

Strategy Studies
Distribution channel marketing strategy – case study (starbucks).
Home > Back
Specialties
Transcript:
What I’m going to share with you in today’s video is one of the most powerful lessons I could ever pass on to you about building a successful business that makes a significant amount of money but please note this video has almost nothing to do with affiliate marketing or selling digital products those are the tools but today I’m going to give you something far more valuable a completely new way to look at your business most people think Starbucks is in the coffee business they’re not coffee is their product but their business is actually distribution and real estate those stores represent Starbucks distribution channel television YouTube Facebook are distribution channels these are the mediums in which marketing messages flow and goods are sold to a participating audience so if Starbucks wants to sell more coffee they must expand their channel by opening more stores without those stores there is no business same with McDonald’s same with Walmart all of these companies have figured out that their real business is their distribution channel through which goods and services are sold we need to remember that as well as it’s the key to building a business that makes four hundred thousand dollars in a week instead of one that only makes four hundred dollars the miracle of building a business in the Internet age is that it allows a single person to build a massive global virtual distribution channel with nothing more than a laptop Cristina a full-time mom with two kids and has spent the past two years writing a few books on parenting tips for new mothers now that her books are done her primary goal has been to sell those books and bring in some revenue most people especially small business owners would agree with that logic you create a product or service and then you focus on selling it but there’s a reason that the average annual revenue for a small business in the US is only forty four thousand dollars and there’s a reason why it is not turned into millions she thinks her business is selling books that’s not her books are a product but a product is never a business here’s what I mean to demonstrate the difference between building a business where the primary focus is on selling books and building a business where the primary focus is on building a distribution channel Cristina could sell her book on amazon.com in the Kindle Store for nine dollars and 95 cents for every sale she makes a 70 percent profit or seven dollars per book in order to make seven thousand dollars per month she would have to find a way to sell 1,000 books per month for 33 books per day she doesn’t get any of her customers information such as their name or email address so her only way to make money is to constantly sell books every single day she might be able to spend some of that seven dollars in profit on advertising but that will decrease her profits down to one dollar or $2 per book if she’s lucky this is not a business and yet it’s what tens of thousands of authors attempt to do each and every day now let’s take another approach instead of focusing on book sales let’s focus on building her distribution channel which in the case is a list of moms who subscribe to her free email newsletter by sending her readers valuable information via email on a regular basis Kristina can build a solid relationship with them she can become known liked and trusted for the value she provides this is called goodwill and goodwill is everything when it comes to the value of your distribution channel because if people know like and trust you they will buy from you on average an email subscriber to Christina’s list will be worth one dollar per month in revenue if she maintains a high level of goodwill if she has a list of 5000 readers she should be able to make around five thousand dollars per month by promoting goods and services that would benefit our readers 20 thousand readers equals twenty thousand dollars per month and so forth over the course of a year that means each subscriber is worth 12 dollars this is possible because people tend to stay in your distribution channel and consume your products and services for as long as you continue to create goodwill so how can we use Christina’s book to build your email list simple if each free email subscriber is worth at least $12 per year and her book customers are only worth $7 total then it makes a heck of a lot more sense to just give away the book for free in exchange for their email address with the addition of a second product that she can offer her new subscribers for $20 to $50 she will be able to afford to actively market her free book on Facebook’s advertising platform and rapidly increase this of her list growth to one hundreds of new subscribers per day within the next 12 months she should have a list of around 100,000 subscribers which should produce around $100,000 per month in revenue any time she creates a new product for comes across someone else that she’d like to recommend she can do so just by sending out a single email but it gets significantly more interesting when you start to focus on turning those free email subscribers into actual customers their value goes from $12 per year to well over $100 to $1,000 so let me walk you through an actual real-world case study the great thing about building a distribution channel that generates revenue rather than a product that generates revenue is that you can leverage the amazing products and services that others have spent the time to create this is typically called affiliate marketing which was pioneered by amazon.com almost 20 years ago basically you can promote someone’s product or service and get paid a commission for every sale if it’s a digital product like an e-book or an online course that commission is typically going to be 50% so if the product costs $50 you’d make a $25 commission when it comes to promoting a product to your list as an affiliate there’s two important rules you need to keep in mind one only promote products that you’ve personally bought and checked out for quality to only promote products because you believe they will provide a real tangible benefit to the people on your list not for money but because you know it will help them achieve their ultimate goal failure to follow these rules will result in the loss of goodwill and could even destroy it completely finally I included a photo with in the email to provide proof that I personally use the product this went a long way in readers minds to solidify the product’s value and credibility anytime you can show photos or a video of your personal use do so it will likely increase your sales by at least 100 to 200 percent you

Get the Strategies
Get the latest posts delivered to your inbox for free.
Ian has marketed for some of the world's best-known brands like Hewlett-Packard, Ryder, Force Factor, and CIT Bank. His content has been downloaded 50,000+ times and viewed by over 90% of the Fortune 500. His marketing has been featured in Forbes, Inc. Magazine, Adweek, Business Insider, Seeking Alpha, Tech Crunch, Y Combinator, and Lifehacker. With over 10 startups under his belt, Ian's been described as a serial entrepreneur— a badge he wears with pride. Ian's a published author and musician and when he's not obsessively testing the next marketing idea, he can be found hanging out with family and friends north of Boston.
Subscribe to Forward Weekly
Related videos, 4 marketing strategy predictions.
Proven Copywriting Formula That Works – The Structure of Persuasive Copy – Dan Lok
How to sell millions without ever opening your mouth copywriting secrets: simple 5-step formula, 5 step formula in copywriting (it’s all psychology), leave a reply.
Get The Marketing Strategies in Your Inbox
Sign up for our 1x a week newsletter (no spam!)
popular videos
- Fundamentals of Marketing Basics (Part 2)
- Best Marketing Strategy Ever! Steve Jobs Think Different / Crazy Ones Speech
- Fundamentals of Marketing Basics (Part 1)
- Top 10 Misleading Marketing Tactics
- Top 10 Marketing Fails: Coke, Ford, Netflix
Get the Guide
You'll learn how to:
- Generate more demand for your product or service
- What channels to start with at first
- Strategies to maximize your lead generation
- And so much more!

Houston, we have a problem... you need to login first!
| | |
Register For This Site
A password will be e-mailed to you.
Get In-Depth Marketing Strategies
Sign up to get in-depth marketing strategies, tactics, and case studies delivered right to your inbox.
100% privacy. We will never spam you!
Copyright @ MarketingStrategy.com 2024. All Right Reserved.
Decoding the Success of Starbucks: A Social Media and Digital Marketing Marketing Case Study
By Aditya Shastri

Introduction
Starbucks Corporation is an American multinational chain of coffeehouses and roastery reserves headquartered in Seattle, Washington. The company operates in over 30,000 locations in 70 countries worldwide as of early 2020.
This blog is an in-depth analysis of Starbucks’ marketing strategies, complete with touching upon their target market, social media strategy, Starbucks’ marketing mix, digital marketing presence, campaigns, and their marketing efforts through the ongoing pandemic.
About the Company
As the world’s largest coffee-house chain, Starbucks is seen to be the main representation of the United States’ second wave of coffee culture. Starbucks coffee houses serve-
- Hot and cold drinks
- Whole-bean coffee
- Microground instant coffee known as VIA
- Caffe lattes
- Full- and loose-leaf teas including Teavana tea products
- Evolution Fresh juices
- Frappuccino beverages
- La Boulange pastries
- Snacks including items such as chips and crackers
- And also some offerings which are seasonal or specific to the locality of the store.
In 2010, the company began its Starbucks Reserve program for single-origin coffees and high-end coffee shops. It planned to open 1,000 Reserve coffee shops by the end of 2017. Starbucks operates six roasteries with tasting rooms and 43 coffee bars.

Let us now get to know how Starbucks made a mark for itself in the Indian market.
Starbucks In India
In the 2010s, Starbucks was keen on entering the Indian market. The company wanted to capitalize on the rise of coffee culture by targeting the niche upper-class segment in India. In 2007, it announced its entry in India but withdrew without any explanation. It was in 2011 that Starbucks finally made a grand entry into the market.
When the world’s biggest bistro chain wanted to enter the Indian market, they entered into a 50-50 joint venture with Asia’s largest coffee grower, Tata Consumer Products Limited.
After successfully launching their brand, the next important step in ensuring they were here to stay, was to nail their target audience.
Starbucks Target Market
Starbucks is a premium coffee brand; its customers are mainly from the upper economic segment or the upper middle class and upper class. The brand targets people who want a peaceful space to drink coffee and lose stress. These are mostly the higher wage-earning professionals, business owners, or other higher-end customers in the 22-50 age group. People with a fast-moving lifestyle want good quality coffee and some space to relax after a hectic day. Starbucks offers all these privileges in a single place. The target audience of Starbucks includes both male and female customers, and a large bunch of these customers are mainly in the 25-45 age group. Mainly the urban, health-conscious, and class-conscious consumers. The truth is, the company has done so well by knowing exactly who its target audience is at any point in time and going all-out to cater to those set of people.
So summed up, their target audience is-
- High-income spenders
- Urban-ish, on the go
- Technology early adopters
- Health-conscious professionals
- Flexible to change
- Reaching Beyond the storefront
Now that we understand their foundation and business, let’s finally begin to uncover the marketing strategies that have led to Starbucks becoming the giant it is today.
Marketing Strategies of Starbucks
Initially, Starbucks’ marketing mix in India was segmenting consumer markets on a socio-economic basis. Concentrating on working professionals and their need for a soothing workspace. Starbucks also segments its market on a geographic and demographic basis by setting up the stores where they can find their target audience mentioned above. Most companies enter a new market by focusing on a single segment, and if they happen to achieve some success, branch out into more segments. Starbucks did the same and now caters to teenagers and young adults as well, by developing its product range and social media marketing presence.
Starbucks’ marketing mix has helped the brand develop a unique market position for its products, where it’s about the brand’s overall differentiated experience. They have positioned themselves as a highly reputed brand. The company’s marketing mix, to target the modern, tech-savvy generation, has also grown the use of digital technology as well as social media for promotions and customer engagement.
Digital Expansion
One of Starbucks’ key priorities is to expand its digital interactions with customers. To do so, it is implementing new ways to attract digitally registered customers beyond the rewards program. For example, the coffee chain is offering mobile order services and leveraging Wi-Fi sign-ins at its brick-and-mortar stores.
Starbucks Social Media Strategy
Most people are familiar with Starbucks on social media. The company’s many social media accounts are known for their distinctive branding, interactive posts, and visually pleasing content. The diverse range of content includes recipes, photography, articles and features. But there’s more than meets the eye. The stream of content can be broken down into a series of campaigns geared at creating a greater sense of brand awareness and community.
Starbucks Product-based Marketing Campaigns
Starbucks focuses on promoting unique and fan-favorite beverages. The brand knows how popular their flagship items are, but more importantly, they know their audience craves this kind of content. They’ve even created social accounts for customers’ favourites -Pumpkin Spiced Latte and Frappuccino- where they push relevant and relatable memes to their die-hard audience. This is also where user-generated content (UGC) comes in. Consumer images of the more Instagrammable products, such as the Unicorn Frappuccino, are often selected to be re-shared via the official channels and also used in influencer campaigns.
Starbucks Corporate Social Responsibility-based campaign
Starbucks uses social change as a marketing tool, positioning itself as open-minded and inclusive. One example is the #ExtraShotOfPride campaign that supports the LGBT+ community.
Community-based campaigns
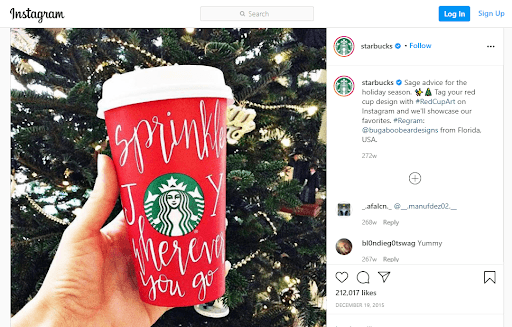
Another facet of Starbucks’ digital strategy is its emphasis on highlighting individuals and communities. Take a look at the #RedCupArt campaign, which not only increases engagement but also provides them with a library of UGC content. They use storytelling to show acts of courage and kindness in American communities, localizing the content. Starbucks puts in conscious efforts to humanize the company by sharing stories on their account which highlights the employees who play an essential role especially when consumers are distrustful of big brands. This sense of community also makes online coffee content social, very similar to how they practically invented the modern coffeehouse culture back in the day.
Festive Marketing
Starbucks has also initiated a new seasonal whole-bean coffee, #StarbucksDiwaliBlend, for their consumers across the country and select global markets. The latest exquisite blend is hand-picked and sourced from Tata Estates in Karnataka and Tamil Nadu. Starbucks Diwali Blend is intended as a tribute to the region’s rich and cultural coffee heritage and expertise.

Starbucks Digital Marketing Presence
Starbucks knows its audience is technologically advanced, which makes it imperative for them to have a strong digital marketing strategy. It’s clear how Starbucks prefers marketing on platforms where they have two-way communication instead of platforms like print and television which is more of one-way communication.
- Instagram – 248K+ followers
- Facebook – 1.1M+ likes
- Twitter – 161K+ followers
- Starbucks posts daily on its social media handles and comes up with challenges and games to engage its customers and increase its fan base
- The posts and engagement are consistent through all platforms and believe in creating an experience as compared to just a promotion channel
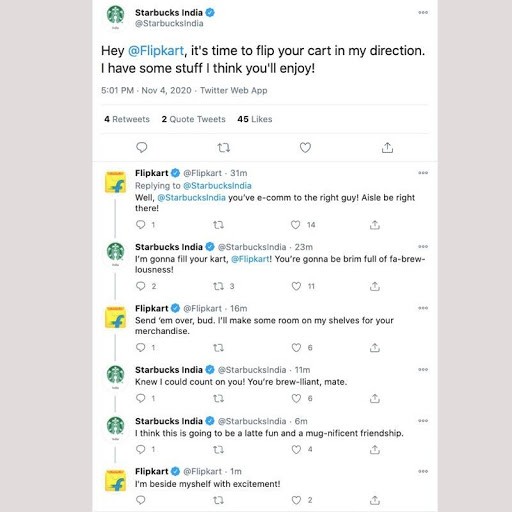
The recent Flipkart Starbucks twitter battle was an example of how active and fun a brand like Starbucks is and shows exactly why the brand is sought after with its target audience, especially the millennials. Outside of campaigns, they show numerous images on their platforms of friends and family enjoying drinks of Starbucks coffee together, interspersed with high-quality content that promotes seasonal products. By doing this, Starbucks has integrated itself into consumers’ social life.
Marketing During Covid-19
We are all aware of how suddenly the Covid-19 pandemic took over the world. All businesses, globally, were hit overnight. And had to figure out how to sustain themselves in these unprecedented times. The pandemic definitely impacted the Indian market heavily but Starbucks constantly improvised to mitigate the economic impact. A case study in itself, these were the steps taken by the coffee giant during the pandemic which proves why it’s the most valued –
CEO Navin Gurnaney announced that they are launching drive-thrus to encourage people to engage with them, and home delivery to make sure they are connected with their customers during the pandemic. The first drive-thru was at Ambala Chandigarh Expressway in Zirakpur. They have also launched their app – Starbucks India App so that customers can easily navigate and purchase their offerings.
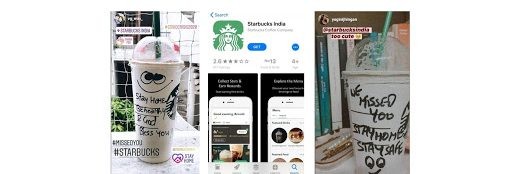
Starbucks Social Media Campaigns.
#reconnectwithstarbucks campaign.
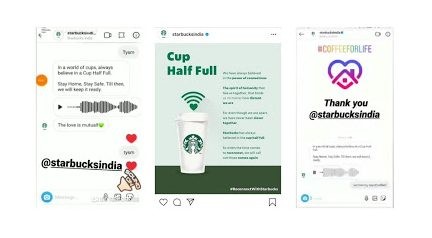
Starbucks launched its social media campaign in 2 phases. The first phase was where they asked their customers to share their ways of reconnecting amidst the pandemic and share their favourite Starbucks memory on their personal Instagram handles with the hashtag #ReconnectWithStarbucks.
In the second phase- “Half Cup Full”- they asked their customers to comment on their favourite beverage on the post. They then sent these customers voice notes of baristas hollering the customers’ names along with their favourite beverage to remind them of the famous in-store experience.
This was a great campaign as it not only reminded the people of all the good memories with Starbucks but also made them feel important and valued.
#StarbucksAtHome and #StarbucksDance
Starbucks launched 1 litre of freshly brewed beverages that could be bought via take-away or ordering through Swiggy and Zomato. 7 flavours were launched at the price of Rs.550 per bottle.
To promote the same, Starbucks launched the #StarbucksDance challenge where it asked its customers to shoot a dance video with the drink and upload them on their personal stories. They promised a year of free Starbucks for the winner.
Strategic Alliances to enhance the experience and reach
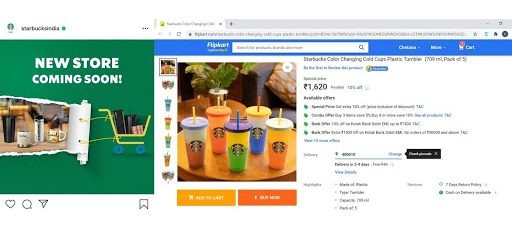
Signature merchandise launch with flipkart.
The pandemic caused a great shift in how people shop and also encouraged people to shop for home-grown products as compared to imported or foreign-based products. Starbucks used this shift to partner with Flipkart, to launch Starbucks Signature Merchandise on the online platform. The product range included custom mugs, tumblers, cold cups, and more. Customers can also soon order coffee brewing equipment from the comfort of their own homes. Starbucks operated in 12 cities only and hence, this was a strategic move to reach out to customers pan India at their homes during the pandemic while taking advantage of the growing dependence on E-Commerce
Standup Comedy Festival
Starbucks recently announced the #StarbucksComedyFestival where few lucky customers can win a free invitation to the comedy festival. The lucky codes would be present on the customer’s invoice. With a popular line-up of hosts like Sapan Verma, Azeem Banatwalla and Rahul Subramanian, customers will now be enthusiastic to shop more at Starbucks and stand a chance to win the invitation.
In conclusion, Starbucks is leading the market because of its dominating global presence and leadership. A consumer’s experience at a Starbucks location is arguably different from any other coffee shop because of its intimate atmosphere, welcoming environment, and unmatched service. Their inviting “ideal coffee shop ambience” should prove to be a sustainable competitive advantage. Starbucks’ implemented strategy of retail locations and on-site partnerships have received greater response rates, giving them the leading seat within the mature industry. Starbucks, thus, has a strong market position through its all-inclusive marketing strategy.
If you liked our analysis of Starbucks’ marketing strategy, be sure to check out the series of case studies on various other companies’ strategies written by our students. IIDE makes its students capable to analyse and curate such campaigns and studies. If you would like to gain these skills yourself, IIDE offers various digital marketing courses for people just like you. Start your journey in upskilling yourself today!
Thank you for reading!
Aditya Shastri
Lead Trainer & Head of Learning & Development at IIDE
Leads the Learning & Development segment at IIDE. He is a Content Marketing Expert and has trained 6000+ students and working professionals on various topics of Digital Marketing. He has been a guest speaker at prominent colleges in India including IIMs...... [Read full bio]
Clicking on the image of the Starbucks cup is my thing too. This blog provides great and deep insights into their strategy.
Starbucks marketing strategy brewed! served! and I’m here for it!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Related Posts

Marketing Mix Of Uniqlo with Updated Company Overview and Explanations
by Aditya Shastri | May 15, 2024
Uniqlo is a Japanese clothing brand known for its high-quality essential pieces formed from the...

