

The Ultimate Guide to Rational Decision-Making (With Steps)

Making decisions is an integral part of our lives. However, how many times do we really stop to think whether our choices are rational or not?
This article dives deep into the concept of rational decision-making, its importance, real-life examples, steps involved, factors influencing it, ways to enhance your skills, potential challenges, and how cognitive biases impact it. Let’s dive in.
What is Rational Decision-Making?
Rational decision-making, at its core, is a multi-step process used to make choices that are logical, informed, and objective. It involves identifying a decision problem, gathering information, evaluating alternatives, and selecting the most rational choice. This is a stark contrast to decisions based on subjectivity or intuition, which may often rely on feelings, emotions, or personal biases.
The goal of rational decision-making is to reach decisions that support your objectives in the most optimal way. The basis of this process is rationality—a concept that propels us to make decisions that provide the maximum benefit or, in other words, the best possible outcome. Rationality encourages us to follow a path that aligns with our goals and values while making decisions. It’s an antidote to impulsive choices or decisions clouded by bias and personal emotions.
While intuitive decisions can sometimes lead to effective outcomes, especially in situations demanding quick responses, rational decision-making allows us to consider all available options, analyze their potential consequences, and make an informed choice. This often leads to decisions that are more aligned with our long-term goals and less likely to result in unintended consequences.
Why is Rational Decision-Making Important?
Rational decision-making is the cornerstone of effective problem-solving and critical thinking. It helps us to make informed choices that are not only beneficial but also ethical, a crucial aspect in both personal and professional life.
In business, rational decision-making can lead to strategies that maximize profit, minimize risk, and promote organizational growth. It ensures resource optimization by aligning decisions with business objectives. Rationality ensures that every decision is data-driven, increasing the likelihood of successful outcomes.
On a personal level, rational decision-making can help us make better choices about our health, finances, relationships, and more. It enables us to make choices that align with our values and life goals, improving our overall quality of life.
Examples of Using Rational Decision-Making
Let’s see how rational decision-making manifests in various spheres.
Business: A company looking to launch a new product will employ rational decision-making. They’ll conduct market research, analyze competitor products, evaluate their resources, and predict potential profits before making a decision. This ensures the decision is based on facts and not just intuition.
Leadership: Leaders use rational decision-making while shaping policies or resolving conflicts. A school principal, for instance, may have to decide whether to enforce a strict no-mobile policy.
They’ll consider the pros and cons, consult with teachers, parents, and students, and make a decision that is most beneficial for the school’s academic environment.
Personal Finance: An individual considering their retirement savings plan would utilize rational decision-making. They might begin by understanding the importance of saving for retirement and gathering information about various options like 401(k)s, IRAs, or traditional savings accounts.
They would evaluate these alternatives, considering factors like potential growth, risk level, and tax benefits. The decision would be based on their financial situation, retirement goals, and risk tolerance, ensuring their choice is not impulsive but grounded in careful consideration and analysis.
Steps Involved in Rational Decision-Making

The rational decision-making process comprises several key steps. Here’s a rundown:
1. Identify the Decision
The first step in rational decision-making is acknowledging that a decision is required. The decision is usually a problem but can also be an opportunity. This is the foundational stage where the problem or situation is recognized, and the need for a decision becomes apparent.
You can’t make a rational decision unless you know exactly what the problem is and the context of the decision that needs to be made. Ask yourself questions such as:
- Why does a decision need to be made?
- What consequences will unfold if no decision is made?
- What desired outcome are we aiming for?
- What stands in the way of achieving it?
Take, for instance, a business observing declining profits. The company identifies the problem and realizes that strategic decisions need to be made to address this issue.
It might ask: What is the reason behind the decreasing profits? What will happen if the situation is not addressed? What are our financial goals, and what is impeding us from achieving them? This level of detailed understanding and clarity sets the stage for the subsequent steps of the decision-making process.
2. Gather Information
Once the decision has been identified, the next step is to gather relevant information about it. This could include data analysis, research, consultations with experts, surveys, etc.
Using the previous example, the business might look into financial statements, assess market trends, and consider feedback from customers. A thorough and unbiased collection of data is critical as it forms the backbone of a rational decision.
3. Identify Alternatives
The third step involves generating a list of potential alternatives. There is often more than one way to address a problem or situation, so it’s important to consider different approaches and options.
For the business facing decreasing profits, alternatives could include cost-cutting, investing in new marketing strategies, introducing new products, or even merging with another company. Creativity and open-mindedness are key in this stage to ensure a wide range of options.
4. Evaluate Alternatives
After generating alternatives, the next crucial step is to evaluate each one. This stage involves a systematic analysis of the pros and cons, feasibility, potential impact, and other factors pertinent to each option. Here, establishing your decision criteria—such as cost-effectiveness, scalability, risk level, and potential return—is key. Once established, these criteria need to be weighed based on their importance to solving the problem at hand.
For example, a business might establish criteria like cost, projected return, and alignment with company values. These criteria would be applied to evaluate the potential impact of different marketing strategies, the feasibility of cost-cutting measures, or the implications of a merger.
This systematic evaluation process, underpinned by established and weighted decision criteria, enables a business to compare and contrast different options effectively. It assists in determining which alternative aligns best with the defined criteria and thus holds the highest potential for success.
5. Choose an Alternative
This step involves making the actual decision among the evaluated alternatives. Typically, the best alternative is the one with the greatest likelihood of solving the issue, paired with the lowest degree of risk.
It’s where the business might choose the most cost-effective marketing strategy that is expected to reach the widest audience. While this stage concludes with a decision, the rational decision-making process is not yet complete.
6. Take Action
This is where the chosen alternative is implemented. It involves carrying out the decision and monitoring its progress.
For the business, this would mean launching the selected marketing strategy and keeping a close eye on metrics such as customer engagement, sales, and profit margins. It’s important to remember that this stage might involve overcoming obstacles and making adjustments as necessary.
7. Review the Decision
The final step of the process is to review and evaluate the results of the decision. This includes analyzing whether the decision has resolved the problem or situation and, if not, considering what adjustments need to be made.
In our business example, this could mean assessing whether the new marketing strategy has indeed increased profits. If it hasn’t, the business might need to revisit previous steps of the process to identify and implement a new decision.
These steps make up the backbone of the rational decision-making process, enabling us to systematically approach our choices, ensuring they are backed by logic and evidence.
Assumptions for Using a Rational Decision-Making Model
To effectively utilize the rational decision-making process, it’s necessary to make several key assumptions. These assumptions create a baseline for the decision-making process and help ensure its effective implementation:
- Complete Information: One must assume that all the information needed to make the decision is available and accessible. This includes details about the problem, potential solutions, and their outcomes.
- Decision-Maker Rationality: The person making the decision is assumed to be rational, meaning they are objective, logical, and aim to make the best choice based on the information available.
- Clear Objectives: The decision-maker is assumed to have clear and consistent objectives or goals that guide the decision-making process.
- Time and Resources: It’s assumed that the decision-maker has adequate time and resources to gather information, evaluate alternatives, and make a decision.
- Decision-Maker Independence: The decision-maker is assumed to have the freedom and authority to make the decision without undue influence or restrictions.
- Stable Environment: The environment in which the decision is being made is assumed to be stable, allowing for reliable predictions about the consequences of each alternative.
- Logical Evaluation: It’s assumed that the decision-maker can logically evaluate the pros and cons of each alternative, weigh them against each other, and make a rational choice.
Other Rational Decision-Making Models
While the steps above cover the basics of rational decision-making, there are several rational decision-making models that have been developed by scholars and researchers over the years.
These models provide structured approaches to making decisions based on logical reasoning and analysis. Here are a few examples:
- The Rational Economic Model: This model assumes that individuals make decisions by maximizing their utility or satisfaction, considering all available information, and weighing the costs and benefits of different alternatives.
- The Bounded Rationality Model: Proposed by Herbert Simon, this model recognizes that humans have limitations in processing information and making fully rational decisions. It suggests that individuals make decisions that are “good enough” rather than optimal, taking into account their cognitive constraints and the available information.
- The Normative Decision Model: This model focuses on the ideal decision-making process, providing a step-by-step framework for making rational decisions. It emphasizes gathering complete information, considering all alternatives, and evaluating the potential outcomes before selecting the best option.
- The Garbage Can Model: This model views decision-making as a chaotic process that occurs in organizations. It suggests that decisions often result from a combination of problems, solutions, participants, and circumstances coming together in a “garbage can” and being resolved opportunistically.
- The Prospect Theory: Proposed by Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky, this model challenges the assumptions of rational decision-making by considering how individuals assess and weigh potential gains and losses. It suggests that people tend to be risk-averse when it comes to gains but risk-seeking when it comes to losses.
These are just a few examples of rational decision-making models. Each model offers a unique perspective and set of principles for approaching decision-making tasks. The choice of model depends on the context, problem complexity, available information, and the decision-makers preferences and constraints.
Factors Influencing Rational Decision-Making
While the idea of making a completely rational decision sounds perfect, in reality, our decisions are often influenced by various factors.
- Information Availability: The amount and quality of information at our disposal can greatly influence our decisions. With limited or incorrect information, we may end up making less-than-optimal decisions.
- Time Constraints: Often, we are pressed for time while making decisions. Under such constraints, we might not go through the full rational decision-making process.
- Cognitive Limitations: Our cognitive capacity to process information and make decisions is limited. We can be overwhelmed with too many alternatives or complex decision scenarios.
- Emotions: Our emotions often play a part in our decisions. We might make irrational choices under emotional distress.
Impact of Cognitive Biases on Rational Decision-Making
Cognitive biases can seriously impact our rational decision-making abilities. These mental shortcuts or “biases” can lead us to make decisions that are not in our best interest.
For instance, confirmation bias can make us pay more attention to information that confirms our pre-existing beliefs and ignore contradicting evidence. Similarly, the anchoring bias can cause us to rely heavily on the first piece of information we receive when making decisions.
Cognitive biases often lead to irrational choices. Being aware of these biases is the first step towards mitigating their impact on our decision-making process.
Potential Challenges in Rational Decision-Making
Rational decision-making, despite its merits, isn’t without its challenges. Some of these include:
- Information Overload: In an age of data deluge, filtering through massive amounts of information to make decisions can be overwhelming.
- Analysis Paralysis: Overanalyzing or overthinking can lead to indecision or delays in decision-making.
- Unpredictable Outcomes: Even with a thorough analysis, outcomes can be unpredictable due to the dynamic nature of our environment.
Developing Rational Decision-Making Skills
Wondering how to become better at making rational decisions? Here are some tips to get you going:
- Improve Critical Thinking: Critical thinking allows us to objectively analyze information and logically derive conclusions. By developing your critical thinking skills, you can better evaluate decision alternatives.
- Practice Mindfulness: Being aware of your thoughts and emotions can help you identify when they are clouding your decision-making process.
- Use Decision-Making Models: Decision-making models can provide a structured approach to rational decision-making. They can help guide you through complex decision scenarios.
Remember, developing rational decision-making skills takes time and practice. Stay patient and keep practicing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Rational decision-making is a structured, logical process that uses evidence and analysis. Intuitive decision-making relies on instinct and gut feelings.
Yes, rational decision-making can be applied in personal situations like choosing a career, managing finances, or making health-related decisions.
Yes, decision-making models like SWOT analysis, decision trees, or cost-benefit analysis can provide structured approaches to enhance rationality.
Wrapping Up
Rational decision-making is a skill that can transform our personal and professional lives, steering us toward more informed and effective choices. Though challenges exist, with awareness and practice, we can significantly improve our decision-making prowess.
By understanding the nuances of rational decision-making, we not only enhance our decision-making abilities but also become better thinkers, planners, and problem-solvers. Now, isn’t that a step towards a more informed and empowered life?
Your Might Also Like
10 goal-setting tips to boost productivity and personal development.

Effective Goal Setting: Unlock Your Full Potential
Smart goals: a comprehensive guide to goal setting and achievement.

Rational Decision Making: The 7-Step Process for Making Logical Decisions
Published: October 17, 2023
Psychology tells us that emotions drive our behavior, while logic only justifies our actions after the fact . Marketing confirms this theory. Humans associate the same personality traits with brands as they do with people — choosing your favorite brand is like choosing your best friend or significant other. We go with the option that makes us feel something.
But emotions can cloud your reasoning, especially when you need to do something that could cause internal pain, like giving constructive criticism, or moving on from something you’re attached to, like scrapping a favorite topic from your team's content calendar.
![what are the steps in the rational problem solving process Download Now: How to Be More Productive at Work [Free Guide + Templates]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/be08853d-7ccb-4ab6-ba13-ef66a1d9b4ff.png)
There’s a way to suppress this emotional bias, though. It’s a thought process that’s completely objective and data-driven. It's called the rational decision making model, and it will help you make logically sound decisions even in situations with major ramifications , like pivoting your entire blogging strategy.
But before we learn each step of this powerful process, let’s go over what exactly rational decision making is and why it’s important.
What is Rational Decision Making?
Rational decision making is a problem-solving methodology that factors in objectivity and logic instead of subjectivity and intuition to achieve a goal. The goal of rational decision making is to identify a problem, pick a solution between multiple alternatives, and find an answer.
Rational decision making is an important skill to possess, especially in the digital marketing industry. Humans are inherently emotional, so our biases and beliefs can blur our perception of reality. Fortunately, data sharpens our view. By showing us how our audience actually interacts with our brand, data liberates us from relying on our assumptions to determine what our audience likes about us.
Rational Decision Making Model: 7 Easy Steps(+ Examples)

1. Verify and define your problem.
To prove that you actually have a problem, you need evidence for it. Most marketers think data is the silver bullet that can diagnose any issue in our strategy, but you actually need to extract insights from your data to prove anything. If you don’t, you’re just looking at a bunch of numbers packed into a spreadsheet.
To pinpoint your specific problem, collect as much data from your area of need and analyze it to find any alarming patterns or trends.
“After analyzing our blog traffic report, we now know why our traffic has plateaued for the past year — our organic traffic increases slightly month over month but our email and social traffic decrease.”
2. Research and brainstorm possible solutions for your problem.
Expanding your pool of potential solutions boosts your chances of solving your problem. To find as many potential solutions as possible, you should gather plenty of information about your problem from your own knowledge and the internet. You can also brainstorm with others to uncover more possible solutions.
Potential Solution 1: “We could focus on growing organic, email, and social traffic all at the same time."
Potential Solution 2: “We could focus on growing email and social traffic at the same time — organic traffic already increases month over month while traffic from email and social decrease.”
Potential Solution 3: "We could solely focus on growing social traffic — growing social traffic is easier than growing email and organic traffic at the same time. We also have 2 million followers on Facebook, so we could push our posts to a ton of readers."
Potential Solution 4: "We could solely focus on growing email traffic — growing email traffic is easier than growing social and organic traffic at the same time. We also have 250,000 blog subscribers, so we could push our posts to a ton of readers."
Potential Solution 5: "We could solely focus on growing organic traffic — growing organic traffic is easier than growing social and email traffic at the same time. We also just implemented a pillar-cluster model to boost our domain’s authority, so we could attract a ton of readers from Google."
3. Set standards of success and failure for your potential solutions.
Setting a threshold to measure your solutions' success and failure lets you determine which ones can actually solve your problem. Your standard of success shouldn’t be too high, though. You’d never be able to find a solution. But if your standards are realistic, quantifiable, and focused, you’ll be able to find one.
“If one of our solutions increases our total traffic by 10%, we should consider it a practical way to overcome our traffic plateau.”
4. Flesh out the potential results of each solution.
Next, you should determine each of your solutions’ consequences. To do so, create a strength and weaknesses table for each alternative and compare them to each other. You should also prioritize your solutions in a list from best chance to solve the problem to worst chance.
Potential Result 1: ‘Growing organic, email, and social traffic at the same time could pay a lot of dividends, but our team doesn’t have enough time or resources to optimize all three channels.”
Potential Result 2: “Growing email and social traffic at the same time would marginally increase overall traffic — both channels only account for 20% of our total traffic."
Potential Result 3: “Growing social traffic by posting a blog post everyday on Facebook is challenging because the platform doesn’t elevate links in the news feed and the channel only accounts for 5% of our blog traffic. Focusing solely on social would produce minimal results.”
Potential Result 4: “Growing email traffic by sending two emails per day to our blog subscribers is challenging because we already send one email to subscribers everyday and the channel only accounts for 15% of our blog traffic. Focusing on email would produce minimal results.”
Potential Result 5: “Growing organic traffic by targeting high search volume keywords for all of our new posts is the easiest way to grow our blog’s overall traffic. We have a high domain authority, Google refers 80% of our total traffic, and we just implemented a pillar-cluster model. Focusing on organic would produce the most results.”
5. Choose the best solution and test it.
Based on the evaluation of your potential solutions, choose the best one and test it. You can start monitoring your preliminary results during this stage too.
“Focusing on organic traffic seems to be the most effective and realistic play for us. Let’s test an organic-only strategy where we only create new content that has current or potential search volume and fits into our pillar cluster model.”
6. Track and analyze the results of your test.
Track and analyze your results to see if your solution actually solved your problem.
“After a month of testing, our blog traffic has increased by 14% and our organic traffic has increased by 21%.”
7. Implement the solution or test a new one.
If your potential solution passed your test and solved your problem, then it’s the most rational decision you can make. You should implement it to completely solve your current problem or any other related problems in the future. If the solution didn’t solve your problem, then test another potential solution that you came up with.
“The results from solely focusing on organic surpassed our threshold of success. From now on, we’re pivoting to an organic-only strategy, where we’ll only create new blog content that has current or future search volume and fits into our pillar cluster model.”
Avoid Bias With A Rational Decision Making Process
As humans, it’s natural for our emotions to take over your decision making process. And that’s okay. Sometimes, emotional decisions are better than logical ones. But when you really need to prioritize logic over emotion, arming your mind with the rational decision making model can help you suppress your emotion bias and be as objective as possible.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

Decision Trees: A Simple Tool to Make Radically Better Decisions

Mental Models: The Ultimate Guide

The Ultimate Guide to Decision Making
![what are the steps in the rational problem solving process How Product Packaging Influences Buying Decisions [Infographic]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hs-fs/hub/53/file-2411322621-png/00-Blog_Thinkstock_Images/product-packaging.png)
How Product Packaging Influences Buying Decisions [Infographic]

The Five Stages of the Consumer Decision-Making Process Explained
Outline your company's marketing strategy in one simple, coherent plan.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)
- Project Management Tools
What is rational decision-making? What are the steps?

