Math Solver
Geogebra math solver.
Get accurate solutions and step-by-step explanations for algebra and other math problems, while enhancing your problem-solving skills!



Get step-by-step solutions to your math problems

Try Math Solver

Get step-by-step explanations
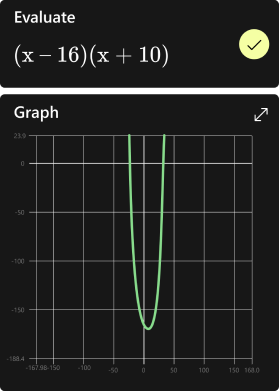
Graph your math problems
Practice, practice, practice

Get math help in your language
Problem Solving in Mathematics
- Math Tutorials
- Pre Algebra & Algebra
- Exponential Decay
- Worksheets By Grade
The main reason for learning about math is to become a better problem solver in all aspects of life. Many problems are multistep and require some type of systematic approach. There are a couple of things you need to do when solving problems. Ask yourself exactly what type of information is being asked for: Is it one of addition, subtraction, multiplication , or division? Then determine all the information that is being given to you in the question.
Mathematician George Pólya’s book, “ How to Solve It: A New Aspect of Mathematical Method ,” written in 1957, is a great guide to have on hand. The ideas below, which provide you with general steps or strategies to solve math problems, are similar to those expressed in Pólya’s book and should help you untangle even the most complicated math problem.
Use Established Procedures
Learning how to solve problems in mathematics is knowing what to look for. Math problems often require established procedures and knowing what procedure to apply. To create procedures, you have to be familiar with the problem situation and be able to collect the appropriate information, identify a strategy or strategies, and use the strategy appropriately.
Problem-solving requires practice. When deciding on methods or procedures to use to solve problems, the first thing you will do is look for clues, which is one of the most important skills in solving problems in mathematics. If you begin to solve problems by looking for clue words, you will find that these words often indicate an operation.
Look for Clue Words
Think of yourself as a math detective. The first thing to do when you encounter a math problem is to look for clue words. This is one of the most important skills you can develop. If you begin to solve problems by looking for clue words, you will find that those words often indicate an operation.
Common clue words for addition problems:
Common clue words for subtraction problems:
- How much more
Common clue words for multiplication problems:
Common clue words for division problems:
Although clue words will vary a bit from problem to problem, you'll soon learn to recognize which words mean what in order to perform the correct operation.
Read the Problem Carefully
This, of course, means looking for clue words as outlined in the previous section. Once you’ve identified your clue words, highlight or underline them. This will let you know what kind of problem you’re dealing with. Then do the following:
- Ask yourself if you've seen a problem similar to this one. If so, what is similar about it?
- What did you need to do in that instance?
- What facts are you given about this problem?
- What facts do you still need to find out about this problem?
Develop a Plan and Review Your Work
Based on what you discovered by reading the problem carefully and identifying similar problems you’ve encountered before, you can then:
- Define your problem-solving strategy or strategies. This might mean identifying patterns, using known formulas, using sketches, and even guessing and checking.
- If your strategy doesn't work, it may lead you to an ah-ha moment and to a strategy that does work.
If it seems like you’ve solved the problem, ask yourself the following:
- Does your solution seem probable?
- Does it answer the initial question?
- Did you answer using the language in the question?
- Did you answer using the same units?
If you feel confident that the answer is “yes” to all questions, consider your problem solved.
Tips and Hints
Some key questions to consider as you approach the problem may be:
- What are the keywords in the problem?
- Do I need a data visual, such as a diagram, list, table, chart, or graph?
- Is there a formula or equation that I'll need? If so, which one?
- Will I need to use a calculator? Is there a pattern I can use or follow?
Read the problem carefully, and decide on a method to solve the problem. Once you've finished working the problem, check your work and ensure that your answer makes sense and that you've used the same terms and or units in your answer.
- Critical Thinking Definition, Skills, and Examples
- Converting Cubic Meters to Liters
- 2nd Grade Math Word Problems
- The Horse Problem: A Math Challenge
- 2020-21 Common Application Essay Option 4—Solving a Problem
- How to Use Math Journals in Class
- The Frayer Model for Math
- Algorithms in Mathematics and Beyond
- "Grandpa's Rubik's Cube"—Sample Common Application Essay, Option #4
- Math Stumper: Use Two Squares to Make Separate Pens for Nine Pigs
- Graphic Organizers in Math
- College Interview Tips: "Tell Me About a Challenge You Overcame"
- Christmas Word Problem Worksheets
- Solving Problems Involving Distance, Rate, and Time
- Innovative Ways to Teach Math
- Study Tips for Math Homework and Math Tests

