
- 71 Good food
- 74 On time delivery
- 70 Correct order

See if this restaurant delivers to you.
Main attractions, sodas and juices, frozen drinks, seared sea scallops, loaded fries, chicken bites, crispy fried calamari, caribben shrimp, the lit 21 wings, camarones al ajillo, volcanic nachos, 5 star vip sampler, piggyback fries, fried mozzarella, colomabian style empanadas, fresh guacamole, garlic pesto flatbread, chorizo flatbread, crispy chicken fingers, lit 21 wings, tostones cup, bang bang shrimp, quesadillas, chicken fingers, chicken cobb salad, the lit 21 house salad, steak salad, over the top taco salad, seared tuna salad, green sea salad, sancocho de pollo soup, french onion soup, azteca soup, chick noodle soup, wild buffalo wrap, high protein wrap, chicken and avocado wrap, steak and chicken wrap, fried fish sandwich, top shelf steak sandwich, pork blt sandwich, chicken sandwich, chicken strip melt, cuban sandwich, braised short rib sandwich, turkey club, the all american burger, the don burger, home-made veggie burger, beef sliders, buffalo sliders, build your own my burger, smokehouse burger, avocado bison burger, teriyaki turkey burger, the lit 21 burger, double grilled cheeseburger, chicken murphy, sauteed salmon, hickory-smoked beef short ribs, 1 by lanf 2 by sea, fettuccini alfredo, top sirloin steak, tilapia and shrimp, shrimp trio, arroz chaufa, grilled pork chops, penne vodka with shrimp, surf and turf, gluten free new york steak, grilled tilapia with spinach and asparagus, cheeseburger, chicken breast, steak diane, mango guava cheesecake, churro cake, tuxedo bombe, double nutty chocolate brownie.

Pineapple Juice
Lemonade juice, pink lemonade, cranberry juice, orange juice, lobster mac & cheese, pan-seared entrees, blackened chicken alfredo pasta, calabrese shrimp pasta, chimichurri skirt steak, surf & turf, lit 21 burger, macaroni & cheese, hand cut fries, cajun fries, yucca fries, mexicano street corn, grilled asparagus, mashed potatoes, vegetable saffron rice, sauteed vegetables, sweet potato fries, lit 21 bulldog, henny colada, pina colada, vodka lemonade, the lit 21 jack daniel’s punch, bacardi mermaid bucket, lit 21 menu info, sponsored restaurants in your area.

Jersey Mike's (1117)

Falafel Guys

Royal Chicken & Biscuit

Charley Bistro

Taqueria Los Gueros

Avenue Pizza

Chopsticks House

Stars N Elites Restaurant Lounge

Jalwa: Modern Indian Dining

Rapin Fritura Restaurant Newark

Kennedy Pizza & Fried Chicken

Eleazar Steakhouse

Giovanni Pizza, Pasta and Grill

Vera Level Bro

New York Fried Chicken and Pizza (Halal)

Sun_island.plate

Tafari Tropics Jamaican Restaurant
Reviews for lit 21, q) does lit 21 (1034 mccarter hwy) deliver, q) does lit 21 (1034 mccarter hwy) offer contact-free delivery, q) is lit 21 (1034 mccarter hwy) eligible for seamless+ free delivery.
- Newark Central Business District
No JavaScript?
No proble... well, actually.
Our site is delivered by JavaScript. To continue, please enable JavaScript in your browser's preferences.
Reload the homepage

Food and Drink Menu
Questions call or text us at (973) 718-2646, 1034 mccarter hwy newark, nj 07102.

Don’t leave so soon. You can test our service for

- Find companies
- Sports Bars
Reviews of Lit 21 in Newark

Overall Rating
Contact info.
1034 McCarter Highway 07102 Newark New Jersey
+1 973-718-2646
Opening hours
Social media, write a review, is this your business.
By claiming this business, you can update and control the information on your profile.
Contact form
Best similar companies nearby, top categories in newark.
- Restaurants
- Bars & Pubs
- American Restaurants
- Bar & Grill
- Fast Food Restaurants
- Family Style Restaurants
- Pizza Restaurants
- Chinese Restaurants
Why choose Yably?
Customer feedback matters - use it to boost your business.
Customer reviews are one of the most important things for your business. Reviews not only have the power to influence consumer decisions but can strengthen a company’s credibility, gain customer trust, and encourage people to interact with your business.
Stand out - Get a Star Rating in Google Search Results
Google 5 Star Ratings in organic search boots traffic to your website and sets you apart from the crowd by inspiring more confidence among potential new customers.
Reputation & Review Monitoring Across Multiple Platforms
Track your ratings and reviews across different review platforms. Starting today, keep track of all your reviews and respond to them directly.
Try it now for free!
Register now and start managing your online reviews across multiple platforms.
- Holiday Rentals
- Restaurants
- Things to do
- Newark Tourism
- Newark Hotels
- Newark Bed and Breakfast
- Newark Holiday Rentals
- Flights to Newark
- Newark Restaurants
- Newark Attractions
- Newark Travel Forum
- Newark Photo
- All Newark Hotels
- Newark Hotel Deals
- Last Minute Hotels in Newark
- Newark Hostels
- Business Hotels Newark
- Family Hotels in Newark
- Newark Green Hotels
- 3-stars Hotels in Newark
- Courtyard (Marriott Bonvoy) Hotels in Newark
- DoubleTree by Hilton Hotels in Newark
- Hilton Hotels in Newark
- Wyndham Hotels in Newark
- Marriott Hotels in Newark
- Newark Hotels with a Pool
- Pet Friendly Hotels in Newark
- Newark Airport and Port Newark Hotels
- Newark Party Hotels
- Newark Oceanfront Hotels
- Motels With Indoor Pools in Newark
- Modern Hotels Newark
- Newark Marathon Hotels
- Luxury Spa Resorts Newark
- Romantic Boutique Hotels in Newark
- Luxury Resorts Newark
- Newark Hotels with Rooftop Pool
- Newark Hotels with Rooftop Bar
- Hotels near Prudential Center
- Hotels near The Newark Museum of Art
- Hotels near Branch Brook Park
- Hotels near Cathedral Basilica of the Sacred Heart
- Hotels near Ironbound
- Hotels near Newark Airport Express
- Hotels near Newark Penn Station
- Hotels near NJ Transit
- Hotels near AirTrain Newark
- Hotels near Newark Public Library
- Hotels near (JFK) John F. Kennedy Intl Airport
- Hotels near (LGA) La Guardia Airport
- Hotels near (EWR) Newark Liberty Intl Airport
- Resorts World Kijal
- Redang Beach Resort
- JW Marriott Hotel Kuala Lumpur
- Alang's Rawa
- Coral Redang Island Resort
- Sea Horizon Resort
- Taiping Bamboo Resort
- Avani Sepang Goldcoast Resort
- Sekeping Serendah Retreat
- Mataking Reef Resort
- M Resort & Hotel
- Redang Reef Resort
- Union Yes Retreat & Training Centre
- The Granite Luxury Hotel Penang
- Lexis Hibiscus Port Dickson
- Popular All-Inclusive Resorts
- Popular Beach Resorts
- Popular Family Resorts
- Popular All-Inclusive Hotels
- Popular Hotels With Waterparks
- Popular Honeymoon Resorts
- Popular Luxury Resorts
- Popular All-Inclusive Family Resorts
- Popular Golf Resorts
- Popular Spa Resorts
- Popular Cheap Resorts
- All Newark Restaurants
- BBQ Restaurants in Newark
- Cafes for Families in Newark
- Cafés in Newark
- Caribbean Restaurants with Delivery in Newark
- Fast Food Restaurants in Newark
- Gluten Free Restaurants in Newark
- Italian Restaurants in Newark
- Late Night Spanish Restaurants in Newark
- Pizza in Newark
- Portuguese Restaurants in Newark
- Seafood Restaurants in Newark
- Spanish Restaurants in Newark
- Vegetarian Restaurants in Newark
- Best Cod in Newark
- Best Meatballs in Newark
- Best Tacos in Newark
- Best Cupcakes in Newark
- Best Waffles in Newark
- Best Crab in Newark
- Best Paella in Newark
- Best Pad Thai in Newark
- Best Clams in Newark
- Best Noodle in Newark
- Best Scallops in Newark
- Best Shrimp in Newark
- Best Hot Dogs in Newark
- Best Dumplings in Newark
- Best Hamburgers in Newark
- Breakfast Restaurants in Newark
- Lunch Restaurants in Newark
- Dinner Restaurants in Newark
- Bakeries in Newark
- Coffee & Tea in Newark
- Desserts in Newark
- Food Delivery Restaurants in Newark
- Kid Friendly Restaurants in Newark
- Late Night Restaurants in Newark
- Restaurants for Group Dining in Newark
- Restaurants for Special Occasions in Newark
- Romantic Restaurants in Newark
- After-hours Restaurants in North Ironbound
- American Restaurants in Newark Central Business District
- Hamburgers in North Ironbound
- Late Night European Restaurants in North Ironbound
- Newark Airport and Port Newark Restaurants
- Newark Central Business District Restaurants
- North Ironbound Restaurants
- GreenLeaders
- Things to Do
- Travel Stories
- Add a Place
- Travel Forum
- Travellers' Choice
- Help Centre
- United States
- New Jersey (NJ)
- Newark
- Newark Restaurants

Ratings and reviews
Food and ambience, location and contact, lit 21, newark - restaurant reviews - tripadvisor.
- Holiday Rentals
- Restaurants
- Things to do
- Newark Tourism
- Newark Hotels
- Newark Guest House
- Newark Holiday Homes
- Newark Flights
- Newark Restaurants
- Newark Attractions
- Newark Travel Forum
- Newark Photos
- All Newark Hotels
- Newark Hotel Deals
- Last Minute Hotels in Newark
- Newark Hostels
- Business Hotels in Newark
- Family Hotels in Newark
- Newark Green Hotels
- 3-stars Hotels in Newark
- Courtyard (Marriott Bonvoy) Hotels in Newark
- DoubleTree by Hilton Hotels in Newark
- Hilton Hotels in Newark
- Wyndham Hotels in Newark
- Marriott Hotels in Newark
- Newark Hotels with a Pool
- Pet Friendly Hotels in Newark
- Newark Airport and Port Newark Hotels
- Newark Central Business District Hotels
- Cheap Motels in Newark
- Cheap Bed and Breakfast in Newark
- Spa Hotels in Newark
- Resorts With Indoor Pools in Newark
- Newark Hotels with Walk-in Shower
- Boutique Resorts in Newark
- Newark Ski Lodges
- Newark Luxury Lodges
- Newark Pet Friendly Campsites
- Newark Cheap Beach Hotels
- Hotels near Prudential Center
- Hotels near The Newark Museum of Art
- Hotels near Branch Brook Park
- Hotels near Cathedral Basilica of the Sacred Heart
- Hotels near Ironbound
- Hotels near Newark Airport Express
- Hotels near Newark Penn Station
- Hotels near NJ Transit
- Hotels near AirTrain Newark
- Hotels near Newark Public Library
- Hotels near (JFK) John F. Kennedy Intl Airport
- Hotels near (LGA) La Guardia Airport
- Hotels near (EWR) Newark Liberty Intl Airport
- Victoria Club Hotel
- Ownland Resort
- Mango Mist Resorts
- Club Mahindra Resort - Tungi, Lonavala, Maharashtra
- Sahyadri Guest House
- Oceano By Trouvaille
- Urbanpod Hotel
- Ratapani Jungle Lodge
- Poovar Island Resort
- Leonia Holistic Destination
- Nirvana Eco and Agro Resort
- Shankus Water Park & Resort
- Haritha Hotel Laknavaram
- Golden Palms Hotel & Spa
- Popular All-Inclusive Resorts
- Popular Beach Resorts
- Popular Family Resorts
- Popular All-Inclusive Hotels
- Popular Hotels With Waterparks
- Popular Honeymoon Resorts
- Popular Luxury Resorts
- Popular All-Inclusive Family Resorts
- Popular Golf Resorts
- Popular Spa Resorts
- Popular Cheap Resorts
- All Newark Restaurants
- BBQ Restaurants in Newark
- Cafes for Families in Newark
- Cafés in Newark
- Caribbean Restaurants with Delivery in Newark
- Fast Food Restaurants in Newark
- Gluten Free Restaurants in Newark
- Italian Restaurants in Newark
- Late Night Spanish Restaurants in Newark
- Pizza in Newark
- Portuguese Restaurants in Newark
- Seafood Restaurants in Newark
- Spanish Restaurants in Newark
- Vegetarian Restaurants in Newark
- Best Cod in Newark
- Best Meatballs in Newark
- Best Tacos in Newark
- Best Cupcakes in Newark
- Best Waffles in Newark
- Best Crab in Newark
- Best Paella in Newark
- Best Pad Thai in Newark
- Best Clams in Newark
- Best Noodle in Newark
- Best Scallops in Newark
- Best Shrimp in Newark
- Best Hot Dogs in Newark
- Best Dumplings in Newark
- Best Hamburgers in Newark
- Breakfast Restaurants in Newark
- Lunch Restaurants in Newark
- Dinner Restaurants in Newark
- Bakeries in Newark
- Coffee & Tea in Newark
- Desserts in Newark
- Food Delivery Restaurants in Newark
- Kid Friendly Restaurants in Newark
- Late Night Restaurants in Newark
- Restaurants for Group Dining in Newark
- Restaurants for Special Occasions in Newark
- Romantic Restaurants in Newark
- After-hours Restaurants in North Ironbound
- American Restaurants in Newark Central Business District
- Hamburgers in North Ironbound
- Late Night European Restaurants in North Ironbound
- Newark Airport and Port Newark Restaurants
- Newark Central Business District Restaurants
- North Ironbound Restaurants
- GreenLeaders
- Things to Do
- Holiday homes
- Travel Stories
- Add a Place
- Travel Forum
- Travellers' Choice
- Help Centre
- United States
- New Jersey (NJ)
- Newark
- Newark Restaurants

Ratings and reviews
Food and ambience, location and contact, lit 21, newark - restaurant reviews - tripadvisor.
Top ways to experience nearby attractions

Also popular with travellers

Lit 21 (Newark, NJ): Address, Phone Number - Tripadvisor
Customer Ratings and Reviews
Ordered food from Lit21 for the first time tonight. I used their website to order. It wasnt complicated. Easy to use. At the end they give you an estimated arrival time which is dope. Food got here before estimated time which was great! We tried the arroz chaufa with chicken and shrimp and some burgers. All the food was delicious! The wings were good too. Burgers on point. Pleasantly surprised! Food hit the spot ????!
Had a Blast here with my friends!! Great vibes and lots of space. Music was on point. Dress code was enforced and everyone looked great! Grown and sexy atmosphere. Free for ladies on a Saturday can’t best that !!!
Lit 21 is a great place for every type of plan you have in mind, want to chill and play with friends while eating and drinking? Go there, great food, amazing staff, great view at the patio, and the nightclub!? The vibe is great, their security is the best! I feel safe there all the time ????????
Nice bar/restaurant on the border of Newark and Harrison, not easy to get to by mass transit so plan on driving. The food is pretty good the two times I've been, especially given the price. From my experience it can range from nearly empty early on weekends to packed on weekdays after work, to the point you'll be waiting a while for your cheque. The servers are great though, very personable and attentive, just a bit overworked.
Soon as I walk in the place was nice. The waiters was very respectful and helpful. The only thing about it that they didn't play the music I like. I enjoyed my Birthday with family and friends. It was clean, the food was good and I will visit again????
Photos of Lit 21

Similar Businesses Nearby
- Divino Tasting Room, Eatery & Lounge 38 Maiden Ln, Newark, NJ 07102, USA
- SAGRES BAR AND GRILL 44 - 50 Prospect Street Corner of Ferry and, Prospect St, Newark, NJ 07105, USA
- Mompou Tapas Bar & Restaurant 77 Ferry St, Newark, NJ 07105, USA
- Lugo Bar/Lounge 99 Bloomfield Ave, Newark, NJ 07104, USA
- Oh! Calamares 102 Kearny Ave, Kearny, NJ 07032, USA
- Catas 538 Market St, Newark, NJ 07105, USA
- La Rouge 972 Broad St, Newark, NJ 07102, USA
- VIVO Tapas KITCHEN • LOUNGE 167 Ferry St, Newark, NJ 07105, USA
Submit a review for Lit 21
- Be specific about your experience and the services that were provided.
- Be truthful - this review will help other consumers as well as the business.
- Be polite - give feedback in a constructive way.
Most Recent
- Power Cross Cafe [Restaurant]
- Compass pizza [Restaurant]
- Mandloi Poha Bhandar [Restaurant]
- Big Daddy D's [Meal takeaway]
- Mega Liquor Vape & Tobacco [Restaurant]
- Boondocks Emporium [Restaurant]
- Market Street Pizza [Restaurant]
- Cruisin I39 [Restaurant]
- Loves by Rockford Airport [Restaurant]
- Ream's Wurst Wagon [Meal takeaway]
Home page . + Add Restaurant . About . Privacy Policy . Terms of Service . Contact Us
© 2024 usarestaurants.info All Rights reserved.
The content displayed in the usarestaurants.info Directory consists of information from third parties, among others from publicly accessible sources, or from customers, who have a presentation page in our directory. usarestaurants.info cannot be held responsible or liable for the accuracy, correctness, usefulness or reliability of the data. The brand names, logos, images and texts are the property of these third parties and their respective owners. If you have any questions or suggestions regarding this matter, you are welcome to contact our customer support team.
usarestaurants.info is not a booking agent, and does not charge any service fees to users of our site.
usarestaurants.info is not responsible for content on external web sites. Taxes, fees not included for deals content.
- The Heights
- Journal Square
- McGinley Square
- Bergen-Lafayette
- West New York
- Featured Listings
- Jersey City
- Food & Drink
Lit 21 Sports Bar and Lounge to Open This Week along Route 21 in Newark

Borders Tex-Mex Cantina advertised that it was the “perfect spot” for graduation celebrations this year. However, the Downtown Newark restaurant, which opened for business two months after the school year began, ended up closing its doors before students in Essex County even took their final exams. Now, following the closure of the city’s only sit-down Tex-Mex restaurant, another business is preparing to open inside.
Lit 21 will soon be in operation in the space, which is located at 1034 McCarter Highway near the Bridge Street Bridge. The business, which describes itself a restaurant, sports bar, and lounge that is “the hottest venue in the tri-state area,” has announced that it will hold a grand opening celebration with DJ Camilo of HOT 97 on Thursday, June 27.
View this post on Instagram The hottest venue has arrived. @lit21nj See you at the Grand opening! June 27th🥂No cover charge. . . . . . . #Newark #Newyork #eatchillplay #nightlife #party #grandopening #fiesta #summer2019 #litlife A post shared by LIT 21 (@lit21nj) on Jun 21, 2019 at 2:26pm PDT
The facade of the building was recently painted and a new sign was installed in front. Lit 21’s logo and name reflect the space’s location along Route 21. Few other details are known yet about the establishment. A representative of Lit 21 could not be reached for comment.
Once home to Rio Rodizio, this restaurant space is one of only a few in Downtown Newark that includes a free surface parking lot for customers, through Lit 21’s Facebook page mentions that there will also be valet parking. Located along a busy state highway, there is not heavy pedestrian traffic in this area, but as we reported when Borders opened, that could change in the years to come if the expansion of Riverfront Park and the construction of the Riverfront Square development move forward.
- 325 Ferry Street’s Luxury Community Captures Cool Ironbound Vibe
- Maplewood’s Cornbread Restaurant to Open Downtown Newark Location
- Developers Set ‘Shaq Tower’ Opening for Mid-June
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

New Images Emerge as Phase One of $336 Million NJPAC Renovation Begins

The Newark that Could Have Been, Part II: Mid-Century Utopias and Motorama Nightmares

The Newark that Could Have Been, Part I: A City Beautiful, Sky-High Ambitions, and Lost Focus
No posts to display.
- Privacy Policy

- 71 Good food
- 74 On time delivery
- 70 Correct order
See if this restaurant delivers to you.
Main attractions, sodas and juices, frozen drinks, seared sea scallops, loaded fries, chicken bites, crispy fried calamari, caribben shrimp, the lit 21 wings, camarones al ajillo, volcanic nachos, 5 star vip sampler, piggyback fries, fried mozzarella, colomabian style empanadas, fresh guacamole, garlic pesto flatbread, chorizo flatbread, crispy chicken fingers, lit 21 wings, tostones cup, bang bang shrimp, quesadillas, chicken fingers, chicken cobb salad, the lit 21 house salad, steak salad, over the top taco salad, seared tuna salad, green sea salad, sancocho de pollo soup, french onion soup, azteca soup, chick noodle soup, wild buffalo wrap, high protein wrap, chicken and avocado wrap, steak and chicken wrap, fried fish sandwich, top shelf steak sandwich, pork blt sandwich, chicken sandwich, chicken strip melt, cuban sandwich, braised short rib sandwich, turkey club, the all american burger, the don burger, home-made veggie burger, beef sliders, buffalo sliders, build your own my burger, smokehouse burger, avocado bison burger, teriyaki turkey burger, the lit 21 burger, double grilled cheeseburger, chicken murphy, sauteed salmon, hickory-smoked beef short ribs, 1 by lanf 2 by sea, fettuccini alfredo, top sirloin steak, tilapia and shrimp, shrimp trio, arroz chaufa, grilled pork chops, penne vodka with shrimp, surf and turf, gluten free new york steak, grilled tilapia with spinach and asparagus, cheeseburger, chicken breast, steak diane, mango guava cheesecake, churro cake, tuxedo bombe, double nutty chocolate brownie.

