

IELTS Reading: Cambridge 13 Test 1 Reading Passage 1, Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website; with best solutions, explanations and bonus tips
This IELTS Reading post deals with a total solution package for IELTS Cambridge 13 Reading test 1 passage 1 . This is a targeted post for candidates who have major difficulties in finding and understanding Reading Answers. This post can guide you the best to understand every Reading answer easily and without much difficulty. Finding IELTS Reading answers is a step-by-step process and I hope this post can help you in this respect.

Reading Passage 1 :
The headline of the passage: case study: tourism new zealand website.
Questions 1-7 ( Completing table with ONE WORD ONLY):
In this type of question, candidates are asked to write only one word to complete a table on the given topic. For this type of question, first, skim the passage to find the keywords in the paragraph concerned with the answer, and then scan to find the exact word.
[ TIPS: Here scanning technique will come in handy. Target the keywords of the questions to find the answers. Remember to focus on Proper nouns, random Capital letters, numbers, special characters of text etc.]
Question 1: allowed businesses to ______ information regularly.
Keywords for these answers: database, allowed businesses, information, regularly,
In paragraph no. 2, we find the mention of the word ‘database’ in the third line. Here, lines 8 & 9, the writer mentions, “In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis….”.
Here, details = information
So, the answer is: update
Question 2: provided a country-wide evaluation of businesses, including their impact on the _________.
Keywords for this answer: database, country-wide evaluation, impact on
The last line of paragraph no. 2 has the answer. Here, the writer suggests, “As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.”
Here, effect = impact
So, the answer is: environment
Question 3: e.g. an interview with a former sports __________.
Keywords for this answer: special features, interview, a former sports
The answer can be found in paragraph 3, lines 1-3. The words ‘interview’ and ‘former’ are formed in line number 2. The writer says, “.. .. . One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga.”
Here, rugby = sports
So, the answer is: captain
Question 4: and an interactive tour of various locations used in ________.
Keywords for this answer: interactive tour, various locations
The answer is in paragraph 3, lines 4-5. The lines say, “…… was an interactive journey through a number of locations chosen for blockbuster films …… ..”.
Here, journey = tour,
A number of locations = various locations,
Chosen for = used in,
So, the answer is: films
Question 5: varied depending on the __________.
Keywords for these answers: driving routes, varied, depending on
Paragraph 3, lines 8-9 has the answer to this question. The lines say, “…. . .the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season ….. . .”.
Here, different = varied,
according to = depending on,
So, the answers are: season
Question 6: including a map showing selected places, details of public transport and local _______.
Keywords for this answer: travel planner, a map, public transport, local
The answer lies in paragraph no. 4, line 4. The paragraph begins with ‘travel planner’. In the subsequent lines, we can find the mention of ‘public transport’. In line no. 4 it says, “… . There were also links to accommodation in the area.”
Here, the phrase ‘in the area’ can be replaced with the word ‘local’.
So, the answer is: accommodation
Question 7: travelers could send a link to their ________.
Keywords for this answer: ‘Your Words’, travelers, send, link to,
The answer is in paragraph no. 4. ‘Your Words’ is the name of a section of the website www.newzealand.com. We can see that the phrase ‘Your Words’ is present in line 6 of paragraph 4. So, we need to read lines 6 & 7 to find the answer.
The author says, “ ….. . . The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.”
Here, anyone could submit = travelers could send a link to
So, the answer is: blog
Questions 8-13: (TRUE/FALSE/NOT GIVEN)
In this type of question, candidates must find out whether:
The statement in the question matches with the account in the text- TRUE The statement contradicts the account in the text- FALSE There is no clear connection of the statement with the account in the text- NOT GIVEN
Question 8: The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists.
Keywords for this answer: the website, aimed, itineraries, travel packages
To find the answer to this question, look for the words itineraries and travel packages. The answer is in Paragraph 6. Here, lines 1 and 2 say, “ The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organizations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests.”
This means that the aim of the website was to allow individuals and travel organizations to do their work on their own, the website did not provide any ready-made itineraries and travel packages.
The statement clearly contradicts the text.
So, the answer is: FALSE
Question 9: It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location.
Keywords for this answer: started searching, geographical location
The answer is not anywhere in the passage. The question is about starting the search in the website.
In paragraph 6 line 3, the author says, “…… visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical locations, but also by the particular nature of the activity.” However, nowhere it says anything about starting the search.
So, the answer is: NOT GIVEN
Question 10: According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation.
Keywords for this answer: 26%, visitor satisfaction, accommodation
** Special answer-finding technique:
There is a number in the question (26%). If the answer is TRUE, 26% has to be in the text. For FALSE, the number will be different; or, the number will be 26% (but it will be related to other matters). If the number is still 26%, yet it doesn’t match with other keywords, the answer will be NOT GIVEN.
The answer is in lines 4, 5 & 6 of paragraph no. 6. Here, the writer says, “This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction , while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26% .”
Here, the lines clearly contradict the question. Transportation and accommodation account for 26%. Visitor satisfaction accounts for 74%. If only accommodation accounted for 26%, we could write TRUE.
Question 11: Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture.
Keywords for this answer: like to, involved, local nature
The answer lies in lines 7-9 of paragraph 6. The author says, “…. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn more about traditional life.”
It means that visitors like to engage in local culture.
So, the answer is: TRUE
Question 12: Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones.
Keywords for this answer: like staying, small hotels
In paragraphs 6 & 7, there is no mention of staying in hotels. There is no comparison between small and large hotels also.
So the answer is: NOT GIVEN
Question 13: Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit.
Keywords for this answer: feel, unlikely, will return, after their visit
The answer is in paragraph 7. Here, lines 4 and 5 states, “Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit .”
Here, the phrase ‘often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit’ means that there is a very low possibility that the visit will happen again.
So the answer is: TRUE
Bonus tips:
You must pay attention to WORD LIMIT. For instance, if you have to complete a sentence using NO MORE THAN TWO WORDS; and the correct answer in the text is ‘dress made of cotton’, you cannot write the answer as ‘dress made of cotton’. You need to change it to ‘cotton dress’.
If you like this post, and need any assistance about IELTS Reading, please make comments below.
Click here for solutions to Cambridge 13 Reading Test 1 Passage 2
Click here for solutions to Cambridge 13 Reading Test 1 Passage 3
Important vocabulary with explanations for Cambridge 13 Test 1 Reading Passage 1, 2, 3
59 thoughts on “ IELTS Reading: Cambridge 13 Test 1 Reading Passage 1, Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website; with best solutions, explanations and bonus tips ”
- Pingback: IELTS Reading: Cambridge 13 Test 1 Reading Passage 2; with best solutions and explanations | IELTS Deal
- Pingback: IELTS Reading: Cambridge 13 Reading Test 1; Passage 3; Artificial artists; with top solutions and explanations | IELTS Deal
thanku really it’s very helpfull
Thank you for help
it was very helpful, thanks!.
Thank u ???
i although questions were all completely explained, i did n’t understand question number 10.
The question asks you to decide whether 26% visitor satisfaction is related to accommodation. We find in the passage, 26% visitor satisfaction is related to accommodation and transport. So, here in the question, transport is missing. This is why the answer is “FALSE’.
u meant that 26% is divided in transportating and accommodation acc. to passage.
There is a number in the question (26%). If the answer is TRUE, 26% has to be in the text. If it is FALSE, the number will be different; or, the number will be 26% (but it will be related to other matters). If the number is still 26%, yet it doesn’t match with other key-words, the answer will be NOT GIVEN.
The answer can be found in lines 4, 5 & 6 of paragraph no. 6. Here, the writer says, “This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%.”
In there,it was written like transport AND accommodation account for remaining 26%. Not ooonly accommodation account for 26% of visitor satisfaction. It is with transport
Thank you so much, it is very helpful
Plzz Sir mainu tusi mcq diya teps diyo reading diya v te listening diya v plzz mainu bht jada problem aa rhi aa ohna nu solve krn ch te ik headings diya v
Hello Kamaljeet, I don’t understand Punjabi much and I didn’t get clearly from what you wrote. But as far as I can understand you, I think you have problems in MCQs. Plz follow my other lessons and surely you’ll get help in this question type. For Headings, I have some good works available in this website.
Hlo sir mainu mcq ch bht problem aa rhi aa te heading ch v plzz mainu ehna dona diya tips dedo menumeration listening ch v mcq di hi problem aundi a jada plzz help me
Super helpful! Thank you so much!
If i add some explanations,
The reason NG isn’t the correct answer: As far as the ‘transport’ was mentioned along with accommodation as one of the factors contributing to the 26% of visitors satisfaction on the paraghagh, we cannot ignore transport’s contribution to the 26%. So, it means there is definitely certain percent related to ‘transport’. And, this means accommodation cannot account for the whole 26%, which is contradicting the sentence of No.10 question. Thereby the evidence to decide whether the No.10 sentence is right or wrong is clearly given on the paragragh, and the answer is F.
I figured it out this way. Hope this helpful to you.
Dear Kimmy, the way you explained can be considered correct. The way I explained it can also be taken as correct.
Hello sir My reading scores had stucked on 5.5 bands and I have exam on 29th June pls share me some tips to crack my ielts.
Dear Rikta, Try to follow these suggestions. 1. give importance in synonyms. 2. learn the tricks of paraphrasing. 3. do not take more than 1 minute in each question. 4. Try to guess some answers. 5. Be careful about proper nouns and use of capital letters. 6. try to practice some mock tests before your exam. 7. Remember you can’t solve all types of questions. so give importance on the types you are comfortable with.
Is it okay to write all your answers in capital letters?
YES, for Reading and Listening. Not for Writing.
Thank you so much! It’s really helpful ??
Its really a most helpful website
I need tips in paragraph type questions nad match the heading
Please share some techniques regarding solving list of heading or match the statement with paragraph…please!
Sir I don’t understand Question 13 What does the question mean ?
Dear Yoon, Thanks for the question. Question 13: Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit. This question means that many visitors fear that they may not return to New Zealand after their visit.
I’m very confused between not given and false. Please give me some tips.
http://ieltsdeal.com/ielts-reading-how-to-find-answers-for-true-false-not-given-or-yes-no-not-given-questions-best-strategies-methodstricks-and-tips/
Thank you Najib for useful support. It is rare that anyone who gives explanation of IELTS reading with tips. Everybody gives simple tips only, what makes difference between you and them. Request explanation on rest of the Cambridge books. Its really really helpful and useful. Your website is unique.
Welcome! And I request you to pray for me. And the rest is coming. Work is going on.
i didn’t understood the answer of quest 10.. can u plz hlp me.. i have doubt that why it is false because it clearly said that 26 % accounts for transport and accommodation
26% = accommdation + transportation, not accommodation alone. Our key word here is’ accommodation’ and it is very much necessary to understand the clear and exact meaning of each question for true/false questions in general.
- Pingback: IELTS Reading: Cambridge 13 Test 1 Reading Passage 2, Why being bored is stimulating and useful, too; with best solutions, explanations and bonus tips | IELTS Deal
Hlo sir muja heading ma bhut didn’t aa Rahe ba
Can you write that in English, please?
hi guys , i have a question is that if i use the word blockbusters instead of films , is it correct ?
blockbusters = films which have broken all sorts of records
It’s really very helpful.
I’m delighted to hear that. Thank you. Here’s my YouTube channel for your consideration: https://www.youtube.com/c/IELTSDeal
where are you from sir?
I’m from Bangladesh.
What is the main different between yesnong and truefalseng?
Thanks alot, this is really explanatory and I find it helpful
Welcome! You can follow my YouTube Channel as well: https://www.youtube.com/c/IELTSDeal/
In fact your website has been of a tremendous help to me. I understood true, false and not given from your website.. But I still need help in the other part too, writing listening n speaking My date is very close that is 2nd Dec n 5th
Thank you so much, it’s really helpful for me!!!
GREAT!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
very helpful
- Pingback: IELTS Reading: Cambridge 13 Reading Test 1; Passage 3; Artificial artists; with top solutions and explanations - IELTS Deal
Thanks for your clear explanation. It really helps to deal with reading tasks. I really appreciate you.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Academic IELTS Reading: Test 2 Passage 1; The Dead Sea Scrolls; with top solutions and best explanations
This Academic IELTS Reading post focuses on solutions to an IELTS Reading Test 2 passage 1 that has a passage titled ‘The Dead Sea Scrolls’. This is a targeted post for Academic IELTS candidates who have major problems locating and understanding Reading Answers in the AC module. This post can guide you the best to understand […]

Academic IELTS Reading: Test 1 Reading passage 3; To catch a king; with best solutions and explanations
This Academic IELTS Reading post focuses on solutions to an IELTS Reading Test 1 Reading Passage 3 titled ‘To catch a king’. This is a targeted post for IELTS candidates who have great problems finding out and understanding Reading Answers in the AC module. This post can guide you the best to understand every Reading answer […]
- Full IELTS Practice Tests
- Practice Tests
IMPLEMENTING THE CYCLE OF SUCCESS: A CASE STUDY
- View Solution
Solution for: IMPLEMENTING THE CYCLE OF SUCCESS: A CASE STUDY
Answer table.
| C | (performance) measures |
| A | productivity |
| C | (') Take Charge (') |
| B | feedback |
| B | employee(s') // staff |
| benchmarking | 30 days |
| service delivery |
Found a mistake? Let us know!
Share this Practice Test
Exam Review

Within Australia, Australian Hotels Inc (AHI) operates nine hotels and employs over 2000 permanent full-time staff, 300 permanent part-time employees and 100 casual staff. One of its latest ventures, the Sydney Airport hotel (SAH), opened in March 1995. The hotel is the closest to Sydney Airport and is designed to provide the best available accommodation, food and beverage and meeting facilities in Sydney's southern suburbs. Similar to many international hotel chains, however, AHI has experienced difficulties in Australia in providing long-term profits for hotel owners, as a result of the country's high labour-cost structure . In order to develop an economically viable hotel organisation model, AHI decided to implement some new policies and practices at SAH.
The first of the initiatives was an organisational structure with only three levels of management - compared to the traditional seven. Partly as a result of this change, there are 25 per cent fewer management positions , enabling a significant saving. This change also has other implications. Communication, both up and down the organisation, has greatly improved. Decision-making has been forced down in many cases to front-line employees. As a result, guest requests are usually met without reference to a supervisor, improving both customer and employee satisfaction.
The hotel also recognised that it would need a different approach to selecting employees who would fit in with its new policies. In its advertisements, the hotel stated a preference for people with some 'service' experience in order to minimise traditional work practices being introduced into the hotel. Over 7000 applicants filled in application forms for the 120 jobs initially offered at SAH. The balance of the positions at the hotel (30 management and 40 shift leader positions) were predominantly filled by transfers from other AHI properties.
A series of tests and interviews were conducted with potential employees, which eventually left 280 applicants competing for the 120 advertised positions. After the final interview, potential recruits were divided into three categories. Category A was for applicants exhibiting strong leadership qualities, Category C was for applicants perceived to be followers, and Category B was for applicants with both leader and follower qualities. Department heads and shift leaders then composed prospective teams using a combination of people from all three categories . Once suitable teams were formed, offers of employment were made to team members.
Another major initiative by SAH was to adopt a totally multi-skilled workforce. Although there may be some limitations with highly technical jobs such as cooking or maintenance, wherever possible, employees at SAH are able to work in a wide variety of positions. A multi-skilled workforce provides far greater management flexibility during peak and quiet times to transfer employees to needed positions. For example, when office staff are away on holidays during quiet periods of the year, employees in either food or beverage or housekeeping departments can temporarily.
The most crucial way, however, of improving the labour cost structure at SAH was to find better, more productive ways of providing customer service. SAH management concluded this would first require a process of ' benchmarking '. The prime objective of the benchmarking process was to compare a range of service delivery processes across a range of criteria using teams made up of employees from different departments within the hotel which interacted with each other. This process resulted in performance measures that greatly enhanced SAH's ability to improve productivity and quality.
The front office team discovered through this project that a high proportion of AHI Club member reservations were incomplete. As a result, the service provided to these guests was below the standard promised to them as part of their membership agreement. Reducing the number of incomplete reservations greatly improved guest perceptions of service.
In addition, a program modelled on an earlier project called ' Take Charge ' was implemented. Essentially, Take Charge provides an effective feedback loop horn both customers and employees. Customer comments, both positive and negative, are recorded by staff. These are collated regularly to identify opportunities for improvement. Just as importantly, employees are requested to note down their own suggestions for improvement. (AHI has set an expectation that employees will submit at least three suggestions for every one they receive from a customer.)
Employee feedback is reviewed daily and suggestions are implemented within 48 hours, if possible, or a valid reason is given for non-implementation. If suggestions require analysis or data collection, the Take Charge team has 30 days in which to address the issue and come up with recommendations.
Although quantitative evidence of AHI's initiatives at SAH are limited at present, anecdotal evidence clearly suggests that these practices are working. Indeed AHI is progressively rolling out these initiatives in other hotels in Australia, whilst numerous overseas visitors have come to see how the program works.
This article has been adapted and condensed fem the article by R Carter (19%), 'Implementing the cycle of success: A case study of the Sheraten Pacific Division', Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources, 34(3): 111-23. Names and other details have been changed and report findings may have been given a different emphasis from the original. W eare grateful to Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources for allowing us to use, file material in this way.
Questions 1-5
Choose the appropriate letters A-D and write them in boxes 1-5 on your answer sheet.
1 The high costs of running AHI's hotels are related to their ...
A management.
D policies. Answer: C Locate
2 SAH's new organisational structure requires ...
A 75% of the old management positions.
B 25% of the old management positions.
C 25% more management positions.
D 5% fewer management positions. Answer: A Locate
3 The SAH's approach to organisational structure required changing practices in ..
A industrial relations.
B firing staff.
C hiring staff.
D marketing. Answer: C Locate
4 The total number of jobs advertised at the SAH was ...
D 280. Answer: B Locate
5 Categories A, B and C were used to select...
A front office staff.
B new teams.
C department heads.
D new managers. Answer: B Locate
Questions 6-13
Complete the following summary of the last four paragraphs of Reading Passage 1 using ONE OR TWO words from the Reading Passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 6-13 on your answer sheet.
WHAT THEY DID AT SAH
Teams of employees were selected from different hotel departments to participate in a 6 exercise.
The information collected was used to compare 7 processes which, in turn, led to the development of 8 that would be used to increase the hotel's capacity to improve 9 as well as quality.
Also, an older program known as ' 10 ' was introduced at SAH. In this program, 11 is sought from customers and staff. Wherever possible 12 suggestions are implemented within 48 hours. Other suggestions are investigated for their feasibility for a period of up to 13
6. Answer: benchmarking Locate 7. Answer: service delivery Locate 8. Answer: (performance) measures Locate 9. Answer: productivity Locate 10. Answer: (') Take Charge (') Locate 11. Answer: feedback Locate 12. Answer: employee(s') // staff Locate 13. Answer: 30 days Locate
Other Tests
- 3 - YES-NO-NOT GIVEN
- 6 - Sentence Completion
- 4 - Summary, form completion
Striking Back at Lightning With Lasers
- Nature & Environment
- 0 unanswered
- 12 - Matching Headings
- 2 - Sentence Completion
Wheel of Fortune
- 5 - Matching Headings
- 8 - Matching Information
Striking the right note
- 10 - Matching Headings
- 3 - Summary, form completion
Neanderthals and modern humans
- 7 - Matching Information
- 4 - TRUE-FALSE-NOT GIVEN
The polar bear
Found a mistake let us know.
Please descibe the mistake as details as possible along with your expected correction, leave your email so we can contact with you when needed.
Describe what is wrong with the practice test:
Please enter description
Enter your name:
Enter your email address:
Please enter a valid email


