State-of-the-art literature review methodology: A six-step approach for knowledge synthesis
- Original Article
- Open access
- Published: 05 September 2022
- Volume 11 , pages 281–288, ( 2022 )

Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Erin S. Barry ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0788-7153 1 , 2 ,
- Jerusalem Merkebu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3707-8920 3 &
- Lara Varpio ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1412-4341 3
28k Accesses
22 Citations
18 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Introduction
Researchers and practitioners rely on literature reviews to synthesize large bodies of knowledge. Many types of literature reviews have been developed, each targeting a specific purpose. However, these syntheses are hampered if the review type’s paradigmatic roots, methods, and markers of rigor are only vaguely understood. One literature review type whose methodology has yet to be elucidated is the state-of-the-art (SotA) review. If medical educators are to harness SotA reviews to generate knowledge syntheses, we must understand and articulate the paradigmatic roots of, and methods for, conducting SotA reviews.
We reviewed 940 articles published between 2014–2021 labeled as SotA reviews. We (a) identified all SotA methods-related resources, (b) examined the foundational principles and techniques underpinning the reviews, and (c) combined our findings to inductively analyze and articulate the philosophical foundations, process steps, and markers of rigor.
In the 940 articles reviewed, nearly all manuscripts (98%) lacked citations for how to conduct a SotA review. The term “state of the art” was used in 4 different ways. Analysis revealed that SotA articles are grounded in relativism and subjectivism.
This article provides a 6-step approach for conducting SotA reviews. SotA reviews offer an interpretive synthesis that describes: This is where we are now. This is how we got here. This is where we could be going. This chronologically rooted narrative synthesis provides a methodology for reviewing large bodies of literature to explore why and how our current knowledge has developed and to offer new research directions.
Similar content being viewed by others

An analysis of current practices in undertaking literature reviews in nursing: findings from a focused mapping review and synthesis
Reviewing the literature, how systematic is systematic.
Reading and interpreting reviews for health professionals: a practical review
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Literature reviews play a foundational role in scientific research; they support knowledge advancement by collecting, describing, analyzing, and integrating large bodies of information and data [ 1 , 2 ]. Indeed, as Snyder [ 3 ] argues, all scientific disciplines require literature reviews grounded in a methodology that is accurate and clearly reported. Many types of literature reviews have been developed, each with a unique purpose, distinct methods, and distinguishing characteristics of quality and rigor [ 4 , 5 ].
Each review type offers valuable insights if rigorously conducted [ 3 , 6 ]. Problematically, this is not consistently the case, and the consequences can be dire. Medical education’s policy makers and institutional leaders rely on knowledge syntheses to inform decision making [ 7 ]. Medical education curricula are shaped by these syntheses. Our accreditation standards are informed by these integrations. Our patient care is guided by these knowledge consolidations [ 8 ]. Clearly, it is important for knowledge syntheses to be held to the highest standards of rigor. And yet, that standard is not always maintained. Sometimes scholars fail to meet the review’s specified standards of rigor; other times the markers of rigor have never been explicitly articulated. While we can do little about the former, we can address the latter. One popular literature review type whose methodology has yet to be fully described, vetted, and justified is the state-of-the-art (SotA) review.
While many types of literature reviews amalgamate bodies of literature, SotA reviews offer something unique. By looking across the historical development of a body of knowledge, SotA reviews delves into questions like: Why did our knowledge evolve in this way? What other directions might our investigations have taken? What turning points in our thinking should we revisit to gain new insights? A SotA review—a form of narrative knowledge synthesis [ 5 , 9 ]—acknowledges that history reflects a series of decisions and then asks what different decisions might have been made.
SotA reviews are frequently used in many fields including the biomedical sciences [ 10 , 11 ], medicine [ 12 , 13 , 14 ], and engineering [ 15 , 16 ]. However, SotA reviews are rarely seen in medical education; indeed, a bibliometrics analysis of literature reviews published in 14 core medical education journals between 1999 and 2019 reported only 5 SotA reviews out of the 963 knowledge syntheses identified [ 17 ]. This is not to say that SotA reviews are absent; we suggest that they are often unlabeled. For instance, Schuwirth and van der Vleuten’s article “A history of assessment in medical education” [ 14 ] offers a temporally organized overview of the field’s evolving thinking about assessment. Similarly, McGaghie et al. published a chronologically structured review of simulation-based medical education research that “reviews and critically evaluates historical and contemporary research on simulation-based medical education” [ 18 , p. 50]. SotA reviews certainly have a place in medical education, even if that place is not explicitly signaled.
This lack of labeling is problematic since it conceals the purpose of, and work involved in, the SotA review synthesis. In a SotA review, the author(s) collects and analyzes the historical development of a field’s knowledge about a phenomenon, deconstructs how that understanding evolved, questions why it unfolded in specific ways, and posits new directions for research. Senior medical education scholars use SotA reviews to share their insights based on decades of work on a topic [ 14 , 18 ]; their junior counterparts use them to critique that history and propose new directions [ 19 ]. And yet, SotA reviews are generally not explicitly signaled in medical education. We suggest that at least two factors contribute to this problem. First, it may be that medical education scholars have yet to fully grasp the unique contributions SotA reviews provide. Second, the methodology and methods of SotA reviews are poorly reported making this form of knowledge synthesis appear to lack rigor. Both factors are rooted in the same foundational problem: insufficient clarity about SotA reviews. In this study, we describe SotA review methodology so that medical educators can explicitly use this form of knowledge synthesis to further advance the field.
We developed a four-step research design to meet this goal, illustrated in Fig. 1 .
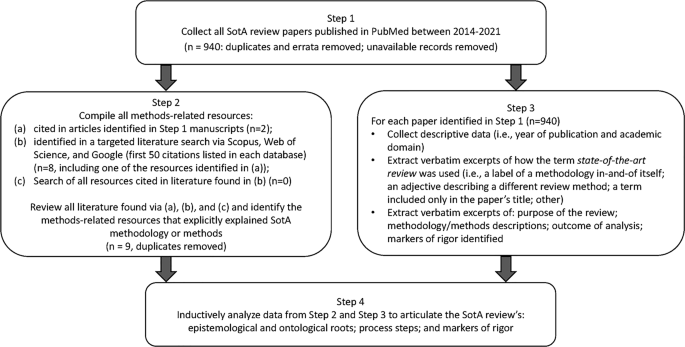
Four-step research design process used for developing a State-of-the-Art literature review methodology
Step 1: Collect SotA articles
To build our initial corpus of articles reporting SotA reviews, we searched PubMed using the strategy (″state of the art review″[ti] OR ″state of the art review*″) and limiting our search to English articles published between 2014 and 2021. We strategically focused on PubMed, which includes MEDLINE, and is considered the National Library of Medicine’s premier database of biomedical literature and indexes health professions education and practice literature [ 20 ]. We limited our search to 2014–2021 to capture modern use of SotA reviews. Of the 960 articles identified, nine were excluded because they were duplicates, erratum, or corrigendum records; full text copies were unavailable for 11 records. All articles identified ( n = 940) constituted the corpus for analysis.
Step 2: Compile all methods-related resources
EB, JM, or LV independently reviewed the 940 full-text articles to identify all references to resources that explained, informed, described, or otherwise supported the methods used for conducting the SotA review. Articles that met our criteria were obtained for analysis.
To ensure comprehensive retrieval, we also searched Scopus and Web of Science. Additionally, to find resources not indexed by these academic databases, we searched Google (see Electronic Supplementary Material [ESM] for the search strategies used for each database). EB also reviewed the first 50 items retrieved from each search looking for additional relevant resources. None were identified. Via these strategies, nine articles were identified and added to the collection of methods-related resources for analysis.
Step 3: Extract data for analysis
In Step 3, we extracted three kinds of information from the 940 articles papers identified in Step 1. First, descriptive data on each article were compiled (i.e., year of publication and the academic domain targeted by the journal). Second, each article was examined and excerpts collected about how the term state-of-the-art review was used (i.e., as a label for a methodology in-and-of itself; as an adjective qualifying another type of literature review; as a term included in the paper’s title only; or in some other way). Finally, we extracted excerpts describing: the purposes and/or aims of the SotA review; the methodology informing and methods processes used to carry out the SotA review; outcomes of analyses; and markers of rigor for the SotA review.
Two researchers (EB and JM) coded 69 articles and an interrater reliability of 94.2% was achieved. Any discrepancies were discussed. Given the high interrater reliability, the two authors split the remaining articles and coded independently.
Step 4: Construct the SotA review methodology
The methods-related resources identified in Step 2 and the data extractions from Step 3 were inductively analyzed by LV and EB to identify statements and research processes that revealed the ontology (i.e., the nature of reality that was reflected) and the epistemology (i.e., the nature of knowledge) underpinning the descriptions of the reviews. These authors studied these data to determine if the synthesis adhered to an objectivist or a subjectivist orientation, and to synthesize the purposes realized in these papers.
To confirm these interpretations, LV and EB compared their ontology, epistemology, and purpose determinations against two expectations commonly required of objectivist synthesis methods (e.g., systematic reviews): an exhaustive search strategy and an appraisal of the quality of the research data. These expectations were considered indicators of a realist ontology and objectivist epistemology [ 21 ] (i.e., that a single correct understanding of the topic can be sought through objective data collection {e.g., systematic reviews [ 22 ]}). Conversely, the inverse of these expectations were considered indicators of a relativist ontology and subjectivist epistemology [ 21 ] (i.e., that no single correct understanding of the topic is available; there are multiple valid understandings that can be generated and so a subjective interpretation of the literature is sought {e.g., narrative reviews [ 9 ]}).
Once these interpretations were confirmed, LV and EB reviewed and consolidated the methods steps described in these data. Markers of rigor were then developed that aligned with the ontology, epistemology, and methods of SotA reviews.
Of the 940 articles identified in Step 1, 98% ( n = 923) lacked citations or other references to resources that explained, informed, or otherwise supported the SotA review process. Of the 17 articles that included supporting information, 16 cited Grant and Booth’s description [ 4 ] consisting of five sentences describing the overall purpose of SotA reviews, three sentences noting perceived strengths, and four sentences articulating perceived weaknesses. This resource provides no guidance on how to conduct a SotA review methodology nor markers of rigor. The one article not referencing Grant and Booth used “an adapted comparative effectiveness research search strategy that was adapted by a health sciences librarian” [ 23 , p. 381]. One website citation was listed in support of this strategy; however, the page was no longer available in summer 2021. We determined that the corpus was uninformed by a cardinal resource or a publicly available methodology description.
In Step 2 we identified nine resources [ 4 , 5 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 ]; none described the methodology and/or processes of carrying out SotA reviews. Nor did they offer explicit descriptions of the ontology or epistemology underpinning SotA reviews. Instead, these resources provided short overview statements (none longer than one paragraph) about the review type [ 4 , 5 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 ]. Thus, we determined that, to date, there are no available methodology papers describing how to conduct a SotA review.
Step 3 revealed that “state of the art” was used in 4 different ways across the 940 articles (see Fig. 2 for the frequency with which each was used). In 71% ( n = 665 articles), the phrase was used only in the title, abstract, and/or purpose statement of the article; the phrase did not appear elsewhere in the paper and no SotA methodology was discussed. Nine percent ( n = 84) used the phrase as an adjective to qualify another literature review type and so relied entirely on the methodology of a different knowledge synthesis approach (e.g., “a state of the art systematic review [ 29 ]”). In 5% ( n = 52) of the articles, the phrase was not used anywhere within the article; instead, “state of the art” was the type of article within a journal. In the remaining 15% ( n = 139), the phrase denoted a specific methodology (see ESM for all methodology articles). Via Step 4’s inductive analysis, the following foundational principles of SotA reviews were developed: (1) the ontology, (2) epistemology, and (3) purpose of SotA reviews.
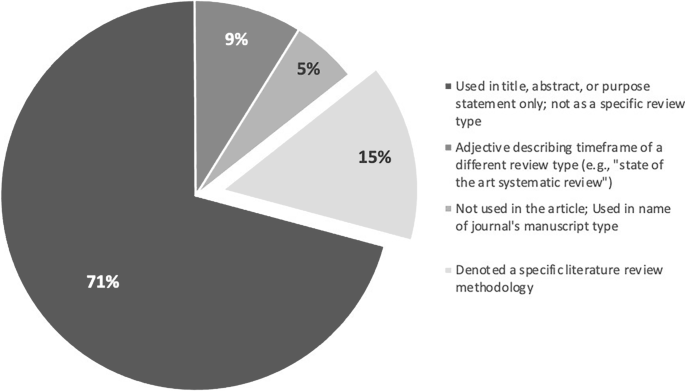
Four ways the term “state of the art” is used in the corpus and how frequently each is used
Ontology of SotA reviews: Relativism
SotA reviews rest on four propositions:
The literature addressing a phenomenon offers multiple perspectives on that topic (i.e., different groups of researchers may hold differing opinions and/or interpretations of data about a phenomenon).