In-depth Marketing Strategy of Bata India – India’s Largest Footwear Company
In this article, we will learn about the marketing strategy of Bata India, the largest footwear...

Airtel: Case Study on its Business Model and Marketing Strategy
Bharti Airtel is one of the three telecom giants of India, known for its distinct and engaging...
" * " indicates required fields
I’m Interested in This Masterclass
By providing your contact details, you agree to our Terms of Use & Privacy Policy
Marketing & Branding
- 17 Feb 2020
Starbucks’ Marketing Strategy: What Your Company Can Learn
Effy Pafitis

This article is part of our ‘Marketing Strategies’ series, an in-depth look at how some of the world’s most successful companies promote their brand and their products.
While a competitive marketing strategy can significantly support the growth of any new company, it can be difficult for entrepreneurs to carve a unique identity for their brand in a crowded marketplace. Fortunately, many businesses offer examples of successful marketing strategies that have helped them excel in this area.
One such organisation is the US coffee giant, Starbucks. The business has leveraged a unique marketing approach to become an iconic brand, renowned for its premium coffee products and excellent customer experience. Indeed, as of February 2020, its strategy has helped the company open nearly 30,000 stores in over 70 countries worldwide, with an impressive 39.8% share of the coffee market in 2019 in the US alone.
To explore how Starbucks has achieved this, we've taken a closer look at their promotion strategy, as well as what you can do to implement these lessons in your own marketing plan .
Starbucks' Marketing Strategy
Founded in Seattle in 1971, Starbucks – one of the first US coffee house franchises at that time – quickly became known for the superior quality of its freshly-roasted, whole bean coffee. Since its establishment, the organisation has focused on a brand-centric marketing strategy, working to build and maintain a distinct identity around its optimal customer service, comfortable in-store environment, and sustainable coffee.
Starbucks continues to achieve this key marketing objective by championing social media marketing and consistently delivering digital campaigns that engage existing and new consumers; indeed, these campaigns frequently utilise user-generated content, transforming buyers into brand ambassadors.
Unique among its main competitors, Starbucks does not invest significantly in offline marketing ; its non-digital promotional communication is predominantly limited to television and print advertisements. Instead, the brand places greater value in bolstering in-store features that lend themselves to positive customer experience and satisfaction – a strategy that is clearly succeeding, with reporting revenues of $26.5bn in 2019.
Customer Profile
In line with Starbucks' market positioning as a premium coffee brand, the company's demographic is typically defined as relatively high-income individuals, primarily between the ages of 25 and 54. They are educated, on-the-go, young professionals and white-collar workers who are willing to pay a premium for handcrafted coffee. Their preferences include personalised in-store interactions and purchasing options that increase buyer convenience.
Starbucks' digital marketing activities and investments support its continued market research, providing valuable customer demographic insights. Online campaign engagements, Starbucks mobile app use and buyer competition entries allow the organisation to consistently evaluate the age, location, income and predilections of its customers.
As mentioned, Starbucks prioritises its online marketing and advertising delivery, raising awareness around its products, promotions, campaigns, social impact principles, merchandise and more. In the fiscal year ending September 2019, the company utilised a global budget of around $246m to this end; here are some of the ways in which that money was spent:
Social Media Marketing
Starbucks uses social media marketing to drive its promotion strategy to consumers. Key platforms utilised throughout include Facebook , Twitter, Instagram and YouTube. In addition to organically posting content, the coffee company invests in paid social media campaigns, using its wealth of demographic data to target particular consumer groups and new audiences.
All creative content prominently displays the now-iconic Starbucks logo , a key driver of its brand recognition and brand equity, and a symbol of its premium status.
The brand also leverages this digital activity to conduct conversations with consumers, fostering closer brand-buyer relationships and contributing to successful consumer retention rates.
Consumer Advocacy
Starbucks cleverly capitalises on user-generated content in its social media marketing practices, influencing impactful consumer advocacy.
Indeed, consumers are encouraged to post photos and videos of their beverages, merchandise and experiences with the brand online. Starbucks then shares this content on its official social media pages, as well as incorporating selected consumer material in their wider marketing campaigns. Consumers whose content is utilised can feel more included in – and valued by – the company, making them more likely to make further purchasing decisions, as well as publish more Starbucks-related content in the future.
User-created content is 2.4 times more likely to be perceived by audiences as authentic, compared to content created directly by a brand. This then creates further trust between the company and potential consumers, encouraging higher sales.
In-Store Marketing

To make its store locations more appealing, welcoming, and functional, Starbucks invests in a variety of in-store marketing efforts.
For instance, the brand began to offer free WiFi in all its stores in 2002, influencing consumers to stay for longer periods after their purchases, and fulfilling buyer preferences for continued connectivity.
Advertising messaging placed inside stores promote new products and loyalty scheme advantages to buyers, too, aiming to drive deeper awareness and generate further demand among existing consumers and, therefore, supporting the brand's customer retention aspirations.
Starbucks also uses the data available from its store locations to fulfil market research objectives , collecting and analysing details around customer sales, preferences and behaviour.
Competitions
Another promotional tool used online and in-store is competitions and sweepstakes. These contests typically encourage consumers to photograph and share content online relating to new store features, campaign banners, seasonal releases and the like.
This is a clever way to boost the online discussion around the brand, drive knowledge of new products, and increase traffic to Starbucks' website and social media pages. By using a dedicated hashtag to track competition entries, digital engagement becomes easier to analyse, clearly depicting how successful each sweepstake was in achieving its particular objective.
Loyalty Programmes and Mobile App Marketing
According to longstanding convention – namely, the 2001 research of Fred Reichheld of management consultancy, Bain & Company – acquiring a new customer can cost anywhere as much as five to 25 times more than retaining an existing one. This is something that Starbucks recognises, investing heavily in its loyalty programme and mobile app to facilitate customer retention.
The company released the first version of its loyalty programme in 2008 – now called Starbucks Rewards – quickly followed by the launch of its dedicated mobile application in 2009. The app's objective was to optimise consumers' end-to-end experience with the brand and allow Starbucks Rewards members to track their loyalty points and gifts easily.
Customers are encouraged to participate in the brand's loyalty scheme and download the app to be eligible for exclusive offers, order discounts, birthday gifts, and complimentary beverages.
Mobile notifications issued from the app also keep loyal users informed of any new announcements, product launches or upcoming rewards.
Finally, the addition of in-app ordering and payment options has increased the in-store convenience experienced by users, addressing modern buyers' demand for efficient service.
With high levels of personalisation supporting its marketing segmentation, Starbucks' mobile app facilitates customer loyalty and differentiation among competitors. The success of the app is evidence of this, boasting 23.4m users in the US alone.
Starbucks' brand-centric marketing approach is executed across various communication channels, predominantly online. Campaigns are consistent in their content type and deployment, always working to maintain the coffee company's premium status, conveying its ethical sourcing principles, promoting its beverages, and influencing loyalty among existing customers.
This focus on maintaining its superior image – while boosting customer experience and satisfaction – has undoubtedly contributed to the steady increase of Starbucks' brand value, which was calculated at around $32.4bn globally in 2018.
Despite selling coffee-related merchandise in all store locations, the company's revenue-by-product-type indicates that its core product leads the way, with global 2019 revenues for beverages totalling around $15.9bn . This is something not lost on the company, reflected in the content focus of its primary marketing campaigns.
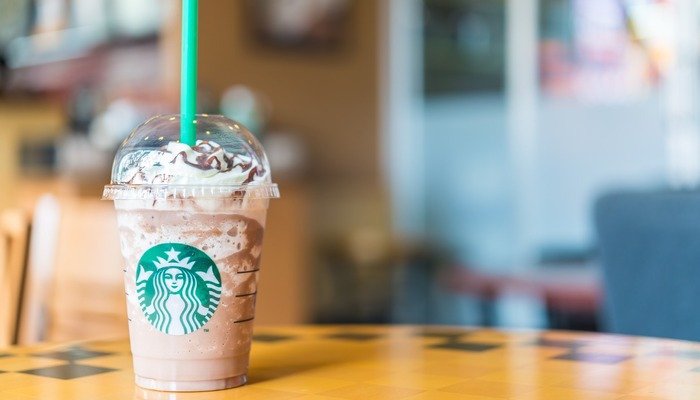
Key Campaign
The 2017 Starbucks Unicorn Frappuccino product campaign is an excellent example of this, also demonstrating the global coverage that Starbucks' digital campaigns garner.
For just four days in April 2017, Starbucks launched an innovative digital campaign around a new, limited-edition beverage created predominantly to drive buzz online. Named the Unicorn Frappuccino , the brightly coloured drink was designed to be both sweet and sour, changing colour from pink to purple once stirred.

Rather than following the traditional digital marketing delivery route of releasing promoted banner ads online or generating awareness through its app, the company leaked attractive images of the product to social news site Reddit before its official release; immediately, this created high levels of consumer anticipation around the product. Except for light promotion through its social media channels, the company then let the media and its buyers do the rest of the work, taking advantage of the free advertising from both of these sources.
Indeed, the new beverage led to over 150,000 consumer posts displaying the hashtag #UnicornFrappuccino on Instagram, even though the drink was only available for purchase in the US, Canada and Mexico. The worldwide exposure, focusing on the aesthetically pleasing nature of the product as well as its scarcity, led to an increase in in-store footfall with consumers scrambling to get their hands on the Frappuccino before it became unavailable.
This higher footfall and sales during the period of April 19th to the 23rd allowed the company to secure new consumers, as well as recapture lost buyers, by reinforcing the brand's market positioning.
The campaign took advantage of the consumer trend of sharing photos of food and drink online, too, something that Starbucks spokespersons confirmed publicly. Indeed, entrepreneurs can take inspiration from this campaign, in particular, and understand that there is real value in making products visually exciting, as well as leveraging digital awareness generated by buyers and spectators alike.
Although the company can often find itself at the centre of PR disputes , Starbucks follows an exemplary marketing plan, tailored specifically to the identity and objectives of the brand. Its compelling strategy indicates how businesses can rely on consistency to maintain strong brand equity and build impressive brand value.
Indeed, rather than limiting the impact of this approach, its steady execution has made the brand renowned for particular principles and levels of quality, allowing existing and new consumers to have an accurate expectation of their in-store experiences both before and after their purchases. As a business owner, you can learn from this; evaluate the digital focus of your brand, and take inspiration from the incredible value of the awareness and demand that can be driven almost exclusively online.
In the meantime, if you still want to learn more about how the world's biggest brands sell their products and engage with audiences, then why not take a look at our breakdown of Red Bull's marketing strategy , too?
What do you think of Starbucks' marketing strategy, and what else can entrepreneurs learn from it? Let us know your thoughts and opinions in the comments below.
Marketing Strategies
Social Media
Case Studies
Food and Drink
Loyalty Marketing
Starbucks Marketing Strategy Unveiled | A Case Study
Jane Ng • 31 October, 2023 • 7 min read
Are you curious about Starbucks marketing strategy? This global coffeehouse chain has transformed the way we consume coffee, with a marketing approach that’s nothing short of genius. In this article, we’ll dive deep into Starbucks marketing strategy, exploring its core elements, the 4 Ps of Starbucks’ Marketing Mix, and its success stories.
Table Of Contents
What is starbucks marketing strategy, key components of starbucks marketing strategy, the 4 ps of starbucks’ marketing mix, starbucks marketing success stories, key takeaways, faqs about starbucks marketing strategy.

Starbucks marketing strategy is all about creating exceptional experiences for its customers. They do this by:
Starbucks’ Core Business Level Strategy
Starbucks is unique in the coffee world because it doesn’t just compete on price. Instead, it stands out by making special and high-quality products. They always aim for something new and innovative, which makes them different from others.
Starbucks Global Expansion Strategy
As Starbucks grows all over the world, it doesn’t use a one-size-fits-all approach. In places like India, China, or Vietnam, they change things up to suit what people there like while keeping the Starbucks style.
1/ Uniqueness and Product Innovation
Starbucks focuses on offering unique products and constant innovation.
- Example: Starbucks’ seasonal drinks like the Pumpkin Spice Latte and the Unicorn Frappuccino are excellent illustrations of product innovation. These limited-time offerings generate excitement and draw in customers seeking something different.

2/ Global Localization
Starbucks adapts its offerings to cater to local tastes while maintaining its core brand identity.
- Example: In China, Starbucks introduced a range of tea-based beverages and mooncakes for the Mid-Autumn Festival , respecting local traditions while keeping the Starbucks experience intact.
3/ Digital Engagement
Starbucks embraces digital channels to enhance customer experiences.
- Example: The Starbucks mobile app is a prime example of digital engagement. Customers can order and pay through the app, earning rewards and receiving personalized offers, simplifying and enriching their visits.
4/ Personalization and the “Name-on-Cup” Strategy

Starbucks connects with customers on a personal level through the famous “ name-on-cup ” approach.
- Example : When Starbucks baristas misspell customers’ names or write messages on cups, it often results in customers sharing their unique cups on social media. This user-generated content showcases personal connections and serves as free, authentic promotion for the brand.
5/ Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing
Starbucks promotes ethical sourcing and sustainability.
- Example: Starbucks’ commitment to buying coffee beans from ethical and sustainable sources is evident through initiatives like C.A.F.E. Practices (Coffee and Farmer Equity) . This reinforces the brand’s commitment to environmental and social responsibility, attracting customers who value sustainability.
Product Strategy
Starbucks offers an array of products, not just coffee. From specialty beverages to snacks, including specialty beverages (e.g., Caramel Macchiato, Flat White), pastries, sandwiches, and even branded merchandise (mugs, tumblers, and coffee beans). Starbucks caters to a wide range of customer preferences. The company continually innovates and customizes its product offerings to maintain a competitive edge.
Price Strategy
Starbucks positions itself as a premium coffee brand. Their pricing strategy reflects this position, charging higher prices compared to many competitors. However, they also offer value through their loyalty program, which rewards customers with free drinks and discounts, promoting customer retention and attracting price-conscious consumers.
Place (Distribution) Strategy
Starbucks’ global network of coffee shops and partnerships with supermarkets and businesses ensures the brand is accessible and convenient for customers. It’s not just a coffee shop; it’s a lifestyle choice.

Promotion Strategy
Starbucks excels in promotion through various methods, including seasonal advertising campaigns, social media engagement, and limited-time offerings. Their holiday promotions, such as the “ Red Cup ” campaign, create anticipation and excitement among customers, increasing footfall and sales.
1/ The Starbucks Mobile App
Starbucks’ mobile app has been a game-changer in the coffee industry. This app seamlessly integrates into the customer experience, allowing users to place orders, make payments, and earn rewards all within a few taps. The convenience offered by the app keeps customers engaged and encourages repeat visits.
Additionally, the app is a data goldmine, providing Starbucks with insights into customer preferences and behaviors, enabling more personalized marketing.
2/ Seasonal and Limited-Time Offerings
Starbucks has mastered the art of creating anticipation and excitement with its seasonal and limited-time offerings. Examples like the Pumpkin Spice Latte (PSL) and the Unicorn Frappuccino have become cultural phenomena. The launch of these unique, time-limited drinks creates a buzz that extends beyond coffee enthusiasts to a broader audience.
Customers eagerly await the return of these offerings, turning seasonal marketing into a potent force for customer retention and acquisition.
3/ My Starbucks Rewards
Starbucks’ My Starbucks Rewards program is a model of loyalty program success. It puts the customer at the center of the Starbucks experience. It offers a tiered system where customers can earn stars for each purchase. These stars translate into various rewards, from free drinks to personalized offers, creating a sense of value for regular patrons. It boosts customer retention, elevates sales, and cultivates brand loyalty.
In addition, it enhances the emotional connection between the brand and its customers. Through personalized offers and birthday rewards, Starbucks makes its customers feel valued and appreciated. This emotional bond encourages not only repeat business but also positive word-of-mouth marketing.
Starbucks marketing strategy is a testament to the power of creating memorable customer experiences. By emphasizing uniqueness, sustainability, personalization, and embracing digital innovations, Starbucks has solidified its position as a global brand that extends far beyond coffee.
To enhance your own business’s marketing strategy, consider incorporating AhaSlides. AhaSlides offers interactive features that can engage and connect with your audience in novel ways. By harnessing the power of AhaSlides, you can gather valuable insights, personalize your marketing efforts, and cultivate stronger customer loyalty.
What is the marketing strategy of Starbucks?
Starbucks’ marketing strategy is built on delivering unique customer experiences, embracing digital innovation, ensuring product quality, and promoting sustainability.
What is Starbucks most successful marketing strategy?
Starbucks’ most successful marketing strategy is personalization through its “name-on-cup” approach, engaging customers and creating social media buzz.
What are the 4 P’s of marketing Starbucks?
Starbucks’ marketing mix consists of Product (diverse offerings beyond coffee), Price (premium pricing with loyalty programs), Place (global network of stores and partnerships), and Promotion (creative campaigns and seasonal offerings).
References: CoSchedule | IIMSkills | Mageplaza | MarketingStrategy.com

A writer who wants to create practical and valuable content for the audience
Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides


