

Why is it important to do a literature review in research?
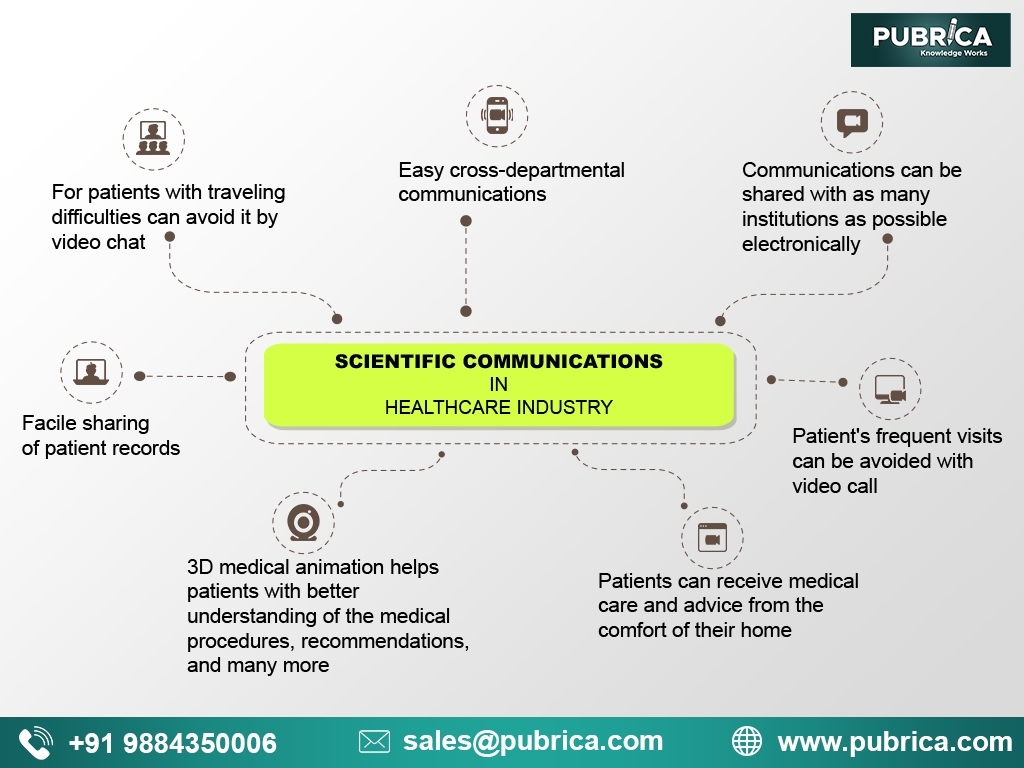
The importance of scientific communication in the healthcare industry
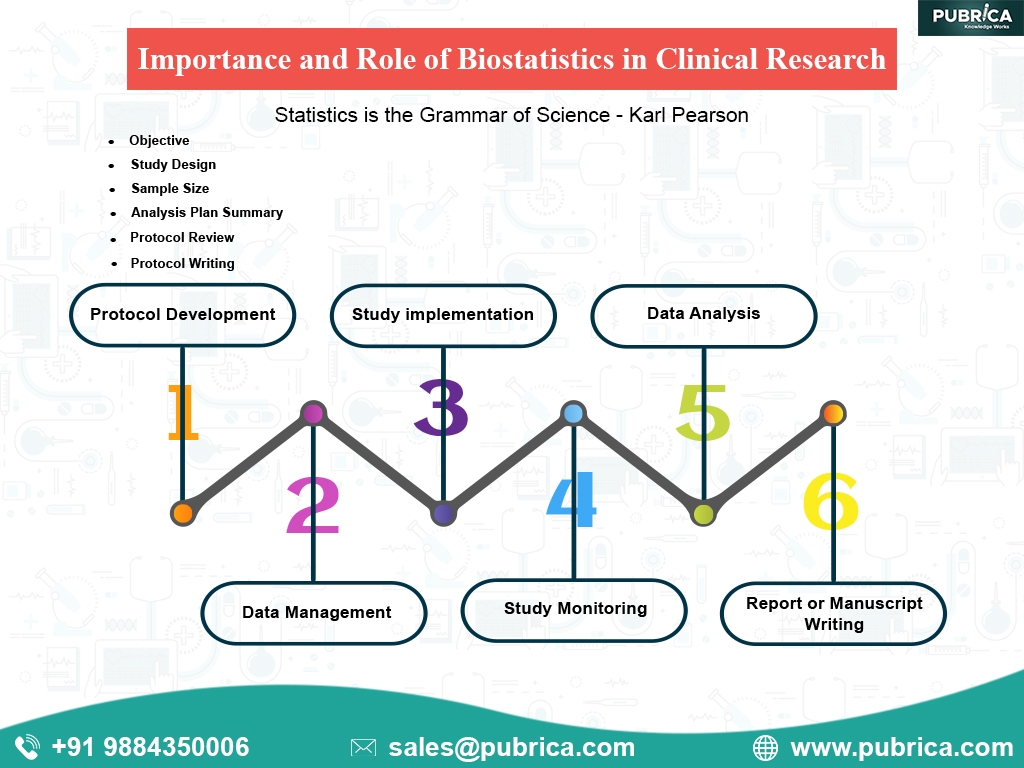
The Importance and Role of Biostatistics in Clinical Research
“A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated research”. Boote and Baile 2005
Authors of manuscripts treat writing a literature review as a routine work or a mere formality. But a seasoned one knows the purpose and importance of a well-written literature review. Since it is one of the basic needs for researches at any level, they have to be done vigilantly. Only then the reader will know that the basics of research have not been neglected.
The aim of any literature review is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of existing knowledge in a particular field without adding any new contributions. Being built on existing knowledge they help the researcher to even turn the wheels of the topic of research. It is possible only with profound knowledge of what is wrong in the existing findings in detail to overpower them. For other researches, the literature review gives the direction to be headed for its success.
The common perception of literature review and reality:
As per the common belief, literature reviews are only a summary of the sources related to the research. And many authors of scientific manuscripts believe that they are only surveys of what are the researches are done on the chosen topic. But on the contrary, it uses published information from pertinent and relevant sources like
- Scholarly books
- Scientific papers
- Latest studies in the field
- Established school of thoughts
- Relevant articles from renowned scientific journals
and many more for a field of study or theory or a particular problem to do the following:
- Summarize into a brief account of all information
- Synthesize the information by restructuring and reorganizing
- Critical evaluation of a concept or a school of thought or ideas
- Familiarize the authors to the extent of knowledge in the particular field
- Encapsulate
- Compare & contrast
By doing the above on the relevant information, it provides the reader of the scientific manuscript with the following for a better understanding of it:
- It establishes the authors’ in-depth understanding and knowledge of their field subject
- It gives the background of the research
- Portrays the scientific manuscript plan of examining the research result
- Illuminates on how the knowledge has changed within the field
- Highlights what has already been done in a particular field
- Information of the generally accepted facts, emerging and current state of the topic of research
- Identifies the research gap that is still unexplored or under-researched fields
- Demonstrates how the research fits within a larger field of study
- Provides an overview of the sources explored during the research of a particular topic
Importance of literature review in research:
The importance of literature review in scientific manuscripts can be condensed into an analytical feature to enable the multifold reach of its significance. It adds value to the legitimacy of the research in many ways:
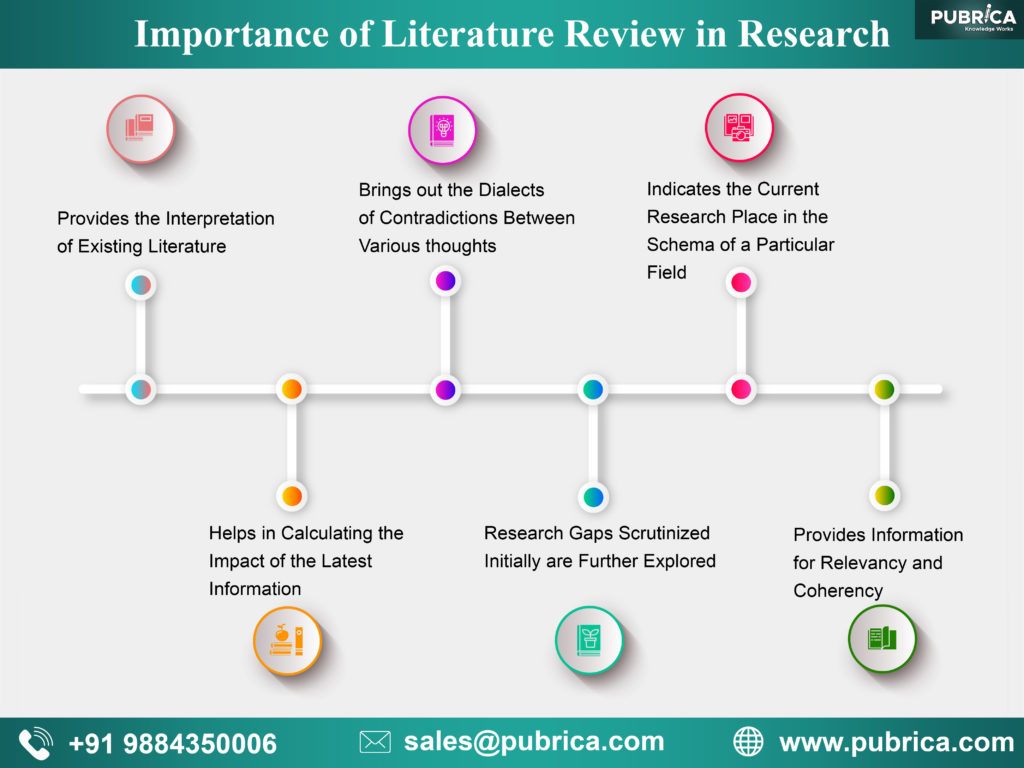
- Provides the interpretation of existing literature in light of updated developments in the field to help in establishing the consistency in knowledge and relevancy of existing materials
- It helps in calculating the impact of the latest information in the field by mapping their progress of knowledge.
- It brings out the dialects of contradictions between various thoughts within the field to establish facts
- The research gaps scrutinized initially are further explored to establish the latest facts of theories to add value to the field
- Indicates the current research place in the schema of a particular field
- Provides information for relevancy and coherency to check the research
- Apart from elucidating the continuance of knowledge, it also points out areas that require further investigation and thus aid as a starting point of any future research
- Justifies the research and sets up the research question
- Sets up a theoretical framework comprising the concepts and theories of the research upon which its success can be judged
- Helps to adopt a more appropriate methodology for the research by examining the strengths and weaknesses of existing research in the same field
- Increases the significance of the results by comparing it with the existing literature
- Provides a point of reference by writing the findings in the scientific manuscript
- Helps to get the due credit from the audience for having done the fact-finding and fact-checking mission in the scientific manuscripts
- The more the reference of relevant sources of it could increase more of its trustworthiness with the readers
- Helps to prevent plagiarism by tailoring and uniquely tweaking the scientific manuscript not to repeat other’s original idea
- By preventing plagiarism , it saves the scientific manuscript from rejection and thus also saves a lot of time and money
- Helps to evaluate, condense and synthesize gist in the author’s own words to sharpen the research focus
- Helps to compare and contrast to show the originality and uniqueness of the research than that of the existing other researches
- Rationalizes the need for conducting the particular research in a specified field
- Helps to collect data accurately for allowing any new methodology of research than the existing ones
- Enables the readers of the manuscript to answer the following questions of its readers for its better chances for publication
- What do the researchers know?
- What do they not know?
- Is the scientific manuscript reliable and trustworthy?
- What are the knowledge gaps of the researcher?
22. It helps the readers to identify the following for further reading of the scientific manuscript:
- What has been already established, discredited and accepted in the particular field of research
- Areas of controversy and conflicts among different schools of thought
- Unsolved problems and issues in the connected field of research
- The emerging trends and approaches
- How the research extends, builds upon and leaves behind from the previous research
A profound literature review with many relevant sources of reference will enhance the chances of the scientific manuscript publication in renowned and reputed scientific journals .
References:
http://www.math.montana.edu/jobo/phdprep/phd6.pdf
journal Publishing services | Scientific Editing Services | Medical Writing Services | scientific research writing service | Scientific communication services
Related Topics:
Meta Analysis
Scientific Research Paper Writing
Medical Research Paper Writing
Scientific Communication in healthcare
pubrica academy
Related posts.

Statistical analyses of case-control studies

PUB - Selecting material (e.g. excipient, active pharmaceutical ingredient) for drug development
Selecting material (e.g. excipient, active pharmaceutical ingredient, packaging material) for drug development

PUB - Health Economics of Data Modeling
Health economics in clinical trials
Comments are closed.

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as you go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface with the option to save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.
- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
| Annotated Bibliography | Literature Review | |
| Purpose | List of citations of books, articles, and other sources with a brief description (annotation) of each source. | Comprehensive and critical analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. |
| Focus | Summary and evaluation of each source, including its relevance, methodology, and key findings. | Provides an overview of the current state of knowledge on a particular subject and identifies gaps, trends, and patterns in existing literature. |
| Structure | Each citation is followed by a concise paragraph (annotation) that describes the source’s content, methodology, and its contribution to the topic. | The literature review is organized thematically or chronologically and involves a synthesis of the findings from different sources to build a narrative or argument. |
| Length | Typically 100-200 words | Length of literature review ranges from a few pages to several chapters |
| Independence | Each source is treated separately, with less emphasis on synthesizing the information across sources. | The writer synthesizes information from multiple sources to present a cohesive overview of the topic. |
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how to structure an essay, leveraging generative ai to enhance student understanding of..., what’s the best chatgpt alternative for academic writing, how to write a good hook for essays,..., addressing peer review feedback and mastering manuscript revisions..., how paperpal can boost comprehension and foster interdisciplinary..., what is the importance of a concept paper..., how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, how to ace grant writing for research funding....
News alert: UC Berkeley has announced its next university librarian
Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Conducting a literature review: why do a literature review, why do a literature review.
- How To Find "The Literature"
- Found it -- Now What?
Besides the obvious reason for students -- because it is assigned! -- a literature review helps you explore the research that has come before you, to see how your research question has (or has not) already been addressed.
You identify:
- core research in the field
- experts in the subject area
- methodology you may want to use (or avoid)
- gaps in knowledge -- or where your research would fit in
It Also Helps You:
- Publish and share your findings
- Justify requests for grants and other funding
- Identify best practices to inform practice
- Set wider context for a program evaluation
- Compile information to support community organizing
Great brief overview, from NCSU
Want To Know More?
- Next: How To Find "The Literature" >>
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 1:10 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/litreview
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved June 24, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
A Guide to Literature Reviews
Importance of a good literature review.
- Conducting the Literature Review
- Structure and Writing Style
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Citation Management Software This link opens in a new window
- Acknowledgements
A literature review is not only a summary of key sources, but has an organizational pattern which combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
The purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
- << Previous: Definition
- Next: Conducting the Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: May 10, 2024 11:34 AM
- URL: https://libguides.mcmaster.ca/litreview

Literature Review - what is a Literature Review, why it is important and how it is done
What are literature reviews, goals of literature reviews, types of literature reviews, about this guide/licence.
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Literature Reviews and Sources
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
- Useful Resources
Help is Just a Click Away
Search our FAQ Knowledge base, ask a question, chat, send comments...
Go to LibAnswers
What is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries. " - Quote from Taylor, D. (n.d) "The literature review: A few tips on conducting it"
Source NC State University Libraries. This video is published under a Creative Commons 3.0 BY-NC-SA US license.
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review?
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
- Baumeister, R.F. & Leary, M.R. (1997). "Writing narrative literature reviews," Review of General Psychology , 1(3), 311-320.
When do you need to write a Literature Review?
- When writing a prospectus or a thesis/dissertation
- When writing a research paper
- When writing a grant proposal
In all these cases you need to dedicate a chapter in these works to showcase what have been written about your research topic and to point out how your own research will shed a new light into these body of scholarship.
Literature reviews are also written as standalone articles as a way to survey a particular research topic in-depth. This type of literature reviews look at a topic from a historical perspective to see how the understanding of the topic have change through time.
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
- Narrative Review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Book review essays/ Historiographical review essays : This is a type of review that focus on a small set of research books on a particular topic " to locate these books within current scholarship, critical methodologies, and approaches" in the field. - LARR
- Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L.K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . San Diego, CA: Plural Publishing.
- Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M.C. & Ilardi, S.S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Malden, MA: Blackwell Pub.
- Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). "Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts," Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53(3), 311-318.
Guide adapted from "Literature Review" , a guide developed by Marisol Ramos used under CC BY 4.0 /modified from original.
- Next: Strategies to Find Sources >>
- Last Updated: Jun 11, 2024 12:14 PM
- URL: https://lit.libguides.com/Literature-Review
The Library, Technological University of the Shannon: Midwest
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
What is the Purpose of a Literature Review?