english-practice.net
Practice English Exercises to Improve Your Skills
english-exercises.net
Practice More English Exercises to Improve Your Skills
englishpracticetest.net
Practice More English Tests to Improve Your Skills
Cambridge Practice Test
Practice Cam Listening Test with Answer & Transcript
Listening Practice Test
Practice Listening Test with Answer & Transcript
Practice Cambridge Reading Test with Answer
Practice Reading Test
Practice Reading Test with Answer
Practice Reading Mock Test with Answer
Speaking Practice Test
Speaking Practice Test with with Band 8-9 Samples
42 Common Topics for ielts Speaking Part 1
100 TOPICS for ielts Speaking Part 2 with Band 8 Sample
70 TOPICS for ielts Speaking Part 2 with Band 8+ Sample Recordings
Vocabulary Words
Most Common Vocabulary Topics for ielts Speaking
Writing Practice Test
Writing Practice Test with Band 8-9 Samples
Writing Mock Test with Band 8-9 Samples
Writing Task 2 Topics with Band 7-8-9 Samples
General Reading Tests
Practice General Reading Test with Answer
Practice Cam 13 Reading Test 01
Cambridge ielts reading
READING PASSAGE 1
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 1-13 which are based on Reading Passage 1 below.
Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website
New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country’s gross domestic product, and is the country’s largest export sector. Unlike other export sectors, which make products and then sell them overseas, tourism brings its customers to New Zealand. The product is the country itself – the people, the places and the experiences. In 1999, Tourism New Zealand launched a campaign to communicate a new brand position to the world. The campaign focused on New Zealand’s scenic beauty, exhilarating outdoor activities and authentic Maori culture, and it made New Zealand one of the strongest national brands in the world.
A key feature of the campaign was the website www.newzealand.com, which provided potential visitors to New Zealand with a single gateway to everything the destination had to offer. The heart of the website was a database of tourism services operators, both those based in New Zealand and those based abroad which offered tourism service to the country. Any tourism-related business could be listed by filling in a simple form. This meant that even the smallest bed and breakfast address or specialist activity provider could gain a web presence with access to an audience of long-haul visitors. In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis, the information provided remained accurate. And to maintain and improve standards, Tourism New Zealand organised a scheme whereby organisations appearing on the website underwent an independent evaluation against a set of agreed national standards of quality. As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.
To communicate the New Zealand experience, the site also carried features relating to famous people and places. One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga. Another feature that attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey through a number of the locations chosen for blockbuster films which had made use of New Zealand’s stunning scenery as a backdrop. As the site developed, additional features were added to help independent travelers devise their own customised itineraries. To make it easier to plan motoring holidays, the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season and indicating distances and times.
Later, a Travel Planner feature was added, which allowed visitors to click and ‘bookmark’ places or attractions they were interested in, and then view the results on a map. The Travel Planner offered suggested routes and public transport options between the chosen locations. There were also links to accommodation in the area. By registering with the website, users could save their Travel Plan and return to it later, or print it out to take on the visit. The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.
The Tourism New Zealand website won two Webby awards for online achievement and innovation. More importantly perhaps, the growth of tourism to New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organisations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests. On the website, visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical location, but also by the particular nature of the activity. This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%. The more activities that visitors undertake, the more satisfied they will be. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn about traditional Maori life. Many long-haul travelers enjoy such learning experiences, which provide them with stories to take home to their friends and family. In addition, it appears that visitors to New Zealand don’t want to be ‘one of the crowd’ and find activities that involve only a few people more special and meaningful.
It could be argued that New Zealand is not a typical destination. New Zealand is a small country with a visitor economy composed mainly of small businesses. It is generally perceived as a safe English-speaking country with a reliable transport infrastructure. Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit. However, the underlying lessons apply anywhere – the effectiveness of a strong brand, a strategy based on unique experiences and a comprehensive and user-friendly website.
Questions 1-7
Complete the table below. Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer.
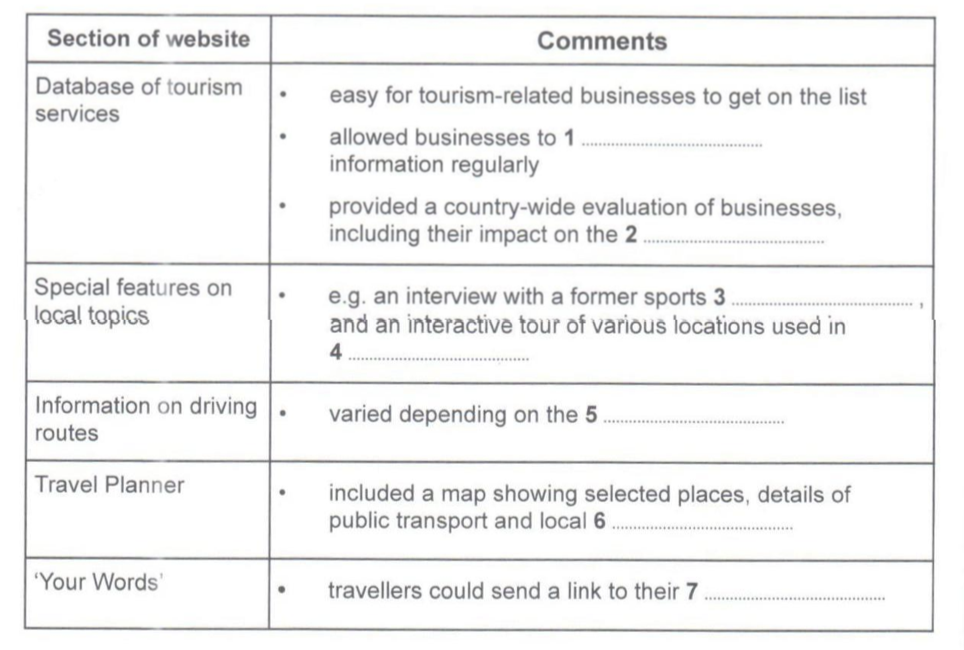
Write your answers in boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet.
| Database of tourism services | • easy for tourism-related businesses to get on the list • allowed businesses to …………………………… information regularly • provided a country-wide evaluation of businesses, including their impact on the ……………………….. |
| Special features on local topics | • e.g. an interview with a former sports ……………………………., and an interactive tour of various locations used in ………………………. |
| Information on driving routes | • varied depending on the …………………………… |
| Travel Planner | • included a map showing selected places, details of public transport and local …………………………. |
| ‘Your Words’ | • travelers could send a link to their ………………………… |
Questions 8-13
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 1?
In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
8 The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists.
9 It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location.
10 According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation.
11 Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture.
12 Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones.
13 Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit.
READING PASSAGE 2
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 14-26 which are based on Reading Passage 2 below.
Why being bored is stimulating – and useful, too
This most common of emotions is turning out to be more interesting than we thought
We all know how it feels – it’s impossible to keep your mind on anything, time stretches out, and all the things you could do seem equally unlikely to make you feel better. But defining boredom so that it can be studied in the lab has proved difficult. For a start, it can include a lot of other mental states, such as frustration, apathy, depression and indifference. There isn’t even agreement over whether boredom is always a low-energy, flat kind of emotion or whether feeling agitated and restless counts as boredom, too. In his book, Boredom: A Lively History , Peter Toohey at the University of Calgary, Canada, compares it to disgust – an emotion that motivates us to stay away from certain situations. ‘If disgust protects humans from infection, boredom may protect them from “infectious” social situations,’ he suggests.
By asking people about their experiences of boredom, Thomas Goetz and his team at the University of Konstanz in Germany have recently identified five distinct types: indifferent, calibrating, searching, reactant and apathetic. These can be plotted on two axes – one running left to right, which measures low to high arousal, and the other from top to bottom, which measures how positive or negative the feeling is. Intriguingly, Goetz has found that while people experience all kinds of boredom, they tend to specialise in one. Of the five types, the most damaging is ‘reactant’ boredom with its explosive combination of high arousal and negative emotion. The most useful is what Goetz calls ‘indifferent’ boredom: someone isn’t engaged in anything satisfying but still feels relaxed and calm. However, it remains to be seen whether there are any character traits that predict the kind of boredom each of us might be prone to.
Psychologist Sandi Mann at the University of Central Lancashire, UK, goes further. ‘All emotions are there for a reason, including boredom,’ she says. Mann has found that being bored makes us more creative. ‘We’re all afraid of being bored but in actual fact it can lead to all kinds of amazing things,’ she says. In experiments published last year, Mann found that people who had been made to feel bored by copying numbers out of the phone book for 15 minutes came up with more creative ideas about how to use a polystyrene cup than a control group. Mann concluded that a passive, boring activity is best for creativity because it allows the mind to wander. In fact, she goes so far as to suggest that we should seek out more boredom in our lives.
Psychologist John Eastwood at York University in Toronto, Canada, isn’t convinced. ‘If you are in a state of mind-wandering you are not bored,’ he says. ‘In my view, by definition boredom is an undesirable state.’ That doesn’t necessarily mean that it isn’t adaptive, he adds. ‘Pain is adaptive – if we didn’t have physical pain, bad things would happen to us. Does that mean that we should actively cause pain? No. But even if boredom has evolved to help us survive, it can still be toxic if allowed to fester.’ For Eastwood, the central feature of boredom is a failure to put our ‘attention system’ into gear. This causes an inability to focus on anything, which makes time seem to go painfully slowly. What’s more, your efforts to improve the situation can end up making you feel worse. ‘People try to connect with the world and if they are not successful there’s that frustration and irritability,’ he says. Perhaps most worryingly, says Eastwood, repeatedly failing to engage attention can lead to state where we don’t know what to do any more, and no longer care.
Eastwood’s team is now trying to explore why the attention system fails. It’s early days but they think that at least some of it comes down to personality. Boredom proneness has been linked with a variety of traits. People who are motivated by pleasure seem to suffer particularly badly. Other personality traits, such as curiosity, are associated with a high boredom threshold. More evidence that boredom has detrimental effects comes from studies of people who are more or less prone to boredom. It seems those who bore easily face poorer prospects in education, their career and even life in general. But of course, boredom itself cannot kill – it’s the things we do to deal with it that may put us in danger. What can we do to alleviate it before it comes to that? Goetz’s group has one suggestion. Working with teenagers, they found that those who ‘approach’ a boring situation – in other words, see that it’s boring and get stuck in anyway – report less boredom than those who try to avoid it by using snacks, TV or social media for distraction.
Psychologist Francoise Wemelsfelder speculates that our over-connected lifestyles might even be a new source of boredom. ‘In modern human society there is a lot of overstimulation but still a lot of problems finding meaning,’ she says. So instead of seeking yet more mental stimulation, perhaps we should leave our phones alone, and use boredom to motivate us to engage with the world in a more meaningful way.
Questions 14-19
Reading Passage 2 has six paragraphs, A-F Choose the correct heading for each paragraph from the list of headings below.
Write the correct number, i-viii , in boxes 14-19 on your answer sheet.
List of Headings
i The productive outcomes that may result from boredom
ii What teachers can do to prevent boredom
iii A new explanation and a new cure for boredom
iv Problems with a scientific approach to boredom
v A potential danger arising from boredom
vi Creating a system of classification for feelings of boredom
vii Age groups most affected by boredom
viii Identifying those most affected by boredom
14 Paragraph A
15 Paragraph B
16 Paragraph C
17 Paragraph D
18 Paragraph E
19 Paragraph F
Questions 20-23
Look at the following people (Questions 20-23 ) and the list of ideas below.
Match each person with the correct idea, A-E .
Write the correct letter, A-E , in boxes 20-23 on your answer sheet.
20 Peter Toohey
21 Thomas Goetz
22 John Eastwood
23 Francoise Wemelsfelder
List of Ideas
A The way we live today may encourage boredom.
B One sort of boredom is worse than all the others.
C Levels of boredom may fall in the future.
D Trying to cope with boredom can increase its negative effects.
E Boredom may encourage us to avoid an unpleasant experience.
Questions 24-26
Complete the summary below. Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 24-26 on your answer sheet.
Responses to boredom
For John Eastwood, the central feature of boredom is that people cannot 24 ……………………………, due to a failure in what he calls the ‘attention system’, and as a result they become frustrated and irritable. His team suggests that those for whom 25 ……………………….. is an important aim in life may have problems in coping with boredom, whereas those who have the characteristic of 26 ……………………….. can generally cope with it.
READING PASSAGE 3
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 27-40 which are based on Reading Passage 3 below.
Artificial artist?
Can computers really create works of art.
The Painting Fool is one of a growing number of computer programs which, so their makers claim, possess creative talents. Classical music by an artificial composer has had audiences enraptured, and even tricked them into believing a human was behind the score. Artworks painted by a robot have sold for thousands of dollars and been hung in prestigious galleries. And software has been built which creates are that could not have been imagined by the programmer.
Human beings are the only species to perform sophisticated creative acts regularly. If we can break this process down into computer code, where does that leave human creativity? ‘This is a question at the very core of humanity,’ says Geraint Wiggins, a computational creativity researcher at Goldsmiths, University of London. ‘It scares a lot of people. They are worried that it is taking something special away from what it means to be human.’
To some extent, we are all familiar with computerised art. The question is: where does the work of the artist stop and the creativity of the computer begin? Consider one of the oldest machine artists, Aaron, a robot that has had paintings exhibited in London’s Tate Modern and the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art. Aaron can pick up a paintbrush and paint on canvas on its own. Impressive perhaps, but it is still little more than a tool to realise the programmer’s own creative ideas.
Simon Colton, the designer of the Painting Fool, is keen to make sure his creation doesn’t attract the same criticism. Unlike earlier ‘artists’ such as Aaron, the Painting Fool only needs minimal direction and can come up with its own concepts by going online for material. The software runs its own web searches and trawls through social media sites. It is now beginning to display a kind of imagination too, creating pictures from scratch. One of its original works is a series of fuzzy landscapes, depicting trees and sky. While some might say they have a mechanical look, Colton argues that such reactions arise from people’s double standards towards software-produced and human-produced art. After all, he says, consider that the Painting Fool painted the landscapes without referring to a photo. ‘If a child painted a new scene from its head, you’d say it has a certain level of imagination,’ he points out. ‘The same should be true of a machine.’ Software bugs can also lead to unexpected results. Some of the Painting Fool’s paintings of a chair came out in black and white, thanks to a technical glitch. This gives the work an eerie, ghostlike quality. Human artists like the renowned Ellsworth Kelly are lauded for limiting their colour palette – so why should computers be any different?
Researchers like Colton don’t believe it is right to measure machine creativity directly to that of humans who ‘have had millennia to develop our skills’. Others, though, are fascinated by the prospect that a computer might create something as original and subtle as our best artists. So far, only one has come close. Composer David Cope invented a program called Experiments in Musical Intelligence, or EMI. Not only did EMI create compositions in Cope’s style, but also that of the most revered classical composers, including Bach, Chopin and Mozart. Audiences were moved to tears, and EMI even fooled classical music experts into thinking they were hearing genuine Bach. Not everyone was impressed however. Some, such as Wiggins, have blasted Cope’s work as pseudoscience, and condemned him for his deliberately vague explanation of how the software worked. Meanwhile, Douglas Hofstadter of Indiana University said EMI created replicas which still rely completely on the original artist’s creative impulses. When audiences found out the truth they were often outraged with Cope, and one music lover even tried to punch him. Amid such controversy, Cope destroyed EMI’s vital databases.
But why did so many people love the music, yet recoil when the discovered how it was composed? A study by computer scientist David Moffat of Glasgow Caledonian University provides a clue. He asked both expert musicians and non-experts to assess six compositions. The participants weren’t told beforehand whether the tunes were composed by humans or computers, but were asked to guess, and then rate how much they liked each one. People who thought the composer was a computer tended to dislike the piece more than those who believed it was human. This was true even among the experts, who might have been expected to be more objective in their analyses.
Where does this prejudice come from? Paul Bloom of Yale University has a suggestion: he reckons part of the pleasure we get from art stems from the creative process behind the work. This can give it an ‘irresistible essence’, says Bloom. Meanwhile, experiments by Justin Kruger of New York University have shown that people’s enjoyment of an artwork increases if they think more time and effort was needed to create it. Similarly, Colton thinks that when people experience art, they wonder what the artist might have been thinking or what the artist is trying to tell them. It seems obvious, therefore, that with computers producing art, this speculation is cut short – there’s nothing to explore. But as technology becomes increasingly complex, finding those greater depths in computer art could become possible. This is precisely why Colton asks the Painting Fool to tap into online social networks for its inspiration: hopefully this way it will choose themes that will already be meaningful to us.
Questions 27-31
Choose the correct letter, A , B , C or D .
Write the correct letter in boxes 27-31 on your answer sheet.
27 What is the writer suggesting about computer-produced works in the first paragraph?
A People’s acceptance of them can vary considerably.
B A great deal of progress has already been attained in this field.
C They have had more success in some artistic genres than in others.
D the advances are not as significant as the public believes them to be.
28 According to Geraint Wiggins, why are many people worried by computer art?
A It is aesthetically inferior to human art.
B It may ultimately supersede human art.
C It undermines a fundamental human quality.
D It will lead to a deterioration in human ability.
29 What is a key difference between Aaron and the Painting Fool?
A its programmer’s background
B public response to its work
C the source of its subject matter
D the technical standard of its output
30 What point does Simon Colton make in the fourth paragraph?
A Software-produced art is often dismissed as childish and simplistic.
B The same concepts of creativity should not be applied to all forms of art.
C It is unreasonable to expect a machine to be as imaginative as a human being.
D People tend to judge computer art and human art according to different criteria.
31 The writer refers to the paintings of a chair as an example of computer art which
A achieves a particularly striking effect.
B exhibits a certain level of genuine artistic skill.
C closely resembles that of a well-known artist.
D highlights the technical limitations of the software.
Questions 32-37
Complete each sentence with the correct ending, A-G below.
Write the correct letter, A-G , in boxes 32-37 on your answer sheet.
32 Simon Colton says it is important to consider the long-term view then
33 David Cope’s EMI software surprised people by
34 Geraint Wiggins criticized Cope for not
35 Douglas Hofstadter claimed that EMI was
36 Audiences who had listened to EMI’s music became angry after
37 The participants in David Moffat’s study had to assess music without
A generating work that was virtually indistinguishable from that of humans.
B knowing whether it was the work of humans or software.
C producing work entirely dependent on the imagination of its creator.
D comparing the artistic achievements of humans and computers.
E revealing the technical details of his program.
F persuading the public to appreciate computer art.
G discovering that it was the product of a computer program
Questions 38-40
Do the following statements agree with the claims of the writer in Reading Passage 3?
In boxes 38-40 on your answer sheet, write
YES if the statement agrees with the claims of the writer
NO if the statement contradicts the claims of the writer
NOT GIVEN if it is impossible to say what the writer thinks about this
38 Moffat’s research may help explain people’s reactions to EMI.
39 The non-experts in Moffat’s study all responded in a predictable way.
40 Justin Kruger’s findings cast doubt on Paul Bloom’s theory about people’s prejudice towards computer art.
Cam 12 Reading Test 04
Cam 13 reading test 02, answer cam 13 reading test 01.
2. environment
6. accommodation
9. NOT GIVEN
12. NOT GIVEN
25. pleasure
26. curiosity
39. NOT GIVEN
View Answers with Explanations
Submit a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Case Study: Tourism New Zealand Website Answers
IELTS Academic Test – Passage 01: Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website reading with answers explanation, location and pdf. This reading paragraph has been taken from our huge collection of Academic & General Training (GT) Reading practice test PDF’s.

Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website
New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country’s gross domestic product, and is the country’s largest export sector. Unlike other export sectors, which make products and then sell them overseas, tourism brings its customers to New Zealand. The product is the country itself – the people, the places and the experiences. In 1999, Tourism New Zealand launched a campaign to communicate a new brand position to the world. The campaign focused on New Zealand’s scenic beauty, exhilarating outdoor activities and authentic Maori culture, and it made New Zealand one of the strongest national brands in the world.
A key feature of the campaign was the website www.newzealand.com, which provided potential visitors to New Zealand with a single gateway to everything the destination had to offer. The heart of the website was a database of tourism services operators, both those based in New Zealand and those based abroad which offered tourism services to the country. Any tourism-related business could be listed by filling in a simple form. This meant that even the smallest bed and breakfast address or specialist activity provider could gain a web presence with access to an audience of long-haul visitors. In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis, the information provided remained accurate. And to maintain and improve standards, Tourism New Zealand organised a scheme whereby organisations appearing on the website underwent an independent evaluation against a set of agreed national standards of quality. As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.
To communicate the New Zealand experience, the site also carried features relating to famous people and places. One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga. Another feature that attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey through a number of the locations chosen for blockbuster films which had made use of New Zealand’s stunning scenery as a backdrop. As the site developed, additional features were added to help independent travellers devise their own customised itineraries. To make it easier to plan motoring holidays, the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season and indicating distances and times.
Later a Travel Planner feature was added, which allowed visitors to click and ‘bookmark’ : paces or attractions they were interested in, and then view the results on a map. The Travel Planner offered suggested routes and public transport options between the chosen locations. There were also links to accommodation in the area. By registering with the website, users could save their Travel Plan and return to it later, or print it out take on the visit. The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.
The Tourism New Zealand website won two Webby awards for online achievement and innovation. More importantly perhaps, the growth of tourism to New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organisations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests. On the website, visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical location, but also by the particular nature of the activity. This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%. The more activities that visitors undertake, the more satisfied they will be. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn about traditional Maori life. Many long-haul travellers enjoy such earning experiences, which provide them with stories to take home to their friends and family. In addition, it appears that visitors to New Zealand don’t want to be ‘one of the crowd’ and find activities that involve only a few people more special and meaningful.
It could be argued that New Zealand is not a typical destination. New Zealand is a small country with a visitor economy composed mainly of small businesses. It is generally perceived as a safe English-speaking country with a reliable transport infrastructure. Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit. However, the underlying lessons apply anywhere-the effectiveness of a strong brand, a strategy based on unique experiences and a comprehensive and user-friendly website.
Questions 1-7
Complete the table below. Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer. Write your answers in boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet.
Questions 8-13
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 1? In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information FALSE if the statement contradicts the information NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
8. The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists.
9. It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location.
10. According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation.
11. Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture.
12. Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones.
13. Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit.
________________
1) IELTS 13 READING PASSAGE – WHY BEING BORED IS STIMULATING ↗
2) IELTS 13 READING PASSAGE – ARTIFICIAL ARTISTS ↗
3) IELTS 13 READING PASSAGE – BRINGING CINNAMON TO EUROPE ↗
4) IELTS 13 READING PASSAGE – OXYTOCIN ↗
5) IELTS 13 READING PASSAGE – MAKING THE MOST OF TRENDS ↗
Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website Answers
Check out Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website reading answers below with explanations and locations given in the text.
- ENVIRONMENT
- ACCOMMODATION
If you want the pdf summary of Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website reading passage and answers, please write your email in the comment section below. We’ll send it across at the speed of light.

ALL THE BEST !
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
IELTS TEST TYPES
✓ IELTS Academic
✓ IELTS General Training
USEFUL LINKS
✓ IELTS Full Form
✓ IELTS Band Score
✓ IELTS Vocabulary
✓ IELTS Grammar
CONNECT WITH US
Pinterest ↗
IELTS® is a registered trademark of The British Council, IDP- IELTS Australia and the University of Cambridge ESOL Examinations (Cambridge ESOL). This site and its owners are not affiliated, approved or endorsed by the University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, IELTS Progress Check, and IDP Education Australia. "IELTS Progress Check" is the name of the official IELTS online practice test and is in no way affiliated with this website. To find out more about the official IELTS online practice test please visit https://www.ieltsprogresscheck.com/.
ABOUT US | PRIVACY POLICY | DISCLAIMER | TERMS | CONTACT US
© 2023 IELTSPROGRESS.COM | All Rights Reserved
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
| Research question | Case study |
|---|---|
| What are the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction? | Case study of wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone National Park |
| How do populist politicians use narratives about history to gain support? | Case studies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and US president Donald Trump |
| How can teachers implement active learning strategies in mixed-level classrooms? | Case study of a local school that promotes active learning |
| What are the main advantages and disadvantages of wind farms for rural communities? | Case studies of three rural wind farm development projects in different parts of the country |
| How are viral marketing strategies changing the relationship between companies and consumers? | Case study of the iPhone X marketing campaign |
| How do experiences of work in the gig economy differ by gender, race and age? | Case studies of Deliveroo and Uber drivers in London |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved June 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
‘Case study: Tourism New Zealand website’- Reading Answer Explanation- CAM- 13

Here are explanations of the Questions of passage named ‘Case study: Tourism New Zealand website’, which is from the Cambridge 13 book. The Questions that have been asked are True/False/Not Given and Blanks. You will find the locations of the Reading Answers, Keywords( highlighted and underlined) and justifications.
READING PASSAGE 1: Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website
| Question | Answer |
| 1 | UPDATE |
| 2 | ENVIRONMENT |
| 3 | CAPTAIN |
| 4 | FILMS |
| 5 | SEASON |
| 6 | ACCOMMODATION |
| 7 | BLOG |
| 8 | FALSE |
| 9 | NOT GIVEN |
| 10 | FALSE |
| 11 | TRUE |
| 12 | NOT GIVEN |
Questions 1-7
Complete the table below. Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet.
| Database of tourism services | • easy for to get on the list • allowed businesses to …………………………… information regularly paragraph Explanation: The answer to this question is in the last third line of the paragraph. ‘In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis…’Here, ‘information’ and ‘details’ are synonyms. Moreover, ‘able to’ means ‘allowed’. Thus, the answer is very clear.
• provided a country-wide evaluation of businesses, including their the ……………………….. paragraph Explanation: The main keyword ‘impact’ has been written as ‘effect’ in the last line of the paragraph. ‘As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered…’Thus, the answer is ‘environment’ Answer: Environment |
| Special features on local topics | with a ……………………………., paragraph Explanation: The main keyword ‘former’ is there in the second line of the paragraph. ‘One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga…’Here, ‘rugby’ is sports. Hence, the answer is clear.
and an interactive of various used in ………………………. paragraph Explanation: The answer to this question is in the third line of the paragraph. ‘attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey… number of the locations chosen for blockbuster films…’Here, ‘tour’ and ‘journey’ are synonyms. Moreover, ‘number of..’ ,means ‘various. Hence, the answer is ‘films’ Answer: Films |
| Information on driving routes | • depending on the …………………………… paragraph Explanation: The location of the answer is in the last line of the paragraph. ‘the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season…’Here, ‘varied’ and ‘different’ are synonyms. This line makes an answer very clear. Hence, the answer is SEASON.
|
| Travel Planner | • included a map showing selected places, details of and local …………………………. paragraph Explanation: The main keyword ‘public transport’ helps to locate the answer in the third line of the paragraph. ‘There were also links to accommodation in the area…’Here, ‘in the area’ is paraphrased as ‘local’. So, the answer is ‘accommodation’
|
| ‘Your Words’ | • travelers could send a to their ………………………… paragraph Explanation: The answer to this question is in the last line of the paragraph. ‘The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand…’Here, ‘could send a link’ means ‘submit …’Thus, the answer is ‘blog’
|
Questions 8-13
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 1?
In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
8 The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists.
Location: 6 th paragraph
Explanation: The main keyword ‘ready-made itineraries’ helps to locate the answer in the first line of the paragraph. ‘The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organisations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests…’The question statement contradicts the passage statement. ‘Create itineraries’ is opposite to the ‘ready-made itineraries’. Thus, the answer is very clear.
Answer: False
9 It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location.
Explanation: The answer to this question is in the second line of the passage. ‘Visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical location, but also by the particular nature of the activity…’Here, the writer does not give information about the starting of search. Hence, no information available.
Answer: Not Given
10 According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation.
Explanation: The main keyword ‘visitor satisfaction’ is in the fourth line of the paragraph. ‘Visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%…’Here, transportation and accommodation account for 26%.But in question statement 26% accounts for accommodation only. Thus, the answer is False.
11 Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture. Location: 6 th paragraph
Explanation: The location of the answer is in the middle line of the paragraph. ‘It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive…’Here, ‘like to become involved in’ is visible as ‘enjoy cultural activities…’Thus, the answer is clear.
Answer: True
12 Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones.
Location: Last paragraph
Explanation: Though the writer talks about the visitors in New Zealand. But there is no information regarding hotels in the New Zealand. Thus, no information available.
13 Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit.
Explanation: The location of the answer is in the second last line of the paragraph. ‘Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit…’Here, ‘often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit…’ makes it clear that there is less possibility that they will return. Thus, the answer is True.
‘About Marine debris or ocean trash’- Reading Answers Explanation- CAM -14
Canada Study Visa Fraud 2023!! Girl to be Deported due to fake offer letter… Click here
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
You cannot copy content of this page
Welcome Guest!
- IELTS Listening
- IELTS Reading
- IELTS Writing
- IELTS Writing Task 1
- IELTS Writing Task 2
- IELTS Speaking
- IELTS Speaking Part 1
- IELTS Speaking Part 2
- IELTS Speaking Part 3
- IELTS Practice Tests
- IELTS Listening Practice Tests
- IELTS Reading Practice Tests
- IELTS Writing Practice Tests
- IELTS Speaking Practice Tests
- All Courses
- IELTS Online Classes
- OET Online Classes
- PTE Online Classes
- CELPIP Online Classes
- Free Live Classes
- Australia PR
- Germany Job Seeker Visa
- Austria Job Seeker Visa
- Sweden Job Seeker Visa
- Study Abroad
- Student Testimonials
- Our Trainers
- IELTS Webinar
- Immigration Webinar
Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website – IELTS Reading Answers
10 min read
Updated On Feb 13, 2024
Share on Whatsapp
Share on Email
Share on Linkedin

Recent IELTS Reading Test with Answers - Free PDF
The IELTS Reading Module offers a fantastic chance to achieve excellent scores. It assesses a candidate’s reading comprehension skills in English. You must comprehend the various question types in order to perform at your best in this area. Ideally, you should not spend more than 20 minutes on a passage.
The Academic passage, Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website reading answers, appeared in an IELTS Test. Try to find the answers to get an idea of the difficulty level of the passages in the actual reading test. If you want more passages to solve, try taking one of our IELTS reading practice tests.
Let’s see how easy this passage is for you and if you can solve it in 20 minutes.
The question types found in this passage are:
- Table Completion (Q. 1-7)
- True/False/Not Given (Q 8-13)
Do you want to revise the steps to solve the Matching Features questions for IELTS Academic Reading?
Check out IELTS Reading Matching Features Questions !
Reading Passage
Case Study: Tourism New Zealand Website
A New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country’s gross domestic product and is the country’s largest export sector. Unlike other export sectors, which make products and then sell them overseas, tourism brings its customers to New Zealand. The product is the country itself – the people, the places, and the experiences. In 1999, Tourism New Zealand launched a campaign to communicate a new brand position to the world. The campaign focused on New Zealand’s scenic beauty, exhilarating outdoor activities and authentic Maori culture, and it made New Zealand one of the strongest national brands in the world.
B A key feature of the campaign was the website www.newzealand.com, which provided potential visitors to New Zealand with a single gateway to everything the destination had to offer. The heart of the website was a database of tourism services operators, both those based in New Zealand and those based abroad which offered tourism service to the country. Any tourism-related business could be listed by filling in a simple form. This meant that even the smallest bed and breakfast address or specialist activity provider could gain a web presence with access to an audience of long-haul visitors. In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis, the information provided remained accurate. And to maintain and improve standards, Tourism New Zealand organised a scheme whereby organisations appearing on the website underwent an independent evaluation against a set of agreed national standards of quality. As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.
C To communicate the New Zealand experience, the site also carried features relating to famous people and places. One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga. Another feature that attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey through a number of the locations chosen for blockbuster films which had made use of New Zealand’s stunning scenery as a backdrop. As the site developed, additional features were added to help independent travelers devise their own customised itineraries. To make it easier to plan motoring holidays, the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season and indicating distances and times.
D Later, a Travel Planner feature was added, which allowed visitors to click and ‘bookmark’ places or attractions they were interested in, and then view the results on a map. The Travel Planner offered suggested routes and public transport options between the chosen locations. There were also links to accommodation in the area. By registering with the website, users could save their Travel Plan and return to it later, or print it out to take on the visit. The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.
E The Tourism New Zealand website won two Webby awards for online achievement and innovation. More importantly perhaps, the growth of tourism to New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
F The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organizations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests. On the website, visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical location, but also by the particular nature of the activity. This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%. The more activities that visitors undertake, the more satisfied they will be. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn about traditional Maori life. Many long-haul travelers enjoy such learning experiences, which provide them with stories to take home to their friends and family. In addition, it appears that visitors to New Zealand don’t want to be ‘one of the crowd’ and find activities that involve only a few people more special and meaningful.
G It could be argued that New Zealand is not a typical destination. New Zealand is a small country with a visitor economy composed mainly of small businesses. It is generally perceived as a safe English-speaking country with reliable transport infrastructure. Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit. However, the underlying lessons apply anywhere – the effectiveness of a strong brand, a strategy based on unique experiences and a comprehensive and user-friendly website.
Questions 1-7
| Database of tourism services | • easy for tourism-related businesses to get on the list • allowed businesses to 1………………………… information regularly • provided a country-wide evaluation of businesses, including their impact on the 2……………………….. |
| Special features on local topics | • e.g. an interview with a former sports 3……………………………., and an interactive tour of various locations used in 4………………………. |
| Information on driving routes | • varied depending on the 5…………………………… |
| Travel Planner | • included a map showing selected places, details of public transport, and local 6…………………………. |
| ‘Your Words’ | • travelers could send a link to their 7………………………… |
Questions 8-13
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage?
In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, write –
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information, FALSE if the statement contradicts the information, NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this.
8 The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists.
9 It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location.
10 According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation.
11 Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture.
12 Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones.
13 Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit.
‘ Case Study Tourism New Zealand website ’ IELTS Reading Answers With Location and Explanation
1 Answer: update
Question type: Table Completion
Answer location: Paragraph B
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the 8th and 9th lines that, “In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis….”.
2 Answer: environment
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the last line that, “As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.”
3 Answer: Captain
Answer location: Paragraph C
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the 1-3 lines that, “….One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga.”
4 Answer: films
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the 4th and 5th lines that, “…… was an interactive journey through a number of locations chosen for blockbuster films …….”.
5 Answer: season
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the 8th and 9th lines that, “…. the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season…..”.
6 Answer: accommodation
Answer location: Paragraph D
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the 4th line that, “….. There were also links to accommodation in the area.”
7 Answer: blog
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the 6th and 7th lines that, “ ….. The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.”
8 Answer: FALSE
Question type: TRUE/FALSE/NOT GIVEN
Answer location: Paragraph F
Answer explanation: The response lies in Paragraph 6. The initial two lines indicate that the website’s purpose was to empower individuals and travel organizations to create their own travel plans. The website did not offer pre-packaged itineraries and travel packages.
This assertion directly opposes the information in the passage.
Hence, the answer is FALSE.
9 Answer: NOT GIVEN
Answer explanation: The answer cannot be located within the text. The question pertains to initiating a search on the website.
In Paragraph 6, line 3, the author mentions, “…visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical locations, but also by the particular nature of the activity.” However, there is no information provided regarding how to start a search.
As a result, the answer is NOT GIVEN.
10 Answer: FALSE
Answer explanation: The answer can be found in lines 4, 5, and 6 of paragraph 6.
In these lines, it is evident that the question is contradicted. Transportation and lodging makeup 26%, while visitor satisfaction makes up 74%. If only lodging constituted 26%, we could affirm that it is TRUE.
Therefore, the correct answer is FALSE.
11 Answer: TRUE
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in lines 7-9 that, “…. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn more about traditional life.”
12 Answer: NOT GIVEN
Answer location: Paragraphs F & G
Answer explanation: Staying in hotels is not discussed, and there is also no comparison made between small and large hotels.
Therefore, the answer is NOT GIVEN.
13 Answer: TRUE
Answer location: Paragraph G
Answer explanation: It is mentioned in the 4th and 5th lines that, “Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit.”
Tips for Answering the Question Types in the ‘Case Study Tourism New Zealand website’ IELTS Reading Answers
Let us check out some quick tips to answer the types of questions in the ‘Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website’ Reading Answers passage.
Table Completion:
The way to solve the table completion questions of the IELTS Reading is similar to Summary Completion. You will be asked to fill in the blanks in a small passage given in the form of a note with the relevant words or numbers. So, let us revise the strategies.
- Read the instructions carefully. It will help you determine the word limit (no more than two, one word, etc.) and important terms like ‘using words from the text’ or ‘from the text’. You have to follow these strictly.
- Go through the incomplete table first. Also, think about keywords and how they could be represented by synonyms or paraphrasing.
- Locate where the information is by scanning quickly . If you can’t, move on.
- Study the reading text by using the skimming and scanning techniques . It will help to establish the answer quickly. When scanning for your answer, make sure you are thinking about paraphrasing and synonyms.
- The answers appear in the same order as the questions . Also, check your spelling and remember that your answer should be grammatically correct.
True/False/Not Given
In IELTS Reading , ‘True, False, Not Given’ questions are based on facts. Several factual statements will be provided to you, and it is up to you to determine whether or not they are accurate by reading the text.
To answer this type of question, you can use the following strategies:
- Read the question and identify the keywords – Before reading the material, have a look at your list of True, False, and Not Given questions.
- Scan the passage for synonyms or paraphrased words of the keywords – When you have highlighted the keywords, swiftly read the text to look for paraphrases or synonyms.
- Match the highlighted words in the questions with their synonyms in the text – Once you find both sets of keywords, cross-check them to find the answer.
Identify the answer – If the facts match, the answer is TRUE, and in case it doesn’t match, it is FALSE. If you are unable to find the answer or unsure of it, mark it NOT GIVEN.
Great work on attempting to solve the ‘Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website’ IELTS reading passage! To crack your IELTS Reading in the first go, try solving more of the Recent IELTS Reading Passages.
Also, check :
- In Praise Of Amateurs IELTS Reading Answers
- The True Cost Of Food Reading Answers
- Climate Change And The Inuit Reading Answers
- Zoo Conservation Programmes Reading Answers
- A Workaholic Economy Reading Answers
Practice IELTS Reading based on question types