By Hadrat Ajao 4 min read · Posted Mar 25, 2024
Decision-making is undertaken by individuals daily, revolving around what to eat, what to wear, whether to go somewhere, what to read, etc. A decision-making process preempts every human action.
The rational decision-making process is often employed when making choices or decisions. The process is based on logic, reason, and carefully considering available information and options. It is a structured approach to making decisions, and it aims to optimize outcomes and reduce the impacts of biases and emotions in decision-making. When a decision is preceded by rational thinking, the results are often a desired outcome and serve a greater good.
This article will review an example of how Lauren utilized rational decision-making.
Lauren is a successful freelancer who has had a particularly successful year in her career. There has been a surge in her clientele. While this is exciting, it also brings some challenges. Lauren needs to make a decision that will significantly shape her future. The surge in her clientele brings both exciting opportunities and challenging choices.
As the offers pour in, one particularly lucrative deal requires Lauren to transition from her cozy home office to a dedicated workspace. The international client offering this two-year contract needs regular face-to-face meetings on a video call, requiring investment in a professional work office with whiteboards and big screen monitors. She had previously worked from her one-room space, but now she needs to build a professional office space. This proposition coincides with a turning point in Lauren's aspirations.
Lauren was planning to purchase a luxurious car, symbolizing her success. The allure of a vehicle that mirrors her blossoming career beckons her. Yet, the decision looms as she realizes that committing to the needed professional office space means putting her automotive dreams on hold. Lauren is torn between two significant investments promising to enhance her professional and personal life. Here, the rational decision-making process becomes Lauren's guiding light.
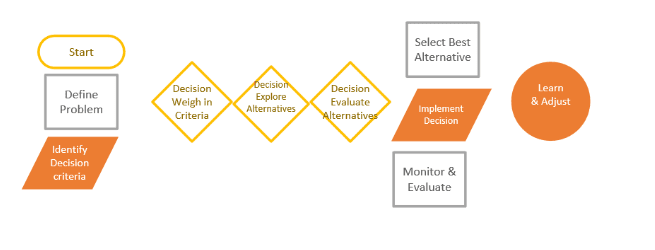
1. Defining the problem: First, Lauren needs to clearly define the issue, which is the decision between spending on office space for her growing clientele vs. Buying a luxurious car.
2. Identifying decision criteria: Next, Lauren determines the key factors influencing her decision, considering the long-term benefits of securing the international deal versus the immediate satisfaction of owning a prestigious car.
3. Weighing in the decision criteria: Lauren assigns a weight to each criterion, acknowledging the potential impact on her career trajectory and personal satisfaction.
4. Exploring alternatives: Lauren explores various scenarios, including negotiating with her clients for a compromise to accommodate their needs and fulfill her aspirations.
5. Evaluating alternatives: She objectively assesses the pros and cons of each alternative, weighing the consequences of delaying the car purchase against the potential gains from securing a long-term client commitment.
6. Selecting the best alternative: With a comprehensive analysis, Lauren makes an informed decision aligning with her goals and priorities.
7. Implementing the decision: Lauren takes the necessary steps to either sign the deal, negotiate terms, or pursue an alternative that suits her clients and satisfies her desires.
8. Monitoring and evaluating: With the decision put in action, Lauren stays vigilant, monitoring the outcomes and adjusting her approach to ensure continued success.
9. Learning and adjusting: Lauren reflects on the experience, learning valuable lessons about balancing professional growth and personal fulfillment. This newfound wisdom guides her future decisions as she navigates the evolving landscape of her freelance career.
By following the rational decision-making steps, Lauren transforms a challenging situation into a strategic choice that aligns with her goals and ensures a sustainable and fulfilling path forward.
Faced with the conflicting choices of building a dedicated office space or the allure of buying a luxurious car, Lauren embarked on a journey of introspection guided by the principles of rational decision-making. The weight of her decision hung in the balance, with the potential to shape her professional trajectory and personal satisfaction. After carefully considering the options and thoroughly evaluating the associated criteria, Lauren chose a path harmonizing with her overarching goals.
Recognizing the transformative potential of the international deal and the enduring impact it could have on her burgeoning career, she boldly decided to prioritize building a dedicated office space.
This choice, rooted in rational analysis, reflected Lauren's commitment to long-term success and her understanding of the sacrifices required for sustained growth. While Lauren temporarily put the luxurious car on hold, she embraced the opportunity to cultivate a thriving professional environment that would undoubtedly yield long-term gains, making her dreams of owning a luxurious car a reality soon enough.
In making this decision, Lauren demonstrated her business acumen, resilience, and foresight. The narrative of her freelance journey had evolved, and with this strategic move, she set the stage for continued prosperity. Lauren embraced her new professional chapter with a sense of purpose and the confidence that comes from deliberate decision-making. Lauren's success was not just about the projects she tackled or the words she penned; it was a testament to her ability to navigate complex choices with wisdom, ensuring a trajectory that promised financial gains and personal fulfillment.
In the grand tapestry of her freelance career, this decision stood out as a defining moment, a testament to Lauren's strategic thinking and unwavering commitment to building a legacy beyond the glossy allure of immediate rewards.
Rational decision-making is an important function especially in the Human Resources management area. This book on Rational Decisions in Organisations details the science and art behind it.
About The Author

Hadrat Ajao
Hello, I am Hadrat, a communication specialist and an article writer for Pitch Labs. I am passionate about street children and abandoned women, with a special focus on the African terrain. I enjoy writing poems and creative stories.
Join Our Community
Looking for something else? Get your questions answered in our free online learning community!
Entrepreneurial Resources
Jumpstart your next business with our free resource library.
Our organization cannot give out official legal/fiscal guidance. All articles are written by volunteers and it may be beneficial to contact professionals to assist your understanding of the information and to guide your action. Pitch Labs bears no responsibility for the results of actions taken based off of article content or any other form of assistance given.
More in Operations
Financial » Accounting
What Are the Different Types of Journals?
Journals help keep business finances in check and up to date. Find out what different types of journals are used by businesses and what’s within them. Read more
Operations » Human Resources
What is an Employee Evaluation and What Is Its Evaluation process?
An employee evaluation is used to rate an employee's areas of strength and need for improvement. It involves preparation, evaluation meeting, evaluation report, follow-up, documentation and implementation, and continuous feedback. Read more
Operations » Project Management Tools
What Are the Seven Key Concepts in Entrepreneurship?
Entrepreneurs play a major role in shaping our world, and entrepreneurship is a force for positive change and empowerment. Entrepreneurs see opportunity in problems and articulate solutions that no one else even identifies. Read more
What is Cognitive Conflict?
Cognitive conflict is the anxiety and tension that affects an individual when cognitive dissonance occurs. Managing such conflict is essential in the workplace. Read more
Recent articles
Technology » Recruitment
What is the role of technology in recruitment?
Overall, technology enhances the recruitment experience for employers and candidates alike, optimizing every step from application to hiring. Read more
Legal » Structures
What is an NGO? Are they typically nonprofits? What are the features of an NGO?
An NGO is an independent, nonprofit organization that promotes humanitarian or social missions throughout the globe. Read more
Legal » Protections
Patent Filing: A Step-By-Step Guide
A patent is a legal protection granted to inventors to protect their intellectual property. Read more
- Getting Started
- Business Plans
- Document Types
- Keeping Records
- Protections
- Regulations
- Entrepreneurship
- Product & Service Management
- Human Resources
- Social Media Tools
- Advertising
- United States of America
- Applications
- Website Building Tools
- Recruitment

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

12.8: The Decision Making Process
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 48738
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Describe the decision making process
“To be or not to be: that is the question.” Hamlet lamented.
“Should I stay or should I go now?” The Clash asked.
“Two roads diverged in a yellow wood,” Robert Frost pointed out.
If you’re struggling to make a decision, you’re in good company. Literature, poetry and pop culture provide plenty of sympathy for your plight. Sadly, while they understand your pain, they don’t always sing you to the correct resolution. When it comes to making a decision, in business or in life, how can you be sure you’re doing the right thing?
Well, we wouldn’t be writing songs about making decisions if it were an easy task. That said, researchers have studied the decision-making process as much as anything else, and they’ve come away with some different ideas and models that help us understand how we can make decisions more carefully and successfully. Let’s take a look at the five best known of those decision making models.
Rational Decision Making
The rational decision making model assumes decisions are based on an objective, orderly, structured information gathering and analysis. The model encourages the decision maker to understand the situation, organize and interpret the information, and then take action. There are eight steps in the rational decision making process:

Bad Hotel REviews
Let’s say that you’re the general manager at a nice hotel. Suddenly, you notice that customers are rating your property two and three stars instead of the customary five stars you and the team are used to earning. You need to make a decision about next steps to solve this issue. Let’s start right at the top of the rational decision making model.
- Understand the issue. The issue is clear to you. Customers are rating their experience at your property online, and they’re not happy. This will surely damage your team’s efforts to generate new business. You need to find a way to earn better customer ratings.
- Define the problem. You and your team sit down and read the last twenty or thirty customer reviews on three different travel sites. It turns out that customers’ unhappiness coincides with a recent increase in rates. They no longer feel they’re getting good value for their money.
- Define the objectives. What criteria will your solution have to meet? Clearly, you want to start getting better ratings from customers. You don’t want to see customers complaining about anything online. Your objective is 100% happiness, 100% five-star ratings.
- Diagnose the problem. This is the stage where you look to determine and understand the root causes of your issue. Perhaps you decide that all customer-facing staff report daily on quality issues. And maybe you consult with operations on additional perks that can be incorporated into the guest experience without giving away too much margin.
- Develop alternatives. You ultimately want to create a lengthy list of alternatives and not decide on one too quickly. You look over your employees’ reports on quality. You wait on operations for recommendations on extra perks. You collect all the data.
- Evaluate alternatives. Once you have all your alternatives on the table, you can start to make a choice. Every employee suggestion, every operations recommendation should be in front of you, and you consider each option carefully.
- Select an alternative. One of your employees has suggested two additional members for the housekeeping staff, as the current level of staff is having difficulty keeping up with the increase precipitated by an office building opening up down the street. A member of your operations team has suggested providing a continental breakfast for business travelers in response to the increase in that customer type. Both seem like good ideas. Which will provide the bigger impact?
- Implement alternative. You decide to hire the two additional members for the housekeeping staff, understanding that your customers view quality in clean rooms and common spaces. You get the budget approved and post for those two jobs. You make a plan to check in at the thirty day mark to see if customers’ ratings have improved.
The goal of the rational decision making model is to eliminate possibilities for error and biases. It assumes the following:
- Managers have all the information about the situation.
- Managers are aware of all alternative options and are equipped to evaluate them properly.
- Managers are looking to make the best possible decision.
- Managers are capable of eliminating misperceptions and biases.
- There are no cost or time constraints.
In a perfect world, where all of those assumptions are met, this model is how the decision making process works best. But we know that those assumptions can’t all be met. And that’s why we have the bounded rationality model.
Bounded Rationality Model
The bounded rationality model assumes numerous organizational and individual factors restrict rational decision making. This is the version of decision making that occurs most often in organizations, because the assumptions of this model are much closer to the truth:
- Early alternatives and solutions are quickly adopted because of perceptual limitations.
- Managers often don’t have access to all the information they need.
- Managers are not aware of all the alternatives and can’t predict the consequences of each one.
- Organizational goals constrain decisions.
- Conflicting goals of multiple stakeholders can force a compromise of a decision.
Because a human being is limited in the amount of information he or she can process, when a complex decision needs to be made, he or she will reduce the problem to a manageable size. By limiting the number of choices and the amount of necessary information, the product is a decision that’s acceptable and satisfactory. This is sometimes referred to as the Satisficing model.
In the bounded rationality model, the same steps are used in the decision making process, only instead of reviewing all information and all alternatives, those aspects are limited to the amount the decision maker is willing to gather.
Linear Model of Decision Making
Linear decision making involves listing positive and negative factors of each decision alternative. If you’ve ever made a list of pros and cons around a certain decision, then you’ve embarked on linear decision making.
In order for it truly to be linear decision making, the decision maker must then assign a numerical “weight” to each of his pros and cons, and arrive at a total score for each side. For instance, let’s say you were trying to decide if you should or should not hire a very experienced but very expensive candidate for a position in your office. Your linear decision making model might look like this:
You’ve assigned the most important reasons a 3 on the positive side, and a –3 for the most important reason on the negative side. This makes it easy for you to tally up both sides and add them together. A positive score suggests you should hire the candidate, and a negative score suggests you should not. Looks like you’re not hiring this candidate!
Intuitive Decision Making
Intuitive decision making is a model that assumes managers make decisions by relying on past experience and their personal assessment of a situation. This model of decision making is often used when there are high levels of uncertainty or complexity around a particular problem, or when the decision is novel and the managers don’t have past experience with this kind of problem.
If managers are faced with uncertain, complex situations and they can’t get the right information to make a good decision quickly, they are apt to rely on hunches and intuition. Given the choice between this model and a linear model (like the one discussed above), managers should reach for the linear model.
Garbage Can Model

