

How Zara became the undisputed king of fast fashion?
Zara is one of the biggest international apparel brands. Zara invites customers from around 93 markets to its organization of 2000+ stores in upscale markets on the planet’s biggest urban communities. With these stores, Zara generates 18 billion Euros annually.
The brand has been fruitful in keeping up its central goal to give quick and reasonable designs in the world of fashion. Zara’s way to deal with configuration is firmly connected to its clients. This story is about how Zara became the undisputed king of Fast fashion.
Fashion is the imitation of a given example and satisfies the demand for social adaptation. . . . The more an article becomes subject to rapid changes of fashion, the greater the demand for cheap products of its kind. — Georg Simmel, “Fashion” (1904)
History of Zara: The Long Story Cut Short
Amancio Ortega launched the first Zara store in 1975 in Central Street in downtown A Coruna, Galicia, Spain. The main Store included low-value look-a-like designs of famous and better-quality dress styles. The store ended up being a triumph and Ortega Began opening more Zara stores throughout Spain.
During the 1980s, Ortega began changing the plan, assembling and dissemination cycle to diminish lead times and respond to new patterns in a snappier manner in what they called “Moment Fashions”.
In 1980 the company started its international expansion through Porto, Portugal in the 1990s, with Mexico in 1992. Since then Ortega has continued to grow and create brands such as Pull & Bear, Bershka , and Oysho . It has acquired groups like Massimo Dutti and Stradivarius . Even though these brands have been contributors to their parent group Inditex’s success, Zara is still the principal growth driver.
Zara’s Customer-driven Value Chain
Product line-up:.
Unlike other Inditex chains, Zara has focused on manufacturing fashion-sensitive products internally. The latest designs were continuously in production as per changing customer’s preferences. Many competitors were producing just a few thousand SKUs whereas Zara was producing several hundred of thousands of SKUs in a year. These SKUs varied as per color, size, and fabric.
Zara’s designs are not dependent on design maestros. Instead, its designers carefully observe the catwalk trends and try to implement them for the mass market. The design team continuously creates variations in a particular season. Thereafter expanding on successful designs.
Fast Supply Chain:
Zara’s flexible supply chain allows it to dispatch new ranges to shops two times per week from its central distribution center that is an approximately 400,000-square-meter facility located in Arteixo, Spain. This kind of business system called vertical integration eliminated the need for local warehouses. The strategy here was to reduce the “bullwhip effect”. Let’s see what the bullwhip effect is:
The bullwhip effect is a distribution channel phenomenon in which demand forecasts yield supply chain inefficiencies. It refers to increasing swings in inventory in response to shifts in consumer demand as one moves further up the supply chain. Wikipedia
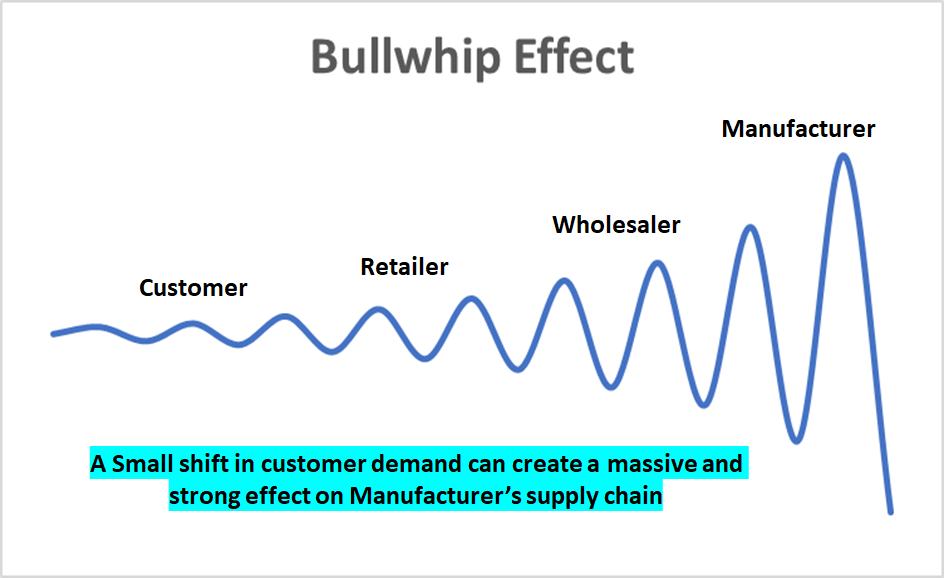
It was a matter of a few weeks and a new design was on the shelf for the customers. Isn’t cool? These designs of clothes and accessories were quickly moved to fancy stores in prime locations but at a cheap price. This strategy has attracted a lot of fashion yet money conscious customers.
We want our customers to understand that if they like something, they must buy it now because it won’t be in the shops the following week. It is all about creating a climate of scarcity and opportunity. Luis Blanc, one of the former Inditex’s international directors
Zara’s Retailing Strategy
Zara instead of focusing on improving its manufacturing efficiency focused on improving its retail strategy. This retailing strategy was about following fashion trends quickly even it means there is an unmet demand. As was previously discussed, this also helped Zara in creating a FOMO for its products. The two components of its retailing strategy were dependent on its upstream operations: Merchandizing and Stores.
Read: The Torchbearers of Sustainable Fashion
Merchandising.
Merchandising is the promotion of goods and/or services that are available for retail sale. It includes the determination of quantities, setting prices for goods and services, creating display designs, developing marketing strategies, and establishing discounts or coupons. Investopedia
- Zara placed emphasis on the freshness of its designs. It wanted to create a sense of exclusivity. It never focused on creating bulk items of one design. Zara had confidence in its fast supply chain of twice a week shipment to the store with the latest designs. Thre quarter of its merchandise gets replaced in just a month. How about that?
The success of your business is based in principle on the idea of offering the latest fashions at low prices, in turn creating a formula for cutting costs: an integrated business in which it is manufactured, distributed, and sold. Amancio Ortega
Fun Fact : An average customer visits a Zara store 17 times in a year where the number is 3-4 times for its competitors.
- Zara understood the importance of store locations very well. Zara prices are not expensive but its store location and design made its products look expensive. The brand wanted its customers to have a premium feel at a reasonable price.
We invest in prime locations. We place great care in the presentation of our storefronts. That is how we project our image. We want our clients to enter a beautiful store, where they are offered the latest fashions. Luis Blanc, one of the former Inditex’s international directors
Store Operations
Zara has stores in most upscale markets and shopping centers in the world. You name it and they have a store there. Champs Elysées in Paris, Regent Street in London, and Fifth Avenue in New York to name a few. As per its latest annual report the value of these properties is valued at almost 8 billion Euros. But the way these stores are managed is a strategy to learn for all retailers.
- We all love grand stores with a lot of variety. Zara has emphasized on creating a grand image of its stores. Imagine a big store at a posh location. How much impressed you would be. The average size of Zara stores has continuously increased over the years. In 2001 the average store size was 910 sq.m whereas in 2018 the size has more than doubled.
Zara’s average store size has increased by 50%: from 1,452m2 in 2012 to 2,184m2 in 2018. That growth has been driven by new store openings – larger flagship stores – as well as the fact that many of the new openings have entailed the absorption of one or more older, smaller units in the same catchment area. Inditex Annual Report
- Zara has tried to standardize the in-store experience with its store window displays and interior presentations. As the season progresses, Zara consistently evolves its interior themes, color schemes, and product placements. All these ideas come from the central team in Spain and regional teams implement with necessary region-based adaptations. So much so that the uniforms of the staff were selected twice in a season by a store manager from the latest collection.

Anti-Marketing Approach of Zara
Zara has able to maintain profitability ~13% whereas its major competitor like H&M is at 6% . This has been possible not only because of its efficient supply chain we discussed above but also because of its no advertising or limited advertising policy.
This is what makes Zara really one of a kind. The organization just spends about 0.3% of deals on promoting and does not have a lot of advertising to discuss. The usual trend in the industry is to spend 3.5% on advertising. Zara never shows its clothes at expensive fashion shows also. It first shows its designs at stores directly. But why does not Zara believe in advertising? There are primarily two reasons:
- First, as we discussed it saves Zara a lot of money. So much so that it has now one of the highest profitability.
- Second, it brings exclusivity and prevents overexposure of a design. Customers feel like if they purchase a shirt at Zara, five others won’t have that equivalent shirt at work or school.
Read: Viral Marketing over the Long-Haul ft. Burger King
Zara is a perfect case study to learn the perfect operations strategy, perfect marketing strategy, perfect pricing strategy, and whatnot. It’s all strategies are so perfect. It is also a perfect example to understand how a traditional brand is evolving itself with time to stay relevant.
As per its annual report , In 2018, Zara launched its global online store, marking a milestone in its commitment to having all of its brands available online worldwide by 2020. Zara continued to earn global accolades for its collections and initiatives, its integrated shopping experience, and its commitment to sustainability, with over 90 million garments put on sale under the Join Life label.
Zara is just not a brand of fast fashion. Its much more than that now. And that’s why it’s actually the true king of fast fashion.
Interested in reading our Advanced Strategy Stories . Check out our collection.
Also check out our most loved stories below

IKEA- The new master of Glocalization in India?
IKEA is a global giant. But for India the brand modified its business strategies. The adaptation strategy by a global brand is called Glocalization

Why do some companies succeed consistently while others fail?
What is Adjacency Expansion strategy? How Nike has used it over the decades to outperform its competition and venture into segments other than shoes?

Nike doesn’t sell shoes. It sells an idea!!
Nike has built one of the most powerful brands in the world through its benefit based marketing strategy. What is this strategy and how Nike has used it?

Domino’s is not a pizza delivery company. What is it then?
How one step towards digital transformation completely changed the brand perception of Domino’s from a pizza delivery company to a technology company?

Why does Tesla’s Zero Dollar Budget Marketing work?
Touted as the most valuable car company in the world, Tesla firmly sticks to its zero dollar marketing. Then what is Tesla’s marketing strategy?

Microsoft – How to Be Cool by Making Others Cool
Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella said, “You join here, not to be cool, but to make others cool.” We decode the strategy powered by this statement.

A marketing aggregator, business story teller, freelancer. I'm pursuing my PGPM, and is a 2nd year marketing student at MDI.
Related Posts

AI is Shattering the Chains of Traditional Procurement

Revolutionizing Supply Chain Planning with AI: The Future Unleashed

Is AI the death knell for traditional supply chain management?
Merchant-focused Business & Growth Strategy of Shopify

Business, Growth & Acquisition Strategy of Salesforce

Hybrid Business Strategy of IBM

Strategy Ingredients that make Natural Ice Cream a King

Investing in Consumer Staples: Profiting from Caution

Storytelling: The best strategy for brands

How Acquisitions Drive the Business Strategy of New York Times

Rely on Annual Planning at Your Peril

How does Vinted make money by selling Pre-Owned clothes?

N26 Business Model: Changing banking for the better

Sprinklr Business Model: Managing Unified Customer Experience

How does OpenTable make money | Business model
How does Paytm make money | Business Model
Write a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Advanced Strategies
- Brand Marketing
- Digital Marketing
- Luxury Business
- Startup Strategies
- 1 Minute Strategy Stories
- Business Or Revenue Model
- Forward Thinking Strategies
- Infographics
- Publish & Promote Your Article
- Write Article
- Testimonials
- TSS Programs
- Fight Against Covid
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and condition
- Refund/Cancellation Policy
- Master Sessions
- Live Courses
- Playbook & Guides
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- April 2003 (Revised December 2006)
- HBS Case Collection
ZARA: Fast Fashion
- Format: Print
- | Pages: 35
Related Work
- Faculty Research
- ZARA: Fast Fashion By: Pankaj Ghemawat and Jose Luis Nueno

How Zara’s strategy made her the queen of fast fashion
Table of contents, here’s what you’ll learn from zara's strategy study:.
- How to come up with disruptive ideas for your industry.
- How finding the right people is more important than developing the best strategy.
- How best to address the sustainability question.
Zara is a privately held multinational clothing retail chain with a focus on fast fashion. It was founded by Amancio Ortega in 1975 and it’s the largest company of the Inditex group.
Amancio Ortega was Inditex’s Chairman until 2011 and Zara’s CEO until 2005. The current CEO of Zara is Óscar García Maceiras and Marta Ortega Pérez, daughter of the founder, is the current Chairwoman of Inditex.
Zara's market share and key statistics:
- Brand value of $25,4 billion in 2022
- Net sales of $19,6 billion in 2021
- 1,939 stores worldwide in 2021
- Over 4 billion annual visits to its website
- Inditex employee count of 165,042 in 2021
{{cta('ba277e9c-bdee-47b7-859b-a090f03f4b33')}}

Humble beginnings: How did Zara start?
Most people date Zara’s birth to 1975, when Amancio Ortega and Rosalia Mera, his then-wife, opened the first shop. But, it’s impossible to study the company’s first steps, its initial competitive advantage, and strategic approach by starting at that point in time.
When the first Zara shop opened, Amancio Ortega already had 22 years of industry experience, ten years as a clever and hard-working employee, and 12 years as a business owner. Rosalia Mera also had 20 years of industry experience.
As an employee , Ortega worked in the clothing industry, first as a gofer and then as a delivery boy. He quickly demonstrated great talent for recognizing fabrics, understanding and serving customers, and making sound business suggestions. Soon, he decided to use his insights to develop his own business instead of his boss’s.
As a business owner , he started GOA Confecciones in 1963, along with his siblings, his wife, and a close friend. They started with a humble workshop making women’s quilted dressing gowns, following a trend at the time Amancio had noticed. Within ten years, that workshop had grown to support a workforce of 500 people.
And then, the couple opened the first Zara shop.
Zara’s competitive positioning strategy in its first year
The opening of the first Zara shop in 1975 wasn’t just a new store to sell clothes. It was the final big move of a carefully planned vertical integration strategy.
To understand how the strategy was formulated , we need to understand Amancio’s first steps. His first business, GOA Confecciones, was a manufacturing business. He was supplying small stores and businesses with his products, and he wasn’t in contact with the end customer.
That brought two challenges:
- A lack of insight into market trends and no direct consumer feedback about preferences.
- Very low-profit margins compared to the 70-80% profit margin of retailers.
Amancio developed several ideas to improve distribution and get a direct relationship with the final purchaser. And he was always updating his factories with the latest technological advancements to offer the highest quality of products at the lowest possible price. But he was missing one essential part to reap the benefits of his distribution practices: a store .
So, in 1972 he opened one under the brand name Sprint . An experiment that quickly proved unsuccessful and, seven years later, was shut down. Although it’s unknown the extent to which Amancio put his ideas to the test, Sprint was a private masterclass in the retail world that gave Amancio insights that would later turn Zara into a global success.
Despite Sprint’s failure, Amancio didn’t abandon the idea of opening his own store mainly because he believed that his advanced production model was vulnerable and the rise of a competitor who could replicate and improve his system was imminent.
Adding a store to his vertical integration strategy would have a twofold effect:
- The store would operate as a direct feedback source. The company would be able to test design ideas before going into mass production while simultaneously getting an accurate pulse of the needs, tastes, and fancies of the customers. The store would simultaneously reduce risk and increase opportunity spotting.
- The company would have reduced operating costs as a retailer. Since the group would control all aspects of the process (from manufacturing to distribution to selling), it would solve key retail challenges with stocking. The savings would then be passed on to the customer. The store would have an operational competitive advantage and become a potential cash cow for the company.
The idea was to claim his spot in prime commercial areas (a core and persistent strategic move for Zara) and target the rising middle class. The market conditions were tough, though, with many family-owned businesses losing their customer base, giant players owning a huge market share, and Benetton’s franchising shops stealing great shop locations and competent potential managers.
So the first Zara store had these defining characteristics that made it the successful final piece of Amancio’s strategy:
- It was located near the factory = delivery of products was optimized
- It was in the city’s commercial heart = more expensive, but with access to affluence
- It was located in the city where Ortegas had the most customer experience = knowing thy customer
- It was visibly attractive = expensive, but a great marketing trick
Amancio’s team lacked experience and expertise in one key factor: display window designing . The display window was a massive differentiator and had to be bold and attractive. So, Amancio hired Jordi Bernadó, a designer with innovative ideas whose work transformed display windows and the sales process.
The Zara shop was a success, laying the foundations for the international expansion of the Inditex group.
Key Takeaway #1: Challenge your industry’s conventional wisdom to create a disruptive strategy
Disrupting an industry isn’t an easy task nor a frequent occurrence.
To do it successfully, you need to:
- Understand the prominent business mode of your industry and the forces that contributed to its development.
- Challenge the assumptions behind it and design a radically different business model.
- Develop ample space for experimentation and failures.
The odds of instantly conquering the industry might be low (otherwise, someone would have already done it), but you’ll end up with out-of-the-box ideas and a higher sensitivity to potential disruptors in your competitive arena.
Recommended reading: How To Write A Strategic Plan + Example
How Zara’s supply chain strategy is at the core of its business strategy
According to many analysts, the Zara supply chain strategy is its most important innovative component.
Amancio Ortega and other senior members of the group disagree. Nevertheless, the Inditex logistics strategy is extraordinarily efficient and plays a crucial role in sustaining its competitive advantage. Most companies in the clothing retail industry take an average of 4-8 weeks between inception and putting the product on the shelf. The group achieves the same in an average of two weeks. That’s nothing short of extraordinary.
Let’s see how Zara developed its logistics and business strategy.
Innovative logistics: how Zara’s supply chain evolved
The logistics methods developed by companies are highly dependent on external factors.
Take, for example, infrastructure. In the early days of Zara, when it was expanding through Spain, the company considered using trains as a transportation system. However, the schedule couldn’t keep up with Zara’s needs, which had the goal of distributing products twice a week to its shops. So transportation by road was the only way.
However, when efficiency is a high priority, it shapes logistics processes more than anything else.
And for Zara, efficient logistics was – and still is – of the highest priority.
Initially, leadership tried outsourcing logistics, but the experiment failed and the company assigned a member of the house with a thorough knowledge of the company's operating philosophy to take charge of the project. The tactic of entrusting important big projects to employees imbued with the company’s philosophy became a defining characteristic.
So, one of Zara’s early strategic decisions was that each shop would make orders twice a week. Since the first store was opened, the company has had the shortest stock rotation times in the industry. That’s what drove the development of its logistics methods. The whole strategy behind Zara relied on quick production and distribution. And the proximity of manufacturing and distribution was essential for the model to work. So Zara had these two centers in the same place.
Even when the brand was expanding around the world, its logistics center remained in Arteixo, Spain, despite being a less-than-ideal location for international distribution. At some point, the growth of the brand, and Inditex as a whole, outpaced Arteixo’s capacity, and the decentralization question came up.
The debate was tough among leadership, but the arguments were strong. Decentralization was necessary because of:
- Safety and security. If there was a fire or any other crippling disaster there (especially on a distribution day), then the company would face serious troubles on multiple fronts.
- Arteixo’s limitations. The company’s center in Arteixo was reaching its capacity limits.
So the company decided to decentralize the manufacturing and distribution of its brands.
Initially, the group made the decision to place differentiated logistics centers where the management of its chain of stores was based, i.e. Bershka would have a different logistics center than Pull&Bear, although they were both part of the Inditex Group. That idea emerged after Massimo Dutti and Stradivarius became part of Inditex. Those brands already had that geographical structure, and since the group integrated them successfully into its strategy and logistics model, it made sense to follow the same pattern with its other brands.
Besides, the proximity of the distribution centers to the headquarters of each brand allowed them to consolidate them based on the growth strategy and purpose of each brand (more on this later).
But just a few years after that, the group decided to build another production center for Zara that forced specialization between the two Zara centers. The specialization was based on location, i.e. each center would manufacture products that would stock the shelves of stores in specific locations.
Zara’s supply chain strategy is so successful because it’s constantly evolving as the group adapts to external circumstances and its internal needs. And just like its iconic fashion, the company always stays ahead of the logistics curve.

Zara’s business strategy transcends its logistics innovations
Zara’s business strategy relies on four key pillars:
- Flexibility of supply
- Instant absorption of market demand
- Response speed
- Technological innovation
Zara is the only brand in the Inditex group that is concerned with manufacturing. It’s the first brand in the clothing sector with a complete vertical organization. And the production model requires the adoption or development of the latest technological innovations.
This requirement is counterintuitive in the clothing sector.
Most people believe that making big investments in a market as mature as clothing is a bad idea. But the Zara production model is very capital and labor intensive. The technological edge derived from that investment gave the company, in the early days, the capability to manufacture over 50% of its own products while maintaining an extremely high stock rotation frequency.
Zara might be one of the best logistics companies in the world, but that particular excellence is a supporting factor, or at least a highly contributing factor, to its successful business strategy.