Pineapple Juice
Lemonade juice, pink lemonade, cranberry juice, orange juice, lobster mac & cheese, pan-seared entrees, blackened chicken alfredo pasta, calabrese shrimp pasta, chimichurri skirt steak, surf & turf, lit 21 burger, macaroni & cheese, hand cut fries, cajun fries, yucca fries, mexicano street corn, grilled asparagus, mashed potatoes, vegetable saffron rice, sauteed vegetables, sweet potato fries, lit 21 bulldog, henny colada, pina colada, vodka lemonade, the lit 21 jack daniel’s punch, bacardi mermaid bucket, lit 21 menu info, sponsored restaurants in your area.

Jersey Mike's (1117)

Panera Bread

Rosemary Restaurant

orale wey mexican rstaurant

Charley Bistro

Rapin Fritura Restaurant Newark

Ah'Pizz Wood Fired Pizza Italian Restaurant & Bar

Casa Nova Grill

Golden Wings Fish And Chicken

El Macho Taqueria & Restaurant

Flavors Soul Food

Hummus Republic

Giovanni Pizza, Pasta and Grill

State Street Grill

Ninos pizza

Kennedy Pizza & Fried Chicken

Napoli Pizza
Reviews for lit 21, q) does lit 21 (1034 mccarter hwy) deliver, q) does lit 21 (1034 mccarter hwy) offer contact-free delivery, q) is lit 21 (1034 mccarter hwy) eligible for grubhub+ free delivery.
- Restaurants Near Me
- Newark Central Business District
No JavaScript?
No proble... well, actually.
Our site is delivered by JavaScript. To continue, please enable JavaScript in your browser's preferences.
Reload the homepage

LIT 21, Newark - Restaurant Reviews, Food Delivery & Takeaway - Tripadvisor
- Holiday Rentals
- Restaurants
- Things to do
- Newark Tourism
- Newark Hotels
- Bed and Breakfast Newark
- Newark Holiday Rentals
- Flights to Newark
- Newark Restaurants
- Newark Attractions
- Newark Travel Forum
- Newark Photos
- All Newark Hotels
- Newark Hotel Deals
- Last Minute Hotels in Newark
- Newark Hostels
- Business Hotels Newark
- Family Hotels Newark
- Newark Green Hotels
- 3-stars Hotels in Newark
- Courtyard (Marriott Bonvoy) Hotels in Newark
- DoubleTree by Hilton Hotels in Newark
- Hilton Hotels in Newark
- Wyndham Hotels in Newark
- Marriott Hotels in Newark
- Newark Hotels with a Pool
- Pet Friendly Hotels in Newark
- Newark Airport and Port Newark Hotels
- Newark Central Business District Hotels
- Newark Cheap Hotels
- Hotels with Shuttle in Newark
- Hotels with Hot Tubs in Newark
- Motels With Indoor Pools in Newark
- Modern Hotels in Newark
- Newark Marathon Hotels
- Luxury Spa Resorts Newark
- Romantic Boutique Hotels Newark
- Exclusive Resorts in Newark
- Newark Hotels with Rooftop Pool
- Hotels near Prudential Center
- Hotels near The Newark Museum of Art
- Hotels near Branch Brook Park
- Hotels near Cathedral Basilica of the Sacred Heart
- Hotels near Ironbound
- Hotels near Newark Airport Express
- Hotels near Newark Penn Station
- Hotels near NJ Transit
- Hotels near AirTrain Newark
- Hotels near Newark Public Library
- Hotels near (JFK) John F. Kennedy Intl Airport
- Hotels near (LGA) La Guardia Airport
- Hotels near (EWR) Newark Liberty Intl Airport
- Ikos Odisia
- Granada Luxury Belek
- Hotel Riu Tequila
- Sandos Papagayo
- H10 Rubicon Palace
- Jiva Beach Resort
- Xoria Deluxe
- Titanic Deluxe Golf Belek
- Holiday Village Majorca - Protur Monte Safari
- Atlantica Holiday Village Rhodes
- Ikos Dassia
- Blue Bay Platinum Hotel
- Hotel Riu Touareg
- Hard Rock Hotel Tenerife - All Inclusive
- Grand Park Lara
- Popular All-Inclusive Resorts
- Popular Beach Resorts
- Popular Family Resorts
- Popular All-Inclusive Hotels
- Popular Hotels With Waterparks
- Popular Honeymoon Resorts
- Popular Luxury Resorts
- Popular All-Inclusive Family Resorts
- Popular Golf Resorts
- Popular Spa Resorts
- Popular Cheap Resorts
- All Newark Restaurants
- BBQ Restaurants in Newark
- Cafes for Families in Newark
- Cafés in Newark
- Caribbean Restaurants with Delivery in Newark
- Fast Food Restaurants in Newark
- Gluten Free Restaurants in Newark
- Italian Restaurants in Newark
- Late Night Spanish Restaurants in Newark
- Pizza in Newark
- Portuguese Restaurants in Newark
- Seafood Restaurants in Newark
- Spanish Restaurants in Newark
- Vegetarian Restaurants in Newark
- Best Cod in Newark
- Best Meatballs in Newark
- Best Tacos in Newark
- Best Cupcakes in Newark
- Best Waffles in Newark
- Best Crab in Newark
- Best Paella in Newark
- Best Pad Thai in Newark
- Best Clams in Newark
- Best Noodle in Newark
- Best Scallops in Newark
- Best Shrimp in Newark
- Best Hot Dogs in Newark
- Best Dumplings in Newark
- Best Hamburgers in Newark
- Breakfast Restaurants in Newark
- Lunch Restaurants in Newark
- Dinner Restaurants in Newark
- Bakeries in Newark
- Coffee & Tea in Newark
- Desserts in Newark
- Food Delivery Restaurants in Newark
- Kid Friendly Restaurants in Newark
- Late Night Restaurants in Newark
- Restaurants for Group Dining in Newark
- Restaurants for Special Occasions in Newark
- Romantic Restaurants in Newark
- After-hours Restaurants in North Ironbound
- American Restaurants in Newark Central Business District
- Hamburgers in North Ironbound
- Late Night European Restaurants in North Ironbound
- Newark Airport and Port Newark Restaurants
- Newark Central Business District Restaurants
- North Ironbound Restaurants
- GreenLeaders
- Things to Do
- Travel Stories
- Add a Place
- Travel Forum
- Travellers' Choice
- Help Centre
- United States
- New Jersey (NJ)
- Newark
- Newark Restaurants

Ratings and reviews
Food and ambience, location and contact, lit 21, newark - restaurant reviews, food delivery & takeaway - tripadvisor.
Hours updated 3 months ago

Today is a holiday! Business hours may be different today.
Review Highlights

“ I arrived there by myself and the bartender, Joshua , was very friendly and accommodating playing music that other customers requested. ” in 2 reviews

“ Went for a drink with my cousin and was pleasantly surprised. ” in 2 reviews

“ I will also suggest they get a game or two maybe some Jenga in there so they can put some good use to the tables :) .. They have popcorn as a snack I didn't have any though. ” in 2 reviews
Location & Hours
Suggest an edit
15325 Washington Ave
San Leandro, CA 94579
Lorenzo Ave & Lewelling Blvd
You Might Also Consider

Bowlero Alameda
tracy r. said "I was quite a bit skeptical after reading the reviews but this location was the closest to us to have our daughters birthday party so we decided to book anyway. I saw several reviews complaining about the lack of staff. I'm guessing…" read more
in Bowling, Arcades, Venues & Event Spaces

alley & vine
KT S. said "I'm going to start this review by saying, everything was exquisite, from the presentation to the dancing flavors on my tongue. Next, here's what we thoroughly enjoyed and devoured: (1) Bites - Crispian bakery toasted epi with house…" read more
in New American, Seafood, Cocktail Bars
Amenities and More
Ask the community.
Ask a question
Yelp users haven’t asked any questions yet about Lit Lounge .
Recommended Reviews
- 1 star rating Not good
- 2 star rating Could’ve been better
- 3 star rating OK
- 4 star rating Good
- 5 star rating Great
Select your rating
Overall rating

Definitely 2000-2010's bay area party vibes. It felt highly nostalgic with the music videos playing hip hop and RnB, along with the caffeinated liquor options and flavored vodka options Got the Margarita and the lotus drink, both were terrible and highly reminiscent of clubbing in SF in the early days. Over sugary and not that strong, poorly balanced. Nothing like whatever the previous yelpers with fancy cocktails and craft beer posted. If you're looking for a good cocktail you can go to viridian in Oakland and get something really good for similar prices but this here you can have a reminder of the sticky club floors and your crazy days Atmosphere here was clean and nostalgic, especially the black toilets, music and drinks. Overall would only probably come back here if they had a DJ or a dance night

Turnt Lotus and Mango Margarita

Mary was awesome and super hospitable, the lounge has a great vibe. The drinks were mixed really well.

Cute new bar in San Lorenzo. Went for a drink with my cousin and was pleasantly surprised. The vibe is cool not crazy hectic. The bartender is attentive! They got a popcorn machine! Cute. They play a good mix of music too! Various TVs on the wall playing music videos. Little space to dance if it get crowded. Overall I thought it was a vibe.

See all photos from Ellie M. for Lit Lounge

I come for the free popcorn lol but no seriously it's a cool spot for some drinks and good (loud) music. Can get pretty busy sometimes, it's a hit or miss.

Joshua-great bartender

Stopped by on a quiet Monday night with my girlfriend, and was not disappointed! The bartender who was working, Joshua (had a necklace with his name so can't get it wrong) was friendly and attentive, resulting in an overall relaxing night with good conversation. The entire establishment was extremely clean, including the restroom Can't complain about drinks, we ordered the basics, a couple beers and some whiskey on the rocks but next time we will try some of their signature drinks. We will definitely come back soon, we actually have an invitation to a birthday party here for next month, so we're glad to have seen the place before then and are looking forward to it. Stay lit!

Cool atmosphere and call employees. Parkin lot small but it's good. Get there before the fake thugs show up to show out for no reason

Not happy with the bartender at Lit never smiled, wasn't a nice one and I did not like that guy at all I will never return again - Sorry Lit Looks nice inside and the vibe was good just get another Bartender who likes people!!

I loooove to check out new bars in town. I stopped by 7/8 to check out the new renovation and name change of this bar. I used to come here years ago when it was the Victorian Pub. Sooo glad someone finally renovated this place. It looks super modern and hip now. Love all the decor and big TV's. The bar looks BEAUTIFUL. And is definitely great for groups and young people that love to take selfies in front of cute backgrounds. Only downside I noticed was that the bar was dead. And there was a lack of genuine hospitality. I walked in the door and wasn't greeted warmly, in a timely manner, nor did I feel welcome. There was NO vibe at all. Anyways, I introduced myself to Owner Josh but it seemed he was too busy chatting up some girl at the bar which is fine. But I had came in this bar in hopes to help his business. Perhaps offer to help with some event planning and social media marketing here and bring in more business or bring a DJ, karaoke, food vendors, game night, singles night etc. For someone that works in hospitality/customer service as well as loves to help promote new businesses. This one is just lacking in the hospitality department for me. As a bartender I always say "Anybody can make a drink, just gotta know how to serve it. Have people leaving better than they came". I'll try this bar 1 more time in a few months, in hopes that they up the hospitality.

Great photo op area to take selfies with your crew

Whack. It has no vibe. It's boring. It's a plain dive bar that has no food and just is average.
From service to bad drinks man very disappointed the guy with tattoos was just wort customer service don't go there .

3.0 miles away from Lit Lounge
Andrea M. said "Much to my disgust, despite me reading the bad reviews about the service on this place to the boy, he still wants to go here for dinner on an early Saturday night. We go, I expect really bad service and meh food. While it took them…" read more
in Bars, Breakfast & Brunch, Mexican

40 Thieves Hookah Lounge
Janelle M. said "My friends and I came across this place on yelp and decided to check it out. The atmosphere here is clean, spacious, and the comfiness of the couches makes you feel like you're hanging out at home. The music in the background was…" read more
in Lounges, Hookah Bars
People Also Viewed

Danny Murry’s Irish Pub

Cunha’s Cocktails

Johnny’s Bar

Why Not Lounge

Curly’s Place

The Stein Lounge

Doucet Saloon

Sunshine’s Lounge
Best of San Leandro
Things to do in San Leandro
Browse Nearby
Restaurants
Things to Do
Other Bars Nearby
Find more Bars near Lit Lounge
- Craft and Criticism
- Fiction and Poetry
- News and Culture
- Lit Hub Radio
- Reading Lists

- Literary Criticism
- Craft and Advice
- In Conversation
- On Translation
- Short Story
- From the Novel
- Bookstores and Libraries
- Film and TV
- Art and Photography
- Freeman’s
- The Virtual Book Channel
- Behind the Mic
- Beyond the Page
- The Cosmic Library
- The Critic and Her Publics
- Emergence Magazine
- Fiction/Non/Fiction
- First Draft: A Dialogue on Writing
- The History of Literature
- I’m a Writer But
- Lit Century
- Tor Presents: Voyage Into Genre
- Windham-Campbell Prizes Podcast
- Write-minded
- The Best of the Decade
- Best Reviewed Books
- BookMarks Daily Giveaway
- The Daily Thrill
- CrimeReads Daily Giveaway

What Should You Read Next? Here Are the Best Reviewed Books of the Week
Featuring new titles by joyce carol oates, r.o. kwon, daniel handler, kevin kwan, and more.

Joyce Carol Oates’ Butcher , R.O. Kwon’s Exhibit , Daniel Handler’s And Then? and Then? What Else? , and Kevin Kwan’s Lies and Weddings all feature among the best reviewed books of the week.
Brought to you by Book Marks , Lit Hub’s home for book reviews.
1. Butcher by Joyce Carol Oates (Knopf)
4 Rave • 2 Positive
“The book has the feverish energy, narrative propulsion and descriptive amplitude—sometimes to excess—of much of her earlier work … Undoubtedly one of her most surreal and gruesome works, sparing no repulsive detail or nefarious impulse. In the end, though, the purview of the novel is larger than one might think, becoming an empathic and discerning commentary on women’s rights, the abuses of patriarchy and the servitude of the poor and disenfranchised. Oates, as is her wont, succeeds in creating a world that is apart from our own yet familiar, making it impossible to dismiss her observations about twisted natures and random acts of violence.”
–Daphne Merkin ( The New York Times Book Review )
2. Exhibit by R.O. Kwon (Riverhead)
3 Rave • 3 Positive • 1 Mixed Read an interview with R.O. Kwon here
“Some readers might sour at the inconclusive ending. But in my mind, nothing is more appropriate for a novel about religion’s hauntings, about religion and art and desire overrunning language and all its forms, including the novel. Kwon understands that these stories cannot have clean endings because something always escapes the telling. We end up silent, tense, gesturing, pointing.”
–Ryan Lackey ( The Los Angeles Review of Books )
3. Lies and Weddings by Kevin Kwan (Doubleday)
2 Rave • 3 Positive • 1 Mixed Read an interview with Kevin Kwan here
“ Lies and Weddings is chock-full of scheming characters and breathtakingly lavish scenes … Kwan remains a cheekily hilarious writer, with footnotes that give each chapter an extra kick … Pure pleasure.”
–Amy Scribner ( BookPage )
1. Undue Burden: Life and Death Decisions in Post-Roe America by Shefali Luthra (Doubleday)
5 Rave • 1 Positive
“ Undue Burden isn’t the first book about abortion rights and it certainly won’t be the last. But one quality that sets it apart is that it offers accounts from all types of people in all types of circumstances … Some of the most affecting sections are those in which Luthra details some of the struggles marginalized patients are going through to access essential reproductive care.”
–Alexis Burling ( The San Francisco Chronicle )
2. And Then? and Then? What Else? by Daniel Handler (Liveright)
3 Rave • 3 Positive
“ And Then? And Then? What Else? is a bit of a grab bag, starting in the middle and ending in the middle, while telling a series of stories that both connect and overlap … Handler is skilled and nuanced as a writer, with a developed voice and point of view. He has never fit the categories, so why would we expect him to start here? … He is frank without being overly revealing and always seeks out some larger integration, a place where thought and feeling might intersect.”
–David L. Ulin ( The Los Angeles Times )
3. In My Time of Dying: How I Came Face to Face with the Idea of an Afterlife by Sebastian Junger (Simon & Schuster)
2 Rave • 2 Positive
“Junger combines riveting operating-room drama, flush with detailed anatomical explanations, with vivid switchbacks to dangerous adventures in his past as well as forays into medical history, his physicist father’s life, quantum mechanics, and the universal elements of near-death experiences. Tracing the ever-wavering lines between science and mystery, reason and spirituality, Junger grapples with the complexity of the brain, the riddle of consciousness, and our views of death. Ardently researched, consummately written, and boldly forthright, this an intensely moving and deeply provocative immersion.”
–Donna Seaman ( Booklist )
- Share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Google+ (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)

Previous Article
Next article, support lit hub..

Join our community of readers.
to the Lithub Daily
Popular posts.

Follow us on Twitter

Ursula K. Le Guin on How to Become a Writer
- RSS - Posts
Literary Hub
Created by Grove Atlantic and Electric Literature
Sign Up For Our Newsletters
How to Pitch Lit Hub
Advertisers: Contact Us
Privacy Policy
Support Lit Hub - Become A Member
Become a Lit Hub Supporting Member : Because Books Matter
For the past decade, Literary Hub has brought you the best of the book world for free—no paywall. But our future relies on you. In return for a donation, you’ll get an ad-free reading experience , exclusive editors’ picks, book giveaways, and our coveted Joan Didion Lit Hub tote bag . Most importantly, you’ll keep independent book coverage alive and thriving on the internet.

