How to Write a Business Report: A Step By Step Guide with Examples


Table of contents

Enjoy reading this blog post written by our experts or partners.
If you want to see what Databox can do for you, click here .
With so much experience under your belt, you already know a lot about business reporting.
So, we don’t want to waste your time pointing out the obvious because we know what you need.
Secrets. Tricks. Best practices.sales rep drilldown business report
The answer to how to write a mind-blowing business report that you don’t need to spend hours and days writing.
A business report that will immediately allow you to identify your strengths and weaknesses.
A report that’ll help you learn more about your business and do more accurate forecasting and planning for the future.
We believe we have just that right here.
With this comprehensive guide, you’ll create effective sales, analytical, and informative business reports (and business dashboards ) that will help you improve your strategies, achieve your goals, and grow your business.
So, let’s dive in.
What Is a Business Report?
Importance of creating business reports, types of business reports, what should be included in a business report, how to write a business report: an 11-step guide.
- Business Report Examples
Although there’s a variety of business reports that differ in many aspects, in short, a business report definition would be the following:
A business report is an informative document that contains important data such as facts, analyses, research findings, and statistics about a business with the goal to make this information accessible to people within a company.
Their main purpose is to facilitate the decision-making process related to the future of the business, as well as to maintain effective communication between people who create the reports and those they report to.
A good business report is concise and well-organized, looks professional, and displays the relevant data you can act on. The point is to reflect upon what you’ve achieved so far (typically, over the past month, quarter or year) and to use the data to create a new strategy or adjust the current one to reach even more business goals.
Business reports should be objective and based on the data. When stating the facts, people rely on numbers rather than giving descriptions. For instance, instead of saying “our conversion rate skyrocketed”, you would display the exact percentages that back up that claim.
Business reporting matters for several reasons, among which the most important ones are:
Recognizing Opportunities to Grow
Detecting issues and solving them quickly, evaluating a potential partner, having a paper trail, keeping things transparent for the stakeholders, setting new company goals.
In fact, over half of the companies that contributed to Databox’s state of business reporting research confirmed that regular monitoring and reporting brought them significant concrete benefits.
If you never look back at what you’ve achieved, you can’t figure out what you’ve done well and what you can leverage in the future for even better results.
When you analyze a specific aspect of your business over a specific time period and present the data you gathered in a report, you can detect an opportunity to grow more easily because you have all the information in one place and organized neatly.
Is it time to introduce new products or services? Is there a way to enhance your marketing strategy? Prepare a report. Can you optimize your finances? Write a financial business report . Whatever decision you need to make, it’s easier when you base it on a report.
Reports are essential for crisis management because they can introduce a sense of calmness into your team. Putting everything on paper makes it easier to encompass all the relevant information and when you know all the facts, you can make a more accurate and effective decision about what to do next.
Writing business reports regularly will also help you identify potential issues or risks and act timely to prevent damage and stop it from escalating. That’s why monthly reporting is better than doing it only once a year.
Having an insight into your finances , operations and other business aspects more regularly allows you to have better control over them and mitigate potential risks more effectively.
Different types of business reports may be accessible to the general public. And if they’re not, specific situations may require a company to send them over to the person requesting them. That may happen if you’re considering a partnership with another company. Before making the final decision, you should learn about their financial health as every partnership poses a certain risk for your finances and/or reputation. Will this decision be profitable?
Having an insight into a company’s business report helps you establish vital business relationships. And it goes the other way around – any potential partner can request that you pull a business report for them to see, so writing business reports can help you prove you’re a suitable business partner.
In business, and especially in large companies, it’s easy to misplace information when it’s communicated verbally. Having a written report about any aspect of your business doesn’t only prevent you from losing important data, but it also helps you keep records so you can return to them at any given moment and use them in the future.
That’s why it’s always good to have a paper trail of anything important you want to share with colleagues, managers, clients, or investors. Nowadays, of course, it doesn’t have to literally be a paper trail, since we keep the data in electronic form.
Writing business reports helps you keep things transparent for the stakeholders, which is the foundation of efficient communication between these two sides.
You typically need to report to different people – sometimes they’re your managers, sometimes they’re a client. But your company’s stakeholders will also require an insight into the performance of your business, and relying on reports will help you maintain favorable business relationships. A business report shows you clearly how your company is performing and there isn’t room for manipulation.
Once you set business goals and the KPIs that help you track your progress towards them, you should remember they’re not set in stone. From time to time, you’ll need to revisit your goals and critical metrics and determine whether they’re still relevant.
When you write a business report and go through it with your team members or managers, you have a chance to do just that and determine if you’re efficient in reaching your goals. Sometimes, new insights will come up while writing these reports and help you identify new objectives that may have emerged.
Depending on your goals and needs, you’ll be writing different types of business reports. Here are five basic types of business reports .
Informational Report
Analytical report, research report, explanatory report, progress report.
Informational reports provide you with strictly objective data without getting into the details, such as explaining why something happened or what the result may be – just pure facts.
An example of this type of business report is a statement where you describe a department within your company: the report contains the list of people working in this department, what their titles are, and what they’re responsible for.
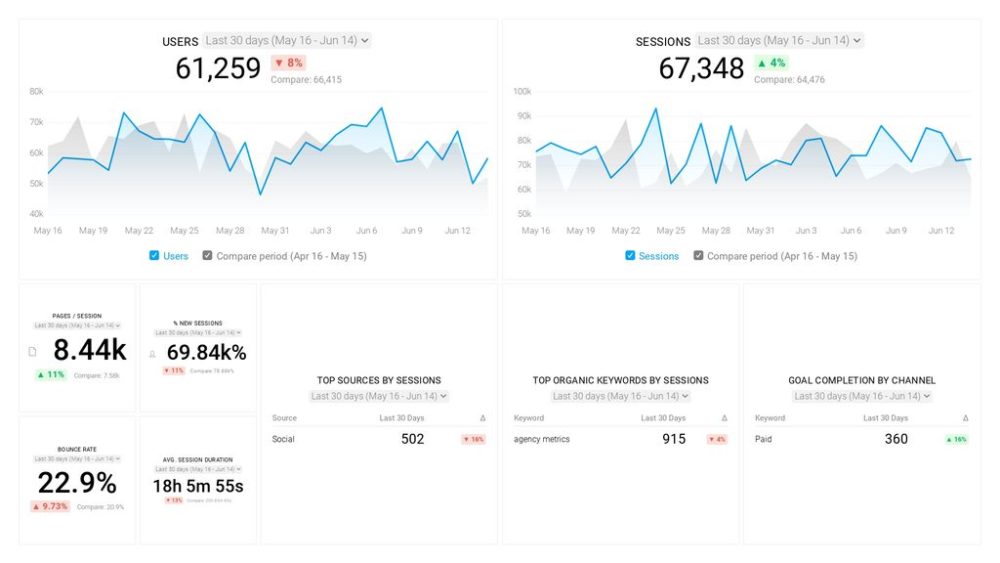
Another example related to a company’s website could look like this Google Analytics website traffic engagement report . As we explained above, this report shows objective data without getting too much into the details, so in this case, just the most important website engagement metrics such as average session duration, bounce rate, sessions, sessions by channel, and so on. Overall, you can use this report to monitor your website traffic, see which keywords are most successful, or how many returning users you have, but without further, in-depth analysis.
Analytical reports help you understand the data you’ve collected and plan for the future based on these insights. You can’t make business decisions based on facts only, so analytical reports are crucial for the decision-making process.
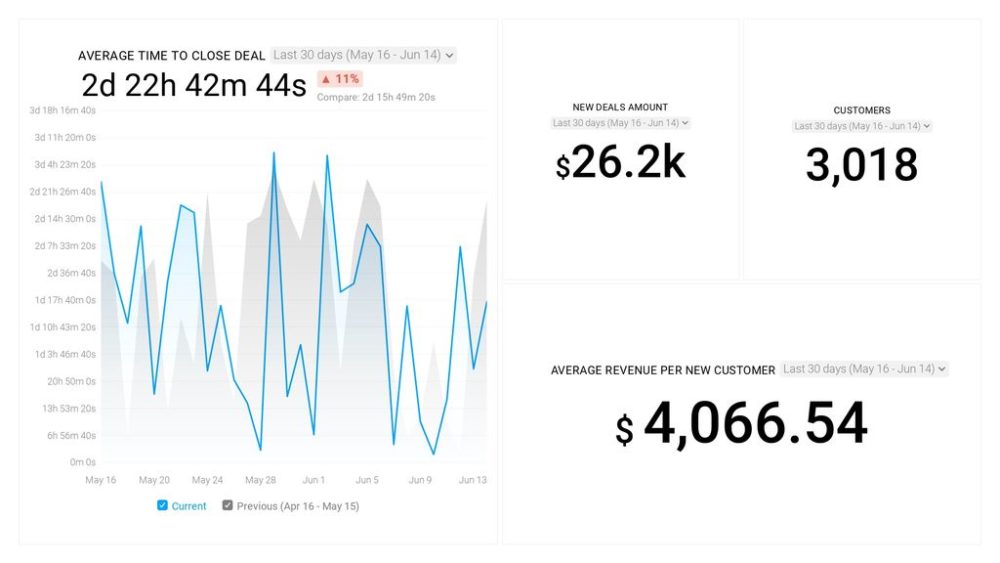
This type of business report is commonly used for sales forecasting. For instance, if you write a report where you identify a drop or an increase in sales, you’ll want to find out why it happened. This HubSpot’s sales analytics report is a good example of what metrics should be included in such a report, like average revenue per new client or average time to close the deal. You can find more web analytics dashboard examples here.
From these business reports, you can find out if you will reach your goals by implementing your current strategy or if you need to make adjustments.
Research is critical when you’re about to introduce a change to your business. Whether it’s a new strategy or a new partner, you need an extensive report to have an overview of all important details. These reports usually analyze new target markets and competition, and contain a lot of statistical data.
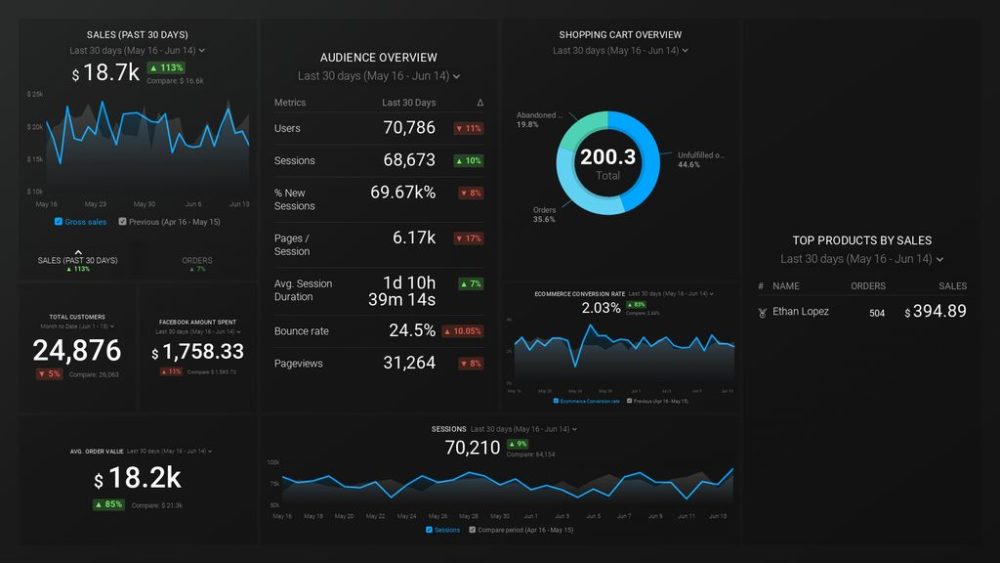
While not the same, here is an example of an ecommerce dashboard that could help track each part of a campaign in detail, no matter whether you are launching a new product, testing a new strategy, and similar. Similar to a research report, it contains key data on your audience (target market), shows your top-selling products, conversion rate and more. If you are an online store owner who is using paid ads, you can rely on this report to monitor key online sales stats in line with Facebook Ads and Google Analytics. See more ecommerce dashboards here.
As you might guess from its name, you write the explanatory report when it’s necessary for you to explain a specific situation or a project you’ve done to your team members. It’s important to write this report in a way that everyone will be able to understand.
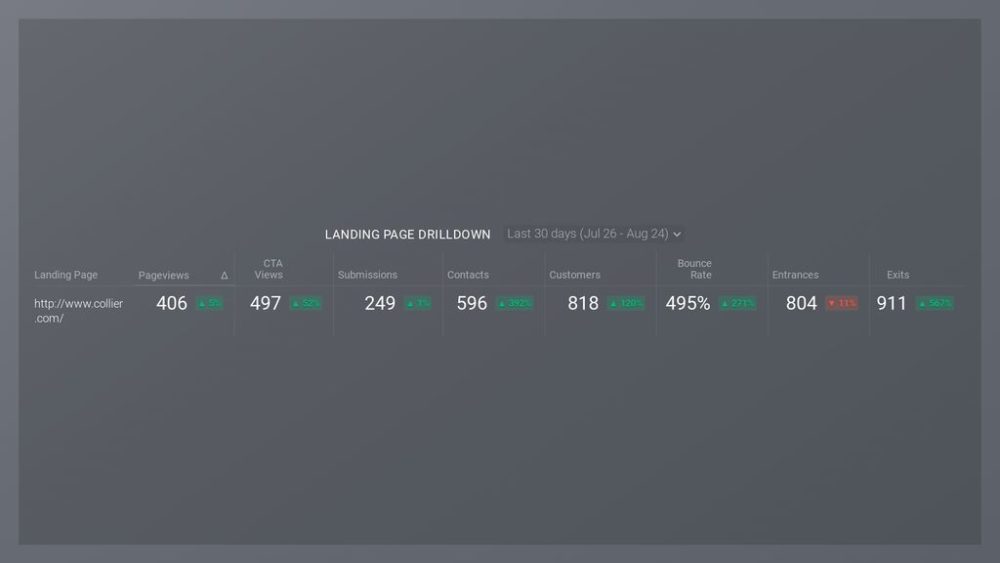
Explanatory reports include elements like research results, reasons and goals of the research, facts, methodology, and more. While not exactly an explanatory report, this example of a HubSpot marketing drilldown report is the closest thing to it, as it helps marketers drill into an individual landing page performance, and identify how good their best landing pages are at converting, or which ones have the best performance.
A progress report is actually an update for your manager or client – it informs them about where you stand at the moment and how things are going. It’s like a checkpoint on your way towards your goal.
These reports may be the least demanding to write since you don’t need to do comprehensive research before submitting them. You just need to sum up your progress up to the point when the report was requested. This business report may include your current results, the strategy you’re implementing, the obstacles you’ve come across, etc. If this is a marketing progress report you can use marketing report templates to provide a more comprehensive overview.
In many companies, progress reports are done on a weekly or even daily basis. Here is an example of a daily sales report from Databox. HubSpot users can rely on this sales rep drilldown business report to see how individual each sales rep is performing and measure performance against goals. Browse through all our KPI dashboards here.
What does a great business report look like? If you’re not sure what sections your report should have, you’ll learn what to include in the following lines.
Business Report Formatting
Different types of reports require different lengths and structures, so your business report format may depend on what elements your report needs to have. For example, progress reports are typically pretty simple, while analytical or explanatory reports are a different story.
However, most reports will start with a title and a table of contents, so the person reading the report knows what to expect. Then, add a summary and move on to the introduction. After you’ve written the body and the conclusion, don’t forget to include suggestions based on your findings that will help your team create an actionable plan as you move forward.
After that, list the references you used while creating the report, and attach any additional documents or images that can help the person reading the report understand it better.
This outline may vary depending on what kind of report you’re writing. Short business reports may not need a table of contents, and informative reports won’t contain any analyses. Also, less formal reports don’t need to follow a strict structure in every situation.
Business Report Contents
When it comes to the contents of your report, keep in mind the person who’s going to read it and try to balance between including all the relevant information, but not overwhelming the reader with too many details.
- The introduction to the report should state the reason why you’re writing it, and what its main goal is. Also, mention what methodology and reporting software you’ve used, if applicable.
- The body of the report is where you’ll expose all your key findings, explain your methodology, share the important data and statistics, and present your results and conclusion.
- The conclusion , similarly to the summary you’ll add at the beginning of the report, briefly singles out the most important points and findings of the report.
If you decide to include more sections like recommendations, this is where you’ll suggest the next steps your team or the company may want to take to improve the results or take advantage of them if they’re favorable.
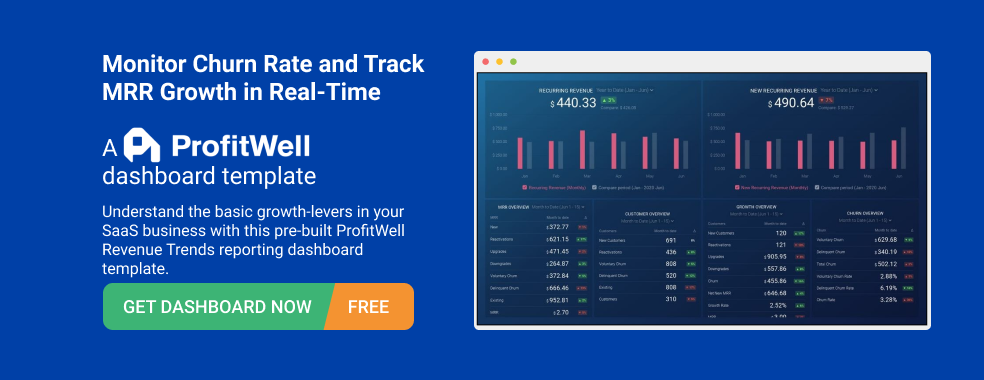
PRO TIP: Are You Tracking the Right Metrics for Your SaaS Company?
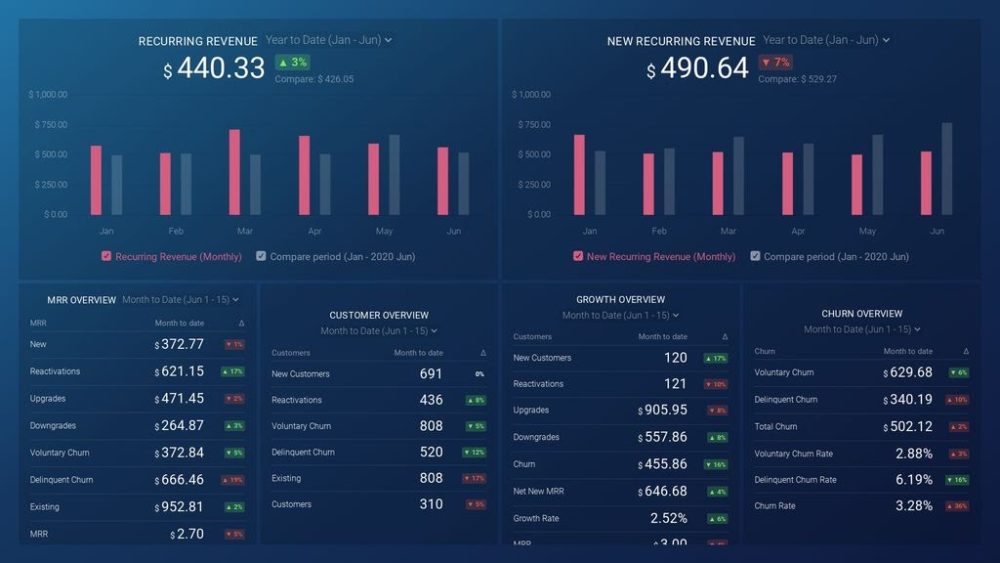
As a SaaS business leader, there’s no shortage of metrics you could be monitoring, but the real question is, which metrics should you be paying most attention to? To monitor the health of your SaaS business, you want to identify any obstacles to growth and determine which elements of your growth strategy require improvements. To do that, you can track the following key metrics in a convenient dashboard with data from Profitwell:
- Recurring Revenue. See the portion of your company’s revenue that is expected to grow month-over-month.
- MRR overview. View the different contributions to and losses from MRR from different kinds of customer engagements.
- Customer overview . View the total number of clients your company has at any given point in time and the gains and losses from different customer transactions.
- Growth Overview . Summarize all of the different kinds of customer transactions and their impact on revenue growth.
- Churn overview. Measure the number and percentage of customers or subscribers you lost during a given time period.
If you want to track these in ProfitWell, you can do it easily by building a plug-and-play dashboard that takes your customer data from ProfitWell and automatically visualizes the right metrics to allow you to monitor your SaaS revenue performance at a glance.
You can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set up the dashboard, follow these 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your Profitwell account with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.
Note : Other than text, make sure you include images, graphs, charts, and tables. These elements will make your report more readable and illustrate your points.
Whether you’re writing a specific type of business report for the first time or you simply want to improve the quality of your reports, make sure you follow this comprehensive guide to writing an effective business report.
- Do Your Research
- Create an Outline
- Determine Formatting Guidelines
- Think of an Engaging Title
- Write the Introduction
- Divide the Body of the Report into Sections
- Choose Illustrations
- Conclude Effectively
- Gather Additional Documentation
- Add a Summary
- Proofread Your Work
Step 1: Do Your Research
A well-planned report is a job half done. That means you need to do research before you start writing: you need to know who you’re writing for and how much they know about the topic of your report. You need to explore the best business dashboard software and templates you can use for your report.
Also, if you believe you will need additional resources and documents to add in the appendix, you should do it during this phase of report writing.
Step 2: Create an Outline
Once you’ve gathered the resources, it’s time to plan the report. Before you start writing, create an outline that will help you stick to the right structure. A business report is complex writing in which you can get lost very easily if you don’t have a clear plan.
Moreover, the report shouldn’t be complicated to read, so sticking to a plan will allow you to keep it concise and clear, without straying from the topic.
Step 3: Determine Formatting Guidelines
Most companies have their in-house formatting that every official document has to follow. If you’re not sure if such rules exist in your company, it’s time you checked with your managers.
If there arent’ any guidelines regarding formatting, make sure you set your own rules to make the report look professional. Choose a simple and readable format and make sure it supports all the symbols you may need to use in the report. Set up proper headings, spacing, and all the other elements you may need in Word or Google Docs.
Pro tip: Google Docs may be easier to share with people who are supposed to read your business report.
Step 4: Think of an Engaging Title
Even if you’re writing a formal business report, the title should be clear and engaging. Reports are typically considered dull as they’re a part of official business documentation, but there’s no reason why you can’t make them interesting to read. Your title should suit the report topic and be in different font size so the reader can recognize it’s a title. Underneath the title, you should add the name of the author of the report.
Step 5: Write the Introduction
A good introductory paragraph for a business report should explain to the reader why you’ve written the report. Use the introduction to provide a bit of background on the report’s topic and mention the past results if there’s been a significant improvement since your last report.
Step 6: Divide the Body of the Report into Sections
As this will be the most comprehensive part of your report, make sure you separate the data into logical sections. Your report is supposed to tell a story about your business, and these sections (such as methodology, hypothesis, survey, findings, and more) will help the data look well-organized and easy to read.
Step 7: Choose Illustrations
Of course, each of these sections should be followed with charts, graphs, tables, or other illustrations that help you make a point. Survey results are typically best displayed in pie charts and graphs, and these enable the reader to visualize the data better. From the formatting point of view, breaking the long text sections with illustrations makes the report more readable.
Pro tip: Using centralized dashboard solutions like Databox can bring your reporting game to the next level. Sign up for a forever-free trial now to see how you can use Databox to track and visualize performance easier than ever before .
Step 8: Conclude Effectively
Finish your report with a to-the-point conclusion that will highlight all the main data from the report. Make sure it’s not too long, as it’s supposed to be a summary of the body of the report. In case you don’t want to add a specific section for recommendations, this is where you can include them, along with your assessments.
Step 9: Gather Additional Documentation
If you’ve determined what additional documents, images, surveys, or other attachments you may need for your report, now is the time to collect them. Request access to those you may not be able to get on time, so you have everything you need by the deadline. Copy the documents you can use in the original form, and scan the documents you need in electronic format.
Step 10: Add a Summary
The summary is usually at the top of the report, but it’s actually something you should write after your report is completed. Only then will you know exactly what your most relevant information and findings are, so you can include them in this brief paragraph that summarizes your report’s main points.
The summary should tell the reader about the objective of the report, the methodology used, and even mention some of the key findings and conclusions.
Step 11: Proofread Your Work
It may seem like common sense, but this final step of the process is often overlooked. Proofreading your work is how you make sure your report will look professional because errors can ruin the overall impression the reader will form about your work, no matter how great the report is.
Look for any spelling or grammatical mistakes you can fix, and if you’re not sure about specific expressions or terminology, use Google to double-check it. Make sure your writing is to-the-point and clear, especially if you’re writing for people who may not know the industry so well. Also, double-check the facts and numbers you’ve included in the report before you send it out or start your reporting meeting.
Business Report Examples (with Ready-to-Use Templates)
Here, we’re sharing a few business reporting examples that you can copy, along with ready-to-use and free-to-download templates. If you don’t know where to start and what to include in different types of business reports, these business report examples are a great way to get started or at least get some inspiration to create yours.
Activity Report Example
Annual report example, project status report example, financial report example, sales report example, marketing report example.
Note : Each of the business report templates shared below can be customized to fit your individual needs with our DIY Dashboard Designer . No coding or design skills are necessary.
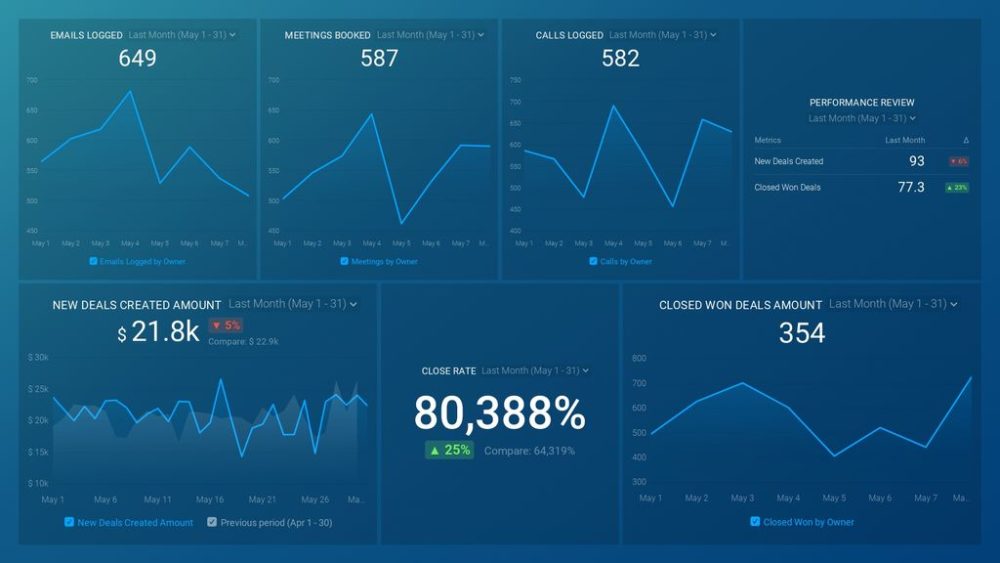
For reporting on sales activity, HubSpot users can rely this streamlined sales activity report that includes key sales metrics, such as calls, meetings, or emails logged by owner. This way, you can easily track the number of calls, meetings, and emails for each sales rep and identify potential leaks in your sales funnel. Check all our sales team activity dashboards here. Or if you are looking for dashboards that track general sales performance, browse through all Databox sales dashboards here.

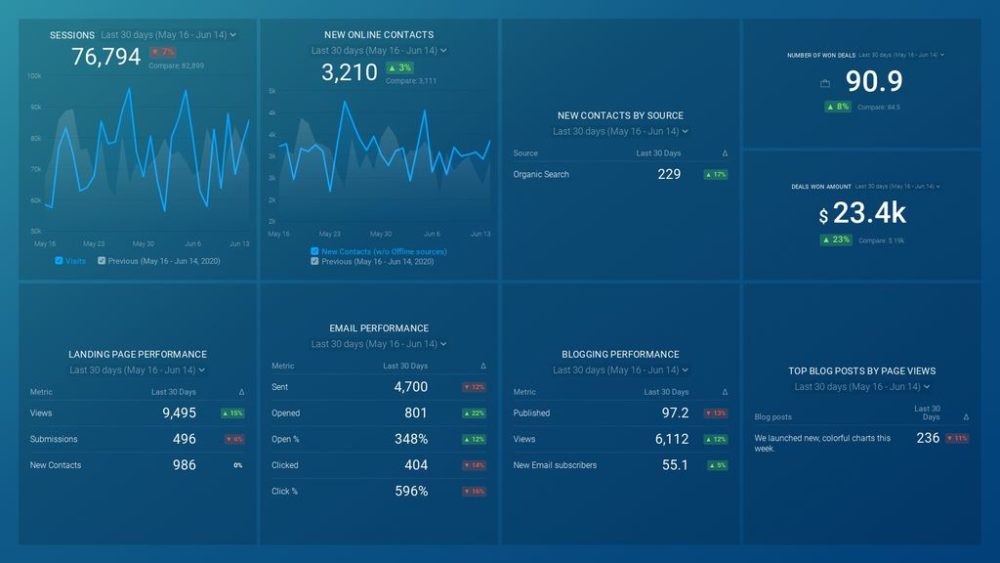
If you’re preparing for annual reporting, you will benefit from choosing this HubSpot annual performance report . It contains all the relevant metrics, such as email and landing page performance, new contacts, top blog posts by page views, and more. See all our performance dashboard templates here.
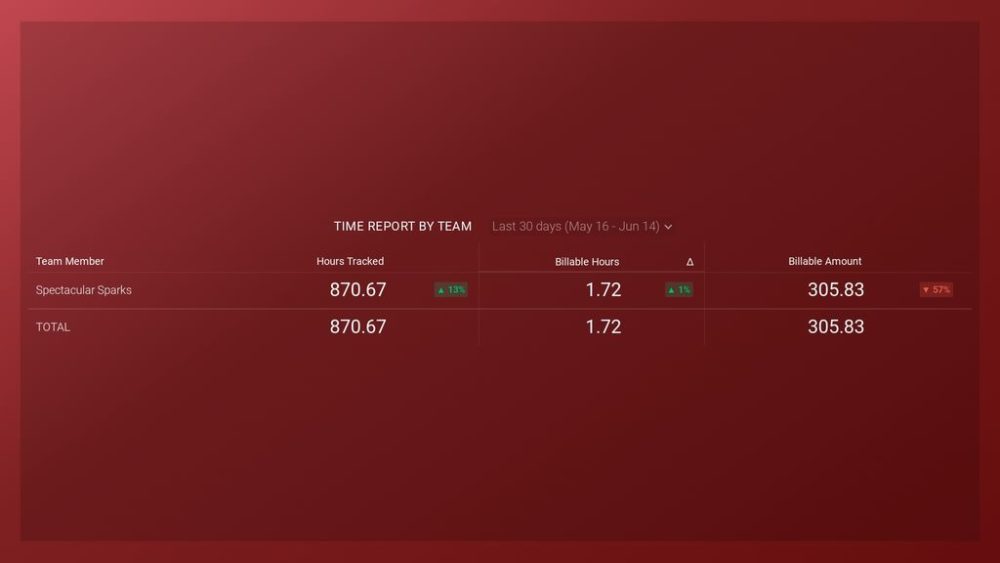
Project status reports can be very similar to progress reports. If you’re in need of one of those, here’s an example of a Project overview dashboard from Harvest that shows that can help you create simple, but well-organized report based on metrics that matter: hours tracked, billable hours, billable amount split by team members., and more. Check out more project management dashboard templates we offer here.
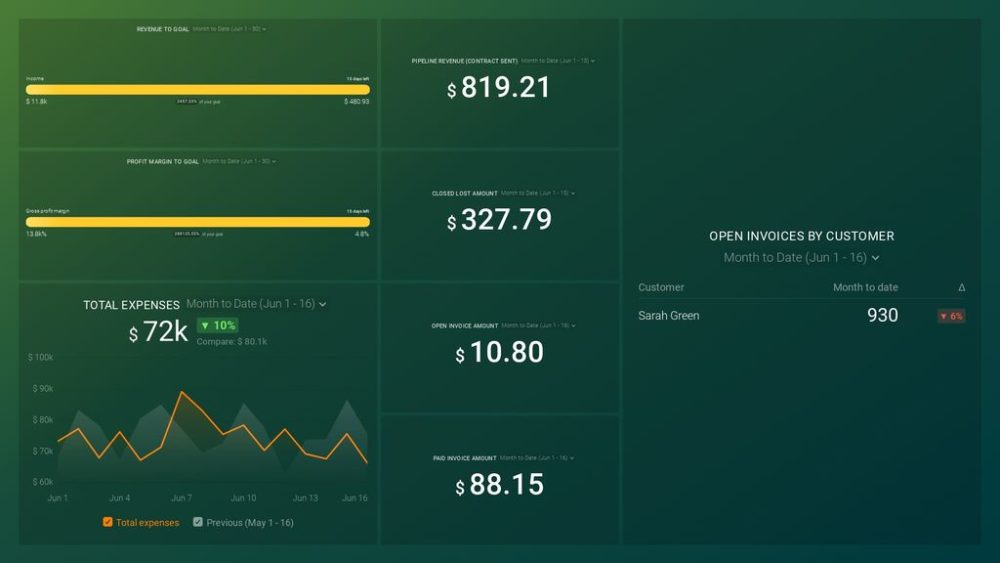
Are you creating a financial report? You will find this QuickBooks + HubSpot integration a great choice for a financial performance dashboard that makes creating a report simple. This dashboard focuses on the essential financial report
ting metrics and answers all your revenue-related questions. See all Databox financial dashboards here.
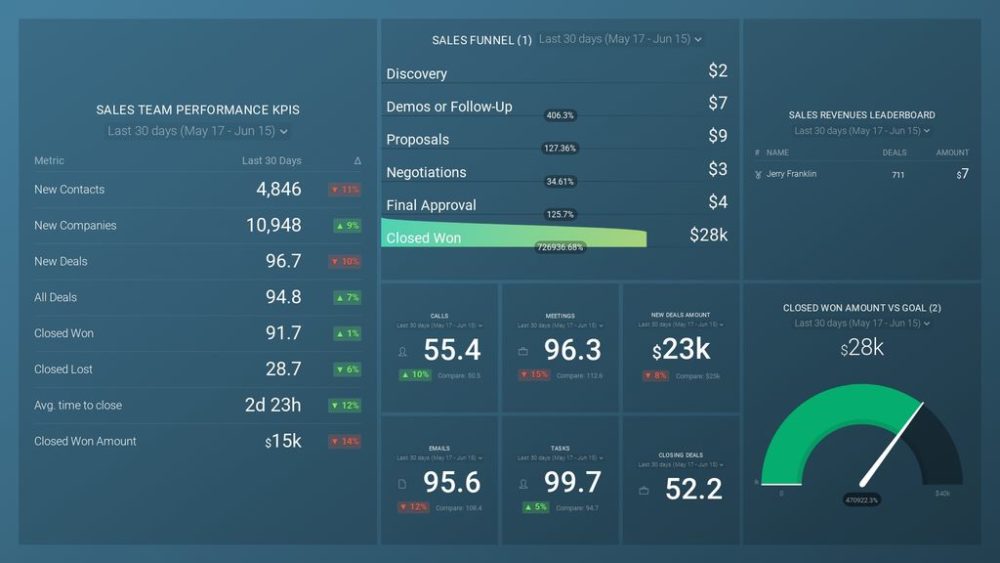
If you’re tracking your sales team’s monthly performance, this sales report template will help you prepare an outstanding report. Check out all the vital productivity KPIs, track your progress towards your goals, and understand well how your current sales pipeline is performing. See all sales performance dashboards we have available here.
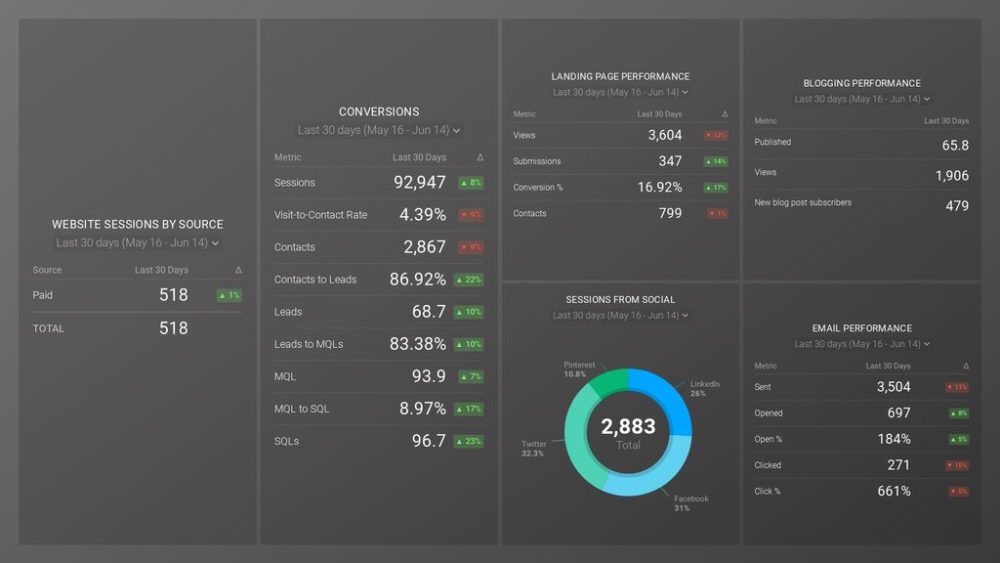
Marketing reports can be easily prepared by using this monthly marketing report template . With HubSpot’s reporting, you can determine where your website traffic is coming from, how your landing pages and specific blog posts are performing, and how successful your email campaigns are. Browse all Databox marketing dashboards or marketing report examples here.
Create a Professional Business Report in No Time with Databox
Does creating a business report still sound like a daunting task? It doesn’t have to be with Databox.
In times when we’re all trying to save our time and energy for things that matter rather than scattering valuable resources on tedious, repetitive tasks, it’s critical to optimize your business process. And we want to help you do just that.
Using a business reporting dashboard enables you to track data from all the different tools you’re using – but in one place. With Databox, you can monitor and report on performance in a single dashboard that is optimized for all your favorite devices and you can create streamlined and beautiful dashboards even if you are not that tech-savvy. (no coding or design skills are required).
Automating business reporting has never been easier. And with Databox, you can do exactly that in just a few clicks. Sign up now and get your first 3 business dashboards for free.
Do you want an All-in-One Analytics Platform?
Hey, we’re Databox. Our mission is to help businesses save time and grow faster. Click here to see our platform in action.
- Databox Benchmarks
- Future Value Calculator
- ROI Calculator
- Return On Ads Calculator
- Percentage Growth Rate Calculator
- Report Automation
- Client Reporting
- What is a KPI?
- Google Sheets KPIs
- Sales Analysis Report
- Shopify Reports
- Data Analysis Report
- Google Sheets Dashboard
- Best Dashboard Examples
- Analysing Data
- Marketing Agency KPIs
- Automate Agency Google Ads Report
- Marketing Research Report
- Social Media Dashboard Examples
- Ecom Dashboard Examples