Step-by-Step Solutions
Use step-by-step calculators for chemistry, calculus, algebra, trigonometry, equation solving, basic math and more.
Gain more understanding of your homework with steps and hints guiding you from problems to answers! Wolfram|Alpha Pro step-by-step solutions not only give you the answers you're looking for, but also help you learn how to solve problems.
Starting at $ 5 .00 /month
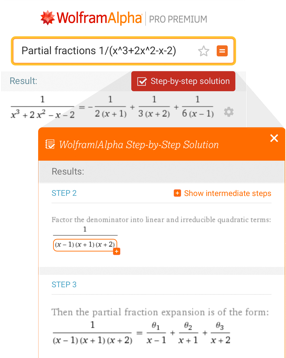
Step-by-Step Solutions Features
Not just answers—step-by-step solutions buttons expand answers and explain how that answer was found.
![steps in problem solving in mathematics [object Object]](https://www.wolframalpha.com/_next/static/images/sbs-solutions_2MB5WFCI.png)
Show Intermediate Steps
Break steps down even further with intermediate steps. These optional additional explanations for individual pieces of step-by-step solutions help guide you.
![steps in problem solving in mathematics [object Object]](https://www.wolframalpha.com/_next/static/images/sbs-intermediate_NnfJanMv.png)
Choose a Method
Explore different ways of finding a solution. Use your classroom's teaching method to guide you through the answer.
![steps in problem solving in mathematics [object Object]](https://www.wolframalpha.com/_next/static/images/sbs-methods_1EfrOjX1.png)
Your own tutor—hints are also frequently provided to not just provide answers, but also to guide you towards finding the solution yourself.
![steps in problem solving in mathematics [object Object]](https://www.wolframalpha.com/_next/static/images/sbs-hints_Ru_Wwd42.png)
Examples of Step-by-Step Solutions
Explore some of the content areas covered by step-by-step solutions, including math, chemistry and physics, or view more examples »
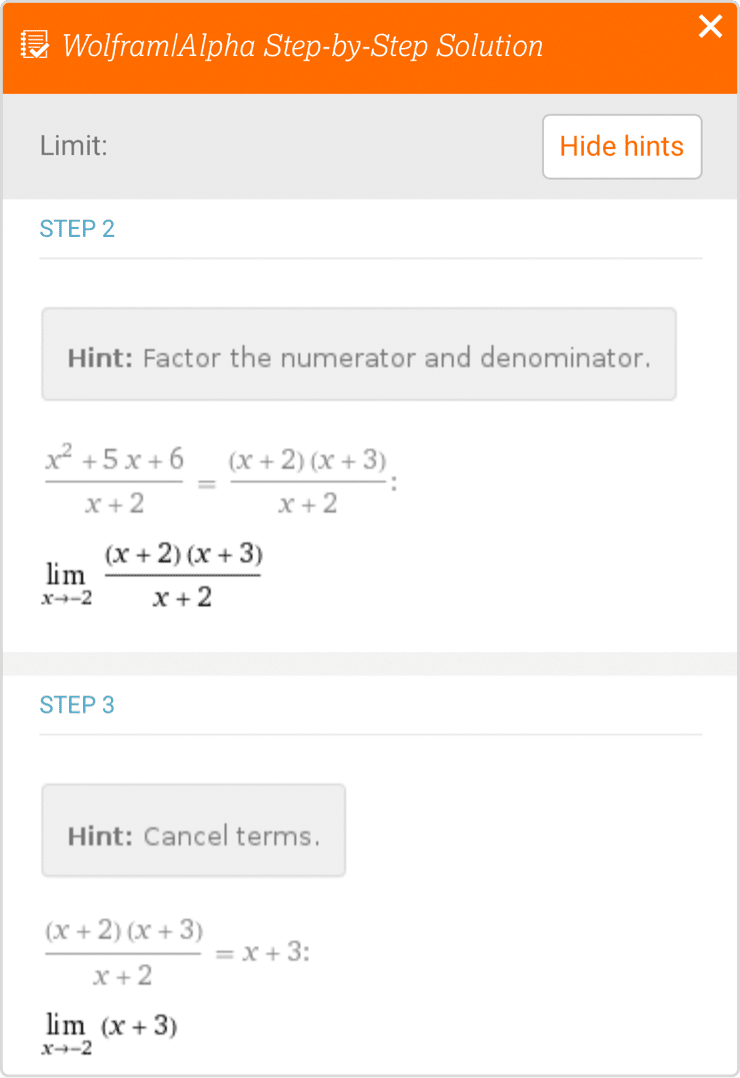
Equation Solving

More Math Topics

- Solve equations and inequalities
- Simplify expressions
- Factor polynomials
- Graph equations and inequalities
- Advanced solvers
- All solvers
- Arithmetics
- Determinant
- Percentages
- Scientific Notation
- Inequalities
Math Topics
More solvers.
- Add Fractions
- Simplify Fractions
Weekly dose of self-improvement
The easy 4 step problem-solving process (+ examples)
This is the 4 step problem-solving process that I taught to my students for math problems, but it works for academic and social problems as well.