Become a member for as low as $5/month

A systematic literature review of empirical research on ChatGPT in education
- Open access
- Published: 26 May 2024
- Volume 3 , article number 60 , ( 2024 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Yazid Albadarin ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0005-8068-8902 1 ,
- Mohammed Saqr 1 ,
- Nicolas Pope 1 &
- Markku Tukiainen 1
Over the last four decades, studies have investigated the incorporation of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into education. A recent prominent AI-powered technology that has impacted the education sector is ChatGPT. This article provides a systematic review of 14 empirical studies incorporating ChatGPT into various educational settings, published in 2022 and before the 10th of April 2023—the date of conducting the search process. It carefully followed the essential steps outlined in the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020) guidelines, as well as Okoli’s (Okoli in Commun Assoc Inf Syst, 2015) steps for conducting a rigorous and transparent systematic review. In this review, we aimed to explore how students and teachers have utilized ChatGPT in various educational settings, as well as the primary findings of those studies. By employing Creswell’s (Creswell in Educational research: planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research [Ebook], Pearson Education, London, 2015) coding techniques for data extraction and interpretation, we sought to gain insight into their initial attempts at ChatGPT incorporation into education. This approach also enabled us to extract insights and considerations that can facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. The results of this review show that learners have utilized ChatGPT as a virtual intelligent assistant, where it offered instant feedback, on-demand answers, and explanations of complex topics. Additionally, learners have used it to enhance their writing and language skills by generating ideas, composing essays, summarizing, translating, paraphrasing texts, or checking grammar. Moreover, learners turned to it as an aiding tool to facilitate their directed and personalized learning by assisting in understanding concepts and homework, providing structured learning plans, and clarifying assignments and tasks. However, the results of specific studies (n = 3, 21.4%) show that overuse of ChatGPT may negatively impact innovative capacities and collaborative learning competencies among learners. Educators, on the other hand, have utilized ChatGPT to create lesson plans, generate quizzes, and provide additional resources, which helped them enhance their productivity and efficiency and promote different teaching methodologies. Despite these benefits, the majority of the reviewed studies recommend the importance of conducting structured training, support, and clear guidelines for both learners and educators to mitigate the drawbacks. This includes developing critical evaluation skills to assess the accuracy and relevance of information provided by ChatGPT, as well as strategies for integrating human interaction and collaboration into learning activities that involve AI tools. Furthermore, they also recommend ongoing research and proactive dialogue with policymakers, stakeholders, and educational practitioners to refine and enhance the use of AI in learning environments. This review could serve as an insightful resource for practitioners who seek to integrate ChatGPT into education and stimulate further research in the field.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Educational technology, a rapidly evolving field, plays a crucial role in reshaping the landscape of teaching and learning [ 82 ]. One of the most transformative technological innovations of our era that has influenced the field of education is Artificial Intelligence (AI) [ 50 ]. Over the last four decades, AI in education (AIEd) has gained remarkable attention for its potential to make significant advancements in learning, instructional methods, and administrative tasks within educational settings [ 11 ]. In particular, a large language model (LLM), a type of AI algorithm that applies artificial neural networks (ANNs) and uses massively large data sets to understand, summarize, generate, and predict new content that is almost difficult to differentiate from human creations [ 79 ], has opened up novel possibilities for enhancing various aspects of education, from content creation to personalized instruction [ 35 ]. Chatbots that leverage the capabilities of LLMs to understand and generate human-like responses have also presented the capacity to enhance student learning and educational outcomes by engaging students, offering timely support, and fostering interactive learning experiences [ 46 ].
The ongoing and remarkable technological advancements in chatbots have made their use more convenient, increasingly natural and effortless, and have expanded their potential for deployment across various domains [ 70 ]. One prominent example of chatbot applications is the Chat Generative Pre-Trained Transformer, known as ChatGPT, which was introduced by OpenAI, a leading AI research lab, on November 30th, 2022. ChatGPT employs a variety of deep learning techniques to generate human-like text, with a particular focus on recurrent neural networks (RNNs). Long short-term memory (LSTM) allows it to grasp the context of the text being processed and retain information from previous inputs. Also, the transformer architecture, a neural network architecture based on the self-attention mechanism, allows it to analyze specific parts of the input, thereby enabling it to produce more natural-sounding and coherent output. Additionally, the unsupervised generative pre-training and the fine-tuning methods allow ChatGPT to generate more relevant and accurate text for specific tasks [ 31 , 62 ]. Furthermore, reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), a machine learning approach that combines reinforcement learning techniques with human-provided feedback, has helped improve ChatGPT’s model by accelerating the learning process and making it significantly more efficient.
This cutting-edge natural language processing (NLP) tool is widely recognized as one of today's most advanced LLMs-based chatbots [ 70 ], allowing users to ask questions and receive detailed, coherent, systematic, personalized, convincing, and informative human-like responses [ 55 ], even within complex and ambiguous contexts [ 63 , 77 ]. ChatGPT is considered the fastest-growing technology in history: in just three months following its public launch, it amassed an estimated 120 million monthly active users [ 16 ] with an estimated 13 million daily queries [ 49 ], surpassing all other applications [ 64 ]. This remarkable growth can be attributed to the unique features and user-friendly interface that ChatGPT offers. Its intuitive design allows users to interact seamlessly with the technology, making it accessible to a diverse range of individuals, regardless of their technical expertise [ 78 ]. Additionally, its exceptional performance results from a combination of advanced algorithms, continuous enhancements, and extensive training on a diverse dataset that includes various text sources such as books, articles, websites, and online forums [ 63 ], have contributed to a more engaging and satisfying user experience [ 62 ]. These factors collectively explain its remarkable global growth and set it apart from predecessors like Bard, Bing Chat, ERNIE, and others.
In this context, several studies have explored the technological advancements of chatbots. One noteworthy recent research effort, conducted by Schöbel et al. [ 70 ], stands out for its comprehensive analysis of more than 5,000 studies on communication agents. This study offered a comprehensive overview of the historical progression and future prospects of communication agents, including ChatGPT. Moreover, other studies have focused on making comparisons, particularly between ChatGPT and alternative chatbots like Bard, Bing Chat, ERNIE, LaMDA, BlenderBot, and various others. For example, O’Leary [ 53 ] compared two chatbots, LaMDA and BlenderBot, with ChatGPT and revealed that ChatGPT outperformed both. This superiority arises from ChatGPT’s capacity to handle a wider range of questions and generate slightly varied perspectives within specific contexts. Similarly, ChatGPT exhibited an impressive ability to formulate interpretable responses that were easily understood when compared with Google's feature snippet [ 34 ]. Additionally, ChatGPT was compared to other LLMs-based chatbots, including Bard and BERT, as well as ERNIE. The findings indicated that ChatGPT exhibited strong performance in the given tasks, often outperforming the other models [ 59 ].
Furthermore, in the education context, a comprehensive study systematically compared a range of the most promising chatbots, including Bard, Bing Chat, ChatGPT, and Ernie across a multidisciplinary test that required higher-order thinking. The study revealed that ChatGPT achieved the highest score, surpassing Bing Chat and Bard [ 64 ]. Similarly, a comparative analysis was conducted to compare ChatGPT with Bard in answering a set of 30 mathematical questions and logic problems, grouped into two question sets. Set (A) is unavailable online, while Set (B) is available online. The results revealed ChatGPT's superiority in Set (A) over Bard. Nevertheless, Bard's advantage emerged in Set (B) due to its capacity to access the internet directly and retrieve answers, a capability that ChatGPT does not possess [ 57 ]. However, through these varied assessments, ChatGPT consistently highlights its exceptional prowess compared to various alternatives in the ever-evolving chatbot technology.
The widespread adoption of chatbots, especially ChatGPT, by millions of students and educators, has sparked extensive discussions regarding its incorporation into the education sector [ 64 ]. Accordingly, many scholars have contributed to the discourse, expressing both optimism and pessimism regarding the incorporation of ChatGPT into education. For example, ChatGPT has been highlighted for its capabilities in enriching the learning and teaching experience through its ability to support different learning approaches, including adaptive learning, personalized learning, and self-directed learning [ 58 , 60 , 91 ]), deliver summative and formative feedback to students and provide real-time responses to questions, increase the accessibility of information [ 22 , 40 , 43 ], foster students’ performance, engagement and motivation [ 14 , 44 , 58 ], and enhance teaching practices [ 17 , 18 , 64 , 74 ].
On the other hand, concerns have been also raised regarding its potential negative effects on learning and teaching. These include the dissemination of false information and references [ 12 , 23 , 61 , 85 ], biased reinforcement [ 47 , 50 ], compromised academic integrity [ 18 , 40 , 66 , 74 ], and the potential decline in students' skills [ 43 , 61 , 64 , 74 ]. As a result, ChatGPT has been banned in multiple countries, including Russia, China, Venezuela, Belarus, and Iran, as well as in various educational institutions in India, Italy, Western Australia, France, and the United States [ 52 , 90 ].
Clearly, the advent of chatbots, especially ChatGPT, has provoked significant controversy due to their potential impact on learning and teaching. This indicates the necessity for further exploration to gain a deeper understanding of this technology and carefully evaluate its potential benefits, limitations, challenges, and threats to education [ 79 ]. Therefore, conducting a systematic literature review will provide valuable insights into the potential prospects and obstacles linked to its incorporation into education. This systematic literature review will primarily focus on ChatGPT, driven by the aforementioned key factors outlined above.
However, the existing literature lacks a systematic literature review of empirical studies. Thus, this systematic literature review aims to address this gap by synthesizing the existing empirical studies conducted on chatbots, particularly ChatGPT, in the field of education, highlighting how ChatGPT has been utilized in educational settings, and identifying any existing gaps. This review may be particularly useful for researchers in the field and educators who are contemplating the integration of ChatGPT or any chatbot into education. The following research questions will guide this study:
What are students' and teachers' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in education?
What are the main findings derived from empirical studies that have incorporated ChatGPT into learning and teaching?
2 Methodology
To conduct this study, the authors followed the essential steps of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020) and Okoli’s [ 54 ] steps for conducting a systematic review. These included identifying the study’s purpose, drafting a protocol, applying a practical screening process, searching the literature, extracting relevant data, evaluating the quality of the included studies, synthesizing the studies, and ultimately writing the review. The subsequent section provides an extensive explanation of how these steps were carried out in this study.
2.1 Identify the purpose
Given the widespread adoption of ChatGPT by students and teachers for various educational purposes, often without a thorough understanding of responsible and effective use or a clear recognition of its potential impact on learning and teaching, the authors recognized the need for further exploration of ChatGPT's impact on education in this early stage. Therefore, they have chosen to conduct a systematic literature review of existing empirical studies that incorporate ChatGPT into educational settings. Despite the limited number of empirical studies due to the novelty of the topic, their goal is to gain a deeper understanding of this technology and proactively evaluate its potential benefits, limitations, challenges, and threats to education. This effort could help to understand initial reactions and attempts at incorporating ChatGPT into education and bring out insights and considerations that can inform the future development of education.
2.2 Draft the protocol
The next step is formulating the protocol. This protocol serves to outline the study process in a rigorous and transparent manner, mitigating researcher bias in study selection and data extraction [ 88 ]. The protocol will include the following steps: generating the research question, predefining a literature search strategy, identifying search locations, establishing selection criteria, assessing the studies, developing a data extraction strategy, and creating a timeline.
2.3 Apply practical screen
The screening step aims to accurately filter the articles resulting from the searching step and select the empirical studies that have incorporated ChatGPT into educational contexts, which will guide us in answering the research questions and achieving the objectives of this study. To ensure the rigorous execution of this step, our inclusion and exclusion criteria were determined based on the authors' experience and informed by previous successful systematic reviews [ 21 ]. Table 1 summarizes the inclusion and exclusion criteria for study selection.
2.4 Literature search
We conducted a thorough literature search to identify articles that explored, examined, and addressed the use of ChatGPT in Educational contexts. We utilized two research databases: Dimensions.ai, which provides access to a large number of research publications, and lens.org, which offers access to over 300 million articles, patents, and other research outputs from diverse sources. Additionally, we included three databases, Scopus, Web of Knowledge, and ERIC, which contain relevant research on the topic that addresses our research questions. To browse and identify relevant articles, we used the following search formula: ("ChatGPT" AND "Education"), which included the Boolean operator "AND" to get more specific results. The subject area in the Scopus and ERIC databases were narrowed to "ChatGPT" and "Education" keywords, and in the WoS database was limited to the "Education" category. The search was conducted between the 3rd and 10th of April 2023, which resulted in 276 articles from all selected databases (111 articles from Dimensions.ai, 65 from Scopus, 28 from Web of Science, 14 from ERIC, and 58 from Lens.org). These articles were imported into the Rayyan web-based system for analysis. The duplicates were identified automatically by the system. Subsequently, the first author manually reviewed the duplicated articles ensured that they had the same content, and then removed them, leaving us with 135 unique articles. Afterward, the titles, abstracts, and keywords of the first 40 manuscripts were scanned and reviewed by the first author and were discussed with the second and third authors to resolve any disagreements. Subsequently, the first author proceeded with the filtering process for all articles and carefully applied the inclusion and exclusion criteria as presented in Table 1 . Articles that met any one of the exclusion criteria were eliminated, resulting in 26 articles. Afterward, the authors met to carefully scan and discuss them. The authors agreed to eliminate any empirical studies solely focused on checking ChatGPT capabilities, as these studies do not guide us in addressing the research questions and achieving the study's objectives. This resulted in 14 articles eligible for analysis.
2.5 Quality appraisal
The examination and evaluation of the quality of the extracted articles is a vital step [ 9 ]. Therefore, the extracted articles were carefully evaluated for quality using Fink’s [ 24 ] standards, which emphasize the necessity for detailed descriptions of methodology, results, conclusions, strengths, and limitations. The process began with a thorough assessment of each study's design, data collection, and analysis methods to ensure their appropriateness and comprehensive execution. The clarity, consistency, and logical progression from data to results and conclusions were also critically examined. Potential biases and recognized limitations within the studies were also scrutinized. Ultimately, two articles were excluded for failing to meet Fink’s criteria, particularly in providing sufficient detail on methodology, results, conclusions, strengths, or limitations. The review process is illustrated in Fig. 1 .
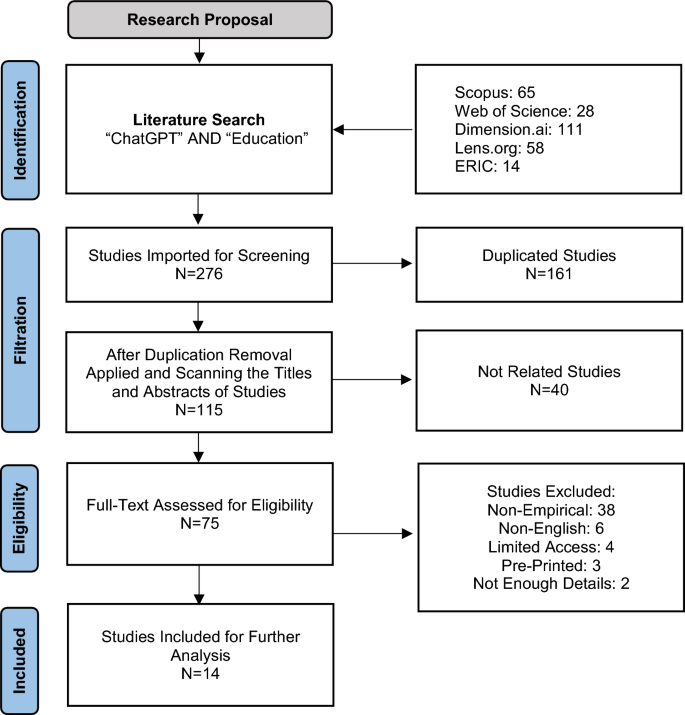
The study selection process
2.6 Data extraction
The next step is data extraction, the process of capturing the key information and categories from the included studies. To improve efficiency, reduce variation among authors, and minimize errors in data analysis, the coding categories were constructed using Creswell's [ 15 ] coding techniques for data extraction and interpretation. The coding process involves three sequential steps. The initial stage encompasses open coding , where the researcher examines the data, generates codes to describe and categorize it, and gains a deeper understanding without preconceived ideas. Following open coding is axial coding , where the interrelationships between codes from open coding are analyzed to establish more comprehensive categories or themes. The process concludes with selective coding , refining and integrating categories or themes to identify core concepts emerging from the data. The first coder performed the coding process, then engaged in discussions with the second and third authors to finalize the coding categories for the first five articles. The first coder then proceeded to code all studies and engaged again in discussions with the other authors to ensure the finalization of the coding process. After a comprehensive analysis and capturing of the key information from the included studies, the data extraction and interpretation process yielded several themes. These themes have been categorized and are presented in Table 2 . It is important to note that open coding results were removed from Table 2 for aesthetic reasons, as it included many generic aspects, such as words, short phrases, or sentences mentioned in the studies.
2.7 Synthesize studies
In this stage, we will gather, discuss, and analyze the key findings that emerged from the selected studies. The synthesis stage is considered a transition from an author-centric to a concept-centric focus, enabling us to map all the provided information to achieve the most effective evaluation of the data [ 87 ]. Initially, the authors extracted data that included general information about the selected studies, including the author(s)' names, study titles, years of publication, educational levels, research methodologies, sample sizes, participants, main aims or objectives, raw data sources, and analysis methods. Following that, all key information and significant results from the selected studies were compiled using Creswell’s [ 15 ] coding techniques for data extraction and interpretation to identify core concepts and themes emerging from the data, focusing on those that directly contributed to our research questions and objectives, such as the initial utilization of ChatGPT in learning and teaching, learners' and educators' familiarity with ChatGPT, and the main findings of each study. Finally, the data related to each selected study were extracted into an Excel spreadsheet for data processing. The Excel spreadsheet was reviewed by the authors, including a series of discussions to ensure the finalization of this process and prepare it for further analysis. Afterward, the final result being analyzed and presented in various types of charts and graphs. Table 4 presents the extracted data from the selected studies, with each study labeled with a capital 'S' followed by a number.
This section consists of two main parts. The first part provides a descriptive analysis of the data compiled from the reviewed studies. The second part presents the answers to the research questions and the main findings of these studies.
3.1 Part 1: descriptive analysis
This section will provide a descriptive analysis of the reviewed studies, including educational levels and fields, participants distribution, country contribution, research methodologies, study sample size, study population, publication year, list of journals, familiarity with ChatGPT, source of data, and the main aims and objectives of the studies. Table 4 presents a comprehensive overview of the extracted data from the selected studies.
3.1.1 The number of the reviewed studies and publication years
The total number of the reviewed studies was 14. All studies were empirical studies and published in different journals focusing on Education and Technology. One study was published in 2022 [S1], while the remaining were published in 2023 [S2]-[S14]. Table 3 illustrates the year of publication, the names of the journals, and the number of reviewed studies published in each journal for the studies reviewed.
3.1.2 Educational levels and fields
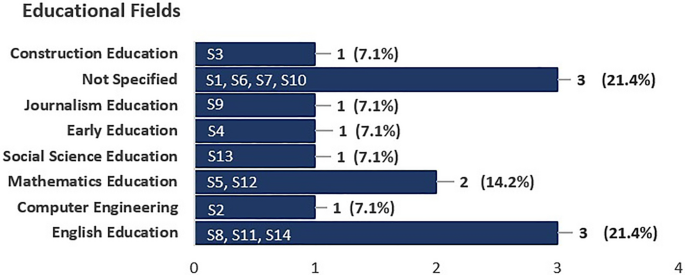
The majority of the reviewed studies, 11 studies, were conducted in higher education institutions [S1]-[S10] and [S13]. Two studies did not specify the educational level of the population [S12] and [S14], while one study focused on elementary education [S11]. However, the reviewed studies covered various fields of education. Three studies focused on Arts and Humanities Education [S8], [S11], and [S14], specifically English Education. Two studies focused on Engineering Education, with one in Computer Engineering [S2] and the other in Construction Education [S3]. Two studies focused on Mathematics Education [S5] and [S12]. One study focused on Social Science Education [S13]. One study focused on Early Education [S4]. One study focused on Journalism Education [S9]. Finally, three studies did not specify the field of education [S1], [S6], and [S7]. Figure 2 represents the educational levels in the reviewed studies, while Fig. 3 represents the context of the reviewed studies.

