Writing a Letter of Support for Grants: Examples and Frameworks | Grantboost

Asking for a grant can be a daunting process. You know that the competition is fierce, and the Grantor’s organization is looking for the best and brightest. You need a team behind you that is as dedicated and committed to your cause as you are. That’s where letters of support come in.

What Is A Letter of Support?
Who normally writes a letter of support, how long should a letter of support be.
- Letter of Support Frameworks
Problem, Solution, and Impact Framework
Personal connection framework.
- Evidence Based Framwork
- Letter of Support for Grants Templates
Examples of Letters of Supports for Grants
- Writing Letters of Support for Grants w/ AI
A letter of support (not to be confused with a Letter of Inquiry ) is a document that advocates for a project, program, or organization and is typically written by an individual or organization outside of the project or organization itself. It is used to supplement a grant proposal and provides additional evidence to support the proposal’s objectives, methods, and potential impact. The letter of support should emphasize the writer’s personal connection to the project and highlight the project’s importance and potential benefits. The letter should be persuasive, clearly written, and provide examples of how the project can make a difference in people’s lives.
Letters of support are a powerful tool in your grant application arsenal. They provide evidence that your project has the backing of respected professionals, organizations, and individuals. They demonstrate that your proposal is not just your own opinion, but that it is supported by the wider community. Most importantly, they show that you have a plan that others are bought into as well.
A letter of support is usually written by an individual or organization outside of the project or organization seeking funding. This can include community leaders, elected officials, experts in the field, or organizations with a similar mission or interest. The writer of the letter should have a personal connection to the project and be able to speak to its importance and potential impact.
It is important to choose a writer who is well-respected and influential in the community, as their support can add credibility to the project and increase the chances of funding. Additionally, the writer should have a clear understanding of the project’s goals, methods, and expected outcomes, as they might be asked to provide specific examples of how the project has made a difference in the community.
In some cases, the grant organization may provide guidelines for who can write a letter of support and what should be included. It is important to carefully review these guidelines and ensure that the writer is able to meet the requirements outlined by the grant organization.
When it comes to the length of a letter of support, there isn’t a strict rule. As a general guideline, it should be no longer than one page, two at the absolute max. The most important thing is to make sure that your letter is concise and to the point. A letter that is too long may be overwhelming and lose the attention of the reader. On the other hand, a letter that is too short may not provide enough detail to convince the grant organization of the merits of your project. This should give you enough space to provide all the necessary details while keeping the letter short and sweet.
Frameworks You Can Use When Writing a Letter of Support
Advocates can follow different frameworks when writing a letter of support. One popular framework is the “Problem, Solution, and Impact” model. In this framework, the letter first introduces the problem that the project is addressing, then outlines the solution proposed by the project, and finally discusses the expected impact of the project. This framework is useful because it presents a clear narrative that connects the problem with the solution and the expected outcome.
Another framework is the “Personal Connection” model, which emphasizes the personal connection between the writer of the letter and the project or organization. This framework can be particularly effective when the writer has a personal relationship with the project or organization, as it can add a sense of authenticity and credibility to the letter.
A third framework is the “Evidence-Based” model, which focuses on providing evidence to support the project’s goals and expected outcomes. This framework typically includes data and statistics that demonstrate the need for the project and the expected impact it will have.
Regardless of the framework chosen, it’s important to keep the focus on the project and its goals. The letter should be written in a clear and concise manner, with a persuasive tone that highlights the project’s importance and potential impact.
The problem, solution, and impact model is a framework that can be used when writing a letter of support for a grant opportunity. This model is particularly effective in highlighting the need for the proposed project, the unique solution being offered, and the potential impact of the project on the community or field.
The components that make up this framwork are:
Problem: The first component of the framework is to clearly identify the problem or need that the project is addressing. This can include data and statistics to support the argument that the problem is significant and widespread. The writer should also explain why the problem is important and how it affects the community or field.
Solution: The second component of the framework is to explain the unique solution that the project is offering. This can include a description of the methods, techniques, or strategies that will be used to address the problem. The writer should also explain why this solution is effective and how it differs from other approaches that have been tried in the past.
Impact: The third and final component of the framework is to discuss the potential impact of the project on the community or field. This can include both short-term and long-term impacts, as well as any specific outcomes or goals that the project aims to achieve. The writer should also explain why the proposed project is likely to be successful and how it will make a difference in people’s lives.
By using the problem, solution, and impact model, the writer can provide a clear and compelling case for why the project is needed, how it will work, and what the potential benefits will be.
Ready to try the Problem, Solution and Impact Model for your letter of support? Check out our template and start crafting your compelling letter today.
The personal connection model is a framework for writing a letter of support that emphasizes the writer’s personal connection to the project or organization. This framework can be particularly effective when the writer has a strong relationship with the project or organization, as it can add a sense of authenticity and credibility to the letter.
The personal connection model typically includes several key components:
Introduction: The letter starts with an introduction that establishes the writer’s relationship to the project or organization. This can include how the writer first became involved with the project, why they believe in the project’s goals, and any personal experiences that have influenced their support.
Personal anecdotes: The letter includes a short personal anecdote or story that illustrate the writer’s connection to the project or organization. These anecdotes can be powerful in demonstrating the importance and impact of the project, as they provide concrete examples of how the project has made a difference in people’s lives.
Emotional appeal: The letter makes an emotional appeal to the reader by highlighting the writer’s passion and commitment to the project or organization. This can include expressing gratitude for the opportunity to be involved with the project and conveying a sense of urgency about the need for funding.
Call to action: The letter concludes with a call to action that encourages the grant organization to fund the project. This can include a clear statement of the project’s goals and expected outcomes, and an invitation to the reader to contact the writer for more information.
When using the personal connection model, it’s important to strike a balance between personal anecdotes and a persuasive tone that highlights the project’s importance and potential impact. The letter should be written in a clear and concise manner, with a focus on how the project will benefit the community or achieve its goals. By emphasizing the writer’s personal connection to the project, the personal connection model can be an effective way to persuade grant organizations to fund important projects.
Click here to access our Personal Connection Model template and start writing your letter of support faster, today.
Evidence Based Framework
The evidence-based model is another framework that can be used when writing a letter of support for grants. This model focuses on presenting evidence to support the need for the proposed project and the effectiveness of the proposed solution. Here are the components that make up a successful evidence-based letter of support:
Background: The first component of the framework is to provide background information on the issue or problem being addressed by the proposed project. This can include data, statistics, and research studies that support the argument that the issue is significant and widespread.
Evidence: The second component of the framework is to provide evidence to support the effectiveness of the proposed solution. This can include studies, research articles, or other types of evidence that demonstrate the potential impact of the proposed project.
Expertise: The third component of the framework is to highlight the expertise of the individuals or organizations involved in the proposed project. This can include descriptions of the qualifications and experience of the project team, as well as any relevant partnerships or collaborations that have been established. Outcomes: The final component of the framework is to describe the specific outcomes or goals that the proposed project aims to achieve. This can include both short-term and long-term outcomes, as well as any specific metrics that will be used to measure success.
By using the evidence-based model, the writer can provide a compelling case for the need for the proposed project and the effectiveness of the proposed solution. This framework can be especially effective when used in combination with other types of evidence, such as personal anecdotes and expert testimonials, to support the argument. Additionally, it is important to ensure that the language used in the letter is clear, concise, and easy to understand, as well as tailored to the specific audience and purpose of the grant application.
Ready to try the Evidence Based Model for your letter of support? Click here to access our template and start crafting a strong, evidence-based argument to support your grant application!
Letters of Support For Grants Templates
If you’re struggling with writing your own letter of support, we encourage you to try some of the templates we’ve provided below. By using them as a guide, you can craft a compelling letters of support that will strengthen any grant application and increase the chances of securing funding.
Problem, Solution, and Impact Template
Dear [Funder’s Name], I am writing in support of [Name of the organization] and their proposed [Name of the project/program]. As someone who is passionate about [Relevant issue], I believe this project has the potential to make a real impact in our community. The problem we are facing is [Brief description of the issue or problem], which has had a negative impact on our community by [Impact of the problem]. This is a pressing issue that demands immediate attention and action. Fortunately, [Name of the organization] has developed an innovative and effective solution to this problem. By [Briefly describe the proposed solution], we can address this issue and make a real impact in our community. The potential impact of this project is significant. [Statistics or data that support the impact of the proposed solution]. If we can successfully implement this project, we can [Positive outcomes that will result from the project]. I strongly believe that [Name of the project/program] is the right solution for our community. [Name of the organization] has a proven track record of success and has the experience and expertise to execute this project with excellence. Thank you for considering this proposal. Your support will make a meaningful difference in the lives of our community members. Sincerely, [Your Name]
Personal Connection Template
Dear [Funder’s Name], I am writing to express my enthusiastic support for [Name of the organization] and their proposed [Name of the project/program]. As someone who has experienced the [Relevant issue], I can personally attest to the urgent need for this project in our community. The team at [Name of the organization] understands the challenges that individuals like me face every day. They have been a trusted resource and source of support for me, and I am grateful for their work. The [Name of the project/program] has the potential to make a real difference in the lives of people like me. By [Briefly describe the proposed solution], this project will provide critical support to those in our community who are most in need. I believe that [Name of the organization] is uniquely positioned to execute this project with excellence. Their expertise, compassion, and dedication to this issue are unparalleled. I am proud to support [Name of the organization] and their efforts to make our community a better place. I hope that you will join me in supporting this important project. Thank you for your consideration. Sincerely, [Your Name]
Evidence-based Template
Dear [Grantor Name], I am writing this letter in support of [Organization Name] and their proposed project [Project Name]. As [Your Position] of [Your Organization Name], I have had the privilege of working alongside the [Organization Name] team and can attest to their expertise in [Field/Area of Work]. The need for [Project Name] is significant and widespread in the [Community/Population] we serve. [Insert statistics or data that supports this claim]. The proposed solution put forth by [Organization Name] has the potential to make a real impact in [Community/Population] and address the issue at its root cause. In support of the proposed solution, I would like to highlight [Insert evidence, such as studies or research articles, that demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed solution]. Additionally, the expertise of the [Organization Name] team is unparalleled in the [Field/Area of Work]. They have a proven track record of success in [Insert examples of previous projects or initiatives that demonstrate expertise]. The specific outcomes and goals of the proposed project include [Insert short-term and long-term outcomes that the project aims to achieve], with a specific focus on [Insert metrics that will be used to measure success]. I wholeheartedly endorse the proposed project [Project Name] by [Organization Name] and believe that it has the potential to make a lasting impact in the [Community/Population] we serve. Thank you for your consideration. Sincerely, [Your Name]
Letter of Support Example: Personal Connection Framework :
Dear John Doe, I am writing to express my enthusiastic support for the Women’s Health Initiative and their proposed Breast Cancer Survivor Support Program. As a breast cancer survivor myself, I can personally attest to the urgent need for this program in our community. The team at the Women’s Health Initiative understands the challenges that individuals like me face every day. They have been a trusted resource and source of support for me, providing critical emotional and physical support during my journey. The Breast Cancer Survivor Support Program has the potential to make a real difference in the lives of survivors in our community. By providing access to counseling, support groups, and educational resources, this program will help women navigate the challenges that come with a breast cancer diagnosis and treatment. I believe that the Women’s Health Initiative is uniquely positioned to execute this program with excellence. Their expertise, compassion, and dedication to women’s health are unparalleled. I am proud to support the Women’s Health Initiative and their efforts to make our community a better place. I hope that you will join me in supporting this important program. Thank you for your consideration. Sincerely, Jane Doe ”
Letter of Support Example: Evidence Based Framework :
Dear John, I am writing to express my strong support for the proposed Literacy for All program, which I believe will have a significant impact on improving the literacy rates in our community. The need for this program is evident from the alarming statistics that indicate that nearly 50% of the adult population in our community lacks basic literacy skills. The Literacy for All program is based on a wealth of research that demonstrates the importance of early childhood literacy interventions, particularly for children from low-income families. Studies have shown that children who are not reading proficiently by third grade are more likely to struggle academically, drop out of school, and face a range of social and economic challenges later in life. The proposed program includes evidence-based strategies such as providing high-quality literacy instruction, offering family literacy programs, and providing access to books and other resources. It is designed to reach children and families in the most vulnerable communities in our area, where the need is greatest. The Literacy for All program has the potential to transform the lives of thousands of children in our community. By improving literacy skills at an early age, we can help set these children on a path toward success in school and in life. I urge you to support this vital program and invest in the future of our community. Thank you for your consideration. Sincerely, Ezenwa ”
Writing Letters of Support w/ AI
At Grantboost, we’re excited to announce the upcoming release of our cutting-edge Proposal generator to the beta stage. It’s a game changer in the world of grant writing, and we’re confident that it will revolutionize the way you write letters of support. With its intuitive design and powerful AI technology, you’ll be able to generate compelling, persuasive letters in minutes. We’re offering it for free to our beta users, so you can see for yourself just how effective it is. This is just the beginning of what Grantboost has in store for the grant writing community, and we can’t wait to see how our technology will help you secure the funding you need to make a difference.
Boost Your Success: Try Free
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Start » strategy, how to write a grant application for your organization.
Writing a strong grant application can help your organization receive the funding it needs to fulfill its mission. These tips will help you get started.

For many organizations, grant writing is the most important component of their entire fundraising strategy. In fact, a single grant application can make or break your organization, so if you’re trying to secure funding for your nonprofit, community organization or research group, it’s important to learn how to write a strong, successful proposal. Here’s what you need to know to get started.
[ Read more: 22 Grants, Loans and Programs to Benefit Your Small Business ]
What to consider before writing a grant application
The best grant proposals are clear, organized documents that illustrate why your organization should receive funds from the grantor. That’s why it’s a good idea to plan in advance and get some things in order. Here are three things to know or accomplish before you start writing your proposal:
- Your audience. First and foremost, get to know the institution that is offering the grant. Consider its goals, values and objectives. Understanding these elements will later help you demonstrate how and why your organization is a good fit.
- The minimum requirements. Research the eligibility expectations for each specific grantor and make sure you meet the minimum requirements. If you find that your organization does not meet these requirements, contact the grantor directly to discuss your options.
- Your organization’s credibility. Compile a list of testimonials, recommendations, data sets and success stories to include with your application. Every grantor is different, but they all want to know their money is being used wisely.
Elements of a grant proposal
Grant applications are organized in specific sections that help the reviewer parse through information quickly and find potential grantees. Here are the main elements to include in a grant proposal:
- Cover letter. Some, but not all, granting organizations ask that you include a cover letter to introduce yourself. This section should establish why you are seeking the available grant, describe your organization or project and illustrate your professionalism.
- Executive summary. Also known as an abstract or overview, the executive summary should state the most important information from the entire proposal. This section should be concise, yet fully describe your goals, what steps you will take, why you need funding and how you will measure progress. It is often best practice to write this section last.
- Needs assessment. The needs assessment, also known as the statement of need, problem statement or literature overview, defines the lack in resources, information or opportunities that you are trying to solve. Include as much data and research as possible and show how your organization is the key link between the problem and the solution.
- Project description. Also known as the project narrative, this section states how you will address the problems described in the needs assessment. The description should include your goals , your projected timeline, how you will measure progress and how you will recognize success. Focus on the impact your work will have on the given issue.
- Budget. This section should clarify why you are asking for funding. State how each dollar will be spent, and illustrate how the cost of labor, materials or equipment is required to fulfill your mission.
- Supplemental documentation. Finally, you may need to provide an appendix with all the supporting materials you’ve included in your application. This may include additional data, business records, employment information, letters of reference, organizational qualifications and so on.
[ Read more: How to Get a Grant to Start a Business ]
It’s important to remember that there are so many factors beyond a nonprofit’s control that influence decision-making...
Arianna Maysonave, Director of Development at Herbicide-Free Campus
4 tips for writing a grant application
- Stick to your mission. It’s not uncommon for inexperienced grant writers to stretch their application too far and create a weak proposal. “Write grants based on your mission,” said Lauren Balkan, Deputy Director of Wellspring Center for Prevention . “Stay true to your mission and then be creative with how to meet that mission within the scope of the grant funding.”
- Build your network. Even if you’re not actively writing a grant application, start meeting with grantors to build a professional relationship. Networking will help you better understand the mission, values and objectives of specific granting organizations, which will give you a head start when you are ready to prepare a proposal. “Relationship building is the number one key to success in securing a grant,” said Arianna Maysonave, Director of Development at Herbicide-Free Campus . “Identify the interest of the grantor long before their grant deadline, and begin connecting with relevant partners months or even years before you expect to receive a grant.”
- Expect to receive rejection letters. Learning how to craft solid grant applications takes time and experience. If your organization doesn’t earn a grant, use it as a learning opportunity. “It’s important to remember that there are so many factors beyond a nonprofit’s control that influence decision-making,” said Maysonave. “Do your best and don’t be afraid to follow up and ask why you weren’t chosen.”
- Learn from your community. Finally, learn from other organizations within your community or industry to better understand what funders are looking for. “Connect to many community groups where organizations come together,” Balkan said. “Workgroups or committees usually provide information about possible funding opportunities, [so] pay attention when similar organizations are talking about their funding and where they get it.”
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
Follow us on Instagram for more expert tips & business owners’ stories.
Applications are open for the CO—100! Now is your chance to join an exclusive group of outstanding small businesses. Share your story with us — apply today .
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Apply for the CO—100!
The CO—100 is an exclusive list of the 100 best and brightest small and mid-sized businesses in America. Enter today to share your story and get recognized.
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
For more business strategies
Best practices for small business ai content creation, funding options and resources for lgbtq+-owned businesses, 7 helpful resources for family-owned businesses.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.

Learn How to Write a Persuasive Letter of Support for Grant
Acquiring funds for your research is an important milestone for every researcher. As the deadline for submitting the grant proposal approaches, there’s a sense of fear that engulfs you into thinking that your application is probably not the best one. While every element of your grant proposal is important to the reviewer, your letter of support for the grant has a potential to strengthen their belief in your research idea. A letter of support may probably not clinch the funding; however, it could make your grant proposal more competitive, especially when it is written by highly influential and renowned individuals or organizations.
What is a Letter of Support for Grant?
A letter of support is a document used to validate the credibility of your research through a third-party testimonial. This testimony should back up your claims of success as well as the promises to deliver results.
The letter implies that other organizations or funders think your proposal has merit. It signifies that your project has the potential of delivering proposed results. In addition, it provides a compelling and persuasive reason for a funder to support your grant proposal .
Who Should Write a Letter of Support for Grant?
Letters of support play a major role in determining whether or not your research project is worthy of funding . Therefore, it is important to identify the right people to write it.
A letter of support can be written by:
- A partner organization
- A major funder
- Another foundation
- A congressional representative
- An outside business such as professional grant writing services
- A key stakeholder
Furthermore, it could be from community leaders who believe in your project, or from people who will receive the services you propose of providing.
What is the Purpose of a Letter of Support for Grant?
A letter of support for grant helps in determining whether your project is worthy of funding.
The purpose of a letter of support is-
- Firstly, to establish a level of credibility
- Secondly, to demonstrate commitment to a research project
- Thirdly, to show that the planned collaboration is genuine
- Lastly, to address the applicant’s qualifications and abilities to complete the proposed research
Which are the Four Categories of Letter of Support for Grant?
Ideally, letter of support for grant are of two types:
- Letters from knowledge partners who are supporting the research with monetary aid
- Letters from a person who supports the research idea.However, depending on where the letters of support are sourced from, they are categorized as:
- Community Leaders: Letters sourced from community leaders help in establishing the proposers’ credibility.
- Collaborative Partners: Letters sourced from collaborative partners help in demonstrating that the proposed project will be beneficial to the service community.
- Contributing Supporters: Letters written by contributing supporters demonstrate tangible resources being dedicated to the project.
- Impacted Constituents: Letters written by impacted constituents help the funder in determining the benefits or repercussions of actions.
Differences Between “Letter of Support” and “Letter of Recommendation”
While confusion may arise from the fact that both letters of support and letters of recommendation provide key information for reviewers of the funding agency, there still are differences between the two.
Key Elements of a “Letter of Support” for Grant
The letter of support consists of three main sections: an opening statement or introduction that identifies the project, one or two main body section of the letter to indicate the relationship of the writer to the project seeking funding, and a closing statement to summarize with key points. However, there are some additional sections such as the header and the salutation. Here we discuss the key elements of a letter of support for grant in sequential order of their occurrence.
A Professional Introduction
The first thing one must do while creating a persuasive letter of support is introduce themselves. Writing an attention-grabbing introduction will encourage the reader to continue reading until the end. The simplest way to start your introduction section is to inform the reader—who you are and why they must care?
The Conclusion
Important points to consider while writing a letter of support for grant.
As letters of support can make a significant difference for applicant/s grant approval, it’s important to consider the following points while writing one.
- It must not be longer than two pages in length.
- Mention correct proposal details.
- Provide any additional details or requirements about the project, if necessary.
- Give a brief description about the role of the letter writer’s organization in the project.
- Discuss expected outcomes from implementation.
- Letter must follow a professional format with the original signature of the writer.
- Most importantly, proofread before sending it out to the potential funder.
Example of “Letter of Support”
Janice Clark XYZ Company 1456 Trafalgar Square Hampstead, London, UK. Dear Dr. Clark, I am pleased to be writing a letter in support of the proposal (name of the project) being submitted to the (name of the program) Program by our (name of department) at (name of institution). We strongly support this grant application and the focus on (mention the purpose of the study). As an organization whose mission is to (state the mission of your organization in alignment to the purpose of the research), we know your true passion is fostering the brilliant minds of tomorrow. We admire your initiatives to fund projects that have greatly benefited the research community. We acknowledge the specific roles and responsibilities fulfilled by us in this partnership. (mention your roles and provisions to the funding point-wise). Sincerely, Clara Montero Senior Director PQR Ltd. Southampton, UK
As you know by now, letters of support can make or break the chances of your project receiving funds, it is important to make sure that these letters are crafted scrupulously. Make sure you follow these tips while gleaning your letter of support or writing one for another applicant. Let us know how this article helped you in formulating a letter of support for grant. You can also visit our Q&A forum for frequently asked questions related to different aspects of research writing and publishing answered by our team that comprises subject-matter experts, eminent researchers, and publication experts.
To write a formal letter of support for a funding application, keep the following in mind: 1. Begin by addressing the letter to the appropriate recipient and state your purpose clearly. 2. Provide specific reasons why the project or initiative is deserving of funding, highlighting its potential impact and benefits. 3. Conclude with a positive statement expressing your confidence in the applicant's abilities to effectively utilize the funds for the intended purpose. Remember to maintain a professional tone and adhere to any specific guidelines provided by the funding organization.
In a letter of support for a grant application, express your strong endorsement for the project or initiative, emphasizing its importance, relevance, and potential positive impact. Highlight the applicant's qualifications, track record, and commitment, while also emphasizing the alignment between their goals and the grant's objectives.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Expert Interviews
Empowering Scholarly Endeavors: Insights on grants, funding, and diversity in academia
Funding plays an indispensable role in a researcher’s career. In our unwavering commitment to improve…