Every problem may be different, but effective problem solving asks the same four questions and follows the same method.
- What’s the problem? If you don’t know exactly what the problem is, you can’t come up with possible solutions. Something is wrong. What are we going to do about this? This is the foundation and the motivation.
- What do you need to know? This is the most important part of the problem. If you don’t know exactly what the problem is, you can’t come up with possible solutions.
- What do you already know? You already know something related to the problem that will help you solve the problem. It’s not always obvious (especially in the real world), but you know (or can research) something that will help.
- What’s the relationship between the two? Here is where the heavy brainstorming happens. This is where your skills and abilities come into play. The previous steps set you up to find many potential solutions to your problem, regardless of its type.
When I used to tutor kids in math and physics , I would drill this problem-solving process into their heads. This methodology works for any problem, regardless of its complexity or difficulty. In fact, if you look at the various advances in society, you’ll see they all follow some variation of this problem-solving technique.
“The gap between understanding and misunderstanding can best be bridged by thought!” ― Ernest Agyemang Yeboah
Generally speaking, if you can’t solve the problem then your issue is step 3 or step 4; you either don’t know enough or you’re missing the connection.
Good problem solvers always believe step 3 is the issue. In this case, it’s a simple matter of learning more. Less skilled problem solvers believe step 4 is the root cause of their difficulties. In this instance, they simply believe they have limited problem-solving skills.
This is a fixed versus growth mindset and it makes a huge difference in the effort you put forth and the belief you have in yourself to make use of this step-by-step process. These two mindsets make a big difference in your learning because, at its core, learning is problem-solving.
Let’s dig deeper into the 4 steps. In this way, you can better see how to apply them to your learning journey.
Step 1: What’s the problem?
The ability to recognize a specific problem is extremely valuable.
Most people only focus on finding solutions. While a “solutions-oriented” mindset is a good thing, sometimes it pays to focus on the problem. When you focus on the problem, you often make it easier to find a viable solution to it.
When you know the exact nature of the problem, you shorten the time frame needed to find a solution. This reminds me of a story I was once told.
When does the problem-solving process start?
The process starts after you’ve identified the exact nature of the problem.
Homeowners love a well-kept lawn but hate mowing the grass.
Many companies and inventors raced to figure out a more time-efficient way to mow the lawn. Some even tried to design robots that would do the mowing. They all were chasing the solution, but only one inventor took the time to understand the root cause of the problem.
Most people figured that the problem was the labor required to maintain a lawn. The actual problem was just the opposite: maintaining a lawn was labor-intensive. The rearrangement seems trivial, but it reveals the true desire: a well-maintained lawn.
The best solution? Remove maintenance from the equation. A lawn made of artificial grass solved the problem . Hence, an application of Astroturf was discovered.
This way, the law always looked its best. Taking a few moments to apply critical thinking identified the true nature of the problem and yielded a powerful solution.
An example of choosing the right problem to work the problem-solving process on
One thing I’ve learned from tutoring high school students in math : they hate word problems.
This is because they make the student figure out the problem. Finding the solution to a math problem is already stressful. Forcing the student to also figure out what problem needs solving is another level of hell.
Word problems are not always clear about what needs to be solved. They also have the annoying habit of adding extraneous information. An ordinary math problem does not do this. For example, compare the following two problems:
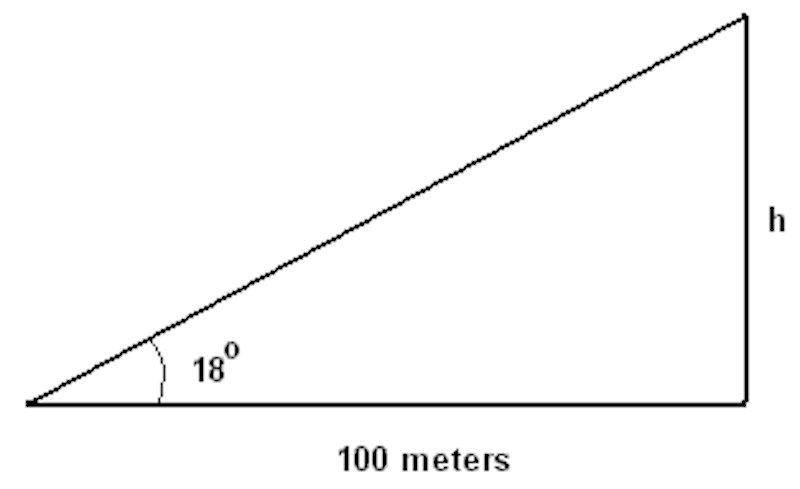
What’s the height of h?
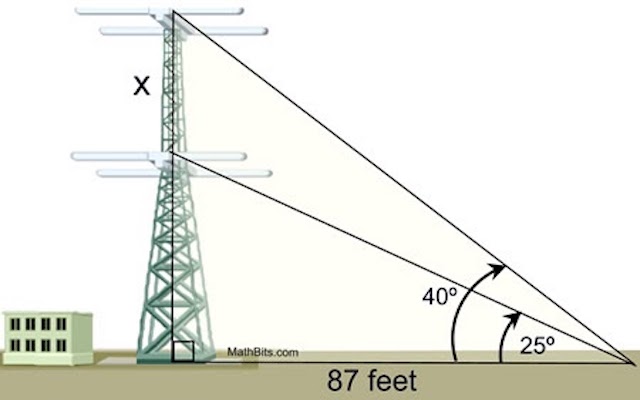
A radio station tower was built in two sections. From a point 87 feet from the base of the tower, the angle of elevation of the top of the first section is 25º, and the angle of elevation of the top of the second section is 40º. To the nearest foot, what is the height of the top section of the tower?
The first is a simple problem. The second is a complex problem. The end goal in both is the same.
The questions require the same knowledge (trigonometric functions), but the second is more difficult for students. Why? The second problem does not make it clear what the exact problem is. Before mathematics can even begin, you must know the problem, or else you risk solving the wrong one.
If you understand the problem, finding the solution is much easier. Understanding this, ironically, is the biggest problem for people.
Problem-solving is a universal language
Speaking of people, this method also helps settle disagreements.
When we disagree, we rarely take the time to figure out the exact issue. This happens for many reasons, but it always results in a misunderstanding. When each party is clear with their intentions, they can generate the best response.
Education systems fail when they don’t consider the problem they’re supposed to solve. Foreign language education in America is one of the best examples.
The problem is that students can’t speak the target language. It seems obvious that the solution is to have students spend most of their time speaking. Unfortunately, language classes spend a ridiculous amount of time learning grammar rules and memorizing vocabulary.
The problem is not that the students don’t know the imperfect past tense verb conjugations in Spanish. The problem is that they can’t use the language to accomplish anything. Every year, kids graduate from American high schools without the ability to speak another language, despite studying one for 4 years.
Well begun is half done
Before you begin to learn something, be sure that you understand the exact nature of the problem. This will make clear what you need to know and what you can discard. When you know the exact problem you’re tasked with solving, you save precious time and energy. Doing this increases the likelihood that you’ll succeed.
Step 2: What do you need to know?
All problems are the result of insufficient knowledge. To solve the problem, you must identify what you need to know. You must understand the cause of the problem. If you get this wrong, you won’t arrive at the correct solution.
Either you’ll solve what you thought was the problem, only to find out this wasn’t the real issue and now you’ve still got trouble or you won’t and you still have trouble. Either way, the problem persists.
If you solve a different problem than the correct one, you’ll get a solution that you can’t use. The only thing that wastes more time than an unsolved problem is solving the wrong one.
Imagine that your car won’t start. You replace the alternator, the starter, and the ignition switch. The car still doesn’t start. You’ve explored all the main solutions, so now you consider some different solutions.
Now you replace the engine, but you still can’t get it to start. Your replacements and repairs solved other problems, but not the main one: the car won’t start.
Then it turns out that all you needed was gas.
This example is a little extreme, but I hope it makes the point. For something more relatable, let’s return to the problem with language learning.
You need basic communication to navigate a foreign country you’re visiting; let’s say Mexico. When you enroll in a Spanish course, they teach you a bunch of unimportant words and phrases. You stick with it, believing it will eventually click.
When you land, you can tell everyone your name and ask for the location of the bathroom. This does not help when you need to ask for directions or tell the driver which airport terminal to drop you off at.
Finding the solution to chess problems works the same way
The book “The Amateur Mind” by IM Jeremy Silman improved my chess by teaching me how to analyze the board.
It’s only with a proper analysis of imbalances that you can make the best move. Though you may not always choose the correct line of play, the book teaches you how to recognize what you need to know . It teaches you how to identify the problem—before you create an action plan to solve it.

The problem-solving method always starts with identifying the problem or asking “What do you need to know?”. It’s only after you brainstorm this that you can move on to the next step.
Learn the method I used to earn a physics degree, learn Spanish, and win a national boxing title
- I was a terrible math student in high school who wrote off mathematics. I eventually overcame my difficulties and went on to earn a B.A. Physics with a minor in math
- I pieced together the best works on the internet to teach myself Spanish as an adult
- *I didn’t start boxing until the very old age of 22, yet I went on to win a national championship, get a high-paying amateur sponsorship, and get signed by Roc Nation Sports as a profession.
I’ve used this method to progress in mentally and physically demanding domains.
While the specifics may differ, I believe that the general methods for learning are the same in all domains.
This free e-book breaks down the most important techniques I’ve used for learning.
Step 3: What do you already know?
The only way to know if you lack knowledge is by gaining some in the first place. All advances and solutions arise from the accumulation and implementation of prior information. You must first consider what it is that you already know in the context of the problem at hand.
Isaac Newton once said, “If I have seen further, it is by standing on the shoulders of giants.” This is Newton’s way of explaining that his advancements in physics and mathematics would be impossible if it were not for previous discoveries.
Mathematics is a great place to see this idea at work. Consider the following problem:
What is the domain and range of y=(x^2)+6?
This simple algebra problem relies on you knowing a few things already. You must know:
- The definition of “domain” and “range”
- That you can never square any real number and get a negative
Once you know those things, this becomes easy to solve. This is also how we learn languages.
An example of the problem-solving process with a foreign language
Anyone interested in serious foreign language study (as opposed to a “crash course” or “survival course”) should learn the infinitive form of verbs in their target language. You can’t make progress without them because they’re the root of all conjugations. It’s only once you have a grasp of the infinitives that you can completely express yourself. Consider the problem-solving steps applied in the following example.
I know that I want to say “I don’t eat eggs” to my Mexican waiter. That’s the problem.
I don’t know how to say that, but last night I told my date “No bebo alcohol” (“I don’t drink alcohol”). I also know the infinitive for “eat” in Spanish (comer). This is what I already know.
Now I can execute the final step of problem-solving.
Step 4: What’s the relationship between the two?
I see the connection. I can use all of my problem-solving strategies and methods to solve my particular problem.
I know the infinitive for the Spanish word “drink” is “beber” . Last night, I changed it to “bebo” to express a similar idea. I should be able to do the same thing to the word for “eat”.
“No como huevos” is a pretty accurate guess.
In the math example, the same process occurs. You don’t know the answer to “What is the domain and range of y=(x^2)+6?” You only know what “domain” and “range” mean and that negatives aren’t possible when you square a real number.
A domain of all real numbers and a range of all numbers equal to and greater than six is the answer.
This is relating what you don’t know to what you already do know. The solutions appear simple, but walking through them is an excellent demonstration of the process of problem-solving.
In most cases, the solution won’t be this simple, but the process or finding it is the same. This may seem trivial, but this is a model for thinking that has served the greatest minds in history.
A recap of the 4 steps of the simple problem-solving process
- What’s the problem? There’s something wrong. There’s something amiss.
- What do you need to know? This is how to fix what’s wrong.
- What do you already know? You already know something useful that will help you find an effective solution.
- What’s the relationship between the previous two? When you use what you know to help figure out what you don’t know, there is no problem that won’t yield.
Learning is simply problem-solving. You’ll learn faster if you view it this way.
What was once complicated will become simple.
What was once convoluted will become clear.