Educational levels in the reviewed studies
Context of the reviewed studies
3.1.3 Participants distribution and countries contribution
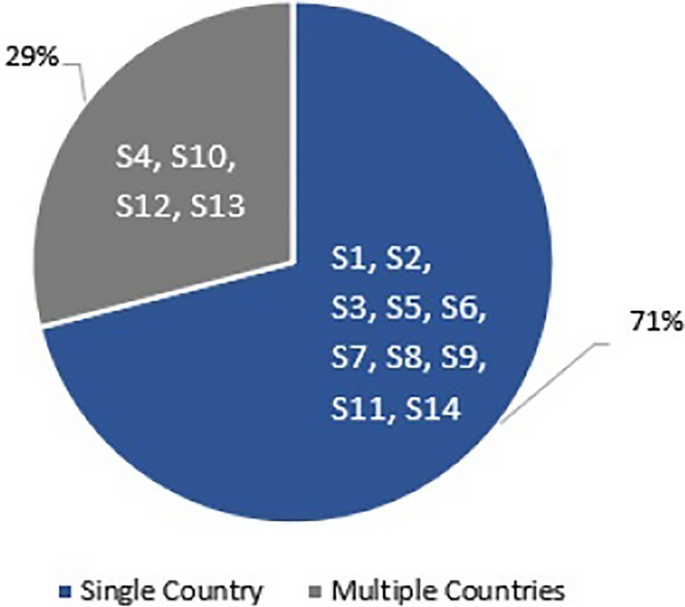
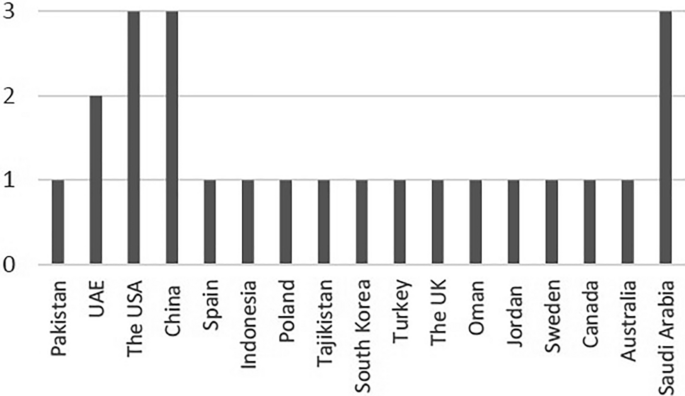
The reviewed studies have been conducted across different geographic regions, providing a diverse representation of the studies. The majority of the studies, 10 in total, [S1]-[S3], [S5]-[S9], [S11], and [S14], primarily focused on participants from single countries such as Pakistan, the United Arab Emirates, China, Indonesia, Poland, Saudi Arabia, South Korea, Spain, Tajikistan, and the United States. In contrast, four studies, [S4], [S10], [S12], and [S13], involved participants from multiple countries, including China and the United States [S4], China, the United Kingdom, and the United States [S10], the United Arab Emirates, Oman, Saudi Arabia, and Jordan [S12], Turkey, Sweden, Canada, and Australia [ 13 ]. Figures 4 and 5 illustrate the distribution of participants, whether from single or multiple countries, and the contribution of each country in the reviewed studies, respectively.
The reviewed studies conducted in single or multiple countries
The Contribution of each country in the studies
3.1.4 Study population and sample size
Four study populations were included: university students, university teachers, university teachers and students, and elementary school teachers. Six studies involved university students [S2], [S3], [S5] and [S6]-[S8]. Three studies focused on university teachers [S1], [S4], and [S6], while one study specifically targeted elementary school teachers [S11]. Additionally, four studies included both university teachers and students [S10] and [ 12 , 13 , 14 ], and among them, study [S13] specifically included postgraduate students. In terms of the sample size of the reviewed studies, nine studies included a small sample size of less than 50 participants [S1], [S3], [S6], [S8], and [S10]-[S13]. Three studies had 50–100 participants [S2], [S9], and [S14]. Only one study had more than 100 participants [S7]. It is worth mentioning that study [S4] adopted a mixed methods approach, including 10 participants for qualitative analysis and 110 participants for quantitative analysis.
3.1.5 Participants’ familiarity with using ChatGPT
The reviewed studies recruited a diverse range of participants with varying levels of familiarity with ChatGPT. Five studies [S2], [S4], [S6], [S8], and [S12] involved participants already familiar with ChatGPT, while eight studies [S1], [S3], [S5], [S7], [S9], [S10], [S13] and [S14] included individuals with differing levels of familiarity. Notably, one study [S11] had participants who were entirely unfamiliar with ChatGPT. It is important to note that four studies [S3], [S5], [S9], and [S11] provided training or guidance to their participants before conducting their studies, while ten studies [S1], [S2], [S4], [S6]-[S8], [S10], and [S12]-[S14] did not provide training due to the participants' existing familiarity with ChatGPT.
3.1.6 Research methodology approaches and source(S) of data
The reviewed studies adopted various research methodology approaches. Seven studies adopted qualitative research methodology [S1], [S4], [S6], [S8], [S10], [S11], and [S12], while three studies adopted quantitative research methodology [S3], [S7], and [S14], and four studies employed mixed-methods, which involved a combination of both the strengths of qualitative and quantitative methods [S2], [S5], [S9], and [S13].
In terms of the source(s) of data, the reviewed studies obtained their data from various sources, such as interviews, questionnaires, and pre-and post-tests. Six studies relied on interviews as their primary source of data collection [S1], [S4], [S6], [S10], [S11], and [S12], four studies relied on questionnaires [S2], [S7], [S13], and [S14], two studies combined the use of pre-and post-tests and questionnaires for data collection [S3] and [S9], while two studies combined the use of questionnaires and interviews to obtain the data [S5] and [S8]. It is important to note that six of the reviewed studies were quasi-experimental [S3], [S5], [S8], [S9], [S12], and [S14], while the remaining ones were experimental studies [S1], [S2], [S4], [S6], [S7], [S10], [S11], and [S13]. Figures 6 and 7 illustrate the research methodologies and the source (s) of data used in the reviewed studies, respectively.
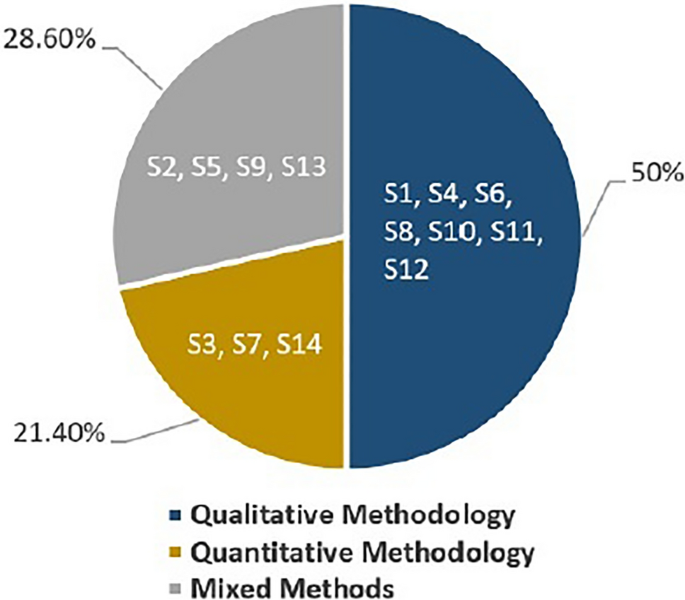
Research methodologies in the reviewed studies
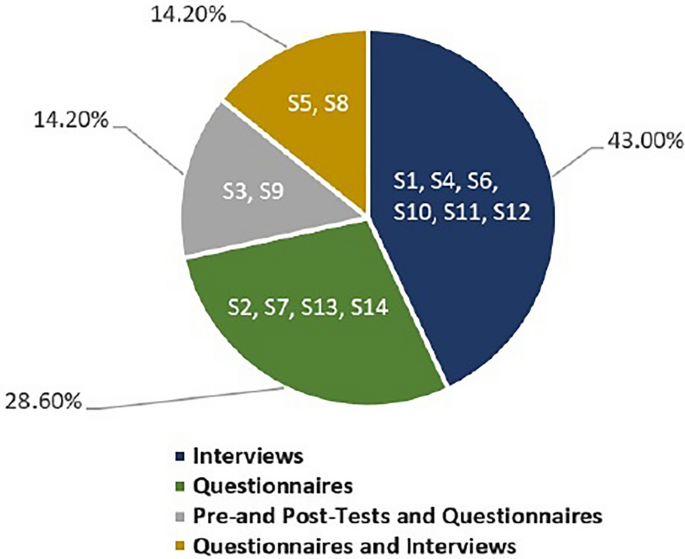
Source of data in the reviewed studies
3.1.7 The aim and objectives of the studies
The reviewed studies encompassed a diverse set of aims, with several of them incorporating multiple primary objectives. Six studies [S3], [S6], [S7], [S8], [S11], and [S12] examined the integration of ChatGPT in educational contexts, and four studies [S4], [S5], [S13], and [S14] investigated the various implications of its use in education, while three studies [S2], [S9], and [S10] aimed to explore both its integration and implications in education. Additionally, seven studies explicitly explored attitudes and perceptions of students [S2] and [S3], educators [S1] and [S6], or both [S10], [S12], and [S13] regarding the utilization of ChatGPT in educational settings.
3.2 Part 2: research questions and main findings of the reviewed studies
This part will present the answers to the research questions and the main findings of the reviewed studies, classified into two main categories (learning and teaching) according to AI Education classification by [ 36 ]. Figure 8 summarizes the main findings of the reviewed studies in a visually informative diagram. Table 4 provides a detailed list of the key information extracted from the selected studies that led to generating these themes.
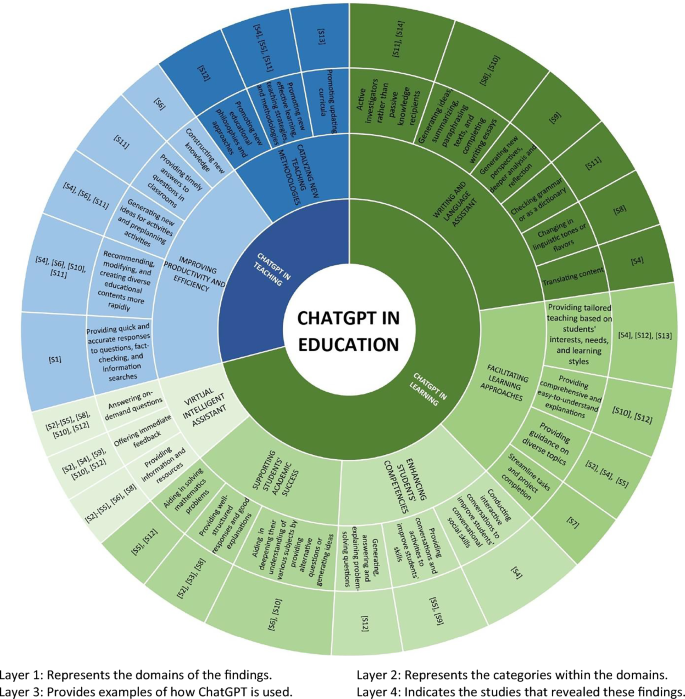
The main findings in the reviewed studies
4 Students' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in learning and main findings from students' perspective
4.1 virtual intelligent assistant.
Nine studies demonstrated that ChatGPT has been utilized by students as an intelligent assistant to enhance and support their learning. Students employed it for various purposes, such as answering on-demand questions [S2]-[S5], [S8], [S10], and [S12], providing valuable information and learning resources [S2]-[S5], [S6], and [S8], as well as receiving immediate feedback [S2], [S4], [S9], [S10], and [S12]. In this regard, students generally were confident in the accuracy of ChatGPT's responses, considering them relevant, reliable, and detailed [S3], [S4], [S5], and [S8]. However, some students indicated the need for improvement, as they found that answers are not always accurate [S2], and that misleading information may have been provided or that it may not always align with their expectations [S6] and [S10]. It was also observed by the students that the accuracy of ChatGPT is dependent on several factors, including the quality and specificity of the user's input, the complexity of the question or topic, and the scope and relevance of its training data [S12]. Many students felt that ChatGPT's answers were not always accurate and most of them believed that it requires good background knowledge to work with.
4.2 Writing and language proficiency assistant
Six of the reviewed studies highlighted that ChatGPT has been utilized by students as a valuable assistant tool to improve their academic writing skills and language proficiency. Among these studies, three mainly focused on English education, demonstrating that students showed sufficient mastery in using ChatGPT for generating ideas, summarizing, paraphrasing texts, and completing writing essays [S8], [S11], and [S14]. Furthermore, ChatGPT helped them in writing by making students active investigators rather than passive knowledge recipients and facilitated the development of their writing skills [S11] and [S14]. Similarly, ChatGPT allowed students to generate unique ideas and perspectives, leading to deeper analysis and reflection on their journalism writing [S9]. In terms of language proficiency, ChatGPT allowed participants to translate content into their home languages, making it more accessible and relevant to their context [S4]. It also enabled them to request changes in linguistic tones or flavors [S8]. Moreover, participants used it to check grammar or as a dictionary [S11].
4.3 Valuable resource for learning approaches
Five studies demonstrated that students used ChatGPT as a valuable complementary resource for self-directed learning. It provided learning resources and guidance on diverse educational topics and created a supportive home learning environment [S2] and [S4]. Moreover, it offered step-by-step guidance to grasp concepts at their own pace and enhance their understanding [S5], streamlined task and project completion carried out independently [S7], provided comprehensive and easy-to-understand explanations on various subjects [S10], and assisted in studying geometry operations, thereby empowering them to explore geometry operations at their own pace [S12]. Three studies showed that students used ChatGPT as a valuable learning resource for personalized learning. It delivered age-appropriate conversations and tailored teaching based on a child's interests [S4], acted as a personalized learning assistant, adapted to their needs and pace, which assisted them in understanding mathematical concepts [S12], and enabled personalized learning experiences in social sciences by adapting to students' needs and learning styles [S13]. On the other hand, it is important to note that, according to one study [S5], students suggested that using ChatGPT may negatively affect collaborative learning competencies between students.
4.4 Enhancing students' competencies
Six of the reviewed studies have shown that ChatGPT is a valuable tool for improving a wide range of skills among students. Two studies have provided evidence that ChatGPT led to improvements in students' critical thinking, reasoning skills, and hazard recognition competencies through engaging them in interactive conversations or activities and providing responses related to their disciplines in journalism [S5] and construction education [S9]. Furthermore, two studies focused on mathematical education have shown the positive impact of ChatGPT on students' problem-solving abilities in unraveling problem-solving questions [S12] and enhancing the students' understanding of the problem-solving process [S5]. Lastly, one study indicated that ChatGPT effectively contributed to the enhancement of conversational social skills [S4].
4.5 Supporting students' academic success
Seven of the reviewed studies highlighted that students found ChatGPT to be beneficial for learning as it enhanced learning efficiency and improved the learning experience. It has been observed to improve students' efficiency in computer engineering studies by providing well-structured responses and good explanations [S2]. Additionally, students found it extremely useful for hazard reporting [S3], and it also enhanced their efficiency in solving mathematics problems and capabilities [S5] and [S12]. Furthermore, by finding information, generating ideas, translating texts, and providing alternative questions, ChatGPT aided students in deepening their understanding of various subjects [S6]. It contributed to an increase in students' overall productivity [S7] and improved efficiency in composing written tasks [S8]. Regarding learning experiences, ChatGPT was instrumental in assisting students in identifying hazards that they might have otherwise overlooked [S3]. It also improved students' learning experiences in solving mathematics problems and developing abilities [S5] and [S12]. Moreover, it increased students' successful completion of important tasks in their studies [S7], particularly those involving average difficulty writing tasks [S8]. Additionally, ChatGPT increased the chances of educational success by providing students with baseline knowledge on various topics [S10].
5 Teachers' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in teaching and main findings from teachers' perspective
5.1 valuable resource for teaching.
The reviewed studies showed that teachers have employed ChatGPT to recommend, modify, and generate diverse, creative, organized, and engaging educational contents, teaching materials, and testing resources more rapidly [S4], [S6], [S10] and [S11]. Additionally, teachers experienced increased productivity as ChatGPT facilitated quick and accurate responses to questions, fact-checking, and information searches [S1]. It also proved valuable in constructing new knowledge [S6] and providing timely answers to students' questions in classrooms [S11]. Moreover, ChatGPT enhanced teachers' efficiency by generating new ideas for activities and preplanning activities for their students [S4] and [S6], including interactive language game partners [S11].
5.2 Improving productivity and efficiency
The reviewed studies showed that participants' productivity and work efficiency have been significantly enhanced by using ChatGPT as it enabled them to allocate more time to other tasks and reduce their overall workloads [S6], [S10], [S11], [S13], and [S14]. However, three studies [S1], [S4], and [S11], indicated a negative perception and attitude among teachers toward using ChatGPT. This negativity stemmed from a lack of necessary skills to use it effectively [S1], a limited familiarity with it [S4], and occasional inaccuracies in the content provided by it [S10].
5.3 Catalyzing new teaching methodologies
Five of the reviewed studies highlighted that educators found the necessity of redefining their teaching profession with the assistance of ChatGPT [S11], developing new effective learning strategies [S4], and adapting teaching strategies and methodologies to ensure the development of essential skills for future engineers [S5]. They also emphasized the importance of adopting new educational philosophies and approaches that can evolve with the introduction of ChatGPT into the classroom [S12]. Furthermore, updating curricula to focus on improving human-specific features, such as emotional intelligence, creativity, and philosophical perspectives [S13], was found to be essential.
5.4 Effective utilization of CHATGPT in teaching
According to the reviewed studies, effective utilization of ChatGPT in education requires providing teachers with well-structured training, support, and adequate background on how to use ChatGPT responsibly [S1], [S3], [S11], and [S12]. Establishing clear rules and regulations regarding its usage is essential to ensure it positively impacts the teaching and learning processes, including students' skills [S1], [S4], [S5], [S8], [S9], and [S11]-[S14]. Moreover, conducting further research and engaging in discussions with policymakers and stakeholders is indeed crucial for the successful integration of ChatGPT in education and to maximize the benefits for both educators and students [S1], [S6]-[S10], and [S12]-[S14].
6 Discussion
The purpose of this review is to conduct a systematic review of empirical studies that have explored the utilization of ChatGPT, one of today’s most advanced LLM-based chatbots, in education. The findings of the reviewed studies showed several ways of ChatGPT utilization in different learning and teaching practices as well as it provided insights and considerations that can facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. The results of the reviewed studies came from diverse fields of education, which helped us avoid a biased review that is limited to a specific field. Similarly, the reviewed studies have been conducted across different geographic regions. This kind of variety in geographic representation enriched the findings of this review.
In response to RQ1 , "What are students' and teachers' initial attempts at utilizing ChatGPT in education?", the findings from this review provide comprehensive insights. Chatbots, including ChatGPT, play a crucial role in supporting student learning, enhancing their learning experiences, and facilitating diverse learning approaches [ 42 , 43 ]. This review found that this tool, ChatGPT, has been instrumental in enhancing students' learning experiences by serving as a virtual intelligent assistant, providing immediate feedback, on-demand answers, and engaging in educational conversations. Additionally, students have benefited from ChatGPT’s ability to generate ideas, compose essays, and perform tasks like summarizing, translating, paraphrasing texts, or checking grammar, thereby enhancing their writing and language competencies. Furthermore, students have turned to ChatGPT for assistance in understanding concepts and homework, providing structured learning plans, and clarifying assignments and tasks, which fosters a supportive home learning environment, allowing them to take responsibility for their own learning and cultivate the skills and approaches essential for supportive home learning environment [ 26 , 27 , 28 ]. This finding aligns with the study of Saqr et al. [ 68 , 69 ] who highlighted that, when students actively engage in their own learning process, it yields additional advantages, such as heightened motivation, enhanced achievement, and the cultivation of enthusiasm, turning them into advocates for their own learning.
Moreover, students have utilized ChatGPT for tailored teaching and step-by-step guidance on diverse educational topics, streamlining task and project completion, and generating and recommending educational content. This personalization enhances the learning environment, leading to increased academic success. This finding aligns with other recent studies [ 26 , 27 , 28 , 60 , 66 ] which revealed that ChatGPT has the potential to offer personalized learning experiences and support an effective learning process by providing students with customized feedback and explanations tailored to their needs and abilities. Ultimately, fostering students' performance, engagement, and motivation, leading to increase students' academic success [ 14 , 44 , 58 ]. This ultimate outcome is in line with the findings of Saqr et al. [ 68 , 69 ], which emphasized that learning strategies are important catalysts of students' learning, as students who utilize effective learning strategies are more likely to have better academic achievement.
Teachers, too, have capitalized on ChatGPT's capabilities to enhance productivity and efficiency, using it for creating lesson plans, generating quizzes, providing additional resources, generating and preplanning new ideas for activities, and aiding in answering students’ questions. This adoption of technology introduces new opportunities to support teaching and learning practices, enhancing teacher productivity. This finding aligns with those of Day [ 17 ], De Castro [ 18 ], and Su and Yang [ 74 ] as well as with those of Valtonen et al. [ 82 ], who revealed that emerging technological advancements have opened up novel opportunities and means to support teaching and learning practices, and enhance teachers’ productivity.
In response to RQ2 , "What are the main findings derived from empirical studies that have incorporated ChatGPT into learning and teaching?", the findings from this review provide profound insights and raise significant concerns. Starting with the insights, chatbots, including ChatGPT, have demonstrated the potential to reshape and revolutionize education, creating new, novel opportunities for enhancing the learning process and outcomes [ 83 ], facilitating different learning approaches, and offering a range of pedagogical benefits [ 19 , 43 , 72 ]. In this context, this review found that ChatGPT could open avenues for educators to adopt or develop new effective learning and teaching strategies that can evolve with the introduction of ChatGPT into the classroom. Nonetheless, there is an evident lack of research understanding regarding the potential impact of generative machine learning models within diverse educational settings [ 83 ]. This necessitates teachers to attain a high level of proficiency in incorporating chatbots, such as ChatGPT, into their classrooms to create inventive, well-structured, and captivating learning strategies. In the same vein, the review also found that teachers without the requisite skills to utilize ChatGPT realized that it did not contribute positively to their work and could potentially have adverse effects [ 37 ]. This concern could lead to inequity of access to the benefits of chatbots, including ChatGPT, as individuals who lack the necessary expertise may not be able to harness their full potential, resulting in disparities in educational outcomes and opportunities. Therefore, immediate action is needed to address these potential issues. A potential solution is offering training, support, and competency development for teachers to ensure that all of them can leverage chatbots, including ChatGPT, effectively and equitably in their educational practices [ 5 , 28 , 80 ], which could enhance accessibility and inclusivity, and potentially result in innovative outcomes [ 82 , 83 ].
Additionally, chatbots, including ChatGPT, have the potential to significantly impact students' thinking abilities, including retention, reasoning, analysis skills [ 19 , 45 ], and foster innovation and creativity capabilities [ 83 ]. This review found that ChatGPT could contribute to improving a wide range of skills among students. However, it found that frequent use of ChatGPT may result in a decrease in innovative capacities, collaborative skills and cognitive capacities, and students' motivation to attend classes, as well as could lead to reduced higher-order thinking skills among students [ 22 , 29 ]. Therefore, immediate action is needed to carefully examine the long-term impact of chatbots such as ChatGPT, on learning outcomes as well as to explore its incorporation into educational settings as a supportive tool without compromising students' cognitive development and critical thinking abilities. In the same vein, the review also found that it is challenging to draw a consistent conclusion regarding the potential of ChatGPT to aid self-directed learning approach. This finding aligns with the recent study of Baskara [ 8 ]. Therefore, further research is needed to explore the potential of ChatGPT for self-directed learning. One potential solution involves utilizing learning analytics as a novel approach to examine various aspects of students' learning and support them in their individual endeavors [ 32 ]. This approach can bridge this gap by facilitating an in-depth analysis of how learners engage with ChatGPT, identifying trends in self-directed learning behavior, and assessing its influence on their outcomes.
Turning to the significant concerns, on the other hand, a fundamental challenge with LLM-based chatbots, including ChatGPT, is the accuracy and quality of the provided information and responses, as they provide false information as truth—a phenomenon often referred to as "hallucination" [ 3 , 49 ]. In this context, this review found that the provided information was not entirely satisfactory. Consequently, the utilization of chatbots presents potential concerns, such as generating and providing inaccurate or misleading information, especially for students who utilize it to support their learning. This finding aligns with other findings [ 6 , 30 , 35 , 40 ] which revealed that incorporating chatbots such as ChatGPT, into education presents challenges related to its accuracy and reliability due to its training on a large corpus of data, which may contain inaccuracies and the way users formulate or ask ChatGPT. Therefore, immediate action is needed to address these potential issues. One possible solution is to equip students with the necessary skills and competencies, which include a background understanding of how to use it effectively and the ability to assess and evaluate the information it generates, as the accuracy and the quality of the provided information depend on the input, its complexity, the topic, and the relevance of its training data [ 28 , 49 , 86 ]. However, it's also essential to examine how learners can be educated about how these models operate, the data used in their training, and how to recognize their limitations, challenges, and issues [ 79 ].
Furthermore, chatbots present a substantial challenge concerning maintaining academic integrity [ 20 , 56 ] and copyright violations [ 83 ], which are significant concerns in education. The review found that the potential misuse of ChatGPT might foster cheating, facilitate plagiarism, and threaten academic integrity. This issue is also affirmed by the research conducted by Basic et al. [ 7 ], who presented evidence that students who utilized ChatGPT in their writing assignments had more plagiarism cases than those who did not. These findings align with the conclusions drawn by Cotton et al. [ 13 ], Hisan and Amri [ 33 ] and Sullivan et al. [ 75 ], who revealed that the integration of chatbots such as ChatGPT into education poses a significant challenge to the preservation of academic integrity. Moreover, chatbots, including ChatGPT, have increased the difficulty in identifying plagiarism [ 47 , 67 , 76 ]. The findings from previous studies [ 1 , 84 ] indicate that AI-generated text often went undetected by plagiarism software, such as Turnitin. However, Turnitin and other similar plagiarism detection tools, such as ZeroGPT, GPTZero, and Copyleaks, have since evolved, incorporating enhanced techniques to detect AI-generated text, despite the possibility of false positives, as noted in different studies that have found these tools still not yet fully ready to accurately and reliably identify AI-generated text [ 10 , 51 ], and new novel detection methods may need to be created and implemented for AI-generated text detection [ 4 ]. This potential issue could lead to another concern, which is the difficulty of accurately evaluating student performance when they utilize chatbots such as ChatGPT assistance in their assignments. Consequently, the most LLM-driven chatbots present a substantial challenge to traditional assessments [ 64 ]. The findings from previous studies indicate the importance of rethinking, improving, and redesigning innovative assessment methods in the era of chatbots [ 14 , 20 , 64 , 75 ]. These methods should prioritize the process of evaluating students' ability to apply knowledge to complex cases and demonstrate comprehension, rather than solely focusing on the final product for assessment. Therefore, immediate action is needed to address these potential issues. One possible solution would be the development of clear guidelines, regulatory policies, and pedagogical guidance. These measures would help regulate the proper and ethical utilization of chatbots, such as ChatGPT, and must be established before their introduction to students [ 35 , 38 , 39 , 41 , 89 ].