Starbucks business model & supply chain analysis
Starbucks is the premier roaster, marketer, and retailer of specialty coffee in the world, operating in 83 markets. Starbucks purchases and roasts high-quality coffees, handcrafted coffee, tea, and other beverages, and a variety of high-quality food items through company-operated stores.
Starbucks also sells a variety of coffee and tea products and licenses its trademarks through other channels, such as licensed stores, as well as grocery and food service through its Global Coffee Alliance with Nestlé S.A. (“Nestlé”). In addition to its flagship Starbucks Coffee brand, Starbucks sells goods and services under the following brands: Teavana, Seattle’s Best Coffee, Ethos, Starbucks Reserve, and Princi.
Starbucks’ primary objective is to maintain Starbucks standing as one of the world’s most recognized and respected brands. Starbucks invests in its brand and operations to achieve long-term targeted revenue and income growth. This includes expanding its global store base, adding stores in both existing, developed markets such as the U.S. and in higher growth markets such as China, and optimizing the mix of company-operated and licensed stores around the world.
By leveraging experiences gained, Starbucks continues to drive beverage, equipment, process, and technology innovation, including in its digital platform. Starbucks regularly offers consumers new, innovative coffee and other products in a variety of forms across new categories, diverse channels, and alternative store formats.
In this strategy story, we decided to decipher the business model and supply chain of Starbucks.
Business Model of Starbucks
Starbucks generated $32.25 billion in revenues in FY22 . The business model of Starbucks consists of company-operated stores and licensed stores. As of FY22, Starbucks had 35,711 stores, comprising 18,253 company-operated stores (51%) and 17,458 licensed stores (49%).
The mix of company-operated versus licensed stores in a given market generally varies based on several factors, including its ability to access desirable local retail space, the complexity, profitability, and expected ultimate size of the market for Starbucks, and its ability to leverage the support infrastructure within a geographic region.
Total net revenues increased $3.2 billion, or 11%, over fiscal 2021, primarily due to higher revenues from company-operated stores ($2.0 billion).
- The growth in company-operated store revenue was driven by an 8% increase in comparable store sales ($1.8 billion), attributed to a 5% increase in average tickets and a 2% increase in similar transactions.
- Licensed stores’ revenue increased by $972 million, primarily driven by higher product and equipment sales and royalty revenues from its licensees.
- Other revenues increased by $249 million, primarily due to higher product sales and royalty revenue in the Global Coffee Alliance and growth in its ready-to-drink business.
Company-operated Stores
Revenue from company-operated stores accounted for 82% of total net revenues during FY22. Starbucks’ retail objective is to be the leading retailer and brand of coffee and tea in each of Starbucks’ target markets by selling the finest quality coffee, tea, and related products, as well as complementary food offerings, and by providing each customer with a unique Starbucks Experience.
The Starbucks Experience is built upon superior customer service, convenience, and a seamless digital experience, as well as safe, clean and well-maintained stores that reflect the personalities of the communities in which they operate, thereby building a high degree of customer loyalty.
Starbucks company-operated stores are typically located in high-traffic, high-visibility locations. Starbucks’ ability to vary the size and format of its stores allows it to locate them in or near various settings, including downtown and suburban retail centers, office buildings, university campuses, and rural and off-highway locations.
Starbucks has plans to increase the efficiency of its business model while elevating the partner and customer experience (the “Reinvention Plan”). Starbucks believes investing in partner wages and training will increase retention and productivity. At the same time, the acceleration of purpose-built store concepts and technological innovations will provide additional convenience and connection with customers.
Today at Investor Day, Starbucks is unveiling their "Reinvention Plan" for the company. Since workers aren't invited to Investor Day, we wanted to share our own vision for the future of Starbucks. pic.twitter.com/fw2bREozkX — Starbucks Workers United (@SBWorkersUnited) September 13, 2022
Starbucks strongly focuses on increasing digital adoption to provide convenience and elevate the customer experience. These strategies align closely with rapidly evolving customer preferences, including higher levels of mobile ordering, more contactless pick-up experiences, and reduced in-store congestion, all of which naturally allow for greater physical distancing.
Starbucks Marketing Mix (4Ps)
Stored Value Cards and Loyalty Program: The Starbucks Card, Starbucks’ branded stored value card program, is designed to provide customers with a convenient payment method, support gifting, and increase the frequency of store visits by cardholders, in part through the related Starbucks Rewards loyalty program where available.
How does Starbucks’ unique promotion strategy aid in its massive success?
Licensed Stores
Revenues from licensed stores accounted for 11% of Starbucks’ net revenues in fiscal 2022. Licensed stores generally have a lower gross margin and a higher operating margin than company-operated stores. Under the licensed business model, Starbucks receives a margin on branded products and supplies sold to the licensed store operator and a royalty on retail sales.
Licensees are responsible for operating costs and capital investments, which more than offset the lower revenues Starbucks receives under the licensed store model. In its licensed store operations, Starbucks seeks to leverage the expertise of its local partners and share its operating and store development experience. Licensees provide improved and, at times, only access to desirable retail space. Most licensees are prominent retailers with the in-depth market knowledge and access.
As part of these arrangements, Starbucks sells coffee, tea, food, and related products to licensees for resale to customers and receives royalties and license fees from the licensees. Starbucks also sells certain equipment, such as coffee brewers and espresso machines, to its licensees for use in their operations.
| Company-operated stores | 26,576.1 | 24,607.0 | 19,164.6 |
| Licensed stores | 3,655.5 | 2,683.6 | 2,327.1 |
| Other | 2,018.7 | 1,770.0 | 2,026.3 |
| Beverage | 19,553.3 | 18,317.0 | 14,337.5 |
| Food | 5,804.2 | 5,053.4 | 3,799.2 |
| Other | 6,890.8 | 5,690.2 | 5,381.3 |
Other Revenues
Other revenues primarily include sales of packaged coffee, tea, and ready-to-drink beverages to customers outside of its company-operated and licensed stores, as well as royalties received from Nestlé under the Global Coffee Alliance and other collaborative partnerships. Others accounted for 7% of Starbucks’ revenue in FY22.
Supply Chain of Starbucks
Starbucks is committed to selling the finest whole bean coffees and coffee beverages. To help ensure compliance with its rigorous coffee standards, Starbucks substantially controls all coffee purchasing, roasting, and packaging and the global distribution of coffee used in its operations, as part of its supply chain strategy.
Nestlé controls the distribution of certain finished goods through the Global Coffee Alliance. Starbucks purchases green coffee beans from multiple coffee-producing regions around the world and custom roasts them to its exacting standards for many blends and single-origin coffees.
Starbucks SWOT Analysis
The price of coffee is subject to significant volatility. Both the premium and the commodity price depend upon the supply and demand at the time of purchase. Supply and price can be affected by multiple factors in the producing countries, including
- water supply quality and availability throughout the coffee production chain,
- natural disasters,
- crop disease, and pests,
- a general increase in farm inputs and costs of production,
- inventory levels, and political and economic conditions.
Depending on market conditions, Starbucks buys coffee using fixed-price and price-to-be-fixed purchase commitments to secure an adequate supply of quality green coffee.
Starbucks prices products on value not cost. Why?
Starbucks depends upon its relationships with coffee producers, outside trading companies, and exporters for the supply of green coffee. To secure the supply chain of high-quality green coffee, Starbucks operates ten farmer support centers.
Farmer support centers are staffed with agronomists and sustainability experts working with coffee farming communities to promote best practices in coffee production designed to improve coffee quality and yields and agronomy support to address climate change and other impacts.
In addition to coffee, Starbucks also purchases significant amounts of dairy and plant-based dairy-free alternative products, particularly fluid milk, oat milk, and almond milk, to support the needs of its company-operated stores.
Starbucks PESTEL Analysis
Products other than whole bean coffees and coffee beverages sold in Starbucks stores include tea and many ready-to-drink beverages purchased from several specialty suppliers, usually under long-term supply contracts. Food products, such as pastries, breakfast sandwiches, and lunch items, are purchased from national, regional, and local sources.
Starbucks also purchases a broad range of paper and plastic products, such as cups and cutlery, from several companies to support the needs of its retail stores and manufacturing and distribution operations. Starbucks is also expanding its use of reusable packaging to reduce landfill waste.

A passionate writer and a business enthusiast having 6 years of industry experience in a variety of industries and functions. I just love telling stories and share my learning. Connect with me on LinkedIn. Let's chat...
Related Posts

How does Instacart work and make money: Business Model

What does Zscaler do | How does Zscaler work | Business Model

What does Chegg do | How does Chegg work | Business Model

What does Bill.com do | How does Bill.com work | Business Model

What does Cricut do | How does Cricut work | Business Model

What does DexCom do? How does DexCom business work?

What does CarMax do? How does CarMax business work?

What does Paycom do? How does Paycom work?
What does FedEx do | How does FedEx work | Business Model

How does Rumble work and make money: Business Model

Dollar General Business Model & Supply Chain Explained

What does C3 AI do | Business Model Explained

What does Aflac do| How does Aflac work| Business Model

How does Booking.com work and make money: Business Model

What does Okta do | How does Okta work | Business Model

What does Alteryx do | How does Alteryx work | Business Model
Write a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Advanced Strategies
- Brand Marketing
- Digital Marketing
- Luxury Business
- Startup Strategies
- 1 Minute Strategy Stories
- Business Or Revenue Model
- Forward Thinking Strategies
- Infographics
- Publish & Promote Your Article
- Write Article
- Testimonials
- TSS Programs
- Fight Against Covid
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and condition
- Refund/Cancellation Policy
- Master Sessions
- Live Courses
- Playbook & Guides
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
Starbucks Marketing Strategy: How Starbucks became the market leader by 'inspiring and nurturing the human spirit'
Learn about starbucks' iconic marketing strategy and advertising campaigns. read how starbucks aces the 4ps of marketing mix - product, price, promotion & placement..
- overview#goto" data-overview-topic-param="history">Brief history
- overview#goto" data-overview-topic-param="believe">What does Starbucks believe in?
- overview#goto" data-overview-topic-param="giant">A global coffee giant
- overview#goto" data-overview-topic-param="strategy">Starbucks' Marketing Strategy
- overview#goto" data-overview-topic-param="iconic">Iconic Marketing Campaigns
- overview#goto" data-overview-topic-param="regular">Thinking beyond regular coffee
- overview#goto" data-overview-topic-param="key">Key Takeaways

If you were to think of coffee, wouldn’t the classic siren logo printed Starbucks cup be the first thing to pop up in your mind? Starbucks is one of the world’s most popular and successful premium coffee brands. It is known for its premium coffee, which is made with fresh ingredients roasted in the Starbucks store every day.
Starbucks is an American multinational coffeehouse chain founded in 1985 and operates in around 80 markets! Starbucks has a whopping 36.7% market share in the United States alone.
You’d likely have a lot of questions now: how did Starbucks coffee manage to become so big? What makes them different from all other mass-market brands?
And most importantly, why is Starbucks the best at what they do? In this case study, we will dive into various aspects of Starbucks' marketing strategy.
A brief history of Starbucks
Starbucks was founded by three men — Jerry Baldwin, Zev Siegl, and Gordon Browker. The trio’s love for coffee and tea was something they had in common.
They drew inspiration from Peet’s Coffee and Tea, a small beverage store founded by a Dutch immigrant. Peet used first-grade coffee and tea beans. Its success cheered the Starbucks founders’ to start one on their own. That’s when, in 1971, they started their first store in Seattle. They named their new business Starbucks, after a fictional character in the Moby-Dick novel.
In the early 1980s, they already opened four stores in Seattle and outranked their competitors. However, at the same time, Siegl decided to part ways to pursue other interests and this led to Starbucks’ struggle for a brief period.
But, in 1984, things began to change for the better when Howard Schultz joined the marketing team as its Director. Schultz had a vision for Starbucks beyond just selling coffee and coffee beans. He wanted to create a unique customer experience that appealed to coffee lovers everywhere.
Schultz's vision came to fruition in 1987 when Starbucks opened its first store outside of Seattle. This marked the beginning of the company's explosive growth. By 1992, there were more than 400 Starbucks stores nationwide.
Going Global
In 1995, Schultz decided to take Starbucks international and opened its first store in Tokyo, Japan. Over the next few years, he opened additional stores in countries all around the world including China, Australia, Italy, Germany, and France.
Today, there are more than 32,000 Starbucks stores in 80 different countries.

What does Starbucks believe in?
Starbucks’ corporate mission is -
“to inspire and nurture the human spirit – one person, one cup, and one neighborhood at a time.”
This statement emphasizes Starbucks’ dedication to providing customer engagement and customer satisfaction.
Also, Starbucks believed that it should be more than just selling coffee and about creating a community space where people can gather and socialize. This sentiment is summed up in its slogan, “The Third Place” and its corporate vision -
"to create moments of connection for everyone who visits our stores."
How Starbucks Became a Global Coffee Giant
As one of the largest chains in the world's coffee market, Starbucks is a company that is always worth taking a closer look at. Now, let’s explore its current business model and pricing strategy.
One thing that sets Starbucks apart from other coffee shops is its focus on customer engagement and experience. From the moment you walk into a store to when you leave, Starbucks employees are there to ensure your experience is perfect. This focus on customer service has helped contribute to the chain's massive success over the years.
But what about its pricing strategy for profits?
Unlike many other consumer chains, Starbucks does not use a discount pricing strategy, and this actually enhances customer perception. That is, it charges exceptional prices for its premium products.
Customers who are willing to pay more for their coffee tend to view it as being of a higher quality. As a result, they perceive Starbucks as a premium coffee brand and are likely to be loyal customers.
While this might be seen as risky by some business owners, its premium pricing strategy has thus far proven to be successful for Starbucks.

So, what makes Starbucks' business model and marketing strategies successful?
Starbucks has always been innovative when it comes to its business model. Rather than just selling coffee, it expanded into food items, drinks, and even music. This means that they can reach a broader customer base, which in turn results in higher customer sales and profits.
Now, the story is no different due to its successful marketing strategies. This keeps the brand exciting and fresh, which helps it stand out from the competition.
There's no denying that Starbucks has a massive success story - but what exactly is the reason behind its successful marketing strategies? Let's take a look at Starbucks' marketing mix:
What is Starbucks' Marketing Strategy?
From the beginning, Starbucks' objective has been to create a "third place" beyond home and work where people can relax and enjoy good coffee.
Starbucks' marketing strategy has been designed to achieve this goal by targeting both regular customers and occasional customers with a consistent brand experience.
In the following sections, let us learn more about its key marketing mix strategies across price, placement, product, and promotion.
1. Starbucks' Promotion
From its very beginning, Starbucks has heavily invested in promotional campaigns. These campaigns include TV commercials, print ads, and radio spots, as well as online marketing brand initiatives such as social media and search engine optimization.
Through its marketing mix, it attracts new customers and keeps the existing ones coming back for more. The premium global coffee brand focused a lot on building customer loyalty and customer retention.
The company sponsors major sporting events such as the Olympics and Wimbledon, and it even partners with other businesses to promote its products.
2. Starbucks' Product
In its early days, Starbucks focused on selling high-quality coffee beans to consumers and businesses. It was not until later that they began to sell brewed coffee beverages. However, today, Starbucks offers a wide variety of drinks and food items, including pastries, sandwiches, and salads.
The company also sells Starbucks coffee beans and brewing equipment to customers who want to make their own coffee at home.
3. Starbucks' Pricing Strategies
One of the factors that have contributed to Starbucks' success is its premium pricing strategy.
To reiterate, Starbucks sets high prices for its products but offers good value for money by providing excellent customer service and a comfortable environment.
That is, it sells coffee at least 25% higher than other value brands and still keeps up a great deal of customer loyalty. However, the chain does offer a few discount programs such as the Starbucks customer rewards program and student beans program at both local and international levels.
4. Starbucks' Placement
Starbucks has placed its stores in strategic locations all over the world. Although it has many brick-and-mortar stores around the world, it also sells its products online through its website and app.
The company has been expanding its delivery services in recent years in order to deliver a good customer experience to its target audience and also reach more customers.
Iconic Marketing Campaigns by Starbucks
Starbucks' marketing campaigns were designed to entice even the ‘I’m not a coffee person’ beyond their natural target audience.
Let's explore some of Starbucks' most innovative marketing tactics that won millions of hearts -
Creative Cup Contests
#thewhitecupcontest.
In 2014, Starbucks ran a promotion called "The White Cup Contest" in which customers were invited to design their own Starbucks coffee cups. The winners would have their designs featured on Starbucks' limited edition products and merchandise.

Source: Consumer Value Creation
#theredcupcontest
Starbucks' red cups became an annual tradition — the symbol of Christmas — and sometimes prompted speculation. Earlier this year they started a #theredcup competition on Instagram. The winner can post a photograph of their RED Cup and use the hashtag theredcupcontest. 40,000 entries collected during the contest were collected on Instagram in 2015.

Source: Iris Worldwide
Tweet-a-coffee campaign
Tweet-to-coffee allows people to pay for coffee online by tweeting @tweetoffee and their friends. This link will give them $5 in rewards. The company's Twitter page received nearly 1 billion tweets. During the first two weeks of operation, there were nearly $180,000 in revenues.

Source: Starbucks Stories
Humans of Starbucks
Starbucks has been on a mission to humanize work for years now. To date, Starbucks is committed to this goal.
To do this, they have launched several initiatives over the years, including their “To Be Human” campaign. It aims to remind employees and customers alike that we are all connected by the shared feeling of humanity.
So far, the “To Be Human” campaign has been implemented in a few different ways. First and foremost, Starbucks has created a series of videos that highlight real-life stories about people connecting over coffee. These videos are being shown in stores all around the world, in an effort to create brand ambassadors organically, and vouch for the importance of connection.
Get into Cause Marketing
Starbucks has also partnered with several charitable organizations like Feeding America and Save The Children UK in order to support causes that align with their beliefs. For example, for every purchase made through their app during December 2018, they donated $1 to one of these charities.
Mobile App and Loyalty Programs
Starbucks knows that retail's future depends in some ways on technology. As another Starbucks marketing strategy, it launched a mobile phone app in 2009 and positioned it in a way that helps customers save time in long queues.

Source: Starbucks Malaysia Twitter
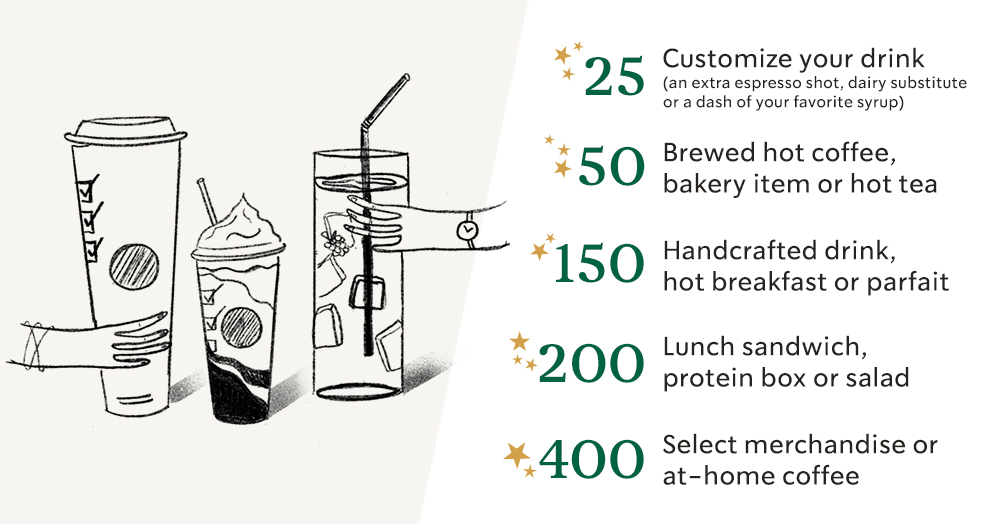
Unlike any other mobile phone app as a business strategy, Starbucks introduced a program on the Starbucks app called 'My Starbucks Rewards' that rewards customers for their continued patronage. In a few seconds, the Starbucks purchases will be rewarded for using the app to pay for their services.
Once they join, they start earning stars for all Starbucks transactions.
On accumulating enough stars, one can redeem them for rewards such as free coffee or free drinks, and food too. Say, for example, you can redeem 12 stars for a free beverage of any size.
Source: Starbucks
Giving back to society, nature, and itself
Starbucks' ecosystem has a long history of being involved in social responsibility programs. It introduced a comprehensive initiative that focuses on four key areas: environmental stewardship, ethical sourcing, community engagement, and employee well-being.
Environmental stewardship:
One of its primary goals is to reduce its environmental impact by becoming more energy efficient and using less packaging materials.
Some of the things that the Starbucks' ecosystem has done in order to achieve this include installing energy-efficient lighting systems and recycling coffee grounds into biodegradable cups.
Ethical sourcing:
Starbucks takes great care to ensure that its products are ethically sourced. This means that they only work with suppliers who meet their high standards for quality and sustainability.
Starbucks also supports sustainable farming practices through programs like Farmer Equity & Loan Assurance (FELA).
Community Engagement:
Starbucks believes in giving back to the communities where they do business. One way they do this is by partnering with local organizations to help fund literacy and education programs.
They have also created unique scholarship opportunities for employees' children who want to pursue higher education.
Employee Well-being:
Starbucks cares about the well-being of its employees just as much as it cares about the environment or ethical sourcing. This is why they offer health insurance plans, flexible working schedules, and training programs designed to help employees grow professionally.
In-store Marketing
While there are many different aspects to Starbucks’ marketing strategy introduced in-store, all of them revolve around one common goal – enticing customers inside the store so they can be sold on the brand!
Starbucks is a prime example of a company that uses in-store marketing to great effect. Their marketing mix includes a variety of elements, such as
Store Layout: The layout of Starbucks stores is very carefully planned out in order to create an inviting environment. It has comfortable seating areas with counters where people can not only drink coffee, but also work or study.
Starbucks also started giving its customers free Wi-Fi in 2002. This encouraged customers to stay longer even after making purchases. Alongside, it attracted working professionals to engage in business or lunch meetings at the outlet all day long!