4-minute read
- 23rd October 2023
If you’re writing a research paper or dissertation , then you’ll most likely need to include a comprehensive literature review . In this post, we’ll review the purpose of literature reviews, why they are so significant, and the specific elements to include in one. Literature reviews can:
1. Provide a foundation for current research.
2. Define key concepts and theories.
3. Demonstrate critical evaluation.
4. Show how research and methodologies have evolved.
5. Identify gaps in existing research.
6. Support your argument.
Keep reading to enter the exciting world of literature reviews!
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a critical summary and evaluation of the existing research (e.g., academic journal articles and books) on a specific topic. It is typically included as a separate section or chapter of a research paper or dissertation, serving as a contextual framework for a study. Literature reviews can vary in length depending on the subject and nature of the study, with most being about equal length to other sections or chapters included in the paper. Essentially, the literature review highlights previous studies in the context of your research and summarizes your insights in a structured, organized format. Next, let’s look at the overall purpose of a literature review.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Literature reviews are considered an integral part of research across most academic subjects and fields. The primary purpose of a literature review in your study is to:
Provide a Foundation for Current Research
Since the literature review provides a comprehensive evaluation of the existing research, it serves as a solid foundation for your current study. It’s a way to contextualize your work and show how your research fits into the broader landscape of your specific area of study.
Define Key Concepts and Theories
The literature review highlights the central theories and concepts that have arisen from previous research on your chosen topic. It gives your readers a more thorough understanding of the background of your study and why your research is particularly significant .
Demonstrate Critical Evaluation
A comprehensive literature review shows your ability to critically analyze and evaluate a broad range of source material. And since you’re considering and acknowledging the contribution of key scholars alongside your own, it establishes your own credibility and knowledge.
Show How Research and Methodologies Have Evolved
Another purpose of literature reviews is to provide a historical perspective and demonstrate how research and methodologies have changed over time, especially as data collection methods and technology have advanced. And studying past methodologies allows you, as the researcher, to understand what did and did not work and apply that knowledge to your own research.
Identify Gaps in Existing Research
Besides discussing current research and methodologies, the literature review should also address areas that are lacking in the existing literature. This helps further demonstrate the relevance of your own research by explaining why your study is necessary to fill the gaps.
Support Your Argument
A good literature review should provide evidence that supports your research questions and hypothesis. For example, your study may show that your research supports existing theories or builds on them in some way. Referencing previous related studies shows your work is grounded in established research and will ultimately be a contribution to the field.
Literature Review Editing Services
Ensure your literature review is polished and ready for submission by having it professionally proofread and edited by our expert team. Our literature review editing services will help your research stand out and make an impact. Not convinced yet? Send in your free sample today and see for yourself!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Perspect Med Educ
- v.7(1); 2018 Feb

Writing an effective literature review
Lorelei lingard.
Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, Health Sciences Addition, Western University, London, Ontario Canada
In the Writer’s Craft section we offer simple tips to improve your writing in one of three areas: Energy, Clarity and Persuasiveness. Each entry focuses on a key writing feature or strategy, illustrates how it commonly goes wrong, teaches the grammatical underpinnings necessary to understand it and offers suggestions to wield it effectively. We encourage readers to share comments on or suggestions for this section on Twitter, using the hashtag: #how’syourwriting?
This Writer’s Craft instalment is the first in a two-part series that offers strategies for effectively presenting the literature review section of a research manuscript. This piece alerts writers to the importance of not only summarizing what is known but also identifying precisely what is not, in order to explicitly signal the relevance of their research. In this instalment, I will introduce readers to the mapping the gap metaphor, the knowledge claims heuristic, and the need to characterize the gap.
Mapping the gap
The purpose of the literature review section of a manuscript is not to report what is known about your topic. The purpose is to identify what remains unknown— what academic writing scholar Janet Giltrow has called the ‘knowledge deficit’ — thus establishing the need for your research study [ 1 ]. In an earlier Writer’s Craft instalment, the Problem-Gap-Hook heuristic was introduced as a way of opening your paper with a clear statement of the problem that your work grapples with, the gap in our current knowledge about that problem, and the reason the gap matters [ 2 ]. This article explains how to use the literature review section of your paper to build and characterize the Gap claim in your Problem-Gap-Hook. The metaphor of ‘mapping the gap’ is a way of thinking about how to select and arrange your review of the existing literature so that readers can recognize why your research needed to be done, and why its results constitute a meaningful advance on what was already known about the topic.
Many writers have learned that the literature review should describe what is known. The trouble with this approach is that it can produce a laundry list of facts-in-the-world that does not persuade the reader that the current study is a necessary next step. Instead, think of your literature review as painting in a map of your research domain: as you review existing knowledge, you are painting in sections of the map, but your goal is not to end with the whole map fully painted. That would mean there is nothing more we need to know about the topic, and that leaves no room for your research. What you want to end up with is a map in which painted sections surround and emphasize a white space, a gap in what is known that matters. Conceptualizing your literature review this way helps to ensure that it achieves its dual goal: of presenting what is known and pointing out what is not—the latter of these goals is necessary for your literature review to establish the necessity and importance of the research you are about to describe in the methods section which will immediately follow the literature review.
To a novice researcher or graduate student, this may seem counterintuitive. Hopefully you have invested significant time in reading the existing literature, and you are understandably keen to demonstrate that you’ve read everything ever published about your topic! Be careful, though, not to use the literature review section to regurgitate all of your reading in manuscript form. For one thing, it creates a laundry list of facts that makes for horrible reading. But there are three other reasons for avoiding this approach. First, you don’t have the space. In published medical education research papers, the literature review is quite short, ranging from a few paragraphs to a few pages, so you can’t summarize everything you’ve read. Second, you’re preaching to the converted. If you approach your paper as a contribution to an ongoing scholarly conversation,[ 2 ] then your literature review should summarize just the aspects of that conversation that are required to situate your conversational turn as informed and relevant. Third, the key to relevance is to point to a gap in what is known. To do so, you summarize what is known for the express purpose of identifying what is not known . Seen this way, the literature review should exert a gravitational pull on the reader, leading them inexorably to the white space on the map of knowledge you’ve painted for them. That white space is the space that your research fills.
Knowledge claims
To help writers move beyond the laundry list, the notion of ‘knowledge claims’ can be useful. A knowledge claim is a way of presenting the growing understanding of the community of researchers who have been exploring your topic. These are not disembodied facts, but rather incremental insights that some in the field may agree with and some may not, depending on their different methodological and disciplinary approaches to the topic. Treating the literature review as a story of the knowledge claims being made by researchers in the field can help writers with one of the most sophisticated aspects of a literature review—locating the knowledge being reviewed. Where does it come from? What is debated? How do different methodologies influence the knowledge being accumulated? And so on.
Consider this example of the knowledge claims (KC), Gap and Hook for the literature review section of a research paper on distributed healthcare teamwork:
KC: We know that poor team communication can cause errors. KC: And we know that team training can be effective in improving team communication. KC: This knowledge has prompted a push to incorporate teamwork training principles into health professions education curricula. KC: However, most of what we know about team training research has come from research with co-located teams—i. e., teams whose members work together in time and space. Gap: Little is known about how teamwork training principles would apply in distributed teams, whose members work asynchronously and are spread across different locations. Hook: Given that much healthcare teamwork is distributed rather than co-located, our curricula will be severely lacking until we create refined teamwork training principles that reflect distributed as well as co-located work contexts.
The ‘We know that …’ structure illustrated in this example is a template for helping you draft and organize. In your final version, your knowledge claims will be expressed with more sophistication. For instance, ‘We know that poor team communication can cause errors’ will become something like ‘Over a decade of patient safety research has demonstrated that poor team communication is the dominant cause of medical errors.’ This simple template of knowledge claims, though, provides an outline for the paragraphs in your literature review, each of which will provide detailed evidence to illustrate a knowledge claim. Using this approach, the order of the paragraphs in the literature review is strategic and persuasive, leading the reader to the gap claim that positions the relevance of the current study. To expand your vocabulary for creating such knowledge claims, linking them logically and positioning yourself amid them, I highly recommend Graff and Birkenstein’s little handbook of ‘templates’ [ 3 ].
As you organize your knowledge claims, you will also want to consider whether you are trying to map the gap in a well-studied field, or a relatively understudied one. The rhetorical challenge is different in each case. In a well-studied field, like professionalism in medical education, you must make a strong, explicit case for the existence of a gap. Readers may come to your paper tired of hearing about this topic and tempted to think we can’t possibly need more knowledge about it. Listing the knowledge claims can help you organize them most effectively and determine which pieces of knowledge may be unnecessary to map the white space your research attempts to fill. This does not mean that you leave out relevant information: your literature review must still be accurate. But, since you will not be able to include everything, selecting carefully among the possible knowledge claims is essential to producing a coherent, well-argued literature review.
Characterizing the gap
Once you’ve identified the gap, your literature review must characterize it. What kind of gap have you found? There are many ways to characterize a gap, but some of the more common include:
- a pure knowledge deficit—‘no one has looked at the relationship between longitudinal integrated clerkships and medical student abuse’
- a shortcoming in the scholarship, often due to philosophical or methodological tendencies and oversights—‘scholars have interpreted x from a cognitivist perspective, but ignored the humanist perspective’ or ‘to date, we have surveyed the frequency of medical errors committed by residents, but we have not explored their subjective experience of such errors’
- a controversy—‘scholars disagree on the definition of professionalism in medicine …’
- a pervasive and unproven assumption—‘the theme of technological heroism—technology will solve what ails teamwork—is ubiquitous in the literature, but what is that belief based on?’
To characterize the kind of gap, you need to know the literature thoroughly. That means more than understanding each paper individually; you also need to be placing each paper in relation to others. This may require changing your note-taking technique while you’re reading; take notes on what each paper contributes to knowledge, but also on how it relates to other papers you’ve read, and what it suggests about the kind of gap that is emerging.
In summary, think of your literature review as mapping the gap rather than simply summarizing the known. And pay attention to characterizing the kind of gap you’ve mapped. This strategy can help to make your literature review into a compelling argument rather than a list of facts. It can remind you of the danger of describing so fully what is known that the reader is left with the sense that there is no pressing need to know more. And it can help you to establish a coherence between the kind of gap you’ve identified and the study methodology you will use to fill it.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Mark Goldszmidt for his feedback on an early version of this manuscript.
PhD, is director of the Centre for Education Research & Innovation at Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, and professor for the Department of Medicine at Western University in London, Ontario, Canada.

- Schools & departments

Literature review
A general guide on how to conduct and write a literature review.
Please check course or programme information and materials provided by teaching staff, including your project supervisor, for subject-specific guidance.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a piece of academic writing demonstrating knowledge and understanding of the academic literature on a specific topic placed in context. A literature review also includes a critical evaluation of the material; this is why it is called a literature review rather than a literature report. It is a process of reviewing the literature, as well as a form of writing.
To illustrate the difference between reporting and reviewing, think about television or film review articles. These articles include content such as a brief synopsis or the key points of the film or programme plus the critic’s own evaluation. Similarly the two main objectives of a literature review are firstly the content covering existing research, theories and evidence, and secondly your own critical evaluation and discussion of this content.
Usually a literature review forms a section or part of a dissertation, research project or long essay. However, it can also be set and assessed as a standalone piece of work.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
…your task is to build an argument, not a library. Rudestam, K.E. and Newton, R.R. (1992) Surviving your dissertation: A comprehensive guide to content and process. California: Sage, p49.
In a larger piece of written work, such as a dissertation or project, a literature review is usually one of the first tasks carried out after deciding on a topic. Reading combined with critical analysis can help to refine a topic and frame research questions. Conducting a literature review establishes your familiarity with and understanding of current research in a particular field before carrying out a new investigation. After doing a literature review, you should know what research has already been done and be able to identify what is unknown within your topic.
When doing and writing a literature review, it is good practice to:
- summarise and analyse previous research and theories;
- identify areas of controversy and contested claims;
- highlight any gaps that may exist in research to date.
Conducting a literature review
Focusing on different aspects of your literature review can be useful to help plan, develop, refine and write it. You can use and adapt the prompt questions in our worksheet below at different points in the process of researching and writing your review. These are suggestions to get you thinking and writing.
Developing and refining your literature review (pdf)
Developing and refining your literature review (Word)
Developing and refining your literature review (Word rtf)
Writing a literature review has a lot in common with other assignment tasks. There is advice on our other pages about thinking critically, reading strategies and academic writing. Our literature review top tips suggest some specific things you can do to help you submit a successful review.
Literature review top tips (pdf)
Literature review top tips (Word rtf)
Our reading page includes strategies and advice on using books and articles and a notes record sheet grid you can use.
Reading at university
The Academic writing page suggests ways to organise and structure information from a range of sources and how you can develop your argument as you read and write.
Academic writing
The Critical thinking page has advice on how to be a more critical researcher and a form you can use to help you think and break down the stages of developing your argument.
Critical thinking
As with other forms of academic writing, your literature review needs to demonstrate good academic practice by following the Code of Student Conduct and acknowledging the work of others through citing and referencing your sources.
Good academic practice
As with any writing task, you will need to review, edit and rewrite sections of your literature review. The Editing and proofreading page includes tips on how to do this and strategies for standing back and thinking about your structure and checking the flow of your argument.
Editing and proofreading
Guidance on literature searching from the University Library
The Academic Support Librarians have developed LibSmart I and II, Learn courses to help you develop and enhance your digital research skills and capabilities; from getting started with the Library to managing data for your dissertation.
Searching using the library’s DiscoverEd tool: DiscoverEd
Finding resources in your subject: Subject guides
The Academic Support Librarians also provide one-to-one appointments to help you develop your research strategies.
1 to 1 support for literature searching and systematic reviews
Advice to help you optimise use of Google Scholar, Google Books and Google for your research and study: Using Google
Managing and curating your references
A referencing management tool can help you to collect and organise and your source material to produce a bibliography or reference list.
Referencing and reference management
Information Services provide access to Cite them right online which is a guide to the main referencing systems and tells you how to reference just about any source (EASE log-in may be required).
Cite them right
Published study guides
There are a number of scholarship skills books and guides available which can help with writing a literature review. Our Resource List of study skills guides includes sections on Referencing, Dissertation and project writing and Literature reviews.
Study skills guides
This article was published on 2024-02-26
The Importance of Literature Review in Academic Writing