Start Preparing for IELTS: Get Your 10-Day Study Plan Today!
Smruti is a passionate and highly skilled content writer working in this field for the past 2 years. She is known for her ability to craft compelling and engaging content. With a keen eye for detail and a deep love for words, Smruti has expertized herself with the latest industry trends. Her commitment to producing high-quality content that resonates with audiences is highly valued.
Explore other Reading Actual Tests

Kasturika Samanta

Akanksha Tripathi
Nehasri Ravishenbagam
Post your Comments
Recent articles.

IELTSMaterial Master Program
1:1 Live Training with Band 9 Teachers
4.9 ( 3452 Reviews )
Our Offices
Gurgaon city scape, gurgaon bptp.
Step 1 of 3
Great going .
Get a free session from trainer
Have you taken test before?
Please select any option
Email test -->
Please enter Email ID
Mobile Band 9 trainer -->
Please enter phone number
Application
Please select any one
Already Registered?
Select a date
Please select a date
Select a time (IST Time Zone)
Please select a time
Mark Your Calendar: Free Session with Expert on
Which exam are you preparing?
Great Going!
Online Case Study Answer Generator for Students
Here Is Your Case Study Analysis
If you want to quickly and effectively carry out case study analyses, you’ve come to the right place. Just for you, we’ve created a free AI-powered tool that can analyze case studies on any subject!
Our app will be the perfect solution for those who don’t want to spend a ton of time structuring their texts and looking for examples. Use it to save time and nerves!
- ️🎉 Benefits of Our Generator
- ️🤖 How to Use
- ️✨ Case Study Definition
- ️🔎 Structure of a Case Study
- ️✍️ Writing Steps
- ️🔝 Top 12 Topics & Examples
- ️🔗 References
🎉 Benefits of Our Case Study Analysis Generator
Our generator is one of the best, and there are many reasons for us to say so:
| 💸 100% free | Not only will you get a perfect case study analysis, but you also won’t have to pay a penny for it. |
|---|---|
| 🚀 Cutting-edge | Our tool has the most advanced AI at its core. It can efficiently analyze case studies of any subject. |
| 🤩 User-friendly | Our app is intuitive and easy to operate. |
| ⏳ Time-saving | Use it and save more time for conducting your research and polishing the results. |
| 🌐 No download | You give our tool any case study task, and it will do the rest just like that. |
🤖 How to Use Our Case Study Answer Generator
Getting a case study analysis has never been easier—see for yourself!
- Paste your case study into the field.
- Add questions or issues you need to address in your analysis.
- Press “Analyze now.”
- Get the results!
Keep in mind that the results provided by the tool are to be used for reference purposes only.
✨ Case Study Analysis Definition
A case study analysis is used to examine a problem and find a solution to it. This type of analysis is typically used in business as well as in other spheres, such as education, healthcare, and social sciences. The main feature of such a study is that it’s rooted in a real-life context.

Researchers use direct observations, interviews, tests, and samples to gather data for their case studies. This information is then used to develop solutions and recommendations backed with evidence.
🔎 Structure of a Case Study Analysis
Usually, a case study analysis consists of 6 parts. Each one is dedicated to a particular aspect and serves its own purpose. Let’s take a closer look at them and see how they differ.
Introduction
An introduction describes the context of the examined topic and provides substantial background on the case study’s subject. When you write it, keep in mind the following questions:
- What is your case study about?
- What is the primary goal of your research?
- Why is it important?
Problem Statement
The next part introduces the main problem or issue the study will be focusing on. Typically, it’s concerned with a challenge faced by an individual or organization in question. The problem statement provides a clear focus for the whole research.
Now, it’s time for the most interesting part—the analysis itself. When it comes to business problems, students can use various approaches, such as:
| Assess the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. | |
| Descriptive statistics | Summarize the main characteristics of the collected data using various measures. |
| Identification of causes | Look for the underlying reasons behind the issue. |
| Stakeholder analysis | Research the perspectives of different stakeholders involved in the case. |

This part presents several ways to resolve the issue in question. The solutions must be realistic and achievable. It’s also worth to mention their pros and cons and thus identify the most potent ones.
Recommendations
This part focuses on the best possible solutions to the problem identified in the previous section. It explains how to implement it in practice and how it will help eliminate the issue. It may also suggest ways to deal with other, minor problems involved in the case.
Conclusions
Now, it’s time for the final part of the analysis: your conclusions . Here is what you need to do:
- Summarize the results of your case study analysis and explain how they relate to the research’s main problem.
- Be sure to emphasize how vital your study is and how it helps to make the issue more manageable.
- Make further suggestions based on your findings.
✍️ How to Write a Case Study
Now you know what to include in your case study. But how do you write one that is truly outstanding? Just follow our step-by-step guide:
1. Pick a Case to Explore
Choosing the right topic is essential. You need to do it early on to ensure that the research subject is sufficiently explored.
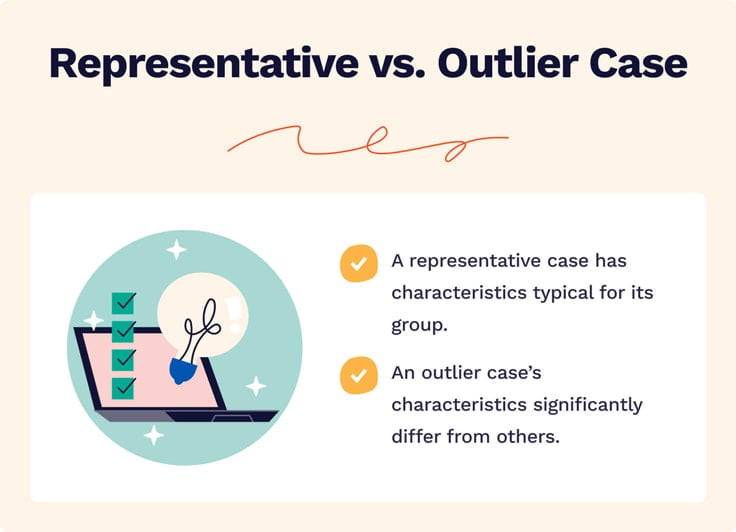
For example, suppose you want to examine how COVID-19 has affected the hospitality sector. In that case, you can choose either a representative case, such as a large hotel chain, or an outlier case, such as a small Bed and Breakfast that has managed to survive the pandemic. The latter case may sound more interesting, but if there's not enough information available on it, it's best to choose the former.
2. Formulate a Problem Statement
Now, you should clearly and concisely formulate the central problem you will be focusing on. To do it, answer the 5 Ws:
- What is the problem you’re researching?
- Who is affected by it?
- Where does it occur?
- When did the problem arise?
- Why is this issue significant?
If you need help with this part of your analysis, you can always use our research problem generator .
3. Gather Evidence & Collect Data
Data gathering can be done through both primary and secondary sources of information . You can use a range of research techniques, such as observations, surveys, and interviews. It is crucial to make sure the data you’ve collected is pertinent to the case study.
4. Describe Your Findings & Analyze Them
Next, you analyze trends and themes in your data. This analysis must be supported by facts and evidence. Use various analysis methods to make your study more in-depth.
5. Provide Solutions & Recommendations
Develop several possible solutions using the information you’ve gathered. Once you’ve done it, answer the following questions:
- What are the pros and cons of these solutions?
- Which one can be the most beneficial?
- How can the entity you’re analyzing implement it in practice?
The more detailed your recommendations are, the better. If possible, try to include aspects such as timeline, resource allocation, and KPIs for monitoring.
🔝 Top 12 Case Study Topics & Examples
Want inspiration for your analysis? Or maybe you need help picking a case to explore? Check out this list of topics with examples!
- Operations and Information Management: A Case Study of CC Music
- Netflix and Blockbuster: Case Study
- Strategic Planning Case Study: Process Management
- HRM Incident: Case Study Analysis
- Case Study Summary: Hiring a Sustainable Development Specialist
- Organizational Change: Qatargas Case Study
- Childhood Development Case Study
- Case Study of Engstrom Auto Mirror Plant and Workplace
- Strategic Marketing: Amazon Go Case Study
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: Case Study
- Social Determinants of Health: Case Study
- Recovering Supply Chain Operations: A Case Study of Nissan
Now you know how to complete a case study! Remember that the tiring process of analyzing can be effectively streamlined if you use our free case study answer generator. Try it out—you won’t regret it!
We also recommend using our transition words maker and personal statement generator to enhance your writing.
❓ Case Study Analysis Generator: FAQ
❓ what questions to answer in a case study.
A case study must either prove or disprove an existing theory. It also aims to find a solution to the research's central question. This question can vary depending on your topic and subject. You present the answer in your research findings and conclusions.
❓ How Do You Write a Case Study Analysis?
First, you introduce your case and provide its background. Then, you gather information and analyze it to develop several solutions. Finally, you propose the best solution and give recommendations on how to implement it. Also, remember to explain how your case study will deepen the existing knowledge.
❓ What Are the 4 Most Important Parts of Case Study?
Every case study begins with the introduction of a topic and its background. Then, you present an analysis of sources that can provide knowledge on the case. The third part is the analysis of collected data. Your case study ends with conclusions based on your findings.
❓ What Are Some Examples of Case Studies?
Case studies are frequently used in psychology to shed light on peculiar circumstances. Famous case study examples include Sigmund Freud's Little Hans as well as John Martin Marlow's study of Phineas Gage, the man who had a railroad spike driven through his brain.
🔗 References
- Case Study: Definition, Examples, Types, and How to Write: Verywell Mind
- What Is a Case Study?: Evidence Based Nursing
- What the Case Study Method Really Teaches: Harvard Business Review
- Using Case Studies to Teach: Boston University
- What Is a Case Study? Definition, Elements and 15 Examples: Indeed
- Writing a Case Study: University of Southern California
- Writing a Case Study – Student Academic Success: Monash University

Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: Jun 3, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

Press ESC to close

Tourism New Zealand Website Case Study Reading Answers : Way to Boost Your IELTS Preparation
For now, we have talked a lot about the speaking & listening sections of the IELTS examination. Today, let’s move forward to know more about the IELTS reading section.
The IELTS reading section is an extremely important yet tough exams but it is not possible for one to not crack it in time. All you need is the right reading practice and by that we mean, a lot of it to make sure that you do not cease anywhere while you’re giving the exam during the final attempt. Along with this, you need to tackle a lot of reading passage’s questions and increase your difficulty level every day to make sure that you are easily able to solve all these questions, no matter what type or any sort of questions you’re presented with.
So, today let’s move forward to know more about it.
Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website Reading Answers
The IELTS reading passage topic: Tourism New Zealand Website” is a very common yet interesting topic in the IELTS examination. In the sections below, this topic is divided into different parts to help you practice in a better yet easy manner for this passage.
Tourism New Zealand Website IELTS Reading Answers: Part 1
New Zealand is a small country with a minimum of just four million inhabitants that are spread across the country in a peaceful manner.
Currently, the total GDP of the country has the highest percentage of tourism in it. Tourism contributes to making up to 9% of this country’s GDP and is the largest export sector of the country. Unlike all the other export sectors, tourism is one such sector in this country which helps to bring a lot of its customers to this country. And while we talk about the other products of this country – they are just people, places, and the experiences that are taken out of it.
In the year 1999, Tourism New Zealand launched a great campaign which was there to help communicate a new brand position to the world. This campaign focused on New Zealand’s scenic beauty, its exhilarating outdoor activities and the authentic Maori culture that is being followed here which helps in making it the most powerful yet the strongest brands in the world.
ALSO, READ What is a Good IELTS Score? Is 7.5 a Good IELTS Score? Here’s All You Need to Know

Tourism New Zealand Website IELTS Reading Answers: Part 2
A key feature of this campaign was the website that was launched during this period for this country, www.newzealand.com. This website helped in providing great potential visitors to the country with a single gateway to each and everything that the destination had to offer to its people.
But the heart of the business is the database of tourism services operators, both of which are based in New Zealand as well as abroad which helps in providing great tourism services to the country. So, any tourism-related form can be filled easily without taking anybody’s help at all. Further, to maintain the standards and improve them, Tourism New Zealand organised a scheme with the help of which organisations that appear on the website underwent an independent evaluation against a set of the national standards of quality that they all agreed on. And due to this, the effect it had on each of the businesses was considered too.
Tourism New Zealand Website IELTS Reading Answers: Part 3
Further, to communicate the New Zealand experience, this site also carried forward various features related to the famous people and places which was one of the most popular interviews that this country had with the former New Zealand All Blacks Rugby Captain “Tana Umaga.”
Another such feature that helped in increasing a lot of attention towards his country is through the help of those blockbuster films that were made here which helps in providing people with an interactive journey through a number of some amazing yet extremely beautiful locations.
A Travel Planner feature was also added to this list which helped the visitors to click and bookmark the places of attraction for them so that when they visit this country, they’ll have a long list of places to roam around. This planner also helps in suggesting routes and public transport options to the readers in order to easily choose between the locations that they have chosen for them.
Also Read: The Life Cycle of a Star: An IELTS Reading Answers Topic with Questions Solved
Tourism New Zealand Website IELTS Reading Answers: Part 4
New Zealand is not just any typical destination where people could come and roam around; it’s an emotion, a feeling for all those four million people residing here. New Zealand is just a small & pretty country with little less population in it and it creates a visitor economy for the tourists which is generally composed of small businesses. It is generally perceived as a safe English-speaking country with reliable transport infrastructure. And because of the long-haul flights, most visitors have to stay for a long period of time in this country, let’s say, for about a period of 20 days so that they can see as much of the country as is possible for them on a one-time long visit to this country.
Tourism New Zealand Website IELTS Reading Questions
Complete the table below.
Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet.
#1. Easy for Tourism-related business to get on the list
#2. Allowed businesses to _____________ information regularly
#3. Provided a countrywide evaluation of businesses, including their impact on the _________________
#4. Special features on local topics
Example – an interview with a former sports _________________, and an interactive tour of various locations used in ____________________________
#5. Information on driving routes that varied depending on the ___________________________
#6. Travel Planner • included a map showing selected places, details of public transport and local ________________
#7. ‘Your Words’ • travelers could send a link to their ________________________
#2. Environment
#3. Captain
#6. Accommodation
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 1?
In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, mention
TRUE – if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE – if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN – if there is no information on this
#8. The website “ www.newzealand.com ” created by the tourism department of New Zealand has been aiming to provide some great deals, itineraries, and good-deal packages for the travel companies as well as for all those travel enthusiasts.
#9. Many of the visitors out of these were found to be searching for the information that they want on the official website by the geographical location of the area.
#10. According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation.
#11. Many-a-times, it has been noticed that many of the visitors to this country become more involved in the local culture of the country and enjoy it a lot.
#12. Many visitors like staying in small hotels as they like the vibe of such hotels a lot rather than those big, grand, and new ones recently built in the country.
#13. Visitors feel it unlikely to return to the country after their first visit here.
#9. Not Given
#12. Not Given
IELTS Preparation Tips: Reading Section
#1.the two “s”.
By the two S here, we mean Skimming and Scanning, that is to skim and scan the lines of the passage. This requires an individual to go through the reading passage in order to get a general understanding of the content and what could be the answers to the questions that follow behind it.
#2.Good Reading Speed
While practising for the IELTS reading section, an individual is asked to read as many passages as he/she can in order to increase their reading speed. This can further help an individual a lot in the future.
#3.Don’t Understand the Full Passage
While sitting in the exam hall, the aim of an individual should not be to understand the entire passage completely because this will put the ability to answer the questions in a timely manner to the test. And after all, your only aim should be to just find the correct answers to the questions.
After reading the above paragraph, we hope that you might have understood it well and have got an idea of how you can further solve the questions related to it or find out the different answers for the various questions being provided. If you have any doubts in your mind regarding the same, just feel free to comment down below and let us know all about it so that we can help you with that in the future because we’ll be more than happy to help you out through this.
Also, if you want more help in any of these reading passages, don’t forget to just check out our other blogs that will help you with the same.
Also Read: The Nature and Aims of Archaeology: Find Reading Answers for IELTS Reading Test

One Comment
helped alott
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Share Article:
About the Author
Sakshi bachani.
Sakshi Bachani is a freelance Content Writer and Teacher. She has completed her Bachelor's degree from Delhi University.. She has been a freelance teacher for the past five years and has worked towards helping young kids achieve their dreams. She had also worked as an Intern teacher with an NGO. Apart from writing and teaching, she really enjoys music, animals, and plants. She even has her own little garden which she loves very dearly and can be sometimes seen buying more plants for herself.
You might also like

Mite Harvestmen Reading Answers: Let’s Prepare with IELTS Mock Test and IELTS Practice Test!

