11 Inspiring UX Case Studies That Every Designer Should Study

A UX case study is a sort of detailed overview of a designer's work. They are often part of a UX designer's portfolio and showcase the designer's skill in managing tasks and problems. From a recruiter's perspective, such a UX portfolio shows the skill, insights, knowledge, and talent of the designer.
Therefore, UX case studies play an important role in the recruitment and demand for designers.

What Makes a Powerful Case Study
Building a UX case study includes showing the design process through compelling stories. They will use plain language to demonstrate how they handled key design issues, offering a comprehensive view of their process. Well done case studies often include:
- A problem statement and solutions with real applications.
- Relevant numbers, data, or testimonials to demonstrate the work and efforts.
- A story that directly connects the problem to the solution.
Any competent UX professional will know that creating a stunning UX case study is about the little details.
11 Best UX Case Studies for Designers
The best way to understand what a good case study looks like is to go over other examples. Each of these UX case study examples shows a designer's insights, basic skills, and other designers' lessons learned through their experience.
1. Promo.com web editor

For this video-creation platform , UX designer Sascha was brought on to revamp v2.0, adding new features that could work alongside the existing UX design. The point was to work on interface details that would help create a user friendly platform, and that users could find simple enough to use.
User personas mapped by the UX designer revealed the most common confusion to be the process of inserting particular features into the video, such as subtitles. The designer's goal, therefore, was to create a platform with improved editor controls.
The designer then used a common text-editor layout to include top and side navigation bars that made it easy to access and implement text editing.
Key Learnings from Promo.com
This case study focuses on addressing a particular problem that customers were currently facing. Its main theme is to show a problem, and how the product designer addressed this problem. Its strength points include:
- clearly highlighting the problem (i.e. inaccessible and limited video-text editor options)
- conduction research to understand the nature of the problem and the kind of solutions customers want
- implementing research insights into the redesign to create a platform that actively served customer needs
2. Productivity tracker app
The main concept behind this UX case study is to address a pre-existing problem through the design of the app. Immediately from the start, the study highlights a common pain point among users: that of a lack of productivity due to device usage.
This UX case study example addressed some of the main problems within existing productivity apps included:a poor UI and UX that made navigation difficult
- a poorly-built information architecture
- limited functions on the mobile application
Key Learnings from the Productivity app case study
The case study highlights the simple design process that was then used to build the app. Wireframes were created, a moldboard developed, and finally, individual pages of the app were designed in line with the initial goals.
3. Postmates Unlimited

This case study clearly identifies the improvements made to the Postmates app in a simple overview before jumping into greater detail. The redesign goal, which it achieved, was to improve the experience and other interface details of the app.
The problems identified included:
- usability that led to high support ticket volume.
- technical app infrastructure issues that prevented scalability.
- lack of efficient product management, such as batching orders.
A UX research course can help understand the kind of research needed for a case study. The app redesign involved bringing couriers in and running usability testing on improvements. The final model, therefore, had input from real users on what worked and what caused issues.
Key Learnings from Postmates
The Postmates redesign works as a great UX case study for the simple way it approaches problem-solving. Following an overview of the work, it addresses the problems faced by users of the app. It then establishes research processes and highlights how changes were made to reduce these issues.
4. TV Guide

Addressing the fragmentation of content across channels, this case study sought to redesign how people consume media. The key problems identified included:
- the overabundance of content across various TV and streaming platforms
- the difficulty in discovering and managing content across all platforms
To deliver on the key goals of content personalization, smart recommendations, and offering cross-platform content search, the design process included conducting interviews, surveys, and checking customer reviews.
The design of TV Guide enables users to get custom recommendations sourced from friends' and family's watchlists.
Key Learnings from TV Guide
Like previous UX design case studies, this one tackled the issue head-on. Describing the research process, it goes into detail regarding the approach used by the UX designers to create the app. It takes readers on a journey, from identifying pain points, to testing solutions, and implementing the final version.
5. The FlexBox Inspector

Designer Victoria discusses how she developed the investigator tool for the Mozilla Firefox browser. Surveys into understanding the problems with the existing CSS Flexbox tool revealed a need for a user-friendly design. Interviews with a senior designer and other designers helped developers understand the features design-focused tools ought to have. A feature analysis revealed what most users look for in such tools.
The final result of the development process was a design that incorporated several new features, including:
- a new layout
- color-coded design
- multiple entry points to make workflow management efficient
Key Learnings from the Flexbox
This UX design case study starts with a clear goal, then addresses multiple user needs. It clearly defines the design process behind each feature developed by the time, and the reasoning for including that feature. To give a complete picture, it also discusses why certain features or processes were excluded.
6. The Current State of Checkouts

This Baymard UX design case study looks into the checkout process in over 70 e-commerce websites. Through competitive analysis, it isolates problem points in the UX design, which, if addressed, could improve the customer's checkout process.
The study found at least 31 common issues that were easily preventable. The study was designed and conducted on a large scale, over 12 years, to incorporate changing design patterns into the review.
Recommendations based on findings include:
- prominent guest checkout option
- simple password requirements
- specific delivery period
- price comparison tool for shipping vs store pickup
Key Learnings from Checkout Case Study
Each identified issue is backed up by data and research to highlight its importance. Further research backs up each recommendation made within the case study, with usability testing to support the idea. As far as UX case studies go, this one provides practical insight into an existing, widely used e-commerce feature, and offers practical solutions.
7. New York Times App

Using a creative illustration website, the designers proposed a landing page feature "Timely" that could counter the problems faced by the NYT app . Its major issues included too much irrelevant content, low usage, and undesirable coverage of content.
The goal behind Timely was to improve user incentives, build long-term loyalty, and encourage reading. Design mapping for the app covered:
- identifying the problem
- understanding audience needs
- creating wireframes
- designing and prototyping
The end result was an app that could help readers get notifications regarding news of interest at convenient moments (at breakfast, before bed). This encouraged interaction and improved readability with short-form articles.
Key Learnings from NYT App
The UX case study proposes a problem solution that works with an existing information architecture, instead adding custom graphics to the mobile app. It leads from a simple problem statement to discuss the project that could address these issues without changing was customers already loved.

UX case studies focused on redesign include the FitBit redesign, which started off by understanding personas and what users expect from a fitness tracker. Developing use cases and personas, Guerilla usability testing was employed to assess pain points.
These pain points were then ranked based on their importance to users and to app performance. They were addressed through:
- Highlighting essential parts and features of the app
- Changing easily missed icons to more recognizable icons
- relabelling tracking options to guide users better to its usage
Key Learnings from Fitbit
While the case study maps user experiences and offers solutions, it does not begin with an intensive research-based approach. The prototype is successful in testing, but problem factors are not identified with research-based statistics, meaning key factors could have been ignored.
9. Rating System UX

The designer behind the rating system UX redesign sought to solve issues with the 5-star rating system. Highlighted issues included:
- the lack of subjective accuracy of a 5-point rating system
- the issue of calculating the average of a zero-star rating
- average ratings are misleading
Better alternatives include:
- 5-star emoticon rating that relates the user experience
- Like/dislike buttons that make approval/disapproval simple
The final design incorporated both these styles to make full use of the rating system.
Key Learnings from Rating System UX
The UX case study stemmed from insight into the limitations of the existing rating system. The new design addressed old issues and incorporated better efficiencies.

The Intuit redesign was focused on making content readable, more engaging, and accessible. Looking into product personalization, the content was found to be lacking aesthetic value, as well as being hard to find. The goal was to create content that was easy to find, clear, and consistent.
The implemented solutions included:
- increased readability with increased body text and header spacing
- table of contents on the sidebar for easier navigation
- visible and prominent search bar
- illustrations and designs for pretty visuals
Key Learnings from Intuit
The Intuit case study approaches the problem from a practical point of view. It begins with isolating problems with the interface, in particular with the content. This is an example of a case study that breaks down problems into broader categories, and solves each problem with a practical solution.