Zara’s business strategy is so much more than its supply chain strategy.
The company created the “fast fashion” term and industry. When other companies were manufacturing their collections once per season, Zara was adapting its collection to suit what people asked for on a weekly basis. The idea was to offer fashionable items at a fair price and faster than everybody else.
Part of its cost-cutting strategic priority was its marketing strategy. Zara didn’t – and still doesn’t – advertise like the rest of the clothing industry. Its marketing strategy starts with choosing the location of the stores and ends with advertising that the sales period has started. In the early years of the brand’s expansion, Amancio would visit potential store locations himself and choose the site to build the Zara shop.
The price was never an issue. If the location was in a commercial center, Zara would build its store there no matter how high the cost was because the company expected to recoup it quickly with increased sales.
Zara’s marketing is its own stores.
The strategy of Zara and her Inditex sisters
Despite Zara’s success (or because of it), Amancio Ortega created – or bought – multiple other brands that he included in the Inditex group, each one with a specific purpose.
- Zara was targeting middle-class women.
- Pull&Bear was targeting young people under twenty-five years old with casual clothing.
- Bershka was targeting rebel teens, especially girls, with hip-hop-style clothing.
- Massimo Dutti was targeting both sexes with more affluence.
- Stradivarius was competing with Bershka, giving Inditex two major brands in the teenage market.
- Oysho was concentrating on women's lingerie.
- Zara Home manufactures home textiles and decor.
Pull&Bear was initially targeting young males between the ages of 14 and 28. Later it extended to young females of the same age and focused on selling leisure and sports clothing. It has the slowest stock turnaround time in the group.
Bershka’s target group was girls between 13 and 23 years of age with highly individualized tastes. Prices were low, but the quality average. Almost a fiasco in the beginning, it underwent a successful strategic turnaround becoming today one of the biggest growth opportunities for the group. And out of all the Inditex chains, Bershka has the most creative designs.
Massimo Dutti was the first retail brand Amancio bought and didn’t create himself. Its strategy is very different from Zara, producing high-quality products and selling them at a high price. It’s an extension of the group’s offer to the higher end of the price spectrum in the fashion industry. It’s also the only Inditex chain brand that advertises regularly.
Stradivarius was the second acquired brand, with the purchase being a defensive move. The chain shares the same target group with Bershka, making it, to this day, a direct competitor.
Oysho started as an underwear and lingerie company. Its product lines evolved to include comfortable night and homewear along with swimwear and a very young children’s line. The brand’s strategy was aggressive from its conception, opening 286 stores in its first six years of existence.
Zara Home is the youngest brand in the Group and the only one outside the clothing sector, though still in the fashion industry. It was launched with the least confidence and with immense prior research. An experiment to extend the Zara brand beyond clothing, it was based on the conservative view that Zara could extend its product categories only to textile items for the home. But it turned out that customers were more accepting of Zara Home selling a wide variety of domestic items. So the brand made a successful strategic pivot.

Key Takeaway #2: The right people are more important than the best strategy
It might not be obvious in the story, but a key reason for Zara's and Inditex’s success has been the people behind them.
For example, a vast number of people in various positions from inside the group claim that Inditex cannot be understood without Amancio Ortega. Additionally, major projects like the development of Zara’s logistics systems and the group's international expansion had such a success precisely because of the people in charge of them.
Zara’s radically different model was a breakthrough because:
- Its leadership had a clear vision and a real strategy to execute it.
- People with a deep understanding of the company’s philosophy led Its largest projects.
Sustainability: Zara’s strategy to make fast fashion sustainable
Building a sustainable business in the fast fashion industry is a tough nut to crack.
To achieve it, Inditex has made sustainability a cornerstone of its business model. Its strategy revolves around the values of collaboration , transparency, and innovation . The group’s ambition is to make a positive impact with a vision of prosperity for the planet and its people by transforming its value chain and industry.
Inditex’s sustainability commitments and strategy to achieve them
Inditex has developed a sustainability roadmap that extends up to 2040 with ambitious goals. Specifically, it has committed to
- 100% consumption of renewable energy in all of its facilities by 2022 (report pending).
- 100% of its cotton to originate from more sustainable sources by 2023.
- 100% of its man-made cellulosic fibers to originate from more sustainable sources by 2023.
- Zero waste from its facilities by 2023.
- 100% elimination of single-use plastic for customers by 2023.
- 100% collection of packaging material for recycling or reuse by 2023.
- 100% of its polyester to originate from more sustainable sources by 2025.
- 100% of its linen to originate from sustainable sources by 2025.
- 25% reduction of water consumption in its supply chain by 2025.
- Net zero emissions by 2040.
The group’s commitments extend beyond environmental issues to how its manufacturing and supplying partners conduct their business . To bring its strategy to fruition, it has set up a new governance and management structure.
The Board of Directors is responsible for approving Inditex’s sustainability strategy. The Sustainability Committee oversees and controls all the proposals around the social, environmental, health, and safety impact of the group’s products, while the Ethics Committee makes sure operations are compliant with the rules of conduct. There is also a Social Advisory Board that includes external independent experts that advises Inditex on sustainability issues.
Finally, Javier Losada, previously the group’s Chief Sustainability Officer and now promoted to Chief Operations Officer, will be leading the sustainability transformation of the group. Javier Losada first joined Inditex back in 1993 and ascended its rank to reach the C-suite.
Inditex is dedicated to its commitment to reducing its environmental impact and seems to be headed in the right direction. The only question is whether it’s fast enough.
Key Takeaway #3: Integrating sustainability with business strategy is a present-day necessity
Governments and international bodies around the world are implementing more stringent environmental regulations, forcing companies to commit to ambitious goals and developing a realistic strategy to achieve them.
The companies that are impacted the least are those that always had sustainability as a high priority .
From the companies that require significant changes in their operations to comply with the new regulations, only those who integrate sustainability into their business strategy and model will succeed.
Why is Zara so successful?

Zara is the biggest Spanish clothing retailer in the world based on sales value. Its success is due to its fast fashion strategy that is based on a strong supply chain and quick market feedback loops.
Zara's customer-centric approach places a strong emphasis on understanding and responding to customer needs and preferences. This is reflected in the company's product design, marketing, and customer service strategies.
Zara made fashionable clothes accessible to the middle class.
Zara’s vision guides its future
Zara's vision, as part of the Inditex Group, is to create a sustainable fashion industry by promoting responsible consumption and production, respecting the environment and people, and contributing to the communities in which it operates.
The company aims to offer the latest fashion trends to its customers at accessible prices while continuously innovating and improving its operations and processes.
Growth by numbers (Inditex)

Digital Innovation and Transformation
Mba student perspectives.
- Assignments
- Assignment: Data and Analytics as…
ZARA: Achieving the “Fast” in Fast Fashion through Analytics

How does fast fashion make any business sense? Zara uses intensive data and analytics to manage a tight supply chain and give customers exactly what they want.
Introduction
Zara’s parent company Inditex has managed to thrive in the last decade while several other fashion retailers have faced declining sales or stagnant growth. Inditex has grown over 220% in annual revenue since 2004, more than its key competitors like H&M, Gap, or Banana Republic (1).
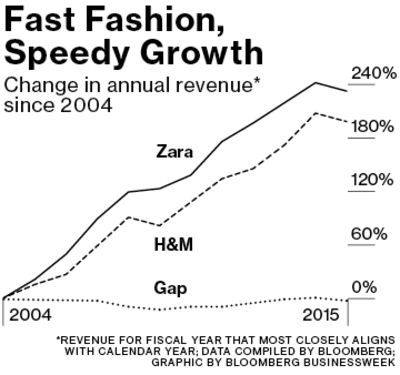
The value of a fast fashion brand is to bring the latest designs and “trendiest trends” into the market as quickly as possible, preferably as soon as they became hot on the catwalk, and to provide these at a reasonable price. The traditional fashion industry is not well equipped to provide such value as it operates on a bi-annual or seasonal basis, with long production lead times due to outsourced manufacturing to low cost-centers. Zara has turned the industry on its head by using data and analytics to track demand on a real-time, localized basis and push new inventory in response to customer pull. This enables them to manage one of the most efficient supply chains in the fashion industry, and to create the fast fashion category as a market leader.
Pathways to a Just Digital Future
How Zara Uses Data
Inditex is a mammoth retailer, producing over 840 million garments in a year, the majority of which are sold by Zara (2). Every item of clothing is tagged with an RFID microchip before it leaves a centralized warehouse, which enables them to track that piece of inventory until it is sold to a customer (3). The data about the sale of each SKU, inventory levels in each store, and the speed at which a particular SKU moves from the shelf to the POS is sent on a real time basis to Inditex’s central data processing center (see picture below). This center is open 24 hours a day and collects information from all 6000+ Inditex stores across 80+ countries and is used by teams for inventory management, distribution, design and customer service improvements (4).

Zara’s Data Processing Center receives real-time data from around the world (4).
When the apparel arrives in store, RFID enables the stockist to determine which items need replenishing and where they are located, which has made their inventory and stock takes 80% faster than before (3). If a customer needs a particular SKU, salespeople are able to serve them better by locating it immediately in store or at a nearby location. Moreover, every Zara location receives inventory replenishments twice a week, which is tailored to that stores real-time updates on SKU-level inventory data.
The sales tracking data is critical in enabling Zara to serve its customers with trends that they actually want, and eliminate designs that don’t have customer pull. Zara’s design team is an egalitarian team of over 350 designers that use inspiration from the catwalk to design apparel on daily basis. Every morning, they dive through the sales data from stores across the world to determine what items are selling and accordingly tailor their designs that day. They also receive qualitative feedback from empowered sales employees that send in feedback and customer sentiment on a daily basis to the central HQ e.g., “customers don’t like the zipper” or “she wishes it was longer” (1).
At the start of the planning process, Zara orders very small batches of any given design from their manufacturers (even just 4-6 of a shirt per store). The majority of Zara’s factories are located proximally in Europe and North Africa, enabling them to manufacture new designs close to home and ship them to their stores within 2-3 weeks. They then test these designs in store, and if the data suggests the designs take off, Zara can quickly order more inventory in the right sizes, in the locations that demanded it. Such store-level data allows Zara to be hyper-local in serving their customer’s needs – as tastes can vary on a neighborhood level. As Inditex’s communication director told the New York Times,
“ Neighborhoods share trends more than countries do. For example, the store on Fifth Avenue in Midtown New York is more similar to the store in Ginza, Tokyo, which is an elegant area that’s also touristic. And SoHo is closer to Shibuya, which is very trendy and young.” (5)
Unlike other retailers that may order inventory based on their hypotheses about tastes at a regional level, Zara is tailors its collections based on the exact zip code and demographic that a given location serves (5).
Zara’s Results vs. Competitors
Zara sells over 11,000 distinct items per year versus its competitors that carry 2,000 to 4,000. However Zara also boasts the lowest year-end inventory levels in the fashion industry. This lean working capital management offsets their higher production costs and enables them to boast rapid sales turnover rates.
At Zara, only 15% to 25% of a line is designed ahead of the season, and over 50% of items are designed and manufactured in the middle of a season based on what becomes popular (2). This is in direct contrast to a close competitor like H&M where 80% of designs are made ahead of the season, and 20% is done in real-time during the season (6). Most other retailers commit 100% of their designs ahead of a season, and are often left with excess inventory that they then have to discount heavily at season-end. Instead, Zara’s quick replenishment cycles create a sense of scarcity which might actually generate more demand:
“With Zara, you know that if you don’t buy it, right then and there, within 11 days the entire stock will change. You buy it now or never.” (5)
- https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2016-11-23/zara-s-recipe-for-success-more-data-fewer-bosses
- http://www.digitalistmag.com/digital-supply-networks/2016/03/30/zaras-agile-supply-chain-is-source-of-competitive-advantage-04083335
- http://static.inditex.com/annual_report_2015/en/our-priorities/innovation-in-customer-services.php
- http://www.refinery29.com/2016/02/102423/zara-facts?utm_campaign=160322-zara-secrets&utm_content=everywhere&utm_medium=editorial&utm_source=email#slide-11
- http://www.nytimes.com/2012/11/11/magazine/how-zara-grew-into-the-worlds-largest-fashion-retailer.html?pagewanted=all
- https://erply.com/in-the-success-stories-of-hm-zara-ikea-and-walmart-luck-is-not-a-key-factor/
Student comments on ZARA: Achieving the “Fast” in Fast Fashion through Analytics
Great post Ravneet – I had never read about Zara’s extremely quick supply chain or hyper-local testing. I have a question for you about fast fashion in general, but especially for Zara since it produces and sells more distinct items than its competitors: it seems that many designers are not fond of the “runway-inspired” fashions sold at these stores and some have even sued stores for copying their designs. Do you think Zara and other brands like it are doing anything wrong, and if not, what recourse do designers have for “imitations” of their work?
Thanks for the post Ravneet. Zara and H&M are beacons of hope for a mostly distressed industry. Do you think Zara’s advantage could be sustained in the event of a full-on assault by the Amazons of the world?
Leave a comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Zara's Secret for Fast Fashion
by Kasra Ferdows, Michael A. Lewis and Jose A.D. Machuca
Editor's note: With some 650 stores in 50 countries, Spanish clothing retailer Zara has hit on a formula for supply chain success that works by defying conventional wisdom. This excerpt from a recent Harvard Business Review profile zeros in on how Zara's supply chain communicates, allowing it to design, produce, and deliver a garment in fifteen days.
In Zara stores, customers can always find new products—but they're in limited supply. There is a sense of tantalizing exclusivity, since only a few items are on display even though stores are spacious (the average size is around 1,000 square meters). A customer thinks, "This green shirt fits me, and there is one on the rack. If I don't buy it now, I'll lose my chance."
Such a retail concept depends on the regular creation and rapid replenishment of small batches of new goods. Zara's designers create approximately 40,000 new designs annually, from which 10,000 are selected for production. Some of them resemble the latest couture creations. But Zara often beats the high-fashion houses to the market and offers almost the same products, made with less expensive fabric, at much lower prices. Since most garments come in five to six colors and five to seven sizes, Zara's system has to deal with something in the realm of 300,000 new stock-keeping units (SKUs), on average, every year.
This "fast fashion" system depends on a constant exchange of information throughout every part of Zara's supply chain—from customers to store managers, from store managers to market specialists and designers, from designers to production staff, from buyers to subcontractors, from warehouse managers to distributors, and so on. Most companies insert layers of bureaucracy that can bog down communication between departments. But Zara's organization, operational procedures, performance measures, and even its office layouts are all designed to make information transfer easy.
Zara's single, centralized design and production center is attached to Inditex (Zara's parent company) headquarters in La Coruña. It consists of three spacious halls—one for women's clothing lines, one for men's, and one for children's. Unlike most companies, which try to excise redundant labor to cut costs, Zara makes a point of running three parallel, but operationally distinct, product families. Accordingly, separate design, sales, and procurement and production-planning staffs are dedicated to each clothing line. A store may receive three different calls from La Coruña in one week from a market specialist in each channel; a factory making shirts may deal simultaneously with two Zara managers, one for men's shirts and another for children's shirts. Though it's more expensive to operate three channels, the information flow for each channel is fast, direct, and unencumbered by problems in other channels—making the overall supply chain more responsive.
In each hall, floor to ceiling windows overlooking the Spanish countryside reinforce a sense of cheery informality and openness. Unlike companies that sequester their design staffs, Zara's cadre of 200 designers sits right in the midst of the production process. Split among the three lines, these mostly twentysomething designers—hired because of their enthusiasm and talent, no prima donnas allowed—work next to the market specialists and procurement and production planners. Large circular tables play host to impromptu meetings. Racks of the latest fashion magazines and catalogs fill the walls. A small prototype shop has been set up in the corner of each hall, which encourages everyone to comment on new garments as they evolve.
The physical and organizational proximity of the three groups increases both the speed and the quality of the design process. Designers can quickly and informally check initial sketches with colleagues. Market specialists, who are in constant touch with store managers (and many of whom have been store managers themselves), provide quick feedback about the look of the new designs (style, color, fabric, and so on) and suggest possible market price points. Procurement and production planners make preliminary, but crucial, estimates of manufacturing costs and available capacity. The cross-functional teams can examine prototypes in the hall, choose a design, and commit resources for its production and introduction in a few hours, if necessary.
Zara is careful about the way it deploys the latest information technology tools to facilitate these informal exchanges. Customized handheld computers support the connection between the retail stores and La Coruña. These PDAs augment regular (often weekly) phone conversations between the store managers and the market specialists assigned to them. Through the PDAs and telephone conversations, stores transmit all kinds of information to La Coruña—such hard data as orders and sales trends and such soft data as customer reactions and the "buzz" around a new style. While any company can use PDAs to communicate, Zara's flat organization ensures that important conversations don't fall through the bureaucratic cracks.
Once the team selects a prototype for production, the designers refine colors and textures on a computer-aided design system. If the item is to be made in one of Zara's factories, they transmit the specs directly to the relevant cutting machines and other systems in that factory. Bar codes track the cut pieces as they are converted into garments through the various steps involved in production (including sewing operations usually done by subcontractors), distribution, and delivery to the stores, where the communication cycle began.
The constant flow of updated data mitigates the so-called bullwhip effect—the tendency of supply chains (and all open-loop information systems) to amplify small disturbances. A small change in retail orders, for example, can result in wide fluctuations in factory orders after it's transmitted through wholesalers and distributors. In an industry that traditionally allows retailers to change a maximum of 20 percent of their orders once the season has started, Zara lets them adjust 40 percent to 50 percent. In this way, Zara avoids costly overproduction and the subsequent sales and discounting prevalent in the industry.
Excerpted with permission from "Rapid-Fire Fulfillment," Harvard Business Review , Vol. 82, No.11, November 2004.
[ Order the full article ]
Kasra Ferdows is the Heisley Family Professor of Global Manufacturing at Georgetown University's McDonough School of Business in Washington DC.
Michael A. Lewis is a professor of operations and supply management at the University of Bath School of Management in the UK.
Jose A.D. Machuca is a professor of operations management at the University of Seville in Spain.
For Fast Response, Have Extra Capacity on Hand
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