Does Your Performance Stack Up?
Are you maximizing your business potential? Stop guessing and start comparing with companies like yours.

A Message From Our CEO
At Databox, we’re obsessed with helping companies more easily monitor, analyze, and report their results. Whether it’s the resources we put into building and maintaining integrations with 100+ popular marketing tools, enabling customizability of charts, dashboards, and reports, or building functionality to make analysis, benchmarking, and forecasting easier, we’re constantly trying to find ways to help our customers save time and deliver better results.
Stefana Zarić is a freelance writer & content marketer. Other than writing for SaaS and fintech clients, she educates future writers who want to build a career in marketing. When not working, Stefana loves to read books, play with her kid, travel, and dance.
Get practical strategies that drive consistent growth
12 Tips for Developing a Successful Data Analytics Strategy

What Is Data Reporting and How to Create Data Reports for Your Business
What is kpi reporting kpi report examples, tips, and best practices.
Build your first dashboard in 5 minutes or less
Latest from our blog
- The State of B2B Content Creation: Navigating the Future of In-House Marketing Innovation May 9, 2024
- New in Databox: Analyze the Performance of Any Metric or KPI with Metric Insights April 22, 2024
- Metrics & KPIs
- vs. Tableau
- vs. Looker Studio
- vs. Klipfolio
- vs. Power BI
- vs. Whatagraph
- vs. AgencyAnalytics
- Product & Engineering
- Inside Databox
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Talent Resources
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- API Documentation

How to Write a Formal Business Report (Template and Examples)
Formal business reports are official documents that guide and inform stakeholders. These reports are valuable tools when solving company problems or making decisions.
You should be clear and include all relevant information to make your report useful in decision-making and problem-solving.
Here are five steps for writing a formal business report:
- Define the purpose and intended audience
- Gather and analyze data
- Create an outline
- Draft the business report
- Revise and format your report
Keep reading to get valuable details under every step and learn to segment your report.
But first, let’s delve deep into formal business reports, the different types, and what differentiates them. We’ll also discuss the elements of a business report and cover valuable tips to perfect your writing skills.
Let’s get started!
Understanding formal business reports
Business reports provide an analysis of the current performance of a business and offer recommended actions to improve operations. A formal business report should include detailed data, analysis, conclusions, and recommendations.
What is a formal and informal business report?
A formal business report is a detailed and organized document that provides information about a specific topic, like research findings, market trends, or a financial situation. It usually includes conclusions based on data collected during the research process.
Formal business reports can present complicated topics in an easy-to-understand format, allowing company executives to make informed decisions. A formal report typically includes an introduction, a body of information, and a conclusion. It should consist of accurate data and reliable sources and be written formally with proper grammar and spelling.
An informal business report does not follow traditional, formal reports’ formal structure and layout. Instead, it is written in an easy-to-understand language and typically includes summaries of key points, along with recommendations or suggestions for further action.
Unlike formal reports, informal business reports do not need to be approved by higher management and can be sent directly to the intended recipient. Businesses often use informal reports to quickly provide updates or summaries of projects, data, or other important information. They are also commonly used when sharing ideas, solutions, or findings that don’t necessarily require a formal response from the receiver.
While informal reports may need more depth and detail than formal reports, they can still communicate important information concisely and clearly.
Types of formal business reports
Formal business reports include different types that may be used to present data, analyze performance, or make recommendations. Examples of formal business reports include annual, research, feasibility, and marketing research reports.
Feasibility Reports
A feasibility report is an analytical document that outlines whether an activity or project has the potential to be successful. It includes cost estimates, expected outcomes, and other factors affecting the project’s success.
Business Plans
A business plan is a formal outline of a company’s objectives and strategies for achieving them. It is used to obtain financing, attract investors, and set goals for the company.
Business plans typically include sections on market analysis, organizational structure, competitive analysis, product or service description, financial projections, marketing strategies, and tactics.
Progress Reports
A progress report is a document that details the current status of a project or activity. It outlines the progress made, challenges encountered, and a timeline for when the project should be completed.
Financial Reports
Financial reports provide information about the company’s financial performance over some time. They include income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
A proposal is a document that outlines how an organization, company, or individual intends to complete a project. It usually includes information such as the purpose of the project, expected outcomes, methods, and associated costs. For example, businesses may use proposals to solicit funding from investors or government agencies.
Market Research Reports
A market research report is a document that provides information about customer needs and competitor activities to develop strategies for the organization. They typically include data on consumer preferences, product demand, market trends, and other relevant factors.
Risk Reports
A risk report is a document that details the potential risks associated with a specific activity or investment. It outlines possible losses and considers how they could affect an organization’s operations. Risk reports may also include measures the organization can take to mitigate losses and recommendations for further actions.
Technical Reports
Technical reports are documents that explain the results of a technical project or investigation in detail. They are used to document the findings of a project and provide a record that can be used as reference material.
Technical reports typically include sections on research methods, results, conclusions, recommendations, and implementation plans.
What are the key differences between writing a business report and writing an academic report?
Business reports inform a decision or provide direction in the form of recommendations. They may include factual data and analysis but are often practical and focus on the actionable steps needed to achieve a goal.
Academic reports take a more analytical approach, emphasizing research and thought-provoking discussions that examine different points of view.
Sources used
When writing business reports, only use real-world sources such as government reports. But when writing academic reports, you may cite theoretical works .
Conciseness
When writing business reports, use concise points with stakeholders in mind . As for academic reports, you may use technical terms and lengthy explanations to support a point.
Academic reports are often longer and more detailed than business reports and may also include recommendations but with a focus on developing new strategies or ideas.
When writing a business report, adhere to the following structure: cover page, table of contents, list of figures, executive summary, introduction, body, conclusion, and recommendations.
But when writing an academic report, follow the structure: introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion.
The purpose of both types of reports is to provide information that is useful and relevant to the target audience. So keep the audience in mind when writing a report; what information do they need to know? How will it help them make decisions or understand a concept better?
Elements of a formal business report
An excellent formal business report organizes information into these sections:
- Table of contents
- List of Figures
- Executive summary
- Introduction
- Recommendation
1. Title page
The title page indicates the company name (and logo), the author’s and readers’ names and positions, and the date.
2. Table of contents
The table of contents lists the sections of a report with their page number and helps jump to a specific title.

3. List of Figures
The list mentions every chart or diagram included in the report and its page number for easy navigation.

4. Executive summary
The executive summary briefly overviews the report’s key points, findings, and conclusions. It helps readers to understand the report’s data without reading the entire document. Therefore, this section should be the last to write since the facts in the report will form the executive summary.

5. Introduction
The introduction outlines the research objectives and methods used to generate data for analysis. It sets the stage for what follows. Unlike the executive summary, it does not mention any conclusion or recommendation.

The body contains an in-depth review of the research results and their implications. It may include an analysis of trends, correlations, pictorial evidence, and other data supporting the report’s conclusions.
7. Conclusion
The conclusion summarizes the data discussed in the body . It is a brief sentence that takes around three to six sentences.
8. Recommendation
The recommendation suggests an action based on the facts presented in the report. It outlines steps or policy changes necessary to solve a problem.
9. Appendix
The appendix contains information that supports your report but would be distracting if you included it in the body. This information may consist of raw data, charts, transcripts, and surveys used for analysis or any additional resources used in the research process. You may also include acronyms used in the report.

10. References/Bibliography
This section consists of all references you used in your report. Citations protect you from plagiarism and give credit to your sources. You can write citations in APA, MLA, and Chicago styles , depending on the style of your formal report.
11. Glossary
The glossary is where you define all technical terms used in the report. Use an asterisk next to words you will describe in the glossary to indicate that the reader should check the glossary for a definition.

How to write a formal business report step-by-step
When writing a formal business report, start by defining the purpose of the report and the intended audience. You then gather data and analyze it before writing the report. Finally, write the report and revise it accordingly.
1. Define the purpose and intended audience
Why are you writing the report? Consider what information you need to include and who will read the report. This will help you structure your document correctly and provide relevant information.
Defining your target audience will help you tailor the language used and choose relevant information to include in the report.
2. Gather and analyze the data
Collect all data relevant to achieving the goal of your report. This should include quantitative and qualitative data, such as customer satisfaction surveys, case studies, performance metrics, or feedback from stakeholders.
Once you have collected all of your data, analyze it and identify any trends or patterns that may be useful in writing the report. You can use various tools and techniques like statistical analysis , gap analysis , or cause-and-effect diagrams .
3. Create an outline
An outline will help you organize your research data, stay on topic, and avoid including unrelated information under a particular title. Besides having a section of each formal business report element above, outline your key points, headings, and subheadings.
Use self-explanatory headings, for example, “ Impact of expanding market share. ”
3. Draft the report
Organize the data you collected during research into the draft report. Start by introducing the topic, providing background information, and the report’s objectives. Then include each of the main points you want to discuss, supported by evidence from the research data.
Have the relevant elements mentioned above and write adequate information under each section. The draft does not have to be perfect; you just need to organize the data roughly.
4. Revise and format your report
After completing your draft, proofread and edit it to remove irrelevant data or add forgotten information. Make sure everything looks good, including the formatting. It also helps to share the business report with someone who can review it and propose necessary changes. Once everything is settled, share the report with your intended audience.
Tips for writing a formal business report
When writing a formal report, use data and evidence to support your argument, add visuals, use consistent fonts and headings, and highlight important information. You should also use clear language that is easy to understand, considering the audience’s background knowledge.
1. Only use credible sources
Credible sources strengthen your report because they are factual, unbiased, and reliable. To identify a credible source, look out for the following markers.
- The source’s author should be an expert in their field.
- The information in the source should be up-to-date.
- The source should include evidence. The author should not have their opinions or speculations.
- A credible source is peer-reviewed by other experts in the field.
2. Use diagrams in formal business reports
Use diagrams like graphs and charts to illustrate relationships between ideas. They are more engaging, easier to understand, and they capture your audience’s attention.
Mind that you don’t clutter your diagrams with too much information. Excess detail will confuse your readers.
Achieve simplicity by:
- Removing backgrounds that cause distractions.
- Removing or lightening gridlines. Gridlines clutter diagrams.
- Reduce the number of colors you use. Only use color on crucial data in the diagram.
- Instead of adding every tiny detail, use symbols and have a key. The key explains what each symbol, figure, or line represents.
3. Use a consistent format
A consistent format makes it easy to follow your report. Keep the format headings and subheadings uniform throughout your report. And make your page margins and font styles consistent.
4. Use bold fonts to highlight
Bold fonts stand out against regular text to draw focus on essential data and make it easier to skim through the report. Use bolding sparingly; otherwise, the effect of highlighting will not work.
Formal business report template
A formal business report template will save both time and energy by providing a framework that simplifies the process of assembling data into a comprehensive document.
Check out this collection of editable business report templates to find one that works for you.
Final Thoughts: Formal Business Report
Formal business reports are essential tools for any business. An excellent report drives company decisions and recommends solutions to company problems. Writing one may be challenging, but this guide gives you a clear pathway to ease the process.
Remember to use visual aids and credible sources to fortify your report. Organize data into the above sections, and use the discussed tips to write your business report like a pro!
You may also like:
- How to Write a Resignation Letter for a Better Opportunity [Samples + Template Included]
- Bullet Form Examples: How to Use Bullet Points Effectively
- How to Write a Subject Line for Job Applications [+Samples]
Get started With 2000 Free Monthly Credit
Want to level up your content game? Get started today with 2000 monthly free credit.
Advanced AI writing tool trained to write better content faster.
- Sentence Rewriter Tool
- Instagram hashtag generator
- LinkedIn headline generator
- Paraphrasing tool
- Acronym generator
- Title generator
- Business name generator
- Slogan generator
- Blog ideas generator
- Job Description Generator
- Brand Style Guide
- Affiliate Program
- Social Media Marketing
- Email Marketing
- Random Generator
- Name Generator
- Summary Generator
- Character Counter
- Word Counter
- Word Finder
- AI Content Detector
Copyright © 2024 WriterBuddy. All rights reserved.

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
Business Communication - How to Write a Powerful Business Report
Business communication -, how to write a powerful business report, business communication how to write a powerful business report.

Business Communication: How to Write a Powerful Business Report
Lesson 8: how to write a powerful business report.
/en/business-communication/how-to-write-a-formal-business-letter/content/
How to write a powerful business report

When a company needs to make an informed decision, it can create a business report to guide its leaders. Business reports use facts and research to study data, analyze performance, and provide recommendations on a company's future.
Watch the video below to learn how to write and format a business report.
The basics of a business report
Business reports are always formal , objective , and heavily researched . Every fact must be clear and verifiable, regardless of whether the report focuses on a single situation or examines the overall performance of an entire company.
Because objectivity is crucial in a business report, avoid subjective descriptions that tell the reader how to feel. For instance, if sales were down last quarter, don’t say “Sales were terrible last quarter,” but rather let the sales data speak for itself. There should also be no personal pronouns, such as “I think we should invest more capital.” A business report should remain impersonal and framed from the company’s perspective.
The structure of a business report
Although the size of a report can range from one page to 100, structure is always important because it allows readers to navigate the document easily. While this structure can vary due to report length or company standards, we’ve listed a common, reliable structure below:
- Front matter : List your name, job title, contact information, and the date of submission. You can also create a title for the report.
- Background : State the background of the topic you’ll be addressing, along with the purpose of the report itself.
- Key findings : Provide facts , data , and key findings that are relevant to the purpose stated in the background. Be clear and specific, especially because the entire report depends on the information in this section.
- Conclusion : Summarize and interpret the key findings, identify issues found within the data, and answer questions raised by the purpose.
- Recommendations : Recommend solutions to any problems mentioned in the conclusion, and summarize how these solutions would work. Although you’re providing your own opinion in this section, avoid using personal pronouns and keep everything framed through the company’s perspective.
- References : List the sources for all the data you've cited throughout the report. This allows people to see where you got your information and investigate these same sources.
Some companies may also require an executive summary after the front matter section, which is a complete summary that includes the report’s background, key findings, and recommendations. This section lets people learn the highlights quickly without having to read the entire document. The size of an executive summary can range from a paragraph to multiple pages, depending on the length of the report.
As mentioned in Business Writing Essentials , revision is key to producing an effective document. Review your writing to keep it focused and free of proofreading errors, and ensure your factual information is correct and presented objectively. We also recommend you get feedback from a colleague before submitting your work because they can spot errors you missed or find new opportunities for analysis or discussion.
Once you’ve revised your content, think about the report’s appearance . Consider turning your front matter section into a cover page to add some visual polish. You can also create a table of contents if the report is lengthy. If you’re printing it out, use quality paper and a folder or binder to hold the report together. To diversify the presentation of your data, try using bulleted lists, graphics, and charts.
Example of a business report
To demonstrate the principles of this lesson, we’ve created a brief business report for you to review.
Let's start by looking at the first page of this two-page report.

The layout of the front matter is simple and effective, while the background sets the stage in a quick, specific manner. The key findings provide the main takeaways that warrant further investigation, along with a chart to add emphasis and visual variety.
Now let's look at the following page.

The conclusion features a little of the writer's opinion on the key findings, although the writing is still centered around the company's perspective. The recommendations are clear and supported by the data, while the references are thorough.
While business reports may seem intimidating, you have the ability to create a thorough, informative document through practice and careful research. Collect the facts and present them in an organized, objective manner, and you’ll help your business make informed decisions.
/en/business-communication/how-to-write-an-effective-business-email/content/
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Marketing 50+ Essential Business Report Examples with Templates
50+ Essential Business Report Examples with Templates
Written by: Sara McGuire May 29, 2023

Reports may not be the most exciting communication format. But they’re important.
To make smart decisions about budgeting, marketing strategies, product development and growth strategies, you can’t rely on gut feeling alone.
And if you’re trying to sway stakeholders, creating a report with a simple, elegant design and creative data visualizations is guaranteed to impress.
This guide will deliver the most essential business report templates you can edit with Venngage, plus design tips and best practices.
Top business report templates (click to jump ahead):
What is a business report?
- Annual reports
- Project status reports
- Budget reports
- Sales reports
- Marketing reports
- Case studies
- White papers
- How to create a business report in 6 steps
- What are the types of business reports
- Business report template FAQs
A business report is a document that delivers important information about a company’s performance, financial health, a particular project, or other aspects that influence its decision-making process.
Business reports come in various formats, such as PowerPoint presentations and online dashboards, offering more than just traditional files and spreadsheets.
They are crucial for organizations as they provide vital details that guide decision-making for business owners and managers.
They act as GPS, highlighting essential aspects like customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and financial figures. Business reports serve different audiences and purposes, delivering information in a clear and engaging format for both internal and external stakeholders.
Want a quick rundown of some of the business report templates in this blog? Check out this video tutorial:
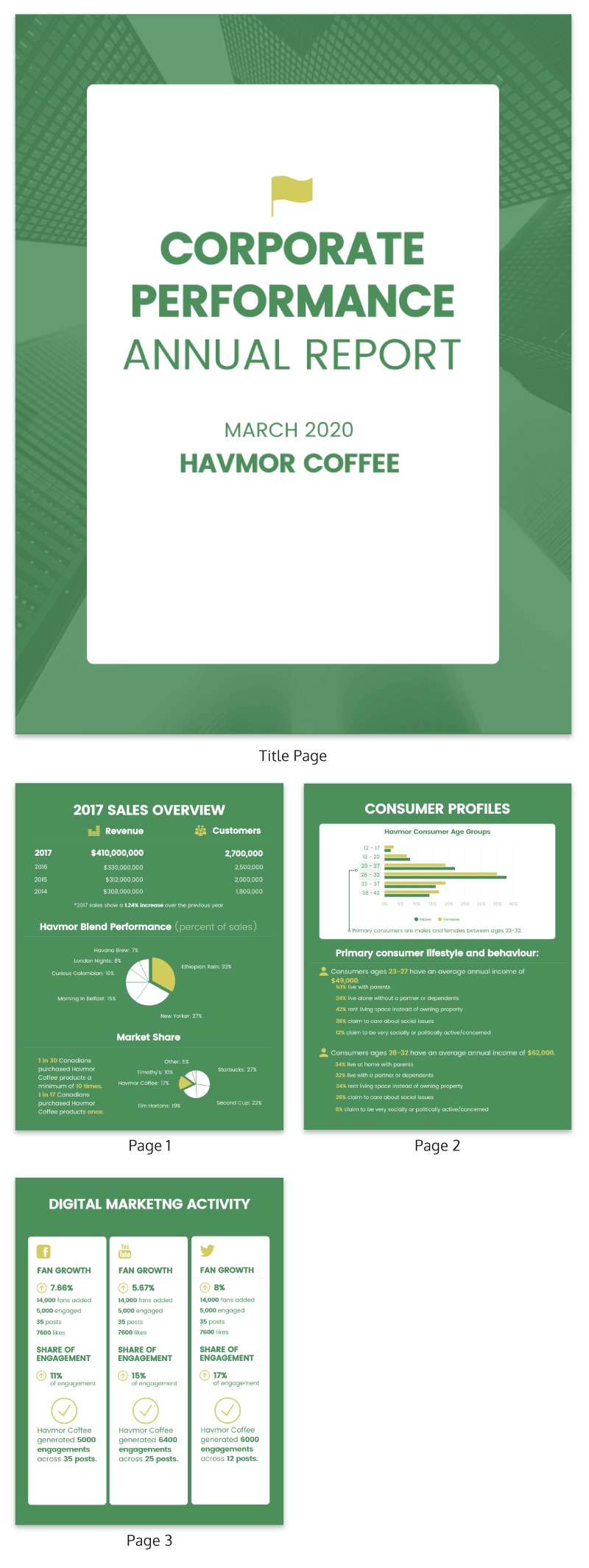
1. Annual Report Templates
An annual report is an all-encompassing document that allows you to reflect on your company’s past year, including:
- Your company’s mission statement
- Your company’s growth (financially, product-wise, culture-wise)
- Your statement of income and cash flow
- Your various business segments
- Information about the company’s directors and executive officers
- Information about your company’s stock and dividends
- Wins and success stories
A lot of that sounds pretty dry, doesn’t it?
There’s actually a lot to be excited about in that list. You’re talking about how your company has grown, your wins (and maybe a few losses), and what’s on the horizon for the coming year.
You can bring that story to life in your annual report design and we have business report samples to inspire you.
This annual business report example uses a variety of charts and unique sections like “program highlights” to tell the agency’s story:

Think about how you can represent your company visually:
- Are there photos you can include of your business in action?
- What fonts and colors reflect your business’s personality?
- Are there icons you can use to illustrate certain concepts?
The below annual report design uses an energizing orange and yellow color scheme and cute icons. The format is highly visual and modern. All this reflects a dynamic company that’s optimistic about the future.
This company annual report template uses a mountain motif to reflect the company’s ambitious goals. Take a look at how the different sections of the report (“Strategy”, “Finance” and “Performance”) are color-coded to make the report easier to scan:

In the business report example below, the sleek, modern design with bold color accents reflects design trends in the games industry, which would appeal to stakeholders.

The same design ideas can be applied to an annual report presentation.
Take this annual report presentation for a coffee shop company. The whole design reflects the coziness of a coffee shop, from the softly filtered photos to the old-fashioned font:

A few annual report best practices:
- Create an eye-catching cover for your report
- Tell your company’s story in your annual report design by using thematic visuals, like background images and icons
- Pick a decorative font for headers and pair it with a more minimalist font for body text
- Look for opportunities to visualize data using infographics , charts and pictograms
Related : Our blog post with 55+ annual report templates , plus design tips and best practices.
2. Project Status Report Templates
Communication is central in any project. Consultants, agencies and freelancers especially want to be as transparent as possible. That is why a project status report template is one of the business report examples we are sharing in the article.
A project status report is crucial for communicating updates on what you’ve accomplished and what’s still pending. It also helps you flag any issues, either current or on the horizon. This helps build trust with the client.
The project status report template below communicates key information in an easy-to-understand format.

The above template lets you alert the client if the project is:
- Suffering from budget or scope creep
- On track in terms of schedule
- Healthy or not i.e. milestones completed on schedule, issues resolved
You can add bullet points on the second page to quickly flag key issues that are impacting project success.
Related : Our post on how to write a project management plan .
Simple Project Status Report Templates
Avoid ad-hoc emails or meetings. Use a simple project status report template to present your latest work and keep everyone on the same page, without endless back and forth.

The project status report below would work well for weekly updates.
This template lets you quickly provide an overview to busy stakeholders, who’ll be able to spot key project issues and progress at a glance.

Project Status Report Template PPT
Big updates might require consultants to communicate the status of a project in person. The below presentation template uses charts and data visualization to get your key points across immediately.
Clients or other stakeholders can see what’s been accomplished and when, while the last slide leaves room for what’s still pending.

A few project status report best practices:
- Include a summary of all important tasks currently in progress. If you have a weekly meeting with the client, this section will probably serve as the jumping-off point for your conversation.
- Stakeholders should be able to tell at a glance if the project is way off schedule or there are too many unresolved issues.
- Document all outstanding problems and concerns. It’s important to have a record in case you run into issues with the client later on.
Related : Our post with 30+ project plan examples plus design tips.
3. Budget Report Templates
This is Business 101: on a quarterly or yearly basis, you should be analyzing your budget, expenses and revenue.
A budget report typically breaks down:
- The different categories of your budget
- The last year or quarter’s spending for each category of your budget
- Areas where you may need to cut or increase spending
- Forecasts for the coming year or quarter
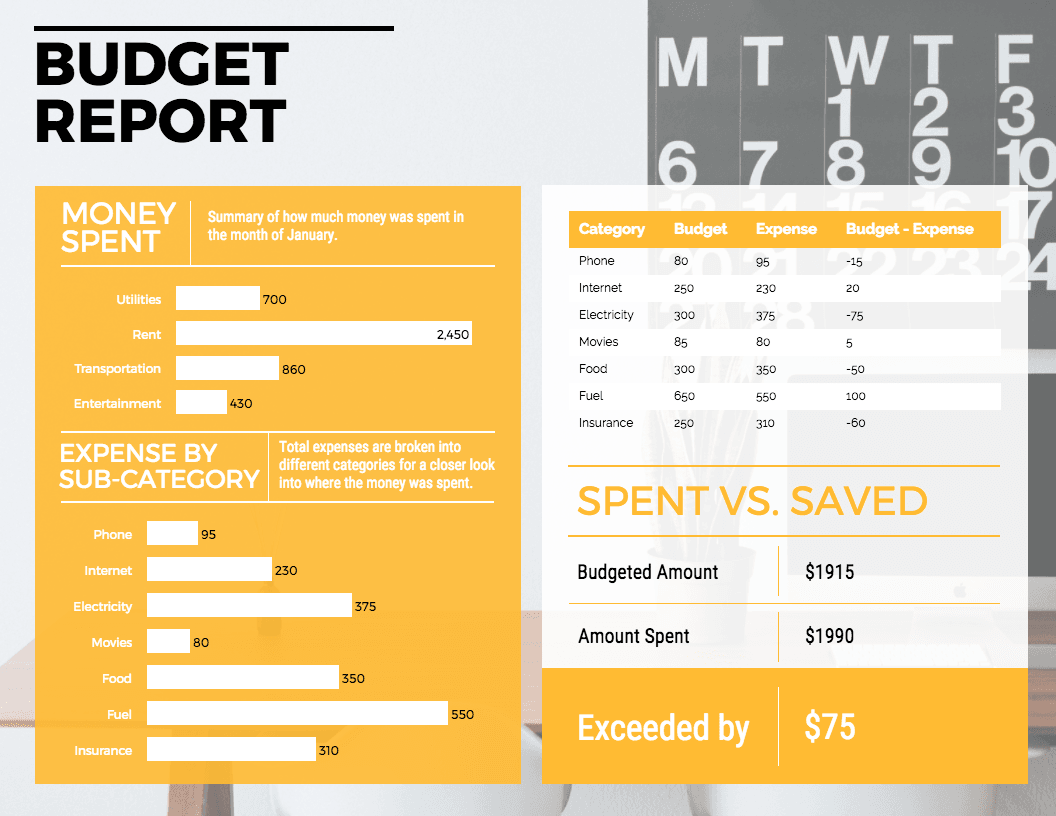
Business Monthly Expenses Template
A full budget report is a bit too dense to pass around a room during a meeting.
But, a visually engaging presentation or one-page summary, like the business report example below, is perfect for keeping your team and stakeholders up to speed.