Source: Tech Log
Product Displays: The products on display at Starbucks are always well organized. This makes it easy for customers to find what they’re looking for and helps them make quick purchase decisions. And, it is so well arranged that it helps with impulsive purchases, just like how you do in supermarkets!
Promotions: Starbucks runs frequent promotions throughout the year in order to attract more customers. These vary from discounts on coffee drinks to freebies like pastries or stickers.
Thinking beyond regular coffee
Starbucks’ success is attributed to its willingness in experimenting with new products and services. For example, they were one of the first companies to offer premium coffee drinks like latte and mocha.
Also, Starbucks launched an instant coffee line called Via which was a big hit among consumers.

Source: Dairy Foods Magazine
By constantly innovating and expanding its product lineup, Starbucks has been able to elevate its customer experience and stay ahead of the competition.
How Starbucks’ marketing strategy makes you hungry?
Starbucks is undeniably one of the most successful coffee chains in the world. But what sets them apart from other coffee shops? The answer is Starbucks' competitive marketing strategy, once again.
Starbucks uses various marketing tactics to make us all crave its coffee, and one of the most effective methods is by making us hungry. But how? Here, we go.
Appetizing Colors: By far, the human tendency has always been to stay healthy and inclined towards nutritious food. The general Starbucks appeal is created through consistent branding with the green color in Starbucks’ brand instantly reminding one of the natural ingredients. This free marketing pull encourages us to eat more, which then leads to us wanting caffeine for energy.
Aroma Marketing:
One of the other main reasons we get hungry at the store is because of the aroma that Starbucks sells. The premium Starbucks coffee tastes are owed to the freshly roasted coffee beans every day.
This creates a Pavlovian response where we start to salivate as soon as we catch a whiff of those delicious aromas.
Key Takeaways from Starbucks for Entrepreneurs
If you're an entrepreneur fascinated by the beverage industry, here are some major takeaways from Starbucks' marketing strategy and its business-
Focus on the Customer: The first lesson is to always focus on the customer. This means putting their needs and wants first and making sure they are happy with your product or service.
Keep Things Simple: Consistent Starbucks' branding and its simple operations helped them become successful worldwide. As an entrepreneur, it's important to maintain consistent branding and keep your business simple and streamlined. This will make it easier to manage and less likely to run into problems down the road.
Be Innovative: Starbucks is constantly innovating and coming up with new products and services that appeal to its customers’ tastes. You should try to adopt innovative and new ways to improve your business.
Offer Unique Products: Another reason for Starbucks' global brand success is its unique and premium coffee products. The company offers a wide range of products that cater to different tastes, which helps to attract new customers and lure the existing ones to come back for more.
- popover#mouseOver mouseout->popover#mouseOut" data-popover-translate-x="-25%" , data-popover-translate-y="-220%"> Copy link
- bottom-bar#toggleTagsSection"> popover#mouseOver mouseout->popover#mouseOut" data-popover-translate-x="-25%" , data-popover-translate-y="-220%"> Copy Link
- bottom-bar#toggleTagsSection">
Test your knowledge through a fun quiz!

You'll love these articles too!

Co-founder & CEO at Flexiple ($3mn+ revenue, bootstrapped) & buildd.co | Helping Startup...
Monster Energy Marketing Strategy: How Monster become a market leader by 'Unleashing the Beast'?
Learn about Monster's iconic marketing strategy and advertising campaigns. Read how Monster aces the 4Ps of marketing mix - Product, Price, Promotion & Placement.

Co-founder at Flexiple, buildd & Remote Tools ($3 million revenue, bootstrapped)
Breaking Down The Maruti Suzuki Marketing Strategy: How they became a brand that rules India's automobile market
Learn about Maruti Suzuki's iconic marketing strategy and advertising campaigns. Read how Maruti Suzuki's aces the 4Ps of marketing mix - Product, Price, Promotion & Placement.

Clinical Research | Data Analytics

Partner at Deloitte | Banking & Capital Markets | Cloud Strategy | FinOps Offering Leader | Board...

Swiggy Business Model: How the Company is Building a Brand That's Hard to Resist
Explore the innovative business strategies behind Swiggy's success, including the company's approach to building a strong brand and delivering unbeatable customer experiences. Learn how Swiggy is disrupting the food delivery industry and solidifying its place as a leader in the market.
Table of Contents
What is the starbucks target market, the rewarding marketing strategies of starbucks, marketing mix, how strong is the starbucks digital marketing presence, marketing during covid-19, starbucks’ strategic alliances that enhanced their reach , exploring starbucks marketing strategy: the success secret.

Ranking 5th on the World's Most Admired Companies list by Fortune, the commitment to consistent branding has made Starbucks a huge success today. Spanning 70 countries worldwide, this American multinational chain of coffeehouses has come a long way in its journey. The Starbucks marketing strategy constitutes a blend of social media marketing , digital marketing , search engine optimization , and right post-marketing analysis.
Replicating the entire Starbucks marketing strategy is nearly impossible for brands with low budgets. However, learning and implementing the core principles and the idea behind the Starbucks marketing strategy can benefit even startups.
Earn the Esteemed Purdue Certification
By knowing exactly who its target audience is at any point and catering to a specific set of people, Starbucks has been able to stand apart from its competitors like Costa and Cafe Coffee Day.
Being a premium coffee brand, Starbucks has most of its customers belonging to the upper economic segment. It targets youngsters and people who seek a peaceful space to drink coffee. Its high-end customers fall in the 22-50 age group, both male and female. Thus, the Starbucks target market constitutes:
- High-income spenders
- Health-conscious professionals
- Technology early adopters
- Coffee-addict youngsters
The Starbucks marketing mix segments its customers on a socio-economic level. The distinguished offline experience and consistent online marketing efforts have made the brand exceptional.
Starbucks' marketing mix very well incorporates the four P's .
- Product: High-quality products justify the premium pricing. They ensure that the coffee tastes better than its competitors. Their Barista Promise of fixing your drink if you don't like it has attracted the masses.
- Price: Starbucks sells their coffee at least 25% higher than other brands. It offers its customers exceptional drinks and food, charges more, and the people are willing to pay.
- Promotion: From social media to TV to ads– the company uses various channels for marketing its products. The mix of marketing media makes them stand out. Compared to other major global brands like Apple, Starbucks spends the least on their marketing but can still make an impact. Why? The robust Starbucks marketing strategy has made all the difference.
- Place: They create a similar premium relaxing environment in every Starbucks location which lures the crowd.
Key Takeaway: Your brand can charge a higher price by providing a premium experience and delivering better products than the competitors.
Digital Expansion
The Starbucks marketing strategy incorporates digital interactions with customers by implementing new ways to attract digitally registered customers. It offers mobile order services and Wi-Fi sign-ins at its stores. The ability to go cashless with Starbucks cards has further accelerated its business.
Starbucks Social Media Strategy
Starbucks' social media accounts exhibit distinctive branding , visually appealing content, and interactive posts that enhance user engagement. The diverse content range has eye-catching photography, videos, recipes, articles and more. In addition to the visual appeal, the Starbuck marketing strategy for social media breaks down the stream of content into a series of campaigns.
Become a Certified Marketing Expert in 8 Months
Starbucks Campaigns
The Starbucks campaigns fall into the following three categories, creating a greater sense of brand awareness :
- Starbucks Product-based Campaigns: The company promotes unique and fan-favorite beverages. It has even created social profiles for customers' favorites -Frappuccino and Pumpkin Spiced Latte. They publish relevant memes for their audience. Utilizing the power and sentiments attached to consumer images, the brand often re-shares them on its official channels.

Starbucks Frappuccino
- Starbucks Corporate Social Responsibility-Based Campaign: Using social change as a marketing tool, Starbucks positions itself as inclusive and open-minded. Its #The ExtraShotOfPride campaign gained popularity by supporting the LGBT+ community.
- Community-based campaigns: Another important facet of the Starbucks marketing strategy is its emphasis on highlighting communities and individuals. They rely on storytelling to depict acts of kindness in communities while localizing the content.
Festive Marketing
Innovative ideas have been the strength of Starbucks. The company initiated a whole-bean coffee campaign– #StarbucksDiwaliBlend as a tribute to Karnataka's rich coffee heritage and expertise.

Starbucks Diwali Blend
Its #SketchTheBlend campaign was launched on Diwali, where customers were urged to share their creativity on the Diwali Blend cup. The best ones could bag five free beverages.

Starbucks Facebook Post on #SketchTheBlend
Key Takeaway: Involving customers via festive marketing is a strong part of the Starbucks marketing strategy too. You can also leverage the opportunity and enhance customer engagement.
Targeting the elite class, Starbucks understands that its audience is technologically advanced. Starbucks' digital marketing provides it with an opportunity for two-way communication, unlike leaflets, magazines, and television, which are more of one-way communication. It has considerable traffic on its social media accounts, including
- Facebook: 36 M+ page likes
- Instagram: 17.8 M followers
- Twitter: 11 M followers

Starbucks Instagram Handle
Consistency is the key to a successful Starbucks marketing strategy. It extends the same to social media handles by posting daily. It has challenges and games that engage its customers and enhance its fan base.
Also, the company publishes engaging posts and connects viewers from one platform to another. Take the following Instagram post as an example. The bright and clean picture is reflective of the Starbucks brand. The caption describes their new espresso shot in a conversational tone.

Starbucks Instagram post
Now any consumer interested in the product would probably like to know more and find the landing page for Starbucks’ blonde espresso .

Starbucks Website Image for Blonde Espresso
The website satisfies the intrigued customer with more information on the blonde espresso and why Starbucks has launched the same. Scrolling down, you would come across videos and several other images. Thus, the company smartly employs marketing tactics to lure its customers and delight them with amazing products.
As the Covid-19 pandemic took over the world, Starbucks geared up with marketing tactics to sustain itself in these unprecedented times. The company constantly improvised, mitigating the economic impact via the following measures:
- Expansion: Starbucks announced launching drive-thrus and home delivery to stay connected with their customers in tough times. They also launched their app in India to help customers easily navigate and purchase their key offerings.
- Starbucks Social Media Campaigns: Seizing the opportunity to expand its user engagement, the company launched the #ReconnectWithStarbucks campaign. They asked their followers to share ideas of reconnecting amidst the pandemic. They also urged them to share their favorite Starbucks memory via Instagram with the hashtag #ReconnectWithStarbucks. Another popular campaign was the “Half Cup Full”. The customers had to comment on their favorite beverage on the Starbucks post, and then to remind the customers of the in-store experience, they sent them voice notes of baristas calling their names along with their favorite beverage.
As a part of the Starbucks marketing strategy, the company makes smart associations that enhance its reach and experience.
Merchandise Launch With Flipkart

Starbucks Merchandise Launch with Flipkart
Taking advantage of the growing dependence on e-commerce during the pandemic, Starbucks partnered with Flipkart and launched Starbucks Signature Merchandise on the platform. It offered a range of products, including custom mugs, cold cups, tumblers, coffee brewing equipment and more. Thus, enabling its customers to order from the comfort of their homes.
A well-crafted Starbucks marketing strategy is one of the prime reasons why the coffee-chain company has a dominating global presence and leadership. Additionally, to stay true to its word, they provide an arguably different atmosphere, unmatched service, and a welcoming environment to every customer who visits their brick-and-mortar stores.
You can establish your business with a stellar marketing strategy and employ the best digital marketing practices. Start your journey in upskilling yourself by enrolling on Simplearn’s PCP Digital Maketing Program in collabration with Purdue University. Boost your career with a unique 6-month course and a placement guarantee.
Our Digital Marketing Courses Duration And Fees
Digital Marketing Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
| Program Name | Duration | Fees |
|---|---|---|
| Cohort Starts: | 8 Months | € 1,699 |
| Cohort Starts: | 8 Months | € 999 |
Recommended Reads
Digital Marketing Career Guide: A Playbook to Becoming a Digital Marketing Specialist
Walmart Marketing Strategy
12 Powerful Instagram Marketing Strategies To Follow in 2021
Introductory Digital Marketing Guide
A Case Study on Netflix Marketing Strategy
What is Digital Marketing and How Does It Work?
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
Post graduate program in digital marketing.
- Joint Purdue-Simplilearn Digital Marketer Certificate
- Become eligible to be part of the Purdue University Alumni Association
IMT Ghaziabad Digital Marketing Program
- Digital Marketing certificate from IMT Ghaziabad
- IMT Ghaziabad Associate Alumni status
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.

- Influencer Marketing
- Celebrity endorsement
- Talent Management
- Web Design and Development
- Our Digital Marketing
- Digital Content
- Search Engine Optimization
- Our Production
- Case Studies
- Affiliation
Starbucks Marketing Strategy: An In-Depth Look at What Makes Starbucks’ Marketing so Effective

With over 34,000 stores across 80 markets, Starbucks has become the world’s most valuable coffee brand worth $28 billion. Its continued growth is fueled by smart, consistent marketing strategies that appeal to diverse demographics worldwide.
This in-depth guide will analyze the key components of Starbucks’ marketing mix that drive its global success. We’ll explore specifics around branding, promotions, products, pricing, partnerships and localization that make Starbucks a case study for effective integrated marketing.
Crafting the Starbucks Brand
Starbucks by the numbers, crafting the starbucks experience, crafting the starbucks brand voice & personality, mastering localization & community connections, optimizing the retail experience, building brand relevance through partnerships, analyzing the starbucks menu strategy, optimizing the starbucks digital experience, integrating traditional media, optimizing social media presence, managing global consistency, evaluating the starbucks pricing strategy, building the starbucks employee culture.

Starbucks fundamentally reshaped consumer expectations around the cafe experience. The brand positioned itself not just as another coffeehouse but as a “third place” between work and home for community, connection and discovery.
Backed by market research, Starbucks knew that customers sought great-tasting coffee and an uplifting space to unwind, socialize or get work done. The brand delivered this through thoughtful store aesthetics, seating layouts, music and more.
Some key ways Starbucks positioned itself as an inviting lifestyle brand include:
- Warm Store Design – Comfy couches and chairs, wood tables, earthy colours and textures that feel energetic yet calm.
- Upbeat Music – Curated playlists spanning genres create a hip, feel-good vibe. Baristas have input on local musical tastes.
- Relaxing Aromas – The smells of freshly roasted coffee and baked goods signal a welcoming refuge.
- Artistic Touches – Local art, handwritten chalkboard menus and decor with regional flair make stores unique.
- Contactless and Mobile Options – Technology like app ordering and in-store kiosks provide convenience without compromising personal connections.
This strategic brand positioning expanded the concept of cafes into community spaces buzzing with positive energy. Starbucks locations are just as suited for a casual chat as heads-down work.
As CEO Howard Schultz said, Starbucks aimed to become a “place for conversation and a sense of community. A third place between work and home.” This brand image resonated widely.
With over 153 million global rewards members and 30 million U.S. app users, Starbucks has tremendous direct consumer insight to continue evolving experiences.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of Stores Worldwide | 35,700+ |
| Number of Employees | 402,000+ |
| Market Value | $109.13 billion |
| Starbucks Rewards Members | 27.4 million |
| U.S. Mobile App Users | 31.2 million |
| Facebook Followers | 36.3 million |
| Instagram Followers | 18.1 million |
Starbucks backs up its brand positioning by delivering an unmatched cafe experience customers crave. Key elements include:
Customer Service
Baristas are extensively trained as coffee experts, not just order takers. They guide customers through selecting beans, roast styles, flavours and preparation methods. Starbucks baristas must pass rigorous knowledge tests demonstrating their mastery. This expertise enhances the craft coffee experience.
Customization
With over 87,000 drink combinations, Starbucks lets customers tailor beverages to their tastes. Options like milk alternatives, sweetness levels, espresso shots and temperature allow personalized orders. Digital apps make customizing easy. This level of personalization builds loyalty.
Technology Integrations
Starbucks seamlessly integrates technologies like mobile order and pay into the experience without dehumanizing service. Customizations and rewards are synchronized across digital platforms and stores. Efficient pickup slots reduce waiting. Rather than being a tradeoff between speed and connection, Starbucks tech enhances both.
Loyalty Program
The Starbucks Rewards program engages customers by rewarding them at various tiers, from free add-ons to free drinks and merchandise. Exclusive offers and early access to new products entice members to visit and pay via the app. The program boasts 26.2 million U.S. members.
Accessibility
From braille menus to ASL video ordering to in-store sign language, Starbucks accommodates diverse needs. Stores have lowered counters, grab bars, ramps and wheelchair-friendly seating. This welcoming accessibility expands their audience.
By perfecting each touchpoint, Starbucks makes customers feel recognized. This drives emotional connections beyond convenience or product quality alone.
- 27.4 million global Starbucks Rewards members
- 28.7 million U.S. rewards members
- Over 87,000 possible drink combinations
- #1 most installed restaurant app in the U.S.
Starbucks’ brand voice and personality convey the optimism and connection its brand stands for. Key characteristics include:
Upbeat Messaging
The copy uses cheerful language like “Let the spring days begin!” and features smiling faces enjoying coffee. Vibrant colours reinforce energy and positivity. Starbucks avoids corporate cliches for a friendly neighbourhood feel.
Millennial Appeal
Starbucks’ social media tone resonates with younger audiences through playful jokes and pop culture references. Responding to user comments fosters relationships beyond broadcasting ads.
Customer Spotlights
User-generated content showing customers enjoying Starbucks in their own lives is frequently featured. This highlights community connections.