- Diversity and Inclusion
- Trending Now
The Silent Struggle: Confronting gender bias in science funding
In the 1990s, Dr. Katalin Kariko’s pioneering mRNA research seemed destined for obscurity, doomed by…

- Industry News
Optimizing Funding Strategies: Clarivate unveils Web of Science Grants Index for researchers
Clarivate Plc, a global leader in providing information services, has recently launched the Web of…

Addressing Socioeconomic Disparities in Academic Funding: Inclusivity in research grant allocation
Research grant allocation is a critical process that determines the distribution of funds to various…

- Thought Leadership
Knowledge Without Walls: Enago’s comprehensive global survey report on open-access publishing
In the ever-evolving landscape of scholarly communication, the global expansion of open-access (OA) publishing has…
Opening Doors to Academic Inclusivity: The significance of open access funding
Investing in Visibility: Incorporating publishing funds effectively in grant…
How to Write an Exceptional Research Scholarship Motivation Letter
How to Write a Data Management Plan During Grant Application

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
RELATED TOPICS
- What is Grant Writing?
- Grant Writing Process
- Grant Writing Templates
- Grant Writing Examples
- Grant Proposal Budget Template
- How to Write a Grant Proposal
- How to Write a Grant Proposal Cover Letter
- Grant Writing Books
- Grant Writer Role
- How to Become a Grant Writer
- Grant Writer Salary
- Grant Writer Resume
- Grant Writing Skills
- Grant Writer LinkedIn Profile
- Grant Writer Interview Questions
- Content Strategist
- How to Become a Content Strategist
- Content Strategist Skills
- Content Strategist Interview Questions
- Content Strategy Manager Overview
- Content Strategy in UX
- Content Strategist Portfolio Examples
- Content Design Overview
- Content Designer
- Content Designer Skills
- Content Design Books
- Technical Documentation
- Knowledge Base Documentation
- Product Documentation
- User Documentation
- Process Documentation
- Process Documentation Templates
- Good Documentation Practices
- HR Document Management Best Practices
- Software Documentation Examples
- How to Test Documentation Usability
- Document Control Overview
- Document Control Process
- Document Control Procedures
- Document Control Numbering
- Document Version Control
- Document Lifecycle Management
- Document Management Software Workflow
- Document Management Practices
- Github Document Management
- HR Document Management
- Confluence Document Management
- What is a Document Management System?
- Document Control Software
- Product Documentation Software
- HR Document Management Software
- Knowledge Base Software
- Internal Knowledge Base Software
- API Documentation Software Tools
- Knowledge Management Tools
- Document Management Software
- What is Software Documentation?
- How to Write Software Documentation
- How to Write API Documentation
- Document Manager
- Documentation Manager
- Documentation Specialist
- Document Control Manager Salary
- Business Writing Overview
- Business Writing Principles
- Best Business Writing Examples
- Best Business Writing Skills
- Best Business Writing Tips
- Types of Business Writing
- Best Business Writing Books
- Proposal Writing Overview
- How to Become a Proposal Writer
- Proposal Writer Role
- Proposal Writer Career Path
- RFP Proposal Writer
- Freelance Proposal Writer
- Remote Proposal Writer
- Government Proposal Writer
- Proposal Writer Salary
- Proposal Writer Job Description Example
- Proposal Writer Interview Questions
- How to Write a Proposal
- Proposal Writer LinkedIn Profile
- Business Proposal Examples
- UX Writing Overview
- Information Architecture
- Information Architecture vs Sitemap
- UX Writing Books
- UX Writing Examples
- UX Writer Overview
- Freelance UX Writer Overview
- UX Writer Career Path
- How to Become a UX Writer
- Google UX Writer
- UX Writer Interview Questions
- Google UX Writer Interview Questions
- UX Writer vs Copywriter
- UX Writer vs Technical Writer
- UX Writer Skills
- UX Writer Salary
- UX Writer Portfolio Examples
- UX Writer LinkedIn Profile
- UX Writer Cover Letter
- Technical Writing Overview
- Types of Technical Writing
- Technical Writing Examples
- Freelance Technical Writing
- Technical Writer Style Guide Examples
- Technical Writing Jobs
- Subject Matter Expert
- Document Development Lifecycle
- Darwin Information Typing Architecture
- Technical Writer Career Path
- How to Become a Technical Writer
- Technical Writer Education Requirements
- English Teacher to Technical Writer
- Software Engineer to Technical Writer
- Technical Writer Salary
- Technical Writer Interview Questions
- Google Technical Writer Interview Questions
- Technical Writer Resume
- Technical Writer Cover Letter
- Technical Writer LinkedIn Profile
- Technical Writer Portfolio
- Senior Technical Writer Salary
- Senior Technical Writer Job Description
- Knowledge Management Overview
- Knowledge Management System
- Knowledge Base Examples
- Knowledge Manager Overview
- Knowledge Manager Resume
- Knowledge Manager Skills
- Knowledge Manager Job Description
- Knowledge Manager Salary
- Knowledge Manager LinkedIn Profile
- Medical Writing Overview
- How to Become a Medical Writer
- Entry-Level Medical Writer
- Freelance Medical Writer
- Medical Writer Resume
- Medical Writer Interview Questions
- Medical Writer Salary
- Senior Medical Writer Salary
- Technical Writer Intern Do
- Entry-level Technical Writer
- Technical Writer
- Senior Technical Writer
- Technical Writer Editor
- Remote Technical Writer
- Freelance Technical Writer
- Software Technical Writer
- Pharmaceutical Technical Writer
- Google Technical Writer
- LinkedIn Technical Writer
- Apple Technical Writer
- Oracle Technical Writer
- Salesforce Technical Writer
- Amazon Technical Writer
- Technical Writing Certification Courses
- Certified Technical Writer
- UX Writer Certification
- Grant Writer Certification
- Proposal Writer Certification
- Business Writing Classes Online
- Business Writing Courses
- Grant Writing Classes Online
- Grant Writing Degree
Home › Writing › What is Grant Writing? › How to Write a Great Grant Proposal Cover Letter
How to Write a Great Grant Proposal Cover Letter
Become a Certified Grant Writer
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Although your grant proposal cover letter isn’t the most exciting part of the grant proposal, it’s still vital to get funding. T he cover letter is the first contact point a potential organization or funder will have with your nonprofit project.
It’s like going out on a date. Sure, looks aren’t everything. Nevertheless, if you utterly don’t care about how you dress, you’re making it harder for yourself.
And just like your looks, you want to make your grant application cover letter simple and focused on impressing a particular person. It’s the first contact with the executive or organization you wish to request funding. If you want them to read your grant proposal request, they’ll have to like the cover letter first.
More crucial steps will come later, presuming the funder reads your cover letter. Although you can search for sample cover letters, they are usually hard to find.
Research shows that about 35% of grant funders funded 50% or more of the received grant requests. So, your grant proposal cover letter needs to be a complete home run. Here’s how.
How to Write a Grant Proposal Cover Letter
First of all, an average grant proposal letter shouldn’t be more than one page long. Cover letters are the pitch of your detailed grant proposal. Think of it as a summary of your book.
Before writing the first paragraph, you should open the letter with the contact’s name, title, address, and other related information. Although this might sound obvious, double-check that the contact information is correct. There are countless examples of rushed letters. You don’t want your project to crumble due to a misspelled executive director name.
Do your research before starting the cover letter. You can quickly find the correct information via a single call, email, or simply by doing some Internet scavenging.
Similarly, address the person with “Dear” and add a personal title such as Mr. or Mrs. Again, it’s cover letter 101, so it will feel even worse if you misspell the first step.
If this doesn’t seem like a big deal, look at it like this. Executives have a keen eye for sloppiness. Since they will skim any cover letter first rather than reading it to the last paragraph, you don’t want mistakes popping out.
The initial information tells the funder you didn’t go in headfirst, and proper addressing tells them you’re a potential candidate. If the letter lacks, you’ll be mistaken for a novice instead of a candidate worthy of doing business.
If you’re interested in learning more about the grant writing process, then take a look at our grant writing certification course.
Get Straight to the Point in Your Grant Proposal Cover Letter
Everybody knows why you’re writing a grant proposal cover letter; it’s in the name. Meaning, there’s no reason to sugarcoat it.
After you nail the introduction, it’s time to introduce yourself and your organization. In the first paragraph, format the content into two sentences maximum. Here, you’ll write who you are and your job title. That’s it.
Next, get right to the point. Describe why your organization or foundation needs the grant, what’s your mission, and most importantly, the budget you’re requesting. Maybe you’re working on a community project, or it’s a charity. Either way, make it brief.
While on the topic, you should create a proposal for grants of all sizes. Even if a smaller grant doesn’t suffice, having it can attract larger grants. There are about 900 federal grant programs . Don’t limit yourself.
Another great touch is to validate your project via research. If you have cold data that justifies your organization’s existence, rarely will anyone find a way to object.
If you’re not 100% sure how to format the paragraph, create a sample cover and share it with friends or co-workers. Write the section, read the grant request introduction, then ask two questions .
- Can you tell me what the project is about? – Although the mission is clear to you as a writer, it might read astrophysical development documents to a fresh pair of eyes.
- How did you feel when you read the requested funding? – This is to see how another person will react. Keep in mind that how your friend and the funder reacts can differ.
Methods, Strategies & Solutions
In the next paragraph, you should explain how you plan to use the grant to the grantor. By doing this, you’re effectively telling the funder that you have a plan in motion. You can also include a graphical modal for visual representation, depending on the format.
Some writers like to use a numbered sample. The format can work both when you’re explaining your goals and strategies:
- The organization’s four main goals
- The project’s five phases
Usually, you want to back up each number with further details. Although an excellent overview, simply including a couple of numbers in your letter won’t suffice. Find the balance between simplicity and complexity. Numbering provides a clear summary, while further details should give the letter a more professional tone.
An additional touch is to offer a timeline where you explain significant milestone and their due dates. You can also do that by using a brief bullet-point format. The timestamps can be months or quarters, depending on the project’s length.
Again, remember you’ll go into full detail in the grant proposal. Although defining strategies and methods isn’t crucial for the cover letter, add it if you can fit it on that one page.
Cover Letters & Necessary Data
After the mission details and budget proposals, it’s time to quickly cover organization info and structure. It can be tedious, but every grant proposal needs it, especially if you grab their attention.
Again, keep it short. Explain your corporate structure and related information in just a couple of sentences, including the founding date. Grant proposals require the data, and although you’re not writing a contract but a cover letter, you still need to present the essential information.
You should also explain how your project matches the funder’s and why the funder should give you the support and funding priority.
As always, double-check the information in your proposal letter, especially if you’re running a nonprofit organization. It’s somewhat easier to get grants for a nonprofit project, but funders are more likely to check the details. Although many think that foundation funding is the primary source for nonprofits, about 80% of income comes from other sources.
If the grant funder likes your cover letter, you want to make it easy for them to contact you about the grant proposal.
Always end all your cover letters with a positive closing line such as “Looking forward to your response.” The goal is for the letter to sound optimistic, grateful, but not needy.
Sign the letter and if your organization has an executive director, have them sign as well.
Cover Letter Tips & Mistakes to Avoid
For the final polish of your proposal, you can do things to give the letter a more personal and professional touch.
Ask for Feedback
Before pressing “send,” have co-workers read the sample of the proposal one more time. Good feedback is hard to find, and once you make contact, the fabled typos become irreversible. Don’t be gun shy to even reach out to your wider community for support.
Send the proposal sample page to anyone you can and collect their feedback. Naturally, you don’t want to spend half of your waking life collecting feedback. Still, a cover letter is just words on a paper without the reader understanding what you want, especially when they’re giving you money.
If still not convinced, it takes between 80 to 200 hours to write a grant proposal, and it can cost several thousand dollars if you’re hiring a grant writer . You don’t want a single page to ruin all the hard work.
Use Plain English
We all want to impress others. But using complex words can easily backfire and ruin your chance.
The point of a proposal letter isn’t to show your vocabulary but to state your case as straightforward as possible. If you’re unsure if you’re overdoing it, some helpful apps and websites will tell you if a sentence is too long or too complex.
Final Formatting
Ensure the dates match since you’ll have a date both in the cover letter and the main grant proposal. You don’t want to send a proposal where the grant proposal has April 5th while the cover letter has November 27th. This goes for other files you’ll send as well.
The cover letter should use single-space and leave space between addresses in the heading. Double-space means less room to write the limited information you need. This doesn’t mean you should delete the area between paragraphs. Give the letter room to breathe.
Although unnecessary, it can be a nice touch if you place your signature in live ink. Leave about three empty spaces the complimentary close and your name for the signature.
Send the Cover Letter in PDF
If you’re emailing the grant proposal letter, email the document in PDF. There’s a chance the foundation will offer to sign documents digitally. Additionally, unlike other text files, PDF is safe from malware. Meaning, a PDF will not only look competent but will also leave a good impression in the eyes of the more “tech-savvy” grant funders.
If you are new to grant writing and are looking to break-in, we recommend taking our Grant Writing Certification Course , where you will learn the fundamentals of being a grant writer, how to write proposals that win grants, and how to stand out as a grant writing candidate.
We offer a wide variety of programs and courses built on adaptive curriculum and led by leading industry experts.
- Work on projects in a collaborative setting
- Take advantage of our flexible plans and community
- Get access to experts, templates, and exclusive events
Become a Certified Technical Writer. Professionals finish the training with a full understanding of how to guide technical writer projects using documentation foundations, how to lead writing teams, and more.
Become a Certified UX Writer. You'll learn how to excel on the job with writing microcopy, content design, and creating conversation chatbots.
Become a Certified Grant Writer. In this course, we teach the fundamentals of grant writing, how to create great grant proposals, and how to stand out in the recruiting process to land grant writing jobs.
Please check your email for a confirmation message shortly.
Join 5000+ Technical Writers
Get our #1 industry rated weekly technical writing reads newsletter.
Your syllabus has been sent to your email
The Ultimate Grant Writing Guide (and How to Find and Apply for Grants)
Securing grants requires strategic planning. Identifying relevant opportunities, building collaborations, and crafting a comprehensive grant proposal are crucial steps. Read our ultimate guide on grant writing, finding grants, and applying for grants to get the funding for your research.
Updated on February 22, 2024

Embarking on a journey of groundbreaking research and innovation always requires more than just passion and dedication, it demands financial support. In the academic and research domains, securing grants is a pivotal factor for transforming these ideas into tangible outcomes.
Grant awards not only offer the backing needed for ambitious projects but also stand as a testament to the importance and potential impact of your work. The process of identifying, pursuing, and securing grants, however, is riddled with nuances that necessitate careful exploration.
Whether you're a seasoned researcher or a budding academic, navigating this complex world of grants can be challenging, but we’re here to help. In this comprehensive guide, we'll walk you through the essential steps of applying for grants, providing expert tips and insights along the way.
Finding grant opportunities
Prior to diving into the application phase, the process of finding grants involves researching and identifying those that are relevant and realistic to your project. While the initial step may seem as simple as entering a few keywords into a search engine, the full search phase takes a more thorough investigation.
By focusing efforts solely on the grants that align with your goals, this pre-application preparation streamlines the process while also increasing the likelihood of meeting all the requirements. In fact, having a well thought out plan and a clear understanding of the grants you seek both simplifies the entire activity and sets you and your team up for success.
Apply these steps when searching for appropriate grant opportunities:
1. Determine your need
Before embarking on the grant-seeking journey, clearly articulate why you need the funds and how they will be utilized. Understanding your financial requirements is crucial for effective grant research.
2. Know when you need the money
Grants operate on specific timelines with set award dates. Align your grant-seeking efforts with these timelines to enhance your chances of success.
3. Search strategically
Build a checklist of your most important, non-negotiable search criteria for quickly weeding out grant options that absolutely do not fit your project. Then, utilize the following resources to identify potential grants:
- Online directories
- Small Business Administration (SBA)
- Foundations
4. Develop a tracking tool
After familiarizing yourself with the criteria of each grant, including paperwork, deadlines, and award amounts, make a spreadsheet or use a project management tool to stay organized. Share this with your team to ensure that everyone can contribute to the grant cycle.
Here are a few popular grant management tools to try:
- Jotform : spreadsheet template
- Airtable : table template
- Instrumentl : software
- Submit : software
Tips for Finding Research Grants
Consider large funding sources : Explore major agencies like NSF and NIH.
Reach out to experts : Consult experienced researchers and your institution's grant office.
Stay informed : Regularly check news in your field for novel funding sources.
Know agency requirements : Research and align your proposal with their requisites.
Ask questions : Use the available resources to get insights into the process.
Demonstrate expertise : Showcase your team's knowledge and background.
Neglect lesser-known sources : Cast a wide net to diversify opportunities.
Name drop reviewers : Prevent potential conflicts of interest.
Miss your chance : Find field-specific grant options.
Forget refinement : Improve proposal language, grammar, and clarity.
Ignore grant support services : Enhance the quality of your proposal.
Overlook co-investigators : Enhance your application by adding experience.
Grant collaboration
Now that you’ve taken the initial step of identifying potential grant opportunities, it’s time to find collaborators. The application process is lengthy and arduous. It requires a diverse set of skills. This phase is crucial for success.
With their valuable expertise and unique perspectives, these collaborators play instrumental roles in navigating the complexities of grant writing. While exploring the judiciousness that goes into building these partnerships, we will underscore why collaboration is both advantageous and indispensable to the pursuit of securing grants.
Why is collaboration important to the grant process?
Some grant funding agencies outline collaboration as an outright requirement for acceptable applications. However, the condition is more implied with others. Funders may simply favor or seek out applications that represent multidisciplinary and multinational projects.
To get an idea of the types of collaboration major funders prefer, try searching “collaborative research grants” to uncover countless possibilities, such as:
- National Endowment for the Humanities
- American Brain Tumor Association
For exploring grants specifically for international collaboration, check out this blog:
- 30+ Research Funding Agencies That Support International Collaboration
Either way, proposing an interdisciplinary research project substantially increases your funding opportunities. Teaming up with multiple collaborators who offer diverse backgrounds and skill sets enhances the robustness of your research project and increases credibility.
This is especially true for early career researchers, who can leverage collaboration with industry, international, or community partners to boost their research profile. The key lies in recognizing the multifaceted advantages of collaboration in the context of obtaining funding and maximizing the impact of your research efforts.
How can I find collaborators?
Before embarking on the search for a collaborative partner, it's essential to crystallize your objectives for the grant proposal and identify the type of support needed. Ask yourself these questions:
1)Which facet of the grant process do I need assistance with:
2) Is my knowledge lacking in a specific:
- Population?
3) Do I have access to the necessary:
Use these questions to compile a detailed list of your needs and prioritize them based on magnitude and ramification. These preliminary step ensure that search for an ideal collaborator is focused and effective.
Once you identify targeted criteria for the most appropriate partners, it’s time to make your approach. While a practical starting point involves reaching out to peers, mentors, and other colleagues with shared interests and research goals, we encourage you to go outside your comfort zone.
Beyond the first line of potential collaborators exists a world of opportunities to expand your network. Uncover partnership possibilities by engaging with speakers and attendees at events, workshops, webinars, and conferences related to grant writing or your field.
Also, consider joining online communities that facilitate connections among grant writers and researchers. These communities offer a space to exchange ideas and information. Sites like Collaboratory , NIH RePorter , and upwork provide channels for canvassing and engaging with feasible collaborators who are good fits for your project.
Like any other partnership, carefully weigh your vetted options before committing to a collaboration. Talk with individuals about their qualifications and experience, availability and work style, and terms for grant writing collaborations.
Transparency on both sides of this partnership is imperative to forging a positive work environment where goals, values, and expectations align for a strong grant proposal.
Putting together a winning grant proposal
It’s time to assemble the bulk of your grant application packet – the proposal itself. Each funder is unique in outlining the details for specific grants, but here are several elements fundamental to every proposal:
- Executive Summary
- Needs assessment
- Project description
- Evaluation plan
- Team introduction
- Sustainability plan
This list of multi-faceted components may seem daunting, but careful research and planning will make it manageable.
Start by reading about the grant funder to learn:
- What their mission and goals are,
- Which types of projects they have funded in the past, and
- How they evaluate and score applications.
Next, view sample applications to get a feel for the length, flow, and tone the evaluators are looking for. Many funders offer samples to peruse, like these from the NIH , while others are curated by online platforms , such as Grantstation.
Also, closely evaluate the grant application’s requirements. they vary between funding organizations and opportunities, and also from one grant cycle to the next. Take notes and make a checklist of these requirements to add to an Excel spreadsheet, Google smartsheet, or management system for organizing and tracking your grant process.
Finally, understand how you will submit the final grant application. Many funders use online portals with character or word limits for each section. Be aware of these limits beforehand. Simplify the editing process by first writing each section in a Word document to be copy and pasted into the corresponding submission fields.
If there is no online application platform, the funder will usually offer a comprehensive Request for Proposal (RFP) to guide the structure of your grant proposal. The RFP:
- Specifies page constraints
- Delineates specific sections
- Outlines additional attachments
- Provides other pertinent details
Components of a grant proposal
Cover letter.
Though not always explicitly requested, including a cover letter is a strategic maneuver that could be the factor determining whether or not grant funders engage with your proposal. It’s an opportunity to give your best first impression by grabbing the reviewer’s attention and compelling them to read further.
Cover letters are not the place for excessive emotion or detail, keep it brief and direct, stating your financial needs and purpose confidently from the outset. Also, try to clearly demonstrate the connection between your project and the funder’s mission to create additional value beyond the formal proposal.
Executive summary
Like an abstract for your research manuscript, the executive summary is a brief synopsis that encapsulates the overarching topics and key points of your grant proposal. It must set the tone for the main body of the proposal while providing enough information to stand alone if necessary.
Refer to How to Write an Executive Summary for a Grant Proposal for detailed guidance like:
- Give a clear and concise account of your identity, funding needs, and project roadmap.
- Write in an instructive manner aiming for an objective and persuasive tone
- Be convincing and pragmatic about your research team's ability.
- Follow the logical flow of main points in your proposal.
- Use subheadings and bulleted lists for clarity.
- Write the executive summary at the end of the proposal process.
- Reference detailed information explained in the proposal body.
- Address the funder directly.
- Provide excessive details about your project's accomplishments or management plans.
- Write in the first person.
- Disclose confidential information that could be accessed by competitors.
- Focus excessively on problems rather than proposed solutions.
- Deviate from the logical flow of the main proposal.
- Forget to align with evaluation criteria if specified
Project narrative
After the executive summary is the project narrative . This is the main body of your grant proposal and encompasses several distinct elements that work together to tell the story of your project and justify the need for funding.
Include these primary components:
Introduction of the project team
Briefly outline the names, positions, and credentials of the project’s directors, key personnel, contributors, and advisors in a format that clearly defines their roles and responsibilities. Showing your team’s capacity and ability to meet all deliverables builds confidence and trust with the reviewers.
Needs assessment or problem statement
A compelling needs assessment (or problem statement) clearly articulates a problem that must be urgently addressed. It also offers a well-defined project idea as a possible solution. This statement emphasizes the pressing situation and highlights existing gaps and their consequences to illustrate how your project will make a difference.
To begin, ask yourself these questions:
- What urgent need are we focusing on with this project?
- Which unique solution does our project offer to this urgent need?
- How will this project positively impact the world once completed?
Here are some helpful examples and templates.
Goals and objectives
Goals are broad statements that are fairly abstract and intangible. Objectives are more narrow statements that are concrete and measurable. For example :
- Goal : “To explore the impact of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance in college students.”
- Objective : “To compare cognitive test scores of students with less than six hours of sleep and those with 8 or more hours of sleep.”
Focus on outcomes, not processes, when crafting goals and objectives. Use the SMART acronym to align them with the proposal's mission while emphasizing their impact on the target audience.
Methods and strategies
It is vitally important to explain how you intend to use the grant funds to fulfill the project’s objectives. Detail the resources and activities that will be employed. Methods and strategies are the bridge between idea and action. They must prove to reviewers the plausibility of your project and the significance of their possible funding.
Here are some useful guidelines for writing your methods section that are outlined in " Winning Grants: Step by Step ."
- Firmly tie your methods to the proposed project's objectives and needs assessment.
- Clearly link them to the resources you are requesting in the proposal budget.
- Thoroughly explain why you chose these methods by including research, expert opinion, and your experience.
- Precisely list the facilities and capital equipment that you will use in the project.
- Carefully structure activities so that the program moves toward the desired results in a time-bound manner.
A comprehensive evaluation plan underscores the effectiveness and accountability of a project for both the funders and your team. An evaluation is used for tracking progress and success. The evaluation process shows how to determine the success of your project and measure the impact of the grant award by systematically gauging and analyzing each phase of your project as it compares to the set objectives.
Evaluations typically fall into two standard categories:
1. Formative evaluation : extending from project development through implementation, continuously provides feedback for necessary adjustments and improvements.
2. Summative evaluation : conducted post-project completion, critically assesses overall success and impact by compiling information on activities and outcomes.
Creating a conceptual model of your project is helpful when identifying these key evaluation points. Then, you must consider exactly who will do the evaluations, what specific skills and resources they need, how long it will take, and how much it will cost.
Sustainability
Presenting a solid plan that illustrates exactly how your project will continue to thrive after the grant money is gone builds the funder's confidence in the project’s longevity and significance. In this sustainability section, it is vital to demonstrate a diversified funding strategy for securing the long-term viability of your program.
There are three possible long term outcomes for projects with correlated sustainability options:
- Short term projects: Though only implemented once, will have ongoing maintenance costs, such as monitoring, training, and updates.
(E.g., digitizing records, cleaning up after an oil spill)
- Projects that will generate income at some point in the future: must be funded until your product or service can cover operating costs with an alternative plan in place for deficits.
(E.g., medical device, technology, farming method)
- Ongoing projects: will eventually need a continuous stream of funding from a government entity or large organization.
(E.g., space exploration, hurricane tracking)
Along with strategies for funding your program beyond the initial grant, reference your access to institutional infrastructure and resources that will reduce costs.
Also, submit multi-year budgets that reflect how sustainability factors are integrated into the project’s design.
The budget section of your grant proposal, comprising both a spreadsheet and a narrative, is the most influential component. It should be able to stand independently as a suitable representation of the entire endeavor. Providing a detailed plan to outline how grant funds will be utilized is crucial for illustrating cost-effectiveness and careful consideration of project expenses.
A comprehensive grant budget offers numerous benefits to both the grantor , or entity funding the grant, and the grantee , those receiving the funding, such as:
- Grantor : The budget facilitates objective evaluation and comparison between multiple proposals by conveying a project's story through responsible fund management and financial transparency.
- Grantee : The budget serves as a tracking tool for monitoring and adjusting expenses throughout the project and cultivates trust with funders by answering questions before they arise.
Because the grant proposal budget is all-encompassing and integral to your efforts for securing funding, it can seem overwhelming. Start by listing all anticipated expenditures within two broad categories, direct and indirect expenses , where:
- Direct : are essential for successful project implementation, are measurable project-associated costs, such as salaries, equipment, supplies, travel, and external consultants, and are itemized and detailed in various categories within the grant budget.
- Indirect : includes administrative costs not directly or exclusively tied to your project, but necessary for its completion, like rent, utilities, and insurance, think about lab or meeting spaces that are shared by multiple project teams, or Directors who oversee several ongoing projects.
After compiling your list, review sample budgets to understand the typical layout and complexity. Focus closely on the budget narratives , where you have the opportunity to justify each aspect of the spreadsheet to ensure clarity and validity.