This UX case study about a social platform tackles a commonly-faced problem from existing platforms. It addresses the issue of recognizing non-monetary user engagement, to help creators identify their user base.
The case study addresses the problem statement and establishes the design process (building wireframes and prototypes) as well as conducting user testing. The final result is to develop "Discover" pages, engaging layouts, and animated interactions to increase usability.
Key Learnings from Jambb
The study goes into detail regarding problem identification, then moves on to propose solutions that take into account the perspective of all stakeholders involved. It then explains why each design decision was made, and proves its efficacy through testing and prototyping.
Key Takeaways
Developing good UX case studies examples is as much about the details you include as the ones you leave out. Going over UX courses can give you a better understanding of what your case study should look like. A good case study should provide an overview of the problem, include numbers and statistics, and offer practical solutions that directly address the problem. The above-discussed UX case studies provide a good example of the dos and don'ts of a well-structured UX design case study that should be part of every UX portfolio .
Additional Resources
Check out these resources to learn more about UX case studies:
8 UX Case Studies to Read
UX Design Case Study
Frequently Asked Questions
Upskill your design team effectively.
Equip your design team with the best-in-class design training that sticks.
Do you know your design team skill level? Send them this quick test & see where their skills stand among 300K+ designers worldwide.
Level up your design career
Get step-by-step guide how to build or advance your UX design career.
Do you know your design skills level? Take a quick test & see where you stand among 300K+ designers worldwide.
Continue reading
The impact of ux design on application success: exploring costs and trends, 7 top ux careers & specialisations: skills, paths & opportunities, 15 figma plugins to boost your design workflow, cookie settings 🍪.
- Interactive UX learning for all levels
- 20+ UX courses and career paths
- Personalized learning & practice
Design-first companies are training their design teams. Are you?
- Measure & identify team skill gaps
- Tailor learning for your team’s needs
- Unlock extensive learning library
- Visualize team growth over time
- Retain your designers
- mindful design
- student success
- product design
- ui/ux design
- watch me work
- design careers
- design inspiration
10 Exceptional Product Design Portfolios with Case Study Breakdowns
After working with many designers throughout my own career and helping many more build their job-ready portfolios, there are a few designers that I keep coming back to for inspiration and some that are inspiring a new generation of UI/UX and Product Designers to enter the field.
I've chosen 10 of our favorite UI/UX and Product Designers—a colorful tapestry of digital product architects that have evolved from graphic designers, marketers, architects, engineers and everything in-between. Their unique backgrounds and journey bring something special to our industry and illustrate how we can all do more meaningful, interesting and impactful work:
There are 10 things in particular that make these 10 designers really stand out:
- They have each honed their craft from the bottom up (whether having gone through a traditional academic program, an online course like DesignerUp , or being self-taught).
- They are all at different stages of their careers (some newly minted and others seasoned veterans).
- They continue to learn, grow, push the envelope, document and share their genuine experiences.
- They each hail from a different background (and sometimes non-design industry) that informs who they are and what they work on as a designer.
- Their evolution is apparent in their work.
- They are passionate about the problems they solve and find joy in connecting with the users they serve.
- They are transparent about their processes, thoughtful in their communication about it and not afraid to show what worked and what didn't.
- They have focused portfolios that reveal their unique point of view as a designer.
- They are a diverse group of designers from different cultural, gender and socio-economic backgrounds.
- They have so much to teach us all about design and how to use it to express authenticity and to understand and help others do the same.
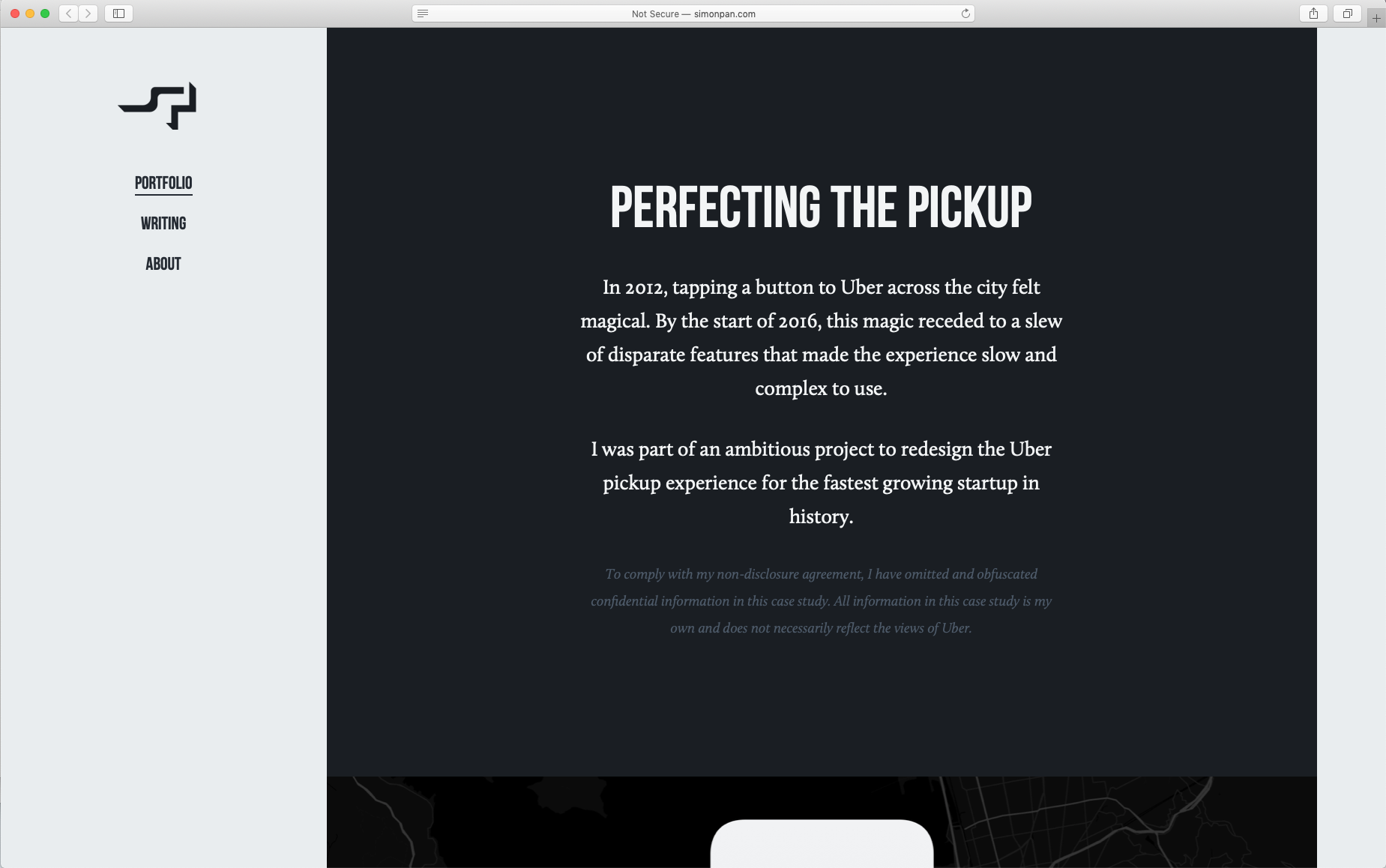
Case Study Format: http://simonpan.com/work/uber/
- The Challenge
- Early Insights
- Reframing the Problem
- The Redesign
- Design Strategy
“In a city as busy as San Francisco, over $1 million was wasted per week because of problematic pickups.”
Madeline Wukusick
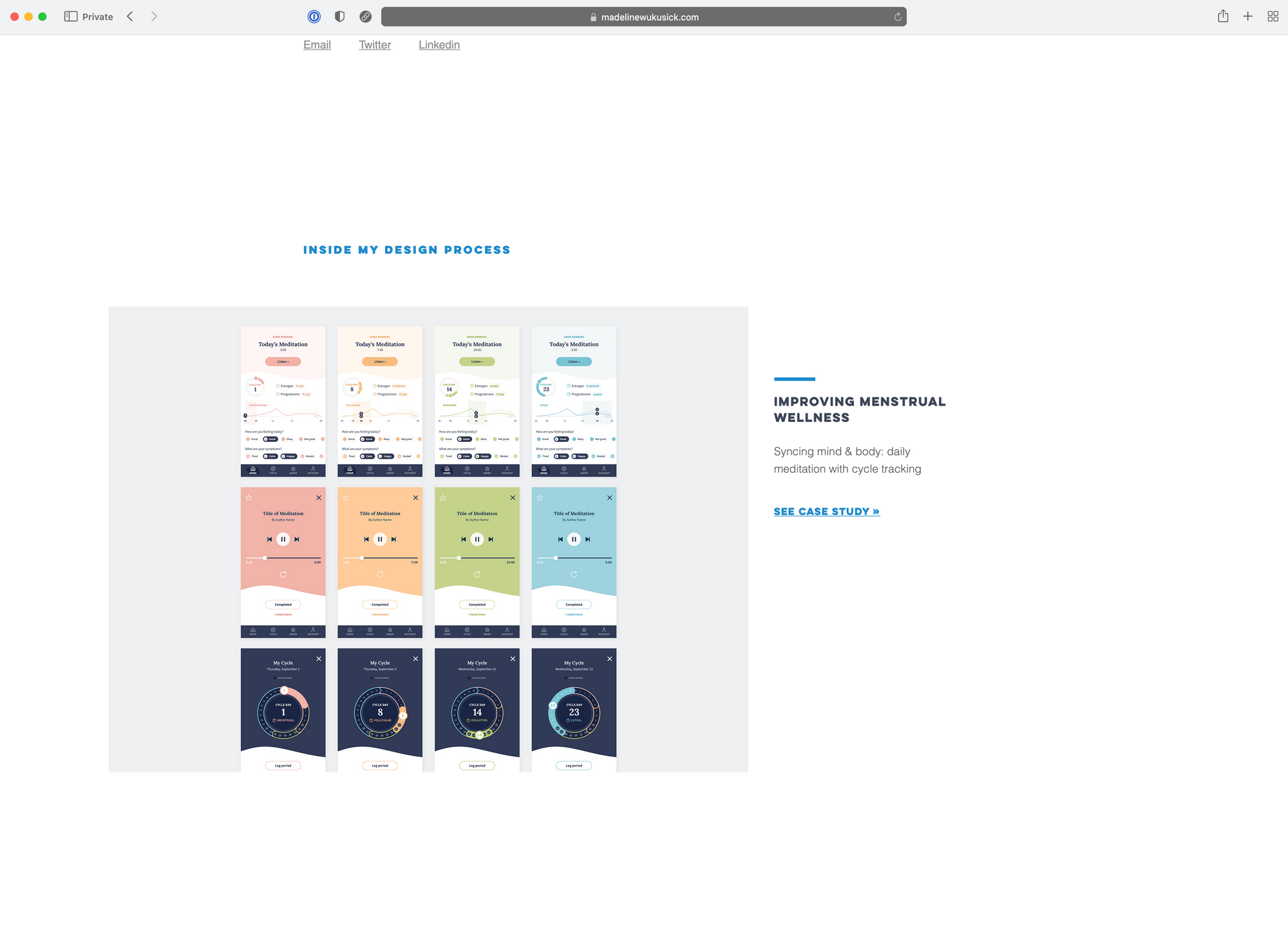
Madeline is a graduate of our DesignerUp Product Design course. She was able to create an incredible portfolio working through our curriculum, blended with her background in graphic and data design that set her up for immediate success landing professional design roles.
Case Study Format:
- The Observed Problem
- The Research
- In the Insights
- The proposed How Might We Statements
- Lean Canvas and Product Strategy
- Business Requirements
- The Solutions and MVP Features
- Things that could be improved
"Thanks for helping me work through these iterations—it's been tremendously helpful! You have such a knack for fine-tuning and teasing out subtle themes that I hadn't noticed before. From these comments, I have a better sense of some of my growth areas to work on and ways in which to push myself. It also helped me realize that I am most interested in hybrid roles, or at least roles with a strong visual component. Really grateful to have discovered this course :-)" - Madeline
Not an Italian mobster; Johny Vino is an engineers' designer. I've been a long time admirer of his work every since his mind-blowing animations and micro-interactions arrested me mid Dribbble scroll many years ago. He is a thoughtful, meticulous designer that understands how to align user and business goals all while transmuting conventional interaction patterns into something that is altogether transcendent yet familiar.
Case Study Format: https://johnyvino.com/
Process, Goal and Task Oriented that varies with each project
- What he worked on
- What he aim to accomplish
- Business Goals
- Representation of complex data
- Integration
Humans are not perfect. I like to apply 3 principles to ever product I design to help me focus on that. Fitt's Law, Mimicry, Aesthetic Usability Effect
Steph Parrott
Steph is a product designer based in Toronto. Currently working on Plantd and most recently at Square in San Francisco.
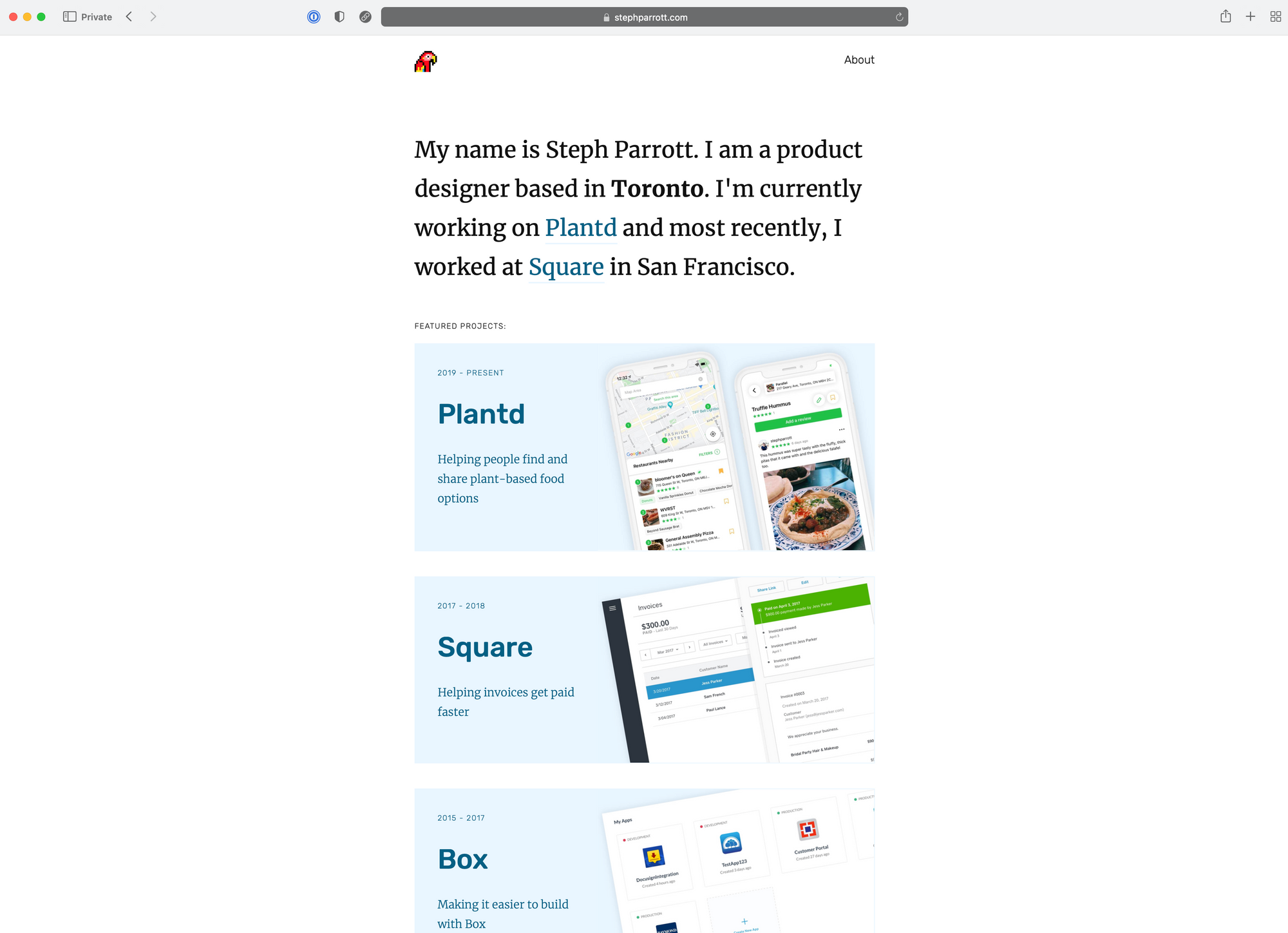
Case Study Format: https://www.stephparrott.com/plantd/
- Roles and Process
- App Overview
- Feature proposal
- Design to Development
- Looking to the future and what's next
"As someone who hasn’t eaten meat in almost 20 years, I’m highly motivated to put in the work to find plant-based options, but for those starting to dabble, how can we except them to do the same?" - Steph
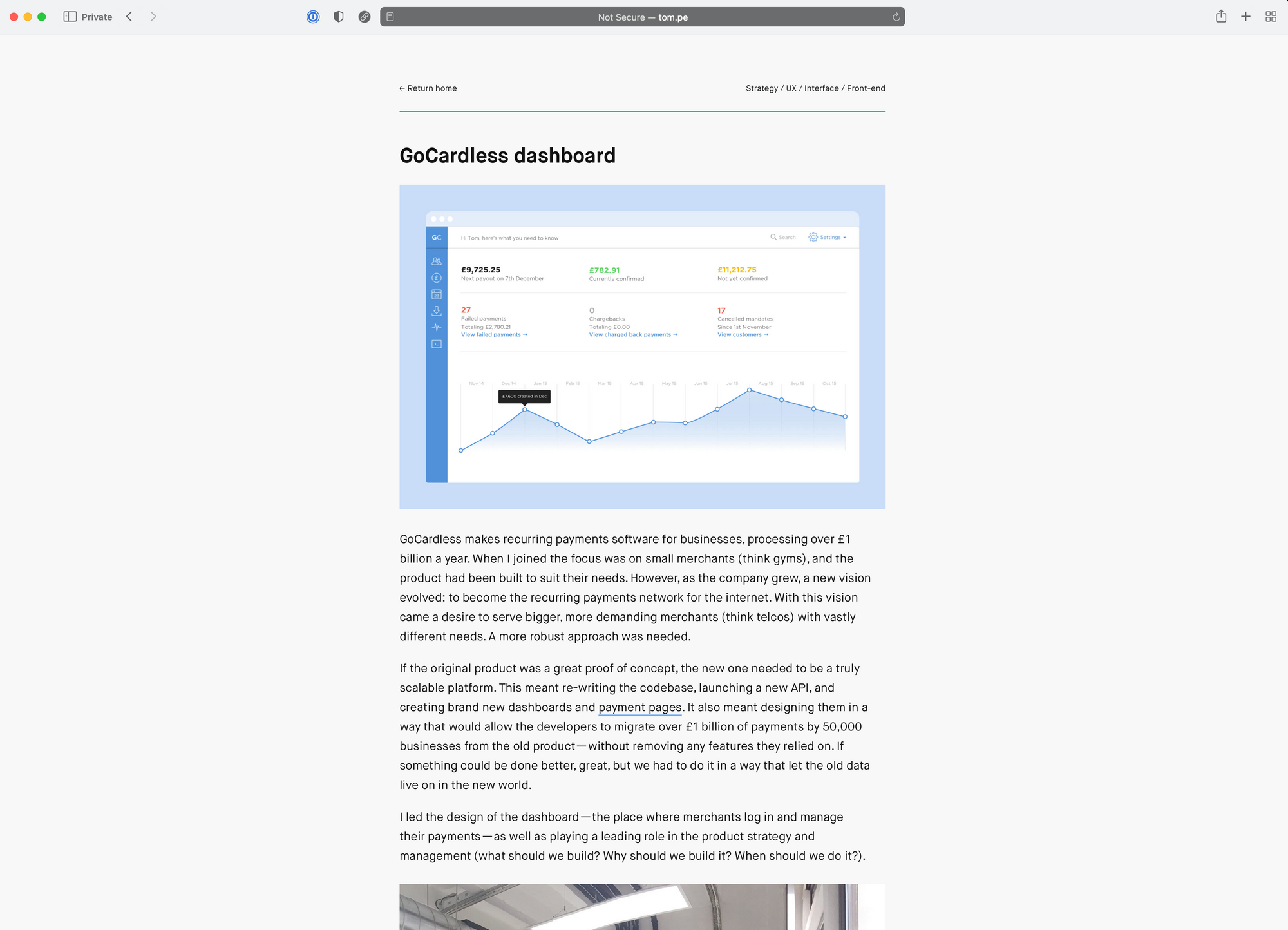
Tom is the co-founder of the community and event series Design Club , and an investor & advisor to Bricklane . He currently works own clients, helping invent, design, and launch new ventures. Before that he held design leadership roles at fashion and fintech startups, and was as a senior designer at a global agency. Case Study Format: http://tom.pe/gc-dashboard.html
- Summary of the problem space, challenges, project and contribution
- Goal and Problem
- Design Principles applied
- Proposed solution and representation of dashboard and data
- Design frameworks used
- Future considerations
"The problem here is that by trying to create something for everyone, we risked helping no one. Avoiding the design equivelant of an identity crisis became a big focus of mine. I'd do this by finding ways to inject a point of view into the product. By knowing what it wasn't, as well as what it was." - Tom Petty
Want to create an incredible portfolio like these full of amazing case studies to get you hired? Enroll in our Product Design Course today!