Local Tone of Voice
While maintaining consistent branding, regional social channels adopt local lingo and references tailored to those markets. Australian channels sound different than Brooklyn stores. Adaptation feels authentic.
Cultural Relevance
Special graphic designs and themes celebrate cultural moments like Black History Month, Pride Month, Diwali and Lunar New Year. This reflects diverse consumer lifestyles.
Sustainability Messaging
Communications highlight sustainability commitments like reduced plastic usage and recyclable cups. But Starbucks avoids preachy language, framing green steps as a shared journey.
This friendly, culturally relevant brand voice crafts hundreds of unique touchpoints between Starbucks and customers daily.
Despite its global scale, Starbucks excels at tailoring experiences to local tastes. They celebrate community connections through:
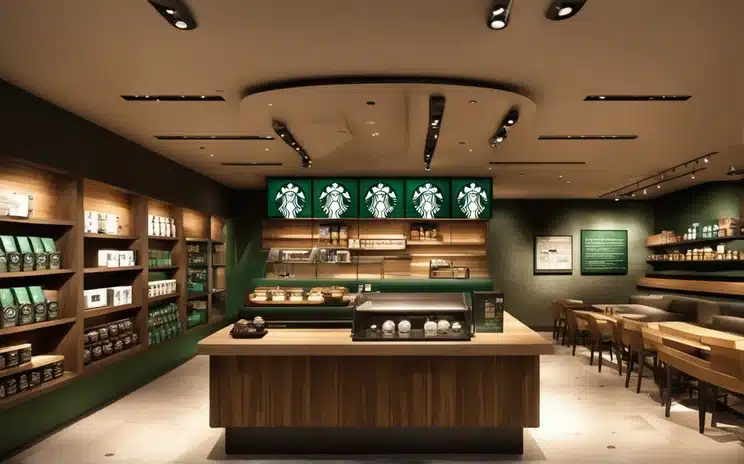

Hyper-Local Store Design
While following Starbucks brand guidelines, details like local artwork, regional materials and neighbourhood names on walls provide local flair. Special collection mugs showcase city landmarks. This customization makes stores feel unique.
Local Food/Drinks
Stores integrate local flavours in offerings like regional coffee beans, seasonal food items or beverages inspired by local tastes. For example, Mumbai stores offer Chai-spiced tea.
Music Curation
Baristas can curate in-store playlists around local music culture, like hip-hop in Atlanta or country in Nashville. Starbucks compiles local songs into playlists.
Community Partnerships
Stores partner with local non-profits for community service projects and fundraising drives. For instance, Austin stores work with Keep Austin Beautiful on neighbourhood cleanups.
Special Events
From art shows to open mics to partnering with local race events, stores integrate into local happenings. During holidays, Starbucks hosts family activities. These connections make stores gathering hubs.
This hyper-local immersion helps Starbucks blend organically into communities worldwide, becoming part of neighbourhoods.
While known for cafes, Starbucks innovates across retail environments. Specialty concepts help reach diverse audiences:
Pickup Stores
Compact Starbucks Pickup locations focus exclusively on mobile order pickup and to-go service. Customers pre-order via the app and grab drinks without waiting in line. Over 2,500 exist in the U.S. alone.
Drive-Thru Stores
In suburban and rural markets, Starbucks Drive-Thru locations offer convenience and speed for commuters. They account for over 60% of U.S. store growth. Starbucks plans to have 9,000 North American drive-thrus by 2025.
Reserve® Roasteries

These stunning flagship locations in Seattle, New York, Tokyo and Milan double as coffee-tasting rooms and entertainment venues. On-site roasting demonstrations, experiential bars and premium Princi food make them creative lab destinations.
Airport Stores
With over 400 airport locations, Starbucks provides travellers with a familiar oasis. New enhancements like mobile ordering improve convenience during layovers.
Testing retail concepts tailored to neighbourhood needs and lifestyles keeps Starbucks accessible everywhere customers need their coffee fix.
Aligning with like-minded brands on creative campaigns and in-store pilots generates buzz while positioning Starbucks as culturally plugged-in:
Blending Spotify’s curated playlists into Starbucks drinks like the Cold Brew Vibes creates engaging crossover moments for youth culture. Over 177,000 Spotify users participated.
Chase Credit Cards
Giving Chase cardholders automatic Starbucks Rewards status and purchase points incentivizes choosing that card. It deepens collaboration between brands.
Ridesharing and coffee go hand-in-hand. Giving drivers Starbucks Rewards for ride referrals and offering coffee giveaways on the Lyft app integrate both brands into daily routines.
Pop-up “Airbnb cafes” in select cities promoted nearby private Airbnb rentals and allowed booking via Starbucks iPads. The partnership united both lifestyle brands.
These co-branding campaigns generate positive press and social engagement while reinforcing Starbucks’ cultural relevance.
Starbucks’ extensive menu evolves constantly to drive sales and attract new customers. Key menu strategies include:
Broad Variety
From traditional espresso beverages to Frappuccinos® to tea infusions, the wide range pleases diverse tastes under one roof. No competitor offers Starbucks a depth of options.
New Products
Starbucks continually rolls out beverages, snacks and accessories, testing consumer response. Successful launches like the Pumpkin Spice Latte or Cold Foam become permanent additions. This innovation keeps the menu fresh.
Regional Flavors
Limited-time beverages incorporate region-inspired ingredients to delight local markets. Examples include coconut milk in Thai drinks or ube flavouring in the Philippines. These specialties excite customers.
Health-Focused
Increasing wellness offerings like plant-based drinks, reduced sugar baked goods and high-protein boxes cater to health-conscious patrons. Even small enhancements like swapping milk for almond milk modernize the menu.
Lifestyle Bundling
Merchandise bundles pairing drinks with items like reusable tumblers, mugs or Spotify gift cards provide gifting occasions and cross-selling opportunities.
Premium Pricing
Starbucks prices most offerings 10-20% higher than competitors. Yet customers readily pay premium prices for the quality and experience. Surge pricing during peak times maximizes revenue.
Through constant innovation and locally tailored options, Starbucks sustains menu excitement globally.
- 1,100+ limited-time/regional drinks per year
- 300+ food items
- 25-35% of sales from seasonal/limited-run drinks

Mobile and digital initiatives help Starbucks build direct connections with customers:
Industry-Leading App
The Starbucks app provides an unmatched mobile experience, letting customers order ahead, collect rewards and pay contactless. Starbucks processed 25% of all U.S. restaurant mobile transactions in 2021.
Personalization
Customers can save favourite locations, customize orders and receive personalized offers through the app. Digital allows 1:1 relationships despite Starbucks’ size.
Rewards Integration
The app houses users’ Rewards program Dashboard. Customers can collect Stars and track benefits in one place. Gamification features like collecting badges keep engagement high.
Order Ahead Functionality
With pre-order pickup, locations have drinks ready right when customers walk in. For commuters, this eliminates waiting in line. Stores see increased visits and ticket sizes from pre-orders.
Seamless Payment
Customers load gift cards and payment methods into the app for tap-to-pay convenience. Starbucks recorded over 9 million mobile transactions per week in 2021. Frictionless payment improves customer lifetime value.
The app offers blind and deaf customers full digital access through voice control and ASL clips. Everyone can independently manage their account.
Digital convenience without dehumanizing service makes Starbucks a gold standard for mobile experience and loyalty.
Although leaner than other QSR brands, Starbucks does advertise across media:
TV Commercials
Cinematic ads illustrate the Starbucks experience. Recent spots spotlight mobile ordering and seasonal beverages. TV builds broad awareness, especially for new menu launches.
Radio Spots
Regional radio ads drive trials of limited-time offerings and cold beverages in warm weather. Frequency can be customized locally.
Out-of-Home Billboard Ads

Billboards in major metro areas promote seasonal drinks and cold coffee in summer. As commuting returns, outdoor ads gain importance.
Direct Mail
Mailing free drink/food vouchers encourages customers to revisit stores and promotes signups. For loyalty members, birthday freebies and member-only coupons increase retention.
Email Marketing
Regular email campaigns highlight new products, local events or member-only perks. Timely, relevant offers keep Starbucks top of mind and drive repeat visits.
Social Media
Organic social content, influencer partnerships and paid social ads build hype for product launches and drive traffic to locations. User-generated content shows real customer moments.
As an established brand, Starbucks focuses media dollars on driving traffic and conversions rather than pure awareness. The combination of national scale and hyper-local personalization makes its advertising relevant.
Read More – Pepsi Marketing Strategy | Refreshing Success Story
Despite its size, Starbucks maintains locally connected social media feeds:
Responsive Engagement
Comments receive prompt responses rather than being ignored. Customer issues get resolved via direct messaging. This fosters positive relationships.
User-Generated Content
User photos and stories showing local Starbucks traditions become featured social content. This highlights community connections.
Localized Content
Regional social channels celebrate local moments like city pride, sports team victories, or landmarks. Localized content fits with each area.
Contests and Polls
Photo contests, coffee preference polls and sweepstakes encourage social sharing, tagging and engagement. User-generated content expands reach.
FOMO Marketing
Limited-time drinks and menu items get introduced on social first to generate buzz. Tempting food and drink photos spark FOMO.
Crowdsourcing Ideas
Polls ask followers for new flavours and food suggestions. Customer ideas becoming reality, like Guava Black Tea Lemonade, get promoted.
Rather than overt sales pitches, Starbucks’s social channels aim for authentic local storytelling and engagement. This community building earns brand love, translating into visits.
While adapting locally, Starbucks ensures brand consistency everywhere:
Product Design
Clean, streamlined cups, mugs, bags, drinks packaging and merchandise, create instant recognition globally. Iconic green and white logo palettes unite locations.
In-Store Signage and Displays
Familiar menu board layouts, ordering flow and digital UI make purchasing seamless across regions. Signage utilizes consistent branding and photography.
Store Aesthetics
Despite unique decor touches, core store elements like materials, seating and lighting create a familiar ambience worldwide. You know you’re in a Starbucks immediately.
Training Consistency
Standardized training programs ensure baristas worldwide share expertise about coffee sourcing, drink preparation and service essentials. Customers expect this mastery.
Technology Systems
Mobile apps, point-of-sale systems and inventory management unify operations for smooth customer experiences globally. Shared infrastructure enables flexibility.
Maintaining brand familiarity attracts global travellers while allowing customization. This glocal strategy powers Starbucks’ worldwide expansion.

Starbucks optimizes pricing through data-driven strategies:
Price Elasticity Analysis
As a premium brand, Starbucks has relative flexibility in pricing. But teams still analyze elasticities, raising prices gradually to avoid volume decline. Premium charges expand as costs rise.
Competitive Benchmarking
While priced above competitors, Starbucks monitors pricing gaps to align with positioning. Cafe-only players get more premium freedom versus QSR chains.
Regional Pricing
Starbucks customizes pricing based on local income levels, competition and labour costs in each market. Low-income regions get discounted value offerings.
Customer Segment Pricing
Rewards members get discounted offers or member prices below general public pricing as an entitlement. Different tiers get tailored pricing incentives.
Time-Based Pricing
Happy hours with half-off discounts drive afternoon traffic when the volume is lower. Surge pricing applies during peak commute times based on demand algorithms.
Bundling Offers
Combining food, accessory and drink items into packages at an inclusive rate provides cost savings over individual purchases. Bundling encourages bigger average orders.
Customers readily accept Starbucks’ premium pricing because it signals the uplifting experience they came for. Value-driven tactics keep options accessible. This strategic balance maximizes profitability.
Starbucks’ strong internal culture empowers passionate employees who deliver outstanding service:
Investing in Barista Training
Extensive training teaches baristas coffee expertise and real hospitality. Training is seen as an investment rather than a cost center. Knowledge programs enhance careers.
Providing Quality Benefits
Uncommon for food service, Starbucks offers benefits like healthcare, stock options, tuition coverage, paid time off, mental health support and rehabilitation assistance even for part-timers.
Fostering Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
From diverse hiring practices to accommodations for disabilities, Starbucks strives for equity and accessibility for all employees to feel welcome and supported.
Enabling Career Growth
About 80% of store managers started as baristas. Internal mobility is encouraged through management apprenticeships and tuition reimbursement for advancing skills.
Rewarding Performance
Bonus challenges reward baristas for success metrics like speed of service, waste reduction or customer connections. Peer recognition also cultivates teamwork.
This people-first foundation enables Starbucks to deliver on ambitious customer experience goals and growth. When employees feel invested, it drives business success.
Through integrated branding, customer experience, partnerships, menu innovation and localized marketing, Starbucks delivers consistent experiences that feel personal worldwide. They elevate coffee into an uplifting community ritual.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Our Services
- Digital Marketing
- Social Media Influencers
- Being Creative
- Celebrity Endorsement
- Content Marketing
- Corporate Film
- Film Making
- Marketing Strategy
- Search engine optimization
- Social media marketing
- Uncategorized
- Web Design Development
- Youtube Marketing