While not always needed, the appendices consist of relevant supplementary materials that are clearly referenced within your grant application. These might include:
- Updated resumes that emphasize staff members' current positions and accomplishments.
- Letters of support from people or organizations that have authority in the field of your research, or community members that may benefit from the project.
- Visual aids like charts, graphs, and maps that contribute directly to your project’s story and are referred to previously in the application.
Finalizing your grant application
Now that your grant application is finished, make sure it's not just another document in the stack Aim for a grant proposal that captivates the evaluator. It should stand out not only for presenting an excellent project, but for being engaging and easily comprehended .
Keep the language simple. Avoid jargon. Prioritizing accuracy and conciseness. Opt for reader-friendly formatting with white space, headings, standard fonts, and illustrations to enhance readability.
Always take time for thorough proofreading and editing. You can even set your proposal aside for a few days before revisiting it for additional edits and improvements. At this stage, it is helpful to seek outside feedback from those familiar with the subject matter as well as novices to catch unnoticed mistakes and improve clarity.
If you want to be absolutely sure your grant proposal is polished, consider getting it edited by AJE .
How can AI help the grant process?
When used efficiently, AI is a powerful tool for streamlining and enhancing various aspects of the grant process.
- Use AI algorithms to review related studies and identify knowledge gaps.
- Employ AI for quick analysis of complex datasets to identify patterns and trends.
- Leverage AI algorithms to match your project with relevant grant opportunities.
- Apply Natural Language Processing for analyzing grant guidelines and tailoring proposals accordingly.
- Utilize AI-powered tools for efficient project planning and execution.
- Employ AI for tracking project progress and generating reports.
- Take advantage of AI tools for improving the clarity, coherence, and quality of your proposal.
- Rely solely on manual efforts that are less comprehensive and more time consuming.
- Overlook the fact that AI is designed to find patterns and trends within large datasets.
- Minimize AI’s ability to use set parameters for sifting through vast amounts of data quickly.
- Forget that the strength of AI lies in its capacity to follow your prompts without divergence.
- Neglect tools that assist with scheduling, resource allocation, and milestone tracking.
- Settle for software that is not intuitive with automated reminders and updates.
- Hesitate to use AI tools for improving grammar, spelling, and composition throughout the writing process.
Remember that AI provides a diverse array of tools; there is no universal solution. Identify the most suitable tool for your specific task. Also, like a screwdriver or a hammer, AI needs informed human direction and control to work effectively.
Looking for tips when writing your grant application?
Check out these resources:
- 4 Tips for Writing a Persuasive Grant Proposal
- Writing Effective Grant Applications
- 7 Tips for Writing an Effective Grant Proposal
- The best-kept secrets to winning grants
- The Best Grant Writing Books for Beginner Grant Writers
- Research Grant Proposal Funding: How I got $1 Million
Final thoughts
The bottom line – applying for grants is challenging. It requires passion, dedication, and a set of diverse skills rarely found within one human being.
Therefore, collaboration is key to a successful grant process . It encourages everyone’s strengths to shine. Be honest and ask yourself, “Which elements of this grant application do I really need help with?” Seek out experts in those areas.
Keep this guide on hand to reference as you work your way through this funding journey. Use the resources contained within. Seek out answers to all the questions that will inevitably arise throughout the process.
The grants are out there just waiting for the right project to present itself – one that shares the funder’s mission and is a benefit to our communities. Find grants that align with your project goals, tell your story through a compelling proposal, and get ready to make the world a better place with your research.

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"

Grant Application Cover Letter
- September 22, 2023

A Grant Application Cover Letter is a formal document that accompanies a grant application, typically addressed to a potential grantor or a funding organization. This letter serves as an introduction to the grant proposal, providing a concise overview of the project or program for which funding is sought.
It plays a critical role in making a first impression and convincing the grantor that the project is worth considering for funding.
The art of crafting a compelling grant application cover letter is integral in navigating the competitive terrain of grant procurement. This initial document serves as a pivotal interface between the applicant and the potential funding entity, reflecting the aspirations, the precision, and the authenticity of the proposed project.
A well-constructed cover letter can be instrumental in shaping favorable impressions, setting the stage for a thorough review of the accompanying application.
The essence of a grant application cover letter is to succinctly communicate the core objectives and anticipated impacts of the proposed endeavor. It acts as a gateway to the intricate details of the application, providing a glimpse into the innovation, relevance, and feasibility embedded within the project.
Given its paramount importance, it is crucial for applicants to meticulously align the content of the cover letter with the ethos and expectations of the funding organization.
In the dynamic landscape of grant procurement, the necessity for clarity, coherence, and congruence in articulating project outlines and objectives cannot be overstated.
The cover letter should resonate with the mission and values of the granting entity, elucidating the synergies between the proposed project and the overarching goals of the funder.
The intricate balance between conciseness and comprehensiveness in presenting the project’s scope and significance is vital in maintaining the interest and curiosity of the reviewers.
The strategic incorporation of pertinent information regarding the applicant’s background, expertise, and the contextual relevance of the project is crucial in establishing credibility and demonstrating commitment.
The inclusion of such elements not only substantiates the feasibility of the project but also reinforces the alignment between the applicant’s capabilities and the project’s demands. It serves to instill confidence in the reviewers about the applicant’s competence and the potential success of the proposed initiative.
Moreover, the articulation of the project’s goals, the anticipated outcomes, and the prospective benefits is essential in elucidating the transformative potential embedded within the proposal.
It provides an opportunity for applicants to showcase the uniqueness and the value proposition of their project, distinguishing it from the plethora of applications. The emphasis on the anticipated impacts and the broader implications of the project fosters a sense of relevance and urgency, compelling the reviewers to delve deeper into the application.
In this realm of incessant competition and evolving expectations, the role of meticulous research and nuanced understanding of the funding organization’s priorities is undeniable. The nuanced tailoring of the cover letter to resonate with the specific interests, values, and mission of the grantor is instrumental in establishing a connection and fostering alignment. The infusion of insights gleaned from thorough research enhances the authenticity and the contextual relevance of the cover letter, optimizing its potential to captivate and convince.
Furthermore, the meticulous attention to detail and adherence to the prescribed guidelines and format is essential in preserving the integrity and the professionalism of the application. The precision in language, the clarity in expression, and the coherence in structure are vital in conveying the seriousness and the sophistication inherent in the proposal. The avoidance of ambiguity, redundancy, and over-complexity is key in maintaining the fluidity and the accessibility of the content.
Understanding the Purpose
A grant application cover letter often serves as the first point of contact between the applicant and the granting institution. The purpose of this crucial document goes beyond merely introducing the project; it acts as a window, revealing the potential, viability, and relevance of the proposed endeavor, and its alignment with the funder’s objectives.
Understanding the purpose of a cover letter in the grant application process is pivotal. It’s the initial framework, setting the tone and providing a concise snapshot of the applicant’s proposal.
This document is vital for creating a strong first impression, reflecting the essence of the project and its potential impact. It lays the groundwork, inviting the grantor to explore the application further, beckoning them into the depths of the envisioned project, its aims, methodologies, and the anticipated outcomes.
Importance of a Cover Letter:
The value of a meticulously crafted cover letter cannot be understated in the world of grant applications. It’s the initial handshake, the first interaction that could make or break the journey of the proposed project. It’s not merely an informative piece but a persuasive document that strives to resonate with the reviewers, subtly conveying the symbiotic alignment between the project’s goals and the funding organization’s mission. It serves to entice, to pique interest, leading the way for the detailed exposition contained within the application.
Role in Creating a First Impression:
First impressions carry immense weight, dictating the subsequent interactions and shaping the perceptions of the reviewers. A well-articulated cover letter is instrumental in constructing a favorable and lasting impression.
It’s the preliminary canvas, painting a vivid picture of the project’s essence, its innovativeness, and its potential to effect meaningful change. The emphasis on clarity, conciseness, and relevance is paramount in ensuring the sustained interest and engagement of the reviewers, steering them towards a deeper exploration of the proposal.
Complementing the Grant Application:
The cover letter and the grant application share a symbiotic relationship, each enhancing the impact of the other. The cover letter serves as a gateway, a concise summary accentuating the pivotal aspects of the project, while the application delves into the intricate details, substantiating the claims and the projections made in the cover letter. This harmonious interplay is crucial in presenting a coherent, comprehensive, and compelling narrative, optimizing the chances of securing the coveted grant.
Setting the Tone:
The tone of the cover letter is a subtle yet powerful element, reflecting the applicant’s approach, attitude, and the level of professionalism. A balanced, respectful, and earnest tone is crucial in establishing rapport and credibility. The infusion of enthusiasm, conviction, and humility can significantly enhance the relatability and the authenticity of the document, fostering a sense of trust and resonance with the reviewers. The deliberate alignment of the tone with the ethos and the expectations of the funding organization is key in optimizing the impact and the persuasiveness of the cover letter.
Essential Components
The crafting of an effective grant application cover letter is akin to constructing a building; every component, every element has a role, ensuring the overall stability, coherence, and impact of the structure. The integral components of a cover letter work in unison to present a well-rounded picture of the project, its relevance, and the prospective benefits, compelling the reviewers to delve deeper into the details provided in the grant application.
A well-structured cover letter is a blend of pertinent information, clear articulation, and strategic emphasis. It consists of several critical elements, each contributing to the overall narrative and impact of the document.
These components, from address to signature, collectively serve to introduce, elucidate, and emphasize the project’s goals, methodologies, anticipated outcomes, and alignment with the funding organization’s mission and values. The meticulous attention to each element ensures the coherence, clarity, and persuasiveness of the cover letter, optimizing its potential to captivate and convince.
Address and Salutation:
The address and salutation set the tone for the interaction, reflecting the professionalism and the attention to detail inherent in the applicant. The accurate addressing of the funding organization and the appropriate salutation are foundational in establishing rapport and conveying respect. The meticulous verification of the organization’s name, the recipient’s title, and the preferred form of address is crucial in avoiding inaccuracies and ensuring a positive first impression.
Introduction:
The introduction serves as the entry point, the initial glimpse into the essence of the proposed project. It’s the succinct articulation of the project’s core objectives, its relevance, and its alignment with the funder’s goals. The strategic emphasis on clarity, conciseness, and relevance in the introduction is vital in capturing the interest of the reviewers and compelling them to explore further. The integration of a hook, a unique angle or insight, can significantly enhance the impact and the memorability of the introduction.
Project Description:
The project description is the heart of the cover letter, providing a concise yet comprehensive overview of the proposed endeavor. It delves into the specifics, elucidating the methodologies, the anticipated outcomes, and the broader implications of the project. The meticulous balancing of detail and brevity is crucial in maintaining the engagement of the reviewers, providing them with a clear understanding of the project’s scope, significance, and feasibility, while fostering a sense of curiosity and anticipation.
Project’s Objectives:
The articulation of the project’s objectives serves to clarify the envisioned outcomes and the intended impacts of the proposal. It’s the clear, coherent presentation of the goals, the transformative potential, and the alignment with the funding organization’s mission. The emphasis on specificity, measurability, attainability, relevance, and time-bound nature of the objectives is essential in conveying the viability and the value proposition of the project, instilling confidence in the reviewers about the prospects of success.
Budget Overview:
The budget overview provides a snapshot of the financial aspects of the project, offering insights into the allocation, utilization, and management of the funds. It’s the transparent, accountable presentation of the financial needs, the justifications, and the anticipated returns on investment. The strategic integration of a budget overview in the cover letter is instrumental in establishing credibility, demonstrating financial acumen, and reinforcing the feasibility and the sustainability of the project.
Closing Remarks and Signature:
The closing remarks and the signature are the final touches, the concluding interactions that re-emphasize the key points and express gratitude for the consideration. The infusion of sincerity, humility, and optimism in the closing remarks is vital in leaving a lasting, positive impression. The professional, respectful signature reflects the earnestness and the commitment of the applicant, serving as a subtle reminder of the authenticity and the integrity inherent in the proposal.
Tailoring the Content
Navigating the nuanced landscape of grant application cover letters necessitates more than just a clear understanding of the project and its components; it requires a meticulous approach to tailoring content. Customizing the narrative to align with the values, interests, and expectations of the granting organization is pivotal in creating resonance and establishing connection.
Tailoring the content of a grant application cover letter is akin to designing a key that perfectly fits a lock. It involves a comprehensive understanding of the funding organization’s mission, goals, and preferences, and aligning the cover letter’s narrative, tone, and emphasis accordingly. This customized approach enhances the relevance and the appeal of the document, optimizing its potential to engage, resonate, and convince. It transforms the cover letter into a dynamic, adaptive entity that speaks directly to the unique needs and aspirations of the grantor.
Understanding the Funder’s Mission:
To tailor content effectively, a profound understanding of the funder’s mission and values is indispensable. This knowledge serves as the foundation upon which the narrative is built, ensuring alignment and coherence with the grantor’s expectations and aspirations. A deep dive into the organization’s objectives, areas of interest, and previous funding initiatives provides insights into their preferences and priorities, enabling the crafting of a narrative that is attuned to their ethos.
Aligning Project Goals:
Once the funder’s mission is discerned, aligning the project’s goals with it is crucial. This involves highlighting the synergies between the proposed project and the grantor’s objectives, emphasizing the mutual benefits and the shared vision. Articulating the project’s objectives in a way that reflects the funder’s interests and values enhances the perceived relevance and value of the proposal, fostering a sense of partnership and shared purpose.
Demonstrating Impact:
The emphasis on the anticipated impacts and benefits of the project is integral in tailoring the content. Demonstrating the transformative potential of the proposal in terms that resonate with the funder’s goals creates a compelling narrative. The quantifiable presentation of the expected outcomes, their broader implications, and their alignment with the grantor’s mission reinforces the feasibility and the significance of the project, instilling confidence and interest in the reviewers.
Using Appropriate Language:
The language used in the cover letter is a subtle yet powerful element in tailoring the content. It reflects the understanding, the respect, and the alignment with the grantor’s culture and values. Adopting a tone and a vocabulary that resonate with the organization’s ethos enhances the relatability and the accessibility of the document. The infusion of terms, phrases, and references that are familiar and valued by the grantor contributes to the authenticity and the appeal of the narrative.
Addressing Specific Criteria:
Funding organizations often have specific criteria and expectations for grant applications. Addressing these explicitly and meticulously in the cover letter is essential in creating a tailored narrative. It demonstrates attentiveness, thoroughness, and alignment with the organization’s standards and requirements. Providing clear, concise responses to the outlined criteria enhances the clarity and the coherence of the document, optimizing its potential to meet the specific needs and expectations of the grantor.
Incorporating Feedback:
If available, incorporating feedback from previous interactions or applications with the funding organization is a strategic move in tailoring content. It reflects adaptability, responsiveness, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Addressing the areas of concern, emphasizing the enhancements made, and reiterating the alignment with the funder’s goals contribute to the credibility and the persuasiveness of the proposal, optimizing its chances of success.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Crafting a compelling grant application cover letter involves navigating around various potential pitfalls. These missteps can significantly hinder the impact and effectiveness of the document, thereby reducing the likelihood of securing the grant.
Identifying common pitfalls in writing grant application cover letters is crucial for avoiding them and enhancing the document’s effectiveness. These pitfalls often revolve around clarity, relevance, conciseness, and alignment with the grantor’s mission and expectations. By being cognizant of these pitfalls and implementing strategic measures, applicants can optimize the cover letter’s coherence, persuasiveness, and appeal, increasing the chances of a favorable reception.
Lack of Clarity:
One common pitfall is the lack of clarity and coherence in presenting the project’s goals, methodologies, and anticipated outcomes. How to Avoid: Prioritize clear, concise articulation of the project’s essence and its alignment with the funder’s mission. Use straightforward language and logical structuring to enhance understanding and engagement.
Neglecting the Funder’s Mission:
Another pitfall is neglecting to align the project’s objectives and impacts with the funder’s mission and values. How to Avoid: Conduct thorough research on the funding organization’s goals, preferences, and previous grants to tailor the content effectively, emphasizing mutual benefits and shared values.
Overloading with Details:
Overloading the cover letter with excessive details and technical jargon can overwhelm the reviewers and obscure the main points. How to Avoid: Maintain a balance between detail and brevity, focusing on the most pivotal aspects of the project. Use accessible language and provide succinct, relevant information to keep the reviewers engaged and informed.
Ignoring Specific Criteria:
Ignoring the specific criteria and guidelines provided by the funding organization can lead to non-compliance and reduced credibility. How to Avoid: Carefully review the application guidelines and address each criterion meticulously, demonstrating attentiveness and alignment with the organization’s standards and expectations.
Overlooking Proofreading:
Submitting a cover letter with errors and inconsistencies can convey a lack of professionalism and attention to detail. How to Avoid: Allocate ample time for proofreading and revisions. Seek feedback from peers or mentors and use editing tools to ensure accuracy, coherence, and polish.
Grant Application Cover Letter Example
Dear Madam Rosy,
I am reaching out on behalf of Girls Empower, a dedicated non-profit organization with a mission to foster learning and development opportunities for young girls from underserved communities.
We believe in the transformative power of education and empowerment to build a foundation for a more equitable, inclusive future. We are fervent advocates of nurturing potential, fostering resilience, and creating platforms for voices waiting to be heard.
We are writing to express our sincere interest in partnering with the Impact Makers Foundation, whose commitment to making a lasting difference aligns seamlessly with our core values and objectives. We humbly seek your support and consideration for a grant amount of $150,000 to launch our initiative titled “E mpowering Futures: Nurturing the Next Generation of Female Leaders.”
The “Empowering Futures” initiative aims to provide holistic education, mentorship, and skill development programs for 200 young girls aged 10-15 in Ohio, focusing on STEM education, leadership training, and personal development. We anticipate that the successful implementation of this project will result in enhanced academic performance, improved self-esteem, and the cultivation of leadership skills among the participants, ultimately contributing to the development of empowered, informed individuals capable of driving positive change in their communities.
We believe our initiative resonates with the mission of the Impact Makers Foundation to cultivate change and foster development in communities in need. The synergies between our goals create a mutual ground for collaboration, wherein we can collectively work towards the empowerment and upliftment of young girls, aiding them in transcending barriers and realizing their fullest potentials.
Our approach combines immersive learning experiences, mentorship programs, and interactive workshops. Each participant will be paired with a mentor to guide them through their journey, fostering a supportive, enriching environment. We anticipate the transformative impact of our program will not only be reflected in the improved academic and personal development of the participants but also in the positive ripple effects it will create within their communities.
The requested grant of $150,000 will be allocated judiciously to cover program development, educational materials, mentorship facilitation, and logistical expenses. We are committed to ensuring transparency, accountability, and optimal utilization of the funds to maximize the impact of the initiative.
We are excited about the prospect of collaborating with the Impact Makers Foundation to bring our shared vision to life. We believe that, together, we can ignite the spark of learning, leadership, and empowerment in the hearts of young girls, creating a wave of positive change that will echo through generations.
We extend our heartfelt gratitude for considering our application and are open to providing any additional information or clarifications required. We eagerly await the opportunity to discuss our proposal further and explore the possibilities of joining hands to make a lasting impact in the lives of the young girls who are the promise of our future.
Thank you for your time, consideration, and dedication to creating a world where every individual has the opportunity to thrive and make a difference.
Joy Martins
Executive Director
Girls Empower
Crafting an articulate and impactful grant application cover letter is truly an art form that combines clarity, coherence, precision, and a deep understanding of both the project at hand and the mission of the funding organization. From understanding the intrinsic purpose of the cover letter to meticulously tailoring the content and avoiding common pitfalls, each step in the process is crucial in constructing a compelling narrative that resonates with the grantors.
This comprehensive exploration has delved into the multifaceted approach required to master the art of writing grant application cover letters.
We’ve navigated through the essential components, the significance of tailoring the content, and the importance of avoiding typical missteps. The insights provided aim to empower individuals and organizations to create powerful, persuasive cover letters that align seamlessly with the values and objectives of funding bodies, thereby optimizing the chances of securing essential grant funding.
Remember, a well-crafted cover letter serves as the gateway to your project, reflecting its essence, its potential, and its alignment with the funder’s mission. It’s the strategic amalgamation of authenticity, alignment, clarity, and relevance that constructs a convincing, memorable narrative.
So, as you embark on your grant application journey, keep in mind the invaluable techniques and insights discussed, and approach the art of writing grant application cover letters with diligence, adaptability, and a profound sense of purpose.
Unlock Your Grant Success!
Join our email list now for exclusive grant-writing tips and unique grant opportunities delivered straight to your inbox. Click here to Subscribe . Don’t miss out!
Elevate Your Grant Writing Game: Dive Deeper with Expert Resources!
If you’ve ever felt the rush of excitement upon spotting a potential grant opportunity, only to be met with the daunting challenge of crafting the perfect proposal, you’re not alone.
Grant writing is both an art and a science, and I’ve distilled years of expertise into a collection of resources tailored to guide you, whether you’re a nonprofit visionary, a rising freelancer, or a small business owner.
Handpicked Titles Just For You:
1. Advanced Grant Writing for Nonprofits : Dive beyond the basics and navigate the intricate nuances to stand out.
2. Becoming the Grant Guru: Embrace your freelance journey with techniques and strategies that ensure success in the grant universe.
3. Mastering Grant Writing: Your nonprofit’s go-to guide for developing compelling proposals that captivate and convince.
4. The Small Business’s Guide to Winning Grants : Tailored insights to ensure your business’s endeavors are backed by the right funding.
Whether you’re taking your first steps in grant writing or seeking to refine your approach, there’s something in this collection for everyone.
Invest in your future now. These titles are available on Amazon, both in Kindle and paperback formats . Arm yourself with the knowledge to not just compete, but to excel.
Dive into a World of Grants Mastery – Grab Your Copies on Amazon
Fuel your passion, secure that funding, and bring your vision to life!
Work With Me: Elevate Your Nonprofit’s Grant Writing Game!
Hello passionate changemakers,
Does your nonprofit organization resonate with these challenges?
1. Feeling overwhelmed by the intricate maze of grant proposal writing?
2. Struggling to secure vital funding due to lackluster proposals?
3. Battling with limited in-house expertise to identify suitable grant opportunities?
4. Frustrated by not knowing how to articulate your mission effectively to potential funders?
If you nodded in agreement to any of these, you’re not alone. But here’s the good news: Together, we can change this narrative.
Why Partner With Me?
I bring to the table a unique blend of expertise and experience. As a seasoned Grant Writing Consultant, I’ve dedicated my career to mastering the art and science of grant writing. But beyond the knowledge, I carry a heartfelt passion for amplifying the impact of nonprofits like yours.
What I Offer:
1. Grant Writing Training: Let’s empower your team! Through comprehensive workshops, I’ll train your staff to craft compelling proposals that captivate, convince, and convert.
2. Personalized Grant Proposal Writing: Leverage my expertise to develop meticulously tailored proposals that reflect your organization’s vision, mission, and impact stories.
3. Strategic Grant Research: Don’t waste hours on unsuitable opportunities. With my deep industry insights, I’ll help identify grants that align with your objectives and values.
4. Report Development: Secure future funding by showcasing your successes. I’ll help you design robust, engaging reports that keep funders connected to your cause.
Our Journey Together:
Our collaboration begins with understanding – diving deep into your organization’s ethos, the communities you serve, and the impact you wish to create. It’s a partnership where your dreams become mine, and together, we’ll weave narratives that resonate, inspire, and secure the resources you need.
Your work in the nonprofit sector is invaluable. Every program initiated, every life touched, every community transformed – it all starts with a well-written proposal that opens doors to necessary funding. Let me be that catalyst for you.
A Future of Possibilities:
Picture this: A future where your nonprofit isn’t just surviving, but thriving. A world where your initiatives are backed by ample funding, and your stories of impact echo in the hearts of donors and communities alike.
So, if you’re ready to ascend the ladder of grant writing success and fuel your organization’s mission with robust funding, I’m here, eager and ready.
Let’s co-create this success story.
Reach out today, and let’s set the stage for a brighter, impactful tomorrow.
Email Address: [email protected]
Related Posts