The garbage can model is one where managers use information about problems, participants, solutions and opportunities haphazardly to generate ideas and potential decisions. Unlike the other decision making models we discussed, the garbage can model does not always lead to satisfactory solutions, because the problem does not always precede alternatives and solutions.
For instance, the corporate office of an organization might have been recently informed of the benefits of going to an “open environment” where people can talk and collaborate freely. Senior management may get behind this idea and start looking for ways to knock down cube walls and make their environment more collaborative before it’s even been determined that their office has issues being collaborative.
As you can see in Figure 2, there is no sequence of steps the way there is in rational decision making, but rather the decision comes by looking at independent streams of events.
Practice Question
https://assessments.lumenlearning.co...essments/13976
These are five well-known models for decision making. Now we’re going to take a look at some of the rules and biases in decision making that, when you’re aware of them, will lead you to stronger decision making skills.
Contributors and Attributions
- The Decision Making Process. Authored by : Freedom Learning Group. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image: Rational Decision Making Process. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Garbage Can Flows. Authored by : Garbagecansarefun. Provided by : Wikimedia Commons. Located at : https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Garbage_Can_Flows.png . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Overview of the Problem-Solving Mental Process
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
- Identify the Problem
- Define the Problem
- Form a Strategy
- Organize Information
- Allocate Resources
- Monitor Progress
- Evaluate the Results
Frequently Asked Questions
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything they can about the issue and then using factual knowledge to come up with a solution. In other instances, creativity and insight are the best options.
It is not necessary to follow problem-solving steps sequentially, It is common to skip steps or even go back through steps multiple times until the desired solution is reached.
In order to correctly solve a problem, it is often important to follow a series of steps. Researchers sometimes refer to this as the problem-solving cycle. While this cycle is portrayed sequentially, people rarely follow a rigid series of steps to find a solution.
The following steps include developing strategies and organizing knowledge.
1. Identifying the Problem
While it may seem like an obvious step, identifying the problem is not always as simple as it sounds. In some cases, people might mistakenly identify the wrong source of a problem, which will make attempts to solve it inefficient or even useless.
Some strategies that you might use to figure out the source of a problem include :
- Asking questions about the problem
- Breaking the problem down into smaller pieces
- Looking at the problem from different perspectives
- Conducting research to figure out what relationships exist between different variables
2. Defining the Problem
After the problem has been identified, it is important to fully define the problem so that it can be solved. You can define a problem by operationally defining each aspect of the problem and setting goals for what aspects of the problem you will address
At this point, you should focus on figuring out which aspects of the problems are facts and which are opinions. State the problem clearly and identify the scope of the solution.
3. Forming a Strategy
After the problem has been identified, it is time to start brainstorming potential solutions. This step usually involves generating as many ideas as possible without judging their quality. Once several possibilities have been generated, they can be evaluated and narrowed down.
The next step is to develop a strategy to solve the problem. The approach used will vary depending upon the situation and the individual's unique preferences. Common problem-solving strategies include heuristics and algorithms.
- Heuristics are mental shortcuts that are often based on solutions that have worked in the past. They can work well if the problem is similar to something you have encountered before and are often the best choice if you need a fast solution.
- Algorithms are step-by-step strategies that are guaranteed to produce a correct result. While this approach is great for accuracy, it can also consume time and resources.
Heuristics are often best used when time is of the essence, while algorithms are a better choice when a decision needs to be as accurate as possible.
4. Organizing Information
Before coming up with a solution, you need to first organize the available information. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? The more information that is available the better prepared you will be to come up with an accurate solution.
When approaching a problem, it is important to make sure that you have all the data you need. Making a decision without adequate information can lead to biased or inaccurate results.
5. Allocating Resources
Of course, we don't always have unlimited money, time, and other resources to solve a problem. Before you begin to solve a problem, you need to determine how high priority it is.
If it is an important problem, it is probably worth allocating more resources to solving it. If, however, it is a fairly unimportant problem, then you do not want to spend too much of your available resources on coming up with a solution.
At this stage, it is important to consider all of the factors that might affect the problem at hand. This includes looking at the available resources, deadlines that need to be met, and any possible risks involved in each solution. After careful evaluation, a decision can be made about which solution to pursue.
6. Monitoring Progress
After selecting a problem-solving strategy, it is time to put the plan into action and see if it works. This step might involve trying out different solutions to see which one is the most effective.
It is also important to monitor the situation after implementing a solution to ensure that the problem has been solved and that no new problems have arisen as a result of the proposed solution.
Effective problem-solvers tend to monitor their progress as they work towards a solution. If they are not making good progress toward reaching their goal, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies .
7. Evaluating the Results
After a solution has been reached, it is important to evaluate the results to determine if it is the best possible solution to the problem. This evaluation might be immediate, such as checking the results of a math problem to ensure the answer is correct, or it can be delayed, such as evaluating the success of a therapy program after several months of treatment.
Once a problem has been solved, it is important to take some time to reflect on the process that was used and evaluate the results. This will help you to improve your problem-solving skills and become more efficient at solving future problems.
A Word From Verywell
It is important to remember that there are many different problem-solving processes with different steps, and this is just one example. Problem-solving in real-world situations requires a great deal of resourcefulness, flexibility, resilience, and continuous interaction with the environment.
Get Advice From The Verywell Mind Podcast
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares how you can stop dwelling in a negative mindset.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
You can become a better problem solving by:
- Practicing brainstorming and coming up with multiple potential solutions to problems
- Being open-minded and considering all possible options before making a decision
- Breaking down problems into smaller, more manageable pieces
- Asking for help when needed
- Researching different problem-solving techniques and trying out new ones
- Learning from mistakes and using them as opportunities to grow
It's important to communicate openly and honestly with your partner about what's going on. Try to see things from their perspective as well as your own. Work together to find a resolution that works for both of you. Be willing to compromise and accept that there may not be a perfect solution.
Take breaks if things are getting too heated, and come back to the problem when you feel calm and collected. Don't try to fix every problem on your own—consider asking a therapist or counselor for help and insight.
If you've tried everything and there doesn't seem to be a way to fix the problem, you may have to learn to accept it. This can be difficult, but try to focus on the positive aspects of your life and remember that every situation is temporary. Don't dwell on what's going wrong—instead, think about what's going right. Find support by talking to friends or family. Seek professional help if you're having trouble coping.
Davidson JE, Sternberg RJ, editors. The Psychology of Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press; 2003. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511615771
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. Published 2018 Jun 26. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process
In this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , Simon London speaks with Charles Conn, CEO of venture-capital firm Oxford Sciences Innovation, and McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin about the complexities of different problem-solving strategies.
Podcast transcript
Simon London: Hello, and welcome to this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , with me, Simon London. What’s the number-one skill you need to succeed professionally? Salesmanship, perhaps? Or a facility with statistics? Or maybe the ability to communicate crisply and clearly? Many would argue that at the very top of the list comes problem solving: that is, the ability to think through and come up with an optimal course of action to address any complex challenge—in business, in public policy, or indeed in life.
Looked at this way, it’s no surprise that McKinsey takes problem solving very seriously, testing for it during the recruiting process and then honing it, in McKinsey consultants, through immersion in a structured seven-step method. To discuss the art of problem solving, I sat down in California with McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin and also with Charles Conn. Charles is a former McKinsey partner, entrepreneur, executive, and coauthor of the book Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything [John Wiley & Sons, 2018].
Charles and Hugo, welcome to the podcast. Thank you for being here.
Hugo Sarrazin: Our pleasure.
Charles Conn: It’s terrific to be here.
Simon London: Problem solving is a really interesting piece of terminology. It could mean so many different things. I have a son who’s a teenage climber. They talk about solving problems. Climbing is problem solving. Charles, when you talk about problem solving, what are you talking about?
Charles Conn: For me, problem solving is the answer to the question “What should I do?” It’s interesting when there’s uncertainty and complexity, and when it’s meaningful because there are consequences. Your son’s climbing is a perfect example. There are consequences, and it’s complicated, and there’s uncertainty—can he make that grab? I think we can apply that same frame almost at any level. You can think about questions like “What town would I like to live in?” or “Should I put solar panels on my roof?”
You might think that’s a funny thing to apply problem solving to, but in my mind it’s not fundamentally different from business problem solving, which answers the question “What should my strategy be?” Or problem solving at the policy level: “How do we combat climate change?” “Should I support the local school bond?” I think these are all part and parcel of the same type of question, “What should I do?”
I’m a big fan of structured problem solving. By following steps, we can more clearly understand what problem it is we’re solving, what are the components of the problem that we’re solving, which components are the most important ones for us to pay attention to, which analytic techniques we should apply to those, and how we can synthesize what we’ve learned back into a compelling story. That’s all it is, at its heart.
I think sometimes when people think about seven steps, they assume that there’s a rigidity to this. That’s not it at all. It’s actually to give you the scope for creativity, which often doesn’t exist when your problem solving is muddled.
Simon London: You were just talking about the seven-step process. That’s what’s written down in the book, but it’s a very McKinsey process as well. Without getting too deep into the weeds, let’s go through the steps, one by one. You were just talking about problem definition as being a particularly important thing to get right first. That’s the first step. Hugo, tell us about that.
Hugo Sarrazin: It is surprising how often people jump past this step and make a bunch of assumptions. The most powerful thing is to step back and ask the basic questions—“What are we trying to solve? What are the constraints that exist? What are the dependencies?” Let’s make those explicit and really push the thinking and defining. At McKinsey, we spend an enormous amount of time in writing that little statement, and the statement, if you’re a logic purist, is great. You debate. “Is it an ‘or’? Is it an ‘and’? What’s the action verb?” Because all these specific words help you get to the heart of what matters.
Want to subscribe to The McKinsey Podcast ?
Simon London: So this is a concise problem statement.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah. It’s not like “Can we grow in Japan?” That’s interesting, but it is “What, specifically, are we trying to uncover in the growth of a product in Japan? Or a segment in Japan? Or a channel in Japan?” When you spend an enormous amount of time, in the first meeting of the different stakeholders, debating this and having different people put forward what they think the problem definition is, you realize that people have completely different views of why they’re here. That, to me, is the most important step.
Charles Conn: I would agree with that. For me, the problem context is critical. When we understand “What are the forces acting upon your decision maker? How quickly is the answer needed? With what precision is the answer needed? Are there areas that are off limits or areas where we would particularly like to find our solution? Is the decision maker open to exploring other areas?” then you not only become more efficient, and move toward what we call the critical path in problem solving, but you also make it so much more likely that you’re not going to waste your time or your decision maker’s time.
How often do especially bright young people run off with half of the idea about what the problem is and start collecting data and start building models—only to discover that they’ve really gone off half-cocked.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah.
Charles Conn: And in the wrong direction.
Simon London: OK. So step one—and there is a real art and a structure to it—is define the problem. Step two, Charles?
Charles Conn: My favorite step is step two, which is to use logic trees to disaggregate the problem. Every problem we’re solving has some complexity and some uncertainty in it. The only way that we can really get our team working on the problem is to take the problem apart into logical pieces.
What we find, of course, is that the way to disaggregate the problem often gives you an insight into the answer to the problem quite quickly. I love to do two or three different cuts at it, each one giving a bit of a different insight into what might be going wrong. By doing sensible disaggregations, using logic trees, we can figure out which parts of the problem we should be looking at, and we can assign those different parts to team members.
Simon London: What’s a good example of a logic tree on a sort of ratable problem?
Charles Conn: Maybe the easiest one is the classic profit tree. Almost in every business that I would take a look at, I would start with a profit or return-on-assets tree. In its simplest form, you have the components of revenue, which are price and quantity, and the components of cost, which are cost and quantity. Each of those can be broken out. Cost can be broken into variable cost and fixed cost. The components of price can be broken into what your pricing scheme is. That simple tree often provides insight into what’s going on in a business or what the difference is between that business and the competitors.
If we add the leg, which is “What’s the asset base or investment element?”—so profit divided by assets—then we can ask the question “Is the business using its investments sensibly?” whether that’s in stores or in manufacturing or in transportation assets. I hope we can see just how simple this is, even though we’re describing it in words.
When I went to work with Gordon Moore at the Moore Foundation, the problem that he asked us to look at was “How can we save Pacific salmon?” Now, that sounds like an impossible question, but it was amenable to precisely the same type of disaggregation and allowed us to organize what became a 15-year effort to improve the likelihood of good outcomes for Pacific salmon.
Simon London: Now, is there a danger that your logic tree can be impossibly large? This, I think, brings us onto the third step in the process, which is that you have to prioritize.
Charles Conn: Absolutely. The third step, which we also emphasize, along with good problem definition, is rigorous prioritization—we ask the questions “How important is this lever or this branch of the tree in the overall outcome that we seek to achieve? How much can I move that lever?” Obviously, we try and focus our efforts on ones that have a big impact on the problem and the ones that we have the ability to change. With salmon, ocean conditions turned out to be a big lever, but not one that we could adjust. We focused our attention on fish habitats and fish-harvesting practices, which were big levers that we could affect.
People spend a lot of time arguing about branches that are either not important or that none of us can change. We see it in the public square. When we deal with questions at the policy level—“Should you support the death penalty?” “How do we affect climate change?” “How can we uncover the causes and address homelessness?”—it’s even more important that we’re focusing on levers that are big and movable.
Would you like to learn more about our Strategy & Corporate Finance Practice ?
Simon London: Let’s move swiftly on to step four. You’ve defined your problem, you disaggregate it, you prioritize where you want to analyze—what you want to really look at hard. Then you got to the work plan. Now, what does that mean in practice?
Hugo Sarrazin: Depending on what you’ve prioritized, there are many things you could do. It could be breaking the work among the team members so that people have a clear piece of the work to do. It could be defining the specific analyses that need to get done and executed, and being clear on time lines. There’s always a level-one answer, there’s a level-two answer, there’s a level-three answer. Without being too flippant, I can solve any problem during a good dinner with wine. It won’t have a whole lot of backing.
Simon London: Not going to have a lot of depth to it.
Hugo Sarrazin: No, but it may be useful as a starting point. If the stakes are not that high, that could be OK. If it’s really high stakes, you may need level three and have the whole model validated in three different ways. You need to find a work plan that reflects the level of precision, the time frame you have, and the stakeholders you need to bring along in the exercise.
Charles Conn: I love the way you’ve described that, because, again, some people think of problem solving as a linear thing, but of course what’s critical is that it’s iterative. As you say, you can solve the problem in one day or even one hour.
Charles Conn: We encourage our teams everywhere to do that. We call it the one-day answer or the one-hour answer. In work planning, we’re always iterating. Every time you see a 50-page work plan that stretches out to three months, you know it’s wrong. It will be outmoded very quickly by that learning process that you described. Iterative problem solving is a critical part of this. Sometimes, people think work planning sounds dull, but it isn’t. It’s how we know what’s expected of us and when we need to deliver it and how we’re progressing toward the answer. It’s also the place where we can deal with biases. Bias is a feature of every human decision-making process. If we design our team interactions intelligently, we can avoid the worst sort of biases.
Simon London: Here we’re talking about cognitive biases primarily, right? It’s not that I’m biased against you because of your accent or something. These are the cognitive biases that behavioral sciences have shown we all carry around, things like anchoring, overoptimism—these kinds of things.
Both: Yeah.
Charles Conn: Availability bias is the one that I’m always alert to. You think you’ve seen the problem before, and therefore what’s available is your previous conception of it—and we have to be most careful about that. In any human setting, we also have to be careful about biases that are based on hierarchies, sometimes called sunflower bias. I’m sure, Hugo, with your teams, you make sure that the youngest team members speak first. Not the oldest team members, because it’s easy for people to look at who’s senior and alter their own creative approaches.
Hugo Sarrazin: It’s helpful, at that moment—if someone is asserting a point of view—to ask the question “This was true in what context?” You’re trying to apply something that worked in one context to a different one. That can be deadly if the context has changed, and that’s why organizations struggle to change. You promote all these people because they did something that worked well in the past, and then there’s a disruption in the industry, and they keep doing what got them promoted even though the context has changed.
Simon London: Right. Right.
Hugo Sarrazin: So it’s the same thing in problem solving.
Charles Conn: And it’s why diversity in our teams is so important. It’s one of the best things about the world that we’re in now. We’re likely to have people from different socioeconomic, ethnic, and national backgrounds, each of whom sees problems from a slightly different perspective. It is therefore much more likely that the team will uncover a truly creative and clever approach to problem solving.
Simon London: Let’s move on to step five. You’ve done your work plan. Now you’ve actually got to do the analysis. The thing that strikes me here is that the range of tools that we have at our disposal now, of course, is just huge, particularly with advances in computation, advanced analytics. There’s so many things that you can apply here. Just talk about the analysis stage. How do you pick the right tools?
Charles Conn: For me, the most important thing is that we start with simple heuristics and explanatory statistics before we go off and use the big-gun tools. We need to understand the shape and scope of our problem before we start applying these massive and complex analytical approaches.
Simon London: Would you agree with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: I agree. I think there are so many wonderful heuristics. You need to start there before you go deep into the modeling exercise. There’s an interesting dynamic that’s happening, though. In some cases, for some types of problems, it is even better to set yourself up to maximize your learning. Your problem-solving methodology is test and learn, test and learn, test and learn, and iterate. That is a heuristic in itself, the A/B testing that is used in many parts of the world. So that’s a problem-solving methodology. It’s nothing different. It just uses technology and feedback loops in a fast way. The other one is exploratory data analysis. When you’re dealing with a large-scale problem, and there’s so much data, I can get to the heuristics that Charles was talking about through very clever visualization of data.
You test with your data. You need to set up an environment to do so, but don’t get caught up in neural-network modeling immediately. You’re testing, you’re checking—“Is the data right? Is it sound? Does it make sense?”—before you launch too far.
Simon London: You do hear these ideas—that if you have a big enough data set and enough algorithms, they’re going to find things that you just wouldn’t have spotted, find solutions that maybe you wouldn’t have thought of. Does machine learning sort of revolutionize the problem-solving process? Or are these actually just other tools in the toolbox for structured problem solving?
Charles Conn: It can be revolutionary. There are some areas in which the pattern recognition of large data sets and good algorithms can help us see things that we otherwise couldn’t see. But I do think it’s terribly important we don’t think that this particular technique is a substitute for superb problem solving, starting with good problem definition. Many people use machine learning without understanding algorithms that themselves can have biases built into them. Just as 20 years ago, when we were doing statistical analysis, we knew that we needed good model definition, we still need a good understanding of our algorithms and really good problem definition before we launch off into big data sets and unknown algorithms.
Simon London: Step six. You’ve done your analysis.
Charles Conn: I take six and seven together, and this is the place where young problem solvers often make a mistake. They’ve got their analysis, and they assume that’s the answer, and of course it isn’t the answer. The ability to synthesize the pieces that came out of the analysis and begin to weave those into a story that helps people answer the question “What should I do?” This is back to where we started. If we can’t synthesize, and we can’t tell a story, then our decision maker can’t find the answer to “What should I do?”
Simon London: But, again, these final steps are about motivating people to action, right?
Charles Conn: Yeah.
Simon London: I am slightly torn about the nomenclature of problem solving because it’s on paper, right? Until you motivate people to action, you actually haven’t solved anything.
Charles Conn: I love this question because I think decision-making theory, without a bias to action, is a waste of time. Everything in how I approach this is to help people take action that makes the world better.
Simon London: Hence, these are absolutely critical steps. If you don’t do this well, you’ve just got a bunch of analysis.
Charles Conn: We end up in exactly the same place where we started, which is people speaking across each other, past each other in the public square, rather than actually working together, shoulder to shoulder, to crack these important problems.
Simon London: In the real world, we have a lot of uncertainty—arguably, increasing uncertainty. How do good problem solvers deal with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: At every step of the process. In the problem definition, when you’re defining the context, you need to understand those sources of uncertainty and whether they’re important or not important. It becomes important in the definition of the tree.
You need to think carefully about the branches of the tree that are more certain and less certain as you define them. They don’t have equal weight just because they’ve got equal space on the page. Then, when you’re prioritizing, your prioritization approach may put more emphasis on things that have low probability but huge impact—or, vice versa, may put a lot of priority on things that are very likely and, hopefully, have a reasonable impact. You can introduce that along the way. When you come back to the synthesis, you just need to be nuanced about what you’re understanding, the likelihood.
Often, people lack humility in the way they make their recommendations: “This is the answer.” They’re very precise, and I think we would all be well-served to say, “This is a likely answer under the following sets of conditions” and then make the level of uncertainty clearer, if that is appropriate. It doesn’t mean you’re always in the gray zone; it doesn’t mean you don’t have a point of view. It just means that you can be explicit about the certainty of your answer when you make that recommendation.
Simon London: So it sounds like there is an underlying principle: “Acknowledge and embrace the uncertainty. Don’t pretend that it isn’t there. Be very clear about what the uncertainties are up front, and then build that into every step of the process.”
Hugo Sarrazin: Every step of the process.
Simon London: Yeah. We have just walked through a particular structured methodology for problem solving. But, of course, this is not the only structured methodology for problem solving. One that is also very well-known is design thinking, which comes at things very differently. So, Hugo, I know you have worked with a lot of designers. Just give us a very quick summary. Design thinking—what is it, and how does it relate?
Hugo Sarrazin: It starts with an incredible amount of empathy for the user and uses that to define the problem. It does pause and go out in the wild and spend an enormous amount of time seeing how people interact with objects, seeing the experience they’re getting, seeing the pain points or joy—and uses that to infer and define the problem.
Simon London: Problem definition, but out in the world.
Hugo Sarrazin: With an enormous amount of empathy. There’s a huge emphasis on empathy. Traditional, more classic problem solving is you define the problem based on an understanding of the situation. This one almost presupposes that we don’t know the problem until we go see it. The second thing is you need to come up with multiple scenarios or answers or ideas or concepts, and there’s a lot of divergent thinking initially. That’s slightly different, versus the prioritization, but not for long. Eventually, you need to kind of say, “OK, I’m going to converge again.” Then you go and you bring things back to the customer and get feedback and iterate. Then you rinse and repeat, rinse and repeat. There’s a lot of tactile building, along the way, of prototypes and things like that. It’s very iterative.
Simon London: So, Charles, are these complements or are these alternatives?
Charles Conn: I think they’re entirely complementary, and I think Hugo’s description is perfect. When we do problem definition well in classic problem solving, we are demonstrating the kind of empathy, at the very beginning of our problem, that design thinking asks us to approach. When we ideate—and that’s very similar to the disaggregation, prioritization, and work-planning steps—we do precisely the same thing, and often we use contrasting teams, so that we do have divergent thinking. The best teams allow divergent thinking to bump them off whatever their initial biases in problem solving are. For me, design thinking gives us a constant reminder of creativity, empathy, and the tactile nature of problem solving, but it’s absolutely complementary, not alternative.
Simon London: I think, in a world of cross-functional teams, an interesting question is do people with design-thinking backgrounds really work well together with classical problem solvers? How do you make that chemistry happen?
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah, it is not easy when people have spent an enormous amount of time seeped in design thinking or user-centric design, whichever word you want to use. If the person who’s applying classic problem-solving methodology is very rigid and mechanical in the way they’re doing it, there could be an enormous amount of tension. If there’s not clarity in the role and not clarity in the process, I think having the two together can be, sometimes, problematic.
The second thing that happens often is that the artifacts the two methodologies try to gravitate toward can be different. Classic problem solving often gravitates toward a model; design thinking migrates toward a prototype. Rather than writing a big deck with all my supporting evidence, they’ll bring an example, a thing, and that feels different. Then you spend your time differently to achieve those two end products, so that’s another source of friction.
Now, I still think it can be an incredibly powerful thing to have the two—if there are the right people with the right mind-set, if there is a team that is explicit about the roles, if we’re clear about the kind of outcomes we are attempting to bring forward. There’s an enormous amount of collaborativeness and respect.
Simon London: But they have to respect each other’s methodology and be prepared to flex, maybe, a little bit, in how this process is going to work.
Hugo Sarrazin: Absolutely.
Simon London: The other area where, it strikes me, there could be a little bit of a different sort of friction is this whole concept of the day-one answer, which is what we were just talking about in classical problem solving. Now, you know that this is probably not going to be your final answer, but that’s how you begin to structure the problem. Whereas I would imagine your design thinkers—no, they’re going off to do their ethnographic research and get out into the field, potentially for a long time, before they come back with at least an initial hypothesis.

Want better strategies? Become a bulletproof problem solver
Hugo Sarrazin: That is a great callout, and that’s another difference. Designers typically will like to soak into the situation and avoid converging too quickly. There’s optionality and exploring different options. There’s a strong belief that keeps the solution space wide enough that you can come up with more radical ideas. If there’s a large design team or many designers on the team, and you come on Friday and say, “What’s our week-one answer?” they’re going to struggle. They’re not going to be comfortable, naturally, to give that answer. It doesn’t mean they don’t have an answer; it’s just not where they are in their thinking process.
Simon London: I think we are, sadly, out of time for today. But Charles and Hugo, thank you so much.
Charles Conn: It was a pleasure to be here, Simon.
Hugo Sarrazin: It was a pleasure. Thank you.
Simon London: And thanks, as always, to you, our listeners, for tuning into this episode of the McKinsey Podcast . If you want to learn more about problem solving, you can find the book, Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything , online or order it through your local bookstore. To learn more about McKinsey, you can of course find us at McKinsey.com.
Charles Conn is CEO of Oxford Sciences Innovation and an alumnus of McKinsey’s Sydney office. Hugo Sarrazin is a senior partner in the Silicon Valley office, where Simon London, a member of McKinsey Publishing, is also based.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Strategy to beat the odds

Five routes to more innovative problem solving

Rational Decision-Making Model: Meaning, Importance And Examples
What is the rational decision-making model? Rational decision-making is a method that organizations, businesses and individuals use to make the…