The literature review holds paramount importance in academic writing for several reasons. Firstly, it serves as a comprehensive survey of existing research, establishing a solid foundation for the author’s work. It helps identify gaps, trends, and debates in the chosen field, guiding researchers toward relevant and valuable contributions. Additionally, a well-crafted literature review demonstrates the author’s understanding of the subject, showcases critical thinking skills, and enhances the credibility of the academic work by contextualizing it within the broader scholarly conversation. Overall, the literature review is an indispensable component that enriches the depth and quality of academic writing.
What is the role of a literature review in academic writing
The literature review plays a crucial role in academic writing by serving several important functions;
- Establishing Context: A literature review provides the context for the research by summarizing and synthesizing existing knowledge on the chosen topic. It helps readers understand the background and the current state of the subject matter.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: Through a literature review, researchers can identify gaps, controversies, or areas where more research is needed. This helps in justifying the significance of the new study and contributing to the existing body of knowledge.
- Formulating Research Questions or Hypotheses: By reviewing existing literature, researchers can derive relevant research questions or hypotheses. This ensures that the study is informed by and contributes to the broader academic discourse.
- Building a Theoretical Framework: A literature review helps in building the theoretical framework for a study by examining and summarizing relevant theories and concepts from previous research. It provides a conceptual foundation for the current research.
- Selecting Methodology: Understanding how previous studies were conducted helps researchers in selecting an appropriate methodology for their own research. It also assists in avoiding potential pitfalls or methodological errors.
- Avoiding Duplication: Researchers can identify what has already been done, preventing duplication of efforts. This helps in ensuring that the new study adds value and contributes to the existing knowledge.
- Critically Evaluating Sources: A literature review involves a critical analysis of the quality and reliability of the sources. This ensures that the information used in the study is credible and relevant.
- Synthesizing Information: A literature review involves synthesizing information from various sources to present a cohesive and comprehensive understanding of the topic. It helps in drawing connections and patterns in the existing research.
- Providing a Historical Perspective: It offers a historical perspective on the development of ideas and concepts within a specific field, allowing readers to trace the evolution of thought over time.
- Supporting or Challenging Arguments: The literature review supports the author’s arguments by presenting evidence from existing research. It may also highlight conflicting findings or alternative perspectives that contribute to a balanced discussion.
In summary, the literature review is a critical component of academic writing, serving as a foundation for the research, guiding methodology, and contributing to the scholarly conversation within a particular field.
How does a literature review contribute to the overall quality of a research paper
A literature review contributes significantly to the overall quality of a research paper in several ways:
- Establishing Credibility: By reviewing relevant and reputable sources, a literature review helps establish the credibility of the research. It shows that the author is well-informed about existing scholarship on the topic.
- Identifying Research Gaps: The literature review identifies gaps, controversies, or unanswered questions in the current body of knowledge. This not only justifies the need for the new study but also highlights its potential contribution to the field.
- Providing Context and Background: A literature review provides context by summarizing and synthesizing existing research. It helps readers understand the historical development, key concepts, and current state of the research topic.
- Guiding Research Questions or Hypotheses: The literature review informs the formulation of research questions or hypotheses by revealing what is already known and what remains unknown in the field. This ensures that the study is focused and relevant.
- Building a Theoretical Framework: It contributes to building a theoretical framework by examining and summarizing relevant theories and concepts. This theoretical foundation helps structure the research and guide the analysis.
- Selecting Appropriate Methodology: Knowledge of how previous studies were conducted informs the choice of methodology for the new research. This ensures that the research design is well-suited to address the specific objectives of the study.
- Avoiding Duplication: The literature review helps prevent duplication of efforts by identifying what has already been studied. This ensures that the new research contributes something novel to the existing body of knowledge.
- Providing a Critical Analysis: A literature review involves critically evaluating the quality, reliability, and relevance of sources. This ensures that only credible and pertinent information is included in the research paper.
- Synthesizing Information: By synthesizing information from diverse sources, a literature review presents a comprehensive and cohesive understanding of the research topic. It helps in drawing connections and identifying patterns in the existing literature.
- Supporting Arguments: The literature review supports the author’s arguments and hypotheses by providing evidence from previous studies. It demonstrates how the current research fits into the broader scholarly conversation.
In essence, a well-executed literature review enhances the overall quality of a research paper by providing a solid foundation, guiding the research process, and ensuring that the study contributes meaningfully to the academic discourse in its respective field.
What are the key objectives of conducting a literature review in academic research
The key objectives of conducting a literature review in academic research include;
- Identifying Existing Knowledge: To review and summarize the current state of knowledge on a particular topic or research question, understanding what is already known.
- Establishing Context: To provide the necessary background and context for the research, helping readers understand the significance of the study.
- Identifying Gaps and Research Questions: To identify gaps, controversies, or areas where further research is needed, which helps in formulating specific research questions or hypotheses.
- Building a Theoretical Framework: To review and synthesize relevant theories and concepts that will form the theoretical foundation of the research.
- Guiding Methodology: To inform the selection of appropriate research methodologies and methods based on the strengths and weaknesses of previous studies.
- Avoiding Duplication: To ensure that the research contributes something new to the existing body of knowledge, preventing unnecessary duplication of previous studies.
- Critical Evaluation: To critically evaluate the quality, reliability, and validity of existing literature, ensuring that only credible sources are used to support the research.
- Synthesizing Information: To synthesize information from diverse sources, presenting a cohesive and comprehensive understanding of the topic.
- Identifying Key Concepts and Variables: To identify and define key concepts, variables, and terms relevant to the research study.
- Understanding Methodological Approaches: To understand how previous studies were conducted, helping researchers learn from successes and pitfalls in methodology.
- Recognizing Trends and Patterns: To identify trends, patterns, and recurring themes in the literature, providing insights into the broader context of the research.
- Contextualizing Findings: To place the research findings in the context of existing knowledge, allowing for a more nuanced interpretation of results.
- Informing Literature Selection: To guide the selection of literature relevant to the research topic, ensuring that the review is focused and comprehensive.
- Supporting or Challenging Arguments: To provide evidence and support for the arguments or hypotheses presented in the research, or to highlight conflicting findings in the literature.
- Contributing to Theoretical Debates: To actively contribute to theoretical debates and discussions within the academic field.
- Enhancing the Rigor of Research: To enhance the overall rigor and validity of the research by basing it on a solid foundation of existing knowledge.
The objectives of a literature review in academic research are multi-faceted, ranging from understanding existing knowledge to guiding the research process and ensuring the credibility and significance of the study.
How does a literature review help establish the research gap in a particular field
A literature review plays a crucial role in identifying and establishing the research gap in a particular field through the following mechanisms;
- Summarizing Existing Knowledge: The literature review provides a comprehensive summary of existing research on a given topic, allowing researchers to understand the current state of knowledge in the field.
- Identifying Patterns and Trends: By reviewing multiple studies, a literature review helps researchers identify patterns, trends, and common themes in the existing literature. This analysis highlights areas where research has been concentrated and areas where it may be lacking.
- Highlighting Consensus and Controversies: The literature review reveals areas where there is a consensus among researchers and areas where there are conflicting findings or ongoing debates. This can point to gaps in understanding that require further investigation.
- Pointing to Unanswered Questions: As researchers analyze the literature, they may come across questions that have not been adequately addressed or answered by existing studies. These unanswered questions signify potential research gaps.
- Examining Methodological Limitations: A thorough literature review involves evaluating the methodologies employed in previous studies. Identifying limitations or gaps in methodology can suggest areas where further research is needed to address these shortcomings.
- Assessing Currency of Information: If there is a lack of recent studies on a specific aspect of a topic, it may indicate that there is a gap in recent research that needs attention.
- Considering Emerging Trends: The literature review allows researchers to identify emerging trends or new developments in the field. These trends may open up avenues for novel research directions.
- Evaluating Geographical or Cultural Gaps: Geographical or cultural gaps in the literature can also indicate areas where further research is needed to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the topic.
- Analyzing Changes Over Time: A temporal analysis of the literature can reveal how research on a particular topic has evolved. Recognizing changes and shifts in focus over time may uncover gaps in understanding that need addressing.
- Seeking Gaps in Application: Researchers can identify gaps in the application of theoretical frameworks or interventions within practical settings. This may suggest opportunities for applied research.
By systematically examining the existing literature and critically evaluating its content, methodologies, and findings, researchers can pinpoint areas where knowledge is incomplete or where further investigation is necessary. Identifying these gaps helps shape the rationale for the new study and positions it within the broader context of the existing body of knowledge.
In what ways does a literature review assist in framing research questions and hypotheses
A literature review assists in framing research questions and hypotheses in several ways;
- Identification of Existing Knowledge: A literature review provides an overview of existing knowledge on a particular topic, helping researchers understand what has already been studied and established in the field.
- Identification of Gaps: By analyzing the existing literature, researchers can identify gaps, limitations, or unanswered questions. These gaps serve as a basis for formulating research questions, as they highlight areas where new knowledge is needed.
- Understanding Theoretical Foundations: The literature review helps researchers understand the theoretical frameworks and concepts that have been used in previous studies. This understanding guides the formulation of research questions that align with established theories or challenge existing paradigms.
- Inspiration from Previous Research: Reviewing the literature provides researchers with insights and inspiration from previous studies. It helps them identify interesting phenomena, patterns, or trends that can lead to the formulation of relevant and meaningful research questions.
- Identification of Variables: Researchers can identify key variables, factors, or elements that have been studied in the literature. This identification informs the formulation of hypotheses and guides the operationalization of variables in the research design.
- Clarity in Focus: A literature review helps researchers narrow down the scope of their study by clarifying the focus and defining the specific aspects of the topic that need further investigation. This clarity contributes to the formulation of precise and focused research questions.
- Understanding Methodologies: By examining the methodologies used in previous studies, researchers gain insights into various research approaches. This understanding guides the selection of an appropriate research methodology for their own study, influencing the formulation of research questions.
- Building on Previous Findings: Researchers may build on or extend previous findings identified in the literature. Formulating research questions in the context of existing research allows for the advancement of knowledge and contributes to the ongoing scholarly conversation.
- Alignment with Research Goals: The literature review helps researchers align their research questions with the overarching goals and objectives of the study. This ensures that the research questions are relevant and contribute meaningfully to the field.
- Contextualizing Hypotheses: Based on the insights gained from the literature review, researchers can formulate hypotheses that are grounded in existing theories or empirical evidence. This contextualization strengthens the rationale for the hypotheses.
A well-conducted literature review informs and guides the process of formulating research questions and hypotheses by providing a foundation of knowledge, highlighting gaps, and offering insights from previous studies. This ensures that the research questions are relevant, theoretically grounded, and contribute to the advancement of the field.
Can a well-conducted literature review enhance the credibility of academic research
Yes! A well-conducted literature review is essential for enhancing the credibility of academic research in several ways;
1. Demonstrates Expertise: A comprehensive review shows you have a deep understanding of the existing knowledge and relevant theory in your field. This establishes you as an authority and positions your research within the broader context.
2. Justifies Significance: By reviewing past studies, you can clarify the gaps in research and highlight why your project addresses a crucial, unanswered question. This strengthens the purpose and originality of your work.
3. Supports Methodological Choices: You can use past research to justify your chosen methods, data collection, and analysis strategies. This demonstrates rigor and helps readers understand how your work builds upon previous findings.
4. Identifies Limitations and Strengths: Recognizing strengths and limitations of earlier studies allows you to position your research strategically. You can address limitations of past work or build upon their strengths, demonstrating a critical and informed approach.
5. Shows Engagement with the Field: Engaging with other scholars' work showcases your awareness of ongoing debates and conversations in your field. This demonstrates you are actively contributing to the advancement of knowledge.
Beyond Credibility:
A strong literature review goes beyond just building trust. It can also:
- Spark new research ideas: Examining diverse perspectives can trigger innovative ways to approach your research question.
- Identify potential challenges: Awareness of previous difficulties can help you anticipate and address similar issues in your study.
- Strengthen your arguments: Referencing relevant findings bolsters your conclusions and persuades readers of their validity.
- Thoroughness matters: Aim for a comprehensive review, including both supportive and opposing viewpoints.
- Critical analysis is key: Don’t just summarize; evaluate, compare, and contrast different studies to demonstrate your critical thinking skills.
- Clarity is crucial: Organize your review logically and present it in a clear, concise, and easy-to-follow manner.
By investing time and effort in conducting a well-structured and insightful literature review, you’ll lay a solid foundation for your research and significantly enhance its credibility and potential impact.
How does the literature review process aid in identifying key theories and concepts relevant to the research topic
The literature review process plays a crucial role in identifying key theories and concepts relevant to your research topic in several ways;
1. Exposure to Existing Knowledge: As you dive into relevant scholarly articles, books, and other sources, you’ll be exposed to the prevailing theories and concepts surrounding your topic. This initial immersion provides a broad understanding of the landscape and potential key players.
2. Identifying Recurring Themes and Ideas: As you analyze and synthesize the collected information, you’ll start noticing recurring themes, terminologies, and arguments. These recurrent elements likely represent the key theories and concepts shaping the field.
3. Recognizing Debates and Contradictions: A good literature review doesn’t shy away from presenting opposing viewpoints and ongoing debates. Recognizing these tensions and contradictions can highlight unresolved questions or emerging concepts, guiding your own research focus.
4. Evaluating Strengths and Weaknesses of Existing Theories: Critically analyzing past research allows you to identify the strengths and limitations of existing theories. This helps you understand which theories are robust and applicable and which areas need further exploration, potentially leading to innovative approaches.
5. Building Upon Previous Work: The literature review allows you to see how different theories and concepts relate to each other and your research question. This knowledge helps you position your work within the existing conversation, building upon established ideas or introducing new ones.
Additional Tips
- Keyword Exploration: Utilize relevant keywords in your search queries to discover important theories and concepts associated with your topic.
- Author Tracking: Pay attention to frequently cited authors and influential figures in your field. Their work often reflects key theories and concepts.
- Consult Experts: Engage with professors, researchers, or librarians specializing in your field. They can provide guidance on prominent theories and suggest relevant sources.
- Conceptual Mapping: Visualize the relationships between concepts and theories you encounter through mind maps or diagrams. This aids in identifying key players and their connections.
What challenges might researchers face when conducting a literature review, and how can these be addressed
Conducting a robust literature review can be an enriching, yet challenging, experience for researchers. Here are some common hurdles and tips on how to overcome them:
1. Information Overload: With the vast amount of published research available, it can be overwhelming to identify, select, and manage relevant sources.
- Develop a focused research question: This helps refine your search terms and target specific areas within the broader field.
- Utilize advanced search techniques: Boolean operators, filters, and keyword variations can improve the precision of your search results.
- Leverage reference management tools: Software like Mendeley or Zotero help organize and annotate your findings efficiently.
2. Bias and Incomplete Coverage: Your search strategy and chosen sources might unintentionally introduce bias towards particular viewpoints or neglect relevant areas.
- Consult with librarians or research experts: They can offer guidance on diverse perspectives and alternative databases beyond the typical search engines.
- Seek out dissenting voices and alternative methodologies: Consider including research that challenges your initial assumptions to ensure a balanced review.
- Be transparent about limitations: Acknowledge potential biases and acknowledge areas where your review might be incomplete.
3. Difficulty Analyzing and Synthesizing Information: Turning information into meaningful insights can be challenging, especially when dealing with conflicting studies or complex concepts.
- Develop a clear analytical framework: This helps you categorize and evaluate studies based on specific criteria like methodology, theoretical perspectives, and findings.
- Identify key themes and arguments: Look for recurring patterns and contrasting viewpoints across different studies.
- Use critical thinking skills: Evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, and potential limitations of each study and its contribution to your understanding.
4. Time Constraints: Conducting a thorough literature review can be time-consuming, especially for students or researchers with limited resources.
- Develop a realistic timeline: Break down the review process into manageable steps and allocate sufficient time for each stage.
- Prioritize sources strategically: Focus on highly relevant and impactful studies initially, then expand your search as needed.
- Seek support from peers or mentors: Discuss your progress and challenges with others to stay motivated and receive feedback.
5. Access to Resources: Paywalled journals and limited library access can pose a barrier for some researchers, particularly those affiliated with smaller institutions.
- Explore open access resources: Numerous online platforms offer free access to scholarly articles and books.
- Utilize interlibrary loan services: Libraries can often borrow materials from other institutions for you.
- Network with other researchers: Share resources and potentially collaborate with colleagues who have access to different databases.
Conducting a well-structured and thoughtful literature review is an iterative process. Don’t be afraid to revisit your search terms, adjust your focus, and seek help when needed. By actively addressing these challenges, you can transform your literature review from a chore into a valuable tool for enriching your research project and enhancing its intellectual contribution.
How does a literature review help researchers avoid duplication of existing studies
A well-conducted literature review serves as a powerful tool for researchers to avoid duplication of existing studies in several ways;
1. Unveiling Existing Knowledge: By diligently exploring past research, researchers gain a comprehensive understanding of what has already been explored and established in their field. This knowledge enables them to identify areas where further investigation is truly needed, preventing them from replicating what’s already known.
2. Building Upon Previous Work: The literature review allows researchers to discover the strengths and weaknesses of past studies. This empowers them to build upon existing findings, addressing identified limitations or extending the investigation in new directions, rather than simply repeating previous efforts.
3. Identifying Gaps and Unanswered Questions: Through critical analysis of past research, researchers can pinpoint areas where knowledge is lacking or existing conclusions remain inconclusive. This guides them towards formulating original research questions that address these gaps and contribute novel insights to the field.
4. Recognizing Methodological Approaches: Examining methodologies employed in earlier studies helps researchers understand the effectiveness and limitations of specific methods. This knowledge allows them to adapt or design innovative approaches that avoid replicating potential flaws or inefficiencies in past studies.
5. Avoiding the “Reinventing the Wheel” Pitfall: By immersing themselves in the existing scholarship, researchers prevent themselves from unknowingly replicating established knowledge or methodologies. This saves valuable time and resources, allowing them to focus on truly innovative and impactful research contributions.
- Utilize systematic review techniques: These involve rigorous search strategies, selection criteria, and data analysis methods to ensure comprehensive coverage and minimize duplication.
- Consult research databases and tools: Many platforms offer features like citation analysis and duplicate detection to help researchers identify overlapping studies.
- Engage with experts and peers: Discussing your research topic and findings with experts or peers can help you identify areas where duplication might occur or suggest alternative directions for your study.
- Clearly define your research question: A well-defined research question ensures your study focuses on a specific gap in knowledge, minimizing the risk of unintentional duplication.
A literature review is not just about summarizing past research; it’s about critically evaluating it and using that knowledge to guide your own original contribution to the field. By diligently conducting your review and embracing its insights, you can avoid the pitfall of duplication and ensure your research makes a distinct and valuable impact.
In what ways does a literature review contribute to the theoretical framework of a research study
A literature review plays a crucial role in shaping and solidifying the theoretical framework of your research study in several key ways;
1. Identifying Relevant Theories and Concepts: Through your exploration of existing research, you’ll encounter prominent theories and concepts related to your topic. These serve as the building blocks for your own theoretical framework.
2. Understanding Established Explanations: The review exposes you to diverse theoretical explanations for the phenomena you’re investigating. This knowledge helps you understand the strengths, weaknesses, and limitations of existing explanations.
3. Selecting and Justifying Your Framework: Based on your understanding of existing theories and the specific focus of your research question, you can select the most relevant theories to form your theoretical framework. The literature review then serves as justification for your choice, demonstrating why these specific theories are best suited to address your research question.
4. Building Upon or Challenging Existing Theories: Depending on your findings, the literature review might support and contribute to established theories by providing new evidence or deeper insights. Alternatively, it might challenge existing theories by highlighting their limitations or offering alternative explanations.
5. Demonstrating Theoretical Coherence: Your literature review should showcase how the chosen theories connect with each other and how they collectively underpin your research question and methodology. This ensures a cohesive and well-reasoned theoretical framework.
6. Highlighting Originality and Significance: By clearly demonstrating how your theoretical framework builds upon, departs from, or refines existing theories, the literature review emphasizes the originality and potential significance of your research contribution.
- Clearly articulate your research question: This guides your search for relevant theories and ensures your framework directly addresses your specific inquiry.
- Engage in critical analysis: Don’t simply accept theories on face value. Evaluate their strengths, weaknesses, and internal consistency through the lens of your research question.
- Consult experts and peers: Discuss your chosen theories and their connection to your research with experts or peers for feedback and refinement.
- Maintain clear connections: Throughout your research, demonstrate how your findings relate back to your theoretical framework, illustrating its explanatory power and validity.
How can a comprehensive literature review help researchers contextualize their findings within the existing body of knowledge
A comprehensive literature review plays a crucial role in contextualizing research findings within the existing body of knowledge by serving several key functions:
1. Setting the Stage: The review provides a historical and theoretical background for your research topic. It establishes the current state of knowledge, key debates, and unresolved questions, creating a framework for understanding your findings.
2. Identifying Comparisons and Contrasts: By showcasing related research and its conclusions, the review allows you to compare your findings to existing knowledge. This highlights similarities, discrepancies, and novel contributions, demonstrating the significance of your study.
3. Explaining Your Results: You can leverage the review to explain your findings in relation to established theories and explanations. This strengthens the validity and generalizability of your conclusions by demonstrating how they fit within the larger picture.
4. Addressing Limitations and Implications: The review helps you identify the limitations of your study and acknowledge areas where further research is needed. It also allows you to discuss the potential implications of your findings for future research and practical applications.
5. Engaging in Scholarly Conversation: By referencing and critically analyzing previous studies, the review showcases your engagement with the existing scholarship. This positions you as a contributor to the ongoing conversation within your field.
- Maintain a Focus: While providing context, ensure your review remains focused on your specific research question and avoids irrelevant tangents.
- Integrate Findings Seamlessly: Weave your research findings into the review naturally, highlighting their unique contribution and connection to established knowledge.
- Acknowledge Different Perspectives: Don’t shy away from presenting contrasting viewpoints or alternative interpretations. This demonstrates a balanced and critical approach.
- Use Clear Language and Structure: Present your review in a way that is easy to understand and navigate for your target audience.
What role does a literature review play in identifying methodological approaches used in previous research studies
A literature review plays a crucial role in identifying methodological approaches used in previous research studies, serving as a foundation for designing your own methodology and demonstrating its significance. Here’s how;
1. Unveiling Existing Methods: By exploring studies relevant to your topic, you’ll discover the diverse methods employed by other researchers. This expands your understanding of how different research questions can be addressed through different methodologies.
2. Evaluating Strengths and Weaknesses: The review allows you to critically analyze the effectiveness and limitations of various methods used in past studies. This helps you understand the suitability of certain approaches for your specific research question and context.
3. Informing Your Choice: Based on your understanding of existing methods and the specific demands of your research question, you can make informed decisions about the most appropriate methodology for your study. This ensures your chosen approach aligns with both theoretical foundations and established practices.
4. Justifying Your Methodology: The literature review becomes a tool for justifying your chosen methods. By showcasing how your approach addresses limitations of past studies or offers a unique perspective, you demonstrate the suitability and potential advantages of your methodology.
5. Avoiding Pitfalls and Inefficiencies: Analyzing past methods helps you identify potential pitfalls or inefficiencies associated with specific approaches. This allows you to adapt existing methods or design new ones that avoid these weaknesses, leading to a more robust and efficient research process.
- Categorize Methods: Organize your findings by grouping similar methodological approaches or research designs. This helps you compare and contrast their applicability.
- Consider Your Research Question: Always evaluate methods through the lens of your specific research question and data needs. Don’t blindly mimic others; choose based on suitability.
- Consult Experts and Peers: Discuss your chosen methodology and its connection to your research question with experts or peers for feedback and refinement.
- Clearly Explain Your Choices: In your research report, clearly explain your chosen methodology, justifying it by referencing relevant past studies and highlighting its unique advantages.
How can a literature review help researchers identify potential sources of bias or limitations in existing studies
A literature review serves as a powerful tool for researchers to identify potential sources of bias and limitations in existing studies by offering several key perspectives;
1. Scrutinizing Design and Methodology: Examining research methods and design choices allows you to pinpoint potential sources of bias. Consider factors like sample selection, data collection procedures, and control groups. Look for imbalances, subjectivity, or lack of randomization that could skew results.
2. Evaluating Data Analysis and Interpretation: Analyze how studies handled data analysis and interpretation of findings. Look for selective reporting of data, subjective interpretations, or questionable statistical methods that might introduce bias or limit the validity of conclusions.
3. Identifying Conflicting Results and Gaps in Evidence: Comparing and contrasting findings across different studies can reveal inconsistencies or discrepancies. These conflicting results might point towards potential biases in specific studies or highlight limitations in the overall body of evidence.
4. Considering Author Bias and Research Context: Be aware of potential author biases related to funding sources, personal beliefs, or institutional affiliations. Examine the broader research context and prevailing discourses to identify potential biases shaping the field.
5. Consulting Quality Assessment Tools: Leverage established tools like the Cochrane Collaboration Risk of Bias tool or the PRISMA checklist to systematically assess the methodological quality of reviewed studies. These tools highlight potential weaknesses and limitations for further consideration.
- Develop a Critical Mindset: Approach your review with a questioning attitude, actively seeking potential flaws and limitations in methodology, analysis, and conclusions.
- Consult Experts and Peers: Discuss your findings and identified biases with experts or peers in your field. Their insights can help you refine your analysis and gain broader perspectives.
- Clearly Report Identified Biases: Don’t shy away from acknowledging and discussing potential biases in existing studies. This demonstrates transparency and strengthens your analysis.
- Use Your Findings to Guide Your Research: Identify and address limitations in previous studies by designing your research to overcome them. This contributes to a more robust and comprehensive understanding of your topic.
What impact does a thorough literature review have on the formulation of a research methodology
A thorough literature review can have a profound impact on the formulation of your research methodology by influencing several key aspects;
1. Identifying Relevant Research Designs: The review exposes you to diverse research designs used in previous studies related to your topic. This broadens your understanding of how specific questions can be addressed and helps you choose the most suitable design for your own research question.
2. Selecting Appropriate Data Collection Methods: By analyzing the methods used in past studies, you gain insights into the effectiveness and limitations of different data collection techniques. This knowledge empowers you to select methods that align with your research design and the type of data you need to answer your question.
3. Considering Sampling Strategies: Exploring how previous studies selected their samples allows you to assess the strengths and weaknesses of different sampling techniques. This informs your decisions regarding sample size, representativeness, and potential biases associated with different sampling strategies.
4. Developing Data Analysis Procedures: Reviewing past studies' analysis methods helps you understand different approaches to data processing, interpretation, and statistical techniques. This allows you to adapt or create appropriate analysis procedures tailored to your specific research question and data type.
5. Anticipating Potential Challenges: Analyzing the limitations and challenges encountered in past studies equips you to proactively address similar issues in your own research. This helps you refine your methodology and plan mitigation strategies to ensure data quality and validity.
6. Justifying Your Chosen Methods: The literature review becomes a foundation for justifying your chosen methods. By highlighting how your approach addresses limitations of past studies or offers a unique perspective, you demonstrate the suitability and potential advantages of your methodology.
- Focus on Methodological Relevance: When analyzing past studies, prioritize those that adopted research designs and methods closest to your own inquiry.
- Consult Experts and Peers: Share your chosen methodology and its connection to your research question with experts or peers for feedback and refinement.
- Maintain Rigor and Transparency: Ensure your chosen methods align with recognized research standards and clearly explain their rationale in your research report.