You can provide an overview of the last period’s spending by category, and highlight the amount you saved or exceeded the budget by.
For example, take a look at this summary budget report slide that uses a thematic background image to make it more engaging:
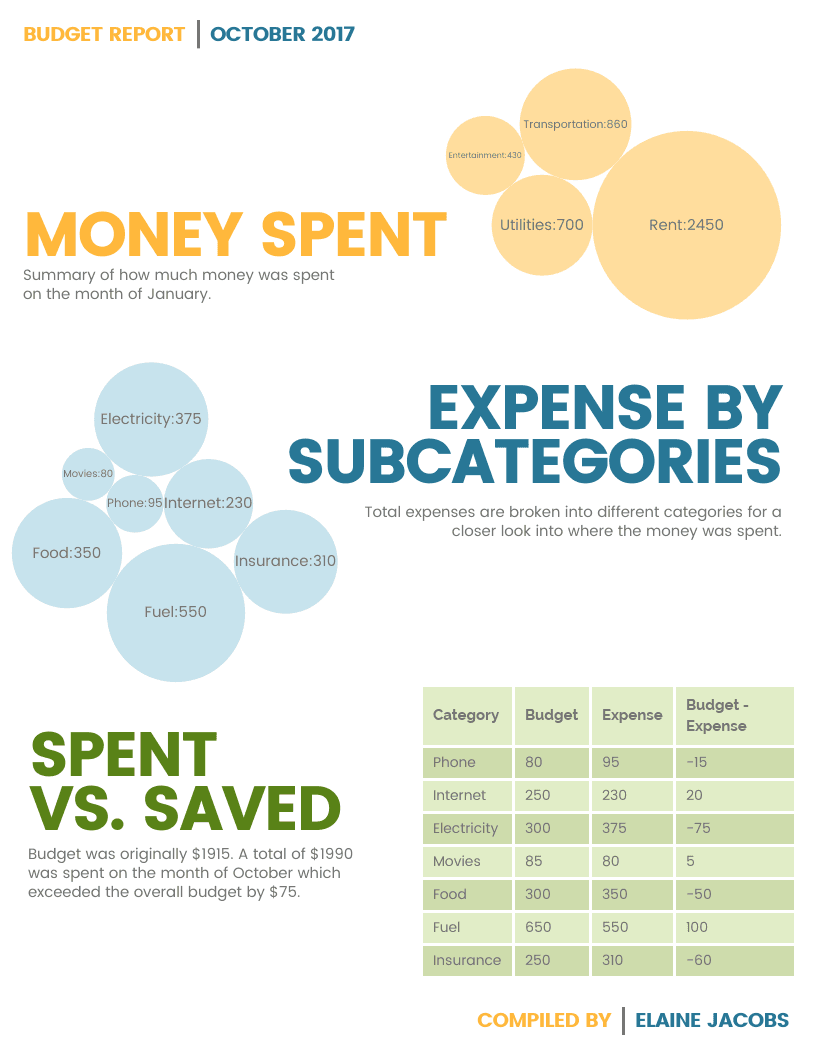
A quick summary page is also the perfect opportunity to creatively visualize data.
While tables are certainly efficient for comparing amounts spent, you could also use a more unusual visual like a bubble chart. This is because unique visuals make memorable business report examples.
Forecast Budget Template
A forecast is an essential business report that shows where a business is headed financially. It’s not a plan for the future, but rather its current short-term direction .
Use this forecast template to project your businesses’ revenue, and take appropriate action.

A few budget report best practices:
- Clearly label the period the report covers (monthly, quarterly, yearly)
- Provide a brief description of each section of your report, to highlight important insights
- Use a table to compare amounts of money saved vs. spent
- Use bar charts, pie charts and bubble charts to visualize budget allotment
- Highlight important insights using contrasting colors, bold fonts and icons
4. Sales Report Templates
If you aren’t tracking your sales on a weekly, monthly, quarterly and yearly basis, it’s time to start.
Creating a sales report for different time periods can help you identify trends, as well as an opportunity for growth. Regularly reporting on your sales can also help your team stay focused on your goals.
What should be included in a sales report?
A sales report typically covers any of the following data:
- An overview of sales goals and whether or not those goals are being met
- Revenue and expenses
- Sales forecasts for the upcoming periods (month, quarter, year)
- Products and services that are selling the most and ones that are lagging
- Number of leads and conversion rates for a given period
- Any challenges or roadblocks
Weekly sales report template
Consider making sales reporting a segment of your weekly team meetings. You may want to provide a quick update for company-wide meetings and a more in-depth report for sales and marketing team meetings.
Here’s an example of what a quick weekly sales report could look like:

The slide simply covers the total sales for the week and compares them to previous weeks to highlight growth.
While this sales report presentation digs deeper into KPIs (key performance indicators) and conversions :
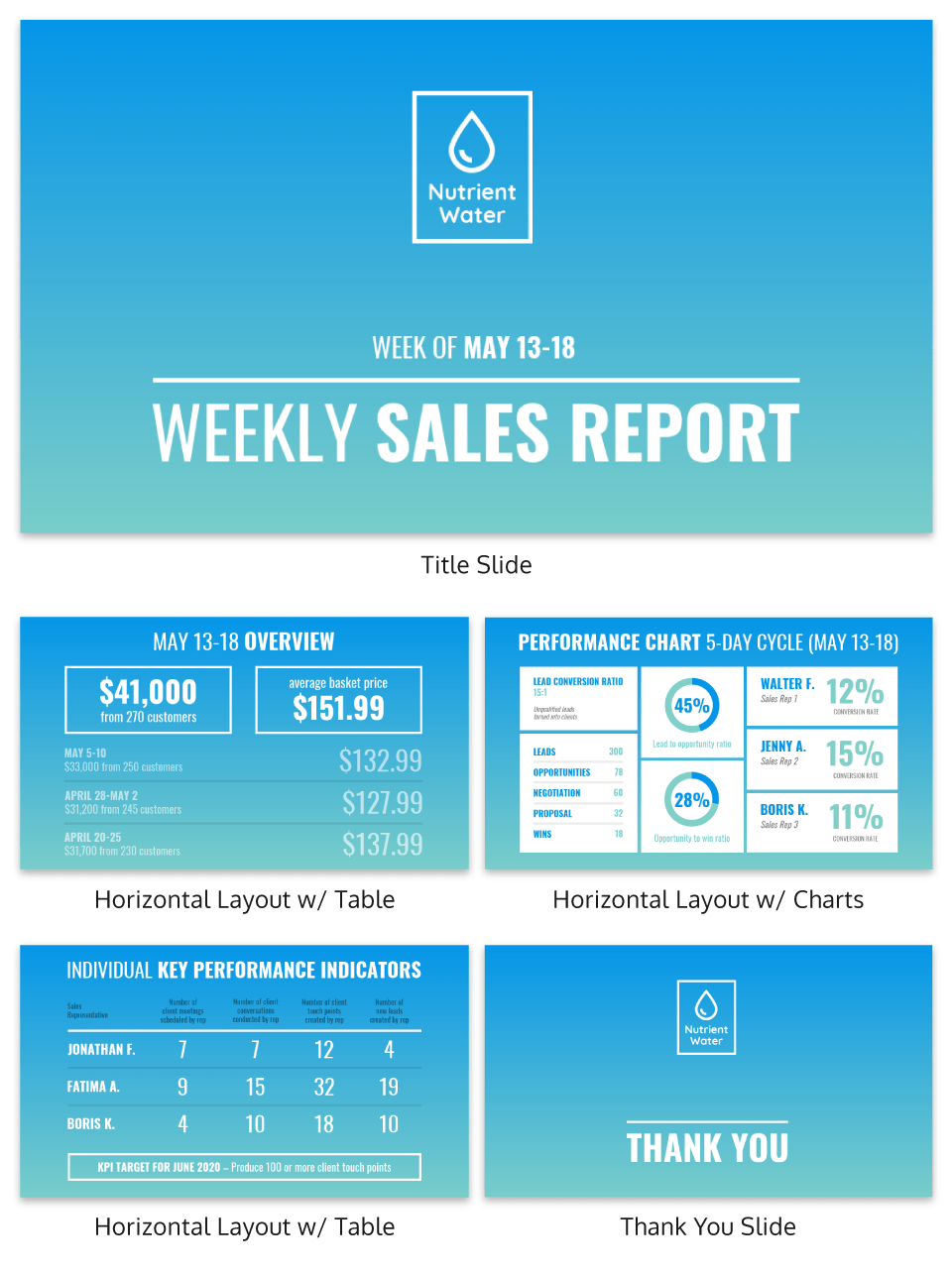
Monthly sales report template
For a monthly, quarterly or yearly sales report, you will probably want to go more in-depth into your metrics as you plan for upcoming periods.
That said, you don’t want to produce a 62-page text-heavy document no one will read. Surprise your client or boss with a fresh new way of doing things that are engaging and concise. You’ll differentiate yourself as an innovator.
For example, the following monthly sales report template uses a variety of charts and tables to keep the data fresh:

The below sales report template will help you visualize key sales metrics using pie charts, bar graphs and tables. The weighted text and icons help organize information in an easily digestible way.
Making your sales report easily accessible will help build your reputation as someone who’s transparent and trustworthy.
A few sales report best practices:
- Clearly identify the time period you are reporting on
- Use descriptive section headers and include descriptions for any charts or tables that need more clarification
- Provide context for readers, explain any major trends they should be aware of, any challenges your team encountered, and how the goals have been impacted
- Use line charts and bar graphs to show changes over time and highlight trends
- Emphasize key metrics in big, bold fonts (for example, the total sales for a given week)
- Use contrasting colors to emphasize keywords or one point on a graph
Related : 5 ways to host a more successful sales demo by using images.
5. Digital Marketing Report Templates
If you’re a SaaS or e-commerce business, I don’t have to tell you how important digital marketing is. It’s the thing that can make or break many small businesses.
In order to scale and grow your business , it’s important to make informed, deliberate digital marketing decisions.
That means always looking for ways to improve your search rankings, grow your social media engagement, and optimize your ad campaigns.
A ‘ digital marketing report ‘ is a pretty broad term for a report that could be an overview of all your digital marketing channels or one particular channel.
A digital marketing report that covers all your main marketing channels could include any (or all) of the following data:
- An overview of your current digital marketing strategy
- Your main marketing goals and whether or not they are being met
- An overview of your conversion metrics, including the number of leads, paid vs. organic leads, and your cost per conversion
- An overview of your traffic metrics, organized by channel
- An SEO overview , including any chhttps://growthbarseo.com/anges in rankings for target keywords
- An overview of PPC campaigns you’re running, including clickthrough rate, ROI and cost per click
- An overview of your social media channels, including engagement metrics and leads from specific channels
For example, take a look at this digital marketing report template that dedicates one page to each channel. Note how the company’s branding has also been incorporated into the design by using the brand’s colors and visuals that reflect the computer theme:

In a digital marketing report that focuses on one specific marketing channel, you will probably want to go more in-depth into each metric.
For example, in a social media report, you should cover:
- A comparison of your performance on specific social media channels like Facebook, Twitter and YouTube (you could try visualizing it with a comparison infographic )
- Specific engagement metrics like impressions, clicks, subscriber count, likes and comments
- An overview of your followers, including demographic information like age, gender and profession
- Conversion metrics from each specific social media channel
The below social media report visualizes some of these key metrics.
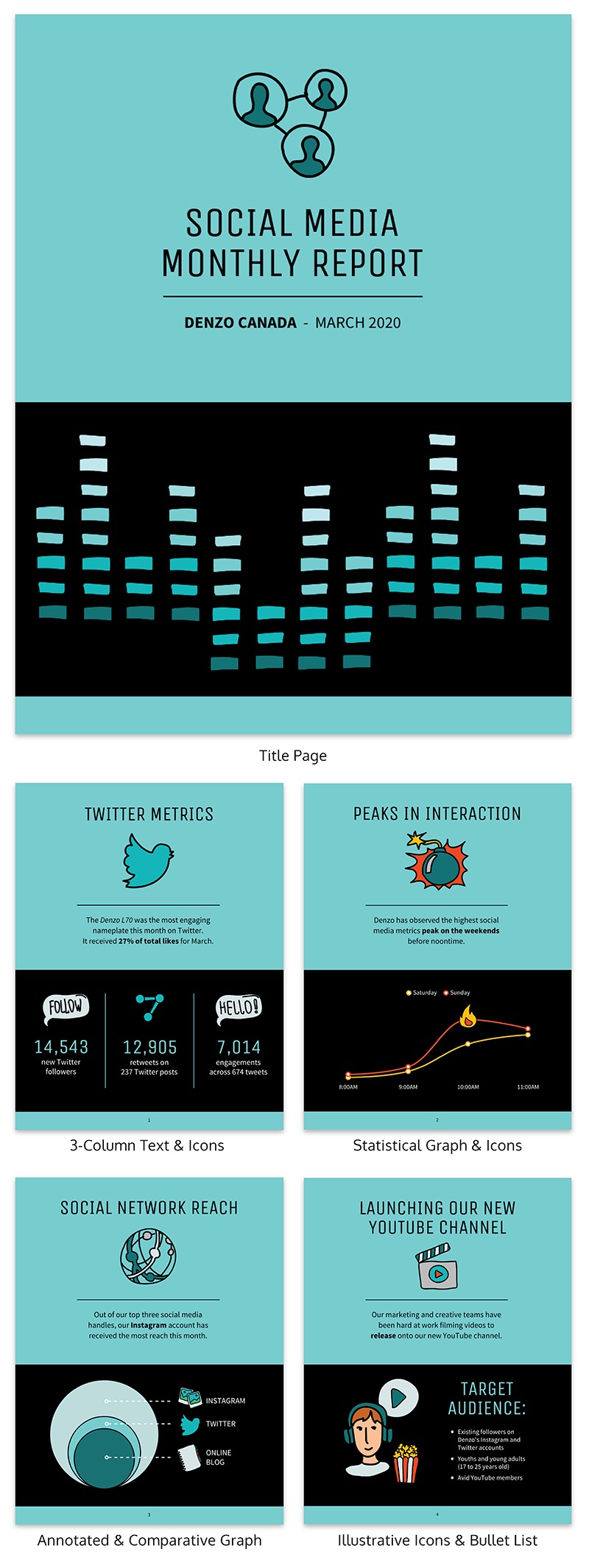
As a consultant, you may be gifted in social media marketing but totally flummoxed by all things design. Look better than you are by using the above template. It’ll help you present your findings in a way that’s effective and professional, while still managing to be playful and engaging.
If you’re concerned about organizing information by channel, here’s an example of a social media marketing report presentation that uses colored columns to make it easy to scan for a specific channel’s metrics:

A few digital marketing report best practices:
- Provide an overview of the performance of all your channels, or a particular channel
- Organize your report by channel (“Organic Search”, “Social Media”, “PPC”) or by specific campaigns/projects
- If your report is long enough, include a table of content to make it easier for readers to navigate your report
- Use bar charts and tables to compare your performance on different marketing channels
- Use icons to emphasize key information and visualize different channels (for example, different social media networks)
- Try to communicate your information concisely and focus on only one topic per page or slide
Related : Our post on what is a marketing plan and how to write and design one for maximum effectiveness.
6. Competitor Analysis Templates
Get the attention of marketers with a competitor analysis report. The best reports show exactly what a company must face off (and beat) to be successful.
A competitor analysis report usually has the following sections:
- Product summary
- Competitor strengths and weaknesses
- Competitor strategies and objectives
- Outlook: is the market growing? Flat? Splintering into niche segments?
The following competitor analysis template neatly organizes these categories into compact sections and highlights important stats. Stakeholders can quickly compare them with their own company’s numbers and get an immediate sense of how they measure up.

Using a pre-designed competitor analysis template is also a great idea for consultants who want to set themselves apart from big consulting firms or boutiques. Visualizing data is a way to set yourself apart as numbers-focused, unique and innovative, as in this business report example.

A few competitor analysis report best practices:
- If you’re listing all competitors, add those entering the market in the next year as well as indirect competitors who sell to the same customers as yours.
- Find customer satisfaction surveys for competitors (usually carried out by trade press) and include their findings.
- Talk to the sales department to get a sense of the competitor’s customers.
- Do informal research on the competitor’s strengths and weaknesses. Talk to journalists who cover this specific industry. Don’t just rely on online information.
Related : Our post on how to create a competitor analysis report (with templates).
7. Case Study Templates
One of the business report examples on our list is the business case study. Though not a report exactly, a case study analyzes a particular aspect of a company or a situation it faced. A consultant may need to write one as part of a corporate training program they’re developing.
Case studies usually focus on one of these situations:
- Startup or early-stage venture
- Merger, joint venture, acquisition
- Market entry or expansion
- New project or product
- Pricing optimization
- Profitability
- Industry landscape
- Growth strategy
What makes case studies unique is how they tell a story. They include background information on the company, a protagonist or key players, the situation and outcomes.
The below case study template has plenty of space for this narrative while using icons and numbers to highlight key details.

Make sure to include a conclusion that contains your key findings. Why did the protagonist make the decisions she made? What were the outcomes? What can we learn from this? Circle back to the key question the case study raises and answer it.
Business case study template
Business case studies are usually teaching tools to show how real companies approached a particular scenario or problem. The case study usually reflects a business theory and demonstrates its real-life application.
For example, the following business case study template shows how a crafts retailer uses earned media to drive engagement-heavy traffic.

This is another version of the above case study. Notice the changes in branding in this business report example that sets it apart from the previous template.

Marketing case study template
Case studies are a powerful form of marketing as they show a potential customer how existing customers are already using your product or service to meet their goals.
For example, this social media marketing case study illustrates how Toy Crates used content marketing to radically increase their sales:

A few case study best practices:
- Outline any constraints and challenges the protagonist of the case study faced that affected her decision (such as a tight deadline).
- Attach supporting documentation, such as financial statements.
- Include an original title, such as “Design Thinking and Innovation at Apple.” The title should mention the company and the subject of the case study.
Related : Our post on how to write and design a case study .
8. Growth Strategy Templates
Setting goals for your business might seem easy in theory… but setting ambitious yet realistic goals can actually be quite challenging.
At Venngage, we follow these 5 steps to set our goals:
- Identifying and set high-level goals.
- Understand which inputs and outputs impact those goals.
- Run experiments to impact those inputs.
- Validate those experiments.
- Foster accountability for the results within the team.
For a more in-depth look at this process read our growth strategy guide .
For example, if you’re a SaaS company, your high-level goals would probably be a specific number for revenue, a number of daily active users or employee count, like in the business report template below:

Once you’ve identified your high-level goals, the next step is to identify your OKRs (Objective Key Results), the metrics that impact your goals. Generally, you will probably want to break down your OKRs by channel.
So, if one of your goals is to hit a certain number of daily active users, your OKRs could be organized by:
- Acquisition OKRs, like organic traffic and paid traffic
- Conversion OKRs, like conversion rate
- Retention OKRs, like retention rate
Once you’ve identified your OKRs, you can come up with experiments to run that will impact those OKRs.
At Venngage, we use a weekly sprint to plan, execute and analyze our growth experiments. But I know other companies that use longer sprints, like two-week or month-long sprints.
Before you run an experiment, you should validate that it’s an experiment worth running. You can do that by identifying which goal it impacts, what resources the experiment will require, and how much effort you anticipate it will take to run the experiment.
This is the exact marketing sprint validator template that our marketing team uses when we schedule growth experiments:
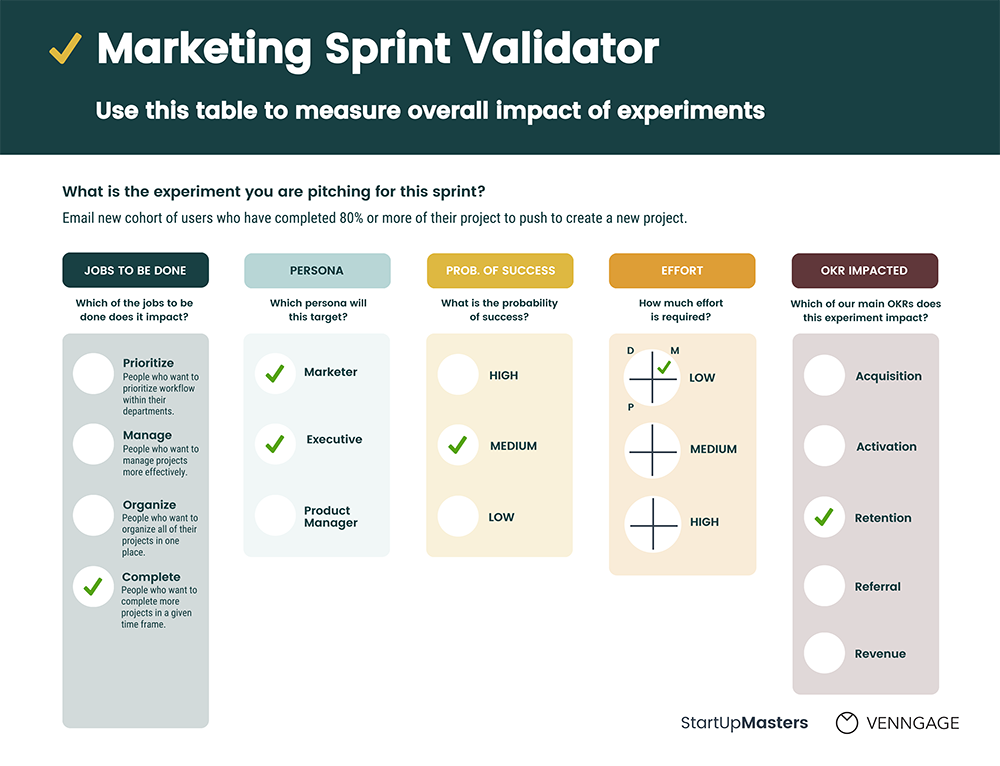
After you’ve run a growth experiment, it’s extremely important to track your results.
At the end of every sprint, take a good chunk of time to analyze your experiments to see what learnings you can take from them. Then, classify an experiment as a “Winner” or “Loser” based on whether or not the results lined up with your hypothesis.
You can use your results from the sprint that just ended to inform your experiments in the upcoming print.
Here’s an example of a sprint release and results template that you could use. Note how each experiment is owned by a team member to foster accountability for the process and results:

A few growth strategy report best practices:
- Divide your growth strategy reports into color-coded columns based on goals, OKRs, or stages in a sprint
- Use icons like checkmarks and x’s to identify winning experiments and losing experiments
- Include brief descriptions on each template, to make it easy to understand
- Attribute each growth experiment to a team member, to foster accountability for the process and results
- Use your company colors, fonts and logo to maintain consistent branding across all of your communications
Related : Our complete guide to developing a growth strategy checklist.

9. Market Research Report Templates
Even after you’ve launched your business, it’s a good idea to do regular market research. You can use your research to plan and refine your marketing strategies, to identify new prospective customers and product plan.
Market research generally involves gathering information about the needs, problems and wants of your customers. This research can help you come up with your customer personas and specific problems you want to solve with your product or service.
You can conduct market research in two ways:
- Qualitative research (calls, focus groups)
- Survey research
For example, many consultants struggle to get buy-in from various stakeholders. The boss may be constantly changing the scope of the project based on a whim, such as the latest article he’s scoured from the internet! Employees may be set in their ways and resistant to incorporate consultants into their workflow.
One way to get clients on board and build trust is to provide stats and research that support your recommendations.
Here’s a market research business report example that lays out the industry landscape and gives clear guidance on the way forward, all backed up by facts.

This cheerful, icon-heavy market research report should help energize reluctant stakeholders. Packaging new (and sometimes daunting) information in fresh ways can help break through resistance.

You may also want to look at competitor statistics and industry trends. This template includes a competitor case study, including website analytics, and a SWOT analysis :

When it comes to creating your market research report, you may want to do an in-depth overview of all of your market research. Or you may want to focus on one area of your research, such as your survey results.
Survey Report Template
This survey report template helps visualize your findings; the pictogram and chart make the findings easy to understand.
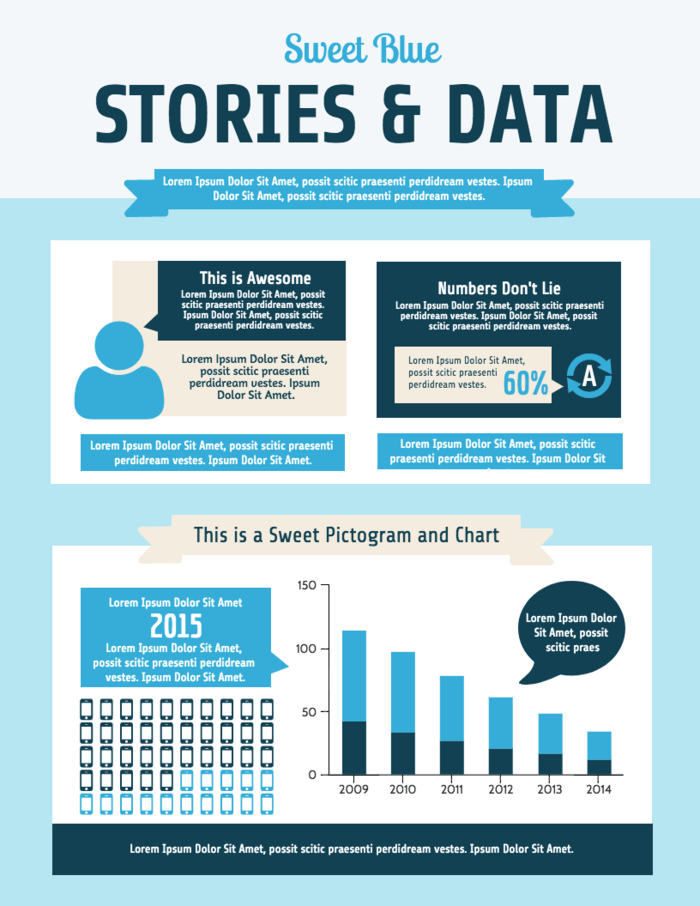
The one-slide market research report identifies the demographics of the survey participants. The report categorizes participants by their jobs, locations, and the topics that they find most engaging. Note how each persona is visualized using an icon:

This business report example highlights how you can give your team and stakeholders a quick overview of your main market and what topics they’re interested in.
One of the purposes of a market research report is to present any conclusions that you came to after analyzing the data.
These could be conclusions about who your target customers are, areas where you can expand your business, and customer needs that aren’t currently being met. The below business report example visualizes this data and also provides space to draw your own conclusions.

Here’s an example of a market research report template that emphasizes key findings in the larger text before providing supporting data:
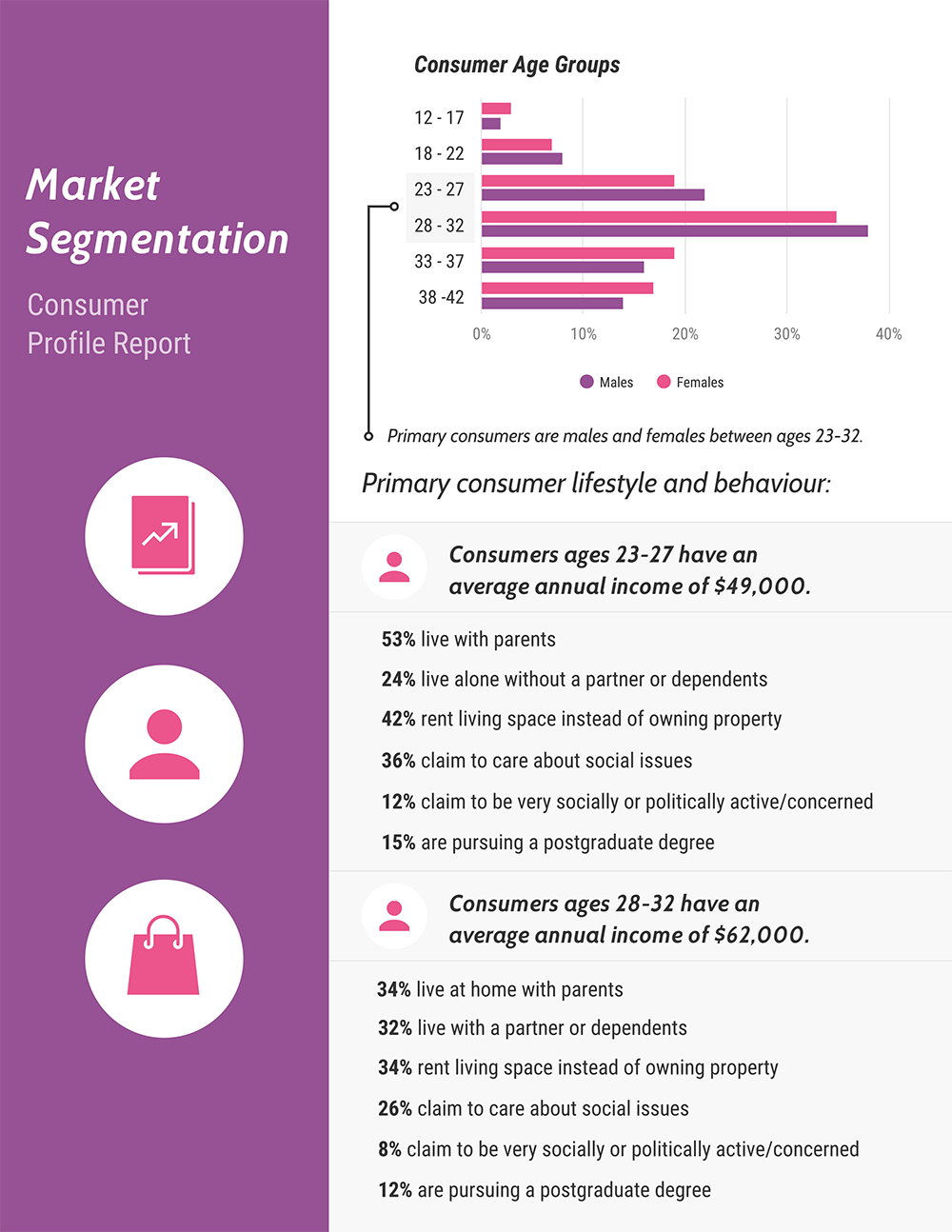
A few market research report best practices:
- Use icons to illustrate your customer personas
- Use charts and graphs to compare demographic information like customer age, gender, location, and occupations
- Include the main conclusions you came from after analyzing your data
- If your market research report is long enough, include a table of contents
- Include a brief summary of your data collection methods , including the sample size
10. White Paper Templates
White papers are great tools to educate and persuade stakeholders. Consultants can also use them to improve their reputation vis-a-vis big consulting firms and boutique firms or use them as lead magnets in Facebook ads etc.
As always, a polished design is much more likely to engage senior leaders or potential clients.
A business report template or consulting report template is the fastest way to produce something that’s both attractive and easy to understand.
The below consulting report example has a full page dedicated to visuals. It’s the perfect way to break up the text and let it breathe. It also reinforces the information.

Browse our library of thousands of professional, free stock photos to swap in images that suit your topic best. Or upload your own.
Our editor makes it simple to adapt any of our business and consulting report templates to your needs. Change the text, fonts, photos, icons, colors, anything you want.
The next business report template is perfect for marketers and marketing consultants. It has an inviting and fun (but still professional) cover page that quickly communicates the content marketing process using icons.

Venngage has an extensive library of thousands of custom, modern and diverse icons you can swap into the above consulting report example. For instance, you could add the Twitter or Facebook logo or a “thumbs up” icon.
Then, click on the template’s chart or graph (pages four and five) to add your own data.
Struggling with organizing information in your reports? It’s important for consultants and marketers to find a way to communicate key takeaways, and not overwhelm your reader with data.
The below consulting report template uses filled text boxes and icons on the third page to highlight top findings.

Different-colored headers also help create a hierarchy of information and add more variety to the design.
A few white paper best practices:
- Create an eye-catching white paper cover page using a background in bold color, photos or icons.
- Add a key takeaways section, with a header and bullet points.
- Visualize data using charts and pictograms in order to highlight key data.
- Incorporate your branding into your white paper template (brand colors and logo).
Related : Our blog post with 20+ white paper examples for even more templates and design tips.
11. Project Plan Templates
A project plan is the best way to keep a project on track.
But, showcasing the steps towards completing a project and showing how each step is actionable and measurable can be tough.
This is especially difficult if you’re a consultant and you don’t have company templates to rely on.
The below project plan template is a simple way to visualize what needs to happen, and when.

The above highly organized project plan template uses bar graphs, icons and color-coding to present information in an accessible way. Once you enter the editor, click on the bar graph to customize the schedule.
The project timeline below also uses icons and color-coding to organize information, though in a slightly different way.
Projects suffer when there’s confusion about deadlines and what’s required at each step. This timeline from a business report sample makes it crystal clear what tasks belong to what step and how long each step should take.

A timeline is a perfect way for your team or client to refer back to the project schedule without having to read through tons of text.
You can also revise your timeline as the project progresses to reflect changes in the schedule.
The below consulting report template has a more traditional format for a project plan. Still, like the timelines, this business report sample relies heavily on visuals to create an easily scannable and understandable project overview.

Scope creep is the enemy of any project’s success (and the bane of many consultant’s existence). That’s why it’s so important to define the project from the very beginning. The consulting report template above has a section to do just that.
Of course, projects change and evolve. The project report below will help you raise any issues as soon as they happen and present solutions. That way, stakeholders can make a decision before the project schedule is seriously derailed.