What is the rational decision-making model? Rational decision-making is a method that organizations, businesses and individuals use to make the best decisions. Rational decision-making, one of many decision-making tools, helps users come up with the most suitable course of action. In this blog, we will look at the meaning of rational decision-making, the importance of rational decision-making and study some rational decision-making examples.
Rational decision-making is a process in which decision-makers go through a set of steps and processes and choose the best solution to a problem. These decisions are based on data analysis and logic, eliminating intuition and subjectivity.
Rational decision-making means that every variable factor, every piece of information about all the available options, has been taken into account.
What Is The Rational Decision-Making Model Used For?
What is the rational decision-making process, non-rational decision making.
The most basic use of the rational decision-making model is to ensure a consistent method of making decisions. This could be used as a standardized decision-making tool across an organization or to ensure that all managers receive the same information to make decisions. The rational decision-making process can be used to maintain a structured, step-by-step approach for every decision.
What Is The Rational Decision-Making Process ?
How the rational decision-making model is implemented can be explained in seven steps:
(There is also an example to help you understand the importance of rational decision-making)
1. Understand and define the scope
Just stating that a problem exists isn’t enough. Solid, accurate data is required to understand and analyze the problem in depth. This lets you know how much attention it requires.
It’s vital to collect as much relevant and accurate data around the problem as possible.
Here’s a rational decision-making example:
Your social media posts aren’t translating to conversions. What could the problem be? Once the analytics reports come in, you realize there isn’t enough engagement. The issue isn’t that your posts are not reaching the right audience, it’s that they don’t engage them. This sets up the next step: figuring out why the problem exists. Why is user engagement low?
2. Research and get feedback
The next step in the rational decision-making process is to delve into the problem. Find out what is causing the problem and how it can be solved. You could start with a brainstorming session and find out what your team thinks.
Rational decision-making example continued:
The budget is good, there are enough views and likes on the posts. So, why is there a lack of engagement? Why aren’t users interacting with the post? Why aren’t they clicking on the CTA?
You might need new types of posts; perhaps the current posts aren’t trendy. Maybe the posts don’t evoke an emotional response from the audience. Or they don’t convey what the product can do for the audience.
Now that you know what the causes could be, you are a step closer. It’s time to collate the data.
The team comes together with their opinions and findings. After a few customer surveys, the major issues are identified as follows:
- Potential consumers don’t know how the product will add value to their lives.
- Potential customers don’t understand the posts’ objectives and aren’t clear on what the product is.
3. List your choices
There are bound to be a host of opinions and innumerable choices about how to address the issue. Consider all of them so that you don’t create more problems later.
This is where you start to use rational decision-making:
Now that the problem has been understood, it’s time to list your options.
You could create a post that showcases what the product does.
You could have an informative GIF that shows that product in action.
You could create additional whitepapers to showcase how the product adds value and thus is beneficial for the customer to buy.
The analytics show that traffic isn’t the issue, so you don’t have to focus on garnering more traffic. Your focus has to be on conversions.
Your color schemes and CTA could be a little more impactful.
Maybe video clips are the way to go?
4. Analyze your options carefully
Now that you have all the options in front of you, cross out the ones that don’t add value or don’t solve the problem. Understand how each of the potential solutions could turn out and what other effects they could have.
Point 6 is about having a back up plan. Once you’ve chosen the plan that is likely to serve you the best, choose the second best option as well. You could use that as your back up, in case things don’t go according to plan.
While it’s great to get a quick solution to a real problem, the solution should be permanent or at least solve the majority of the issue.
The example of the rational decision-making process continued:
This is where you set about deciding the benefits of each of your choices mentioned above.
A video clip post would mean additional costs.
Redesigning the graphics may lead to more views and interaction but dilute your following.
A whitepaper is a good idea, but it doesn’t help with conversions. It’s ideal for customers to click on the CTA.
While GIFs are very popular, the image you choose has to convey the right information and be impactful. You may need to rework the branding for this to work.
While it would be great to have a post that showcases how the product works, it can’t be overly technical.
5. Understand the results you want
This is where the importance of rational decision-making comes into play. Understand what you expect from the solutions. There has to be a clear outcome because of the decision that is made. Knowing what you expect from your actions is important. It’s always a good idea to test the solution to see if it resolves the problem entirely.
Rational decision-making model example continued:
The best course of action might be to assign different teams for the different potential solutions.
One team could create a GIF, while the other works on the video clip and another on the ‘how to use’ post.
Once the teams have all made rough drafts, a productive critiquing session could be conducted. The teams can then look at each others’ solutions and point out the merits and drawbacks of each.
This way a general consensus can be reached and the best option or options can be selected. It is also advisable to use predictive social media tools. There are algorithms and equations that could help predict the success of a post to some degree.
6. Have a backup plan
While this may not always be necessary and can be a little cost-intensive, it may be worthwhile to have a backup plan if the solution doesn’t give you the intended results. This means that you should either have another strategy in place, created using the rational decision-making model .
Even though your plan has been made after careful thought, there is a chance that it either does not go as per plan or that an external factor interferes and throws your plan into chaos.
Try to have a back-up plan to make sure that your business isn’t impacted.
Now that you’ve decided to go with a combination of a GIF and an information-based post, go ahead and begin drafting your white paper as well.
7. Implement
Once the team has done all the work and created the solution, implement it. Implementing this plan means that everyone has to be on board. This means that everyone should be informed and be willing to contribute in executing the plan. The plan won’t work if everyone isn’t working toward the same goal.
As logic and data have been used to reach the decision, it’s likely going to be the most effective one.
Non -Rational Decision-Making
Non-rational decision-making is quite simply the opposite of rational decision-making . Non-rational decision-making is generally used when there isn’t enough information available or when there isn’t enough time to carry out the research and analysis required to employ rational decision-making methods.
Non-rational decision-making can be used when the person or team making the decisions has experienced that issue before or their collective experience allows them to predict what the outcome of their decision would be.
To sum it up, rational decision making can be the difference between a high performance culture driven by results and an unorganized setting. If you would like to drive decisions that guarantee results, you have to employ strategies that kindle organizational objectives based on real data. Let’s sum up the steps explained in this post about the importance of rational decision-making.
- Understand and define the scope
- Research and get feedback
- List your choices
- Analyze your options carefully
- Understand the results you want
Now that you have some idea of what the rational decision-making process is, you may be curious to find out how to make better decisions for your business. To understand more about the importance of rational decision-making , take a look at Harappa’s Making Decisions course. It delves deep into how the best decisions can be reached. The course is for you if you’re looking to get into business and learn how to use rational decision-making.
Explore Harappa Diaries to learn more about topics such as How To Define Problem , Steps involved in Ethical Decision Making , Importance Of Decision Making and How To Overcome Indecisiveness to classify problems and solve them efficiently.

- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
8 Steps in the Decision-Making Process

- 04 Feb 2020
Strong decision-making skills are essential for newly appointed and seasoned managers alike. The ability to navigate complex challenges and develop a plan can not only lead to more effective team management but drive key organizational change initiatives and objectives.
Despite decision-making’s importance in business, a recent survey by McKinsey shows that just 20 percent of professionals believe their organizations excel at it. Survey respondents noted that, on average, they spend 37 percent of their time making decisions, but more than half of it’s used ineffectively.
For managers, it’s critical to ensure effective decisions are made for their organizations’ success. Every managerial decision must be accompanied by research and data , collaboration, and alternative solutions.
Few managers, however, reap the benefits of making more thoughtful choices due to undeveloped decision-making models.
Access your free e-book today.
Why Is Making Decisions Important?
According to Harvard Business School Professor Leonard Schlesinger, who’s featured in the online course Management Essentials , most managers view decision-making as a single event, rather than a process. This can lead to managers overestimating their abilities to influence outcomes and closing themselves off from alternative perspectives and diverse ways of thinking.
“The reality is, it’s very rare to find a single point in time where ‘a decision of significance’ is made and things go forward from there,” Schlesinger says. “Embedded in this work is the notion that what we’re really talking about is a process. The role of the manager in managing that process is actually quite straightforward, yet, at the same time, extraordinarily complex.”
If you want to further your business knowledge and be more effective in your role, it’s critical to become a strong decision-maker. Here are eight steps in the decision-making process you can employ to become a better manager and have greater influence in your organization.
Steps in the Decision-Making Process
1. frame the decision.
Pinpointing the issue is the first step to initiating the decision-making process. Ensure the problem is carefully analyzed, clearly defined, and everyone involved in the outcome agrees on what needs to be solved. This process will give your team peace of mind that each key decision is based on extensive research and collaboration.
Schlesinger says this initial action can be challenging for managers because an ill-formed question can result in a process that produces the wrong decision.
“The real issue for a manager at the start is to make sure they are actively working to shape the question they’re trying to address and the decision they’re trying to have made,” Schlesinger says. “That’s not a trivial task.”
2. Structure Your Team
Managers must assemble the right people to navigate the decision-making process.
“The issue of who’s going to be involved in helping you to make that decision is one of the most central issues you face,” Schlesinger says. “The primary issue being the membership of the collection of individuals or group that you’re bringing together to make that decision.”
As you build your team, Schlesinger advises mapping the technical, political, and cultural underpinnings of the decision that needs to be made and gathering colleagues with an array of skills and experience levels to help you make an informed decision. .
“You want some newcomers who are going to provide a different point of view and perspective on the issue you’re dealing with,” he says. “At the same time, you want people who have profound knowledge and deep experience with the problem.”
It’s key to assign decision tasks to colleagues and invite perspectives that uncover blindspots or roadblocks. Schlesinger notes that attempting to arrive at the “right answer” without a team that will ultimately support and execute it is a “recipe for failure.”
3. Consider the Timeframe
This act of mapping the issue’s intricacies should involve taking the decision’s urgency into account. Business problems with significant implications sometimes allow for lengthier decision-making processes, whereas other challenges call for more accelerated timelines.
“As a manager, you need to shape the decision-making process in terms of both of those dimensions: The criticality of what it is you’re trying to decide and, more importantly, how quickly it needs to get decided given the urgency,” Schlesinger says. “The final question is, how much time you’re going to provide yourself and the group to invest in both problem diagnosis and decisions.”
4. Establish Your Approach
In the early stages of the decision-making process, it’s critical to set ground rules and assign roles to team members. Doing so can help ensure everyone understands how they contribute to problem-solving and agrees on how a solution will be reached.
“It’s really important to get clarity upfront around the roles people are going to play and the ways in which decisions are going to get made,” Schlesinger says. “Often, managers leave that to chance, so people self-assign themselves to roles in ways that you don’t necessarily want, and the decision-making process defers to consensus, which is likely to lead to a lower evaluation of the problem and a less creative solution.”

5. Encourage Discussion and Debate
One of the issues of leading a group that defaults to consensus is that it can shut out contrarian points of view and deter inventive problem-solving. Because of this potential pitfall, Schlesinger notes, you should designate roles that focus on poking holes in arguments and fostering debate.
“What we’re talking about is establishing a process of devil’s advocacy, either in an individual or a subgroup role,” he says. “That’s much more likely to lead to a deeper critical evaluation and generate a substantial number of alternatives.”
Schlesinger adds that this action can take time and potentially disrupt group harmony, so it’s vital for managers to guide the inner workings of the process from the outset to ensure effective collaboration and guarantee more quality decisions will be made.
“What we need to do is establish norms in the group that enable us to be open to a broader array of data and decision-making processes,” he says. “If that doesn’t happen upfront, but in the process without a conversation, it’s generally a source of consternation and some measure of frustration.”
Related: 3 Group Decision-Making Techniques for Success
6. Navigate Group Dynamics
In addition to creating a dynamic in which candor and debate are encouraged, there are other challenges you need to navigate as you manage your team throughout the decision-making process.
One is ensuring the size of the group is appropriate for the problem and allows for an efficient workflow.
“In getting all the people together that have relevant data and represent various political and cultural constituencies, each incremental member adds to the complexity of the decision-making process and the amount of time it takes to get a decision made and implemented,” Schlesinger says.
Another task, he notes, is identifying which parts of the process can be completed without face-to-face interaction.
“There’s no question that pieces of the decision-making process can be deferred to paper, email, or some app,” Schlesinger says. “But, at the end of the day, given that so much of decision-making requires high-quality human interaction, you need to defer some part of the process for ill-structured and difficult tasks to a face-to-face meeting.”
7. Ensure the Pieces Are in Place for Implementation
Throughout your team’s efforts to arrive at a decision, you must ensure you facilitate a process that encompasses:
- Shared goals that were presented upfront
- Alternative options that have been given rigorous thought and fair consideration
- Sound methods for exploring decisions’ consequences
According to Schlesinger, these components profoundly influence the quality of the solution that’s ultimately identified and the types of decisions that’ll be made in the future.
“In the general manager’s job, the quality of the decision is only one part of the equation,” he says. “All of this is oriented toward trying to make sure that once a decision is made, we have the right groupings and the right support to implement.”

8. Achieve Closure and Alignment
Achieving closure in the decision-making process requires arriving at a solution that sufficiently aligns members of your group and garners enough support to implement it.
As with the other phases of decision-making, clear communication ensures your team understands and commits to the plan.
In a video interview for the online course Management Essentials , Harvard Business School Dean Nitin Nohria says it’s essential to explain the rationale behind the decision to your employees.
“If it’s a decision that you have to make, say, ‘I know there were some of you who thought differently, but let me tell you why we went this way,’” Nohria says. “This is so the people on the other side feel heard and recognize the concerns they raised are things you’ve tried to incorporate into the decision and, as implementation proceeds, if those concerns become real, then they’ll be attended to.”

How to Improve Your Decision-Making
An in-depth understanding of the decision-making process is vital for all managers. Whether you’re an aspiring manager aiming to move up at your organization or a seasoned executive who wants to boost your job performance, honing your approach to decision-making can improve your managerial skills and equip you with the tools to advance your career.
Do you want to become a more effective decision-maker? Explore Management Essentials —one of our online leadership and management courses —to learn how you can influence the context and environment in which decisions get made.
This article was update on July 15, 2022. It was originally published on February 4, 2020.

About the Author
Our content is reader-supported. Things you buy through links on our site may earn us a commission
Join our newsletter
Never miss out on well-researched articles in your field of interest with our weekly newsletter.
- Project Management
- Starting a business
Get the latest Business News
Mastering problem solving and decision making.

© Copyright Carter McNamara, MBA, PhD, Authenticity Consulting, LLC .
Sections of This Topic Include
- Test – What is Your Personal Decision-Making Style?
- Guidelines to Rational Problem Solving and Decision-Making
- Rational Versus Organic Approach to Problem Solving and Decision Making
- General Guidelines to Problem Solving and Decision-Making
- Various Methods and Tools for Problem-Solving and Decision Making
- General Resources for Problem-Solving and Decision Making
Also, consider
- Related Library Topics
- (Also see the closely related topics Decision Making , Group-Based Problem Solving, and Decision Making and Planning — Basics .)
What is Your Personal Decision-Making Style?
There are many styles of making decisions, ranging from very rational and linear to organic and unfolding. Take this online assessment to determine your own style.
Discover Your Decision-Making Style
Do you want to improve or polish your style? Consider the many guidelines included below.
Guidelines to Problem-Solving and Decision Making (Rational Approach)
Much of what people do is solve problems and make decisions. Often, they are “under the gun”, stressed, and very short of time. Consequently, when they encounter a new problem or decision they must make, they react with a decision that seemed to work before. It’s easy with this approach to get stuck in a circle of solving the same problem over and over again. Therefore, it’s often useful to get used to an organized approach to problem-solving and decision-making.
Not all problems can be solved and decisions made by the following, rather rational approach. However, the following basic guidelines will get you started. Don’t be intimidated by the length of the list of guidelines. After you’ve practiced them a few times, they’ll become second nature to you — enough that you can deepen and enrich them to suit your own needs and nature.
(Note that it might be more your nature to view a “problem” as an “opportunity”. Therefore, you might substitute “problem” for “opportunity” in the following guidelines.)
1. Define the problem
This is often where people struggle. They react to what they think the problem is. Instead, seek to understand more about why you think there’s a problem.
Define the problem: (with input from yourself and others). Ask yourself and others, the following questions:
- What can you see that causes you to think there’s a problem?
- Where is it happening?
- How is it happening?
- When is it happening?
- With whom is it happening? (HINT: Don’t jump to “Who is causing the problem?” When we’re stressed, blaming is often one of our first reactions. To be an effective manager, you need to address issues more than people.)
- Why is it happening?
- Write down a five-sentence description of the problem in terms of “The following should be happening, but isn’t …” or “The following is happening and should be: …” As much as possible, be specific in your description, including what is happening, where, how, with whom and why. (It may be helpful at this point to use a variety of research methods.)
Defining complex problems:
If the problem still seems overwhelming, break it down by repeating steps 1-7 until you have descriptions of several related problems.
Verifying your understanding of the problems:
It helps a great deal to verify your problem analysis for conferring with a peer or someone else.
Prioritize the problems:
If you discover that you are looking at several related problems, then prioritize which ones you should address first.
Note the difference between “important” and “urgent” problems. Often, what we consider to be important problems to consider are really just urgent problems. Important problems deserve more attention. For example, if you’re continually answering “urgent” phone calls, then you’ve probably got a more “important” problem and that’s to design a system that screens and prioritizes your phone calls.
Understand your role in the problem:
Your role in the problem can greatly influence how you perceive the role of others. For example, if you’re very stressed out, it’ll probably look like others are, too, or, you may resort too quickly to blaming and reprimanding others. Or, you are feel very guilty about your role in the problem, you may ignore the accountabilities of others.
2. Look at potential causes for the problem
- It’s amazing how much you don’t know about what you don’t know. Therefore, in this phase, it’s critical to get input from other people who notice the problem and who are affected by it.
- It’s often useful to collect input from other individuals one at a time (at least at first). Otherwise, people tend to be inhibited about offering their impressions of the real causes of problems.
- Write down your opinions and what you’ve heard from others.
- Regarding what you think might be performance problems associated with an employee, it’s often useful to seek advice from a peer or your supervisor in order to verify your impression of the problem.
- Write down a description of the cause of the problem in terms of what is happening, where, when, how, with whom, and why.
3. Identify alternatives for approaches to resolve the problem
At this point, it’s useful to keep others involved (unless you’re facing a personal and/or employee performance problem). Brainstorm for solutions to the problem. Very simply put, brainstorming is collecting as many ideas as possible, and then screening them to find the best idea. It’s critical when collecting the ideas to not pass any judgment on the ideas — just write them down as you hear them. (A wonderful set of skills used to identify the underlying cause of issues is Systems Thinking.)
4. Select an approach to resolve the problem
- When selecting the best approach, consider:
- Which approach is the most likely to solve the problem for the long term?
- Which approach is the most realistic to accomplish for now? Do you have the resources? Are they affordable? Do you have enough time to implement the approach?
- What is the extent of risk associated with each alternative?
(The nature of this step, in particular, in the problem solving process is why problem solving and decision making are highly integrated.)
5. Plan the implementation of the best alternative (this is your action plan)
- Carefully consider “What will the situation look like when the problem is solved?”
- What steps should be taken to implement the best alternative to solving the problem? What systems or processes should be changed in your organization, for example, a new policy or procedure? Don’t resort to solutions where someone is “just going to try harder”.
- How will you know if the steps are being followed or not? (these are your indicators of the success of your plan)
- What resources will you need in terms of people, money, and facilities?
- How much time will you need to implement the solution? Write a schedule that includes the start and stop times, and when you expect to see certain indicators of success.
- Who will primarily be responsible for ensuring the implementation of the plan?
- Write down the answers to the above questions and consider this as your action plan.
- Communicate the plan to those who will involved in implementing it and, at least, to your immediate supervisor.
(An important aspect of this step in the problem-solving process is continual observation and feedback.)
6. Monitor implementation of the plan
Monitor the indicators of success:
- Are you seeing what you would expect from the indicators?
- Will the plan be done according to schedule?
- If the plan is not being followed as expected, then consider: Was the plan realistic? Are there sufficient resources to accomplish the plan on schedule? Should more priority be placed on various aspects of the plan? Should the plan be changed?
7. Verify if the problem has been resolved or not
One of the best ways to verify if a problem has been solved or not is to resume normal operations in the organization. Still, you should consider:
- What changes should be made to avoid this type of problem in the future? Consider changes to policies and procedures, training, etc.
- Lastly, consider “What did you learn from this problem-solving?” Consider new knowledge, understanding, and/or skills.
- Consider writing a brief memo that highlights the success of the problem-solving effort, and what you learned as a result. Share it with your supervisor, peers and subordinates.
Rational Versus Organic Approach to Problem Solving
A person with this preference often prefers using a comprehensive and logical approach similar to the guidelines in the above section. For example, the rational approach, described below, is often used when addressing large, complex matters in strategic planning.
- Define the problem.
- Examine all potential causes for the problem.
- Identify all alternatives to resolve the problem.
- Carefully select an alternative.
- Develop an orderly implementation plan to implement the best alternative.
- Carefully monitor the implementation of the plan.
- Verify if the problem has been resolved or not.
A major advantage of this approach is that it gives a strong sense of order in an otherwise chaotic situation and provides a common frame of reference from which people can communicate in the situation. A major disadvantage of this approach is that it can take a long time to finish. Some people might argue, too, that the world is much too chaotic for the rational approach to be useful.
Some people assert that the dynamics of organizations and people are not nearly so mechanistic as to be improved by solving one problem after another. Often, the quality of an organization or life comes from how one handles being “on the road” itself, rather than the “arriving at the destination.” The quality comes from the ongoing process of trying, rather than from having fixed a lot of problems. For many people, it is an approach to organizational consulting. The following quote is often used when explaining the organic (or holistic) approach to problem solving.
“All the greatest and most important problems in life are fundamentally insoluble … They can never be solved, but only outgrown. This “outgrowing” proves that further investigation to require a new level of consciousness. Some higher or wider interest appeared on the horizon and through this broadening of outlook, the insoluble lost its urgency. It was not solved logically in its own terms, but faded when confronted with a new and stronger life urge.” From Jung, Carl, Psychological Types (Pantheon Books, 1923)
A major advantage of the organic approach is that it is highly adaptable to understanding and explaining the chaotic changes that occur in projects and everyday life. It also suits the nature of people who shun linear and mechanistic approaches to projects. The major disadvantage is that the approach often provides no clear frame of reference around which people can communicate, feel comfortable and measure progress toward solutions to problems.
Additional Guidelines for Problem-Solving and Decision Making
Recommended articles.
- Ten Tips for Beefing Up Your Problem-Solving Tool Box
- Problem Solving Techniques (extensive overview of various approaches)
- Key Questions to Ask Before Selecting a Solution to a Business Problem
Additional Articles
- Problem-solving and Decision-Making:
- Top 5 Tips to Improve Concentration
- Problem Solving and Decision Making – 12 Great Tips!
- Powerful Problem Solving
- Creative Problem-Solving
- Leadership Styles and Problem Solving (focus on creativity)
- Forget About Causes, Focus on Solutions
- Ten Tips for Beefing Up Your Problem-Solving ToolBox
- Coaching Tip: Four-Question Method for Proactive Problem Solving
- Coaching Tip — How to Bust Paralysis by Analysis
- Appreciative Inquiry
- Powerful Problem-Solving
- Problem-Solving Techniques
- Guidelines for Selecting An Appropriate Problem-Solving Approach
- Factors to Consider in Figuring Out What to Do About A Problem
- A Case for Reengineering the Problem-Solving Process (Somewhat Advanced)
- Courseware on Problemistics (The art & craft of problem dealing)
- Adapt your leadership style
- Organic Approach to Problem Solving
- Make Good Decisions, Avoid Bad Consequences
- Priority Management: Are You Doing the Right Things?
General Guidelines for Decision Making
- Decision-Making Tips
- How We Sometimes Fool Ourselves When Making Decisions (Traps We Can Fall Into)
- More of the Most Common Decision-Making Mistakes (more traps we can fall into)
- When Your Organization’s Decisions Are in the Hands of Devils
- Flawed Decision-making is Dangerous
- Five Tips for Making Better Decisions
- Study Says People Make Better Decisions With a Full Bladder
- What Everyone Should Know About Decision Making
Various Tools and Methods for Problem Solving and Decision Making
(Many people would agree that the following methods and tools are also for decision-making.)
- Cost Benefit Analysis (for deciding based on costs)
- De Bono Hats (for looking at a situation from many perspectives
- Delphi Decision Making (to collect the views of experts and distill expert-based solutions)
- Dialectic Decision Making (rigorous action planning via examining opposite points of view) Fishbone Diagram —
- 5 Steps to build Fishbone Diagram
- Fishbowls (for groups to learn by watching modeled behaviors)
- Grid Analysis (for choosing among many choices)
- Pareto Principle (for finding the options that will make the most difference — (20/80 rule”)
- For solving seemingly unsolvable contradictions
- Rational Decision Making
- SWOT Analysis (to analyze strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats)
- Work Breakdown Structure (for organizing and relating many details)
General Resources for Problem Solving and Decision Making
- The Ultimate Problem-Solving Process Guide: 31 Steps and Resources
- list of various tools
- long list of tools
- Decision Making Tools
- Decision Making
- Group Decision Making and Problem Solving
- Inquiry and Reflection
- Mental Models (scan down to “Mental Models”)
- Questioning
- Research Methods
- Systems Thinking
Learn More in the Library’s Blogs Related to Problem Solving and Decision Making
In addition to the articles on this current page, also see the following blogs that have posts related to this topic. Scan down the blog’s page to see various posts. Also, see the section “Recent Blog Posts” in the sidebar of the blog or click on “Next” near the bottom of a post in the blog. The blog also links to numerous free related resources.
- Library’s Career Management Blog
- Library’s Coaching Blog
- Library’s Human Resources Blog
- Library’s Spirituality Blog
For the Category of Innovation:
To round out your knowledge of this Library topic, you may want to review some related topics, available from the link below. Each of the related topics includes free, online resources.
Also, scan the Recommended Books listed below. They have been selected for their relevance and highly practical nature.
- Recommended Books
Cheapest Insurance
Businesses, especially those specializing in providing one form of service or the other, stand the risk of being sued for insurance claims, damages, or accidents that occur while providing a service. That’s where general liability insurance comes in, and it helps businesses cover these claims without the business owners taking out private funds. Although general …