Garett MacGillivray
Much like myself and other designers of a particular generation, Aussie/Canadian Garett MacGillivray has been around the block and through the evolution of graphic designer, web design, UI/UX Designers and now landed squarely as a full stack Product Designer.
Case Study Format: https://aucadian.com.au/project/goloop
- Exploration and Ideation
- Component Library
- B2B product interface
I've had many labels throughout my career in the digital industry. It's safe to say that I enjoy crafting digital experiences.
Elise is a Bay Area designer that jumped to the bay from NYU. She comes from an advertising and marketing background and has fine tuned her communication skills and processes vast knowledge of the tech and digital product industry has a whole having been on the broadcasting and marketing side of things.
Case Study Format: http://www.elisefu.com/work-komeeda/
- Impact/Metrics
- User testing
- User research
- Information Architecture
- Implementation
- Major Findings
- Formal User Testing
I was driven to design because I felt excited and rewarding to learn about people’s goals and desires, help them solve problems and make their lives easier.
Latiesha Caston
Latisha is a User Experience Designer passionate about holistic, accessible, and inclusive design, based in Seattle.
Case Study Format: https://www.latieshacaston.com/veggie-grill-online-ordering-experience
- The Problem
- The High-level Goal
- The approach
- Pain Points
- Optimizing flow and improving architecture
- Interaction model breakdown
- Looking to the future
"Our high level goal was to design a holistic order-ahead experience that keeps the core of what we've built, while delivering on opportunities, addressing pain points, and setting the stage for the future." - Latisha
Karolis Kosas

Having recently joined the amazing design team at Stripe as a Product designer, Karolis's portfolio is clean and minimal and his case studies really understand the mental model of the user, getting into their heads and revealing the friction points they are feeling and how he can insert a solution that improves on the experience with compromising the soul of the designer.
Case Study Format: http://karoliskosas.com/cinemaclub/
- prototyping
- Built the product from zero
Visual communication is a self-sufficient organism capable of adapting and evolving based on the input of multiple sources.Acting in such context, the designer is an initiator, establishing methods and boundaries for the system to establish itself as an independent entity.
Rohit Singh
One of o ur very own graduates ! Rohit Singh is an up and coming product designer with a focus on helping early-stage startups and new businesses blossom.
Rohit outlines his process for creating an MVP for his digital product from scratch, which serves as a sort of physical and virtual library for the poorest class of India.
Case Study Format: https://work.khadush.in/booksite-an-online-physical-book-sharing-platform/
- Inspiration
- User Interviews
- Lean Canvas
- Visual Design
- Final Words
I specialize in helping early stage startups validate their riskiest assumptions using leading design methods
After analyzing all of these case studies and working with 100s of designers in our product design course to get them ready for the job application process, we've created our own tried-and-true templates to make it easy for designers to replicate the successful format and structure of these top portfolios using Notion .
Each of these amazing portfolios tells the story of the product designer, their evolution, their process and shows what they bring to the world. But it's not easy doing what they do or knowing exactly how to show and tell who you are as designer. Having a solid design education and getting feedback from the design community is the best way to ensure that your work is up to par and being presented in a way the shows your skills and your worth.
Have a look at our partners' advice over at Pathrise on building a strong UX design portfolio .
The best design resources, in your inbox
Tips, tricks, articles and freebies. It's all happening in the DesignerUp Newsletter. View the archives →
We'll only send the occasional email and promise not to spam.
© Copyright 2022 DesignerUp. All Rights Reserved.

50+ Design Thinking Case Study Examples
Design Thinking Case Studies demonstrate the value of the Design Thinking methodology. They show how this Design Thinking methodology helps creatively solve problems and improve the success rate of innovation and increase collaboration in corporations, education, social impact work and the public sector by focusing on the needs of humans.
There are many Design Thinking Case Study examples on the web, but few meet the criteria for a robust case study: a clear description of the methodology, steps undertaken, experimentation through rapid prototypes and testing with people and finally documented results from the process. In this section, we have been selective about the design thinking case study examples that we highlight. We look for Design Thinking Case Studies that demonstrate how a problem was tackled and wherever possible the results or effect that the project produced. Our goal in curating this section of Design Thinking Case Study examples is quality over quantity.
Browse this page to view all Design Thinking Case Study examples, or if you are looking for Design Thinking Case Studies in a specific industry or marketing vertical, then rather start with the Design Thinking Case Studies Index .
If you have an interesting application of Design Thinking that you have a case study for, we would be happy to publish it.
Submit your Design Thinking Case Study for publication here.

Design Thinking Case Study Index
Welcome to the Design Thinking Case Study Index. There are many Design Thinking Case Studies on the internet. Many are retrofitted descriptions of what occurred, rather than evidence of the Design Thinking process in action. In order to bring a higher standard to the practice of Design Thinking, we require stronger evidence and rigor. Only members can post and must provide strong evidence in the Design Thinking Case Study that the Design Thinking process was used to create the original idea for the product or service solution. The criteria that needs to be proved to make your project a Design Thinking Case Study are:

The Guardian: Benefits of Design Thinking
Design thinking helped The Guardian newspaper and publishing group change their funding model, boost revenue and adapt their culture and engage on an emotional level with their readers. In this case study, Alex Breuer, Executive Creative Director and Tara Herman, Executive Editor, Design explain how design thinking was able to achieve these goals for The Guardian.
Read more...

Tackling the Opioid Crisis at the Human and Systems Levels
How the Lummi Tribal clinic used design to address opioid overdoses

Applying Design Thinking Internally
Applying Design Thinking internally, within a group, community or to ourselves. This is a new application of the Design Thinking Methodology.
An internal application in this sense can have two meanings. First, the internal application of design thinking tactics within a group, organization or community, and second, the internal application of design thinking to one’s own self and life.
Can Design Thinking help you solve your own problems?

The Use of Design Thinking in MNCH Programs, Ghana
Responding to growing interest among designers, global health practitioners, and funders in understanding the potential benefits of applying design thinking methods and tools to solving complex social problems, the Innovations for Maternal, Newborn, and Child Health (MNCH) Initiative (Innovations) developed and piloted innovative interventions to address common barriers to improving the effectiveness of basic MNCH health services in low-resource settings.
Société Générale's Time Tracking Nightmare Solved
In 2017, employees, managers, and partners of Société Générale Global Solution Centre agreed that invoices based on time tracking and project allocation were a chronic and painful challenge.
At SG-GSC, customers were billed for the time each assigned employee worked. The process of collecting the time worked by those employees (HCC) was a complicated and difficult ordeal. It consumed 21 days per month for senior employees. These employees had to navigate different systems, many types of contracts, high staff mobility, and a variety of processes between business lines.

How to Stimulate Innovation in Your Organization With Design Thinking
In this use case the cities of Aalborg and Rotterdam share their findings obtained from design thinking initiatives. This is based on empirical research as part of an evaluation. The use case is written for other professionals in the field of design in public organizations.
One of the main targets of the Interreg NSR project Like! is to create a digital innovative culture in which citizens are engaged, and more inclusive services are build. To reach this the municipalities started several initiatives with design thinking. In these initiatives one of the objectives was to find out how design thinking can help us to develop innovative and inclusive services. To research what design thinking contributed, we evaluated the pilots with participants.

The Impact of Design Thinking on Innovation: A Case Study at Scania IT
Organizational culture represents a crucial factor for the introduction of innovation throughout the organization via Design Thinking and agile way of working. Thus, the organization must establish a culture that encompasses a shared vision with values that create a commitment to learn, experiment and accept failure.

Oral B - Putting the User At the Center of Innovation
Oral B wanted to integrate digital technology into their electric toothbrush. The Brands first thoughts were to help users to track how well they were brushing their teeth. Future Facility, a product design firm in the UK suggested a different approach. Focus on the pain points of electric toothbrush users.
This case study discusses the importance of placing the user at the center of your innovation activities.

Design Thinking at Innogy
eCarSharing: Energy Solutions for the New Generation
In 2015, Itai Ben-Jacob pitched his own ideas for a viable business model and developed the idea for innogy’s eCarSharing project in a design thinking workshop. His goal was to explore one of innogy’s innovation focus areas, ‘urban mobility.’
Together with fellow innovation hub members he organized a series of design thinking workshops to wade through the expansive topic of urban concepts – one of them focusing on mobility: “ We wanted to understand urban mobility – what does it actually entail? What type of business should we start? “

Building Cape Town’s Resilience Qualities Through Design Thinking.
This case study focuses on a Design Thinking Workshop for primary school learners. The aim of the workshops was to provide learners with a new set of skills which they can employ when problem solving for real world challenges.
Building resilience is essential for cities that face increasing uncertainty and new challenges that threaten the well-being of its citizens. This is especially important when looking at the diversity and complexity of potential shocks and stresses.
Cape Town’s efforts to build skills in design thinking supports the creation of locally-relevant and innovative solutions that contribute to building resilient individuals and communities in Cape Town.

Designing Waste Out of the Food System
The average American wastes enough food each month to feed another person for 19 days. Through a number of projects with The Rockefeller Foundation and other organizations, IDEO designers from across the U.S. devised novel ways to tackle food waste.

B2B Design Thinking: Product Innovation when the User is a Network
When B2B companies talk about user experience, they are really considering the aggregated needs of multiple people and roles in a large ecosystem. But what happens when those objectives are vastly different for every individual?
“Humans don’t stop being humans just because they entered an office building.”

Self-Checkout: Improving Scan Accuracy Through Design
In this unique applied research study, academics and designers partnered with four of ECR’s Retailer members to immerse themselves in the self-checkout experience, understanding from the perspectives of the shopper and self-checkout supervisors, their journey from entry to exit, and their design challenges and frustrations.

Co-designing OTP Bank’s Strategic Plan for Growth
This is an example of accelerating a transformation through co-design. Eighty-two professionals gathered, representing OTP’s whole organization. Together, they were able to achieve months of work in just three days.
OTP Bank Romania (OTP) was at a key turning point in late 2018. The organization was undergoing changes in its leadership team. This new team helped them develop an ambitious goal:
OTP Bank will double its market share in 5 years.
They gathered for two Discovery sessions in December 2018. In these sessions, a carefully selected senior team chose three market segments to focus on. Then they built these segments into Personas.

IDEO: Journey to Mastery
While this is not a case study as such, it sits in our case study section as it is an important piece of information from a consultancy that played a large part in popularizing Design Thinking. In their Journey to Mastery section, IDEO discuss and shine a light on the shortcomings of the design thinking term and how it has been applied. I.e that it is not designing and that just knowing and using the practice does not in itself produce amazing solutions to problems.
It is worth a read to understand some of the nuance that is important to successful design thinking work.

Singapore Government: Building Service Platforms Around Moments in Life
In 2017, the product development team at Singapore’s Government Technology Agency (GovTech) was tasked to develop a tool to consolidate citizen-facing services previously delivered by different government agencies onto a single platform. The initiative, Moments of Life, sought to make it easier for citizens to discover and access relevant services during important changes in their lives by reducing fragmentation and being more anticipatory in the delivery of those services.
Organizing the delivery of services around a citizen’s journey, rather than fitting their delivery to existing processes, required extensive interagency collaboration beyond functional silos.

Mayo Clinic: Design Thinking in Health Care – Case Study
In the early 2000s, Mayo Clinic physician Nicholas LaRusso asked himself a question: if we can test new drugs in clinical trials, can we in a similarly rigorous way test new kinds of doctor-patient interactions?
Consequently, the Mayo Clinic set up a skunkworks outpatient lab called SPARC. Within 6 years it had grown to an enterprise wide department called the Center for Innovation a dedicated research and design-oriented institute that studies the processes of health care provision, from the initial phone call, to the clinic visit, to the diagnosis and treatment of the problem, to follow-up and preventive care.

Design Thinking and Participation in Switzerland: Lessons Learned from Three Government Case Studies
Olivier Glassey, Jean-Henry Morin, Patrick Genoud, Giorgio Pauletto
This paper examines how design thinking and serious game approaches can be used to support participation.
In these case studies the authors discovered the following results.
Perceived usefulness. Based on informal discussions and debriefing sessions following all workshops, it is clear that the vast majority of workshop participants explicitly stated that both the actual outcome of the workshop and the methods used would significantly contribute to enhancing their performance in their work. Some workshops have actually led to follow up workshops or concrete actions based on the outcome.