In summary, our review has delved into the utilization of ChatGPT, a prominent example of chatbots, in education, addressing the question of how ChatGPT has been utilized in education. However, there remain significant gaps, which necessitate further research to shed light on this area.
7 Conclusions
This systematic review has shed light on the varied initial attempts at incorporating ChatGPT into education by both learners and educators, while also offering insights and considerations that can facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. From the analysis of 14 selected studies, the review revealed the dual-edged impact of ChatGPT in educational settings. On the positive side, ChatGPT significantly aided the learning process in various ways. Learners have used it as a virtual intelligent assistant, benefiting from its ability to provide immediate feedback, on-demand answers, and easy access to educational resources. Additionally, it was clear that learners have used it to enhance their writing and language skills, engaging in practices such as generating ideas, composing essays, and performing tasks like summarizing, translating, paraphrasing texts, or checking grammar. Importantly, other learners have utilized it in supporting and facilitating their directed and personalized learning on a broad range of educational topics, assisting in understanding concepts and homework, providing structured learning plans, and clarifying assignments and tasks. Educators, on the other hand, found ChatGPT beneficial for enhancing productivity and efficiency. They used it for creating lesson plans, generating quizzes, providing additional resources, and answers learners' questions, which saved time and allowed for more dynamic and engaging teaching strategies and methodologies.
However, the review also pointed out negative impacts. The results revealed that overuse of ChatGPT could decrease innovative capacities and collaborative learning among learners. Specifically, relying too much on ChatGPT for quick answers can inhibit learners' critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Learners might not engage deeply with the material or consider multiple solutions to a problem. This tendency was particularly evident in group projects, where learners preferred consulting ChatGPT individually for solutions over brainstorming and collaborating with peers, which negatively affected their teamwork abilities. On a broader level, integrating ChatGPT into education has also raised several concerns, including the potential for providing inaccurate or misleading information, issues of inequity in access, challenges related to academic integrity, and the possibility of misusing the technology.
Accordingly, this review emphasizes the urgency of developing clear rules, policies, and regulations to ensure ChatGPT's effective and responsible use in educational settings, alongside other chatbots, by both learners and educators. This requires providing well-structured training to educate them on responsible usage and understanding its limitations, along with offering sufficient background information. Moreover, it highlights the importance of rethinking, improving, and redesigning innovative teaching and assessment methods in the era of ChatGPT. Furthermore, conducting further research and engaging in discussions with policymakers and stakeholders are essential steps to maximize the benefits for both educators and learners and ensure academic integrity.
It is important to acknowledge that this review has certain limitations. Firstly, the limited inclusion of reviewed studies can be attributed to several reasons, including the novelty of the technology, as new technologies often face initial skepticism and cautious adoption; the lack of clear guidelines or best practices for leveraging this technology for educational purposes; and institutional or governmental policies affecting the utilization of this technology in educational contexts. These factors, in turn, have affected the number of studies available for review. Secondly, the utilization of the original version of ChatGPT, based on GPT-3 or GPT-3.5, implies that new studies utilizing the updated version, GPT-4 may lead to different findings. Therefore, conducting follow-up systematic reviews is essential once more empirical studies on ChatGPT are published. Additionally, long-term studies are necessary to thoroughly examine and assess the impact of ChatGPT on various educational practices.
Despite these limitations, this systematic review has highlighted the transformative potential of ChatGPT in education, revealing its diverse utilization by learners and educators alike and summarized the benefits of incorporating it into education, as well as the forefront critical concerns and challenges that must be addressed to facilitate its effective and responsible use in future educational contexts. This review could serve as an insightful resource for practitioners who seek to integrate ChatGPT into education and stimulate further research in the field.
Data availability
The data supporting our findings are available upon request.
Abbreviations
- Artificial intelligence
AI in education
Large language model
Artificial neural networks
Chat Generative Pre-Trained Transformer
Recurrent neural networks
Long short-term memory
Reinforcement learning from human feedback
Natural language processing
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
AlAfnan MA, Dishari S, Jovic M, Lomidze K. ChatGPT as an educational tool: opportunities, challenges, and recommendations for communication, business writing, and composition courses. J Artif Intell Technol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37965/jait.2023.0184 .
Article Google Scholar
Ali JKM, Shamsan MAA, Hezam TA, Mohammed AAQ. Impact of ChatGPT on learning motivation. J Engl Stud Arabia Felix. 2023;2(1):41–9. https://doi.org/10.56540/jesaf.v2i1.51 .
Alkaissi H, McFarlane SI. Artificial hallucinations in ChatGPT: implications in scientific writing. Cureus. 2023. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.35179 .
Anderson N, Belavý DL, Perle SM, Hendricks S, Hespanhol L, Verhagen E, Memon AR. AI did not write this manuscript, or did it? Can we trick the AI text detector into generated texts? The potential future of ChatGPT and AI in sports & exercise medicine manuscript generation. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2023;9(1): e001568. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjsem-2023-001568 .
Ausat AMA, Massang B, Efendi M, Nofirman N, Riady Y. Can chat GPT replace the role of the teacher in the classroom: a fundamental analysis. J Educ. 2023;5(4):16100–6.
Google Scholar
Baidoo-Anu D, Ansah L. Education in the Era of generative artificial intelligence (AI): understanding the potential benefits of ChatGPT in promoting teaching and learning. Soc Sci Res Netw. 2023. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4337484 .
Basic Z, Banovac A, Kruzic I, Jerkovic I. Better by you, better than me, chatgpt3 as writing assistance in students essays. 2023. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.04536 .
Baskara FR. The promises and pitfalls of using chat GPT for self-determined learning in higher education: an argumentative review. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Ilmu Keguruan IAIM Sinjai. 2023;2:95–101. https://doi.org/10.47435/sentikjar.v2i0.1825 .
Behera RK, Bala PK, Dhir A. The emerging role of cognitive computing in healthcare: a systematic literature review. Int J Med Inform. 2019;129:154–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2019.04.024 .
Chaka C. Detecting AI content in responses generated by ChatGPT, YouChat, and Chatsonic: the case of five AI content detection tools. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.2.12 .
Chiu TKF, Xia Q, Zhou X, Chai CS, Cheng M. Systematic literature review on opportunities, challenges, and future research recommendations of artificial intelligence in education. Comput Educ Artif Intell. 2023;4:100118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2022.100118 .
Choi EPH, Lee JJ, Ho M, Kwok JYY, Lok KYW. Chatting or cheating? The impacts of ChatGPT and other artificial intelligence language models on nurse education. Nurse Educ Today. 2023;125:105796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2023.105796 .
Cotton D, Cotton PA, Shipway JR. Chatting and cheating: ensuring academic integrity in the era of ChatGPT. Innov Educ Teach Int. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2190148 .
Crawford J, Cowling M, Allen K. Leadership is needed for ethical ChatGPT: Character, assessment, and learning using artificial intelligence (AI). J Univ Teach Learn Pract. 2023. https://doi.org/10.53761/1.20.3.02 .
Creswell JW. Educational research: planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative and qualitative research [Ebook]. 4th ed. London: Pearson Education; 2015.
Curry D. ChatGPT Revenue and Usage Statistics (2023)—Business of Apps. 2023. https://www.businessofapps.com/data/chatgpt-statistics/
Day T. A preliminary investigation of fake peer-reviewed citations and references generated by ChatGPT. Prof Geogr. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/00330124.2023.2190373 .
De Castro CA. A Discussion about the Impact of ChatGPT in education: benefits and concerns. J Bus Theor Pract. 2023;11(2):p28. https://doi.org/10.22158/jbtp.v11n2p28 .
Deng X, Yu Z. A meta-analysis and systematic review of the effect of Chatbot technology use in sustainable education. Sustainability. 2023;15(4):2940. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15042940 .
Eke DO. ChatGPT and the rise of generative AI: threat to academic integrity? J Responsib Technol. 2023;13:100060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrt.2023.100060 .
Elmoazen R, Saqr M, Tedre M, Hirsto L. A systematic literature review of empirical research on epistemic network analysis in education. IEEE Access. 2022;10:17330–48. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3149812 .
Farrokhnia M, Banihashem SK, Noroozi O, Wals AEJ. A SWOT analysis of ChatGPT: implications for educational practice and research. Innov Educ Teach Int. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2195846 .
Fergus S, Botha M, Ostovar M. Evaluating academic answers generated using ChatGPT. J Chem Educ. 2023;100(4):1672–5. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00087 .
Fink A. Conducting research literature reviews: from the Internet to Paper. Incorporated: SAGE Publications; 2010.
Firaina R, Sulisworo D. Exploring the usage of ChatGPT in higher education: frequency and impact on productivity. Buletin Edukasi Indonesia (BEI). 2023;2(01):39–46. https://doi.org/10.56741/bei.v2i01.310 .
Firat, M. (2023). How chat GPT can transform autodidactic experiences and open education. Department of Distance Education, Open Education Faculty, Anadolu Unive . https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8707-5918
Firat M. What ChatGPT means for universities: perceptions of scholars and students. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.22 .
Fuchs K. Exploring the opportunities and challenges of NLP models in higher education: is Chat GPT a blessing or a curse? Front Educ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2023.1166682 .
García-Peñalvo FJ. La percepción de la inteligencia artificial en contextos educativos tras el lanzamiento de ChatGPT: disrupción o pánico. Educ Knowl Soc. 2023;24: e31279. https://doi.org/10.14201/eks.31279 .
Gilson A, Safranek CW, Huang T, Socrates V, Chi L, Taylor A, Chartash D. How does ChatGPT perform on the United States medical Licensing examination? The implications of large language models for medical education and knowledge assessment. JMIR Med Educ. 2023;9: e45312. https://doi.org/10.2196/45312 .
Hashana AJ, Brundha P, Ayoobkhan MUA, Fazila S. Deep Learning in ChatGPT—A Survey. In 2023 7th international conference on trends in electronics and informatics (ICOEI) . 2023. (pp. 1001–1005). IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/icoei56765.2023.10125852
Hirsto L, Saqr M, López-Pernas S, Valtonen T. (2022). A systematic narrative review of learning analytics research in K-12 and schools. Proceedings . https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-3383/FLAIEC22_paper_9536.pdf
Hisan UK, Amri MM. ChatGPT and medical education: a double-edged sword. J Pedag Educ Sci. 2023;2(01):71–89. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.2.31280.23043/1 .
Hopkins AM, Logan JM, Kichenadasse G, Sorich MJ. Artificial intelligence chatbots will revolutionize how cancer patients access information: ChatGPT represents a paradigm-shift. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1093/jncics/pkad010 .
Househ M, AlSaad R, Alhuwail D, Ahmed A, Healy MG, Latifi S, Sheikh J. Large Language models in medical education: opportunities, challenges, and future directions. JMIR Med Educ. 2023;9: e48291. https://doi.org/10.2196/48291 .
Ilkka T. The impact of artificial intelligence on learning, teaching, and education. Minist de Educ. 2018. https://doi.org/10.2760/12297 .
Iqbal N, Ahmed H, Azhar KA. Exploring teachers’ attitudes towards using CHATGPT. Globa J Manag Adm Sci. 2022;3(4):97–111. https://doi.org/10.46568/gjmas.v3i4.163 .
Irfan M, Murray L, Ali S. Integration of Artificial intelligence in academia: a case study of critical teaching and learning in Higher education. Globa Soc Sci Rev. 2023;8(1):352–64. https://doi.org/10.31703/gssr.2023(viii-i).32 .
Jeon JH, Lee S. Large language models in education: a focus on the complementary relationship between human teachers and ChatGPT. Educ Inf Technol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11834-1 .
Khan RA, Jawaid M, Khan AR, Sajjad M. ChatGPT—Reshaping medical education and clinical management. Pak J Med Sci. 2023. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.39.2.7653 .
King MR. A conversation on artificial intelligence, Chatbots, and plagiarism in higher education. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2023;16(1):1–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12195-022-00754-8 .
Kooli C. Chatbots in education and research: a critical examination of ethical implications and solutions. Sustainability. 2023;15(7):5614. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075614 .
Kuhail MA, Alturki N, Alramlawi S, Alhejori K. Interacting with educational chatbots: a systematic review. Educ Inf Technol. 2022;28(1):973–1018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11177-3 .
Lee H. The rise of ChatGPT: exploring its potential in medical education. Anat Sci Educ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.2270 .
Li L, Subbareddy R, Raghavendra CG. AI intelligence Chatbot to improve students learning in the higher education platform. J Interconnect Netw. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0219265921430325 .
Limna P. A Review of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Education during the Digital Era. 2022. https://ssrn.com/abstract=4160798
Lo CK. What is the impact of ChatGPT on education? A rapid review of the literature. Educ Sci. 2023;13(4):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13040410 .
Luo W, He H, Liu J, Berson IR, Berson MJ, Zhou Y, Li H. Aladdin’s genie or pandora’s box For early childhood education? Experts chat on the roles, challenges, and developments of ChatGPT. Early Educ Dev. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409289.2023.2214181 .
Meyer JG, Urbanowicz RJ, Martin P, O’Connor K, Li R, Peng P, Moore JH. ChatGPT and large language models in academia: opportunities and challenges. Biodata Min. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13040-023-00339-9 .
Mhlanga D. Open AI in education, the responsible and ethical use of ChatGPT towards lifelong learning. Soc Sci Res Netw. 2023. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4354422 .
Neumann, M., Rauschenberger, M., & Schön, E. M. (2023). “We Need To Talk About ChatGPT”: The Future of AI and Higher Education. https://doi.org/10.1109/seeng59157.2023.00010
Nolan B. Here are the schools and colleges that have banned the use of ChatGPT over plagiarism and misinformation fears. Business Insider . 2023. https://www.businessinsider.com
O’Leary DE. An analysis of three chatbots: BlenderBot, ChatGPT and LaMDA. Int J Intell Syst Account, Financ Manag. 2023;30(1):41–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/isaf.1531 .
Okoli C. A guide to conducting a standalone systematic literature review. Commun Assoc Inf Syst. 2015. https://doi.org/10.17705/1cais.03743 .
OpenAI. (2023). https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt
Perkins M. Academic integrity considerations of AI large language models in the post-pandemic era: ChatGPT and beyond. J Univ Teach Learn Pract. 2023. https://doi.org/10.53761/1.20.02.07 .
Plevris V, Papazafeiropoulos G, Rios AJ. Chatbots put to the test in math and logic problems: A preliminary comparison and assessment of ChatGPT-3.5, ChatGPT-4, and Google Bard. arXiv (Cornell University) . 2023. https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2305.18618
Rahman MM, Watanobe Y (2023) ChatGPT for education and research: opportunities, threats, and strategies. Appl Sci 13(9):5783. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13095783
Ram B, Verma P. Artificial intelligence AI-based Chatbot study of ChatGPT, google AI bard and baidu AI. World J Adv Eng Technol Sci. 2023;8(1):258–61. https://doi.org/10.30574/wjaets.2023.8.1.0045 .
Rasul T, Nair S, Kalendra D, Robin M, de Oliveira Santini F, Ladeira WJ, Heathcote L. The role of ChatGPT in higher education: benefits, challenges, and future research directions. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.29 .
Ratnam M, Sharm B, Tomer A. ChatGPT: educational artificial intelligence. Int J Adv Trends Comput Sci Eng. 2023;12(2):84–91. https://doi.org/10.30534/ijatcse/2023/091222023 .
Ray PP. ChatGPT: a comprehensive review on background, applications, key challenges, bias, ethics, limitations and future scope. Internet Things Cyber-Phys Syst. 2023;3:121–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iotcps.2023.04.003 .
Roumeliotis KI, Tselikas ND. ChatGPT and Open-AI models: a preliminary review. Future Internet. 2023;15(6):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi15060192 .
Rudolph J, Tan S, Tan S. War of the chatbots: Bard, Bing Chat, ChatGPT, Ernie and beyond. The new AI gold rush and its impact on higher education. J Appl Learn Teach. 2023. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.23 .
Ruiz LMS, Moll-López S, Nuñez-Pérez A, Moraño J, Vega-Fleitas E. ChatGPT challenges blended learning methodologies in engineering education: a case study in mathematics. Appl Sci. 2023;13(10):6039. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106039 .
Sallam M, Salim NA, Barakat M, Al-Tammemi AB. ChatGPT applications in medical, dental, pharmacy, and public health education: a descriptive study highlighting the advantages and limitations. Narra J. 2023;3(1): e103. https://doi.org/10.52225/narra.v3i1.103 .
Salvagno M, Taccone FS, Gerli AG. Can artificial intelligence help for scientific writing? Crit Care. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-023-04380-2 .
Saqr M, López-Pernas S, Helske S, Hrastinski S. The longitudinal association between engagement and achievement varies by time, students’ profiles, and achievement state: a full program study. Comput Educ. 2023;199:104787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2023.104787 .
Saqr M, Matcha W, Uzir N, Jovanović J, Gašević D, López-Pernas S. Transferring effective learning strategies across learning contexts matters: a study in problem-based learning. Australas J Educ Technol. 2023;39(3):9.
Schöbel S, Schmitt A, Benner D, Saqr M, Janson A, Leimeister JM. Charting the evolution and future of conversational agents: a research agenda along five waves and new frontiers. Inf Syst Front. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-023-10375-9 .
Shoufan A. Exploring students’ perceptions of CHATGPT: thematic analysis and follow-up survey. IEEE Access. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2023.3268224 .
Sonderegger S, Seufert S. Chatbot-mediated learning: conceptual framework for the design of Chatbot use cases in education. Gallen: Institute for Educational Management and Technologies, University of St; 2022. https://doi.org/10.5220/0010999200003182 .
Book Google Scholar
Strzelecki A. To use or not to use ChatGPT in higher education? A study of students’ acceptance and use of technology. Interact Learn Environ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2023.2209881 .
Su J, Yang W. Unlocking the power of ChatGPT: a framework for applying generative AI in education. ECNU Rev Educ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/20965311231168423 .
Sullivan M, Kelly A, McLaughlan P. ChatGPT in higher education: Considerations for academic integrity and student learning. J ApplLearn Teach. 2023;6(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.17 .
Szabo A. ChatGPT is a breakthrough in science and education but fails a test in sports and exercise psychology. Balt J Sport Health Sci. 2023;1(128):25–40. https://doi.org/10.33607/bjshs.v127i4.1233 .
Taecharungroj V. “What can ChatGPT do?” analyzing early reactions to the innovative AI chatbot on Twitter. Big Data Cognit Comput. 2023;7(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc7010035 .
Tam S, Said RB. User preferences for ChatGPT-powered conversational interfaces versus traditional methods. Biomed Eng Soc. 2023. https://doi.org/10.58496/mjcsc/2023/004 .
Tedre M, Kahila J, Vartiainen H. (2023). Exploration on how co-designing with AI facilitates critical evaluation of ethics of AI in craft education. In: Langran E, Christensen P, Sanson J (Eds). Proceedings of Society for Information Technology and Teacher Education International Conference . 2023. pp. 2289–2296.
Tlili A, Shehata B, Adarkwah MA, Bozkurt A, Hickey DT, Huang R, Agyemang B. What if the devil is my guardian angel: ChatGPT as a case study of using chatbots in education. Smart Learn Environ. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-023-00237-x .
Uddin SMJ, Albert A, Ovid A, Alsharef A. Leveraging CHATGPT to aid construction hazard recognition and support safety education and training. Sustainability. 2023;15(9):7121. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097121 .
Valtonen T, López-Pernas S, Saqr M, Vartiainen H, Sointu E, Tedre M. The nature and building blocks of educational technology research. Comput Hum Behav. 2022;128:107123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2021.107123 .
Vartiainen H, Tedre M. Using artificial intelligence in craft education: crafting with text-to-image generative models. Digit Creat. 2023;34(1):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/14626268.2023.2174557 .
Ventayen RJM. OpenAI ChatGPT generated results: similarity index of artificial intelligence-based contents. Soc Sci Res Netw. 2023. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4332664 .
Wagner MW, Ertl-Wagner BB. Accuracy of information and references using ChatGPT-3 for retrieval of clinical radiological information. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1177/08465371231171125 .
Wardat Y, Tashtoush MA, AlAli R, Jarrah AM. ChatGPT: a revolutionary tool for teaching and learning mathematics. Eurasia J Math, Sci Technol Educ. 2023;19(7):em2286. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/13272 .
Webster J, Watson RT. Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: writing a literature review. Manag Inf Syst Quart. 2002;26(2):3.
Xiao Y, Watson ME. Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. J Plan Educ Res. 2017;39(1):93–112. https://doi.org/10.1177/0739456x17723971 .
Yan D. Impact of ChatGPT on learners in a L2 writing practicum: an exploratory investigation. Educ Inf Technol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-11742-4 .
Yu H. Reflection on whether Chat GPT should be banned by academia from the perspective of education and teaching. Front Psychol. 2023;14:1181712. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1181712 .
Zhu C, Sun M, Luo J, Li T, Wang M. How to harness the potential of ChatGPT in education? Knowl Manag ELearn. 2023;15(2):133–52. https://doi.org/10.34105/j.kmel.2023.15.008 .
Download references
The paper is co-funded by the Academy of Finland (Suomen Akatemia) Research Council for Natural Sciences and Engineering for the project Towards precision education: Idiographic learning analytics (TOPEILA), Decision Number 350560.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Computing, University of Eastern Finland, 80100, Joensuu, Finland
Yazid Albadarin, Mohammed Saqr, Nicolas Pope & Markku Tukiainen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
YA contributed to the literature search, data analysis, discussion, and conclusion. Additionally, YA contributed to the manuscript’s writing, editing, and finalization. MS contributed to the study’s design, conceptualization, acquisition of funding, project administration, allocation of resources, supervision, validation, literature search, and analysis of results. Furthermore, MS contributed to the manuscript's writing, revising, and approving it in its finalized state. NP contributed to the results, and discussions, and provided supervision. NP also contributed to the writing process, revisions, and the final approval of the manuscript in its finalized state. MT contributed to the study's conceptualization, resource management, supervision, writing, revising the manuscript, and approving it.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yazid Albadarin .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
See Table 4
The process of synthesizing the data presented in Table 4 involved identifying the relevant studies through a search process of databases (ERIC, Scopus, Web of Knowledge, Dimensions.ai, and lens.org) using specific keywords "ChatGPT" and "education". Following this, inclusion/exclusion criteria were applied, and data extraction was performed using Creswell's [ 15 ] coding techniques to capture key information and identify common themes across the included studies.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Albadarin, Y., Saqr, M., Pope, N. et al. A systematic literature review of empirical research on ChatGPT in education. Discov Educ 3 , 60 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s44217-024-00138-2
Download citation
Received : 22 October 2023
Accepted : 10 May 2024
Published : 26 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s44217-024-00138-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Large language models
- Educational technology
- Systematic review
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Advertisement
Supported by
Jenny Erpenbeck’s ‘Kairos’ Wins the International Booker Prize
Translated by Michael Hofmann, it’s the first novel originally written in German to win the major literary award.
- Share full article