Check out our blog post with 15+ project plan templates for even more examples and design tips.
A few project plan best practices:
- Plot your project schedule visually using a timeline.
- Use color to categorize tasks and milestones.
- Use icons to illustrate steps in a process.
- Insert charts to track the duration of each phase of a project.
- Pick a flexible template that you can update as the project progresses and things change.
Related : Our post on the four phases of the project life cycle .
12. Business Proposal Templates
A business proposal is a document that presents your product or service as the solution to a client’s problem. The goal of a business proposal is to persuade a prospective client to buy your product or service. These proposals can be either solicited or unsolicited.
The contents of a business proposal report will vary depending on the problem.
Typically, a business proposal will include these sections:
- Information about your company (mission, qualifications, competitive edge)
- A detailed description of your client’s problem
- The cost of your product/service
- The methodology of how you propose to solve the client’s problem
- A timeline of your approach to solving the problem
A few business report examples and design tips:
Create an engaging title page for your business proposal. Think of it as the cover of a book or a movie poster. This will be your prospective client’s first impression of your business.
Use a design that tells a story about your company’s mission and the people you serve. For example, the cover for this business proposal template shows a happy team working together:

Meanwhile, this simple business proposal example uses icons to illustrate what the company does. The motif is carried throughout the rest of the proposal design:

Use visuals to highlight the emotion behind the problem
Businesses are made up of people, and people are emotionally charged. When identifying the problem, use imagery to highlight the frustration, confusion, or dissatisfaction behind the problem. This will show empathy towards the people you’re proposing your solution to.
This business report sample page from a business proposal contrasts one image to illustrate the “problem” with a more cheerful image for the “solution”:

This marketing business proposal uses a variety of visuals like icons, bold typography and photos to tell a story:

Related : Our post on consulting proposal templates or our guide to creating a business proposal .
How to create a business report in 6 steps?
Creating a business report can seem daunting, especially if you’ve never done it before. don’t let the word “business” intimidate you – these steps can be used for writing a report in any field!
Step 1: Define the purpose and scope of your report
Know the purpose of your report. Are you aiming to share the results of a project? Analyze performance? Recommend specific actions? Whatever the goal, keep it in mind as you go through the process. Also, consider the scope of your report. Decide what information you’ll be including, as well as what you can leave out.
Example: Let’s say your boss wants a report on your team’s sales performance during the last quarter. Your purpose might be to analyze the numbers and identify trends, areas for improvement, or opportunities for growth.
Step 2: Gather relevant data and information
Now that you know what you’re aiming for, it’s time to gather the information you’ll need. This might involve pulling data from internal systems, interviewing colleagues, or even conducting your research. Remember, the quality of your report depends on the accuracy and relevance of the information you provide, so double-check your sources and make sure you’ve got everything you need.
Example: For our sales performance report, you’ll need to collect data on product sales, individual and team performance, and any factors that may have influenced sales during the quarter.
Step 3: Organize your content
Next up is organizing all that information into a logical and easy-to-follow structure. This will depend on the specific requirements of your report, but some common components are an introduction, executive summary, main body, conclusion, and recommendations. A clear and logical structure helps readers easily understand and follow your report.
Example: In a sales performance report, you might start with an executive summary highlighting sales growth (or declines), outline individual team member’s performance, and then delve into a more detailed analysis of factors and trends.
Step 4: Write the report
When writing your report, start by developing a clear and concise writing style, avoiding jargon and buzzwords. Keep your audience in mind – make sure your report is easily digestible for your intended readers.
Example: When writing about sales performance, share facts and figures in simple terms that everyone can understand. Instead of saying, “Our sales team demonstrated a 12.3% compound annual growth rate,” say, “Our sales team increased their sales by 12.3% each year.”
Step 5: Add visual aids
To make your report more engaging and easier to understand, consider adding visual aids like graphs, charts, or images. These can help break up large blocks of text and highlight key findings or trends.
Example: For your sales performance report, you might create a bar chart showing sales growth over time or a pie chart displaying individual team members’ contributions.
Step 6: Review and refine
Last but not least, review your report. Does it achieve the purpose you set at the beginning? Are there any gaps in the information? Are there areas that could be clearer or more concise? Address any issues you find and refine your report until it meets your goals and is easy to understand for your target audience.
Example: In your sales performance report, if you find that you haven’t adequately explored the impact of a new product launch on sales, go back and add that analysis to provide a more comprehensive view.
What are the types of business reports?
Different types of business reports cater to various purposes, including monitoring performance, making decisions, and more, offering a range of options beyond standard reports.
1. Informational reports
The primary purpose of informational reports is, well, to inform. These reports provide all the nitty-gritty details of specific aspects of your business without any conclusions or opinions.
Examples include daily sales reports, inventory levels, or even project updates. This is the essential “just the facts, ma’am” type of report you need to stay in the loop.
2. Analytical reports
Analytical reports give you a more in-depth look at the data to help you make decisions. These reports come with all the bells and whistles – charts, graphs, and recommendations based on thorough analysis. Analytical reports are what you whip out when you need to decide whether to invest in a new project, evaluate your marketing efforts, or diagnose challenges within the company. The goal of such a report is to help you make smarter decisions for the growth and development of your business.
3. Summaries & reviews:
If you’re a little short on time and need a quick overview of your business’s performance, summary reports are your best bet. These reports condense the crucial details from other reports at regular intervals (monthly, quarterly, or annually) and present them in a digestible format.
4. Research reports
As the name suggests, these in-depth reports dig into specific topics or issues relevant to your business. Research reports are great when exploring new markets, considering new product development, or requiring a detailed evaluation of business practices. These reports act as guides for making major decisions that could significantly impact your company’s direction and success.
5. Progress reports
Let’s say you’ve got a fantastic project idea underway. You’ll need to keep track of every stage of it to ensure it’s smooth sailing ahead. Enter progress reports. They track the achievements, setbacks, and future plans of ongoing projects. These are essential for keeping everyone – from employees to investors – in the loop.
Business report template FAQs
1. what are the best practices for creating a business report.
You could open up Google doc, record your metrics and make a few points of analysis, send it to your team and call it a day. But is that the most effective way to report on your findings?
Many people may not even read those types of reports. Not to mention, a plain old report probably won’t impress stakeholders.
It’s important to brand yourself (and stand out from your competition). And then there’s the ever-important need to create buy-in from stakeholders and convince them of your recommendations.
That’s why it pays to make your reports as engaging as possible. That means visualizing data , processes , and concepts to make them easier to understand and more fun to look at, as you’ve seen from the business report examples in this post.

You can do that easily by getting started with a business report template or consulting report template .
There are two big reasons why it’s a good idea to create a highly visual business report:
- You will be able to organize, analyze and summarize your findings .
- You will be able to communicate your reports more effectively with your team, stakeholders and customers.
For example, the below business report template shows four different ways you can visualize information. It’s much more captivating and easily digested than a block of text.
And don’t worry about how time-consuming designing a report might be. If you start with a solid business report template, you can repurpose that template over and over again.
Use the template as a framework, then customize your information and design to fit your specific needs. Then, use a chart tool to convert cumbersome data into clear visuals.
Just like in the above business report sample, you’ll have a succinct, powerful (and polished) report that stakeholders can understand at a glance.
2. How do you design a business report template?
Incorporate your branding into the design
Part of building a strong brand is using consistent branding across all of your content, both internal and public-facing. You can incorporate your branding into your business report design by importing your logo and using your brand colors and fonts.
Our My Brand Kit feature automatically imports company logos and fonts from any website. You can then apply them to your design with one click.
Stick to only one topic per page or slide
When creating a report, it’s easy to try and cram a bunch of text onto one page. But then you run the risk of creating an impenetrable wall of text.
Instead, focus on only one topic per page or slide. If you find that even that makes your page look too cramped, then try breaking up your information into two pages or looking for ways to better summarize your information .
Put functionality first
When you’re designing a business report, you should look for opportunities to visualize data and creatively present information. That being said, the primary goal of your business report should still be to communicate information clearly.
Use design elements such as icons or fonts in different sizes, weights and colors to highlight, emphasize and categorize information, not obscure it. If a page you’re working on looks cluttered or confusing, take another stab at it.
Remember that functionality comes first, and that includes using the right visuals for your information.
3. What is the best business report maker?
You can make a business report online using a number of tools. As we have mentioned, a great business report is visually appealing, includes icons, images, clear fonts, easy-to-understand charts and graphs, as well as being branded.
Venngage is the one-stop design solution when it comes to creating reports. The business report examples in this article highlight how easy it is to design a variety of reports for every type of organization and activity. Make design simple by using Venngage.
More business communication guides:
- The Ultimate Guide to Consulting Proposals (2024)
- 20+ White Paper Examples [Design Guide + White Paper Templates]
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Structure a Business Report

5-minute read
- 14th March 2019
The content of a business report will depend on what you are writing about. Even the writing style may depend on who you are writing for (although clear, concise and formal is usually best). However, there is a general structure that most business reports follow. In this post, then, we’ll look at how to structure a business report for maximum clarity and professionalism.
1. Title Page
Every business report should feature a title page . The title itself should clearly set out what the report is about. Typically, you should also include your name and the date of the report.
Most business reports begin with a summary of its key points. Try to include:
- A brief description of what the report is about
- How the report was completed (e.g., data collection methods)
- The main findings from the research
- Key conclusions and recommendations
A paragraph or two should suffice for this in shorter business reports. However, for longer or more complex reports, you may want to include a full executive summary .
3. Table of Contents
Short business reports may not need a table of contents, especially if they include a summary. But longer reports should set out the title of each section and the structure of the report. Make sure the headings here match those used in the main text. You may also want to number the sections.
4. Introduction
The introduction is the first part of the report proper. Use it to set out the brief you received when you were asked to compile the report. This will frame the rest of the report by providing:
- Background information (e.g., business history or market information)
- The purpose of the report (i.e., what you set out to achieve)
- Its scope (i.e., what the report will cover and what it will ignore)
These are known as the “terms of reference” for the business report.
5. Methods and Findings
If you are conducting original research, include a section about your methods. This may be as simple as setting out the sources you are using and why you chose them. But it could also include how you have collected and analyzed the data used to draw your conclusions.
After this, you will need to explain your findings. This section will present the results of your research clearly and concisely, making sure to cover all the main points set out in the brief.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
One tip here is to break the findings down into subsections, using headings to guide the reader through your data. Using charts and illustrations , meanwhile, can help get information across visually, but make sure to label them clearly so the reader knows how they relate to the text.
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
The last main section of your report will cover conclusions and recommendations. The conclusion section should summarize what you have learned from the report. If you have been asked to do so, you should also recommend potential courses of action based on your conclusions.
If you are not sure what to suggest here, think back to the objectives set out in your brief.
7. References
If you have used any third-party sources while writing your report, list them in a bibliography after the main report. This could include other business documents, academic articles, or even news reports. The key is to show what you have based your findings and conclusions upon.
8. Appendices (If Applicable)
Finally, you may have gathered extra documentation during your research, such as interview transcripts, marketing material, or financial data. Including this in the main report would make it too long and unfocused, but you can add it to an appendix (or multiple appendices) at the end of the document. It will then be available should your reader need it.
Summary: How to Structure a Business Report
If you are writing a business report, aim to structure it as follows:
- Title Page – Include a clear, informative title, your name, and the date.
- Summary – A brief summary of what the report is about, the data collection methods used, the findings of the report, and any recommendations you want to make.
- Table of Contents – For longer reports, include a table of contents.
- Introduction –Set out the brief you were given for the report.
- Methods and Findings – A description of any methods of data collection and analysis used while composing the report, as well as your findings.
- Conclusions and Recommendations – Any conclusions reached while writing the report, plus recommendations for what to do next (if required).
- References – Sources used in your report listed in a bibliography.
- Appendices – If you have supporting material (e.g., interview transcripts, raw data), add it to an appendix at the end of the document.
Don’t forget, too, that a business report should be clear, concise, and formal. And if you would like help making sure that your business writing is easy to read and error free, just let us know .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