Grants for Land Conservation
Grants for land conservation are a vital lifeline for preserving natural landscapes, ecosystems, and biodiversity. These financial resources support a wide range of activities, from purchasing land to protect it

Grants for Journalism
Grants for journalism are financial awards or funds provided to individuals, groups, or organizations to support the production of high-quality, public-interest journalism. These grants are essential for sustaining investigative reporting,

Grant Writing Academy is offering you full resources you need to win free money and boost your nonprofit impact.
No thanks, I’m not interested!
Calypso Tree
11 free grant letter of support templates & examples.
Boost your grant chances with our grant letter of support templates and expert guide. Learn how to get strong, persuasive letters.
Are you struggling to get those crucial letters of support for your grant? You know they’re important, but how do you get busy people to write glowing recommendations for your project? That’s where we come in! Think of letters of support as supercharged references for your grant proposal.
Table of Contents
What’s a Letter of Support?
It’s a short, official letter written by someone who believes in your project. This could be a local business owner, another nonprofit, a teacher – anyone who knows your work and thinks your project will make a difference. Good letters of support add a powerful boost to your application!
Key Elements of an Effective Letter of Support
Here’s a key components of a letter of support, focusing on what each section accomplishes:
Opening and Introduction
Writer’s Credentials:
- Why it matters: Establishes the writer as a knowledgeable, credible voice. This isn’t just anyone, but someone whose opinion holds weight in relation to the project.
- Example: “As Director of the City Parks Department…” or “As a teacher at [School Name] for 15 years…”
Clear Endorsement:
- Why it matters: No beating around the bush! Immediate enthusiasm sets a positive tone and grabs the grant reviewer’s attention.
- Example: “I wholeheartedly support [Organization]’s grant proposal for the [Project Name] initiative.”
Understanding of the Project
Demonstrate Knowledge:
- Why it matters: Shows the writer didn’t just sign a generic letter. They took the time to understand the project’s purpose and methods.
- Example: “Your plan to expand after-school tutoring aligns perfectly with our district’s focus on improving reading scores…”
- Why it matters: Strengthens the support by connecting the writer/their organization to the project’s mission.
- Example: “As a company committed to sustainability, we’re excited about your community recycling program…”
Value and Impact
Benefit to the Community:
- Why it matters: Moves beyond “This is a good idea” to showing how it solves a real problem or improves lives in the community the grant serves.
- Example: “This playground renovation will provide a safe, accessible play space in an area where children desperately need it.”
Unique Contributions:
- Why it matters: This is where the writer seals the deal! Shows they’re not just cheerleading, but will actively help make the project successful.
- Example: “Our organization can offer marketing expertise, a network of volunteers, and the use of our community center…”
Commitment and Collaboration
Level of Commitment:
- Why it matters: Vagueness is the enemy here. Are they offering money, volunteer hours, specific skills?
- Example: “We pledge $5000 toward this project, along with…”
Tangible Examples:
- Why it matters: Proves the commitment is genuine, not just empty words.
Reiterate Support:
- Why it matters: Leaves the grant reviewer with a strong final impression of the writer’s belief in the project.
Contact Information:
- Why it matters: Shows a willingness to answer further questions and makes follow-up easy.
When to Ask for Support Letters
Letters of support can seriously boost your chances of winning grant money. But when’s the right time to ask for them?
- The Grant Requires It: Duh! Some grant applications specifically say you need letters of support. Read the instructions carefully!
- You Want to Stand Out: Even if letters aren’t required, strong ones can make your application way more impressive than the competition.
- You Have Awesome Partners: If you’re already working with businesses, other nonprofits, or experts who love your project, ask them to write a letter! This shows the grant funders you’re a team player.
- You Need Specific Help: Maybe you need a space to hold events, volunteers, or someone to donate supplies. A letter of support can promise those things, making your grant application stronger.
Things to Remember:
- Ask Early! Don’t wait until the last minute. Give your partners time to write a thoughtful letter.
- Make It Easy: If possible, provide a short template or some bullet points of the key info to include.
- It’s Not Just About the Letter: Build real relationships with your partners. That makes their support genuine, which shines through in their writing.

Why You Need Letters of Support for Your Grant
Think of your grant application like applying for a really important job. Letters of support are like glowing recommendations from people who know you and your work. Here’s why they matter:
- Shows You’re Legit: These letters prove that other people in your community believe in your project and think you can pull it off.
- Teamwork Power: Grant funders want to see you have partners. This shows your project is connected to the community and has a better chance of long-term success.
- Why Your Project is Special: A good letter of support doesn’t just say, “This is cool.” It explains exactly how your project solves a problem and why the person writing the letter wants to be part of that.
- Standing Out: Lots of people apply for grants! Strong letters of support can give you the edge and show that your project deserves the money.
- Extra Info: Sometimes these letters mention things about your project that aren’t in the main application. This gives the grant people a fuller picture!
Who’s the Perfect Person to Write Your Support Letter?
Choosing the right people to ask is key to getting awesome letters of support. Here’s how to find them:
- Mission Match: Look for people or groups whose work is similar to your project’s goals. Example: If you’re building a playground, a school principal or child health organization would be a good fit.
- The Helper Squad: Who have you worked with on successful projects in the past? They already know you rock!
- Boost Your Business: Could your project help a local business? Maybe they attract more customers, or you’ll need to buy supplies from them. Showing that benefit makes them more likely to help.
- Community Stars: Is there a well-known teacher, community leader, or organization that people respect? Their support carries a lot of weight.
How to Write a Great Grant Letters of Support?
Here’s how to make those letters powerful:
Step 1: Introduce Yourself with Impact
- Who are you?: Your title and organization – make sure it’s clear why your opinion matters.
- Pump Up the Enthusiasm!: Start strong with “I’m totally excited to support [Project Name]…”
Step 2: Make It Personal
- Why Does This Project Matter to YOU?: Connect it to your own work, expertise, or your organization’s mission.
- Real-World Change: Explain how this project will make a positive difference in the community.
Step 3: Show Off Your Superpowers
- How Will You Help?: Be specific! Offer money, volunteer time, supplies, your special skills, or a place to meet.
- Prove Your Awesome: Mention a past project you helped with that was a success (if you have one!).
Step 4: The Grand Finale
- Summarize Your Support: Remind them in a few sentences why you believe in this project.
- Easy to Contact: Include your email or phone number so the grant people can reach out with questions.
Need more grant writing guidance? Check out our full suite of resources [Link]”.
Common Mistakes in Grant Letters of Support (And How to Fix Them!)
You’ve asked someone to write a letter supporting your grant project – awesome! But there are a few ways these letters can fall flat. Here’s what to avoid:
Mistake #1: Generic Praise
Problem: Saying “This project is great” isn’t very helpful. The best letters are personal.
How to Fix It:
- Ask for specifics: Suggest the writer explain why the project matters to them and fits their organization’s goals.
- Give them a nudge: Ask if they have a past success story that relates to your project. They can mention that!
Mistake #2: No Real Promises
Problem: Just saying “We support this idea” is weak. Funders want to see action!
- Be upfront: When you ask for the letter, clearly state what kind of help you need (money, volunteers, supplies, etc.).
- Make it easy: Give the writer a few options for how they could help. This gets their ideas flowing.
Mistake #3: Misaligned Expertise
Problem: A letter from someone who has nothing to do with your project is confusing.
- Choose wisely: Pick people or organizations whose work or mission connects to your project’s goals.
- Explain the connection: When you ask for the letter, briefly mention why you think their expertise would be a perfect fit.
Mistake #4: Neglecting Proofreading
Problem: Sloppy mistakes make your whole project seem less professional.
- Stress the importance: Let the writer know a polished letter makes them look good too!
- Lend a hand: If they’re short on time, offer to proofread their letter before it goes out.
Extra Tips:
- Templates Help, But Don’t Be a Robot: A basic template is a good start, but make sure the final letter sounds like a real person wrote it.
- Don’t Rush: Give your partners time to write something great. Rushed letters are rarely amazing.
- Say Thanks! A thank-you note after shows you’re grateful and makes them more likely to help out again in the future.
Free Grant Letter of Support Templates & Examples
Templates are like a recipe for writing a letter of support. Here’s a simple one:

Grant letter of support template
Grant Letter of Support Templates Concise and Impactful

Basic Grant Letter of Support Templates Concise and Impactful
Grant Letter of Support Templates Emphasis on Expertise

Basic Grant Letter of Support Templates Emphasis on Expertise
Basic Grant Letter of Support Templates Focus on Partnership

Environmental grant letter of support template

environmental grant letter of support template
Gates Foundation grant letter of support Sample

Gates Foundation grant letter of support format
Letter of support for educational grant

letter of support for grant example

Nonprofit grant letter of support template

nonprofit grant letter of support template
Research grant letter of support template

research grant letter of support template
Sample NIH grant letter of support Letter

Sample NIH grant letter of support Letter guidelines
Why Use Templates
Here’s why:
- Saves Time: Templates give your partners a basic outline, so they don’t have to write a letter from scratch. This is great for busy people!
- Makes Sure Nothing’s Missing: A good template reminds the writer to include all the important stuff – who they are, why they support your project, and how they’ll help.
- Looks More Pro: If you need several letters, templates help them all sound similar and polished. This makes a stronger impression on the grant funders.
- Don’t Forget to Customize! Templates are a starting point. The best letters still feel personal and show the unique connection between your project and the partner
Important Tips to Make Your Support Letters
- Customize!: Templates are a helpful start, but the best letters feel personal. Add details about why YOU care about the project and how your unique skills will help.
- Choose Wisely: Choose people or organizations who are truly excited about your project, not just anyone who will say yes. Their enthusiasm will come through in the letter.
- Check for Mistakes: Typos or confusing sentences make your whole project seem less polished. Read your letter out loud to catch errors, or ask a friend to help edit.
The Winning Formula
A strong letter of support can make a huge difference when you’re applying for a grant. Download some templates, start writing, and show everyone why your project deserves support!

The content creator team at calipsotree.com is dedicated to making topics accessible to everyone, with over 9 years of experience in writing and breaking down complex concepts into easy-to-understand articles that answer readers’ financial questions.
About The Author
Calypsotree.com.
The content creator team at calipsotree.com is dedicated to making topics accessible to everyone, with over 9 years of experience in writing and breaking down complex concepts into easy-to-understand articles that answer readers' financial questions.
Related Articles
15 Best Sorority Recommendation Letter Example
12+ Example Persuasive Letters: Templates and Tips to Get Results
How to Write an Effective Grant Proposal Cover Letter
Make It Brief but Inviting
Image by Ran Zheng é The Balance 2020
- Nonprofit Organizations
- Retail Small Business
- Restauranting
- Real Estate
- Import/Export Business
- Freelancing & Consulting
- Food & Beverage
- Event Planning
- Construction
- Operations & Success
- Becoming an Owner
When Do You Include a Cover Letter?
Attributes of a good cover letter, formatting your cover letter, how long should the cover letter be, sample cover letter, mistakes to avoid in your cover letter, make your cover letter stand out.
Joanne Fritz is an expert on nonprofit organizations and philanthropy. She has over 30 years of experience in nonprofits.
Although the main parts of your grant proposal will take up most of your time and energy, don't shortchange your cover letter. Attention to the subtler points of putting the proposal package together can make or break a funding request. Don't turn off your funder with a sloppy cover letter.
Mim Carlson and Tori O'Neal-McElrath, authors of Winning Grants, Step by Step , point out that the cover letter should:
- Introduce your organization to the correct person.
- Assure the funder that this project has the support of your board of directors .
- State what you are asking for - how much and for what.
Use a cover letter for proposals to corporations and foundations, but not for federal or state grant applications. Those funders only want what they ask for, and they rarely ask for a cover letter.
Your cover letter should:
- Get to the point quickly
- Does not repeat the information that is in the proposal
- Tell the reader how well you understand the funder and how your grant fulfills the funder's requirements
Beverly A. Browning, the author of Grant Writing for Dummies , suggests that you write the cover letter after you've completed the entire proposal, and when you are in a reflective mood. Browning says:
"As you consider your great achievement (the finished funding request), let the creative, right side of your brain kick in and connect your feelings of accomplishment to the person who will help make your plans come true."
- Use your organization's letterhead. Put the same date on the cover letter that is on the completed grant application. That is the date you will send the grant proposal to the grantor. Using the same date makes all the documents in your proposal package consistent.
- For the inside address (goes at the top of the letter) use the foundation or corporate contact person's name and title, followed by the funding source's name, address, city, state, and zip code. Double-check this information with a telephone call or an email. Such information changes frequently, so make sure you have the current name and address.
- In your salutation, use "Dear" plus the personal title (Mr., Ms., Mrs., Dr., Messrs., etc.), followed by the last name. It is critical that you address the letter to a particular person. Call the foundation or corporate office to make sure you have the right person and the correct personal title. These details may seem unimportant, but they do matter.
- Your first paragraph should be short and focused. Introduce your organization (its legal name, which will be your corporate name ) and tell the funder how much money you are requesting and why. Include a sentence or two about what your organization does, and then include one research-based point that shows there is a need for what your organization does.
- Write one or two more brief paragraphs. State your project's purpose and how it fits with the funder's mission or funding priorities. Include the fact that your board of directors fully supports the project.
- End your letter with a summarizing paragraph. Add what this funding partnership can mean for your project's target audience. You might want to include an invitation for a site visit as well.
- Use a closing such as "Sincerely."
- The letter should be signed by the executive director or the board president, or both. Below the signature, type the signer's first name, middle initial, last name, and job title. Although the ED or board president should sign the letter, do include the contact information for the best person to answer questions at the end of the last paragraph.
- At the bottom of the letter, include the word, "ENCLOSURE" (in all caps).
Limit your cover letter to one page with three or four paragraphs. It should be a quick read.
The tone and specifics of your cover letter may vary depending on whether you've been invited to submit a full proposal after sending a Letter of Inquiry (LOI) , or if this project is your organization's first approach to this particular foundation.
Mary Smith, PhD
Program Officer
Community Foundation
4321 Common Lane
Some City, YZ 55555
Dear Dr. Smith:
The Some City Senior Center respectfully requests a grant of $50,000 for our Senior Latino Community Outreach Pilot Project.
As the largest senior center in Any County, serving over 450 seniors every day, we are aware of the changing demographics in our service area. And we are committed to growing and adapting our center to meet emerging needs. The Senior Latino Community Outreach Pilot Project will allow us to pilot a one-year effort to determine if our center can effectively:
Provide comprehensive access to health and social services to seniors in the Latino communities served by our center, and
Raise and fully integrate the cultural competency of the board, staff, and volunteers of the Some City Senior Center.
Our board of directors is enthusiastic about this program and eager to launch it so we can become the most inclusive and culturally competent center for seniors in all of our communities that need these services. Should we find at the end of our pilot year that this program is, in fact, successful, our board has committed to including a portion of the project's yearly expenses into our annual operating budget so that the program becomes an integral part of our core services.
Through this project, the Center will become the primary referral given by Health Access Latinos, Families of Any County, and three community clinics within a fifteen-mile radius of our center. We will also accept referrals of Spanish-speaking seniors from any other community agency in our immediate service area.
Thank you for your consideration of our request. I will follow up with you in the next week to answer any questions you might have, as well as to learn whether we might meet with you to discuss the merits of our proposal. Meanwhile, should you have any questions, please feel free to contact Connie Jones, our Director of Development, at (555) 555-5555, x555, or cjones@scsc.org.
Jane Lovely
Executive Director
*Letter reprinted (with modifications) with permission from Winning Grants, Step by Step, Second Edition, Tori O'Neal-McElrath, Jossey-Bass, 2008.
- Writing too much. A cover letter is not a dissertation, nor is it a full proposal. Keep it short and to the point Tip: Have someone else read it. Do they understand it?
- Using big words . If you've been to graduate school, you learned to write in a complicated way. Don't do that here. You're not trying to impress someone with your erudition. You only want to state your case as naturally as possible. If you don't know when you're overcomplicating your writing, use an app such as Hemingway . It will tell you when your sentences are hard to read and when you are too wordy.
- Making Grammatical Mistakes . If you're not sure of your grammar, don't take chances. Use the grammar check in WORD, and, also run your draft through an app such as Grammarly . There is a free version, but the paid version goes well beyond the necessary grammar check.
Sad to say, but your grant proposal may be among hundreds or thousands that a typical foundation will see during an average year. Your cover letter can make the difference in getting to the next step towards funding. But how can you make it stand out?
Don't try anything "cute," as foundation officials will not be impressed.
The cover letter would not be appropriate for a story about a client , although you should have a story for other parts of your proposal, such as the description of the problem. Include a paragraph about why your organization is the one that can best accomplish this mission. Survey your competitive organizations and assess just how and where you excel. That may be in the strength of your staff and volunteers, your experience with this particular problem, or the community support you enjoy.
You don't need to mention the names of competitors or criticize them. Just highlight your strengths. This would be a good time to consult with others around the office. Pull a few people together and brainstorm how your nonprofit excels.
Fundamentally, the cover letter should be forward moving, easy-to-read and compel the reader into the larger proposal. Don't put any obstacles in the way of the reader that might deter them from reading further.
Free Grant Proposal Templates
By Andy Marker | February 1, 2018
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
With grant proposals, individuals and organizations can solicit funds from foundations, government entities, corporations, and other sources for projects such as scientific research, humanitarian programs, academic study, social services, and professional development. Since grant funding can be a critical component for financing an organization or allowing research to progress, crafting an effective grant proposal is key. Whether you’re creating a lengthy proposal for a government agency, using a letter format for a private foundation, or entering info into an online application, a grant proposal helps potential funders understand the importance of your project and what you plan to achieve.
To help guide you through this process, a number of grant writing templates are available below, including proposal, application, and budget forms. These free, printable templates can provide structure, offer a professional presentation, and save you time and money. You’ll find templates in Microsoft Excel, Word, and PDF formats, all of which you can customize to suit your organization and project.
Grant Proposal Templates
Generic grant proposal template.