Asili: Addressing an Entire Ecosystem of Need in a Rural Community

Design Thinking in HR at Deutche Telekom
Reza Moussavian, a senior HR and IT executive at Deutsch Telekom explains the company's journey and how important Design Thinking is as a business strategy for HR. Reza Moussavian's presentation provides great examples of issues tackled in HR and the results achieved. The presenter claims that there is not a singe issue that Deutche Telekom tackles in HR now that does not start with a Design Thinking methodology.
"Design Thinking solves 5% of our problems." says Reza Moussavian, "What we found out was that the magic was really in the implementation phase. We had to learn how to keep the momentum, the spirit and the fire from the co-creation workshops alive through the long implementation phase. Success is really about technology, transformation and leadership skills."

Design Thinking in Education: Perspectives, Opportunities and Challenges
This very informative article discusses design thinking as a process and mindset for collaboratively finding solutions for wicked problems in a variety of educational settings. Through a systematic literature review the article organizes case studies, reports, theoretical reflections, and other scholarly work to enhance our understanding of the purposes, contexts, benefits, limitations, affordances, constraints, effects and outcomes of design thinking in education.
Specifically, the review pursues four questions:

Design Thinking in the Classroom: What can we do about Bullying?
As children move from kindergarten, through middle school, and to high school, instruction shifts from stories to facts, from speculation to specifics, and imagination fades from focus. Design Thinking provides an alternative model to traditional ways of learning academic content by challenging students to find answers to complex, nuanced problems with multiple solutions and by fostering students’ ability to act as change agents.
Design Thinking is all about building creative confidence — a sense that “I can change the world.” In the Bullies & Bystanders Design Challenge, the students discovered that changing themselves might be even more important.

Following One School District's Approach to Innovation for the 21st Century
In her doctoral paper Loraine Rossi de Campos explores the use of Design Thinking in a school district for a 4-5 grade school.

India: Using ‘Design Thinking’ to Enhance Urban Redevelopment.
The discourse on urban planning and development has evolved over the last century with top-down methods of planning urban spaces giving way to bottom-up approaches that involve residents and other stakeholders in the design process. While the notion of participation and user involvement is considered critical to the design of appropriate and acceptable urban forms, there is no clear consensus in the literature on the methodology to be used to involve users and stakeholders in the design process. In this paper, we propose that the use of ‘Design-Thinking’ – a methodology for Human-Centred Design that is often used in product design and related industries – may be an effective methodology for engaging stakeholders in the urban design domain.

E*Trade: From Idea to Investment in 5 Minutes
Why the Financial Services Sector Should Embrace Design Thinking. Financial institutions need to evolve rapidly or risk disruption at the hands of nimble Fintech start-up companies.
In this article Kunal Vaed, The Street, describes how E*Trade used design thinking to enable the company to help investors get smarter by going from the idea of investing to an investment in 5 minutes.
E*Trade's Adaptive Portfolio service offering provides a good example of the work and results that E*Trade achieved with Design Thinking.

Fidelity Labs: Optimizing near-term savings goals
Thanks to providers like Fidelity, people can rely on easy, convenient systems to stay on track with their retirement savings. But when it comes to saving for important near-term goals (think: vacation, house, or wedding), people tend to be less organized.
Fidelity Labs tackled this problem and defined the challenge as: "How might we improve the experience of saving for near-term goals? How might we make it easier, faster, and better?"

Design for Action: MassMutual and Intercorp Group
How to use design thinking to make great things actually happen by Tim Brown and Roger L. Martin. In this great HBR article, the authors look at design thinking in Finance with two case studies, one from MassMutual and the other from Intercorp. Group of Peru.
In this article highlighting the development of the acceptance of Design Thinking, they discuss how Design Thinking helps to create the artifact that creates the new solution as well as the intervention/s that brings the artifact to life.

How to Use Design Thinking to Make Great Things Actually Happen
Ever since it became clear that smart design led to the success of many products, companies have been employing it in other areas, from customer experiences, to strategy, to business ecosystems. But as design is used in increasingly complex contexts, a new hurdle has emerged: gaining acceptance (for the new solutions).

4 Design Thinking Case Studies in Healthcare: Nursing
The 4 case studies by Penn Nursing illustrate how nurses can be really powerful collaborators and generators of solutions within Healthcare. The videos describe the main attributes that nurses bring to the problem solving table

Philips: Improving the Patient Experience
Philips Ambient Experience service offers hospitals a way to radically improve the patient experience and results that they can achieve from their CT scanning suites. The best way to understand what it is is to watch this video and this video discussing the latest addition to the service. The white paper from Philips is also a good source of information on the Ambient Experience Service.

IBM: Design Thinking Adaptation and Adoption at Scale
How IBM made sense of ‘generic design thinking’ for tens of thousands of people.
Generic design thinking often faces heavy resistance from influential skeptics, gets misunderstood or not understood at all, or less dire, it gets picked up with an unreflected euphoria and is applied as a “silver bullet” to all kinds of problems and projects (the famous “methodology misfit” we also see with Scrum for example). The big hangover often comes after the first experimentation budgets are expended and at worst a blame game starts.

Design Thinking in Public Engagement: Two Case Studies
Dave Robertson presents two case studies with the British Columbia Government (Canada). One with the Ministry of Transportation discussing their (public servant centered website), the other solving the problem of finding a solution to where to place a power substation.
Dave shows how he was stuck working in the public sector as a consultant and how creativity expressed through the Design Thinking methodology helped him to see a different, more effective way of creating solutions.

Bank of America Helps Customers Keep the Change
How do you encourage new customers to open bank accounts? In 2004, Bank of America used the Design Thinking methodology to look at the problem from a human centered perspective when they assigned design agency IDEO to boost their enrollment numbers: a problem that at the time, lacked any user perspective on why it was so hard for customers to save.

Redesigning The Employment Pass Application in Singapore
The Ministry of Manpower’s Work Pass Division (WPD) used design thinking as a tool to develop better ways to support foreigners who choose Singapore as a destination to live, work and set up businesses. The case reveals: Design thinking can potentially transform the perception and meaning of public service.
The team found out that the service redesign process required a better understanding of the decision points of both users and non-users. This involved taking a closer look at the opportunities and difficulties facing users, including those who had succeeded and failed within it, or had encountered problems or avoided it.

The US Tax Forms Simplification Project
This case concerns one of the earliest attempts by design thinkers at designing a large, complex system. It shows that design approaches in the public sector can look back at a long history. And it reveals how design thinking within the organization must include members of the whole organization in the design process.
Design has a long tradition and a rich history in the public sector. Nearly 40 years ago, when the US Congress passed the Paperwork Reduction Act into law, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) turned to designers in an effort to implement the new policy and to improve its relationship with taxpayers.

A Tough Crowd: Using Design Thinking to Help Traditional German Butchers
Between 2004 and 2014, more than 4000 butcher shops were forced to shut down in Germany. When last was the butcher shop redesigned? The process started in the 1990s, as supermarkets became the favored spot for meat-shopping. As if a dramatic loss of market share was not enough, the industry as a whole started suffering from a serious image crisis. It was time to apply design Thinking to the traditional German Butcher Shop.
The initial problem statement read “Create the meat shop 2.0, an up-to-date version of the classic butcher business”.

IDEO: Using Design Thinking to Create a Better Car
The challenge.
Remove roadblocks that can compromise the in-car experience for the Lincoln car company.
The final product, the Lincoln MKC luxury crossover, is credited with helping the Lincoln brand outpace growth in the luxury segment by more than two-to-one over competitors.
THE OUTCOME
A pop-up studio where IDEO designers helped departments communicate and collaborate more effectively.

Transforming Constructivist Learning into Action: Design Thinking in Education
In an ever changing society of the 21st century, there is a demand to equip students with meta competences going beyond cognitive knowledge. Education, therefore, needs a transition from transferring knowledge to developing individual potentials with the help of constructivist learning. A Scheer, C Noweski, C Meinel , University of Potsdam, Germany.
Design Thinking is the most effective method of teaching constructivist learning.

Scaling Design Thinking in the Enterprise, a 5 Year Study
During Julie Baher's five years at Citrix between 2010 to 2015, she was fortunate to gain first-hand experience leading a transformation in product strategy to a customer-centered approach. It began when several senior executives attended the design thinking boot camp at Stanford’s d-school, returning with a new vision for the product development processes. Julie goes into detail about how they scaled up the customer centric methodology across the organizations 8,000 employees.

Developing Environmental Sustainability Strategies
Developing environmental sustainability strategies, the Double Diamond method of LCA and design thinking: a case study from aged care. Journal of Cleaner Production, 85, 67-82. Stephen J. Clune*, Simon Lockrey.

Developing an App for Type II Diabetes
Development and testing of a mobile application to support diabetes self-management for people with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a design thinking case study. Numerous mobile applications have been developed to support diabetes-self-management. However, the majority of these applications lack a theoretical foundation and the involvement of people with diabetes during development. The aim of this study was to develop and test a mobile application (app) supporting diabetes self-management among people with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes using design thinking. The article was written by Mira Petersen and Nana F. Hempler.

Improving UX in Public Transportation
In this case study the project leaders goal was to improve the experience of bus users on Madrid's EMT system by offering a technological solution to increase the users’ satisfaction with regard to accessibility during the bus trip as well as when waiting for the bus to arrive.

Transforming Life Insurance through Design Thinking
To some fintechs, non-insurance incumbents, and venture capitalists, the industry’s challenges suggest opportunity. The life insurance value chain is increasingly losing share to these players, who are chipping away at the profit pool.
How might incumbent life insurers keep pace in today’s fast-moving competitive environment and meet customers’ changing needs?
Deploying the Design Thinking methodology in the insurance sector could be the key to helping save insurance from itself. Here's what McKinsey has to say about design thinking in insurance in their article "Transforming Life Insurance through Design Thinking".
"Better addressing the evolving needs of consumers can help incumbents win their loyalty—and protect against new competitors.

Bringing Design Thinking to the Insurance World
Pancentric helped Jelf kick-off a several-year digital transformation journey by getting to know not just their customers better, but their own staff, too. Jelf has dozens of offices around the UK, all with specialties in insuring different kinds of commercial businesses. For our project team trying to determine a roadmap of new developments, there was no easy overview of how each office operated or what the entire customer experience looked like.

The Features of Design Thinking in Fast Moving Consumer Goods Brand Development
This paper investigates what features of design thinking are employed in FMCG brand development via stakeholder interviews in three domains: agencies, companies, and retailers. This paper concludes with suggestions of how design thinking can be embraced in FMCG brand development.

A Chain of Innovation The Creation of Swiffer
This is a great case study that underlines the complexity of bringing game changing products to market. It helps to provide an understanding of just how much more is needed that a simple five step process of idea generation.
Read more from Continuum , the Design Firm responsible for the Swiffer

The Guardian: Using Design to Reaffirm Values
The Guardian's redesign, which launched in January 2018, illustrated the business impact when design is valued. The Guardian has a strong culture of design and increasingly, how design thinking can contribute to organizational change and development.
20+ Outstanding UX/UI Design Case Studies

Discover an expertly curated collection of 20+ inspirational UX/UI design case studies that will empower you to create outstanding case studies for your own portfolio.
- Comprehensive end-to-end case studies covering research, ideation, design, testing, and conclusions.
- Perfect for designers building portfolios and looking for inspiration to create their own case studies.
- Learn new methods and techniques, improve your understanding, and apply them to your projects.
- Gain insights from the successes and challenges of accomplished designers.
Want to get access to 30+ more case studies including smart tagging system?
Download full version
All case studies included in this collection are sourced from real designers' portfolios and are used for the purpose of learning and inspiration. The original authors retain all rights to their work.

- Get in touch
- Enterprise & IT
- Banking & Financial Services
- News media & Entertainment
- Healthcare & Lifesciences
- Networks and Smart Devices
- Education & EdTech
- Service Design
- UI UX Design
- Data Visualization & Design
- User & Design Research
- In the News
- Our Network
- Voice Experiences
- Golden grid
- Critical Thinking
- Enterprise UX
- 20 Product performance metrics
- Types of Dashboards
- Interconnectivity and iOT
- Healthcare and Lifesciences
- Airtel XStream
- Case studies
Data Design
- UCD vs. Design Thinking
Work & Case Studies: The proof is in the pudding and the pudding is here!
Enterprise & it.
Agility Transfora: A 360° enterprise management platform
Healthcare & Lifesciences
Healthshots: Demystifying wellness for the Millennial Indian Women
QuaQua: Designing a new age Virtual Travel Experience

