- CBSE Maths Important Questions
- Class 8 Maths
- Chapter 2: Linear Equations One Variable

Important Questions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable
CBSE Important Questions about Maths Chapter 2 – Linear equations in one variable is provided here for all the Class 8 students. To score well in the final exams, students can practise these important questions. All the questions given here are as per the CBSE syllabus and NCERT curriculum. All these questions have been prepared based on the exam perspective.
Linear equations in one variable are the algebraic expressions which have only one variable. These equations are easy to solve. Let us see some of the questions here to practise well.
Get all the chapters here: Important Questions for Class 8 Maths .
Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Important Questions With Answers
Question. 1 : Solve the following linear equations:
(i) x – 11 =7
(ii) z + 8 = 9
(iii) 11x = 121
(i) x – 11 = 7
Question. 2 : Solve: y/11 = 11
Solution: y/11 = 11
y = 11 × 11
Question. 3 : Solve: 23x/2 = 46
Solution: 23x/2 = 46
x = (46 × 2)/23
Question.4 : Solve 1.2 = z/1.4
Solution: 1.2 = z/1.4
z = 1.2 × 1.4
Question.5 : Solve 7x – 12 = 16
Solution: 7x -12 = 16
7x = 16 + 12
Question.6 : Solve 7z – 5 = 16
Solution: 7z – 5 = 16
Question.7 : 10 + 6p = 22
Solution: 10 + 6p = 22
6p = 22 – 10
Question.8 : 11 – 5x + 3x + 4x =18
Solution: 11 – 5x + 3x + 4x = 18
11 – 5x + 7x = 18
2x = 18 -11
Question.9 : (x – 2) + (x – 3) + (x – 9) = 0
Solution: (x – 2) + (x – 3) + (x – 9) = 0
x – 2 + x – 3 + x – 9 = 0
3x – 2 – 3 – 9 = 0
3x – 14 = 0
Question.10: (2x-2)+(3x-3)+(9x-9) = 1
Solution: (2x-2)+(3x-3)+(9x-9) = 1
2x – 2 + 3x – 3 + 9x – 9 = 1
14x – 14 = 1
14x = 1 + 14
Question.11 : Solve each of the following equations:
(i)x+2 = -11
Solution: x + 2 = -11
(ii) 2x – 1/6 = 3
Solution: 2x – 1/6 = 3
2x = 3 + 1/6
(iii)7x – 7 = 21
Solution: 7x – 7 = 21
7x = 21 + 7
(iv) -7x = 84
Solution: -7x = 84
(v) 18+ 7x = -3
Solution: 18+ 7x = -3
7x = -3 -18
(vi) 3(x-4) = 21
Solution: 3(x-4) = 21
3x – 12 = 21
3x = 21 + 12
(vii) 3x/2 – 2x/3 = 8
Solution: 3x/2 – 2x/3 = 8
(9x – 4x)/6 = 8
(Viii) 3x-9 = 4x – 3
Solution: 3x-9 = 4x – 3
3x – 4x = -3 + 9
x = – 6
(ix) 3(2x – 3) = 4(2x + 4)
Solution: 3(2x – 3) = 4(2x + 4)
6x – 9 = 8x + 16
6x – 8x = 16 + 9
Question.12: Solve each of the following equations and check your solution by substituting in the equation.
(i) x/2-10=1/2
Solution: x/2 – 10 = 1/2
(x – 20)/2 = 1/2
x – 20 = 1
(ii) x/3-x/2=6
x/3 – x/2 =6
(2x – 3x)/6 = 6
x = – 36
(iii) 6x-9-2(1+x)=x-9
Solution: 6x – 9 -2(1+x) = x -9
6x -9 -2 – 2x = x – 9
6x – 2x – x = -9 + 9 + 2
(iv) 2(x+2)+5(x+5)=4(x-8)+2(x-2)
Solution: 2(x+2)+5(x+5) = 4(x-8)+2(x-2)
2x + 4 + 5x + 25 = 4x – 32 + 2x – 4
2x + 5x -4x – 2x = -32 – 4 -4 – 25
7x – 6x = -65
x = – 65
(v) (3+x)/(2x-3) = -1/2
Solution: (3+x)/(2x-3) = -1/2 2 (3 + x) = -1 (2x – 3)
6 + 2x = -2x + 3
(vi) (x-7)/3 = (x-1)/5
Solution: (x-7)/3 = (x-1)/5
5(x-7) = 3(x-1)
5x – 35 = 3x – 3
5x – 3x = -3 + 35
Word Problems
Question.13: A positive number is 5 time another number. If 21 is added to both the numbers, then one of the new numbers become twice of other new numbers. Find the original numbers.
Solution: Let the smaller number be x And another number = 5x
If 21 is added to both the numbers then as per the given condition;
5x+21 = 2×(x+21)
5x + 21 = 2x + 42
5x – 2x = 42 – 21
x = 21/3= 7
Therefore, the positive number is = 5×7 = 35
Question.14: The sum of three consecutive multiples of 8 is 888. Find the multiple.
Solution: Let the multiples be x, x+8, x+16
Given, the sum of three consecutive multiples of 8 is 888
x+x+8+x+16=888
Therefore the multiples are:
Question.15: Five years ago, Anu was thrice as old as Sonu. After ten years, Anu will be twice as old as Sonu. How old are Anu and Sonu?
Let us assume the present ages of Anu is x and Sonu is y.
According to the question:
x – 5 = 3(y – 5)
x – 5 = 3y – 15
x= 3y -10 ……………….. (1)
Again, as per question;
x + 10 = 2(y + 10)
x + 10 = 2y + 20
x – 2y = 10
(3y – 10) – 2y = 10 (from equation 1)
3y-2y =10+10
Substitute, y=20 in equation 1,
x = 3(20) -10
x =60 – 10
Hence, the present ages of Anu is 50 years and of Sonu is 20 years.
Question 16: Three consecutive integers are as such they are taken in increasing order and multiplied by 2, 3, and 4, respectively, they add up to 56. Find these numbers.
Solution: Let us say the three consecutive numbers be x, x+1 and x+2.
Now as per the given question;
2 × (x)+3 × (x+1)+4 × (x+2)=56 9x + 11 = 56 9x = 56-11 9x = 45 x = 45/9 x= 5
Therefore, the three consecutive numbers are 5, 6 and 7.
Question 17: The perimeter of a rectangular swimming pool is 154 meters. Its length is 2m more than twice its breadth. What are the length and the breadth of the pool?
Solution: Let the breadth of the pool =x
Length of the pool will be 2+2x.
Given, Perimeter of the pool = 154 m
We know, for a given rectangle,
Perimeter=2(length+breath) By using this formula, we get;
154=2(2+2x+x)
Hence, the breadth of the pool is 25m
and Length=2+2×25=52m
Question 18: Sum of two numbers is 95. If one exceeds the other by 15, find the numbers.
Solution: Let first number be x
So, second number will be x+15
As per the given question; x+x+15=95 x+x=95-15 2x=80 x=80/2 x=40
First number = 40
Second number = x+15=40+15=55
Hence, 40 + 55 = 95
Question 19: The numbers are in the ratio 4:3. If they differ by 18, find these numbers.
Solution: Let the numbers be 4x and 3x
According to the question, the two numbers are differed by 18. Thus,
4x – 3x = 18
=> x = 18
4x = 4 × 18 = 72
3x = 3 × 18 = 54
Therefore, the two numbers are 72 and 54
Question 20: Three consecutive integers add up to 57. What are these integers?
Let us say the three consecutive numbers be x-1, x and x+1
Now, as per the given question,
x-1+x+x+1=57
x-1=19-1=18
x+1=19+1=20
The three consecutive numbers are 18,19 and 20.
Question 21: There is a narrow rectangular plot. The length and breadth of the plot are in the ratio of 11:4. At the rate of Rs. 100 per meter it will cost the village panchayat Rs. 75000 to fence the plot. What are the dimensions of the plot?
Solution: Let the common ratio be x.
Thus, the length and breadth of a rectangular plot be 11x and 4x.
We know that perimeter of rectangal = 2(length + breadth)
Therefore, the perimeter of the plot here is:
= 2(11x + 4x)
Given that Cost of fencing the plot at the rate of rs.100 per metre is 75000.
⇒ 100 × Perimeter = 75000
⇒ 100 × 30x = 75000
⇒ 3000x = 75000
Length of rectangular plot = 11x = 275m
Breadth of rectangular plot = 4x = 100m
Hence, the dimensions of the rectangular plot are 275m and 100m respectively.
Question 22: Convert the following statements into equations.
(a) 3 added to a number is 11
(b) 2 subtracted from a number is equal to 15.
(c) 3 times a number decreased by 2 is 4.
(d) 2 times the sum of the number x and 7 is 13.
(a) x +3 = 11
(b) x – 2 = 15
(c) 3x – 2 = 4
(d) = 2(x+7) = 13
Question 23: Amina thinks of a number and subtracts 5/2 from it. She multiplies the result by 8. the final result is 3 times her original number. Find the number.
Solution: Let the number thought by Amina be x
She subtracts 5/2 from the number.
x – 5/2
Now, she multiplies the result by 8
8(x – 5/2)
The result obtained is three times her original number;
8(x – 5/2) = 3x
8x – 20 = 3x
Hence, the number is 4.
Question 24: A number is 12 more than the other. Find the numbers if their sum is 48.
Solution: Let the first number be x and the second number be x + 12
As per the given question;
Sum of the two numbers = 48
x + x + 12 = 48
2x + 12 = 48
2x = 48 – 12
Therefore, x = 18 and x+12= 18+12=30
So the answer is 18 and 30.
Question 25: The sum of three consecutive odd numbers is 51. Find the numbers.
Solution: Let the three consecutive odd numbers are x, x+2 and x+4.
As per the given question, the sum all the three numbers is 51
x+x+2+x+4=51
x=(51-6)/3=45/3 =15
Hence the numbers are:
Therefore, the required three consecutive odd numbers are 15,17 and 19.
Question 26: Jane is 6 years older than her younger sister. After 10 years, the sum of their ages will be 50 years. Find their present ages.
Solution: Let the age of Jane’s younger sister is x.
Age of Jane will be x + 6
As per the question, after 10 years the sum of their ages will be 50.
After 10 years,
age of Jane = x + 16
age of her younger sister = x + 10
x + 16 + x +10 = 50
2x + 26 = 50
Hence, the present age of Jane’s younger sister is 12 years.
And of Jane’s is 12+6 = 18 years.
Question 27: The denominator of a fraction is greater than the numerator by 8. If the numerator is increased by 17 and denominator is decreased by 1, the number obtained is 3/2. Find the fraction.
Solution: Let numerator of a fraction be x.
Denominator = ( x + 8 )
Fraction = Numerator/Denominator = x/x+8
According to the question,
(x + 17) / (x + 8 – 1) = 3/2
(x + 17) / (x + 7) = 3/2
2 ( x + 17 ) = 3 ( x + 7 )
2x + 34 = 3x + 21
3x – 2x = 34 – 21
Numerator = x = 13
Denominator = X + 8 = 13+8 = 21
Fraction = 13/21
Question 28: A sum of Rs.2700 is to be given in the form of 63 prizes. If the prize is of either Rs.100 or Rs.25, find the number of prizes of each type.
Solution: Let the number of prizes of Rs. 100 be =x, and worth rs.25 be y.
Given that,
100x+25y= 2700
Simplify the above equation, we get
4x+y= 108 ….(1)
x+y= 63 ….(2)
Now, solve equation (1) and (2), we get
Now, substitute x= 15 in equation (2), we get
Hence, the number of prizes worth Rs. 1oo is 15 and the number of prizes worth Rs. 25 is 48.
Question 29: In an isosceles triangle, the base angles are equal, and the vertex angle is 80 degrees. Find the measure of the base angles.
Solution: Let the base angle of the isosceles triangle is x.
Since the two sides of the isosceles triangle are equal, therefore its base angles are also equal. By angle sum property of triangle, we know;
Hence, the measure of both the base angles is equal to 50 degrees.
Extra Practice Questions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable
1. The tens and unit digits of a number are the same. By adding the number to its reverse, you get the sum 110. Calculate the number.
2. A man sold his bicycle for an amount that is over Rs 988 by half the price that he paid for it. He made a profit of Rs, 300. Now, what was the original cost of the bicycle?
3. Sum of two numbers were given as 2490. If 6.5% of one number is equal to 8.5% of another number, then find the value of both the numbers.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
It is good for periodic tests and exams ☺️
It is very useful for exams
Really thank you Nice question
really help my kid in exam very nice
Useful questions!!!!!
Very thanks
Nice questions it’s really help mm
Helpful and interesting. I benefited and have fun doing them, thanks you!❤
Nice practice questions before exam
Please can you make some more questions
Thank you this helped study for exams
These sums help to test ourselves before exams.
Yaa , thank you . it helped us to do revision before exam .👍😊
Good Questions Really helpful
thanks for your help, it helped to to prepare for my mid term examinations.
Very good Questions
Helped me score full marks for the maths exam
Thank you sir , for your great support
It was a good experience
this helped to learn more about linear equations now i will be prepared for the exams with byjus thank you very much next time i want only question no amswers
Thank you so much it help me to much
Thank you They were very helpful
exellent super i scored full marks in this Maths exam
Thank u, They were very helpful 👍.
These questions are very helpful, by doing such questions we can solve any type of questions in exams thanks a lot.
very helpful thanks:)
It was very useful
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 2 Class 8 Linear Equations in One Variable
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Updated for new NCERT - 2023-24 Book.
Get NCERT Solutions of all Exercise Questions and Examples of Chapter 2 Class 8 Linear Equations in One Variable free at Teachoo. Answers to each and every question with detailed explanation for your understanding. Best answers guaranteed!
We studied Equations and Expressions in Algebra ( Chapter 9 Class 8 ). Equation has an = sign, expression does not have it
In this chapter, we will learn
- What is an Equation
- What is a Linear Equation
- What is a Linear Equation in one variable
- Solving Linear Equations - by taking variables on one side, numbers on the side
- Making Equations from Statements , and then Solving.
- Perimeter and Area Questions
- Fraction questions - where we need to find Numerator or Denominator
- Cost, Sale, Profit Questions
- Questions where we have Consecutive Numbers
- Questions involving Consecutive Multiples
- Coins and Currency Notes Questions
- Questions where numbers are added or subtracted
- Questions where a Two Digit number is given, and we reverse its digits
- Questions involving Age
Click on an exercise or topic link below to start doing the chapter.
Note: Important Questions of this chapter have been marked. When you click on a link, at the bottom of the page there is a list with arrows. In that list, you can find all the questions of that exercise and find Important Questions marked as blue.
Serial order wise
Concept wise.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable
NCERT solutions for class 8 maths chapter 2 linear equations in one variable tell us that a Mathematical equation can come in many different forms with several variables, differing degrees, number of coefficients , etc. However, a linear equation in one variable is defined as a mathematical expression in which the highest power of the polynomial is 1 and it consists of a single variable. These solutions greatly emphasize on the meaning of a linear equation in one variable and how to effectively solve problems based on the same. As mentioned before there can be many types of linear equations and each has its own method of solving. Thus, students need to go through the NCERT solutions class 8 maths chapter 2 in order to get a good understanding of the procedures. This is a very important chapter because as kids proceed to higher grades they will have to build on the concepts taught in this lesson to solve problems on sister chapters such as linear equations in two variables .
Class 8 maths NCERT solutions chapter 2 comprises a well-structured and detailed explanation of all the NCERT textbook questions. They have been presented using vernacular language so that these solutions can be comprehended by kids of all intelligence levels. NCERT solutions Chapter 2 linear equations in one variable also give real-life applications of the topic helping students to get a holistic view of it. In this article, we will take a deeper look into the subtopics associated with this lesson and also you can find some of these in the exercises given below.
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.1
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.2
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.3
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.4
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.5
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.6
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 PDF
An important topic covered in this chapter is how to interpret a word problem into a linear mathematical equation and what techniques have to be applied in order to solve them. The NCERT solutions class 8 maths chapter 2 acts as a guide for kids when they solve NCERT problems. As these are well-crafted solutions students can refer to them for clarity of concepts. Given below are the exercise-wise links to all the NCERT solutions .
☛ Download Class 8 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 2
NCERT Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Download PDF

NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2
As this chapter is long and has various methods and formulas required to solve a linear equation students need to regularly visit the above links and practice the solutions. This will help them gain confidence thus, helping kids to get the best possible score in an examination. A detailed breakdown of all the components in the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 linear equations in one variable is given below.
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.1 - 12 Questions
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.2 - 16 Questions
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.3 - 10 Questions
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.4 - 10 Questions
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.5 - 10 Questions
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.6 - 7 Questions
☛ Download Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 NCERT Book
Topics Covered: The important topics covered under class 8 maths NCERT solutions chapter 2 are solving equations with only numbers on one side, applications of linear equations, determining the value of an equation with variables on both sides, and simplifying linear equations .
Total Questions: Class 8 maths chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable has a total of 65 well-researched questions out of which 20 are straightforward, 38 are of a medium level, and 7 complex problems.
List of Formulas in NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2
NCERT solutions class 8 maths chapter 2 does not have formulas that need to be memorized as kids have to rely on their calculation and analytical skills in order to solve the problem sums. However, there are some pointers and steps that need to be kept in mind while attempting any question in this particular lesson. Given below are the necessary steps that kids need to follow for going through the NCERT solutions for class 8 maths chapter 2.
- In case of a problem sum read the question with care so as to translate it into the correct mathematical linear equation.
- In an equation take all the terms with variables on one side and the constant on the other side of the equal sign to solve it.
- Always simplify an equation into the standard form of a linear equation, i.e., ax + b = 0 before solving it.
Important Questions for Class 8 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 2
Ncert solutions for class 8 maths video chapter 2, faqs on ncert solutions class 8 maths chapter 2, why are ncert solutions class 8 maths chapter 2 important.
While solving sums kids are bound to hit some form of a roadblock due to doubt or an incorrect result. In order to combat this confusion, the NCERT solutions class 8 maths chapter 2 is important. They give a step-by-step solution to all NCERT textbook questions helping kids to identify and work on their pain points.
Do I Need to Practice all Questions Provided in NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable?
The questions in the NCERT coursebook are handpicked by experts. They cover a wide variety of topics to give students an all-around experience. Thus, it is imperative to practice all problems in the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable to build a robust mathematical foundation for this lesson.
What are the Important Topics Covered in NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2?
All topics in the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 are essential as they cover different aspects of linear equations. However, kids need to reserve an ample amount of time to practice converting a word problem to a linear equation and the methods that can be used to solve the same.
How Many Questions are there in NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable?
There are a total of 65 sums in the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable that have been split into 6 exercises. Each exercise covers a different topic. The questions are a mix of easy and difficult to give children the opportunity of exploring the different ways in which a problem can be framed.
How CBSE Students can utilize NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 effectively?
To effectively utilize the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 kids must go through the solved examples, highlights, and theory that the exercises are based on. Once they get an understanding of the underlying concepts students can proceed to practicing the NCERT questions and using the solutions as a reference.
Why Should I Practice NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable Chapter 2?
Practice is the road to perfection. Students must revise the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Linear Equations in One Variable Chapter 2 so that they can clear their concepts and solve problems with ease. If kids practice these solutions with dexterity and sincerity they are sure to ace any exam be it home or competitive.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- RS Aggarwal Class 8 Mathematics Solutions for Chapter-8 Linear Equations
- RS Aggarwal Solutions