Ed Latimore
I’m a writer, competitive chess player, Army veteran, physicist, and former professional heavyweight boxer. My work focuses on self-development, realizing your potential, and sobriety—speaking from personal experience, having overcome both poverty and addiction.
Follow me on Twitter.

Pimsleur language system review—old but still good
The Pimsleur language program offers a framework you can use to learn a language. I’ve used the program. Here are my experiences.

Pimsleur vs Duolingo: Choosing the best language learning app
Pimsleur and Duolingo are two popular language-learning apps to help you learn a new language. This guide will help you decide which app will work best for you.

My Chess.com Chess Improvement Plan
This is a plan that I’ll be implementing to improve my rating on Chess.com in the rapid and daily games. Not for OTB but could work.

Or search by topic
Number and algebra
- The Number System and Place Value
- Calculations and Numerical Methods
- Fractions, Decimals, Percentages, Ratio and Proportion
- Properties of Numbers
- Patterns, Sequences and Structure
- Algebraic expressions, equations and formulae
- Coordinates, Functions and Graphs
Geometry and measure
- Angles, Polygons, and Geometrical Proof
- 3D Geometry, Shape and Space
- Measuring and calculating with units
- Transformations and constructions
- Pythagoras and Trigonometry
- Vectors and Matrices
Probability and statistics
- Handling, Processing and Representing Data
- Probability
Working mathematically
- Thinking mathematically
- Mathematical mindsets
- Cross-curricular contexts
- Physical and digital manipulatives
For younger learners
- Early Years Foundation Stage
Advanced mathematics
- Decision Mathematics and Combinatorics
- Advanced Probability and Statistics
A Guide to Problem Solving
When confronted with a problem, in which the solution is not clear, you need to be a skilled problem-solver to know how to proceed. When you look at STEP problems for the first time, it may seem like this problem-solving skill is out of your reach, but like any skill, you can improve your problem-solving with practice. How do I become a better problem-solver? First and foremost, the best way to become better at problem-solving is to try solving lots of problems! If you are preparing for STEP, it makes sense that some of these problems should be STEP questions, but to start off with it's worth spending time looking at problems from other sources. This collection of NRICH problems is designed for younger students, but it's very worthwhile having a go at a few to practise the problem-solving technique in a context where the mathematics should be straightforward to you. Then as you become a more confident problem-solver you can try more past STEP questions. One student who worked with NRICH said: "From personal experience, I was disastrous at STEP to start with. Yet as I persisted with it for a long time it eventually started to click - 'it' referring to being able to solve problems much more easily. This happens because your brain starts to recognise that problems fall into various categories and you subconsciously remember successes and pitfalls of previous 'similar' problems." A Problem-solving Heuristic for STEP Below you will find some questions you can ask yourself while you are solving a problem. The questions are divided into four phases, based loosely on those found in George Pólya's 1945 book "How to Solve It". Understanding the problem
- What area of mathematics is this?
- What exactly am I being asked to do?
- What do I know?
- What do I need to find out?
- What am I uncertain about?
- Can I put the problem into my own words?
Devising a plan
- Work out the first few steps before leaping in!
- Have I seen something like it before?
- Is there a diagram I could draw to help?
- Is there another way of representing?
- Would it be useful to try some suitable numbers first?
- Is there some notation that will help?
Carrying out the plan STUCK!
- Try special cases or a simpler problem
- Work backwards
- Guess and check
- Be systematic
- Work towards subgoals
- Imagine your way through the problem
- Has the plan failed? Know when it's time to abandon the plan and move on.
Looking back
- Have I answered the question?
- Sanity check for sense and consistency
- Check the problem has been fully solved
- Read through the solution and check the flow of the logic.
Throughout the problem solving process it's important to keep an eye on how you're feeling and making sure you're in control:
- Am I getting stressed?
- Is my plan working?
- Am I spending too long on this?
- Could I move on to something else and come back to this later?
- Am I focussing on the problem?
- Is my work becoming chaotic, do I need to slow down, go back and tidy up?
- Do I need to STOP, PEN DOWN, THINK?
Finally, don't forget that STEP questions are designed to take at least 30-45 minutes to solve, and to start with they will take you longer than that. As a last resort, read the solution, but not until you have spent a long time just thinking about the problem, making notes, trying things out and looking at resources that can help you. If you do end up reading the solution, then come back to the same problem a few days or weeks later to have another go at it.
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&
High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
Free ready-to-use math resources
Hundreds of free math resources created by experienced math teachers to save time, build engagement and accelerate growth
20 Effective Math Strategies To Approach Problem-Solving
Katie Keeton
Math strategies for problem-solving help students use a range of approaches to solve many different types of problems. It involves identifying the problem and carrying out a plan of action to find the answer to mathematical problems.
Problem-solving skills are essential to math in the general classroom and real-life. They require logical reasoning and critical thinking skills. Students must be equipped with strategies to help them find solutions to problems.
This article explores mathematical problem solving strategies, logical reasoning and critical thinking skills to help learners with solving math word problems independently in real-life situations.
What are problem-solving strategies?
Problem-solving strategies in math are methods students can use to figure out solutions to math problems. Some problem-solving strategies:
- Draw a model
- Use different approaches
- Check the inverse to make sure the answer is correct
Students need to have a toolkit of math problem-solving strategies at their disposal to provide different ways to approach math problems. This makes it easier to find solutions and understand math better.
Strategies can help guide students to the solution when it is difficult ot know when to start.