A Case Study on Zara's Digital Transformation

This case study examines Zara’s current retail strategy and digital transformation. It details Zara’s current in-store and eCommerce retail strategy, the impact of digital on the retail environment and customer experience, and the growth opportunity provided by eCommerce. By providing a competitive analysis of the current market, this paper presents key opportunities, strategic questions, and possible solutions for retail brands to improve their digital strategy. This paper received First Class Honors in the Digital Marketing Strategy course at Trinity Business School.
Related Papers
Lea Valentine F Steinlein
Dinh Nam Nguyen
The successful implementation of an integrated supply chain strategy enhances total control over the operations and thus enhances speed and flexibility. The objective of this study is twofold: first to identify the constituents that mold the fast fashion retailing business model, and second to discuss how global leader of fast fashion retailing Inditex-Zara's product offering is strongly supported by integration of various supply chain operations. The findings suggest that vertical integration through ownership of various operational stages including product design and development, production operation, logistics and distribution channel; appropriate sourcing strategy to meet product needs; application of process/product modularity practices in product design, material procurement and manufacturing to ensure manufacturing flexibility; flexible logistics capability; and all of these seamlessly integrated and coordinated by a centralized IT infrastructure can significantly raise overall supply chain flexibility and responsiveness. Inditex-Zara's super-responsive supply chain reduces 'bullwhip effect', order-to-delivery lead time to stores, ensures lean inventory and high level of responsiveness to adapt and deliver products to stores with latest fashion trends and customer feedbacks at a rapid speed. Thus Inditex-Zara is able to successfully counter the negative effects of short product life cycles, high product variety, demand uncertainty and thus able to closely match product supply to the stores with market demand. This contributes to lower inventory backlogs; avoid mark-down losses and/or inventory stock out.
josep valor
Florida Tax Review
Rifat Azam , Orly Mazur
The growth of the digital economy, and, in particular, cloud computing, has put a significant strain on sales taxation and other consumption tax systems. The borderless, anonymous, and digital nature of cloud computing raises questions about the paradigm used to determine the character of the transaction and the location where consumption, and therefore, taxation occurs. From an American perspective, the effective resolution of these issues continues to grow in importance in light of the recent U.S. Supreme Court decision in South Dakota v. Wayfair and the growing number of U.S. businesses transacting overseas in jurisdictions that impose value-added taxes (VATs). The cloud magnifies difficulties with VAT compliance and enforcement, as businesses increasingly are subject to VAT laws in multiple jurisdictions. Tax authorities therefore have to collect from remote vendors who have numerous opportunities for VAT avoidance and evasion. The outcome of these challenges is unfair competition, a burden on international trade, and a huge gap in VAT revenues. In this important article, we closely analyze these cutting-edge challenges and contribute to the debate on how to tax the digital economy. We argue that while the approaches taken by both the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development, of which the United States is a member, and the European Union introduce some noteworthy improvements to the current system, more substantial measures are necessary. Thus, we propose a range of fundamental changes that include improving the existing registration-based VAT system through the enhanced use of new technologies, replacing the current system with a blockchain real-time basis VAT system, and shifting the VAT collection burden from suppliers to payment intermediaries. As the digital transformation of the economy accelerates, each of these changes will help adapt consumption taxation to the modern realities of our digital era.
Theodora A Christou
This report is prepared for the World Bank Legal Department’s Thematic Working Group on Technology and Innovation in Development. The research paper explores the legal issues and considerations the World Bank should take into account when considering financing projects with components that involve disruptive technologies. The report highlights legal and regulatory issues which may either enable or which may impede the adoption or creation of disruptive technologies, particularly in emerging market economies. The authors of the report are Professor Ian Walden and Dr Theodora A Christou, members of the Cloud Legal Project at the Centre for Commercial Law Studies, Queen Mary University London
Administrative Sciences
Dag Øivind Madsen
The Industry 4.0 (I4.0) concept is concerned with the fourth industrial revolution in manufacturing, in which technological trends such as digitalization, automation and artificial intelligence are transforming production processes. Since the concept's introduction at the Hannover Fair in Germany in 2011, I4.0 has enjoyed a meteoric rise in popularity and is currently high on the agenda of governments, politicians and business elites. In light of these observations, some commentators have asked the question of whether I4.0 is a concept that is hyped up and possibly just the latest in a long line of fashionable management concepts introduced over the course of the last few decades. Therefore, the aim of this paper is to provide a critical outside-in look at the emergence and rise of I4.0. Theoretically, these processes are viewed through the lens of management fashion, a theoretical perspective well suited to examinations of evolutionary trajectories of management concepts and ideas. The findings indicate that the I4.0 concept has quickly become highly popular and is dominating much of the popular management discourse. The concept has migrated out of the specialized manufacturing discourse to become a more general concept with mainstream appeal and applicability, evidenced by a multitude of neologisms such as Work 4.0 and Innovation 4.0. The numbers 4.0 have spread in a meme-like fashion, evidenced by the fact that the combination of a noun and the numbers 4.0 are used to signal and usher in discussions about the future of business and society. While there is much evidence that clearly shows that the concept has had a wide-ranging impact at the discursive level, the currently available research is less clear about what impact the concept has had so far on industries and organizations worldwide.
Heart (British Cardiac Society)
Reme Revista Mineira de Enfermagem
Silvia Bocchi
RELATED PAPERS
Journal of Korean Tunnelling and Underground Space Association
Current issues of scientific support for the state anti-corruption policy in the Russian Federation
Telelbachillerato Caracheo Cortazar
CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research - Zenodo
Yamandú Acosta
American journal of medical genetics. Part A
Deborah Wenkert
Journal of Materials Science
Arpita tiwari
Analytica Chimica Acta
Journal of Molecular Structure: THEOCHEM
HAMBATAN DAN PERENCANAAN PEMBANGUNAN DAERAH EFEKTIVITAS PEMBERDAYAAN MASYARAKAT 0LEH KELOMPOK SADAR WISATA (POKDARWIS) DALAM MENGEMBANGKAN PARIWISATA BERKELANJUTAN
Anggun Selfi Febriyani
Jimmy Robot
Sai Lakshmi 1430
Ovidius University Annals: Economic Sciences Series
Alina Elena Ionascu
Dunia keperawatan: Jurnal Keperawatan dan Kesehatan
Arif Imam Hidayat
New England Journal of Medicine
Márcia Boechat
NMIMS Assignments Solutions
IFAC Proceedings Volumes
B. Castillo-toledo
Journal of Communications Technology and Electronics
Đorđe Grozdić
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE on eGOVERNMENT & eGOVERNANCE (ICEBEG-2013)
Sosyal Bilimler Araştırmaları Derneği (Social Sciences Research Society)
Abdulla Hassan Hamad
Materials Advances
Neeleshwar Sonnathi
riyana rajput
Scientific Research Journal
saidu yakubu
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Zara Case Study: How Zara Lead The Fast Fashion Market?
Supti Nandi
Updated on: April 8, 2024

You asked, and we listened! Get ready to dive into the fascinating world of Zara with our highly requested Zara Case Study.
Recently, Zara has been trending in Instagram reels and YouTube shorts for its funky model poses. You must have seen it too! Have you wondered what made this Spanish brand so famous?

You may say that Zara works on the concept of fast fashion, which makes it win in the competitive market.
Well, that’s true but it is not the only reason. Let’s uncover the secrets behind Zara’s success through the Zara Case Study.
Let’s begin!
(A) Zara: A Brief Overview
Zara, a notable name in the fashion industry, is a Spanish retailer known for its distinctive approach to clothing and accessories. Operating on a fast fashion model, Zara excels in swiftly adapting to evolving fashion trends, setting it apart in the market. With a vertically integrated process, the brand manages everything from design to production in-house, allowing for efficient and responsive operations.
You’ll find Zara stores globally, each offering a diverse range of trendy and affordable clothing for men, women, and children. The brand’s commitment to delivering fashion-forward pieces at accessible prices caters to a broad audience, reflecting its significance in the industry.
Do you know what is fast fashion?
Fast fashion is a business model characterized by quickly producing affordable, trendy clothing items to meet rapidly changing consumer demands.
Zara works in the same way. We will look into its details in the upcoming section. Before that, let’s go through the profile of Zara-
What makes Zara stand out is its ability to balance responsiveness in manufacturing, a well-structured supply chain, and a keen understanding of consumer preferences. This combination has established Zara as a trendsetting and influential player in the fashion landscape. Its adaptability and dedication to making fashion trends accessible have solidified Zara’s place as a recognizable and influential name in the fashion industry.
(B) Zara Case Study: History & Evolution
Zara’s journey began with a dress-making factory called Inditex, established by Ortega in 1963. Over the years, Zara expanded its presence from Spain to Portugal and eventually to other European countries, the United States, and France.
Today, Zara boasts nearly 6,500 stores across 88 countries worldwide.
Let’s dive into the history of Zara in detail-
Zara is the flagship brand of the Inditex group, which is one of the world’s largest fashion retail conglomerates.
The head office of Zara is located in Arteixo, in the province of A Coruña, Galicia, Spain. Inditex also owns other popular brands like Massimo Dutti, Pull&Bear, Bershka, and Stradivarius.
(C) Brand Philosophy of Zara
Do you know why Zara stands out among its competitors? Due to its brand philosophy! Sara’s success hinges on several key principles-
Zara’s strategy is strikingly different from traditional fashion retailers. Reason? Fast fashion concept and in-house production of clothes! Go through the next section for detailed information.
(D) Zara Business Model: Effective Working Strategies
In this section, we will dive into the business model of Zara to determine its working strategies that played a huge role in its success-
Let’s dive into the details-
(D.1) Fast Fashion Model
Zara is known for its “ Fast Fashion ” approach. It releases new collections frequently, sometimes launching over 22 new product lines per year. This agility allows Zara to respond swiftly to changing trends and customer preferences.
- Rapid Trend Replication: Harnessing cutting-edge information technology, Zara excels at swiftly replicating prevailing fashion trends. This enables the brand to stay ahead of the curve, delivering the latest styles to customers promptly.
- Group Design Approach: Departing from the conventional individual designer model, Zara adopts a collaborative approach. Teams of designers work in synergy, fostering enhanced creativity and efficiency in product development. This collective effort ensures a diverse range of products aligned with dynamic market demands.
- Cost-Effective Materials: Zara strategically utilizes affordable materials without compromising on quality. This approach allows the brand to maintain competitive pricing while delivering products that meet or exceed industry standards. The focus on cost-effective yet quality materials contributes to Zara’s accessibility and broad customer appeal.
- Competitive Pricing: Zara optimizes its production costs by outsourcing to countries with cost-effective labor. This global approach not only supports competitive pricing but also facilitates the brand’s ability to swiftly adapt to market demands. The combination of efficient production and competitive pricing reinforces Zara’s position as a leader in the fast fashion landscape.

(D.2) Product Range

Let’s briefly look at its product range too-
- Clothing: From chic dresses and tailored suits to casual wear and activewear.
- Accessories: Including bags, shoes, belts, and jewelry.
- Beauty Products: Fragrances and cosmetics.
- Perfumes: Zara has its line of fragrances.
(D.3) Vertical Integration: In-House Operations & Logistics
Zara’s way of doing business centers on something called vertical integration. Here is how it works-
- Design: Zara takes charge of creating its designs, meaning it controls how its clothes look and stay on-trend. This ensures that what you find in Zara stores reflects the latest fashion trends.
- Manufacturing: Zara doesn’t just design; it also makes its clothes in-house. This is a big deal because it lets Zara make changes to its products fast. If there’s a new trend or customer feedback, Zara can respond quickly, which is pretty cool.
- Shipping and Distribution: Zara doesn’t stop at making the clothes; it handles everything from getting them to the store to making sure they’re sent to the right places. This full control of the supply chain ensures that the clothes you see in Zara are not only stylish but also reach the stores efficiently.
In short, the fast fashion concept, vertical integration, and supply chain efficiency helped Zara to achieve impressive milestones.
(E) Revenue Model of Zara: How does Zara make money?
Do you know Zara earned Rs.2,562.50 crore in India? That’s not all. It earned over 23 billion euros from its stores worldwide.
That’s quite amazing! Isn’t it?
But how does Zara earn such a whopping amount of money? Due to its impressive revenue model.
Let’s go through them one by one-
Let’s briefly dive into Zara’s finances for the years 2022 & 2021-
That’s how Zara is going through its purple patch in terms of revenues!
(F) Zara Marketing Strategies
Zara, the renowned Spanish fashion retailer, has crafted a distinctive marketing strategy that contributes to its global success. In this section, we will delve into the key elements of Zara’s marketing approach-
(F.1) Fast Fashion Strategy
The fast fashion model functions as a highly effective marketing strategy for Zara in several ways. First and foremost, the rapid turnover of collections, with over twenty product lines per year, creates a sense of urgency and novelty for customers. This continual introduction of fresh styles not only keeps Zara top-of-mind but also fosters a dynamic shopping experience, encouraging frequent visits to discover the latest trends.
Moreover, the quick response to changing trends and customer preferences positions Zara as a trendsetter, appealing to fashion-conscious consumers. The ability to swiftly translate runway trends into accessible and affordable pieces reinforces Zara’s image as a go-to destination for staying in vogue.
Additionally, the limited production batches contribute to an atmosphere of exclusivity, prompting customers to make timely purchases to secure unique and in-demand items. This scarcity-driven approach enhances the perceived value of Zara’s offerings.
In essence, the fast fashion model serves as a powerful marketing tool for Zara by creating a sense of immediacy, exclusivity, and trend relevance, fostering customer loyalty and consistently attracting a diverse audience seeking the latest in fashion.
(F.2) In-Store Experience

Zara places a strong emphasis on crafting an exceptional in-store experience, carefully curating showrooms to exude an atmosphere that is both exclusive and professional. The meticulous design choices contribute to an ambiance that goes beyond a mere shopping space, creating an environment where customers feel engaged and inspired.
The meticulous attention to detail is aimed at ensuring that every aspect of the in-store setting is carefully considered, from layout to lighting.
This focus on the in-store ambiance goes beyond aesthetics—it becomes a vital part of Zara’s marketing strategy. The thoughtfully designed physical stores act as powerful marketing tools in themselves, drawing in customers by providing a memorable and immersive shopping environment.
By enticing shoppers to explore the latest trends in this carefully curated setting, Zara not only enhances the overall customer experience but also reinforces its brand image as a trendsetting and sophisticated fashion destination!
(F.3) Affordability & Differentiation
Zara strategically positions itself by prioritizing affordable pricing while maintaining a commitment to quality. This dual emphasis allows the brand to resonate with a wide range of customers. By providing stylish clothing at reasonable prices, Zara ensures accessibility, making fashion-forward designs attainable for a diverse audience.
The effectiveness of this marketing strategy lies in Zara’s ability to differentiate itself in the market. The brand stands out not only for its trendsetting designs but also for its adept balance of fashion-forward aesthetics and accessible costs.
This unique blend positions Zara as a go-to destination for those seeking both style and value, enhancing the brand’s appeal and solidifying its market presence. The affordability and differentiation strategy contribute to Zara’s ability to capture a broad customer base and maintain its status as a leading player in the competitive fashion landscape.
(F.4) Word of Mouth and Limited Advertising

Zara strategically leverages the power of word of mouth and customer recommendations as primary drivers of its marketing efforts. In a departure from traditional advertising-heavy approaches, Zara relies on the subtlety of customer satisfaction and positive experiences to promote its brand.
This unique strategy involves cultivating a strong and positive buzz around Zara’s collections, encouraging customers to share their experiences and recommendations. The reliance on word of mouth creates an authentic and organic promotion of the brand, fostering a sense of trust and credibility among potential customers.
The limited advertising approach doesn’t diminish Zara’s impact; rather, it aligns with the brand’s commitment to providing an outstanding in-store experience and quality products. The positive buzz generated by satisfied customers becomes a powerful force, driving foot traffic to Zara’s stores and contributing to the brand’s sustained success in the competitive fashion market.
(F.5) Social Media Marketing
Zara actively embraces social media platforms as a crucial component of its marketing strategy. The brand leverages platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter to engage directly with its audience, creating a dynamic online presence.
The strategy involves regular updates across these platforms, keeping followers informed about the latest arrivals, ongoing trends, and behind-the-scenes glimpses into Zara’s fashion world. By maintaining an active and visually appealing presence, Zara not only stays connected with its audience but also cultivates a sense of anticipation and excitement around its offerings.
In addition to direct engagement, Zara strategically collaborates with influencers. These collaborations amplify Zara’s reach, tapping into the influencers’ follower base and creating a ripple effect of brand awareness.
Through this multi-faceted approach, Zara effectively utilizes social media not just as a promotional tool but as a means to foster a dynamic and interactive relationship with its audience, contributing to the brand’s overall success in the digital landscape.
(F.6) Personalization & Community Engagement
Zara adopts a customer-centric strategy by customizing its offerings to cater to local tastes and preferences. This personalization ensures that Zara’s collections resonate with diverse communities, creating a more inclusive and relatable shopping experience.
Community engagement takes center stage in Zara’s approach. Events like fashion shows or store openings play a pivotal role in fostering a sense of belonging among customers. By actively involving the community in these events, Zara goes beyond being a retailer and becomes an integral part of the local fabric.
Crucially, Zara prioritizes customer feedback. Actively listening to what customers have to say, the brand adapts and evolves its offerings based on this valuable input. This responsiveness not only enhances the overall customer experience but also reinforces a sense of collaboration between Zara and its community.
In essence, Zara’s commitment to personalization and community engagement contributes to a brand image rooted in customer satisfaction and a genuine connection with the diverse communities it serves.
(G) Sustainability Efforts: Crucial Part of Zara Case Study
Do you know what Zara is famous for apart from fashion? Its sustainability efforts to preserve mother nature! Let’s look at the sustainability efforts of Zara-
Thus, Zara is increasingly conscious of sustainability. The brand aims to reduce its environmental impact by using eco-friendly materials and promoting recycling. Such initiatives resonate with socially aware consumers.
(H) Challenges Faced by Zara
The journey of Zara was not free of challenges. Let’s look at some of the major challenges of Zara-
Zara brilliantly addressed those challenges to produce effective results that ultimately helped them grow their business.
(I) Summing Up: Zara Case Study
Zara’s remarkable success in leading the fashion market can be attributed to its unique blend of rapid fashion cycles, vertical integration, and a customer-centric approach. By staying ahead of trends with its fast fashion model, ensuring control over the entire production process, and tailoring offerings to local tastes, Zara captures a diverse and loyal customer base.
The brand’s commitment to affordability, engaging in-store experiences, and strategic use of social media further solidify its market leadership. Zara’s story showcases the power of adaptability, responsiveness, and a strong connection with customers in navigating the dynamic landscape of the fashion industry!
Related Posts:
Apart from selling clothes and accessories at higher prices, still it is among the favourite ones for many!
Contact Info: Axponent Media Pvt Ltd, 706-707 , 7th Floor Tower A , Iris Tech Park, Sector 48, Sohna Road, Gurugram, India, Pin - 122018
© The Business Rule 2024
Case Flash Forward: Zara: Fast Fashion
By: Baker Library
Each Case Flash Forward provides educators and students with a brief, 2-3 page update of key changes at a particular company covered in a related case study. It is a compilation of…
- Length: 4 page(s)
- Publication Date: Oct 1, 2015
- Discipline: Strategy
- Product #: 8553-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Educator Copy
$2.62 per student
degree granting course
$4.60 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
Each Case Flash Forward provides educators and students with a brief, 2-3 page update of key changes at a particular company covered in a related case study. It is a compilation of publicly-available content prepared by an experienced editor. This Case Flash Forward provides an update on Inditex and Zara, including significant developments, current executives, key readings, and basic financials.
Oct 1, 2015 (Revised: Apr 26, 2023)
Discipline:
Geographies:
Industries:
Apparel accessories, Retail trade
Harvard Business School
8553-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Information Systems Management » Case Study of Zara : Application of Business Intelligence in Retail Industry
Case Study of Zara : Application of Business Intelligence in Retail Industry
ZARA is a Spanish clothing and accessories retailer based in Arteixo, Galicia. Founded in 24 May ,1975 by Amancio Ortega and RosalÃa Mera, the brand is renowned for it’s ability to deliver new clothes to stores quickly and in small batches. Zara needs just two weeks to develop a new product and get it to stores, compared to the six-month industry average, and launches around 10,000 new designs each year. Zara was described by Louis Vuitton Fashion Director Daniel Piette as “possibly the most innovative and devastating retailer in the world. The company produces about 450 million items a year for its 1,770 stores in 86 countries.
The Zara has made of use of Information Systems (IS) and to advance in many areas. This has resulted in huge success for the company. This included application of Business intelligence (BI) involves technologies, practices for collection, integration and applications to analyze and present business information. The main aim of business intelligence is to promote better business decision making.
BI describes a group of information on concepts and methods to better decision making in business. This is achieved by employing a fact based support systems. The intelligence systems are data-driven and sometimes used in executive information systems. Predictive views on business operations can be provided by use of BI systems. predictive views on business operations can be provided by use of BI systems since historical and current data has been gathered into a data bank performance management benchmarking is done whereby information on other companies in the same industry is gathered.

Since the Zara’s have large network and therefore dealing with large volumes of data, an enterprise information system has been employed in the firm. This is generally a type of computing systems that involves an enterprise class that is, typically offering total quality service handling large volumes of data and able to sustain a big organization. With this system, a technology platform is provided which enables the enterprise is provided to that information can be shared in all useful levels of management enterprise systems are important in removing the problem of fragmentation of information. This happens when there are numerous information systems in an enterprise. The problem is solved by developing a standard data structure.
The Zara being big organization, the enterprise systems is housed in many different data centers, and includes content management system as the main application. The Zara team comprises technology professionals. These include content specialists, network and system engineers, flash developers, database business analysts and administrators, software developers, quality assurance managers and computer and applications support technicians. All these specialists work in tandem to bring about competitive advantage to business by allowing for quick-response capability.
The Zara is devoted to integrating information technology appropriately into all areas of its operations and activities. The range of services and resources available to its clients is attributed to the commitment of integration of IT properly in the organization. The client services group in the Zara partners with staff and clients to identify and meet each group’s technological requirements. This group of technical advisors associates with departments to execute a roadmap for a team’s technological vision and then defines this vision within entity projects.
Much support is required for invariable innovation. The Zara IT group is devoted to developing community through technology and operates closely with business associates. The IT group is devoted to developing community through technology and operates closely with business associates. The IT group has technical support and tools they require to come up with new ideas and spread the ideas to the wider community worldwide. This ensures that client needs are realized. A constantly growing state-of-the-art technology infrastructure has enabled the firm to develop and maintain a fully integrated organization/ enterprise. The infrastructure has enabled the firm to develop and maintain a fully integrated organization/ enterprise. The infrastructure entails a core of systems and attempts designed to produce the flexibility and capacity for innovation and growth.
The Zara thrives in an environment of change, experimentation and learning that is spreading over the boundaries for the application of IT in their business in the enterprises an easy-to-use modular tools, templates and platforms that involve all sides of life at the Zara firms including career development , administration and operations are implemented and developed.
In the Zara other web-based solutions are deployed with an advance knowledge management thereby making a big shift in the quality and speed of work in how the enterprises function. In the exploding growth of the software market a new world growth for the software market a new world of connectivity is realized in the Zara. The urgency of the business recognizing the importance of corporate portal has enabled linkage of information, data, people and knowledge to provide business solutions. The corporate portals come from consumer portals like Alta-vista, yahoo! and Lycos.
The portals (gateways) show the importance of letting clients have a wide scope of varied information on the web. This has given rise to the increase in multitasking, receiving information and checking from varied sources and thereby getting involved in projects that cross geographical boundaries with this technology the needs of the community, employees and even the extended network that is more advanced are served.
The Zara is possibly the most devastating and innovative retailer in the world. With more than 1000 shops world wide, the Zara has turned controlled over garment factories into a competitive advantage by making and designing the garments. By making the garments itself, it can quickly react to varying market trends. The Zara has been able to succeed in building a massive brand , without promotion or advertising but through the information systems and information technology.
Related posts:
- Application of Big Data in Retail Industry
- Case Study of Zara: Sustainability in Fast Fashion Industry
- Case Study: Zara’s Entry into Indian Retail Fashion Market
- Case Study of FedEx: Pioneer of Internet Business in the Global Transportation and Logistics Industry
- Case Study of Zara: A Better Fashion Business Model
- Case Study: Success of Starbucks Mobile Payment Application
- Case Study of Zara: Use of Technology to Improve Operational Responsiveness
- Case Study: The International Growth of Zara
- Case Study: Zara’s Operational Model
- How Internet of Things (IoT) Transforms the Retail Industry?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- TOP CATEGORIES
- AS and A Level
- University Degree
- International Baccalaureate
- Uncategorised
- 5 Star Essays
- Study Tools
- Study Guides
- Meet the Team
- Business Studies
Zara case study
[Type text]
Prof: Ahmed El Melegy
Ammar Al-Areqi 4491
Zara Case Study
1. Discuss the nature of competition and demand in the apparel industry? While most apparel manufacturers were migrating manufacturing to Asia to gain cost efficiency, Zara recognized that speed, flexibility and innovation were key to establishing a stronghold of the market. Although manufacturing in Spain and Portugal has a cost premium of 10 to 15 percent, the local production means the company can react to market changes faster than the competition, ensure tighter connectivity between design and manufacturing, and produce greater flexibility in product distribution
2. What are Zara core competencies and competitive capabilities? has remained focused on its core fashion philosophy that creativity and quality design together with a rapid response to market demands will yield profitable results. In order to realized these results Zara developed a that incorporated the following three goals for operations: develop a system the requires short lead times, decrease quantities produced to decrease inventory risk, and increase the number of available styles and/or choice. These goals helped to formulate a unique value proposition, to combine moderate prices with the ability to offer new clothing styles faster than its competitors. These goals helped to shape Zara’s current business model.