Use this template as a guide for preparing a grant proposal. It includes typical sections, such as a statement of need, project description, goals and objectives, and budget. There’s also room to add a detailed timeline. This template provides a basic outline that you can easily modify for a range of proposals.
Download Generic Grant Proposal Template
Word | PDF
Nonprofit Grant Proposal Template

Many nonprofit organizations rely on grants to pay for operating expenses and provide community services. This grant proposal template for nonprofits includes sections for adding organizational background information, details about the community or population that will be served, measurable goals, and more. Remove or add sections as needed to create a customized template.
Download Nonprofit Grant Proposal Template
Research Grant Proposal Template
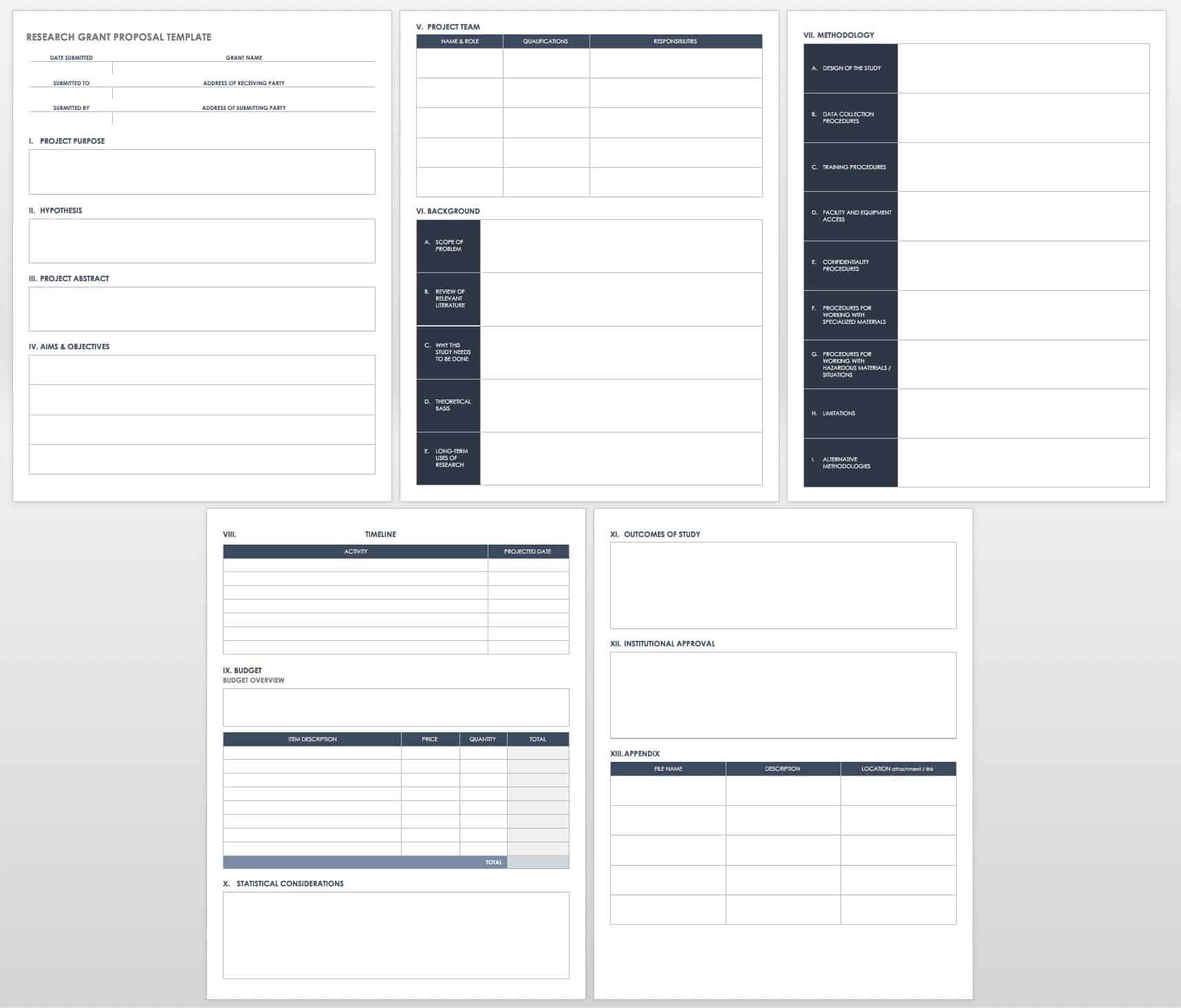
Present your hypothesis, literature review, research plans, and projected outcomes with this research grant proposal. This template could be adjusted to suit a scientific research proposal or academic grant application. Depending on the application requirements, you may be able to submit this document as a formal proposal, or you can use it to compile and organize all of the information that will go into your final proposal.
Download Research Grant Proposal Template
Technology Grant Proposal Template
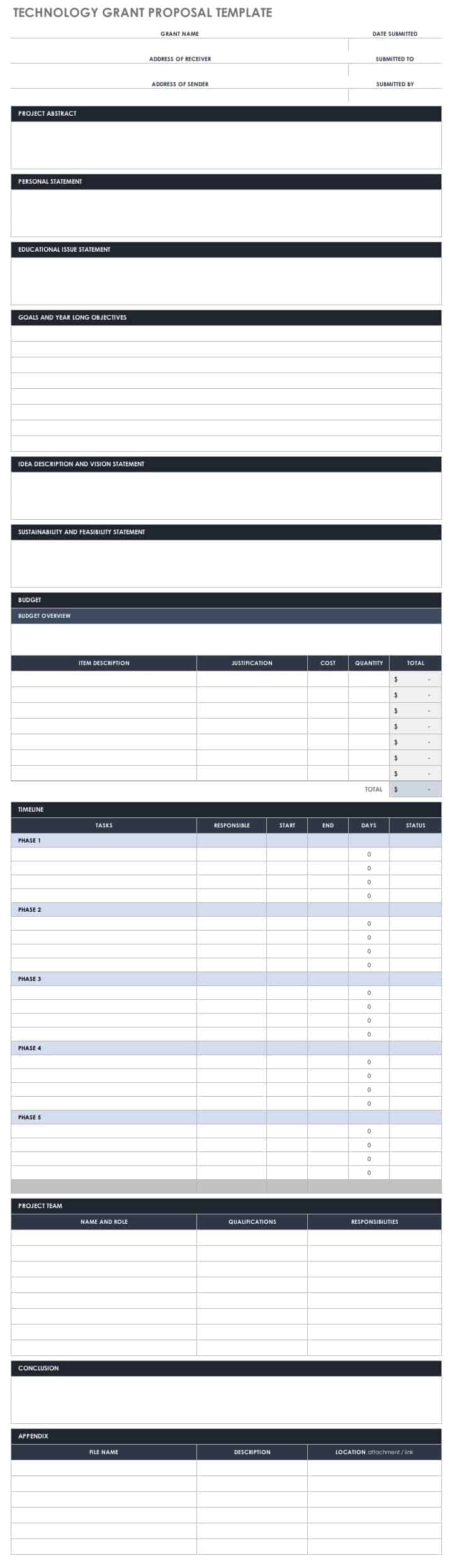
This technology grant proposal template is geared toward teachers and schools seeking funding for technology to use in the classroom. You can use the template to describe educational goals, technology needs, program sustainability, and budget requirements. The proposal also includes a timeline section to add a detailed schedule.
Download Technology Grant Proposal Template
Grant Budget Templates
Grant proposal budget template.
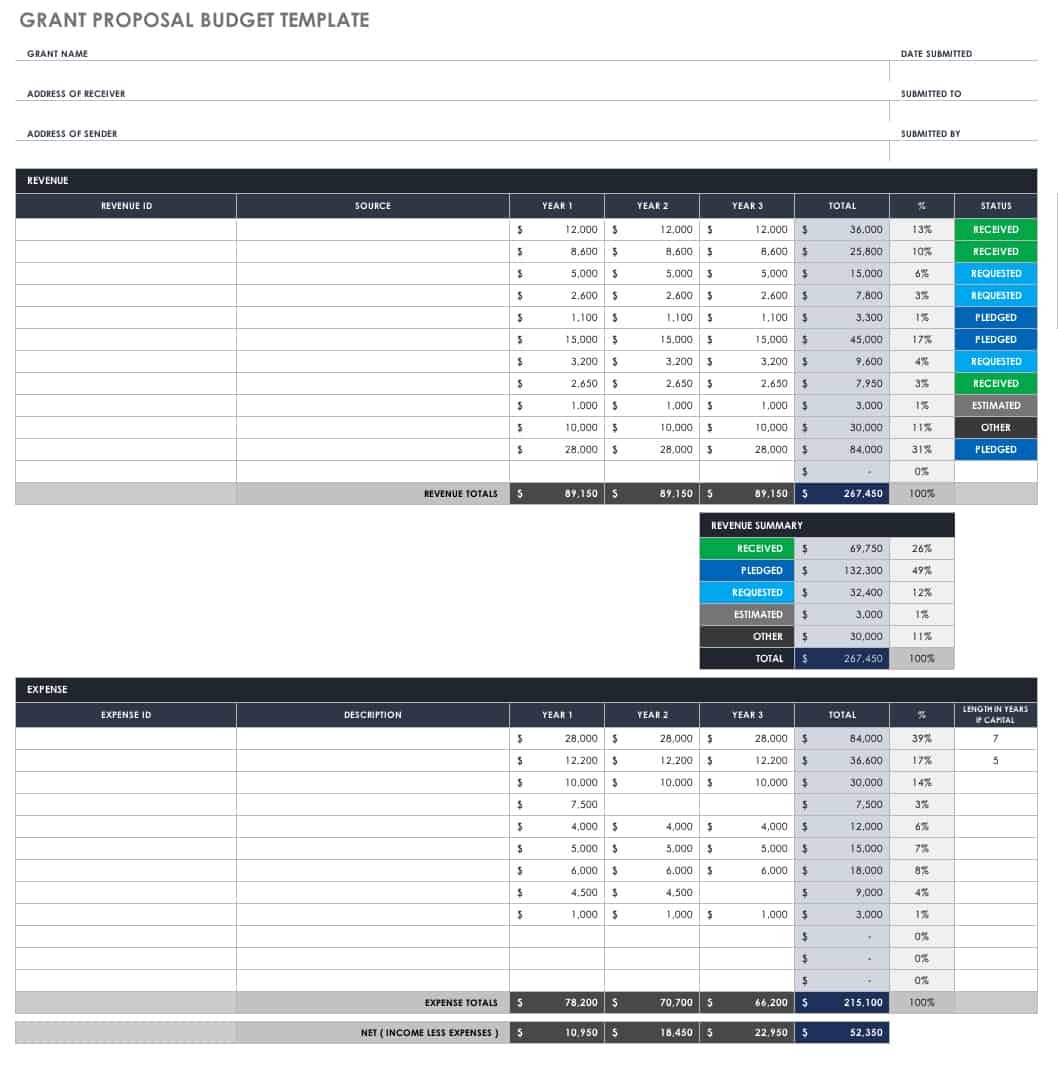
Create an itemized grant proposal budget that shows income and expenses over the course of a given time period. Enter funding sources and amounts along with specific costs, and the template will automatically calculate the totals. You can use this template for planning purposes, or submit it as part of a larger grant proposal.
Download Grant Proposal Budget Template
Grant Budget Revision Template
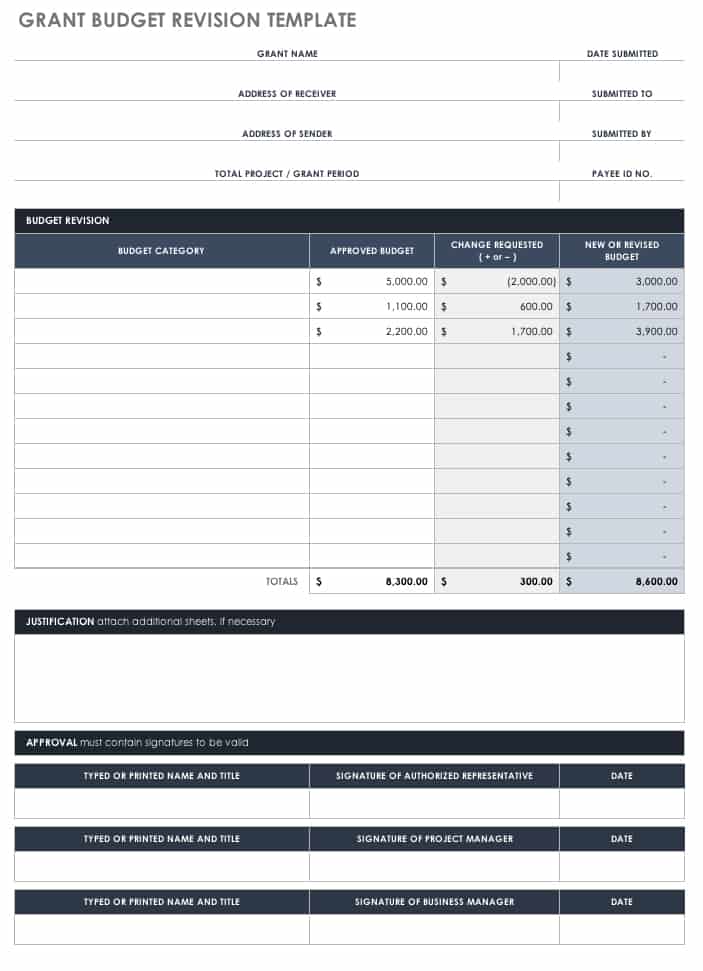
If you need to request a budget revision, this template is designed to show how funds will be adjusted by reducing the amounts allotted to one or more categories and increasing funds to others. Some grant makers require a revised budget so that they can approve how funds will be used. This template also includes room for adding organization and grant details.
Download Grant Budget Revision Template
Nonprofit Cash Flow Projection Template
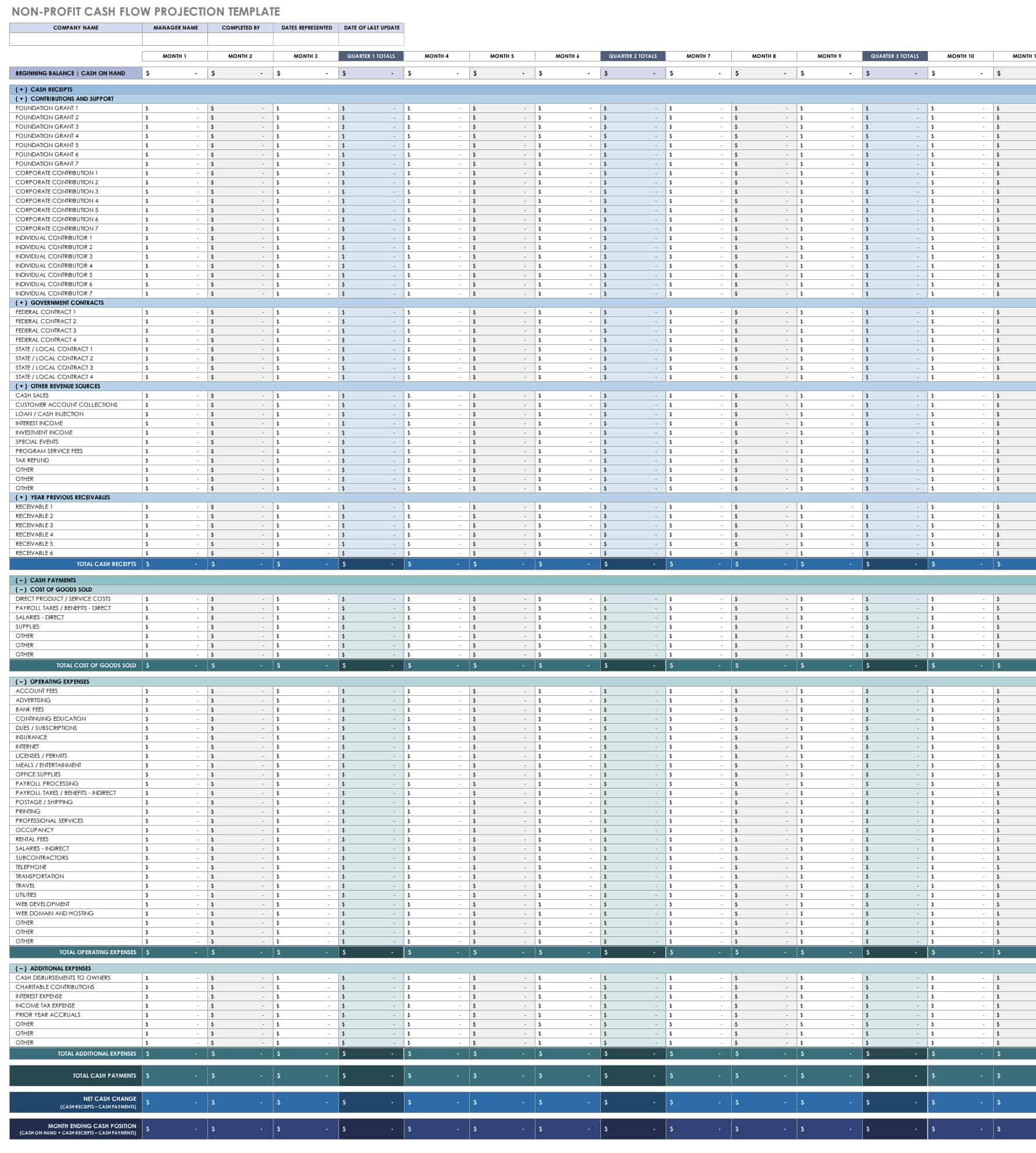
Nonprofits can use this cash flow template for financial planning over a 12-month period. The template shows revenue and expenses on a monthly, quarterly, and annual basis. The template also lists common funding sources along with operating costs, which can be edited to accommodate any type of organization.
Download Nonprofit Cash Flow Projection Template
Grant Application Templates
Grant application template.
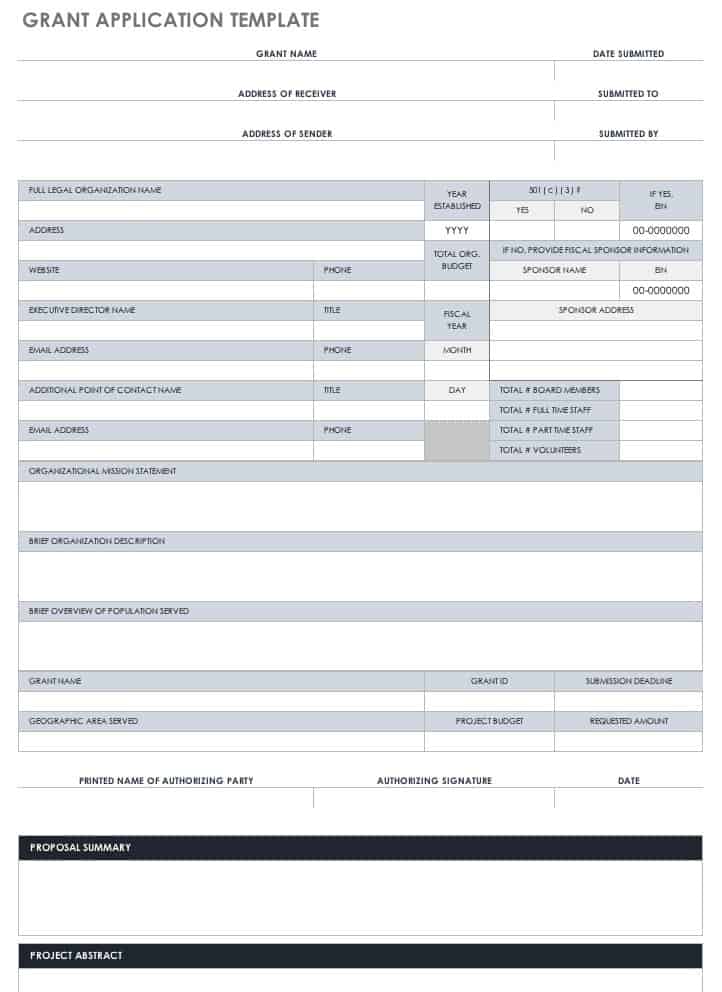
This template is intended for grant makers who want to create a grant application. It has sections for collecting applicant contact information, organizational details, and a thorough proposal, including a budget. Customize the application to cover whatever questions and information need to be reviewed to accurately assess a proposal.
Download Grant Application Template
Excel | PDF
Grant RFP Template
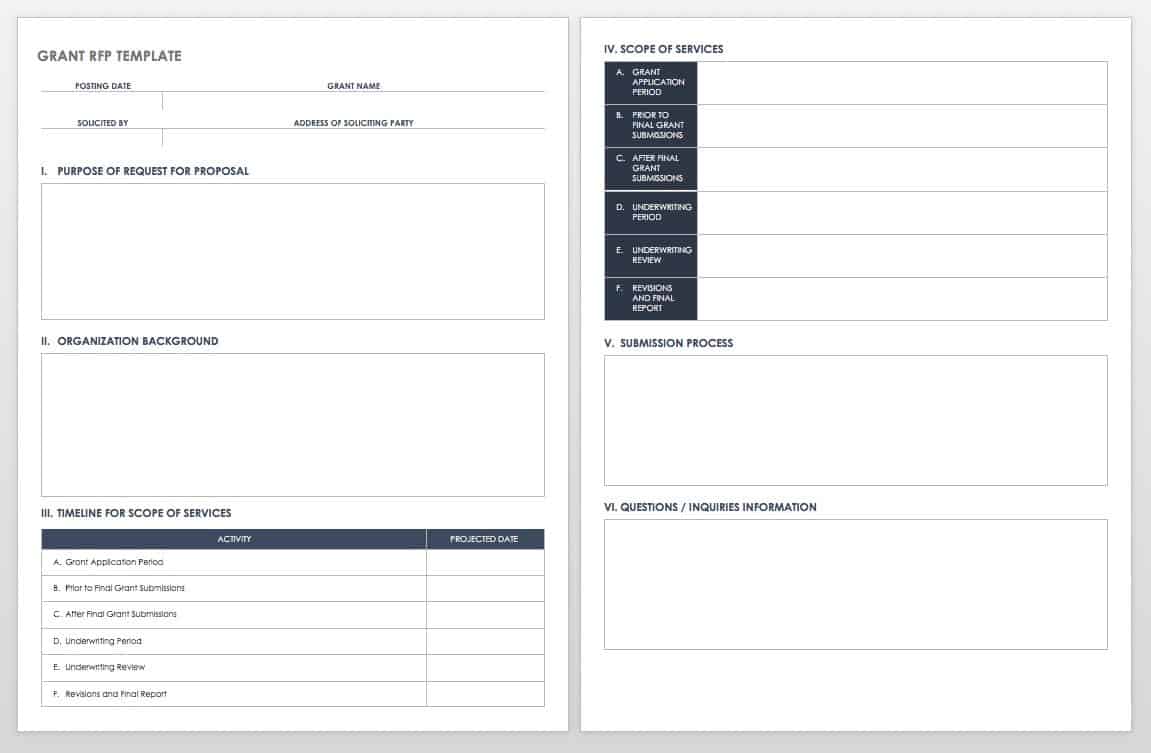
Grant makers can follow this outline to create a request for proposal template. Include submission instructions, agency background information, the timeline for reviewing proposals, and any requirements for proposal content and formatting. Applicants will also want to know what criteria will be used for evaluating proposals.
Download Grant RFP Template - Word
Grant Report and Evaluation Templates
Grant proposal checklist and evaluation form.
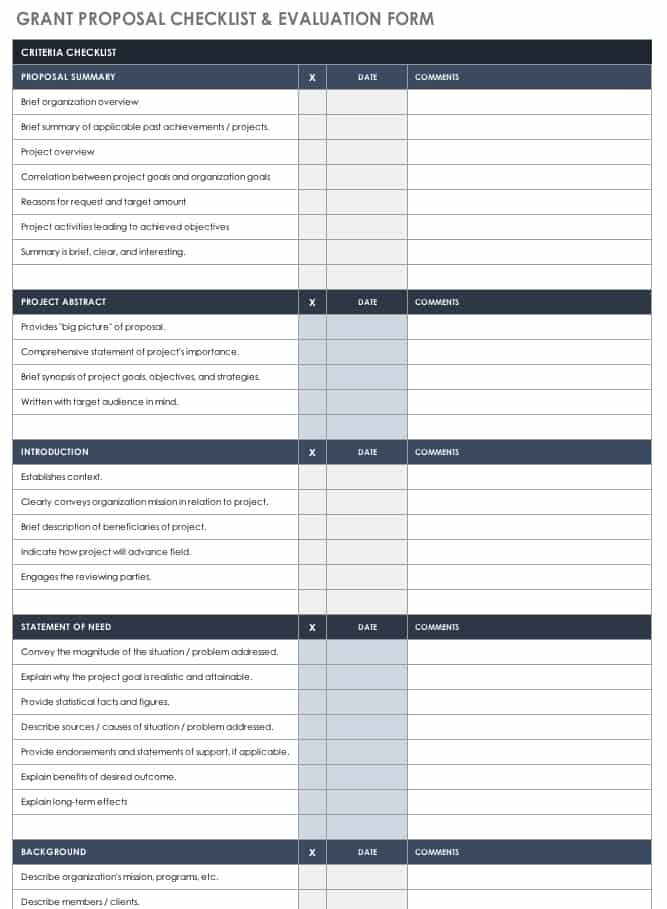
Once you have completed a proposal, use this checklist to ensure that all application requirements have been met and to evaluate the proposal’s quality and effectiveness. Consider soliciting feedback on your proposal from stakeholders or others who may be less familiar with the project and, therefore, more objective. Taking a moment to review a proposal may help reduce errors or omissions that could cost more time and money in the long run.
Download Grant Proposal Checklist and Evaluation Form
Excel | PDF
Grant Report Template
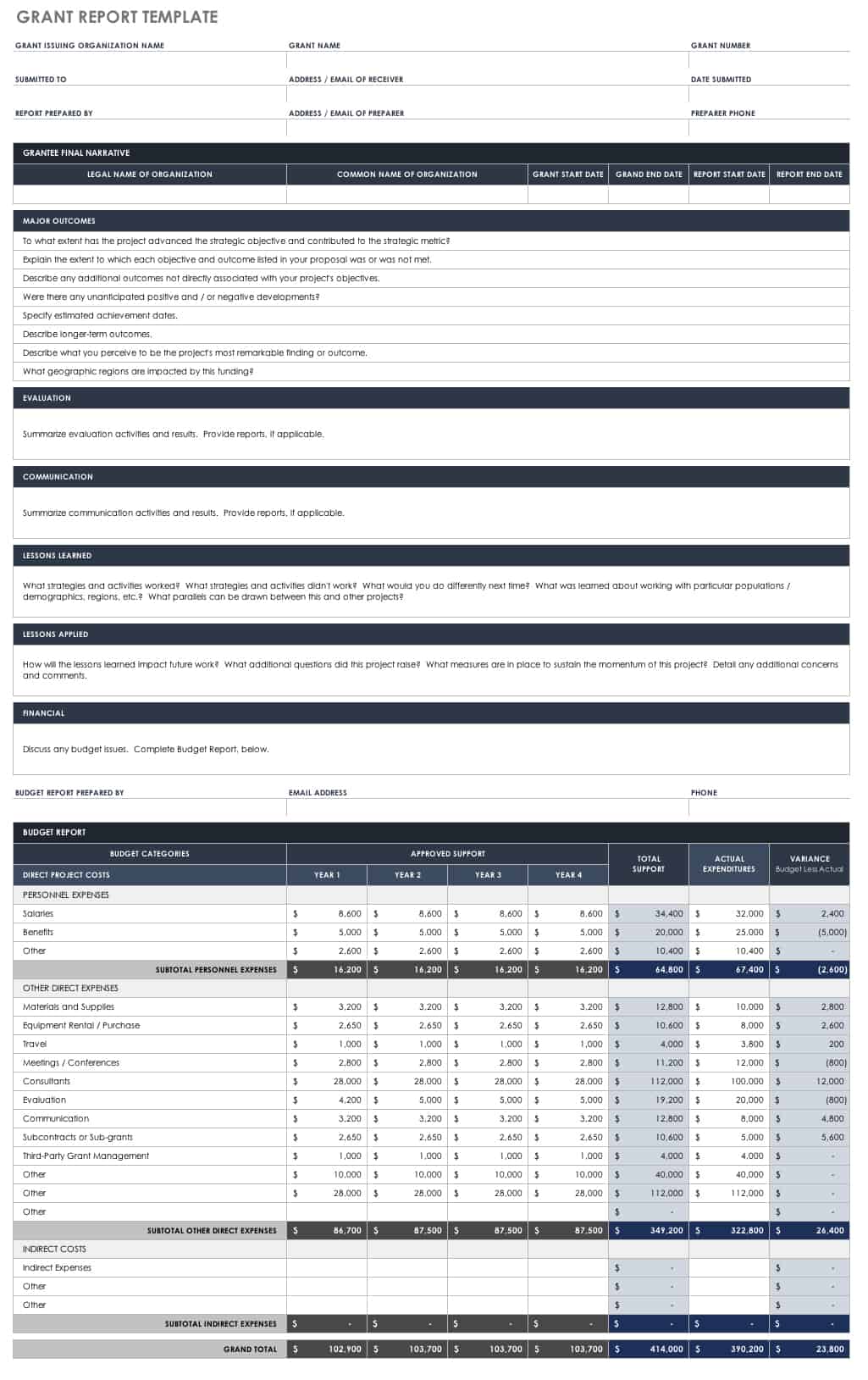
Grantees may be required to submit an interim or final report describing the progress and outcomes of a project. This simple template provides an outline for creating a comprehensive report, including a financial update that shows how funds have been spent. Grant makers can provide this form to grantees so they have a template to follow for creating a narrative report.
Download Grant Report Template
Grant Applications and Eligibility
Grant writing varies across disciplines, and proposals range from lengthy reports to brief letters that summarize project details. A science grant proposal might be 50 pages long and include a thorough literature review, background information for key personnel, research methodology, and more. The National Science Foundation, for instance, has extensive guidelines for grant applications, and its policies and procedures are outlined in a comprehensive guide for grant applicants.
An application for a global grant from the Rotary Club, on the other hand, is much shorter, and the information required depends on the type of project to be funded. The scope of a project, the amount of funding being awarded, the type of grant maker, and other factors influence what is required from grant seekers.
Businesses are generally not eligible for grants unless they qualify for funding through local government initiatives or are involved in research and development projects that are relevant to federal programs. Some states offer small-business grants to woman- or minority-owned businesses as well as for certain industries. If your company qualifies for federal or state funding, creating a business grant proposal would entail following the guidelines for a specific grant.
Some organizations will accept a common grant application form, which allows for a standardized proposal that saves time for both grant makers and grant seekers. When researching grant opportunities, it is important to understand and follow the application requirements so that your efforts aren’t undermined by technical errors, missing information, or mistakes in the submission process.
Mastering the Grant Writing Process
Writing grants may seem to adhere to a series of linear steps, but unless you are applying for a one-time grant and will not use grant funding in the future, grant writing is a circular process that follows a funding cycle. The process begins with a goal or need that gets translated into a proposal, which is reviewed by the agency or foundation supplying the grant, and then accepted or rejected.
Whether the proposal is accepted or not, the grant writing process continues into the next funding cycle as you revise and resubmit earlier grants or apply for new ones. Nonprofit organizations, ongoing research studies, and other groups that rely on grants as a primary funding source may need to keep a calendar and dedicate a writer to planning and securing grants.
To write an effective proposal, it is helpful to not only find grant opportunities that are relevant to your project, but also understand the funding source and gear your proposal to that audience. If a funder is available to meet in person prior to your organization submitting a proposal, that can go a long way toward providing a more personal context to your project and developing an ongoing relationship. Above all, the proposal should describe a project that can realistically be carried out by the applicant based on experience, qualifications, and financial resources.
As stated earlier, grant proposals vary widely and the content is largely dictated by the application requirements of a particular funder. However, there are commonalities among grant proposals. Here is a look at some of the information typically included:
- Cover Letter: Unless you have already had a face-to-face meeting or other contact with a funder, the cover letter is the first impression of your organization and project. Provide a brief summary that emphasizes your vision and objective.
- Proposal Summary: Although included at the beginning of a proposal, an abstract or executive summary section is often written last. It provides a brief overview of a project, including how the project fits with funding criteria.
- Literature Review: Academic and scientific research grants typically include a literature review that lists and evaluates sources of preliminary research that are related to the project.
- Statement of Need: The need statement is your opportunity to show a funder why your project is important. It explains the issue, and also provides background information and relevant research or evidence to support your proposal. You present the argument for why your project should be awarded funding over other proposals.
- Organization Description and Staff: Organizational history, background and qualifications for key personnel, and a program’s mission and track record for similar projects may all be important to illustrate a trustworthy reputation and your ability to successfully implement the proposed project. You may need a separate section to outline specific roles and responsibilities.