The ultimate guide to problem solving techniques
Download these ready-to-go problem solving techniques that every student should know. Includes printable tasks for students including challenges, short explanations for teachers with questioning prompts.
20 Math Strategies For Problem-Solving
Different problem-solving math strategies are required for different parts of the problem. It is unlikely that students will use the same strategy to understand and solve the problem.
Here are 20 strategies to help students develop their problem-solving skills.
Strategies to understand the problem
Strategies that help students understand the problem before solving it helps ensure they understand:
- The context
- What the key information is
- How to form a plan to solve it
Following these steps leads students to the correct solution and makes the math word problem easier .
Here are five strategies to help students understand the content of the problem and identify key information.
1. Read the problem aloud
Read a word problem aloud to help understand it. Hearing the words engages auditory processing. This can make it easier to process and comprehend the context of the situation.
2. Highlight keywords
When keywords are highlighted in a word problem, it helps the student focus on the essential information needed to solve it. Some important keywords help determine which operation is needed. For example, if the word problem asks how many are left, the problem likely requires subtraction. Ensure students highlight the keywords carefully and do not highlight every number or keyword. There is likely irrelevant information in the word problem.
3. Summarize the information
Read the problem aloud, highlight the key information and then summarize the information. Students can do this in their heads or write down a quick summary. Summaries should include only the important information and be in simple terms that help contextualize the problem.
4. Determine the unknown
A common problem that students have when solving a word problem is misunderstanding what they are solving. Determine what the unknown information is before finding the answer. Often, a word problem contains a question where you can find the unknown information you need to solve. For example, in the question ‘How many apples are left?’ students need to find the number of apples left over.
5. Make a plan
Once students understand the context of the word problem, have dentified the important information and determined the unknown, they can make a plan to solve it. The plan will depend on the type of problem. Some problems involve more than one step to solve them as some require more than one answer. Encourage students to make a list of each step they need to take to solve the problem before getting started.
Strategies for solving the problem
1. draw a model or diagram.
Students may find it useful to draw a model, picture, diagram, or other visual aid to help with the problem solving process. It can help to visualize the problem to understand the relationships between the numbers in the problem. In turn, this helps students see the solution.
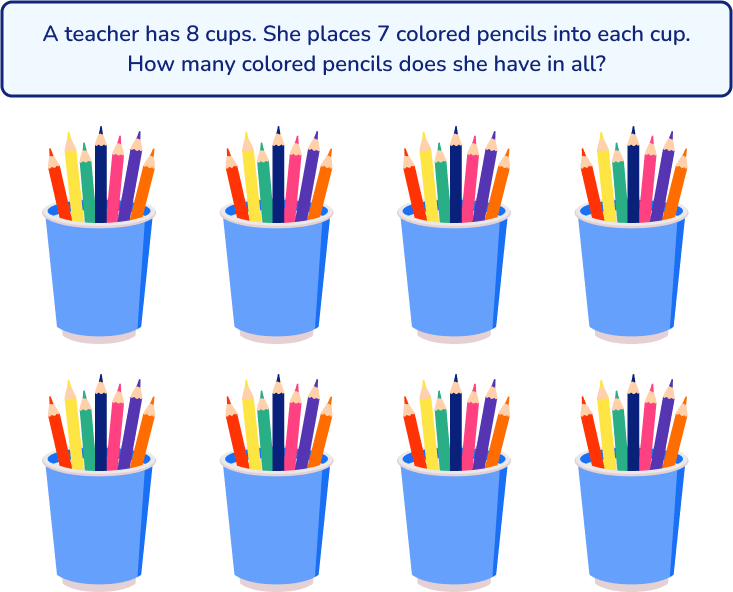
Similarly, you could draw a model to represent the objects in the problem:
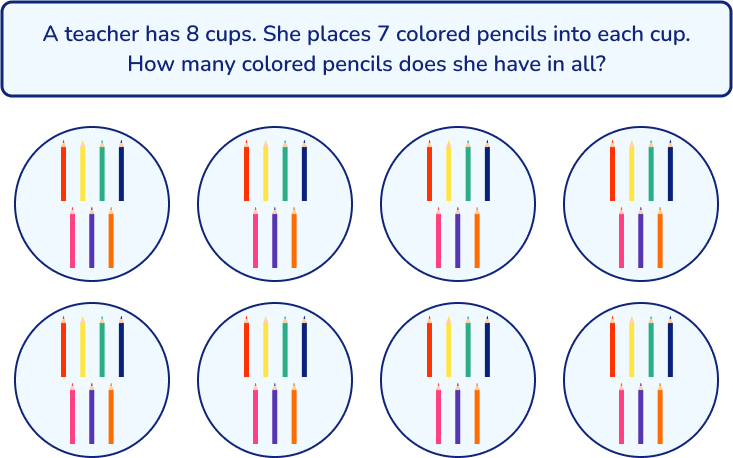
2. Act it out
This particular strategy is applicable at any grade level but is especially helpful in math investigation in elementary school . It involves a physical demonstration or students acting out the problem using movements, concrete resources and math manipulatives . When students act out a problem, they can visualize and contectualize the word problem in another way and secure an understanding of the math concepts. The examples below show how 1st-grade students could “act out” an addition and subtraction problem:
| The problem | How to act out the problem |
| Gia has 6 apples. Jordan has 3 apples. How many apples do they have altogether? | Two students use counters to represent the apples. One student has 6 counters and the other student takes 3. Then, they can combine their “apples” and count the total. |
| Michael has 7 pencils. He gives 2 pencils to Sarah. How many pencils does Michael have now? | One student (“Michael”) holds 7 pencils, the other (“Sarah”) holds 2 pencils. The student playing Michael gives 2 pencils to the student playing Sarah. Then the students count how many pencils Michael is left holding. |
3. Work backwards
Working backwards is a popular problem-solving strategy. It involves starting with a possible solution and deciding what steps to take to arrive at that solution. This strategy can be particularly helpful when students solve math word problems involving multiple steps. They can start at the end and think carefully about each step taken as opposed to jumping to the end of the problem and missing steps in between.
For example,

To solve this problem working backwards, start with the final condition, which is Sam’s grandmother’s age (71) and work backwards to find Sam’s age. Subtract 20 from the grandmother’s age, which is 71. Then, divide the result by 3 to get Sam’s age. 71 – 20 = 51 51 ÷ 3 = 17 Sam is 17 years old.
4. Write a number sentence
When faced with a word problem, encourage students to write a number sentence based on the information. This helps translate the information in the word problem into a math equation or expression, which is more easily solved. It is important to fully understand the context of the word problem and what students need to solve before writing an equation to represent it.
5. Use a formula
Specific formulas help solve many math problems. For example, if a problem asks students to find the area of a rug, they would use the area formula (area = length × width) to solve. Make sure students know the important mathematical formulas they will need in tests and real-life. It can help to display these around the classroom or, for those who need more support, on students’ desks.
Strategies for checking the solution
Once the problem is solved using an appropriate strategy, it is equally important to check the solution to ensure it is correct and makes sense.
There are many strategies to check the solution. The strategy for a specific problem is dependent on the problem type and math content involved.
Here are five strategies to help students check their solutions.
1. Use the Inverse Operation
For simpler problems, a quick and easy problem solving strategy is to use the inverse operation. For example, if the operation to solve a word problem is 56 ÷ 8 = 7 students can check the answer is correct by multiplying 8 × 7. As good practice, encourage students to use the inverse operation routinely to check their work.
2. Estimate to check for reasonableness
Once students reach an answer, they can use estimation or rounding to see if the answer is reasonable. Round each number in the equation to a number that’s close and easy to work with, usually a multiple of ten. For example, if the question was 216 ÷ 18 and the quotient was 12, students might round 216 to 200 and round 18 to 20. Then use mental math to solve 200 ÷ 20, which is 10. When the estimate is clear the two numbers are close. This means your answer is reasonable.
3. Plug-In Method
This method is particularly useful for algebraic equations. Specifically when working with variables. To use the plug-in method, students solve the problem as asked and arrive at an answer. They can then plug the answer into the original equation to see if it works. If it does, the answer is correct.