a. The high turnover of its products.
b. Low level of inventory due to fast supply chain- 1 week final production cycle, two day outbound logistics, fast adaption of leading trends. c. Effective distribution system d. Commitment of its employee’s e. scanning the fashion trends, market trends and meeting the consumer demands relating to fashionable clothes. f. Flexible production system.
This is a preview of the whole essay
3. How does Zara model differ from its competitors? What are the pros and cons of the current model? Zara’s core business model is vertically integrated, it specializes in speed and efficiency and the fast fashion trend. Zara’s approach to information technology is consistent with its core business model Zara’s core business model is vertically integrated; it specializes in speed and efficiency and the fast fashion trend. Zara does have a competitive advantage over its competitors in regards to operations. The local strategic partnerships that Zara maintains with manufacturers in Europe allow for a product throughput time of 3-4 weeks from conception to distribution. To make this happen, the company designs and cuts its fabric in-house and it acquires fabrics in only four colors to keep costs low. The proximity of these suppliers gives Zara great flexibility in adapting their product lines based on up to date market trends and consumer behavior. It also decreases costs of holding inventory. Zara’s competitors, through outsourcing to Asian countries such as China, sacrifice the benefits of proximity for low labor and production costs. Though there is a cost advantage in their approach in regards to labor, the lack of flexibility in changing orders based on current trends hinders their operational efficiencies. Inventory costs are higher for competitors because orders are placed for a whole season well in advance and then held in distribution facilities until periodic shipment to stores. This proximity effect and the flexibility that it gives Zara is fundamental to their basic concept to respond quickly to shifts in consumer demand and has provided them with a competitive edge in comparison to their peers. Zara has differentiated itself from its competitors by adding value in the every step right from manufacturing to distribution to sales.
4. How does Zara design its supply chain?
The main driver for Zara’s success is its dynamic supply chain with its intended outcome of focusing on a shorter response time. Zara has used its supply chain management to generate instant fashions: cheap, trendy clothing using a high wage paradigm. Recognizing the consumers demand for fashion products at the right time, Zara has developed a supply chain that is capable of getting a trend from the catwalk to their stores in 30 days, in comparison to 4 – 12 months from its industry competitors. This is beneficial to Zara in two instances; firstly, less availability leads to increased desirability and secondly, with smaller amounts being produced at any one time means that there is less to be added at the end of season sales. Zara only discounts 18% of its total product range, half the level of its competitors. Time has already been noted as one of the fundamental drivers to achieve a competitive advantage, in the case of Zara, an agile supply chain has been developed. Here Zara focuses on flexibility and relies on being market sensitive, as opposed to the traditional method of being forecast driven. Zara recognizes the need for quick response; therefore just 40% of its total garments, mainly the products with the least transient appeal are manufactured in the Far East region, whilst the remainders are produced in Spain using Zara’s own highly automated factories in pursuit of achieving a strategy capable of the most effective quick-response system.
In conclusion, Zara has maintained an upper hand over its competitors by the response to the changing market trends and fashion and by vertical integration. Zara, with its present IT infrastructure has been effective and able to be consistent with its core business. However, depending on an unreliable change from the supplier side, obsolete OS will not be compatible for future improvements or growth. Although, there no immediate need to change the current system, Zara should not invest more in the current obsolete IT infrastructure. It should adopt the change to the new OS eventually. Making a gradual change to the new system will increase Zara’s efficiency, without facing the sudden setback of implementing the change at once.

Document Details
- Author Type Student
- Word Count 918
- Page Count 2
- Level International Baccalaureate
- Subject Business Studies
- Type of work Research assignment (e.g. EPQs)
Related Essays

Nivea Case Study

Business Case Study: Coffee

Case Study - increasing Apple's profitability.

Case Study of BP
Short and sweet: multiple mini case studies as a form of rigorous case study research
- Original Article
- Open access
- Published: 15 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Sebastian Käss ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0640-3500 1 ,
- Christoph Brosig ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7809-0796 1 ,
- Markus Westner ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6623-880X 2 &
- Susanne Strahringer ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9465-9679 1
Case study research is one of the most widely used research methods in Information Systems (IS). In recent years, an increasing number of publications have used case studies with few sources of evidence, such as single interviews per case. While there is much methodological guidance on rigorously conducting multiple case studies, it remains unclear how researchers can achieve an acceptable level of rigour for this emerging type of multiple case study with few sources of evidence, i.e., multiple mini case studies. In this context, we synthesise methodological guidance for multiple case study research from a cross-disciplinary perspective to develop an analytical framework. Furthermore, we calibrate this analytical framework to multiple mini case studies by reviewing previous IS publications that use multiple mini case studies to provide guidelines to conduct multiple mini case studies rigorously. We also offer a conceptual definition of multiple mini case studies, distinguish them from other research approaches, and position multiple mini case studies as a pragmatic and rigorous approach to research emerging and innovative phenomena in IS.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Case study research has become a widely used research method in Information Systems (IS) research (Palvia et al. 2015 ) that allows for a comprehensive analysis of a contemporary phenomenon in its real-world context (Dubé and Paré, 2003 ). This research method is particularly useful due to its flexibility in covering complex phenomena with multiple contextual variables, different types of evidence, and a wide range of analytical options (Voss et al. 2002 ; Yin 2018 ). Although case study research is particularly useful for studying contemporary phenomena, some researchers feel that it lacks rigour, particularly in terms of the validity of findings (Lee and Hubona 2009 ). In response to these criticisms, Yin ( 2018 ) provides comprehensive methodological steps to conduct case studies rigorously. In addition, many other publications with a partly discipline-specific view on case study research, offer guidelines for achieving rigour in case study research, e.g., Benbasat et al. ( 1987 ), Dubé and Paré ( 2003 ), Pan and Tan ( 2011 ), or Voss et al. ( 2002 ). Most publications on case study methodology converge on four criteria for ensuring rigour in case study research: (1) construct validity, (2) internal validity, (3) external validity, and (4) reliability (Gibbert et al. 2008 ; Voss et al. 2002 ; Yin 2018 ).
A key element of rigour in case study research is to look at the unit of analysis of a case from multiple perspectives in order to draw informed conclusions (Dubois and Gadde 2002 ). Case study researchers refer to this as triangulation, for example, by using multiple sources of evidence per case to support findings (Benbasat et al. 1987 ; Yin 2018 ). However, in our own research experience, we have come across numerous IS publications with a limited number of sources of evidence per case, such as a single interview per case. Some researchers refer to these studies as mini case studies (e.g., McBride 2009 ; Weill and Olson 1989 ), while others refer to them as multiple mini cases (e.g., Eisenhardt 1989 ). We were unable to find a definition or conceptualisation of this type of case study. Therefore, we will refer to this type of case study as a multiple mini case study (MMCS). Interestingly, many researchers use these MMCSs to study emerging and innovative phenomena.
From a methodological perspective, multiple case study publications with limited sources of evidence, also known as MMCSs, may face criticism for their lack of rigour (Dubé and Paré 2003 ). Alternatively, they may be referred to as “marginal case studies” (Piekkari et al. 2009 , p. 575) if they fail to establish a connection between theory and empirical evidence, provide only limited context, or merely offer illustrative aspects (Piekkari et al. 2009 ). IS scholars advocate conducting case study research in a mindful manner by balancing methodological blueprints and justified design choices (Keutel et al. 2014 ). Consequently, we propose MMCSs as a mindful approach with the potential for rigour, distinguishing them from marginal case studies. The following research question guides our study:
RQ: How can researchers rigorously conduct MMCSs in the IS discipline?
As shown in Fig. 1 , we develop an analytical framework by synthesising methodological guidance on how to rigorously conduct multiple case study research. We then address three aspects of our research question: For aspect (1), we analyse published MMCSs in the IS discipline to derive a "Research in Practice" definition of MMCSs and research situations for MMCSs. For aspect (2), we use the analytical framework to analyse how researchers in the IS discipline ensure that existing MMCSs follow a rigorous methodology. For aspect (3), we discuss the methodological findings about rigorous MMCSs in order to derive methodological guidelines for MMCSs that researchers in the IS discipline can follow.
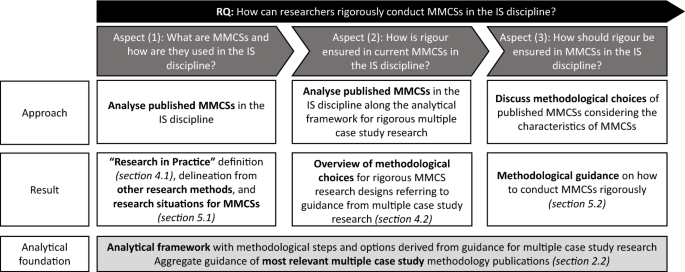
Overview of the research approach
We approach these aspects by introducing the conceptual foundation for case study research in Sect. 2 . We define commonly accepted criteria for ensuring validity in case study research, introduce the concept of MMCSs, and distinguish them from other types of case studies. Furthermore, as a basis for analysis, we present an analytical framework of methodological steps and options for the rigorous conduct of multiple case study research. Section 3 presents our methodological approach to identifying published MMCSs in the IS discipline. In Sect. 4 , we first define MMCSs from a research in practice perspective (Sect. 4.1 ). Second, we present an overview of methodological options for rigorous MMCSs based on our analytical framework (Sect. 4.2 ). In Sect. 5 , we differentiate MMCSs from other research approaches, identify research situations of MMCSs (i.e., to study emerging and innovative phenomena), and provide guidance on how to ensure rigour in MMCSs. In our conclusion, we clarify the limitations of our study and provide an outlook for future research with MMCSs.
2 Conceptual foundation
2.1 case study research.
Case study research is about understanding phenomena by studying one or multiple cases in their context. Creswell and Poth ( 2016 ) define it as an “approach in which the investigator explores a bounded system (a case) or multiple bounded systems (cases) over time, through detailed, in-depth data collection” (p. 73). Therefore, it is suitable for complex topics with little available knowledge, needing an in-depth investigation, or where the research subject is inseparable from its context (Paré 2004 ). Additionally, Yin ( 2018 ) states that case study research is useful if the research focuses on contemporary events where no control of behavioural events is required. Typically, this type of research is most suitable for how and why research questions (Yin 2018 ). Eventually, the inferences from case study research are based on analytic or logical generalisation (Yin 2018 ). Instead of drawing conclusions from a representative statistical sample towards the population, case study research builds on analytical findings from the observed cases (Dubois and Gadde 2002 ; Eisenhardt and Graebner 2007 ). Case studies can be descriptive, exploratory, or explanatory (Dubé and Paré 2003 ).
The contribution of research to theory can be divided into the steps of theory building , development and testing , which is a continuum (Ridder 2017 ; Welch et al. 2011 ), and case studies are useful at all stages (Ridder 2017 ). In theory building, there is no theory to explain a phenomenon, and the researcher identifies new concepts, constructs, and relationships based on the data (Ridder 2017 ). In theory development, a tentative theory already exists that is extended or refined (e.g., by adding new antecedents, moderators, mediators, and outcomes) (Ridder 2017 ). In theory testing, an existing theory is challenged through empirical investigation (Ridder 2017 ).
In case study research, there are different paradigms for obtaining research results, either positivist or interpretivist (Dubé and Paré 2003 ; Orlikowski and Baroudi 1991 ). The positivist paradigm assumes that a set of variables and relationships can be objectively identified by the researcher (Orlikowski and Baroudi 1991 ). In contrast, the interpretivist paradigm assumes that the results are inherently rooted in the researcher’s worldview (Orlikowski and Baroudi 1991 ). Nowadays, researchers find that there are similar numbers of positivist and interpretivist case studies in the IS discipline compared to almost 20 years ago when positivist research was perceived as dominant (Keutel et al. 2014 ; Klein and Myers 1999 ). As we aim to understand how to conduct MMCSs rigorously, we focus on methodological guidance for positivist case study research.
The literature proposes a four-phased approach to conducting a case study: (1) the definition of the research design, (2) the data collection, (3) the data analysis, and (4) the composition (Yin 2018 ). Table 1 provides an overview and explanation of the four phases.
Case studies can be classified based on their depth and breadth, as shown in Fig. 2 . We can distinguish five types of case studies: in-depth single case studies , marginal case studies , multiple case studies , MMCSs , and extensive in-depth multiple case studies . Each type has distinct characteristics, yet the boundaries between the different types of case studies is blurred. Except for the marginal case studies, the italic references in Fig. 2 are well-established publications that define the respective type and provide methodological guidance. The shading is to visualise the different types of case studies. The italic references in Fig. 2 for marginal case studies refer to publications that conceptualise them.
Simplistic conceptualisation of MMCS
In-depth single case studies focus on a single bounded system as a case (Creswell and Poth 2016 ; Paré 2004 ; Yin 2018 ). According to the literature, a single case study should only be used if a case meets one or more of the following five characteristics: it is a critical, unusual, common, revelatory, or longitudinal case (Benbasat et al. 1987 ; Yin 2018 ). Single case studies are more often used for descriptive research (Dubé and Paré 2003 ).
A second type of case studies are marginal case studies , which generally have low depth (Keutel et al. 2014 ; Piekkari et al. 2009 ). Marginal case studies lack a clear link between theory and empirical evidence, a clear contextualisation of the case, and are often used for illustration purposes (Keutel et al. 2014 ; Piekkari et al. 2009 ). Therefore, marginal case studies provide only marginal insights with a lack of generalisability.
In contrast, multiple case studies employ multiple cases to obtain a broader picture of the researched phenomenon from different perspectives (Creswell and Poth 2016 ; Paré 2004 ; Yin 2018 ). These multiple case studies are often considered to provide more robust results due to the multiplicity of their insights (Eisenhardt and Graebner 2007 ). However, often discussed criticisms of multiple case studies are high costs, difficult access to multiple sources of evidence for each case, and long duration (Dubé and Paré 2003 ; Meredith 1998 ; Voss et al. 2002 ). Eisenhardt ( 1989 ) considers four to ten in-depth cases as a suitable number of cases for multiple case study research. With fewer than four cases, the empirical grounding is less convincing, and with more than ten cases, researchers quickly get overwhelmed by the complexity and volume of data (Eisenhardt 1989 ). Therefore, methodological literature views extensive in-depth multiple case studies as almost infeasible due to their high complexity and resource demands, which can easily overwhelm the research team and the readers (Stake 2013 ). Hence, we could not find a methodological publication outlining the approach for this case study type.
To solve the complexity and resource issues for multiple case studies, a new phenomenon has emerged: MMCS . An MMCS is a special type of multiple case study that focuses on an investigation's breadth by using a relatively high number of cases while having a somewhat limited depth per case. We characterise breadth not only by the number of cases but also by the variety of the cases. Even though there is no formal conceptualisation of the term, we understand MMCSs as a type of multiple case study research with few sources of evidence per case. Due to the limited depth per case, one can overcome the resource and complexity issues of classical multiple case studies. However, having only some sources of evidence per case may be considered a threat to rigour. Therefore, in this publication, we provide suggestions on how to address these threats.
2.2 Rigour in case study research
Rigour is essential for case study research (Dubé and Paré 2003 ; Yin 2018 ) and, in the early 2000s, researchers criticised case study research for inadequate rigour (e.g., Dubé and Paré 2003 ; Gibbert et al. 2008 ). Based on this, various methodological publications provide guidance for rigorous case study research (e.g., Dubé and Paré 2003 ; Gibbert et al. 2008 ).
Methodological literature proposes four criteria to ensure rigour in case study research: Construct validity , internal validity , external validity , and reliability (Dubé and Paré 2003 ; Gibbert et al. 2008 ; Yin 2018 ). Table 2 outlines these criteria and states in which research phase they should be addressed (Yin 2018 ). Methodological literature agrees that all four criteria must be met for rigorous case study research (Dubé and Paré 2003 ).
The methodological literature discusses multiple options for achieving rigour in case study research (e.g., Benbasat et al. 1987 ; Dubé and Paré 2003 ; Eisenhardt 1989 ; Yin 2018 ). We aggregated guidance from multiple sources by conducting a cross-disciplinary literature review to build our analytical foundation (cf. Fig. 1 ). This literature review aims to identify the most relevant multiple case study methodology publications from a cross-disciplinary and IS-specific perspective. We focus on the most cited methodology publications, while being aware that this may over-represent disciplines with a higher number of case study publications. However, this approach helps to capture an implicit consensus among case study researchers on how to conduct multiple case studies rigorously. The literature review produced an analytical framework of methodological steps and options for conducting multiple case studies rigorously. Appendix A Footnote 1 provides a detailed documentation of the literature review process. The analytical framework derived from the set of methodological publications is presented in Table 3 . We identified required and optional steps for each research stage. The analytical framework is the basis for the further analysis of MMCS and an explanation of all methodological steps is provided in Appendix B. Footnote 2
3 Research methodology
For our research, we analysed published MMCSs in the IS discipline with the goal of understanding how these publications ensured rigour. This section outlines the methodology of how we identified our MMCS publications.
First, we searched bibliographic databases and citation indexing services (Vom Brocke et al. 2009 ; Vom Brocke et al. 2015 ) to retrieve IS-specific MMCSs (Hanelt et al. 2015 ). As shown in Fig. 3 , we used two sets of keywords, the first set focusing on multiple case studies and the second set explicitly on mini case studies. We decided to follow this approach as many MMCSs are positioned as multiple case studies, avoiding the connotation “mini” or “short”. We restricted our search to completed research publications written in English from litbaskets.io size “S”, a set of 29 highly ranked IS journals (Boell and Wang 2019 ) Footnote 3 and leading IS conference proceedings from AMCIS, ECIS, HICSS, ICIS, and PACIS (published until end of June 2023). We focused on these outlets, as they can be taken as a representative sample of high quality IS research (Gogan et al. 2014 ; Sørensen and Landau 2015 ).