The reality of the phenomenon itself cannot be completely perceived or understood (i.e., due to limitations [e.g., the capabilities of current technologies, a research team’s disciplinary orientation] we can only perceive a limited part of the phenomenon).
The reality of the phenomenon is a subjective and inter-subjective construction (i.e., what we understand about a phenomenon is built by individuals and so their individual subjectivities shape that understanding).
The context in which the review was conducted informs the review (e.g., a SotA review of literature about gender identity and sexual function will be synthesized differently by researchers in the domain of gender studies than by scholars working in sex reassignment surgery).
As these propositions suggest, SotA scholars bring their experiences, expectations, research purposes, and social (including academic) orientations to bear on the synthesis work. In other words, a SotA review synthesizes the literature based on a specific orientation to the topic being addressed. For instance, a SotA review written by senior scholars who are experts in the field of medical education may reflect on the turning points that have shaped the way our field has evolved the modern practices of learner assessment, noting how the nature of the problem of assessment has moved: it was first a measurement problem, then a problem that embraced human judgment but needed assessment expertise, and now a whole system problem that is to be addressed from an integrated—not a reductionist—perspective [ 12 ]. However, if other scholars were to examine this same history from a technological orientation, learner assessment could be framed as historically constricted by the media available through which to conduct assessment, pointing to how artificial intelligence is laying the foundation for the next wave of assessment in medical education [ 30 ].
Given these foundational propositions, SotA reviews are steeped in a relativist ontology—i.e., reality is socially and experientially informed and constructed, and so no single objective truth exists. Researchers’ interpretations reflect their conceptualization of the literature—a conceptualization that could change over time and that could conflict with the understandings of others.
Epistemology of SotA reviews: Subjectivism
SotA reviews embrace subjectivism. The knowledge generated through the review is value-dependent, growing out of the subjective interpretations of the researcher(s) who conducted the synthesis. The SotA review generates an interpretation of the data that is informed by the expertise, experiences, and social contexts of the researcher(s). Furthermore, the knowledge developed through SotA reviews is shaped by the historical point in time when the review was conducted. SotA reviews are thus steeped in the perspective that knowledge is shaped by individuals and their community, and is a synthesis that will change over time.
Purpose of SotA reviews
SotA reviews create a subjectively informed summary of modern thinking about a topic. As a chronologically ordered synthesis, SotA reviews describe the history of turning points in researchers’ understanding of a phenomenon to contextualize a description of modern scientific thinking on the topic. The review presents an argument about how the literature could be interpreted; it is not a definitive statement about how the literature should or must be interpreted. A SotA review explores: the pivotal points shaping the historical development of a topic, the factors that informed those changes in understanding, and the ways of thinking about and studying the topic that could inform the generation of further insights. In other words, the purpose of SotA reviews is to create a three-part argument: This is where we are now in our understanding of this topic. This is how we got here. This is where we could go next.
The SotA methodology
Based on study findings and analyses, we constructed a six-stage SotA review methodology. This six-stage approach is summarized and guiding questions are offered in Tab. 1 .
Stage 1: Determine initial research question and field of inquiry
In Stage 1, the researcher(s) creates an initial description of the topic to be summarized and so must determine what field of knowledge (and/or practice) the search will address. Knowledge developed through the SotA review process is shaped by the context informing it; thus, knowing the domain in which the review will be conducted is part of the review’s foundational work.
Stage 2: Determine timeframe
This stage involves determining the period of time that will be defined as SotA for the topic being summarized. The researcher(s) should engage in a broad-scope overview of the literature, reading across the range of literature available to develop insights into the historical development of knowledge on the topic, including the turning points that shape the current ways of thinking about a topic. Understanding the full body of literature is required to decide the dates or events that demarcate the timeframe of now in the first of the SotA’s three-part argument: where we are now . Stage 2 is complete when the researcher(s) can explicitly justify why a specific year or event is the right moment to mark the beginning of state-of-the-art thinking about the topic being summarized.
Stage 3: Finalize research question(s) to reflect timeframe
Based on the insights developed in Stage 2, the researcher(s) will likely need to revise their initial description of the topic to be summarized. The formal research question(s) framing the SotA review are finalized in Stage 3. The revised description of the topic, the research question(s), and the justification for the timeline start year must be reported in the review article. These are markers of rigor and prerequisites for moving to Stage 4.
Stage 4: Develop search strategy to find relevant articles
In Stage 4, the researcher(s) develops a search strategy to identify the literature that will be included in the SotA review. The researcher(s) needs to determine which literature databases contain articles from the domain of interest. Because the review describes how we got here , the review must include literature that predates the state-of-the-art timeframe, determined in Stage 2, to offer this historical perspective.
Developing the search strategy will be an iterative process of testing and revising the search strategy to enable the researcher(s) to capture the breadth of literature required to meet the SotA review purposes. A librarian should be consulted since their expertise can expedite the search processes and ensure that relevant resources are identified. The search strategy must be reported (e.g., in the manuscript itself or in a supplemental file) so that others may replicate the process if they so choose (e.g., to construct a different SotA review [and possible different interpretations] of the same literature). This too is a marker of rigor for SotA reviews: the search strategies informing the identification of literature must be reported.
Stage 5: Analyses
The literature analysis undertaken will reflect the subjective insights of the researcher(s); however, the foundational premises of inductive research should inform the analysis process. Therefore, the researcher(s) should begin by reading the articles in the corpus to become familiar with the literature. This familiarization work includes: noting similarities across articles, observing ways-of-thinking that have shaped current understandings of the topic, remarking on assumptions underpinning changes in understandings, identifying important decision points in the evolution of understanding, and taking notice of gaps and assumptions in current knowledge.
The researcher(s) can then generate premises for the state-of-the-art understanding of the history that gave rise to modern thinking, of the current body of knowledge, and of potential future directions for research. In this stage of the analysis, the researcher(s) should document the articles that support or contradict their premises, noting any collections of authors or schools of thinking that have dominated the literature, searching for marginalized points of view, and studying the factors that contributed to the dominance of particular ways of thinking. The researcher(s) should also observe historical decision points that could be revisited. Theory can be incorporated at this stage to help shape insights and understandings. It should be highlighted that not all corpus articles will be used in the SotA review; instead, the researcher(s) will sample across the corpus to construct a timeline that represents the seminal moments of the historical development of knowledge.
Next, the researcher(s) should verify the thoroughness and strength of their interpretations. To do this, the researcher(s) can select different articles included in the corpus and examine if those articles reflect the premises the researcher(s) set out. The researcher(s) may also seek out contradictory interpretations in the literature to be sure their summary refutes these positions. The goal of this verification work is not to engage in a triangulation process to ensure objectivity; instead, this process helps the researcher(s) ensure the interpretations made in the SotA review represent the articles being synthesized and respond to the interpretations offered by others. This is another marker of rigor for SotA reviews: the authors should engage in and report how they considered and accounted for differing interpretations of the literature, and how they verified the thoroughness of their interpretations.
Stage 6: Reflexivity
Given the relativist subjectivism of a SotA review, it is important that the manuscript offer insights into the subjectivity of the researcher(s). This reflexivity description should articulate how the subjectivity of the researcher(s) informed interpretations of the data. These reflections will also influence the suggested directions offered in the last part of the SotA three-part argument: where we could go next. This is the last marker of rigor for SotA reviews: researcher reflexivity must be considered and reported.
SotA reviews have much to offer our field since they provide information on the historical progression of medical education’s understanding of a topic, the turning points that guided that understanding, and the potential next directions for future research. Those future directions may question the soundness of turning points and prior decisions, and thereby offer new paths of investigation. Since we were unable to find a description of the SotA review methodology, we inductively developed a description of the methodology—including its paradigmatic roots, the processes to be followed, and the markers of rigor—so that scholars can harness the unique affordances of this type of knowledge synthesis.
Given their chronology- and turning point-based orientation, SotA reviews are inherently different from other types of knowledge synthesis. For example, systematic reviews focus on specific research questions that are narrow in scope [ 32 , 33 ]; in contrast, SotA reviews present a broader historical overview of knowledge development and the decisions that gave rise to our modern understandings. Scoping reviews focus on mapping the present state of knowledge about a phenomenon including, for example, the data that are currently available, the nature of that data, and the gaps in knowledge [ 34 , 35 ]; conversely, SotA reviews offer interpretations of the historical progression of knowledge relating to a phenomenon centered on significant shifts that occurred during that history. SotA reviews focus on the turning points in the history of knowledge development to suggest how different decisions could give rise to new insights. Critical reviews draw on literature outside of the domain of focus to see if external literature can offer new ways of thinking about the phenomenon of interest (e.g., drawing on insights from insects’ swarm intelligence to better understand healthcare team adaptation [ 36 ]). SotA reviews focus on one domain’s body of literature to construct a timeline of knowledge development, demarcating where we are now, demonstrating how this understanding came to be via different turning points, and offering new research directions. Certainly, SotA reviews offer a unique kind of knowledge synthesis.
Our six-stage process for conducting these reviews reflects the subjectivist relativism that underpins the methodology. It aligns with the requirements proposed by others [ 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 ], what has been written about SotA reviews [ 4 , 5 ], and the current body of published SotA reviews. In contrast to existing guidance [ 4 , 5 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 ], our description offers a detailed reporting of the ontology, epistemology, and methodology processes for conducting the SotA review.
This explicit methodology description is essential since many academic journals list SotA reviews as an accepted type of literature review. For instance, Educational Research Review [ 24 ], the American Academy of Pediatrics [ 25 ], and Thorax all lists SotA reviews as one of the types of knowledge syntheses they accept [ 27 ]. However, while SotA reviews are valued by academia, guidelines or specific methodology descriptions for researchers to follow when conducting this type of knowledge synthesis are conspicuously absent. If academics in general, and medical education more specifically, are to take advantage of the insights that SotA reviews can offer, we need to rigorously engage in this synthesis work; to do that, we need clear descriptions of the methodology underpinning this review. This article offers such a description. We hope that more medical educators will conduct SotA reviews to generate insights that will contribute to further advancing our field’s research and scholarship.
Cooper HM. Organizing knowledge syntheses: a taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowl Soc. 1988;1:104.
Google Scholar
Badger D, Nursten J, Williams P, Woodward M. Should all literature reviews be systematic? Eval Res Educ. 2000;14:220–30.
Article Google Scholar
Snyder H. Literature review as a research methodology: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res. 2019;104:333–9.
Grant MJ, Booth A. A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Info Libr J. 2009;26:91–108.
Sutton A, Clowes M, Preston L, Booth A. Meeting the review family: exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements. Health Info Libr J. 2019;36:202–22.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Prisma Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000097.
Tricco AC, Langlois E, Straus SE, World Health Organization, Alliance for Health Policy and Systems Research. Rapid reviews to strengthen health policy and systems: a practical guide. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017.
Jackson R, Feder G. Guidelines for clinical guidelines: a simple, pragmatic strategy for guideline development. Br Med J. 1998;317:427–8.
Greenhalgh T, Thorne S, Malterud K. Time to challenge the spurious hierarchy of systematic over narrative reviews? Eur J Clin Invest. 2018;48:e12931.
Bach QV, Chen WH. Pyrolysis characteristics and kinetics of microalgae via thermogravimetric analysis (TGA): a state-of-the-art review. Bioresour Technol. 2017;246:88–100.
Garofalo C, Milanović V, Cardinali F, Aquilanti L, Clementi F, Osimani A. Current knowledge on the microbiota of edible insects intended for human consumption: a state-of-the-art review. Food Res Int. 2019;125:108527.
Carbone S, Dixon DL, Buckley LF, Abbate A. Glucose-lowering therapies for cardiovascular risk reduction in type 2 diabetes mellitus: state-of-the-art review. Mayo Clin Proc. 2018;93:1629–47.
Hofkens PJ, Verrijcken A, Merveille K, et al. Common pitfalls and tips and tricks to get the most out of your transpulmonary thermodilution device: results of a survey and state-of-the-art review. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2015;47:89–116.
Schuwirth LW, van der Vleuten CP. A history of assessment in medical education. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2020;25:1045–56.