Popular Posts

Starbucks Company’s Brand and Distribution Strategy
| 📄 Words: | 1126 |
|---|---|
| 📝 Subject: | |
| 📑 Pages: | 5 |
| 💼 Companies: |
This paper uses the case study of Starbucks Corporation as a first-class marketer of coffee to evaluate its brand today and its distribution strategy over time. Discover Starbucks distribution channels, strategic priorities, and its success factors.
Background Information
Analysis of starbucks brand, starbucks distribution strategy over time, video voice-over.
Starbucks Corporation is regarded as a first-class roaster, retailer, and marketer of speciality coffee (MarketLine 2014). The company has operations in more than 62 countries across Europe, North America, Asia Pacific, Latina America, Africa, and the Middle East. Starbucks is reputed to be one of the leading brands dealing with coffee products and snacks in the world.
According to MarketLine (2014), the industry Starbucks operates in is at a mature stage. It experiences a medium level of concentration. Several factors determine demand in the industry. They entail the disposable income and prices of the product on the international market. In this paper, the author uses the case study of Starbucks to evaluate its brand today and its distribution strategy over time.
The company has one of the major brands in the world. It possesses several key competencies. One of them is the capability to push its products in the market through differentiation. The company offers a premium product mix made up of high-quality snacks and beverages (MarketLine 2014). According to Garthwaite, Busse, and Brown (2012), Starbucks brand is built and driven by quality and depiction of prestige. Cobb (2008) further postulates that brand equity is founded on the sale of high-quality coffee and related products.
The ‘finest quality’ attribute is achieved by providing every customer with a unique Starbucks experience (Cobb 2008). According to Lingley (2009), the experience is derived from the offering of supreme customer services in clean and well-maintained outlets and stores. The attributes reflect the culture of the various communities the company operates in. It builds a high degree of customer loyalty, bordering on a cult following (Lingley 2009).
Moon and Quelch (2006) argue that the Starbucks experience is best captured in the company’s “live free” mantra. The phrase reflects the coffee culture advanced by the organisation. Also, it highlights the three components of the company’s branding strategy. According to Moon and Quelch (2006), one of the key components of this branding approach is the coffee itself. The company sources coffee from the best growers in the world, including those in Africa and South America. Also, the entity works closely with the coffee producers to ensure the supply of a high-quality product.
The other component of Starbucks branding strategy is based on customer experience. According to Moon and Quelch (2006), Starbuck’s loyal customers visit its outlets as often as eighteen times in a month. The reason is that the company identifies and customises the customers’ requirements, creating an experience that is equal to intimacy. The experience keeps these consumers going back for the brand.
The third aspect of Starbucks’ strategy is the atmosphere associated with the brand. Moon and Quelch (2006) advance that although customers frequent Starbucks for coffee, the reason why they remain is the ambience of the company’s restaurants and outlets. Lingley (2009) agrees that Starbucks outlets have an aura of exclusivity. In addition to having a cup of decent coffee, people also frequent the outlets to network.
The three components of Starbucks branding strategy have turned the brand and the products into highly differentiated phenomena. It lowers the threat of substitution (Cobb, 2008). Starbucks’ major strategy entails building strong customer connections. The initiatives have facilitated the attainment of a high footfall since customers increasingly frequent the company outlets in search of the exclusive experience.
According to Lingley (2009), a key strategy that Starbucks has adhered to from its conception is product differentiation. Differentiators are founded on a premium product mix, supreme customer service, high-quality products, and locations. In essence, these attributes have led to the establishment of a premium value brand, which is very costly for competitors to imitate. As a result, Starbucks has built a formidable brand, which qualifies as one of its major strengths in the industry. The brand boosts the competitiveness of the company in the global market.
According to Garthwaite et al. (2012), as early as 1996, the company embarked on the growth process pegged on two initiatives. The initiatives entailed selling products through channels of mass distribution. The other approach was based on the dramatic expansion of the retail footprint (Garthwaite et al., 2012).
Alliances are used by the company to support its marketing approaches. According to Lingley (2009), strategic alliances form the basis of the company’s growth and long-term success. They promote brand recognition in the industry. One of the earliest alliances formed by Starbucks was the joint venture with Pepsi-Cola North America Division. The partnership was aimed at marketing the company’s Frappuccino bottled coffee drink (Garthwaite et al. 2012). By September 1998, the company had engaged in an exclusive long-term licensing agreement with Kraft Foods. However, the partnership was terminated in 2010 (Garthwaite et al., 2012).
According to Cobb (2008), Starbucks occupies the position of industry segment and product quality leader. The company does not engage in aggressive marketing through traditional means. On the contrary, it focuses on word-of-mouth branding, high-level marketing, partnerships, and key alliances (Lingley, 2009).
According to Lingley (2009), the company has formed key alliances with companies and various social groups. Consequently, exposure of the brand has been broadened. Also, the reputation of the brand has improved. The alliances and partnerships have facilitated exposure of Starbucks products and name regularly to new and potential customers.
Starbucks has established distribution channels through shrewd strategic alliances and smart acquisitions (Lingley 2009). Instead of focusing on the franchising model, the firm’s operations focus on company-oriented stores and joint ventures in international markets (Cobb, 2008). For instance, the company has acquired several strategically placed entities. Such alliances aim to enhance product diversification (Lingley, 2009).
Starbucks has experienced numerous successes in its differentiation focus strategy. However, in 2009, the company embarked on other growth initiatives, which increased the diversity of the products offered (Garthwaite et al., 2012). Consequently, some of the distribution approaches have been diversified. Such approaches include online music retailing.
Starbucks has built very strong values about human resource management. Such moves have enhanced the success of the distribution strategy. For instance, the relationships have led to successful employment of the company’s strategy, which entails organic expansion across the international markets (Cobb, 2008). The reason is that the links facilitate the establishment of close unions with both internal and external suppliers. Also, horizontal integration through alliance and smart acquisitions has facilitated the maintenance of the company’s objective of a recognised and respected global brand.
The successes of Starbucks can be attributed to functional corporate governance, a focused distribution strategy, and a strong brand. The industry’s trends are changing. However, the diverse marketing and distribution strategies employed by the company have effectively responded to these changes. However, it is important for Starbucks to brace for increased competition, especially concerning costs and product quality.
Cobb, C 2008, ‘Wake up and smell the publicity: a look at Starbucks’ brand revitalisation’, Public Relations Tactics, vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 18-26.
Garthwaite, C, Busse, M & Brown, J 2012, Starbucks: a story of growth , Kellogg School of Management, New York.
Lingley, R 2009, Marketing strategy and alliances analysis of Starbucks Corporation, Web.
MarketLine 2014, Company profile: Starbucks Corporation , Web.
Moon, Y & Quelch, J 2006, Starbucks: delivering customer service , Harvard Business School, New York.
Cite this paper
Select style
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
BusinessEssay. (2023, June 15). Starbucks Company’s Brand and Distribution Strategy. https://business-essay.com/starbucks-companys-brand-and-its-distribution-strategy/
"Starbucks Company’s Brand and Distribution Strategy." BusinessEssay , 15 June 2023, business-essay.com/starbucks-companys-brand-and-its-distribution-strategy/.
BusinessEssay . (2023) 'Starbucks Company’s Brand and Distribution Strategy'. 15 June.
BusinessEssay . 2023. "Starbucks Company’s Brand and Distribution Strategy." June 15, 2023. https://business-essay.com/starbucks-companys-brand-and-its-distribution-strategy/.
1. BusinessEssay . "Starbucks Company’s Brand and Distribution Strategy." June 15, 2023. https://business-essay.com/starbucks-companys-brand-and-its-distribution-strategy/.
Bibliography
BusinessEssay . "Starbucks Company’s Brand and Distribution Strategy." June 15, 2023. https://business-essay.com/starbucks-companys-brand-and-its-distribution-strategy/.
- Apple Decision Making
- Samsung Group Global Market Developments
- New Zealand’ Energy Drinks Industry Marketing
- BlackBerry Brand Management and Competition
- Kitchen Fashionable Furniture Company’s Marketing Plan
- Unilever Company: “Dove” Brand Evolution
- Product Development Life Cycle Phases
- Alibaba Brand Image & New Strategy Analysis
- Emirates and Etihad Airlines’ Brand Management
- Dettol Brand Loyalty
Marketing strategy of 'Starbucks Coffe'
Research paper (undergraduate), 2008, 24 pages, grade: 1,0, dr. khanh pham-gia (author), table of contents, executive summary, list of abbreviations.
List of Tables and Figures
1 Introduction
2 Main Part 2.1 The effect of Starbucks’ entry into the grocery market 2.2 The “Starbucks’ experience” and new retail channels 2.3 Key factors for Starbucks’ success 2.3.1 New definition of coffee store 2.3.2 Strategy for store expansion 2.3.3 Innovation in products and store concepts 2.4 Problems of the rapid expansion and their solutions
3 Conclusion
4 ITM Checklist
illustration not visible in this excerpt
List of Figures
Figure 1 – Store expansion of Starbucks in the last 20 years. (Self created from data of Starbucks Corporation)
Starbucks is the world leader in the premium coffee market and has an amazing success story. In this study the key factors for the successes of Starbucks are analyzed. The distribution strategy of Starbucks, e.g. through coffee stores, grocery markets, and new retail channels, is investigated. Additionally, problems of the rapid expansion of Starbucks in national and international markets and their solutions are discussed.
Starbucks sells not only its coffee; it sells the “Starbucks’ experience”. The company is successful to convey its vision to the customers. It can convince customers paying more for high-quality products and a new life style. Starbucks reached its goal to establish and leverage its powerhouse premium brand through rapid expansion of retail operations, introduction of new products and store concepts, as well as development of new distribution channels.
Starbucks has revolutionized the coffee business. The main marketing strategy is to represent Starbucks’ store as a “third place” between work and home. The company could increase the market share in existing markets and open stores in new markets rapidly. Additionally, Starbucks always tries to expand its products portfolio. The company cooperates and takes alliances with other companies to develop and distribute new products. As the result, Starbucks has developed from a local coffee bean roaster and retailer in the US to a multinational coffee and coffeehouse chain with more than 14,000 stores in 42 countries.
The rapid expansion of Starbucks leads unfortunately to some serious problems. The company has to fight with the commoditization of Starbucks’ brand because of a series of decisions which are necessary for the rapid business growth. Getting back to the score, being smarter in efforts of time, money, and resources, pushing innovation, and doing things necessary to once again differentiate Starbucks from all others are the keys for business success in the future.
In a sunny day in May 2002, people lined up on the Pariser Plaza in Berlin and waited for the opening of the first Starbucks coffeehouse in Germany. Howard Schultz, the founder and chairman of Starbucks Corporation, told customers about his wonderful vision and success story. [1] In 1983 he visited Italy and drank his first espresso in a coffee bar in Milan. He was immediately impressed and deeply inspired with the Italian coffee culture. He lauded: “There was nothing like this in America. It was an extension of people’s front porch. It was an emotional experience”. [2] He applied successfully the concept of Italian espresso bar to the United States. He built Starbucks from a local coffee bean roaster and retailer in Seattle to a famous international corporation with 7.8 billion USD sales and 894 million USD earning. The “Espresso bar idea” combined with the “American way of business” brought Howard Schultz a private property of 700 million USD, and Starbucks became a strong brand worldwide. [3]
The fact, that not every coffee bar gets success automatically, could be shown in a counter-example of Jacobs’s coffeehouse “J-Cups” at rail station Zoo in Berlin. In a bar with modern design, coffee with milk and sugar comes in a flash from the coffee maker by pushing a button and can be served quickly to the customer. However, the most customers want to enjoy the moment, as their coffee is brewed. They love relaxing by drinking a cup of coffee in a convenient atmosphere. The Jacobs’s coffee bar with its modern silver metallic cyber look should be closed because of a low number of customers. [4]
These examples demonstrate the reality in the hard-fought coffee market and the changing needs of customers. Coffee drinking is not only a demand and a habit; it is also a part of quality of life and a life style nowadays. Only companies, which can satisfy it, will survive and those, who can set early a business trend, will earn profits and grow.
The object of this study is to analyze the key factors for the successes of Starbucks. The strategies of Starbucks to distribute coffee, such as through coffee stores, grocery markets, and new retail channels, as well as their benefits and consequences are studied. Furthermore, problems of the rapid expansion of Starbucks in national and international markets and their solutions are discussed.
2 Main Part
2.1 the effect of starbucks’ entry into the grocery market.
The Seattle-based Starbucks Corporation is nowadays a multinational coffee and coffeehouse chain with 14,400 stores in 42 countries. The company is world leader in the premium specialty coffee market. Starbucks purchases and roasts high-quality whole bean coffees and distributes them predominantly through its own retail stores. In its coffee stores, Starbucks offers a variety of hot and cold beverages with different flavors and customized modifications e.g. fresh-brewed coffee, Italian style espresso, cappuccino, macchiato, Frappuccino, non-coffee blended beverages, and teas. Customers can also buy pastries, sandwiches, snacks, coffee beans and other items like mugs, tumblers, books, music and films. [5] The company receives 77 % of the sales with beverages and 13 % with goodies like sandwiches and cakes. [6]
Beside the distribution in company-operated or licensed retail stores, Starbucks sells coffee and tea products through other channels including a specialty sales group and supermarkets. In the US, the company distributes its products in grocery markets, where 80 % of America’s groceries are sold. Starbucks started in 1998 a partnership with the grocery-product giant Kraft Foods Inc., the largest branded food and beverage Company in the US and the second largest worldwide. This allows Starbucks to supplies its coffee products, while Kraft Foods is responsible for distribution, accounting, in-store merchandising, promotion and marketing. [7] Using this way, Starbucks can get entry into 25,000 U.S. supermarkets quickly. The company fills a super premium coffee niche where Kraft Foods was not presented. Furthermore, both companies get benefits from the co-branding and can leverage their strong brands. [8] In this study, it should be discussed, how the entry into the grocery market affects the Starbucks’ customer relationship.
According to the trade group Specialty Coffee Association of America, there is a big market for selling coffee beans to home users. About 75 % of 300 million cups of coffee, which Americans drink a day, are made at home. For Starbucks, distribution of its coffee in grocery markets is a good possibility to attract new customers to its brand. New customers can test Starbucks coffee at home. Its high-quality and various blends would encourage them to visit Starbucks stores and enjoy coffee there. A similar trend could be observed in Japan. The launching of a cold coffee drink led to increasing sales at Starbucks stores in Japan. Hence, Starbucks is not concerned about the possibly negative influence of the distribution in grocery market on the sales at coffee stores. [9]
The Starbucks’ main marketing strategy is to represent its store as a “third place” between work and home. People can take a refreshing break and relax by drinking a cup of fresh-brewed coffee in a homelike and socialized environment. They enjoy the life in a coffee store with warm wall colors, soft and cuddly armchair, coffee flavor, convenient music in the background and friendly baristas. Each week, 44 million customers visit a Starbucks coffeehouse, 10 % of them twice a day. A typical Starbucks customer comes to favorite store 18 times a month. [10] , [11] But how can Starbucks reach these loyal customers outside the stores, namely in their “first place” (home) or “second place” (work)? The solution is that regular customers would continue enjoying their favorite Starbucks coffee if they could buy and brew it self. Thus, the sale of coffee beans in grocery market for home brewing can continue building the relationship with the customer outside the stores. That helps Starbucks being within the sphere of customers whenever they have a need for a cup of coffee, said Lopez, the Starbucks’ senior vice president and head of global consumer products. 9
Owens, the analyst of Morningstar responsible for analysis of Starbucks business, stated that no sign of negative impact of increasing mass-market reach on the Starbucks’ brand could be observed. The company seems to be managing its growth in grocery market without devaluing the brand. However, the quality of products, which are sold outside the stores, should be considered. For example, a pre-made, bottled Frappucino from supermarket will never taste as good as a fresh Frappuccino made by a barista in a coffee store. Starbucks takes this problem seriously and distributes its coffee in grocery market only when a flavor-lock bag technology is available. Using this technology coffee can be kept fresh for a long time in retail stores. In addition, Starbucks does not offer its coffee in open dispensing kiosks, where exposure to light and air can lead to a degradation of the coffee’s flavor. With ensuring the quality of products sold at grocery markets, Starbucks can continue expanding its reach to new and existing customers without diluting the premium brand. [12] , [13]
2.2 The “Starbucks’ experience” and new retail channels
Starbucks sells not only its coffee; it sells the “Starbucks’ experience”. The company is successful to convey its vision to the customers. It can convince customers paying more for high-quality products and a new life style. The goal of Starbucks is to establish and leverage its powerhouse premium brand through rapid expansion of retail operations, introduction of new products and store concepts, as well as development of new distribution channels. [14]
Starbucks uses different channels to distribute its products outside the company-operated stores. These include arrangements with foodservice companies, licensed partners, grocery channel, warehouse club accounts, direct-to-customer market channels, joint ventures and other specialty operations. The deal with Kraft Foods allows that Starbucks’ products are available on grocery shelves. Both companies accomplished marketing and promotion activities, e.g. radio advertising campaign or launching touch-screen marketing tools in supermarkets with info about specific bean types and blends. That helps customers to understand about Starbucks experience and shows them how they can bring that experience home. [15] , [16] Beside the cooperation with Kraft Foods to sell its coffee products in supermarkets, Starbucks delivers whole bean and ground coffees to office coffee distributors, institutional foodservice companies, hotels, airlines, retailers and restaurants. In 2001, the company had already 5,500 foodservice accounts which brought Starbucks 31 % of its specialty revenues. Additionally, the distribution to warehouse club chains ensured the company 13 % of specialty revenues. [17]
[1] Steinborn, D. (2003). Der Kaffe-König. Available from http://www.zeit.de/2003/17/Starbucks?page=all (accessed on 08.01.2008).
[2] Kotler et. al (2006), p. 691.
[3] Dowideit, M. (2007). Starbucks trauert Kaffehaus-Romantik nach. Available from http://www.welt.de/wirtschaft/article736978/Starbucks_trauert_Kaffeehaus-Romantik_nach.html (accessed on 08.01.2008).
[4] Huhn (2001). Expansion mit Espresso. Available from http://www.zeit.de/2001/47/200147_coffeeshop.xml?page=all (accessed on 08.01.2008).
[5] Available from http://www.starbucks.com/aboutus/overview.asp (accessed on 08.01.2008).
[6] Siedenburg, B. (2007). Der Blueberry-Herkules. Available from http://www.focus.de/finanzen/news/starbucks_aid_57627.html (accessed on 08.01.2008).
[7] Tice, C. (2001). Grocery sales steamin’ at Starbucks. Available from http://www.bizjournals.com/seattle/stories/2001/01/29/story2.html (accessed on 08.01.2008).
[8] Kotler et. al (2004), p. 49.
[9] Linn, A. (2007). Starbucks aims to increase its reach. Available from http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/17263863/ (accessed on 08.01.2008).
[10] Kotler et. al (2004), p. 49 & 310.
[11] Schüller, T. (2007). Der Kaffee ist fertig (EuramS). Available from http://www.finanzen.net/nachricht/Der_Kaffee_ist_fertig_EuramS__640464 (accessed on 08.01.2008).
[12] Linn, A. (2007). Starbucks aims to increase its reach. Available from http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/17263863/ (accessed on 08.01.2008).
[13] Tice, C. (2001). Grocery sales steamin’ at Starbucks. Available from http://www.bizjournals.com/seattle/stories/2001/01/29/story2.html (accessed on 08.01.2008).
[14] Kotler et. al (2004), p. 49 & 277.
[15] Company press release (2003). Netkey retail solution for Kraft and Starbucks featured in BRANDWEEK. Available from http://www.netkey.com/company/news_detail.aspx? count=4&ctid=12&ntkid=303 (accessed on 08.01.2008).
[16] Tice, C. (2001). Grocery sales steamin’ at Starbucks. Available from http://www.bizjournals.com/seattle/stories/2001/01/29/story2.html (accessed on 08.01.2008).
[17] International guild of hospitality and restaurant managers. Available from http://www.hospitalityguild.com/Financial/Restaurants/Starbucks%20Corporation.htm (accessed on 08.01.2008).
- No comments yet.

Similar texts

Situational Analysis and Marketing Strategy of Lorenz Bahlsen GmbH & Co KG

The Marketing Strategy of Oatly

E-Marketing Strategy for Reg Vardy

Analysis of Nokia‘s Corporate, business, and marketing strategies

Country of Origin Effects as Key Success Factor for Marketing Strategies

The Marketing Strategy of the foreign Hypermarket Wal-Mart in China

Marketing Strategy for Set up Photovoltaic Solar Energy Systems in Turkey

Marketing Strategies for Indian Software Development Companies in Entering We...

Evaluation of the Marketing Strategy of Tesla Motors Inc

Amazon Case Study. "The Best Marketing Strategies Aren’t Top Down, They’...

International Marketing Strategies to Go Global

Marketing Strategies of Online Shopping in UK on Customer Behavior

Harley-Davidson Marketing Strategy in the US and China

The Impact of Technology on Marketing Strategy

International Marketing Strategy

Current and Past Marketing Strategies of Microsoft

Marketing strategy of Sony for portable audio device business

Applied Marketing Strategy - The Rocker Hotel Sunderland

Amazon Marketing Strategy
Upload papers
Your term paper / thesis:
- Publication as eBook and book - High royalties for the sales - Completely free - with ISBN - It only takes five minutes - Every paper finds readers
Publish now - it's free