The search process for published MMCSs in the IS discipline
Second, we screened the obtained set of IS publications to identify MMCSs. We only included publications with positivist multiple cases where the majority of cases was captured with only one primary source of evidence. Further, we excluded all publications which were interview studies rather than case studies (i.e., they do not have a clearly defined case). In some cases, it was unclear from the full text whether a publication fulfils this requirement. Therefore, we contacted the authors and clarified the research methodology with them. Eventually, our final set contained 50 publications using MMCSs.
For qualitative data analysis, we employed axial coding (Recker 2012 ) based on the pre-defined analytical framework shown in Table 3 . For the coding, we followed the explanations of the authors in the manuscripts. The coding was conducted and reviewed by two of the authors. We coded the first five publications of the set of IS MMCS publications together and discussed our decisions. After the initial coding was completed, we checked the reliability and validity by re-coding a sample of the other author’s set. In this sample, we achieved inter-coder reliability of 91% as a percent agreement in the decisions made (Nili et al. 2020 ). Hence, we consider our coding as highly consistent.
In the results section, we illustrate the chosen methodological steps for each MMCS type (descriptive, exploratory, and explanatory). For this purpose, we selected three publications based on two criteria: only journal publications, as they have more details about their methodological steps and publications which applied most of the analytical framework’s methodology steps. This led to three exemplary IS MMCS publications: (1) McBride ( 2009 ) for descriptive MMCSs, (2) Baker and Niederman ( 2014 ) for exploratory MMCSs, and (3) van de Weerd et al. ( 2016 ) for explanatory MMCSs.
4.1 MMCS from a “Research in Practice" perspective
In this section, we explain MMCSs from a "Research in Practice" perspective and identify different types based on our sample of 50 MMCS publications. As outlined in Sect. 2.1 , an MMCS is a special type of a multiple case study, which focuses on an investigation’s breadth by using a relatively high number of cases while having a limited depth per case. In the most extreme scenario, an MMCS only has one source of evidence per case. Moreover, breadth is not only characterised by the number of cases, but also by the variety of the cases. MMCSs have been used widely but hardly labelled as such, i.e., only 10 of our analysed 50 MMCS publications explicitly use the terms mini or short case in the manuscript . Multiple case study research distinguishes between descriptive, exploratory, and explanatory case studies (Dubé and Paré 2003 ). The MMCSs in our sample follow the same classification with three descriptive, 40 exploratory, and seven explanatory MMCSs. Descriptive and exploratory MMCSs are used in the early stages of research , and exploratory and explanatory MMCSs are used to corroborate findings .
Descriptive MMCSs provide little information on the methodological steps for the design, data collection, analysis, and presentation of results. They are used to illustrate novel phenomena and create research questions, not solutions, and can be useful for developing research agendas (e.g., McBride 2009 ; Weill and Olson 1989 ). The descriptive MMCS publications analysed contained between four to six cases, with an average of 4.6 cases per publication. Of the descriptive MMCSs analysed, one did not state research questions, one answered a how question and the third answered how and what questions. Descriptive MMCSs are illustrative and have a low depth per case, resulting in the highest risk of being considered a marginal case study.
Exploratory MMCSs are used to explore new phenomena quickly, generate first research results, and corroborate findings. Most of the analysed exploratory MMCSs answer what and how questions or combinations. However, six publications do not explicitly state a research question, and some MMCSs use why, which, or whether research questions. The analysed exploratory MMCSs have three to 27 cases, with an average of 10.2 cases per publication. An example of an exploratory MMCS is the study by Baker and Niederman ( 2014 ), who explore the impacts of strategic alignment during merger and acquisition (M&A) processes. They argue that previous research with multiple case studies (mostly with three cases) shows some commonalities, but much remains unclear due to the low number of cases. Moreover, they justify the limited depth of their research with the “proprietary and sensitive nature of the questions” (Baker and Niederman 2014 , p. 123).
Explanatory MMCSs use an a priori framework with a relatively high number of cases to find groups of cases that share similar characteristics. Most explanatory MMCSs answer how questions, yet some publications answer what, why, or combinations of the three questions. The analysed explanatory MMCSs have three to 18 cases, with an average of 7.2 cases per publication. An example of an explanatory MMCS publication is van de Weerd et al. ( 2016 ), who researched the influence of organisational factors on the adoption of Software as a Service (SaaS) in Indonesia.
4.2 Applied MMCS methodology in IS publications
4.2.1 overarching.
In the following sections, we present the results of our analysis. For this purpose, we mapped our 50 IS MMCS publications to the methodological options (Table 3 ) and present one example per MMCS type. We extended some methodological steps with options from methodology-in-use. A full coding table can be found in Appendix D Footnote 4 . Tables 4 , 5 , 6 and 7 summarise the absolute and percentual occurrences of each methodological option in descriptive, exploratory, and explanatory IS MMCS publications. All tables are structured in the same way and show the number of absolute and, in parentheses, the percentual occurrences of each methodological option. The percentages may not add up to 100% due to rounding. The bold numbers show the most common methodological option for each MMCS type and step. Most publications were classified in previously identified options. Some IS MMCS publications lacked detail on methodological steps, so we classified them as "step not evident". Only 16% (8 out of 50) explained how they addressed validity and reliability threats.
4.2.2 Research design phase
There are six methodological steps in the research design phase, as shown in Table 4 . Descriptive MMCSs usually define the research question (2 out of 3, 67%), clarify the unit of analysis (2 out of 3, 67%), bound the case (2 out of 3, 67%), or specify an a priori theoretical framework (2 out of 3, 67%). The case replication logic is mostly not evident (2 out of 3, 67%). Descriptive MMCS use a criterion-based selection (1 out of 3, 33%), a maximum variation selection (1 out of 3, 33%), or do not specify the selection logic (1 out of 3, 33%). Descriptive MMCSs have a high risk of becoming a marginal case study due to their illustrative nature–our chosen example is not different. McBride ( 2009 ) does not define the research question, does not have a priori theoretical framework, nor does he justify the case replication and the case selection logic. However, he clarifies the unit of analysis and extensively bounds each case with significant context about the case organisation and its setup.
The majority of exploratory MMCSs define the research question (34 out of 40, 85%) clarify the unit of analysis (35 out of 40, 88%), and specify an a priori theoretical framework (33 out of 40, 83%). However, only a minority (6 out of 40, 15%) follow the instructions of bounding the case or justify the case replication logic (13 out of 40, 33%). The most used case selection logic is the criterion-based selection (23 out of 40, 58%), followed by step not evident (5 out of 40, 13%), other selection approaches (3 of 40, 13%), maximum variation selection (3 out of 40, 13%), a combination of approaches (2 out of 40, 5%), snowball selection (2 out of 40, 5%), typical case selection (1 out of 40, 3%), and convenience-based selection (1 out of 40, 3%). Baker and Niederman ( 2014 ) build their exploratory MMCS on previous multiple case studies with three cases that showed ambiguous results. Hence, Baker and Niederman ( 2014 ) formulate three research objectives instead of defining a research question. They clearly define the unit of analysis (i.e., the integration of the IS function after M&A) but lack the bounding of the case. The authors use a rather complex a priori framework, leading to a high number of required cases. This a priori framework is also used for the “theoretical replication logic [to choose] conforming and disconfirming cases” (Baker and Niederman 2014 , p. 116). A combination of maximum variation and snowball selection is used to select the cases (Baker and Niederman 2014 ). The maximum variation is chosen to get evidence for all elements of their rather complex a priori framework (i.e., the breadth), and the snowball sampling is chosen to get more details for each framework element.
All explanatory MMCS s define the research question, clarify the unit of analysis, and specify an a priori theoretical framework. However, only one (14%) bounds the case. The case replication logic is mostly a mixture of theoretical and literal replication (3 out of 7, 43%) and one (14%) MMCS does a literal replication. For 43% (3 out of 7) of the publications, the step is not evident. Most explanatory MMCSs use criterion-based selection (4 out of 7, 57%), followed by maximum variation selection (2 out of 7, 29%) and snowball selection (1 out of 7, 14%). In their publication, van de Weerd et al. ( 2016 ) define the research question and clarify the unit of analysis (i.e., the influence of organisational factors on SaaS adoption in Indonesian SMEs). Further, they specify an a priori framework (i.e., based on organisational size, organisational readiness, and top management support) to target the research (van de Weerd et al. 2016 ). A combination of theoretical (between the groups of cases) and literal (within the groups of cases) replication was used. To strengthen the findings, van de Weerd et al. ( 2016 ) find at least one other literally replicated case for each theoretically replicated case.
To summarize this phase, we see that in all three types of MMCSs, the majority of publications define the research question, clarify the unit of analysis, and specify an a priori theoretical framework. Moreover, descriptive MMCSs are more likely to bound the case than exploratory and explanatory MMCSs. However, only a minority across all MMCSs justify the case replication logic, whereas the majority does not. Most MMCSs justify the case selection logic, with criterion-based case selection being the most often applied methodological option.
4.2.3 Data collection phase
In the data collection phase, there are four methodological steps, as summarised in Table 5 .
One descriptive MMCS applies triangulation via multiple sources, whereas for the majority (2 out of 3, 67%), the step is not evident. One (33%) of the analysed descriptive MMCSs creates a full chain of evidence, none creates a case study database, and one (33%) uses a case study protocol. McBride ( 2009 ) applies triangulation via multiple sources, as he followed “up practitioner talks delivered at several UK annual conferences” (McBride 2009 , p. 237). Therefore, we view the follow-up interviews as the primary source of evidence per case, as dedicated questions to the unit of analysis can be asked per case. Triangulation via multiple sources was then conducted by combining practitioner talks and documents with follow-up interviews. McBride ( 2009 ) does not create a full chain of evidence, a case study database, nor a case study protocol. This design decision might be rooted in the objective of a descriptive MMCS to illustrate and open up new questions rather than find clear solutions (McBride 2009 ).
Most exploratory MMCSs triangulate via multiple sources (20 out of 40, 50%) or via multiple investigators (4 out of 40, 10%). Eight (20%) exploratory MMCSs apply multiple triangulation types and for eight (20%), no triangulation is evident. At first glance, a triangulation via multiple sources may seem contradictory to the definition of MMCSs–yet it is not. MMCSs that triangulate via multiple sources have one source per case as the primary, detailed evidence (e.g., an interview), which is combined with easily available supplementary sources of evidence (e.g., public reports and documents (Baker and Niederman 2014 ), press articles (Hahn et al. 2015 ), or online data (Kunduru and Bandi 2019 )). As this leads to multiple sources of evidence, we understand this as a triangulation via multiple sources; however, on a different level than triangulating via multiple in-depth interviews per case. Only a minority of exploratory MMCSs create a full chain of evidence (14 out of 40, 35%), and a majority (23 out of 40, 58%) use a case study database or a case study protocol (20 out of 40, 50%). Baker and Niederman ( 2014 ) triangulate with multiple sources (i.e., financial reports as supplementary sources) to increase the validity of their research. Further, the authors create a full chain of evidence from their research question through an identical interview protocol to the case study’s results. For every case, an individual case report is created and stored in the case study database (Baker and Niederman 2014 ).
All explanatory MMCSs triangulate during the data collection phase, either via multiple sources (2 out of 7, 29%) or a combination of multiple investigators and sources (5 out of 7, 71%). Interestingly, only three explanatory MMCSs (43%) create a full chain of evidence. All create a case study database (7 out of 7, 100%) and the majority creates a case study protocol (6 out of 7, 86%). In their explanatory MMCS, van de Weerd et al. ( 2016 ) use semi-structured interviews as the primary data collection method. The interview data is complemented “with field notes and (online) documentation” (van de Weerd et al. 2016 , p. 919), e.g., data from corporate websites or annual reports. Moreover, a case study protocol and a case study database in NVivo are created to increase reliability.
To summarise the data collection phase, we see that most (40 out of 50, 80%) of MMCSs apply some type of triangulation. However, only 36% (18 out of 50) of the analysed MMCSs create a full chain of evidence. Moreover, descriptive MMCSs are less likely to create a case study database (0 out of 3, 0%) or a case study protocol (1 out of 3, 33%). In contrast, most exploratory and explanatory MMCS publications create a case study database and case study protocol.
4.2.4 Data analysis phase
There are three methodological steps (cf. Table 6 ) for the data analysis phase, each with multiple methodological options.
One descriptive MMCS (33%) corroborates findings through triangulation, and two do not (67%). Further, one (33%) uses a rich description of findings as other corroboration approaches, whereas for the majority (2 out of 3, 67%), the corroboration with other approaches is not evident. Descriptive MMCSs mostly do not define their within-case analysis strategy (2 out of 3, 67%). However, pre-defined patterns are used to conduct a cross-case analysis (2 out of 3, 67%). In the data analysis, McBride ( 2009 ) triangulates via multiple sources of evidence (i.e., talks at practitioner conferences and resulting follow-up interviews), but does not apply other corroboration approaches or provides methodological explanations for the within or cross-case analysis. This design decision might be rooted in the illustrative nature of his descriptive MMCS and the focus on analysing each case standalone.
Exploratory MMCSs mostly corroborate findings through a combination of triangulation via multiple investigators and sources (15 out of 40, 38%) or triangulation via multiple sources (9 out of 40, 23%). However, for ten (25%) exploratory MMCSs, this step is not evident. For the other corroboration approaches, a combination of approaches is mostly used (15 out of 40, 38%), followed by rich description of findings (11 out of 40, 28%), peer review (6 out of 40, 15%), and prolonged field visits (1 out of 40, 3%). For five (13%) publications, other corroboration approaches are not evident. Pattern matching (17 out of 40, 43%) and explanation building (5 out of 40, 13%) are the most used methodological options for the within-case analysis. To conduct a cross-case analysis, 11 (28%) MMCSs use a comparison of pairs or groups of cases, nine (23%) pre-defined patterns, and six (15%) structure their data along themes. Interestingly, for 14 (35%) exploratory MMCSs, no methodological step to conduct the cross-case analysis is evident. Baker and Niederman ( 2014 ) use a combination of triangulation via multiple investigators (“The interviews were coded by both researchers independently […], with a subsequent discussion to reach complete agreement” (Baker and Niederman 2014 , p. 117)) and sources to increase internal validity. Moreover, the authors use a rich description of the findings. An explanation-building strategy is used for the within-case analysis, and the cross-case analysis is done based on pre-defined patterns (Baker and Niederman 2014 ). This decision for the cross-case analysis is justified by a citation of Dubé and Paré ( 2003 , p. 619), who see it as “a form of pattern-matching in which the analysis of the case study is carried out by building a textual explanation of the case.”
Explanatory MMCSs corroborate findings through a triangulation via multiple sources (4 out of 7, 57%) or a combination of multiple investigators and sources (3 out of 7, 43%). For the other corroboration approaches, a rich description of findings (3 out of 7, 43%), a combination of approaches (3 out of 7, 43%), or peer review (1 out of 7, 14%) are used. To conduct a within-case analysis, pattern matching (5 out of 7, 71%) or explanation building (1 out of 7, 14%) are used. For the cross-case analysis, pre-defined patterns (3 out of 7, 43%) and a comparison of pairs or groups of cases (2 out of 7, 29%) are used; yet, for two (29%) explanatory MMCSs a cross-case analysis step is not evident. van de Weerd et al. ( 2016 ) corroborate their findings through a triangulation via multiple sources, a combination of rich description of findings and solicitation of participants’ views (“summarizing the interview results of each case company for feedback and approval” (van de Weerd et al. 2016 , p. 920)) as other corroboration approaches. Moreover, for the within-case analysis, the authors “followed an explanation-building procedure to strengthen […] [the] internal validity” (van de Weerd et al. 2016 , p. 920). For the cross-case, the researchers compare groups of cases. They refer to this approach as an informal qualitative comparative analysis.
To summarize the results of the data analysis phase, we see that some type of triangulation is used by most of the MMCSs, with source triangulation (alone or in combination with another approach) being the most often used methodological option. For the within-case analysis, pattern matching (22 of 50, 44%) is the most often used methodological option. For the cross-case analysis, pre-defined patterns are most often used (14 out of 50, 28%). However, depending on the type of MMCS, there are differences in the options used and some methodological options are never used (e.g., time-series analysis and solicitation of participants’ views).
4.2.5 Composition phase
We can find two methodological steps for the composition phase, as summarized in Table 7 .
Descriptive MMCSs do not apply triangulation in the composition phase (3 out of 3, 100%), nor do they use the methodological step to let key informants review the draft of the case study report (3 of 3, 100%). Also, the descriptive MMCS by McBride ( 2009 ) does not apply any of the methodological steps.
Exploratory MMCSs mostly use triangulation via multiple sources (25 out of 40, 63%), a combination of multiple sources and theories (2 out of 40, 5%), triangulation via multiple investigators (1 out of 40, 3%), and a combination of multiple sources and methods (1 out of 40, 3%). However, for 11 (28%) exploratory MMCS publications, no triangulation step is evident. Moreover, the majority (24 out of 40, 85%) do not let key informants review a draft of the case study report. Baker and Niederman ( 2014 ) do not use triangulation in the composition phase nor let key informants review the draft of the case study report. An example of an exploratory publication that applies both methodological steps is the publication by Kurnia et al. ( 2015 ). The authors triangulate via multiple sources and let key informants review their interview transcripts and the case study report to increase construct validity.
Explanatory MMCSs mostly use triangulation via multiple sources (5 out of 7, 71%) and for two (29%), the step is not evident. Furthermore, only two MMCS (29%) publications let key informants review the draft of the case study report, whereas the majority (5 out of 7, 71%) do not. In their publication , van de Weerd et al. ( 2016 ) use both methodological steps of the composition phase. The authors triangulate via multiple sources by presenting interview snippets from different cases for each result in the case study manuscript. Moreover, each case and the final case study report were shared with key informants for review and approval to reduce the risk of misinterpretations and increase construct validity.
To summarize, most exploratory and explanatory MMCSs use triangulation in the composition phase, whereas descriptive MMCSs do not. Moreover, only a fraction of all MMCSs let key informants review a draft of the case study report (8 out of 50, 16%).
5 Discussion
5.1 mmcs from a “research in practice" perspective, 5.1.1 delineating mmcs from other research approaches.
In this section, we delineate MMCSs from related research approaches. In the subsequent sections, we outline research situations for which MMCSs can be used and the benefits MMCSs provide.
Closely related research approaches from which we delineate MMCSs are multiple case studies , interviews, and vignettes . As shown in Fig. 2 , MMCSs differ from multiple case studies in that they focus on breadth by using a high number of cases with limited depth per case. In the most extreme situation, an MMCS only has one primary source of evidence per case. Moreover, MMCSs can also consider a greater variety of cases. In contrast, multiple case studies have a high depth per case and multiple sources of evidence per case to allow for a source triangulation (Benbasat et al. 1987 ; Yin 2018 ). Moreover, multiple case studies mainly focus on how and why research questions (Yin 2018 ), whereas MMCSs can additionally answer what, whether, and which research questions. The rationale why MMCSs are used for more types of research questions is their breadth, allowing them to also answer rather explorative research questions.
Distinguishing MMCSs from interviews is more difficult . Yet, we see two differences. First, interview studies do not have a clear unit of analysis. Interview studies may choose interviewees based on expertise (expert interviews), whereas case study researchers select informants based on the ability to inform about the case (key informants) (Yin 2018 ). Most of the 50 analysed MMCS (88%) specify their unit of analysis. Second, MMCSs can use multiple data collection methods (e.g., observations, interviews, documents), while interviews only use one (the interview) (Lamnek and Krell 2010 ). An example showing these delineation difficulties between MMCSs and interviews is the publication of Demlehner and Laumer ( 2020 ). The authors claim to take “a multiple case study approach including 39 expert interviews” (Demlehner and Laumer 2020 , p. 1). However, our criteria classify this as an interview study. Demlehner and Laumer ( 2020 ) contend that the interviewees were chosen using a “purposeful sampling strategy” (p. 5). However, case study research selects cases based on replication logic, not sampling (Yin 2018 ). Moreover, the results are not presented on a per-case basis (as usual for case studies); instead, the findings are presented on an aggregated level, similar to expert interviews. Therefore, we would not classify this publication as an MMCS but find that it is a very good example to discuss this delineation.
MMCSs differ from vignettes, which are used for (1) data collection , (2) data analysis , and (3) research communication (Klotz et al. 2022 ; Urquhart 2001 ). Researchers use vignettes for data collection as stimuli to which participants react (Klotz et al. 2022 ), i.e., a carefully constructed description of a person, object, or situation (Atzmüller and Steiner 2010 ; Hughes and Huby 2002 ). We can delineate MMCS from vignettes for data collection based on this definition. First, MMCSs are not used as a stimulus to which participants can react, as in MMCSs, data is collected without the stimulus requirement. Furthermore, vignettes for data collection are carefully constructed, which contradicts the characteristics of MMCS, that are all based on collected empirical data and not constructed descriptions.
A data analysis vignette is used as a retrospective tool (Klotz et al. 2022 ) and is very short, which makes it difficult to analyse deeper relationships between constructs. MMCSs differ from vignettes for data analysis in two ways. First, MMCSs are a complete research methodology with four steps, whereas vignettes for data analysis cover only one step (the data analysis) (e.g., Zamani and Pouloudi 2020 ). Second, vignettes are too short to conduct a thorough analysis of relationships, whereas MMCSs foster a more comprehensive analysis, allowing for a deeper analysis of relationships.
Finally, a vignette used for research communication “(1) is bounded to a short time span, a location, a special situation, or one or a few key actors, (2) provides vivid, authentic, and evocative accounts of the events with a narrative flow, (3) is rather short, and (4) is rooted in empirical data, sometimes inspired by data or constructed.” (Klotz et al. 2022 , p. 347). Based on the four elements for the vignettes’ definition, we can delineate MMCS from vignettes used for research communication. First, MMCSs are not necessarily bounded to a short time span, location, special situation, or key actors; instead, with MMCSs, a clearly defined case bounded in its context is researched. Second, the focus of MMCSs is not on the narrative flow; instead, the focus is on describing (c.f., McBride ( 2009 )), exploring (c.f., Baker and Niederman ( 2014 )), or explaining (c.f., van de Weerd et al. ( 2016 )) a phenomenon. Third, while MMCSs do not have the depth of multiple case studies, they are much more comprehensive than vignettes (e.g., the majority of analysed publications (42 of 50, 84%) specify an a priori theoretical framework). Fourth, every MMCS must be based on empirical data, i.e., all of our 50 MMCSs collect data for their study and base their results on this data. This is a key difference from vignettes, which can be completely fictitious (Klotz et al. 2022 ).
5.1.2 MMCS research situations
The decision to use an MMCS as a research method depends on the research context. MMCSs can be used in the early stages of research (descriptive and exploratory MMCS) and to corroborate findings (exploratory and explanatory MMCS). Academic literature has yet to agree on a uniform categorisation of research questions. For instance, Marshall and Rossman ( 2016 ) distinguish between descriptive, exploratory, explanatory, and emancipatory research questions. In contrast, Yin ( 2018 ) distinguishes between who , what , where , how , and why questions, where he argues that the latter two are especially suitable for explanatory case study research. MMCSs can answer more types of research questions than Yin ( 2018 ) proposed. The reason for this is rooted in the higher breadth of MMCSs, which allows MMCSs to also answer rather exploratory what , whether , or which questions, besides the how and why questions that are suggested by Yin ( 2018 ).
For descriptive MMCSs , the main goal of the how and what questions is to describe the phenomenon. However, in our sample of analysed MMCSs, the analysis stops after the description of the phenomenon. The main goal of the five types of exploratory MMCS research questions is to investigate little-known aspects of a particular phenomenon. The how and why questions analyse operational links between different constructs (e.g., “How do different types of IS assets account for synergies between business units to create business value?” (Mandrella et al. 2016 , p. 2)). Exploratory what questions can be answered by case study research and other research methods (e.g., surveys or archival analysis) (Yin 2018 ). Nevertheless, all whether and which MMCS research questions can also be re-formulated as exploratory what questions. The reason why many MMCSs answer what , whether , or which research questions lies in the breadth (i.e., higher number and variety of cases) of MMCS, that allow them to answer these rather exploratory research questions to a satisfactory level. Finally, the research questions of the explanatory MMCSs aim to analyse operational links (i.e., how or why something is happening). This is also in line with the findings of Yin ( 2018 ) for multiple case study research. However, for MMCSs, this view must be extended, as explanatory MMCSs are also able to answer what questions. We explain this with the higher breadth of MMCS.
To discuss an MMCS’s contribution to theory, we use the idea of the theory continuum proposed by Ridder ( 2017 ) (cf. Section 2.1 ). Despite being used in the early phase of research (descriptive and exploratory), we do not recommend using MMCSs to build theory . We argue that for theory building, data with “as much depth as […] feasible” (Eisenhardt 1989 , p. 539) is required on a per-case basis. However, a key characteristic of MMCSs is the limited depth per case, which conflicts with the in-depth requirements of theory building. Moreover, a criterion for theory building is that there is no theory available which explains the phenomenon (Ridder 2017 ). Nevertheless, in our analysed MMCSs, 84% (42 out of 50) have an a priori theoretical framework. Furthermore, for theory building, the recommendation is to use between four to ten cases; with more, “it quickly becomes difficult to cope with the complexity and volume of the data” (Eisenhardt 1989 , p. 545). However, a characteristic of MMCSs is to have a relatively high number of cases, i.e., the analysed MMCSs often have more than 20 cases, which is significantly above the recommendation for theory building.
The next phase in the theory continuum is theory development , where a tentative theory is extended or refined (Ridder 2017 ). MMCSs should and are used for theory development, i.e., 84% (42 out of 50) of analysed MMCS publications have an a priori theoretical framework extended and refined using the MMCS. An MMCS example for theory development is the research of Karunagaran et al. ( 2016 ), who use a combination of the diffusion of innovation theory and technology organisation environment framework as tentative theories to research the adoption of cloud computing. As Ridder ( 2017 ) outlined, for theory development, literal replication and pattern matching should be used. Both methodological steps are used by Karunagaran et al. ( 2016 ) to identify the mechanisms of cloud adoption more precisely.
The next step in the theory continuum is theory testing , where existing theory is challenged by finding anomalies that existing theory cannot explain (Ridder 2017 ). The boundaries between theory development and testing are often blurred (Ridder 2017 ). In theory testing, the phenomenon is understood, and the research strategy focuses on testing if the theory also holds under different circumstances, i.e., hypotheses can be formed and tested based on existing theory (Ridder 2017 ). In multiple case study research, theory testing uses theoretical replication with pattern matching or addressing rival explanations (Ridder 2017 ). In our MMCS publications, no publication addresses rival explanations, and only a few apply theoretical replication and pattern matching–yet not for theory testing. A few publications claim to test propositions derived from an a priori theoretical framework (e.g., Schäfferling et al. 2011 ; Spiegel and Lazic 2010 ; Wagner and Ettrich-Schmitt 2009 ). However, these publications either do not state their replication logic (e.g., Spiegel and Lazic 2010 ; Wagner and Ettrich-Schmitt 2009 ) or use a literal replication (e.g., Schäfferling et al. 2011 ), both of which weaken the value of their theory testing.
5.1.3 MMCS research benefits
MMCSs are beneficial in multiple research situations and can be an avenue to address the frequent criticism of multiple case study research of being time-consuming and costly (Voss et al. 2002 ; Yin 2018 ).
Firstly, MMCSs can be used for time-critical topics where it is beneficial to publish results quicker and discuss them instead of conducting in-depth multiple case studies (e.g., COVID-19 (e.g., dos Santos Tavares et al. 2021 ) or emergent technology adoption (e.g., Bremser 2017 )). Especially with COVID-19, research publishing saw a significantly higher speed due to special issues of journals and faster review processes. Further, due to the fast technological advancements, there is a higher risk that the results are obsolete and of less practical use when researched with time-consuming multiple in-depth case studies.
Secondly, MMCSs can be used in research situations when it is challenging to gather in-depth data from multiple sources of evidence for each case due to the limited availability of sources of evidence or limited accessibility of sources of evidence. When researching novel phenomena (e.g., the adoption of new technologies in organisations), managers and decision-makers are usually interviewed as sources of evidence. However, in most organisations, only one (or very few) decision-makers have the ability to inform and should be interviewed, limiting the potential sources of evidence per case. These decision-makers often have limited availability for multiple in-depth interviews. Furthermore, the sources of evidence are often difficult to access, as professional organisations have regulations that prevent sharing documents with researchers.
Thirdly, MMCSs can be beneficial when the research framework is complex and requires many cases for validation (e.g., Baker and Niederman ( 2014 ) validate their rather complex a priori framework with 22 cases) or when previous research has led to contradictory results . Therefore, in both situations, a higher breadth of cases is required to also research combinatorial effects (e.g., van de Weerd et al. 2016 ). However, conducting an in-depth multiple case study would take time and effort. Therefore, MMCSs can be a mindful way to collect many cases, but in the same vein, being time and cost-efficient.
5.2 MMCS research rigour
Table 8 outlines two types of methodological steps for MMCSs. The first are methodological steps, where MMCSs should follow multiple case study methodological guidance (e.g., clarify the unit of analysis ), while the second is unique to MMCSs due to its characteristics. This section focuses on the latter, exploring MMCS characteristics, problems, validity threats, and proposed solutions.
The characteristics of MMCSs of having only one primary source of evidence per case prevents MMCSs from using source triangulation, which is often used in multiple case study research (Stake 2013 ; Voss et al. 2002 ; Yin 2018 ). By only having one source of evidence, researchers can fail to develop a sufficient set of operational measures and instead rely on subjective judgements, which threatens construct validity (Yin 2018 ). The threats to construct validity must be addressed throughout the MMCS research process. To do so, we propose to use easily accessible supplementary data or other triangulation approaches to increase construct validity in a MMCS. For the other triangulation approaches, we see that the majority of publications use supplementary data (e.g., publicly available documents) as further sources of evidence, multiple investigators, multiple methods (e.g., quantitative and qualitative), multiple theories, or combinations of these (cf. Tables 5 , 6 and 7 ). Having one or, in the best case, all of them reduces the risk of reporting spurious relationships and subjective judgements of the researchers, as a phenomenon is analysed from multiple perspectives. Besides the above-mentioned types of triangulation, we propose to apply a new type of triangulation, which is specific to MMCSs and triangulates findings across similar cases combined to groups instead of multiple sources per case. We propose that all reported findings have to be found in more than one case in a group of cases. This is also in line with previous methodological guidelines, which suggest that findings should only be reported if they have at least three confirmations (Stake 2013 ). To triangulate across multiple cases in one group, researchers have to identify multiple similar cases by applying a literal case replication logic to reinforce similar results. One should also apply a theoretical replication to compare different groups of literally replicated cases (i.e., searching for contrary results). Therefore, researchers have to justify their case replication logic . However, in our sample of MMCS, the majority (32 of 50, 64%) does not justify their replication logic, whereas the remaining publications use either literal replication (8 of 50, 16%), theoretical replication (6 of 50, 12%), or a combination (4 of 50, 8%). We encourage researchers to use a combination of literal and theoretical replication because it allows triangulation across different groups of cases. An exemplary MMCS that uses this approach is the publication of van de Weerd et al. ( 2016 ), who use theoretical replication to find cases with different outcomes (e.g., adoption and non-adoption) and use literal replication to find cases with similar characteristics and form groups of them.
Two further methodological steps, which are not exclusive to MMCS but recommended for increasing the construct validity, are creating a chain of evidence and letting key informants review a draft of the case study report . Only 36% (18 out of 50) of the analysed MMCS publications establish a chain of evidence. One reason for this lower usage may be that the majority (35 out of 50, 70%) of the publications analysed are conference proceedings. While we understand that these publications face space limitations, we note that no publication offers a supplementary appendix with in-depth insights. However, we encourage researchers to create a full chain of evidence with as much transparency as possible. Therefore, online directories for supplementary appendices could be a valuable addition. As opposed to a few years ago, these repositories today are widely available and using them for such purposes could become a good research practice for qualitative research. Interestingly, only 16% (8 of 50) analysed MMCS publications let key informants review the draft of the case study report . As MMCSs only have one source of evidence per case, misinterpretations and subjective judgement by the researcher have a significantly higher impact on the results compared to multiple case study research. Therefore, MMCS researchers should let key informants review the case study report before publishing.
MMCSs only have few (one) sources of evidence per case, so the risk of focusing on spurious relationships is higher, threatening internal validity (Dubé and Paré 2003 ). This threat to internal validity must be addressed in the data analysis phase. In the context of MMCSs, researchers may aggregate fewer data points to obtain a within-case overview. Therefore, having a clear perspective of the existing data points and rigorously applying the within-case analysis methodological steps (e.g., pattern matching) is even more critical. However, due to the limited depth of data at MMCSs, the within-case analysis must be combined with an analysis across groups of cases (to allow triangulation via multiple groups of cases). For MMCSs, we propose not doing the cross-case analysis on a per-case basis. Instead, we propose to build groups of similar cases across which researchers could conduct an analysis across groups of cases. This solidifies internal validity in case study research (Eisenhardt 1989 ) by viewing and synthesising insights from multiple perspectives (Paré 2004 ; Yin 2018 ).
Another risk of MMCSs is the relatively high number of cases (i.e., we found up to 27 for exploratory MMCSs) that is higher than Eisenhardt’s ( 1989 ) recommendation of maximal ten cases in multiple case study research. With more than ten in-depth cases, researchers struggled to manage the complexity and data volume, resulting in models with low generalisability and reduced external validity (Eisenhardt 1989 ). We propose to use two methodological steps to address the threat to external validity.
First, like Yin’s ( 2018 ) recommendation to use theory for single case studies, we suggest an a priori theoretical framework for MMCSs. 84% (42 out of 50) of the analysed MMCS publications use such a framework. An a priori theoretical framework has two advantages: it simplifies research by pre-defining constructs and relationships, and it enables analytical techniques like pattern matching. Second, instead of doing the within and then cross-case analysis on a per-case basis, for MMCSs, we propose first doing the within-case analysis and then forming groups of similar cases. Then, the cross-case analysis is performed on the formed groups of cases. To form case groups, replication logic (literal and theoretical) must be chosen carefully. Cross-group analysis (with at least two cases per group) can increase the generalisability of results.
To increase MMCS reliability, a case study database and protocol should be created, similar to multiple case studies. To ensure higher reliability, researchers should document MMCS design decisions in more detail. As outlined in the results section, the documentation on why design decisions were taken is often relatively short and should be more detailed. This call for better documentation is not exclusive to MMCSs, as Benbasat et al. ( 1987 ) and Dubé and Paré ( 2003 ) also criticised this for multiple case study research.To ensure rigour in MMCS, we suggest following the steps for multiple case study research. However, MMCSs have unique characteristics, such as an inability to source triangulate on a per-case level, a higher risk of marginal cases, and difficulty in managing a high number of cases. Therefore, for some methodological steps (cf. Table 8 ), we propose MMCS-specific methodological options. First, MMCS should include supplementary data per case (to increase construct validity). Second, instead of doing a cross-case analysis, we propose to form groups of similar cases and focus on the cross-group analysis (i.e., in each group, there must be at least two cases). Third, researchers should justify their case replication logic , i.e., a combination of theoretical replication (to form different groups) and literal replication (to find the same cases within groups) should be conducted to allow for this cross-group analysis.
6 Conclusion
Our publication contributes to case study research in the IS discipline and beyond by making four methodological contributions. First, we provide a conceptual definition of MMCSs and distinguish them from other research approaches. Second, we provide a contemporary collection of exemplary MMCS publications and their methodological choices. Third, we outline methodological guidelines for rigorous MMCS research and provide examples of good practice. Fourth, we identify research situations for which MMCSs can be used as a pragmatic and rigorous approach.
Our findings have three implications for research practice: First, we found that MMCSs can be descriptive, exploratory, or explanatory and can be considered as a type of multiple case study. Our set of IS MMCS publications shows that this pragmatic approach is advantageous in three situations. First, for time-sensitive topics, where rapid discussion of results, especially in the early stages of research, is beneficial. Second, when it is difficult to collect comprehensive data from multiple sources for each case, either because of limited availability or limited accessibility to the data source. Third, in situations where the research setting is complex, many cases are needed to validate effects (e.g., combinatorial effects) or previous research has produced conflicting results. It is important, however, that the pragmatism of the MMCS should not be misunderstood as a lack of methodological rigour.
Second, we have provided guidelines that researchers can follow to conduct MMCSs rigorously. As we observe an increasing number of MMCSs being published, we encourage their authors to clarify their methodological approach by referring to our analytical MMCS framework. Our analytical framework helps researchers to justify their approach and to distinguish it from approaches that lack methodological rigour.
Third, throughout our collection of MMCS publications, we contacted several authors to clarify their case study research methodology. In many cases, these publications lacked critical details that would be important to classify them as MMCS or marginal cases. Many researchers responded that some details were not mentioned due to space limitations. While we understand these constraints, we suggest that researchers still present these details, for example, by considering online appendices in research repositories.
Our paper has five limitations that could be addressed by future research. First, we focus exclusively on methodological guidelines for positivist multiple case study research. Therefore, we have not explicitly covered methodological approaches from other research paradigms.
Second, we aggregated methodological guidance on multiple case study research from the most relevant publications by citation count only. As a result, we did not capture evidence from publications with far fewer citations or that are relevant in specific niches. However, our design choice is still justified as the aim was to identify established and widely accepted methodological strategies to ensure rigour in case study research.
Third, the literature reviews were keyword-based. Therefore, concepts that fall within our understanding of MMCS but do not include the keywords used for the literature search could not be identified. However, due to the different search terms and versatile search approaches, our search should have captured the most relevant contributions.
Fourth, we selected publications from highly ranked IS MMCS publications and proceedings of leading IS conferences to analyse how rigour is ensured in MMCSs in the IS discipline. We therefore excluded all other research outlets. As with the limitations arising from the keyword-based search, we may have omitted IS MMCS publications that refer to short or mini case studies. However, the limitation of our search is justified as it helps us to ensure that all selected publications have undergone a substantial peer review process and qualify as a reference base in IS.
Fifth, we coded our variables based on the characteristics explicitly stated in the manuscript (i.e., if authors position their MMCS as exploratory, we coded it as exploratory). However, for some variables, researchers do not have a consistent understanding (e.g., the discussion of what constitutes exploratory research by cf., Sarker et al. ( 2018 )). Therefore, we took the risk that MMCS may have different understandings of the coded variables.
For the future, our manuscript on positivist MMCSs provides researchers with guidance for an emerging type of case study research. Based on our study, we can identify promising areas for future research. By limiting ourselves to the most established strategies for ensuring rigour, we also invite authors to enrich our methodological guidelines with other, less commonly used steps. In addition, future research could compare the use of MMCSs in IS with other disciplines in order to solidify our findings.
Data availability
Provided at https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.24916458
The information can be found in the online Appendix: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.24916458 .
litbaskets.io is a web interface that allows searching for literature across the top 847 IS journals. It offers ranging from 2XS (Basket of Eight) to 3XL (847) essential IS journals and a full list of 29 journals which are the basis for this study can be found in Appendix C ( https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.24916458 ).
Atzmüller C, Steiner PM (2010) Experimental vignette studies in survey research. Method Eur J Res Methods Behav Soc Sci. https://doi.org/10.1027/1614-2241/a000014
Article Google Scholar
Baker EW, Niederman F (2014) Integrating the IS functions after mergers and acquisitions: analyzing business-IT alignment. J Strateg Inf Syst 23(2):112–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsis.2013.08.002
Benbasat I, Goldstein DK, Mead M (1987) The case research strategy in studies of information systems. MIS Q 11(3):369–386. https://doi.org/10.2307/248684
Boell S, Wang B (2019) www.litbaskets.io , an IT artifact supporting exploratory literature searches for information systems research. In: Proceedings ACIS 2019
Bremser CP, Gunther Rothlauf F (2017) Strategies and influencing factors for big data exploration. In: proceedings AMCIS 2017
Vom Brocke J, Simons A, Niehaves B, Riemer K, Plattfaut R, Cleven A (2009) Reconstructing the giant: on the importance of rigour in documenting the literature search process. In: Proceedings ECIS 2009
Creswell JW, Poth CN (2016) Qualitative inquiry and research design: choosing among five approaches, 4th edn. Sage Publications, California
Google Scholar
Demlehner Q, Laumer S (2020) Shall we use it or not? Explaining the adoption of artificial intelligence for car manufacturing purposes. In: Proceedings ECIS 2020
Dubé L, Paré G (2003) Rigor in information systems positivist case research: current practices, trends, and recommendations. MIS Q 27(4):597–636. https://doi.org/10.2307/30036550
Dubois A, Gadde L-E (2002) Systematic combining: an abductive approach to case research. J Bus Res 55(7):553–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0148-2963(00)00195-8
Eisenhardt KM (1989) Building theories from case study research. Acad Manag Rev 14(4):532–550. https://doi.org/10.2307/258557
Eisenhardt KM, Graebner ME (2007) Theory building from cases: opportunities and challenges. Acad Manag J 50(1):25–32. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2007.24160888
Gibbert M, Ruigrok W, Wicki B (2008) What passes as a rigorous case study? Strateg Manag J 29(13):1465–1474. https://doi.org/10.1002/smj.722
Gogan JL, McLaughlin MD, Thomas D (2014) Critical incident technique in the basket. In: Proceedings ICIS 2014
Hahn C, Röher D, Zarnekow R (2015) A value proposition oriented typology of electronic marketplaces for B2B SaaS applications. In: Proceedings AMCIS 2015
Hanelt A, Hildebrandt B, Polier J (2015) Uncovering the role of IS in business model innovation: a taxonomy-driven approach to structure the field. In: Proceedings ECIS 2015
Hughes R, Huby M (2002) The application of vignettes in social and nursing research. J Adv Nurs 37(4):382–386. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2648.2002.02100.x
Karunagaran S, Mathew S, Lehner F (2016) Differential adoption of cloud technology: a multiple case study of large firms and SMEs. In: Proceedings ICIS 2016
Keutel M, Michalik B, Richter J (2014) Towards mindful case study research in IS: a critical analysis of the past ten years. Eur J Inf Syst 23(3):256–272. https://doi.org/10.1057/ejis.2013.26
Klein HK, Myers MD (1999) A set of principles for conducting and evaluating interpretive field studies in information systems. MIS Q 23(1):67–93. https://doi.org/10.2307/249410
Klotz S, Kratzer S, Westner M, Strahringer S (2022) Literary sketches in information systems research: conceptualization and guidance for using vignettes as a narrative form. Inf Syst Manag. https://doi.org/10.1080/10580530.2021.1996661
Kunduru SR, Bandi RK (2019) Fluidity of power structures underpinning public discourse on social media: a multi-case study on twitter discourse in India. In: Proceedings AMCIS 2019
Kurnia S, Karnali RJ, Rahim MM (2015) A qualitative study of business-to-business electronic commerce adoption within the indonesian grocery industry: a multi-theory perspective. Inf Manag 52(4):518–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2015.03.003
Lamnek S, Krell C (2010) Qualitative sozialforschung: mit online-materialien, 6th edn. Beltz Verlangsgruppe, Germany
Lee AS, Hubona GS (2009) A scientific basis for rigor in information systems research. MIS Q 33(2):237–262. https://doi.org/10.2307/20650291
Mandrella M, Zander S, Trang S (2016) How different types of IS assets account for synergy-enabled value in multi-unit firms: mapping of critical success factors and key performance indicators. In: Proceedings AMCIS 2016
Marshall C, Rossman GB (2016) Designing qualitative research, 6th edn. SAGE Publications, Inc., California
McBride N (2009) Exploring service issues within the IT organisation: four mini-case studies. Int J Inf Manag 29(3):237–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2008.11.010
Meredith J (1998) Building operations management theory through case and field research. J Oper Manag 16:441–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-6963(98)00023-0
Nili A, Tate M, Barros A, Johnstone D (2020) An approach for selecting and using a method of inter-coder reliability in information management research. Int J Inf Manage 54:102154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102154
Orlikowski WJ, Baroudi JJ (1991) Studying information technology in organizations: research approaches and assumptions. Inf Syst Res 2(1):1–28
Palvia P, Daneshvar Kakhki M, Ghoshal T, Uppala V, Wang W (2015) Methodological and topic trends in information systems research: a meta-analysis of IS journals. Commun Assoc Inf Syst 37(1):30. https://doi.org/10.17705/1CAIS.03730
Pan SL, Tan B (2011) Demystifying case research: a structured–pragmatic–situational (SPS) approach to conducting case studies. Inf Organ 21(3):161–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infoandorg.2011.07.001
Paré G (2004) Investigating information systems with positivist case research. Commun Assoc Inf Syst 13(1):18. https://doi.org/10.17705/1CAIS.01318
Piekkari R, Welch C, Paavilainen E (2009) The case study as disciplinary convention: evidence from international business journals. Organ Res Methods 12(3):567–589. https://doi.org/10.1177/109442810831990
Recker J (2012) Scientific research in information systems: a beginner’s guide. Springer, Berlin
Ridder H-G (2017) The theory contribution of case study research. Bus Res 10(2):281–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40685-017-0045-z
dos Santos Tavares AP, Fornazin M, Joia LA (2021) The good, the bad, and the ugly: digital transformation and the Covid-19 pandemic. In: Proceedings AMCIS 2021
Sarker S, Xiao X, Beaulieu T, Lee AS (2018) Learning from first-generation qualitative approaches in the IS discipline: an evolutionary view and some implications for authors and evaluators (PART 1/2). J Assoc Inf Syst 19(8):752–774. https://doi.org/10.17705/1jais.00508
Schäfferling A, Wagner H-T, Schulz M, Dum T (2011) The effect of knowledge management systems on absorptive capacity: findings from international law firms. In: Proceedings PACIS 2011
Sørensen C, Landau JS (2015) Academic agility in digital innovation research: the case of mobile ICT publications within information systems 2000–2014. J Strateg Inf Syst 24(3):158–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsis.2015.07.001
Spiegel F, Lazic M (2010) Incentive and control mechanisms for mitigating relational risk in IT outsourcing relationships. In: Proceedings AMCIS 2010
Stake RE (2013) Multiple case study analysis. The Guilford Press
Urquhart C (2001) Bridging information requirements and information needs assessment: Do scenarios and vignettes provide a link? Inf Res 6(2):6–2
van de Weerd I, Mangula IS, Brinkkemper S (2016) Adoption of software as a service in indonesia: examining the influence of organizational factors. Inf Manag 53(7):915–928. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2016.05.008
Vom Brocke J, Simons A, Riemer K, Niehaves B, Plattfaut R, Cleven A (2015) Standing on the shoulders of giants: challenges and recommendations of literature search in information systems research. Commun Assoc Inf Syst 37(1):9. https://doi.org/10.17705/1CAIS.03709
Voss C, Tsikriktsis N, Frohlich M (2002) Case research in operations management. Int J Oper Prod Manag 22(2):195–219
Wagner H-T, Ettrich-Schmitt K (2009) Integrating value-adding mobile services into an emergency management system for tourist destinations. In: Proceedings ECIS 2009
Welch C, Piekkari R, Plakoyiannaki E. et al (2011) Theorising from case studies: Towards a pluralist future for international business research. J Int Bus Stud 42, 740–762. https://doi.org/10.1057/jibs.2010.55
Weill P, Olson MH (1989) Managing investment in information technology: mini case examples and implications. MIS Q 13(1):3–17. https://doi.org/10.2307/248694
Yin RK (2018) Case study research and applications: design and methods, 5th edn. Sage Publications, California
Zamani E, Pouloudi N (2020) Generative mechanisms of workarounds, discontinuance and reframing: a study of negative disconfirmation with consumerised IT. Inf Syst J 31(3):284–428. https://doi.org/10.1111/isj.12315
Download references
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL. No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany
Sebastian Käss, Christoph Brosig & Susanne Strahringer
OTH Regensburg, Seybothstr 2, 93053, Regensburg, Germany
Markus Westner
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Literature search and analyses were performed by the first two authors, and reviewed by the other two. All authors contributed to the interpretation and the discussion of the results. The first draft of the manuscript was written by the first two authors and all authors commented on the previous versions of the manuscript and critically revised the work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Susanne Strahringer .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this study.
Ethical approval
Not Applicable, no human participants.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Käss, S., Brosig, C., Westner, M. et al. Short and sweet: multiple mini case studies as a form of rigorous case study research. Inf Syst E-Bus Manage (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10257-024-00674-2
Download citation
Received : 24 January 2024
Accepted : 23 February 2024
Published : 15 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10257-024-00674-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Case study research
- Multiple mini case study
- Short case study
- Methodological guidance
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Share Podcast