If students use the equation 20m+80=300 to solve this problem and find that m = 11, they can plug that value back into the equation to see if it is correct. 20m + 80 = 300 20 (11) + 80 = 300 220 + 80 = 300 300 = 300 ✓
4. Peer Review
Peer review is a great tool to use at any grade level as it promotes critical thinking and collaboration between students. The reviewers can look at the problem from a different view as they check to see if the problem was solved correctly. Problem solvers receive immediate feedback and the opportunity to discuss their thinking with their peers. This strategy is effective with mixed-ability partners or similar-ability partners. In mixed-ability groups, the partner with stronger skills provides guidance and support to the partner with weaker skills, while reinforcing their own understanding of the content and communication skills. If partners have comparable ability levels and problem-solving skills, they may find that they approach problems differently or have unique insights to offer each other about the problem-solving process.
5. Use a Calculator
A calculator can be introduced at any grade level but may be best for older students who already have a foundational understanding of basic math operations. Provide students with a calculator to allow them to check their solutions independently, accurately, and quickly. Since calculators are so readily available on smartphones and tablets, they allow students to develop practical skills that apply to real-world situations.
Step-by-step problem-solving processes for your classroom
In his book, How to Solve It , published in 1945, mathematician George Polya introduced a 4-step process to solve problems.
Polya’s 4 steps include:
- Understand the problem
- Devise a plan
- Carry out the plan
Today, in the style of George Polya, many problem-solving strategies use various acronyms and steps to help students recall.
Many teachers create posters and anchor charts of their chosen process to display in their classrooms. They can be implemented in any elementary, middle school or high school classroom.
Here are 5 problem-solving strategies to introduce to students and use in the classroom.
How Third Space Learning improves problem-solving
Resources .
Third Space Learning offers a free resource library is filled with hundreds of high-quality resources. A team of experienced math experts carefully created each resource to develop students mental arithmetic, problem solving and critical thinking.
Explore the range of problem solving resources for 2nd to 8th grade students.
One-on-one tutoring
Third Space Learning offers one-on-one math tutoring to help students improve their math skills. Highly qualified tutors deliver high-quality lessons aligned to state standards.
Former teachers and math experts write all of Third Space Learning’s tutoring lessons. Expertly designed lessons follow a “my turn, follow me, your turn” pedagogy to help students move from guided instruction and problem-solving to independent practice.
Throughout each lesson, tutors ask higher-level thinking questions to promote critical thinking and ensure students are developing a deep understanding of the content and problem-solving skills.
Problem-solving
Educators can use many different strategies to teach problem-solving and help students develop and carry out a plan when solving math problems. Incorporate these math strategies into any math program and use them with a variety of math concepts, from whole numbers and fractions to algebra.
Teaching students how to choose and implement problem-solving strategies helps them develop mathematical reasoning skills and critical thinking they can apply to real-life problem-solving.
READ MORE : 8 Common Core math examples
There are many different strategies for problem-solving; Here are 5 problem-solving strategies: • draw a model • act it out • work backwards • write a number sentence • use a formula
Here are 10 strategies of problem-solving: • Read the problem aloud • Highlight keywords • Summarize the information • Determine the unknown • Make a plan • Draw a model • Act it out • Work backwards • Write a number sentence • Use a formula
1. Understand the problem 2. Devise a plan 3. Carry out the plan 4. Look back
Some strategies you can use to solve challenging math problems are: breaking the problem into smaller parts, using diagrams or models, applying logical reasoning, and trying different approaches.
Related articles

Why Student Centered Learning Is Important: A Guide For Educators

13 Effective Learning Strategies: A Guide to Using them in your Math Classroom

Differentiated Instruction: 9 Differentiated Curriculum And Instruction Strategies For Teachers