Class 8 RS Aggarwal Mathematics Linear Equations solutions - free PDF download
Mathematics is a high-scoring subject in which pupils achieve the highest possible score on the exam. When it comes to test preparation, it is the most difficult moment for most students, as they struggle to solve problems. As a result, our skilled teachers at Vedantu created helpful aids to assist students in easily preparing the RS Aggarwal Class 8 Mathematics Solutions for Chapter-8 Linear Equations for their exams. All of the answers are designed and adhere to the most recent CBSE patterns. When students learn on a regular basis, they might acquire simple tactics and shortcut ways. This Chapter's PDFs are available here, and students can download them for free using the link on Vedantu’s site.
Solutions to Linear Equations for Class 8 RS Aggarwal
Scoring good marks in the math final examination becomes easy with the help of RS Aggarwal Class 8 Mathematics Solution Chapter 8. It is recommended that students should practice all the sums given in every math Chapter to score well in the examination. They can download Chapter 8 Class 8 Mathematics RS Aggarwal Solutions PDF from Vedantu. Students can refer to the RS Aggarwal Mathematics Class 8 Chapter 8 Solutions,to clear all their doubts from the Chapter. You can download the RS Aggarwal Class 8 Mathematics Chapter 8 solutions PDF from Vedantu for free. You may also be able to download NCERT Solution and NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics . Subjects like Science, Mathematics, English will become easy to study if you have access to NCERT Solution for Class 8 Science , Mathematics solutions and solutions of other subjects.
Exercise-Wise Solutions
We have provided step by step solutions for all exercise questions given in the PDF of Class 8 RS Aggarwal Chapter-8 Linear Equations. All the Exercise questions with solutions in Chapter-8 Linear Equations are given below:
Exercise (Ex 8A) 8.1
Exercise (Ex 8B) 8.2
Exercise (Ex 8C) 8.3
Learn More About Linear Equations:
When it comes to the topic of Linear Equations, then there are some concepts that students should be familiar with before they start solving sums. If you want to learn those topics, then you can refer to the thoroughly discussed topics below. All answers given in the RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics Chapter 8 PDF file are accurate and reliable.
According to experts, Linear Equations can be defined as equations of the first order. This means that equations are defined for lines in any particular coordinate system. In other words, a Linear Equation is an equation for a straight line.
Usually, the general representation of the straight-line equation can be written as y = mx + b. In this equation, m is the slope of the line and b is the y-intercept. Also, Linear Equations can have the highest exponent value of 1. Some examples of Linear Equations are:
3x - y + z = 4
Similarly, when an equation has a homogenous variable, which can also mean that there is only one variable, then this type of equation is known as a Linear Equation in one variable. This further means that a line equation can be achieved by relating zero to a linear polynomial over any particular field. This can be used to obtain the coefficients.
If a student finds solutions to Linear Equations, then that will result in the generation of values. These values when substituted for the unknown values would make the equation true. When it comes to the case of one variable, then there is also a single solution.
However, in the case of Linear Equations with two variables, the solutions can be calculated as the Cartesian coordinates of a point of the Euclidean plane. It should be noted here that Linear Equations can be present in one variable, two variables, and three variables. The examples for all of these Linear Equations are:
Linear Equation in One Variable: 3x + 5 = 0, 97x = 47, and 32x + 8 = 0.
Linear Equation in Two Variables: 6x + 9y - 11 = 0, y + 7x = 3, and 3a + 5t = 2.
Linear Equation in Three Variables: 3x + 12y = 2z, x + y + t = 0, and a - 4b = z.
The equation of a straight line can be given by:
Here, m is the slope of the line, b is the y-intercept, and x and y are the coordinates of the x-axis and the y-axis, respectively.
Further, if a straight line is parallel to the x-axis, then the x coordinate should be equal to zero. Hence, this means that:
Also, if the line is parallel to the y-axis, then the y coordinate will be zero. This means that:
The slope of the line can also be defined as being equal to the ratio of change in y coordinates and the change in x coordinates. An individual can evaluate the value of a slope by using the following formula.
M = (y 2 - y 1 ) / (x 2 - x 1 )
From this formula, it is clear that the slop shows the rise of a line in the plane. This is seen along with the distance covered on the x-axis. Students should remember that the slope of a line is also known as a gradient.
There are other important formulas related to Linear Equations that students should be familiar with. To help students, we have created a table of all those formulas. And that table is mentioned below.
In this table, m is the slope of a line, and xo and yo are the intercepts of the x-axis and y-axis, respectively.
There are several methods that one should follow to solve Linear Equations in one variable. As a general rule, both sides of the equation should be balanced for solving a Linear Equation. After that, students should solve the equation by using several mathematical operations on both sides of the equation. This should be done in a manner that does not have any effect on the balance of the equation. For example, if one has to solve the equation (2x - 10) / 2 = 3 (x - 1), then this can be done by following the steps that are mentioned below.
Step 1: Begin by clearing the fraction.
X - 5 = 3 (x - 1)
Step 2: Simplify both sides of the equation.
2x - 5 = 3x - 3
Step 3: Isolate the value of x.
In the case of Linear Equations with two variables, then there are different methods in which those equations can be solved. And those ways are:
Method of substitution.
Determinant methods.
Method of elimination.
Cross multiplication method.
Also, when it comes to solving Linear Equations in three variables, then those equations can be solved by using the matrix method. Students will get to learn about those methods in other Classes in the future.
Get the Solutions on Vedantu
There are three exercises in RS Aggarwal Class 8 Chapter 8. In all of these exercises, students are tested on their knowledge of Linear Equations. If a student has any doubts while solving these exercises, then the student may take the help of experts at Vedantu. We provide students with solved R S Aggarwal Class 8 Chapter 8 Solutions PDF for free.
Benefits of Downloading Class 8 Mathematics RS Aggarwal Chapter 8 From Vedantu:
There are many benefits that students can get from downloading Class 8 Mathematics R S Aggarwal Chapter 8 from Vedantu. Some of these benefits are listed below.
All answers are 100% accurate and reliable.
Answers are accompanied by an explanation section that can help students to further understand the answer in a better light.
Answers are written by the best subject matter experts in India.