SUGGESTED VIDEO
What does it take to create impact through design.
Here’s a capture of those moments from our studios & network across the world, that provide insight into what it takes to create global impact through Design.
Financial Services
SBI Smart Money: Trading App designed to facilitate more transactions
Education & Learning
Manorama Yearbook: Re-imagining digital for India’s gold standard knowledge bank
Zoylo: Designing the digital healthcare ecosystem
News, Media & Entertainment
Airtel XStream: Impacting 100 Million users through superior UX Design
GE Configurator: Defining workflows for a fortune company
Analyttica TreasureHunt: An intelligence marketplace
SUGGESTED READ
Design in the age of digitization: the next agenda for industry 4.0.
User Experience design is at the cusp of making this great re-make actualize. Design thinking as an approach is an imperative solution that enterprises could leverage to reinvent themselves while being in synergy with new-age technologies.
Airtel Payments Bank: Powering India’s first payments bank with Design
Zafin Analytics: Data Design for financial institutions
Pearl Academy: Frontlining creative education with a new-age digital identity
Tata ClassEdge: Redefining a class-leading product
Reliance Smart Money: Redefining investment category
Lock The Deal: Re-defining distribution systems through digital experiences
Zee5: New age entertainment for the Indian audience
Godrej U & Us: Pioneering augmented reality shopping experience
Abt Healthcare Toolkit: Mitigating infant mortality through Design
Axis Bank: Transformation of experience across platforms and ecosystems
Networks & Smart Devices
Roamware: Empowering telecom providers through predictive Roaming analytics
Engagedly: Insight led product proposition
Gamification in Education: Why, What and How?
With the Edtech industry growing in size, gamification is bound to gain and accredit to some of those brownie points. Why gamify educational technologies and experiences in the first place?
Axis Bank RM: Empowering Relationship Managers through a range of apps
Axis Direct: On a mission to demistify investments
Extramarks: Digital transformation of a leading EDTech solution
Linchpin app: Enterprise learning, made engaging and fun
Religare Securities: Re-imagining the trader’s favorite online portal
Mediport: Everything healthcare, at fingertips
KryptoGraphe: Cryptocurrency Portfolio Tracker
Globetouch Connect : Driving seamless global connectivity
IDBI Federal: Transforming a legacy product
Figo: Roaming, with no strings attached
Avanti Cardiogym: User Centered Design for fitness enthusiasts
Playablo: Enabling learning through gamification
Hindustan Times: Transformative design for the legacy newspaper
Finodex: Smart investment tools for the smart user
Dr. Reddy’s: Vendor engagement portal that delivers trust
The power of interconnectivity in the global world
The successful integration of emerging technologies like IoT, AR, VR and AI needs a complex network of highly sophisticated services and providers underpinned by reliable connections.
Pidilite: Corporate website, differently approached
Telegraph: Reaching out and across through superior UX
Yupp TV: Entertainment for the Indian diaspora
Hero Fincorp SimplyCash: End to end digital lending platform
Sun Pharma Genie: Internal employee portal to engage and delight
GSMA Mobile Connect: Making authentication secure and powerful
Infozech: User Centered Design across solutions for the telecom industry
Reliance Life Insurance: Self service to empower users
Zeta Interactive: Research led user relevance
Leadership across Industries
News media & entertainment.
News portals and apps, Media & Entertainment portals and apps, OTT, Mobile TV, Music, Streaming.
ERP, Utilities, HRMS, Planning tools, Data & Analytics, LMS, Enterprise systems, Productivity suites.
Medical devices, Hospital management systems, Pharma, Wearable tech, Personal healthcare, Fitness, Wellness.
Networks & Smart devices
Telecom, Home automation, Data networks, M2M, IoT, Utilities, Law enforcement, Defense & Border security.
Education & Edtech
Institutions, Portals, Apps, Learning management, Gamified learning, MOOCs, Universities, Learning centers.
Banking & Financial Services
Fintechs, Banks, Insurance, Payments, Wallets, Lending, Trading, Investment, Blockchain, Currencies, Wealth management.
UI UX DESIGN
User & design research, service design.
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue we'll assume that you accept this. Learn more
Recent Tweets
Sign up for our newsletter.
Subscribe to our newsletter to stay updated with the latest insights in UX, CX, Data and Research.
Get in Touch
Thank you for subscribing.
You will be receive all future issues of our newsletter.
Thank you for Downloading.
One moment….
While the report downloads, could you tell us…
Limited Time Offer! Save up to 50% Off annual plans.* View Plans
Save up to 50% Now .* View Plans
How To Write A Case Study For Your Design Portfolio
Case studies are an important part of any designer’s portfolio. Read this article to learn everything you need to know to start writing the perfect case study.

When you’re putting together your online design portfolio , design case studies are a great way to showcase your experience and skills. They also give potential clients a window into how you work.
By showing off what you can do and your design process, case studies can help you land more clients and freelance design jobs —so it can be smart to dedicate an entire section of your online portfolio website to case studies.
Getting Started
So—what is a design case study and how do they fit in your portfolio.
Let’s get some definitions out of the way first, shall we? A design case study is an example of a successful project you’ve completed. The exact case study format can vary greatly depending on your style and preferences, but typically it should outline the problem or assignment, show off your solution, and explain your approach.
One of the best ways to do that is to use a case study design that’s similar to a magazine article or long-form web article with lots of images throughout. When building your case study portfolio, create a new page for each case study. Then create a listing of all your case studies with an image and link to each of them. Now, let’s get into the nitty-gritty of creating these case studies.
Choose Your Best Projects
To make your online portfolio the best it can be , it’s good to be picky when choosing projects for case studies. Since your portfolio will often act as your first impression with potential clients, you only want it to showcase your best work.
If you have a large collection of completed projects, you may have an urge to do a ton of case studies. There’s an argument to be made in favor of that, since it’s a way to show off your extensive experience. In addition, by including a wide variety of case studies, it’s more likely that potential clients will be able to find one that closely relates to their business or upcoming project.
But don’t let your desire to have many case studies on your portfolio lead you to include projects you’re not as proud of. Keep in mind that your potential clients are probably busy people, so you shouldn’t expect them to wade through a massive list of case studies. If you include too many, you can never be sure which ones potential clients will take a look at. As a result, they may miss out on seeing some of your best work.
There’s no hard-and-fast rule for how many case studies to include. It’ll depend on the amount of experience you have, and how many of your completed projects you consider to be among your best work.
Use Your Design Expertise
When creating the case study section of your portfolio, use your designer’s eye to make everything attractive and easily digestible. One important guideline is to choose a layout that will enable you to include copy and image captions throughout.
Don’t have your portfolio up and running yet and not sure which portfolio platform is best for you? Try one that offers a free trial and a variety of cool templates that you can play around with to best showcase your design case studies.
If you don’t provide context for every image you include, it can end up looking like just a (somewhat confusing) image gallery. Case studies are more than that—they should explain everything that went into what you see in the images.
Check Out Other Case Study Examples for Inspiration
Looking at case study examples from successful designers is a great way to get ideas for making your case study portfolio more effective. Pay special attention to the case study design elements, including the layout, the number of images, and amount of copy. This will give you a better idea of how the designer keeps visitors interested in the story behind their projects.
To see some great case study examples, check out these UX designer portfolios .
Try a Case Study Template
There are plenty of resources online that offer free case study templates . These templates can be helpful, as they include questions that’ll help you ensure you’ve included all the important information.
However, most of them are not tailored to designers. These general case study templates don’t have the formatting you’ll want (i.e. the ability to include lots of images). Even the ones that are aimed at designers aren’t as effective as creating your own design. That’s why case study templates are best used as a starting point to get you thinking, or as a checklist to ensure you’ve included everything.
How to Write Case Studies
Maintain your usual tone.
You should write your case studies in the same personal, authentic (yet still professional!) tone of voice as you would when creating the About Me section of your portfolio . Don’t get bogged down in too much technical detail and jargon—that will make your case studies harder to read.
Since your case studies are part of your online portfolio, changing your usual tone can be jarring to the reader.
Instead, everything on your portfolio should have a consistent style. This will help you with creating brand identity . The result will be potential clients will be more connected to your writing and get the feeling that they’re learning what makes you unique.
Provide Some Context
Case studies are more effective when you include some information at the beginning to set the stage. This can include things like the date of the project, name of the client, and what the client does. Providing some context will make the case study more relatable to potential clients.
Also, by including the date of the project, you can highlight how your work has progressed over time. However, you don’t want to bog down this part of the case study with too much information. So it only really needs to be a sentence or two.
Explain the Client’s Expectations
Another important piece of information to include near the beginning of your case study is what the client wanted to accomplish with the project. Consider the guidelines the client provided, and what they would consider a successful outcome.
Did this project involve unique requirements? Did you tailor the design to suit the client’s brand or target audience? Did you have to balance some conflicting requirements?
Establishing the client’s expectations early on in the case study will help you later when you want to explain how you made the project a success.
Document Your Design Process
As you write your case study, you should take a look at your process from an outsider’s point of view. You already know why you made the decisions you did, so it may feel like you’re explaining the obvious. But by explaining your thought process, the case study will highlight all the consideration you put into the design project.
This can include everything from your initial plan to your inspiration, and the changes you made along the way. Basically, you should think about why you took the approach you did, and then explain it.
At this point, consider mentioning any tricks you use to make your design process more efficient . That can include how you managed your time, how you communicated with clients, and how you kept things on track.
Don’t Be Afraid to Mention Challenges
When writing a case study, it can be tempting to only explain the parts that went flawlessly. But you should consider mentioning any challenges that popped up along the way.
Was this project assigned with an extremely tight deadline? Did you have to ask the client to clarify their desired outcome? Were there revisions requested?
If you have any early drafts or drawings from the project saved, it can be a good idea to include them in the case study as well—even if they show that you initially had a very different design in mind than you ended up with. This can show your flexibility and willingness to go in new directions in order to achieve the best results.
Mentioning these challenges is another opportunity to highlight your value as a designer to potential clients. It will give you a chance to explain how you overcame those challenges and made the project a success.
Show How the Project’s Success Was Measured
Case studies are most engaging when they’re written like stories. If you followed the guidelines in this article, you started by explaining the assignment. Next, you described the process you went through when working on it. Now, conclude by going over how you know the project was a success.
This can include mentioning that all of the client’s guidelines were met, and explaining how the design ended up being used.
Check if you still have any emails or communications with the client about their satisfaction with the completed project. This can help put you in the right mindset for hyping up the results. You may even want to include a quote from the client praising your work.
Start Writing Your Case Studies ASAP
Since case studies involve explaining your process, it’s best to do them while the project is still fresh in your mind. That may sound like a pain; once you put a project to bed, you’re probably not looking forward to doing more work on it. But if you get started on your case study right away, it’s easier to remember everything that went into the design project, and why you made the choices you did.
If you’re just starting writing your case studies for projects you’ve completed in the past, don’t worry. It will just require a couple more steps, as you may need to refresh your memory a bit.
Start by taking a look at any emails or assignment documents that show what the client requested. Reviewing those guidelines will make it easier to know what to include in your case study about how you met all of the client’s expectations.
Another helpful resource is preliminary drafts, drawings, or notes you may have saved. Next, go through the completed project and remind yourself of all the work that went into achieving that final design.
Draw Potential Clients to See Your Case Studies
Having a great portfolio is the key to getting hired . By adding some case studies to your design portfolio, you’ll give potential clients insight into how you work, and the value you can offer them.
But it won’t do you any good if they don’t visit your portfolio in the first place! Luckily, there are many ways you can increase your chances. One way is to add a blog to your portfolio , as that will improve your site’s SEO and draw in visitors from search results. Another is to promote your design business using social media . If you’re looking to extend your reach further, consider investing in a Facebook ad campaign , as its likely easier and less expensive than you think.
Once clients lay eyes on all your well-written, beautifully designed case studies, the work will come roaring in!
Want to learn more about creating the perfect design portfolio? 5 Designers Reveal How to Get Clients With Your Portfolio 20 Design Portfolios You Need to See for Inspiration Study: How Does the Quality of Your Portfolio Site Influence Getting Hired?

A Guide to Improving Your Photography Skills
Elevate your photography with our free resource guide. Gain exclusive access to insider tips, tricks, and tools for perfecting your craft, building your online portfolio, and growing your business.
Get the best of Format Magazine delivered to your inbox.

Beyond the Rule of Thirds: 30 Creative Techniques for Composition

Inspiring Still Life Photography Portfolios: Crafting a Quality Online Presence

10 Inspiring Examples and Expert Tips for Crafting A Powerful Artist Statement

Get Inspired by 10 Fashion Design Portfolios That Capture the Essence of Contemporary Style

Should I Catalog My Art?

Making Your Site Design More Accessible

6 Inspiring Portfolios by Members of BWP (Black Women Photographers)
*Offer must be redeemed by May 31st, 2024 at 11:59 p.m. PST. 50% discount off the subscription price of a new annual Pro Plus plan can be applied at checkout with code PROPLUSANNUAL, 38% discount off the price of a new annual Pro plan can be applied with code PROANNUAL, and 20% discount off the price of a new Basic annual plan can be applied with code BASICANNUAL. The discount applies to the first year only. Cannot be combined with any other promotion.
- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
All About Process: Dissecting Case Study Portfolios
A portfolio is more than a cache of images, it’s a way to demonstrate design skills and problem solving to clients. We show how to elevate portfolios by explaining the inner workings of a case study.

By Adnan Puzic
Adnan is a UI/UX expert with a bold aesthetic and a passion for designing digital products for startups and corporations.
PREVIOUSLY AT
Designers have portfolios. It’s a precondition of our profession. We all know we need one, so we get to work assembling images and writing project descriptions. Then, we put our work on the web for all to see, tiny shrines to individual talent and creativity.
It’s a familiar process, a rite of passage, but why do we need portfolios in the first place?
If we’re honest, we must admit that most of our portfolio design decisions are influenced by what other designers are doing. That’s not necessarily bad, but if we don’t understand why portfolios look the way they do, we’re merely imitating.
We may produce dazzling imagery, but we also risk a portfolio experience that’s like strolling through an art gallery. “Look at the pretty pictures…”
The number one audience that design portfolios must please? Non-designers.
These are the people who seek our services, the ones working for the businesses and organizations that invest in our problem solving abilities.
Non-designers need more than beauty from a design portfolio; they need clarity and assurance. They need to come away believing in a designer’s expertise, their design process, and ability to solve problems in an efficient manner.
Luckily, it’s not difficult to design a portfolio to meet those needs.
The Advantages of a Case Study
What is a case study?
A case study is a tool that a designer may use to explain his involvement in a design project, whether as a solo designer or part of a team. It is a detailed account, written in the designer’s own voice (first person), that examines the client’s problem, the designer’s role, the problem solving process, and the project’s outcome.
Who can use a case study?
The beauty of the case study framework is that it’s adaptable to multiple design disciplines. It organizes need-to-know information around common categories and questions that are applicable to all kinds of design projects—from UX research to visual identities .
At its core, a case study is a presentation format for communicating the journey from problem to solution. Details within the framework may change, but the momentum is always moving towards clarity and uncovering a project’s most important whats , whys , and hows .