- Project Narrative: This is where you would include a lengthier project or program description, providing a detailed look at what the project entails, specific goals, and other information. You may include some of the sections listed here, such as personnel information, objectives, and measurements for success.
- Goals and Objectives: Breaking down goals into definitive and measurable results outlines the vision for a project as well as tangible outcomes. Grant proposals from nonprofits and other organizations involved in community projects may also include a description of the community being served, information on how it will benefit, and research on the potential for community involvement.
- Methods and Strategies: Grant makers will want to see how you plan to achieve goals and objectives. You may decide to include a logic model, which offers a condensed version of your proposal outline, to provide a visual representation of the key elements of your project and how they will lead to the intended outcomes. Clarify connections among methodology, objectives, and outcomes.
- Project Timeline: A timeline for your action plan can help funders visualize the stages of your project. This may be especially useful for research projects carried out over the course of several years. You may also want to include a budget timeline.
- Evaluation: Create an evaluation plan and describe what metrics will be used to assess a project’s effectiveness or impact.
- Sustainability Plan: If a project will continue into the future, create a plan for ongoing sustainability after grant funds have been used — doing so shows funders that a project is viable for the long term.
- Other Funding: Grant makers may want to see what other sources of funding you expect to receive for your project.
- Budget: The proposal budget shows estimated expenses along with sources of revenue. It provides an itemized look at how funds will be allotted and utilized.
- Appendix: References and additional materials can be included in the appendix.
Before submitting a completed proposal, grant writers can do their own review to ensure that the proposal meets the necessary criteria and application requirements. Grant makers will in turn conduct their review process and select which proposals to fund. Once funding is awarded, the grant maker and the grantee sign an agreement that describes the terms of the grant.
There are many sample grant proposal templates online that provide examples of successful applications. For instance, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) offers a variety of sample proposals for scientific research, as well as small-business funding for research and development.
Top 5 Grant Writing Tips
If you are new to grant writing, here are some tips to keep in mind as you develop your proposals:
- Give yourself plenty of time. Researching grant opportunities and gathering the information needed for an effective proposal can be a time-consuming process. Start earlier than you think you need to, and create a schedule to keep your grant writing process on track.
- Keep trying. If your proposal is rejected, revise it and apply again. Persistence can pay off, and you don’t need to wait for the results of one application before applying for a different grant. Sending proposals to a diverse selection of funders may also increase your chances of being selected.
- Details matter. Be specific about how funding will be used, goals will be achieved, and data will be collected, as well as your timeline of action steps. Grant makers want to know exactly how their money will be used, what impact the project or program will have, and why the project is important.
- Follow the rules. Follow grant application guidelines exactly, including answering required questions, providing requested information, and sticking to a submission timeline.
- Pay attention to formatting. The format of your proposal may be dictated by grant guidelines or a preset application, but make sure it is organized with clear headings. Information should be easily accessible and appropriate for the given audience.
One final tip: Create a reusable template that can be adjusted for a variety of grant applications.
Improve Grant Proposal Management with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
How to Leverage Impactful Letters of Support For Your Grant Applications
Customer Success Manager at Instrumentl
Reviewed by:
November 17, 2023
Last Updated:
Table of Contents
A strong letter of support can make or break your ability to land funding.
Really, it can be that powerful, and for small or medium-sized nonprofits, it’s important to leave a lasting impression on as many funders as possible to get your organization off the ground.
A letter of support should highlight successful partnerships, the differences you’ve made, and the impact you can still have with a funder’s support. You want to knock potential funders out of the park with these letters and inspire them to be a part of the change within your organization.
In this article, we’ll share all you need to know about creating and soliciting a letter of support for a grant, including:
- What is a letter of support for a grant
- Why do funders ask for letters of support in their RFPs
- Key components every letter of support should include
- Who should you ask for a letter of support?
- How to ask for a letter of support
Let’s dig in!

What is a Letter of Support for a Grant?
A letter of support for a grant is a testimonial from another person or organization. It serves as a character witness, backing up your claims with tangible evidence that your organization is able to do what you say it can do.

This document is an important part of a grant proposal, and it adds another layer of credibility to your organization’s application. Think of it almost like a letter of reference.
The letter implies that other organizations or funders think your proposal has merit. It signifies that your project has the potential of delivering proposed results. In addition, it provides a compelling and persuasive reason for a funder to support your grant proposal.
A letter of support for a grant is supporting documentation, and it should work in tandem with other parts of your organization’s application, like a letter of inquiry .
A letter of support can make your grant application stand out. It can show just how much potential your organization has with the right funding, perfect for those small to medium sized organizations that are still finding their footing.
Why Do Funders Ask For Letters Of Support In Their RFPs?
Funders like proof that your organization is able to accomplish the goals that you talk about in your cover letter and throughout your application, especially if you’ve been in the game for a shorter amount of time.
After reading your letter of support, funders should be inspired to be part of your mission, vision, and the difference you can make in the world around you.
Your letter boosts your credibility—others are willing to speak on your behalf, providing additional assurance to the grant committee that you walk the talk .
Additionally, many times, the partnership illustrated in the letter can lend additional weight during the application process.
- It shows that others are willing to invest in your organization with their time, money, or both.
- It also is an excellent indication of the future working relationship funders might have with your organization, should they accept your proposal.
A lot of information can be packed in a letter of support for a grant, so it’s critical that you take the time to leverage it properly.
Find Your Next Grant
17K Live Grants on Instrumentl
150+ Grants Added Weekly

Key Components Every Letter of Support Should Include
Writing a letter of support is more of an art form than a science, kind of like when it comes to writing an impactful needs statement . As you consider how to write a letter of support for a grant, there are several elements that should always be included.
- Project Endorsement : A clear statement on why the person supports the project, including the formal project title.
- Authority of the Supporter : A brief statement on why the person can speak to the subject, including information on the relationship to the organization.
- Alignment with Funding Priorities : Information on how the project aligns with the specific grant requirements, complete with specific examples of how the organization has accomplished similar work in the past or plans to do it in the future.
- Personal Anecdotes : Following the alignment with funding priorities, include information about how you have personally witnessed the work and why they support it.
- Call to Action : Invite the funder to be part of the difference, including any relevant information about why they chose to support it.
Ensure that the letter of support demonstrates a clear alignment between the goals of the grant proposal and the mission, values, and objectives of the supporting organization or individual. Provide concrete evidence and highlight the potential for impact. Personalize the letter and avoid making generic statements without clear alignment with the grant proposal.” - Jacob Chase, CEO Chase Consulting Solutions
Lastly, the letter of support should be written on a formal letterhead or come from an official business email address. This letter of support for a grant example will help lend legitimacy to the note and demonstrate that your organization is ready to grow.
Want to get better at grants?
Get access to weekly advice and grant writing templates.