Optima Tax Relief Review – Pros, Cons, & Cost Compared
Considering Optima Tax Relief for your IRS debt issues? Before you decide, check out this review! Dealing with tax debt can be incredibly stressful, and finding the right help is crucial. We’ve explored the ins and outs of tax debt relief and discovered that while there’s a mix of good and bad, Optima Tax Relief …

Community Tax Services Review 2024: Pros, Cons, & Alternates
Community Tax Relief is a comprehensive tax debt relief company providing various services to help you manage tax debt. Whether it’s negotiating tax liabilities, planning future taxes, filing returns, or optimizing your business’s accounting practices, Community Tax is equipped to assist. With a track record of serving over 100,000 clients and managing over $800 million …

Larson Tax Relief Review for 2024: Pros, Cons, & Pricing
If you’re dealing with complex business taxes or intricate personal tax issues, Larson Tax Relief could be a valuable resource. Larson’s tax relief programs and professional tax services are designed to address a wide range of business and personal income tax challenges. They commit to guiding you personally through each stage of the process and …

Anthem Tax Services Review for 2024: Pros, Cons, & Pricing
Do you have a tax debt of $10,000 or more? Anthem Tax Services might be your solution, helping you arrange a payment plan to reduce your tax liability or possibly both. What sets them apart? If Anthem Tax Services doesn’t secure a favorable outcome for you, they’ll refund your payment. This assurance stands out as …

10 Best SEO Competitor Analysis Tools Tested by Experts
Are you struggling to keep up with your competitors and match their success rate? Competitor analysis tools enable you to monitor, assess, and draw insights from your competitors’ tactics. This knowledge can supercharge your marketing campaigns and help you win! With so many competitor analysis tools available, finding the perfect fit for your brand can …

6 Best SEO Audit Tools Tried & Tested by Experts
If you’re like most people, the term “audit” might send a shiver down your spine, conjuring images of stressful financial scrutiny. However, if you’re an SEO professional, the same word likely sparks excitement, evoking thoughts of discovering valuable marketing insights. Digital marketers rely heavily on tools that provide these insights, enabling us to understand what …

7 Best SEO Reporting Tools Tested by Experts for 2024
Do you send your clients multiple Excel files filled with endless metrics, values, and comments? That’s not the best way to highlight the value of your services. A data-rich, visually appealing SEO report is a much more effective alternative. Now, the big question is: which SEO reporting tool should you use? I’ve scoured the market …

6 Best California Credit Repair Companies Ranked for 2024
If you’re looking for the top credit repair company in California, you’re in the right spot. From Creditrepair.com to Credit Pros, I’ll help you find the perfect match for your needs. Here are the top six credit repair companies in California, USA. >> Improve Credit Rating With CreditRepair.com >> 6 Best Credit Repair Companies CA …

8 Best Keyword Research Tools Tested by SEO Experts in 2024
A vast array of keyword research tools are available, catering to all levels of expertise, from beginners to seasoned SEO professionals. These tools vary widely, from the overly basic and somewhat ineffective to those that are incredibly useful and powerful. The most effective keyword research tools do more than just help you find relevant keywords; …

Semrush Review 2024: Pros, Cons, Pricing, & Alternates
Thinking about giving Semrush a spin for your SEO or digital marketing needs? Let’s dive into a hands-on review that might help you figure out if it’s the right tool for your business. We’ll explore various features of Semrush and pinpoint which aspects could be especially beneficial for certain types of enterprises. Ready to discover …

10 Best Tax Relief Services Ranked for Pros, Cons, & Fees
Grappling with a hefty tax debt can be overwhelming, especially when your finances are tight. Luckily, there’s professional assistance out there for those buried under thousands of dollars in IRS debt. Several tax pros work at tax relief firms. They can negotiate with the IRS and state tax agencies on your behalf to arrange payment …

6 Best SEO Tools for You to Try in 2024: Tested by Experts
In some professions, you might rely solely on your wit, physical prowess, or sheer ambition. SEO marketing, however, isn’t one of those fields. In today’s digital landscape, marketers depend heavily on the right tools. These tools are essential for tracking performance metrics, diagnosing issues, suggesting enhancements, reporting progress, and automating the repetitive tasks that are …

Credit Saint Review: Pros, Cons, & Features Compared
If you’ve faced challenges with past credit issues and are constantly hassled by collection companies, Credit Saint’s credit repair and monitoring packages are helpful. The company specializes in directly contacting credit bureaus to dispute inaccuracies on your credit report and works to have them removed. In this article, we’ve thoroughly reviewed Credit Saint, exploring the …

6 Best Cost Segregation Companies Ranked & Rated for 2024
Are you thinking about cost segregation for your commercial or investment real estate? The top cost segregation firms can maximize your tax benefits while ensuring compliance with IRS regulations. In this article, I’ve put together a list of six outstanding cost segregation companies known for their reliability and efficiency. They can significantly assist you in …
Privacy Overview
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Leadership |
- 7 important steps in the decision makin ...
7 important steps in the decision making process

The decision making process is a method of gathering information, assessing alternatives, and making a final choice with the goal of making the best decision possible. In this article, we detail the step-by-step process on how to make a good decision and explain different decision making methodologies.
We make decisions every day. Take the bus to work or call a car? Chocolate or vanilla ice cream? Whole milk or two percent?
There's an entire process that goes into making those tiny decisions, and while these are simple, easy choices, how do we end up making more challenging decisions?
At work, decisions aren't as simple as choosing what kind of milk you want in your latte in the morning. That’s why understanding the decision making process is so important.
What is the decision making process?
The decision making process is the method of gathering information, assessing alternatives, and, ultimately, making a final choice.
Decision-making tools for agile businesses
In this ebook, learn how to equip employees to make better decisions—so your business can pivot, adapt, and tackle challenges more effectively than your competition.

The 7 steps of the decision making process
Step 1: identify the decision that needs to be made.
When you're identifying the decision, ask yourself a few questions:
What is the problem that needs to be solved?
What is the goal you plan to achieve by implementing this decision?
How will you measure success?
These questions are all common goal setting techniques that will ultimately help you come up with possible solutions. When the problem is clearly defined, you then have more information to come up with the best decision to solve the problem.
Step 2: Gather relevant information
Gathering information related to the decision being made is an important step to making an informed decision. Does your team have any historical data as it relates to this issue? Has anybody attempted to solve this problem before?
It's also important to look for information outside of your team or company. Effective decision making requires information from many different sources. Find external resources, whether it’s doing market research, working with a consultant, or talking with colleagues at a different company who have relevant experience. Gathering information helps your team identify different solutions to your problem.
Step 3: Identify alternative solutions
This step requires you to look for many different solutions for the problem at hand. Finding more than one possible alternative is important when it comes to business decision-making, because different stakeholders may have different needs depending on their role. For example, if a company is looking for a work management tool, the design team may have different needs than a development team. Choosing only one solution right off the bat might not be the right course of action.
Step 4: Weigh the evidence
This is when you take all of the different solutions you’ve come up with and analyze how they would address your initial problem. Your team begins identifying the pros and cons of each option, and eliminating alternatives from those choices.
There are a few common ways your team can analyze and weigh the evidence of options:
Pros and cons list
SWOT analysis
Decision matrix
Step 5: Choose among the alternatives
The next step is to make your final decision. Consider all of the information you've collected and how this decision may affect each stakeholder.
Sometimes the right decision is not one of the alternatives, but a blend of a few different alternatives. Effective decision-making involves creative problem solving and thinking out of the box, so don't limit you or your teams to clear-cut options.
One of the key values at Asana is to reject false tradeoffs. Choosing just one decision can mean losing benefits in others. If you can, try and find options that go beyond just the alternatives presented.
Step 6: Take action
Once the final decision maker gives the green light, it's time to put the solution into action. Take the time to create an implementation plan so that your team is on the same page for next steps. Then it’s time to put your plan into action and monitor progress to determine whether or not this decision was a good one.
Step 7: Review your decision and its impact (both good and bad)
Once you’ve made a decision, you can monitor the success metrics you outlined in step 1. This is how you determine whether or not this solution meets your team's criteria of success.
Here are a few questions to consider when reviewing your decision:
Did it solve the problem your team identified in step 1?
Did this decision impact your team in a positive or negative way?
Which stakeholders benefited from this decision? Which stakeholders were impacted negatively?
If this solution was not the best alternative, your team might benefit from using an iterative form of project management. This enables your team to quickly adapt to changes, and make the best decisions with the resources they have.
Types of decision making models
While most decision making models revolve around the same seven steps, here are a few different methodologies to help you make a good decision.
Rational decision making models
This type of decision making model is the most common type that you'll see. It's logical and sequential. The seven steps listed above are an example of the rational decision making model.
When your decision has a big impact on your team and you need to maximize outcomes, this is the type of decision making process you should use. It requires you to consider a wide range of viewpoints with little bias so you can make the best decision possible.
Intuitive decision making models
This type of decision making model is dictated not by information or data, but by gut instincts. This form of decision making requires previous experience and pattern recognition to form strong instincts.
This type of decision making is often made by decision makers who have a lot of experience with similar kinds of problems. They have already had proven success with the solution they're looking to implement.
Creative decision making model
The creative decision making model involves collecting information and insights about a problem and coming up with potential ideas for a solution, similar to the rational decision making model.
The difference here is that instead of identifying the pros and cons of each alternative, the decision maker enters a period in which they try not to actively think about the solution at all. The goal is to have their subconscious take over and lead them to the right decision, similar to the intuitive decision making model.
This situation is best used in an iterative process so that teams can test their solutions and adapt as things change.
Track key decisions with a work management tool
Tracking key decisions can be challenging when not documented correctly. Learn more about how a work management tool like Asana can help your team track key decisions, collaborate with teammates, and stay on top of progress all in one place.
Related resources

Fiedler’s Contingency Theory: Why leadership isn’t uniform
What is management by objectives (MBO)?

How to find alignment on AI
Grant management: A nonprofit’s guide

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
14.3 Problem Solving and Decision Making in Groups
Learning objectives.
- Discuss the common components and characteristics of problems.
- Explain the five steps of the group problem-solving process.
- Describe the brainstorming and discussion that should take place before the group makes a decision.
- Compare and contrast the different decision-making techniques.
- Discuss the various influences on decision making.
Although the steps of problem solving and decision making that we will discuss next may seem obvious, we often don’t think to or choose not to use them. Instead, we start working on a problem and later realize we are lost and have to backtrack. I’m sure we’ve all reached a point in a project or task and had the “OK, now what?” moment. I’ve recently taken up some carpentry projects as a functional hobby, and I have developed a great respect for the importance of advanced planning. It’s frustrating to get to a crucial point in building or fixing something only to realize that you have to unscrew a support board that you already screwed in, have to drive back to the hardware store to get something that you didn’t think to get earlier, or have to completely start over. In this section, we will discuss the group problem-solving process, methods of decision making, and influences on these processes.
Group Problem Solving
The problem-solving process involves thoughts, discussions, actions, and decisions that occur from the first consideration of a problematic situation to the goal. The problems that groups face are varied, but some common problems include budgeting funds, raising funds, planning events, addressing customer or citizen complaints, creating or adapting products or services to fit needs, supporting members, and raising awareness about issues or causes.
Problems of all sorts have three common components (Adams & Galanes, 2009):
- An undesirable situation. When conditions are desirable, there isn’t a problem.
- A desired situation. Even though it may only be a vague idea, there is a drive to better the undesirable situation. The vague idea may develop into a more precise goal that can be achieved, although solutions are not yet generated.
- Obstacles between undesirable and desirable situation. These are things that stand in the way between the current situation and the group’s goal of addressing it. This component of a problem requires the most work, and it is the part where decision making occurs. Some examples of obstacles include limited funding, resources, personnel, time, or information. Obstacles can also take the form of people who are working against the group, including people resistant to change or people who disagree.
Discussion of these three elements of a problem helps the group tailor its problem-solving process, as each problem will vary. While these three general elements are present in each problem, the group should also address specific characteristics of the problem. Five common and important characteristics to consider are task difficulty, number of possible solutions, group member interest in problem, group member familiarity with problem, and the need for solution acceptance (Adams & Galanes, 2009).
- Task difficulty. Difficult tasks are also typically more complex. Groups should be prepared to spend time researching and discussing a difficult and complex task in order to develop a shared foundational knowledge. This typically requires individual work outside of the group and frequent group meetings to share information.
- Number of possible solutions. There are usually multiple ways to solve a problem or complete a task, but some problems have more potential solutions than others. Figuring out how to prepare a beach house for an approaching hurricane is fairly complex and difficult, but there are still a limited number of things to do—for example, taping and boarding up windows; turning off water, electricity, and gas; trimming trees; and securing loose outside objects. Other problems may be more creatively based. For example, designing a new restaurant may entail using some standard solutions but could also entail many different types of innovation with layout and design.
- Group member interest in problem. When group members are interested in the problem, they will be more engaged with the problem-solving process and invested in finding a quality solution. Groups with high interest in and knowledge about the problem may want more freedom to develop and implement solutions, while groups with low interest may prefer a leader who provides structure and direction.
- Group familiarity with problem. Some groups encounter a problem regularly, while other problems are more unique or unexpected. A family who has lived in hurricane alley for decades probably has a better idea of how to prepare its house for a hurricane than does a family that just recently moved from the Midwest. Many groups that rely on funding have to revisit a budget every year, and in recent years, groups have had to get more creative with budgets as funding has been cut in nearly every sector. When group members aren’t familiar with a problem, they will need to do background research on what similar groups have done and may also need to bring in outside experts.
- Need for solution acceptance. In this step, groups must consider how many people the decision will affect and how much “buy-in” from others the group needs in order for their solution to be successfully implemented. Some small groups have many stakeholders on whom the success of a solution depends. Other groups are answerable only to themselves. When a small group is planning on building a new park in a crowded neighborhood or implementing a new policy in a large business, it can be very difficult to develop solutions that will be accepted by all. In such cases, groups will want to poll those who will be affected by the solution and may want to do a pilot implementation to see how people react. Imposing an excellent solution that doesn’t have buy-in from stakeholders can still lead to failure.
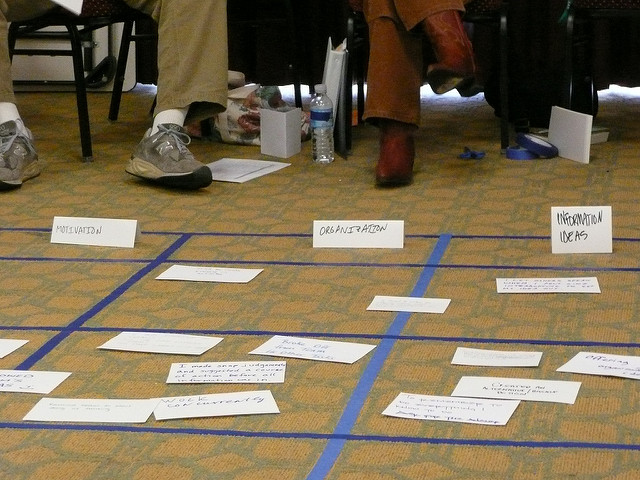