How do case studies benefit designers?
Many clients don’t understand all that goes into the design process. And while they certainly don’t need to know everything , a case study provides a big-picture overview and sets up realistic expectations about what it takes to design an elegant solution.
A case study can also be a handy presentation aide that a designer may use when interviewing a potential client. The format allows a designer to talk about their work and demonstrate their expertise in a natural and logical progression. “Here’s what I did, how it helped, and how I might apply a similar approach with you.”
Are there any drawbacks to using case studies?
Don’t let a case study turn into a ca-a-a-a-a-se study. The whole project should be digestible within 1-2 minutes max. If necessary, provide links to more detailed documents so that interested visitors may explore further.
A lot of design work, especially digital, is created within multidisciplinary teams, so designers need to be clear about their role in a project. Blurring the lines of participation gives clients false expectations.
Many make the mistake of treating portfolios as repositories of all of their past projects, but three to five case studies documenting a designer’s most outstanding work is enough to satisfy the curiosity of most potential clients (who simply don’t have time to mine through everything a designer ever did).
Case studies are professional documents, not tell-all manuscripts, and there are some things that simply shouldn’t be included. Descriptions of difficult working relationships, revelations of company-specific information (i.e., intellectual property), and contentious explanations of rejected ideas ought to be left out.

Crafting a Customer-centric Case Study
It’s one thing to know what a case study is and why it’s valuable. It’s an entirely different and more important thing to know how to craft a customer-centric case study. There are essentials that every case study must include if clients are to make sense of what they’re seeing.
What are the core elements of a case study?
Introduce the client.
Present the design problem.
Recap your role.
Share the solution you designed.
Walk through the steps of your design process.
Describe the results.
Note any key learnings.
Wrap it all up with a short conclusion.
Happily, the core elements also outline a case study presentation format that’s simple, repeatable, and applicable to multiple disciplines. Let’s look closer:
- Who was the client?
- What industry are they in?
- What goods or services do they provide?
- Keep this section brief.
- What was the client’s problem?
- Why was it important that the problem be solved?
- Are there any additional background tidbits that might be helpful or interesting?
- What, specifically, were you hired to do?
- What were the constraints? Time. Budgetary. Technological. Etc.
- Before diving into your process, summarize the solution you designed.
- Make the summary short but powerful.
- Don’t give all the good parts away, and don’t be afraid to use language that makes your audience curious about the rest of the project.
- Go through the various steps of your discipline specific process.
- Again, summarize what you did, but don’t overload. Find a balance between informational and interesting.
- If you can, try to make each step introduce a question that only the following step can answer.

- Use this section to share a more robust description of the results of your design process.
- Be direct, avoid jargon, and don’t get too carried away with the amount of text you include.
- Don’t go overboard here, but if there are interesting things that you learned during the process, include them.
- If they won’t be helpful for the client, leave them out.
- Quickly summarize the project, and invite potential customers to contact you.
- It doesn’t hurt to provide a call to action and a contact link.
*Note: This isn’t the only case study format, just one that works. It’s helpful for people to encounter a predictable framework so they can focus on what they’re looking at as opposed to interpreting an inventive presentation structure.
The Value of Overlooked Details
Want to create a case study with a top notch user experience? Don’t underestimate the value of design details. Design projects are more than problem-meets-solution. They’re deeply human endeavors, and it makes a difference to clients when they see that a designer goes above and beyond in their work.
Share client feedback.
How did the client feel about your working relationship and the solution you provided? When you deliver top-notch work and nurture trust, get client feedback and include it in the case study as a testimonial.
If something you designed blew your client away, weave a testimonial into the case study (along with an image of what you made). This combo is proof positive to potential customers that you can deliver.
Explain positive metrics.
Not all design work has direct metrics that prove its success, but if your work does, and the results are impressive, include them. Just make sure that you don’t mislead (easy to do with statistics), and be careful that the metrics make sense to your audience.

Show unselected work.
Sometimes, amazing work from the design process doesn’t make it through to the finished product. These unused artifacts are helpful because they show an ability to explore a range of concepts.
Highlight unglamorous design features.
Not every aspect of design is glamorous. Like a pinky finger, small details may seem insignificant but they’re actually indispensable. Highlight these and recap why they matter.
Link to live projects.
It can be highly persuasive for a client to experience your work doing it’s thing out in the real world. Don’t hesitate to include links to live projects. Just make sure that your role in the project is clear, especially when you didn’t design everything you’re linking to.
Win Clients and Advance Careers with Case Study Portfolios
Designers need clients. We need their problems, their insights, their feedback, and their investments in the solutions we provide.
Since clients are so important, we ought to think about them often and strive to make entering into partnership with us as easy and painless as possible. Design portfolios are a first impression, an opportunity to put potential clients at ease and show that we understand their needs.

Case studies push our design portfolios past aesthetic allure to a level where our skills, communication abilities, and creativity instill trust and inspire confidence. Even better, they take clients out of a passive, browsing mindset to a place where “That looks cool,” becomes “That’s someone I’d like to work with.”
Further Reading on the Toptal Blog:
- UX Portfolio Tips and Best Practices
- Ditch MVPs, Adopt Minimum Viable Prototypes (MVPrs)
- Breaking Down the Design Thinking Process
- The Best UX Designer Portfolios: Inspiring Case Studies and Examples
- Influence with Design: A Guide to Color and Emotions
Understanding the basics
How do i create a design portfolio.
Nowadays, it’s best to create a design portfolio online. Options vary: Some designers use a service like Behance or a WYSIWYG website builder like Squarespace, while others build custom sites with CSS. It’s also important that online design portfolios be responsive for multiple screen sizes.
How do I create an online portfolio for free?
Websites like Behance and Dribbble (among others) are free options for designers to publish online portfolios. Some designers have opted to forgo traditional web portfolios and instead document their work on social platforms like Instagram and Facebook. Free sites also take care of design portfolio layout.
How do you organize a design portfolio?
A designer ought to organize his portfolio according to his strengths. This means highlighting his best and most relevant work. Remember that design portfolios should be made with potential clients in mind. Avoid overly technical project descriptions, images without context, and excessively long case studies.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Many design portfolios consist of short project summaries and process images, but case studies are a way for designers to show their problem-solving skills to clients in greater detail. This is achieved by defining the client’s problem and the designer’s role, along with an overview of the designer’s process.
What are the advantages of a case study?
Case studies combine descriptive text and images and allow designers to demonstrate the details of their design processes to potential clients. They are also a great way for designers to highlight problem solving and small, but powerful, design features that may otherwise be overlooked.
- VisualDesign
- DesignProcess
Adnan Puzic
Sarajevo, Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Member since September 28, 2015
About the author
World-class articles, delivered weekly.
By entering your email, you are agreeing to our privacy policy .
Toptal Designers
- Adobe Creative Suite Experts
- Agile Designers
- AI Designers
- Art Direction Experts
- Augmented Reality Designers
- Axure Experts
- Brand Designers
- Creative Directors
- Dashboard Designers
- Digital Product Designers
- E-commerce Website Designers
- Full-Stack Designers
- Information Architecture Experts
- Interactive Designers
- Mobile App Designers
- Mockup Designers
- Presentation Designers
- Prototype Designers
- SaaS Designers
- Sketch Experts
- Squarespace Designers
- User Flow Designers
- User Research Designers
- Virtual Reality Designers
- Visual Designers
- Wireframing Experts
- View More Freelance Designers
Join the Toptal ® community.
5 Key Parts of a Great Design Case Study