10k+ grant writers have already subscribed
Who Should You Ask For A Letter Of Support?
There are a number of people or organizations that you could ask for a letter of support for a grant. Assess the grant requirements to determine who would be the most impactful.
- Collaborators and Partners can speak to what you’re doing, how you’re doing it, and how it feels to be a part of the project on a personal level. This is particularly impactful because potential funders will see themselves in these letters.
- Community Leaders and Stakeholders can share more about the impact that your project has had or will have in the community. They should inspire funders to be a part of the solution.
- Beneficiaries or Clients can demonstrate how it feels to benefit from the project and the difference it makes in their lives.
- Local Government Officials can lend formal legitimacy to a project, demonstrating it is important to the local community and has garnered strong support.
- Prominent Figures in the Field can illustrate how your project is making waves in the industry and how it caught the attention of industry leaders and other influential people.
- Funders or Previous Funders can offer wisdom about why they partnered with you, what you accomplished together, and why they recommend supporting you.
- Key Volunteers or Advisors can share a unique view of why they choose to offer their time and expertise with your organization over others.
- Prominent Local Businesses can talk about why they support you and how their partnership is beneficial to both organizations.
- Foundations or Similar Organizations can speak to the greater need in the industry and how you are uniquely situated to address a specific issue.
- Supportive Individuals with Influence can add legitimacy to your application, showing they believe in you and recruiting others in their network to do the same.
At the end of the day, your organization’s letter of support needs to add value to your grant application. It needs to add another dimension to your submission that will help differentiate you from others.
Related: You can learn more about landing stellar support letters in our webinar with Rachel Waterman, CEO and Founder of GDS Grants .
How To Ask For A Letter Of Support
It can be intimidating to ask for a letter of support, so here are some steps you can take to make the process seem more manageable.
Choose Your Targets Carefully
Pick people that you trust and know will speak positively about your organization. The more familiar they are with your project, the more they can speak from the heart.
You want people/orgs who align with the work you are talking about. You want leaders in your community. You want people who are passionate about your org and the work you are doing.” - Amanda Day, Co-owner, HayDay Services
Make a Personal Connection
Leverage actual stories, anecdotes, and data in your ask. You are reaching out to them for a reason, so be sure to make it clear this isn’t a generic ask. A personal touch can go a long way.
Explain Your Project
Be clear about your upcoming project, including its objectives, critical details, projected impact, and more. Share its impact, especially how it addresses a critical need or gap in the field. These details will help inform their letter.
Offer to Draft the Letter
It can be difficult to know how to write a letter of support for a grant, and many individuals or organizations will welcome an initial draft to help ensure the project details are accurate. They’ll review, provide additional feedback, and place it on their letterhead when it’s finalized.
Make it easy and painless for them. Give a sample letter with plug-and-play verbiage that they can quickly revise,” - Teresa Huff , Nonprofit Strategist / Grant Writing Simplified Podcast Host
Set a Deadline
Be generous with the deadline, knowing that this likely isn’t going to be a high priority for them. Make sure it is well before the application deadline to give you some wiggle room.
Express Gratitude
Thank them for their time, consideration, and partnership. Their support has been critical, and it will help carry you forward as you land your next big grant.
Make sure your ask is authentic and genuine. If you pick right, most people will be honored that you asked and write you the best letter of support for grants they can.
Wrapping Up: Go Win More Funding With Impactful Letters of Support
By now, you should:
- Understand the basics of a letter of support .
- Know the critical components every letter should include.
- Feel comfortable asking someone to write you a letter.
The letter of support for a grant is only one element of the overall application; however, it’s one that adds nuance, dimension, and credibility that can help your organization stand out and grow.
To continue learning, read our article on how to build a grant application timeline strategy so you never miss another deadline.

Amelie Heurteux
Amelie Heurteux, a Customer Success Manager at Instrumentl, works day in and day out training nonprofits and grant writers how to efficiently prospect new funders and streamline their grant tracking and management processes.
Become a Stronger Grant Writer in Just 5 Minutes
17,502 open grants waiting for you.
Find grant opportunities to grow your nonprofit
10 Ready-to-Use Cold Email Templates That Break The Ice With Funders
Transform funder connections with our 10 expert-crafted cold email templates. Engage, build bonds, showcase impact, and elevate conversations effortlessly.
Related posts
5 mistakes you’re making with your grant writing – and what to do instead.
Grant writing can be complex, and even seasoned professionals make mistakes. In this article, we'll highlight five common errors and provide actionable solutions to improve your grant writing game.
How To Write A Grant Acceptance Letter: What Nonprofits Often Miss
Handwritten thank-you notes can make one feel genuinely appreciated. In cultivating funder relationships, communication is paramount. Crafting a gracious grant acceptance letter lays the foundation for a long-term relationship, potentially leading to sustainable funding. In this article, we'll guide you through crafting memorable and effective grant acceptance letters, empowering you to nurture relationships with your funders and build a robust network of support.
5 Tips For Using AI To Write Grants: 4 Experts Putting It To The Test
These days, it feels like Artificial Intelligence (AI) is everywhere. We spoke to four industry experts to learn how they are—or are not—using AI to support their grant-seeking efforts.
Try Instrumentl
The best tool for finding & organizing grants
128 reviews | High Performer status on g2.com


How to Start Grant Writing (+ Templates)
As a nonprofit, it’s a good idea to have a variety of revenue sources to fund your missions. One source can be grants. And if you’re looking for support for a specific project or position within your organization, you may have grant writing on the brain.
If you’re new to this process, you could have a lot of questions: How do I start grant writing? Is grant writing difficult? What does grant writing consist of?
Well, you’ve come to the right place! Below, we’ll cover everything you need to know about grant writing:
- Key essentials about grant writing
- Tips, tricks, and strategies
- A grant application template to get you started
In no time, you’ll be well on your way to writing your first grant!
Looking for templates you can use for your grant application? Download our FREE Grant Application Template bundle, which includes:
- A cover letter template
- A grant proposal template
Fill in the form below to get your copy!

Download Your FREE Grant Application Template

What Is Grant Writing?
Grant writing is the process of writing a grant. But, you might wonder, what is a grant? A grant is a funding opportunity that foundations, businesses, and individuals make available to nonprofits to support their missions. It’s like a cash award for a great idea!
Grant writing is about building the case for a potential funder to support your work. Writing a grant involves putting together a proposal that tells the grantmaker the details of your project idea, how much money you need to fund it, and the impact it will make in the community.
You might also need to write a cover letter, but not all grant applications require one. We’ll dive into that more later in this article, so stay tuned!
Different Types of Nonprofit Grant Writing
You may find yourself writing for different types of grants. Some support specific project types, causes, or neighborhoods. Others may take a broader funding focus and accept proposals for any activity supporting the “public good.”
As you’re researching grants to apply for, you’ll want to be familiar with the three main types of nonprofit grants:
- Operating support or unrestricted funding : This kind of grant supports the day-to-day operations of your work. Unrestricted funding is the bread and butter of any nonprofit! If you snag this type of grant, it means the grantmaker trusts you to use the funding for whatever best supports your nonprofit rather than for specific line items or projects. These grant funds can be hard to find, since funders tend to like measuring impact through specific projects. But if you stumble across one, receiving it can make a huge difference to your nonprofit’s work!
- Capital support : Think of capital support as brick and mortar funding! These grants help your nonprofit purchase, renovate, or build needed facilities. They’re often for larger amounts. Because of that, they can require some extra details. Mainly, you’ll need to show the grantmaker that they can trust you to use it well!
- Program development grants or restricted funding : Have a specific project or staffing position to fund ? These grants are restricted to specific purposes, so are a great option for those needs. For example, you might write a grant to fund a new after-school art program. Based on the grantmaker’s restrictions, the grant might cover the costs of purchasing paint, paper, and other art supplies to use in the program, but not the rent for the space where you’re hosting it.
Why Is Applying for Grants Important? Is it Right for Me?
There are several reasons why grant writing is important. Grant writing can:
- Diversify your sources of revenue : Having a variety of revenue sources helps prevent financial emergencies . If one stream dries up, other sources are there to support you. Grants can give your nonprofit something to fall back on should, say, your individual donor contributions decrease during an economic downturn.
- Serve as a source of non-dues revenue : If you’re a membership organization, grant writing lets you secure funding outside of dues . You can use this funding to create better programming to recruit more members to your organization. Win, win!
- Help carry out what may seem like big dreams, programs, or initiatives : Sometimes a sizable grant set aside for a specific purpose is the resource you need to finally see a big project through. This is especially true if you’re already running a tight ship with your day-to-day expenses and don’t have the wiggle room to expand. Continuing with the art program example, a grant could help you buy a new kiln to start a ceramics program or fund an artist-in-residence program.
- Offer funding without a required payback period : Particularly for capital projects, grants can provide a solution to what you might otherwise have to finance through a loan. It definitely takes strain off your budget to avoid monthly loan payments!
- Increase the visibility of your organization : A lot of times, grantmakers will share press releases on which nonprofits they fund. They may also share your work on their social media and other marketing channels. This added bonus to the funding helps you reach a wider audience.
- Increase the credibility of your organization : Have you ever trusted a business or organization more because a peer recommended it? So many of us do—including grantmakers!. As you find success with your grant writing, you build your nonprofit’s credibility and it may become easier to secure additional funding in the future.
How do I know if applying for a grant is right for me?
While any nonprofit, big or small, can apply for a grant, it’s important to keep in mind that grants are best for long-term projects and goals. If you’re looking for immediate financial aid, a grant won’t be able to support you the way you need. This is because the application cycle can be long, and you don’t want to be waiting if you’re in a pinch!
Where can I look for nonprofit grants?
There are many places you can look for nonprofit grant writing opportunities. Here are a few to get you started:
- Google Alerts : Set up a Google Alert to receive a notification whenever new opportunities come up for your selected keywords. For example, if you’re funding an after school art program, you might set up alerts for “art program funding opportunity,” “after school art grants,” or “art grants for children.”
- Government-Based Grant Foundations : Your state, province, or country will usually have a database for grant writing opportunities. If you’re based in the United States, Grants.gov is a great place to start.
- Search Engines : You can find a lot of opportunities with some simple search engine research. Use keywords like the same ones you’ve used to set up Google Alerts.
- Your Existing Network : You may have current donors or members who serve on foundation boards or run their own philanthropic opportunities. Reach out to your supporters and ask them about grants they know of that could fit your nonprofit.
- Board Members : Board members are another great resource. See if the companies they work for offer grant writing opportunities. They may also have connections at other foundations or to friends in their network who offer grants to nonprofits like yours!
- Other Nonprofits : Need some ideas on who might fund you? Take a look at nonprofits similar to yours to see where they’re getting their funding.
- GrantWatch : GrantWatch is an online database that keeps current information on available grant writing opportunities within 60 different categories. It makes it easy to search for grants that could be good for your nonprofit.
- GuideStar : This online database provides information on nonprofits everywhere. It’s a great way to identify similar nonprofits to yours and see where they’re receiving their grants. You can also use it to identify foundations that provide grants and learn more about them and who they have funded in the past.
- Philanthropy News Digest : This free online service posts requests for proposals and grant notices for US-based nonprofit and grantmaking organizations. You can sign up for its newsletter and alerts and easily view the most recent opportunities by category and application deadline.
- Candid’s Regional Giving Dashboards : This online service offers overviews of regional funding opportunities across the United States. Not based in the US? Keep an eye on it, as it may expand to include global opportunities in the future as well.
Essential Elements of a Grant
Usually, the two core elements of a grant are the grant proposal and the grant cover letter . Below, we’ve covered the essential parts of each of these components.
Nonprofit Grant Writing Cover Letter
Depending on your grant application, the cover letter may not be necessary. However, if your grant writing involves a cover letter, it should typically be one page in length and written on your nonprofit’s official letterhead.
Your cover letter is an overview of your funding ask. It grabs your potential funder’s attention and makes them want to look into your project. Think of it like a friendly elevator pitch that lands you an interview to learn more!
Here’s what you’ll typically want to include in your cover letter:
- Brief project description
- Expected impact of the grant
- Requested grant support amount
- Outline of what is included in your attached proposal
- Mention of past grants you’ve received
- Your contact information
- Signature of your Executive Director or Development Director
Nonprofit Grant Writing Proposal
If your cover letter is what gets your foot in the door for an interview, we can think of the grant proposal as what gets you the job!
Your grant proposal builds the case for why the grantmaker should fund your project. It provides essential, persuasive details that give heft to anything already mentioned in your cover letter. Some grant funders will provide you with their own template for your application. Others may simply ask for a proposal. Be ready for both!
What is included may vary slightly by funder, but typically a proposal involves:
- Overview/Abstract
- Statement of Need/Need Assessment
- Project Description
- Budget & Budget Allocation
- Organizational Background
- Supporting Documents
Don’t forget to grab your FREE copy of The Nonprofit Grant Writing Cover Letter and Proposal Templates here.
Tips and Strategies for Grant Writing
Whether you decide to use a template or decide to free-style it, there are some key tips and strategies you want to keep in mind. Grant writing can feel intimidating, so it’s important you go in with the right information. This way, you’ll have the confidence that you’ll be writing a strong application.
In this section, we’ll cover key pointers for each stage of grant writing, including:
- How to prepare for grant writing
- Grant writing strategy and planning
- Writing your grant
How to Prepare for Grant Writing
Before you even start mapping out your grant application, there are a few steps to take to prepare. You’ll want to:
- Understand the audience, purpose, and expectations of your grant proposal : Read as much as you can to learn who will be reading your grant application and what they’re looking for. Know the purpose of the grant funding and the expectations the grantmaker will have if you receive the award. This can even help you find the right person to address your cover letter to, making it a lot more personal than using “Dear Foundation” as your salutation!
- Tailor your proposal for a specific objective : Even if you’re applying for unrestricted funds, aim to be detailed in your funding ask. Framing your grant writing around a specific objective builds the case for why you should get the funding and the type of impact it’ll have for your nonprofit.
- Understand the application’s guidelines and rules and follow them to a tee : Grantmakers typically have many high-quality applications to review. It can be hard for them to narrow it down to a winner! Avoid simple mistakes that could move you from the “yes” pile to the “no” pile, like getting the time zone wrong for the deadline or forgetting to include supplemental materials. You want your hard work to have the best chance possible! Have questions about the grant application’s rules? Reach out to the grant officer for clarification. Asking questions isn’t a weakness! It shows the grantmaker you pay attention and care enough to submit the best application possible.
- Be realistic : As you review a grant’s guidelines, rules, and purpose, ask yourself whether your project is truly the right fit for that grant. There’s no need to waste your time writing the grant or the grantmaker’s time reviewing the application if your project doesn’t align with the grant’s goals.
Grant Writing Strategy and Planning
Before writing your grant, know what you need to cover within it. Having these answers before you start writing will make sure you cover the core ideas needed in your grant application. And ultimately, this makes sure you give the funder all the information they need to be convinced to award you the funding!
As well, during this stage, you’ll want to strategize and plan accordingly to make sure you’ve given yourself enough time. Set out time to draft and refine your grant application before your submission is due.
As you get started, make sure you know your answers to the following:
- What is YOUR grant application timeline? This is one of the first and most important questions to ask yourself. Know when grant application periods open and close. Consider whether you have one or multiple grants to write during that period. Then, create a timeline for yourself so you have ample time to prepare your application with minimal stress and to not miss a deadline!
- Why are you asking for the grant? From the beginning to the end of your grant writing process, focus on this question and build it into your entire narrative. Basically, you want to clearly know your need and how to convey it.
- What will the impact and benefits be? On top of communicating what your needs are, you should be able to clearly state how this grant will address them. Help your funder envision the future they will help you create!
- What will be your plan of action once you get the grant? Be prepared to start your project as soon as you receive the grant. Having a timeline for when different events and activities will occur demonstrates that you have an actionable plan to use the grant in a timely and effective manner.
- What is your financial budget and plan for the funding received? You should be prepared with a detailed budget for your project. Rather than asking for a lump sum of money, be able to explain the different pieces that go into creating that total. Using the after-school art program example, you’ll want to share how much funding will go toward paint, brushes, paper, staff time, marketing , and rent.
Writing Your Grant
As you actually start writing your grant, there are some tips that can help strengthen your application. To write a successful grant application:
- Be specific : Show that you’ve put thought and care into your funding proposal by being specific. For example, rather than saying you want to fund art opportunities for children, share how you will create those opportunities. You will begin an after school art program for children ages 5 to 10 in New York City that will employ three local artists who specialize in painting, collaging, and ceramics.
- Be concise : While you want to be specific, you also want to be concise. Don’t make the funder search for the most relevant information in your grant application. Make every sentence count.
- Avoid redundancy and repetition : One way to tighten up your application is to review it for repetition. Have you already explained something clearly in an earlier part of your application? No need to say the same thing again! If you’re building on it in a way that’s crucial to your application, keep it short and simple by adding a phrase like “as stated earlier”.
- Make a clear ask : Don’t be shy about making your ask! Clearly state your need. For example: We are asking for a $5,000 donation to support an after-school art program. You can also use bullet points to draw attention to your ask and make it easy to understand.
- Lead with your core idea : Start with your clear objective for the grant proposal and then make sure everything else you write links back to that core idea. Think of it as you would the thesis for an essay.
- Demonstrate your past successes : When relevant, feel free to brag on your organization’s past successes with grants a bit! Mention others you’ve received and how you’ve put them to use. This shows the grantmaker that in the past, others have seen promise in your projects or mission. It also shows you’ve been able to use that money to make a positive difference. Funders may be more likely to give to an organization that already has experience managing grant funds.
Start Grant Writing With Smart Preparation and Strategy
We hope you found this guide to grant writing helpful! Yes, getting started with grant writing can feel like a lot, but with some simple preparation and strategy, you can take the process step by step for a successful submission and award!
Want to keep up to date with other nonprofit tips? Make sure to check out other articles on our blog !
And if you’re looking for additional ways to diversify your nonprofit funding and sources of income, check out our resource How to Write the Perfect Donation Letter (+ Examples & Template) .
Related Organizational Management Articles

30 Free Nonprofit Webinars for June 2024
Nonprofit Succession Planning: A Step-by-Step Guide

Strategic Planning for Nonprofits

The Membership Growth Report:
Benchmarks & insights for growing revenue and constituents.