Group problem solving can be a confusing puzzle unless it is approached systematically.
Muness Castle – Problem Solving – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Group Problem-Solving Process
There are several variations of similar problem-solving models based on US American scholar John Dewey’s reflective thinking process (Bormann & Bormann, 1988). As you read through the steps in the process, think about how you can apply what we learned regarding the general and specific elements of problems. Some of the following steps are straightforward, and they are things we would logically do when faced with a problem. However, taking a deliberate and systematic approach to problem solving has been shown to benefit group functioning and performance. A deliberate approach is especially beneficial for groups that do not have an established history of working together and will only be able to meet occasionally. Although a group should attend to each step of the process, group leaders or other group members who facilitate problem solving should be cautious not to dogmatically follow each element of the process or force a group along. Such a lack of flexibility could limit group member input and negatively affect the group’s cohesion and climate.
Step 1: Define the Problem
Define the problem by considering the three elements shared by every problem: the current undesirable situation, the goal or more desirable situation, and obstacles in the way (Adams & Galanes, 2009). At this stage, group members share what they know about the current situation, without proposing solutions or evaluating the information. Here are some good questions to ask during this stage: What is the current difficulty? How did we come to know that the difficulty exists? Who/what is involved? Why is it meaningful/urgent/important? What have the effects been so far? What, if any, elements of the difficulty require clarification? At the end of this stage, the group should be able to compose a single sentence that summarizes the problem called a problem statement . Avoid wording in the problem statement or question that hints at potential solutions. A small group formed to investigate ethical violations of city officials could use the following problem statement: “Our state does not currently have a mechanism for citizens to report suspected ethical violations by city officials.”
Step 2: Analyze the Problem
During this step a group should analyze the problem and the group’s relationship to the problem. Whereas the first step involved exploring the “what” related to the problem, this step focuses on the “why.” At this stage, group members can discuss the potential causes of the difficulty. Group members may also want to begin setting out an agenda or timeline for the group’s problem-solving process, looking forward to the other steps. To fully analyze the problem, the group can discuss the five common problem variables discussed before. Here are two examples of questions that the group formed to address ethics violations might ask: Why doesn’t our city have an ethics reporting mechanism? Do cities of similar size have such a mechanism? Once the problem has been analyzed, the group can pose a problem question that will guide the group as it generates possible solutions. “How can citizens report suspected ethical violations of city officials and how will such reports be processed and addressed?” As you can see, the problem question is more complex than the problem statement, since the group has moved on to more in-depth discussion of the problem during step 2.
Step 3: Generate Possible Solutions
During this step, group members generate possible solutions to the problem. Again, solutions should not be evaluated at this point, only proposed and clarified. The question should be what could we do to address this problem, not what should we do to address it. It is perfectly OK for a group member to question another person’s idea by asking something like “What do you mean?” or “Could you explain your reasoning more?” Discussions at this stage may reveal a need to return to previous steps to better define or more fully analyze a problem. Since many problems are multifaceted, it is necessary for group members to generate solutions for each part of the problem separately, making sure to have multiple solutions for each part. Stopping the solution-generating process prematurely can lead to groupthink. For the problem question previously posed, the group would need to generate solutions for all three parts of the problem included in the question. Possible solutions for the first part of the problem (How can citizens report ethical violations?) may include “online reporting system, e-mail, in-person, anonymously, on-the-record,” and so on. Possible solutions for the second part of the problem (How will reports be processed?) may include “daily by a newly appointed ethics officer, weekly by a nonpartisan nongovernment employee,” and so on. Possible solutions for the third part of the problem (How will reports be addressed?) may include “by a newly appointed ethics commission, by the accused’s supervisor, by the city manager,” and so on.
Step 4: Evaluate Solutions
During this step, solutions can be critically evaluated based on their credibility, completeness, and worth. Once the potential solutions have been narrowed based on more obvious differences in relevance and/or merit, the group should analyze each solution based on its potential effects—especially negative effects. Groups that are required to report the rationale for their decision or whose decisions may be subject to public scrutiny would be wise to make a set list of criteria for evaluating each solution. Additionally, solutions can be evaluated based on how well they fit with the group’s charge and the abilities of the group. To do this, group members may ask, “Does this solution live up to the original purpose or mission of the group?” and “Can the solution actually be implemented with our current resources and connections?” and “How will this solution be supported, funded, enforced, and assessed?” Secondary tensions and substantive conflict, two concepts discussed earlier, emerge during this step of problem solving, and group members will need to employ effective critical thinking and listening skills.
Decision making is part of the larger process of problem solving and it plays a prominent role in this step. While there are several fairly similar models for problem solving, there are many varied decision-making techniques that groups can use. For example, to narrow the list of proposed solutions, group members may decide by majority vote, by weighing the pros and cons, or by discussing them until a consensus is reached. There are also more complex decision-making models like the “six hats method,” which we will discuss later. Once the final decision is reached, the group leader or facilitator should confirm that the group is in agreement. It may be beneficial to let the group break for a while or even to delay the final decision until a later meeting to allow people time to evaluate it outside of the group context.
Step 5: Implement and Assess the Solution
Implementing the solution requires some advanced planning, and it should not be rushed unless the group is operating under strict time restraints or delay may lead to some kind of harm. Although some solutions can be implemented immediately, others may take days, months, or years. As was noted earlier, it may be beneficial for groups to poll those who will be affected by the solution as to their opinion of it or even to do a pilot test to observe the effectiveness of the solution and how people react to it. Before implementation, groups should also determine how and when they would assess the effectiveness of the solution by asking, “How will we know if the solution is working or not?” Since solution assessment will vary based on whether or not the group is disbanded, groups should also consider the following questions: If the group disbands after implementation, who will be responsible for assessing the solution? If the solution fails, will the same group reconvene or will a new group be formed?

Once a solution has been reached and the group has the “green light” to implement it, it should proceed deliberately and cautiously, making sure to consider possible consequences and address them as needed.
Jocko Benoit – Prodigal Light – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Certain elements of the solution may need to be delegated out to various people inside and outside the group. Group members may also be assigned to implement a particular part of the solution based on their role in the decision making or because it connects to their area of expertise. Likewise, group members may be tasked with publicizing the solution or “selling” it to a particular group of stakeholders. Last, the group should consider its future. In some cases, the group will get to decide if it will stay together and continue working on other tasks or if it will disband. In other cases, outside forces determine the group’s fate.
“Getting Competent”
Problem Solving and Group Presentations
Giving a group presentation requires that individual group members and the group as a whole solve many problems and make many decisions. Although having more people involved in a presentation increases logistical difficulties and has the potential to create more conflict, a well-prepared and well-delivered group presentation can be more engaging and effective than a typical presentation. The main problems facing a group giving a presentation are (1) dividing responsibilities, (2) coordinating schedules and time management, and (3) working out the logistics of the presentation delivery.
In terms of dividing responsibilities, assigning individual work at the first meeting and then trying to fit it all together before the presentation (which is what many college students do when faced with a group project) is not the recommended method. Integrating content and visual aids created by several different people into a seamless final product takes time and effort, and the person “stuck” with this job at the end usually ends up developing some resentment toward his or her group members. While it’s OK for group members to do work independently outside of group meetings, spend time working together to help set up some standards for content and formatting expectations that will help make later integration of work easier. Taking the time to complete one part of the presentation together can help set those standards for later individual work. Discuss the roles that various group members will play openly so there isn’t role confusion. There could be one point person for keeping track of the group’s progress and schedule, one point person for communication, one point person for content integration, one point person for visual aids, and so on. Each person shouldn’t do all that work on his or her own but help focus the group’s attention on his or her specific area during group meetings (Stanton, 2009).
Scheduling group meetings is one of the most challenging problems groups face, given people’s busy lives. From the beginning, it should be clearly communicated that the group needs to spend considerable time in face-to-face meetings, and group members should know that they may have to make an occasional sacrifice to attend. Especially important is the commitment to scheduling time to rehearse the presentation. Consider creating a contract of group guidelines that includes expectations for meeting attendance to increase group members’ commitment.
Group presentations require members to navigate many logistics of their presentation. While it may be easier for a group to assign each member to create a five-minute segment and then transition from one person to the next, this is definitely not the most engaging method. Creating a master presentation and then assigning individual speakers creates a more fluid and dynamic presentation and allows everyone to become familiar with the content, which can help if a person doesn’t show up to present and during the question-and-answer section. Once the content of the presentation is complete, figure out introductions, transitions, visual aids, and the use of time and space (Stanton, 2012). In terms of introductions, figure out if one person will introduce all the speakers at the beginning, if speakers will introduce themselves at the beginning, or if introductions will occur as the presentation progresses. In terms of transitions, make sure each person has included in his or her speaking notes when presentation duties switch from one person to the next. Visual aids have the potential to cause hiccups in a group presentation if they aren’t fluidly integrated. Practicing with visual aids and having one person control them may help prevent this. Know how long your presentation is and know how you’re going to use the space. Presenters should know how long the whole presentation should be and how long each of their segments should be so that everyone can share the responsibility of keeping time. Also consider the size and layout of the presentation space. You don’t want presenters huddled in a corner until it’s their turn to speak or trapped behind furniture when their turn comes around.
- Of the three main problems facing group presenters, which do you think is the most challenging and why?
- Why do you think people tasked with a group presentation (especially students) prefer to divide the parts up and have members work on them independently before coming back together and integrating each part? What problems emerge from this method? In what ways might developing a master presentation and then assigning parts to different speakers be better than the more divided method? What are the drawbacks to the master presentation method?
Decision Making in Groups
We all engage in personal decision making daily, and we all know that some decisions are more difficult than others. When we make decisions in groups, we face some challenges that we do not face in our personal decision making, but we also stand to benefit from some advantages of group decision making (Napier & Gershenfeld, 2004). Group decision making can appear fair and democratic but really only be a gesture that covers up the fact that certain group members or the group leader have already decided. Group decision making also takes more time than individual decisions and can be burdensome if some group members do not do their assigned work, divert the group with self-centered or unproductive role behaviors, or miss meetings. Conversely, though, group decisions are often more informed, since all group members develop a shared understanding of a problem through discussion and debate. The shared understanding may also be more complex and deep than what an individual would develop, because the group members are exposed to a variety of viewpoints that can broaden their own perspectives. Group decisions also benefit from synergy, one of the key advantages of group communication that we discussed earlier. Most groups do not use a specific method of decision making, perhaps thinking that they’ll work things out as they go. This can lead to unequal participation, social loafing, premature decisions, prolonged discussion, and a host of other negative consequences. So in this section we will learn some practices that will prepare us for good decision making and some specific techniques we can use to help us reach a final decision.
Brainstorming before Decision Making
Before groups can make a decision, they need to generate possible solutions to their problem. The most commonly used method is brainstorming, although most people don’t follow the recommended steps of brainstorming. As you’ll recall, brainstorming refers to the quick generation of ideas free of evaluation. The originator of the term brainstorming said the following four rules must be followed for the technique to be effective (Osborn, 1959):
- Evaluation of ideas is forbidden.
- Wild and crazy ideas are encouraged.
- Quantity of ideas, not quality, is the goal.
- New combinations of ideas presented are encouraged.
To make brainstorming more of a decision-making method rather than an idea-generating method, group communication scholars have suggested additional steps that precede and follow brainstorming (Cragan & Wright, 1991).
- Do a warm-up brainstorming session. Some people are more apprehensive about publicly communicating their ideas than others are, and a warm-up session can help ease apprehension and prime group members for task-related idea generation. The warm-up can be initiated by anyone in the group and should only go on for a few minutes. To get things started, a person could ask, “If our group formed a band, what would we be called?” or “What other purposes could a mailbox serve?” In the previous examples, the first warm up gets the group’s more abstract creative juices flowing, while the second focuses more on practical and concrete ideas.
- Do the actual brainstorming session. This session shouldn’t last more than thirty minutes and should follow the four rules of brainstorming mentioned previously. To ensure that the fourth rule is realized, the facilitator could encourage people to piggyback off each other’s ideas.
- Eliminate duplicate ideas. After the brainstorming session is over, group members can eliminate (without evaluating) ideas that are the same or very similar.
- Clarify, organize, and evaluate ideas. Before evaluation, see if any ideas need clarification. Then try to theme or group ideas together in some orderly fashion. Since “wild and crazy” ideas are encouraged, some suggestions may need clarification. If it becomes clear that there isn’t really a foundation to an idea and that it is too vague or abstract and can’t be clarified, it may be eliminated. As a caution though, it may be wise to not throw out off-the-wall ideas that are hard to categorize and to instead put them in a miscellaneous or “wild and crazy” category.
Discussion before Decision Making
The nominal group technique guides decision making through a four-step process that includes idea generation and evaluation and seeks to elicit equal contributions from all group members (Delbecq & Ven de Ven, 1971). This method is useful because the procedure involves all group members systematically, which fixes the problem of uneven participation during discussions. Since everyone contributes to the discussion, this method can also help reduce instances of social loafing. To use the nominal group technique, do the following:
- Silently and individually list ideas.
- Create a master list of ideas.
- Clarify ideas as needed.
- Take a secret vote to rank group members’ acceptance of ideas.
During the first step, have group members work quietly, in the same space, to write down every idea they have to address the task or problem they face. This shouldn’t take more than twenty minutes. Whoever is facilitating the discussion should remind group members to use brainstorming techniques, which means they shouldn’t evaluate ideas as they are generated. Ask group members to remain silent once they’ve finished their list so they do not distract others.
During the second step, the facilitator goes around the group in a consistent order asking each person to share one idea at a time. As the idea is shared, the facilitator records it on a master list that everyone can see. Keep track of how many times each idea comes up, as that could be an idea that warrants more discussion. Continue this process until all the ideas have been shared. As a note to facilitators, some group members may begin to edit their list or self-censor when asked to provide one of their ideas. To limit a person’s apprehension with sharing his or her ideas and to ensure that each idea is shared, I have asked group members to exchange lists with someone else so they can share ideas from the list they receive without fear of being personally judged.
During step three, the facilitator should note that group members can now ask for clarification on ideas on the master list. Do not let this discussion stray into evaluation of ideas. To help avoid an unnecessarily long discussion, it may be useful to go from one person to the next to ask which ideas need clarifying and then go to the originator(s) of the idea in question for clarification.
During the fourth step, members use a voting ballot to rank the acceptability of the ideas on the master list. If the list is long, you may ask group members to rank only their top five or so choices. The facilitator then takes up the secret ballots and reviews them in a random order, noting the rankings of each idea. Ideally, the highest ranked idea can then be discussed and decided on. The nominal group technique does not carry a group all the way through to the point of decision; rather, it sets the group up for a roundtable discussion or use of some other method to evaluate the merits of the top ideas.
Specific Decision-Making Techniques
Some decision-making techniques involve determining a course of action based on the level of agreement among the group members. These methods include majority, expert, authority, and consensus rule. Table 14.1 “Pros and Cons of Agreement-Based Decision-Making Techniques” reviews the pros and cons of each of these methods.

Majority rule is a simple method of decision making based on voting. In most cases a majority is considered half plus one.
Becky McCray – Voting – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Majority rule is a commonly used decision-making technique in which a majority (one-half plus one) must agree before a decision is made. A show-of-hands vote, a paper ballot, or an electronic voting system can determine the majority choice. Many decision-making bodies, including the US House of Representatives, Senate, and Supreme Court, use majority rule to make decisions, which shows that it is often associated with democratic decision making, since each person gets one vote and each vote counts equally. Of course, other individuals and mediated messages can influence a person’s vote, but since the voting power is spread out over all group members, it is not easy for one person or party to take control of the decision-making process. In some cases—for example, to override a presidential veto or to amend the constitution—a super majority of two-thirds may be required to make a decision.
Minority rule is a decision-making technique in which a designated authority or expert has final say over a decision and may or may not consider the input of other group members. When a designated expert makes a decision by minority rule, there may be buy-in from others in the group, especially if the members of the group didn’t have relevant knowledge or expertise. When a designated authority makes decisions, buy-in will vary based on group members’ level of respect for the authority. For example, decisions made by an elected authority may be more accepted by those who elected him or her than by those who didn’t. As with majority rule, this technique can be time saving. Unlike majority rule, one person or party can have control over the decision-making process. This type of decision making is more similar to that used by monarchs and dictators. An obvious negative consequence of this method is that the needs or wants of one person can override the needs and wants of the majority. A minority deciding for the majority has led to negative consequences throughout history. The white Afrikaner minority that ruled South Africa for decades instituted apartheid, which was a system of racial segregation that disenfranchised and oppressed the majority population. The quality of the decision and its fairness really depends on the designated expert or authority.
Consensus rule is a decision-making technique in which all members of the group must agree on the same decision. On rare occasions, a decision may be ideal for all group members, which can lead to unanimous agreement without further debate and discussion. Although this can be positive, be cautious that this isn’t a sign of groupthink. More typically, consensus is reached only after lengthy discussion. On the plus side, consensus often leads to high-quality decisions due to the time and effort it takes to get everyone in agreement. Group members are also more likely to be committed to the decision because of their investment in reaching it. On the negative side, the ultimate decision is often one that all group members can live with but not one that’s ideal for all members. Additionally, the process of arriving at consensus also includes conflict, as people debate ideas and negotiate the interpersonal tensions that may result.
Table 14.1 Pros and Cons of Agreement-Based Decision-Making Techniques
“Getting Critical”
Six Hats Method of Decision Making
Edward de Bono developed the Six Hats method of thinking in the late 1980s, and it has since become a regular feature in decision-making training in business and professional contexts (de Bono, 1985). The method’s popularity lies in its ability to help people get out of habitual ways of thinking and to allow group members to play different roles and see a problem or decision from multiple points of view. The basic idea is that each of the six hats represents a different way of thinking, and when we figuratively switch hats, we switch the way we think. The hats and their style of thinking are as follows:
- White hat. Objective—focuses on seeking information such as data and facts and then processes that information in a neutral way.
- Red hat. Emotional—uses intuition, gut reactions, and feelings to judge information and suggestions.
- Black hat. Negative—focuses on potential risks, points out possibilities for failure, and evaluates information cautiously and defensively.
- Yellow hat. Positive—is optimistic about suggestions and future outcomes, gives constructive and positive feedback, points out benefits and advantages.
- Green hat. Creative—tries to generate new ideas and solutions, thinks “outside the box.”
- Blue hat. Philosophical—uses metacommunication to organize and reflect on the thinking and communication taking place in the group, facilitates who wears what hat and when group members change hats.
Specific sequences or combinations of hats can be used to encourage strategic thinking. For example, the group leader may start off wearing the Blue Hat and suggest that the group start their decision-making process with some “White Hat thinking” in order to process through facts and other available information. During this stage, the group could also process through what other groups have done when faced with a similar problem. Then the leader could begin an evaluation sequence starting with two minutes of “Yellow Hat thinking” to identify potential positive outcomes, then “Black Hat thinking” to allow group members to express reservations about ideas and point out potential problems, then “Red Hat thinking” to get people’s gut reactions to the previous discussion, then “Green Hat thinking” to identify other possible solutions that are more tailored to the group’s situation or completely new approaches. At the end of a sequence, the Blue Hat would want to summarize what was said and begin a new sequence. To successfully use this method, the person wearing the Blue Hat should be familiar with different sequences and plan some of the thinking patterns ahead of time based on the problem and the group members. Each round of thinking should be limited to a certain time frame (two to five minutes) to keep the discussion moving.
- This decision-making method has been praised because it allows group members to “switch gears” in their thinking and allows for role playing, which lets people express ideas more freely. How can this help enhance critical thinking? Which combination of hats do you think would be best for a critical thinking sequence?
- What combinations of hats might be useful if the leader wanted to break the larger group up into pairs and why? For example, what kind of thinking would result from putting Yellow and Red together, Black and White together, or Red and White together, and so on?
- Based on your preferred ways of thinking and your personality, which hat would be the best fit for you? Which would be the most challenging? Why?
Influences on Decision Making
Many factors influence the decision-making process. For example, how might a group’s independence or access to resources affect the decisions they make? What potential advantages and disadvantages come with decisions made by groups that are more or less similar in terms of personality and cultural identities? In this section, we will explore how situational, personality, and cultural influences affect decision making in groups.
Situational Influences on Decision Making
A group’s situational context affects decision making. One key situational element is the degree of freedom that the group has to make its own decisions, secure its own resources, and initiate its own actions. Some groups have to go through multiple approval processes before they can do anything, while others are self-directed, self-governing, and self-sustaining. Another situational influence is uncertainty. In general, groups deal with more uncertainty in decision making than do individuals because of the increased number of variables that comes with adding more people to a situation. Individual group members can’t know what other group members are thinking, whether or not they are doing their work, and how committed they are to the group. So the size of a group is a powerful situational influence, as it adds to uncertainty and complicates communication.
Access to information also influences a group. First, the nature of the group’s task or problem affects its ability to get information. Group members can more easily make decisions about a problem when other groups have similarly experienced it. Even if the problem is complex and serious, the group can learn from other situations and apply what it learns. Second, the group must have access to flows of information. Access to archives, electronic databases, and individuals with relevant experience is necessary to obtain any relevant information about similar problems or to do research on a new or unique problem. In this regard, group members’ formal and information network connections also become important situational influences.