By Alex Marshall
Reporting from London
Jenny Erpenbeck’s “ Kairos ,” a novel about a torrid love affair in the final years of East Germany, won on Tuesday the International Booker Prize, the renowned award for fiction translated into English.
Erpenbeck shares the award of 50,000 British pounds, about $63,500, with Michael Hofmann, who translated the book into English. The pair received the prize during a ceremony at the Tate Modern art museum in London.
After receiving the award, the pair seemed lost for words. Erpenbeck thanked Hofmann, and Hofmann thanked Erpenbeck: “I want to thank Jenny for her trust in me,” he said. “Er, that’s about the size of it.”
Eleanor Wachtel, the chair of the judges, said in a news conference that “Kairos” was more than a simple evocation of a romance. The “self-absorption of the lovers” — a student and a 50-something novelist — and “their descent into a destructive vortex” tracks the history of East Germany before the collapse of the Berlin Wall, she said.
Like that country, Wachtel added, the couple’s relationship “starts with optimism and trust, then unravels so badly.”
“What makes ‘Kairos’ so unusual is that it’s both beautiful and uncomfortable, personal and political, psychological and very moving,” Wachtel said. The judging panel deliberated for half an hour before deciding to give “Kairos” the prize, she added.
“Kairos” beat five other shortlisted titles , including Jente Posthuma’s “What I’d Rather Not Think About,” translated from Dutch by Sarah Timmer Harvey, about a woman grieving her twin brother, and Hwang Sok-yong’s “Mater 2-10,” translated from Korean by Sora Kim-Russell and Youngjae Josephine Bae, which traces North and South Korean history through a family of railway workers.
After its publication in English last year, some reviewers praised “Kairos” as the latest novel to suggest Erpenbeck could be a future winner of the Nobel Prize in Literature. Dwight Garner, in The New York Times , said that Erpenbeck was “among the most sophisticated and powerful novelists we have.” “Kairos,” he added, was so moving it had “a subterranean force.”
“I don’t generally read the books I review twice,” Garner said, “but this one I did.”
Established in 2005, the International Booker Prize is separate from the Booker Prize, which recognizes fiction written in English. Originally awarded for a writer’s entire body of work, in 2016 the international prize became an annual award for the best novel translated into English. Past winners have included Han Kang’s “ The Vegetarian, ” translated from Korean by Deborah Smith, and Olga Tokarczuk’s “ Flights ,” translated from Polish by Jennifer Croft.
Erpenbeck is the first German novelist to win the award, while Hofmann is the first male translator to receive the honor.
Erpenbeck, 57, grew up in Berlin in what was then the German Democratic Republic, or East Germany, and the country has provided either a setting or context for much of her fiction, including 2017’s “ Go, Went, Gone ” about a professor befriending a group of African refugees in present day Berlin.
In a recent interview with The Times , Erpenbeck said that the tumult around the Berlin Wall’s collapse led to her becoming a writer, as she grappled with what it meant to lose “the system that I knew, that I grew up in.”
Stories about the fall of the Berlin Wall focus on the idea of freedom, Erpenbeck said in a recent interview for the Booker Prize’s website , but that was “not the only” story that could be told.
“Kairos,” she added, was “also about what follows the happy end.”
Alex Marshall is a Times reporter covering European culture. He is based in London. More about Alex Marshall
Explore More in Books
Want to know about the best books to read and the latest news start here..
An assault led to Chanel Miller’s best seller, “Know My Name,” but she had wanted to write children’s books since the second grade. She’s done that now with “Magnolia Wu Unfolds It All.”
When Reese Witherspoon is making selections for her book club , she wants books by women, with women at the center of the action who save themselves.
The Nobel Prize-winning author Alice Munro, who died on May 14 , specialized in exacting short stories that were novelistic in scope , spanning decades with intimacy and precision.
“The Light Eaters,” a new book by Zoë Schlanger, looks at how plants sense the world and the agency they have in their own lives.
Each week, top authors and critics join the Book Review’s podcast to talk about the latest news in the literary world. Listen here .
- Case report
- Open access
- Published: 25 May 2024
Wandering spleen presenting in the form of right sided pelvic mass and pain in a patient with AD-PCKD: a case report and review of the literature
- Yitagesu aberra shibiru ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3645-9115 1 ,
- Sahlu wondimu 1 &
- Wassie almaw 1
Journal of Medical Case Reports volume 18 , Article number: 259 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
77 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Wandering spleen is a rare clinical entity in which the spleen is hypermobile and migrate from its normal left hypochondriac position to any other abdominal or pelvic position as a result of absent or abnormal laxity of the suspensory ligaments (Puranik in Gastroenterol Rep 5:241, 2015, Evangelos in Am J Case Rep. 21, 2020) which in turn is due to either congenital laxity or precipitated by trauma, pregnancy, or connective tissue disorder (Puranik in Gastroenterol Rep 5:241, 2015, Jawad in Cureus 15, 2023). It may be asymptomatic and accidentally discovered for imaging done for other reasons or cause symptoms as a result of torsion of its pedicle and infarction or compression on adjacent viscera on its new position. It needs to be surgically treated upon discovery either by splenopexy or splectomy based on whether the spleen is mobile or not.
Case presentation
We present a case of 39 years old female Ethiopian patient who presented to us complaining constant lower abdominal pain especially on the right side associated with swelling of one year which got worse over the preceding few months of her presentation to our facility. She is primiparous with delivery by C/section and a known case of HIV infection on HAART. Physical examination revealed a right lower quadrant well defined, fairly mobile and slightly tender swelling. Hematologic investigations are unremarkable. Imaging with abdominopelvic U/S and CT-scan showed a predominantly cystic, hypo attenuating right sided pelvic mass with narrow elongated attachment to pancreatic tail and absent spleen in its normal position. CT also showed multiple different sized purely cystic lesions all over both kidneys and the pancreas compatible with AD polycystic kidney and pancreatic disease.
With a diagnosis of wandering possibly infarcted spleen, she underwent laparotomy, the finding being a fully infarcted spleen located on the right half of the upper pelvis with twisted pedicle and dense adhesions to the adjacent distal ileum and colon. Release of adhesions and splenectomy was done. Her post-operative course was uneventful.
Wandering spleen is a rare clinical condition that needs to be included in the list of differential diagnosis in patients presenting with lower abdominal and pelvic masses. As we have learnt from our case, a high index of suspicion is required to detect it early and intervene by doing splenopexy and thereby avoiding splenectomy and its related complications.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Wandering spleen is a rare clinical entity characterized by hypermobility of the spleen as a result of absence or abnormal laxity of its suspensory ligaments which in turn can be congenital or precipitated by a number of risk factors like repeated pregnancy, trauma, surgery or connective tissue disorder. The spleen therefore migrates from its normal left hypochondriac position, to other parts of the peritoneal cavity especially the pelvis [ 3 ]. Since the first case report in 1667, there have been less than 600 cases reported in the literature so far [ 1 , 3 ].
Wandering spleen can have different clinical presentations ranging from asymptomatic incidental finding on imaging to features of acute abdomen as a result of complete torsion of the pedicle and total infarction of the spleen or complete obstruction of adjacent hollow viscus due to pressure effect. Less dramatic presentation includes chronic lower abdominal pain, swelling and symptoms of partial obstruction of bowel especially of the colon [ 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 ].
Diagnosis is confirmed by imaging usually abdominal ultrasound or CT which reveals that the spleen is absent from its normal anatomical position but seen somewhere else in the new location within the peritoneal cavity [ 3 , 9 , 10 ]. Once diagnosed, surgical intervention is required either by splenopexy or splenectomy depending on the viability of the organ [ 3 , 5 ] and can be done laparoscopically or by laparotomy.
Owing to its rarity, a high index of suspicion is required and this condition should always be considered as a possible differential diagnosis in patients presenting with lower abdominal swelling and pain. We present this case to share our experience in diagnosing and managing such a rare pathology and once again bring it to the attention of fellow clinicians handling this sort of abdominal conditions.
Case summary
Our patient is a 39 years old female Primi-para Ethiopian, who presented with lower abdominal dull aching pain of one-year duration which got worse over the last few months associated with right lower abdominal swelling, easy fatigability, LGIF, loss of appetite and weight. She is a known case of RVI on HAART for the past 18yrs and hypertensive for the last 8 years for which she was taking enalapril and atenolol. Her only child was delivered by C/section 10 years ago.
On examination , she looked chronically sick with her vitals in the normal range. The abdomen was flat with a lower midline surgical scar and a visible round mass on the right paraumblical and lower quadrant areas. The mass was well defined, smooth surfaced, slightly tender and mobile (Fig. 1 —black arrow).
Black arrow shows the splenic mass, red arrow shows the stomach, cyan arrow shows previous CS scar
Her hematologic tests revealed WBC of 8.7 × 103, Hgb of 12.3 and PLT count of 544 × 10 3 . Serum electrolyte and liver function tests were all in the normal range. Creatinine was 1.4 mg/dl.
Abdominal ultrasound
Multiple bilateral renal, liver and pancreatic cysts. An ehcocomplex mainly hypoechoic, 13 cmx8cm well defined right sided abdomino-pelvic mass, with absent color Doppler flow. Spleen was not visualized in its normal anatomic site.
Contrast enhanced abdomino-pelvic CT
Described the mass as a hypoattenuating, well circumscribed lesion with no contrast enhancement located at right abdomino pelvic cavity (Fig. 2 ). Its long torsed pedicle could be traced to the region of the tail of the pancreas and the spleen was missing from its normal location. (Fig. 3 ) Majority of the renal parenchyma is almost replaced with different sized cystic lesions with imperceptible wall causing bilateral renal enlargement. (Fig. 3 ) The liver and the pancreas too is filled with similar cysts. The portal vein were not visualized and replaced by periportal enlarged collateral vessels. (Figs. 3 , 4 ).
Infarcted spleen
Absent spleen in the splenic fossa
Spleen seen in the abdomino-pelvic cavity
With a diagnosis of wandering spleen located in the right abdomino pelvic region with torsion of the pedicle and infarction, she was admitted and underwent laparotomy. Intraoperatively, dense adhesion encountered between the anterior abdominal wall, omentum, the wandering spleen and small bowel. The spleen was whitish, distended and grossly infarcted with its long stalk torsed > 360°. (Fig. 5 ) Adhesions were gently released and splenectomy done. The splenic mass was sent for biopsy.
The intra-op picture of our patient upon exploration
She was discharged on the 3rd postoperative day and her post-operative course was uneventful. She was seen after a month on follow up clinic with no report of complication. Her biopsy result showed splenic tissue. She got her pentavelant vaccine on the third week.
Wandering spleen is a rare clinical entity characterized by splenic hypermobility from its left hypochondriac position to any other abdominal or pelvic position caused by absent or abnormal laxity of the suspensory ligaments [ 1 , 2 ].
The first case of wandering spleen was reported by Von Horne in 1667. So far less than 600 cases are reported world wide [ 1 , 3 ].
Anatomically a normal spleen is found in the left hypochondriac region suspended by ligaments to the stomach, kidney, pancreas, colon and left hemi-diaphram by the gastrosplenic, splenorenal, pancreaticosplenic, splenocolic, splenophreni ligaments and presplenic folds [ 1 ]. Our patient presented with RLQ palpable abdominal mass which is against the commonest presentation being in the LLQ of the abdomen (Fig. 1 ).
It could result from either a developmental failure of the embryonic septum transversum to fuse properly with the posterior abdominal wall which results in absent/lax ligaments [ 4 ] or from acquired conditions that result in lax suspensory ligaments as in pregnancy or connective tissue disorders [ 3 ]. The spleen is found in any quadrant of the abdomen or the pelvis though mostly in the left quadrants attached only by a long and loose vascular pedicle. Our patient presented with RLQ mass.
It is mostly seen in multiparous women [ 4 ] though the incidence is found to be nearly equal in both sexes in the prepubertal age group [ 3 ]. Our patient was a Para 1 mother and presented with 01 year history of abdominal pain which got worse in the past 06 months. Otherwise she had no any other pressure symptoms. She had visible umbilical area mass which was mobile up on examination
Wandering spleen can have different presentation ranging from asymptomatic incidental finding on imaging or upon surgical exploration for other surgical conditions to a presentation that mimics acute abdomen [ 3 , 5 ]. Mostly it presents as an on and of type acute/ subacute non-specific abdominal pain due to torsion and spontaneous de-torsion of the loose splenic pedicle [ 3 , 4 ]. This chronic torsion results in congestion and splenomegaly [ 3 , 5 ]. Hence patients could have palpable mobile mass [ 6 ] which is the typical presentation of this patient. The other presentations are usually related to the mass effect of the enlarged spleen and patients could present with GOO, bowel obstruction, pancreatitis and urinary symptoms [ 3 , 6 ].
In some cases it is reported to be associated with some other disorders like gastric volvulus [ 7 ] and distal pancreatic volvulus [ 8 ].
Ultrasound is one of the imaging modalities to investigate patients whom we suspect had wandering spleen. It usually shows absent spleen in the splenic fossa and a comma shaped spleen in the abdomen or pelvis [ 9 ]. Doppler study might help us see the vascular condition and ads up to a better preoperative plan. CT scan shows absence of the spleen in the left upper quadrant, ovoid or comma-shaped abdominal mass, enlarged spleen, a whirled appearance of non-enhancing splenic vessels and signs of splenic hypo-perfusion: homogenous or heterogeneous decreased enhancement depending on the degree of infarction [ 3 , 9 , 10 ].
Our patient was scanned with US and showed 13*8 cm large midline abdomino-pelvic well defined oval mass which was predominantly solid with areas of cystic component with absent color Doppler flow. Otherwise the spleen was not visualized in the splenic fossa. Bilateral kidney and liver has multiple different sized cystic lesions. With this image Abdomino-pelvic CT was done and shows spleen is located in the lower abdomen and appears to have torsed vascular pedicle and the whole splenic parenchyma is hypodense and no enhancement seen. Majority of the renal parenchyma is almost replaced with different sized cystic lesions with imperceptible wall causing bilateral renal enlargement. The whole liver is filled with cystic lesions with imperceptible wall. The portal veins were not visualized and replaced by periportal enlarged collateral vessels (Figs. 6 , 7 ).
Usually surgical management is the rule once a patient is diagnosed with wandering spleen [ 3 , 5 ]. Most patients; 65% as reported in some studies will have torsion of the vascular pedicle at some point of their life [ 5 , 6 ]. Hence splenopexy or splenectomy shall be considered when a wandering spleen is found incidentally up on surgical exploration for some other purposes [ 6 ]. Complicated wandering spleen like infarcted, signs of hypersplenism, huge in size and splenic vein thrombosis needs splenectomy while others can be managed with splenopexy [ 3 , 5 , 6 ]. Nowadays though laparoscopic technique is the gold standard, open technique can be used for splenopexy and splenectomy [ 3 , 5 ].
Partial infraction of a wandering spleen might necessitate partial splenectomy and splenopexy or splenectomy and splenic implantation [ 6 , 11 ].
The spleen might get fixed by different methods [ 8 , 9 ].
Simple splenic fixation involves simple tacking the splenic capsule to the peritoneum
Retroperitoneal pouch splenopexy- Tissue [ 11 , 12 ]/Mesh splenopexy (sandwich technique) [ 13 ].
Omental and peritoneal pouch splenic fixation [ 14 ].
In our case, Spleen was absent from the normal anatomic splenic fossa and the spleen in the abdomino-pelvic area looks infarcted. Hence she was managed with splenectomy and the patient was extubated on table and having a stable postoperative course .
Wandering spleen is a rare form of splenic pathology. Such a rare pathology presents commonly as an acute torsion with infarction. Spleen in the RLQ with chronic torsion and infarction is a very rare presentation for wandering spleen. In addition there is no report of such a presentation in a patient with AD-PCKD.
Recommendation
We recommend Clinicians to consider wandering spleen in their differential diagnosis in a patient presenting with RLQ abdominal mass and chronic abdominal pain.
Availability of supporting data
Data related with this case report is available at Addis ababa university, Tikur Ambesa Tertiary Hospital.
Abbreviations
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
Blood pressure
Low grade intermittent fever
High active anti-retroviral therapy
Right lower quadrant
Retro viral infection
Hypertension
White blood cell count
Puranik AK, et al . Wandering spleen: a surgical enigma. Gastroenterol Rep. 2015;5:241.
Google Scholar
Evangelos K, et al . Wandering spleen volvulus: a case report and literature review of this diagnostic challenge. Am J Case Rep. 2020;21: e925301.
Jawad M. Wandering spleen: a rare case from the emergency department. Cureus. 2023;15(1): e33246.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ayaz UY, et al . Wandering spleen in a child with symptoms of acute abdomen. Med Ultrasonogr. 2012;14:64.
Masroor M, Sarwari MA. Torsion of the wandering spleen as an abdominal emergency: a case report. BMC Surg. 2021;21:289.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Blouhos K, et al . Ectopic spleen: an easily identifiable but commonly undiagnosed entity until manifestation of complications. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2014;8:451–4.
Article Google Scholar
Uc A. Gastric volvulus and wandering spleen. Am J Gastroenrterol. 1998;93:1146–8.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Alqadi GO, Saxena AK. Is laparoscopic approach for wandering spleen in children an option? J Min Access Surg. 2019;15:93.
Awan M, et al . Torsion of wandering spleen treated by laparoscopic splenopexy. Int J Surgery Case Rep. 2019;62:58.
Taori K, et al . Wandering spleen with torsion of vascular pedicle: early diagnosis with multiplaner reformation technique of multislice spiral CT. Abdom Imaging. 2004;29:09428925.
Fonseca AZ, et al . Torsion of a wandering spleen treated with partial splenectomy and splenopexy. J Emerg Med. 2013;44:e33.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Seashore JH, McIntosh S. Elective splenopexy for wandering spleen. J Pediatr Surg. 1990;25:270–2.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Soleimani M. Surgical treatment of patients with wandering spleen: report of six cases with a review of the literature. Surg Today. 2007;37:261.
Peitgen K. Laparoscopic splenopexy by peritoneal and omental pouch construction for intermittent splenic torsion (“wandering spleen”). Surg Endosc. 2001;15:413.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the managing team of this patient including all the ward staffs who played a great role in the peri-operative management of this patient. We also appreciate the support of our consultants, residents and member of the department of surgery and HPB unit. Our kind gratitude goes to the family of this patient for their unreserved support in post-operative period that helped for the fast recovery of this patient
Funding is not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Yitagesu aberra shibiru, Sahlu wondimu & Wassie almaw
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Dr. Yitagesu Aberra, Main author of this case report, is an HPB surgery fellow in the department of surgery, college of health science, Addis Ababa University who was the leading surgeon in the management of this patient. Dr. Sahlu Wendimu is an HPB surgery subspecialist and Assistant professor of General Surgery who was the consultant in duty during the management of this patient. Dr.Wassie Almaw is a 2nd year pediatric surgery resident attaching at HPB surgery unit who took part in the management of this patient.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yitagesu aberra shibiru .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethical clearance is not applicable but we took oral and written consent from the patient for case presentation and publication.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
There is no competing interest in this case presentation.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
shibiru, Y.a., wondimu, S. & almaw, W. Wandering spleen presenting in the form of right sided pelvic mass and pain in a patient with AD-PCKD: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Reports 18 , 259 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-024-04580-6
Download citation
Received : 02 December 2023
Accepted : 02 May 2024
Published : 25 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-024-04580-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Wandering spleen
- Splenic torsion
- Splenic infarction
- Splenectomy
Journal of Medical Case Reports
ISSN: 1752-1947
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Case Report
- Open access
- Published: 10 May 2024
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome with central nervous system symptom onset: a case report and literature review
- Dawei Shan 1 ,
- Weibi Chen 1 ,
- Gang Liu 1 ,
- Huimin Zhang 1 ,
- Shuting Chai 1 &
- Yan Zhang 1
BMC Neurology volume 24 , Article number: 158 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
564 Accesses
Metrics details
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is a natural focal disease transmitted mainly by tick bites, and the causative agent is SFTS virus (SFTSV). SFTS can rapidly progress to severe disease, with multiple-organ failure (MOF) manifestations such as shock, respiratory failure, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and death, but cases of SFTS patients with central nervous system (CNS) symptoms onset and marked persistent involuntary shaking of the perioral area and limbs have rarely been reported.
Case presentation
A 69-year-old woman with fever and persistent involuntary shaking of the perioral area and limbs was diagnosed with SFTS with CNS symptom onset after metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and peripheral blood identified SFTSV. The patient developed a cytokine storm and MOF during the course of the disease, and after aggressive antiviral, glucocorticoid, and gamma globulin treatments, her clinical symptoms improved, her laboratory indices returned to normal, and she had a good prognosis.
This case gives us great insight that when patients with CNS symptoms similar to those of viral encephalitis combined with thrombocytopenia and leukopenia are encountered in the clinic, it is necessary to consider the possibility of SFTS involving the CNS. Testing for SFTSV nucleic acid in CSF and blood (mNGS or polymerase chain reaction (PCR)) should be carried out, especially in critically ill patients, and treatment should be given accordingly.
Peer Review reports