FAQs on RS Aggarwal Class 8 Mathematics Solutions for Chapter-8 Linear Equations
1. Is solving Class 8 RS Aggarwal Chapter 8 Linear Equations beneficial for exams?
Solving Chapter 8 Linear Equations of Class 8 RS Aggarwal is critical in understanding the concepts of the Chapter perfectly. The Chapter is important from the exam perspective as well as for strengthening the foundation for higher studies. Hence, students RS Aggarwal textbook problems to learn how to solve any type of question from the Chapter. RS Aggarwal Chapter 8 Linear Equation exercises allow students to score well in the exams. Class 8 students must solve RS Aggarwal questions for Chapter 8 Linear Equations for proper revision and doubt clearance.
2. Why should I download Class 8 RS Aggarwal solutions for Chapter 8 Linear Equations?
Students must download RS Aggarwal Solutions for Chapter 8 Linear Equations to get the solutions to exercise questions. These are available on popular ed-tech platforms like Vedantu. At Vedantu, RS Aggarwal Linear Equations problems are explained in a fairly simple manner so that students can understand them on their own. The solutions allow students to practice the Chapter for better understanding of concepts. For clearing any doubts regarding Class 8 RS Aggarwal Chapter 8 Linear Equations, students can refer to the solutions available in the free PDF format.
3. What are the learning objectives of RS Aggarwal Mathematics Chapter 8 of Class 8?
With the help of Chapter 8 Linear Equations, students will learn how to solve Linear Equations in one variable. Linear Equations are a crucial part of Algebra. Solving the problems of the Chapter improves arithmetic skills as well as problem-solving abilities. Students will get to know how to frame Linear Equations based on the problem statement. It also ensures that students are able to solve problems where some equations are involved.
4. From where can one avail RS Aggarwal solutions for Class 8 Mathematics Chapter 8 Linear Equations?
There are many ed-tech platforms that offer RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics. However, Vedantu is becoming the students’ favorite platform where one can find the well-curated solutions prepared by expert teachers. These mentors have a vast knowledge of the subject and are also well-experienced. RS Aggarwal Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics Chapter 8 Linear Equations include solved exercise problems. This helps students to easily solve the Chapter. Vedantu provides a step-by-step solution to make it easier for students to grasp the knowledge. Vedantu’s RS Aggarwal Solutions are 100% correct. You can download the PDF for free.
5. What is the most effective method for learning Chapter 8? Factorization in RS Aggarwal's Class 8 Mathematics Chapter 7?
Class 8 Mathematics Chapter-7, RS Aggarwal Factorisation is a fascinating Chapter that necessitates a full comprehension of the principles as well as the practice of a variety of numerical based on the same notion. The bigger the number of questions you practise after fully understanding the subject or theory of the Chapter, the stronger your grip on it will be. This can tremendously assist you in gaining confidence and improving your exam performance. After you've completed all of the Chapters, you should work on the previous year papers and mocks available on Vedantu to improve your speed and efficiency, as well as your total subject score.
Register here
In case you want to be notified about school in your locality then please register here.
- Are you a Parent or Student?
- Are you a Teacher?
- Are you a School Supplier?

- Our other Domains Olympiad Preparation Math Square Science Square English Square Cyber Square School Square Scholar Square Global Olympiads NCERT Solutions CBSE Sample Papers
- Join WhatsApp Channel
- Apply for CREST Olympiads

Linear Equations

- An equation which has only one variable is called Linear Equation
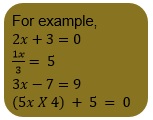
Solving equations which have linear equations on one side and numbers on the other side
EXAMPLE 1: Solve 3x + 15 = 1
- We need to keep the variable on the left side and numerical terms on the right side. Because of this, we have to transport 15 to the right side by changing its sign i.e., -15. => 3x + 15 = 1 => 3x = 1-15
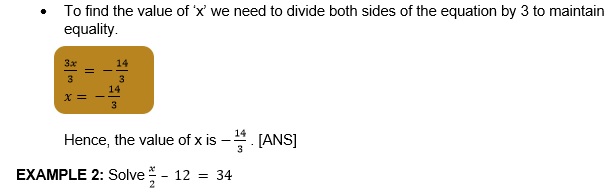
- We need to keep the variable on the left side and numerical terms on the right side. Because of this, we have to transport -12 to the other side by changing its sign i.e., +12.

Solving equations having variables having the variable on both sides
EXAMPLE 1: Solve .
- Simplify the given equation. => =>
- Bring the variable terms on the left side of the equation and the other numerical terms on the right side of the equation. => =>
- Now, to find the value of ‘x’ we need to divide both sides of the equation by 6 to maintain equality.

Application of Linear Equations
Linear equations are used to find the value of an unknown quantity. Have a look at the following examples:
EXAMPLE 1: The sum of the digits of a 2 digit number 13. The numbers obtained by interchanging the digits is 14 more than the given number. Find the number.
SOLUTION: Let the digit at units place be x and the number at tens place be y.
=> y + x = 13 [sum is 13 given] => y = 13 – x [Transposing x to the other side by changing its sign] Thus, the formed number is= [Since x is at ones place and y=13-x is at tens place] After interchanging the digits, the number is= [Now x is at tens place & y=13-x is at one's place] The interchanged number is greater than the original number by 14. [Given]
New number Old number Difference
- Simplify => => => =>
- Transpose the variable term ‘x’ on the left side of the equation and other numerical terms on the right side of the equation by changing their sign. => 18x – 117 = 14 => 18x = 131
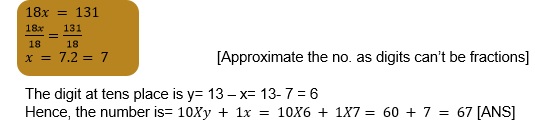
EXAMPLE 2: The distance between town A and town B is 123 km. Two buses begin their journey from these towns and move directly toward each other. From town A, the bus is moving at a speed of 45 km per hour and from town B, the bus is moving at 67 km per hour. Assuming the buses start at the same time, find how far is their meeting point from town A. SOLUTION: Let the buses meet after t hours.
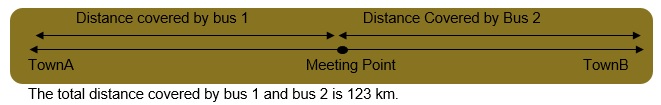
We know that distance= speed X time Distance covered by bus 1 = 45 X t Distance covered by bus 2 = 67 X t Therefore, 45t + 67t = 123
The distance travelled by bus 1 from city A to the meeting point= speed of bus 1 X time taken by it to reach the meeting point. =45 X 1.098= 49.41 km Thus, the distance of reaching point from town A is 49.41km. [ANS]
Reducing Equation to Simpler Form