The urgency of a decision can have a major influence on the decision-making process. As a situation becomes more urgent, it requires more specific decision-making methods and types of communication.
Judith E. Bell – Urgent – CC BY-SA 2.0.
The origin and urgency of a problem are also situational factors that influence decision making. In terms of origin, problems usually occur in one of four ways:
- Something goes wrong. Group members must decide how to fix or stop something. Example—a firehouse crew finds out that half of the building is contaminated with mold and must be closed down.
- Expectations change or increase. Group members must innovate more efficient or effective ways of doing something. Example—a firehouse crew finds out that the district they are responsible for is being expanded.
- Something goes wrong and expectations change or increase. Group members must fix/stop and become more efficient/effective. Example—the firehouse crew has to close half the building and must start responding to more calls due to the expanding district.
- The problem existed from the beginning. Group members must go back to the origins of the situation and walk through and analyze the steps again to decide what can be done differently. Example—a firehouse crew has consistently had to work with minimal resources in terms of building space and firefighting tools.
In each of the cases, the need for a decision may be more or less urgent depending on how badly something is going wrong, how high the expectations have been raised, or the degree to which people are fed up with a broken system. Decisions must be made in situations ranging from crisis level to mundane.
Personality Influences on Decision Making
A long-studied typology of value orientations that affect decision making consists of the following types of decision maker: the economic, the aesthetic, the theoretical, the social, the political, and the religious (Spranger, 1928).
- The economic decision maker makes decisions based on what is practical and useful.
- The aesthetic decision maker makes decisions based on form and harmony, desiring a solution that is elegant and in sync with the surroundings.
- The theoretical decision maker wants to discover the truth through rationality.
- The social decision maker emphasizes the personal impact of a decision and sympathizes with those who may be affected by it.
- The political decision maker is interested in power and influence and views people and/or property as divided into groups that have different value.
- The religious decision maker seeks to identify with a larger purpose, works to unify others under that goal, and commits to a viewpoint, often denying one side and being dedicated to the other.
In the United States, economic, political, and theoretical decision making tend to be more prevalent decision-making orientations, which likely corresponds to the individualistic cultural orientation with its emphasis on competition and efficiency. But situational context, as we discussed before, can also influence our decision making.

Personality affects decision making. For example, “economic” decision makers decide based on what is practical and useful.
One Way Stock – Tough Decisions Ahead – CC BY-ND 2.0.
The personalities of group members, especially leaders and other active members, affect the climate of the group. Group member personalities can be categorized based on where they fall on a continuum anchored by the following descriptors: dominant/submissive, friendly/unfriendly, and instrumental/emotional (Cragan & Wright, 1999). The more group members there are in any extreme of these categories, the more likely that the group climate will also shift to resemble those characteristics.
- Dominant versus submissive. Group members that are more dominant act more independently and directly, initiate conversations, take up more space, make more direct eye contact, seek leadership positions, and take control over decision-making processes. More submissive members are reserved, contribute to the group only when asked to, avoid eye contact, and leave their personal needs and thoughts unvoiced or give into the suggestions of others.
- Friendly versus unfriendly. Group members on the friendly side of the continuum find a balance between talking and listening, don’t try to win at the expense of other group members, are flexible but not weak, and value democratic decision making. Unfriendly group members are disagreeable, indifferent, withdrawn, and selfish, which leads them to either not invest in decision making or direct it in their own interest rather than in the interest of the group.
- Instrumental versus emotional. Instrumental group members are emotionally neutral, objective, analytical, task-oriented, and committed followers, which leads them to work hard and contribute to the group’s decision making as long as it is orderly and follows agreed-on rules. Emotional group members are creative, playful, independent, unpredictable, and expressive, which leads them to make rash decisions, resist group norms or decision-making structures, and switch often from relational to task focus.
Cultural Context and Decision Making
Just like neighborhoods, schools, and countries, small groups vary in terms of their degree of similarity and difference. Demographic changes in the United States and increases in technology that can bring different people together make it more likely that we will be interacting in more and more heterogeneous groups (Allen, 2011). Some small groups are more homogenous, meaning the members are more similar, and some are more heterogeneous, meaning the members are more different. Diversity and difference within groups has advantages and disadvantages. In terms of advantages, research finds that, in general, groups that are culturally heterogeneous have better overall performance than more homogenous groups (Haslett & Ruebush, 1999). Additionally, when group members have time to get to know each other and competently communicate across their differences, the advantages of diversity include better decision making due to different perspectives (Thomas, 1999). Unfortunately, groups often operate under time constraints and other pressures that make the possibility for intercultural dialogue and understanding difficult. The main disadvantage of heterogeneous groups is the possibility for conflict, but given that all groups experience conflict, this isn’t solely due to the presence of diversity. We will now look more specifically at how some of the cultural value orientations we’ve learned about already in this book can play out in groups with international diversity and how domestic diversity in terms of demographics can also influence group decision making.
International Diversity in Group Interactions
Cultural value orientations such as individualism/collectivism, power distance, and high-/low-context communication styles all manifest on a continuum of communication behaviors and can influence group decision making. Group members from individualistic cultures are more likely to value task-oriented, efficient, and direct communication. This could manifest in behaviors such as dividing up tasks into individual projects before collaboration begins and then openly debating ideas during discussion and decision making. Additionally, people from cultures that value individualism are more likely to openly express dissent from a decision, essentially expressing their disagreement with the group. Group members from collectivistic cultures are more likely to value relationships over the task at hand. Because of this, they also tend to value conformity and face-saving (often indirect) communication. This could manifest in behaviors such as establishing norms that include periods of socializing to build relationships before task-oriented communication like negotiations begin or norms that limit public disagreement in favor of more indirect communication that doesn’t challenge the face of other group members or the group’s leader. In a group composed of people from a collectivistic culture, each member would likely play harmonizing roles, looking for signs of conflict and resolving them before they become public.
Power distance can also affect group interactions. Some cultures rank higher on power-distance scales, meaning they value hierarchy, make decisions based on status, and believe that people have a set place in society that is fairly unchangeable. Group members from high-power-distance cultures would likely appreciate a strong designated leader who exhibits a more directive leadership style and prefer groups in which members have clear and assigned roles. In a group that is homogenous in terms of having a high-power-distance orientation, members with higher status would be able to openly provide information, and those with lower status may not provide information unless a higher status member explicitly seeks it from them. Low-power-distance cultures do not place as much value and meaning on status and believe that all group members can participate in decision making. Group members from low-power-distance cultures would likely freely speak their mind during a group meeting and prefer a participative leadership style.
How much meaning is conveyed through the context surrounding verbal communication can also affect group communication. Some cultures have a high-context communication style in which much of the meaning in an interaction is conveyed through context such as nonverbal cues and silence. Group members from high-context cultures may avoid saying something directly, assuming that other group members will understand the intended meaning even if the message is indirect. So if someone disagrees with a proposed course of action, he or she may say, “Let’s discuss this tomorrow,” and mean, “I don’t think we should do this.” Such indirect communication is also a face-saving strategy that is common in collectivistic cultures. Other cultures have a low-context communication style that places more importance on the meaning conveyed through words than through context or nonverbal cues. Group members from low-context cultures often say what they mean and mean what they say. For example, if someone doesn’t like an idea, they might say, “I think we should consider more options. This one doesn’t seem like the best we can do.”
In any of these cases, an individual from one culture operating in a group with people of a different cultural orientation could adapt to the expectations of the host culture, especially if that person possesses a high degree of intercultural communication competence (ICC). Additionally, people with high ICC can also adapt to a group member with a different cultural orientation than the host culture. Even though these cultural orientations connect to values that affect our communication in fairly consistent ways, individuals may exhibit different communication behaviors depending on their own individual communication style and the situation.
Domestic Diversity and Group Communication
While it is becoming more likely that we will interact in small groups with international diversity, we are guaranteed to interact in groups that are diverse in terms of the cultural identities found within a single country or the subcultures found within a larger cultural group.
Gender stereotypes sometimes influence the roles that people play within a group. For example, the stereotype that women are more nurturing than men may lead group members (both male and female) to expect that women will play the role of supporters or harmonizers within the group. Since women have primarily performed secretarial work since the 1900s, it may also be expected that women will play the role of recorder. In both of these cases, stereotypical notions of gender place women in roles that are typically not as valued in group communication. The opposite is true for men. In terms of leadership, despite notable exceptions, research shows that men fill an overwhelmingly disproportionate amount of leadership positions. We are socialized to see certain behaviors by men as indicative of leadership abilities, even though they may not be. For example, men are often perceived to contribute more to a group because they tend to speak first when asked a question or to fill a silence and are perceived to talk more about task-related matters than relationally oriented matters. Both of these tendencies create a perception that men are more engaged with the task. Men are also socialized to be more competitive and self-congratulatory, meaning that their communication may be seen as dedicated and their behaviors seen as powerful, and that when their work isn’t noticed they will be more likely to make it known to the group rather than take silent credit. Even though we know that the relational elements of a group are crucial for success, even in high-performance teams, that work is not as valued in our society as the task-related work.
Despite the fact that some communication patterns and behaviors related to our typical (and stereotypical) gender socialization affect how we interact in and form perceptions of others in groups, the differences in group communication that used to be attributed to gender in early group communication research seem to be diminishing. This is likely due to the changing organizational cultures from which much group work emerges, which have now had more than sixty years to adjust to women in the workplace. It is also due to a more nuanced understanding of gender-based research, which doesn’t take a stereotypical view from the beginning as many of the early male researchers did. Now, instead of biological sex being assumed as a factor that creates inherent communication differences, group communication scholars see that men and women both exhibit a range of behaviors that are more or less feminine or masculine. It is these gendered behaviors, and not a person’s gender, that seem to have more of an influence on perceptions of group communication. Interestingly, group interactions are still masculinist in that male and female group members prefer a more masculine communication style for task leaders and that both males and females in this role are more likely to adapt to a more masculine communication style. Conversely, men who take on social-emotional leadership behaviors adopt a more feminine communication style. In short, it seems that although masculine communication traits are more often associated with high status positions in groups, both men and women adapt to this expectation and are evaluated similarly (Haslett & Ruebush, 1999).
Other demographic categories are also influential in group communication and decision making. In general, group members have an easier time communicating when they are more similar than different in terms of race and age. This ease of communication can make group work more efficient, but the homogeneity may sacrifice some creativity. As we learned earlier, groups that are diverse (e.g., they have members of different races and generations) benefit from the diversity of perspectives in terms of the quality of decision making and creativity of output.
In terms of age, for the first time since industrialization began, it is common to have three generations of people (and sometimes four) working side by side in an organizational setting. Although four generations often worked together in early factories, they were segregated based on their age group, and a hierarchy existed with older workers at the top and younger workers at the bottom. Today, however, generations interact regularly, and it is not uncommon for an older person to have a leader or supervisor who is younger than him or her (Allen, 2011). The current generations in the US workplace and consequently in work-based groups include the following:
- The Silent Generation. Born between 1925 and 1942, currently in their midsixties to mideighties, this is the smallest generation in the workforce right now, as many have retired or left for other reasons. This generation includes people who were born during the Great Depression or the early part of World War II, many of whom later fought in the Korean War (Clarke, 1970).
- The Baby Boomers. Born between 1946 and 1964, currently in their late forties to midsixties, this is the largest generation in the workforce right now. Baby boomers are the most populous generation born in US history, and they are working longer than previous generations, which means they will remain the predominant force in organizations for ten to twenty more years.
- Generation X. Born between 1965 and 1981, currently in their early thirties to midforties, this generation was the first to see technology like cell phones and the Internet make its way into classrooms and our daily lives. Compared to previous generations, “Gen-Xers” are more diverse in terms of race, religious beliefs, and sexual orientation and also have a greater appreciation for and understanding of diversity.
- Generation Y. Born between 1982 and 2000, “Millennials” as they are also called are currently in their late teens up to about thirty years old. This generation is not as likely to remember a time without technology such as computers and cell phones. They are just starting to enter into the workforce and have been greatly affected by the economic crisis of the late 2000s, experiencing significantly high unemployment rates.
The benefits and challenges that come with diversity of group members are important to consider. Since we will all work in diverse groups, we should be prepared to address potential challenges in order to reap the benefits. Diverse groups may be wise to coordinate social interactions outside of group time in order to find common ground that can help facilitate interaction and increase group cohesion. We should be sensitive but not let sensitivity create fear of “doing something wrong” that then prevents us from having meaningful interactions. Reviewing Chapter 8 “Culture and Communication” will give you useful knowledge to help you navigate both international and domestic diversity and increase your communication competence in small groups and elsewhere.
Key Takeaways
- Every problem has common components: an undesirable situation, a desired situation, and obstacles between the undesirable and desirable situations. Every problem also has a set of characteristics that vary among problems, including task difficulty, number of possible solutions, group member interest in the problem, group familiarity with the problem, and the need for solution acceptance.
The group problem-solving process has five steps:
- Define the problem by creating a problem statement that summarizes it.
- Analyze the problem and create a problem question that can guide solution generation.
- Generate possible solutions. Possible solutions should be offered and listed without stopping to evaluate each one.
- Evaluate the solutions based on their credibility, completeness, and worth. Groups should also assess the potential effects of the narrowed list of solutions.
- Implement and assess the solution. Aside from enacting the solution, groups should determine how they will know the solution is working or not.
- Before a group makes a decision, it should brainstorm possible solutions. Group communication scholars suggest that groups (1) do a warm-up brainstorming session; (2) do an actual brainstorming session in which ideas are not evaluated, wild ideas are encouraged, quantity not quality of ideas is the goal, and new combinations of ideas are encouraged; (3) eliminate duplicate ideas; and (4) clarify, organize, and evaluate ideas. In order to guide the idea-generation process and invite equal participation from group members, the group may also elect to use the nominal group technique.
- Common decision-making techniques include majority rule, minority rule, and consensus rule. With majority rule, only a majority, usually one-half plus one, must agree before a decision is made. With minority rule, a designated authority or expert has final say over a decision, and the input of group members may or may not be invited or considered. With consensus rule, all members of the group must agree on the same decision.
Several factors influence the decision-making process:
- Situational factors include the degree of freedom a group has to make its own decisions, the level of uncertainty facing the group and its task, the size of the group, the group’s access to information, and the origin and urgency of the problem.
- Personality influences on decision making include a person’s value orientation (economic, aesthetic, theoretical, political, or religious), and personality traits (dominant/submissive, friendly/unfriendly, and instrumental/emotional).
- Cultural influences on decision making include the heterogeneity or homogeneity of the group makeup; cultural values and characteristics such as individualism/collectivism, power distance, and high-/low-context communication styles; and gender and age differences.
- Scenario 1. Task difficulty is high, number of possible solutions is high, group interest in problem is high, group familiarity with problem is low, and need for solution acceptance is high.
- Scenario 2. Task difficulty is low, number of possible solutions is low, group interest in problem is low, group familiarity with problem is high, and need for solution acceptance is low.
- Scenario 1: Academic. A professor asks his or her class to decide whether the final exam should be an in-class or take-home exam.
- Scenario 2: Professional. A group of coworkers must decide which person from their department to nominate for a company-wide award.
- Scenario 3: Personal. A family needs to decide how to divide the belongings and estate of a deceased family member who did not leave a will.
- Scenario 4: Civic. A local branch of a political party needs to decide what five key issues it wants to include in the national party’s platform.
- Group communication researchers have found that heterogeneous groups (composed of diverse members) have advantages over homogenous (more similar) groups. Discuss a group situation you have been in where diversity enhanced your and/or the group’s experience.
Adams, K., and Gloria G. Galanes, Communicating in Groups: Applications and Skills , 7th ed. (Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill, 2009), 220–21.
Allen, B. J., Difference Matters: Communicating Social Identity , 2nd ed. (Long Grove, IL: Waveland, 2011), 5.
Bormann, E. G., and Nancy C. Bormann, Effective Small Group Communication , 4th ed. (Santa Rosa, CA: Burgess CA, 1988), 112–13.
Clarke, G., “The Silent Generation Revisited,” Time, June 29, 1970, 46.
Cragan, J. F., and David W. Wright, Communication in Small Group Discussions: An Integrated Approach , 3rd ed. (St. Paul, MN: West Publishing, 1991), 77–78.
de Bono, E., Six Thinking Hats (Boston, MA: Little, Brown, 1985).
Delbecq, A. L., and Andrew H. Ven de Ven, “A Group Process Model for Problem Identification and Program Planning,” The Journal of Applied Behavioral Science 7, no. 4 (1971): 466–92.
Haslett, B. B., and Jenn Ruebush, “What Differences Do Individual Differences in Groups Make?: The Effects of Individuals, Culture, and Group Composition,” in The Handbook of Group Communication Theory and Research , ed. Lawrence R. Frey (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1999), 133.
Napier, R. W., and Matti K. Gershenfeld, Groups: Theory and Experience , 7th ed. (Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin, 2004), 292.
Osborn, A. F., Applied Imagination (New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons, 1959).
Spranger, E., Types of Men (New York: Steckert, 1928).
Stanton, C., “How to Deliver Group Presentations: The Unified Team Approach,” Six Minutes Speaking and Presentation Skills , November 3, 2009, accessed August 28, 2012, http://sixminutes.dlugan.com/group-presentations-unified-team-approach .
Thomas, D. C., “Cultural Diversity and Work Group Effectiveness: An Experimental Study,” Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology 30, no. 2 (1999): 242–63.
Communication in the Real World Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