Here are five of the most important areas that go beyond the basics of case study writing and get into the more challenging parts that can provide a far greater reward.
When done right, case studies are seriously complex and represent hundreds of hours of design work. At their start, they can feel like a disorganized, overwhelming mess.
Step by step, they transform into a piece of work a designer can truly be proud of because it tells the story of their growth over the project. Being able to effectively communicate and illustrate that unique story is key to a designer’s success in the interview process, and a way for them to stand out from competitors.
I’ve lost track of how many case studies I’ve reviewed in my time at Designation — it’s probably somewhere close to 1,000 by now — and in all that time, I’ve seen many important parts of case study writing come into focus.
Below are five of the most important areas that go beyond the basics of case study writing and get into the more challenging parts that can provide a far greater reward. Together, they can turn good designers into great design storytellers—and set them up for greater success later on as professionals.
Show your process assets purposefully.
Assets are your opportunity to show rather than tell—explain a big chunk of the process in a visual form. Assets can take many forms, and the more diversity in them, the more engaging for readers.
They include photographs, which can backup descriptions of on-site research, interviews, and teamwork; screenshots of in-progress work and art boards; sketches showing rough ideas that were fleshed out later; Post-it notes and affinity diagrams; wireframes, sometimes with color added for extra clarity for the reader; animated gifs showing microinteractions and user flows through the product; charts and tables; and so many others.
When focusing on a design or visual case study image like this shows a surprising amount of information and process—how creatively messy it can be to sketch, sorting to find ideas worthy of development, fleshing the strong ones out, and applying design elements and patterns to them.
A case study without showing assets is incomplete, but one that shows assets without explaining them is almost worse, because a designer always needs to explain their importance to the process.
The best way to do that is to use captions for each asset. But captions must always be a part of the overall story; they shouldn’t only repeat information that the asset already shows. They must provide a unique insight, and further the story for the reader. By doing this, it activates the caption and justifies its existence and the work it takes to write them by the designer.
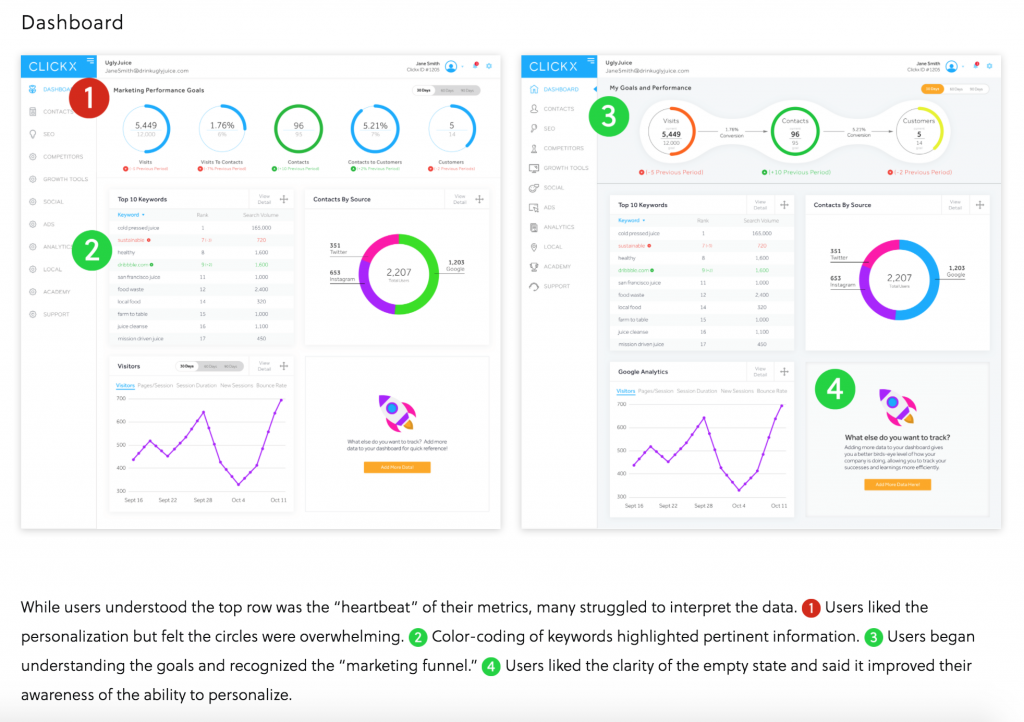
This designer used two forms of captions to illustrate their screens: Annotations that point out specific areas of concern from testers who looked at them, and a caption below that collected and synthesized them for easier comprehension.
Provide a competitive benchmark for the study.
Designers often like to downplay the research and analysis of competitors that happens near the beginning of a project because it doesn’t directly focus on the work they created. This is an unfortunate mistake because it’s a huge part of the story and it often leads directly to designers making research or design decisions later in the process.
Furthermore, designers should show off that they have a deep understanding of the competition whenever they work on a product; that they know what’s happening in the landscape and how their product fits in. Showing logos or only mentioning names of competitors isn’t anywhere near enough; designers need to discuss in detail what competitors do well, and analyze the areas in which they need improvement. Designers can provide screenshots of competitors’ products, but they need to go further and annotate or comment on them, to show a more detailed analysis.
They can’t ignore out-of-category competitors too, because that research often leads to innovative ideas that can catapult their product over in-category competitors’.
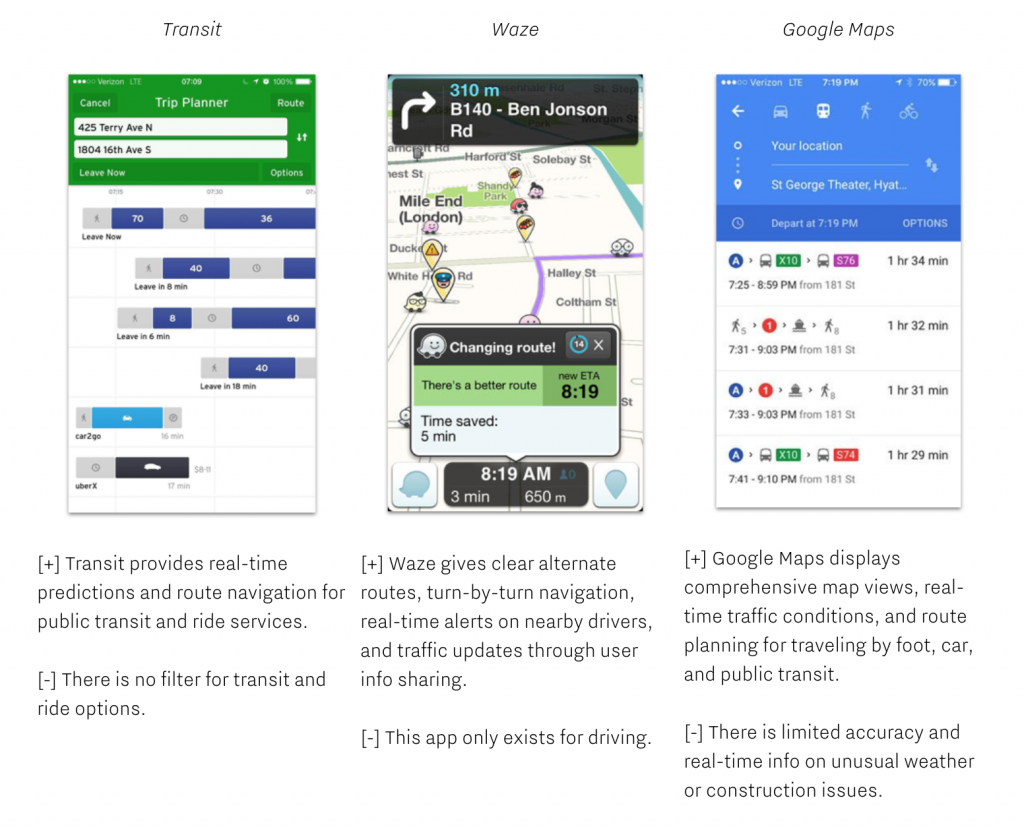
This designer looked at three competitors and called out unique areas of strength and weakness from each one, especially as they led the designer to make design decisions later in the process.
Finally, all that analysis requires synthesis, which means explaining the opportunities the designer saw for their own product after looking at the competition. This helps the designer more formally describe the end of the competitive research phase of a project and how that helped them refocus on their own product.
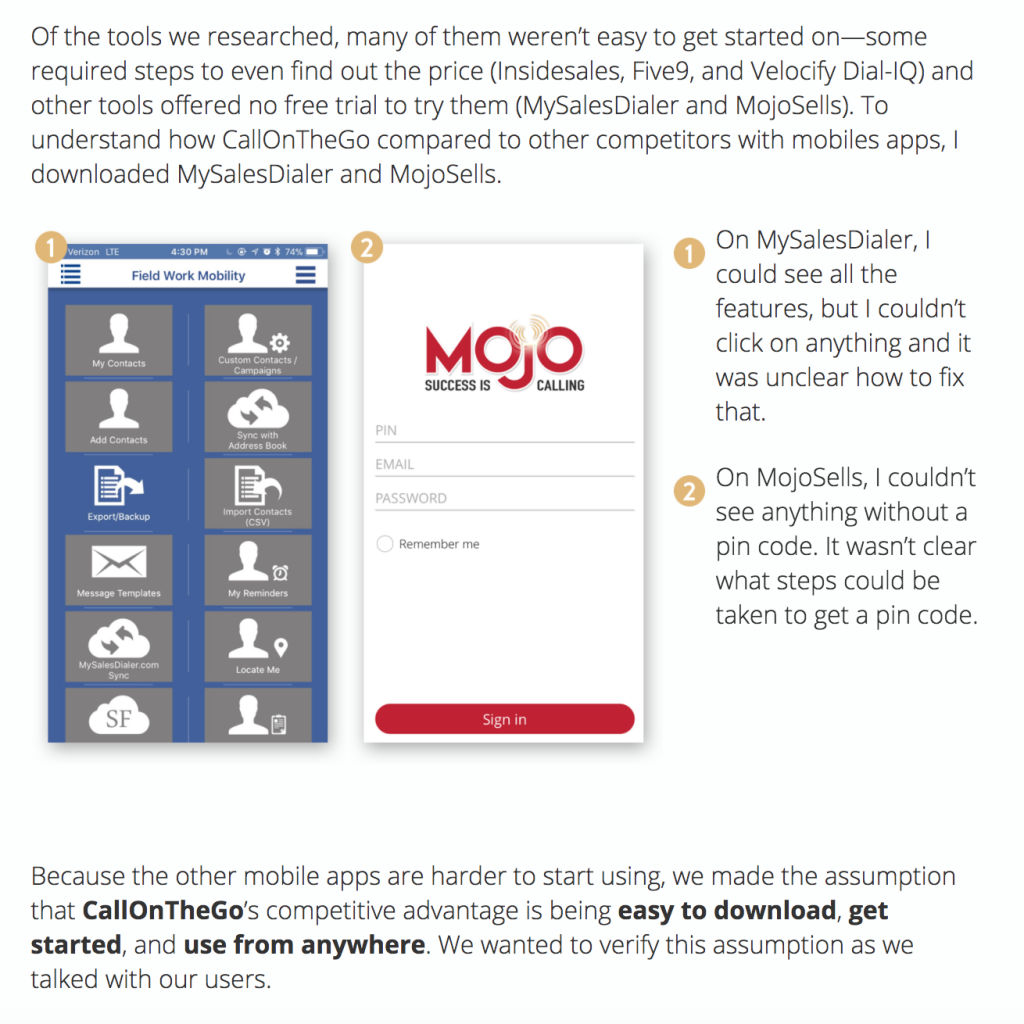
The designer analyzed competitors’ images in the center of this screen, but the text at the bottom presents what they did with that analysis: They derived an important design principle from it, which heavily impacted the next phase of their work.
Be team-centered in user experience design.
Almost every project done at Designation is done as part of a team because almost every project done as a professional designer is done as part of a team. It’s crucial for designers to reflect that in their case studies. Designers must write “we” when talking about group actions, and “I” when talking about personal design decisions or insights. In other words, we encourage designers to use “I” when they talk about where they led their team, and “we” when they supported another team member leading their team.
This is a great example of team-centered writing, where the designer discusses how the team worked together to generate concepts. She then switches to individual writing to indicate which concept she took charge of. Both extremes of this spectrum are bad in a case study—ones that only say “we” look like the designer didn’t think for themselves, and ones that only say “I” look like the designer isn’t a team player. So that balance has to always be found. Employers look for teamwork skills as much as they look for hard design skills, and a case study can be an excellent place to find records of them.
Don’t designsplain.
This is a big one. A lot of designers fall into the trap of explaining a basic element of the design process or design deliverables to the reader. You might be asking yourself: Why is this problematic? It’s because the intended readership of a designer’s case study is a hiring manager, design director, or someone else looking for evidence the designer will make a good fit for their team.
That means the designer needs to make an educated assumption that the reader is already familiar with design—and write their case study with that in mind. Unless it’s a part of their design process that was extremely unusual or the designer came up with it themselves, a designer has to assume the reader’s already familiar with it. If they don’t, they risk looking like the case study condescends to the reader, and that’s not purposeful writing.
One easy way to avoid this is for a designer to always avoid second-person writing —using “you” and “your”—which is a little too conversational for a case study anyway. They keep the focus on themselves and their work, and tell a stronger story in doing so.
Get the details right.
It might be cheating a little to clump a bunch of little steps together like this, but it’s important at the end of the case study writing process to micro-edit and make sure every detail is taken care of.
That’s why designers utilize tools like Figma to to tell their story in a professional way.
That’s making sure every word is spelled right, every publication title is italicized, and every piece of software is properly capitalized. But it’s also doing tasks like using contractions as often as possible throughout the text, removing extra spaces from between words or in front of paragraphs, knowing when to use a semicolon or an em dash, and making sure all dumb quotes are taken care of. And using writing tools like Hemingway, Grammarly, and GradeProof are a huge gift to anyone who needs a little help to take care of tricky grammar and get rid of run-on sentences.
Though tedious and time-consuming, the best way to take care of these details is to go through the complete draft and look to make one editing change at a time. Trying to edit for multiple needs causes the designer’s attention to be split in many directions—and makes them much less effective as self-editors.
Digital Designer Case Studies Conclusion
Writing effective, powerful case studies is a craft, and like all crafts, it rarely comes naturally to people. It takes skill and work, and staying in practice. The tools, resources, feedback, and processes we give every designer at Designation are able to be used for years and decades to come, so a designer can turn any work they produce into a case study anytime during their long career.
Remember: Hiring managers don’t look for designers with superpowers; they look for designers who are committed to designing better and better for as long as they practice design. And case studies are the absolute best metric for a designer to see how far they’ve come and how much they’ve learned, from tool to tool, project to project, and job to job.
Disclaimer: The information in this blog is current as of February 26, 2020. Current policies, offerings, procedures, and programs may differ.

About Flatiron School
Related posts.

Learn to Code Python: Free Lesson for Beginners

What Does a Web Developer Do?

Design for Good: Exploring Social Impact Design
Related resources.

Behind JavaScript, HTML/CSS, and SQL, Python is the fourth most popular language with 44.1% of developers. Check out this article on how you can learn this popular programming language for free.

Web development is more than just coding fancy graphics. Discover the different roles behind the scenes, from crafting user-friendly applications to building the brains of the operation.

Social impact design isn't just about aesthetics; it's about using design thinking to tackle complex social issues and improve lives. Dive deeper and see how design can become a powerful tool for positive change.
Privacy Overview
InVisionApp, Inc.
Inside Design
Designing case studies that attract more clients
• may 23, 2016.
W hether you’re looking for a studio job or you want to get some new freelance clients , you need a good portfolio. I’m talking more than just a series of curated images with a short description of the project. I know you can do better than that.
- It can serve as the final presentation of your project when it comes time to send off your final work to the client
- More content on the page means your portfolio piece ranks higher in search results
- By showcasing your process, you’re giving clients a better idea of how you work, which lays down their expectations for future projects
- It gives you the opportunity to prove your worth and show that you can satisfy your customers’ needs
- It can help lead the user to contact you for a new project with a tailored call to action
In this article, I’ll go over the key elements that make a good case study and the steps you need to take to get more clients from your design portfolio .
Read more from Dina Rodriguez: The art of hand lettering .
Document your process.
The easiest way to create your case study: document your process along the way. This includes taking screenshots and photographs of your process while keeping detailed notes that explain your design decisions.
“The easiest way to create a case study: document your process along the way.”
So at every stage of the project when you make an internal revision, document it and explain why you made it. By explaining your process in this way, you’re able to keep yourself in check to ensure that you’re making the right decisions based on your client’s goals and not your personal aesthetic or gut feeling.
To keep your notes and images organized you can use Behance’s WIP (Work In Progress) feature that allows you to show your work in its early stages, and get feedback on it from your followers that can help guide the artistic direction.
This has been especially helpful for me because it simplifies the process of putting my ideas together while making connections with other creative professionals online. Check out the example above where you can see my process of creating my 26 Letters piece for my new homepage.
Your case study doubles as your final presentation
Another added benefit to creating case studies is that they also serve as an excellent final presentation to give to your client once production is complete. For me, this always wows my clients because it proves that my project perfectly aligns with their expectations and goals. And that makes it really hard for them to ask for revisions later on.
“Case studies also serve as an excellent final presentation for clients.”
Then, once the client approves my artwork and pays the final installment, I can easily reuse my presentation to post a detailed case study in my portfolio. Double win!
Here’s a sample of a recent logo design case study I created for Paper Tiger Mentoring that showcases the steps I took to complete the design. Notice how much more engaging this is and how my revisions have reasons behind them. It’s hard to argue with a final result when everything you made reflects what’s most appropriate to attract my client’s demographic.
So rather than just sending your client the final static image of your project, why not create a case study that serves as the final presentation instead? Think of how much better of an impression it would make to send your client the beautiful final result in addition to showing the steps you took to get there.
The 6 key principles to the perfect case study
Now that you understand the importance of case studies, let’s break down the key elements that will get your portfolio noticed and keep the project inquiries rolling in.
1. Provide a meaningful overview for the non-readers
The project overview is the first piece of content on the page that allows your visitors to get some additional information about the project and understand what was accomplished. Keep this short and to the point so that the skimmers and browsers can get a quick look at what your project is all about without having to read the full case study.
Here’s an example of how I introduced my hand-lettered logo design project for Say Something Marketing . Notice that I provide some key information before I start to talk about my process like industry, creation date, project duties, and objective. You can either break down the info like how I have here, or provide just a few lines for your overview. Just be sure to include the problems that your client is trying to solve so that you can talk about your process with their goals in mind.
Along with this introduction, it’s important to show the final result upfront before going into the beginning stages of your process. You don’t want to make the user scroll down to the bottom of the page in order to see the final result of your beautiful work.
2. Show pictures—lots and lots of pictures
People love seeing the evolution of a project and how it came to life. Watching a project form step-by-step is not only engaging, it also makes you more relatable when you show the mistakes you made along the way.
So don’t worry if one of your process shots isn’t perfect or camera-ready. It’s a work in progress—it’s not supposed to be perfect on the first try. Check out my process for creating my Stop Staring Poster . It has imperfections, but that’s what makes the final result so much more interesting.
3. Describe the reason behind your decisions
This is why you have an in-depth onboarding process before starting production so you can get a detailed and clear view of what your client wants. In order to land your ideal clients, you need a questionnaire that sets the tone of the project moving forward and gives you everything you need to determine if it’s the right project for you. This way you can over deliver on a project because it’s custom-made to attract their audience.
4. Top it off with a client testimonial
“A good testimonial creates trust.”
Most of us ask for testimonials, and if we follow up and pester our customers enough, we get testimonials. But without asking the right questions to probe our clients, our testimonials usually end up looking something like this:
Dina did a great job on this project. I’m very happy and plan to work with her again.
Now that isn’t a bad review, but it doesn’t sell my services or tell a good story of how I am to work with. This is because most clients don’t know how to give testimonials, so as professionals we need to guide them to provide testimonials that will inspire potential clients to hire us.
Here are the 3 basic questions you should ask in order to get a powerful testimonial:
- Discuss your experience working with me.
- What did you like most about your final project?
- Would you hire me again? If so, why?
By asking these questions, I’m able to get a testimonial that tells a vivid story. Check out one of my previous client testimonials for a logo design project I created for BrandScape :
Dina invested hours learning about my brand personality, mission, and style. She was completely transparent about her process and always kept me involved. It was up to Dina to really translate everything we’d discussed to a logo, and the end result blew me away. The script is playful but clean, and the colors pop beautifully. The logo is visually distinct and professional, and I’m excited to display it every chance I get! I’m so grateful to have had the opportunity to work with Dina for such a unique product, and I plan to work with her again.
Now that’s a testimonial that sells! About 3 days after posting this project and testimonial, I received 5 new inquiries. And they just keep rolling on in—all from one excellent case study.
5. Don’t forget the call to action
Just like any other page on your site, you need a call to action (CTA) to help guide the user to contact you. For me, 82% of the people who look at 3 or more of my projects in my portfolio submit a project request. So having a CTA on your portfolio page is one of the most important pieces of content that will help you get new clients.
“Your portfolio page has to have a call to action.”
If you’ve followed the above steps in your case study, you should have enticed your user enough to contact you. Now all you need is to serve up a custom pitch of your services on the bottom of the page with a link to your questionnaire.
There are several ways to make your call to actions stand out , but with each project you should have a custom-written call to action that speaks directly to your user. For example, if a client is looking at my portfolio and is checking out one of my hand-lettered logo designs, they’re most likely interested in hiring me for a similar project.
Rather than having a nonspecific CTA such as “Like what you see? Contact me today for a free quote,” try presenting a more personalized message like “Interested in a hand-lettered logo design that’s custom made to attract your audience? Contact me today for a free quote.”
See the difference? If you were a potential client looking for a logo design , which one would you click on?
6. SEO is important, too
SEO is an often overlooked step when adding new projects to your portfolio. It’s a necessary part of web design that can help you get more organic traffic to your portfolio site.
Your portfolio is filled with work that other clients in those industries want. So a good starting point is to use descriptive long-tail keywords like “logo design for app” or “web design for restaurants.” You already have the content and images to reel them in, and now all you need are some keywords to get their attention on Google.
You can test out search terms by using tools such as Wordtracker and the Google Adwords Keyword Tool . I won’t go into the nuts and bolts of search engine optimization here. (For a crash course in SEO that won’t overwhelm you, check out this article .
Blast your newest project across the internet
After you’ve posted your case study online, the work is only about 90% complete. That extra 10% is going to get new eyes on your portfolio and help you get your work noticed. This means posting your work everywhere your designs are welcomed.
So get active on Facebook, Twitter, and Google+; post your portfolio pieces to Behance , Dribbble , and deviantART . Get creative and film your process and put the video on YouTube or livestream it using Periscope . You could even create a slideshow of your artwork and share it on Slideshare or put together a PDF presentation and upload it to Scribd . The more you link out your newest portfolio piece, the more people you can get looking at your work.
The great thing about marketing yourself isn’t just getting more clients—it’s building a following of other like-minded designers. Tons of designers and art directors are always on the lookout for people to pass design work onto. Once you start forming a good network, you’ll find that more projects will automatically start coming to you, rather than you frantically searching and begging for work.
This was originally published on Letter Shoppe .
Collaborate in real time on a digital whiteboard Try Freehand
Get awesome design content in your inbox each week, give it a try—it only takes a click to unsubscribe., thanks for signing up, you should have a thank you gift in your inbox now-and you’ll hear from us again soon, get started designing better. faster. together. and free forever., give it a try. nothing’s holding you back..
- Watch Videos
- Meet Our Expert Guests
- Inside An Architect’s Office
- Showroom Feature: Focus on Fulton
- Shop the Marketplace
- In-Depth Product Profiles
- Chair Reviews
- Product Roundups
- Expert Insights
- Tips & Trends