Collecting Ant Specimens Reading Answers: Let’s Prepare to Ace the IELTS Exam

Organic Farming and Chemical Fertilizers Reading Answers: Let’s Score Well in the IELTS Exam!
Other stories, is ielts speaking test face to face here’s how you can ace it & achieve 8+ band score, why being bored is stimulating and useful too ielts reading answers.
How To Answer A Case Study
We totally understand the dire need of students to find credible help with their case studies. Whether they are the students of a college or a university, time and again, you will be asked to make your case studies effectively. This brings to the question as to who will answer a case study impressively? Students can find several online companies that guarantee some great tips for answering your case studies nicely, but not all of them are to rely on.
We bet we have the best step to step guide with us that can easily get you to the end of your case study solutions . The following tips will promise to help you efficiently with your case, irrespective of how difficult they are. Precisely, when it comes to the question of how to answer a case study, it’s all about words. So, do not hesitate in using the correct and researched words to leave a lasting impact.
How To Answer A Consulting Case Study On Three Major Types
Case studies are not an easy task to fulfill in your academic life. If students dare to take it lightly, chances are you will not be able to impress your teachers. However, case studies do not come as easy as they sound. There are three significant types of case studies that are popular among students.
1. Legal Case Study
2. Nursing Case Study
3. Management Case Study
These are the common subjects that will lead to stress in your college or university life. With so much other stuff to do, students don’t feel happy about the pressure of finding a fruitful answer to the case study. There is no doubt it’s quite a challenging situation for any student who has to make a flawless case study. That’s why we usually advise our students to get online help for their case study writing. Because of it, they can have fewer chances of flunking in these exams.
The Helpful 15 Tips On How To Answer A Case Study
When students have no option but to write a persuasive case study, it is preferable to set out on a journey to get external help for it. You can get easy help online. You will be pleased to know that our writing help has some best case study assignment writers who can distress you in a matter of a few hours. But, the most vital thing to know is that a student should know the basic formulas to find good answers to your case studies on their own.
We have collected some fabulous notable tips for our students can help them for years with their case studies:
1. Use Conventional Tone: The foremost thing while writing case studies is to use a professional tone to have a lasting impact on your papers.
2. Use Your Words Only: It is equally important for a student to use simple and their wording while writing case studies.
3. Don’t Be Too Precise: Sometimes, providing proper sentences gives an understandable image to your case studies. Hence, soon use shorter or confusing sentences.
4. Use Examples: The students should support their case studies with relevant examples. The examples can be given through a video, statements which should prove your opinions as well.
5. Accurate Grammar: Your writing is the crucial thing, Don’t engage in poorly written content. Use proper English without any grammatical errors or spelling mistakes.
6. No Acronyms: Students should avoid using acronyms while writing their case studies.
7. Use Life Experiences: Your practical life experiences are important to make a compelling case study. Try to use live examples to give a more impactful expression to your case studies.
8. Justified Statements Are Necessary: The best way to answer a case study is to agree or disagree with the justified statements.
9. Make Complete Sentences: It is also an important point to make a flawless case study paper. While writing, try to make complete sentences.
10. No Spelling Flaws: Bad grammar or wrong spellings are not tolerable. Hence, students should do keen writing with no spelling mistakes.
11. Proper Answers: Try to give proper answers to the questions.
12. Adequate Justifications: Justifications are crucial. Make adequate justifications to avoid any confusion.
13. Sufficient Reasoning: The reasoning should be enough while writing a case study.
14. No indefinite Answers: Indefinite answers cause a hell of a lot of confusion and complexity in a case study. That’s why the students should avoid making indefinite answers.
15. Provide Proper Conversations: It is also vital to contribute as much as possible in conversations.
How To Properly Answer A Case Study
Precisely, a good case study is a scenario that students will analyze out of a professional concept. However, it is blended with useful questions that demand definite answers. There can be a sample case study assignment online that can always help a student while writing one but, it is equally important to know the proper way of answering a case study.
- Reading a case study is the foremost important thing. Later analyze the question carefully too.
- It is mandatory to identify the issue of the case study thoroughly
- A bridge is vital to link the theory to practice
- Planning of the answers comes next.
- Start making your case study answers
- Proofread and edit it carefully to avoid mistakes
- Submit the case studies to your tutors.
How To Answer A Case Study Interview
This aspect is a bit tricky. In a case study interview, you will be given a case and will be asked to analyze the situation with possible solutions.
Here are some common and most useful tips about answering the interview questions:
- Listening carefully to the questions is the key
- Asl the proper questions
- Highlight your approach
- do brainstorming
- Don't lose focus
- Be attentive to feedback
- Prove your quantitative skills
- Summarize in detail
To write a productive case study is hard, but if you choose online help for it, this task becomes really easy. Be a smarter version of yourself and find great ways of handling the answers to your case study problems. We have a proficient team that can make this hectic task to answer your case study a piece of cake. Don’t be late to avail of our quality help.
Importance OF Case Study
How To Write A Case Study For Assignment
How To Write Case Study In MBA
How To Solve A Case Study

Key Study Skills
- Assignment Calculator
- Managing nervousness
- Allocating time and using the marking system
- Using the reading time effectively
- Answering multi-choice and short answer questions
- Answering essay and case study questions in exams
- Managing exam stress
- Academic Skills for Success
Answering essay questions in exams
Writing an essay in an exam is similar in many ways to writing an essay for an assignment: It needs to be clearly structured, and your ideas need to be linked and supported by evidence.
Essay questions in exams
- Read the question through carefully to make sure you are answering what has been asked. Missing one part of a question can cost you a lot of marks.
- Make a quick plan of the points you want to include in your answer.
- Use essay structure: introduction, points, conclusion. But if you run out of time, it can be a good idea to write notes.
- Get right to the point from the beginning. Use the words from the question to write your first sentence. For example:
Question: What do you think is the most important intercultural communication issue in New Zealand? First sentence: At present in New Zealand the most important intercultural communication issue is...
- Remember to include one idea per paragraph, and to begin each paragraph with a clear topic sentence.
- Make sure your writing is legible.
- Grammar, punctuation and spelling are not as important as in an assignment but should still be of a good standard.
Answering case study questions
Exam questions that ask you to anlayse case studies (also called scenarios) are usually designed to test your ability to relate theories and concepts to real-world situations.
Preparing for case studies before the exam:
- Start by identifying the theories and concepts covered in your course. Organise and review the information you have on these theories/concepts so you understand them.
- Practice reading case studies and identifying relevant information. It's probably useful to practice doing this with a time limit as you will have one in your exam.
- Practice relating concepts and theories to real-world situations: ask lecturers and check textbooks for practice examples. It is also worth checking past exams for your course to see if there are examples of case study questions.
During the exam
- Take time to plan: Have a clear idea of how much time you have to answer the question. Then plan to spend some time reading the exam question, the case study and planning your answer. Take time to make sure you have understood the case study and know what the exam question is asking you to do:
- Read the exam question(s)
- Then skim read the case study to get the general idea. Highlight or underline key points
- Reread the question to make sure you understand it and to focus your attention when you reread the case study.
- Reread the case study carefully. Make a note of any ideas that you think of.
- Answer the question linking relevant theories and concepts to specific information from the case study. Usually you will need to write your answers in clearly formed paragraphs which have a clear topic that is well-supported with evidence and examples.
- Instead of simply describing or restating information from the case itself, use specific details or examples to support the points you are trying to make. This is where you link theory to the facts from the case study.
- << Previous: Answering multi-choice and short answer questions
- Next: Managing exam stress >>
Unitec Private Bag 92025 Victoria Street West Auckland 1142 Unitec website
- Last Updated: Feb 14, 2023 11:36 AM
- URL: https://guides.unitec.ac.nz/studyskills
Exams Know-how
Case Study Tour...
Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website - IELTS Reading Answers
The IELTS Reading Module offers a fantastic chance to achieve excellent scores. It assesses a candidate’s reading comprehension skills in English. You must comprehend the various question types in order to perform at your best in this area. Ideally, you should not spend more than 20 minutes on a passage. The Academic passage, Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website reading answers, appeared in an IELTS Test. Try to find the answers to get an idea of the difficulty level of the passages in the actual reading test. If you want more passages to solve, try taking one of our IELTS reading practice tests.
The IELTS Reading test is essential for anybody planning to study, work, or relocate to English-speaking nations. Mastery of this part necessitates strong linguistic abilities and efficient reading comprehension techniques. In this situation, understanding reading passages and correctly recognizing responses is critical. This article will examine "Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website" and how it relates to IELTS reading. By analyzing the passage and critiquing example responses, we want to give valuable insights and tactics to assist test takers in effectively traversing this area. This article provides thorough information for improving reading comprehension and eventually succeeding on the IELTS Reading exam, from understanding the material to breaking down sample responses.
Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website Reading Passage
Paragraph 1
New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country’s gross domestic product and is the country’s largest export sector. Unlike other export sectors, which make products and then sell them overseas, tourism brings its customers to New Zealand. The product is the country itself – the people, the places and the experiences. In 1999, Tourism New Zealand launched a campaign to communicate a new brand position to the world. The campaign focused on New Zealand’s scenic beauty, exhilarating outdoor activities and authentic Maori culture, and it made New Zealand one of the strongest national brands in the world.
Paragraph 2
A key feature of the campaign was the website www.newzealand.com, which provided potential visitors to New Zealand with a single gateway to everything the destination had to offer. The heart of the website was a database of tourism services operators, both those based in New Zealand and those based abroad which offered tourism services to the country. Any tourism-related business could be listed by filling in a simple form. This meant that even the smallest bed and breakfast address or specialist activity provider could gain a web presence with access to an audience of long-haul visitors. In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis, the information provided remained accurate. And to maintain and improve standards, Tourism New Zealand organized a scheme whereby organizations appearing on the website underwent an independent evaluation against a set of agreed national standards of quality. As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.
Paragraph 3
To communicate the New Zealand experience, the site also carried features relating to famous people and places. One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga. Another feature that attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey through a number of the locations chosen for blockbuster films which had made use of New Zealand’s stunning scenery as a backdrop. As the site developed, additional features were added to help independent travelers devise their own customized itineraries. To make it easier to plan motoring holidays, the site cataloged the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season and indicating distances and times.
Paragraph 4
Later, a Travel Planner feature was added, which allowed visitors to click and ‘bookmark’ places or attractions they were interested in, and then view the results on a map. The Travel Planner offered suggested routes and public transport options between the chosen locations. There were also links to accommodation in the area. By registering with the website, users could save their Travel Plan and return to it later, or print it out to take on the visit. The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog about their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.
Paragraph 5
The Tourism New Zealand website won two Webby awards for online achievement and innovation. More importantly, perhaps, the growth of tourism in New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
Paragraph 6
The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organizations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests. On the website, visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical location, but also by the particular nature of the activity. This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%. The more activities that visitors undertake, the more satisfied they will be. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn about traditional Maori life. Many long-haul travelers enjoy such learning experiences, which provide them with stories to take home to their friends and family. In addition, it appears that visitors to New Zealand don’t want to be ‘one of the crowd’ and find activities that involve only a few people more special and meaningful.
Paragraph 7
It could be argued that New Zealand is not a typical destination. New Zealand is a small country with a visitor economy composed mainly of small businesses. It is generally perceived as a safe English-speaking country with a reliable transport infrastructure. Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit. However, the underlying lessons apply anywhere – the effectiveness of a strong brand, a strategy based on unique experiences and a comprehensive and user-friendly website.
IELTS Exam Fees in India
Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website Reading Questions
Questions 1-7
- Complete the table below.
- Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer.
- Write your answers in boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet.
| Database of tourism services | • easy for tourism-related businesses to get on the list • allowed businesses to 1…………………………… information regularly • provided a country-wide evaluation of businesses, including their impact on the 2……………………….. |
| Special features on local topics | • e.g. an interview with a former sports 3……………………………., and an interactive tour of various locations used in 4……………………….v |
| Information on driving routes | • varied depending on the 5…………………………… |
| Travel Planner | • included a map showing selected places, details of public transport and local 6…………………………. |
| ‘Your Words’ | • travelers could send a link to their 7………………………… |
Questions 8-13
- Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 1?
- In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, write
- TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
- FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
- NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
8 The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists. 9 It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location. 10 According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation. 11 Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture. 12 Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones. 13 Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit.
Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website Reading Answers
In this section, the case study tourism New Zealand website reading answers with explanations, are given to evaluate your errors.
(Note: The text in italics mentions the location and referring lines written in the reading passage)
1. Answer:Update Explanation: participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis, the information provided remained accurate. The given answer is located in 8-10 lines of the 2nd paragraph.
2. Answer: Environment Explanation: As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered. The given answer is located in the last 2 lines of the 2nd paragraph.
3. Answer:Captain Explanation: One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga.The given answer is located in the 2-3 lines of the 3rd paragraph.
4. Answer: Flims Explanation:Attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey through a number of the locations chosen for blockbuster films. The given answer is located in the 4-5 line of the 3rd paragraph.
5. Answer: Seasons Explanation: The site cataloged the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season and indicating distances and times. The given answer is located in the last 3 lines of the 3rd paragraph.
6. Answer: Accommodation Explanation: There were also links to accommodation in the area. The given answer is located in the 4-5 lines of the 4th paragraph.
7. Answer: Blog Explanation: The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website. The given answer is located in the last 3 lines of the 4th paragraph.
8. Answer: False Explanation: The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organizations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests. The given answer is located in the first 3 lines of the 6th paragraph.
9. Answer: Not given
10. Answer: False Explanation: Visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%. The given answer is located in the 5-7 lines of the 6th paragraph.
11. Answer: True Explanation: It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive. The given answer is located in the 7-9 lines of the 6th paragraph.
12. Answer: Not given
13. Answer: True Explanation: Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit. The given answer is located in the 4-6 lines of the 7th paragraph.
Difference Between IELTS vs GMAT
Tips for the IELTS Reading Test
Below are some tips to help you improve your band score in the IELTS reading test:
- Mark essential words as you read the section. It helps you keep your attention on the critical points.
- Look over the questions quickly before you read them. Find keywords in the questions to help you learn.
- Keep track of time. Make good use of your time for each part, and don’t spend too much on any one question.
- Skim the sentence before entering the details. Know what the primary thought is and how the information is put together.
- Begin with the easiest questions for you. It makes sure you get those questions before moving on to harder ones.
To summarize, mastering the IELTS Reading test involves a combination of successful tactics, persistent practice, and confidence. You may quickly and accurately explore the chapters by establishing strong skimming and scanning methods, growing your vocabulary, and becoming familiar with various questions. Identify and manage your time effectively, remain calm under pressure, and systematically address each question. Yocket's extensive study materials and professional assistance may provide additional support and tools to help you succeed in your IELTS. With effort and the correct resources, you may confidently take the IELTS Reading exam and attain your goal score. Visit Yocket today and take your IELTS preparation to the next level.
FAQ's on Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website - IELTS Reading Answers
How many parts does the IELTS Reading test have?
There are three parts to the IELTS Reading test, each with a different written text. From sections one to three, these sentences get more complicated and complex as you read them. Quickly read through the questions to know what to expect. You can read more quickly and easily with this.
How can I qualify for the IELTS Reading test?
To prepare for the IELTS Reading test, practice reading various literature, such as academic articles, newspapers, and magazines. Familiarize yourself with various question forms and use efficient reading skills, including skimming, scanning, and paraphrasing.
What sorts of questions might I expect on the IELTS Reading test?
The IELTS Reading test has a variety of question formats, including multiple-choice, matching headers, True/False/Not Given, sentence completion, summary completion, and more. These questions measure reading abilities, such as comprehending key concepts, accessing particular material, and recognizing viewpoints or attitudes.
What is the IELTS Reading test, and what does it cover?
The IELTS Reading exam measures a candidate's ability to comprehend and interpret written English content. It is divided into three sections, each with distinct content: an article, an essay, and an advertisement. Test takers must attentively read each section and respond to text-related questions.
More Topics
Top Premium Admits
The University of Edinburgh
Yocketers Admitted
Scholarships granted

Nandita Shekar
Columbia University

Sharwari Bhosale
Cornell University

Atharva Thodge
Articles you might like
The Indian Dream To Go For Higher Studies Abroad?
Hold all the aces before you depart for your higher studies
What After SAT / ACT Exam? | Things to do for Studies Abroad
Upcoming Events
Scholarships and Other Funding Strategies 2025
June 15th, 7:00 pm IST | 1hr
Fireside chat with Brown uni admitted student
June 21st, 3:00 pm IST | 1hr
Looking for Funding options: Scholarships, RA & TA are the way forward!
July 2nd, 5:00 pm IST | 1hr
- Practice Test
- Useful Tips – Tricks
- Full Writing Review
- General Writing Task
- Writing Task 1
- Writing Task 2
- Writing Exercises
- Writing Sample – Topics
- Writing Vocabulary
- Speaking Vocabulary
- Intro Question
- Speaking Part 1
- Speaking Part 2
- Speaking Part 2 – Audio
- Speaking Part 3
- IELTS Books
- Recent Exams
- IELTS Vocabulary
- Essay from Examiners
- IELTS Ideas
IELTS App - For Mobile
Ready for the IELTS exam with our IELTS app. Over 2 million downloads