How does the literature review process contribute to the synthesis of information from various sources
The literature review process plays a crucial role in synthesizing information from various sources by several key mechanisms;
1. Critical Evaluation and Comparison: You don’t simply summarize each source individually; you actively compare and contrast their findings, methodologies, and theoretical perspectives. This helps you identify commonalities, inconsistencies, and unique contributions of each source.
2. Identification of Key Themes and Arguments: Through in-depth analysis, you uncover recurring themes, arguments, and concepts across different sources. This allows you to synthesize diverse information into a cohesive understanding of the overall knowledge landscape surrounding your topic.
3. Building Connections and Relationships: You go beyond just presenting findings side-by-side. You actively build connections between different sources, highlighting how they support, contradict, or expand upon each other’s ideas. This creates a richer and more nuanced understanding of the topic.
4. Integrating Theories and Explanations: You don’t just list theories; you evaluate their strengths and weaknesses within the context of your research question. By integrating relevant theories from different sources, you create a robust theoretical framework that informs your own research and analysis.
5. Constructing New Knowledge: Synthesis is not just about summarizing; it’s about drawing new insights and interpretations based on the combined information. By critically analyzing and creatively connecting across sources, you can formulate original perspectives and contribute to the advancement of knowledge.
- Utilize Visual Tools: Mind maps, concept maps, or diagrams can help visualize relationships between different sources and key findings.
- Develop a Coding System: Categorize different sources based on themes, methodologies, or viewpoints to facilitate comparison and synthesis.
- Write Critically and Analytically: Don’t simply paraphrase; analyze, evaluate, and interpret the information from different sources in light of your research question.
- Maintain Transparency and Source Attribution: Clearly acknowledge the sources you use and ensure proper citation practices throughout your review.
By engaging in these active synthesis processes, the literature review becomes much more than a collection of summaries. It transforms into a powerful tool for generating new knowledge, refining your research question, and contributing meaningfully to the existing body of scholarship.
What strategies can researchers employ to critically evaluate and synthesize diverse literature in their field
Researchers can employ a variety of strategies to critically evaluate and synthesize diverse literature in their field;
Evaluation Strategies
- Scrutinize Methodology: Analyze the research design, sample selection, data collection, and analysis methods used in each source. Consider potential biases, limitations, and strengths of each approach.
- Evaluate Theoretical Frameworks: Examine the theoretical perspectives underpinning each study. Are they well-justified? Do they align with other studies and your own research question?
- Assess Findings and Claims: Don’t accept results at face value. Critically evaluate the evidence and arguments presented, considering alternative interpretations and potential counter-arguments.
- Consider Author Credibility: Look at the author’s expertise and publication history in the field. Are they respected figures? Do they have potential biases or conflicts of interest?
- Compare and Contrast Sources: Actively compare findings, methodologies, and conclusions across different sources. Identify similarities, discrepancies, and unique contributions of each study.
Synthesis Strategies
- Identify Recurring Themes and Arguments: As you analyze sources, look for common threads, concepts, and debates emerging across the literature. Organize your findings around these themes for clarity.
- Build Connections and Relationships: Don’t present sources in isolation. Highlight how they relate to each other, building a cohesive understanding of the topic. Show how they support, contradict, or expand upon each other’s ideas.
- Develop a Synthesis Framework: Create a structure to organize your synthesis, such as chronological analysis, thematic comparison, or methodological critique. This framework will guide your analysis and presentation.
- Integrate and Interpret: Go beyond simply summarizing. Use the combined information to draw new insights, interpretations, and conclusions relevant to your research question.
- Utilize Visual Tools: Mind maps, concept maps, or diagrams can help visualize relationships between sources, themes, and key findings.
- Consult Experts and Peers: Discuss your findings and interpretations with scholars or colleagues in your field. Their feedback can refine your analysis and identify potential blind spots.
- Utilize Specialized Tools: Software like NVivo or ATLAS.ti can help manage and analyze large amounts of literature data.
- Maintain Transparency and Citation: Clearly acknowledge the sources you use and ensure proper citation practices throughout your work.
- Focus on Quality Over Quantity: Don’t aim for an exhaustive review at the expense of depth. Prioritize high-quality, relevant sources that offer significant insights.
How does a literature review contribute to the identification of key variables and concepts in a research study
A well-conducted literature review plays a crucial role in identifying key variables and concepts for your research study in several ways;
1. Unveiling Relevant Domains and Theories: By immersing yourself in the existing scholarship, you’ll encounter various theories and concepts surrounding your topic. These serve as starting points for identifying potential variables relevant to your research question.
2. Identifying Relationships and Interactions: Through your analysis, you’ll discover how different concepts and variables are linked within existing studies. This helps you understand potential interactions and dependencies between factors you might investigate.
3. Examining Measurements and Operationalizations: Reviewing past research methods allows you to see how specific variables have been operationalized and measured. This informs your own choices regarding how to define and measure relevant variables in your study.
4. Recognizing Contextual Factors: The literature review exposes you to various contextual factors that might influence the variables you’re interested in. This awareness helps you identify potential moderator or control variables that need consideration in your research design.
5. Spotlighting Gaps and Untapped Potential: Analyzing past studies can reveal areas where specific variables haven’t been fully explored or their interactions haven’t been examined. This highlights opportunities for you to explore novel variables or investigate existing ones from a unique perspective.
- Develop a Focused Research Question: A clear and specific research question guides your search for relevant variables and ensures you don’t get overwhelmed by too much information.
- Utilize Key Terms and Search Operators: Explore the literature using relevant keywords and Boolean operators to refine your search and target specific concepts or variables.
- Consult With Experts and Peers: Discuss your research topic and potential variables with experts or colleagues in your field. Their insights can point you towards important concepts and suggest different perspectives.
- Conduct Thematic Analysis: Organize your findings by grouping related concepts and variables. This visualizes their connections and helps you identify key elements for your research.
- Maintain Theoretical Coherence: Ensure the identified variables and concepts align with your chosen theoretical framework, demonstrating their relevance to your research question.
The literature review is not just about passively collecting information; it’s about actively analyzing and making connections. By critically engaging with existing research, you’ll unearth the key variables and concepts that form the foundation of your study, ensuring its relevance, depth, and potential to add new knowledge to your field.
Can a literature review help researchers recognize trends and emerging themes in a particular academic field
Yes! A well-conducted literature review can be a powerful tool for researchers to recognize trends and emerging themes in a particular academic field. Here’s how;
1. Identifying Patterns and Recurring Concepts: As you delve into existing research, you’ll naturally start noticing recurring themes, ideas, and methodologies being employed across different studies. These patterns can point towards emerging trends gaining traction within the field.
2. Tracking Shifts in Focus and Emphasis: By comparing older studies with recent ones, you can identify shifts in the field’s focus. Are there new research questions gaining prominence? Are specific methodologies gaining favor? Recognizing these shifts can highlight emerging trends.
3. Analyzing Debates and Controversies: Examining ongoing debates and controversies within the literature can reveal areas where new knowledge is being actively sought. These discussions often point towards potential trends in the field as researchers explore various solutions or interpretations.
4. Recognizing Gaps and Unexplored Areas: A thorough literature review often uncovers gaps in previous research or areas where existing knowledge remains incomplete. Identifying these gaps can lead you to potential new trends as researchers strive to address them with their studies.
5. Utilizing Bibliometrics and Citation Analysis: Analyzing citation patterns and trends in publication dates can reveal which areas are attracting increasing attention and potential emerging trends that are gaining momentum within the field.
- Develop a Broad Search Strategy: Don’t limit yourself to specific journals or disciplines. Cast a wider net to capture diverse perspectives and identify potential trends across different subfields.
- Use Critical Analysis: Don’t simply accept trends at face value. Analyze their potential causes, implications, and validity. Are they supported by evidence, or are they merely hype?
- Consult Experts and Peers: Discuss your findings and interpretations with scholars or colleagues in your field. Their insights can help you confirm or refine your understanding of emerging trends.
- Consider the Broader Context: Analyze how emerging trends within your field connect with developments in other disciplines or societal changes. This adds context and depth to your understanding.
- Stay Updated: Regularly review new literature and attend conferences to keep informed of the latest developments and emerging trends in your field.
What is the significance of staying updated on the latest literature when conducting a literature review
Staying updated on the latest literature holds immense significance for conducting a thorough and impactful literature review in several ways;
1. Ensuring Comprehensiveness and Relevance: The field of research is constantly evolving, with new studies, methodologies, and theoretical frameworks emerging regularly. By incorporating the latest literature, you ensure your review encompasses the most current knowledge and findings, leading to a more comprehensive and relevant understanding of your topic.
2. Identifying Novel Research Questions and Gaps: Recent publications often highlight new areas of inquiry and potential shortcomings in existing knowledge. Staying updated helps you identify gaps in research and formulate innovative research questions that address these unresolved issues, contributing to the advancement of your field.
3. Avoiding Outdated Information and Biases: Relying solely on older literature might lead you to perpetuate outdated understandings or miss vital advancements that challenge previous biases. Staying updated ensures your review reflects the current state of knowledge and avoids misinterpretations based on superseded information.
4. Demonstrating Rigor and Expertise: Incorporating recent, high-quality studies into your review showcases your awareness of the latest developments and strengthens the credibility of your work. It demonstrates your commitment to conducting a thorough and well-informed analysis.
5. Fostering Collaboration and Networking: Engaging with the latest literature opens doors for collaboration with researchers exploring similar topics and methodologies. Utilizing new tools and platforms for scholarly communication allows you to connect with diverse perspectives and potentially contribute to ongoing research projects.
Strategies for Staying Updated
- Develop Targeted Alerts: Set up automatic notifications for new publications in relevant journals, databases, and author profiles.
- Attend Conferences and Workshops: Participate in academic events to gain insights into ongoing research and network with experts.
- Utilize Literature Review Tools: Leverage software like Mendeley or Zotero to efficiently manage your references and receive updates related to your research interests.
- Subscribe to Author Blogs and Newsletters: Follow prominent researchers in your field to stay informed about their latest work and insights.
- Join Online Communities and Forums: Engage in discussions with fellow researchers to share knowledge, exchange ideas, and learn about emerging trends.
Staying updated on the latest literature is not a one-time task; it’s an ongoing process. By actively engaging with new developments and incorporating them into your research, you can ensure your literature review remains relevant, impactful, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in your field.
How does the literature review process contribute to the overall rigor and validity of academic research
The literature review process plays a crucial role in ensuring the rigor and validity of academic research in several key ways;
1. Establishing Context and Foundation: A comprehensive literature review provides the context and theoretical foundation for your research. It demonstrates your understanding of the existing body of knowledge, relevant debates, and established methodologies. This ensures your research isn’t conducted in isolation and builds upon existing knowledge, contributing to the overall understanding of your field.
2. Preventing Duplication and Redundancy: By thoroughly exploring past research, you can identify areas where research is already saturated and avoid replicating what has already been done. This prevents unnecessary duplication of effort and ensures your research focuses on addressing genuine gaps in knowledge.
3. Justifying Your Research Question and Methodology: The literature review allows you to justify the significance of your research question and the chosen methodology. You can demonstrate how your study addresses limitations in previous research, offers unique insights, or employs innovative approaches, ultimately contributing to the advancement of knowledge.
4. Identifying Potential Biases and Limitations: A critical analysis of existing research helps you identify potential biases and limitations in previous studies. By acknowledging these limitations and outlining strategies to address them in your own research, you demonstrate awareness and enhance the trustworthiness of your findings.
5. Ensuring Transparency and Traceability: The literature review showcases the sources and evidence upon which your research is built. This transparency allows other researchers to assess the validity of your arguments, replicate your findings, and build upon your work, contributing to the overall scientific process.
6. Building Credibility and Expertise: A well-researched and well-presented literature review showcases your understanding of the field and your ability to critically evaluate existing knowledge. This establishes your credibility as a researcher and strengthens the impact of your findings.
7. Enhancing Argumentation and Communication: Your knowledge gleaned from the literature review enriches your arguments by providing them with historical context, theoretical underpinnings, and comparisons to related work. This improves communication and ensures your research resonates with other scholars in the field.
8. Informing Data Analysis and Interpretation: By understanding how past research has approached similar topics, you can develop a more informed approach to analyzing your own data and interpreting your findings. This helps you ensure your conclusions are well-grounded and supported by existing knowledge.
Tips for developing academic writing skills
What are the 5 parts of the research paper
How do I write a research paper
How to incorporate data and statistics in research papers
What are the steps for writing a research paper
How to prepare a research paper outline
How to write a research paper outline
How to write a research paper
- Library Homepage
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide: Literature Reviews?
- Literature Reviews?
- Strategies to Finding Sources
- Keeping up with Research!
- Evaluating Sources & Literature Reviews
- Organizing for Writing
- Writing Literature Review
- Other Academic Writings
What is a Literature Review?
So, what is a literature review .
"A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available or a set of summaries." - Quote from Taylor, D. (n.d)."The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting it".
- Citation: "The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting it"
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Each field has a particular way to do reviews for academic research literature. In the social sciences and humanities the most common are:
- Narrative Reviews: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific research topic and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weaknesses, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section that summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Book review essays/ Historiographical review essays : A type of literature review typical in History and related fields, e.g., Latin American studies. For example, the Latin American Research Review explains that the purpose of this type of review is to “(1) to familiarize readers with the subject, approach, arguments, and conclusions found in a group of books whose common focus is a historical period; a country or region within Latin America; or a practice, development, or issue of interest to specialists and others; (2) to locate these books within current scholarship, critical methodologies, and approaches; and (3) to probe the relation of these new books to previous work on the subject, especially canonical texts. Unlike individual book reviews, the cluster reviews found in LARR seek to address the state of the field or discipline and not solely the works at issue.” - LARR
What are the Goals of Creating a Literature Review?
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
- Baumeister, R.F. & Leary, M.R. (1997). "Writing narrative literature reviews," Review of General Psychology , 1(3), 311-320.
When do you need to write a Literature Review?
- When writing a prospectus or a thesis/dissertation
- When writing a research paper
- When writing a grant proposal
In all these cases you need to dedicate a chapter in these works to showcase what has been written about your research topic and to point out how your own research will shed new light into a body of scholarship.
Where I can find examples of Literature Reviews?
Note: In the humanities, even if they don't use the term "literature review", they may have a dedicated chapter that reviewed the "critical bibliography" or they incorporated that review in the introduction or first chapter of the dissertation, book, or article.
- UCSB electronic theses and dissertations In partnership with the Graduate Division, the UC Santa Barbara Library is making available theses and dissertations produced by UCSB students. Currently included in ADRL are theses and dissertations that were originally filed electronically, starting in 2011. In future phases of ADRL, all theses and dissertations created by UCSB students may be digitized and made available.
Where to Find Standalone Literature Reviews
Literature reviews are also written as standalone articles as a way to survey a particular research topic in-depth. This type of literature review looks at a topic from a historical perspective to see how the understanding of the topic has changed over time.
- Find e-Journals for Standalone Literature Reviews The best way to get familiar with and to learn how to write literature reviews is by reading them. You can use our Journal Search option to find journals that specialize in publishing literature reviews from major disciplines like anthropology, sociology, etc. Usually these titles are called, "Annual Review of [discipline name] OR [Discipline name] Review. This option works best if you know the title of the publication you are looking for. Below are some examples of these journals! more... less... Journal Search can be found by hovering over the link for Research on the library website.
Social Sciences
- Annual Review of Anthropology
- Annual Review of Political Science
- Annual Review of Sociology
- Ethnic Studies Review
Hard science and health sciences:
- Annual Review of Biomedical Data Science
- Annual Review of Materials Science
- Systematic Review From journal site: "The journal Systematic Reviews encompasses all aspects of the design, conduct, and reporting of systematic reviews" in the health sciences.
- << Previous: Overview
- Next: Strategies to Finding Sources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 5, 2024 11:44 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucsb.edu/litreview
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jun 20, 2024 9:08 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral

- Become Involved |
- Give to the Library |
- Staff Directory |
- UNF Library
- Thomas G. Carpenter Library
Conducting a Literature Review
Benefits of conducting a literature review.
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Summary of the Process
- Additional Resources
- Literature Review Tutorial by American University Library
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It by University of Toronto
- Write a Literature Review by UC Santa Cruz University Library
While there might be many reasons for conducting a literature review, following are four key outcomes of doing the review.
Assessment of the current state of research on a topic . This is probably the most obvious value of the literature review. Once a researcher has determined an area to work with for a research project, a search of relevant information sources will help determine what is already known about the topic and how extensively the topic has already been researched.
Identification of the experts on a particular topic . One of the additional benefits derived from doing the literature review is that it will quickly reveal which researchers have written the most on a particular topic and are, therefore, probably the experts on the topic. Someone who has written twenty articles on a topic or on related topics is more than likely more knowledgeable than someone who has written a single article. This same writer will likely turn up as a reference in most of the other articles written on the same topic. From the number of articles written by the author and the number of times the writer has been cited by other authors, a researcher will be able to assume that the particular author is an expert in the area and, thus, a key resource for consultation in the current research to be undertaken.
Identification of key questions about a topic that need further research . In many cases a researcher may discover new angles that need further exploration by reviewing what has already been written on a topic. For example, research may suggest that listening to music while studying might lead to better retention of ideas, but the research might not have assessed whether a particular style of music is more beneficial than another. A researcher who is interested in pursuing this topic would then do well to follow up existing studies with a new study, based on previous research, that tries to identify which styles of music are most beneficial to retention.
Determination of methodologies used in past studies of the same or similar topics. It is often useful to review the types of studies that previous researchers have launched as a means of determining what approaches might be of most benefit in further developing a topic. By the same token, a review of previously conducted studies might lend itself to researchers determining a new angle for approaching research.
Upon completion of the literature review, a researcher should have a solid foundation of knowledge in the area and a good feel for the direction any new research should take. Should any additional questions arise during the course of the research, the researcher will know which experts to consult in order to quickly clear up those questions.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Aug 29, 2022 8:54 AM
- URL: https://libguides.unf.edu/litreview

Get Started
Take the first step and invest in your future.

Online Programs
Offering flexibility & convenience in 51 online degrees & programs.

Prairie Stars
Featuring 15 intercollegiate NCAA Div II athletic teams.