Arena A, Prete F, Rambaldi E, et al. Nanostructured zirconia-based ceramics and composites in dentistry: a state-of-the-art review. Nanomaterials. 2019;9:1393.
Bahraminasab M, Farahmand F. State of the art review on design and manufacture of hybrid biomedical materials: hip and knee prostheses. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2017;231:785–813.
Maggio LA, Costello JA, Norton C, Driessen EW, Artino AR Jr. Knowledge syntheses in medical education: a bibliometric analysis. Perspect Med Educ. 2021;10:79–87.
McGaghie WC, Issenberg SB, Petrusa ER, Scalese RJ. A critical review of simulation-based medical education research: 2003–2009. Med Educ. 2010;44:50–63.
Krishnan DG, Keloth AV, Ubedulla S. Pros and cons of simulation in medical education: a review. Education. 2017;3:84–7.
National Library of Medicine. MEDLINE: overview. 2021. https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medline/medline_overview.html . Accessed 17 Dec 2021.
Bergman E, de Feijter J, Frambach J, et al. AM last page: a guide to research paradigms relevant to medical education. Acad Med. 2012;87:545.
Maggio LA, Samuel A, Stellrecht E. Systematic reviews in medical education. J Grad Med Educ. 2022;14:171–5.
Bandari J, Wessel CB, Jacobs BL. Comparative effectiveness in urology: a state of the art review utilizing a systematic approach. Curr Opin Urol. 2017;27:380–94.
Elsevier. A guide for writing scholarly articles or reviews for the educational research review. 2010. https://www.elsevier.com/__data/promis_misc/edurevReviewPaperWriting.pdf . Accessed 3 Mar 2020.
American Academy of Pediatrics. Pediatrics author guidelines. 2020. https://pediatrics.aappublications.org/page/author-guidelines . Accessed 3 Mar 2020.
Journal of the American College of Cardiology. JACC instructions for authors. 2020. https://www.jacc.org/pb-assets/documents/author-instructions-jacc-1598995793940.pdf . Accessed 3 Mar 2020.
Thorax. Authors. 2020. https://thorax.bmj.com/pages/authors/ . Accessed 3 Mar 2020.
Berven S, Carl A. State of the art review. Spine Deform. 2019;7:381.
Ilardi CR, Chieffi S, Iachini T, Iavarone A. Neuropsychology of posteromedial parietal cortex and conversion factors from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease: systematic search and state-of-the-art review. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2022;34:289–307.
Chan KS, Zary N. Applications and challenges of implementing artificial intelligence in medical education: integrative review. JMIR Med Educ. 2019;5:e13930.
World Health Organization. Framework for action on interprofessional education and collaborative practice. 2010. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/framework-for-action-on-interprofessional-education-collaborative-practice . Accessed July 1 2021.
Hammersley M. On ‘systematic’ reviews of research literatures: a ‘narrative’ response to Evans & Benefield. Br Educ Res J. 2001;27:543–54.
Chen F, Lui AM, Martinelli SM. A systematic review of the effectiveness of flipped classrooms in medical education. Med Educ. 2017;51:585–97.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8:19–32.
Matsas B, Goralnick E, Bass M, Barnett E, Nagle B, Sullivan E. Leadership development in US undergraduate medical education: a scoping review of curricular content and competency frameworks. Acad Med. 2022;97:899–908.
Cristancho SM. On collective self-healing and traces: How can swarm intelligence help us think differently about team adaptation? Med Educ. 2021;55:441–7.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank Rhonda Allard for her help with the literature review and compiling all available articles. We also want to thank the PME editors who offered excellent development and refinement suggestions that greatly improved this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Anesthesiology, F. Edward Hébert School of Medicine, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, MD, USA
Erin S. Barry
School of Health Professions Education (SHE), Maastricht University, Maastricht, The Netherlands
Department of Medicine, F. Edward Hébert School of Medicine, Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, MD, USA
Jerusalem Merkebu & Lara Varpio
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Erin S. Barry .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
E.S. Barry, J. Merkebu and L. Varpio declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
The opinions and assertions contained in this article are solely those of the authors and are not to be construed as reflecting the views of the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences, the Department of Defense, or the Henry M. Jackson Foundation for the Advancement of Military Medicine.
Supplementary Information
40037_2022_725_moesm1_esm.docx.
For information regarding the search strategy to develop the corpus and search strategy for confirming capture of any available State of the Art review methodology descriptions. Additionally, a list of the methodology articles found through the search strategy/corpus is included
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Barry, E.S., Merkebu, J. & Varpio, L. State-of-the-art literature review methodology: A six-step approach for knowledge synthesis. Perspect Med Educ 11 , 281–288 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40037-022-00725-9
Download citation
Received : 03 December 2021
Revised : 25 July 2022
Accepted : 27 July 2022
Published : 05 September 2022
Issue Date : October 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40037-022-00725-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- State-of-the-art literature review
- Literature review
- Literature review methodology
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 7 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
Research Methods
- Getting Started
- Literature Review Research
- Research Design
- Research Design By Discipline
- SAGE Research Methods
- Teaching with SAGE Research Methods
Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- What is NOT a Literature Review?
- Purposes of a Literature Review
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Literature Reviews vs. Systematic Reviews
- Systematic vs. Meta-Analysis
Literature Review is a comprehensive survey of the works published in a particular field of study or line of research, usually over a specific period of time, in the form of an in-depth, critical bibliographic essay or annotated list in which attention is drawn to the most significant works.
Also, we can define a literature review as the collected body of scholarly works related to a topic:
- Summarizes and analyzes previous research relevant to a topic
- Includes scholarly books and articles published in academic journals
- Can be an specific scholarly paper or a section in a research paper
The objective of a Literature Review is to find previous published scholarly works relevant to an specific topic
- Help gather ideas or information
- Keep up to date in current trends and findings
- Help develop new questions
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Helps focus your own research questions or problems
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Suggests unexplored ideas or populations
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
- Identifies critical gaps, points of disagreement, or potentially flawed methodology or theoretical approaches.
- Indicates potential directions for future research.
All content in this section is from Literature Review Research from Old Dominion University
Keep in mind the following, a literature review is NOT:
Not an essay
Not an annotated bibliography in which you summarize each article that you have reviewed. A literature review goes beyond basic summarizing to focus on the critical analysis of the reviewed works and their relationship to your research question.
Not a research paper where you select resources to support one side of an issue versus another. A lit review should explain and consider all sides of an argument in order to avoid bias, and areas of agreement and disagreement should be highlighted.
A literature review serves several purposes. For example, it
- provides thorough knowledge of previous studies; introduces seminal works.
- helps focus one’s own research topic.
- identifies a conceptual framework for one’s own research questions or problems; indicates potential directions for future research.
- suggests previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, quantitative and qualitative strategies.
- identifies gaps in previous studies; identifies flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches; avoids replication of mistakes.
- helps the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research.
- suggests unexplored populations.
- determines whether past studies agree or disagree; identifies controversy in the literature.
- tests assumptions; may help counter preconceived ideas and remove unconscious bias.
As Kennedy (2007) notes*, it is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the original studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally that become part of the lore of field. In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews.
Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are several approaches to how they can be done, depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study. Listed below are definitions of types of literature reviews:
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply imbedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews.
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical reviews are focused on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [content], but how they said it [method of analysis]. This approach provides a framework of understanding at different levels (i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches and data collection and analysis techniques), enables researchers to draw on a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection and data analysis, and helps highlight many ethical issues which we should be aware of and consider as we go through our study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyse data from the studies that are included in the review. Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?"
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to concretely examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review help establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
* Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147.
All content in this section is from The Literature Review created by Dr. Robert Larabee USC
Robinson, P. and Lowe, J. (2015), Literature reviews vs systematic reviews. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, 39: 103-103. doi: 10.1111/1753-6405.12393

What's in the name? The difference between a Systematic Review and a Literature Review, and why it matters . By Lynn Kysh from University of Southern California

Systematic review or meta-analysis?
A systematic review answers a defined research question by collecting and summarizing all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria.
A meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of these studies.
Systematic reviews, just like other research articles, can be of varying quality. They are a significant piece of work (the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination at York estimates that a team will take 9-24 months), and to be useful to other researchers and practitioners they should have:
- clearly stated objectives with pre-defined eligibility criteria for studies
- explicit, reproducible methodology
- a systematic search that attempts to identify all studies
- assessment of the validity of the findings of the included studies (e.g. risk of bias)
- systematic presentation, and synthesis, of the characteristics and findings of the included studies
Not all systematic reviews contain meta-analysis.
Meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects of health care than those derived from the individual studies included within a review. More information on meta-analyses can be found in Cochrane Handbook, Chapter 9 .
A meta-analysis goes beyond critique and integration and conducts secondary statistical analysis on the outcomes of similar studies. It is a systematic review that uses quantitative methods to synthesize and summarize the results.
An advantage of a meta-analysis is the ability to be completely objective in evaluating research findings. Not all topics, however, have sufficient research evidence to allow a meta-analysis to be conducted. In that case, an integrative review is an appropriate strategy.
Some of the content in this section is from Systematic reviews and meta-analyses: step by step guide created by Kate McAllister.
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Research Design >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2023 4:07 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.udel.edu/researchmethods
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral

Research Methods: Literature Reviews
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Literature Reviews
- Scoping Reviews
- Systematic Reviews
- Scholarship of Teaching and Learning
- Persuasive Arguments
- Subject Specific Methodology
A literature review involves researching, reading, analyzing, evaluating, and summarizing scholarly literature (typically journals and articles) about a specific topic. The results of a literature review may be an entire report or article OR may be part of a article, thesis, dissertation, or grant proposal. A literature review helps the author learn about the history and nature of their topic, and identify research gaps and problems.
Steps & Elements
Problem formulation
- Determine your topic and its components by asking a question
- Research: locate literature related to your topic to identify the gap(s) that can be addressed
- Read: read the articles or other sources of information
- Analyze: assess the findings for relevancy
- Evaluating: determine how the article are relevant to your research and what are the key findings
- Synthesis: write about the key findings and how it is relevant to your research
Elements of a Literature Review
- Summarize subject, issue or theory under consideration, along with objectives of the review
- Divide works under review into categories (e.g. those in support of a particular position, those against, those offering alternative theories entirely)
- Explain how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others
- Conclude which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of an area of research
Writing a Literature Review Resources
- How to Write a Literature Review From the Wesleyan University Library
- Write a Literature Review From the University of California Santa Cruz Library. A Brief overview of a literature review, includes a list of stages for writing a lit review.
- Literature Reviews From the University of North Carolina Writing Center. Detailed information about writing a literature review.
- Undertaking a literature review: a step-by-step approach Cronin, P., Ryan, F., & Coughan, M. (2008). Undertaking a literature review: A step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing, 17(1), p.38-43
Literature Review Tutorial
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliographies
- Next: Scoping Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Feb 29, 2024 12:00 PM
- URL: https://guides.auraria.edu/researchmethods
1100 Lawrence Street Denver, CO 80204 303-315-7700 Ask Us Directions
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.

- University of Texas Libraries

Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE: Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: May 30, 2024 9:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Wiley Open Access Collection

An overview of methodological approaches in systematic reviews
Prabhakar veginadu.
1 Department of Rural Clinical Sciences, La Trobe Rural Health School, La Trobe University, Bendigo Victoria, Australia
Hanny Calache
2 Lincoln International Institute for Rural Health, University of Lincoln, Brayford Pool, Lincoln UK
Akshaya Pandian
3 Department of Orthodontics, Saveetha Dental College, Chennai Tamil Nadu, India
Mohd Masood
Associated data.
APPENDIX B: List of excluded studies with detailed reasons for exclusion
APPENDIX C: Quality assessment of included reviews using AMSTAR 2
The aim of this overview is to identify and collate evidence from existing published systematic review (SR) articles evaluating various methodological approaches used at each stage of an SR.
The search was conducted in five electronic databases from inception to November 2020 and updated in February 2022: MEDLINE, Embase, Web of Science Core Collection, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, and APA PsycINFO. Title and abstract screening were performed in two stages by one reviewer, supported by a second reviewer. Full‐text screening, data extraction, and quality appraisal were performed by two reviewers independently. The quality of the included SRs was assessed using the AMSTAR 2 checklist.
The search retrieved 41,556 unique citations, of which 9 SRs were deemed eligible for inclusion in final synthesis. Included SRs evaluated 24 unique methodological approaches used for defining the review scope and eligibility, literature search, screening, data extraction, and quality appraisal in the SR process. Limited evidence supports the following (a) searching multiple resources (electronic databases, handsearching, and reference lists) to identify relevant literature; (b) excluding non‐English, gray, and unpublished literature, and (c) use of text‐mining approaches during title and abstract screening.