5 Math Mastery Strategies To Incorporate Into Your 4th and 5th Grade Classrooms
Ultimate Guide to Metacognition [FREE]
Looking for a summary on metacognition in relation to math teaching and learning?
Check out this guide featuring practical examples, tips and strategies to successfully embed metacognition across your school to accelerate math growth.
Pólya’s How to Solve It
George Pólya was a great champion in the field of teaching effective problem solving skills. He was born in Hungary in 1887, received his Ph.D. at the University of Budapest, and was a professor at Stanford University (among other universities). He wrote many mathematical papers along with three books, most famously, “How to Solve it.” Pólya died at the age 98 in 1985. [1]
In 1945, Pólya published the short book How to Solve It , which gave a four-step method for solving mathematical problems:
- Understand the problem.
- Devise a plan.
- Carry out the plan.
- Looking back.
This is all well and good, but how do you actually do these steps?!?! Steps 1. and 2. are particularly mysterious! How do you “make a plan?” That is where you need some tools in your toolbox, and some experience to draw upon.
Much has been written since 1945 to explain these steps in more detail, but the truth is that they are more art than science. This is where math becomes a creative endeavor (and where it becomes so much fun). We will articulate some useful problem solving strategies, but no such list will ever be complete. This is really just a start to help you on your way. The best way to become a skilled problem solver is to learn the background material well, and then to solve a lot of problems!
We have already seen one problem solving strategy, which we call “Wishful Thinking.” Do not be afraid to change the problem! Ask yourself “what if” questions:
- What if the picture was different?
- What if the numbers were simpler?
- What if I just made up some numbers?
You need to be sure to go back to the original problem at the end, but wishful thinking can be a powerful strategy for getting started.
This brings us to the most important problem solving strategy of all:
Problem Solving Strategy 2 (Try Something!). If you are really trying to solve a problem, the whole point is that you do not know what to do right out of the starting gate. You need to just try something! Put pencil to paper (or stylus to screen or chalk to board or whatever!) and try something. This is often an important step in understanding the problem; just mess around with it a bit to understand the situation and figure out what is going on.
And equally important: If what you tried first does not work, try something else! Play around with the problem until you have a feel for what is going on.
Problem 2 (Payback)
Last week, Alex borrowed money from several of his friends. He finally got paid at work, so he brought cash to school to pay back his debts. First he saw Brianna, and he gave her 1/4 of the money he had brought to school. Then Alex saw Chris and gave him 1/3 of what he had left after paying Brianna. Finally, Alex saw David and gave him 1/2 of what he had remaining. Who got the most money from Alex?
Think/Pair/Share
After you have worked on the problem on your own for a while, talk through your ideas with a partner (even if you have not solved it). What did you try? What did you figure out about the problem?
This problem lends itself to two particular strategies. Did you try either of these as you worked on the problem? If not, read about the strategy and then try it out before watching the solution.
Problem Solving Strategy 3 (Draw a Picture). Some problems are obviously about a geometric situation, and it is clear you want to draw a picture and mark down all of the given information before you try to solve it. But even for a problem that is not geometric, like this one, thinking visually can help! Can you represent something in the situation by a picture?
Draw a square to represent all of Alex’s money. Then shade 1/4 of the square — that’s what he gave away to Brianna. How can the picture help you finish the problem?
After you have worked on the problem yourself using this strategy (or if you are completely stuck), you can watch someone else’s solution.
Problem Solving Strategy 4 (Make Up Numbers). Part of what makes this problem difficult is that it is about money, but there are no numbers given. That means the numbers must not be important. So just make them up!
You can work forwards: Assume Alex had some specific amount of money when he showed up at school, say $100. Then figure out how much he gives to each person. Or you can work backwards: suppose he has some specific amount left at the end, like $10. Since he gave Chris half of what he had left, that means he had $20 before running into Chris. Now, work backwards and figure out how much each person got.
Watch the solution only after you tried this strategy for yourself.
If you use the “Make Up Numbers” strategy, it is really important to remember what the original problem was asking! You do not want to answer something like “Everyone got $10.” That is not true in the original problem; that is an artifact of the numbers you made up. So after you work everything out, be sure to re-read the problem and answer what was asked!
Problem 3 (Squares on a Chess Board)
How many squares, of any possible size, are on a 8 × 8 chess board? (The answer is not 64… It’s a lot bigger!)
Remember Pólya’s first step is to understand the problem. If you are not sure what is being asked, or why the answer is not just 64, be sure to ask someone!
Think / Pair / Share
After you have worked on the problem on your own for a while, talk through your ideas with a partner (even if you have not solved it). What did you try? What did you figure out about the problem, even if you have not solved it completely?
It is clear that you want to draw a picture for this problem, but even with the picture it can be hard to know if you have found the correct answer. The numbers get big, and it can be hard to keep track of your work. Your goal at the end is to be absolutely positive that you found the right answer. You should never ask the teacher, “Is this right?” Instead, you should declare, “Here’s my answer, and here is why I know it is correct!”
Problem Solving Strategy 5 (Try a Simpler Problem). Pólya suggested this strategy: “If you can’t solve a problem, then there is an easier problem you can solve: find it.” He also said: “If you cannot solve the proposed problem, try to solve first some related problem. Could you imagine a more accessible related problem?” In this case, an 8 × 8 chess board is pretty big. Can you solve the problem for smaller boards? Like 1 × 1? 2 × 2? 3 × 3?
Of course the ultimate goal is to solve the original problem. But working with smaller boards might give you some insight and help you devise your plan (that is Pólya’s step (2)).
Problem Solving Strategy 6 (Work Systematically). If you are working on simpler problems, it is useful to keep track of what you have figured out and what changes as the problem gets more complicated.
For example, in this problem you might keep track of how many 1 × 1 squares are on each board, how many 2 × 2 squares on are each board, how many 3 × 3 squares are on each board, and so on. You could keep track of the information in a table:
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 9 | 4 | 1 | 0 | ||
Problem Solving Strategy 7 (Use Manipulatives to Help You Investigate). Sometimes even drawing a picture may not be enough to help you investigate a problem. Having actual materials that you move around can sometimes help a lot!
For example, in this problem it can be difficult to keep track of which squares you have already counted. You might want to cut out 1 × 1 squares, 2 × 2 squares, 3 × 3 squares, and so on. You can actually move the smaller squares across the chess board in a systematic way, making sure that you count everything once and do not count anything twice.
Problem Solving Strategy 8 (Look for and Explain Patterns). Sometimes the numbers in a problem are so big, there is no way you will actually count everything up by hand. For example, if the problem in this section were about a 100 × 100 chess board, you would not want to go through counting all the squares by hand! It would be much more appealing to find a pattern in the smaller boards and then extend that pattern to solve the problem for a 100 × 100 chess board just with a calculation.
If you have not done so already, extend the table above all the way to an 8 × 8 chess board, filling in all the rows and columns. Use your table to find the total number of squares in an 8 × 8 chess board. Then:
- Describe all of the patterns you see in the table.
- Can you explain and justify any of the patterns you see? How can you be sure they will continue?
- What calculation would you do to find the total number of squares on a 100 × 100 chess board?
(We will come back to this question soon. So if you are not sure right now how to explain and justify the patterns you found, that is OK.)

Problem 4 (Broken Clock)
This clock has been broken into three pieces. If you add the numbers in each piece, the sums are consecutive numbers. ( Consecutive numbers are whole numbers that appear one after the other, such as 1, 2, 3, 4 or 13, 14, 15.)
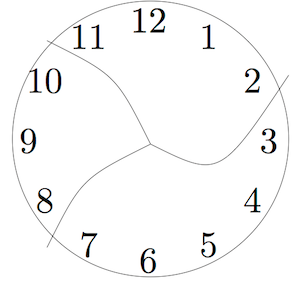
Can you break another clock into a different number of pieces so that the sums are consecutive numbers? Assume that each piece has at least two numbers and that no number is damaged (e.g. 12 isn’t split into two digits 1 and 2.)
Remember that your first step is to understand the problem. Work out what is going on here. What are the sums of the numbers on each piece? Are they consecutive?
After you have worked on the problem on your own for a while, talk through your ideas with a partner (even if you have not solved it). What did you try? What progress have you made?
Problem Solving Strategy 9 (Find the Math, Remove the Context). Sometimes the problem has a lot of details in it that are unimportant, or at least unimportant for getting started. The goal is to find the underlying math problem, then come back to the original question and see if you can solve it using the math.
In this case, worrying about the clock and exactly how the pieces break is less important than worrying about finding consecutive numbers that sum to the correct total. Ask yourself:
- What is the sum of all the numbers on the clock’s face?
- Can I find two consecutive numbers that give the correct sum? Or four consecutive numbers? Or some other amount?
- How do I know when I am done? When should I stop looking?
Of course, solving the question about consecutive numbers is not the same as solving the original problem. You have to go back and see if the clock can actually break apart so that each piece gives you one of those consecutive numbers. Maybe you can solve the math problem, but it does not translate into solving the clock problem.
Problem Solving Strategy 10 (Check Your Assumptions). When solving problems, it is easy to limit your thinking by adding extra assumptions that are not in the problem. Be sure you ask yourself: Am I constraining my thinking too much?
In the clock problem, because the first solution has the clock broken radially (all three pieces meet at the center, so it looks like slicing a pie), many people assume that is how the clock must break. But the problem does not require the clock to break radially. It might break into pieces like this:
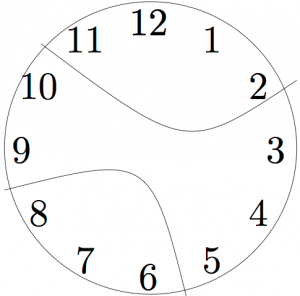
Were you assuming the clock would break in a specific way? Try to solve the problem now, if you have not already.
- Image of Pólya by Thane Plambeck from Palo Alto, California (Flickr) [CC BY 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons ↵
Mathematics for Elementary Teachers Copyright © 2018 by Michelle Manes is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
























IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Solution. Step 1: Understanding the problem. We are given in the problem that there are 25 chickens and cows. All together there are 76 feet. Chickens have 2 feet and cows have 4 feet. We are trying to determine how many cows and how many chickens Mr. Jones has on his farm. Step 2: Devise a plan.
To solve math problems step-by-step start by reading the problem carefully and understand what you are being asked to find. Next, identify the relevant information, define the variables, and plan a strategy for solving the problem. en. Related Symbolab blog posts. Practice Makes Perfect.
Get accurate solutions and step-by-step explanations for algebra and other math problems with the free GeoGebra Math Solver. Enhance your problem-solving skills while learning how to solve equations on your own. Try it now!
Get math help in your language. Works in Spanish, Hindi, German, and more. Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app.
In 1945, Pólya published the short book How to Solve It, which gave a four-step method for solving mathematical problems: First, you have to understand the problem. After understanding, then make a plan. Carry out the plan. ... Make sure you use Polya's 4 problem solving steps. (12 points) Problem Solving Strategy 2 (Draw a Picture).
QuickMath will automatically answer the most common problems in algebra, equations and calculus faced by high-school and college students. The algebra section allows you to expand, factor or simplify virtually any expression you choose. It also has commands for splitting fractions into partial fractions, combining several fractions into one and ...
An identity is an equation that is satisfied by all numbers from its replacement set. Example 1 Consider the equation 2x-1 = x+2. The replacement set here is the set of all real numbers. The equation is conditional since, for example, 1 is a member of the replacement set but not of the solution set. Example 2 Consider the equation (x-1) (x+1 ...
Mathematician George Pólya's book, "How to Solve It: A New Aspect of Mathematical Method," written in 1957, is a great guide to have on hand.The ideas below, which provide you with general steps or strategies to solve math problems, are similar to those expressed in Pólya's book and should help you untangle even the most complicated math problem.
Starting at $5.00 /month. Get step-by-step answers and hints for your math homework problems. Learn the basics, check your work, gain insight on different ways to solve problems. For chemistry, calculus, algebra, trigonometry, equation solving, basic math and more.
QuickMath offers a step-by-step math problem solver for various equations and expressions, simplifying complex math tasks.
Consider the problem-solving steps applied in the following example. I know that I want to say "I don't eat eggs" to my Mexican waiter. That's the problem. I don't know how to say that, but last night I told my date "No bebo alcohol" ("I don't drink alcohol"). I also know the infinitive for "eat" in Spanish (comer).
A Guide to Problem Solving. When confronted with a problem, in which the solution is not clear, you need to be a skilled problem-solver to know how to proceed. When you look at STEP problems for the first time, it may seem like this problem-solving skill is out of your reach, but like any skill, you can improve your problem-solving with practice.
In 1945, Pólya published the short book How to Solve It, which gave a four-step method for solving mathematical problems: First, you have to understand the problem. After understanding, then make a plan. Carry out the plan. Look back on your work.
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Start 7-day free trial on the app. Download free on Amazon. Download free in Windows Store.
Here are five strategies to help students check their solutions. 1. Use the Inverse Operation. For simpler problems, a quick and easy problem solving strategy is to use the inverse operation. For example, if the operation to solve a word problem is 56 ÷ 8 = 7 students can check the answer is correct by multiplying 8 × 7.
Provide step-by-step solutions to math word problems Graphing Plot and analyze functions and equations with detailed steps Geometry Solve geometry problems, proofs, and draw geometric shapes Math Help Tailored For You Practice Practice and improve your math skills through interactive personalized exercises and quizzes
Problem Solving Strategy 6 (Work Systematically). If you are working on simpler problems, it is useful to keep track of what you have figured out and what changes as the problem gets more complicated. For example, in this problem you might keep track of how many 1 × 1 squares are on each board, how many 2 × 2 squares on are each board, how ...
Polya's four step method for problem solving is. 1) Understand the Problem-Make sure you understand what the question is asking and what information will be used to solve the problem. 2) Devise a ...
Join millions of users in problem solving! +. > < ...
Problem identification. Problem analysis. Plan development. Plan implementation. Plan evaluation. Following this 5-step problem-solving approach helps to guide school teams of educators and administrators in engaging in data-based decision making: a core principle of the MTSS framework.
This creates a math problem solver that's more accurate than ChatGPT, more flexible than a math calculator, and provides answers faster than a human tutor. Sign up for free here. Problem Solver Subjects. Our math problem solver that lets you input a wide variety of math math problems and it will provide a step by step answer.
Is this problem similar to another problem you have solved? Step 2: Devise a Plan: Below are some strategies one might use to solve a problem. Can one (or more) of the following strategies be used? (A strategy is defined as an artful means to an end.) 1.
Learn the steps you can follow to solve any math word problem.We hope you are enjoying this video! For more in-depth learning, check out Miacademy.co (https:...
In the past, we would teach the concepts and procedures and then assign one-step "story" problems designed to provide practice on the content. Next, we would teach problem solving as a collection of strategies such as "draw a picture" or "guess and check.". Eventually, students would be given problems to apply the skills and strategies.
Basic properties of functions, graphs; with emphasis on linear, quadratic, trigonometric, exponential functions and their inverses. Emphasis on multi-step problem solving. Recommended: completion of Department of Mathematics' Guided Self-Placement. Offered: AWSpS.
About the Curricula. A curriculum is how standards, or learning goals, for every grade and subject are translated into day-to-day activities. As part of the NYC Solves initiative, all high schools will use Illustrative Mathematics and districts will choose a comprehensive, evidence-based curricula for middle school math instruction from an approved list.
Ai Tutor Math Solver, the all-in-one app that empowers you to conquer any mathematical challenge. Don't just get an answer, understand the "why" behind it. Ai Tutor Math Solver breaks down each problem into clear, step-by-step explanations, allowing you to grasp the concepts and solve similar problems independently.