Junee Community Network
Writing a ‘Letter of Support’ for a Grant Application
This is the second of a two-part series — This article will explain how to actually write a ‘Letter of Support’ for another organisation to include with their grant application.
The first article in the series, “Requesting a ‘Letter of Support’ for a Grant Application” explains how to ask other Community Groups, Businesses and other Partners, for a ‘Letter of Support’ for a project to show to grant providers that other groups will also benefit from your project receiving funding.
Why you might be asked to write a ‘Letter of Support’
Many grant and funding providers now try and get the ‘biggest bang for their buck’ so they look for projects that can assist or benefit many different groups, various demographics and not just a single entity.
By having multiple entities express support for a particular project shows the grant provider that more than one group in the community may benefit from the funding of the project. It also shows that the applicant and the actual project does actually have support of a larger number of people.
Some Letters of Support may also be used to show that a landlords’ permission has been sought and obtained; or that local council or other relevant authorities have also been advised of a project and their permission or support is granted. Often these ‘permission approvals’ need to be completed on a specific form supplied by the Grant Provider.
What to include in a Letter of Support
Always write a Letter of Support on your organisation’s formal letterhead… NEVER write it as an email!!! and especially do NOT write it as a direct reply to the original email request.
- Full LEGAL name of your organisation This seems obvious, but many organisations abbreviate their “name” and they shouldn’t. If your legal name, as listed on your Certificate of Incorporation, is “Dragon Breeders and Trainers of Fairyland Inc” then list it as such and NOT just a shortened version (eg “Dragon Breeders of Fairyland”) that you may use in day to day discussions
- Organisation’s Logo Ensure you have a high-quality version of the logo and that you are using the proper version
- ABN and/or Incorporation Number If you have both, list both. If you only have an Incorporation Number, list that. It allows others to easily look your group up with ASIC and verify your group’s status
- Website Address (or Facebook Page URL) ALWAYS list your website in your letterhead — this is where others can find out more about your organisation. Ideally you’ll have your own domain and website, but an active Facebook page that is publicly visible can suffice in many circumstances.
- Postal Address List the association’s PO Box if you have one, otherwise it should be the address registered with Fair Trading (usually your Public Officer’s address)
- Primary Telephone Number List the phone number you normally give out for the organisation (often the Secretary’s mobile if you don’t have a dedicated number)
- Primary Email Address List the main email address for the organisation eg [email protected]. As with the website having your own domain is better, but if you don’t then a gmail.com address with your organisation name can suffice eg [email protected]
Date, Addressed to, and Subject
Insert the date at the top of the letter… I use a long format like April 10, 2020 so there can be no confusion (It’s so annoying trying to translate 10/04/2020 — if that’s written by an American that date converts to October 4th. Virtually anywhere else that is 10th of April.)
Next address the Letter of Support as per the directions received from organisation submitting the grant.
Usually it will be addressed to the President or Secretary of the organisation submitting the grant application. Occasionally, it may need to be addressed directly to Grant Provider (but you would still normally supply the letter to the applicant for them to include in their application). In rare circumstances it may be as simple as addressing it as “To whom it may concern” — but ONLY do this as a last resort!
After the address include a single line referencing the reason for the Letter, using the supplied Project Name – basically a “Re: Grant Application for new Dragon Breeding Cages”
I tend to list the project name rather than the specific grant name (this way it can easily be resubmitted to another funding channel if the first grant is unsuccessful) — UNLESS you’ve specifically been asked to reference the actual grant eg “re: Westros Development Fund Round 23 — Dragon Breeding Cages”
[Letterhead above] October 31, 2020 Mr Mushu Ghidorah Dragon Breeders and Trainers of Fairyland Inc 151 Kirkham Road Camelot NSW 2011 RE: Grant Application for new Dragon Breeding Cages
Note that I put the address on a single line… and I didn’t worry about a Dear John (or Dear Mr Smith) — if space is tight and you’re trying to keep the Letter on a single page, these can be simple ways of getting a few extra lines back.
Alternatively if you are trying space the Letter out a little, add the Dear line and spilt the address over two lines (with Suburb, State and Postcode on the second line).
Introduction about your organisation
The first paragraph should be a very brief introduction to your organisation — It should be NO MORE than 30-50 words long and only contain two or three sentences.
It should simply establish your organisation’s credibility and relevance to the project. It does not need to explain every aspect of your organisation — that’s what your website is for!
The Society of WereWolf Protection was founded in 626AD to protect the misunderstood changelings, commonly referred to as Werewolves. Since this time we have seen the werewolf population steady grow over the generations, but we have much work still ahead of us to see werewolves fully accepted amongst regular society.
Why you support the project
This is the most important part of the Letter of Support!
The next couple of paragraphs should explain why your organisation supports this particular project .
It maybe that your organisation can utilise the cages when Dragon Breeding Season is not happening, or you see a need for more dragons to be bred each year so they can help protect your castle’s treasure room, so having more dragons born each year would help your organisation.
We fully support the Dragon Breeders project of building new Dragon Breeding cages in the aeries of Camelot Castle. During the spring months, which is breeding season for werewolves, we welcome your offer to allow us access to these nests so our pack mothers have a warm and safe place to raise their cubs during those early, formative months.
If your organisation is contributing in any way towards the project, be sure to mention that — If you are providing in kind support (a discount on goods supplied, or volunteering time and labour to assist with the project) or if you are providing a co-contribution towards the project (ie your organisation has provided $5,000 cash towards the project) mention this.
Grant providers are looking at getting the best value out of the funding they provide — so the more community groups, local residents and others can directly benefit from a single project, the better — so if your organisation will benefit from the proposed project getting funded, clearly explain how and why it will benefit your own group .
Wish the grant applicant well
At the end of the Letter, usually as the second last paragraph you may wish the grant application all the best with their application to highlight the fact you understand that the grant applicant is actually seeking external funding for their project. If space is tight on the page, this paragraph can be dropped, or reduced to a single line of “We wish you well with your funding application”.
On behalf of the Society for Werewolf Protection, we wish Dragon Breeders and Trainers of Fairyland all the best with your application for funding to purchase new breeding cages and we look forward to seeing your dragon population grow in the coming decades.
Direct contact details
If the author of the letter can’t be contacted directly using the details in the Letterhead, or are only available during certain times, then include a single sentence listing the best method to be contacted and suitable times (remembering that processing of the grant application and any follow up regarding it may not occur for up to six months after the you’ve written the letter).
An example could be
“Should further information be required, I may be contacted directly on 0400 666 666. I am usually available between 8am and 1pm most week days.
Signature and Title
The final segment of the letter should include a complementary close, your signature and your title/position within the organisation.
If the letter is addressed to “Dear Sir/Madam” or “To whom it may concern” then use “Yours faithfully,” as your complementary close.
If it was addressed to a personal name eg “Dear Mr Smith” or “Dear James” then you should use “Yours sincerely,” Australians (along with Britain and most Commonwealth countries) usually put the Yours first, but you’ll often see Americans place the Yours after the faithfully or sincerely eg “Faithfully yours,” — neither style is wrong but putting the Yours first reads better to Australians.
Next, you need to sign the letter.
Ideally you should have a ‘real signature’ — either scanned in as an image from a real signature or drawn using a mouse, touchpad or stylus on a computer or tablet.
Mac users can create a graphic version of their signature from inside Preview (an app for reading and basic editing of PDFs and images that is included with Mac OS). It is accessed from the Tools Menu → Annotate → Signature.
If scanning a physical copy from paper, be sure to;
- Use a black pen with at least 1mm tip but no more than 2mm (eg a ‘ sharpie ‘ is ideal)
- Make the signature at least 2.5cm (1-inch) tall
- Use a light blue or light green sheet of paper, if you have access to it; otherwise use an ‘ultra-white’ sheet
- Crop the scanned signature so there is minimal white space around it
- Using a good graphic application create an ‘Alpha-background’ or ‘Transparency’ around the outside of the signature AND in the spaces inside the characters (This is why we recommended the light blue or green paper — so you can see which areas have been made transparent)
- Save the edited signature as a .PDF or .PNG WITH a Transparent background
You can now insert the signature into your document and if you have the transparent background, it can even be overlapped on top of printed name and title, just like a physical letter.
Alternatively, it is becoming more common these days to just use a font that resembles cursive handwriting to create a signature for electronic documents.
There are a number of ‘handwriting script’ fonts included with Windows and Microsoft Office that could substitute for a signature, including Bradley Hand ITC , Brush Script MT , Lucida Handwriting , Freestyle Script , Mistral , Palace Script MT , Rage Italic , and Vivaldi . Mac users will have the same fonts available if they have installed Microsoft Office or there are similar fonts included with Mac OS.
Pick one and stay with it for all your future ‘signatures’
After your signature, list your name and then on the next line list the title (or position) you hold with your organisation, followed by a comma and your organisation’s name.
Yours faithfully, [signature] Mieczysław Stilinski President, Society for Werewolf Protection Inc
Document Format
Remember not everyone uses Microsoft Word and even different versions of Word can display the layout differently on a different computer. Likewise, fonts you used may not be available on someone else’s system.
The Letter of Support should be a minimum of half a page long (including letterhead) but ideally no longer than a single page . There are always exceptions to this rule, but 95% of the time a single page is sufficient and any longer can actually have a negative effect.
Some tips for helping make the letter fit on a single page;
- Re-word paragraphs to make them shorter — This is the BEST option
- Remove ‘blank lines’ from in between paragraphs and set the Spacing Before or After Paragraph to 8 or 9pts (never go below 5pts)
- Reduce line spacing to 0.9 lines (never go lower)
- Reduce the font size (but never go below 11pt for your main body text)
- Change page margins (don’t go below 1.2cm, or ½-inch)
- If your ‘ corporate identity standards ‘ lets you, reduce your letterhead — if your logo is more than 3cm tall, can it be reduced???
Keep Copies!
ALWAYS keep a copy of the Letter of Support … both as the original wordpressing document (eg Microsoft Word, Apple Pages or Google Doc) and as the PDF you sent.
Usually, it would need to be presented at your next Committee Meeting and minuted as “Outbound Correspondence” as it was written on organisational letterhead and written on behalf of the organisation.
You can also refer back to it later if you need to write another ‘Letter of Support’ for someone else — you can then simply copy and paste relevant segments into the new letter.
Occasionally the organisation that requested the Letter may come back to you for an updated version (often just with a new date or perhaps addressed to a different funding provider) so they can submit the same project to another grant so you can then quickly and easily supply the new version. BTW: Most grant providers and assessors will usually accept a Letter of Support (and other documentation) that is six, or even 12-months, old — but read the individual grant guidelines!
Don’t be afraid to say “NO!” to a request for a Letter of Support!
Hopefully, you won’t need to say “No” to a request for a Letter of Support, but occasionally you may need to politely decline such a request.
The project in question may not align with your own organisational goals; or you may just feel you can’t provide a quality letter for this particular project.
Sometimes, you may not have the time to write the Letter of Support before the deadline — you might be writing your own application for the same grant but for a very different project, or the appropriate authorised person who would need to sign the letter on behalf your organisation (eg the President) is on leave and won’t be back until after the deadline.
As mentioned, politely decline , and if possible, give a quick explanation why you can’t supply a Letter of Support. Just be up front and honest as to why you can’t/won’t supply a Letter of Support and if it is just this project that you can’t supply a Letter, or if it is a general policy.
Example of a Letter of Support

Further Reading
This article is part of a two-part series on Letters of Support for Grant Applications.
Part 1: Requesting a ‘Letter of Support’ for a Grant Application Part 2: Writing a ‘Letter of Support’ for a Grant Application [This Article]
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Mastodon (Opens in new window)
By Nicholas Pyers
Related post, request an official portrait of hm king charles iii (and australian flags), share your news, upgrade your nfp’s banking procedures for the 21st century, recent posts, junee community network contract terminated with junee business and trades, abc riverina’s free kick friday: promote your community event for free, results of essential energy’s community choices for 2023, essential energy community choices 2022 now open for voting.
You May Want Javascript For This
Your browser currently has Javascript turned off. While some things, like signing petitions, will work without Javascript you may encounter errors. If you do, enabling JavaScript should get around the problems.

Enter Your Return Address
- You may receive email updates from Kearny ACES, the sponsor of this letter campaign.
- Edit Subscription Preferences Close Preferences
- Opt in to email updates from Kearny ACES
Support Kearny’s Hud. Co. Open Space Grant Application for funding to purchase the former Skinner Brothers site and Rapp’s Boat Yard along Passaic Riverbank Park!
The purchase of both privately owned properties along the Passaic River will allow the Town of Kearny to expand Riverbank Park and make a continuous greenspace from Bergen Ave. to Route 7/Belleville Turnpike.
This would provide Kearny residents and visitors more open space and recreational opportunities to enjoy.
Send a message to Hudson County's Open Space Trust Fund Advisory Committee supporting the Town of Kearny's application for grant funding to purchase these properties and expand Riverbank Park! Letters of Support will only be accepted until 5pm on June 7, 2024.
Sponsored by

- Policy & Compliance
- Changes Coming To NIH Applications and Peer Review In 2025
Changes Coming to NIH Applications and Peer Review in 2025
This page serves as a central location where you can learn more about multiple changes coming in 2025 that will affect the submission and review of NIH grant applications.
These changes include updates to the peer review and submission of most research project grants, fellowships, and training grants; Common Forms for NIH biographical sketch and Current and Pending (Other) Support; updated instructions for reference letters; and the transition to FORMS-I application instructions. Although each of these initiatives has specific goals, they are all meant to simplify, clarify, and/or promote greater fairness towards a level playing field for applicants throughout the application and review processes.
Upcoming Webinars
Learn more and have the opportunity to ask questions at the following upcoming webinars:
- June 5, 2024 : Webinar on Updates to NIH Training Grant Applications (registration open)
- September 19, 2024 : Webinar on Revisions to the Fellowship Application and Review Process (registration open)
Simplified Review Framework for Most Research Project Grants (RPGs)
NIH is implementing a simplified framework for the peer review of the majority of competing research project grant (RPG) applications, beginning with submissions with due dates on or after January 25, 2025.

Revisions to the NIH Fellowship Application and Review Process
NIH is revising the fellowship review criteria used to evaluate fellowship applications and modifying the PHS Fellowship Supplemental Form to align with the restructured review criteria beginning with submissions with due dates on or after January 25, 2025.

Updates to Training Grant Applications
The NIH Training Program applications are undergoing changes that take effect for submissions with due dates on or after January 25, 2025.

Updates to Reference Letter Instructions for Referees
NIH is updating the instructions for reference letters submitted for due dates on or after January 25, 2025 to provide more structure so letters will better assist reviewers in understanding the candidate’s strengths, weaknesses, and potential to pursue a productive career in biomedical science. Updated instructions will be posted on the NIH Grants page for Reference Letters as soon as they are available (later in 2024).

Updated Application Forms and Instructions (FORMS-I)
NIH is updating application forms to support many of the changes coming in 2025. These new forms will provide the needed form fields to efficiently implement policy updates and align form instructions and field labels with current terminology. Updated application forms will be posted with active funding opportunities in the Fall of 2024, and updated instructions will be available on the How to Apply - Application Guide at that time.

Common Forms for Biographical Sketch and Current and Pending (Other) Support
NIH is adopting the Biographical Sketch Common Form and the Current and Pending (Other) Support Common Form in 2025. Information on the timing and details of implementation are expected in the coming months.

NIH will provide applicants with plenty of training and resources throughout 2024. The below resources discuss the collective changes coming in January 2025. Additional resources for each initiative can be found on their respective pages.
- Overview of Grant Application and Review Changes for Due Dates on or after January 25, 2025: NOT-OD-24-084
- Drop-in slides on changes coming in 2025 (PowerPoint)
This page last updated on: May 17, 2024
- Bookmark & Share
- E-mail Updates
- Help Downloading Files
- Privacy Notice
- Accessibility
- National Institutes of Health (NIH), 9000 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, Maryland 20892
- NIH... Turning Discovery Into Health
There is still time to to apply for financial aid! Learn more

- WebGrants 4 Students
- California Dream Act Application
- California Chafee Grant for Foster Youth Application
- California Military Department GI Bill Award Program Application
- WebGrants for Institutions
- Register to vote
Cal Grant Programs
The Cal Grant is a California-specific financial aid allocation that does not need to be paid back. Cal Grant applicants must apply using the FAFSA or CA Dream Act Application by the deadline and meet all eligibility, financial, and minimum GPA requirements of either program. Grants are for students attending Universities of California, California State Universities or California Community Colleges, or qualifying independent and career colleges or technical schools in California.
There are three kinds of Cal Grants — A, B and C — but you don’t have to figure out which one to apply for. Your eligibility will be based on your FAFSA or CA Dream Act Application responses, your verified Cal Grant GPA, the type of California colleges you list on your application and whether you’re a recent high school graduate.
Eligibility Requirements
Cal Grants are for students who are pursuing an undergraduate degree or vocational or career training, and do not have to be repaid. In addition to meeting the financial criteria and Cal Grant requirements, you must:
- submit the FAFSA or CA Dream Act Application and your verified Cal Grant GPA by the deadline
- be a U.S. citizen or eligible noncitizen or meet AB540 eligibility criteria
- be a California resident for 1 year
- attend a qualifying California college
- not have a bachelor’s or professional degree
- have financial need at the college of your choice
- have family income and assets below the minimum levels
- be enrolled or plan to enroll in a program leading to an undergraduate degree or certificate
- be enrolled or plan to enroll at least half time
- not owe a refund on any state or federal grant or be in default on a student loan
- not be incarcerated
- maintain the Satisfactory Academic Progress standards as established by the school. Recipients who do not meet the standards are ineligible for Cal Grant payment and will not use eligibility during the terms they are ineligible for payment.
More questions? Cal Grant FAQ
Cal Grant Community College Entitlement Award For students enrolling at a CA Community College starting
The Cal Grant Community College Entitlement Award is for students attending a California Community College (CCC). Applicants must submit a FAFSA or CA Dream Act Application, plus a verified Cal Grant GPA to the California Student Aid Commission by September 2.
Who is considered for a Community College Entitlement Award
- Students must be enrolled at a California Community College
- Students who meet the general Cal Grant eligibility requirements, which can be found here
Cal Grant High School Entitlement Award For current high school seniors and recent high school graduates
The Cal Grant High School Entitlement Award is for current high school seniors and recent high school graduates. Applicants must submit a high school GPA, FASFA or CADAA to the California Student Aid Commission by March 2.
Who is considered for a High School Entitlement Award
- Current High school seniors and last year’s high school graduates
- Students who meet the general Cal Grant eligibility requirements
Cal Grant Transfer Entitlement Award For students who plan to transfer directly from a California Community College to a 4-Year University
This grant is for students who plan to transfer directly from a California Community College to a 4-Year University that offers a bachelor degree in the academic year that they are applying for the award. Deadline is March 2 and applicants must submit a FAFSA or CA Dream Act Application and have a minimum GPA of 2.4.
Cal Grant Competitive Awards For students who are not eligible for the Cal Grant Entitlement awards
This is a competitive award and limited to 13,000 awards each academic year. To be considered for the award, you must meet the general Cal Grant eligibility requirements and complete a FAFSA or CA Dream Act Application . Only students who are not awarded a Cal Grant Entitlement award can be considered. To see more information about the Cal Grant Entitlement Programs, click here .
Cal Grant B Foster Youth Award For Current and Former Foster Youth
The Cal Grant B Foster Youth award allows students who are current and former foster youth to be eligible for increased Cal Grant eligibility. Foster youth have until their 26 birthday to apply.
On July 1, 2018 California expanded the Cal Grant Program to allow students who are current and former foster youth to be eligible for increased Cal Grant eligibility.
- Resources for Foster Youth Students
Cal Grant C Award Free Money For students who are pursuing an Occupational or Technical Program
The Cal Grant C program provides FREE MONEY to students pursuing an occupational or technical program. Students must apply for FAFSA or CA Dream Act Application to apply. No GPA requirement.
Are you interested in pursuing an occupational or technical program that could bring you closer to your dream job? The California Student Aid Commission provides State financial aid for those who meet certain income, asset, and other financial aid standards to attend college. The Cal Grant C program provides FREE MONEY to students pursuing an occupational or technical program.
- Cal Grant C Priority Occupational List
- Cal Grant C Occupational List
- Request new password
- Support portal

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
If you're planning to write a cover letter for your grant proposal, here are some helpful steps you can follow: 1. Use a formal header. At the top of a grant proposal cover letter, most professionals choose to include a formal header. In this section, you can include elements such as: Your contact information.
The letter should be persuasive, clearly written, and provide examples of how the project can make a difference in people's lives. Letters of support are a powerful tool in your grant application arsenal. They provide evidence that your project has the backing of respected professionals, organizations, and individuals.
Here are some tips on how to start a good cover letter for a grant: Use a formal header. Begin your cover letter with a professional header that includes your organization's name, address, phone number, and email. Address the funder personally. If possible, address the cover letter to a specific person by their name and title.
Attach the PDF to the email and mention it in the email body. 3. Personalize Your Message. In the email body, provide a personalized introduction and context for the support letter. Address the recipient by name, express your connection to the nonprofit, and briefly explain the purpose of the letter. 4.
4 tips for writing a grant application. Stick to your mission. It's not uncommon for inexperienced grant writers to stretch their application too far and create a weak proposal. "Write grants based on your mission," said Lauren Balkan, Deputy Director of Wellspring Center for Prevention.
A Grant Proposal Cover Letter is a formal document that provides information about a proposed project or mission. It is submitted to government agencies, foundations, or organizations that provide grants. The grant proposal cover letter is submitted with the grant proposal or application document. It provides vital information about the project, its background, purpose, and goals. The grant ...
To write a formal letter of support for a funding application, keep the following in mind: 1. Begin by addressing the letter to the appropriate recipient and state your purpose clearly. 2. Provide specific reasons why the project or initiative is deserving of funding, highlighting its potential impact and benefits. 3.
Following are some examples: Sample 01. Dear Grant Review Committee, I am writing to express my enthusiastic support for the grant application titled "Impact of Urbanization on Local Bee Populations," submitted by Dr. Marcus Yi, a distinguished colleague at the University of Springfield.
Your application must include letters of support from your institution, key personnel, collaborators, and other significant contributors. Reference Letters. Some types of programs, such as fellowships (F) or mentored research career development (K) awards, require you to request letters of reference before you apply. Additional Letters. Beyond ...
A grant inquiry letter may be required to get approval from a grant-making organization before sending a grant proposal. Business proposal software can help you handle all related documents (support letters, résumés of key personnel, and so on) that are required for a successful grant application. Why should you seek grant funding
First of all, an average grant proposal letter shouldn't be more than one page long. Cover letters are the pitch of your detailed grant proposal. Think of it as a summary of your book. Before writing the first paragraph, you should open the letter with the contact's name, title, address, and other related information.
The date on the cover letter should match the date of your proposal or application. The letter should be contained to one page, consisting of 3-4 paragraphs. Find the appropriate contact person at the funding organization so you can address your letter to a specific person. The address of the funder should be placed at the top of the letter.
Letters of support from people or organizations that have authority in the field of your research, or community members that may benefit from the project. Visual aids like charts, graphs, and maps that contribute directly to your project's story and are referred to previously in the application. Finalizing your grant application
Include a sentence or two about what your organization does, and one research-based point that shows the need that your organization addresses. Limit your cover letter to one page with three or four paragraphs. Use the same date that you'll be sending the complete grant application to the funding source.
What is It? A letter of support is a document written by a third party to explain why a nonprofit organization deserves to receive funding for its programs and services.. It is written to boost the nonprofit's application or proposal for a grant. In addition, the third-party organization or business writing the support letter is required to demonstrate that the nonprofit can successfully ...
Include letters of commitment in your application that clearly spell out the roles of the collaborators. The grant application should contain a signed letter from each collaborator to the applicant that lists the contribution he or she intends to make and his or her commitment to the work. These letters are often the primary assurance the ...
A Grant Application Cover Letter is a formal document that accompanies a grant application, typically addressed to a potential grantor or a funding organization. This letter serves as an introduction to the grant proposal, providing a concise overview of the project or program for which funding is sought. It plays a critical role in making a ...
Offer money, volunteer time, supplies, your special skills, or a place to meet. Prove Your Awesome: Mention a past project you helped with that was a success (if you have one!). Step 4: The Grand Finale. Summarize Your Support: Remind them in a few sentences why you believe in this project.
Formatting Your Cover Letter. Use your organization's letterhead. Put the same date on the cover letter that is on the completed grant application. That is the date you will send the grant proposal to the grantor. Using the same date makes all the documents in your proposal package consistent. For the inside address (goes at the top of the ...
Cover Letter: Unless you have already had a face-to-face meeting or other contact with a funder, the cover letter is the first impression of your organization and project. Provide a brief summary that emphasizes your vision and objective. ... Follow grant application guidelines exactly, including answering required questions, providing ...
Ensure that the letter of support demonstrates a clear alignment between the goals of the grant proposal and the mission, values, and objectives of the supporting organization or individual. Provide concrete evidence and highlight the potential for impact. Personalize the letter and avoid making generic statements without clear alignment with ...
Nonprofit Grant Writing Cover Letter. Depending on your grant application, the cover letter may not be necessary. However, if your grant writing involves a cover letter, it should typically be one page in length and written on your nonprofit's official letterhead. Your cover letter is an overview of your funding ask.
The Letter of Support should be a minimum of half a page long (including letterhead) but ideally no longer than a single page. There are always exceptions to this rule, but 95% of the time a single page is sufficient and any longer can actually have a negative effect. Some tips for helping make the letter fit on a single page;
Articles and resources that equip current and prospective members of the federal grant community with information, answers, and tools to make your job easier. Read the latest in our "What is a Grant?" Blog Series Read the latest in our Federal Grant Writing Tips Blog Series. Grant Searching Made Easy: Mastering Keywords on Grants.gov. 4/11/2024 ...
1. Tell Success Stories. Always tell as many success stories as possible, even if it can only be told on the cover or in the introduction. Successes demonstrate the organization's impact on a ...
Policies and procedures, grant announcements, contract solicitations, special initiatives, call for partners, small business innovation research, and research dissertations, ... Grant application process guidance and application basics. Grant Application Basics; Application Forms; Application Deadlines & Important Dates;
Your request was flagged as suspicious; sorry about that! Please prove you are a human below.
NIH is updating the instructions for reference letters submitted for due dates on or after January 25, 2025 to provide more structure so letters will better assist reviewers in understanding the candidate's strengths, weaknesses, and potential to pursue a productive career in biomedical science. ... Overview of Grant Application and Review ...
The Cal Grant is a California-specific financial aid allocation that does not need to be paid back. Cal Grant applicants must apply using the FAFSA or CA Dream Act Application by the deadline and meet all eligibility, financial, and minimum GPA requirements of either program. Grants are for students attending Universities of California, California State Universities or California Community ...
The Community Eligibility Provision (CEP) is a non-pricing meal service option for schools and school districts in low-income areas. CEP allows the nation's highest poverty schools and districts to serve breakfast and lunch at no cost to all enrolled students without collecting household applications.