The overview identified limited SR‐level evidence on various methodological approaches currently employed during five of the seven fundamental steps in the SR process, as well as some methodological modifications currently used in expedited SRs. Overall, findings of this overview highlight the dearth of published SRs focused on SR methodologies and this warrants future work in this area.
1. INTRODUCTION
Evidence synthesis is a prerequisite for knowledge translation. 1 A well conducted systematic review (SR), often in conjunction with meta‐analyses (MA) when appropriate, is considered the “gold standard” of methods for synthesizing evidence related to a topic of interest. 2 The central strength of an SR is the transparency of the methods used to systematically search, appraise, and synthesize the available evidence. 3 Several guidelines, developed by various organizations, are available for the conduct of an SR; 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 among these, Cochrane is considered a pioneer in developing rigorous and highly structured methodology for the conduct of SRs. 8 The guidelines developed by these organizations outline seven fundamental steps required in SR process: defining the scope of the review and eligibility criteria, literature searching and retrieval, selecting eligible studies, extracting relevant data, assessing risk of bias (RoB) in included studies, synthesizing results, and assessing certainty of evidence (CoE) and presenting findings. 4 , 5 , 6 , 7
The methodological rigor involved in an SR can require a significant amount of time and resource, which may not always be available. 9 As a result, there has been a proliferation of modifications made to the traditional SR process, such as refining, shortening, bypassing, or omitting one or more steps, 10 , 11 for example, limits on the number and type of databases searched, limits on publication date, language, and types of studies included, and limiting to one reviewer for screening and selection of studies, as opposed to two or more reviewers. 10 , 11 These methodological modifications are made to accommodate the needs of and resource constraints of the reviewers and stakeholders (e.g., organizations, policymakers, health care professionals, and other knowledge users). While such modifications are considered time and resource efficient, they may introduce bias in the review process reducing their usefulness. 5
Substantial research has been conducted examining various approaches used in the standardized SR methodology and their impact on the validity of SR results. There are a number of published reviews examining the approaches or modifications corresponding to single 12 , 13 or multiple steps 14 involved in an SR. However, there is yet to be a comprehensive summary of the SR‐level evidence for all the seven fundamental steps in an SR. Such a holistic evidence synthesis will provide an empirical basis to confirm the validity of current accepted practices in the conduct of SRs. Furthermore, sometimes there is a balance that needs to be achieved between the resource availability and the need to synthesize the evidence in the best way possible, given the constraints. This evidence base will also inform the choice of modifications to be made to the SR methods, as well as the potential impact of these modifications on the SR results. An overview is considered the choice of approach for summarizing existing evidence on a broad topic, directing the reader to evidence, or highlighting the gaps in evidence, where the evidence is derived exclusively from SRs. 15 Therefore, for this review, an overview approach was used to (a) identify and collate evidence from existing published SR articles evaluating various methodological approaches employed in each of the seven fundamental steps of an SR and (b) highlight both the gaps in the current research and the potential areas for future research on the methods employed in SRs.
An a priori protocol was developed for this overview but was not registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO), as the review was primarily methodological in nature and did not meet PROSPERO eligibility criteria for registration. The protocol is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. This overview was conducted based on the guidelines for the conduct of overviews as outlined in The Cochrane Handbook. 15 Reporting followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta‐analyses (PRISMA) statement. 3
2.1. Eligibility criteria
Only published SRs, with or without associated MA, were included in this overview. We adopted the defining characteristics of SRs from The Cochrane Handbook. 5 According to The Cochrane Handbook, a review was considered systematic if it satisfied the following criteria: (a) clearly states the objectives and eligibility criteria for study inclusion; (b) provides reproducible methodology; (c) includes a systematic search to identify all eligible studies; (d) reports assessment of validity of findings of included studies (e.g., RoB assessment of the included studies); (e) systematically presents all the characteristics or findings of the included studies. 5 Reviews that did not meet all of the above criteria were not considered a SR for this study and were excluded. MA‐only articles were included if it was mentioned that the MA was based on an SR.
SRs and/or MA of primary studies evaluating methodological approaches used in defining review scope and study eligibility, literature search, study selection, data extraction, RoB assessment, data synthesis, and CoE assessment and reporting were included. The methodological approaches examined in these SRs and/or MA can also be related to the substeps or elements of these steps; for example, applying limits on date or type of publication are the elements of literature search. Included SRs examined or compared various aspects of a method or methods, and the associated factors, including but not limited to: precision or effectiveness; accuracy or reliability; impact on the SR and/or MA results; reproducibility of an SR steps or bias occurred; time and/or resource efficiency. SRs assessing the methodological quality of SRs (e.g., adherence to reporting guidelines), evaluating techniques for building search strategies or the use of specific database filters (e.g., use of Boolean operators or search filters for randomized controlled trials), examining various tools used for RoB or CoE assessment (e.g., ROBINS vs. Cochrane RoB tool), or evaluating statistical techniques used in meta‐analyses were excluded. 14
2.2. Search
The search for published SRs was performed on the following scientific databases initially from inception to third week of November 2020 and updated in the last week of February 2022: MEDLINE (via Ovid), Embase (via Ovid), Web of Science Core Collection, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, and American Psychological Association (APA) PsycINFO. Search was restricted to English language publications. Following the objectives of this study, study design filters within databases were used to restrict the search to SRs and MA, where available. The reference lists of included SRs were also searched for potentially relevant publications.
The search terms included keywords, truncations, and subject headings for the key concepts in the review question: SRs and/or MA, methods, and evaluation. Some of the terms were adopted from the search strategy used in a previous review by Robson et al., which reviewed primary studies on methodological approaches used in study selection, data extraction, and quality appraisal steps of SR process. 14 Individual search strategies were developed for respective databases by combining the search terms using appropriate proximity and Boolean operators, along with the related subject headings in order to identify SRs and/or MA. 16 , 17 A senior librarian was consulted in the design of the search terms and strategy. Appendix A presents the detailed search strategies for all five databases.
2.3. Study selection and data extraction
Title and abstract screening of references were performed in three steps. First, one reviewer (PV) screened all the titles and excluded obviously irrelevant citations, for example, articles on topics not related to SRs, non‐SR publications (such as randomized controlled trials, observational studies, scoping reviews, etc.). Next, from the remaining citations, a random sample of 200 titles and abstracts were screened against the predefined eligibility criteria by two reviewers (PV and MM), independently, in duplicate. Discrepancies were discussed and resolved by consensus. This step ensured that the responses of the two reviewers were calibrated for consistency in the application of the eligibility criteria in the screening process. Finally, all the remaining titles and abstracts were reviewed by a single “calibrated” reviewer (PV) to identify potential full‐text records. Full‐text screening was performed by at least two authors independently (PV screened all the records, and duplicate assessment was conducted by MM, HC, or MG), with discrepancies resolved via discussions or by consulting a third reviewer.
Data related to review characteristics, results, key findings, and conclusions were extracted by at least two reviewers independently (PV performed data extraction for all the reviews and duplicate extraction was performed by AP, HC, or MG).
2.4. Quality assessment of included reviews
The quality assessment of the included SRs was performed using the AMSTAR 2 (A MeaSurement Tool to Assess systematic Reviews). The tool consists of a 16‐item checklist addressing critical and noncritical domains. 18 For the purpose of this study, the domain related to MA was reclassified from critical to noncritical, as SRs with and without MA were included. The other six critical domains were used according to the tool guidelines. 18 Two reviewers (PV and AP) independently responded to each of the 16 items in the checklist with either “yes,” “partial yes,” or “no.” Based on the interpretations of the critical and noncritical domains, the overall quality of the review was rated as high, moderate, low, or critically low. 18 Disagreements were resolved through discussion or by consulting a third reviewer.
2.5. Data synthesis
To provide an understandable summary of existing evidence syntheses, characteristics of the methods evaluated in the included SRs were examined and key findings were categorized and presented based on the corresponding step in the SR process. The categories of key elements within each step were discussed and agreed by the authors. Results of the included reviews were tabulated and summarized descriptively, along with a discussion on any overlap in the primary studies. 15 No quantitative analyses of the data were performed.
From 41,556 unique citations identified through literature search, 50 full‐text records were reviewed, and nine systematic reviews 14 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 were deemed eligible for inclusion. The flow of studies through the screening process is presented in Figure 1 . A list of excluded studies with reasons can be found in Appendix B .

Study selection flowchart
3.1. Characteristics of included reviews
Table 1 summarizes the characteristics of included SRs. The majority of the included reviews (six of nine) were published after 2010. 14 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 Four of the nine included SRs were Cochrane reviews. 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 The number of databases searched in the reviews ranged from 2 to 14, 2 reviews searched gray literature sources, 24 , 25 and 7 reviews included a supplementary search strategy to identify relevant literature. 14 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 26 Three of the included SRs (all Cochrane reviews) included an integrated MA. 20 , 21 , 23
Characteristics of included studies
SR = systematic review; MA = meta‐analysis; RCT = randomized controlled trial; CCT = controlled clinical trial; N/R = not reported.
The included SRs evaluated 24 unique methodological approaches (26 in total) used across five steps in the SR process; 8 SRs evaluated 6 approaches, 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 while 1 review evaluated 18 approaches. 14 Exclusion of gray or unpublished literature 21 , 26 and blinding of reviewers for RoB assessment 14 , 23 were evaluated in two reviews each. Included SRs evaluated methods used in five different steps in the SR process, including methods used in defining the scope of review ( n = 3), literature search ( n = 3), study selection ( n = 2), data extraction ( n = 1), and RoB assessment ( n = 2) (Table 2 ).
Summary of findings from review evaluating systematic review methods
There was some overlap in the primary studies evaluated in the included SRs on the same topics: Schmucker et al. 26 and Hopewell et al. 21 ( n = 4), Hopewell et al. 20 and Crumley et al. 19 ( n = 30), and Robson et al. 14 and Morissette et al. 23 ( n = 4). There were no conflicting results between any of the identified SRs on the same topic.
3.2. Methodological quality of included reviews
Overall, the quality of the included reviews was assessed as moderate at best (Table 2 ). The most common critical weakness in the reviews was failure to provide justification for excluding individual studies (four reviews). Detailed quality assessment is provided in Appendix C .
3.3. Evidence on systematic review methods
3.3.1. methods for defining review scope and eligibility.
Two SRs investigated the effect of excluding data obtained from gray or unpublished sources on the pooled effect estimates of MA. 21 , 26 Hopewell et al. 21 reviewed five studies that compared the impact of gray literature on the results of a cohort of MA of RCTs in health care interventions. Gray literature was defined as information published in “print or electronic sources not controlled by commercial or academic publishers.” Findings showed an overall greater treatment effect for published trials than trials reported in gray literature. In a more recent review, Schmucker et al. 26 addressed similar objectives, by investigating gray and unpublished data in medicine. In addition to gray literature, defined similar to the previous review by Hopewell et al., the authors also evaluated unpublished data—defined as “supplemental unpublished data related to published trials, data obtained from the Food and Drug Administration or other regulatory websites or postmarketing analyses hidden from the public.” The review found that in majority of the MA, excluding gray literature had little or no effect on the pooled effect estimates. The evidence was limited to conclude if the data from gray and unpublished literature had an impact on the conclusions of MA. 26
Morrison et al. 24 examined five studies measuring the effect of excluding non‐English language RCTs on the summary treatment effects of SR‐based MA in various fields of conventional medicine. Although none of the included studies reported major difference in the treatment effect estimates between English only and non‐English inclusive MA, the review found inconsistent evidence regarding the methodological and reporting quality of English and non‐English trials. 24 As such, there might be a risk of introducing “language bias” when excluding non‐English language RCTs. The authors also noted that the numbers of non‐English trials vary across medical specialties, as does the impact of these trials on MA results. Based on these findings, Morrison et al. 24 conclude that literature searches must include non‐English studies when resources and time are available to minimize the risk of introducing “language bias.”