Ask These Questions Before Choosing a Manufacturing Location
How to grapple with the complexities of moving operations in a tightly woven global economy.
- Apple Podcasts
In today’s global economy, what are the factors that go into choosing a production location?
In this episode, Harvard Business School professor Willy Shih draws on his case study about China-based automotive glass maker Fuyao to discuss this core strategic question. The company must decide between two options to fulfill its upcoming contracts: its new Ohio factory or its factory based out of Tianjin, China. Unlike the Ohio factory, the Chinese factory produces below the cost target, but it also incurs extensive shipping costs and requires a far greater amount of inventory holding.
Shih explains how to account for product life cycles and the length of your inventory pipelines when selecting a manufacturing location. He also discusses how to assess other possible risks that could cause delays or increase production costs—like customs delays and labor strikes.
Key episode topics include: strategy, cross-cultural management, global strategy, operations and supply chain management, China, shipping, production planning, inventory pipeline.
HBR On Strategy curates the best case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, to help you unlock new ways of doing business. New episodes every week.
- Listen to the original HBR Cold Call episode: China-based Fuyao Glass Considers Manufacturing in the U.S. (2020)
- Find more episodes of Cold Call
- Discover 100 years of Harvard Business Review articles, case studies, podcasts, and more at HBR.org
HANNAH BATES: Welcome to HBR On Strategy , case studies and conversations with the world’s top business and management experts, hand-selected to help you unlock new ways of doing business.
In today’s global economy, what are the factors that go into choosing a production location? That’s the strategic decision facing Wen Li. She’s the global sales manager for Fuyao Glass, the world’s largest automotive glass producer.
She must decide where to fulfill upcoming contracts: In Fuyao’s new Ohio factory, where production rates are lower due to a newer employee base? Or their factory in Tianjin, China, which produces faster and cheaper but would incur shipping costs and require enormous inventory management?
Today, we bring you a conversation about a core strategic question facing managers who oversee supply chains, with Harvard Business School professor Willy Shih.
In this episode, you’ll learn how to account for product life cycles and the length of your inventory pipelines when you select a manufacturing location. You’ll also learn how to assess other possible risks that could cause delays or increase production costs – like customs delays, labor strikes, and political conditions that could lead to tariffs.
Since this episode originally aired on Cold Call in January 2020, global trade and U.S. and Chinese production have continued to shift. But the case study and its larger lessons in supply chain strategy are as relevant as ever. Here it is.
BRIAN KENNY: During the run up to the 2016 presidential election, candidate Donald Trump promised to reinvigorate the economy by bringing American manufacturing jobs back to the U.S. It was the cornerstone of his Make America Great campaign. Three years later, the results are mixed. The New York Times reports that companies have relocated just under 145,000 factory jobs to the U.S. On the other hand, the administration’s trade war with China may have undercut those gains by compelling some U.S. companies to move their manufacturing operations from China to other Asian countries with low-cost labor and easier access to Asian markets. In a highly polarized political environment, there is considerable debate over how to measure the effect of any reshoring trends by U.S. companies. But this isn’t just a concern for U.S. business leaders, the repatriation of American firms and the U.S. China trade war, have business leaders around the world grappling with the complexities of moving operations in a tightly woven global economy. Bottom line, it’s really complicated. Today we’ll hear from professor Willy Shih, about his case entitled, Fuyao Glass America: Sourcing Decision. I’m your host, Brian Kenny, and you’re listening to Cold Call , recorded live in Klarman Hall Studio at Harvard Business School.
BRIAN KENNY: Professor Shih is an expert in manufacturing and product development who also spent 28 years in industry at some of the largest technology firms in the world. And you know your way around a manufacturing floor. Is that right, Willy?
WILLY SHIH: Well, I’ve seen quite a few, so some people think I’m an expert.
BRIAN KENNY: And we’re going to talk about that more today. Thanks for joining me.
WILLY SHIH: Oh my pleasure. Thank you for having me.
BRIAN KENNY: We’ve had you on the show before, so I’m glad that you came back. I thought this case was really interesting because it kind of flips the script a little bit on the repatriation of companies to the U.S. Because here we have a Chinese company making the very same complicated decision, but from the other side of the Pacific. So I thought that was kind of an interesting flip on this. But let me ask you this, to start the way we always do, can you tell us what’s happening as the case opens? Who’s the protagonist and what’s on her mind?
WILLY SHIH: The case is actually Wen Li, who is the protagonist, who is the global sales manager for Fuyao Glass and she is preparing for a meeting with the chairman. And the question is really, they have opened this new factory in Moraine, Ohio and they are a Chinese company. Most of their other factories are in China and they’ve made some ventures abroad. But this factory in Moraine was really their stake in the American market. And so the question in front of her is, they have just won a new bid, which they priced very aggressively, should they supply it out of Ohio, which is more expensive at the moment or should they supply it out of China, where they actually have very established, mature facilities and they can deliver it at a much lower cost.
BRIAN KENNY: And that raises a whole host of issues that we’re going to get into that I thought were really interesting and sort of unintended consequences of some of the decisions that business leaders are being forced to make these days in the current environment. But I’m wondering, how did you hear about Fuyao? What prompted you to write the case and how does it relate to the work that you do here at Harvard Business School?
WILLY SHIH: What I was looking for as I was looking for a case that would teach about sort of the fundamental tenets of trade and globalization. Right, so we were looking for something that would illustrate those core issues, tradability of goods, to what extent do I need to manufacture something locally that I’m going to consume locally or can I make it in some other part of the world? The notion of labor arbitrage. When I have labor costs in one part of the world, which are very different than where I might want to sell, does it make sense to ship product long distances to do that? And then the third question that we really wanted to teach was about the tradeoff between using more labor or using more capital. And this is heavily influenced by your local labor costs and market conditions, to what extent do I invest more in automation? Or would I rather do more with labor because labor is less expensive and more flexible? We wanted to illustrate those three concepts. Okay. And what appealed to me about the Fuyao setting is, it’s the traditional offshoring narrative. It’s about a company that is trying to move jobs and manufacturing from its home base to another country. And it faces all the same challenges. The very popular narrative we heard in America for the last 15 years in particular, except it’s reversed. Here’s a Chinese company offshoring jobs to the U.S. and the chairman in China, by the way, is facing the same type of political issues there. How could you be shipping Chinese jobs to America? But it illustrates all those same key concepts that we wanted to in a narrative that’s just backwards.
BRIAN KENNY: So let’s talk about Fuyao. They make glass, they make glass for cars, at least in the case they may make glass for other things as well.
WILLY SHIH: Fuyao is an automotive glass maker and so they focus only on the automotive glass market. Automotive glasses are a little different than the type of glass that you have for windows. Window glass is normally are just flat sheets of glass, it’s made by a process called Float Glass, The Pilkington Float Glass Process. When you make automotive glass, usually what you have to do is you have to first cut it and shape it to match the style of the vehicle. So every vehicle that’s produced, usually, you have to produce custom cut windows for that vehicle. And then the other thing you have to do is you have to treat it specially. So for example your front windshield is safety glass. So that’s actually two sheets of glass with a layer of a polymer in between so that if you strike it with some object, it won’t shatter, rather it’ll hold all the shards of glass in place. So there’s an assembly process associated with it. And then there’s also the tempering process where you really try to change the physical properties of the glass through a heat cycling so that it won’t shatter on impact, it’ll be stronger. So you start with float glasses, the raw material, and then you bend it and you cut it and you do these various processes. And then also you will add things like features, right? So for example, sometimes you want to embed heating wires in it so you can have defrosting. Or some of the newer windshields now will have moisture sensors embedded in them to trigger your windshield wipers and things like that. So there’s lots of features as well.
BRIAN KENNY: Even displays…
WILLY SHIH: Even displays.
BRIAN KENNY: My side mirrors tell me if there’s a car in the lane before I change.
WILLY SHIH: Right. So then what you can do is you can embed features like that. So Fuyao is a specialist, okay. And at the time of the case, they had almost 65% market share in China of all the automotive glass sold in China. Now that’s particularly significant because at the time of the case, China was already the largest automotive market in the world. At the time of the case, China was around 28 million vehicles produced and sold every year, whereas the U.S. is typically around 16 to 17 million vehicles sold per year. But we only manufacture 11 million and change in the U.S. and the rest are imported. So from a manufacturing scale standpoint, China is actually much larger market.
BRIAN KENNY: And I’m sure a lot of people listening to our conversation are driving in their cars. I would just say, look around you, there’s so much glass in a car. Until I read the case, I hadn’t really thought about that. And then I was still driving home after reading the case and I thought, “Wow, this thing is probably 50% glass it seems like-”
WILLY SHIH: Well, there’s a lot of glass, there’s increasing use of glass in fact, especially for skylights, there are some vehicles who have very large skylights. And so you can imagine the kind of the mechanical strength you need to have for that. But then also if you look at the side windows, there’s a lot of complexity. You have a lot of these corner cuts and a lot of curve shaping and stuff. So there’s actually quite a bit of manufacturing complexity because for each set of auto glass for a vehicle program, right. So for an individual model car, you have to do a set of molds and you have to do custom cutting and you have to make it match that particular vehicle. So each one of these orders and this case concerns the particular order for the glass set for a particular model. Once you win that, then you have to have a production plan and you then have to choose which factory you want to source it from because the auto maker will expect to work with that line in that factory for the life of that model.
BRIAN KENNY: What was it like on the manufacturing room floor?
WILLY SHIH: So, I’ve been in several of the Fuyao factories. For example, the one in Moraine is an enormous facility. If you think about the processes that you need to make all these parts, you have raw glass coming in to Moraine and it’s trucked in from a factory in Mount Zion, Illinois, for the case of Ohio, but then you have cutting and you have washing. You have a lot of automated tools which will handle those sheets because frankly, handling sheets of glass like that is not easy. And for the volumes that people are talking about, you like to have some automation. So you’ll have initial cutting and washing, you’ll have long lines where machines will handle the bending of the glass. And then eventually you’ll cut them to shape and then you’ll have a separate lines where you’ll say, I’ll make the front windshields, where I’m going to take two pieces that are cut to match. And then workers will grab first the first layer, and they’ll put a sheet of that plastic in between, they’ll put a second layer of glass on and then they’ll trim it and set it up to go into an oven where I can heat it to fuse everything together. So it takes quite a bit of space. If you look in the factory in China versus the factory in Ohio, because labor is more expensive in Ohio, they’ve chosen to automate more steps. In China, for example, there’ll be more workers handling windshields or window parts, whereas in Ohio there’s a kind of more machine automation. And Ohio is also a newer plant.
BRIAN KENNY: Which is another sort of dimension to the whole bringing jobs back to the U.S. Automation obviously is having a big impact on how many jobs, how many workers are needed to perform a produce a product or perform a task.
WILLY SHIH: Right. Labor is much more expensive in the U.S. so it’s easier for a manufacturer to justify more investments than automation.
BRIAN KENNY: How much more expensive is it? The case gets into, does it?
WILLY SHIH: Well, the case talks about it and the case talks about the labor rate differential being about 7:1. It’s down considerably from the early 2000s when a typical labor rate ratio would be 10:1 maybe even 20:1. That gap has certainly narrowed.
BRIAN KENNY: What about the raw materials that are needed to make the glass?
WILLY SHIH: Well, raw materials are pretty basic for glass, it’s basically purified sand, limestone and some other materials. Okay. And so the key raw material for auto glass is something called float glass. Okay. And that’s something where you mix sand and other minor elements and you fuse them in a hot oven and then you pour it into a bath of molten tin. The glass then just kind of floats off that onto a line where you try to control the thickness and you use the molten tin as a way of having a very flat surface and not requiring a lot of polishing. And that was a process developed by the Pilkington Company in the UK, it’s called the Pilkington Flood Glass Process. It’s widely used by most glass manufacturers. In the case of Fuyao, they have their own float glass plants because they believe very much in vertical integration. So they’ll make their own float glass. They have their own sand mines in China. Right. Because they want to control all that
BRIAN KENNY: So, this becomes one of the considerations obviously, that they have to think about when they think about where to locate this plant. So why don’t we dive into that, that set of questions specifically. First of all, I’m just curious about Wen Li’s background, I mean this is obviously a big job, big decisions with big consequences. How did she prepare for that?
WILLY SHIH: It is a big job. She actually started out as a consultant, but her father had a family business in Shandong Province in China and he had a health emergency. And I’ve never delved into the details of that, but this family business was a printing and packaging business. And so when he had this health emergency, she had to step in, for a number of years she was running that business, which was actually great training for her. She told me that she had to do a lot of restructuring of that business and really get it into profitability. She then got recruited into Fuyao and as I mentioned, one of her early tasks was when the Beijing government told them they had to move this factory to Tianjin. So she really worked closely with the Tianjin government and then with the team in setting up that whole Tianjin facility.
BRIAN KENNY: So now she’s thrust into a different situation where she has to make a recommendation to the owner of the company about where to locate this plant, what are some of the things that she has to consider?
WILLY SHIH: Well, I think the key questions really revolve around the costs. If you look at the Moraine factory, it’s relatively new, it’s still in its ramp up phase. For this particular order that they want, that they are looking at, the cost to produce it in Moraine is roughly 50% higher than it would be to produce it in Tianjin for example. It’s considerably cheaper to produce it in Tianjin and ship it than it is to produce it in Moraine. But the Tianjin factory is quite mature. They’ve gotten better in their yields, they’ve gotten better in their labor efficiency and all those metrics which contribute to cost, whereas Moraine is still coming up the learning curve. And I think the key question is, do I bet that they’re going to get there? And potentially lose money on this contract if they don’t get there? Or it takes them longer, or do I go with a safe thing and stick with Tianjin and source it from China. Now they’re already doing other business in Moraine, so it’s not like there’s no work for the factory in Moraine. It’s more kind of an incremental order that they bid very aggressively for, and so where should I put it?
BRIAN KENNY: So, they have a lot of stake there though because they did bid aggressively for this and they’ve got to prove that they can do it. How guaranteed is it that those pieces of glass are ever going to get across the ocean and to where they need to be in time to meet the order?
WILLY SHIH: Well, that’s one of the other challenges facing them, right? Because if I source this glass from Tianjin, and by the way, they have been supplying U.S. and European makers for a while, even before they had this factory in Moraine. So they have been shipping auto glass around the world, but it takes some amount of time. So I am going to have inventory in my pipeline and that subjects me to a lot of risks. Maybe there’s a longshoreman strike that holds up my inventory clearing customs and coming into the country. Maybe the U.S. has an administration that decides they’re going to apply tariffs to it. Okay. So that my costs go up.
BRIAN KENNY: That could happen.
WILLY SHIH: If you’re a company that is a supplier to one of the big three U.S. automakers or to a number of other automakers, I know somebody who is intimately familiar with some of these contracts. Tariffs are the responsibility of the supplier. If you’re General Motors, that’s not your problem. Because in your purchasing agreement you say two years supplier, if you have to pay tariffs it’s your problem. That’s not what is in the cost that I will be prepared to absorb. Right. So, that’s a risk. In some sense you have to give the chairman of Fuyao some amount of credit for building this factory in Moraine, actually well ahead of when the trade war really got heated up. In some respects, and I’ve talked to him about that, he was in a hurry to do it. And I would say, they were ahead of the curve in that thought process.
BRIAN KENNY: I want to talk about this from the customer’s perspective. So if I’m GM and I’m entertaining bids from different suppliers, do I have a say on this and how much do I care about where they’re sourcing the materials as long as I’ve got this ironclad guarantee that I’m going to get my stuff when I need it.
WILLY SHIH: A company like a GM or any of the major automakers, what they want is they want a quality product, at the right price, delivered dependably. So you can imagine every car out there needs its windshield and its windows. So if you are not able to deliver on time exactly when they need it, you’re going to stop their production line. So the major automakers often impose very stiff fines, if you’re unable to deliver. It could cost you $1 million a day if you shut down somebody’s production line. But if you step back and say, as a major automaker, what does that really mean? It means I need suppliers who can really be good partners for me. Oftentimes they’ll say, I want you for a particular model or maybe a range of models. I want you to source it locally. Some other automakers like BMW, for example, will say, I want you to source from these plants around the world to supply my plants around the world and they will designate ones that they have inspected that they’re comfortable with. Right. So your customers have actually a fair amount of influence in terms of where they would like you to manufacture a particular order or a particular set of products.
BRIAN KENNY: How crowded is this marketplace? Who competes with Fuyao?
WILLY SHIH: Well, Fuyao is a pretty big player in China. They’re relatively smaller elsewhere. They’re trying to grow to become a global player. Other companies that you would typically find in the U.S. would be companies like Guardian Industries. Okay. Or Saint-Gobain, which is a very large global player. Asahi Glass, Nippon Sheet Glass. So there are other manufacturers out there, many of them tend to be kind of regional rather than global. Saint-Gobain is fairly global, but you see a lot of regional players.
BRIAN KENNY: So, the experience of knowing how to operate in overseas markets, whether it’s in the direction of China to the U.S. or the other way around, it’s pretty valuable.
WILLY SHIH: Yes. I think it’s very valuable in this industry in particular.
BRIAN KENNY: Have you discussed this in class?
WILLY SHIH: We just taught the case yesterday. One of the surprises to me was a reticence amongst students to have long supply chains. Okay. And it wasn’t pervasive by any means, but I saw to me a surprising number of people who were not big fans of global sourcing and long supply chains. Now having said that, I also had students in my classes who have worked at companies like at Apple. Okay. Or garment companies who have long used global sourcing. Garments are one of those lead products that always are one of the first seek low cost countries for manufacturing. So it was a mix. But I was surprised by the number of people who are very conscious of the length of the supply chain in terms of distance and time in how that could impact your responsiveness to customer needs because of that kind of long inventory pipeline. On the other hand, if they were comfortable with the long inventory pipeline, kind of a reticence on paying for premium shipping. And one of the things I was trying to point out is if I have high value cargo, I might choose to assemble it in a low cost country because I can save a lot and then I’ll high value or high time value, I can ship it by air cargo and I can have it here, cleared customs in a store in 48 hours. I mean we have firms like Zara: Fast Fashion, who have built their whole business model on, I’m going to source in places which are attractive for various reasons. And then I will just get it into store very quickly using air cargo or somebody like Apple who predominantly ships iPhones and iPads by air cargo. Because my product life cycles are short and you know, I need to assemble it somewhere where labor is not expensive, but I need to get them to market fast.
BRIAN KENNY: And ultimately the customer probably pays whatever that tariff is.
WILLY SHIH: Well, we had that discussion in one of my classes about, would you pay more to get this in a day instead of 30 days and ultimately most students agreed, well, I probably would pay more. Right? But for a company, if they become a product manager somewhere someday and a lot of students aspire to those types of roles, these are the types of decisions you have to make every day about where do I source my product? What do I want to pay for in terms of supply chain flexibility and responsiveness? So those were the things that we were trying to explore.
BRIAN KENNY: There’s a little footnote to this case too that you let me know about which is that, this is the subject already of a documentary.
WILLY SHIH: It turns out there’s a documentary that has gotten very great reviews so far. It’s called American Factory. And it highlights kind of the challenges of a Chinese company coming into the U.S. where you have very different cultures. You have to span that cultural divide. You have a whole host of issues. There’s a union organizing campaign around the factory. There’s struggles getting the factory to the performance level that they need. So it’ll be a-
BRIAN KENNY: It kind of gets to a lot of the issues in the case.
WILLY SHIH: Gets to a lot of issues in the case, it’s a very nice complement to the case.
BRIAN KENNY: And this film will be on Netflix eventually for-
WILLY SHIH: It is already on Netflix. In fact, when we taught the case a number of students in each of my sections had seen the movie, and so but they were still–
BRIAN KENNY: –Very enterprising of them. Willy, thank you for joining me.
WILLY SHIH: Thank you for having me.
HANNAH BATES: That was Harvard Business School professor Willy Shih – in conversation with Brian Kenny on Cold Call .
We’ll be back next Wednesday with another hand-picked conversation about business strategy from Harvard Business Review. If you found this episode helpful, share it with your friends and colleagues, and follow our show on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, or wherever you get your podcasts. While you’re there, be sure to leave us a review.
When you’re ready for more podcasts, articles, case studies, books, and videos with the world’s top business and management experts, you’ll find it all at HBR.org.
This episode was produced by Anne Saini and me, Hannah Bates. Ian Fox is our editor. Special thanks to Maureen Hoch, Erica Truxler, Ramsey Khabbaz, Nicole Smith, Anne Bartholomew, and you – our listener. See you next week.
- Subscribe On:
Latest in this series
This article is about strategy.
- Cross-cultural management
- Global strategy
- Operations and supply chain management
Partner Center
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
This article is part of the research topic.
Measuring Diets and Food Choice in the Context of a Changing World
Measuring and Shaping the Nutritional Environment via Food Sales Logs: Case Studies of Campus-Wide Food Choice and a Call to Action Provisionally Accepted