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is a natural focal disease transmitted mainly by tick bites, and the causative agent is a novel Bunyavirus, also known as SFTS virus (SFTSV), belonging to the Phenuiviridae family and the Bandavirus genus, which was first isolated from patient serum by the Chinese Centre for Disease Control and Prevention in 2010 [ 1 ]. The main features of SFTS include fever, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia and gastrointestinal symptoms, and in severe cases, patients may present with multiple‑organ failure (MOF) symptoms such as shock, respiratory failure, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and death, with a mortality rate of 5–30% in East Asia [ 2 , 3 ]. SFTS may also present with central nervous system (CNS) involvement, which can severely affect the patient’s disease progression and prognosis and is manifested by seizures, psychiatric symptoms, cognitive impairment, and disorders of consciousness [ 4 , 5 ]. However, reports of patients who present with CNS symptoms as the first symptom and with marked persistent involuntary shaking of the perioral area and limbs are rare.
A 69-year-old female patient was admitted to the hospital with fever for 4 days, involuntary shaking around the mouth and limbs for 3 days, and mental abnormalities for 1 day. The patient was admitted to the emergency department of another hospital 4 days before admission because of fever, where her body temperature reached 38.7 °C and she showed poor mental status, less talking, a loss of appetite, but no headache, vomiting, and limb twitching. A routine blood examination showed a white blood cell (WBC) count of 2.28 × 10 9 /L and a platelet count of 165 × 10 9 /L. When given a cooling infusion for symptomatic treatment, her body temperature would temporarily return to normal. Three days before admission, she experienced persistent involuntary trembling around the mouth and lips, as well as trembling of the tongue and extremities. The trembling of the lips, mouth, and both distal upper limbs was especially bothersome and was aggravated by emotional excitement and accompanied by slurred speech. Two days before admission, she had persistent fever, with a body temperature up to 39.6 °C, and the effect of antipyretic drugs was not good. A routine blood examination performed in another hospital showed a WBC count of 1.78 × 10 9 /L and a platelet count of 81 × 10 9 /L, which was significantly decreased compared with the count from the previous examination. One day prior to admission, the patient experienced babbling, restlessness, irritability, and a decline in time and place orientation and calculation power.
The patient had a many-year history of hypertension, diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidaemia; denied a history of working and living in hilly, forested and mountainous areas and travelling; denied a recent history of mosquito bites; and reported a history of close contact with a pet dog in the last month.
Neurological examination after admission showed that the patient had normal arousal but had unclear speech, hyperactivity, irritability. Her time and place orientation and calculation power decreased. The patient was uncooperative in the pharyngeal reflex examination, and involuntary tongue twitching could be seen when the tongue was stretched out. The remaining cranial nerve examination did not show any abnormalities. Perioral and limb involuntary shaking was obvious and persistent, especially in the perioral area and distal part of both upper limbs. Bilateral tendon reflexes were symmetrical, bilateral pathological signs were negative, and meningeal irritation signs were negative.
On admission, viral encephalitis was considered, and intravenous acyclovir antiviral therapy (0.5 g, q8h) was empirically administered. A comprehensive examination revealed that the patient had MOF: (1) Her platelet count further decreased to 63 × 10 9 /L (normal: 100–300 × 10 9 /L), toxic granules were seen in some granulocytes of the peripheral blood smear, and heterogeneous lymphocytes accounted for 21% of the total. (2) She had impaired liver function with elevated liver enzymes (alanine aminotransferase (ALT), 76 IU/L (normal: 5–40 IU/L); aspartate aminotransferase (AST), 188 IU/L (normal: 8–40 IU/L); and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (γ-GT), 177 IU/L (normal: 7–50 IU/L)), which was treated with magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate injection and vitamin C for liver protection. (3) She had acute myocardial injury, with an increased heart rate of > 120 beats/minute and markedly elevated myocardial enzyme and B-type natriuretic peptide levels (myoglobin, 299 ng/mL (normal: 25–58 ng/mL); troponin T, 209 ng/L (normal: 0–14 ng/L); and B-type natriuretic peptide, 9,355 pg/mL (normal: 0-125 pg/mL)). Electrocardiograms (ECGs) showed various atypical manifestations, such as short PR intervals; atrial premature, mild ST-segment depression in leads V2V3; and T-wave changes in multiple leads. Cardiac ultrasound showed a normal left ventricular ejection fraction but abnormal segmental motion of the left ventricular wall, biventricular diastolic insufficiency and a small amount of pericardial effusion. Coenzyme Q10 and trimetazidine were given to improve myocardial energy metabolism, and fluid intake and output were closely monitored. (4) The patient had a bacterial infection of the lungs, combined with type I respiratory failure, which were treated with tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation immediately to assist respiration and antibiotic antimicrobial therapy. The patient did not have prolonged hypoxic injury. (5) She had impaired renal function, with elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) (17.33 mmol/L) (normal: 1.7–8.3 mmol/L) and urinary protein. We administered measures to ensure fluid intake and without the use of nephrotoxic drugs. (6) She had impaired pancreatic function, with elevated lipase (56.5 U/L) (normal: 5.6–51.3 U/L); we administered acid-suppressing drugs to inhibit pancreatic secretion and reduce the load and damage to pancreatic tissue. (7) She had abnormal coagulation, with a prolonged prothrombin time (PT) and thrombin time (TT) (15.7 s (normal: 11–15 s) for PT and 22.6 s (normal: 14–21 s) for TT), decreased fibrinogen (1.8 g/L) (normal: 2–4 g/L), and markedly elevated plasma D-dimer (9.01 µg/mL) (normal: 0.01–0.5 µg/mL) and fibrinogen degradation products (FDPs) (28.36 µg/mL) (normal: 0–5 µg/mL). (8) A thrombus had formed in her right peroneal vein and the intermuscular veins of the right and left calves, for which low molecular heparin anticoagulation was given. (9) Her muscle enzyme profiles were variably elevated (creatine kinase (CK), 335 IU/L (normal: 24–195 IU/L); lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), 1347 IU/L (normal: 109–245 IU/L); and alpha-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase (α-HBDH), 645 IU/L (normal: 72–182 IU/L)), correlating with inflammatory response-mediated organ damage. (10) The patient experienced a cytokine storm, with significantly increased inflammatory factors (ferritin > 1500 ng/mL (normal: 11-306.8 ng/mL), interleukin (IL)-6 = 49.88 pg/mL (normal: 0–20 pg/mL), IL-8 = 45.99 pg/mL (normal: 0-21.4 pg/mL), and IL-10 = 25.67 pg/mL (normal: 0-5.9 pg/mL), interferon (IFN)-α = 9.76 pg/mL (normal: 0-7.9 pg/mL), and IFN-γ = 18.7 pg/mL (normal: 0-17.3 pg/mL)) in serum (Table 1 ). (11) Finally, the patient showed an electrolyte balance disorder, as evidenced by hypernatremia (154 mmol/L) (normal: 135–145 mmol/L), hyperchloremia (119 mmol/L) (normal: 96–108 mmol/L), hypocalcaemia (1.92 mmol/L) (normal: 2.03–2.67 mmol/L), and hypophosphatemia (0.54 mmol/L) (normal: 0.84–1.65 mmol/L), and treatments included calcium supplementation, phosphorus supplementation, nasal administration of plain water, and a reduction of sodium and chlorine intake.
Lumbar puncture was performed on the second day after admission (Table 2 ). Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was colourless and clear, with a pressure of 190 mmH 2 O (normal: 80–180 mmH 2 O) and a WBC count of 3 × 10 6 /L. CSF cytology showed scattered lymphocytes and a few mononuclear cells. The glucose level and protein counts were normal, chloride was slightly elevated (134 mmol/L) (normal: 118–128 mmol/L), immunoglobulins (Ig) were slightly elevated (IgA, 1.03 mg/dL (normal: 0-0.2 mg/dL); IgM, 0.22 mg/dL (normal: 0-0.2 mg/dL); and IgG, 6.68 mg/dL (normal: 0.48–5.86 mg/dL)), and CSF cytokine levels of IL-6 (27.46 pg/mL) (normal: 0–20 pg/mL) and IL-8 (546.93 pg/mL) (normal: 0-21.4 pg/mL) were elevated. CSF was negative for an autoimmune encephalitis antibody profile (NMDAR, CASPR2, AMPAR1, AMPAR2, LGI1, GABABR, DPPX, and IgLON5), neuroparaneoplastic syndrome antibody profile (Hu, Ri, Yo, CV2, Amphiphysin, GAD65, PNMA2, Recoverin, SOX1, Titin, Tr, and Zic4), and CNS demyelination antibody profile (AQP4, GFAP, MBP, and MOG). Metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) showed that the number of sequences of a novel Bunyavirus of the Bandavirus genus was 59 in the blood and 12 in the CSF. We also excluded acute febrile illnesses by serum and CSF mNGS, such as dengue fever, chikungunya fever, EB virus infection, renal syndrome hemorrhagic fever, and rickettsial disease.
A diagnosis of SFTS that started with symptoms of CNS and encephalitis due to a novel Bunyavirus was considered based on the patient’s clinical presentation and laboratory test results. With immediate effect, acyclovir was adjusted to the broad-spectrum antiviral drug Foscarnet sodium (3 g, q8h); intravenous infusion of dexamethasone (10 mg qd for five days) and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) (0.4 g/kg for five days) were administered to regulate immune function and inhibit the cytokine storm; nifedipine and benidipine hydrochloride were given to reduce the viral-induced calcium inflow to inhibit viral replication, reduce the viral load and increase the platelet count; clonazepam (1 mg, q8h) was given to relieve the patient’s obvious symptoms of involuntary shaking; and adequate symptomatic supportive therapy was given to ensure adequate calorie and protein intake and to maintain water, electrolyte, blood glucose and acid‒base balance.
After 3 days of hospitalization, the patient’s platelet and WBC counts began to rise gradually and returned to normal levels. After 5 days of hospitalization, the patient’s involuntary shaking and psychiatric symptoms were less severe than before, but compliance with activities was still poor, and her cognitive level still had not returned to normal. After 11 days of hospitalization, the lung infection was better than before, and ventilator withdrawal training was started. After 12 days of hospitalization, cranial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed, which showed slightly high signals in the bilateral anterior temporal lobe, temporal lobe hook gyrus, insular cortex, and bilateral thalamus on fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) and diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) (Fig. 1 a-f). After 13 days of hospitalization, a blood sample was negative for novel Bunyavirus nucleic acid. After 16 days of hospitalization, her condition was significantly better than before, she could perform activities as instructed and answer questions correctly, her time and place orientation returned to normal, and her cognitive level was better than before. A electroencephalogram (EEG) was performed, and a full-lead low-wave amplitude state was observed (Fig. 2 ). After 17 days of hospitalization, the ventilator was completely withdrawn, and the tracheal tube was removed. A repeat lumbar puncture 3 weeks after hospitalization showed a pressure of 110 mmH 2 O, a WBC count of 4 × 10 6 /L, a normal protein count, a slightly elevated glucose level (5.19 mmol/L, compared with a glucose of 7.9 mmol/L over the same period), a slightly elevated chlorine level (130 mmol/L), and a return of Ig to normal. The levels of cytokines IL-6 (4.35 pg/mL) and IL-8 (96.17 pg/mL) decreased significantly compared with the previous levels, and the levels of whole-blood cytokines returned to the normal range (IL-6, 12.22 pg/mL; IL-8, 4.62 pg/mL; IL-10, 1.27 pg/mL; IFN-α, 0 pg/mL; and IFN-γ, 1.14 pg/mL) in serum (Table 1 ). No further novel Bunyaviruses were detected by mNGS of the CSF. Meanwhile, MOF gradually recovered, and liver, heart, lung, kidney, pancreas and coagulation function; the muscle enzyme profile; inflammatory factors; and electrolyte levels gradually returned to normal levels.
After antiviral therapy, immunotherapy, life support and symptomatic treatment, the patient’s vital signs were stable 3 weeks after admission, with clear speech and normal higher cortical function to perform tasks correctly on command. The muscle strength of all four limbs was grade 5, muscle tone was normal, bilateral tendon reflexes existed symmetrically, an ataxia test was normal, bilateral pathological signs were negative, and meningeal irritation signs were negative. She was discharged from the hospital in 23 days after admission. The patient was followed up 1 month after she was discharged from the hospital and is now back to her normal living conditions, with normal functioning of the higher cortex, the ability to take care of herself, and the ability to perform all of the activities she regularly engages in.
Cranial MRI of the patient 12 days after admission. Bilateral anterior temporal lobe (a and d) , temporal lobe leptomeningeal gyrus (a and d) , insular cortex (b and e) , and bilateral thalamus (c and f) FLAIR and DWI sequences with slightly high signals
Sixteen-lead resting-state EEG of the patient 16 days after admission. Simultaneous display an EEG record in monopolar and bipolar montages. A low-amplitude state can be seen in all leads. (a) monopolar montage EEG, (b) bipolar montage EEG
Discussion and conclusions
SFTS is an infectious disease caused by SFTSV infection. The epidemic period is mainly in May-August, and SFTSV is mainly transmitted by tick bites to humans. In recent years, interpersonal and human-animal transmission has also been found. An epidemiological survey of SFTS found that 48% of the patients had had close contact with their pets within two weeks of the onset of the disease [ 6 ]. The general population is susceptible, with a higher risk of infection in residents living in areas such as hills, mountains and forests and in people who spend time outdoors. In this case, SFTSV was isolated from blood and CSF. There was no history of tick bites or travel in the wild, but there was a history of close contact with a pet dog within the past month, and we hypothesized that the infected dog might have been the source of SFTSV in this patient.
The pathogenesis of CNS involvement in SFTS patients is unclear. Previous studies have demonstrated that Bunyaviruses have neurological properties of attack, and Park et al. found viral transcripts of novel Bunyaviruses in the brain and spinal cord of an aged model ferret. It is hypothesized that novel Bunyaviruses also involve the CNS, with consequent symptoms [ 7 ]. Possible mechanisms by which SFTSV attacks the CNS include direct invasion, cytokine storms, and impaired immune function. Kaneko et al. [ 8 ] performed an autopsy on a patient with SFTS with rapid CNS involvement, and the pathological findings revealed a massive infiltration of macrophages with high haematoxylin content and inflammatory cells around the microvessels of the cerebral pontine, fibrin deposition in the vessels, and focal degenerative lesions in some neuronal cells. In a variety of brain tissues, positive SFTSV nucleocapsid protein antigens were observed in the immunoblasts infiltrating the vascular lumen, suggesting that SFTSV can invade the CNS directly for disease development. The availability of agents that recognize these antigens also suggest immunoassays are possible and available for serodiagnosis. For example, serum enzyme linked immunosorbent assay or immunofluorescence to determine SFTSV antigens and antibodies have been used for clinical diagnosis [ 9 ]. Several studies [ 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ] have found that the blood levels of several cytokines, including IFN-α, IFN-γ, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP)-1, are elevated in patients with SFTS, and IL-8 and MCP-1 levels in the CSF are significantly higher than the blood of those who present with CNS symptoms [ 10 ], suggesting that a cytokine storm may increase vascular permeability and prompt SFTSV to cross the blood‒brain barrier (BBB) and invade the CNS. SFTSV was found in the CSF of this patient, suggesting that the virus had invaded the patient’s CNS. The patient’s blood levels of IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IFN-α, and IFN-γ were markedly elevated compared with normal ranges; IL-6 and IL-8 were elevated in the CSF; and CSF IL-8 levels were significantly higher than the blood levels, which was consistent with the results of a previous study [ 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ], further suggesting that the cytokine storms induced by multiple elevated cytokines may increase BBB vascular permeability and contribute to the SFTSV invasion of the CNS. In patients with SFTS complicated by neurological involvement, protein and glucose levels in the CSF are normal and that an increase in leukocytes in the CSF may be uncommon. However, in the case of a high suspicion both on a clinical and epidemiological level in countries where the infection exists, in these patients the search for MCP-1 and IL-8 in the CSF and serum is indicated and CSF viral RNA detection are recommended.
According to the course of infection, SFTS can be divided into four periods: the incubation period, the febrile period, the MOF period, and the recovery period [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 16 ]. Patients with SFTS can present with neurological symptoms, which usually appear approximately 5 days after the onset of the disease (Table 3 ) and are often regarded as a complication of SFTS, which has been referred to as SFTS-associated encephalopathy/encephalitis (SFTSAE) [ 10 ]. SFTSAE mainly manifests as headache, seizures, mental abnormality, irritability, limb convulsions, cognitive impairment, and impaired consciousness, with an incidence of approximately 19.1-57.02% [ 4 , 5 , 11 , 17 ]. Most patients with SFTSAE develop impaired consciousness, such as coma, before their condition is taken seriously, which leads to a poor prognosis for the patients [ 4 , 18 ]. Most clinicians rely on the clinical manifestations to make the clinical diagnosis. SFTSV has rarely been isolated from CSF. We screened studies and case reports of SFTS with CNS involvement and found no reports of disease onset with CNS symptoms such as marked persistent involuntary shaking of the perioral area and extremities. In this case, the patient first presented with fever, followed by persistent involuntary tremors of the perioral area and limbs and mental behavioural abnormalities such as rambling, irritability and agitation; furthermore, the whole-genome sequence of SFTSV was found by mNGS of blood and CSF. The case reported here is a case of SFTS with CNS symptoms onset, accompanied by perioral and extremity persistent involuntary shaking, which has not been previously reported in the literature. It has been reported in the literature that SFTS patients can have tremors of limbs and muscles [ 8 , 17 , 19 ], but most of them occurred in the middle and late stages of the disease, and the tremor amplitude was small. In this case, the patient had large-amplitude involuntary shaking of the limbs that was persistent and intensified during agitation, which immediately attracted the clinician’s attention. An additional movie file shows this in more detail [see Additional file 1 ]. However, the specific underlying mechanism is not clear, and a description of similar symptoms of viral encephalitis and an analysis of the underlying mechanism have not been found before; therefore, further studies are needed. The course of the disease in this patient was consistent with the general pattern, with the clinical experience of the febrile period, the MOF period, and the recovery period. The febrile period lasted approximately 4 days, followed by MOF involving the liver, heart, lungs, kidneys, and pancreas, and then the recovery period began approximately 2 weeks after the disease onset, with clinical symptoms gradually returning to normal.
There are fewer reports on neurological-related ancillary investigations (CSF, cranial imaging, and EEG) in SFTS patients with CNS involvement, and we analyse this because SFTS patients rarely start with CNS symptoms and go directly to the neurology department and because such patients are generally more severely ill, making it difficult for them to cooperate in completing the relevant investigations. In a few previous studies, lumbar puncture CSF tests in SFTS patients with CNS symptoms were mostly normal, with few abnormal changes in leukocyte counts, sugars and proteins [ 10 , 20 ]. Park et al. [ 10 ] analysed head imaging and EEG in a series of SFTS patients presenting with CNS symptoms, and no new focal lesions were seen on imaging in any of the brain parenchyma, suggesting that the imaging was not specific and that the EEG in the majority of the patients showed a slow-wave background rhythm (δ-θ), a common feature of encephalitis/encephalopathy. In this patient, two lumbar punctures were performed successively, and no CSF leukocyte abnormalities were observed in any of them either; it was presumed that SFTSV infection was less likely to involve the meninges. We performed cranial MRI and EEG on the patient 12 and 16 days after admission, respectively, and slightly high signals were observed in the bilateral anterior temporal lobes, temporal lobe hook gyrus, insular cortex, and bilateral thalamus in the FLAIR and DWI sequences of cranial MRI, all of which were consistent with the general imaging manifestations of viral encephalitis and were presumed to be related to viral invasion. In addition, we should consider the similarities and differences between the above MRI changes and cortical laminar necrosis associated with hypoxia or hypotension. We found that both had MRI high signals distributed along the cortex. However, this patient’s cranial MRI showed cortical high signals only in FLAIR and DWI sequences, and no abnormal signal was found in T1WI, which was the most obvious difference from cortical laminar necrosis. Furthermore, the patient did not show hypotension or significant hypoxic injury, so the changes on cranial MRI were more likely to be inflammatory changes of viral encephalitis and less relevant to cortical laminar necrosis. The background rhythm of the EEG was an α rhythm, and the whole leads were in low amplitude, which was different from previous studies [ 10 ]. It was presumed that the patient’s brain inflammation had tended to recover at that time, but the suppression of cortical function was remained.
There are no specific drugs for the treatment of CNS symptoms in SFTS, and symptomatic supportive treatment is the mainstay. In vitro and ex vivo studies have found that nifedipine or benidipine hydrochloride can inhibit SFTSV replication, reduce viral load, increase platelet counts, and reduce morbidity and mortality, as confirmed in a retrospective clinical study [ 21 , 22 ]. Glucocorticoids can inhibit the cytokine storms caused by the overproduction of cytokines and reduce patient mortality [ 12 , 13 , 23 ], and a Japanese report documented that three SFTS patients with impaired consciousness recovered without any neurological sequelae after short-term glucocorticoid treatment. However, the authors also suggested that the dosage should be minimized and the duration of administration should be shortened to inhibit cytokine storms and provide systemic benefit, rather than high doses or prolonged use, to avoid side effects [ 24 ]. Gamma globulin, which triggers complement activation and viral neutralization and influences the differentiation process of Schwann cells to increase their regenerative potential [ 25 ], has been used to treat other virus-induced encephalitides and can be used for the treatment of CNS symptoms in SFTS. Two successful cases of combined glucocorticoid and IVIG therapy were reported in Korea [ 26 ]. Two case reports documented that plasma exchange therapy reduced cytokine levels but not viral load, presumably making plasma exchange more effective at an early stage [ 27 , 28 ]. However, these are case reports, and the findings should be confirmed by large-scale randomized controlled studies. In this case, the patient was given the broad-spectrum antiviral drug foscarnet sodium, intravenous infusion of dexamethasone and IVIG to regulate the immune function of the body and inhibit the inflammatory storm, nifedipine and benidipine hydrochloride to inhibit viral replication and reduce the viral load, and other symptomatic treatments. The patient’s clinical manifestations and laboratory indicators gradually improved.