Equations reducible to linear form

- Now, simplify => 6x + 12 + 12x + 15 = 14x + 16 => 18x + 27 = 14x +16
- Transpose the variable term ‘x’ to the left side and the numerical terms on the right side of the equation by changing their sign. => 18x – 14x = 16 – 27 => 4x = 11
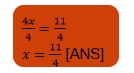
Practice these questions
Q3) Three numbers are in the ratio 1:2:3. If the sum of the largest and the smallest equals the second and 45. Find the numbers.
Q4) Find the number whose 1/6 th part decreased 7 equals its 8/9 th part diminished by 1.
Q5) The difference between two numbers is 23. And the quotient obtained by dividing the larger number by the smaller one is 4. Find the numbers.
Q6) A man cycles to the office from his house at a speed of 5km per hour and reaches 6 minutes late. If he cycles at a speed of 7km/hr, he reaches 8 minutes early. What is the distance between the office and his house? Q7) Suraj is now half as old as his father. 20 years ago, Suraj’s father was six times Suraj’s age. What are their ages now? Q8) The perimeter of an isosceles triangle is 91cm. If the length of each equal side is 2cm more than the length of its base. Find the lengths of the sides of the triangle. Q9) The age of a boy in months is equal to the age of his grandfather in years. If the difference between their ages is 66 years, find their ages.
- The basic principle used in solving any linear equation is that any operation performed on one side of the equation must also be performed on the other side of the equation.
- Any term in an equation can be transposed from one side to other side by changing its sign.
- In cross multiplication, we multiply the numerator of LHS by the denominator of RHS and the denominator of LHS by the numerator of RHS and the resultant expression are equal to each other.
- Practical problems are based on the relations between some known and unknown quantities. We convert such problems into equations and then solve them.
Quiz for Linear Equations
Your Score: 0 /10
Other Chapters of Class 8
Quick Links

SchoolPlus Program
Yearlong program for Olympiads preparation & to build necessary skills for future.

Olympiad Exam Dates
Time to mark your calendar with the upcoming Olympiads exam schedule.

LIVE Classes for Olympiads
Take your Olympiad preparation to next-level by taking LIVE Classes.

Olympiad Test Series
Assess your performance by taking topic-wise and full length mock tests.

India’s First Summer Olympiads
Know your true potential by participating in Unicus Olympiads for classes 1-11.
Asia’s Biggest Winter Olympiads
Give wings to your innovation by appearing in CREST Olympiads for Prep/KG to classes 1-10.
- Equation Problems of Age
Equation Problems of Age are part of the quantitative aptitude section. In the equation problems of age, the questions are such that they result in equations. These equations could become either linear or non-linear and they will have solutions that will represent the age of the people in the question. In the following sections, we will some of the examples of these problems and also learn about the various shortcuts that we can use to solve them. Let us start with some easier examples and concepts below.
Suggested Videos
Equations are a convenient way to represent conditions or relations between two or more quantities . An equation could have one, two or more unknowns. The basic rule is that if the number of unknowns is equal to the number of conditions, then these equations are solvable, otherwise not. We will see some important examples here but first, let us see the following tricks.
If the age of a person is ‘x’, then ‘n’ years after today, the age = x + n. Similarly, n years in the past, the age of this would have been x – n years.
Example 1: A father and his son decide to sum their age. The sum is equal to sixty years. Six years ago the age of the father was five times the age of the son. Six years from now the son’s age will be:
A) 23 years B) 19 years C) 20 years D) 22 years
Answer: Suppose that the present age of the son is = x years. Then the father’s age is (60 -x) years. Notice that we are trying to reduce the problem into as few variables as possible. As per the second condition of the question, we have:
The age of the father six years ago = (60 – x) – 6 years = 54 – x years.
Similarly the age of the son six years ago will be x – 6 years. Therefore as per the second condition , we have;
54 – x = 5(x – 6) or 54 – x = 5x – 30 and we can write 6x = 84
Hence, we have x = 14 years. Thus the son’s age after 6 years = (x+ 6) = (14 + 6) = 20 years. Hence the correct option is C) 20 years.
More Solved Examples
Example 2: The difference in the age of two people is 20 years. If 5 years ago, the elder one of the two was 5 times as old as the younger one, then their present ages are equal to:
A) 20 and 30 years respectively
B) 30 and 10 years respectively
C) 15 and 35 years respectively
D) 32 and 22 years respectively
Answer: The first step is to find the equation. Let the age of the younger person be x. Then the age of the second person will be (x + 20) years. Five years ago their ages would have been x – 5 years and x + 20 years. Therefore as per the question, we have: 5 (x – 5) = (x + 20 – 5) or 4x = 40 or x = 10. Therefore the ages are 10 years for the younger one and (10 + 20) years = 30 years for the elder one.
Example 3: Yasir is fifteen years elder than Mujtaba. Five years ago, Yasir was three times as old as Mujtaba. Then Yasir’s present age will be:
A) 29 years B) 30 years C) 31 years D) 32 years
Answer: Let the age of Yasir be = x years. Then the age of Mujtaba will be equal to x – 15 years. Now let us move on to the second condition. Five years ago the age of Yasir will be equal to x – 5 years. Also, the age of Mujtaba five years ago will be x – 15 – 6 years = x – 21 years. As per the question, we have:
3(x – 21) = x – 5 or 3x – 63 = x – 5. Therefore we have: 2x = 58 and hence x = 29 years. Therefore Yasir’s present age is 29 years and the correct option is A) 29 years.
Example 4: Ten years ago, the age of a person’s mother was three times the age of her son. Ten years hence, the mother’s age will be two times the age of her son. The ratio of their present ages will be:
A) 10:19 B) 9: 5 C) 7: 4 D) 7: 3
Answer: Let the age of the son ten years ago be equal to x years. Therefore the age of the mother ten years ago will be equal to 3x. Following this logic, we see that the present age of the son will be equal to x + 10 years and that of the mother will be equal to 3x + 10 years.
The second condition says that ten years from the present, the mother’s age will be twice that of her son. After ten year’s the mother’s age will be 3x + 10 + 10 years and that of the son will be x + 10 + 10 years. As per the question we have:
(3x + 10) +10 = 2 [(x + 10) + 10] or (3x + 20) = 2[x + 20]. In other words , we can write:
x = 20 years. Thus the present age of the mother = 3(20) + 10 = 70 years. Also the present age of the son = 20 + 10 = 30 years. Thus the ratio is 7:3 and the correct option is D) 7:3.
Practice Questions
Q 1: The age of a man is 24 years more than his son. In two years, the father’s age will be twice that of his son. Then the present age of his son is: A) 18 years B) 21 years C) 22 years D) 24 years
Ans: C) 22 years.
Q 2: After 15 years Ramesh’s age will be 5 times his age 5 years ago. What is the present age of Ramesh? A) 5 years B) 10 years C) 15 years D) 20 years
Ans: B) 10 years
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Age Problems
- Age Problems Practice Questions
- Proportion Based Age Problems
- Ratio Based Age Problems
6 responses to “Ratio Based Age Problems”
3 peoples ages = 100,the older is 5 years older than the second,the age of the third is half of the seconds age ,whats the age of the thrid person ?
The ages of zaira and angel are in the ratio 7:9. Five years ago, the sum of their ages is 54. What are their present ages?
Am I crazy or is Q1 not the right answer? I got 24. I even looked this up elsewhere and people were reporting 24 is the correct answer (or rather none of the above in this case).
5 Read the information given. Form simultaneous equations and solve :
Present age of Raju is X years
Present age of Sanju is y years
Add 4 years , to their ages
The ratio of their ages is
Equation 121
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Existence, sign and asymptotic behaviour for a class of integro-differential elliptic type problems
- Published: 05 May 2024
- Volume 63 , article number 122 , ( 2024 )
Cite this article