Popular Last 24h
Ielts speaking part 1 topic: dream –answers with audio, listening full test 10 - section 2, writing task 2: today, many people do not know their neighbors in large cities., writing task 1: the average daily sales of selected food items at the brisk café, by season, [ebook] ielts academic writing task 1 samples pdf, writing task 1: information about various professions in the u.k. and their salaries, ielts speaking part 3: a time you took risk.
- IELTS Test/Skills FAQs
- IELTS Scoring in Detail
- Forecast Speaking – 2023
- List IELTS Speaking Part 3
- List IELTS Speaking Part 1
- IELTS Writing 2023 – Actual Test
Our Telegram
Join our community for IELTS preparation and share and download materials.
The information on this site is for informational purposes only. IELTS is a registered trademark of the University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, and IDP Education Australia. This site and its owners are not affiliated, approved or endorsed by University of Cambridge ESOL, the British Council, or IDP Education Australia.
Latest Articles
Ielts speaking part 3: tips to answer questions, cue card – describe a gift you bought for someone, cue card – describe a place where you like to go shopping, ielts writing task 1 (process wasted glass bottles) – band 9, ielts speaking part 1: rubbish/ plastic garbage, most popular, describe a film that made you laugh, describe a person whom you met for the first time and made you happy, topic: experience is the best teacher, describe something difficult you would like to succeed in doing, in many countries,today there are many highly qualified graduates without employment..
ieltspracticeonline All Rights Reserved

All You Wanted to Know About How to Write a Case Study

What do you study in your college? If you are a psychology, sociology, or anthropology student, we bet you might be familiar with what a case study is. This research method is used to study a certain person, group, or situation. In this guide from our dissertation writing service , you will learn how to write a case study professionally, from researching to citing sources properly. Also, we will explore different types of case studies and show you examples — so that you won’t have any other questions left.
What Is a Case Study?
A case study is a subcategory of research design which investigates problems and offers solutions. Case studies can range from academic research studies to corporate promotional tools trying to sell an idea—their scope is quite vast.
What Is the Difference Between a Research Paper and a Case Study?
While research papers turn the reader’s attention to a certain problem, case studies go even further. Case study guidelines require students to pay attention to details, examining issues closely and in-depth using different research methods. For example, case studies may be used to examine court cases if you study Law, or a patient's health history if you study Medicine. Case studies are also used in Marketing, which are thorough, empirically supported analysis of a good or service's performance. Well-designed case studies can be valuable for prospective customers as they can identify and solve the potential customers pain point.
Case studies involve a lot of storytelling – they usually examine particular cases for a person or a group of people. This method of research is very helpful, as it is very practical and can give a lot of hands-on information. Most commonly, the length of the case study is about 500-900 words, which is much less than the length of an average research paper.
The structure of a case study is very similar to storytelling. It has a protagonist or main character, which in your case is actually a problem you are trying to solve. You can use the system of 3 Acts to make it a compelling story. It should have an introduction, rising action, a climax where transformation occurs, falling action, and a solution.
Here is a rough formula for you to use in your case study:
Problem (Act I): > Solution (Act II) > Result (Act III) > Conclusion.
Types of Case Studies
The purpose of a case study is to provide detailed reports on an event, an institution, a place, future customers, or pretty much anything. There are a few common types of case study, but the type depends on the topic. The following are the most common domains where case studies are needed:

- Historical case studies are great to learn from. Historical events have a multitude of source info offering different perspectives. There are always modern parallels where these perspectives can be applied, compared, and thoroughly analyzed.
- Problem-oriented case studies are usually used for solving problems. These are often assigned as theoretical situations where you need to immerse yourself in the situation to examine it. Imagine you’re working for a startup and you’ve just noticed a significant flaw in your product’s design. Before taking it to the senior manager, you want to do a comprehensive study on the issue and provide solutions. On a greater scale, problem-oriented case studies are a vital part of relevant socio-economic discussions.
- Cumulative case studies collect information and offer comparisons. In business, case studies are often used to tell people about the value of a product.
- Critical case studies explore the causes and effects of a certain case.
- Illustrative case studies describe certain events, investigating outcomes and lessons learned.
Need a compelling case study? EssayPro has got you covered. Our experts are ready to provide you with detailed, insightful case studies that capture the essence of real-world scenarios. Elevate your academic work with our professional assistance.

Case Study Format
The case study format is typically made up of eight parts:
- Executive Summary. Explain what you will examine in the case study. Write an overview of the field you’re researching. Make a thesis statement and sum up the results of your observation in a maximum of 2 sentences.
- Background. Provide background information and the most relevant facts. Isolate the issues.
- Case Evaluation. Isolate the sections of the study you want to focus on. In it, explain why something is working or is not working.
- Proposed Solutions. Offer realistic ways to solve what isn’t working or how to improve its current condition. Explain why these solutions work by offering testable evidence.
- Conclusion. Summarize the main points from the case evaluations and proposed solutions. 6. Recommendations. Talk about the strategy that you should choose. Explain why this choice is the most appropriate.
- Implementation. Explain how to put the specific strategies into action.
- References. Provide all the citations.
How to Write a Case Study
Let's discover how to write a case study.

Setting Up the Research
When writing a case study, remember that research should always come first. Reading many different sources and analyzing other points of view will help you come up with more creative solutions. You can also conduct an actual interview to thoroughly investigate the customer story that you'll need for your case study. Including all of the necessary research, writing a case study may take some time. The research process involves doing the following:
- Define your objective. Explain the reason why you’re presenting your subject. Figure out where you will feature your case study; whether it is written, on video, shown as an infographic, streamed as a podcast, etc.
- Determine who will be the right candidate for your case study. Get permission, quotes, and other features that will make your case study effective. Get in touch with your candidate to see if they approve of being part of your work. Study that candidate’s situation and note down what caused it.
- Identify which various consequences could result from the situation. Follow these guidelines on how to start a case study: surf the net to find some general information you might find useful.
- Make a list of credible sources and examine them. Seek out important facts and highlight problems. Always write down your ideas and make sure to brainstorm.
- Focus on several key issues – why they exist, and how they impact your research subject. Think of several unique solutions. Draw from class discussions, readings, and personal experience. When writing a case study, focus on the best solution and explore it in depth. After having all your research in place, writing a case study will be easy. You may first want to check the rubric and criteria of your assignment for the correct case study structure.
Read Also: ' WHAT IS A CREDIBLE SOURCES ?'
Although your instructor might be looking at slightly different criteria, every case study rubric essentially has the same standards. Your professor will want you to exhibit 8 different outcomes:
- Correctly identify the concepts, theories, and practices in the discipline.
- Identify the relevant theories and principles associated with the particular study.
- Evaluate legal and ethical principles and apply them to your decision-making.
- Recognize the global importance and contribution of your case.
- Construct a coherent summary and explanation of the study.
- Demonstrate analytical and critical-thinking skills.
- Explain the interrelationships between the environment and nature.
- Integrate theory and practice of the discipline within the analysis.
Need Case Study DONE FAST?
Pick a topic, tell us your requirements and get your paper on time.
Case Study Outline
Let's look at the structure of an outline based on the issue of the alcoholic addiction of 30 people.
Introduction
- Statement of the issue: Alcoholism is a disease rather than a weakness of character.
- Presentation of the problem: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there.
- Explanation of the terms: In the past, alcoholism was commonly referred to as alcohol dependence or alcohol addiction. Alcoholism is now the more severe stage of this addiction in the disorder spectrum.
- Hypotheses: Drinking in excess can lead to the use of other drugs.
- Importance of your story: How the information you present can help people with their addictions.
- Background of the story: Include an explanation of why you chose this topic.
- Presentation of analysis and data: Describe the criteria for choosing 30 candidates, the structure of the interview, and the outcomes.
- Strong argument 1: ex. X% of candidates dealing with anxiety and depression...
- Strong argument 2: ex. X amount of people started drinking by their mid-teens.
- Strong argument 3: ex. X% of respondents’ parents had issues with alcohol.
- Concluding statement: I have researched if alcoholism is a disease and found out that…
- Recommendations: Ways and actions for preventing alcohol use.
Writing a Case Study Draft
After you’ve done your case study research and written the outline, it’s time to focus on the draft. In a draft, you have to develop and write your case study by using: the data which you collected throughout the research, interviews, and the analysis processes that were undertaken. Follow these rules for the draft:

- Your draft should contain at least 4 sections: an introduction; a body where you should include background information, an explanation of why you decided to do this case study, and a presentation of your main findings; a conclusion where you present data; and references.
- In the introduction, you should set the pace very clearly. You can even raise a question or quote someone you interviewed in the research phase. It must provide adequate background information on the topic. The background may include analyses of previous studies on your topic. Include the aim of your case here as well. Think of it as a thesis statement. The aim must describe the purpose of your work—presenting the issues that you want to tackle. Include background information, such as photos or videos you used when doing the research.
- Describe your unique research process, whether it was through interviews, observations, academic journals, etc. The next point includes providing the results of your research. Tell the audience what you found out. Why is this important, and what could be learned from it? Discuss the real implications of the problem and its significance in the world.
- Include quotes and data (such as findings, percentages, and awards). This will add a personal touch and better credibility to the case you present. Explain what results you find during your interviews in regards to the problem and how it developed. Also, write about solutions which have already been proposed by other people who have already written about this case.
- At the end of your case study, you should offer possible solutions, but don’t worry about solving them yourself.
Use Data to Illustrate Key Points in Your Case Study
Even though your case study is a story, it should be based on evidence. Use as much data as possible to illustrate your point. Without the right data, your case study may appear weak and the readers may not be able to relate to your issue as much as they should. Let's see the examples from essay writing service :
With data: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there. Without data: A lot of people suffer from alcoholism in the United States.
Try to include as many credible sources as possible. You may have terms or sources that could be hard for other cultures to understand. If this is the case, you should include them in the appendix or Notes for the Instructor or Professor.
Finalizing the Draft: Checklist
After you finish drafting your case study, polish it up by answering these ‘ask yourself’ questions and think about how to end your case study:
- Check that you follow the correct case study format, also in regards to text formatting.
- Check that your work is consistent with its referencing and citation style.
- Micro-editing — check for grammar and spelling issues.
- Macro-editing — does ‘the big picture’ come across to the reader? Is there enough raw data, such as real-life examples or personal experiences? Have you made your data collection process completely transparent? Does your analysis provide a clear conclusion, allowing for further research and practice?
Problems to avoid:
- Overgeneralization – Do not go into further research that deviates from the main problem.
- Failure to Document Limitations – Just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study, you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis.
- Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications – Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings.
How to Create a Title Page and Cite a Case Study
Let's see how to create an awesome title page.
Your title page depends on the prescribed citation format. The title page should include:
- A title that attracts some attention and describes your study
- The title should have the words “case study” in it
- The title should range between 5-9 words in length
- Your name and contact information
- Your finished paper should be only 500 to 1,500 words in length.With this type of assignment, write effectively and avoid fluff
Here is a template for the APA and MLA format title page:
There are some cases when you need to cite someone else's study in your own one – therefore, you need to master how to cite a case study. A case study is like a research paper when it comes to citations. You can cite it like you cite a book, depending on what style you need.
Citation Example in MLA Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing, 2008. Print.
Citation Example in APA Hill, L., Khanna, T., & Stecker, E. A. (2008). HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing.
Citation Example in Chicago Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies.
Case Study Examples
To give you an idea of a professional case study example, we gathered and linked some below.
Eastman Kodak Case Study
Case Study Example: Audi Trains Mexican Autoworkers in Germany
To conclude, a case study is one of the best methods of getting an overview of what happened to a person, a group, or a situation in practice. It allows you to have an in-depth glance at the real-life problems that businesses, healthcare industry, criminal justice, etc. may face. This insight helps us look at such situations in a different light. This is because we see scenarios that we otherwise would not, without necessarily being there. If you need custom essays , try our research paper writing services .
Get Help Form Qualified Writers
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. If you’re having trouble with your case study, help with essay request - we'll help. EssayPro writers have read and written countless case studies and are experts in endless disciplines. Request essay writing, editing, or proofreading assistance from our custom case study writing service , and all of your worries will be gone.
Don't Know Where to Start?
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. Request ' write my case study ' assistance from our service.
What Is A Case Study?
How to cite a case study in apa, how to write a case study.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
.webp)
Bird Flu (H5N1) Explained: Bird Flu Has Killed Dozens Of Dairy Cows In Multiple States, Report Says
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Here’s the latest news about a global outbreak of H5N1 bird flu that started in 2020, and recently spread among cattle in U.S. states and marine mammals across the world, which has health officials closely monitoring it and experts concerned the virus could mutate and eventually spread to humans, where it has proven rare but deadly.
A sign warns of a outbreak of bird flu.
June 6 Dozens of cows infected with bird flu have either died or been slaughtered in Colorado, Ohio, Michigan, South Carolina and Texas, which is unusual since—unlike poultry—cows cost more to slaughter and around 90% usually make a full recovery, Reuters reported .
June 5 A new study examining the 2023 bird flu outbreak in South America that killed around 17,400 elephant seal pups and 24,000 sea lions found the disease spread between the animals in several countries, the first known case of transnational virus mammal-to-mammal bird flu transmission.
May 30 Another human case of bird flu has been detected in a dairy farm worker in Michigan—though the cases aren’t connected—and this is the first person in the U.S. to report respiratory symptoms connected to bird flu, though their symptoms are “resolving,” according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
May 23 A new study with mice suggests that drinking infected milk can spread the disease—and that a certain type of pasteurization may not always be effective in killing the virus.
May 22 Michigan reported bird flu in a farmworker—the second U.S. human case tied to transmission from dairy cows—though the worker had a mild infection and has since recovered.
May 21 Australia reported its first human case of bird flu after a child became infected in March after traveling to India, though the child has since recovered after suffering from a “severe infection,” according to the Victorian Department of Health.
May 16 The USDA conducted a study, and discovered that after high levels of the virus was injected into beef, no trace was left after the meat was cooked medium to well done, though the virus was found in meat cooked to lower temperatures.
May 14 The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released influenza A waste water data for the weeks ending in April 27 and May 4, and found several states like Alaska, California, Florida, Illinois and Kansas had unusually high levels, though the agency isn’t sure if the virus came from humans or animals, and isn’t able to differentiate between influenza A subtypes, meaning the H5N1 virus or other subtypes may have been detected.
May 10 The Food and Drug Administration announced it will commit an additional $8 million to ensure the commercial milk supply is safe, while the Department of Agriculture said it will pay up to $28,000 per farm to help mitigate the spread of the disease, totaling around $98 million in funds.
May 9 Some 70 people in Colorado are being monitored for bird flu due to potential exposure, and will be tested for the virus if they show any symptoms, the Colorado Department of Public Health told Forbes—it was not immediately clear how or when the people were potentially exposed.
May 1 The Department of Agriculture said it tested 30 grocery store ground beef products for bird flu and they all came back negative, reaffirming the meat supply is safe.
May 1 The Food and Drug Administration confirmed dairy products are still safe to consume, announcing it tested grocery store samples of products like infant formula, toddler milk, sour cream and cottage cheese, and no live traces of the bird flu virus were found, although some dead remnants were found in some of the food—though none in the baby products.
April 30 Wenqing Zhang, head of the World Health Organization's Global Influenza Programme, said during a news briefing "there is a risk for cows in other countries to be getting infected," with the bird flu virus, since it’s commonly spread through the movement of migratory birds.
April 29 The Department of Agriculture told Forbes it will begin testing ground beef samples from grocery stores in states with cow outbreaks, and test ground beef cooked at different temperatures and infected with the virus to determine if it's safe to eat.
April 24 The USDA said cow-to-cow transmission may be occurring due to the cows coming into contact with raw milk—and warned against humans and other animals, including pets, consuming unpasteurized milk to prevent potential infection.
April 18 Jeremy Farrar, chief scientist for the World Health Organization, said during a press conference the threat of bird flu spreading between humans was a “great concern,” since it’s evolved and has increasingly been infecting mammals (on land and sea), which means it could possibly spread to humans.
April 1 The CDC reported the second U.S. human case of bird flu in a Texas dairy farmer who became infected after contracting the virus from infected dairy cows, but said the person was already recovering.
Get Forbes Breaking News Text Alerts: We’re launching text message alerts so you'll always know the biggest stories shaping the day’s headlines. Sign up here .
Can Bird Flu Spread Between Humans?
Bird flu doesn’t “transmit easily from person-to-person,” according to the World Health Organization. Bird flu rarely affects humans, and most previous cases came from close contact with infected poultry, according to the CDC. Because human-to-human spread of bird flu poses “pandemic potential,” each human case is investigated to rule out this type of infection. Though none have been confirmed, there are a few global cases—none in the U.S.—where human-to-human transmission of bird flu was thought to be “probable,” including in China , Thailand , Indonesia and Pakistan .
Is Bird Flu Fatal To Humans?
It is very deadly. Between January 2003 and March 28, 2024 there have been 888 human cases of bird flu infection in humans, according to a report by the World Health Organization. Of those 888 cases, 463 (52%) died. To date, only two people in the U.S. have contracted H5N1 bird flu, and they both were infected after coming into contact with sick animals. The most recent case was a dairy worker in Texas who became ill in March after interacting with sick dairy cows, though he only experienced pink eye. The first incident happened in 2022 when a person in Colorado contracted the disease from infected poultry, and fully recovered.
Is It Safe To Drink Milk Infected With Bird Flu?
Raw, unpasteurized milk is unsafe to drink, but pasteurized milk is fine, according to the FDA. Bird flu has been detected in both unpasteurized and pasteurized milk, but the FDA recommends manufacturers against making and selling unpasteurized milk since there’s a possibility consuming it may cause bird flu infection. However, the virus remnants in pasteurized milk have been deactivated by the heat during the pasteurization process , so this type of milk is still believed safe to consume.
Is It Safe To Consume Meat Infected With Bird Flu?
The CDC warns against eating raw meat or eggs from animals “confirmed or suspected” of having bird flu because of the possibility of transmission. However, no human has ever been infected with bird flu from eating properly prepared and cooked meat, according to the agency. The possibility of infected meat entering the food supply is “extremely low” due to rigorous inspection, so properly handled and cooked meat is safe to eat, according to the USDA. To know when meat is properly cooked, whole beef cuts must be cooked to an internal temperature of 145 degrees Fahrenheit, ground meat must be 160 degrees and poultry must be cooked to 165 degrees. Rare and medium rare steaks fall below this temperature. Properly cooked eggs with an internal temperature of 165 degrees Fahrenheit kills bacteria and viruses including bird flu, according to the CDC. “It doesn’t matter if they may or may not have [avian] influenza… runny eggs and rare pieces of meat” are never recommended, Francisco Diez-Gonzalez, director and professor for the Center for Food Safety at the University of Georgia, told Forbes. To “play it safe,” consumers should only eat fully cooked eggs and make sure “the yolks are firm with no runny parts,” Daisy May, veterinary surgeon with U.K.-based company Medivet, said .
What Are Bird Flu Symptoms In Humans?
Symptoms of bird flu include a fever, cough, headache, chills, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, runny nose, congestion, sore throat, nausea or vomiting, diarrhea, pink eye, muscle aches and headache. However, the CDC advises it can’t be diagnosed based on symptoms alone, and laboratory testing is needed. This typically includes swabbing the nose or throat (the upper respiratory tract), or the lower respiratory tract for critically ill patients.
How Is Bird Flu Affecting Egg Prices?
This year’s egg prices have increased as production decreased due to bird flu outbreaks among poultry, according to the USDA. A dozen large, grade A eggs in the U.S. costed around $2.99 in March, up almost a dollar from the fall. However, this price is down from a record $4.82 in January 2023, which was also spiked by bird flu outbreaks . Earlier this month, Cal-Maine Foods—the country’s largest egg producer—temporarily halted egg production after over one million egg-laying hens and chickens were killed after being infected with bird flu.
Why Do Poultry Farmers Kill Chickens With Bird Flu?
Once chickens have been infected with bird flu, farmers quickly kill them to help control the spread of the virus, since bird flu is highly contagious and fatal in poultry. The USDA pays farmers for all birds and eggs that have to be killed because of bird flu, as an incentive to responsibly try and curb the spread of the disease. The USDA has spent over $1 billion in bird flu compensation for farmers since 2022, according to the nonprofit Food & Environment Reporting Network.
Is There A Vaccine For The Bird Flu (h5n1)?
The FDA has approved a few bird flu vaccines for humans. The U.S. has a stockpile of vaccines for H5N1 bird flu, but it wouldn’t be enough to vaccinate all Americans if an outbreak were to happen among humans. If a human outbreak does occur, the government plans to mass produce vaccines, which can take at least six months to make enough for the entire population. CSL Seqirus, the maker of one of the approved vaccines, expects to have 150 million vaccines ready within six months of an announcement of a human bird flu pandemic. Although there are approved vaccines for other variants designed for birds, there are none for the H5N1 variant circulating. However, the USDA began trials on H5N1 animal-specific vaccines in 2023.
Key Background
As of May 30, more than 92 million poultry (primarily chickens) in 48 states have been euthanized because of bird flu since 2022, and 57 dairy cow herds across nine states have tested positive, according to data from the CDC (unlike chickens, cows appear to recover from the virus). The USDA believes wild migratory birds are the original source of the cow outbreaks that recently has experts concerned it may mutate and spread more easily in humans, though the CDC said its risk to the public remains low . Farrar called the cattle infections in the U.S. a “huge concern,” urging public health officials to continue closely monitoring the situation “because it may evolve into transmitting in different ways.” The increased number of mammal bird flu infections since 2022 “could indicate that the virus is looking for new hosts, and of course, moving closer to people,” Andrea Garcia, vice president of science, medicine and public health for the American Medical Association, said . The first report of a walrus dying from bird flu was detected in April on one of Norway’s Arctic Islands, and the first U.S. dolphin infected with bird flu died back in 2022, according to a report published April 18. More than 10 human bird flu cases were reported to the World Health Organization in 2023, and all but one survived. Bird flu has devastated bird populations, and 67 countries reported the deaths of 131 million poultry in 2022 alone. Although bird flu typically infects wild birds and poultry, it’s spread to other animals during the outbreak, and at least 10 countries have reported outbreaks in mammals since 2022. Around 17,400 elephant seal pups died from bird flu in Argentina in 2023, and at least 24,000 sea lions died in South America the same year. Besides cattle, bird flu has been detected in over 200 other mammals—like seals, raccoons and bears—in the U.S. since 2022. Although rare, even domestic pets like dogs and cats are susceptible to the virus, and the FDA warns against giving unpasteurized milk to cats to avoid possible transmission.
On June 5, WHO confirmed the first human death of a strain of bird flu that’s never before been seen in humans and is separate from H5N1. A 59-year-old man in Mexico contracted H5N2, and died on April 24 after being hospitalized and developing a fever, diarrhea, nausea, shortness of breath and general discomfort. Cases of H5N2 have been reported in poultry in Mexico, but the man had no history with poultry or animals, WHO said. It’s unclear how he became infected. He was bedridden for weeks prior to the infection, and suffered from several other health conditions.
Further Reading
Another Bird Flu Variant Reaches Humans: What To Know About H5N2—After First-Ever Confirmed Death
WHO Warns Threat Of Bird Flu Spreading To Humans Is ‘Great Concern’ (Forbes)
One In Five Milk Samples From Across US Had Traces Of Bird Flu Virus, FDA Says (Forbes)
Can Pets Get Bird Flu? Here’s What To Know (Forbes)
Avian H5N1 (Bird) Flu: Why Experts Are Worried—And What You Should Know (Forbes)