Find your Fit
UIS has over 85 student and 10 greek life organizations, and many volunteer opportunities.

Arts & Culture
Celebrating the arts to create rich cultural experiences on campus.

Give Like a Star
Your generosity helps fuel fundraising for scholarships, programs and new initiatives.

Bragging Rights
UIS was listed No. 1 in Illinois and No. 3 in the Midwest in 2023 rankings.
- Quick links Applicants & Students Important Apps & Links Alumni Faculty and Staff Community Admissions How to Apply Cost & Aid Tuition Calculator Registrar Orientation Visit Campus Academics Register for Class Programs of Study Online Degrees & Programs Graduate Education International Student Services Study Away Student Support Bookstore UIS Life Dining Diversity & Inclusion Get Involved Health & Wellness COVID-19 United in Safety Residence Life Student Life Programs UIS Connection Important Apps UIS Mobile App Advise U Canvas myUIS i-card Balance Pay My Bill - UIS Bursar Self-Service Email Resources Bookstore Box Information Technology Services Library Orbit Policies Webtools Get Connected Area Information Calendar Campus Recreation Departments & Programs (A-Z) Parking UIS Newsroom The Observer Connect & Get Involved Update your Info Alumni Events Alumni Networks & Groups Volunteer Opportunities Alumni Board News & Publications Featured Alumni Alumni News UIS Alumni Magazine Resources Order your Transcripts Give Back Alumni Programs Career Development Services & Support Accessibility Services Campus Services Campus Police Facilities & Services Registrar Faculty & Staff Resources Website Project Request Web Services Training & Tools Academic Impressions Career Connect CSA Reporting Cybersecurity Training Faculty Research FERPA Training Website Login Campus Resources Newsroom Campus Calendar Campus Maps i-Card Human Resources Public Relations Webtools Arts & Events UIS Performing Arts Center Visual Arts Gallery Event Calendar Sangamon Experience Center for Lincoln Studies ECCE Speaker Series Community Engagement Center for State Policy and Leadership Illinois Innocence Project Innovate Springfield Central IL Nonprofit Resource Center NPR Illinois Community Resources Child Protection Training Academy Office of Electronic Media University Archives/IRAD Institute for Illinois Public Finance
Request Info

Literature Review

- Request Info Request info for.... Undergraduate/Graduate Online Study Away Continuing & Professional Education International Student Services General Inquiries
The purpose of a literature review is to collect relevant, timely research on your chosen topic, and synthesize it into a cohesive summary of existing knowledge in the field. This then prepares you for making your own argument on that topic, or for conducting your own original research.
Depending on your field of study, literature reviews can take different forms. Some disciplines require that you synthesize your sources topically, organizing your paragraphs according to how your different sources discuss similar topics. Other disciplines require that you discuss each source in individual paragraphs, covering various aspects in that single article, chapter, or book.
Within your review of a given source, you can cover many different aspects, including (if a research study) the purpose, scope, methods, results, any discussion points, limitations, and implications for future research. Make sure you know which model your professor expects you to follow when writing your own literature reviews.
Tip : Literature reviews may or may not be a graded component of your class or major assignment, but even if it is not, it is a good idea to draft one so that you know the current conversations taking place on your chosen topic. It can better prepare you to write your own, unique argument.
Benefits of Literature Reviews
- Literature reviews allow you to gain familiarity with the current knowledge in your chosen field, as well as the boundaries and limitations of that field.
- Literature reviews also help you to gain an understanding of the theory(ies) driving the field, allowing you to place your research question into context.
- Literature reviews provide an opportunity for you to see and even evaluate successful and unsuccessful assessment and research methods in your field.
- Literature reviews prevent you from duplicating the same information as others writing in your field, allowing you to find your own, unique approach to your topic.
- Literature reviews give you familiarity with the knowledge in your field, giving you the chance to analyze the significance of your additional research.
Choosing Your Sources
When selecting your sources to compile your literature review, make sure you follow these guidelines to ensure you are working with the strongest, most appropriate sources possible.
Topically Relevant
Find sources within the scope of your topic
Appropriately Aged
Find sources that are not too old for your assignment
Find sources whose authors have authority on your topic
Appropriately “Published”
Find sources that meet your instructor’s guidelines (academic, professional, print, etc.)
Tip: Treat your professors and librarians as experts you can turn to for advice on how to locate sources. They are a valuable asset to you, so take advantage of them!
Organizing Your Literature Review
Synthesizing topically.
Some assignments require discussing your sources together, in paragraphs organized according to shared topics between them.
For example, in a literature review covering current conversations on Alison Bechdel’s Fun Home , authors may discuss various topics including:
- her graphic style
- her allusions to various literary texts
- her story’s implications regarding LGBT experiences in 20 th century America.
In this case, you would cluster your sources on these three topics. One paragraph would cover how the sources you collected dealt with Bechdel’s graphic style. Another, her allusions. A third, her implications.
Each of these paragraphs would discuss how the sources you found treated these topics in connection to one another. Basically, you compare and contrast how your sources discuss similar issues and points.
To determine these shared topics, examine aspects including:
- Definition of terms
- Common ground
- Issues that divide
- Rhetorical context
Summarizing Individually
Depending on the assignment, your professor may prefer that you discuss each source in your literature review individually (in their own, separate paragraphs or sections). Your professor may give you specific guidelines as far as what to cover in these paragraphs/sections.
If, for instance, your sources are all primary research studies, here are some aspects to consider covering:
- Participants
- Limitations
- Implications
- Significance
Each section of your literature review, in this case, will identify all of these elements for each individual article.
You may or may not need to separate your information into multiple paragraphs for each source. If you do, using proper headings in the appropriate citation style (APA, MLA, etc.) will help keep you organized.
If you are writing a literature review as part of a larger assignment, you generally do not need an introduction and/or conclusion, because it is embedded within the context of your larger paper.
If, however, your literature review is a standalone assignment, it is a good idea to include some sort of introduction and conclusion to provide your reader with context regarding your topic, purpose, and any relevant implications or further questions. Make sure you know what your professor is expecting for your literature review’s content.
Typically, a literature review concludes with a full bibliography of your included sources. Make sure you use the style guide required by your professor for this assignment.

- Library Catalogue
Academic writing: What is a literature review?
A review of the literature in a discipline is not the same as an annotated bibliography of sources, though an annotated bibliography can be a type of literature review. The purpose of a lit review is not only to tell your reader the state of scholarship about a given topic, but also to organize and evaluate the major points, parts, or arguments of each source. From the University of Toronto Writing Centre’s Tips on Conducting the Literature Review :
"A literature review is a piece of discursive prose , not a list describing or summarizing one piece of literature after another. It's usually a bad sign to see every paragraph beginning with the name of a researcher. Instead, organize the literature review into sections that present themes or identify trends, including relevant theory. You are not trying to list all the material published, but to synthesize and evaluate it according to the guiding concept of your thesis or research question."
A lit review may serve as a stand-alone piece or article. For example, see this published Stand-Alone Literature Review (content note: this literature review focuses on the topic of abuse against women with disabilities). However, more often a lit review is part of a larger research publication. For example, see this published research article that includes a Literature Review (content note: this article discusses depression among college students).
What should a literature review include?
Introduction: Explain why this research topic is important. Outline what direction your review will take: i.e., what aspects of the topic you’re focusing on.
Body : Present your summaries and evaluations of the sources in a clear, logical, and coherent manner. Some options for organizing your review include chronological, order of importance, two sides of a controversial problem, differences in perspective or viewpoint. Your review must “read” like a coherent paper, not a list.
Note: Most literature reviews describe only the main findings, relevant methodological issues, and/or major conclusions of other research.
Ensure your final list of references includes all sources you’ve discussed, and use the citation style required in your discipline.
Don’t provide a lot of detail about the procedures used in your sources. Don’t mention every study conducted on the topic. Include only the ones that are most relevant for the purpose and scope of your review.
Plan and organize your literature review
- Define your central problem, issue, or focus (create a research question or thesis statement)
- Consider audience expectations. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are.
- summarize the “gist” or main ideas of the source
- comment on the source’s usefulness, relevance, methodology, and/or findings in the context of your question or issue
- Do not use a “list-like” approach in drafting your lit review. Rather, organize your information logically to address your research question, thesis, or central issue. For more, see the Writeonline.ca guide to Literature Reviews and the Monash University Learn HQ mini-module on Literature Reviews (including sections on the process of writing a literature review, structuring a literature review, and the language of literature reviews).
Revise your literature review, keeping in mind these tips for effective writing
- Pay attention to sentence structure
- Use the active and passive voices appropriately
- Reduce or omit wordy, redundant phrases
- Proofread for common punctuation and expression errors
For more about literature reviews, including definitions, protocols and guidelines, search strategies, and managing citations, see the Library's Literature reviews for graduate students .

- Academic Writing Guides
How to Write a Literature Review? A Beginner’s Guide
Sooner or later in your academic path, you will be required to compose a literature review. So, it’s important to approach this task well-prepared and understand how to write a literature review inside out.
Are you interested in how to write lit review projects correctly and cover the subject comprehensively, from all angles? This article will explore the concept of review of literature , dwell on how to write a literature review in line with your professor’s expectations, and share a universal literature review template for your usage.
What Is the Purpose of a Literature Review?
To understand what should be included in a literature review , you need to understand its purpose and value in a larger work. A well-researched and written lit review usually addresses the following objectives:
- Inform . The fundamental purpose of any review of literature is to provide the foundation of knowledge on a specific topic or phenomenon. You explore what people have learned about it from prior studies and summarize those findings to inform your readers.
- Give credit . Another purpose of a lit review is to identify researchers who have contributed to the advancement of research on your chosen literature review topic and have produced the most valuable findings. This way, you pay tribute to those researchers and showcase your knowledge of the most considerable influencers.
- Identify gaps . By performing a thorough review of literature , you may not only discover what is known about your topic but also find out what it yet to be learned about it. As a result of reviewing the available evidence, you may identify gaps for addressing through your academic inquiry.
- Identify patterns . Those who know how to write a literature review can also effectively embrace data trends and patterns in the collected dataset. As a result, they can present a more nuanced analysis of the existing knowledge in your literature review and uncover dependencies that inform people’s understanding of certain phenomena and processes.
- Contextualize research . When you perform lit review writing, you can also create a spot for your own study within the broad field of your academic research interest. This way, you show to your readers that you can effectively navigate the landscape of your academic area.
These purposes lay the foundation for understanding how to write a literature review that will attain all academic goals. You simply need to use this list as your checklist for structuring an impactful lit review and including all vital data in it.
How to Write a Literature Review?
Now, we come to the main topic of this article – how to write a good literature review for dissertation projects, research papers, and other works. Follow the steps we’ve covered below to arrive at a consistent, logical piece of lit review .
Identify Relevant Sources
Any literature review writing starts with academic research. You should look for sources that explore your topic from various angles and provide valuable literature review findings to expand your knowledge on the subject. It’s best to look for subject-specific books first and then go through academic databases that publish journal articles. This way, you will start with the evidence of the highest reliability level and move on to expand your literature review dataset conveniently.
Screen Sources for Quality
The best solution on how to write a literature review without challenges is to rely on high-quality evidence. Your task is to research extensively in reliable academic databases to find peer-reviewed academic journals and books written by experts in your field. Don’t over-rely on online sources in your literature review, like blogs or opinion pieces, because they rarely possess the needed degree of credibility for an academic review. By choosing only industry-approved sources from qualified professionals, you can build a solid foundation for your writing and impress the audience.
Determine Data Patterns and Gaps
How to write a literature review of value for your readers? One of the best approaches is to go beyond mere summarization of what other researchers have found on the subject and to apply critical thinking and data categorization. This way, you will manage to uncover existing patterns and trends and examine those dependencies in your literature review. A systematic, critical approach is always evaluated much higher than a simple outline of what people say on your subject.
Draft an Outline
Now, it’s time to compose an outline for a literature review . The outline should include the main concepts you’re planning to cover in the literature review text and should structure the narrative consistently. By means of composing an outline before the actual writing process, you give yourself a hands-on roadmap for composing a logically flowing piece. As a result of using an outline, you will write the literature review faster and will avoid the risk of going off-topic.
Compose the Review
With a good and detailed outline, you should have no more problems or concerns about how to write a literature review . The writing process should go quickly and smoothly when you have all your evidence at your fingertips, categorized by themes and requiring only proper summarization in the text.
We recommend starting with a broad introduction to the topic and concepts related to it. You should give definitions and explain the topic’s features and components that require attention in the research process. After that, you may briefly outline the main sections of your review and then proceed to the exploration of each section in depth.
At times, your professor will give you a specific structure for review writing – such as the general introduction, coverage of theories, and then coverage of empirical evidence. At times, it may be a review of the data search strategy and a report on the identified resources that follow. In any case, you should follow the tutor’s prompt closely to ensure compliance with the task.
Make Use of This Generic Literature Review Template
Looking for a universal, ready-to-use literature review template ? Here is an effective literature review template that everyone can apply with minor tweaks to produce a high-quality review of literature .
LITERATURE REVIEW TEMPLATE
Introduction
- Introduce the topic of your literature review
- Examine its significance for your academic area
- Determine the scope of your literature review inquiry
- Give a brief outline of subtopics and sections included in your literature review
Body of the literature review
- Describe the subtopic and indicate how it relates to your literature review’s main idea
- Summarize the evidence available about it
- Compare the available data and voice your opinion
Conclusion
- Summarize the main points and findings from your literature review
- State the main contribution you have managed to achieve
- Identify the research gaps your literature review has revealed
Use this literature review template to pump your writing muscle and get ready for new literature review challenges.
More Pro Tips for Writing a Literature Review
If you’re still unsure about how to do a literature review with excellence, these pro tips may improve your understanding of this task type.
- Mind the audience . Understanding how to do a literature review for a research paper often has little to do with how to write literature review for thesis . This difference is explained by the fact that these types of academic work are of different lengths and pursue different scholarly goals. This way, you may need to cover only some basic seminal research in the review of literature for a research paper but will need to dig deeper into theoretical and applied research with deeper analysis and more critical thinking when dealing with a thesis.
- Mind the length . How long should a literature review be ? This is a vital question that you should answer before starting the outlining and writing process. Ask your professor if you’re not sure or apply the rule of thumb, where this section usually takes from 15% to 25% of the entire paper.
- Mind the structure . It’s important to cover all lit review aspects that your professor wants to see in the paper; otherwise, you risk getting a low grade even if your literature review is comprehensive and interesting. What should a literature review include ? In most cases, you will be required to cover some seminal research works in your literature review to show that you understand who the pioneers in the field are, and what contribution they have made to the topic’s exploration. Next, you should examine relevant theories that inform studies in your subject. At the end of the literature review, you should typically cite a variety of studies of applied nature, thus showing what empirical research is conducted in your academic field.
With these recommendations at your disposal, you’re sure to become much more proficient in how to do a lit review . If you need more help with a literature review project, welcome to use our professional and quick literature review writing service . Our experts know everything about how to write a literature review , so they will handle your literature review task with ease within the timeframe you set for them.