3.3.2. Methods for searching studies
Crumley et al. 19 analyzed recall (also referred to as “sensitivity” by some researchers; defined as “percentage of relevant studies identified by the search”) and precision (defined as “percentage of studies identified by the search that were relevant”) when searching a single resource to identify randomized controlled trials and controlled clinical trials, as opposed to searching multiple resources. The studies included in their review frequently compared a MEDLINE only search with the search involving a combination of other resources. The review found low median recall estimates (median values between 24% and 92%) and very low median precisions (median values between 0% and 49%) for most of the electronic databases when searched singularly. 19 A between‐database comparison, based on the type of search strategy used, showed better recall and precision for complex and Cochrane Highly Sensitive search strategies (CHSSS). In conclusion, the authors emphasize that literature searches for trials in SRs must include multiple sources. 19
In an SR comparing handsearching and electronic database searching, Hopewell et al. 20 found that handsearching retrieved more relevant RCTs (retrieval rate of 92%−100%) than searching in a single electronic database (retrieval rates of 67% for PsycINFO/PsycLIT, 55% for MEDLINE, and 49% for Embase). The retrieval rates varied depending on the quality of handsearching, type of electronic search strategy used (e.g., simple, complex or CHSSS), and type of trial reports searched (e.g., full reports, conference abstracts, etc.). The authors concluded that handsearching was particularly important in identifying full trials published in nonindexed journals and in languages other than English, as well as those published as abstracts and letters. 20
The effectiveness of checking reference lists to retrieve additional relevant studies for an SR was investigated by Horsley et al. 22 The review reported that checking reference lists yielded 2.5%–40% more studies depending on the quality and comprehensiveness of the electronic search used. The authors conclude that there is some evidence, although from poor quality studies, to support use of checking reference lists to supplement database searching. 22
3.3.3. Methods for selecting studies
Three approaches relevant to reviewer characteristics, including number, experience, and blinding of reviewers involved in the screening process were highlighted in an SR by Robson et al. 14 Based on the retrieved evidence, the authors recommended that two independent, experienced, and unblinded reviewers be involved in study selection. 14 A modified approach has also been suggested by the review authors, where one reviewer screens and the other reviewer verifies the list of excluded studies, when the resources are limited. It should be noted however this suggestion is likely based on the authors’ opinion, as there was no evidence related to this from the studies included in the review.
Robson et al. 14 also reported two methods describing the use of technology for screening studies: use of Google Translate for translating languages (for example, German language articles to English) to facilitate screening was considered a viable method, while using two computer monitors for screening did not increase the screening efficiency in SR. Title‐first screening was found to be more efficient than simultaneous screening of titles and abstracts, although the gain in time with the former method was lesser than the latter. Therefore, considering that the search results are routinely exported as titles and abstracts, Robson et al. 14 recommend screening titles and abstracts simultaneously. However, the authors note that these conclusions were based on very limited number (in most instances one study per method) of low‐quality studies. 14
3.3.4. Methods for data extraction
Robson et al. 14 examined three approaches for data extraction relevant to reviewer characteristics, including number, experience, and blinding of reviewers (similar to the study selection step). Although based on limited evidence from a small number of studies, the authors recommended use of two experienced and unblinded reviewers for data extraction. The experience of the reviewers was suggested to be especially important when extracting continuous outcomes (or quantitative) data. However, when the resources are limited, data extraction by one reviewer and a verification of the outcomes data by a second reviewer was recommended.
As for the methods involving use of technology, Robson et al. 14 identified limited evidence on the use of two monitors to improve the data extraction efficiency and computer‐assisted programs for graphical data extraction. However, use of Google Translate for data extraction in non‐English articles was not considered to be viable. 14 In the same review, Robson et al. 14 identified evidence supporting contacting authors for obtaining additional relevant data.
3.3.5. Methods for RoB assessment
Two SRs examined the impact of blinding of reviewers for RoB assessments. 14 , 23 Morissette et al. 23 investigated the mean differences between the blinded and unblinded RoB assessment scores and found inconsistent differences among the included studies providing no definitive conclusions. Similar conclusions were drawn in a more recent review by Robson et al., 14 which included four studies on reviewer blinding for RoB assessment that completely overlapped with Morissette et al. 23
Use of experienced reviewers and provision of additional guidance for RoB assessment were examined by Robson et al. 14 The review concluded that providing intensive training and guidance on assessing studies reporting insufficient data to the reviewers improves RoB assessments. 14 Obtaining additional data related to quality assessment by contacting study authors was also found to help the RoB assessments, although based on limited evidence. When assessing the qualitative or mixed method reviews, Robson et al. 14 recommends the use of a structured RoB tool as opposed to an unstructured tool. No SRs were identified on data synthesis and CoE assessment and reporting steps.
4. DISCUSSION
4.1. summary of findings.
Nine SRs examining 24 unique methods used across five steps in the SR process were identified in this overview. The collective evidence supports some current traditional and modified SR practices, while challenging other approaches. However, the quality of the included reviews was assessed to be moderate at best and in the majority of the included SRs, evidence related to the evaluated methods was obtained from very limited numbers of primary studies. As such, the interpretations from these SRs should be made cautiously.
The evidence gathered from the included SRs corroborate a few current SR approaches. 5 For example, it is important to search multiple resources for identifying relevant trials (RCTs and/or CCTs). The resources must include a combination of electronic database searching, handsearching, and reference lists of retrieved articles. 5 However, no SRs have been identified that evaluated the impact of the number of electronic databases searched. A recent study by Halladay et al. 27 found that articles on therapeutic intervention, retrieved by searching databases other than PubMed (including Embase), contributed only a small amount of information to the MA and also had a minimal impact on the MA results. The authors concluded that when the resources are limited and when large number of studies are expected to be retrieved for the SR or MA, PubMed‐only search can yield reliable results. 27
Findings from the included SRs also reiterate some methodological modifications currently employed to “expedite” the SR process. 10 , 11 For example, excluding non‐English language trials and gray/unpublished trials from MA have been shown to have minimal or no impact on the results of MA. 24 , 26 However, the efficiency of these SR methods, in terms of time and the resources used, have not been evaluated in the included SRs. 24 , 26 Of the SRs included, only two have focused on the aspect of efficiency 14 , 25 ; O'Mara‐Eves et al. 25 report some evidence to support the use of text‐mining approaches for title and abstract screening in order to increase the rate of screening. Moreover, only one included SR 14 considered primary studies that evaluated reliability (inter‐ or intra‐reviewer consistency) and accuracy (validity when compared against a “gold standard” method) of the SR methods. This can be attributed to the limited number of primary studies that evaluated these outcomes when evaluating the SR methods. 14 Lack of outcome measures related to reliability, accuracy, and efficiency precludes making definitive recommendations on the use of these methods/modifications. Future research studies must focus on these outcomes.
Some evaluated methods may be relevant to multiple steps; for example, exclusions based on publication status (gray/unpublished literature) and language of publication (non‐English language studies) can be outlined in the a priori eligibility criteria or can be incorporated as search limits in the search strategy. SRs included in this overview focused on the effect of study exclusions on pooled treatment effect estimates or MA conclusions. Excluding studies from the search results, after conducting a comprehensive search, based on different eligibility criteria may yield different results when compared to the results obtained when limiting the search itself. 28 Further studies are required to examine this aspect.
Although we acknowledge the lack of standardized quality assessment tools for methodological study designs, we adhered to the Cochrane criteria for identifying SRs in this overview. This was done to ensure consistency in the quality of the included evidence. As a result, we excluded three reviews that did not provide any form of discussion on the quality of the included studies. The methods investigated in these reviews concern supplementary search, 29 data extraction, 12 and screening. 13 However, methods reported in two of these three reviews, by Mathes et al. 12 and Waffenschmidt et al., 13 have also been examined in the SR by Robson et al., 14 which was included in this overview; in most instances (with the exception of one study included in Mathes et al. 12 and Waffenschmidt et al. 13 each), the studies examined in these excluded reviews overlapped with those in the SR by Robson et al. 14
One of the key gaps in the knowledge observed in this overview was the dearth of SRs on the methods used in the data synthesis component of SR. Narrative and quantitative syntheses are the two most commonly used approaches for synthesizing data in evidence synthesis. 5 There are some published studies on the proposed indications and implications of these two approaches. 30 , 31 These studies found that both data synthesis methods produced comparable results and have their own advantages, suggesting that the choice of the method must be based on the purpose of the review. 31 With increasing number of “expedited” SR approaches (so called “rapid reviews”) avoiding MA, 10 , 11 further research studies are warranted in this area to determine the impact of the type of data synthesis on the results of the SR.
4.2. Implications for future research
The findings of this overview highlight several areas of paucity in primary research and evidence synthesis on SR methods. First, no SRs were identified on methods used in two important components of the SR process, including data synthesis and CoE and reporting. As for the included SRs, a limited number of evaluation studies have been identified for several methods. This indicates that further research is required to corroborate many of the methods recommended in current SR guidelines. 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 Second, some SRs evaluated the impact of methods on the results of quantitative synthesis and MA conclusions. Future research studies must also focus on the interpretations of SR results. 28 , 32 Finally, most of the included SRs were conducted on specific topics related to the field of health care, limiting the generalizability of the findings to other areas. It is important that future research studies evaluating evidence syntheses broaden the objectives and include studies on different topics within the field of health care.
4.3. Strengths and limitations
To our knowledge, this is the first overview summarizing current evidence from SRs and MA on different methodological approaches used in several fundamental steps in SR conduct. The overview methodology followed well established guidelines and strict criteria defined for the inclusion of SRs.
There are several limitations related to the nature of the included reviews. Evidence for most of the methods investigated in the included reviews was derived from a limited number of primary studies. Also, the majority of the included SRs may be considered outdated as they were published (or last updated) more than 5 years ago 33 ; only three of the nine SRs have been published in the last 5 years. 14 , 25 , 26 Therefore, important and recent evidence related to these topics may not have been included. Substantial numbers of included SRs were conducted in the field of health, which may limit the generalizability of the findings. Some method evaluations in the included SRs focused on quantitative analyses components and MA conclusions only. As such, the applicability of these findings to SR more broadly is still unclear. 28 Considering the methodological nature of our overview, limiting the inclusion of SRs according to the Cochrane criteria might have resulted in missing some relevant evidence from those reviews without a quality assessment component. 12 , 13 , 29 Although the included SRs performed some form of quality appraisal of the included studies, most of them did not use a standardized RoB tool, which may impact the confidence in their conclusions. Due to the type of outcome measures used for the method evaluations in the primary studies and the included SRs, some of the identified methods have not been validated against a reference standard.
Some limitations in the overview process must be noted. While our literature search was exhaustive covering five bibliographic databases and supplementary search of reference lists, no gray sources or other evidence resources were searched. Also, the search was primarily conducted in health databases, which might have resulted in missing SRs published in other fields. Moreover, only English language SRs were included for feasibility. As the literature search retrieved large number of citations (i.e., 41,556), the title and abstract screening was performed by a single reviewer, calibrated for consistency in the screening process by another reviewer, owing to time and resource limitations. These might have potentially resulted in some errors when retrieving and selecting relevant SRs. The SR methods were grouped based on key elements of each recommended SR step, as agreed by the authors. This categorization pertains to the identified set of methods and should be considered subjective.
5. CONCLUSIONS
This overview identified limited SR‐level evidence on various methodological approaches currently employed during five of the seven fundamental steps in the SR process. Limited evidence was also identified on some methodological modifications currently used to expedite the SR process. Overall, findings highlight the dearth of SRs on SR methodologies, warranting further work to confirm several current recommendations on conventional and expedited SR processes.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Supporting information
APPENDIX A: Detailed search strategies
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The first author is supported by a La Trobe University Full Fee Research Scholarship and a Graduate Research Scholarship.
Open Access Funding provided by La Trobe University.
Veginadu P, Calache H, Gussy M, Pandian A, Masood M. An overview of methodological approaches in systematic reviews . J Evid Based Med . 2022; 15 :39–54. 10.1111/jebm.12468 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Open access
- Published: 04 June 2024
What are medical students taught about persistent physical symptoms? A scoping review of the literature
- Catie Nagel 1 ,
- Chloe Queenan 1 &
- Chris Burton 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 618 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
133 Accesses
Metrics details
Persistent Physical Symptoms (PPS) include symptoms such as chronic pain, and syndromes such as chronic fatigue. They are common, but are often inadequately managed, causing distress and higher costs for health care systems. A lack of teaching about PPS has been recognised as a contributing factor to poor management.
The authors conducted a scoping review of the literature, including all studies published before 31 March 2023. Systematic methods were used to determine what teaching on PPS was taking place for medical undergraduates. Studies were restricted to publications in English and needed to include undergraduate medical students. Teaching about cancer pain was excluded. After descriptive data was extracted, a narrative synthesis was undertaken to analyse qualitative findings.