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.

Cambridge IELTS 13 Academic Reading Test 1 with Answers
Cambridge ielts 13 academic reading test 1, reading passage 1, case study: tourism new zealand website.
New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country’s gross domestic product, and is the country’s largest export sector. Unlike other export sectors, which make products and then sell them overseas, tourism brings its customers to New Zealand. The product is the country itself – the people, the places and the experiences. In 1999, Tourism New Zealand launched a campaign to communicate a new brand position to the world. The campaign focused on New Zealand’s scenic beauty, exhilarating outdoor activities and authentic Maori culture, and it made New Zealand one of the strongest national brands in the world.
A key feature of the campaign was the website www.newzealand.com, which provided potential visitors to New Zealand with a single gateway to everything the destination had to offer. The heart of the website was a database of tourism services operators, both those based in New Zealand and those based abroad which offered tourism service to the country. Any tourism-related business could be listed by filling in a simple form. This meant that even the smallest bed and breakfast address or specialist activity provider could gain a web presence with access to an audience of long-haul visitors. In addition, because participating businesses were able to update the details they gave on a regular basis, the information provided remained accurate. And to maintain and improve standards, Tourism New Zealand organised a scheme whereby organisations appearing on the website underwent an independent evaluation against a set of agreed national standards of quality. As part of this, the effect of each business on the environment was considered.
To communicate the New Zealand experience, the site also carried features relating to famous people and places. One of the most popular was an interview with former New Zealand All Blacks rugby captain Tana Umaga. Another feature that attracted a lot of attention was an interactive journey through a number of the locations chosen for blockbuster films which had made use of New Zealand’s stunning scenery as a backdrop. As the site developed, additional features were added to help independent travelers devise their own customised itineraries. To make it easier to plan motoring holidays, the site catalogued the most popular driving routes in the country, highlighting different routes according to the season and indicating distances and times.
Later, a Travel Planner feature was added, which allowed visitors to click and ‘bookmark’ places or attractions they were interested in, and then view the results on a map. The Travel Planner offered suggested routes and public transport options between the chosen locations. There were also links to accommodation in the area. By registering with the website, users could save their Travel Plan and return to it later, or print it out to take on the visit. The website also had a ‘Your Words’ section where anyone could submit a blog of their New Zealand travels for possible inclusion on the website.
The Tourism New Zealand website won two Webby awards for online achievement and innovation. More importantly perhaps, the growth of tourism to New Zealand was impressive. Overall tourism expenditure increased by an average of 6.9% per year between 1999 and 2004. From Britain, visits to New Zealand grew at an average annual rate of 13% between 2002 and 2006, compared to a rate of 4% overall for British visits abroad.
The website was set up to allow both individuals and travel organisations to create itineraries and travel packages to suit their own needs and interests. On the website, visitors can search for activities not solely by geographical location, but also by the particular nature of the activity. This is important as research shows that activities are the key driver of visitor satisfaction, contributing 74% to visitor satisfaction, while transport and accommodation account for the remaining 26%. The more activities that visitors undertake, the more satisfied they will be. It has also been found that visitors enjoy cultural activities most when they are interactive, such as visiting a marae (meeting ground) to learn about traditional Maori life. Many long-haul travelers enjoy such learning experiences, which provide them with stories to take home to their friends and family. In addition, it appears that visitors to New Zealand don’t want to be ‘one of the crowd’ and find activities that involve only a few people more special and meaningful.
It could be argued that New Zealand is not a typical destination. New Zealand is a small country with a visitor economy composed mainly of small businesses. It is generally perceived as a safe English-speaking country with a reliable transport infrastructure. Because of the long-haul flight, most visitors stay for longer (average 20 days) and want to see as much of the country as possible on what is often seen as a once-in-a-lifetime visit. However, the underlying lessons apply anywhere – the effectiveness of a strong brand, a strategy based on unique experiences and a comprehensive and user-friendly website.
Questions 1-7
Complete the table below. Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet.
| Database of tourism services | • easy for tourism-related businesses to get on the list • allowed businesses to …………………………… information regularly • provided a country-wide evaluation of businesses, including their impact on the ……………………….. |
| Special features on local topics | • e.g. an interview with a former sports ……………………………., and an interactive tour of various locations used in ………………………. |
| Information on driving routes | • varied depending on the …………………………… |
| Travel Planner | • included a map showing selected places, details of public transport and local …………………………. |
| ‘Your Words’ | • travelers could send a link to their ………………………… |
Questions 8-13
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage 1?
In boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information FALSE if the statement contradicts the information NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
8 The website www.newzealand.com aimed to provide ready-made itineraries and packages for travel companies and individual tourists. 9 It was found that most visitors started searching on the website by geographical location. 10 According to research, 26% of visitor satisfaction is related to their accommodation. 11 Visitors to New Zealand like to become involved in the local culture. 12 Visitors like staying in small hotels in New Zealand rather than in larger ones. 13 Many visitors feel it is unlikely that they will return to New Zealand after their visit.
READING PASSAGE 2
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 14-26 which are based on Reading Passage 2 below.
Why being bored is stimulating – and useful, too
This most common of emotions is turning out to be more interesting than we thought
We all know how it feels – it’s impossible to keep your mind on anything, time stretches out, and all the things you could do seem equally unlikely to make you feel better. But defining boredom so that it can be studied in the lab has proved difficult. For a start, it can include a lot of other mental states, such as frustration, apathy, depression and indifference. There isn’t even agreement over whether boredom is always a low-energy, flat kind of emotion or whether feeling agitated and restless counts as boredom, too. In his book, Boredom: A Lively History , Peter Toohey at the University of Calgary, Canada, compares it to disgust – an emotion that motivates us to stay away from certain situations. ‘If disgust protects humans from infection, boredom may protect them from “infectious” social situations,’ he suggests.
By asking people about their experiences of boredom, Thomas Goetz and his team at the University of Konstanz in Germany have recently identified five distinct types: indifferent, calibrating, searching, reactant and apathetic. These can be plotted on two axes – one running left to right, which measures low to high arousal, and the other from top to bottom, which measures how positive or negative the feeling is. Intriguingly, Goetz has found that while people experience all kinds of boredom, they tend to specialise in one. Of the five types, the most damaging is ‘reactant’ boredom with its explosive combination of high arousal and negative emotion. The most useful is what Goetz calls ‘indifferent’ boredom: someone isn’t engaged in anything satisfying but still feels relaxed and calm. However, it remains to be seen whether there are any character traits that predict the kind of boredom each of us might be prone to.
Psychologist Sandi Mann at the University of Central Lancashire, UK, goes further. ‘All emotions are there for a reason, including boredom,’ she says. Mann has found that being bored makes us more creative. ‘We’re all afraid of being bored but in actual fact it can lead to all kinds of amazing things,’ she says. In experiments published last year, Mann found that people who had been made to feel bored by copying numbers out of the phone book for 15 minutes came up with more creative ideas about how to use a polystyrene cup than a control group. Mann concluded that a passive, boring activity is best for creativity because it allows the mind to wander. In fact, she goes so far as to suggest that we should seek out more boredom in our lives.
Psychologist John Eastwood at York University in Toronto, Canada, isn’t convinced. ‘If you are in a state of mind-wandering you are not bored,’ he says. ‘In my view, by definition boredom is an undesirable state.’ That doesn’t necessarily mean that it isn’t adaptive, he adds. ‘Pain is adaptive – if we didn’t have physical pain, bad things would happen to us. Does that mean that we should actively cause pain? No. But even if boredom has evolved to help us survive, it can still be toxic if allowed to fester.’ For Eastwood, the central feature of boredom is a failure to put our ‘attention system’ into gear. This causes an inability to focus on anything, which makes time seem to go painfully slowly. What’s more, your efforts to improve the situation can end up making you feel worse. ‘People try to connect with the world and if they are not successful there’s that frustration and irritability,’ he says. Perhaps most worryingly, says Eastwood, repeatedly failing to engage attention can lead to state where we don’t know what to do any more, and no longer care.
Eastwood’s team is now trying to explore why the attention system fails. It’s early days but they think that at least some of it comes down to personality. Boredom proneness has been linked with a variety of traits. People who are motivated by pleasure seem to suffer particularly badly. Other personality traits, such as curiosity, are associated with a high boredom threshold. More evidence that boredom has detrimental effects comes from studies of people who are more or less prone to boredom. It seems those who bore easily face poorer prospects in education, their career and even life in general. But of course, boredom itself cannot kill – it’s the things we do to deal with it that may put us in danger. What can we do to alleviate it before it comes to that? Goetz’s group has one suggestion. Working with teenagers, they found that those who ‘approach’ a boring situation – in other words, see that it’s boring and get stuck in anyway – report less boredom than those who try to avoid it by using snacks, TV or social media for distraction.
Psychologist Francoise Wemelsfelder speculates that our over-connected lifestyles might even be a new source of boredom. ‘In modern human society there is a lot of overstimulation but still a lot of problems finding meaning,’ she says. So instead of seeking yet more mental stimulation, perhaps we should leave our phones alone, and use boredom to motivate us to engage with the world in a more meaningful way.
Questions 14-19
Reading Passage 2 has six paragraphs, A-F Choose the correct heading for each paragraph from the list of headings below.
Write the correct number, i-viii , in boxes 14-19 on your answer sheet.
List of Headings
i The productive outcomes that may result from boredom
ii What teachers can do to prevent boredom
iii A new explanation and a new cure for boredom
iv Problems with a scientific approach to boredom
v A potential danger arising from boredom
vi Creating a system of classification for feelings of boredom
vii Age groups most affected by boredom
viii Identifying those most affected by boredom
14 Paragraph A 15 Paragraph B 16 Paragraph C 17 Paragraph D 18 Paragraph E 19 Paragraph F
Questions 20-23
Look at the following people (Questions 20-23 ) and the list of ideas below.
Match each person with the correct idea, A-E .
Write the correct letter, A-E , in boxes 20-23 on your answer sheet.
20 Peter Toohey
21 Thomas Goetz
22 John Eastwood
23 Francoise Wemelsfelder
List of Ideas
A The way we live today may encourage boredom.
B One sort of boredom is worse than all the others.
C Levels of boredom may fall in the future.
D Trying to cope with boredom can increase its negative effects.
E Boredom may encourage us to avoid an unpleasant experience.
Questions 24-26
Complete the summary below. Choose ONE WORD ONLY from the passage for each answer.
Write your answers in boxes 24-26 on your answer sheet.
Responses to boredom
For John Eastwood, the central feature of boredom is that people cannot 24 ……………………………, due to a failure in what he calls the ‘attention system’, and as a result they become frustrated and irritable. His team suggests that those for whom 25 ……………………….. is an important aim in life may have problems in coping with boredom, whereas those who have the characteristic of 26 ……………………….. can generally cope with it.
READING PASSAGE 3
You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 27-40 which are based on Reading Passage 3 below.
Artificial artist?
Can computers really create works of art?
The Painting Fool is one of a growing number of computer programs which, so their makers claim, possess creative talents. Classical music by an artificial composer has had audiences enraptured, and even tricked them into believing a human was behind the score. Artworks painted by a robot have sold for thousands of dollars and been hung in prestigious galleries. And software has been built which creates are that could not have been imagined by the programmer.
Human beings are the only species to perform sophisticated creative acts regularly. If we can break this process down into computer code, where does that leave human creativity? ‘This is a question at the very core of humanity,’ says Geraint Wiggins, a computational creativity researcher at Goldsmiths, University of London. ‘It scares a lot of people. They are worried that it is taking something special away from what it means to be human.’
To some extent, we are all familiar with computerised art. The question is: where does the work of the artist stop and the creativity of the computer begin? Consider one of the oldest machine artists, Aaron, a robot that has had paintings exhibited in London’s Tate Modern and the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art. Aaron can pick up a paintbrush and paint on canvas on its own. Impressive perhaps, but it is still little more than a tool to realise the programmer’s own creative ideas.
Simon Colton, the designer of the Painting Fool, is keen to make sure his creation doesn’t attract the same criticism. Unlike earlier ‘artists’ such as Aaron, the Painting Fool only needs minimal direction and can come up with its own concepts by going online for material. The software runs its own web searches and trawls through social media sites. It is now beginning to display a kind of imagination too, creating pictures from scratch. One of its original works is a series of fuzzy landscapes, depicting trees and sky. While some might say they have a mechanical look, Colton argues that such reactions arise from people’s double standards towards software-produced and human-produced art. After all, he says, consider that the Painting Fool painted the landscapes without referring to a photo. ‘If a child painted a new scene from its head, you’d say it has a certain level of imagination,’ he points out. ‘The same should be true of a machine.’ Software bugs can also lead to unexpected results. Some of the Painting Fool’s paintings of a chair came out in black and white, thanks to a technical glitch. This gives the work an eerie, ghostlike quality. Human artists like the renowned Ellsworth Kelly are lauded for limiting their colour palette – so why should computers be any different?
Researchers like Colton don’t believe it is right to measure machine creativity directly to that of humans who ‘have had millennia to develop our skills’. Others, though, are fascinated by the prospect that a computer might create something as original and subtle as our best artists. So far, only one has come close. Composer David Cope invented a program called Experiments in Musical Intelligence, or EMI. Not only did EMI create compositions in Cope’s style, but also that of the most revered classical composers, including Bach, Chopin and Mozart. Audiences were moved to tears, and EMI even fooled classical music experts into thinking they were hearing genuine Bach. Not everyone was impressed however. Some, such as Wiggins, have blasted Cope’s work as pseudoscience, and condemned him for his deliberately vague explanation of how the software worked. Meanwhile, Douglas Hofstadter of Indiana University said EMI created replicas which still rely completely on the original artist’s creative impulses. When audiences found out the truth they were often outraged with Cope, and one music lover even tried to punch him. Amid such controversy, Cope destroyed EMI’s vital databases.
But why did so many people love the music, yet recoil when the discovered how it was composed? A study by computer scientist David Moffat of Glasgow Caledonian University provides a clue. He asked both expert musicians and non-experts to assess six compositions. The participants weren’t told beforehand whether the tunes were composed by humans or computers, but were asked to guess, and then rate how much they liked each one. People who thought the composer was a computer tended to dislike the piece more than those who believed it was human. This was true even among the experts, who might have been expected to be more objective in their analyses.
Where does this prejudice come from? Paul Bloom of Yale University has a suggestion: he reckons part of the pleasure we get from art stems from the creative process behind the work. This can give it an ‘irresistible essence’, says Bloom. Meanwhile, experiments by Justin Kruger of New York University have shown that people’s enjoyment of an artwork increases if they think more time and effort was needed to create it. Similarly, Colton thinks that when people experience art, they wonder what the artist might have been thinking or what the artist is trying to tell them. It seems obvious, therefore, that with computers producing art, this speculation is cut short – there’s nothing to explore. But as technology becomes increasingly complex, finding those greater depths in computer art could become possible. This is precisely why Colton asks the Painting Fool to tap into online social networks for its inspiration: hopefully this way it will choose themes that will already be meaningful to us.
Questions 27-31
Choose the correct letter, A , B , C or D .
Write the correct letter in boxes 27-31 on your answer sheet.
27 What is the writer suggesting about computer-produced works in the first paragraph?
A People’s acceptance of them can vary considerably. B A great deal of progress has already been attained in this field. C They have had more success in some artistic genres than in others. D the advances are not as significant as the public believes them to be.
28 According to Geraint Wiggins, why are many people worried by computer art?
A It is aesthetically inferior to human art. B It may ultimately supersede human art. C It undermines a fundamental human quality. D It will lead to a deterioration in human ability.
29 What is a key difference between Aaron and the Painting Fool?
A its programmer’s background B public response to its work C the source of its subject matter D the technical standard of its output
30 What point does Simon Colton make in the fourth paragraph?
A Software-produced art is often dismissed as childish and simplistic. B The same concepts of creativity should not be applied to all forms of art. C It is unreasonable to expect a machine to be as imaginative as a human being. D People tend to judge computer art and human art according to different criteria.
31 The writer refers to the paintings of a chair as an example of computer art which
A achieves a particularly striking effect. B exhibits a certain level of genuine artistic skill. C closely resembles that of a well-known artist. D highlights the technical limitations of the software.
Questions 32-37
Complete each sentence with the correct ending, A-G below.
Write the correct letter, A-G , in boxes 32-37 on your answer sheet.
32 Simon Colton says it is important to consider the long-term view then
33 David Cope’s EMI software surprised people by
34 Geraint Wiggins criticized Cope for not
35 Douglas Hofstadter claimed that EMI was
36 Audiences who had listened to EMI’s music became angry after
37 The participants in David Moffat’s study had to assess music without
A generating work that was virtually indistinguishable from that of humans.
B knowing whether it was the work of humans or software.
C producing work entirely dependent on the imagination of its creator.
D comparing the artistic achievements of humans and computers.
E revealing the technical details of his program.
F persuading the public to appreciate computer art.
G discovering that it was the product of a computer program
Questions 38-40
Do the following statements agree with the claims of the writer in Reading Passage 3?
In boxes 38-40 on your answer sheet, write
YES if the statement agrees with the claims of the writer NO if the statement contradicts the claims of the writer NOT GIVEN if it is impossible to say what the writer thinks about this
38 Moffat’s research may help explain people’s reactions to EMI.
39 The non-experts in Moffat’s study all responded in a predictable way.
40 Justin Kruger’s findings cast doubt on Paul Bloom’s theory about people’s prejudice towards computer art.
Cambridge IELTS 13 Academic Reading Test 1 Answers
1. update 2. environment 3. captain 4. films 5. season 6. accommodation 7. blog 8. FALSE 9. NOT GIVEN 10. FALSE 11. TRUE 12. NOT GIVEN 13. TRUE 14. iv 15. vi 16. i 17. v 18. viii 19. iii 20. E
Practice with Expert IELTS Tutors Online
Apply Code "IELTSXPRESS20" To Get 20% off on IELTS Mock Test