- Essay Writing Guides


File(s) under embargo
Reason: Interested in publishing within the next year.
until file(s) become available
ASSESSING THE IMPACT OF STRUCTURED REVISION AFTER PEER REVIEW ON FIRST YEAR BIOLOGY LAB STUDENT SCIENTIFIC WRITING SELF-EFFICACY AND UTILITY VALUE
Scientific writing is a core competency within the undergraduate biology curriculum (AAAS, 2010), as it has wide-ranging applications in academic and professional life, alongside being a powerful tool for formative learning (Wingate, 2010). Due to its importance in critical analysis and understanding of biological concepts, developing scientific writing is necessary for success within the biological sciences disciplines (Clemmons et al., 2020). Peer review has emerged as a common pedagogical technique to address the need for scientific writing training. The expansive literature on peer review indicates its ability to engage students in critical thinking, increase writing confidence, and improve academic performance on writing assignments (Dochy et al., 1999; S. Gielen et al., 2010; van Zundert et al., 2010). Research on the usage of scaffolded curriculum within peer review has shown increased review validity from students (Cho et al., 2006; Liu & Li, 2014), and integrated plans to revise leads to increased revisions (Wu & Schunn, 2021) and the incorporation of more feedback that is correct (Jurkowski, 2018). However, despite the breadth of peer review research, the number of quasi-experimental and experimental studies assessing the benefits and perceptions of revision is small (Double et al., 2020; van Zundert et al., 2010). This study provides a detailed look at the effects of scaffolded peer review and structured revision on student perceptions of scientific writing self-efficacy and the utility value of the peer review process. After performing peer review, students were given either a supported revision worksheet, wherein students list the feedback received and if it is useful for revisions, or a general revision worksheet, where students list their planned revisions. Quantitative surveys and qualitative reflection questions were administered to gauge the scientific writing ability and the perceived usefulness of peer review and were compared between treatment groups. Little to no difference was found in how students perceived their scientific writing self-efficacy and the utility value of the peer review process. Despite the lack of differences, analysis of the themes within responses reveals alignment with the theoretical frameworks guiding this research. This study provides a rich account of the characteristics of scientific writing self-efficacy and utility value in undergraduate biology students during peer review and revision, which have implications for the future development of an effective scaffolded peer review curriculum.
Degree Type
- Master of Science
- Biological Sciences
Campus location
- West Lafayette
Advisor/Supervisor/Committee Chair
Additional committee member 2, additional committee member 3, usage metrics.
- Science, technology and engineering curriculum and pedagogy
- Other biological sciences not elsewhere classified

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
The Science of Strong Business Writing
- Bill Birchard

Lessons from neurobiology
Brain scans are showing us in new detail exactly what entices readers. Scientists can see a group of midbrain neurons—the “reward circuit”—light up as people respond to everything from a simple metaphor to an unexpected story twist. The big takeaway? Whether you’re crafting an email to a colleague or an important report for the board, you can write in a way that delights readers on a primal level, releasing pleasure chemicals in their brains.
Bill Birchard is an author and writing coach who’s worked with many successful businesspeople. He’s drawn on that experience and his review of the scientific literature to identify eight features of satisfying writing: simplicity, specificity, surprise, stirring language, seductiveness, smart ideas, social content, and storytelling. In this article, he shares tips for using those eight S’s to captivate readers and help your message stick.
Strong writing skills are essential for anyone in business. You need them to effectively communicate with colleagues, employees, and bosses and to sell any ideas, products, or services you’re offering.
- Bill Birchard is a business author and book-writing coach. His Writing for Impact: 8 Secrets from Science That Will Fire Up Your Reader’s Brain will be published by HarperCollins Leadership in April 2023. His previous books include Merchants of Virtue, Stairway to Earth, Nature’s Keepers, Counting What Counts, and others. For more writing tactics, see his website .
Partner Center

- Conferences
- Editorial Process
- Recent Advances
- Sustainability
- Academic Resources

What Are The Benefits of Academic Editing?
Publication journeys can differ greatly from author to author. Some can be relatively straightforward, whereas others can feel like a never-ending process of returns, revisions, and resubmissions. Academic editing can ease this process and benefit authors in a number of ways.
Here, we take a look at the features of academic editing services and how they benefit authors.
What is academic editing?
Academic editing is much more in-depth than language editing services. It’s a dedicated service seeing authors through from pre-publication to post-publication, entailing two rounds of editing and checks—a language edit followed by a specialist edit—as well as post-editing support for various aspects of the publication process.
The English editing component ensures that the language of the research is up to a publishable standard. It then undergoes a quality check by a senior language editor, who then passes it on to a PhD-holding specialist editor.
The specialist Academic Editor, who has expertise in the same field as the authors, makes content-specific and technical changes, also providing an analysis of the structure, terminology, coherence, etc. They then compile this information into a report, which the author can refer to and implement.
This edit then goes through another quality check, this time by a senior Academic Editor, and the paper and report are then returned to the author, taking a total of around 5 days.
As part of the academic editing package, authors are also entitled to free English language re-editing if the author is dissatisfied, as well as complimentary editing to cover letters and reviewer responses.
What are the benefits of academic editing?
Academic editing is the best way to prepare your research for publication. Below are detailed the major benefits of using this specialist service.
1. Academic report
The Academic Editor’s report is a great resource for authors, providing invaluable insights that will help the author’s manuscript withstand the scrutiny of peer review. It covers all aspects of the paper, with detailed feedback on each section, as well as figures, tables, references, structure, titles, and terminology.
This enables authors to make important changes prior to submission, and thus makes it more likely to pass the peer review process. This ensures a smoother publication journey for authors, reducing the chance of it being sent back for revisions.
2. Two rounds of editing
The combination of language and specialist editing ensures that every aspect of the paper is of publishable standard prior to submission. Poor expression and grammar in a paper can detract from its overall quality. So, by choosing academic editing, authors can be confident not only that the content of their paper meets the highest academic standards, but also that it has high readability and will be understood by the intended audience.
This is also strengthened by the quality control process, with a senior language editor and senior PhD-holding editor checking over each and every paper before being sent back to the author. This ensures that high quality standards are met for both language and content and thus high author satisfaction.
3. Specialist knowledge
Academic Editors are carefully selected for each paper. They are PhD holders with relevant expertise in the same field as the author, and thus are well qualified to heighten its potential. They help to ensure that the paper is logical and consistent, refining its structure and coherence.
This helps to ensure that the paper will stand out in its field. Academic Editors understand the nuances of their subject areas and thus can make sure that research is communicated clearly, professionally, and accurately.
4. Post-editing support
Another major benefit of academic editing is the support received after the paper has been edited and returned to authors. Professional support is offered for several aspects of the publishing process—for example, cover letters and reviewer responses. Free English language re-editing is also offered if the author requests it.
Choosing editing services
There are several considerations when it comes to choosing the right editing service for your research. If you want a comprehensive service that best prepares your paper for peer review and publication, academic editing is the most appropriate option.
Through the combination of language and specialist editing, the structure, coherence, and readability of the paper are all significantly improved, allowing authors to be confident in their work upon submission.

If you want to prepare your research for publication, MDPI Author Services offers high-quality academic editing by PhD specialists in your field. This service offers an in-depth report compiled by the Academic Editor, reviewing each section in detail as well as structure, terminology, and more.
Our team of highly skilled English editors have edited over 60,000 papers, with a 97% author satisfaction rate. Our services are available to both MDPI authors and those publishing with other journals. Visit the link above to get a free quote today.
Related posts

Open Science
MDPI Papers Cited in the News – June 2024

Mushrooms for Gut Health

Academic Resources , Open Access , Open Science
Open Access in South Korea

International Women in Engineering Day 2024

Academic Resources , Journals , Open Science
Why Journal Metrics are Important and How to Use Them

Insights from MDPI Top 5 Picks: May 2024
Long-Term Effects of Prenatal Exposure to Amphetamine

Optimizing Biological Control of Soybean Crop Pest Species

Academic Resources , English Resources , Open Science
Author Services Guide To Word Classes

