted with a web page displaying the logo of your modem's manufacturer.
How To Fix Wi-Fi and Cellular Data Not Working on iPhone 15 Pro Max. 1. Enable and Disable Airplane Mode. Turn Airplane Mode on and off again. It resets your iPhone's network connection ...