Also Check: Cambridge IELTS 14 Academic Reading Test 4 with Answers
Practice: Practice Cambridge IELTS 4 Listening Test 4 with Answers ca
Oh hi there! It’s nice to meet you.
Sign up to receive awesome content in your inbox, every week.
We promise not to spam you or share your Data. 🙂
Check your inbox or spam folder to confirm your subscription.
Oh Hi there! It’s nice to meet you.
We promise not to Spam or Share your Data. 🙂
Related Posts

Pacific Navigation and Voyaging IELTS Reading

The Accidental Scientists IELTS Reading with Answers

Cambridge IELTS 18 Academic Reading Test 4
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Yes, add me to your mailing list
Start typing and press enter to search
Many blame social media for poor mental health among teenagers, but the science is murky
If Jordy had a switch to instantly shut down social media, she would flip it.
"I'd switch it off, 100 per cent, even if it was for a week, just so people could have that taste of what it would be like," she said.
Now in her first year out of school, the 18-year-old studies nursing at university and works at a local cafe in Charleville, a small town 745 kilometres west of Brisbane, where she has lived most of her life.
Like Australian teenagers everywhere, she has another life online.
"It's like a second world, really," she said.
"You have reality and then you have social media — two extremely different things."
At the moment, she spends an average of five-and-a-half hours a day on her phone, but it's lower than her peak during high school.
"When I first got a phone I was on it constantly, probably like seven hours, eight hours a day," she said.
She has cut back since then because that second world was not always kind, especially when it came to body image — and despite the fact her parents were always strict about phone usage.
"Growing up, I've always been a big girl … and a sporty person — I'm pretty healthy," she said.
"But when we see images, it tends to be just very thin, skinny people.
"It can just take you down, with the click of your fingers."
Jordy was also being bullied at school, but social media meant it could happen around the clock, no matter where she was.
"A group of boys at my school had tagged me on TikTok telling me to go kill myself," she said.
"It was just so heartbreaking. I was just like, 'I go to school with you every day, we've never had an issue in the past.' That's probably the worst thing that's happened."
Jordy's mental health was tanking, and she began to withdraw from activities she used to love, like footy training or seeing friends.
"I just felt so scared to talk to my mum … I was just like, 'I don't want my mum to think I'm using social media the wrong way'," she said.
No matter how bad things got, logging off still felt impossible.
"It was like that fear of missing out, I guess. I think that's the addiction thing, right?" she said.
"You sort of just have to be on your phone to socialise."
Does more screen time cause worse mental health in teenagers?
Teen mental health has deteriorated at an accelerating rate in the last two decades — more or less exactly since social media and smartphones started to become widespread in 2007.
For obvious reasons, many people, especially concerned parents, have leapt to the conclusion that tech is the culprit.
But the science is surprisingly murky, even though there is a link — research shows more screen time is associated with higher rates of depression in adolescents.
"What we know about the link is there's a link, and that's pretty much what we know," said Aliza Werner-Seidler, a senior researcher at the Black Dog Institute.
"We have really good correlational data, there is a strong linear relationship, particularly in young girls.
"What we don't know is about causation — so is young people's mental health leading them to spend more time on social media and screens, or is it actually the other way around?
"We don't know the direction of the effect."
Dr Werner-Seidler is one of thousands of researchers around the world trying to solve that mystery.
Even if many people are convinced they already know the answer because of their own experience online.
"Personally I would say that it's both," Jordy said.
After a session doomscrolling perfect bodies on TikTok, she "would feel horrible" about herself.
"But then I'd continue to use it and then it made me feel even worse."
After 17 years, why don't we have the answers yet?
Despite 17 years of widespread smartphones and social media, researchers still don't have enough data to definitively say whether they're to blame for deteriorating teen mental health.
Getting those long-term studies done is particularly difficult because trends, algorithms and habits change so quickly.
"When I started this work, TikTok wasn't even a thing … Snapchat, really has only taken off in the last decade or so," Dr Werner-Seidler said.
"It's a very fast-moving field. And so it's very, very difficult to get a handle on it before the next thing comes out."
Part of the problem is that studies have focused on overall screen time, instead of looking at what people were doing online.
"Are they FaceTiming with Grandma? Are they viewing distressing content? Are they being groomed online?" Dr Werner-Seidler said.
"This idea of nuance and it matters what people do and how they do it and how long for and with whom.
"We can't tell any of this information just by looking at how long young people spend on screens."
What social media companies know but don't say
The National Mental Health Commission has been investigating the relationship between digital tech and teen mental health.
On Friday it released its findings after months of consultation, noting the lack of longitudinal evidence and calling for further research to be made a "top priority".
Frustratingly for Dr Werner-Seidler, and other researchers in this area, the data that might solve the mystery does exist — but they can't access it.
"Big tech companies have all of this information," she said.
"If they were to share it with academics and scientists, we would be able to learn so much more, so much more quickly."
The data that has so far emerged in other ways, courtesy of lawsuits and whistleblowers such as Frances Haugen in 2021, has been disturbing.
Ms Haugen, a former Facebook employee, revealed detailed internal research showing Instagram was harmful for teenage girls.
One slide from an in-house presentation reportedly said: "We make body image issues worse for one in three teen girls."
The peak body for Australia's technology industry — whose members include social media companies Meta, Snapchat and TikTok — has defended the sector's contribution to public research.
"DIGI's relevant members have long-standing research and community partnerships in mental health and online safety, and specific policies … informed by that work," a spokesperson said.
Depending on the platform, those policies might include parental controls, avenues to report inappropriate content and seek help, customisable settings, and age limits.
Adherence to those age limits has been mostly voluntary, and the federal government is spending $6.5 million on an age verification trial in the hopes of introducing a higher standard of proof.
Some social media companies are trying to get ahead of any future legislation.
Facebook's parent company Meta announced this week it would no longer allow Facebook users to edit their birthdate to say they're over 18 without verification — a feature that's been in place on Instagram in Australia since last year.
A window for change
The public and political mood when it comes to big tech has rarely been darker.
"I've never seen the appetite [for change] as strong as it is right now," said Alice Dawkins, executive director of Reset Tech Australia.
She says there's a window for change with the federal government currently reviewing its key legislation, the Online Safety Act.
"Our online safety laws are geared at protecting people from [one] another online … [but] there's virtually nothing that can be done about protecting people from the tech itself."
As it stands, companies are rarely obliged to share information on how their products, and not just the people using them, may cause harm.
"It's highly exceptional — think about other sectors, like food, like medicine, like toys — it's incredibly routine in those sectors to have risk assessment and risk mitigation of products," Ms Dawkins said.
"There's compounding public awareness of the problem … it's never been a more appropriate time for the government to legislate."
Dr Werner-Seidler said that for now, internal data was being used by big tech to keep users scrolling for as long as possible.
"These are commercial big companies [and] they use a whole bunch of engagement strategies to keep people coming back, and that is their goal," she said.
The conversation you need to have with your kids
Jordy eventually found the courage to tell her mum what was happening to her online.
"When it got really bad I was just like, 'Mum, I need to show you … this is what's happening.'"
After that, her parents insisted she cut back her screen time but, despite everything that had already happened, she still fought it.
"I was so mean to her … I would get so angry, I'd be like, 'Mum, it's not your life,'" she said.
But that was before Jordy noticed a big improvement in her mood and her grades.
"I'm thankful every day that my mum did what she did.
"You can't ever change the fact that your kids are going to use social media," said Jordy, although boundaries were useful in her case.
"Saying to your kids, 'What are you using social media for? Why do you have to be on social media?'
"For parents out there that are struggling, I think it's that conversation you need to have with your kids.
"As a kid, you're going to get frustrated, but it's really just parents trying to protect their kids from what's out there."
Mental health disorders among young people have soared by nearly 50 per cent in 15 years. The ABC is talking to youth, parents, and researchers about what's driving this pattern, and what can be done to turn things around.
- X (formerly Twitter)
Related Stories
'there's a radicalisation happening online': fears hardcore porn could be behind rising rates of teen sexual assaults.
Why are girls suffering so much right now? The problem is bigger than you think
Teen circadian rhythms are different to the rest of us and could be key to improving their sleep and wellbeing
- Federal Government
- Mental Health
- Mental Wellbeing
- Social Media

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Reading Passage 1: The headline of the passage: Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website Questions 1-7 (Completing table with ONE WORD ONLY):In this type of question, candidates are asked to write only one word to complete a table on the given topic. For this type of question, first, skim the passage to find the keywords in the paragraph concerned with the answer, and then scan to find the ...
The Academic passage 'Implementing The Cycle Of Success: A Case Study ' is a reading passage that appeared in an IELTS Test.Try to find the answers to get an idea of the difficulty level of the passages in the actual reading test. If you want more passages to solve, try taking one of our IELTS reading practice tests. Implementing The Cycle Of Success: A Case Study
Answers. Check out your IMPLEMENTING THE CYCLE OF SUCCESS: A CASE STUDY reading answers below with locations and explanations given in the text. 1. C 8. (performance) measures 2. A 9. productivity 3. C 10. (') Take Charge (') 4. B 11. feedback 5. B 12. employee(s') // staff 6. benchmarking 13. 30 days 7. service delivery
Answer: employee (s') // staff Locate. 13. Answer: 30 days Locate. IMPLEMENTING THE CYCLE OF SUCCESS: A CASE STUDY reading practice test has 13 questions belongs to the Education subject. In total 13 questions, 8 questions are Matching Information form, 5 questions are Sentence Completion form.
Implementing The Cycle of Success A Case Study Reading Answers Explanation. 1. The high costs of running AHI's hotels are related to their … Answer: staff Supporting Sentence: Similar to many international hotel chains, however, AHI has experienced difficulties in Australia in providing long-term profits for hotel owners, as a result of the country's high labour-cost structure.
READING PASSAGE 1. You should spend about 20 minutes on Questions 1-13 which are based on Reading Passage 1 below. Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website. New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world.
When faced with a case study question, it's important to approach it in a structured and logical manner. Here are some tips on how to answer case study questions effectively: 1. Understand the question: Start by carefully reading and understanding the case study question. Break it down into smaller parts and make sure you fully comprehend ...
Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website. New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country's gross domestic product, and is the country's largest export sector. Unlike other export sectors, which make ...
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are sometimes also used.
March 4, 2023. 'Case study: Tourism New Zealand website'- Reading Answer Explanation- CAM- 13. Here are explanations of the Questions of passage named 'Case study: Tourism New Zealand website', which is from the Cambridge 13 book. The Questions that have been asked are True/False/Not Given and Blanks.
The Academic passage, Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website reading answers, appeared in an IELTS Test. Try to find the answers to get an idea of the difficulty level of the passages in the actual reading test. If you want more passages to solve, try taking one of our IELTS reading practice tests. Let's see how easy this passage is for you ...
🤖 How to Use Our Case Study Answer Generator. Getting a case study analysis has never been easier—see for yourself! Paste your case study into the field.; Add questions or issues you need to address in your analysis.; Press "Analyze now."; Get the results!; Keep in mind that the results provided by the tool are to be used for reference purposes only.
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity.
Identify the key problems and issues in the case study. Formulate and include a thesis statement, summarizing the outcome of your analysis in 1-2 sentences. Background. Set the scene: background information, relevant facts, and the most important issues. Demonstrate that you have researched the problems in this case study. Evaluation of the Case
Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website Reading Answers. The IELTS reading passage topic: Tourism New Zealand Website" is a very common yet interesting topic in the IELTS examination. In the sections below, this topic is divided into different parts to help you practice in a better yet easy manner for this passage. Tourism New Zealand Website ...
Try to use live examples to give a more impactful expression to your case studies. 8. Justified Statements Are Necessary: The best way to answer a case study is to agree or disagree with the justified statements. 9. Make Complete Sentences: It is also an important point to make a flawless case study paper.
Then plan to spend some time reading the exam question, the case study and planning your answer. Take time to make sure you have understood the case study and know what the exam question is asking you to do: Read the exam question(s) Then skim read the case study to get the general idea. Highlight or underline key points
Ideally, you should not spend more than 20 minutes on a passage. The Academic passage, Case Study Tourism New Zealand Website reading answers, appeared in an IELTS Test. Try to find the answers to get an idea of the difficulty level of the passages in the actual reading test. If you want more passages to solve, try taking one of our IELTS ...
A CASE STUDY. Within Australia, Australian Hotels Inc (AHI) operates nine hotels and employs over 2000 permanent full-time staff, 300 permanent part-time employees and 100 casual staff. ... Complete the following summary of the last four paragraphs of Reading Passage 36 using ONE OR TWO WORDS from the Reading Passage for each answer.
Explain what you will examine in the case study. Write an overview of the field you're researching. Make a thesis statement and sum up the results of your observation in a maximum of 2 sentences. Background. Provide background information and the most relevant facts. Isolate the issues.
John T. Schiller, a National Institutes of Health researcher and pioneer in the study of cancer-causing viruses, said pathogens known to cause cancer persist in the body long-term.
Timeline. June 5 A new study examining the 2023 bird flu outbreak in South America that killed around 17,400 elephant seal pups and 24,000 sea lions found the disease spread between the animals in ...
READING PASSAGE 1 . Case Study: Tourism New Zealand website. New Zealand is a small country of four million inhabitants, a long-haul flight from all the major tourist-generating markets of the world. Tourism currently makes up 9% of the country's gross domestic product, and is the country's largest export sector.
The rise of social media and smartphones has coincided with an accelerating decline in teenagers' mental health — and researchers are trying to figure out whether the technology is to blame.