What Are Business Reports & Why They Are Important: Examples & Templates
Table of Contents
1) What Is A Business Report?
2) Types Of Business Reports
3) Business Reports Examples & Samples
4) Why Do You Need Business Reports?
5) How To Setup A Business Report?
6) Challenges Of Business Reports
In your daily operations, you likely notice your processes and ‘activities’ constantly changing – sales trends and volume, marketing performance metrics, warehouse operational shifts, or inventory management changes, among many others.
All these little alterations in your organizational activities are impacting the global well-being of your company, your warehouse, your restaurant, or even your healthcare facility. Whether you manage a big or small company, business reports must be incorporated to establish goals, track operations, and strategy to get an in-depth view of the overall company state.
But with so much information being collected daily from every department, static business reports created manually will not give your company the fresh insights it needs to stay competitive. Businesses that want to succeed in today’s crowded market need to leverage the power of their insights in an accessible and efficient way. This is where modern business reports created with interactive data visualizations come to the rescue.
Traditional means of reporting are tedious and time-consuming. Due to how the human brain processes information, presenting insights in charts or graphs to visualize significant amounts of complex information is more accessible and intuitive. Thanks to modern, user-friendly online data analysis tools armed with powerful visualizations, companies can benefit from interactive reports that are accessible and understandable for everyone without needing prior technical skills.
Here, we take the time to define a business report, explore visual report examples, and look at how to create them for various needs, goals, and objectives. In the process, we will use online data visualization software to interact with and drill deeper into bits and pieces of relevant data. Let's get started.
What Is A Business Report?
A business report is a tool that helps collect and analyze historical and current data from a company’s operations, production, and more. Through various types of business reports, organizations make critical decisions to ensure growth and operational efficiency.
To understand the best uses for these reports, it’s essential to properly define them. According to authors Lesikar and Pettit, “A corporate-style report is an orderly, objective communication of factual information that serves some organizational purpose”. It organizes information for a specific business purpose. While some reports will go into a more detailed approach to analyzing the functionality and strategies of a department, other examples of business reports will be more concentrated on the bigger picture of organizational management, for example, investor relations. That’s where the magic of these kinds of reports truly shines: no matter for which company goal you need, their usage can be various and, at the same time, practical.
Traditional business reports are often static and text reach (bullet points, headings, subheadings, etc.). Classically formatted in sections such as the summary, table of contents, introduction, body, and conclusion, this report format is no longer the most efficient when it comes to extracting the needed insights to succeed in this fast-paced world. On one hand, by the time these reports have been finished, the insights included within them might not be useful anymore. On the other hand, the fact that it is mostly text and numbers makes them hard to understand, making the analysis strategy segregated and inefficient.
The visual nature of modern business dashboards leaves all the aforementioned issues in the past. Thanks to interactive data visualizations and modern business intelligence solutions , the analysis sequence can be done fast and efficiently while empowering non-technical users to rely on digital insights for their decision-making process.
Your Chance: Want to test professional business reporting software? Explore our 14-day free trial. Benefit from great business reports today!
Types Of Business Reports?
Before creating your business outcome reports, it is important to consider your core goals and objectives. This way, you can pick the correct type of report for each situation. Here, we present you with five common types of visual reports that you can use for different analytical purposes.
1. Analytical reports
Analytical reports are reporting tools that use qualitative and quantitative data to analyze the performance of a business strategy or as support when a company needs to make important decisions. A modern analytical dashboard created with top reporting software can include statistics, historical data, as well as forecasts, and real-time information. Let’s look into it with a sales example.
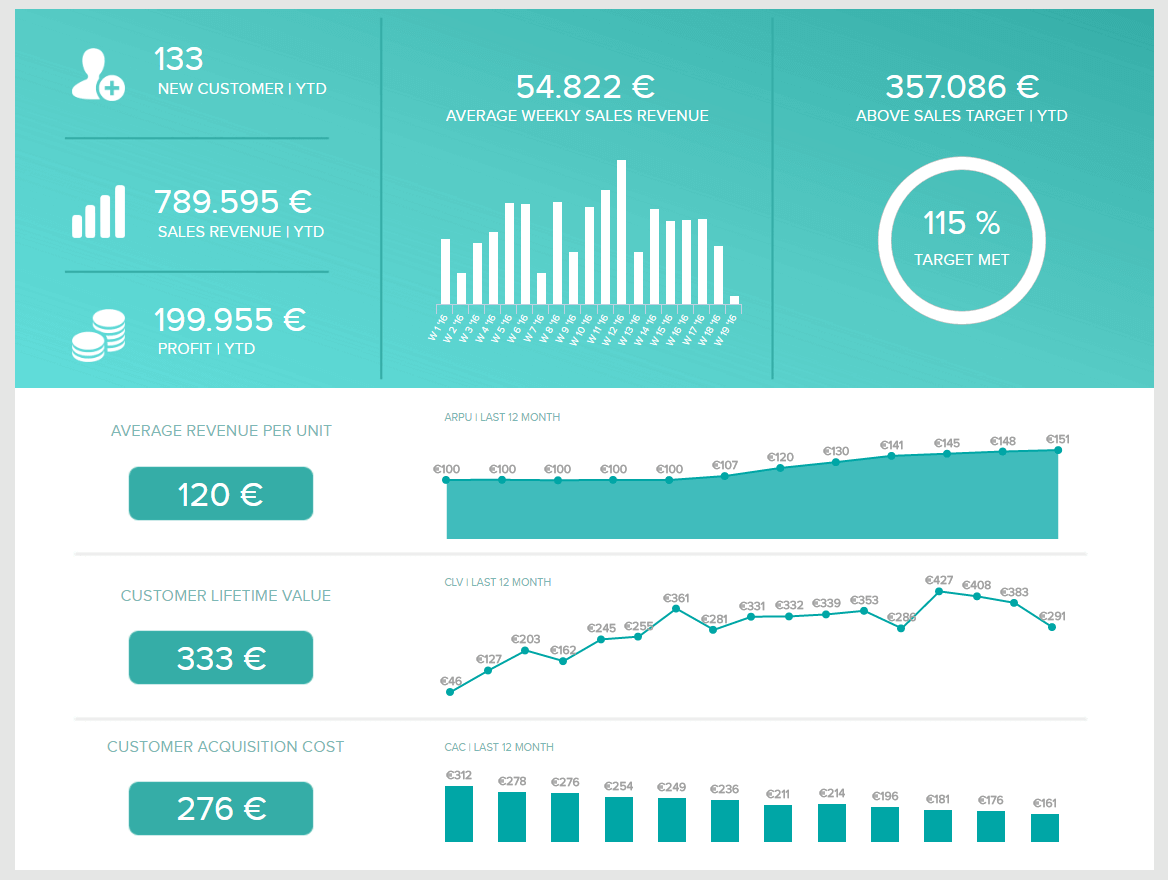
**click to enlarge**
This visually appealing business analysis report contains relevant sales KPIs to measure performance, such as the average revenue per unit, the customer lifetime value, acquisition costs, and some sales targets to be met. The value of this analytical report lies in the fact that you get a lot of relevant metrics in a single dashboard. The data can be filtered and explored on different time frames such as daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly, depending on the discussion that it needs to support.
With this kind of sample in hand, managers can quickly understand if they are meeting their targets, find improvement opportunities, get a bigger picture of their sales, and find efficient ways to proceed with new strategies.
2. Research reports
Next in our types of business reports that we will discuss is a research report. Companies often use these kinds of reports to test the viability of a new product, study a new geographical area to sell, or understand their customer’s perception of their brand image. To generate this type of report, managers often contact market research agencies to gather all the relevant information related to the studied topic. This brand analysis dashboard is a great example.
The image above is a business report template of a brand analysis. Here, we can see the results of a survey that was conducted to understand the brand’s public perception on different topics. The value of this market research dashboard lies in its interactivity. Often, research reports are depicted in long and static PowerPoint presentations. With a modern market research dashboard like this one, all the info can be filtered upon need, and the whole presentation of results can be done on one screen. For example, if you want to know the brand awareness of a particular region or age group, you just have to click on the graphs, and the entire dashboard will be filtered based on this information. Like this, the analysis sequence is fast, interactive, and efficient.
3. Industry reports
Following on from the research topic, our next type is an industry report. Benchmarks and targets are excellent ways to measure a company’s performance and success. But, these targets need to be based on realistic values, especially considering how crowded and competitive today’s markets are. For this purpose, companies perform industry reports. By getting a clear picture of the average industry numbers, such as the competitive landscape, industry size, economic indicators, and trends, they can plan smart strategies and create realistic targets for performance.
Let's take this industry report by Technavio about the Global Ice Cream Market as an example. Here, we can see relevant numbers concerning the ice cream market, how COVID-19 impacted it, and what is expected to happen between the years 2020-2024. For example, the business report sample shows that the pandemic has positively impacted the ice cream market and that it grew 4.33% during 2020. The report also shows that there is increasing popularity of plant-based ice cream and that this trend is driving market growth. This is invaluable information for an ice cream company as they can invest in new products with almost certain success.
4. Progress reports
Next, we have progress reports. Unlike our other examples, this type of business report is not necessarily based on deep research or advanced analytics but rather on delivering a clear picture of the performance of a particular area or business goal. Their visual nature makes them the perfect tool to support meetings or business discussions as they provide a glance into the status of different metrics. A common use of progress reports is with KPI scorecards . Let’s look at an example.
The image above is a business report example of a balanced scorecard. The goal here is to quickly understand the development of metrics related to 4 key business areas: financial, customers, learning and growth, and internal objectives. Each of these metrics is displayed in a current value and compared to a set target. Paired with this, the template has five colors for the performance status. This allows anyone who uses this report to quickly understand just by looking at the colors if the target is being met.
5. By business function
Getting a bigger picture of a company’s performance is a great benefit of the best business reports. But, apart from helping the company as a whole, the real value of these reports lies in the fact that they empower departments to leverage the power of data analysis for their decision-making process. Instead of the sales department, human resources, or logistics, your entire organization will be data-driven. Let’s look at it with a business report example by function on marketing.
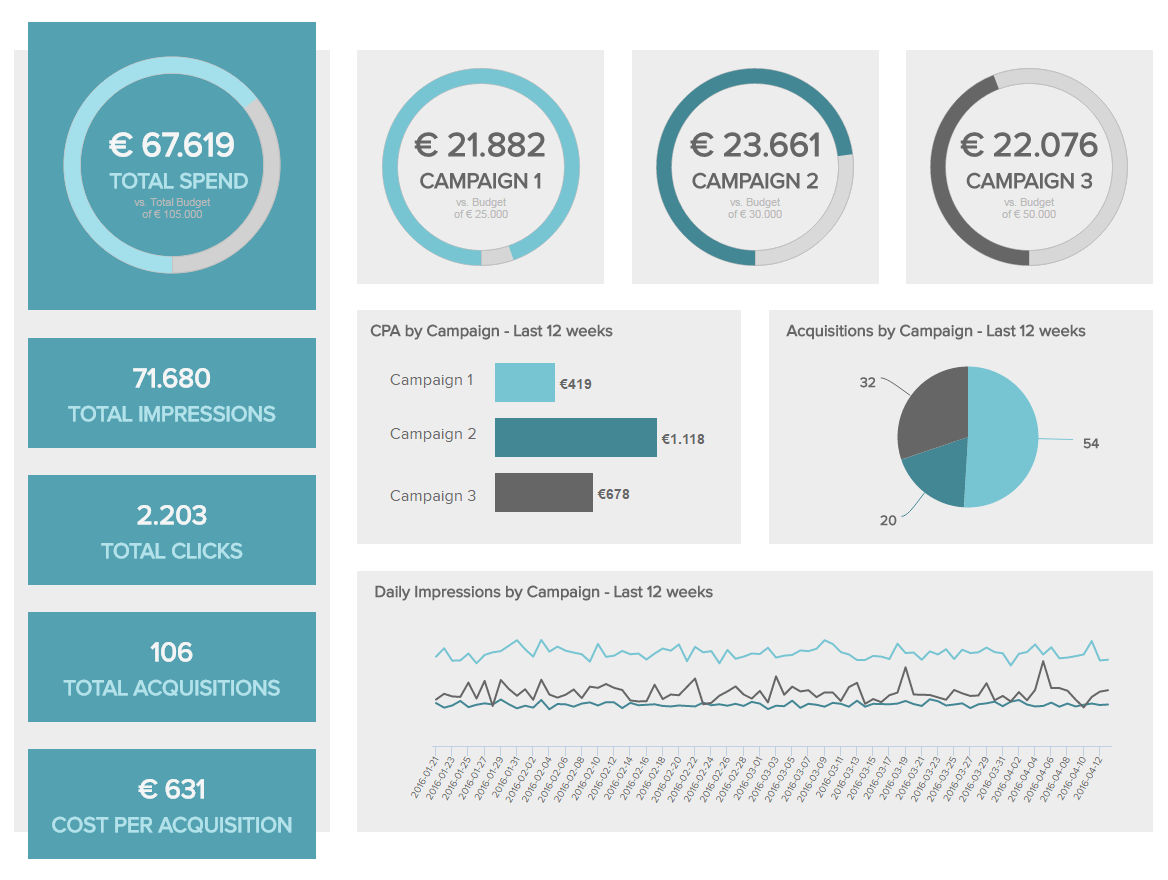
Created with modern marketing dashboard software , this example entirely focuses on the development of marketing campaigns. With metrics such as the total number of impressions, clicks, acquisitions, and cost per acquisition being depicted on intuitive gauge charts, you quickly get a clear understanding of the performance of your campaigns. Through this, you can spot any inefficiencies before they become bigger issues and find improvement opportunities to ensure your marketing efforts are paying off. If you want to dig even deeper, this interactive business report can be filtered for specific campaigns so you only see related insights, making this dashboard the perfect tool to support team meetings.
Business Report Examples And Templates
We’ve answered the question, ‘What is a business report?’ and now, it’s time to look at some real-world examples.
The examples of business reports that we included in this article can be utilized in many different industries; the data can be customized based on the factual information of the specific department, organization, company, or enterprise. Interdepartmental communication can then effectively utilize findings, and the content can be shared with key stakeholders.
Now that we know what they are, let's go over some concrete, real-world instances of visuals you will need to include in your reports.
1. Visual financial business report example
This first example focuses on one of the most vital and data-driven departments of any company: finance. It gathers the most essential financial KPIs a manager needs to have at his fingertips to make an informed decision: gross profit margin, operational expenses ratio (OPEX), both earning before interests (EBIT) and net profit margins, and the income statement. Next to these are the revenue evolution over a year compared to its target predefined, the annual evolution of operational expenses for various internal departments as well as the evolution of the EBIT compared to its target.
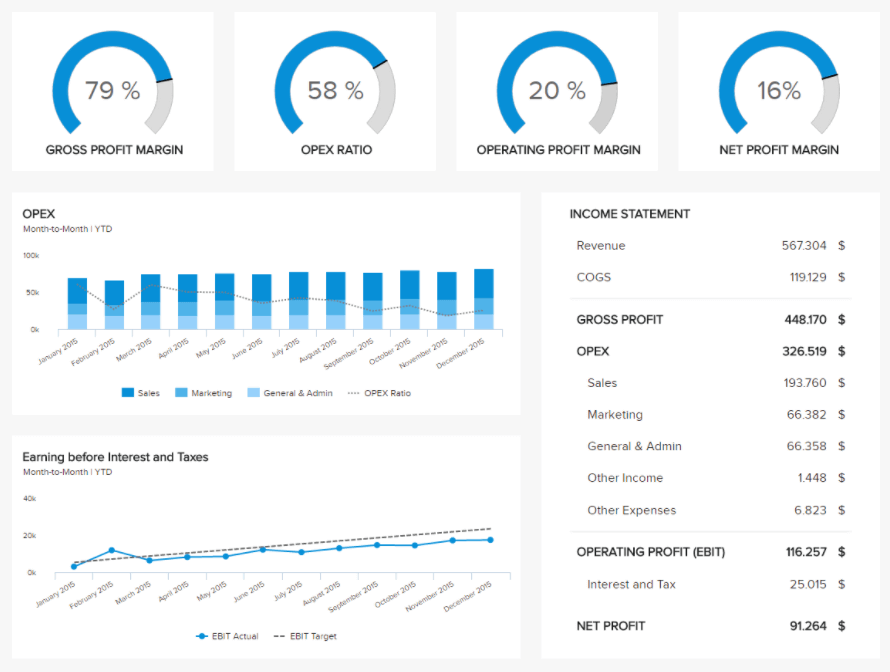
The different sets of visual representations of data can clearly point out particular trends or actions that need to be taken to stay on the financial track of a company. All your financial analysis can be integrated into a single visual. When the presentation becomes interactive, clicks will provide even deeper insights into your financial KPIs and the desired outcomes to make a company healthy in its financial operations. The importance of this finance dashboard lies in the fact that every finance manager can easily track and measure the whole financial overview of a specific company while gaining insights into the most valuable KPIs and metrics. Empowering a steadfast and operation-sensitive plan is among the most important goals a company can have, and finance is right in the middle of this process.
Thanks to all this information displayed on a single dashboard, your report is greatly enhanced and backed with accurate information for you to make sound decisions. It becomes easier to implement a solid and operation-sensitive management plan.
2. Visual investor's business report layout
As mentioned earlier, holding an account of your activity, performance, and organization’s assets is important for people outside of the company to understand how it works. When these people are investors, it is all the more critical to have a clean and up-to-date report for them to know how successful is the company they invest in and for you to increase your chances of having more funds. This example provides just that: an exact overview of the most important insights and specific values in a particular time frame.
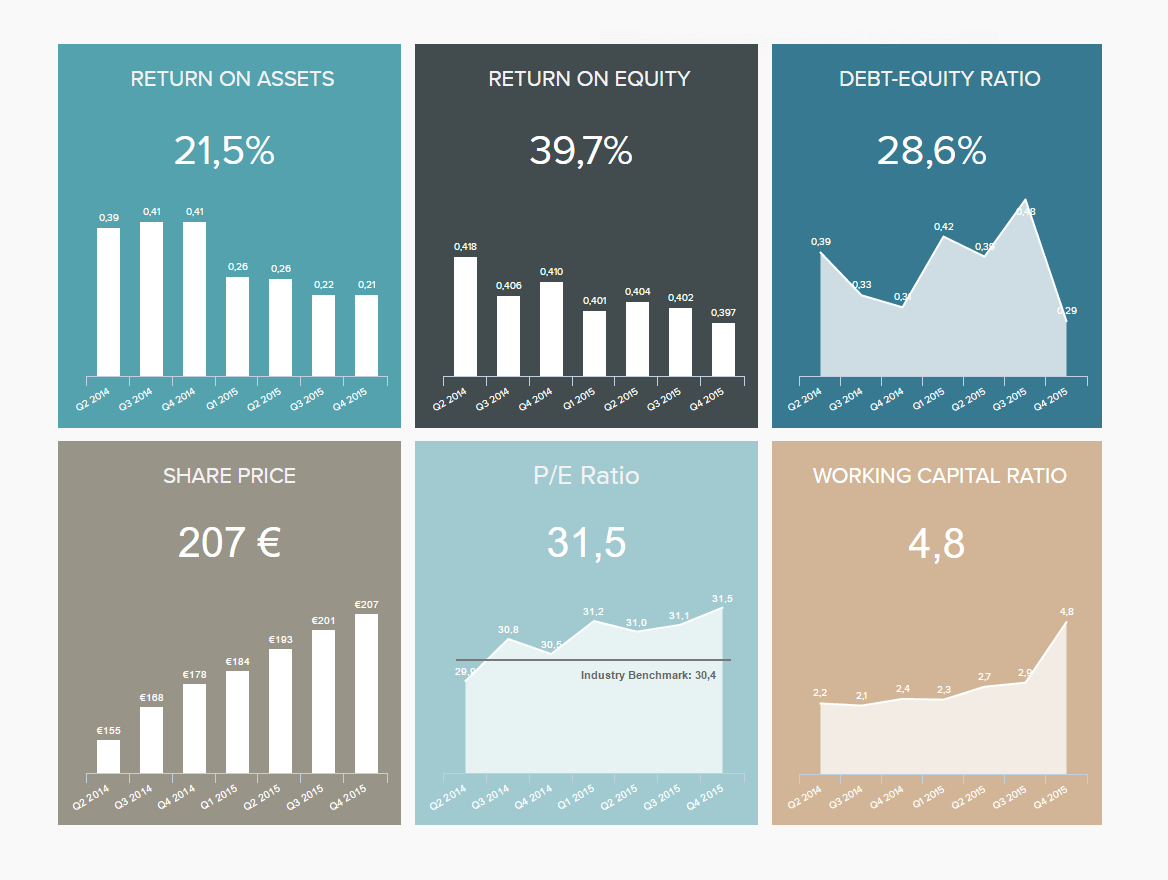
Calculating and communicating KPIs about the overall company situation is what this investors’ relationship dashboard tries to focus on. You learn about the return on equity and return on asset, the debt-equity ratio, and the working capital ratio, but also see the evolution of a share price over time. Each of these metrics is crucial for a potential shareholder, and if they are not monitored regularly and kept under control, it is easy to lose investors’ interest. Tracking them and visualizing them through a modern dashboard is a competitive advantage for your investors’ reports. You can even see on this visual a clear set of data, so you don’t have to dig through numerous amounts of spreadsheets, but clearly see the specific development over time, the percentage gained or lost, ratios, and returns on investments. Not to be limited just to these data, you can always customize and make sample business reports for your specific needs.
3. Visual management report example
The management KPIs presented below focus on the revenue and customer overview seen through a specified quarter of a year. With just a click, you can easily change your specific date range and make an overview of different months or years.
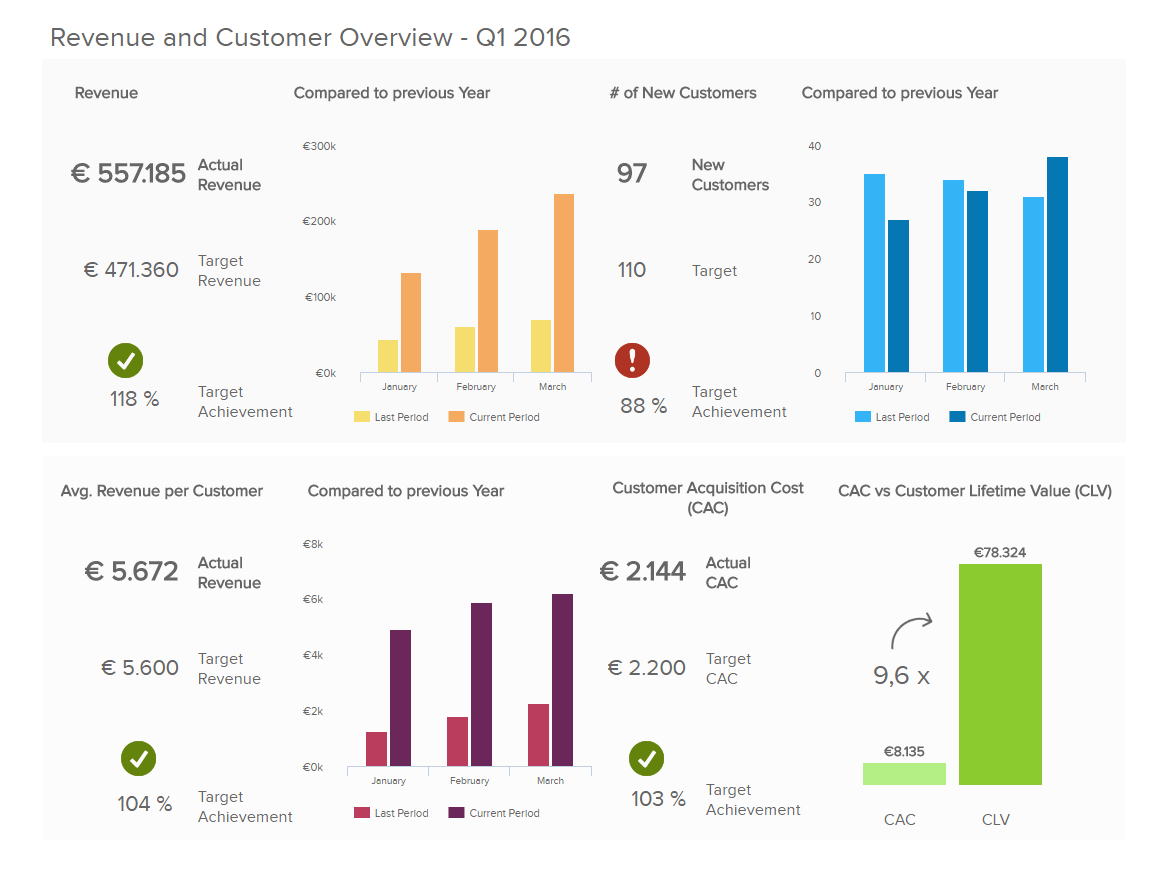
When analyzing insights on a more specific level, you can easily spot if the revenue is approaching your target value, compare it to the previous year, and see how much of the target you still need to work on. The average number of your revenue per customer compared to your targets can also identify on a more specific level how much you need to adjust your strategy based on your customers’ value. If you see your values have exceeded your goals, you can concentrate on KPIs that haven’t yet reached your target achievement. In this specific example, we have gained insights into how to present your management data, compare them, and evaluate your findings to make better decisions.
This clear overview of data can set apart the success of your management strategy since it is impossible to omit vital information. By gathering all your findings into a single CEO dashboard , the information presented is clear and specific to the management’s needs. The best part of this example report is seen through its interactivity: the more you click, the more data you can present, and the more specific conclusions you can look for.
These report templates that we have analyzed and presented in this article can be a roadmap to effectively create your own report or customize your data to tailor your needs and findings.
4. SaaS management dashboard
The next in our rundown of dynamic business report examples comes from our specialized SaaS metrics dashboard .
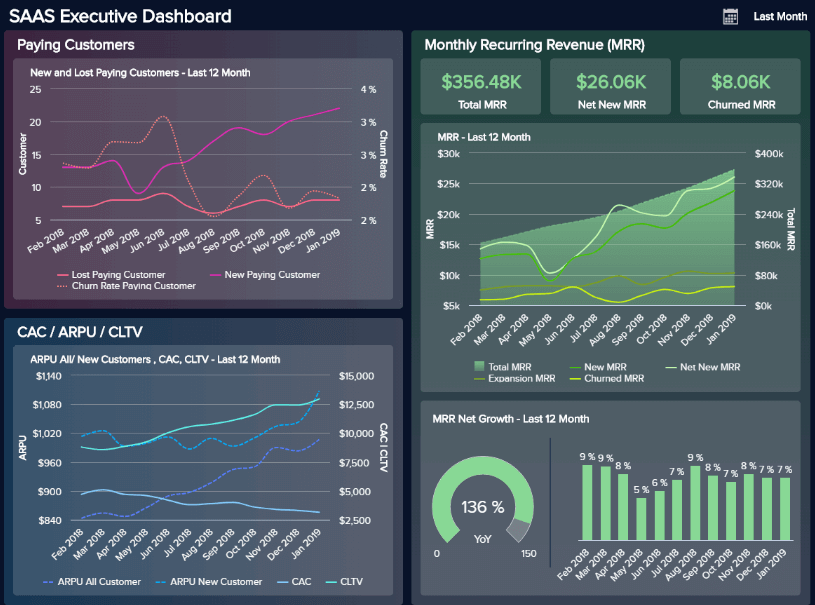
A SaaS company report example that packs a real informational punch, this particular report format offers a panoramic snapshot of the insights and information every ambitious software-as-a-service business needs to succeed.
With visual KPIs that include customer acquisition costs, customer lifetime value, MMR, and APRU, here, you will find everything you need to streamline your company’s initiatives at a glance. This is an essential tool for both short- and long-term evolution.
5. Sales KPI dashboard
Niche or sector aside, this most powerful of online business reports samples will empower your sales team to improve productivity while increasing revenue on a sustainable basis.
A powerful daily business activity report as well as a tool for long-term growth, our sales dashboard boasts a cohesive mix of visualizations built to boost your business's bottom line.
With centralized access to sales graphs and charts based on churn rates, revenue per sales rep, upselling & cross-selling, and more, this is a company report format that will help you push yourself ahead of the pack (and stay there). It’s a must-have tool for any modern sales team.
6. Retail store dashboard company report example
Retail is another sector that pays to utilize your data to its full advantage. Whatever branch of retail you work in, knowing how to generate a report is crucial, as is knowing which types of reports to work with.
Our interactive retail dashboard is one of our finest visual report examples, as it offers a digestible window of insight into the retail-centric unit as well as transaction-based information that can help you reduce costs while boosting your sales figures over time.
Ideal for target setting and benchmarking as well as strategy formulation, this is an unrivaled tool for any retailer navigating their activities in our fast-paced digital age. If you’re a retailer looking for steady, positive growth, squeezing every last drop of value from your retail metrics is essential—and this dashboard will get you there.
7. Customer service team dashboard
As a key aspect of any successful organizational strategy, optimizing your customer service communications across channels is essential. That’s where our customer service analytics report comes into play.
Making your customer service efforts more efficient, effective, and responsive will not only drastically improve your consumer loyalty rates but also set you apart from your competitors.
One of the best ways to achieve a mean, lean, well-oiled consumer-facing machine is by giving your customer service representatives the tools to perform to the best of their abilities at all times. Armed with a balanced mix of KPIs to track and enhance service performance, this most powerful of business report samples will help you drive down response times while improving your first call resolution rates. It’s a combination that will result in ongoing growth and success.
8. Employee performance dashboard
In addition to your customers, your employees are the beating heart of your organization. Our employee dashboard will give you the power to track the ongoing value and productivity of your internal talent.
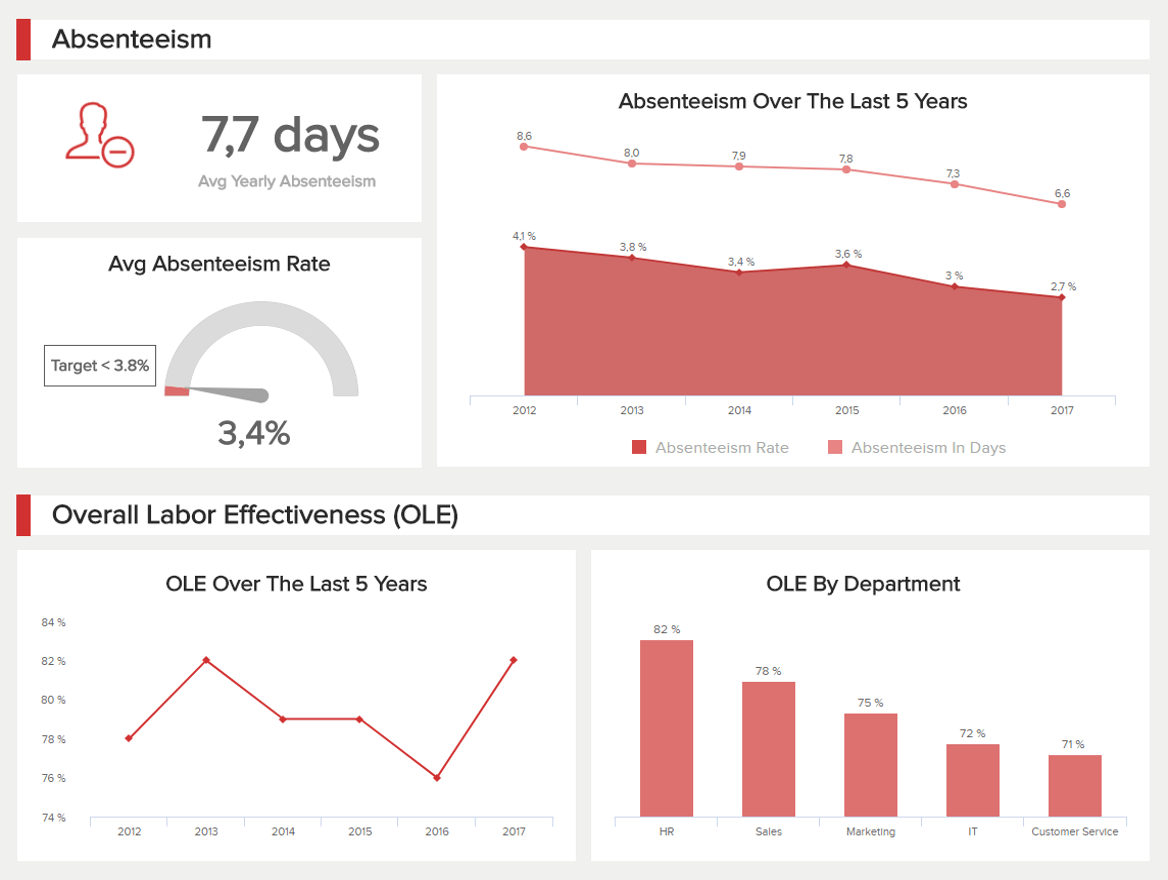
An ideal formal business report example for any modern HR department, this telling dashboard will give you deep insight into how your employees perform and behave over specific timeframes.
Here, you can examine trends in absenteeism rates, track overtime hours by age group, monitor your training costs, and explore peaks and troughs in productivity across the entire workforce. This melting pot of at-a-glance information will empower you to provide training exactly where it’s needed and get to the heart of any issue that’s affecting productivity or engagement levels.
Working with this business report format example consistently will ultimately ensure you get the very best return on investment (ROI) from your internal talent.
9. Marketing KPI dashboard
Without a solid multichannel marketing strategy, it’s unlikely that you’ll ever see a consistently healthy ROI from your promotional efforts. Shooting in the dark regarding marketing will also see you fall behind the competition. Enter our marketing dashboard .
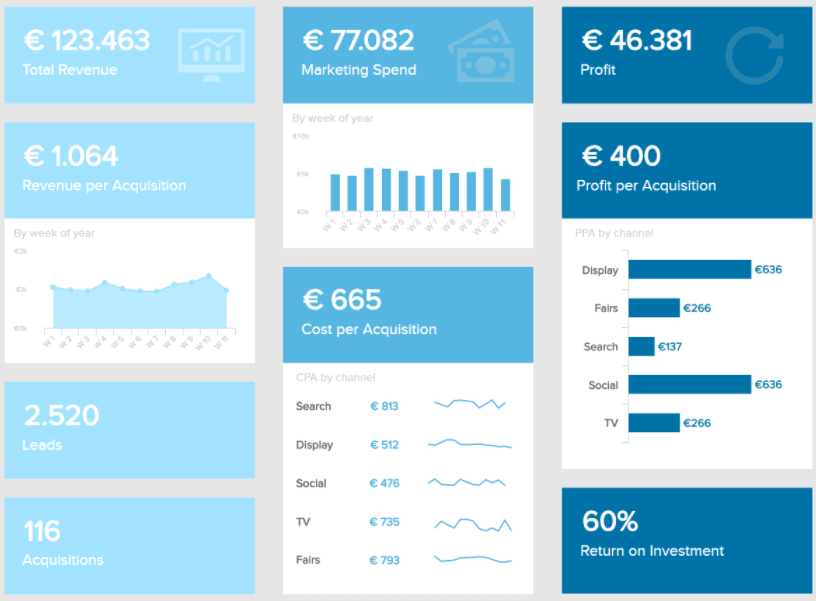
This business report format template brimming with insight, lets you set accurate performance benchmarks while uncovering a wealth of insight from one intuitive dashboard.
To optimize your promotional campaigns and activities, talking to specific audience segments and using the right touchpoints at precisely the right time is essential. Without a targeted approach, all you’re doing is throwing your time and money away.
This effective company report example offers a balanced overview of your campaigns’ performance by offering the tools to dig deep into vital metrics like cost per acquisition (CPA), customer lifetime value (CLTV), and ROI.
This perfect storm of metrics will show you where your communications or campaigns are failing to drive engagement and where they’re yielding positive results. Armed with this critical information, you can optimize all of your efforts to make the biggest possible impact across channels. An essential report design for any modern organization looking to scale swiftly and consistently.
10. Warehouse KPI dashboard
Being a warehouse manager or decision-maker is a high-pressure job where every decision counts. To keep your fulfillment activities and initiatives fluid, functional, and primed for organizational growth, sweating your data correctly is a must.
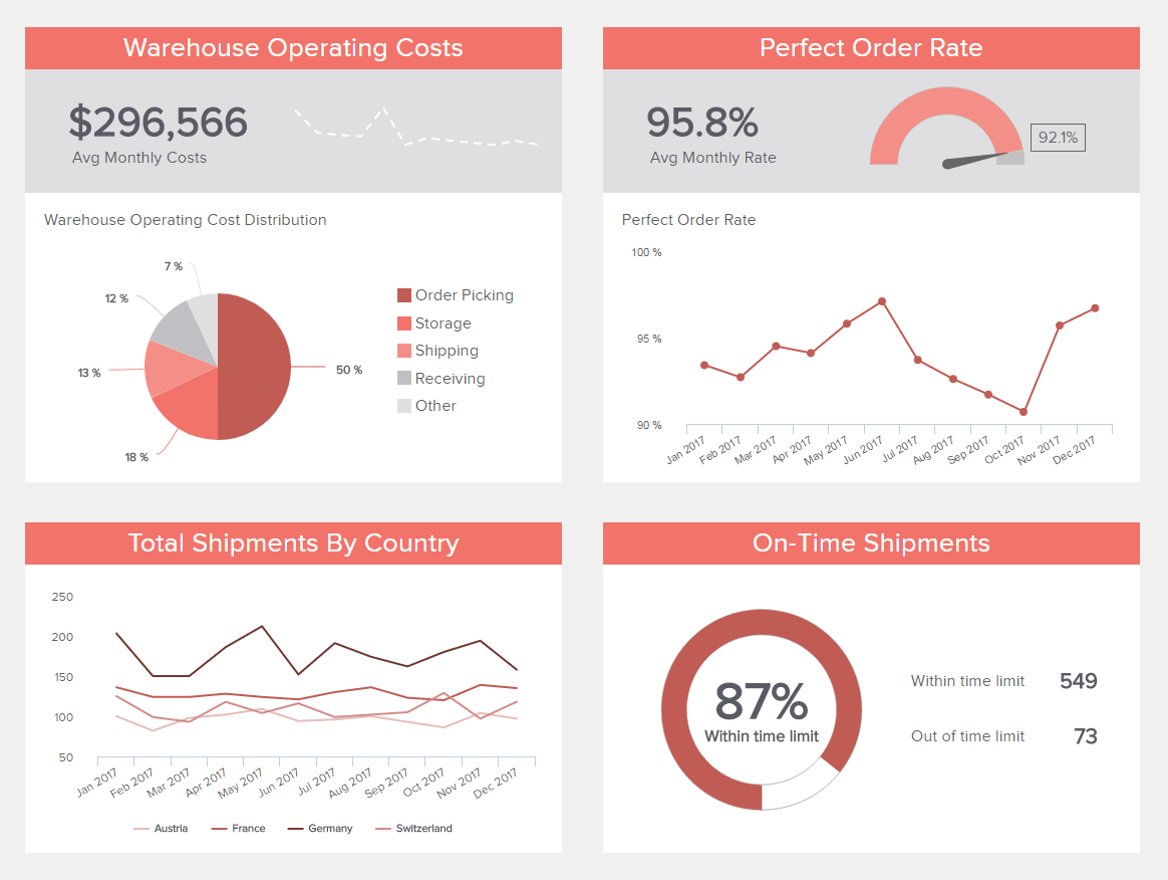
Our warehouse KPI dashboard is a business report sample that aids both real-time decision-making and longer-term strategic planning.
With a powerful selection of logistics-based KPIs, this highly visual business report structure features metrics based on on-time shipment rates, a breakdown of warehouse costs, the number of shipments made over a specified timeframe, and a perfect order rate.
By making this kind of business reports formats a core part of your daily operations, you can eliminate unnecessary costs or activities while boosting overall productivity and significantly improving the success, as well as accuracy, of your warehouse operations. It is an invaluable tool that will help consistently deliver on your fulfillment promises, improving your brand reputation in the process.
11. Cybersecurity dashboard
In our hyper-connected digital age, failing to invest in adequate cybersecurity solutions is the same as leaving your front door wide open when you’re on holiday.
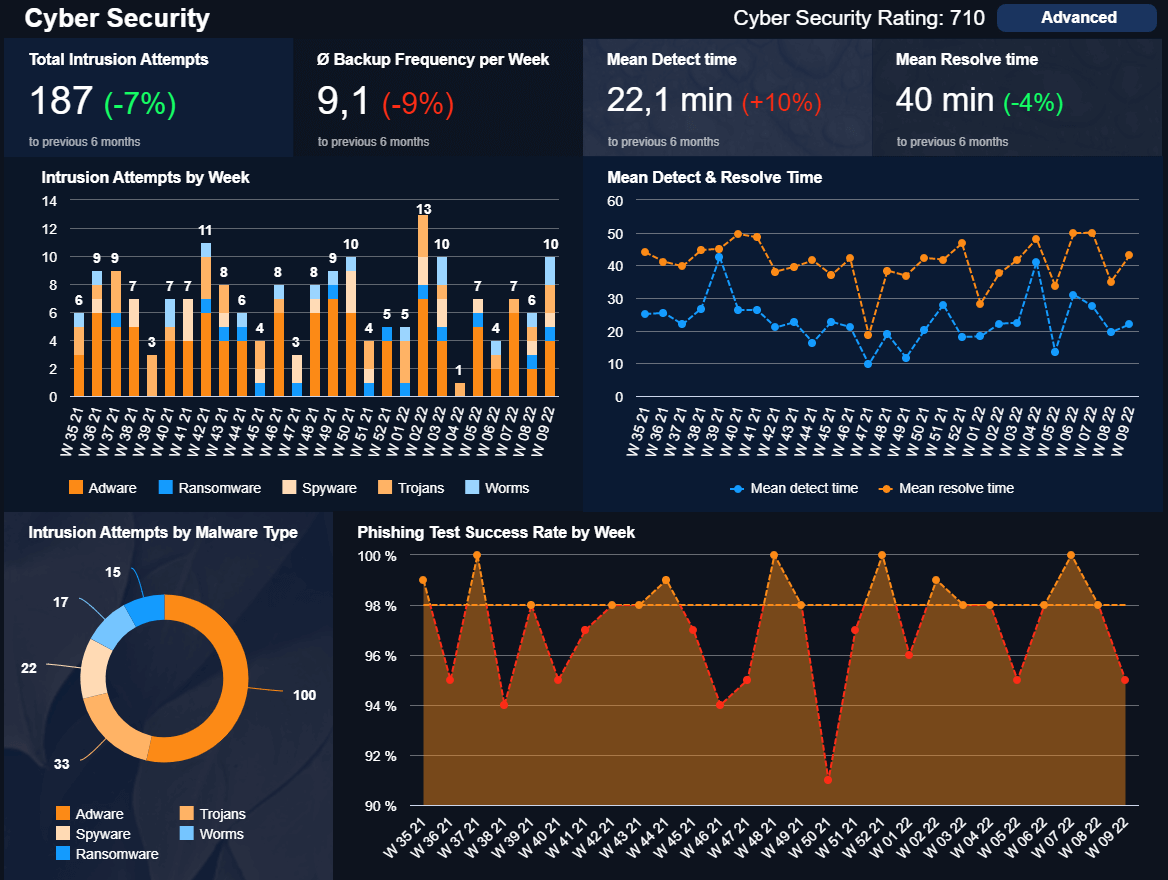
To avoid the devastating impact of organizational cyber attacks or informational breaches, our cyber security IT dashboard will ensure your company is fortified from every angle. This most vital of business report examples will help you fend off any prospective acts of cybercrime while monitoring for any attacks or abnormalities in real-time.
Here, you can keep on top of your cybersecurity rating, track your phishing test success rates, understand how long it takes you to identify an attack (and improve your responsivity), look at how often you backup your company's sensitive information, and discover the most common intrusion rates related to your company from a cohesive space. It’s an essential analysis tool designed to keep your company safe, secure, and happy.
12. CEO dashboard
The CEO is the highest leadership position in an organization. As such, they need to get a complete overview of the entire operations and performance to ensure everything is running smoothly and on track to meet expected goals. Our next example is a scorecard report tracking relevant metrics related to finances, marketing, customer service, and human resources.
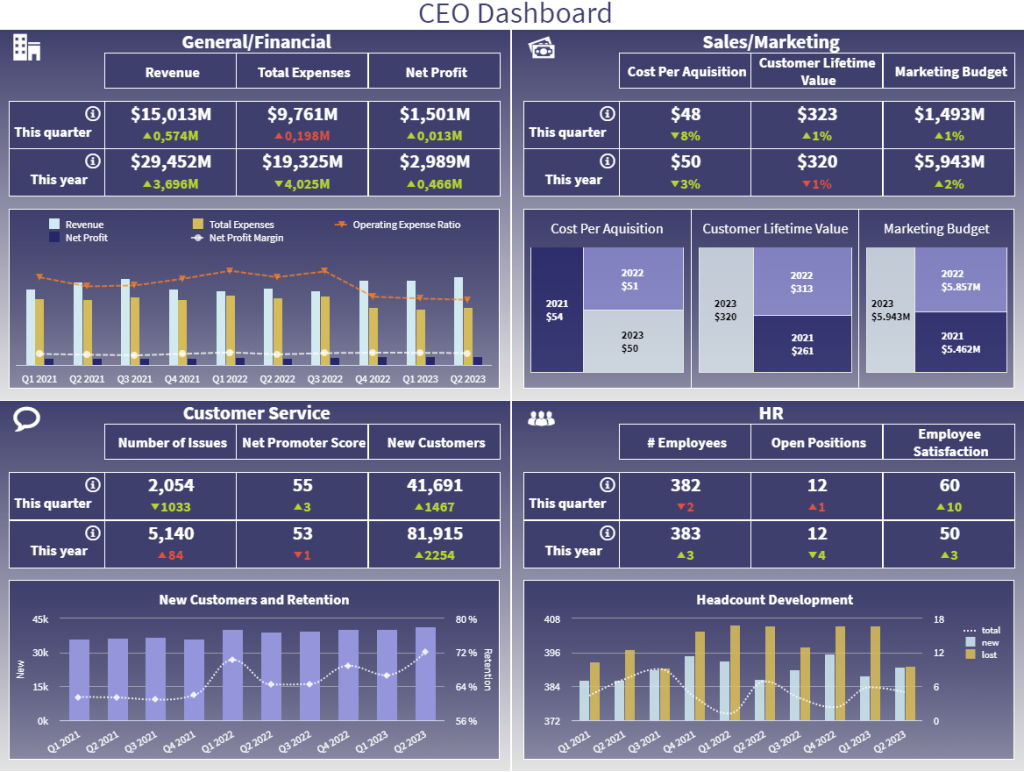
What makes this template so valuable for the CEO is the fact that it offers a long-term view with benchmarks for quarterly and annual performance. This way, leadership can evaluate the development of the different strategies and spot any inefficiencies at a glance by looking at the green or red colors depicted on each KPI. Plus, each section of the scorecard offers a detailed breakdown of additional information to help dive deeper into the reasons behind a specific result.
For instance, we can see that there is an increase in the total expenses in the current quarter. However, when taking a deeper look at the yearly breakdown, we can see that the operating expenses ratio has been decreasing for the past three months. Therefore, the quarterly increase is nothing to worry about.
13. Manufacturing production dashboard
As a production company, you must ensure every aspect of the process is efficiently carried out at its maximum capacity. This means, ensuring machines are working properly, the right amounts of products are being produced, and the least amount are being returned by customers. Our next template aims to help with that task by offering a 360-degree view into a company’s production processes.
With insights into production volume vs. quantity ordered, top 5 machines by production volume, and return items by reason, the manufacturing manager can spot inefficiencies and identify trends to optimize production and ensure the highest possible ROI.
For example, looking at the top machines by production can help you spot the ones that might need some maintenance and plan that maintenance time without affecting production. On the other hand, analyzing the returned items by reason can also help improve customer experience and satisfaction. If you see a large amount of returns due to a broken product, it means you need to improve the quality of your materials or the packaging when they are sent to the customer to keep it safer.
14. IT project management dashboard
Completing a project successfully relies heavily on the team being connected to keep tasks moving at the expected speed. The issue is that it often involves multiple meetings that end up taking a lot of time that could be implemented actually completing the tasks. Our next sample aims to tackle that issue by providing a real-time overview of project development metrics.
At the top of the report, we see a breakdown of the different stages of the project with a development percentage and a projected launch date. This is great information to have as it can inform the team about the status of the entire project and any external stakeholders as well.
We then get insights into the project budget, overdue tasks, upcoming deadlines, and employee workload. This is invaluable information that can help optimize any bottlenecks and increase overall efficiency. For instance, we can see that Georg and Nancy are 10+ days overdue with their tasks which is not good for the project. However, a deeper look shows us that these two employees are the ones with the biggest workload, which means they might need some help from other team members to speed up their tasks.
15. HR diversity dashboard
Diversity in the workplace has become a big priority for organizations and prospective talents. Each year, more and more businesses realize the value of having employees from different backgrounds and cultures as a way to boost their strategies and overall growth. That being said, to be considered a diverse company, you need to ensure your workforce feels comfortable and that the same opportunities are being given to all. Enters our last business report template.

The template above offers a view into different diversity management metrics from recruitment to talent management. Through this insightful report, HR managers can test the success of their diversity strategies and spot any areas of improvement to ensure the highest level of employee satisfaction. The template is highly interactive and offers insights into diversity by gender, ethnicity, and disabilities.
Analyzing the content of the report, we can see that black employees are the ones with the highest voluntary turnover rate. This is something that needs to be looked into to find the reasons why these employees are not feeling comfortable at the company. On the other hand, we can see that the organization is 1% above the 2% industry standard for hiring employees with disabilities. This is a great indicator, and it can translate into a low 7% of voluntary leaves by these workers.
Now that we’ve looked at report samples, let’s consider the clear-cut business-boosting benefits of these essential analytical tools. These perks will make your company stronger, more fluent, and more efficient on a sustainable basis.
Why Do You Need Business Reports?