10 Modeling Problem Solving
We’ve discussed in previous chapters how part of a tutor’s task is to model good learning habits. When tutors are organized, use good time management, and leverage resources, we demonstrate the skills that students can use to be successful learners.
Problem-solving is an additional skill that tutors model for students. An organized and- intentional problem-solving approach helps us to efficiently work through challenges, and many of us effectively problem solve without much thought given to our approach. 1 However, it makes sense to take a step back and do our best to model problem-solving best-practices. Remember that repeated demonstration of a tutor’s problem-solving strategies can help students learn from our example.
We know the tutor’s role is not to solve a student’s problem for them. How do we model good problem-solving, without actually solving the problem ourselves? It’s tricky, but not impossible. We can empower students to work their way through any problem by asking good questions and walking them through the steps of the process.
The Rational Problem-Solving Process
Problem-solving is something many of us have taught ourselves through practice. However, there are many scholars and professionals who have examined and broken down effective problem-solving strategies into a series of logical steps. 2 We can check our own process by reflecting on what has been written about best-practices in problem-solving, and maybe make changes to be more consistent and effective. This can better prepare tutors to guide a student through the process when we apply it in a tutoring session.
Step 1: Define the Problem
It may seem obvious to state that the first step in solving a problem is to notice that we have a problem. Unless we take time to understand precisely what is wrong, however, we may find ourselves creating a solution that doesn’t actually fix anything. It’s very common to dive straight into devising a solution only to find that we’ve solved the wrong problem. Alternatively, we might develop a solution only to discover that the real problem is bigger than we thought.
A good practice for starting out is to try to define the problem in words. By writing or stating a problem definition, we’re challenged to identify the root cause, and this information can guide us in developing effective solutions.
In a tutoring session, sometimes the problem can take a variety of forms. The problem could be:
- the literal problem given in a student’s homework assignment (a word problem in math, or a case study in biology, for example.)
- a lack of clarity in assignment instructions.
- the student not having a strategy for planning a project or starting a paper.
- the student lacking confidence to tackle their homework or study independently
Keep in mind that the form the “problem” takes will change based on the student’s needs and goals. If the problem is that the student doesn’t understand something, the first step is to identify precisely what they don’t understand. If the problem is that something is missing, then understanding exactly what necessary parts are missing is the first step.
In a tutoring session this may mean asking the student to start the process, or begin describing the concept from the beginning, until they reach the point where things become unclear. Together, you can determine where the gaps are, and begin to develop a problem definition.
Step 2: Pull from Existing Knowledge
After we’ve identified and defined the problem, the next step is to ask ourselves what we already know about the situation. Take an inventory. What information do we already have? What can we learn from the context? What resources have we been given?
When working with a student, pulling from existing knowledge might involve reviewing the concepts already covered and the student’s existing knowledge of the course material. It may also mean reaching into material and experiences outside of the student’s course.
Some helpful questions to guide this step include:
- What does the student know about topics related to the course material?
- What experience might the student have from prior courses?
- In what context might the student have heard these ideas discussed in their everyday lives or in popular culture?
When we encourage students to step back and really take account of everything they already know about the problem and its context, they can be surprised at how much knowledge they actually bring.
Step 3: Refer to support materials
Once we’ve pulled from the knowledge we already have, we can expand our search for supporting knowledge to outside resources. Are there reference materials we can access? Are there experts we can consult?
The first thing we can encourage students to do is to refer to their course texts, notes, study guides, and materials provided by the class instructor. These are often the best places to start because they’re most likely to provide relevant information. Once these resources have been referenced, we can also encourage students to look for information and guidance from other academic resources.
Students often forget that they can reference what others have written about their problem. Outside textbooks and supporting texts may offer similar ideas presented in a different way, and this could help the student approach the problem with new understanding or perspective. Online research and reference materials are good places to look for clarification of rules, theories, laws, formulas, processes, and examples. While these sources may not be quite as specific to a student’s class assignment, they can sometimes provide confirmation or clarity in areas where a student might need it.
Students should be made to feel free to leverage other academic supports as well. They are already leveraging one aspect of this support when they come to see a tutor. Other supports may include making use of the library or computer center, visiting their instructor’s office hours to ask questions, or even reaching out to other classmates. It’s always helpful for tutors to remind the student that these other supports are available and to encourage them to use these resources.
If a student is unsure or intimidated by contacting an instructor or a classmate, or is uncomfortable learning how to use other support resources, encouragement from a tutor can often be the nudge a student needs. Remind them of these supports and offer to help them access them where appropriate.
Step 4: Brainstorm Solutions
There’s usually more than one way to solve a problem, and it’s helpful to brainstorm multiple solutions to find the one that works best.
It’s important that tutors allow students to take an active role in developing their own solutions to the problem. This is where our Socratic questioning skills become really crucial and can help the students to apply what they know to the problem they’ve identified. The tutor’s role here is to facilitate the solution-generating process, contributing where appropriate, and helping to guide the student in a productive direction.
It is possible that the student will suggest a solution that we know will not solve the problem. Depending on the nature and scale of the problem, it may not always be appropriate for us to tell the student that we think it won’t work. Guiding the student through the problem-solving process is about helping students to engage with the process itself. That way, they can feel confident applying it on their own, even when a helpful tutor isn’t around to give hints. It’s up to each tutor in each situation to decide when it is appropriate to expedite the process by providing insights into solutions, and when it is best to allow students to test their solutions to determine their effectiveness.
Step 5: Test a Solution
Choose a solution and try it out. Maybe it will work! Maybe it doesn’t. Having a variety of solutions to try is why we brainstorm more than one. Though trial and error can sometimes feel frustrating, it is in the testing of our solutions that we often learn the most. We’re able to better understand the parts that work, the parts that don’t, and hopefully learn the reasons why. This can result in solutions that are more efficient and better suited to our needs.
Solution-testing is an opportunity for students to learn from mistakes in a safe, low-risk way. Often mistakes in class result in deducted points, a bad grade, or maybe an embarrassing moment in from t of classmates. As a guide through the problem-solving process, tutors can help students to see mistakes as necessary and helpful steps on the way to a solution that works, rather than as failures. It’s important that the tutor help the student see mistakes as progress, especially when a student becomes discouraged. This helps the student maintain a growth mindset while identifying ways to improve.
Step 6: Revising the Solution
When a solution doesn’t work, it may not mean the whole idea was bad. Maybe it needs some revisions and refining, but doesn’t always need to be discarded. We can use what we learned from solution-testing to make effective revisions.
This may mean we guide a student back to previous steps in the problem-solving process. Students may once more need to pull from existing knowledge, revisit those support materials, or look at some of the alternative solutions that the student developed.
Step 7: Revisit the Problem
We’ve got a solution that works! Did it fix our problem? If yes, then great!
Sometimes, however, a solution may “work,” without fixing our problem.
When this happens, we need to revisit the problem definition. Do we really understand it? Is there a detail we didn’t consider when developing our solutions? Did we misinterpret what the problem actually is when we crafted our problem definition?
At this point, perhaps we need to revise the solution once more. Sometimes in our process of researching and brainstorming, we can get off course, and taking time to refer to the initial problem can help us recalibrate our efforts and get us back on track.
Other times we may need re-define our problem. Perhaps after developing and testing several solutions, it becomes clear that the real problem is different than what we initially thought it was. Or perhaps our solutions address parts of the problem, but don’t get to the deeper root of the issue.
When a student has worked through the problem-solving process and still feels stuck, tutors can guide them to revisit the problem and clarify the initial goal. Returning to previous steps of the process as needed is normal and often necessary. Ensuring students that they’re still correctly applying the process, even when they need to jump back and forth between these steps, can help keep them from getting discouraged.
Quickwrite Exercise
Think back to a time you solved a problem in the past. It could be an obstacle you encountered in an academic setting (completing an assignment, researching for a paper, troubleshooting a technical problem) or in your personal life.
Take a moment to reflect:
- Did you use pieces of the rational problem solving process, without knowing?
- If you could go back and approach the problem again, how would you implement this problem solving approach? What would it look like? How would it have been different?
Facilitating the Problem-Solving Process
The rational problem-solving process is an excellent tool to help tutors guide students through problems big and small. This organized way of approaching the task can help us make sure we’re heading in a productive direction, from solving a math problem to developing a strategy to finish a research paper. How do we ensure we’re empowering students to use this process on their own?
It can be helpful to both tutors and students to use the process as a checklist during a problem-solving session. We can name each step as we move through, and make it clear to the student the purpose of each activity. This doesn’t mean we turn a session of math tutoring into a lesson on the problem-solving process, but explicitly stating the names of each step can make it clear to the student the purpose of each activity, and help them to become familiar with the process. If we “narrate” our process as we go, students can experience a guided problem-solving process during their tutoring session and be encouraged to apply it independently.
Once we’ve guided a student through the process, we can then provide opportunities for the student to take charge. We can prompt the student to move from step to step, supporting them in their problem-solving efforts along the way. This guided practice can help students to become well-versed in the process itself, and to feel more comfortable applying it independently. 3
Something to Try
In your next session, when a student comes to you with a problem, use your Socratic questioning skills to walk the student through the problem solving process. (This may be something you’re already implementing naturally!)
Be deliberate about each step. Assist the student in defining the problem, guide the student to collect their existing knowledge, help the student pull from reference materials available, etc.
How does it work for you?
Practicing the Problem-Solving Process
Don’t forget, that while this process is an excellent tool for helping students to solve problems during a session, it can also help tutors to problem-solve during a session!
Perhaps you encounter a student faced with a problem you yourself don’t know how to solve. No worries! The problem-solving process works just the same.
We can apply it to challenges with assignments, and we can also apply it to other issues we encounter during a tutoring session. Every student is unique, and it may take some problem-solving to learn how to best work with each student. Identifying the “problem,” pulling from our knowledge, consulting our supports, brainstorming, and testing solutions are all ways tutors can determine how best to assist students.
- Dane, E., Baer, M., Pratt, M. G., and Oldham, G. R. (2011). Rational versus intuitive problem solving: How thinking “off the beaten path” can stimulate creativity. Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts. 5 (1), 3–12. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0017698.
- Uzonwanne F.C. (2016). Rational Model of Decision Making. In: Farazmand A. (eds) Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-31816-5_2474-1.
- Klegeris, A., Bahniwal, M., and Hurren, H. (2017). Improvement in Generic Problem-Solving Abilities of Students by Use of Tutor-less Problem-Based Learning in a Large Classroom Setting. Life Sciences Education. 12(1), 1-116. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.12-06-0081.
Additional Resources:
McNamera, C. (2020). Problem Solving and Decision Making (Solving Problems and Making Decisions). Free Management Library. Authenticity Consulting LLC. https://managementhelp.org/personalproductivity/problem-solving.htm . Accessed 26 Apr. 2021.
Nezu C., Palmatier, A., and Nezu, A. (2004). Social Problem-Solving Training for Caregivers. In Chang, D’Zurilla, & Sanna (Eds.) Social Problem Solving: Theory, Research, and Training. (223-238). American Psychological Association. https://doi.org/10.1037/10805-013 .
Nezu, A., Nezu, C., and D’Zurilla, T. (2007). Solving Life’s problems: a 5 Step Guide to Enhanced Well-Being. Springer Publishing Company LLC. https://www.springerpub.com/solving-life-s-problems-9780826114891.html .
Scott, G. M., Lonergan, D. C., and Mumford, M.D. (2010). Conceptual Combination: Alternative Knowledge Structures, Alternative Heuristics. Creativity Research Journal. 17(1), 79-98. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1207/s15326934crj1701_7 .
Tutor Handbook Copyright © 2021 by Penny Feltner and gapinski is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 4 min read
The Problem-Solving Process
Looking at the basic problem-solving process to help keep you on the right track.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
Problem-solving is an important part of planning and decision-making. The process has much in common with the decision-making process, and in the case of complex decisions, can form part of the process itself.
We face and solve problems every day, in a variety of guises and of differing complexity. Some, such as the resolution of a serious complaint, require a significant amount of time, thought and investigation. Others, such as a printer running out of paper, are so quickly resolved they barely register as a problem at all.

Despite the everyday occurrence of problems, many people lack confidence when it comes to solving them, and as a result may chose to stay with the status quo rather than tackle the issue. Broken down into steps, however, the problem-solving process is very simple. While there are many tools and techniques available to help us solve problems, the outline process remains the same.
The main stages of problem-solving are outlined below, though not all are required for every problem that needs to be solved.
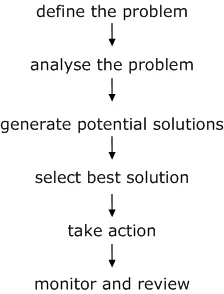
1. Define the Problem
Clarify the problem before trying to solve it. A common mistake with problem-solving is to react to what the problem appears to be, rather than what it actually is. Write down a simple statement of the problem, and then underline the key words. Be certain there are no hidden assumptions in the key words you have underlined. One way of doing this is to use a synonym to replace the key words. For example, ‘We need to encourage higher productivity ’ might become ‘We need to promote superior output ’ which has a different meaning.
2. Analyze the Problem
Ask yourself, and others, the following questions.
- Where is the problem occurring?
- When is it occurring?
- Why is it happening?
Be careful not to jump to ‘who is causing the problem?’. When stressed and faced with a problem it is all too easy to assign blame. This, however, can cause negative feeling and does not help to solve the problem. As an example, if an employee is underperforming, the root of the problem might lie in a number of areas, such as lack of training, workplace bullying or management style. To assign immediate blame to the employee would not therefore resolve the underlying issue.
Once the answers to the where, when and why have been determined, the following questions should also be asked:
- Where can further information be found?
- Is this information correct, up-to-date and unbiased?
- What does this information mean in terms of the available options?
3. Generate Potential Solutions
When generating potential solutions it can be a good idea to have a mixture of ‘right brain’ and ‘left brain’ thinkers. In other words, some people who think laterally and some who think logically. This provides a balance in terms of generating the widest possible variety of solutions while also being realistic about what can be achieved. There are many tools and techniques which can help produce solutions, including thinking about the problem from a number of different perspectives, and brainstorming, where a team or individual write as many possibilities as they can think of to encourage lateral thinking and generate a broad range of potential solutions.
4. Select Best Solution
When selecting the best solution, consider:
- Is this a long-term solution, or a ‘quick fix’?
- Is the solution achievable in terms of available resources and time?
- Are there any risks associated with the chosen solution?
- Could the solution, in itself, lead to other problems?
This stage in particular demonstrates why problem-solving and decision-making are so closely related.
5. Take Action
In order to implement the chosen solution effectively, consider the following:
- What will the situation look like when the problem is resolved?
- What needs to be done to implement the solution? Are there systems or processes that need to be adjusted?
- What will be the success indicators?
- What are the timescales for the implementation? Does the scale of the problem/implementation require a project plan?
- Who is responsible?
Once the answers to all the above questions are written down, they can form the basis of an action plan.
6. Monitor and Review
One of the most important factors in successful problem-solving is continual observation and feedback. Use the success indicators in the action plan to monitor progress on a regular basis. Is everything as expected? Is everything on schedule? Keep an eye on priorities and timelines to prevent them from slipping.
If the indicators are not being met, or if timescales are slipping, consider what can be done. Was the plan realistic? If so, are sufficient resources being made available? Are these resources targeting the correct part of the plan? Or does the plan need to be amended? Regular review and discussion of the action plan is important so small adjustments can be made on a regular basis to help keep everything on track.
Once all the indicators have been met and the problem has been resolved, consider what steps can now be taken to prevent this type of problem recurring? It may be that the chosen solution already prevents a recurrence, however if an interim or partial solution has been chosen it is important not to lose momentum.
Problems, by their very nature, will not always fit neatly into a structured problem-solving process. This process, therefore, is designed as a framework which can be adapted to individual needs and nature.
Join Mind Tools and get access to exclusive content.
This resource is only available to Mind Tools members.
Already a member? Please Login here

Gain essential management and leadership skills
Busy schedule? No problem. Learn anytime, anywhere.
Subscribe to unlimited access to meticulously researched, evidence-based resources.
Join today and save on an annual membership!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Better Public Speaking

How to Build Confidence in Others
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
How to create psychological safety at work.
Speaking up without fear
How to Guides
Pain Points Podcast - Presentations Pt 1
How do you get better at presenting?
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Communications planning.
Getting the Right Message Across in the Right Way
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The rational decision-making process comprises several key steps. Here's a rundown: 1. Identify the Decision. The first step in rational decision-making is acknowledging that a decision is required. The decision is usually a problem but can also be an opportunity.
Rational Decision Making Model: 7 Easy Steps (+ Examples) 1. Verify and define your problem. To prove that you actually have a problem, you need evidence for it. Most marketers think data is the silver bullet that can diagnose any issue in our strategy, but you actually need to extract insights from your data to prove anything.
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
Here, the rational decision-making process becomes Lauren's guiding light. The rational decision-making process typically involves several vital steps. 1. Defining the problem: First, Lauren needs to clearly define the issue, which is the decision between spending on office space for her growing clientele vs. Buying a luxurious car. 2.
In essence, rational behavior intertwines psychology and logic, fostering a rational approach to problem-solving. It's not just about the decisions made but how and why they are made. Understanding this concept is the first step in mastering rational decision making and embedding it into your decision-making arsenal. Step 2: People Face Trade-offs
The rational decision making model assumes decisions are based on an objective, orderly, structured information gathering and analysis. The model encourages the decision maker to understand the situation, organize and interpret the information, and then take action. There are eight steps in the rational decision making process:
The problem or the issue that needs solving needs to be defined clearly to make all the other steps in the process make sense. Defining the problem is the foundation of the entire rational ...
Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below. Step. Characteristics. 1. Define the problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically.
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
When we do problem definition well in classic problem solving, we are demonstrating the kind of empathy, at the very beginning of our problem, that design thinking asks us to approach. When we ideate—and that's very similar to the disaggregation, prioritization, and work-planning steps—we do precisely the same thing, and often we use ...
Abstract. Rational decision making requires executing an appropriate decision-making process to select the best alternative. This can be challenging when information is uncertain or when time is limited. This article describes three important perspectives on decision making: (i) the problem-solving perspective, (ii) the decision-making process ...
A team's problem-solving process can be disrupted by a number of non-task-related factors. Team members may support a position because of their ... which shows the main steps in a formal, rational, problem-solving model. Problem Recognition, Definition, and Analysis Problem recognition, definition, and analysis are key processes in effec-
Problem definition and formulation (PDF) represents the first of the four rational problem-solving skills. The overarching goal of training in PDF is to help a person to better understand the nature of the problem and to set realistic goals. Although the tasks involved in this aspect of the problem-solving process may be the most complex and challenging, they are also perhaps the most important.
Rational decision-making is a process in which decision-makers go through a set of steps and processes and choose the best solution to a problem. These decisions are based on data analysis and logic, eliminating intuition and subjectivity. ... The next step in the rational decision-making process is to delve into the problem. Find out what is ...
Steps in the Decision-Making Process. 1. Frame the Decision. Pinpointing the issue is the first step to initiating the decision-making process. Ensure the problem is carefully analyzed, clearly defined, and everyone involved in the outcome agrees on what needs to be solved. This process will give your team peace of mind that each key decision ...
Guidelines to Problem-Solving and Decision Making (Rational Approach) Much of what people do is solve problems and make decisions. Often, they are "under the gun", stressed, and very short of time. ... (An important aspect of this step in the problem-solving process is continual observation and feedback.) 6. Monitor implementation of the plan.
When the problem is clearly defined, you then have more information to come up with the best decision to solve the problem. Read: 22 types of business objectives to measure success Step 2: Gather relevant information Gathering information related to the decision being made is an important step to making an informed decision.
Step 2: Analyze the Problem. During this step a group should analyze the problem and the group's relationship to the problem. Whereas the first step involved exploring the "what" related to the problem, this step focuses on the "why.". At this stage, group members can discuss the potential causes of the difficulty.
The rational problem-solving process is an excellent tool to help tutors guide students through problems big and small. This organized way of approaching the task can help us make sure we're heading in a productive direction, from solving a math problem to developing a strategy to finish a research paper.
The decision-making process typically involves several sequential steps. Here's a breakdown of these steps: 1. Identification of the Decision: Recognize that a decision needs to be made. This could be prompted by a problem, opportunity, or a need for improvement. 2.
Join today and save on an annual membership! Although problem-solving is something everyone does on a daily basis, many people lack confidence in their ability. Here we look at the basic problem-solving process to help keep you on the right track.
Here are the seven steps of the rational approach: Define the problem. Identify possible causes. Brainstorm options to solve the problem. Select an option. Create an implementation plan. Execute the plan and monitor the results. Evaluate the solution. Read more: Effective Problem Solving Steps in the Workplace.
Rational decision making is a multi-step process for making logically sound decisions that aims to follow the orderly path from problem identification through solution. ... Identifying the decision criteria that will be important in solving the problem. The decision maker must determine the relevant factors to take into account when making the ...