- Márcio A. L. Bahia 1 ,
- Marcos T. O. Pimenta 2 &
- João R. Santos Junior 3
72 Accesses
Explore all metrics
In this work we study existence, sign and asymptotic behaviour of solutions for a class of elliptic problems of the integral-differential type under the presence of a parameter. A careful analysis of the influence of the referred parameter on the structure of the set of solutions is made, by considering different reaction terms. Among our main contributions are: (1) a positive answer to Remark 2.4 in Allegretto and Barabanova (Proc R Soc Edinb A 126(3):643–663, 1996); (2) a detailed treatment of the associated eigenvalue problem; (3) The first result involving the existence of a ground-state solution for this class of problems.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Similar content being viewed by others

General Solution to a Nonlocal Linear Differential Equation of First-Order
Fractional integration and optimal estimates for elliptic systems
Nonlinear eigenvalue problems for (p, 2)-equations and laplace equations with perturbations, data availability.
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Allegretto, W., Barabanova, A.: Positivity of solutions of elliptic equations with nonlocal terms. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. A 126 (3), 643–663 (1996)
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Allegretto, W., Shen, B., Haswell, P., Robinson, A.M.: Numerical modelling and optimization of micromachined thermal conductivity pressure sensor. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 13 (10), 1247–1256 (1994)
Article Google Scholar
Alves, C.O., Correa, F.J.S.A., Santos Júnior, J.R.: Remark on a class of integro-differential problems. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 506 , 125723 (2022)
Amann, H.: Fixed point equations and nonlinear eigenvalue problems in ordered Banach spaces. SIAM 18 (4), 621–704 (1976)
Brezis, H.: Functional Analysis, Sobolev Spaces and Partial Differential Equations, Universitext. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Google Scholar
Catchpole, E.A.: A Cauchy problem for an ordinary integro-differential equation. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. A 72 , 39–55 (1972/73)
Chafee, N.: The electric ballast resistor: homogeneous and nonhomogeneous equilibra. In: Nonlinear Differential Equations, pp. 97–1277. Academic Press, New York (1981)
Correa, F.J.S.A., Lima, N.A., de Lima, R.N.: Existence of solutions of integro-differential semilinear elliptic equations. Appl. Anal. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1080/00036811.2021.2005786
Chipot, M., Rodrigues, J.F.: On a class of nonlocal nonlinear elliptic problems. RAIRO - Modélisation mathématique et analyse numérique 26 (3), 447–467 (1992)
MathSciNet Google Scholar
dos Santos, G.C.G., Lima, N.A., de Lima, R.N.: Existence and multiple of solutions for a class integro-differential equations with singular term via variational and Galerkin method. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Mapp. 69 , 103752 (2023)
Fiedler, B., Polác̆ik, P.: Complicated dynamics of scalar reaction diffusion equations with a nonlocal term. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. Sect. A Math. 115 (1–2), 167–192 (1990)
Furter, J., Grinfeld, M.: Local vs. nonlocal interactions in population dynamics. J. Math. Biol. 27 , 65–80 (1989)
Freitas, P.: A nonlocal Sturm-Liouville eigenvalue problem. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. Sect. A Math. 124 , 169–188 (1994)
Szulkin, A., Weth, T.: The method of Nehari manifold. In: Gao, D.Y., Montreanu, D. (eds.) Handbook of Nonconvex Analysis and mappings, pp. 597–632. International Press, Boston (2010)
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Programa de Doutorado em Matemática, Instituto de Ciências Exatas e Naturais, Universidade Federal do Pará, Avenida Augusto corrêa 01, Belém, PA, 66075-110, Brazil
Márcio A. L. Bahia
Departamento de Matemática e Computação, Faculdade de Ciências e Tecnologia, Universidade Estadual Paulista - UNESP, Rua Roberto Simonsen, 305, Presidente Prudente, SP, 19060-900, Brazil
Marcos T. O. Pimenta
Faculdade de Matemática, Instituto de Ciências Exatas e Naturais, Universidade Federal do Pará, Avenida Augusto corrêa 01, Belém, PA, 66075-110, Brazil
João R. Santos Junior
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to João R. Santos Junior .
Additional information
Communicated by P. H. Rabinowitz.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
João R. Santos was partially supported by CNPq/Brazil 307045/2021-8, Brazil. M. T. O. Pimenta was partially supported by CNPq/Brazil 303788/2018-6 and FAPESP 2019/14330-9, Brazil.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Bahia, M.A.L., Pimenta, M.T.O. & Junior, J.R.S. Existence, sign and asymptotic behaviour for a class of integro-differential elliptic type problems. Calc. Var. 63 , 122 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00526-024-02730-8
Download citation
Received : 13 June 2023
Accepted : 27 March 2024
Published : 05 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s00526-024-02730-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Mathematics Subject Classification
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Class 8 Math (India) - Hindi
Course: class 8 math (india) - hindi > unit 2.
- Two-step equation word problem: garden (Hindi)
Word problems linear equations (basic)
- Sums of consecutive integers (Hindi)
- Sums of consecutive integers
- Two-step equation word problem: oranges (Hindi)
- Linear equations word problems (advanced)
- Your answer should be
- an integer, like 6
- a simplified proper fraction, like 3 / 5
- a simplified improper fraction, like 7 / 4
- a mixed number, like 1 3 / 4
- an exact decimal, like 0.75
- a multiple of pi, like 12 pi or 2 / 3 pi