A total of 1116 studies were found, after exclusion, from 3 databases. A further 28 studies were found by searching the grey literature and by citation analysis. After screening for relevance, a total of 57 studies were included in the review. The most commonly taught condition was chronic non-cancer pain, but overall, there was a widespread lack of teaching and learning on PPS. Several factors contributed to this lack including: educators and learners viewing the topic as awkward, learners feeling that there was no science behind the symptoms, and the topic being overlooked in the taught curriculum. The gap between the taught curriculum and learners’ experiences in practice was addressed through informal sources and this risked stigmatising attitudes towards sufferers of PPS.
Faculties need to find ways to integrate more teaching on PPS and address the barriers outlined above. Teaching on chronic non-cancer pain, which is built on a science of symptoms, can be used as an exemplar for teaching on PPS more widely. Any future teaching interventions should be robustly evaluated to ensure improvements for learners and patients.
Peer Review reports
Persistent Physical Symptoms (PPS) are symptoms which are disproportionate to currently recognised pathology and are common in all fields of medicine. The term encompasses single symptoms such as pain, dizziness or fatigue, and established syndromes including fibromyalgia and irritable bowel syndrome. It is increasingly understood that PPS arise from complex interactions between the brain and body [ 1 , 2 ]. While historically terms such as “medically unexplained symptoms” have been in common use, most symptoms can actually be explained [ 3 ] and PPS is a more acceptable term to patients [ 4 ].
PPS are common and present to nearly every medical specialty. They represent the primary reason for presentation in around 45% of general practice consultations and between 30 and 70% of presentations to neurology, gynaecology, and rheumatology outpatient clinics [ 5 ]. People with PPS suffer unduly in a medical system that is predisposed to ‘body part medicine,’ [ 6 ] resulting in what Balint referred to as the “collusion of anonymity.” [ 7 ] In other words, patients who pass from specialist to specialist, without any doctor taking full responsibility for holistic care. Patients with PPS consult more frequently [ 8 ] and tend to have a higher rate of referral to secondary care [ 9 ]. This is costly, both in financial terms and in terms of the emotional work for patients and clinicians [ 10 , 11 ]. Patients with PPS often have a poor experience of the health system and can be left feeling marginalised and even stigmatised [ 12 ].
Doctors find it difficult to consult and manage patients with persistent physical symptoms [ 8 ]. The absence of a common language of explanation to reconcile patients’ lived experience with doctors’ biomedical models, is particularly problematic [ 13 ]. It is plausible that difficulties may arise, or be perpetuated by, issues in each of the three domains of learning: cognitive (knowledge), psychomotor (skills) and affective (attitudes) [ 14 ].
The shifting perspectives, particularly around “medically unexplained symptoms” may account for historical uncertainty, however recent adoption of more consistent language and underlying models of symptoms mean that a common curriculum should be possible [ 15 ]. It is the authors’ experience that little teaching and learning at the undergraduate level has previously taken place on this topic. We wanted to find out if this was still the case, by reviewing the current medical education literature.
We carried out a scoping review with narrative synthesis following the approach of Arksey & O’Malley [ 16 ]. The PRISMA-ScR guidelines were used to structure reporting [ 17 ].
Research questions
The aim of the review was to explore the published literature regarding undergraduate medical teaching and learning on persistent physical symptoms. The specific research questions were:
What teaching and learning on persistent physical symptoms has been described for medical undergraduates?
What teaching methods have been used and how have these been evaluated?
Search strategy
We used a Population, Concept, and Context (PCC) framework to structure a systematic search. The population was undergraduate medical students, the concept was persistent physical symptoms, and the context was teaching and learning. A variety of synonyms were used in order to be inclusive, given the constant evolution of terms for persistent physical symptoms. We used adjacency searching and truncation methods in order to broaden the search as widely as possible and to account for different spellings of words or use of phrases across the international context. Search concepts were then combined using Boolean operators. No date range was used, so all studies before 31 March 2023 were included. Inclusion criteria were: studies relating to the teaching and learning of Persistent Physical Symptoms; medical students included in the population; available in the English language. Exclusion criteria were: studies about cancer or terminal pain without the inclusion of other forms of chronic or persistent pain; population not including medical students; letters to the editor, and papers which were not available in the English language. See Table 1 for the full search strategy.
Sources of evidence
Two authors searched for published literature in MEDLINE, PsycINFO, and Web of Science. Additionally, we searched Google and Google Scholar in order to include any grey literature or sources that had not been picked up by the previous search method. We employed citation analysis, by following backward citations from included papers and analysed the citations of any existing literature reviews.
Study selection
We used a two-stage screening process to identify eligible papers: first at title and abstract level and then at full text. This method was undertaken separately by two reviewers.
Literature reviews were excluded to avoid duplicated representation of primary data, but citations in these reviews were analysed to ensure consistent inclusion of studies and to check for any additional sources.
Charting the data: summary and synthesis
Summary findings for each full text article were charted to determine the most relevant items for extraction. This was an iterative process given the high degree of heterogeneity between the studies. Charting was conducted by two reviewers independently. Discrepancies in charting and data extraction were discussed in review meetings and a consensus was reached regarding which data to include for analysis.
Reviewers extracted descriptive data including: country of origin, whether the study was experimental or observational, the characteristics of the study participants, and whether any teaching intervention was evaluated. Other study characteristics were noted, such as the symptom or syndrome represented, as well as the type of study or intervention.
The expectation was that there would be a lack of teaching and learning on the subject of persistent physical symptoms. For this reason, the scoping review aimed to capture the greatest breadth of studies, rather than exclude studies based on quality criteria. If a teaching intervention was used, we did look at whether this was evaluated using a validated tool.
Following the extraction of descriptive data, a narrative synthesis was undertaken to identify other key findings. An inductive, iterative approach was taken in order to identify themes relating back to the research question. Manual coding was undertaken by two authors independently, followed by a discussion with all authors to arrive at an interpretation of the findings.
Search strategy, study selection, and data extraction
Searches identified 1390 unique titles. Studies were limited to English language and human participants, leading to 274 being excluded. First stage screening excluded a further 1080 studies. It was not possible to retrieve one study and six were excluded on full text. Ten further records were identified through a grey literature search using Google and Google Scholar and 18 were found through citation searching, three of which were from a previous literature review [ 15 ]. This resulted in 57 publications for inclusion in the review. See the PRISMA flow diagram in Fig. 1 for a summary of these findings.
PRISMA Diagram
Adapted from Page MJ, et al. [ 17 ]
Descriptive analysis
Study types.
The studies included for review were highly heterogeneous in their nature. 15/57 (26%) studies employed a teaching intervention, with the remaining either being observational or qualitative. 8/57 (14%) studies described or evaluated the teaching curriculum, 13/57 (22%), included an assessment of the current level of learner knowledge. 9/57 (16%) used qualitative methods with learners and 6/57 (11%) with medical educators. One literature review on assessing knowledge, perceptions and attitudes to pain was found [ 15 ]. The citations of this review were checked and the three new sources [ 18 , 19 , 20 ] were included for review. Sources within this literature review that did not meet the eligibility criteria were excluded. The findings of the review itself were noted for congruity, but not formally analysed.
Study characteristics
23/57(40%) of studies took place in USA and 13/57 (23%) in the UK. Six studies took place in Scandinavia and four in Canada, four in Australia and one in New Zealand, India, and Nigeria respectively. Some studies were based in more than one country e.g. Australia and New Zealand [ 21 ]. Publication dates ranged from 1992 to 2022. See Table 2 for a summary of the descriptive data.
Teaching and learning methods
A wide range of teaching and learning methods were discussed in the literature. These are fully described in Table 3 , but included lectures, workshops, reflective practice, and forum theatre.
Evaluation of teaching studies
Four studies used validated tools to assess learner attitudes towards patients with PPS, but only one used such a tool to evaluate a teaching intervention [ 22 ]. Morris, Rankin, and Briggs used the HC-PAIRS attitudinal questionnaire to assess learner attitudes towards patients with chronic low back pain [ 18 , 23 , 24 ]. Whereas Friedberg et al. [ 22 ] used the Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Attitudes Test (CFSAT) and paired t-test to analyse learner attitudes before and after a teaching intervention. The remaining educational interventions either did not use a validated tool for evaluation or were not formally evaluated. See Table 3 for more details.
Thematic synthesis
All studies identified a lack of teaching about persistent physical symptoms (PPS) at undergraduate level. The narrative synthesis identified four themes: An awkward problem, an absence of science, being easily overlooked, and a hidden curriculum.
An awkward problem
PPS was consistently viewed as an awkward problem. Medical educators and learners found it difficult to understand, particularly when referring to the symptoms as ‘unexplained.’ Some educators described PPS as too complex or too confusing, even ‘dangerous’ to introduce at an undergraduate level and stated the need to focus on the easily ‘explainable.’ [ 25 ] Chronic non-cancer pain was the dominant condition represented in the literature, but despite theoretical concepts of chronic pain being more established, learners found the subject challenging, even ‘unpleasant.’ [ 26 , 27 ].
The absence of science
Four studies highlighted that learners infer patients with PPS have ‘no science’ behind their symptoms. In the study by Vasanthy [ 28 ], clinical role models in Kerala were found to have a ‘nihilistic’ attitude towards people with fibromyalgia and regarded the condition as benign and unimportant. This finding was echoed by UK studies [ 29 , 30 , 31 ] where the impact of a lack of teaching and negative role modelling was evident:
“You can’t really train someone for it because there is no science behind it” [ 30 ].
One final year medical student stated that fibromyalgia was “not a medical issue” intimating that it had no place in the taught curriculum [ 29 ]. Learners understood the need to be supportive and for good communication, but only as a way of achieving relational congruence, not epistemic congruence [ 8 ]. Terminology may be important and in one study learners’ attitudes towards PPS varied depending on the diagnostic label [ 32 ]. As an example, learners thought that people with myalgic encephalopathy were less likely to recover than those with chronic fatigue syndrome [ 32 ].
Easily overlooked
Even without the overt attitudinal barriers described in some studies, PPS as a topic is overlooked in undergraduate medical education. The most common barrier was an already overloaded teaching curriculum [ 25 , 33 ]. PPS was not deemed a priority area by educational leaders and [ 33 ] even when they recognised its importance, they cited a lack of ownership of the topic and a lack of coordination between teaching specialties as a barrier to implementing teaching. This was in contrast to chronic non-cancer pain teaching which usually did have clear ownership by pain specialists and established interdisciplinary relationships [ 34 ]. The experience of learners in the clinical setting was that they were shielded from patients with PPS or directed towards patients with other more easily defined clinical problems [ 28 ].
Stigma and the hidden curriculum
Given the vacuum of formal teaching, learners were taking on stigmatised messages about sufferers of PPS, frequently from role models in the clinical placement setting. Stenhoff and colleagues described a cycle of negativity created by the lack of teaching on the subject of chronic fatigue, which resulted in negative behaviour by clinical role models, in turn perpetuating negative attitudes in the next generation of learners [ 31 ]. Whilst learners recognised the problematic nature of the attitudes towards people with PPS, they lacked the tools to challenge negative stereotypes [ 29 , 30 , 35 ]. Learners experienced a mismatch between formal teaching on the topic and their experience on placement, where these conditions were frequently encountered. They addressed the gap by seeking information about PPS from informal sources, such as their own or their families’ experiences or from the internet [ 36 ]. This lack of explicit teaching and the influence of informal sources has been termed by some authors as the ‘hidden curriculum’ [ 29 , 30 , 31 , 36 ] and this has had a significant impact on learners’ attitudes towards people suffering with PPS.
Suggestions for improvement: relationship to domains of learning
The findings of the narrative synthesis map onto Bloom’s revised three domains of learning [ 14 ].
Knowledge (cognitive)
A number of studies demonstrate success in teaching on the topic of chronic non-cancer pain. Teaching interventions tended to include a foundation of knowledge such as teaching on pain mechanisms, pharmacology, and pain management [ 37 , 38 ]. Such theory-driven interventions led to improved scores on assessment [ 39 ]. Methods of teaching should be considered in the explicitly taught curriculum. Authors recommended an integrated approach [ 40 , 41 ] and one which drew on the skills and knowledge from a variety of disciplines [ 37 , 42 ]. Curriculum mapping was recommended by Howman et al. [ 33 ] in order to identify ways in which this integration could be implemented. The need for an holistic approach which emphasises the importance of empathy [ 41 ] and the biopsychosocial was also widely recognised [ 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 ]. Learners cited a lack of assessment as an indicator that PPS was either unimportant or uncommon [ 29 , 33 ] and therefore any teaching intervention should include assessment in order to drive learning and engagement.