- 1 Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne, Switzerland
- 2 Université de Fribourg, Switzerland
- 3 Microsoft Research (United States), United States
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
Although diets influence health and the environment, measuring and changing nutrition is challenging. Traditional measurement methods face challenges, and designing and conducting behavior-changing interventions is conceptually and logistically complicated. Situated local communities such as university campuses offer unique opportunities to shape the nutritional environment and promote health and sustainability. The present study investigates how passively sensed food purchase logs typically collected as part of regular business operations can be used to monitor and measure on-campus food consumption and understand food choice determinants.First, based on 38 million sales logs collected on a large university campus over eight years, we perform statistical analyses to quantify spatio-temporal determinants of food choice and characterize harmful patterns in dietary behaviors, in a case study of food purchasing at EPFL campus. We identify spatial proximity, food item pairing, and academic schedules (yearly and daily) as important determinants driving the on-campus food choice. The case studies demonstrate the potential of food sales logs for measuring nutrition and highlight the breadth and depth of future possibilities to study individual food-choice determinants. We describe how these insights provide an opportunity for stakeholders, such as campus offices responsible for managing food services, to shape the nutritional environment and improve health and sustainability by designing policies and behavioral interventions. Finally, based on the insights derived through the case study of food purchases at EPFL campus, we identify five future opportunities and offer a call to action for the nutrition research community to contribute to ensuring the health and sustainability of on-campus populations-the very communities to which many researchers belong.
Keywords: food choice, Measurement, Monitoring, determinants, Digital traces, Health, sustainability, policy
Received: 30 May 2023; Accepted: 14 May 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Gligorić, Zbinden, Chiolero, Kiciman, White, Horvitz and West. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Dr. Kristina Gligorić, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne, Lausanne, 1015, Vaud, Switzerland
People also looked at
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Study Suggests Genetics as a Cause, Not Just a Risk, for Some Alzheimer’s
People with two copies of the gene variant APOE4 are almost certain to get Alzheimer’s, say researchers, who proposed a framework under which such patients could be diagnosed years before symptoms.