These reports also enable data collection by documenting the progress you make. Through them, you have the means to compare different periods and activity, growth, etc. You can better see which products or services are more successful than others, which marketing campaign outperforms which other, and which markets or segments require more attention. Collecting all this data is indispensable – and by doing so, you build a paper trail of your past (or, namely, a data trail). They let people outside the company (like banks or investors) know about your activity and performance and enable stakeholders to understand your organization’s tangible and intangible assets.
- Risk assessment & opportunity: With a business report, you can increase the understanding of risks and opportunities within your company . Sample reports accentuate the link between financial and non-financial performance: they streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve overall cohesion in an informed, commercially ‘safe’ way.
- Trends & connections: Business report samples can help you compare your performance to other internal units or companies in the same sector. On a more specific level, a report template can help you dig thoroughly into operational metrics and details and discover correlations that would be otherwise overlooked. In today’s hyper-connected digital age, gaining a deeper insight into your data will empower you to formulate strategies that will accelerate key areas of your business growth through trend identification. This fact alone highlights the importance of a business analysis report.
- Business intelligence (BI): If used correctly, the best BI tools will answer a vital question: ‘Will I survive on the market?’ By creating a business report of a company built to improve your BI activities and answer essential organizational questions, you will gain the ability to tackle deeper specific insights that can bring operational value and control the overall expenditures. By knowing how to set up such a report with specific samples and templates, you can provide building blocks to establish a successful business intelligence strategy.
- Buy-in: While there are many different types of business reports for a company, they all have one common trait: gathering data and tracking the business activities related to something specific. By working with the right reports, users can perform in-depth visual analyses of many key areas or functions and provide informed recommendations that will ultimately improve efficiency and encourage innovation. Regardless of how good or beneficial an idea might be , getting buy-in from senior executives or external partners is often a major roadblock to progress. However, a good report template presents a level of depth and presentation that is both factual and convincing and will encourage buy-in from the people with the power to sign off on new strategies, initiatives, or ideas.
- Operational efficiency: The more factual the report is, the clearer the data. When your data is well organized and crystal clear, it’s possible to interpret your business activities cost-effectively, reducing the time required to analyze findings while saving countless working hours sifting through metrics for actionable insights. A good template presents an in-depth analysis where the writers show how they have interpreted their findings. For example, a marketing report can reduce the time needed to analyze a specific campaign, while an HR report can provide insights into the recruiting process and evaluate, for example, why the cost per hire increased?
- Specificity: When you create a business information report, you are giving yourself a key opportunity to address specific issues that are often used when decisions need to be made. As author Alan Thomson says, “A company report conveys information to assist in business decision-making. [It] is the medium in which to present this information.” They have several purposes: some record information to plan for the future, some record past information to understand a situation, and others present a solution to a pressing problem. Some executive dashboards are for daily usage, while a monthly business report template will help you pinpoint your activities on a more gradual, incremental basis. They are all essential to commercial success, as they bring clarity to complex analysis. As mentioned earlier, the clearer the data, the more cost-effective results will be, so keeping in mind the exact data to incorporate into this kind of report should be essential in deciding what kind of report to generate. You can find multiple key performance indicator examples in different industries, which should be considered when creating that kind of report. You can also generate an interdepartmental report or between businesses to compare industry values and see how your company stands in the market.
- Accuracy & consistency: In The Age of Information, data is a vast landscape, and if you want to use it to your advantage, aiming for consistency and accuracy is key. If your data is off or presents hit-and-miss findings, it could cost your company in the long run. Working with an online dashboard tool to produce your reports is an incredible advantage for the ease of use, the time saved, and, most importantly, the accuracy of the information you will use. As you work with real-time data, everything on your report will be up-to-date, and the decisions you will take will be backed with the latest info. Business report examples are significantly helpful when you need to explore your data and perform data analyses to extract actionable insights. They will deliver an important added value to your report thanks to the visualization of your findings, bringing more clarity and comprehension to the analyses, which is their primary purpose.
- Engagement: As intuitive, digestible, and visual tools, business-centric reporting tools are easier to understand and tell a story that is far more likely to resonate with your audience. While exploring your data, with deeper insights generated with just a few clicks, the report doesn’t have to be dull, boring, and lost in hundreds of pages or spreadsheets of data. If you create a report that is clean and customized, you will bring more value than by printing or searching through a spreadsheet. Achieving a design like this is simple with the right KPI dashboard software . Imagine yourself in a meeting with 200 pages of analysis from the last 5 years of business management. One participant asks you a specific question regarding your operational costs dating 3 years back. And you’re sitting there, trying to find that specific piece of information that can make or break your business meeting. With business dashboards , you cannot go wrong. All the information you need is generated with a click, within a click.
- Benchmarking: If you know how to set up a business-centric report with efficiency, you will gain the ability to set defined, accurate benchmarks. By frequently setting targets based on your most important organizational goals and working with visual reporting tools, you will keep your organization flowing while catalyzing your overall growth and productivity levels.
- Communication: One of the best uses of these tools is improving internal collaboration and communication. By gaining 24/7 access to your most essential business data while enhancing the way you analyze and present it, you will empower everyone in the business with better access to information, which, in turn, will enhance internal communication and collaboration.
- Innovation: The intuitive nature of these reports makes them the most efficient way to steer a progressive analytical strategy. As such, it’s easier (and quicker) to uncover hidden insights, spot trends, and hone in on critical information. It’s this speed, ease, and accuracy that frees creativity and improves innovation across the organization, accelerating growth as a result.
These reports can also be of many different types, but they all have one common trait: gathering data and tracking the organizational activities related to something specific. From there, their author(s) will often perform an analysis and provide recommendations to the organizations.
How To Generate A Business Report
The primary importance of a corporate-centric report lies in gaining confidence and clarity. Before starting to create it, it’s vital to establish the goals and the audience. Knowing who you want to direct it to is key in its elaboration, from the tone, vocabulary/jargon you choose to the data you will focus on. A report to external stakeholders, to the CEOs, or to the technical engineers’ team will be drastically different from one another.
Likewise, the scope varies according to the objective of the report. State beforehand the needs and goals to direct you on the right path. It should be impartial and objective, with a planned presentation or dashboard reporting tool , which enables an interactive flow of data and immediate access to every piece of information needed to generate clear findings.
To help you write your daily, weekly, or monthly business-centric report template with confidence, let’s go over some essential steps and tips you should focus on:
1. Consider your audience
First of all, if you want to understand how to do a business report the right way, you have to think of your audience from the outset. Your reporting efforts must make sense and offer direct value to the end viewer or user - otherwise, they’ll be meaningless. That said, it’s critical that you take the time to consider who will use the reporting tool most and which information or features will add the most value, helping improve the organization in the process. Take the time to understand your audience, and your reporting tools will not only meet expectations but exceed them - one well-placed visualization at a time.
2. Determine and state the purpose
As we stated in the previous paragraph, defining the needs of your audience is vital to reporting success. As we said, a report usually assists in decision-making and addresses certain issues. You can state them at the beginning of the report. The more clear and specific the goal, the better the content will be. You won’t lose time adjusting information when you present your purpose in a clear and well-defined manner.
3. Use a mix of real-time and historical data
Another key component of this report is making sure you’re free of any informational blind spots. So many companies work with one form of metric, stunting their organizational progress in the process. To drill down deep into detailed pockets of information and gain a panoramic view of specific trends or patterns, working with a balanced mix of historical and real-time data is key. Doing so will empower you to capitalize on potential strengths while learning from historical weaknesses. This balanced approach will also give you the tools to develop strategies that return the best possible ROI while making powerful decisions under pressure.
4. Set actionable targets and goals
Once you’ve curated your informational sources and defined your audience, you should set actionable goals. Setting the right benchmarks will help you track your ongoing success with pinpoint accuracy while defining goals or targets will give you the insight you need to work with the right KPIs while ensuring your company is moving in the right direction. Taking the time to set actionable goals and targets that align with your organizational strategy will ensure your reports offer a consistently healthy ROI.
5. Define your reporting frequency
Another key component of successful organizational reporting is deciding how often you will analyze your metrics and information. Depending on the function or the goals you’re looking to achieve, you should decide whether your dashboard will serve as a daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly reporting tool. Setting the right frequency will ensure your analytical strategy is fully streamlined while connecting you with the insights that count most at exactly the right time. The best modern reporting tools also offer automated functionality, helping to monitor insights and offer alerts without human intervention - the best way to save time while ensuring you never miss a critical piece of information again.
6. Gather and organize the information
Now that the purpose and scope are clearly defined, you can start gathering the data in any form that can address the issue. Thanks to that information, you will carry out data analysis to understand what lies beneath and to extract valuable insights. These findings need to be balanced and justifiable – what significance they have to the report's purpose. Identifying key performance indicators for a specific company, organizing, comparing, and evaluating them on the needed level, can be one of the most important parts of creating this kind of report. An example of a business report that shows how to extract and define your analysis can be found above in the article, where we presented our visuals.
7. Present your findings
Explain how you uncovered them and how you interpreted them that way. Answer the original issue by detailing the action to take to overcome it and provide recommendations leading to a better decision-making process. A best practice to present the insights you have drawn out is using dashboards that communicate data visually in a very efficient way. A dashboard software like datapine can precisely answer that need while helping you with data exploration at the same time, which is a crucial part. When you click on a specific part of the dashboard, you can easily access your data in a more in-depth approach.
Comparing your findings is also one of the features you can use if you are asking yourself what has changed in relation to a specific period. When you assess these datasets in just a few clicks on your monitor, the whole reporting process and measurement of your strategy can be done in minutes, not days. Evaluating findings in today’s digital world has become one of the main focuses of businesses wanting to stay competitive in the market. The faster you can do that, the more information you gain, and the more successful your actions will become.
8. Align your visualizations
Expanding on presenting your findings, it’s also important to get your design elements right when considering how to write a business report. As a rule of thumb, your most essential at-a-glance insights should be at the top of your dashboard, and you should aim to be as clean, concise, and minimal as possible with your presentation to avoid cluttering or confusion. To improve your visual storytelling and bring every key element of your report together cohesively, getting your dashboard design just right is vital. Our essential guide to data visualization methods will help to steer your efforts in the right direction.
9. Proofread your reports
When you’re looking at a polished example of a business report, you’ll notice that every element of design and content is immaculate and makes complete logical sense. That said, to get the best returns for your analytical efforts, proofreading your reports is vital. Work through your report with a fine-toothed comb and ask trusted colleagues in your organization to do the same. Once you’ve carefully proofread your entire report, you can collectively tighten up any sloppy design elements, typos, misleading copy, and bad visual placements. Doing so is vital because it will make your examples of business reports slick, actionable, accurate, and built for success.
10. Be responsive
While modern reporting dashboards are dynamic and interactive in equal measure, it’s important that you also remain robust and responsive when writing a business-based report. What does this mean, exactly? It means that in the digital age, the landscape is always changing. As such, if you want to get the most from your reports or dashboards, you must commit to editing and updating them according to the changes around you. In an informational context, what is relevant today may be redundant tomorrow, so to remain powerful and relevant, your reports must always be optimized for success. When you write a business-style report, you should understand that, to some extent, you will need to rewrite it repeatedly. Remember, commit to regularly assessing your reports, and success will be yours for the taking.
You can easily find a sample of a business report on the Internet, but not all of them fit your needs. Make sure, at any moment, that the report you want to create is accurate, objective, and complete. It should be well-written, in a way that holds the reader’s attention and meets their expectations, with a clear structure.
Common Challenges Of Business Reports
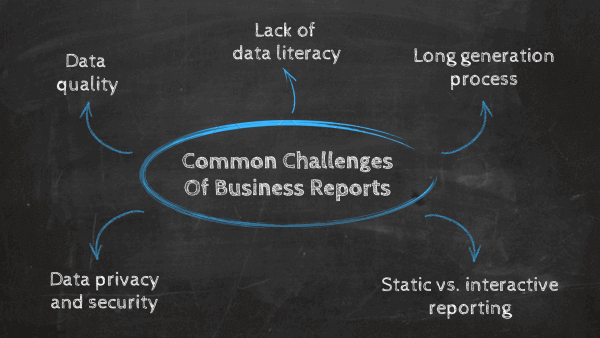
As we just learned from the previous section, generating a successful report requires carefully following some steps and considerations. This often comes with challenges and limitations that users face during the generation and analysis process. To help you be aware of those challenges and how to overcome them efficiently, we will list some of the most common ones below.
- Data quality
All the time and effort dedicated to the reporting process will be for nothing if you are not working with high-quality information. Believe it or not, according to recent reports , 41% of companies cite inconsistent data across technologies as their biggest challenge. With only 16% labeling the data they are using as “very good”.
This presents a huge challenge as the consequences of poor data quality can be quite expensive since organizations are basing their most important strategic decisions on unreliable insights.
To prevent this issue from affecting you, it is essential to invest time and money in implementing a thoughtful data quality management plan to ensure your information is constantly checked under specified guidelines. Putting extra attention to the cleaning and constant manipulation of the information is also a huge aspect of the process.
- Lack of data literacy
Another big challenge that businesses face when implementing reporting practices is the level of literacy of their employees. As mentioned earlier in the post, the success of the entire process relies heavily on the entire workforce being involved in it and collaborating with each other. The issue is that generating a report and analyzing the data can be very intimidating for non-technical employees who often don’t have the necessary skills or confidence to integrate data-driven activities into their daily work.
That is why carrying out a careful analysis of the literacy level across your workforce can help you understand the actual situation and offer training instances to anyone who needs it. Paired with that, investing in self-service BI tools that allow any user, regardless of their technical knowledge, to generate a business report with just a few clicks is a great way to approach this challenge.
- Long generation processes
It is not a secret that manually generating a business report can take a lot of time and effort. In fact, in some cases, when a report is finally completed, the information in it might not be entirely valuable anymore. Luckily, this challenge has been tackled a long time ago thanks to the power of automation.
Modern online reporting tools offer users the possibility to automatically generate a report in a matter of seconds, eliminating any form of manual work. All they need to do is connect their data sources, select the KPIs they want to display, and enjoy a visually appealing and fully functional report in just a few clicks. This enables organizations to focus on the important part, which is extracting powerful insights to inform their strategies.
- Static vs. interactive business reports
Traditionally, these reports generated with tools such as Excel or PowerPoint have been static and full of text and complex numbers. Making it impossible to extract deeper conclusions from them or act on fresh insights. This is not to say that they are completely unuseful, but their historical and static perspective makes them less effective, especially considering how agile decision-making can represent a huge competitive advantage for organizations today.
To help you make the most out of your data-driven efforts and tackle this common limitation, we recommend you invest in tools that offer dynamic reports. BI reporting tools , such as datapine, give you the ability to generate interactive real-time reports, like the ones we saw earlier, which can be easily filtered to explore different periods or lower levels of data. This will give you the power to extract deeper and fresh insights to boost your strategies and growth.
- Ensuring data security and privacy
In the digital age we live in, we need to be fully aware of the risks of using online tools to manage our business’s operations. Studies have shown an increasing trend in cyberattacks and data breaches that has left decision-makers concerned about how they manage their sensitive data. One of these attacks can significantly impact an organization’s reputation but also incur considerable costs that can be hard to come back from. According to recent research, these types of breaches cost businesses an average of $4.35 million in 2022.
All of this makes security and privacy a big challenge for businesses of all sizes. Especially regarding their report-related activities, as they contain sensitive information about the company and its clients. Luckily, modern SaaS BI tools offer high levels of security to help you keep your data secure at all times, from the moment it is generated to the time it is shared with different stakeholders. Therefore, it is important to consider this topic before investing in such a tool.
Key Takeaways Professional Business Reports
"Once we know something, we find it hard to imagine what it was like not to know it." - Chip & Dan Heath , Authors of Made to Stick, Switch.
We live in a data-driven world, and as a business, it’s up to you to move with the times. If you ignore the power of smart data analytics, you are only stunting your own commercial progress.
We’ve explored many shining business reports examples, and one thing is abundantly clear: if you embrace the power of digital reporting, your company will be bigger, better, and exponentially more informed. The more confident and informed you are as a business, the better you will be able to respond to constant change. In today’s digital world, it doesn’t matter what sector you work in. If you’re rigid in your approach to data, you will get left behind. Digital reporting dashboards are the only way forward.
So, you now know what business reports are, how to structure and write them , and how they can benefit your business. Committing to the right reporting and information delivery can have a significant impact on your organization and orientate its strategy better. For more ideas about business reporting in a more specific, function-related way, you can dig deeper into some of our popular articles on sales reports and marketing reports !
Don’t miss out on that opportunity and start now with datapine’s online reporting software , and benefit from a free 14-day trial ! You won’t regret it.
👀 Turn any prompt into captivating visuals in seconds with our AI-powered visual tool ✨ Try Piktochart AI!
- Piktochart Visual
- Video Editor
- AI Design Generator
- Infographic Maker
- Banner Maker
- Brochure Maker
- Diagram Maker
- Flowchart Maker
- Flyer Maker
- Graph Maker
- Invitation Maker
- Pitch Deck Creator
- Poster Maker
- Presentation Maker
- Report Maker
- Resume Maker
- Social Media Graphic Maker
- Timeline Maker
- Venn Diagram Maker
- Screen Recorder
- Social Media Video Maker
- Video Cropper
- Video to Text Converter
- Video Views Calculator
- AI Brochure Maker
- AI Document Generator
- AI Flyer Generator
- AI Infographic
- AI Instagram Post Generator
- AI Newsletter Generator
- AI Report Generator
- AI Timeline Generator
- For Communications
- For Education
- For eLearning
- For Financial Services
- For Healthcare
- For Human Resources
- For Marketing
- For Nonprofits
- Brochure Templates
- Flyer Templates
- Infographic Templates
- Newsletter Templates
- Presentation Templates
- Resume Templates
- Business Infographics
- Business Proposals
- Education Templates
- Health Posters
- HR Templates
- Sales Presentations
- Community Template
- Explore all free templates on Piktochart
- Course: What is Visual Storytelling?
- The Business Storyteller Podcast
- User Stories
- Video Tutorials
- Need help? Check out our Help Center
- Earn money as a Piktochart Affiliate Partner
- Compare prices and features across Free, Pro, and Enterprise plans.
- For professionals and small teams looking for better brand management.
- For organizations seeking enterprise-grade onboarding, support, and SSO.
- Discounted plan for students, teachers, and education staff.
- Great causes deserve great pricing. Registered nonprofits pay less.
What is a Business Report? (Examples, Tips and How to Make One)

According to a recent survey by Zapier , 76% of respondents said they spend 1-3 hours a day simply moving data from one place to another. Additionally, 73% of workers spend 1-3 hours just trying to find relevant data or a particular document. Another survey by TrackVia found that 44% of workers spend more than one day per week on manual, administrative tasks such as generating reports .
Fortunately, there are tools available to automate the report creation process and produce high-quality reports efficiently. However, it’s essential to understand the key factors that make a report effective and distinguish your report from the rest, without relying on plain Excel/PowerPoint tools.
Are you ready to take your report writing skills to the next level?
A business report is a document that presents information in a structured format, typically written for a specific audience or purpose. Business reports are used to convey data, research findings, recommendations, and other types of information in a clear, concise, and organized manner.
Business reports may be written for a variety of contexts. They may vary in length and complexity, depending on the type of information being presented and the intended audience.
You can also jump right into creating business reports by selecting a template and following along this guide, or create a report using our AI-powered report maker for free today.
Table of Contents
General business reporting templates, specialized business reporting examples, other reports, what makes a great business report format, what are the five main parts of a business report, how to present the report in a more visual way, and now, over to you.
- Progress reports : These are reports used to easily track progress on a particular project or activity, and can be divided into daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly progress reports.

- Feasibility reports: These are reports that assess the feasibility of a particular project or initiative, such as a new product or service.

- Executive Summary Reports: These reports provide a brief summary of a larger report in business management. They are typically used to provide key decision-makers with a quick overview of the report topic.

- Financial reports : These are reports that present financial information, such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, which measure performance of the company.

- Annual reports : These are reports that provide an overview of an organization’s performance over the course of a year, including company goals, new insights, and average revenue.

- Sales and Marketing Reports : These reports provide relevant information on sales and marketing activities, such as sales forecasts, customer overview demographics, marketing report and market research, typically created by sales rep.

- Human Resources Reports : These reports provide information on employee-related matters, such as recruitment, training, and performance management.

- Incident Reports: These reports document workplace incidents, such as accidents, injuries, or security breaches. They may be used for legal or insurance purposes.
- Environmental Reports: These reports assess the environmental impact of a company’s operations. They may include information on energy consumption, waste management, and carbon emissions.

- Investigative reports : These are reports that investigate a particular issue, such as a workplace incident or accident.

- Academic reports: This is an analytical report used in academic settings to convey research findings, such as lab reports, research reports, and case studies.
- Technical reports: These are reports that communicate technical information, such as engineering reports, scientific reports, and project reports. It may contain all the relevant explanatory reports and research methods.

There are several elements that make a great formal business report, including:
Clear purpose and scope
A report can contain a lot of information, it is important not to lose the bigger picture. It should be easy to access the report’s main points through a table of contents at the introduction.
Define the purpose and scope of the entire report : Determine the objectives of the report and the information that needs to be collected to achieve those objectives.
Accurate and relevant metrics/data
Identify the sources of information : Determine where the critical information can be found. Sources can include primary sources such as surveys, interviews, and experiments, or secondary sources such as books, articles, and online databases.
Collect the historical data: Gather the necessary data by conducting interviews, surveys, experiments, analytical reports, or other means. Be sure to record and organize the data in a systematic and organized manner.
The gathering of relevant data is often time consuming. It would be good to collaborate on this process and assign multiple stakeholders different portions of the report so that the information gathering isn’t spent on analytical reports by one individual only. Piktochart has the ability to help you collaborate in teams specifically for this purpose.
Comprehensive analysis
Analyze the data : Once the data has been collected, conduct an in depth analysis to identify patterns, trends, and relationships. Use statistical tools, software, or other analysis methods to make sense of the data.
Go from big picture to small details. It is good practice to create an outline of the report and what should be communicated in official document before going into the actuals of putting the report together.
Break the analysis down into multiple pages. Use a page to convey one main point instead of cramming in multiple charts and figures.
Clear and concise writing
Interpret and present the findings : Draw conclusions based on the data and present the findings in a clear and organized manner. Use charts, tables, graphs, and other visual aids to help convey the factual information.
For example, one may opt for the use of bullet points sparingly and opt to make the sentences shorter and without jargon. A visual layout of two columns may also help in some cases.
Effective communication in research report
A report can be consumed digitally or via print. If it’s consumed digitally e.g. in a single dashboard , you can provide a TLDR summary or explanatory report for the readers via email so that they would know what to expect.
Visual aids
The best option here is to go with diagrams, images, tables and charts that help to convey the main point of a particular page.
If the report is hosted online, it is also possible to include other videos or audio content to get the viewers interested.
Recommendations and conclusions
Revise and finalize the report: Review and revise the report to ensure that it is accurate, complete, and well-organized. Be sure to proofread for spelling errors, grammar mistakes, and punctuation.
It is important to address the concerns that the key decision maker has about the progress report and aid decision making process. The language and tone of the report should always be future-looking and positive. You can do this by balancing potential risks and key opportunity areas.
Professional formatting and presentation
Aim to use brand colors and fonts throughout the whole presentation. These “tiny” signals give the impression that the report has been professionally designed.
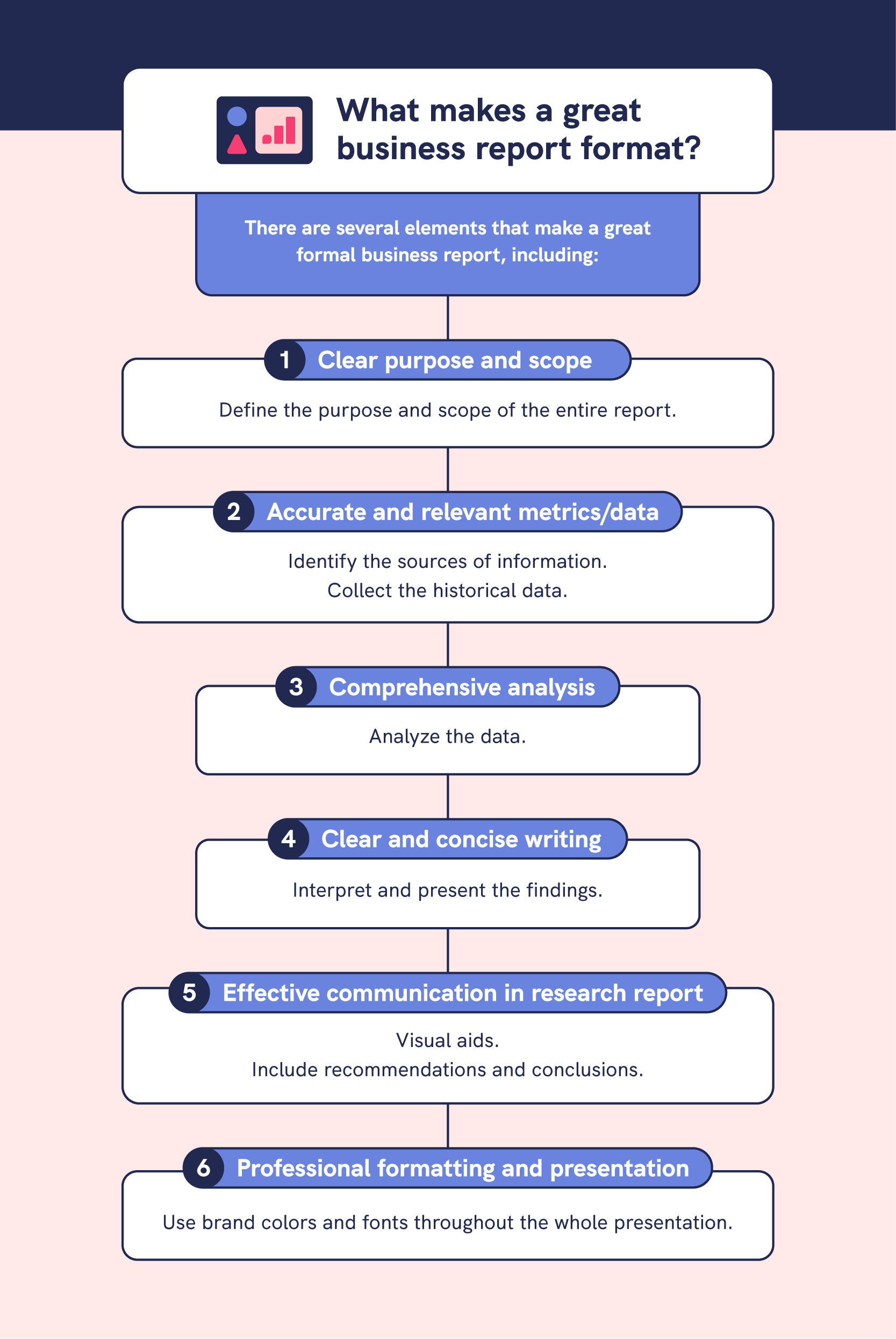
Business reporting typically includes:
- Introduction that provides background information. The title and table of contents can go here. Occasionally, it also includes some brief opening remarks from the leadership team.

- Main body that presents the data or findings. This can be broken down into several pages and it is best to present one salient piece of information per page. The aim is not to reduce the number of pages, but to go for concise writing so that there is a strong message per page.
- Conclusion that summarizes the key points.

An important part of conclusion is recommendations for further action. A report would be incomplete if it does not bear any future-forward messages for the business/activity.

While there is no specific format that has to be followed, Piktochart has some great business report examples for you to get started. Sign up to access more professionally designed templates of presentations , infographics , social media graphics and more.
Use charts and diagrams
Visual aids such as pie charts, bar graphs, and line graphs can help to convey complex information in a clear and concise manner.
Choose the right type of chart or diagram
There are many different types of charts and diagrams available, including bar charts, pie charts, line graphs, scatter plots, flowcharts, and more. Choose the type of chart or diagram that best represents the data you are presenting and is most appropriate for your audience.

Keep it simple
While charts and diagrams can be useful for presenting complex information, it’s important to keep them simple and easy to understand. Avoid cluttering your chart or diagram with too much information, and use clear and concise labels and titles.
Use appropriate scaling
When creating a chart or diagram, it’s important to use appropriate scaling to ensure that the data is accurately represented. Make sure that the scale of the chart or diagram is appropriate for real value of the data you are presenting, and avoid distorting the data by using uneven scales.
Provide context
Charts and diagrams can be difficult to interpret without proper context. Make sure to provide context for your data by including clear and concise explanations of what the chart or diagram represents and how it relates to the rest of the report.
Use color strategically
Color can be a powerful tool for highlighting key data points or drawing attention to important information. However, it’s important to use color strategically and sparingly to avoid overwhelming your audience.
Use color sparingly
Color can help to highlight important information and make the report more visually appealing.
While color can be a powerful tool for emphasizing important information, using too much color can be overwhelming and distracting. Use color strategically to draw attention to key data points, headings, or other elements that you want to emphasize.

Choose colors carefully
When selecting colors, consider the target audience and purpose of the report.
Stick to a color scheme that is appropriate for the subject matter and aligns with the company’s branding. Avoid using too many bright or bold colors, which can be jarring to the reader.
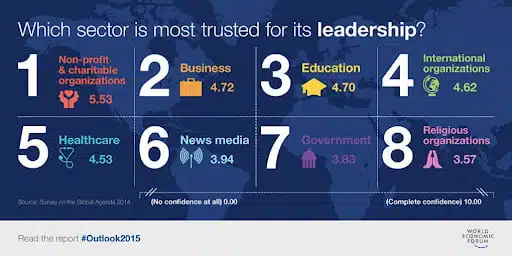
Use contrast
One of the most effective ways to use color in a business report is to create contrast between different elements. For example, use a bold color for headings or subheadings to make them stand out from the surrounding text.

Use color to organize information
Color can be a useful tool for organizing information and making it easier to scan. Consider using color to create sections or categories within the report, or to distinguish between different types of data.
Be consistent
To avoid confusion, it’s important to be consistent in your use of color throughout the report. Use the same colors for the same types of information, and make sure that the colors you use are consistent with the company’s in house format or branding guidelines.
Use a consistent layout
Using a consistent layout throughout the report broken down by headings and subheadings can help to make it more visually appealing and easier to follow.
A single-column format is often used because it is easier to read and allows for a more logical flow of information. It also allows for the use of larger fonts and more white space, which can help improve readability.
In some exceptions, some reports may use a multi-column layout, typically with two columns, if they contain a large amount of data or if the report is intended to be read on a digital device, such as a tablet or computer screen. A multi-column format can help improve the organization of the data and make it easier to compare information across different sections.
Choose an appropriate and concise length
Do not cram too much information within a single page. Here are some more helpful tips on the language that you can use for business reports.
Use active voice
Active voice makes your writing clearer and more concise, and it can help you communicate your ideas more effectively.
For example, instead of writing “The report was analyzed,” write “We analyzed such a report.”

Avoid overly technical language
While some technical language may be necessary, avoid using jargon or technical terms that your readers may not be familiar with. If you must use technical terms, provide clear definitions or explanations.
Use simple, clear sentences
Avoid long, convoluted sentences that are difficult to understand. Instead, use simple, straightforward sentences that clearly communicate your ideas.
Don’t use more words than necessary to convey your message. A sentence should not contain more than 20-30 words (unless you’re writing a technical or academic report).
The average length of an annual report is 10,000 words (50 pages) for a smaller company and 50,000 (150 pages+) words for an enterprise. Typically, not every page contains text, as some may have more charts/tables.

Use bullet points, tables, and graphs to help convey your ideas concisely.
Use appropriate tone
The tone of your report should be professional and objective. Avoid using emotional language or language that is overly informal.
For example, “I’m totally excited to announce that our new product is going to blow the competition out of the water! It’s absolutely amazing and customers are going to love it.”

This sentence uses informal language (“totally excited”) and emotionally charged language (“blow the competition out of the water,” “absolutely amazing,” “customers are going to love it”) that may not be appropriate for a business report.
Ultimately, the language you use in your business reports should be tailored to your audience and the purpose of the most professional business report itself. Consider who will be reading the formal business report and what information they need to know, and adjust your language accordingly.
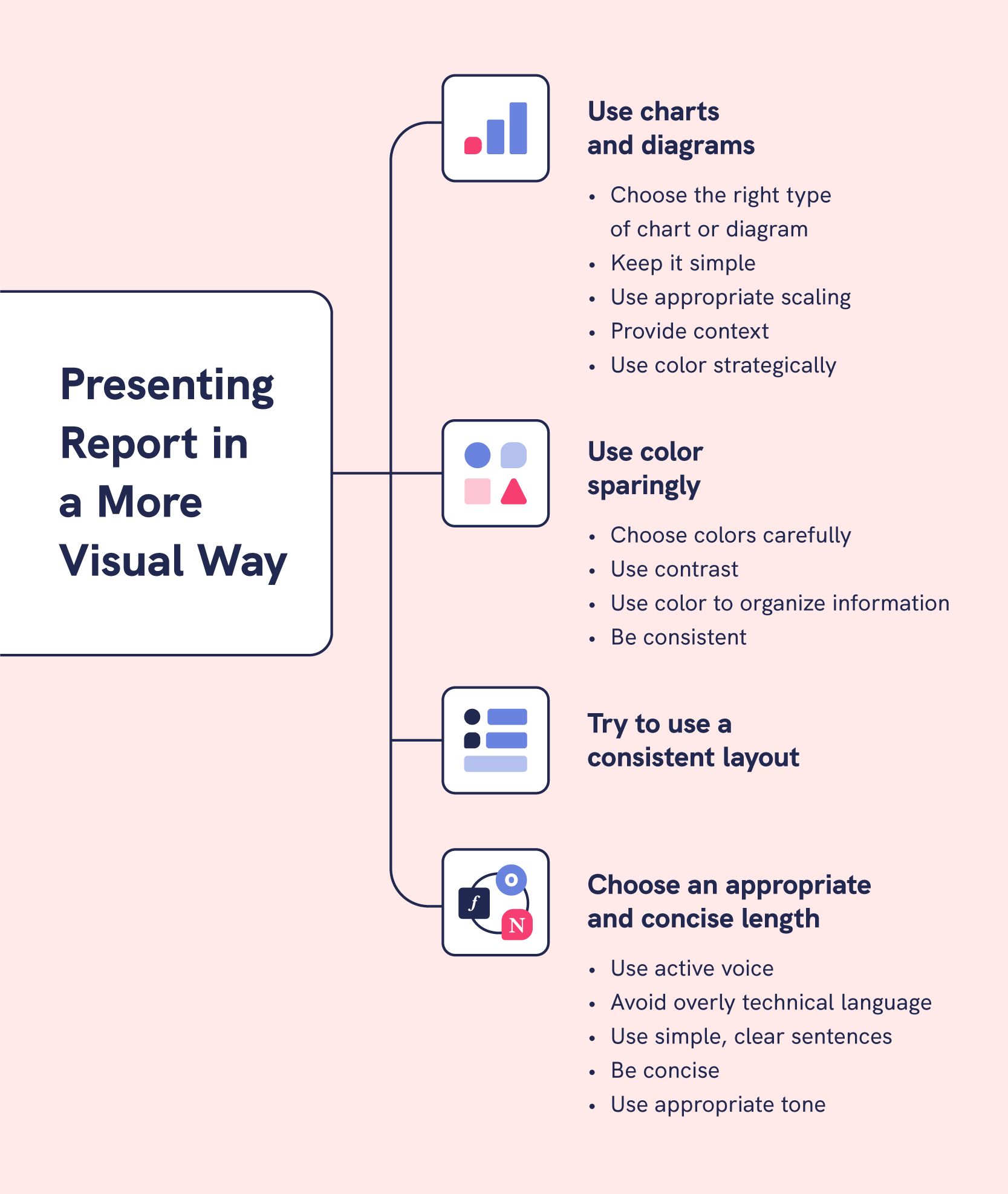
For more information, you can check out a step by step guide to create your business report sample. You can also browse our template gallery and select a template to get started.
CTA: Check out Piktochart’s business report template gallery to get you started! https://piktochart.com/templates/reports/

Other Posts
10 Best Sales Report Templates for Tracking Revenue, KPIs & Growth

10 Types of HR Reports (With Templates and Examples)

7 Captivating Report Design Ideas And Tips (With Templates and Examples)

What is a Business Report: How To Write it? (Examples & Format)
Table of Contents
This is a detailed guide to what is a business report, explained with examples, types, importance, and features, and how to write it with elements and a checklist.
Definition of business report
“A business report is an orderly, objective communication of factual information that serves some business purpose”. By Raymond Vincent Lesikar, and John D. Pettit
What is a Business Report?
A business report is a formal document that provides an analysis of a specific business issue or situation. It typically includes detailed information on the topic at hand such as data, research, and other relevant sources.
Business reports are used to make business decisions, identify problems or opportunities, or track progress toward goals. They are often written for an internal audience, such as managers or executives, but may also be shared with external stakeholders, such as investors or clients.
Business reports should be well-structured, concise, and objective, presenting findings and recommendations in a clear and easily understandable format. They may include charts, graphs, and other visual aids to help illustrate key points.
Difference between Market Report and Business Report
A business report typically focuses on a specific company’s performance, operations, and financial results. It can provide information on topics such as sales trends, revenue growth, expenses, and profitability.
In contrast, a market report focuses on the broader market landscape and provides information on the trends, opportunities, and challenges in a specific industry. Market reports can include information on market size, growth potential, competition, and consumer behavior.
While both reports aim to provide useful information for decision-making, their focus and scope are different, with business reports focusing on internal operations, and market reports focusing on external market factors.
Difference between a Business Report and a Business Plan
A business report is a document that provides detailed information on a specific aspect of a company’s operations, such as financial results, sales trends, customer feedback, or employee performance. It is used for decision-making, tracking progress, and communicating with stakeholders.
On the other hand, a business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, and tactics for achieving success. It typically includes an analysis of the market, a description of the company’s products or services, an overview of the management team, and a financial plan that details how the company will generate revenue and manage expenses over time.
How to Write a Business Report
Writing a business report can be a valuable tool for analyzing and presenting information related to a company’s performance or a specific business project. Here are some steps to follow when writing a business report:
1) Determining the purpose: Before writing the report, it’s important to define the purpose of the report. The writer must know what type of report they are writing and why it is being written. This helps in better research and writing.
2) Check target audience: After determining the purpose of the report, the writer must keep in mind who the report will be addressed. This can help in effectively conveying the message to the concerned persons.
3) Gather information: The writer must then gather data and conduct research. It is necessary to use credible sources such as industry reports, financial statements, or market research studies to collect relevant data.
4) Analysis of the supportive information: This is the main body of the report where the writer will present their findings. They must make sure to use data and statistics to support conclusions. This section can include charts, graphs, and tables to make the information easy to understand.
5) Findings and recommendations: Once the writer has presented their findings, they can draw conclusions and make recommendations based on the analysis. This is where they can suggest ways to improve the company’s performance or make recommendations for future business projects.
6) Determining report format: Before writing the report, the writer must determine what kind of business report it is. This is done so they can structure the report in a logical and easy-to-follow way. They can create outlines that include headings, subheadings, and sections to organize the information in a clear and concise manner.
Elements of a Business Report
A business report consists of three main elements – Front Matter, Body of the Report, and Back Matter.
The format of a business report is as follows:
(A)Front Matter: The front matter of a business report is the first section of the report and provides essential information about the report’s contents and purpose. It includes the following elements:
- Cover Page: This is the first page of the report, typically including the title, author or authors, date, and company logo.
- Title Page: It follows the cover page and provides more detailed information about the report.
- Table of Contents: It is also included in the front matter and provides an outline of the report’s contents, including headings and subheadings with page numbers.
- Executive Summary: It provides a brief overview of the report’s main findings, conclusions, and recommendations.
A portion of the executive summary in the business report: An executive summary is a brief overview of a business report that highlights the main points and conclusions of the report. It is usually the first section of the report that the reader sees and is often used as a standalone document for busy executives who need to quickly understand the report’s key findings. The purpose of an executive summary is to provide a concise and clear picture of the main purpose of the report, the methods used to gather data, the key findings and conclusions, and the recommendations based on those conclusions.
(B) Body of the Report: The body of a business report is the main section of the report where the writer presents the data, analysis, and interpretation of the findings in a clear and concise manner. It contains the following elements:
- Introduction: The introduction gives a background on the problem or issue being addressed in the report, the objectives of the report, and an explanation of the report’s scope.
- Methodology: It is a description of the research methods used to gather data and information for the report.
- Results: This section highlights the presentation of the findings or data gathered during the research phase, including tables, graphs, and other visual aids to support the information.
The importance of tables and graphs in a business report: Tables and graphs are important elements in a business report because they can help to communicate complex data and information in a visual and easy-to-understand way. They are useful for presenting large amounts of data in a clear and concise manner, making it easier for the reader to interpret and understand the information presented.
- Discussion: An analysis and interpretation of the results, including the significance of the findings and their implications.
- Conclusion: The conclusion contains a summary of the main points made in the report, including the conclusions drawn from the analysis and any recommendations for action.
- Recommendations: Finally, the recommendation section contains specific actions or strategies that are proposed to address the problem or issue being investigated in the report.
(C) Back Matter: The back matter of a business report is the section that comes after the main body of the report and includes any additional information that may be useful for the reader. This section may include
- Appendices: This contains additional materials such as charts, graphs, or data that support the report but are not included in the main body of the document.
- References: This contains all the citations and references used in the research and collection of data for the report.
- Glossary: A glossary lists the technical terms used in the report with their meanings and descriptions.
Must Read : What are the parts of a business report
How should headings be used in business reports?
Headings are an essential tool for organizing a business report and making it easy to read and navigate. Headings should be clear and descriptive, giving the reader a sense of what each section will cover.
They should also be formatted in a way that makes them stand out from the rest of the text, such as by using bold or larger font sizes. They should be used consistently throughout the report to guide the reader through the various sections and sub-sections.
When using headings in a business report, it is important to follow a logical and hierarchical structure. The main heading of the report should clearly state the purpose of the report and provide an overview of the main points that will be covered. Subheadings should be used to break down the report into smaller sections, each covering a specific topic related to the overall theme of the report.
Examples of business reports
Below we have listed business reports of some top companies along with the business performance metrics.