Sign Up For Our Newsletter
- Advertise With Us

- Company Directory
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Sign In / Join Now
Industrial Design Case Study: A Package Management System
Formation design group tackles hellopackage.
These days an ID firm might be called on to design a system, rather than a product. Package Solutions is a company seeking to solve the problems of delivering packages to multi-resident buildings and student housing. They hired Formation Design Group to work out the solutions.
"The rapid growth of e-commerce has overwhelmed last mile package delivery, particularly in multifamily residential communities," the firm writes. "Formation worked with Package Solutions to streamline their user experience and commercialize their cutting edge package tracking technology."

Beyond the Room
Using contextual research as a basis, Formation conceptualized a multitude of mobile application features to improve resident experience, create opportunities for additional revenue and provide new amenities. The mobile application empowers residents, carriers, and staff to interact with the HelloPackage system while away from the community. Beyond package delivery, the system engages with residents to provide useful features that fit seamlessly into the rhythm of life in a multifamily community.

Creating Community
Using the HelloPackage app residents can send, receive, transfer or redirect their packages. The system allows trusted roommates, neighbors and staff to retrieve packages for each other and rewards them with points redeemable for merchandise stored on secured shelves and other benefits. Features like these build community, increase package throughput, and ultimately allow people to get their stuff in the way that works best for them.

An Adaptable Platform
HelloPackage's hardware was designed to be minimal, attractive and adaptable. The system is based on a simple kit of parts that can be combined to adapt to any space. The system can be easily expanded to scale with a community's needs. Sheet metal construction provides an efficient, durable platform with limitless design and aesthetic possibilities.
This integrated hardware/software system makes managing packages easier for community staff, carriers and ultimately for the resident/recipient.

The solution is a powerful combination of software & hardware that revolutionizes the package delivery experience for apartment staff, residents and carriers.

<iframe title="vimeo-player" src="https://player.vimeo.com/video/320496682?h=32a09cd291" width="640" height="360" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>
You can see more of Formation's work here .
- o Favorite This
Join over 240,000 designers who stay up-to-date with the Core77 newsletter.
Test it out; it only takes a single click to unsubscribe
Directory Company Profiles
Core77 Directory

We are a multidisciplinary product innovation and development firm that brings bold ideas to market....
Copenhagen Institute of Interaction Design (CIID) is an international hub of creative minds. We shar...
Artefact is a strategy + design firm. Design is powerful. It determines how we experience life, and ...
Founded in 2007, Ammunition is led by partners Robert Brunner and Matt Rolandson. Our work is create...
BlueMap design is a multi-disciplinary product development firm. Founded by Simon Yan in 2001, the f...
Aruliden is a global design agency born in 2006. We are a collection of people who care deeply about...
We're a full-service branding and creative agency. We specialize in building brands, companies and o...
- m Sign In with Twitter
- U Sign In with Linkedin
- j Sign In with Core77 Account
- Email or Username
- Password Forgot password?
- Keep me signed in
Don't have an account? Join Now
Create a Core77 Account
- Y Join Now with Facebook
- m Join Now with Twitter
- U Join Now with Linkedin
- j Join Now with Email
- Email Not Public
- Confirm Password
Already have an account? Sign In
By creating a Core77 account you confirm that you accept the Terms of Use
Reset Password
Please enter your email and we will send an email to reset your password.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
As far as UX case studies go, this one provides practical insight into an existing, widely used e-commerce feature, and offers practical solutions. 7. New York Times App. Using a creative illustration website, the designers proposed a landing page feature "Timely" that could counter the problems faced by the NYT app.
After analyzing all of these case studies and working with 100s of designers in our product design course to get them ready for the job application process, we've created our own tried-and-true templates to make it easy for designers to replicate the successful format and structure of these top portfolios using Notion.
50+ Design Thinking Case Study Examples. Design Thinking Case Studies demonstrate the value of the Design Thinking methodology. They show how this Design Thinking methodology helps creatively solve problems and improve the success rate of innovation and increase collaboration in corporations, education, social impact work and the public sector by focusing on the needs of humans.
About. Discover an expertly curated collection of 20+ inspirational UX/UI design case studies that will empower you to create outstanding case studies for your own portfolio. Comprehensive end-to-end case studies covering research, ideation, design, testing, and conclusions. Perfect for designers building portfolios and looking for inspiration ...
Design in the age of digitization: The next agenda for Industry 4.0. User Experience design is at the cusp of making this great re-make actualize. Design thinking as an approach is an imperative solution that enterprises could leverage to reinvent themselves while being in synergy with new-age technologies. READ ARTICLE.
Now that you know why case studies are so important, here is what you need to know to design a top-notch case study for your next client! . 1. Understand Your Client's Needs. . It's always a good idea to make sure that you really understand the message your client is looking to display with their case study. .
Case Study 1: Airbnb. Airbnb's one of the popular Design Thinking Case Studies that you can aspire from. Airbnb disrupted the traditional hotel industry by applying Design Thinking principles to create a platform that connects travellers with unique accommodations worldwide. The founders of Airbnb, Brian Chesky, Joe Gebbia, and Nathan ...
UX case studies are examples of design work which designers include in their portfolio. To give recruiters vital insights, designers tell compelling stories in text and images to show how they handled problems. Such narratives showcase designers' skills and ways of thinking and maximize their appeal as potential hires.
What's Great About This UX Designer Portfolio. Rahul's case studies are very detailed and walk people through his design process in an easily consumable way. Some designers make the mistake of adding way too much text to their case studies-most reviewers/ recruiters are busy and simply don't have the time to go through that much detail.
When you're putting together your online design portfolio, design case studies are a great way to showcase your experience and skills.They also give potential clients a window into how you work. By showing off what you can do and your design process, case studies can help you land more clients and freelance design jobs—so it can be smart to dedicate an entire section of your online ...
A case study is a tool that a designer may use to explain his involvement in a design project, whether as a solo designer or part of a team. It is a detailed account, written in the designer's own voice (first person), that examines the client's problem, the designer's role, the problem solving process, and the project's outcome.
Here are five of the most important areas that go beyond the basics of case study writing and get into the more challenging parts that can provide a far greater reward. Reading Time 7 mins. When done right, case studies are seriously complex and represent hundreds of hours of design work. At their start, they can feel like a disorganized ...
The best way to write a case study is to tell it like a story. This way, your case studies become a vessel through which recruiters can imagine a future working with you, since they get to experience and understand exactly how you solve a design problem. Your recruiters will also enjoy the familiarity and structure of a story arc, and they'll ...
4. Top it off with a client testimonial. Client testimonials are proof that you can provide work that satisfies your customers. A good testimonial creates trust and has the power to convince even your "tough sell" visitors that your service can make a difference in your customer's life.
A case study should be concise and easy to read, providing only the essential information that prospective clients need to know about the project and how you work. You should be aiming to write a maximum of three paragraphs for each section below. If you need to, you can go over that limit. But, it's important to remember that the more text ...
Antonio Vidakovik's case study has some of the best visuals, making it a great example to follow as you work on your portfolio. His user flow charts have a simple design, but they feature bright colors and succinct descriptions of each step. Vidakovik also does a good job explaining his user interface design decisions.
A case study allows you, the designer, ... This is the final "thing", the finished design work. Show the final photos, mockups, screenshots, prototypes, or screen recordings.
This means the normal rules of design apply. Use fonts, colors, and icons to create an interesting and visually appealing case study. In this case study example, we can see how multiple fonts have been used to help differentiate between the headers and content, as well as complementary colors and eye-catching icons.
In our Designing for Social Systems program, at the d.school, we develop and teach design practices that integrate methods from human-centered design, systems thinking, and strategic planning, grounded in a commitment to equity and anti-racism. These case studies highlight meaningful work and hard-fought impact by some of our program ...
A Non-Profit Taking on Disability, Recreates its Office To Achieve Better Days. Alexis Ramos - May 28, 2019. In an attempt to set a precedent for all future developments, Easterseals tapped interior architecture firm H. Hendy Associates to fully remodel the 40,000 square foot, two-story office in Irvine, California. Case Studies.
15 Real-Life Case Study Examples. Now that you understand what a case study is, let's look at real-life case study examples. In this section, we'll explore SaaS, marketing, sales, product and business case study examples with solutions. Take note of how these companies structured their case studies and included the key elements.
Case study examples. Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study: Amazon Web Services, Inc. provides companies with cloud computing platforms and APIs on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
A case study design similar to multiple-case design, is cross-case design ... Researchers may feel more comfortable generalising if they work with typical cases, that is, if the case being studied can be shown to be similar to other cases in terms of relevant characteristics. However, the difficulty lies in the demonstration whether a ...
NYU Tandon has connected the ASUS ProArt Display PA348CGV with the Puget Systems computer. Using the ultra-wide display, the students are able to see their creations from a cinematic perspective. The wide monitor allows them to display any of their software anywhere they want on the screen and run it with a 120Hz refresh rate.
About the journal. Foster Interdisciplinary Design Discussions: Create a space for interdisciplinary discussions on fundamental design elements, including process, cognition, and philosophy, while emphasising research, theory, and innovative outcomes. Explore Design's Theoretical Evolution: Assess the history and future of design by examining ...
This case study describes and discusses how student-faculty partnerships can be strengthened through design thinking and the establishment of shared ignorance, i.e., an awareness of how none of the involved parties understands the problem or knows the optimum solution of the partnership project. As a case, we use a student-faculty project that aimed to develop course material for an electrical ...
These days an ID firm might be called on to design a system, rather than a product. Package Solutions is a company seeking to solve the problems of delivering packages to multi-resident buildings and student housing. They hired Formation Design Group to work out the solutions. "The rapid growth of e-commerce has overwhelmed last mile package delivery, particularly in multifamily residential ...
As Bloomberg notes, the case study method is employed across disciplines, including education, health care, social work, history, sociology, management studies, and organizational studies. When you look at lists of most-read and most-cited articles you will find that this flexible approach is widely used and published.
The urban design of the Core Area of Suzhou Science and Technology City was selected as a case study. Located west of Suzhou and on the east bank of Taihu Lake, Suzhou Science and Technology City is a national innovation center in the Yangtze River Delta aiming at green and low-carbon development.