- Free Case Studies
- Business Essays
Write My Case Study
Buy Case Study
Case Study Help
- Case Study For Sale
- Case Study Services
- Hire Writer
Starbucks Marketing Strategy
Prepared for: Starbucks Coffee Submitted: Thursday, 2nd February 2012 Prepared by: • Velisya (551496) • Aktalisa Tifany (548994) • Steffany Ciputri (551288) • Gabriela Tiffany (546561) Executive Summary This essay discuss about how Starbucks utilizes its marketing mix in order to gain market share.
Starbucks, which has been in the coffeehouse industry for 41 years, face higher competition than before. Even so, Starbucks is able to not only survive through this, but they are able to be “one of the most valuable global brands” (Theodore 2002).In its maturity stage, they are capable of expanding their consumer base despite the fact of increasing competition. Through the augmentation of their products they could gain consumer loyalty. Starbucks uses price-skimming strategy in which they set higher price compared to others to indicate higher quality.
We Will Write a Custom Case Study Specifically For You For Only $13.90/page!
Thus, this shows that Starbucks utilizes its pricing as their signaling device. In addition, Starbucks does not frequently use traditional means of advertising. In fact, they do not spend a lot on advertising and only depend upon their customer through their word of mouth advertising.Starbucks distributes their product widely in places that enables consumers to easily reach them and for them to reach their customers. It uses vertical marketing system in which it distributes their product through direct and indirect channel. Therefore, by using their marketing mix efficiently, Starbucks is able to increase its consumer loyalty, brand equity and also the rate of adoption.
Table of Contents Cover Page1 Executive Summary2 Table of Contents3 Overview4 The External Environment4 Customer Analysis & Evaluation5 Marketing Mix6-10 Product6-7 Price8 Promotion9 Place10 Conclusion11References12 Overview Starbucks, which first originated from Seattle in 1971, is a company that specializes on its coffeehouses. Providing high quality coffee, good ambience and genuine service to their customers. Over time, Starbucks diversify its products into tea, ice creams, juices and savory delights. However, this essay will only focus on its coffee products. Being the largest in the coffeehouse industry, Starbucks coffee receives massive competition from other producers. This essay will discuss how Starbucks uses its marketing mix to sell and compete against other competitors.
The External Environment With its high level of competition, Starbucks needs to utilize its marketing mix in an even better way. Some of its direct competitors include Gloria Jeans, Hudson’s Coffee and Coffee Beans. Its indirect competitors being Redbull, Monster and Nescafe bottled coffee. Major competitors in the future could be Gloria Jean’s that is now expanding in the market. Starbucks should take into account the replacement products that may threaten the future of their products. These include energy drinks such as Redbull and Monster.
Since it is more widely distributed in convenient stores and has a longer shelf life, these products tend to attract more consumers from the younger generation. As Starbucks has good positioning in the market, it will be difficult for replacement products to take over its market share. Most coffee houses are not only about its coffee anymore, they are also widely known as places for people to socialize, and therefore the location of the Starbucks shops should be easily found and the place should be comfortable. Since it is dealing with food and beverages, it is important for Starbucks to ensure the quality and taste of its products.Once customers have positive experience with Starbucks, people may spread the positive feedback and promote to people around them, minimizing the need to use mass media promotion. In addition, due to high competition in the coffee house industry, Starbucks has to be cautious in setting its prices.
If the price is too high and is beyond consumers’ price range, they might switch to other competitors, and if it is too low, it may signal low quality. Compared to the other coffeehouses, Starbucks has a greater augmentation layer. Now, Starbucks has provided ice creams, alcoholic beverages, teas and juices in addition to coffee.Not many companies has this wide range of products sold in the market. Customer Analysis and Evaluation The target market for Starbucks Coffee used to be the established customers, which includes the middle to high economic class of the society such as the elderly and the professional workers who enjoys high quality coffee.
However, as their business expands, its customers are becoming more diversified. Starbucks’ target market moves towards the “younger, less well-educated, and in a lower income bracket than their more established customers,” (Moon).Starbucks position itself as a brand which provides high quality products and is environmentally conscious. Nowadays, people are becoming more environmentally friendly due to higher knowledge on global warming. Therefore, Starbucks is able to improve its brand image by using a recycled packaging.
Through time, Starbucks reposition itself not to be too concentrated on coffee itself but to diversify their products. This is shown by changing their brand logo in 2011. Because its product is in its maturity stage it is important for them to diversify its products and differentiate themselves against competitors.Consumers are exposed to different types of goods everyday. They do not always make the same purchase everyday. They make decisions and efforts to choose the products that suit the most.
In the purchase decision theory, Starbucks coffee is classified as a minor re-purchase group. The customers make routine purchase of the good without searching for other options. In this case, the customers are said to be brand loyal. Brand loyalty is the result of a satisfying post-purchase evaluation. Starbucks has developed strong brand loyalty and convenience to its customers by providing great distribution and coffeehouse experience.Furthermore, consumers perceive Starbucks as an environmentally responsible company that sells high quality products.
Consumer perception is essential since it influences Starbucks’ positioning in the market. Loyal consumers of Starbucks have influenced others through word of mouth advertising. This tempts other people who are not a frequent purchaser to buy coffee from Starbucks. Those new customers may even become loyal towards the brand if they have a positive post-purchase experience. Product Starbucks has a wide range of coffee products. It has packed coffee beans, cold and hot coffee drink, and blended coffee.
For the packed coffee beans, Starbucks offers Coffee from Latin America, Africa, and Asia/Pacific. For the hot drinks, it has Flat White, Caffe Americano, Cappuccino, Caffe Latte, Caffe Mocha, Caramel Machiato, Brewed Coffee, White Chocolate Mocha, Espresso, Espresso Machiato, Espresso Con Panna, Caffe Misto. For the cold beverages, it has Iced Latte, Iced Cafe Mocha, Iced Caramel Machiato, Iced Americano, and Iced Cream Brulee Macchiato. Moreover, Starbucks also has its Frappucino Blended Coffee that has different flavours such as, caramel, mocha, dark mocha, white chocolate mocha, java chip, and espresso.During customers’ first purchase, coffee is a shopping product. They search for the brand that suits them the most and compare the qualities of different brands.
Then, after several acts of buying, they become familiar with the brand and repeat their purchase (routinised response behavior). Thus, coffee becomes a convenience product that people buy regularly and become loyal to the brand. The loyalty of the consumers increases the brand equity of a product. The core product of Starbucks coffee is the coffee itself. The expected products are the quality, flavor, and aroma.
Customers who purchase Starbucks coffee expect a high quality coffee full of nice aroma and rich in flavor. Starbucks creates a homely atmosphere in its cafe where people can socialize and enjoy their coffee Starbucks coffee is considered to be a highly augmented product. The augmented products are the brand, the packaging, and the intangible service. Starbucks coffee could be considered as a low involvement product because it is relatively cheap and as a daily product, it would not really impact the consumers’ lifestyle. Brand increases customers’ awareness towards a particular product and the ability to recall the product simultaneously.Starbucks changes its logo over the years.
When it first established in 1987, the logo was brown circle with a picture of a mermaid in the middle. Then in 1987, Starbucks changed its logo color into green and add the company’s name. In 2011, Starbucks changed its logo again by removing the company’s name from its logo. The new logo is more eye catchy than the old one. The purpose of this is to catch consumers’ attentions. Starbucks brand is synonymous with high quality and environmental friendly.
Starbucks uses recycled packaging for its product. The coffee beans and drinks are packaged in recycled bag and cups.In 1971, Starbucks first launched its coffee to the consumers. During the introduction stage, only coffee beans were sold. At that stage, it was really risky to start a business because of the high cost and low sales.
Moreover, Starbucks needed to encourage their customers to sample its product and build brand awareness by distributing its goods. Innovators were the type of consumers that sample the products. The characteristics for this type of consumers are willing to try new product and risk taker. As time goes by, Starbucks coffee product entered the growth stage and consumers start to recognize the product.In 1992, Starbucks expanded its market by opening 17,000 cafes in 49 countries that serve hot and cold drinks.
They also launched new product: Frapucinno. Frapucinno was first a failed product, nonetheless, customers like it. Starbucks coffee products are now in their maturity stage. The cost drops significantly and sales increases. At this stage, Starbucks maintains its brand differentiation and keeps inventing new products to increase market share. One of it most popular innovations are themed drinks for many occasions such as Christmas and summer holiday which are only available during certain periods.
Furthermore, during the maturity stage, product augmentation is highly important so that sales would not decline. Starbucks should create more types of coffee drink and new flavors. For example, Coffee milkshake and fruit flavored coffee. Moreover, Starbucks should also launch a diet coffee for health conscious consumers. Starbucks should reduce the sugar in their coffee drinks because lately, people are becoming more aware on their health and start to decrease their sugar intake. Price Price is really important since it has huge impact towards the customers, it stimulates customers’ intention to purchase.
Starbucks coffee can be categorized as an expensive coffee compared to other brands. But still, its demand is very high. Firstly, it is because their perceived value and benefits that exceeds the perceived costs. This means the high cost of Starbucks coffee is worth the quality of its coffee. Eventhough Starbucks coffee’s price is higher than others, a lot of customers still keep on buying Starbucks coffee, thus it can be concluded that Starbucks’ customers are less price sensitive, thus Starbucks’ coffee is price inelastic.Starbucks uses its pricing as their signaling device, they are telling customers that their high price indicates their coffee’s high quality.
However, by using pricing as signaling device, Starbucks has to prove this with their product’s performance, and it has been proven through its high quality coffee. Starbucks also uses skimming pricing strategy, which indicates that their products are unique and this is proven by being the only one coffeehouse industries that create Frapucinno. Their duration of skimming strategy depends on competitors and product positioning.Based on Starbucks situation, their skimming strategy clearly depends on its product positioning since they set their price high in order to position their product as a high quality product. They have proved it for years by providing a high quality coffee compared to their other competitors’.
Secondly, due to Starbucks worldwide-known brand, which is associated with its great quality coffee. By seeing the brand “Starbucks”, customers straight away think towards the high quality of Starbucks’ coffee and therefore it gives customers a sense of security by reducing their risk of purchase.A lot of consumers purchase Starbucks coffee on the basis of its brand name, thus it increases their brand loyalty , therefore affect their overall brand equity to a certain degree. Despite the higher price of Starbucks’ coffee compared to the others, people still buy Starbucks coffee since the benefit outweigh their cost meaning the quality of its coffee worth the cost. Therefore, Starbucks’ brand has differentiated its products and due to this brand loyalty, Starbucks, which its coffee can be categorized as a low involvement good has minimize customer’s cognitive activity and therefore decreases its price.
In this way, consumer behavior overlaps with pricing. Therefore, it can be concluded that due to its high price, Starbucks are targeting group of people with middle to high income. Based on the current situations of Starbucks, they are now in the maturity growing stage, in which the number of competitors has reached its peak resulting in strong price competition that might ignite price wars. Starbucks has been a successful company for long period of time, they have raised high revenue and generate profit. They have raised 10% profits for 3 months to January 2012. Its revenue also increases by 16% to $3.
4 billion. (BBC News 2012)Thus, they are able to eliminate its new competitors by setting a price war. They are able to drop its price and keep it longer than the new competitors resulting in the loss for the new competitors since they are not even able to breakeven. Its post-purchase decision behaviour is such that customers repeat the purchase as a result of positive experience, due to its price that is still affordable and worth the quality of the coffee. Lastly, Starbucks should create more special offers and vouchers so that it will attract new consumers who have never tried Starbucks before.
Promotion Promotion is one of the most important parts of marketing. It is how the company communicates, delivers message to its customers. While other companies pay a large amount of money for their promotions through mass media, Starbucks’ approach in its promotion relies more on its own customers’ word-of-mouth. Unlike perhaps other companies that boast their growth plans and revenues, Starbucks have been trying to promote its values and also its commitments to the community and customers, and word-of-mouth tends to support this strategy (Tewell, Odom & Snider 2006: 18).Due to its already famous brand recognition in the market, its company image and especially its logo is already well-known. Recently, Starbucks decided to change its logo as a way to rejuvenate its image in the market and also because it is trying to reach wider range of target market.
Now, not only it sells coffee, Starbucks has been trying to create and sell more varieties of drinks, foods, ice-cream and even alcoholic beverage (BBC News 2011). This move also serves as a means to reposition itself in the market and to differentiate the company from its competitors, such as Gloria Jeans.Thus, the word “coffee” is no longer printed in its logo. Not only changing its logo, Starbucks is trying to make its image better through its ‘go-green’ packaging that is environmentally friendly (Tewell, Odom & Snider 2006: 13). It would not only increase its social responsibility which gives positive impact to the nature but also would give a positive boost to the company’s image. Promotion tends to play an important role for a company mostly when it is in its maturity stage.
One reason is that there would be only a little differentiation between that company, in this case Starbucks, and its competitors. Therefore promotion would help customers recall its products when they are making their pre-purchase decisions, and Starbucks is doing this by depending on word-of-mouth promotion. The more Starbucks advertise its product, the more aware the customers would be about it. The interesting displays or banners and vouchers could attract new customers and those that have bought and like Starbucks’ products tend to tell their experience to friends.At this moment, Starbucks attract more customers’ attention and awareness through the word-of-mouth advertising rather than using mass media, although it does have a website and it can also be accessible through social networking sites.
Customers have acknowledged the products and will continue to deliver this knowledge through word-of-mouth. This word-of-mouth advertising is mostly due to the customers’ acceptance and positive reviews, and it has been proven to be an external influence that plays positive and important role to Starbucks.In addition to all that, Starbucks make other attempts to advertise such as verbal offers by the employees, collection of stamps from each purchase, etc. Overall of Starbucks’ promotion, it mostly applies a ‘word of mouth’ strategy which is a very effective way in promoting their products. Starbucks just spend very little on advertising as its brand is already well known by most people.
Place For a product to be able to satisfy consumer needs, it must distributed strategically in places where it is easy for consumers to reach the producers and for producers to do the same thing.Starbucks distribute its product selectively to more than one but less than all the intermediaries who are willing to carry Starbuck’s Product, exposing their brand in selected outlet that is closely related. Starbucks is a Franchise organization, which uses contractual vertical marketing system. This means that there is a legally binding contract, which keeps the entire Starbucks store together, and works towards the same goal. Starbucks has both direct and indirect marketing channel.Its direct channel being the Starbucks outlet and its indirect channel being the bottled Starbucks Frappuccino and its instant coffee which is available in vending machines and other convenient stores such as Seven Eleven.
Channel selection is very important as it affect other elements of the marketing mix. By distributing enough products for consumers at the time and place they needed, Starbucks is able to strengthen their brand equity. Thus, it minimizes the behavioral effort for purchasing decision and also increases the intangible benefits for consumer, which includes time and place utility.Through this, Starbucks is able to increase the value of their product. This leads to customers being satisfied and they are likely to advertise Starbucks to others through word of mouth advertising. Peter Maslen (cited in Karolefski 2002), the President of Starbucks Coffee International says that, “[Starbucks depend] on repeat purchase and loyalty [,] we don’t do advertising or traditional marketing, we depend very much on the in-store experience and building loyalty that way.
Therefore, by distributing enough products for consumers at the time and place they needed and also providing customers with a good coffeehouse experience, Starbucks is able to improve its brand equity. In the growing maturity stage of its product life cycle, Starbucks dominates the market share. Having a high level of capital to fund their expansion, Starbucks is able to find the right spot where their targeted consumers are located. In fact, as of Decemberr 2011 Starbucks has “more than 17,000 retail stores in over 55 countries” (Starbucks 2011).Through its expansion, Starbucks is able to provide a relative advantage and better satisfaction for their consumers through convenience. In their growing maturity stage, Starbucks have a wider distribution channel that increases consumer loyalty, brand equity and the rate of adoption.
Starbucks has a more diversified customer base over time. To reach an even wider customer base, Starbucks locates its stores conveniently whereby segments of their consumers would be able to enjoy their products. Most of its stores are located in shopping malls and city areas where most of their consumers gather.Additionally, through its product distribution on indirect channel, consumers with time constraint can easily purchase their product without going to their outlets. When the consumers of Starbucks evaluate their alternatives, they are likely to compare it from the evoked set, for example Gloria Jean’s.
In terms of place, Starbucks have a relative advantage, as they are able to distribute their products at many different locations. Customer would be able to save time and it decreases the purchasing effort for customers.Therefore, Starbucks is able to comply with the changing behavior of consumer who wants everything to be readily available at convenient places. Conclusion Over the past few years, Starbucks is becoming more diversified by producing new products and attracting more customers. Starbucks has uses its marketing mix efficiently and capture a huge share of the market. Currently, Starbucks Coffee is in its maturity stage of its PLC.
In order to survive in the market, they have higher augmentation. They also set their price higher than their competitors to indicate higher quality coffee.Although Starbucks does not spend a lot on advertising, but still its brand is widely known through word of mouth advertising. By widely distributing their products in convenient locations, Starbucks is able to increase its consumer loyalty, brand equity and also the rate of adoption. Starbucks is a good example for other company in the way they use their marketing strategy. By using their marketing mix efficiently, they are capable of gaining consumer loyalty, brand equity and also the rate of adoption.
References BBC News. 2012. ‘Starbucks profits rise 10%’. Retrieved January 27, 2012, from http://www. bc. co.
uk/news/business-16752929 BBC News. 2011. ‘Starbucks drops its name and the word coffee from logo’. Retrieved January 6, 2011, from http://www. bbc. co.
uk/news/business-12125440. Karolefski, J. 2002. ‘Starbucks: Conquering New Grounds’. Retrieved 30 Jan 2012, from http://www.
brandchannel. com/features_effect. asp? pf_id=78. Lofthouse, R. (n.
d. ) 2011, ‘HOW ONE BRAND CHANGED THE WORLD’ – CNBC Business. Financial & Business News – CNBC Business. Retrieved January 31, 2012, from http://www. cnbcmagazine. com/story/how-one-brand-changed-the-world/1297/1/ Moon, Youngme, and Quelch J.
Starbucks: Delivering Customer Service’. Harvard College. Boston: Harvard Business School, 2003. 1-20. Starbucks Company, ‘Starbucks Company Profile’ (PDF file), downloaded from http://www.
starbucks. com/about-us/company-information, accessed 31 January, 2012. Tewell, K. , Odom, B. & Snider, K.
2006. ‘Starbucks Marketing Plan’. Retrieved December 12, 2006, from http://www. franklincollege. edu/pwp/BOdom/SampleWorkStarbucks.
pdf. Theodore, S. ‘Expanding the coffee experience: Starbucks keeps sales brewing with new products, innovation and global expansion [Electronic version]’. Beverage Industry, 2002. P.
Related posts:
- Starbucks Case
- Case Study: Arnott’s Emporio Marketing Strategy
- Whirlpool’s global marketing strategy
- The ‘Apple, Inc’ Should Continue to Implement ‘Hunger Marketing’ Strategy in China
- Marketing Starbucks Case Study
- Starbucks Strategy & Internal Intiatives to Teturn to Profitable Growth
Quick Links
Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Testimonials
Our Services
Case Study Writing Services
Case Studies For Sale
Our Company
Welcome to the world of case studies that can bring you high grades! Here, at ACaseStudy.com, we deliver professionally written papers, and the best grades for you from your professors are guaranteed!
[email protected] 804-506-0782 350 5th Ave, New York, NY 10118, USA
Acasestudy.com © 2007-2019 All rights reserved.

Hi! I'm Anna
Would you like to get a custom case study? How about receiving a customized one?
Haven't Found The Case Study You Want?
For Only $13.90/page

Marketing Mix
Ai generator.
- Practice Questions

The Marketing Mix is a crucial concept in marketing that involves the strategic integration of four primary elements: product, price, place, and promotion. These elements help businesses create a balanced approach to delivering value to customers and achieving their objectives. A Product Marketing Strategy focuses on defining and promoting a product’s unique features and benefits to target customers effectively. A Marketing Strategy Report outlines detailed plans and analyses to guide marketing efforts and measure performance. A Marketing Strategy Business Plan integrates these elements into a comprehensive roadmap for achieving business goals and sustaining competitive advantage.
What Is Marketing Mix?
The Marketing Mix is a set of strategic tools used to achieve marketing objectives by balancing four key elements: product, price, place, and promotion. It supports a Marketing Strategy and a Business Marketing Strategy by ensuring cohesive and targeted efforts to meet customer needs and drive business growth.
Examples of Marketing Mix