Topics for writing Business Reports Importance of the communication process ? Non-verbal aspect of business communication? Modes of the communication process? Changing patterns of business correspondence? Types of barriers in business communication ? How to overcome barriers of communication in an organization ?
Most common types of Business Reports
In business communication, there are many different types of business reports , with each type designed to provide specific information about a particular aspect of a company’s operations. Some common types of business reports include:
1) I nformational Report: This type of business report provides factual information on a particular topic or issue, without making any recommendations or drawing conclusions.
Further Reading : How to Write an informational report
2) Analytical Report: These reports use data and analysis to draw conclusions and make recommendations. It typically includes an executive summary, introduction, methods and results sections, and a conclusion with recommendations.
3) Routine Report: These reports are produced on a regular basis, such as weekly or monthly. It typically provides updates on specific activities or tasks, such as progress on a project or sales figures for a given period.
4) Informal Business Report: An informal business report is less structured and formal than other types of business reports. It may be used for internal communication between colleagues or departments and can include memos, emails, or short notes.
5) Short Report : This type of business report is concise and to the point, typically no more than five pages in length. It is often used to communicate a specific issue or recommendation quickly and may include only the most essential information.
Must Read : List of different types of business reports with classification
Importance of Business Reports
Business reports are an important tool for organizations to communicate and document important information related to the business. Some of the key reasons why business reports are important to include:
- Evaluation: Business reports can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of specific initiatives or programs by tracking progress toward goals and measuring outcomes.
- Communicating with stakeholders: Business reports can be used to communicate important information to a range of stakeholders, including investors, customers, suppliers, and employees.
- Supports decision-making: Business reports can provide the information and analysis needed to make informed decisions about business operations, investments, and strategies.
- Providing a record of performance: Business reports can provide a historical record of the organization’s performance, documenting trends and changes over time.
Must Read : What is the importance of a business report
Characteristics of Business Reports
A good business report should have the following characteristics:
1) Purpose: Business reports are written with a specific purpose in mind, such as informing a decision, presenting research findings, or providing updates on a project or initiative.
2) Audience: Reports are tailored to the needs and interests of the intended audience, which may include executives, managers, stakeholders, or external clients.
3) Structure: The report must have a clear and standardized structure, which typically includes an introduction, background information, results, analysis, recommendations, and conclusions.
4) Objectivity: Reports are expected to be objective and unbiased, and to present information and analysis in an accurate and factual manner.
Must Read : What are the characteristics of a good business report
Advantages and Disadvantages of Business Reports:
In this section, we will look at a few advantages and disadvantages of business reports .
Advantages:
- Business reports provide clear and concise information about various aspects of a business, such as financial performance, market trends, customer satisfaction, and employee productivity.
- Business reports can be used to share information among employees, departments, and stakeholders. This facilitates communication and collaboration, allowing everyone to stay informed and work together towards common goals.
Disadvantages:
- Business reports can be time-consuming to create, especially if they require extensive research and analysis. This can be a burden on employees who are already busy with their regular responsibilities.
- Depending on the length and complexity of the report, it can be overwhelming for readers to process and understand all of the information contained within it. This can be especially true if the report is full of technical jargon or financial data that may not be familiar to all readers.
Must Read : Advantages and disadvantages of business reports
What is a Small Business Report
A short business report is a concise document that provides a brief summary of key information related to a specific business topic. Short reports are typically between one and five pages in length and are often used to communicate information to a specific audience.
Short business reports typically include an introduction that highlights the context of the report, a summary of the key points or findings, and a conclusion or recommendation. They may also include supporting data, such as charts, graphs, or tables, to help illustrate key points.
Must Read : What is a small report and how to write a small report with examples
What is the Significance of Business Report Writing in Business Success?
Business report writing is a critical tool for achieving success in business. Reports provide valuable information to business owners and managers that can be used to make informed decisions, identify improvement areas, and create growth strategies.
They also facilitate communication within the organization, allowing employees and stakeholders to stay informed about the business’s progress and work together towards common goals. Business reports can be used to help plan for the future and set goals, and promote accountability by tracking and reporting on performance metrics.
Checklist for making your Business Report Reader-Friendly
Here is a checklist for making your business report reader-friendly:
- Use clear and concise language: Avoid using technical jargon and complex language that may be difficult for readers to understand. Use simple, clear language that is easy to read and comprehend.
- Organize your report effectively: Use headings, subheadings, and bullet points to break up your report into smaller, more digestible sections. This makes it easier for readers to navigate and find the information they are looking for.
- Use visual aids: Incorporate graphs, charts, and tables to help illustrate key points and make the information more engaging. This can help readers understand complex data more easily.
- Proofread your report: Ensure that your report is free of grammatical errors, typos, and other mistakes. This can help make your report appear more professional and increase the credibility of the information contained within it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) what is the purpose of a business report.
Ans: The purpose of a business report is to communicate relevant information about a company’s performance, activities, or other important data to various stakeholders, including executives, shareholders, employees, customers, or external partners. They also help in decision-making, evaluation, and keeping a record of business activities.
Q2) What are the important principles of a business report?
Ans: The important principles of the business report are the principle of objectivity, the principle of knowing your target audience, the principle of planning & framework, the principle of clarity, the principle of organizing your report, and the principle of evaluating information.
Q3) What are the 5 main parts of a business report?
Ans: The 5 main parts of a business report include a title page, executive summary, table of contents, findings, and discussion, and finally, the conclusion and recommendations.
Share Your Read Share this content
- Opens in a new window
Aditya Soni
You might also like.

10 Differences Between Formal & Informal Reports + Examples

11 Characteristics of a Good Business Report

24 Types of Business Reports With Samples & Writing Structure
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

How to Write a Business Report
A business report is a collection of data and analyses that helps make relevant information easily accessible to a company. There are many different types of business reports, but this guide will show you the basic outline.
Before You Begin:
- Think about your audience and their expectations, and plan your report accordingly. For example, are they expecting a formal or informal report? Do they have an understanding of the vocabulary/terms used? Do they require more background information? Do they need to be heavily persuaded?
- What is the purpose of the report? Make sure this is clear.
- Gather and organize your supporting information/data/visuals.
- Focus on the facts.
- Make sure to be clear and concise, so the report is easy for everyone to read and understand.
- Use a professional, standard font in a readable size.
Components of a Business Report
- Table of Contents: Depending on the length of the report, you might want to consider including a table of contents. This will make finding specific information easier for readers.
- Tip: Even though this is the first section, consider writing this section after you have finished the report. This will help you determine which points are the most important to address.
- Introduction: This section outlines what you will be going over in your report. It includes the main points, chosen report structure, and, most importantly, the objective of your report.
- Conclusion: In the conclusion, be sure to briefly summarize all of the main points in the order they were presented in the report.
- Recommendations: This section is where you provide your recommendations or suggestions based on the findings you noted in earlier sections. Indicate the potential benefits for the company to applying your suggestions.
- References: Be sure to cite all sources used in the report in this section.
- Appendices: In the Appendix, you can add relevant documents, surveys, graphs, etc. that you referenced in the report.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Finance and Business
- Business Skills
- Business Writing
How to Write a Business Report
Last Updated: March 22, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Sarah Evans . Sarah Evans is a Public Relations & Social Media Expert based in Las Vegas, Nevada. With over 14 years of industry experience, Sarah is the Founder & CEO of Sevans PR. Her team offers strategic communications services to help clients across industries including tech, finance, medical, real estate, law, and startups. The agency is renowned for its development of the "reputation+" methodology, a data-driven and AI-powered approach designed to elevate brand credibility, trust, awareness, and authority in a competitive marketplace. Sarah’s thought leadership has led to regular appearances on The Doctors TV show, CBS Las Vegas Now, and as an Adobe influencer. She is a respected contributor at Entrepreneur magazine, Hackernoon, Grit Daily, and KLAS Las Vegas. Sarah has been featured in PR Daily and PR Newswire and is a member of the Forbes Agency Council. She received her B.A. in Communications and Public Relations from Millikin University. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 741,661 times.
Business reports are one of the most effective ways to communicate in today’s business world. Although business reports' objectives are broad in scope, businesses or individuals can use them to help make important decisions. To write an effective business report, you first need to understand what it is and how it can be used.
Deciding What Type of Report to Write

- For example, you want a 3D printer for your division. To convince your manager to requisition one, you would write a justification/recommendation report to formally ask the management team for the printer.

- For instance, say pharmaceutical company X wants to partner with pharmaceutical company Y but has some concerns. Company X doesn’t want to partner with a company that has current financial problems or has had financial problems in the past. Company X conducts an investigation and uses an investigative report to discuss in-depth financial information on company Y and its directors.

- For instance, CALPERS (California Public Employees Retirement System) needed to show its board of administration that it followed all applicable laws and rules in 2010. It put together an annual compliance report to show their activities for the year.

- Can this project be completed within its budget?
- Will the project be profitable?
- Can this project be completed within the allotted time frame?

- For example, a business might conduct a company-wide study on whether to ban smoking in its employee lounge. The person who writes up the study would produce a research studies report.

- For instance, a pharmaceutical sales representative might provide a monthly summary of his or her sales calls.

- As an example, a state’s governing body would like a situational report after a hurricane.

- For instance, ABC Auto Manufacturing, Inc., wants to open a plant in Asia. The report might narrow down three country options based on the company’s needs. The report would then conclude which of the three countries is the best location for the new plant.
Writing a Business Report

- Regardless of the answer, you need to make your objective concise. If it is muddled, then your report will only confuse your audience, which risks damaging the report's credibility.
- For instance, you may want to accomplish receiving a larger advertising budget for your department. Your report should focus on the current advertising budget and how you might effectively use a larger budget.

- Remember that regardless of your audience, no bottom line speaks louder than money to a company or client.
- For instance, say you want to implement a job-share program for your division. You decide your target audience is the company’s HR director, CEO and COO. Consider how much they likely know about job-share programs already. The answer will set the tone for the report. If your company has never considered a job-share program, then the report will be both informational and strategic. If the company has considered a job-share program, then the report will be less informational and more persuasive.

- Data may come internally, which means you'll be able to collect it quite quickly. Sales figures, for example, should be available from the sales department with a phone call, meaning you can receive your data and plug it into your report quickly.
- External data may also be available internally. If a department already performs customer analysis data collection, borrow that department's. You don't need to conduct the research on your own. This will be different for every type of business, but the writer of a business report often doesn't need to conduct firsthand research.
- For instance, if you are writing a justification/recommendation report, then you have to research all the benefits of your proposed idea and incorporate the research into your report.

- Break up relevant data into separate sections. A business report can't be a big flood of figures and information. Organizing the data into separate sections is key to the success of a well-written business report. For example, keep sales data separate from customer analysis data, each with its own header.
- Organize the report into appropriate section headers, which may be read through quickly as standalone research, but also supporting the basic objective of the report together.
- Since some of the sections may depend upon analysis or input from others, you can often work on sections separately while waiting for the analysis to be completed.

- Any goals should include specific, measurable actions. Write out any changes in job descriptions, schedules or expenses necessary to implement the new plan. Each statement should directly indicate how the new method will help to meet the goal/solution set forth in the report.

- The executive summary gets its name because it's likely the only thing a busy executive would read. Tell your boss everything important here, in no more than 200-300 words. The rest of the report can be perused if the boss is more curious.

- Generally speaking, visual figures are a great idea for business reports because the writing and the data itself can be a little dry. Don’t go overboard, though. All infographics should be relevant and necessary.
- Use boxes on pages with a lot of text and no tables or figures. A page full of text can be tiresome for a reader. Boxed information can also effectively summarize important points on the page.

- Use the appropriate formatting for the citations in your report, based on your industry.

- For example, don’t overuse fancy words or make your sentences too wordy.
- Avoid using slang.
- If your report and audience are both closely tied to a specific industry, it's appropriate to use jargon or technical terms. But you have to take care to not overuse jargon and technical terms.
- Generally, business writing is written in the passive voice , and this is one of the few instances where passive writing is usually better than active writing.
- You can often miss errors while proofreading your own work due to the familiarity from writing it. Consider asking someone else in your department who wants the report to succeed to read over it as well. Be open to the feedback. It's better to hear about mistakes from a co-worker than from a boss. Review each comment from the peer review and rewrite the report, taking comments into consideration.

- This applies to any graphs or charts included in the report as well.
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

Expert Interview

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about business writing, check out our in-depth interview with Sarah Evans .
- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/formal-business-report-example
- ↑ https://openoregon.pressbooks.pub/lbcctechwriting/chapter/7-7-feasibility-reports/
- ↑ https://www.adelaide.edu.au/writingcentre/ua/media/44/learningguide-businessreportwriting.pdf
- ↑ http://wac.colostate.edu/teaching/tipsheets/writing_business_reports.pdf
- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/student-resources/writing-speaking-resources/how-to-write-a-business-report
About This Article

To write a business report, start with an introduction that presents a clear idea, problem, or objective. Next, present the facts, focusing on one main idea per paragraph, and discuss benefits and possible risks associated with your objective. Then, present your research and proposed solutions. Be sure to organize the data into separate sections based on subject matter and include section headers for readability. Finally, summarize the main points of your report in the conclusion. For tips on formatting different kinds of business reports, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jackson Yakx Weno
Sep 21, 2017
Did this article help you?

Grace Avellino
Apr 11, 2016
Mar 27, 2021
Apr 22, 2017
Afful Samuel
Jun 3, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
Money blog: Gen Z would rather deliver parcels than work in restaurants, top chef claims
A reader seeks help as her employer of 24 years is bringing in a new clock-in system to pay her by the minute. Read this and all the latest personal finance and consumer news in the Money blog - and share your own problem or dispute below.
Monday 13 May 2024 11:35, UK
- Free childcare applications open for new age band
- Money Problem: My workplace is bringing in new clock-in system to pay us by the minute - is this allowed?
Essential reads
- How to make sure your car passes its MOT
- 'Loud budgeting': The money-saving trend that has nothing to do with giving up your daily coffee
- How to avoid a holiday data roaming charge (while still using the internet)
- Best of the Money blog - an archive
Ask a question or make a comment
Restaurants might only be able to open three or four days a week due to staffing problems, Michel Roux Jr has warned.
Speaking to The Telegraph as he gears up to open his new restaurant Chez Rouz, the Michelin starred chef admitted the industry needs to change to accommodate flexible working hours.
"Just because I worked 80 hours a week or more doesn't mean the next generation should," he said.
"Quite the contrary. That is something that we have to address in our industry."
But, he warned that the move will come at a cost...
"It will mean ultimately that going out is going to be more expensive, and that maybe your favourite restaurant is no longer open seven days a week - it's only open three or four days a week," he said.
The industry is known for its long, unsociable working hours, and Roux Jr explained that the real issue hit after the pandemic, with people no longer wanting to work weekends.
"People don't want to work unsociable hours and would rather work delivering parcels as and when they want to. It's as simple as that," he added.
Earlier this year, Roux Jr said goodbye to his famous restaurant Le Gavroche in London.
It had been opened by his father Albert Roux and uncle Michel Roux in 1967.
Now, he said it's "brave" to open a new restaurant, with the market "very, very tough".
"I really feel for anyone that is brave enough to open up a restaurant now. It's incredibly difficult," he added.
Chez Rouz at The Langham in Marylebone, central London, is due to open on 22 May.
By James Sillars , business news reporter
A pause for breath on the FTSE 100 after a 3% gain over the course of past week that took the index to a fresh record closing high.
The rally of recent weeks - significant for London's standing and pension pots alike - has been broad based and reflects several factors.
A major driver has been sterling's weakness versus the US dollar.
The US currency has been strong as the Federal Reserve, its central bank, has hinted it will be some time yet before it begins to cut interest rates.
Language out of the Bank of England last week sparked a flurry of bets that UK rates could be cut as early as next month.
A weaker pound boosts dollar-earning constituents on the FTSE 100 because they get more for their money when dollars are converted to pounds.
Also at play is the view that UK stocks represent good value, as they are cheaper compared to many of their international peers.
A few moments ago, the FTSE 100 was trading 6 points lower at 8,423.
A major talking point is the possibility of the Chinese fast fashion firm Shein listing in London.
According to Reuters, the company has shifted its focus to the UK after receiving a lukewarm reception in the United States.
The news agency, citing two sources, reported that Shein was stepping up its preparations for an initial public offering in London that would be expected to be one of the biggest carried out globally this year.
By Emily Mee , Money team
No one likes the date in their calendar when their MOT rolls around.
But to make things a little less stressful, consumer expert Scott Dixon - known as The Complaints Resolver - has given us some tips on what to look out for to help your vehicle pass with flying colours.
Some of the most common failures are faulty steering, brakes, suspension, worn or damaged tyres, cracked windscreens and faulty lights.
Mr Dixon recommends you get your car serviced a couple of weeks before your MOT, in case there are any complex or costly issues.
This will give you time to get them fixed and get your car through first time without any advisories.
Aside from taking your car for a service, there are also some easy checks you can run yourself...
Listen for unusual clunks while you're driving - this could be a sign of a damaged suspension.
You could also check by pushing the car down on each corner. It should return to normal without bouncing a few times.
Another option is to look with a torch under the wheel arch, as this should reveal any obvious defects.
Blown bulbs are a common MOT failure, but they're cheap to fix.
Walk around your car and check all the bulbs are working - this includes the headlights, sidelights, brake lights, indicators and the number plate bulb.
Mr Dixon says it's "not an easy job" to change the lightbulbs yourself on most modern cars, as the MOT will also check the positioning of the light. Therefore he recommends getting this done professionally.
Squealing or grinding noises may be a sign your brake pads need replacing.
You should also check whether your car stops in a straight line, or whether it pulls in different directions.
Don't forget about the handbrake, too. Test it out on a slope and see if it securely holds the car. If it doesn't, you should get it adjusted.
It's easy to check if your wipers work okay, but you should also make sure to inspect the blades for tears and rips.
They should be able to clean the windows with no smears.
Mr Dixon says you don't need to pay Halfords to change your wiper blade as you can "do it yourself in seconds". All you need to do is look for a YouTube tutorial.
He also recommends buying the Bosch wiper blades, as he says these are good quality and will also be a sign you've looked after your car well when you come to sell it.
One thing to look out for is tread depth. You can do this by looking for the "wear bar" that sits between the tread.
If it's close to 1.6mm and is low, you should get the tyre replaced so it's not flagged as an advisory.
Also check for perished tyre walls, which can happen when a vehicle is standing for any length of time.
Uneven tyre wear is another potential issue, and if there are signs of this you should get the tyre replaced and tracking and suspension checked.
These must be in good condition and working order, with no tears or knots.
Registration plates
Your number plates should be clean and visible with a working light bulb at the rear. You may need to give them a wipe and replace the bulb if necessary.
This should be in good condition, without damage such as loose bumpers or sharp edges.
Mr Dixon advises against using automatic car washes during your car's lifetime, saying they "wreck your car".
"It's not just your paintwork but they can also damage the wiper blades and the bodywork," he says.
Check for warning lights
You'll need to take your vehicle to a trusted garage or mechanic for this.
Exhaust emissions
Some diesel vehicles can fail their MOTs based on emissions. To avoid this, you can buy a fuel treatment pack and take your car for a good run to clear the fuel lines and tank.
Driving for at least 30 to 50 minutes at a sustained speed on a motorway or A-road should help to clear the filter.
You should make sure the driver's view of the road isn't obstructed, so check for stone chips at eye level and remove any obstructions such as air fresheners and mobile phone cradles.
What else should you think about?
Make sure your car is clean beforehand, as a tester can refuse to do your MOT if the vehicle is filthy and full of rubbish.
Giving your car a clean can also give you a chance to inspect it, Mr Dixon says.
Another thing to do is to check last year's MOT for any advisories that might crop up this time.
These potential issues will still be there - so it's best not to ignore them.
You can check your vehicle's MOT history using https://car-check.co.uk .
Every Monday we get an expert to answer your money problems or consumer disputes. Find out how to submit yours at the bottom of this post. Today's question is...
I have worked at a bank for 24 years - the facilities are outsourced. This new company is bringing in a system where the staff have to click in and out and are then paid by the minute? Is this allowed? Amber
Ian Jones, director and principal solicitor at Spencer Shaw Solicitors, has picked this one up...
Your rights depend on your contract and what it says about payment. Does it specify an annual salary, or payment by time? Does it allow for changes to how payment is calculated?
If the contract does not allow for this type of payment, your employer may be trying to vary the contract of employment unlawfully.
If you're directly employed by the bank, and your pay arrangements are changing because of a new monitoring system, this would be an internal contract variation. If you work in the facilities department and the new contractor is taking over as your employer, the Transfer of Undertakings (Protection of Employment) Regulations (TUPE) 2006 may apply.
In this case, your current terms, conditions and previous service will transfer to the new employer.
TUPE may make the issue sound more complicated but, in practice, either way the changes will be valid only if the employee agrees to them.
If you have not agreed to the change, then this could be a breach of contract. This could give rise to a successful claim in the civil courts or the employment tribunal.
If the breach is serious (for example, you're paid less than agreed in the original contract) and you resign in response, this could amount to constructive dismissal for which a claim can be made in the employment tribunal.
It would be sensible to get the contract reviewed by a solicitor for advice. But act swiftly - if you continue working for the employer, you are effectively waiving the breach and accepting the change to your contract.
To make it possible to pay by the minute, employees may be monitored while at work. When collecting and processing data and using it to make a decision, the employer must comply with data protection laws. If not, the employee could be entitled to compensation, depending on the breach, or the employer could be at risk of a sanction by the regulator the Information Commissioner's Office.
This feature is not intended as financial advice - the aim is to give an overview of the things you should think about. Submit your dilemma or consumer dispute via:
- The form above - make sure you leave a phone number or email address
- Email [email protected] with the subject line "Money blog"
- WhatsApp us here .
Please make sure you leave your contact details as we cannot follow up consumer disputes without them.
We're back for another week of consumer news, personal finance tips and all the latest on the economy.
This is how the week in the Money blog is shaping up...
Today : Every week we ask industry experts to answer your Money Problems . Today, a reader's employer is bringing in a new clock-in system to pay workers by the minute - but is this allowed?
Tuesday : This week's Basically... explains everything you need to know about the PIP.
Wednesday : We speak to one of London's top chefs for his Cheap Eats at home and in the capital.
Thursday : Savings Champion founder Anna Bowes will be back with her weekly insight into the savings market.
Friday : We'll have everything you need to know about the mortgage market this week with the guys from Moneyfacts.
Running every weekday, Money features a morning markets round-up from the Sky News business team and regular updates and analysis from our business, City and economic correspondents, editors and presenters - Ed Conway , Mark Kleinman , Ian King , Paul Kelso and Adele Robinson .
You'll also be able to stream Business Live with Ian King on weekdays at 11.30am and 4.30pm.
Bookmark news.sky.com/money and check back from 8am, and through the day, each weekday.
The Money team is Emily Mee, Bhvishya Patel, Jess Sharp, Katie Williams, Brad Young and Ollie Cooper, with sub-editing by Isobel Souster. The blog is edited by Jimmy Rice.
By Jess Sharp , Money team
Money saving trends are constantly popping up on social media - but one in particular has been gaining huge amounts of attention.
Created accidentally by a comedian, loud budgeting is breaking down the taboo of speaking about money.
The idea is based on being firmer/more vocal about your financial boundaries in social situations and setting out what you are happy to spend your money on, instead of "Keeping up with the Joneses".
On TikTok alone, videos published under the hashtag #loudbudgeting have garnered more than 30 million views - and that figure is continuing to climb.
We spoke to Lukas Battle - the 26-year-old who unintentionally created the trend as part of a comedy sketch.
Based in New York, he came up with the term in a skit about the "quiet luxury" hype, which had spread online in 2023 inspired by shows like Succession.
The term was used for humble bragging about your wealth with expensive items that were subtle in their design - for example, Gwyneth Paltrow's £3,900 moss green wool coat from The Row, which she wore during her ski resort trial...
"I was never a big fan of the quiet luxury trend, so I just kind of switched the words and wrote 'loud budgeting is in'. I'm tired of spending money and I don't want to pretend to be rich," Lukas said.
"That's how it started and then the TikTok comments were just obsessed with that original idea."
This was the first time he mentioned it...
Lukas explained that it wasn't about "being poor" but about not being afraid of sharing your financial limits and "what's profitable for you personally".
"It's not 'skip a coffee a day and you'll become a millionaire'."
While talking money has been seen as rude or taboo, he said it's something his generation is more comfortable doing.
"I've seen more debate around the topic and I think people are really intrigued and attracted by the idea," he said.
"It's just focusing your spending and time on things you enjoy and cutting out the things you might feel pressured to spend your money on."
He has incorporated loud budgeting into his own life, telling his friends "it's free to go outside" and opting for cheaper dinner alternatives.
"Having the terminology and knowing it's a trend helps people understand it and there's no awkward conversation around it," he said.
The trend has been a big hit with so-called American "finfluencers", or "financial influencers", but people in the UK have started practising it as well.
Mia Westrap has taken up loud budgeting by embarking on a no-buy year and sharing her finances with her 11.3k TikTok followers.
Earning roughly £2,100 a month, she spends around £1,200 on essentials, like rent, petrol and car insurance, but limits what else she can purchase.
Clothes, fizzy drinks, beauty treatments, makeup, dinners out and train tickets are just some things on her "red list".
The 26-year-old PHD student first came across the idea back in 2017, but decided to take up the challenge this year after realising she was living "pay check to pay check".
She said her "biggest fear" in the beginning was that her friends wouldn't understand what she was doing, but she found loud budgeting helped.
"I'm still trying my best to just go along with what everyone wants to do but I just won't spend money while we do it and my friends don't mind that, we don't make a big deal out of it," she said.
So far, she has been able to save £1,700, and she said talking openly about her money has been "really helpful".
"There's no way I could have got this far if I wasn't baring my soul to the internet about the money I have spent. It has been a really motivating factor."
Financial expert John Webb said loud budgeting has the ability to help many "feel empowered" and create a "more realistic" relationship with money.
"This is helping to normalise having open and honest conversations about finances," the consumer affair manager at Experien said.
"It can also reduce the anxiety some might have by keeping their financial worries to themselves."
However, he warned it's important to be cautious and to take the reality of life into consideration.
"It could cause troubles within friendship groups if they're not on the same page as you or have different financial goals," he said.
"This challenge isn't meant to stop you from having fun, but it is designed to help people become more conscious and intentional when it comes to money, and reduce the stigma around talking about it."
Rightmove's keyword tool shows Victorian-era houses are the most commonly searched period properties, with people drawn to their ornate designs and features.
Georgian and Edwardian-style are second and third respectively, followed by Tudor properties. Regency ranked in fifth place.
Rightmove property expert Tim Bannister said: "Home hunters continue to be captivated by the character and charm of properties that we see in period dramas.
"Victorian homes remain particularly popular, characterised by their historic charm, solid construction, and spacious interiors. You'll often find Victorian houses in some of the most desirable locations which include convenient access to schools and transport links."
Throughout the week Money blog readers have shared their thoughts on the stories we've been covering, with the most correspondence coming in on...
- A hotly contested debate on the best brand of tea
- Downsizing homes
- The cost of Michelin-starred food
Job interview mistakes
On Wednesday we reported on a new £12m ad from PG Tips in response to it falling behind rivals such as Twinings, Yorkshire Tea and Tetley....
We had lots of comments like this...
How on earth was the PG Tips advert so expensive? I prefer Tetley tea, PG Tips is never strong enough flavour for me. Shellyleppard
The reason for the sales drop with PG Tips could be because they increased the price and reduced the quantity of bags from 240 to 180 - it's obvious. Royston
And then this question which we've tried to answer below...
Why have PG Tips changed from Pyramid shape tea bags, to a square? Sam
Last year PG Tips said it was changing to a square bag that left more room for leaves to infuse, as the bags wouldn't fold over themselves.
We reported on data showing how downsizing could save you money for retirement - more than £400,000, in some regions, by swapping four beds for two.
Some of our readers shared their experiences...
We are downsizing and moving South so it's costing us £100k extra for a smaller place, all money from retirement fund. AlanNorth
Interesting read about downsizing for retirement. We recently did this to have the means to retire early at 52. However, we bought a house in the south of France for the price of a flat in our town in West Sussex. Now living the dream! OliSarah
How much should we pay for food?
Executive chef at London's two-Michelin-starred Ikoyi, Jeremy Chan, raised eyebrows when he suggested to the Money blog that Britons don't pay enough for restaurant food.
Ikoyi, the 35th best restaurant in the world, charges £320 for its tasting menu.
"I don't think people pay enough money for food, I think we charge too little, [but] we want to always be accessible to as many people as possible, we're always trying our best to do that," he said, in a piece about his restaurant's tie up with Uber Eats...
We had this in...
Are they serious? That is two weeks' worth of food shopping for me, if the rich can afford this "tasting menu" then they need to be taxed even more by the government, it's just crazy! Steve T
If the rate of pay is proportionate to the vastly overpriced costs of the double Michelin star menu, I would gladly peel quail eggs for four-hour stints over continuing to be abused as a UK supply teacher. AndrewWard
Does this two-star Michelin star chef live in the real world? Who gives a toss if he stands and peels his quails eggs for four hours, and he can get the best turbot from the fishmonger fresh on a daily basis? It doesn't justify the outrageous price he is charging for his tasting menu. Topaztraveller
Chefs do make me laugh, a steak is just a steak, they don't make the meat! They just cook it like the rest of us, but we eat out because we can't be bothered cooking! StevieGrah
Finally, many of you reacted to this feature on common mistakes in job interviews...
Those 10 biggest mistakes people make in interviews is the dumbest thing I've ever read. They expect all that and they'll be offering a £25k a year job. Why wouldn't I want to know about benefits and basic sick pay? And also a limp handshake? How's that relevant to how you work? Jre90
Others brought their own tips...
Whenever I go for an interview I stick to three points: 1. Be yourself 2. Own the interview 3. Wear the clothes that match the job you are applying Kevin James Blakey
From Sunday, eligible working parents of children from nine-months-old in England will be able to register for access to up to 15 free hours of government-funded childcare per week.
This will then be granted from September.
Check if you're eligible here - or read on for our explainer on free childcare across the UK.
Three and four year olds
In England, all parents of children aged three and four in England can claim 15 hours of free childcare per week, for 1,140 hours (38 weeks) a year, at an approved provider.
This is a universal offer open to all.
It can be extended to 30 hours where both parents (or the sole parent) are in work, earn the weekly minimum equivalent of 16 hours at the national minimum or living wage, and have an income of less than £100,000 per year.
Two year olds
Previously, only parents in receipt of certain benefits were eligible for 15 hours of free childcare.
But, as of last month, this was extended to working parents.
This is not a universal offer, however.
A working parent must earn more than £8,670 but less than £100,000 per year. For couples, the rule applies to both parents.
Nine months old
In September, this same 15-hour offer will be extended to working parents of children aged from nine months. From 12 May, those whose children will be at least nine months old on 31 August can apply to received the 15 hours of care from September.
From September 2025
The final change to the childcare offer in England will be rolled out in September 2025, when eligible working parents of all children under the age of five will be able to claim 30 hours of free childcare a week.
In some areas of Wales, the Flying Start early years programme offers 12.5 hours of free childcare for 39 weeks, for eligible children aged two to three. The scheme is based on your postcode area, though it is currently being expanded.
All three and four-year-olds are entitled to free early education of 10 hours per week in approved settings during term time under the Welsh government's childcare offer.
Some children of this age are entitled to up to 30 hours per week of free early education and childcare over 48 weeks of the year. The hours can be split - but at least 10 need to be used on early education.
To qualify for this, each parent must earn less than £100,000 per year, be employed and earn at least the equivalent of working 16 hours a week at the national minimum wage, or be enrolled on an undergraduate, postgraduate or further education course that is at least 10 weeks in length.
All three and four-year-olds living in Scotland are entitled to at least 1,140 hours per year of free childcare, with no work or earnings requirements for parents.
This is usually taken as 30 hours per week over term time (38 weeks), though each provider will have their own approach.
Some households can claim free childcare for two-year-olds. To be eligible you have to be claiming certain benefits such as Income Support, Jobseeker's Allowance or Universal Credit, or have a child that is in the care of their local council or living with you under a guardianship order or kinship care order.
Northern Ireland
There is no scheme for free childcare in Northern Ireland. Some other limited support is available.
Working parents can access support from UK-wide schemes such as tax credits, Universal Credit, childcare vouchers and tax-free childcare.
Aside from this, all parents of children aged three or four can apply for at least 12.5 hours a week of funded pre-school education during term time. But over 90% of three-year-olds have a funded pre-school place - and of course this is different to childcare.
What other help could I be eligible for?
Tax-free childcare - Working parents in the UK can claim up to £500 every three months (up to £2,000 a year) for each of their children to help with childcare costs.
If the child is disabled, the amount goes up to £1,000 every three months (up to £4,000 a year).
To claim the benefit, parents will need to open a tax-free childcare account online. For every 80p paid into the account, the government will top it up by 20p.
The scheme is available until the September after the child turns 11.
Universal credit - Working families on universal credit can claim back up to 85% of their monthly childcare costs, as long as the care is paid for upfront. The most you can claim per month is £951 for one child or £1,630 for two or more children.
Tax credits - People claiming working tax credit can get up to 70% of what they pay for childcare if their costs are no more than £175 per week for one child or £300 per work for multiple children.
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free

Trump could face a $100 million tax bill after the IRS says he tried to write off the same losses twice on his Chicago skyscraper
- Trump could face a $100 million tax bill after the IRS said he tried to write off the same losses twice.
- The losses are tied to the 92-story Trump International Hotel and Tower in Chicago.
- The IRS conducted a "high-level legal review" before it began their inquiry, the Times reported.