What Are Preprints?
Add comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Privacy Preference Center
Privacy preferences.
From sharing the latest MDPI blog news, to showcasing our most popular articles, the newsletters will keep you in the loop with everything good going on in the science world.
Fall 2024 Semester
Undergraduate courses.
Composition courses that offer many sections (ENGL 101, 201, 277 and 379) are not listed on this schedule unless they are tailored to specific thematic content or particularly appropriate for specific programs and majors.
- 100-200 level
ENGL 151.S01: Introduction to English Studies
Tuesday and Thursday, 11 a.m.-12:15 p.m.
Sharon Smith
ENGL 151 serves as an introduction to both the English major and the discipline of English studies. In this class, you will develop the thinking, reading, writing and research practices that define both the major and the discipline. Much of the semester will be devoted to honing your literary analysis skills, and we will study and discuss texts from several different genres—poetry, short fiction, the novel, drama and film—as well as some literary criticism. As we do so, we will explore the language of the discipline, and you will learn a variety of key literary terms and concepts. In addition, you will develop your skills as both a writer and researcher within the discipline of English.
ENGL 201.ST1 Composition II: The Mind/Body Connection
In this section of English 201, students will use research and writing to learn more about problems that are important to them and articulate ways to address those problems. The course will focus specifically on issues related to the mind, the body and the relationship between them. The topics we will discuss during the course will include the correlation between social media and body image; the efficacy of sex education programs; the degree to which beliefs about race and gender influence school dress codes; and the unique mental and physical challenges faced by college students today. In this course, you will be learning about different approaches to argumentation, analyzing the arguments of others and constructing your own arguments. At the same time, you will be honing your skills as a researcher and developing your abilities as a persuasive and effective writer.
ENGL 201.S10 Composition II: Environmental Writing
Monday/Wednesday/Friday 1-1:50 p.m.
Gwen Horsley
English 201 will help students develop the ability to think critically and analytically and to write effectively for other university courses and careers. This course will provide opportunities to develop analytical skills that will help students become critical readers and effective writers. Specifically, in this class, students will:
- Focus on the relationships between world environments, land, animals and humankind.
- Read various essays by environmental, conservational and regional authors.
- Produce student writings.
Students will improve their writing skills by reading essays and applying techniques they witness in others’ work and those learned in class. This class is also a course in logical and creative thought. Students will write about humankind’s place in the world and our influence on the land and animals, places that hold special meaning to them or have influenced their lives and stories of their own families and their places and passions in the world. Students will practice writing in an informed and persuasive manner, in language that engages and enlivens readers by using vivid verbs and avoiding unnecessary passives, nominalizations and expletive constructions.
Students will prepare writing assignments based on readings and discussions of essays included in "Literature and the Environment " and other sources. They may use "The St. Martin’s Handbook," as well as other sources, to review grammar, punctuation, mechanics and usage as needed.
ENGL 201.13 Composition II: Writing the Environment
Tuesday and Thursday 9:30-10:45 a.m.
Paul Baggett
For generations, environmentalists have relied on the power of prose to change the minds and habits of their contemporaries. In the wake of fires, floods, storms and droughts, environmental writing has gained a new sense of urgency, with authors joining activists in their efforts to educate the public about the grim realities of climate change. But do they make a difference? Have reports of present and future disasters so saturated our airwaves that we no longer hear them? How do writers make us care about the planet amidst all the noise? In this course, students will examine the various rhetorical strategies employed by some of today’s leading environmental writers and filmmakers. And while analyzing their different arguments, students also will strengthen their own strategies of argumentation as they research and develop essays that explore a range of environmental concerns.
ENGL 201 Composition II: Food Writing
S17 Tuesday and Thursday 12:30-1:45 p.m.
S18 Tuesday and Thursday 2-3:15 p.m.
Jodi Andrews
In this composition class, students will critically analyze essays about food, food systems and environments, food cultures, the intersections of personal choice, market forces and policy and the values underneath these forces. Students will learn to better read like writers, noting authors’ purpose, audience organizational moves, sentence-level punctuation and diction. We will read a variety of essays including research-intensive arguments and personal narratives which intersect with one of our most primal needs as humans: food consumption. Students will rhetorically analyze texts, conduct advanced research, reflect on the writing process and write essays utilizing intentional rhetorical strategies. Through doing this work, students will practice the writing moves valued in every discipline: argument, evidence, concision, engaging prose and the essential research skills for the 21st century.
ENGL 221.S01 British Literature I
Michael S. Nagy
English 221 is a survey of early British literature from its inception in the Old English period with works such as "Beowulf" and the “Battle of Maldon,” through the Middle Ages and the incomparable writings of Geoffrey Chaucer and the Gawain - poet, to the Renaissance and beyond. Students will explore the historical and cultural contexts in which all assigned reading materials were written, and they will bring that information to bear on class discussion. Likely themes that this class will cover include heroism, humor, honor, religion, heresy and moral relativity. Students will write one research paper in this class and sit for two formal exams: a midterm covering everything up to that point in the semester, and a comprehensive final. Probable texts include the following:
- The Norton Anthology of English Literature: The Middle Ages. Ed. Alfred David, M. H. Abrams, and Stephen Greenblatt. 9th ed. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 2012.
- The Norton Anthology of English Literature: The Sixteenth Century and Early Seventeenth Century. Ed. George M. Logan, Stephen Greenblatt, Barbara K Lewalski, and M. H. Abrams. 9th ed. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 2012.
- The Norton Anthology of English Literature: The Restoration and the Eighteenth Century. Ed. George M. Logan, Stephen Greenblatt, Barbara K Lewalski, and M. H. Abrams. 9th ed. New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 2012.
- Gibaldi, Joseph. The MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers. 6th ed. New York: The Modern Language Association of America, 2003.
- Any Standard College Dictionary.
ENGL 240.S01 Juvenile Literature Elementary-5th Grade
Monday, Wednesday and Friday noon-12:50 p.m.
April Myrick
A survey of the history of literature written for children and adolescents, and a consideration of the various types of juvenile literature. Text selection will focus on the themes of imagination and breaking boundaries.
ENGL 240.ST1 Juvenile Literature Elementary-5th Grade
Randi Anderson
In English 240 students will develop the skills to interpret and evaluate various genres of literature for juvenile readers. This particular section will focus on various works of literature at approximately the K-5 grade level. We will read a large range of works that fall into this category, as well as information on the history, development and genre of juvenile literature.
Readings for this course include classical works such as "Hatchet," "Little Women", "The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe" and "Brown Girl Dreaming," as well as newer works like "Storm in the Barn," "Anne Frank’s Diary: A Graphic Adaptation," "Lumberjanes," and a variety of picture books. These readings will be paired with chapters from "Reading Children’s Literature: A Critical Introduction " to help develop understanding of various genres, themes and concepts that are both related to juvenile literature and also present in our readings.
In addition to exposing students to various genres of writing (poetry, historical fiction, non-fiction, fantasy, picture books, graphic novels, etc.) this course will also allow students to engage in a discussion of larger themes present in these works such as censorship, race and gender. Students’ understanding of these works and concepts will be developed through readings, research, discussion posts, exams and writing assignments designed to get students to practice analyzing poetry, picture books, informational books and transitional/easy readers.
ENGL 241.S01: American Literature I
Tuesday and Thursday 12:30-1:45 p.m.
This course provides a broad, historical survey of American literature from the early colonial period to the Civil War. Ranging across historical periods and literary genres—including early accounts of contact and discovery, narratives of captivity and slavery, poetry of revolution, essays on gender equality and stories of industrial exploitation—this class examines how subjects such as colonialism, nationhood, religion, slavery, westward expansion, race, gender and democracy continue to influence how Americans see themselves and their society.
Required Texts
- The Norton Anthology of American Literature: Package 1, Volumes A and B Beginnings to 1865, Ninth Edition. (ISBN 978-0-393-26454-8)
ENGL 283.S01 Introduction to Creative Writing
Steven Wingate
Students will explore the various forms of creative writing (fiction, nonfiction and poetry) not one at a time in a survey format—as if there were decisive walls of separation between then—but as intensely related genres that share much of their creative DNA. Through close reading and work on personal texts, students will address the decisions that writers in any genre must face on voice, rhetorical position, relationship to audience, etc. Students will produce and revise portfolios of original creative work developed from prompts and research. This course fulfills the same SGR #2 requirements ENGL 201; note that the course will involve a research project. Successful completion of ENGL 101 (including by test or dual credit) is a prerequisite.
ENGL 283.S02 Introduction to Creative Writing
Jodilyn Andrews
This course introduces students to the craft of writing, with readings and practice in at least two genres (including fiction, poetry and drama).
ENGL 283.ST1 Introduction to Creative Writing
Amber Jensen, M.A., M.F.A.
This course explores creative writing as a way of encountering the world, research as a component of the creative writing process, elements of craft and their rhetorical effect and drafting, workshop and revision as integral parts of writing polished literary creative work. Student writers will engage in the research practices that inform the writing of literature and in the composing strategies and writing process writers use to create literary texts. Through their reading and writing of fiction, poetry and creative nonfiction, students will learn about craft elements, find examples of those craft elements in published works and apply these elements in their own creative work, developed through weekly writing activities, small group and large group workshop and conferences with the instructor. Work will be submitted, along with a learning reflection and revision plan in each genre and will then be revised and submitted as a final portfolio at the end of the semester to demonstrate continued growth in the creation of polished literary writing.
- 300-400 level
ENGL 424.S01 Language Arts Methods grades 7-12
Tuesday 6-8:50 p.m.
Danielle Harms
Techniques, materials and resources for teaching English language and literature to middle and secondary school students. Required of students in the English education option.
AIS/ENGL 447.S01: American Indian Literature of the Present
Thursdays 3-6 p.m.
This course introduces students to contemporary works by authors from various Indigenous nations. Students examine these works to enhance their historical understanding of Indigenous peoples, discover the variety of literary forms used by those who identify as Indigenous writers, and consider the cultural and political significance of these varieties of expression. Topics and questions to be explored include:
- Genre: What makes Indigenous literature indigenous?
- Political and Cultural Sovereignty: Why have an emphasis on tribal specificity and calls for “literary separatism” emerged in recent decades, and what are some of the critical conversations surrounding such particularized perspectives?
- Gender and Sexuality: What are the intersecting concerns of Indigenous Studies and Women, Gender and Sexuality Studies, and how might these research fields inform one another?
- Trans-Indigeneity: What might we learn by comparing works across different Indigenous traditions, and what challenges do such comparisons present?
- Aesthetics: How do Indigenous writers understand the dynamics between tradition and creativity?
- Visual Forms: What questions or concerns do visual representations (television and film) by or about Indigenous peoples present?
Possible Texts
- Akiwenzie-Damm, Kateri and Josie Douglas (eds), Skins: Contemporary Indigenous Writing. IAD Press, 2000. (978-1864650327)
- Erdrich, Louise, The Sentence. Harper, 2021 (978-0062671127)
- Harjo, Joy, Poet Warrior: A Memoir. Norton, 2021 (978-0393248524)
- Harjo, Sterlin and Taika Waititi, Reservation Dogs (selected episodes)
- Talty, Morgan. Night of the Living Rez, 2022, Tin House (978-1953534187)
- Wall Kimmerer, Robin. Braiding Sweet Grass, Milkweed Editions (978-1571313560)
- Wilson, Diane. The Seed Keeper: A Novel. Milkweed Editions (978-1571311375)
- Critical essays by Alexie, Allen, Cohen, Cox, King, Kroeber, Ortiz, Piatote, Ross and Sexton, Smith, Taylor, Teuton, Treuer, Vizenor, and Womack.
ENGL 472.S01: Film Criticism
Tuesdays 2-4:50 p.m.
Jason McEntee
Do you have an appreciation for, and enjoy watching, movies? Do you want to study movies in a genre-oriented format (such as those we typically call the Western, the screwball comedy, the science fiction or the crime/gangster, to name a few)? Do you want to explore the different critical approaches for talking and writing about movies (such as auteur, feminist, genre or reception)?
In this class, you will examine movies through viewing and defining different genres while, at the same time, studying and utilizing different styles of film criticism. You will share your discoveries in both class discussions and short writings. The final project will be a formal written piece of film criticism based on our work throughout the semester. The course satisfies requirements and electives for all English majors and minors, including both the Film Studies and Professional Writing minors. (Note: Viewing of movies outside of class required and may require rental and/or streaming service fees.)
ENGL 476.ST1: Fiction
In this workshop-based creative writing course, students will develop original fiction based on strong attention to the fundamentals of literary storytelling: full-bodied characters, robust story lines, palpable environments and unique voices. We will pay particular attention to process awareness, to the integrity of the sentence, and to authors' commitments to their characters and the places in which their stories unfold. Some workshop experience is helpful, as student peer critique will be an important element of the class.
ENGL 479.01 Capstone: The Gothic
Wednesday 3-5:50 p.m.
With the publication of Horace Walpole’s "The Castle of Otranto " in 1764, the Gothic officially came into being. Dark tales of physical violence and psychological terror, the Gothic incorporates elements such as distressed heroes and heroines pursued by tyrannical villains; gloomy estates with dark corridors, secret passageways and mysterious chambers; haunting dreams, troubling prophecies and disturbing premonitions; abduction, imprisonment and murder; and a varied assortment of corpses, apparitions and “monsters.” In this course, we will trace the development of Gothic literature—and some film—from the eighteenth-century to the present time. As we do so, we will consider how the Gothic engages philosophical beliefs about the beautiful and sublime; shapes psychological understandings of human beings’ encounters with horror, terror, the fantastic and the uncanny; and intervenes in the social and historical contexts in which it was written. We’ll consider, for example, how the Gothic undermines ideals related to domesticity and marriage through representations of domestic abuse, toxicity and gaslighting. In addition, we’ll discuss Gothic texts that center the injustices of slavery and racism. As many Gothic texts suggest, the true horrors of human existence often have less to do with inexplicable supernatural phenomena than with the realities of the world in which we live.
ENGL 485.S01: Undergraduate Writing Center Learning Assistants
Flexible Scheduling
Nathan Serfling
Since their beginnings in the 1920s and 30s, writing centers have come to serve numerous functions: as hubs for writing across the curriculum initiatives, sites to develop and deliver workshops and resource centers for faculty as well as students, among other functions. But the primary function of writing centers has necessarily and rightfully remained the tutoring of student writers. This course will immerse you in that function in two parts. During the first four weeks, you will explore writing center praxis—that is, the dialogic interplay of theory and practice related to writing center work. This part of the course will orient you to writing center history, key theoretical tenets and practical aspects of writing center tutoring. Once we have developed and practiced this foundation, you will begin work in the writing center as a tutor, responsible for assisting a wide variety of student clients with numerous writing tasks. Through this work, you will learn to actively engage with student clients in the revision of a text, respond to different student needs and abilities, work with a variety of writing tasks and rhetorical situations, and develop a richer sense of writing as a complex and negotiated social process.
Graduate Courses
Engl 572.s01: film criticism, engl 576.st1 fiction.
In this workshop-based creative writing course, students will develop original fiction based on strong attention to the fundamentals of literary storytelling: full-bodied characters, robust story lines, palpable environments and unique voices. We will pay particular attention to process awareness, to the integrity of the sentence and to authors' commitments to their characters and the places in which their stories unfold. Some workshop experience is helpful, as student peer critique will be an important element of the class.
ENGL 605.S01 Seminar in Teaching Composition
Thursdays 1-3:50 p.m.
This course will provide you with a foundation in the pedagogies and theories (and their attendant histories) of writing instruction, a foundation that will prepare you to teach your own writing courses at SDSU and elsewhere. As you will discover through our course, though, writing instruction does not come with any prescribed set of “best” practices. Rather, writing pedagogies stem from and continue to evolve because of various and largely unsettled conversations about what constitutes effective writing and effective writing instruction. Part of becoming a practicing writing instructor, then, is studying these conversations to develop a sense of what “good writing” and “effective writing instruction” might mean for you in our particular program and how you might adapt that understanding to different programs and contexts.
As we read about, discuss and research writing instruction, we will address a variety of practical and theoretical topics. The practical focus will allow us to attend to topics relevant to your immediate classroom practices: designing a curriculum and various types of assignments, delivering the course content and assessing student work, among others. Our theoretical topics will begin to reveal the underpinnings of these various practical matters, including their historical, rhetorical, social and political contexts. In other words, we will investigate the praxis—the dialogic interaction of practice and theory—of writing pedagogy. As a result, this course aims to prepare you not only as a writing teacher but also as a nascent writing studies/writing pedagogy scholar.
At the end of this course, you should be able to engage effectively in the classroom practices described above and participate in academic conversations about writing pedagogy, both orally and in writing. Assessment of these outcomes will be based primarily on the various writing assignments you submit and to a smaller degree on your participation in class discussions and activities.
ENGL 726.S01: The New Woman, 1880–1900s
Thursdays 3–5:50 p.m.
Katherine Malone
This course explores the rise of the New Woman at the end of the nineteenth century. The label New Woman referred to independent women who rebelled against social conventions. Often depicted riding bicycles, smoking cigarettes and wearing masculine clothing, these early feminists challenged gender roles and sought broader opportunities for women’s employment and self-determination. We will read provocative fiction and nonfiction by New Women writers and their critics, including authors such as Sarah Grand, Mona Caird, George Egerton, Amy Levy, Ella Hepworth Dixon, Grant Allen and George Gissing. We will analyze these exciting texts through a range of critical lenses and within the historical context of imperialism, scientific and technological innovation, the growth of the periodical press and discourse about race, class and gender. In addition to writing an argumentative seminar paper, students will complete short research assignments and lead discussion.
ENGL 792.ST1 Women in War: Female Authors and Characters in Contemporary War Lit
In this course, we will explore the voices of female authors and characters in contemporary literature of war. Drawing from various literary theories, our readings and discussion will explore the contributions of these voices to the evolving literature of war through archetypal and feminist criticism. We will read a variety of short works (both theoretical and creative) and complete works such as (selections subject to change): "Eyes Right" by Tracy Crow, "Plenty of Time When We Get Home" by Kayla Williams, "You Know When the Men are Gone" by Siobhan Fallon, "Still, Come Home" by Katie Schultz and "The Fine Art of Camouflage" by Lauren Johnson.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
"A substantive, thorough, sophisticated literature review is a precondition for doing substantive, thorough, sophisticated research". Boote and Baile 2005 . Authors of manuscripts treat writing a literature review as a routine work or a mere formality. But a seasoned one knows the purpose and importance of a well-written literature review.
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
Besides the obvious reason for students -- because it is assigned! -- a literature review helps you explore the research that has come before you, to see how your research question has (or has not) already been addressed. You identify: core research in the field. experts in the subject area. methodology you may want to use (or avoid)
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
INTRODUCTION. Writing the literature review (LR) is often viewed as a difficult task that can be a point of writer's block and procrastination in postgraduate life.Disagreements on the definitions or classifications of LRs may confuse students about their purpose and scope, as well as how to perform an LR.Interestingly, at many universities, the LR is still an important element in any ...
A literature review is not only a summary of key sources, but has an organizational pattern which combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem.
In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your ...
A literature review is a critical summary and evaluation of the existing research (e.g., academic journal articles and books) on a specific topic. It is typically included as a separate section or chapter of a research paper or dissertation, serving as a contextual framework for a study.
Mapping the gap. The purpose of the literature review section of a manuscript is not to report what is known about your topic. The purpose is to identify what remains unknown—what academic writing scholar Janet Giltrow has called the 'knowledge deficit'—thus establishing the need for your research study [].In an earlier Writer's Craft instalment, the Problem-Gap-Hook heuristic was ...
A literature review is a piece of academic writing demonstrating knowledge and understanding of the academic literature on a specific topic placed in context. A literature review also includes a critical evaluation of the material; this is why it is called a literature review rather than a literature report.
A literature review is a piece of academic writing demonstrating knowledge and understanding of the academic literature on a specific topic placed in context. A literature review also includes a critical evaluation of the material; this is why it is called a literature review rather than a literature report.
The literature review holds paramount importance in academic writing for several reasons. Firstly, it serves as a comprehensive survey of existing research, establishing a solid foundation for the author's work. It helps identify gaps, trends, and debates in the chosen field, guiding researchers toward relevant and valuable contributions.
In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your ...
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
lls the reader, and why it is necessary.3.2 Evaluate the nine basic steps taken to wr. te a well-constructed literature review.3.3 Conduct an electronic search using terms, phrases, Boolean operators, and filters.3.4 Evaluate and identify the parts of an empirical research journal article, and use that kn.
While there might be many reasons for conducting a literature review, following are four key outcomes of doing the review. Assessment of the current state of research on a topic. This is probably the most obvious value of the literature review. Once a researcher has determined an area to work with for a research project, a search of relevant ...
Typically, a literature review concludes with a full bibliography of your included sources. Make sure you use the style guide required by your professor for this assignment. The purpose of a literature review is to collect relevant, timely research on your chosen topic, and synthesize it into a cohesive summary of existing knowledge in the field.
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
genres of writing. All disciplines use literature reviews. Most commonly, the literature review is a part of a research paper, article, book, thesis or dissertation. Sometimes your instructor may ask you to simply write a literature review as a stand-alone document. This handout will consider the literature review as a section of a larger ...
The importance of literature review in academic writing of different categories, levels, and purposes cannot be overemphasized. The literature review establishes both the relevance and justifies ...
A literature review helps you create a sense of rapport with your audience or readers so they can trust that you have done your homework. As a result, they can give you credit for your due diligence: you have done your fact-finding and fact-checking mission, one of the initial steps of any research writing.
In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. Critically read and annotate your sources with your research question or central issue in mind. Effective annotations. summarize the "gist" or main ideas of the ...
Some Issues in Liter ature R eview. 1. A continuous and time consuming process runs. through out r esearch work (more whil e selecting. a resear ch problem and writing 'r eview of. liter ature ...
Sooner or later in your academic path, you will be required to compose a literature review. So, it's important to approach this task well-prepared and understand how to write a literature review inside out.. Are you interested in how to write lit review projects correctly and cover the subject comprehensively, from all angles? This article will explore the concept of review of literature ...
Scientific writing is a core competency within the undergraduate biology curriculum (AAAS, 2010), as it has wide-ranging applications in academic and professional life, alongside being a powerful tool for formative learning (Wingate, 2010). Due to its importance in critical analysis and understanding of biological concepts, developing scientific writing is necessary for success within the ...
Strong writing skills are essential for anyone in business. You need them to effectively communicate with colleagues, employees, and bosses and to sell any ideas, products, or services you're ...
Academic editing is the best way to prepare your research for publication. Below are detailed the major benefits of using this specialist service. 1. Academic report. The Academic Editor's report is a great resource for authors, providing invaluable insights that will help the author's manuscript withstand the scrutiny of peer review.
Undergraduate CoursesComposition courses that offer many sections (ENGL 101, 201, 277 and 379) are not listed on this schedule unless they are tailored to specific thematic content or particularly appropriate for specific programs and majors.100-200 levelENGL 151.S01: Introduction to English StudiesTuesday and Thursday, 11 a.m.-12:15 p.m.Sharon SmithENGL 151 serves as an introduction to both ...