- Apple iPhone: Regular updates with new features to maintain market interest.
- Coca-Cola: Consistent taste and branding across all markets.
- Tesla: High-tech electric vehicles with a focus on innovation and sustainability.
- Nike Shoes: Extensive range of athletic footwear tailored to various sports.
- Samsung Galaxy: Competitive smartphone features and continuous innovation.
- Lego Sets: Diverse themes and collaboration with popular franchises.
- McDonald’s Menu: Localized menu items catering to regional tastes.
- Amazon Kindle: Continuous improvement in e-reader technology and features.
- Starbucks Coffee: Variety of coffee blends and seasonal offerings.
- Toyota Prius: Emphasis on hybrid technology and fuel efficiency.
- Walmart: Everyday low pricing strategy.
- Apple: Premium pricing to position products as high-end.
- IKEA: Affordable pricing with a do-it-yourself assembly model.
- Dollar Tree: Uniform pricing of $1 for all items.
- Netflix: Subscription pricing tiers based on content access and quality.
- Zara: Competitive pricing for trendy fashion items.
- Costco: Membership-based pricing for bulk purchases.
- AirAsia: Low-cost airline pricing with add-ons for additional services.
- H&M: Affordable fashion with frequent sales promotions.
- Adobe Creative Cloud: Subscription model with various pricing plans.
- Amazon: Extensive online presence with a global reach.
- Starbucks: Strategic placement of stores in high-traffic areas.
- Walmart: Large number of retail stores across various regions.
- IKEA: Large warehouse stores in suburban locations.
- McDonald’s: Worldwide presence with local franchise models.
- Nike: Flagship stores in major cities and online shopping options.
- Apple: Exclusive Apple Stores and authorized resellers.
- Tesla: Direct-to-consumer sales model with showrooms in high-end locations.
- Target: Accessible store locations in urban and suburban areas.
- Costco: Membership warehouses in strategic locations.
- Coca-Cola: Global advertising campaigns and sponsorships.
- Nike: Endorsements from top athletes and sports teams.
- Apple: High-profile product launches and keynote events.
- Pepsi: Engaging social media marketing and influencer partnerships.
- Toyota: Comprehensive advertising across TV, digital, and print media.
- Samsung: Innovative product demos and experiential marketing.
- Netflix: Original content promotion through various media channels.
- L’Oréal: Influencer collaborations and beauty tutorials.
- Red Bull: Extreme sports sponsorships and event marketing.
- Google: Digital advertising and targeted online marketing campaigns.
7 Ps of marketing Mix with Examples
Product: The tangible or intangible goods or services offered by a business.
- Apple iPhone: High-tech smartphones with regular updates and innovative features.
- Nike Shoes: Diverse range of athletic footwear catering to different sports and fashion trends.
Price: The amount of money customers must pay to acquire the product.
- Apple: Premium pricing to position products as high-end and exclusive.
Place: The distribution channels used to deliver the product to customers.
- Amazon: Extensive online marketplace with a global reach.
- Starbucks: Strategic store locations in high-traffic areas and urban centers.
Promotion: The activities undertaken to make the product known to potential customers.
- Coca-Cola: Global advertising campaigns and sponsorships of major events.
- Nike: Endorsements from top athletes and high-visibility sports sponsorships.
People: The staff and salespeople who work for the business and interact with customers.
- Ritz-Carlton: Exceptional customer service with well-trained staff.
- Disney: Cast members who enhance the guest experience at theme parks.
Process: The procedures and processes involved in delivering the product or service to the customer.
- McDonald’s: Efficient and standardized service process for quick food delivery.
- Amazon: Streamlined online shopping and fast delivery processes.
Physical Evidence: The environment and tangible cues that customers use to evaluate the quality of the product or service.
- Starbucks: Cozy and inviting store ambiance with comfortable seating and Wi-Fi.
- Apple Stores: Sleek, modern retail spaces designed to showcase products and enhance customer experience.
Marketing mix examples of companies
Product: High-tech consumer electronics, including iPhones, iPads, MacBooks, and accessories. Emphasis on innovation, design, and user experience.
Price: Premium pricing strategy to position products as high-end and exclusive.
Place: Exclusive Apple Stores, online store, and authorized resellers worldwide.
Promotion: High-profile product launches, keynote events, and targeted advertising campaigns emphasizing product quality and innovation.
People: Knowledgeable and well-trained staff in Apple Stores providing excellent customer service.
Process: Seamless integration of hardware, software, and services, streamlined purchasing process both online and in stores.
Physical Evidence: Sleek, modern Apple Stores with minimalist design, product packaging, and branding that conveys quality and innovation.
Product: Wide variety of products ranging from electronics to groceries. Continuous expansion of product categories and services.
Price: Competitive pricing, dynamic pricing strategies, and frequent discounts.
Place: Extensive online marketplace accessible globally, with efficient distribution centers and logistics. Promotion: Digital advertising, personalized marketing, and Prime membership benefits.
People: Customer service teams and AI-driven support systems to handle customer inquiries efficiently.
Process: Streamlined purchasing process with easy navigation, one-click ordering, and fast delivery options. Physical Evidence: User-friendly website and app design, clear product listings, and reliable delivery services.
Marketing mix case study
Offerings: Starbucks provides a wide range of high-quality coffee beverages, teas, pastries, and snacks. They also sell coffee beans, branded merchandise, and seasonal items. Starbucks focuses on product innovation, regularly introducing new flavors, limited-time offers, and seasonal beverages like the Pumpkin Spice Latte.
Example: The introduction of cold brew coffee and nitro cold brew catered to the growing trend for cold coffee beverages, attracting a new segment of customers looking for premium cold coffee options.
Strategy: Starbucks uses a premium pricing strategy to reflect the high quality of its products and the overall customer experience. While their prices are higher compared to fast-food coffee options, they offer perceived value through quality, ambiance, and service.
Example: Despite higher prices, customers are willing to pay for the unique Starbucks experience, including the customization of drinks and the comfortable store environment.
Distribution Channels: Starbucks has a vast network of company-owned and licensed stores located in high-traffic areas such as city centers, malls, and airports. They also offer products through grocery stores and online platforms.
Example: The strategic placement of Starbucks stores in urban areas, college campuses, and high-traffic retail locations ensures accessibility and convenience for customers.
4. Promotion
Advertising and Promotions: Starbucks employs a mix of traditional advertising, digital marketing, social media engagement, and customer loyalty programs. They focus on storytelling and creating a connection with their audience.
Example: The Starbucks Rewards program encourages repeat purchases by offering points for every transaction, which can be redeemed for free items. This program also provides personalized offers based on purchase history.
Staff and Customer Service: Starbucks places a strong emphasis on hiring and training baristas to deliver excellent customer service. Employees, known as partners, are trained to create a welcoming atmosphere and to personalize customer orders.
Example: Baristas are trained to remember regular customers’ names and preferences, enhancing the personalized experience and fostering customer loyalty.
Operational Efficiency: Starbucks ensures a smooth and efficient service process, from ordering to delivery. This includes mobile ordering and payment options through the Starbucks app, reducing wait times and improving customer convenience.
Example: The Starbucks app allows customers to place orders in advance and pick them up at a designated time, streamlining the ordering process and enhancing convenience.
7. Physical Evidence
Environment and Branding: Starbucks stores are designed to provide a comfortable and inviting environment with free Wi-Fi, relaxing music, and cozy seating. The store layout and design reflect the brand’s identity and enhance the overall customer experience.
Example: The ambiance of Starbucks stores, with their modern décor and cozy atmosphere, encourages customers to spend time in the store, whether for socializing, working, or relaxing.
Process of marketing mix
Market research and analysis.
Understanding the Market: Conduct thorough research to understand the market dynamics, customer needs, preferences, and behavior. Analyze competitors, market trends, and potential opportunities.
Example: A tech company conducts surveys, focus groups, and competitor analysis to identify gaps in the market for a new wearable device.
Strategic Planning
Setting Objectives: Define clear, measurable marketing objectives aligned with business goals. This could include increasing market share, launching a new product, or entering a new market.
Example: A cosmetics company sets an objective to increase its market share by 10% within a year by introducing a new line of organic skincare products.
Product Development
Design and Testing: Develop a product that meets the identified needs. This includes designing, prototyping, and testing the product to ensure it meets quality standards.
Example: An automotive company develops and tests electric vehicles to ensure they meet safety and performance standards before launching.
Pricing Models
Determining Price Points: Establish pricing strategies based on cost, value perception, competition, and market demand. Consider various pricing models like cost-plus, value-based, or dynamic pricing.
Example: A software company adopts a subscription-based pricing model, offering different tiers based on features and usage levels.
Channel Selection
Choosing Distribution Channels: Select the most effective channels to reach target customers. This could include direct sales, online platforms, retail stores, or third-party distributors.
Example: A fashion brand decides to sell its products through its e-commerce site, partnered boutiques, and online marketplaces like Amazon.
Promotional Tactics
Creating Campaigns: Develop integrated marketing campaigns using a mix of advertising, public relations, sales promotions, and digital marketing to reach and engage customers.
Example: A beverage company launches a multi-channel promotional campaign featuring TV ads, social media contests, influencer partnerships, and in-store promotions.
Customer Engagement
Building Relationships: Focus on creating and maintaining strong relationships with customers through personalized interactions, loyalty programs, and excellent customer service.
Example: A retail chain implements a loyalty program that rewards customers with points for every purchase, which can be redeemed for discounts or special offers.
Feedback and Improvement
Collecting and Analyzing Feedback: Gather customer feedback through surveys, reviews, and social media interactions. Use this feedback to make continuous improvements to products and marketing strategies. Example: A smartphone manufacturer regularly collects customer feedback on new models and uses the insights to enhance future designs and features.
Performance Measurement
Monitoring and Evaluation: Track the performance of marketing activities using key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales figures, market share, customer acquisition cost, and return on investment (ROI).
Example: An online education platform monitors metrics like enrollment rates, user engagement, and customer satisfaction to evaluate the success of its marketing efforts.
Example: Integrated Marketing Communication in Product Marketing
Context: Launching a New Fitness App
Market Research and Analysis:
- Conduct surveys and focus groups to understand the needs of fitness enthusiasts.
- Analyze competitors’ apps to identify unique selling points.
Strategic Planning:
- Set an objective to achieve 100,000 downloads within the first six months.
Product Development:
- Design the app with features like personalized workout plans, nutrition tracking, and social sharing.
- Test the app with a beta group to gather feedback and make necessary improvements.
Pricing Models:
- Offer a freemium model with basic features available for free and premium features accessible through a subscription.
Channel Selection:
- Distribute the app through major app stores like Apple App Store and Google Play Store.
- Partner with fitness influencers and blogs for wider reach.
Promotional Tactics:
- Launch a comprehensive promotional campaign including social media ads, influencer partnerships, email marketing, and in-app promotions.
Customer Engagement:
- Create a community within the app where users can share their progress and tips.
- Offer personalized customer support to address user queries and issues.
Feedback and Improvement:
- Collect user feedback through in-app surveys and app store reviews.
- Continuously update the app based on user feedback to improve functionality and user experience.
Performance Measurement:
- Track KPIs such as download numbers, active users, user retention rate, and customer satisfaction scores.
Marketing strategy
A marketing strategy is a comprehensive plan designed to promote and sell products or services to target customers through Email Marketing Strategy . It encompasses various tactics and actions aimed at achieving business objectives, such as increasing sales, building brand awareness, and gaining a competitive advantage.
1. Market Research and Analysis
Objective: Understand the market, customer needs, preferences, and behavior.
- Conduct surveys and focus groups.
- Analyze competitors and industry trends.
- Segment the market to identify target audiences.
- Example: A tech company surveys potential users to understand their needs before launching a new product.
2. Setting Objectives
Objective: Define clear, measurable marketing goals aligned with overall business objectives.
- Set SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals.
- Align marketing goals with sales targets and growth plans.
- Example: A clothing retailer sets a goal to increase online sales by 20% in the next six months.
3. Identifying Target Audience
Objective: Determine the specific group of customers to focus marketing efforts on.
- Create customer personas.
- Use demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral segmentation.
- Example: A cosmetics brand identifies young, urban women as its primary target audience for a new skincare line.
4. Developing the Marketing Mix (4 Ps)
Objective: Craft a balanced approach using Product, Price, Place, and Promotion.
- Product: Develop or refine products to meet customer needs.
- Price: Set competitive and profitable pricing strategies.
- Place: Choose distribution channels to reach the target audience effectively.
- Promotion: Design campaigns to communicate with customers and encourage purchases.
- Example: An electronics company launches a new gadget, prices it competitively, sells it through online and retail stores, and promotes it via social media ads and influencer partnerships.
5. Implementing the Strategy
Objective: Execute the planned marketing activities and campaigns.
- Develop a detailed action plan with timelines.
- Allocate resources and budget for each activity.
- Coordinate efforts across marketing, sales, and other departments.
- Example: A food delivery service implements a promotional campaign involving discounts, social media advertising, and partnerships with local influencers.
Weaknesses of the marketing mix
1. static framework.
Limitation: The traditional marketing mix (4 Ps) is relatively static and may not adapt well to the dynamic and fast-paced nature of modern markets.
Impact: It might not address rapidly changing consumer behaviors, technological advancements, or emerging market trends effectively.
Example: A business relying solely on the 4 Ps may struggle to keep up with the shift from brick-and-mortar to e-commerce platforms.
2. Overemphasis on Internal Factors
Limitation: The marketing mix focuses primarily on internal factors (product, price, place, promotion) and may overlook external factors such as economic conditions, regulatory changes, and competitive actions.
Impact: Businesses might miss critical market insights and fail to respond to external threats or opportunities. Example: A company might set a high price for a product without considering a looming economic downturn that reduces consumer purchasing power.
3. Lack of Customer Focus
Limitation: The original 4 Ps framework does not explicitly include the customer’s perspective, potentially leading to strategies that do not align with customer needs and preferences.
Impact: This can result in lower customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Example: A product might be developed based on the company’s capabilities rather than customer demand, leading to poor sales performance.
4. Neglect of Service Elements
Limitation: The 4 Ps were initially designed for tangible products and do not adequately address the nuances of service marketing, which requires additional elements such as people, processes, and physical evidence (7 Ps). Impact: Service-oriented businesses might find the traditional marketing mix insufficient for addressing their specific challenges.
Example: A hospital might struggle to fully capture the importance of patient care experience using only the 4 Ps framework.
What Are The Four Ps of Marketing?
1. Product: The goods or services a business offers to meet customer needs.
Example: A smartphone with features like a high-quality camera, long battery life, and sleek design.
2. Price: The amount of money customers pay to buy the product.
Example: A competitive price of $699 for a new smartphone to attract buyers.
3. Place: Where and how the product is sold and delivered to customers.
Example: Selling the smartphone through online stores, electronics retailers, and mobile carrier shops.
4. Promotion: The activities used to make customers aware of the product and encourage them to buy it.
Example: Advertising the smartphone through social media, TV commercials, and online ads, and offering special discounts.
The four Ps as the four Cs
1. product to customer.
Traditional P: Product focuses on the features and benefits of what a company offers.
Customer Perspective: Understand and fulfill customer needs and desires.
Example: Instead of just focusing on the features of a smartphone (Product), consider what the customer actually needs, such as a high-quality camera for photography enthusiasts or long battery life for business travelers.
2. Price to Cost
Traditional P: Price is the amount customers pay for a product.
Customer Perspective: Cost considers the customer’s total expenditure, including price, time, effort, and perceived value.
Example: For a streaming service, consider not only the subscription fee (Price) but also the value it provides in terms of content variety and the convenience of access (Cost).
3. Place to Convenience
Traditional P: Place involves the distribution channels used to deliver the product to customers.
Customer Perspective: Convenience focuses on how easily customers can obtain and use the product.
Example: Offering online shopping and fast home delivery (Convenience) instead of just focusing on retail store locations (Place).
Comparison Table
| Developing a smartphone that meets specific customer needs, like a high-quality camera for photographers. | ||
| Considering the total cost of a streaming service, including subscription fee and value of content. | ||
| Offering online shopping and fast home delivery options for increased customer convenience. | ||
| Engaging with customers via social media and personalized email campaigns to build relationships. |
What is the marketing mix?
The marketing mix consists of four key elements: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion, which businesses use to develop effective marketing strategies.
How does the marketing mix help businesses?
It helps businesses meet customer needs, promote products effectively, and achieve their marketing and business objectives.
Why is product important in the marketing mix?
The product element ensures that the goods or services offered meet customer needs and preferences, driving satisfaction and loyalty.
What factors influence pricing strategies?
Pricing strategies are influenced by production costs, competitor pricing, perceived value, and market demand.
How does place impact the marketing mix?
Place involves choosing the right distribution channels to ensure products are easily accessible to target customers.
What are common promotional tactics?
Promotional tactics include advertising, sales promotions, public relations, personal selling, and digital marketing.
How do businesses choose the right distribution channels?
They consider factors like target audience, product type, and market coverage to select effective distribution channels.
Why is branding part of the product element?
Branding creates a unique identity and image, helping differentiate the product and build customer loyalty.
How do businesses ensure effective promotion?
By using a mix of advertising, sales promotions, and digital marketing to reach and engage their target audience.
What role does customer feedback play in the marketing mix?
Customer feedback helps businesses refine their product, pricing, place, and promotion strategies to better meet market needs.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn What is Distribution Channel Strategy - In Marketing to make a passive income stream for long term income. This distribution channels in marketing is t...
With over 10 startups under his belt, Ian's been described as a serial entrepreneur— a badge he wears with pride. Ian's a published author and musician and when he's not obsessively testing the next marketing idea, he can be found hanging out with family and friends north of Boston. Marketing Strategy Starbucks. 0.
Introduction. Starbucks Corporation is an American multinational chain of coffeehouses and roastery reserves headquartered in Seattle, Washington. The company operates in over 30,000 locations in 70 countries worldwide as of early 2020. This blog is an in-depth analysis of Starbucks' marketing strategies, complete with touching upon their ...
Starbucks' Marketing Strategy. Founded in Seattle in 1971, Starbucks - one of the first US coffee house franchises at that time - quickly became known for the superior quality of its freshly-roasted, whole bean coffee. Since its establishment, the organisation has focused on a brand-centric marketing strategy, working to build and maintain ...
Strategic Analysis Of Starbucks Corporation Starbucks, with its size and scale, has the power to take advantage of its suppliers but it maintains a Fair trade certified coffee under its coffee and farmer equity (C.A.F.E) program, which gives its suppliers a fair partnership status, which yields them some moderately, low power. 7
4/ Personalization and the "Name-on-Cup" Strategy. Starbucks connects with customers on a personal level through the famous " name-on-cup " approach. Example: When Starbucks baristas misspell customers' names or write messages on cups, it often results in customers sharing their unique cups on social media. This user-generated content ...
Starbucks generated $32.25 billion in revenues in FY22. The business model of Starbucks consists of company-operated stores and licensed stores. As of FY22, Starbucks had 35,711 stores, comprising 18,253 company-operated stores (51%) and 17,458 licensed stores (49%). The mix of company-operated versus licensed stores in a given market generally ...
Decoding Starbucks' Marketing Strategy Success: Beyond the Coffee — Relevantly Facebook Marketing. Case Study. In an ever-evolving digital landscape, Starbucks stands out as a beacon of successful digital marketing. From its engaging social media presence to creative in-store experience, the Starbucks marketing strategy has continuously ...
Learn about Starbucks' iconic marketing strategy and advertising campaigns. Read how Starbucks aces the 4Ps of marketing mix - Product, Price, Promotion & Placement. ... In this case study, we will dive into various aspects of Starbucks' marketing strategy. A brief history of Starbucks. Starbucks was founded by three men — Jerry Baldwin, Zev ...
We believe that Starbucks should seek to expand its international presence and revenue, so it's not overdependent on its U.S. consumers. Key words: Starbucks, Marketing Mix Strategies, Michael Porter's Five Forces, Case Analysis Introduction: The first Starbucks opened its doors on March 31, 1971, by three friends, Jerry Baldwin, Gordon
Distribution Channel Marketing Strategy — Case Study (Starbucks) Tom Morgan ...
Table 2.Ten sub-types and their id's, selected features ("purchase requirement," "channel"), and projected success rate. Choice of channel (i.e., social media, mobile app, webpage, and email) for delivering single offers is a determining factor for a successful promotion (see Figure 4).For each subtype, a fixed set of channels were used to sent out single offers, and those that were ...
The Starbucks marketing strategy constitutes a blend of social media marketing, digital marketing, search engine optimization, and right post-marketing analysis. Replicating the entire Starbucks marketing strategy is nearly impossible for brands with low budgets. However, learning and implementing the core principles and the idea behind the ...
Starbucks Marketing Strategy: An In-Depth Look at What Makes Starbucks' Marketing so Effective. With over 34,000 stores across 80 markets, Starbucks has become the world's most valuable coffee brand worth $28 billion. Its continued growth is fueled by smart, consistent marketing strategies that appeal to diverse demographics worldwide.
The goal is to drive digitally registered customers into stores during non-peak hours. Offers are geared toward premium products, serving as a gateway to more profitable skus. Second, as alluded above, Starbucks views email as the first phase in its omnichannel retailing strategy. It is their first digital channel, not their last.
Key Topics Marketing Strategy Retailing Corporate Social Responsibility Globalisation Starbucks is the essential success story of the American capitalist dream. From humble beginnings in 1971 as a Seattle coffee store, it's become a multinational with over 21,000 outlets in 63 countries. Its brand is universally known. How did they do it?
That prepaid sum is up over 50% from 2019 levels and itself nearly covers Starbucks combined FY2021 and FY2022 capital expenditures. Starbucks CFO Rachel Ruggeri detailed, "Capital expenditures ...
Strategic Marketing: A Case Study of Starbucks. The document discusses Starbucks' global expansion and marketing strategies. It covers Starbucks' product levels including their core, actual and augmented products. It also discusses their product classification, individual product decisions around attributes, branding, packaging and services.
Starbucks Company's Brand and Distribution Strategy. This paper uses the case study of Starbucks Corporation as a first-class marketer of coffee to evaluate its brand today and its distribution strategy over time. Discover Starbucks distribution channels, strategic priorities, and its success factors.
Starbucks is the world leader in the premium coffee market and has an amazing success story. In this study the key factors for the successes of Starbucks are analyzed. The distribution strategy of Starbucks, e.g. through coffee stores, grocery markets, and new retail channels, is investigated.
A "channel steward" is a player in the chain who is best positioned to look out for the interests of all involved and devise a win-win strategy. Distribution strategy needs the attention of high-level executives—not just a product manager. Think of the Internet as a complementary go-to-market tool, not a total solution.
Starbucks uses price-skimming strategy in which they set higher price compared to others to indicate higher quality. We Will Write a Custom Case Study Specifically. For You For Only $13.90/page! order now. Thus, this shows that Starbucks utilizes its pricing as their signaling device.
Starbucks Distribution Channel Strategy Starbucks utilizes a multi-channel distribution strategy to reach its customers. This strategy includes both direct and indirect ... Wheaties Case Study. Introduction to Marketing 100% (10) 1. T5)DQ1 - Discussion Question ... Write 250 words utilizing your research findings for the marketing mix of ...
Starbucks: Strategic store locations in high-traffic areas and urban centers. ... Marketing mix case study 1. Product. ... Distribution Channels: Starbucks has a vast network of company-owned and licensed stores located in high-traffic areas such as city centers, malls, and airports. They also offer products through grocery stores and online ...