By Pam Belluck
Scientists are proposing a new way of understanding the genetics of Alzheimer’s that would mean that up to a fifth of patients would be considered to have a genetically caused form of the disease.
Currently, the vast majority of Alzheimer’s cases do not have a clearly identified cause. The new designation, proposed in a study published Monday, could broaden the scope of efforts to develop treatments, including gene therapy, and affect the design of clinical trials.
It could also mean that hundreds of thousands of people in the United States alone could, if they chose, receive a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s before developing any symptoms of cognitive decline, although there currently are no treatments for people at that stage.
The new classification would make this type of Alzheimer’s one of the most common genetic disorders in the world, medical experts said.
“This reconceptualization that we’re proposing affects not a small minority of people,” said Dr. Juan Fortea, an author of the study and the director of the Sant Pau Memory Unit in Barcelona, Spain. “Sometimes we say that we don’t know the cause of Alzheimer’s disease,” but, he said, this would mean that about 15 to 20 percent of cases “can be tracked back to a cause, and the cause is in the genes.”
The idea involves a gene variant called APOE4. Scientists have long known that inheriting one copy of the variant increases the risk of developing Alzheimer’s, and that people with two copies, inherited from each parent, have vastly increased risk.
The new study , published in the journal Nature Medicine, analyzed data from over 500 people with two copies of APOE4, a significantly larger pool than in previous studies. The researchers found that almost all of those patients developed the biological pathology of Alzheimer’s, and the authors say that two copies of APOE4 should now be considered a cause of Alzheimer’s — not simply a risk factor.
The patients also developed Alzheimer’s pathology relatively young, the study found. By age 55, over 95 percent had biological markers associated with the disease. By 65, almost all had abnormal levels of a protein called amyloid that forms plaques in the brain, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s. And many started developing symptoms of cognitive decline at age 65, younger than most people without the APOE4 variant.
“The critical thing is that these individuals are often symptomatic 10 years earlier than other forms of Alzheimer’s disease,” said Dr. Reisa Sperling, a neurologist at Mass General Brigham in Boston and an author of the study.
She added, “By the time they are picked up and clinically diagnosed, because they’re often younger, they have more pathology.”
People with two copies, known as APOE4 homozygotes, make up 2 to 3 percent of the general population, but are an estimated 15 to 20 percent of people with Alzheimer’s dementia, experts said. People with one copy make up about 15 to 25 percent of the general population, and about 50 percent of Alzheimer’s dementia patients.
The most common variant is called APOE3, which seems to have a neutral effect on Alzheimer’s risk. About 75 percent of the general population has one copy of APOE3, and more than half of the general population has two copies.
Alzheimer’s experts not involved in the study said classifying the two-copy condition as genetically determined Alzheimer’s could have significant implications, including encouraging drug development beyond the field’s recent major focus on treatments that target and reduce amyloid.
Dr. Samuel Gandy, an Alzheimer’s researcher at Mount Sinai in New York, who was not involved in the study, said that patients with two copies of APOE4 faced much higher safety risks from anti-amyloid drugs.
When the Food and Drug Administration approved the anti-amyloid drug Leqembi last year, it required a black-box warning on the label saying that the medication can cause “serious and life-threatening events” such as swelling and bleeding in the brain, especially for people with two copies of APOE4. Some treatment centers decided not to offer Leqembi, an intravenous infusion, to such patients.
Dr. Gandy and other experts said that classifying these patients as having a distinct genetic form of Alzheimer’s would galvanize interest in developing drugs that are safe and effective for them and add urgency to current efforts to prevent cognitive decline in people who do not yet have symptoms.
“Rather than say we have nothing for you, let’s look for a trial,” Dr. Gandy said, adding that such patients should be included in trials at younger ages, given how early their pathology starts.
Besides trying to develop drugs, some researchers are exploring gene editing to transform APOE4 into a variant called APOE2, which appears to protect against Alzheimer’s. Another gene-therapy approach being studied involves injecting APOE2 into patients’ brains.
The new study had some limitations, including a lack of diversity that might make the findings less generalizable. Most patients in the study had European ancestry. While two copies of APOE4 also greatly increase Alzheimer’s risk in other ethnicities, the risk levels differ, said Dr. Michael Greicius, a neurologist at Stanford University School of Medicine who was not involved in the research.
“One important argument against their interpretation is that the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in APOE4 homozygotes varies substantially across different genetic ancestries,” said Dr. Greicius, who cowrote a study that found that white people with two copies of APOE4 had 13 times the risk of white people with two copies of APOE3, while Black people with two copies of APOE4 had 6.5 times the risk of Black people with two copies of APOE3.
“This has critical implications when counseling patients about their ancestry-informed genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease,” he said, “and it also speaks to some yet-to-be-discovered genetics and biology that presumably drive this massive difference in risk.”
Under the current genetic understanding of Alzheimer’s, less than 2 percent of cases are considered genetically caused. Some of those patients inherited a mutation in one of three genes and can develop symptoms as early as their 30s or 40s. Others are people with Down syndrome, who have three copies of a chromosome containing a protein that often leads to what is called Down syndrome-associated Alzheimer’s disease .
Dr. Sperling said the genetic alterations in those cases are believed to fuel buildup of amyloid, while APOE4 is believed to interfere with clearing amyloid buildup.
Under the researchers’ proposal, having one copy of APOE4 would continue to be considered a risk factor, not enough to cause Alzheimer’s, Dr. Fortea said. It is unusual for diseases to follow that genetic pattern, called “semidominance,” with two copies of a variant causing the disease, but one copy only increasing risk, experts said.
The new recommendation will prompt questions about whether people should get tested to determine if they have the APOE4 variant.
Dr. Greicius said that until there were treatments for people with two copies of APOE4 or trials of therapies to prevent them from developing dementia, “My recommendation is if you don’t have symptoms, you should definitely not figure out your APOE status.”
He added, “It will only cause grief at this point.”
Finding ways to help these patients cannot come soon enough, Dr. Sperling said, adding, “These individuals are desperate, they’ve seen it in both of their parents often and really need therapies.”
Pam Belluck is a health and science reporter, covering a range of subjects, including reproductive health, long Covid, brain science, neurological disorders, mental health and genetics. More about Pam Belluck
The Fight Against Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s is the most common form of dementia, but much remains unknown about this daunting disease..
How is Alzheimer’s diagnosed? What causes Alzheimer’s? We answered some common questions .
A study suggests that genetics can be a cause of Alzheimer’s , not just a risk, raising the prospect of diagnosis years before symptoms appear.
Determining whether someone has Alzheimer’s usually requires an extended diagnostic process . But new criteria could lead to a diagnosis on the basis of a simple blood test .
The F.D.A. has given full approval to the Alzheimer’s drug Leqembi. Here is what to know about i t.
Alzheimer’s can make communicating difficult. We asked experts for tips on how to talk to someone with the disease .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn how Zara, the fast fashion pioneer, achieved success with its unique strategy and supply chain management. Read the case study on ResearchGate.
Zara's 'Fast Fashion' Business Model. Zara's business model is basically based on the principle that it can sell "medium quality fashion clothing at affordable prices". Basically vertical integration and the ability to come up with a quick-response is a key factor to Zara's successful business model otherwise they would be no ...
In 2010, amidst the growth of ecommerce and the emergence of new, purely online, fashion players, Zara launched its first online store, Zara.com. Since then, Zara's online business had grown at a fast pace. By 2018, 12% of Inditex Group's total sales came from the online channel. Since the inception of the first online store, Inditex ...
Fashion retailer ZARA has achieved spectacular growth via a distinctive design-on-demand operating model. This case describes this model and outlines a number of challenges facing the company, with a particular emphasis on its international expansion. ... David J., and Guillermo D"Andrea. "Zara." Harvard Business School Case 503-050, March 2003 ...
Source: Harvard Business School. Product #: 503050-PDF-ENG. Length: 26 page (s) Fashion retailer ZARA has achieved spectacular growth via a distinctive design-on-demand operating model. This case describes this model and outlines.
This story is about how Zara became the undisputed king of Fast fashion. Fashion is the imitation of a given example and satisfies the demand for social adaptation. . . . The more an article becomes subject to rapid changes of fashion, the greater the demand for cheap products of its kind. — Georg Simmel, "Fashion" (1904)
Powered by ZARA's success, Inditex has expanded into 39 countries, making it one of the most global retailers in the world. But in 2002, it faces important questions concerning its future growth. ... Harvard Business School Case 703-497, April 2003. (Revised December 2006.) Educators; Purchase; Related Work. April 2003 (Revised December 2006 ...
ZARA'S CASE STUDY | CATÓLICA-LISBON SCHOOL OF BUSINESS AND ECONOMICS ZARA'S CASE STUDY The Leader in the Fast Fashion Concept Author: Maria Joana Mascarenhas de Lemos ... studies. I will start by doing an exploratory interview to the Marketing Director of Zara in Portugal, Dr. Pedro Vidigal, to better understand how the company, Inditex ...
Zara is a privately held multinational clothing retail chain with a focus on fast fashion. It was founded by Amancio Ortega in 1975 and it's the largest company of the Inditex group. Amancio Ortega was Inditex's Chairman until 2011 and Zara's CEO until 2005. The current CEO of Zara is Óscar García Maceiras and Marta Ortega Pérez ...
Zara uses intensive data and analytics to manage a tight supply chain and give customers exactly what they want. Introduction. Zara's parent company Inditex has managed to thrive in the last decade while several other fashion retailers have faced declining sales or stagnant growth. Inditex has grown over 220% in annual revenue since 2004 ...
703-497 ZARA: Fast Fashion 4 Inditex combined. The latter two companies were perhaps the most pan-European apparel retailers but had yet to achieve market shares of more than 2%-3% in more than two or three major countries.
In May 2021, SHEIN overtook Amazon as the most downloaded shopping app on the US iOS and Android app stores. During the pandemic in 2020, SHEIN achieved substantial sales growth and is now catching up with the fast-fashion giant Zara. This case first briefly discusses the apparel and fast-fashion industry and the creation of the fast-fashion model by Zara. Then it covers SHEIN's historical ...
This excerpt from a recent Harvard Business Review profile zeros in on how Zara's supply chain communicates, allowing it to design, produce, and deliver a garment in fifteen days. In Zara stores, customers can always find new products—but they're in limited supply. There is a sense of tantalizing exclusivity, since only a few items are on ...
By examining Zara as a case study from a negative perspective, important lessons and insights can be gained in the following areas: Business strategy and development New: Zara's success is based ...
2018. This case study examines Zara's current retail strategy and digital transformation. It details Zara's current in-store and eCommerce retail strategy, the impact of digital on the retail environment and customer experience, and the growth opportunity provided by eCommerce. By providing a competitive analysis of the current market, this ...
Zara - Introduction. Founded in 1975, ZARA, a Spanish clothing and accessories retailer was originally the brainchild of the Inditex Group owned by Amancio Ortega. Headquartered in A Coruña, Galicia, Spain, Inditex is the world's largest fashion retailer with ZARA as its international flagship chain store. Beginning with the single store ...
There are currently 2085 Zara stores in 96 countries around the world. In 2020, Zara was the leading brand of the Inditex group — with an annual net income of over 14 billion euros. Bringing "attractive and responsible fashion, as well as improving the customer's experience, are Zara's priorities.".
Zara brilliantly addressed those challenges to produce effective results that ultimately helped them grow their business. (I) Summing Up: Zara Case Study. Zara's remarkable success in leading the fashion market can be attributed to its unique blend of rapid fashion cycles, vertical integration, and a customer-centric approach.
Each Case Flash Forward provides educators and students with a brief, 2-3 page update of key changes at a particular company covered in a related case study. It is a compilation of publicly-available content prepared by an experienced editor. This Case Flash Forward provides an update on Inditex and Zara, including significant developments, current executives, key readings, and basic financials.
ZARA: FAST FASHION. 1. Introduction. In my short study case I will start by illustrating Zara's present situation (according to the case), then I will continue with a brief analysis of the internal and external environments; in the next step I will develop some alternative ways of action and I will end by presenting my recommendations regarding the adaptation of the Zara's business model ...
I have added some links to great resources (courses, statistics, videos, and articles) on Zara, fashion analytics, data analytics, and a non-fashion related case study. Inditex 2021 Report Inditex ...
Evaluating business ethics and CSR: Case Zara. January 2019; Authors: ... Journal o f International Women´s Studies, 19(6). Kant, I., 1785. ... This case study examines the grievances of young ...
ZARA is a Spanish clothing and accessories retailer based in Arteixo, Galicia. Founded in 24 May ,1975 by Amancio Ortega and RosalÃa Mera, the brand is renowned for it's ability to deliver new clothes to stores quickly and in small batches. Zara needs just two weeks to develop a new product and get it to stores, compared to the six-month ...
Prof: Ahmed El Melegy. Ammar Al-Areqi 4491. Zara Case Study. 1. Discuss the nature of competition and demand in the apparel industry? While most apparel manufacturers were migrating manufacturing to Asia to gain cost efficiency, Zara recognized that speed, flexibility and innovation were key to establishing a stronghold of the market.
15 Real-Life Case Study Examples. Now that you understand what a case study is, let's look at real-life case study examples. In this section, we'll explore SaaS, marketing, sales, product and business case study examples with solutions. Take note of how these companies structured their case studies and included the key elements.
Case study research is one of the most widely used research methods in Information Systems (IS). In recent years, an increasing number of publications have used case studies with few sources of evidence, such as single interviews per case. While there is much methodological guidance on rigorously conducting multiple case studies, it remains unclear how researchers can achieve an acceptable ...
In this episode, Harvard Business School professor Willy Shih draws on his case study about China-based automotive glass maker Fuyao to discuss this core strategic question. The company must ...
Streamline customer self-service processes and reduce operational costs by automating responses for customer service queries through generative AI-powered chatbots, voice bots, and virtual assistants. Learn more. Analyze unstructured customer feedback from surveys, website comments, and call transcripts to identify key topics, detect sentiment ...
The case studies demonstrate the potential of food sales logs for measuring nutrition and highlight the breadth and depth of future possibilities to study individual food-choice determinants. ... The present study investigates how passively sensed food purchase logs typically collected as part of regular business operations can be used to ...
May 6, 2024 Updated 12:19 p.m. ET. Scientists are proposing a new way of understanding the genetics of Alzheimer's that would mean that up to a fifth of patients would be considered to have a ...