Skills (psychomotor)
Learners valued the addition of skills-based teaching and engaged best with teaching that was experiential [ 47 ] and included either patients with PPS or simulated patients [ 45 , 48 , 49 ]. In one study the focus of the teaching was on interactive, practical teaching for emotionally demanding consultations and the skills taught in such a programme could be transferable to the PPS context [ 49 ]. Approaches to help learners find a common language of explanation [ 13 ] will not only bridge the epistemic gap between clinicians and patients [ 8 ], but should give learners greater confidence and satisfaction in consultations where PPS are the focus.
Attitudes (affective) and the role of reflection
Reflection is a key transferable skill that graduates should acquire as part of their undergraduate training [ 50 ]. Both learners and educators voiced a great deal of anxiety regarding teaching and managing patients with PPS. Some authors utilised reflective logs and visual art as a way of teaching about chronic pain [ 51 ] and learners valued the deep insights provided by this method. Skills in reflection might help to ameliorate the negative emotions felt by learners, especially if combined with a taught framework that helps them understand concepts such as internal bias and cognitive dissonance [ 52 ].
Summary of main findings
This review found that teaching on persistent physical symptoms in undergraduate medical education is inconsistent and incomplete. We identified four important themes: an awkward problem, the absence of science, easily overlooked, and the hidden curriculum. Mapping these to teaching and learning domains provides a coherent framework for undergraduate teaching of these common conditions. Where teaching does take place, this is more frequently on the topic of chronic non-cancer pain. A number of studies have demonstrated improved knowledge [ 39 ], skills [ 49 ], and attitudes [ 51 ] as a result of this teaching [ 34 , 47 ], but high quality evaluation of such teaching and learning is lacking.
Strengths and limitations
This scoping review has addressed a gap in the literature. By undertaking a search of three databases, the grey literature, and citation analysis, a wide range of sources were included for initial screening. Two researchers independently undertook the search strategy before comparing findings which has helped to ensure a robust and systematic approach. Narrative synthesis was undertaken by three researchers, one with expertise in the field of persistent physical symptoms.
The majority of the studies identified were from the USA and UK. Papers that were not accessible in English were excluded, which may explain this finding. Where teaching and learning evaluations had taken place, this was on a small scale usually within one institution. Only one study [ 22 ] used a validated tool to evaluate the efficacy of the teaching intervention.
Implications for practice, policy, and research
There is a lack of teaching on PPS in undergraduate medical education. As a result, medical graduates are ill-equipped to recognise, consult for, and manage this group of conditions. Given the prevalence of PPS across medical specialties this is a priority area that needs to be addressed, whilst acknowledging the barriers that exist to implementation.
The solutions offered up in the literature include the need to consider whole-person care, in order to avoid fragmentation and the “collusion of anonymity” [ 7 ] described above. For this reason, teaching on PPS should be integrated into the core curriculum and draw on a variety of disciplines.
A better understanding of the science behind PPS [ 1 , 2 ] is needed for both educators and learners. There is also a need to move learners beyond reductionist models of communication skills towards more theory-driven approaches of person-centredness, as identified by Bansal [ 53 ]. We need to convey to learners that skilled communication is not about platitudes, but can make a difference to recovery and addresses the current epistemic gap between clinicians and their patients [ 8 , 13 ].
Future educational research should focus on the most effective methods to improve the knowledge base of both educators and students and how best to evaluate the success of future teaching interventions. Skills in person-centred communication and explanation [ 3 ] need to be taught, alongside those in reflection and challenging prejudice.
We identified four important themes which underpin the challenges of teaching medical undergraduates about persistent physical symptoms. Educational faculties need to find ways to integrate teaching into current programmes and work around the existing barriers to successful implementation and evaluation of teaching about these common and limiting conditions. Examples of successful teaching on chronic non-cancer pain were found in the literature. These tended to articulate the science behind symptoms and often included experiential elements. Such examples should be used to inform an approach for teaching about other forms of PPS. Importantly, robust evaluation that accounts for the complexity of the taught environment is needed to ensure our teaching is making a difference, both for our learners and the patients they will go on to encounter.
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Henningsen P, et al. Persistent physical symptoms as Perceptual Dysregulation: a Neuropsychobehavioral Model and its clinical implications. Psychosom Med. 2018;80(5):422–31.
Article Google Scholar
Burton C et al. Functional somatic disorders: discussion paper for a new common classification for research and clinical use BMC Medicine, 2020;18(1).
Morton L, et al. A taxonomy of explanations in a general practitioner clinic for patients with persistent medically unexplained physical symptoms. Patient Educ Couns. 2017;100(2):224–30.
Picariello F, Ali S, Moss-Morris R, Chalder T. The most popular terms for medically unexplained symptoms: the views of CFS patients. J Psychosom Res. 2015;78(5):420–6.
Haller H, Cramer H, Lauche R, Dobos G. Somatoform disorders and medically unexplained symptoms in primary care. Deutsches Ärzteblatt international, 2015.
Oldham J. Reform reform: an essay by John Oldham. BMJ: Br Med J. 2013;347:f6716.
Balint M. The doctor, his patient and the illness . 2000, Edinburgh: Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 2000.
Johansen M-L, Risor MB. What is the problem with medically unexplained symptoms for GPs? A meta -synthesis of qualitative studies. Patient Educ Couns. 2017;100(4):647–54.
Verhaak PFM. Persistent presentation of medically unexplained symptoms in general practice. Fam Pract. 2006;23(4):414–20.
Mcgorm K, et al. Patients repeatedly referred to secondary care with symptoms unexplained by organic disease: prevalence, characteristics and referral pattern. Fam Pract. 2010;27(5):479–86.
Barsky AJ, Orav EJ, Bates DW. Somatization increases medical utilization and costs Independent of Psychiatric and Medical Comorbidity. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62(8):903.
Polakovská L, Řiháček T. What is it like to live with medically unexplained physical symptoms? A qualitative meta-summary. Psychology & Health. 2021:pp. 1–17.
Salmon P. Conflict, collusion or collaboration in consultations about medically unexplained symptoms: the need for a curriculum of medical explanation. Patient Educ Couns. 2007;67(3):246–54.
Anderson L. A taxonomy for learning, teaching, and assessing: a revision of Bloom’s . Pearson new international ed. 2014, Harlow, Essex: Pearson.
Ung A, Salamonson Y, Hu W, Gallego G. Assessing knowledge, perceptions and attitudes to pain management among medical and nursing students: a review of the literature. Br J Pain. 2016;10(1):8–21.
Arksey H, O’Malley L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2005;8(1):19–32.
Page MJ et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ, 2021:p. n71.
Briggs AM, et al. Low back pain-related beliefs and likely practice behaviours among final-year cross-discipline health students. Eur J Pain. 2013;17(5):766–75.
Murinson BB, et al. A new program in pain medicine for medical students: integrating core curriculum knowledge with emotional and reflective development. Pain Med. 2011;12(2):186–95.
Watt-Watson J, et al. An integrated undergraduate pain curriculum, based on IASP curricula, for six Health Science Faculties. Pain. 2004;110(1):140–8.
Shipton EE, et al. Pain medicine content, teaching and assessment in medical school curricula in Australia and New Zealand. Volume 18. BMC Medical Education; 2018:1.
Friedberg F, Sohl SJ, Halperin PJ. Teaching medical students about medically unexplained illnesses: a preliminary study. Med Teach. 2008;30(6):618–21.
Morris H, Ryan C, Lauchlan D, Field M. Do medical student attitudes towards patients with chronic low back pain improve during training? A cross-sectional study. BMC Med Educ. 2012;12(1):10.
Rankin L, Fowler CJ, Stålnacke B-M, Gallego G. What influences chronic pain management? A best–worst scaling experiment with final year medical students and general practitioners. Br J Pain. 2019;13(4):214–25.
Joyce E, et al. Training tomorrow’s doctors to explain ‘medically unexplained’ physical symptoms: an examination of UK medical educators’ views of barriers and solutions. Patient Educ Couns. 2018;101(5):878–84.
Corrigan C, et al. What can we learn from First-Year Medical Students’ perceptions of Pain in the primary care setting? Pain Med. 2011;12(8):1216–22.
Wilson JF, et al. Medical students’ attitudes toward pain before and after a brief course on pain. Pain. 1992;50(3):251–6.
Vasanthy B, Parameswaran Nair VC. Fibromyalgia: perspective of patients, medical students and professionals. Journal of evidence based Medicine and Healthcare. J Evid Based Med Healthc. 2018;5(34):2463–7.
Silverwood V et al. ‘If it’s a medical issue I would have covered it by now’: learning about fibromyalgia through the hidden curriculum: a qualitative study. BMC Med Educ, 2017;17(1).
Shattock L, et al. They’ve just got symptoms without science’: medical trainees’ acquisition of negative attitudes towards patients with medically unexplained symptoms. Patient Educ Couns. 2013;91(2):249–54.
Stenhoff AL, Sadreddini S, Peters S, Wearden A. Understanding medical students’ views of chronic fatigue syndrome: a qualitative study. J Health Psychol. 2015;20(2):198–209.
Jason LA, et al. Evaluating attributions for an illness based upon the name: chronic fatigue syndrome, myalgic Encephalopathy and Florence Nightingale Disease. Am J Community Psychol. 2002;30(1):133–48.
Howman M, et al. Teaching about medically unexplained symptoms at medical schools in the United Kingdom. Med Teach. 2012;34(4):327–9.
Vargovich AM, et al. Difficult conversations: Training Medical students to assess, educate, and treat the patient with Chronic Pain. Acad Psychiatry. 2019;43(5):494–8.
Yon K, et al. Improving teaching about medically unexplained symptoms for newly qualified doctors in the UK: findings from a questionnaire survey and expert workshop. BMJ Open. 2017;7(4):e014720.
Emorinken A, et al. Assessment of Undergraduate Medical Students Knowledge and Awareness of Fibromyalgia. J Evol Med Dent Sci. 2022;11(5):551–6.
Comer L. Content analysis of chronic pain content at three undergraduate medical schools in Ontario. Can J Pain. 2017;1(1):75–83.
Kolber BJ, Janjic JM, Pollock JA, Tidgewell KJ. Summer undergraduate research: a new pipeline for pain clinical practice and research. BMC Med Educ, 2016;16(1).
Weiner DK, et al. E-Learning Module on Chronic Low Back Pain in older adults: evidence of Effect on Medical Student Objective Structured Clinical Examination performance. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62(6):1161–7.
Pöyhiä R, Niemi-Murola L, Kalso E. The outcome of pain related undergraduate teaching in Finnish medical faculties. Pain. 2005;115(3):234–7.
Murinson BB, et al. Recommendations for a New Curriculum in Pain Medicine for Medical students: toward a Career distinguished by competence and Compassion. Pain Med. 2013;14(3):345–50.
Morley-Forster P et al. Mitigating the risk of opioid abuse through a balanced undergraduate pain medicine curriculum. J Pain Res, 2013:p. 791.
Wojtowicz AA, et al. Perceptions of clinical training in biopsychosocial treatment of pediatric functional abdominal pain: a survey of medical students. Clin Pract Pediatr Psychol. 2020;8:37–44.
Google Scholar
Dwyer CPM-P, Phoebe E, Durand H, Gormley EM, Slattery BW, Harney OM, MacNeela P, McGuire BE. Factors influencing the application of a Biopsychosocial Perspective in Clinical Judgement of Chronic Pain: interactive management with medical students. Pain Physician. 2017;20(6):E951–60.
Ali N, Thomson DI. A comparison of the knowledge of chronic pain and its management between final year physiotherapy and medical students. Eur J Pain. 2009;13(1):38–50.
Tauben DJ, Loeser JD. Pain Education at the University of Washington School of Medicine. J Pain. 2013;14(5):431–7.
Stevens DL, et al. Medical students retain pain assessment and management skills long after an experiential curriculum: a controlled study. Pain. 2009;145(3):319–24.
Bradner M, et al. Chronic non-malignant pain: it’s complicated. Clin Teach. 2019;16(5):530–2.
Baessler F, et al. Are we preparing future doctors to deal with emotionally challenging situations? Analysis of a medical curriculum. Patient Educ Couns. 2019;102(7):1304–12.
GMC, Outcomes for Graduates . 2018.
Lempp H, Potter J, Petit P, Hester J. Exploring chronic pain with patients: medicine meets art. Med Educ. 2010;44(11):1139–40.
Syed M. Black box thinking: marginal gains and the secrets of high performance. London: John Murray; 2016.
Bansal A, et al. Optimising planned medical education strategies to develop learners’ person-centredness: A realist review. Medical Education, 2021.
Turner GH, Weiner DK. Essential components of a Medical Student Curriculum on Chronic Pain Management in older adults: results of a modified Delphi process. Pain Med. 2002;3(3):240–52.