The prognosis of patients with SFTS is related to numerous factors, and studies have shown that advanced age; significant elevations in ALT, AST, CK, CK-MB, LDH, γ-GT, and BUN; low platelet count; persistent lowering of blood calcium; and the presence of CNS symptoms are all important influences that can lead to a poor prognosis [ 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 ]. Most of these are commonly used to monitor cardiac, hepatic and renal function, and significant abnormalities in their results indicate more severe organ damage and dysfunction. In addition, there is a statistically significant difference in serum viral copy number between deceased and non-dead patients. The mean viral copy number was higher in deceased patients than in surviving patients, and patients with higher copy numbers had higher mortality rates [ 35 , 36 ]. It was shown that the serum viral load detected by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) on admission was higher in SFTSAE patients than in non-encephalitis patients [ 11 ]. The above suggests a relationship between patient serum number of SFTSV RNA copies and encephalitis CNS symptoms and mortality in SFTS patients. CNS symptoms are often considered to be associated with fatal outcomes in patients with SFTS [ 33 ], and early diagnosis and treatment of neurological symptoms can help reduce mortality. Advanced age; long intervals between onset and admission; comorbid diabetes mellitus or subcutaneous haemorrhage; pulmonary rales; low platelet count; elevated neutrophil percentages and LDH, CK, and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels; and decreased chloride concentrations are significantly associated with the development of CNS symptoms and should be taken into consideration in clinical practice [ 11 , 17 ]. We believe that changes in platelet count and CK-MB should be monitored in patients with SFTSAE. As shown in previous, decreased platelet counts and high CK-MB levels are risk factors for poor prognosis in patients with SFTS. The presence of encephalitis is evidence of a more critical condition. Monitoring changes in platelet counts may provide an initial indication of the direction of the patient’s regression. It has been found that in cardiac enzyme profiles, patients presenting with CNS symptoms have elevated CK levels earlier than LDH and AST levels, and elevated liver enzyme levels later than cardiac enzymes [ 17 ]. Therefore, early monitoring of CK-MB levels may have a predictive effect on the development of CNS symptoms in patients. Although the mortality rate of SFTS patients presenting with CNS symptoms is significantly higher [ 11 ], several studies have found [ 11 , 37 , 38 ] that the long-term prognosis of surviving patients is good, with no obvious sequelae after active treatment. In this case, the patient’s laboratory indicators were consistent with the factors leading to a poor prognosis, and the CNS symptoms were prominent, suggesting that the condition was critical, but with timely administration of treatment, the patient’s condition eventually returned to normal.
In summary, we report a case of SFTS in a patient who started with CNS symptoms accompanied by marked persistent involuntary perioral and extremity shaking, and the whole-genome sequence of SFTSV was found by mNGS of both serum and CSF (It is important to note that hospitals where mNGS analysis is unavailable should use real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR to detect SFTS-specific nucleic acids in serum and CSF.). This has given us great insight into the fact that SFTS should be considered a possible cause when patients present with common CNS symptoms of viral encephalitis, such as mental behavioural abnormalities, convulsions, and cognitive deficits, or rare symptoms, such as persistent involuntary shaking of the perioral area and limbs in the rare case of this patient, combined with thrombocytopenia and leukopenia. Prompt lumbar puncture examination for SFTSV should be performed, and appropriate treatment should be given aggressively to reduce mortality.
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome
severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus
multiple-organ failure
disseminated intravascular coagulation
central nervous system
metagenomic next-generation sequencing
cerebrospinal fluid
alanine aminotransferase
aspartate aminotransferase
gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
electrocardiogram
blood urea nitrogen
prothrombin time
thrombin time
fibrinogen degradation products
creatine kinase
lactate dehydrogenase
alpha-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase
interleukin
immunoglobulin
intravenous immunoglobulin
magnetic resonance imaging
fluid attenuated inversion recovery
diffusion weighted imaging
electroencephalogram
tumour necrosis factor
monocyte chemotactic protein
blood-brain barrier
severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome -associated encephalopathy/ encephalitis
polymerase chain reaction
C-reactive protein
Yu XJ, Liang MF, Zhang SY, Liu Y, Li JD, Sun YL, et al. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(16):1523–32.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yang T, Huang H, Jiang L, Li J. Overview of the immunological mechanism underlying severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (review). Int J Mol Med. 2022;50(3).
Li H, Lu QB, Xing B, Zhang SF, Liu K, Du J, et al. Epidemiological and clinical features of laboratory-diagnosed severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2011-17: a prospective observational study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18(10):1127–37.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Casel MA, Park SJ, Choi YK. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus: emerging novel phlebovirus and their control strategy. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(5):713–22.
Fei X, Feng B, Fang K, Ren W. Risk factors for mortality in severe fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome patients with Central Nervous System complications. Med Sci Monit. 2023;29:e938427.
Kobayashi Y, Kato H, Yamagishi T, Shimada T, Matsui T, Yoshikawa T, et al. Severe fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome, Japan, 2013–2017. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26(4):692–9.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Park SJ, Kim YI, Park A, Kwon HI, Kim EH, Si YJ, et al. Ferret animal model of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome phlebovirus for human lethal infection and pathogenesis. Nat Microbiol. 2019;4(3):438–46.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Kaneko M, Shikata H, Matsukage S, Maruta M, Shinomiya H, Suzuki T, et al. A patient with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis-associated involvement of the central nervous system. J Infect Chemother. 2018;24(4):292–7.
Guang C, Tao C, Sainan S, Ke M, Xiaojing W, Di W et al. Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Chin J Clin Infect Dis. 2022:253–63.
Park SY, Kwon JS, Kim JY, Kim SM, Jang YR, Kim MC, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome-associated encephalopathy/encephalitis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2018;24(4):432.e1-.e4.
Article Google Scholar
Cui N, Liu R, Lu QB, Wang LY, Qin SL, Yang ZD, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus-related human encephalitis. J Infect. 2015;70(1):52–9.
Sun Y, Jin C, Zhan F, Wang X, Liang M, Zhang Q, et al. Host cytokine storm is associated with disease severity of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. J Infect Dis. 2012;206(7):1085–94.
Deng B, Zhang S, Geng Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Yao W, et al. Cytokine and chemokine levels in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(7):e41365.
Kwon JS, Kim MC, Kim JY, Jeon NY, Ryu BH, Hong J, et al. Kinetics of viral load and cytokines in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. J Clin Virol. 2018;101:57–62.
Liu MM, Lei XY, Yu H, Zhang JZ, Yu XJ. Correlation of cytokine level with the severity of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Virol J. 2017;14(1):6.
Li J, Li S, Yang L, Cao P, Lu J. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus: a highly lethal bunyavirus. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2021;47(1):112–25.
Fei X, Fang K, Ni X, Ren WH. Risk factors of neurological complications in severe fever patients with thrombolytic syndrome: a single-Center Retrospective Study in China. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e932836.
Liu MM, Lei XY, Yu XJ. Meta-analysis of the clinical and laboratory parameters of SFTS patients in China. Virol J. 2016;13(1):198.
Li DX. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: a newly discovered emerging infectious disease. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015;21(7):614–20.
Deng B, Zhou B, Zhang S, Zhu Y, Han L, Geng Y, et al. Clinical features and factors associated with severity and fatality among patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome Bunyavirus infection in Northeast China. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(11):e80802.
Takayama-Ito M, Saijo M. Antiviral drugs against severe fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Virus infection. Front Microbiol. 2020;11:150.
Li H, Zhang LK, Li SF, Zhang SF, Wan WW, Zhang YL, et al. Calcium channel blockers reduce severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) related fatality. Cell Res. 2019;29(9):739–53.
Hayden A, Park S, Giustini D, Lee AY, Chen LY. Hemophagocytic syndromes (HPSs) including hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) in adults: a systematic scoping review. Blood Rev. 2016;30(6):411–20.
Nakamura S, Azuma M, Maruhashi T, Sogabe K, Sumitani R, Uemura M, et al. Steroid pulse therapy in patients with encephalopathy associated with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. J Infect Chemother. 2018;24(5):389–92.
Tzekova N, Heinen A, Bunk S, Hermann C, Hartung HP, Reipert B, et al. Immunoglobulins stimulate cultured Schwann cell maturation and promote their potential to induce axonal outgrowth. J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12:107.
Kim UJ, Kim DM, Ahn JH, Kang SJ, Jang HC, Park KH, et al. Successful treatment of rapidly progressing severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome with neurological complications using intravenous immunoglobulin and corticosteroid. Antivir Ther. 2016;21(7):637–40.
Choi S, Kim MC, Kwon JS, Kim JY, Lee KH, Kim SH. Case Report: use of plasma Exchange followed by Convalescent Plasma Therapy in a critically ill patient with severe fever and Thrombocytopenia Syndrome-Associated Encephalopathy: Cytokine/Chemokine concentrations, viral loads, and antibody responses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018;99(6):1466–8.
Park SY, Choi W, Chong YP, Park SW, Wang EB, Lee WJ, et al. Use of plasma therapy for severe fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome Encephalopathy. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016;22(7):1306–8.
Jia B, Yan X, Chen Y, Wang G, Liu Y, Xu B, et al. A scoring model for predicting prognosis of patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11(9):e0005909.
Seo JW, Kim D, Yun N, Kim DM. Clinical update of severe fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome. Viruses. 2021;13(7).
Choi SJ, Park SW, Bae IG, Kim SH, Ryu SY, Kim HA, et al. Severe fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in South Korea, 2013–2015. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2016;10(12):e0005264.
Wang L, Wan G, Shen Y, Zhao Z, Lin L, Zhang W, et al. A nomogram to predict mortality in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome at the early stage-A multicenter study in China. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019;13(11):e0007829.
Gai ZT, Zhang Y, Liang MF, Jin C, Zhang S, Zhu CB, et al. Clinical progress and risk factors for death in severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome patients. J Infect Dis. 2012;206(7):1095–102.
Chen Y, Jia B, Liu Y, Huang R, Chen J, Wu C. Risk factors associated with fatality of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: a meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(51):89119–29.
Yoshikawa T, Fukushi S, Tani H, Fukuma A, Taniguchi S, Toda S, et al. Sensitive and specific PCR systems for detection of both Chinese and Japanese severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus strains and prediction of patient survival based on viral load. J Clin Microbiol. 2014;52(9):3325–33.
Saijo M. Pathophysiology of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome and development of specific antiviral therapy. J Infect Chemother. 2018;24(10):773–81.
Youdong X, Xiaofeng D, Xiyuan N, Zhengdong L. Analysis of the risk factors and prognosis for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome associated encephalopathy. J Infect Chemother. 2023;29(5):464–8.
Kawaguchi T, Matsuda M, Takajo I, Kawano A, Kariya Y, Kubo K, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome with myocardial dysfunction and encephalopathy: a case report. J Infect Chemother. 2016;22(9):633–7.
Kim UJ, Kim DM, Kim SE, Kang SJ, Jang HC, Park KH, et al. Case report: detection of the identical virus in a patient presenting with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome encephalopathy and the tick that bit her. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):181.
Sun Y, Guo B, Yan H, Wu AL, Yao WW, Chen K, et al. Patient with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection and central nervous system disturbance in Dongyang, Zhejiang Province, China, 2017. Virol J. 2019;16(1):129.
Wang C, Gong L, Zeng Z, Zhang J, Guan H, Chen L, et al. Genome-based analysis of SFTSV causing severe encephalitis with brain lesions. J Neurovirol. 2020;26(2):181–7.
Download references
This project was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2020YFC2005403), and by China Association for Promotion of Health Science and Technology (JKHY2023001).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Neurology, Xuanwu Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, 100053, China
Dawei Shan, Weibi Chen, Gang Liu, Huimin Zhang, Shuting Chai & Yan Zhang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Dawei Shan and Yan Zhang contributed to the conception and design of the manuscript. Dawei Shan collected the data and drafted the manuscript. Yan Zhang, Weibi Chen, Gang Liu, Huimin Zhang and Shuting Chai reviewed and modified the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript revision and read and approved the final submitted version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yan Zhang .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Informed consent was obtained from the patient to publish this case, and approval for this study was provided by Research Ethics Committee of the Xuanwu Hospital of Capital Medical University.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and the accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor of this journal.
Competing interests
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or nonfinancial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12883_2024_3664_MOESM1_ESM.mp4
Supplementary Material 1. File name: Additional file 1. File format: mp4. Title of data: Video of patient with persistent involuntary shaking of the perioral area and limbs. Description of data: We took this video on day 2 after the patient was admitted to the hospital. The patient develops persistent involuntary shaking of the perioral area and limbs, especially in the perioral area and distal limbs, which is aggravated by agitation and is accompanied by slurred speech.
Supplementary Material 2. CARE Checklist of information to include when writing this case report.
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Shan, D., Chen, W., Liu, G. et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome with central nervous system symptom onset: a case report and literature review. BMC Neurol 24 , 158 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-024-03664-6
Download citation
Received : 30 November 2023
Accepted : 02 May 2024
Published : 10 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-024-03664-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome
- Novel bunyaviruses
- Central nervous system
- Encephalitis
- Involuntary shaking
BMC Neurology
ISSN: 1471-2377
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Start your review of Lit 21. Overall rating. 148 reviews. 5 stars. 4 stars. 3 stars. 2 stars. 1 star. Filter by rating. Search reviews. Search reviews. Wanda R. Elite 24. Alameda, CA. 132. 270. 393. Feb 8, 2024. 2 photos. In the heart of Newark, New Jersey, perched with a grand view of Kearney, Lit 21 is a good choice.
Start your review of Lit 21. Overall rating. 147 reviews. 5 stars. 4 stars. 3 stars. 2 stars. 1 star. Filter by rating. Search reviews. Search reviews. Dee C. Union, NJ. 0. 1. 1. Mar 10, 2023. 1 photo. By FAR ONE OF THE WORST EXPERIENCES IV EVER Had Interested in celebrating NYE with friends I called and spoke with a hostess who explained the ...
BulgogiZip Barbeque, Chicken Wings, Korean. Deluxe Diner Cafe, Breakfast, Vegetarian. Chinatown Diner Chinese, Vegetarian. Latest reviews, photos and 👍🏾ratings for Lit 21 at 1034 McCarter Hwy in Newark - view the menu, ⏰hours, ☎️phone number, ☝address and map.
Lit 21, Newark, New Jersey. 8,885 likes · 293 talking about this · 10,349 were here. EAT-CHILL-PLAY #ALWAYSLIT
Reviews for Lit 21. 65 ratings. 71 Good food; 74 On time delivery; 70 Correct order; Sort by: Most recent. J. Janet. Mar 17, 2020. 2 reviews. The Chicken Wing appetizer was fantastic! The Lit 21 sauce was delicious. If it were in a bottle I would buy it. Even though I ordered late, the chicken was fresh and the skin crispy.
Lit 21 - Contact Us; Search for: Twitter YouTube Facebook Instagram. Lit 21 - Newark, NJ lit21admin 2024-05-20T23:22:59+00:00. Food and Drink Menu. Questions? Call or Text us at (973) 718-2646. 1034 McCarter Hwy Newark, NJ 07102. Call Us. Text Us. View All Events.
Get information on Lit 21 - Newark. Ratings & Reviews, phone number, website, address & opening hours. ... Lit 21. Lounges. Write review. Write a message. Please call back. Overall Rating. 3.82 /5. Satisfying. 2382 reviews from 4 other sources. Contact info. 1034 McCarter Highway 07102 Newark New Jersey
Lit 21 has gotten off to an uneven start thus far, with a 3.5-star rating out of three reviews on Yelp. Yelper Kenton F. wrote, "This is a cool spot. The liquor isn't watered down and the food ...
Lit 21, Newark: See unbiased reviews of Lit 21, one of 614 Newark restaurants listed on Tripadvisor.
Lit 21, Newark: See unbiased reviews of Lit 21, one of 754 Newark restaurants listed on Tripadvisor.
Lit 21 #11 of 28 Nightlife in Newark. Bars & Clubs. Write a review. Be the first to upload a photo. Upload a photo. Suggest edits to improve what we show. Improve this listing. Top ways to experience nearby attractions. SPECIAL OFFER. 7-Day Philadelphia, D.C, Niagara Falls, Boston Tour from New York. 6. Historical Tours.
Lit 21 #11 of 28 Nightlife in Newark. Bars & Clubs. Write a review. Be the first to upload a photo. Upload a photo. Revenue impacts the experiences featured on this page, learn more. Top ways to experience nearby attractions. The Psychiatric History of New York Walking Tour. 16. Recommended.
148 reviews (973) 718-2646. Website. More. Directions Advertisement. 1034 McCarter Hwy Newark, NJ 07102 Open until 3:00 AM. Hours. Sun 12:00 PM -2:00 AM ... For Jersey, Lit 21 is a vibe for anyone who loves Hip Hop/Rap, Reggae-ton and Denbow. It s theme is more towards the Spanish Caribbean from music and food !
Glassdoor has 2 Lit 21 reviews submitted anonymously by Lit 21 employees. Read employee reviews and ratings on Glassdoor to decide if Lit 21 is right for you. Glassdoor
Get address, phone number, hours, reviews, photos and more for Lit 21 | 1034 McCarter Hwy, Newark, NJ 07102, USA on usarestaurants.info
Lit 21 will soon be in operation in the space, which is located at 1034 McCarter Highway near the Bridge Street Bridge. The business, which describes itself a restaurant, sports bar, and lounge that is "the hottest venue in the tri-state area," has announced that it will hold a grand opening celebration with DJ Camilo of HOT 97 on Thursday ...
View Lit 21's April 2024 deals and menus. Support your local restaurants with Grubhub! Order delivery online from Lit 21 in Newark instantly with Grubhub! ... Reviews for Lit 21. 65 ratings. 71 Good food; 74 On time delivery; 70 Correct order; Sort by: Most recent. J. Joel. Mar 05, 2023. 1 review.
Lit 21 #11 of 28 Nightlife in Newark. Bars & Clubs. Write a review. Be the first to upload a photo. Upload a photo. Suggest edits to improve what we show. Improve this listing. Top ways to experience nearby attractions. SPECIAL OFFER. 7-Day Philadelphia, D.C, Niagara Falls, Boston Tour from New York. 6. Historical Tours.
Order takeaway and delivery at Lit 21, Newark with Tripadvisor: See unbiased reviews of Lit 21, ranked #0 on Tripadvisor among 763 restaurants in Newark.
There are no reviews for Lit 21, New Jersey yet. Be the first to write a review! Write a Review. Food and ambience. Enhance this page - Upload photos! Add a photo. Location and contact. 1034 McCarter Highway, Newark, NJ 7102. Improve this listing. Be the first to write a review .
Lit 21. Unclaimed. Review. Save. Share. 0 reviews. 1034 McCarter Highway, Newark, NJ 7102 + Add phone number + Add website + Add hours Improve this listing. Enhance this page - Upload photos! Add a photo.
202 views, 5 likes, 0 loves, 1 comments, 0 shares, Facebook Watch Videos from Lit 21: LIT Brunch ️ 壟 Every Saturday and Sunday enjoy the best view in Newark alongside our $3 Mimosas and Brunch Menu...
Start your review of Lit Lounge. Overall rating. 27 reviews. 5 stars. 4 stars. 3 stars. 2 stars. 1 star. Filter by rating. Search reviews. Search reviews. Tina A. Elite 24. San Francisco, CA. 299. 1099. 1392. Feb 13, 2024. 2 photos. Definitely 2000-2010's bay area party vibes. It felt highly nostalgic with the music videos playing hip hop and ...
Pure pleasure.". -Amy Scribner ( BookPage) **. Nonfiction. 1. Undue Burden: Life and Death Decisions in Post-Roe America by Shefali Luthra. (Doubleday) 5 Rave • 1 Positive. " Undue Burden isn't the first book about abortion rights and it certainly won't be the last.
Fish and seafood products are one of the most common causes of listeriosis in humans. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted using scientific literature to summarize available data on the prevalence of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria sp. in fish, fish products and fish processing environment. Meta-analysis models were used to estimate the mean prevalence of the pathogen and ...
To conduct this study, the authors followed the essential steps of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA 2020) and Okoli's [] steps for conducting a systematic review.These included identifying the study's purpose, drafting a protocol, applying a practical screening process, searching the literature, extracting relevant data, evaluating the quality ...
May 21, 2024. Jenny Erpenbeck's " Kairos ," a novel about a torrid love affair in the final years of East Germany, won on Tuesday the International Booker Prize, the renowned award for ...
Wandering spleen is a rare clinical entity in which the spleen is hypermobile and migrate from its normal left hypochondriac position to any other abdominal or pelvic position as a result of absent or abnormal laxity of the suspensory ligaments (Puranik in Gastroenterol Rep 5:241, 2015, Evangelos in Am J Case Rep. 21, 2020) which in turn is due to either congenital laxity or precipitated by ...
Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) is a natural focal disease transmitted mainly by tick bites, and the causative agent is SFTS virus (SFTSV). SFTS can rapidly progress to severe disease, with multiple-organ failure (MOF) manifestations such as shock, respiratory failure, disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) and death, but cases of SFTS patients with central nervous ...