Former President Donald Trump could face a $100 million tax bill after the IRS said he twice sought to write off the same losses on his struggling 92-story Chicago skyscraper, according to a New York Times and ProPublica report.
The Trump International Hotel and Tower Chicago, built on the site of the former Chicago Sun-Times headquarters, opened during the Great Recession in 2009. The vast condo-hotel project was saddled with cost overruns, according to the report.
In the IRS inquiry, acquired by The Times and ProPublica, the agency said Trump tried to claim tax benefits from financial losses associated with the project and that he practically wrote off those losses twice.
Trump's first tax write-off for the Chicago tower came in his 2008 tax return, when sales at the building faltered below expectations. Trump claimed that his share of investment in the structure amounted to what the tax code classified as "worthless" — largely because the debt he incurred on the building demonstrated that he wouldn't profit.
In that year's tax return, Trump noted that he lost up to $651 million on the project, according to The Times and ProPublica.
The Times and ProPublica reported that there weren't any signs that the IRS initially pushed back against Trump's first claim, which surprised tax experts who spoke with the outlets.
Related stories
Trump and his tax advisors in 2010 tried to obtain additional benefits from the skyscraper project by transitioning the company that owned the building into a new partnership. But Trump wielded the levers of power for both companies. And for the next decade, he used the business move to try to claim $168 million in new losses.
Because of the nature of Trump's claims, the IRS conducted a "high-level legal review" before they began their inquiry, according to the report.
After looking at the inquiry, The Times and ProPublica — and tax experts — concluded that the revision pursued by the IRS would give Trump an updated tax bill exceeding $100 million, excluding any additional penalties.
Eric Trump, the executive vice president of the Trump Organization, responded to the report, stating that the company was "confident" in its actions regarding the Chicago skyscraper.
"This matter was settled years ago, only to be brought back to life once my father ran for office," he said in a statement to the Times and ProPublica. "We are confident in our position, which is supported by opinion letters from various tax experts, including the former general counsel of the IRS."
Business Insider reached out to the Trump campaign for comment.
News of the IRS inquiry comes during a presidential year in which Trump is set to once again be on the ballot, with his personal finances and the extent of his wealth continuing to be a major point of discussion in the race.
A court ordered Trump, in January, to pay $83.3 million in defamation damages to the writer E. Jean Carroll. (In a separate civil trial last year, a New York jury found the former president liable for the sexual abuse of Carroll.)
And, in February, a New York judge ordered Trump to pay $355 million in penalties for what the judge said was a scheme by the former president to fraudulently inflate the value of his properties. Prosecutors in April then accepted a $175 million bond from Trump in the civil fraud case, which the ex-president posted to block the larger judgment as he goes through the appeals process.
Watch: The biggest revelations from Trump's tax returns
- Main content

How to Start an LLC in Texas 2024: Step-by-Step Guide
Featured partner.
Advertiser disclosure
Newsweek.com is part of an affiliate sales network and receives compensation through featured partners. This may impact how and where links appear across articles. Newsweek.com does not include all financial companies or all available financial offers.
Swyft Filings
On Swyft Filings’s Website
Swyft Filings intuitive platform helps you launch your business easily.
- Free BOI (Beneficial Ownership Information) Report
- Free Trademark Filings
- Access to 250+ customizable legal documents
- Privacy Protection with Virtual Mailbox
- Get your business up and running in just 9 minutes with Swyft Filings’ streamlined process.
- Obtain all necessary paperwork required for opening your business bank account.
- Utilize Swyft Filings’ range of tools and integrations to optimize your operations efficiently.
- Swyft Filings boasts a 10-day faster processing time compared to the industry average of leading competitors.
Vault’s Viewpoint
- Starting an LLC business in Texas helps reduce the owner’s personal liability.
- Registration for a Texas LLC is done with the Secretary of State.
- Make sure that you have a registered agent who is available during business hours to receive legal documents on behalf of the company.
How to Start an LLC Business in Texas
Step 1: choose a business name for the llc.
Before registering your business, ensure its intended name (or something very similar) isn’t already taken in The Texas Secretary of State’s business name search . Texas requires businesses to operate under unique names and not infringe upon one another by being too similar.
When choosing a business name, keep in mind that you must adhere to approved naming schemes to be a compliant LLC. This means that the LLC’s name must contain one of the following designations at the end of the name:
- Limited Liability Company
- Limited Company
- Limited Liability Co.
The way this works is you choose the company’s name and add one of the aforementioned phrases as the suffix. For example, a company might be called “Mary’s Flower Shop LLC.” Note that the name itself must be different, not just the suffix. If “Mary’s Flower Shop Ltd. Co” already exists, “Mary’s Flower Shop LLC” would be too similar.
Names must not be offensive or misleading. For example, the name cannot insinuate that you are a government agency by containing the word “Treasury” in it. Additionally, names are not allowed to use trademarked or restricted terms such as bank, trust, trust company, Olympic, University, or veteran. The only exception is if the governing committee gives express permission to do so.
Step 2: Select a Registered Agent
Every Texas LLC must have a registered agent, the designated person who will receive legal documents for the company. Legal documents include tax documents or lawsuit notices. The registered agent must have a physical street address in Texas and be there during normal business hours. Documents may be delivered in person or via mail.
Registered agents cannot be the LLC itself. They must be individuals who are Texas residents over the age of 18. This could be you or a member of the LLC, as long as they meet the requirements. If none of the members are willing to be the registered agent, the LLC can hire a third-party agency that is registered as an agent service company authorized to conduct business in the state. Some LLCs will also hire a business attorney to be the registered agent.
Any registered agent should expressly consent to the role and keep this with the organization’s records. In this consent, you will list the LLC’s name, a statement from the registered agent’s consent, the name of the person who will be the registered agent, the signature of the registered agent and the date of execution.
Step 3: File the Certificate of Formation
A certificate of formation (otherwise known as articles of organization) must be filed with the Secretary of State. The articles of organization can be completed online by going to SOSDirec , or you can mail them in directly to the Secretary of State at:
Secretary of State
P.O. Box 13697
Austin, TX 78711
The form may also be filed in person at:
James Earl Rudder Office Building
1019 Brazos
Austin, Texas 78701
The Secretary of State’s business and nonprofit forms have all of the required information for registering each type of business, but in general, you can expect to provide the following information for an LLC’s certificate of formation:
- Organization’s name
- Organization’s type
- Registered agent’s name and street address
- Directors’ name and address
- The value of the authorized shares
- Organization’s purpose
- Mailing address
- The organizer of the entity
- Signature of organizer
Note that the information in the certificate of formation becomes public record after the form is filed. People can search for the company and find details about it from the Secretary of State. To keep information private, a virtual address can be used except for the address of the registered agent, which must be searchable.
Step 4: Write an Operating Agreement for the LLC
An operating agreement is not required in Texas but is generally a good idea, especially if the organization has more than one member. The operating agreement, which may also be called a company agreement, is an internal document that outlines how the company works and states each member’s duties and responsibilities.
An operating agreement is a useful document that can eliminate confusion because it states what each will do, how members can exit the company and whether or not they can decide to sell their shares or must get all members’ approval. The company falls under the default Texas law if there is no operating agreement.
In the operating agreement, make sure to include the following:
- Percentage of members’ ownership
- Voting rights and responsibilities
- Powers and duties of members and managers
- How profits and losses and distributed
- When and where meetings will be held
- Rules on buyouts, sellouts and distributions
Step 5: Obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN)
Once your business entity is formed, you will want to obtain an employer identification number (EIN). You do this by going directly to the IRS and completing form SS-4 or by completing the online application .
The EIN is a nine-digit number similar to a Social Security number that’s used when filing taxes and opening bank accounts or getting loans for the LLC . It is also required when filing for state unemployment taxes and certain permits and contracts with vendors.
On the subject of taxes, note that the LLC has the option to pay taxes as a pass-through entity to its members or as a corporation. If it is a pass-through entity, the income and expenses are reported on the members’ personal tax returns on Schedule C. Even with this tax structure, it’s a wise idea to get an EIN so that the company is represented on its own and helps avoid members’ personal identity theft.
Step 6: File a Beneficial Ownership Information (BOI) Report
As of January 1, 2024, all new LLCs must file a BOI report to the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network within 90 days of their LLC’s formation/registration. LLCs created before January 1, 2024, have until January 1, 2025, to file their BOI report.
This law is meant to impede criminals who use LLCs as shell companies. Filing your BOI report is free. Failure to comply will result in civil fines of $500 per day and can get as serious as criminal penalties of $10,000 and two years in prison.
Step 7: Open a Bank Account
Once you have an EIN, you will want to open a business bank account . The business bank account should receive all income for the company and pay all expenses. Avoid mixing personal assets with the business. While an LLC limits the liability of personal assets of members, this can be convoluted and diminished if the business owner and the LLC commingle assets.
How Much Does It Cost to File an LLC in Texas?
The cost of registering an LLC varies from state to state, and in Texas, it costs $300 to file an LLC directly with the state of Texas. If you use a business registration service, there will be an additional fee associated with the registration. Note that there are no monthly or annual fees that you must pay in Texas, but, you may need to pay annual franchise taxes instead. Visit the Texas Comptroller’s website and complete Form 05-285 to pay your annual franchise taxes.
Frequently Asked Questions
How quickly can i start an llc business in texas.
Filing online can expedite services, but it can take up to 40 days for the Secretary of State to approve new LLCs.
Is an LLC Worth It in Texas?
Having an LLC in Texas is worth having because it reduces your personal liability in the company’s operations. If the company falls into debt or is sued, your personal assets are safe from being confiscated.
Do I Need a Business License if I Have an LLC in Texas?
Texas does not require a general business license to operate in the state. However, depending on the type of business that you have, you may need specialty licenses or permits, such as a liquor license.
The post How to Start an LLC in Texas 2024: Step-by-Step Guide first appeared on Newsweek Vault .


Trump May Owe $100 Million From Double-Dip Tax Breaks, Audit Shows
A previously unknown focus of an I.R.S. audit is a dubious accounting maneuver that effectively meant taking the same write-offs twice on a Chicago skyscraper.
The I.R.S. believes that former President Donald J. Trump violated a law meant to prevent double-dipping on tax-reducing losses. Credit... Jamie Kelter Davis for The New York Times
Supported by
- Share full article
By Russ Buettner and Paul Kiel
This article was published in partnership with ProPublica. Russ Buettner of The New York Times has spent years reporting on the former president’s finances, including decades of his tax returns. Paul Kiel of ProPublica has reported on the I.R.S. and the ways the ultrawealthy avoid taxes since 2018.
- May 11, 2024
Former President Donald J. Trump used a dubious accounting maneuver to claim improper tax breaks from his troubled Chicago tower, according to an Internal Revenue Service inquiry uncovered by The New York Times and ProPublica. Losing a yearslong audit battle over the claim could mean a tax bill of more than $100 million.
Listen to this article, read by Eric Jason Martin
The 92-story, glass-sheathed skyscraper along the Chicago River is the tallest and, at least for now, the last major construction project by Mr. Trump. Through a combination of cost overruns and the bad luck of opening in the teeth of the Great Recession, it was also a vast money loser.
But when Mr. Trump sought to reap tax benefits from his losses, the I.R.S. has argued, he went too far and in effect wrote off the same losses twice.
The first write-off came on Mr. Trump’s tax return for 2008. With sales lagging far behind projections, he claimed that his investment in the condo-hotel tower met the tax code definition of “worthless,” because his debt on the project meant he would never see a profit. That move resulted in Mr. Trump reporting losses as high as $651 million for the year, The Times and ProPublica found.
There is no indication the I.R.S. challenged that initial claim, though that lack of scrutiny surprised tax experts consulted for this article. But in 2010, Mr. Trump and his tax advisers sought to extract further benefits from the Chicago project, executing a maneuver that would draw years of inquiry from the I.R.S. First, he shifted the company that owned the tower into a new partnership. Because he controlled both companies, it was like moving coins from one pocket to another. Then he used the shift as justification to declare $168 million in additional losses over the next decade.
The issues around Mr. Trump’s case were novel enough that, during his presidency, the I.R.S. undertook a high-level legal review before pursuing it. The Times and ProPublica, in consultation with tax experts, calculated that the revision sought by the I.R.S. would create a new tax bill of more than $100 million, plus interest and potential penalties.
Mr. Trump’s tax records have been a matter of intense speculation since the 2016 presidential campaign, when he defied decades of precedent and refused to release his returns, citing a long-running audit. A first, partial revelation of the substance of the audit came in 2020, when The Times reported that the I.R.S. was disputing a $72.9 million tax refund that Mr. Trump had claimed starting in 2010. That refund, which appeared to be based on Mr. Trump’s reporting of vast losses from his long-failing casinos, equaled every dollar of federal income tax he had paid during his first flush of television riches, from 2005 through 2008, plus interest.

The reporting by The Times and ProPublica about the Chicago tower reveals a second component of Mr. Trump’s quarrel with the I.R.S. This account was pieced together from a collection of public documents, including filings from the New York attorney general’s suit against Mr. Trump in 2022, a passing reference to the audit in a congressional report that same year and an obscure 2019 I.R.S. memorandum that explored the legitimacy of the accounting maneuver. The memorandum did not identify Mr. Trump, but the documents, along with tax records previously obtained by The Times and additional reporting, indicated that the former president was the focus of the inquiry.
It is unclear how the audit battle has progressed since December 2022, when it was mentioned in the congressional report. Audits often drag on for years, and taxpayers have a right to appeal the I.R.S.’s conclusions. The case would typically become public only if Mr. Trump chose to challenge a ruling in court.
In response to questions for this article, Mr. Trump’s son Eric, executive vice president of the Trump Organization, said: “This matter was settled years ago, only to be brought back to life once my father ran for office. We are confident in our position, which is supported by opinion letters from various tax experts, including the former general counsel of the I.R.S.”
An I.R.S. spokesman said federal law prohibited the agency from discussing private taxpayer information.
The outcome of Mr. Trump’s dispute could set a precedent for wealthy people seeking tax benefits from the laws governing partnerships. Those laws are notoriously complex, riddled with uncertainty and under constant assault by lawyers pushing boundaries for their clients. The I.R.S. has inadvertently further invited aggressive positions by rarely auditing partnership tax returns.
The audit represents yet another potential financial threat — albeit a more distant one — for Mr. Trump, the Republicans’ presumptive 2024 presidential nominee. In recent months, he has been ordered to pay $83.3 million in a defamation case and another $454 million in a civil fraud case brought by the New York attorney general, Letitia James. Mr. Trump has appealed both judgments. (He is also in the midst of a criminal trial in Manhattan, where he is accused of covering up a hush-money payment to a porn star in the weeks before the 2016 election.)
Beyond the two episodes under audit, reporting by The Times in recent years has found that, across his business career, Mr. Trump has often used what experts described as highly aggressive — and at times, legally suspect — accounting maneuvers to avoid paying taxes. To the six tax experts consulted for this article, Mr. Trump’s Chicago accounting maneuvers appeared to be questionable and unlikely to withstand scrutiny.
“I think he ripped off the tax system,” said Walter Schwidetzky , a law professor at the University of Baltimore and an expert on partnership taxation.
From ‘$1.2 Billion’ to ‘Worthless’
Mr. Trump struck a deal in 2001 to acquire land and a building that was then home to the Chicago Sun-Times newspaper. Two years later, after publicly toying with the idea of constructing the world’s tallest building there, he unveiled plans for a more modest tower, with 486 residences and 339 “hotel condominiums” that buyers could use for short stays and allow Mr. Trump’s company to rent out. He initially estimated that construction would last until 2007 and cost $650 million.
Mr. Trump placed the project at the center of the first season of “The Apprentice” in 2004 , offering the winner a top job there under his tutelage. “It’ll be a mind-boggling job to manage,” Mr. Trump said during the season finale. “When it’s finished in 2007, the Trump International Hotel and Tower, Chicago, could have a value of $1.2 billion and will raise the standards of architectural excellence throughout the world.”
As his cost estimates increased, Mr. Trump arranged to borrow as much as $770 million for the project — $640 million from Deutsche Bank and $130 million from Fortress Investment Group, a hedge fund and private equity company. He personally guaranteed $40 million of the Deutsche loan. Both Deutsche and Fortress then sold off pieces of the loans to other institutions, spreading the risk and potential gain.
Mr. Trump planned to sell enough of the 825 units to pay off his loans when they came due in May 2008. But when that date came, he had sold only 133. At that point, he projected that construction would not be completed until mid-2009, at a revised cost of $859 million.
He asked his lenders for a six-month extension. A briefing document prepared for the lenders, obtained by The Times and ProPublica, said Mr. Trump would contribute $89 million of his own money, $25 million more than his initial plan. The lenders agreed.
But sales did not pick up that summer, with the nation plunged into the financial crisis that would become the Great Recession. When Mr. Trump asked for another extension in September, his lenders refused.
Two months later, Mr. Trump defaulted on his loans and sued his lenders, characterizing the financial crisis as the kind of catastrophe, like a flood or hurricane, covered by the “force majeure” clause of his loan agreement with Deutsche Bank. That, he said, entitled him to an indefinite delay in repaying his loans. Mr. Trump went so far as to blame the bank and its peers for “creating the current financial crisis.” He demanded $3 billion in damages.
At the time, Mr. Trump had paid down his loans with $99 million in sales but still needed more money to complete construction. At some point that year, he concluded that his investment in the tower was worthless, at least as the term is defined in partnership tax law.
Mr. Trump’s worthlessness claim meant only that his stake in 401 Mezz Venture, the L.L.C. that held the tower, was without value because he expected that sales would never produce enough cash to pay off the mortgages, let alone turn a profit.
When he filed his 2008 tax return, he declared business losses of $697 million. Tax records do not fully show which businesses generated that figure. But working with tax experts, The Times and ProPublica calculated that the Chicago worthlessness deduction could have been as high as $651 million, the value of Mr. Trump’s stake in the partnership — about $94 million he had invested and the $557 million loan balance reported on his tax returns that year.
When business owners report losses greater than their income in any given year, they can retain the leftover negative amount as a credit to reduce their taxable income in future years. As it turned out, that tax-reducing power would be of increasing value to Mr. Trump. While many of his businesses continued to lose money, income from “The Apprentice” and licensing and endorsement agreements poured in: $33.3 million in 2009, $44.6 million in 2010 and $51.3 million in 2011.
Mr. Trump’s advisers girded for a potential audit of the worthlessness deduction from the moment they claimed it, according to the filings from the New York attorney general’s lawsuit. Starting in 2009 Mr. Trump’s team excluded the Chicago tower from the frothy annual “statements of financial condition” that Mr. Trump used to boast of his wealth, out of concern that assigning value to the building would conflict with its declared worthlessness, according to the attorney general’s filing. (Those omissions came even as Mr. Trump fraudulently inflated his net worth to qualify for low-interest loans, according to the ruling in the attorney general’s lawsuit.)
Mr. Trump had good reason to fear an audit of the deduction, according to the tax experts consulted for this article. They believe that Mr. Trump’s tax advisers pushed beyond what was defensible.
The worthlessness deduction serves as a way for a taxpayer to benefit from an expected total loss on an investment long before the final results are known. It occupies a fuzzy and counterintuitive slice of tax law. Three decades ago, a federal appeals court ruled that the judgment of a company’s worthlessness could be based in part on the opinion of its owner. After taking the deduction, the owner can keep the “worthless” company and its assets. Subsequent court decisions have only partly clarified the rules. Absent prescribed parameters, tax lawyers have been left to handicap the chances that a worthlessness deduction will withstand an I.R.S. challenge.
There are several categories, with a declining likelihood of success, of money taxpayers can claim to have lost.
The tax experts consulted for this article universally assigned the highest level of certainty to cash spent to acquire an asset. The roughly $94 million that Mr. Trump’s tax returns show he invested in Chicago fell into this category.
Some gave a lower, though still probable, chance of a taxpayer prevailing in declaring a loss based on loans that a lender agreed to forgive. That’s because forgiven debt generally must be declared as income, which can offset that portion of the worthlessness deduction in the same year. A large portion of Mr. Trump’s worthlessness deduction fell in this category, though he did not begin reporting forgiven debt income until two years later, a delay that would have further reduced his chances of prevailing in an audit.
The tax experts gave the weakest chance of surviving a challenge for a worthlessness deduction based on borrowed money for which the outcome was not clear. It reflects a doubly irrational claim — that the taxpayer deserves a tax benefit for losing someone else’s money even before the money has been lost, and that those anticipated future losses can be used to offset real income from other sources. Most of the debt included in Mr. Trump’s worthlessness deduction was based on that risky position.
Including that debt in the deduction was “just not right,” said Monte Jackel , a veteran of the I.R.S. and major accounting firms who often publishes analyses of partnership tax issues.
A Second Bite at the Apple
Mr. Trump continued to sell units at the Chicago Tower, but still below his costs. Had he done nothing, his 2008 worthlessness deduction would have prevented him from claiming that shortfall as losses again. But in 2010, his lawyers attempted an end-run by merging the entity through which he owned the Chicago tower into another partnership, DJT Holdings L.L.C. In the following years, they piled other businesses, including several of his golf courses, into DJT Holdings.
Those changes had no apparent business purpose. But Mr. Trump’s tax advisers took the position that pooling the Chicago tower’s finances with other businesses entitled him to declare even more tax-reducing losses from his Chicago investment.
His financial problems there continued. More than 100 of the hotel condominiums never sold. Sales of all units totaled only $727 million, far below Mr. Trump’s budgeted costs of $859 million. And some 70,000 square feet of retail space remained vacant because it had been designed without access to foot or vehicle traffic. From 2011 through 2020, Mr. Trump reported $168 million in additional losses from the project.
Those additional write-offs helped Mr. Trump avoid tax liability for his continuing entertainment riches, as well as his unpaid debt from the tower. Starting in 2010, his lenders agreed to forgive about $270 million of those debts. But he was able to delay declaring most of that income until 2014 and spread it out over five years of tax returns, thanks to a provision in the Obama administration’s stimulus bill responding to the Great Recession. In 2018, Mr. Trump reported positive income for the first time in 11 years. But his income tax bill still amounted to only $1.9 million, even as he reported a $25 million gain from the sale of his late father's assets.
It’s unclear when the I.R.S. began to question the 2010 merger transaction, but the conflict escalated during Mr. Trump’s presidency.
The I.R.S. explained its position in a Technical Advice Memorandum , released in 2019, that identified Mr. Trump only as “A.” Such memos, reserved for cases where the law is unclear, are rare and involve extensive review by senior I.R.S. lawyers. The agency produced only two other such memos that year.
The memos are required to be publicly released with the taxpayer’s information removed, and this one was more heavily redacted than usual. Some partnership specialists wrote papers exploring its meaning and importance to other taxpayers, but none identified taxpayer “A” as the then-sitting president of the United States. The Times and ProPublica matched the facts of the memo to information from Mr. Trump’s tax returns and elsewhere.
The 20-page document is dense with footnotes, calculations and references to various statutes, but the core of the I.R.S.’s position is that Mr. Trump’s 2010 merger violated a law meant to prevent double dipping on tax-reducing losses. If done properly, the merger would have accounted for the fact that Mr. Trump had already written off the full cost of the tower’s construction with his worthlessness deduction.
In the I.R.S. memo, Mr. Trump’s lawyers vigorously disagreed with the agency’s conclusions, saying he had followed the law.
If the I.R.S. prevails, Mr. Trump’s tax returns would look very different, especially those from 2011 to 2017. During those years, he reported $184 million in income from “The Apprentice” and agreements to license his name, along with $219 million from canceled debts. But he paid only $643,431 in income taxes thanks to huge losses on his businesses, including the Chicago tower. The revisions sought by the I.R.S. would require amending his tax returns to remove $146 million in losses and add as much as $218 million in income from condominium sales. That shift of up to $364 million could swing those years out of the red and well into positive territory, creating a tax bill that could easily exceed $100 million.
The only public sign of the Chicago audit came in December 2022, when a congressional Joint Committee on Taxation report on I.R.S. efforts to audit Mr. Trump made an unexplained reference to the section of tax law at issue in the Chicago case. It confirmed that the audit was still underway and could affect Mr. Trump’s tax returns from several years.
That the I.R.S. did not initiate an audit of the 2008 worthlessness deduction puzzled the experts in partnership taxation. Many assumed the understaffed I.R.S. simply had not realized what Mr. Trump had done until the deadline to investigate it had passed.
“I think the government recognized that they screwed up,” and then audited the merger transaction to make up for it, Mr. Jackel said.
The agency’s difficulty in keeping up with Mr. Trump’s maneuvers, experts said, showed that this gray area of tax law was too easy to exploit.
“Congress needs to radically change the rules for the worthlessness deduction,” Professor Schwidetzky said.
Susanne Craig contributed reporting.
Read by Eric Jason Martin
Narration produced by Anna Diamond and Krish Seenivasan
Engineered by Steven Szczesniak
Russ Buettner is an investigative reporter. Since 2016, his reporting has focused on the finances of Donald. J. Trump, including articles that revealed tax avoidance schemes evidenced on several decades of his tax returns. In 2019, he shared a Pulitzer Prize for work that revealed the vast inheritance Mr. Trump had received from his father. More about Russ Buettner
Advertisement
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 2: Create an Outline. Once you've gathered the resources, it's time to plan the report. Before you start writing, create an outline that will help you stick to the right structure. A business report is complex writing in which you can get lost very easily if you don't have a clear plan.
When writing a formal report, use data and evidence to support your argument, add visuals, use consistent fonts and headings, and highlight important information. You should also use clear language that is easy to understand, considering the audience's background knowledge. 1. Only use credible sources.
Add your name, the names of the other people who worked on it and the date under the title. Write an index or table of contents: A table of contents or index is essential in any business report, especially if the document is long and complex. Add a list of each section of the document under the title and ensure the page numbers accurately match ...
Front matter: List your name, job title, contact information, and the date of submission. You can also create a title for the report. Background: State the background of the topic you'll be addressing, along with the purpose of the report itself. Key findings: Provide facts, data, and key findings that are relevant to the purpose stated in ...
These reports provide all the nitty-gritty details of specific aspects of your business without any conclusions or opinions. Examples include daily sales reports, inventory levels, or even project updates. This is the essential "just the facts, ma'am" type of report you need to stay in the loop. 2. Analytical reports.
In this post, then, we'll look at how to structure a business report for maximum clarity and professionalism. 1. Title Page. Every business report should feature a title page. The title itself should clearly set out what the report is about. Typically, you should also include your name and the date of the report. 2.
Level Up Your Team. See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Through bullet points, graphs, and FAQs, great business reports list key findings and relevant information from executive or team meetings to share with others. Learn about the importance of business reports and how to write concise reports.
When you write a business-style report, you should understand that, to some extent, you will need to rewrite it repeatedly. Remember, commit to regularly assessing your reports, and success will be yours for the taking. You can easily find a sample of a business report on the Internet, but not all of them fit your needs. Make sure, at any ...
Give your report a title. Depending on the brief, you may receive the title of the report or you may write it yourself. At the beginning of the report, make sure the title is clear and visible. The report should also include your name, the names of others who worked on it, and the date it was written.
A business report is a document that presents information in a structured format, typically written for a specific audience or purpose. Business reports are used to convey data, research findings, recommendations, and other types of information in a clear, concise, and organized manner. Business reports may be written for a variety of contexts.
3. Add a title. You might get the title of the report with the brief or you may write it yourself. Make sure the title is clear and visible at the beginning of the report. You should also add your name and the names of others who have worked on the report and the date you wrote it. 4.
Check out the list of steps in writing your business reports on your company's behalf: 1. Identify the type of report you want to write. You need to discover the type of solution you're looking to determine with your report. A recommendation or periodic report is advised for solutions that your company should take, where it allows you to factor ...
A business report is a formal document that provides an analysis of a specific business issue or situation. It typically includes detailed information on the topic at hand such as data, research, and other relevant sources. Business reports are used to make business decisions, identify problems or opportunities, or track progress toward goals.
Tip: Even though this is the first section, consider writing this section after you have finished the report. This will help you determine which points are the most important to address. Introduction: This section outlines what you will be going over in your report. It includes the main points, chosen report structure, and, most importantly ...
Review each comment from the peer review and rewrite the report, taking comments into consideration. 11. Create a table of contents. Format the business report as formally as possible, creating a table of contents to make it easy to reference and flip through your report.
Business acumen. A business report is a document in which the author analyses a business issue and gives recommendations based on that analysis. It may also be referred to as writing a business case or a manager's briefing. HR practitioners are likely to write business reports to summarise their investigations into a particular situation (for ...
In this video, you'll learn more about writing a powerful business report. Visit https://www.gcflearnfree.org/business-communication/how-to-write-a-powerful-...
Writing an effective business report is a necessary skill for communicating ideas in the business environment. Reports usually address a specific issue or problem, and are often commissioned when a decision needs to be made. They present the author's findings in relation to the issue or problem and then
How to write a business report. When it comes to writing a business report, prepare to compile research and break up the contents of the document by section. If the report has multiple sections, consider including a summary or abstract at the start of the report. Traditionally, bullet points, headings, and subheadings are also good tools to ...
The following is the format of a business report: Step 1: Create a plan before writing. Before commencing the report, identify the purpose of the report. Find out the objective to accomplish with ...
When planning your report, you may find it helpful to follow these steps: Analyse the problem and identify the purpose of the report. Analyse the audience and the issue. Prepare a work plan and a draft outline. Collect and sort the information you require. Evaluate and organise the information. Revise the draft outline and restructure it if ...
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out ...
By James Sillars, business news reporter. A pause for breath on the FTSE 100 after a 3% gain over the course of past week that took the index to a fresh record closing high. The rally of recent ...
Many business owners are still concerned about the downstream impact the collapse of the Francis Scott Key Bridge accident will have on their bottom lines.
New York CNN —. ABC News President Kim Godwin is skating on thinner and thinner ice. Debra OConnell, the well-liked and respected media veteran who was tapped by Burbank in February for a newly ...
Chun-Teh Chen/Moment Editorial/Getty Images. Trump could face a $100 million tax bill after the IRS said he tried to write off the same losses twice. The losses are tied to the 92-story Trump ...
1 Month $1. Vault's Viewpoint How to Start an LLC Business in Texas Step 1: Choose a Business Name for the LLC Before registering your business, ensure its intended name (or something very ...
A previously unknown focus of an I.R.S. audit is a dubious accounting maneuver that effectively meant taking the same write-offs twice on a Chicago skyscraper. The I.R.S. believes that former ...
Eddy Cue, the Apple executive known as Cook's closest confidant, has privately told colleagues that Ternus should be the next CEO, according to a person with knowledge of the matter. Apple has ...