Niemi-Murola L, et al. Training medical students to manage a chronic pain patient: both knowledge and communication skills are needed. Eur J Pain. 2006;10(2):167–167.
Saypol B, Schmulson DD. A review of three educational projects using interactive theater to improve physician-patient communication when treating patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2015;107(5):268–73.
Bradshaw YS, et al. Deconstructing one Medical School’s Pain Curriculum: II. Partnering with medical students on an evidence-guided redesign. Pain Med. 2017;18(4):664–79.
Leeds FS, et al. A patient-narrative Video Approach to Teaching Fibromyalgia. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2020;7:238212052094706.
Gadde U, et al. Implementing an interactive introduction to complementary medicine for chronic Pain Management into the Medical School Curriculum. MedEdPORTAL. 2020;16(1):11056.
Campbell WI. What do medical-students know about chronic pain and its management. Ulster Med J. 1992;61(2):139–43.
Chibnall JT, Tait RC, Ross LR. J Behav Med. 1997;20(3):257–71.
Niemi-Murola L, Nieminen JT, Kalso E, Pöyhiä R. Medical undergraduate students’ beliefs and attitudes toward pain - how do they mature? Eur J Pain. 2007;11(6):700–6.
Amber KT, Brooks L, Chee J, Ference TS. Assessing the perceptions of Fibromyalgia Syndrome in United States among Academic Physicians and Medical students: where are we and where are we headed? J Musculoskelet Pain. 2014;22(1):13–9.
Amber KT, Brooks L, Ference TS. Does Improved confidence in a Disease relate to increased knowledge? Our experience with medical students: table 1. Pain Med. 2014;15(3):483–4.
Adillón C, Lozano È, Salvat I. Comparison of pain neurophysiology knowledge among health sciences students: a cross-sectional study. BMC Res Notes, 2015. 8(1).
Argyra E, et al. How does an undergraduate Pain Course Influence Future Physicians’ awareness of Chronic Pain concepts? A comparative study. Pain Med. 2015;16(2):301–11.
Briggs EV, et al. Current pain education within undergraduate medical studies across Europe: advancing the provision of Pain Education and Learning (APPEAL) study. BMJ Open. 2015;5(8):e006984.
Hollingshead NA et al. Examining influential factors in providers’ chronic pain treatment decisions: a comparison of physicians and medical students. BMC Med Educ, 2015. 15(1).
Rankin L, Stålnacke B-M, Fowler CJ, Gallego G. Differences in Swedish and Australian medical student attitudes and beliefs about chronic pain, its management, and the way it is taught. Scandinavian J Pain. 2018;18(3):533–44.
Cristóvão I, Reis-Pina P. O Ensino Da Dor Crónica em Portugal: as Perspectivas Dos Estudantes De Medicina E dos internos do Ano Comum. Acta Med Port. 2019;32(5):338.
Gustafsson Sendén M, Renström EA. Gender bias in assessment of future work ability among pain patients – an experimental vignette study of medical students’ assessment. Scandinavian J Pain. 2019;19(2):407–14.
Lechowicz K, et al. Acute and Chronic Pain Learning and Teaching in Medical School—An observational cross-sectional study regarding Preparation and Self-confidence of clinical and Pre-clinical Medical Students. Medicina. 2019;55(9):533.
Storrar A, Rayment D, Mallam E. 47 undergraduate teaching and perceptions of functional neurological disorders. Members’ POSTER abstracts. BMJ Publishing Group Ltd; 2019.
Muirhead N, Muirhead J, Lavery G, Marsh B. Medical School Education on myalgic encephalomyelitis. Medicina. 2021;57(6):542.
Simons J, et al. Disorders of gut-brain interaction: highly prevalent and burdensome yet under‐taught within medical education. United European Gastroenterology Journal, 2022.
Lambson R. Chronic fatigue syndrome: where do your views lie? An experience from a UK Medical Student. Int J Med Students. 2015;3(2):117–8.
Raber I, et al. Qualitative Assessment of Clerkship Students’ perspectives of the topics of Pain and Addiction in their preclinical curriculum. Acad Psychiatry. 2018;42(5):664–7.
Rice K, et al. Medical trainees’ experiences of Treating People with Chronic Pain: a lost opportunity for Medical Education. Acad Med. 2018;93(5):775–80.
Sallay V, et al. Medical educators’ experiences on medically unexplained symptoms and intercultural communication—an expert focus group study. Volume 22. BMC Medical Education. 2022;1.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
CN is undertaking an In Practice Fellowship which has been funded by the NIHR (Reference number NIHR301019). This is an educational award and does not fund direct research costs.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Primary Care Research Group, Division of Population Health, School of Medicine, University of Sheffield, Regent Court, 30 Regent Street, S1 4DA, Sheffield, UK
Catie Nagel, Chloe Queenan & Chris Burton
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Chris Burton: review and editing (equal); formal analysis (supporting). Catie Nagel: Conceptualisation (lead); Methodology (lead); writing – original draft (lead); formal analysis (lead); writing – review and editing (lead). Chloe Queenan: review and editing (supporting); formal analysis (supporting).
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Catie Nagel .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, authors’ information, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Nagel, C., Queenan, C. & Burton, C. What are medical students taught about persistent physical symptoms? A scoping review of the literature. BMC Med Educ 24 , 618 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05610-z
Download citation
Received : 03 November 2023
Accepted : 27 May 2024
Published : 04 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05610-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Scoping review
- Narrative synthesis
- Undergraduate
- Persistent physical symptoms
- Medically unexplained symptoms
- Chronic pain
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy for reducing pain susceptibility and increasing social engagement in patients with chronic low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Affiliations.
- 1 School of Rehabilitation, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, Shangdong, China.
- 2 Department of Rehabilitation, University Town Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan, Shangdong, China.
- PMID: 37960716
- PMCID: PMC10637560
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035269
Background: The objective of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy in improving social engagement and pain susceptibility in patients with chronic low back pain (≥6 months duration).
Methods: From the initial to January 2023, 5 databases were searched for randomized controlled trials, literature screening, quality evaluation, and data extraction were performed by 2 independent researchers throughout, Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.4 software, standardized mean difference (SMD) was calculated for different indicators, and the combined experimental and control groups were calculated using random-effects models or fixed-effects models effect sizes, and forest plots were drawn to present the results.
Results: A total of 16 studies containing 2527 patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain, all of whom had pain lasting longer than 6 months, were included, and after treatment, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) was superior to other treatments in improving social participation [SMD = -0.30, 95%CI (-0.60, -0.01), Z = 2.02, P = .04]. There was no significant difference from other treatments in improving patient depression [SMD = -0.07, 95%CI (-0.19, 0.05), Z = 1.11, P = .27] and anxiety [SMD = -0.07, 95%CI (-0.30, 0.16), Z = 0.52, P = .57]. Three papers describe the superiority of CBT over other treatments in improving sleep quality, but the metrics could not be combined due to too little literature.
Conclusion: CBT can improve patients' social participation and pain susceptibility to some extent, but it does not show advantages for managing negative emotions (depression, anxiety). Due to the limited number and low quality of included literature, the above findings still need to be validated by conducting a large sample of high-quality RCTs.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Publication types
- Meta-Analysis
- Systematic Review
- Anxiety Disorders / therapy
- Chronic Pain* / psychology
- Chronic Pain* / therapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy* / methods
- Low Back Pain* / therapy
- Social Participation

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
As mentioned previously, there are a number of existing guidelines for literature reviews. Depending on the methodology needed to achieve the purpose of the review, all types can be helpful and appropriate to reach a specific goal (for examples, please see Table 1).These approaches can be qualitative, quantitative, or have a mixed design depending on the phase of the review.
The general literature review is a synthesis and analysis of published research on a relevant clinical issue, and is a common format for academic theses at the bachelor's and master's levels in nursing, physiotherapy, occupational therapy, public health and other related fields. ... The data analysis methods described here are based on ...
A literature review is defined as "a critical analysis of a segment of a published body of knowledge through summary, classification, and comparison of prior research studies, reviews of literature, and theoretical articles." (The Writing Center University of Winconsin-Madison 2022) A literature review is an integrated analysis, not just a summary of scholarly work on a specific topic.
Literature reviews allow scientists to argue that they are expanding current. expertise - improving on what already exists and filling the gaps that remain. This paper demonstrates the literatu ...
This. paper discusses literature review as a methodology for conducting research and o ffers an overview of different. types of reviews, as well as some guidelines to how to both conduct and ...
A vital step for any systematic review is the analysis and synthesis of the available evidence and depends on the number of studies that will be included in the review; the type of research method(s) used by individual studies (if applicable) and the quality of the evidence, and the chosen analytical or visualisation technique.
Introduction Researchers and practitioners rely on literature reviews to synthesize large bodies of knowledge. Many types of literature reviews have been developed, each targeting a specific purpose. However, these syntheses are hampered if the review type's paradigmatic roots, methods, and markers of rigor are only vaguely understood. One literature review type whose methodology has yet to ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
A formal literature review is an evidence-based, in-depth analysis of a subject. There are many reasons for writing one and these will influence the length and style of your review, but in essence a literature review is a critical appraisal of the current collective knowledge on a subject. Rather than just being an exhaustive list of all that ...
9.3. Types of Review Articles and Brief Illustrations. EHealth researchers have at their disposal a number of approaches and methods for making sense out of existing literature, all with the purpose of casting current research findings into historical contexts or explaining contradictions that might exist among a set of primary research studies conducted on a particular topic.
In the field of research, the term method represents the specific approaches and procedures that the researcher systematically utilizes that are manifested in the research design, sampling design, data collec-tion, data analysis, data interpretation, and so forth. The literature review represents a method because the literature reviewer chooses ...
What kinds of literature reviews are written? Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified.
A literature review goes beyond basic summarizing to focus on the critical analysis of the reviewed works and their relationship to your research question. ... A meta-analysis is the use of statistical methods to summarize the results of these studies. Systematic reviews, just like other research articles, can be of varying quality. ...
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
Elements of a Literature Review. Summarize subject, issue or theory under consideration, along with objectives of the review; Divide works under review into categories (e.g. those in support of a particular position, those against, those offering alternative theories entirely) Explain how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
Literature reviews establish the foundation of academic inquires. However, in the planning field, we lack rigorous systematic reviews. In this article, through a systematic search on the methodology of literature review, we categorize a typology of literature reviews, discuss steps in conducting a systematic literature review, and provide suggestions on how to enhance rigor in literature ...
1. INTRODUCTION. Evidence synthesis is a prerequisite for knowledge translation. 1 A well conducted systematic review (SR), often in conjunction with meta‐analyses (MA) when appropriate, is considered the "gold standard" of methods for synthesizing evidence related to a topic of interest. 2 The central strength of an SR is the transparency of the methods used to systematically search ...
sources that inform a literatur e synthesis comprising the following four major source. type s to inform research syntheses: talk, observations, drawings/photographs/videos, and. documents, and we ...
Methodology: type of study design or method. ... Refer to a systematic review or meta-analysis guidelines such as PRISMA or one that applies to your discipline. ... Remember, the literature review is an iterative process. You may need to revisit parts of this search, find new or additional information, or update your research question based on ...
2. Materials and methods. The SLR applied in this research was based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA), which is an evidence-based minimum set to assist authors to report several systematic reviews and meta-analyses (Pati & Lorusso, Citation 2018).PRISMA focuses on the methods to be applied by authors to ensure complete and transparent reporting ...
Background Persistent Physical Symptoms (PPS) include symptoms such as chronic pain, and syndromes such as chronic fatigue. They are common, but are often inadequately managed, causing distress and higher costs for health care systems. A lack of teaching about PPS has been recognised as a contributing factor to poor management. Methods The authors conducted a scoping review of the literature ...
guide to the actual analysis that a general literature review requires. Below we present a step-by-step guide for analysing data for two different types of research ques-tions. The data analysis methods described here are based on basic content analysis as described by Elo and Kyng€as 4 and Graneheim and Lundman,5 and the integrative review
Bitemark analysis involves the examination of both patterned injuries and contextual circumstances, combining morphological and positional data. Considering the uniqueness of human dentition, bitemarks caused by teeth on skin or impressions on flexible surfaces could assist in human identification. Aims: to investigate the available literature systematically and evaluate the scientific ...
Background: The objective of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy in improving social engagement and pain susceptibility in patients with chronic low back pain (≥6 months duration). Methods: From the initial to January 2023, 5 databases were searched for randomized controlled trials, literature screening, quality evaluation, and data extraction were ...