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Word Problems. Question.13: A positive number is 5 time another number. If 21 is added to both the numbers, then one of the new numbers become twice of other new numbers. ... Extra Practice Questions For Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable. 1. The tens and unit digits of a number are the same. By adding the number to its ...
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type. Question 1. Identify the algebraic linear equations from the given expressions. (a) x 2 + x = 2 is not a linear equation. (b) 3x + 5 = 11 is a linear equation. (c) 5 + 7 = 12 is not a linear equation as it does not contain variable.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable Exercise 2.1. Ex 2.1 Class 8 Maths Question 1. Solve the equation: x - 2 = 7. Solution: Given: x - 2 = 7. ⇒ x - 2 + 2 = 7 + 2 (adding 2 on both sides) ⇒ x = 9 (Required solution) Ex 2.1 Class 8 Maths Question 2. Solve the equation: y + 3 = 10.
Updated for new NCERT - 2023-24 Book. Get NCERT Solutions of all Exercise Questions and Examples of Chapter 2 Class 8 Linear Equations in One Variable free at Teachoo. Answers to each and every question with detailed explanation for your understanding. Best answers guaranteed! We studied Equations and Expressions in Algebra ( Chapter 9 Class 8 ...
2.1 Introduction. In the introduction part of NCERT Maths Class 8 Chapter 2, you will be reminded of algebraic equations and expressions of earlier days. Those are of the format shown below: Expresions - 5x + y, x + y, y + y2, etc. Equations - 5x + y = 10, x + y = -2, y + y2= 9 etc.
This will help them gain confidence thus, helping kids to get the best possible score in an examination. A detailed breakdown of all the components in the NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 linear equations in one variable is given below. Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.1 - 12 Questions. Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Ex 2.2 - 16 Questions.
There are 6 problems in Chapter 2 of the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths that deal with linear equations in one variable. The key ideas presented in this chapter are: 2.1 The Start 2.2 Solving Equations with Numbers and Linear Expressions on One Side 2.3 Some Applications Solving Equations with a Variable on Both Sides, Section 2.4 2.5 A Few Additional Uses 2.6 Simplification Equations ...
These solutions for Linear Equations In One Variable are extremely popular among class 8 students for Math Linear Equations In One Variable Solutions come handy for quickly completing your homework and preparing for exams. All questions and answers from the NCERT Book of class 8 Math Chapter 2 are provided here for you for free.
Learn. Linear graphs word problems. Modeling with tables, equations, and graphs. Linear graphs word problem: cats. Linear equations word problems: volcano. Linear equations word problems: earnings. Modeling with linear equations: snow. Linear function example: spending money. Fitting a line to data.
Class 8 (Old) 14 units · 96 skills. Unit 1. Rational numbers. Unit 2. Linear equations in one variable. Unit 3. Understanding quadrilaterals. Unit 4. Data handling. ... Word problems linear equations (basic) Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Sums of consecutive integers Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Linear equations word problems ...
Solving Chapter 8 Linear Equations of Class 8 RS Aggarwal is critical in understanding the concepts of the Chapter perfectly. The Chapter is important from the exam perspective as well as for strengthening the foundation for higher studies. Hence, students RS Aggarwal textbook problems to learn how to solve any type of question from the Chapter.
Linear equations word problems. Google Classroom. Andrei wants to fill a glass tank with spherical marbles and then fill the remaining space with water. The variable w models the amount of water (in liters) Andrei uses if he uses n marbles. w = 32 − 0.05 n. What is the volume of each marble? liters. Learn for free about math, art, computer ...
To eliminate the denominator terms, multiply both sides of the equation by the LCM of 6 and 8. Application of Linear Equations. Linear equations are used to find the value of an unknown quantity. Have a look at the following examples: EXAMPLE 1: The sum of the digits of a 2 digit number 13. The numbers obtained by interchanging the digits is 14 ...
Solution. (a) If ax = b, then x = b a. Since, a and b are positive integers. So, b a is also positive integer, Hence, the solution of the given equation has to be always positive. Question. 8 Linear equation in one variable has. (a) only one variable with any power. (b) only one term with a variable.
Unit test. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.
Answer: The first step is to find the equation. Let the age of the younger person be x. Then the age of the second person will be (x + 20) years. Five years ago their ages would have been x - 5 years and x + 20 years. Therefore as per the question, we have: 5 (x - 5) = (x + 20 - 5) or 4x = 40 or x = 10.
Date. Topic. January 16. Introduction to CIVL 7/8111 Introduction to mathematical modeling - engineering applications and equilibrium of a spring mass system. January 21. Martin Luther King Day - No Class. January 23. Introduction to mathematical modeling Equilibrium of a spring mass system and plane trusses.
In this work we study existence, sign and asymptotic behaviour of solutions for a class of elliptic problems of the integral-differential type under the presence of a parameter. A careful analysis of the influence of the referred parameter on the structure of the set of solutions is made, by considering different reaction terms. Among our main contributions are: (1) a positive answer to Remark ...
Word problems linear equations (basic) A positive number is 5 times another number. If we add 2 to both the numbers, then one of them becomes 4 times the other. Find the smaller number. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more.