Present Perfect Tense
What is the present perfect tense.
- John has taken Sarah's advice.
- They have fixed the fence.
Table of Contents

More Examples of the Present Perfect Tense
Video lesson, comparing the present perfect tense and the simple past tense, forming the present perfect tense, interactive verb conjugation tables, the other present tenses.
- The board has decided to uphold the appeal.
- I have taken the wrong path.
Are you a visual learner? Do you prefer video to text? Here is a list of all our grammar videos .
- Janet has run two miles.
- Janet ran two miles.
- David has worked alongside two of the world's finest scientists in the field of entomology.
- David worked alongside two of the world's finest scientists in the field of entomology.
- I have worked.
- She has painted.
Forming the Past Participle (Regular Verbs)
- jump > jumped
- paint > painted
- chat > chatted
- stop > stopped
- sew > sewed
- play > played
- fix > fixed
- incur > incurred
- prefer > preferred
- open > opened
- enter > entered
- swallow > swallowed
- thrive > thrived
- guzzle > guzzled
- cry > cried
- fry > fried
Forming the Past Participle (Irregular Verbs)
- arise > arisen
- catch > caught
- choose > chosen
- know > known
The Negative Version
- The board has not decided to uphold the appeal.
- I have not taken the wrong path.
The Question Version
- Has the board decided to uphold the appeal?
- Have I taken the wrong path?
- Why has the board decided to uphold the appeal?
- How have I taken the wrong path?
Infographic for the Present Perfect Tense

Top 10 Regular Verbs
Top 10 Irregular Verbs
All 4 Past Tenses
| Person | Simple Past | Past Progressive Tense | Past Perfect Tense | Past Perfect Progressive Tense |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| is for a completed activity that happened in the past. | is for an ongoing activity in the past. Often, it is used to set the scene for another action. | is for emphasizing that an action was completed before another took place. | is for showing that an ongoing action in the past has ended. |
All 4 Present Tenses
| Person | Simple Present | Present Progressive Tense | Present Perfect Tense | Present Perfect Progressive Tense |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| is mostly for a fact or a habit. | is for an ongoing action in the present. | is for an action that began in the past. (Often, the action continues into the present.) | is for a continuous activity that began in the past and continues into the present (or finished very recently). |
All 4 Future Tenses
| Person | Simple Future | Future Progressive Tense | Future Perfect Tense | Future Perfect Progressive Tense |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| is for an action that will occur in the future. | is for an ongoing action that will occur in the future. | is for an action that will have been completed at some point in the future. | is for an ongoing action that will be completed at some specified time in the future. |
| The 4 | Example |
|---|---|
| I go | |
| I am going | |
| present perfect tense | I have gone |
| I have been going |

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
You might also like...
Help us improve....

Was something wrong with this page?

Use #gm to find us quicker .

Create a QR code for this, or any, page.
mailing list
grammar forum
teachers' zone
Confirmatory test.
This test is printable and sendable
expand to full page
show as slides
download as .doc
print as handout
send as homework
display QR code
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Present Perfect Tense | Examples & Use
Present Perfect Tense | Examples & Use
Published on April 4, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on September 25, 2023.
The present perfect tense is a verb form used to refer to a past action or situation that has a present consequence. It’s typically used to indicate experience up to the present, recent actions, or a change that occurred over a period of time.
The present perfect is formed using the auxiliary verb “have” and the past participle of the main verb (e.g., “I have eaten”). However, the third person singular (e.g., “he,” “she,” and “it”) uses “has” instead of “have.”
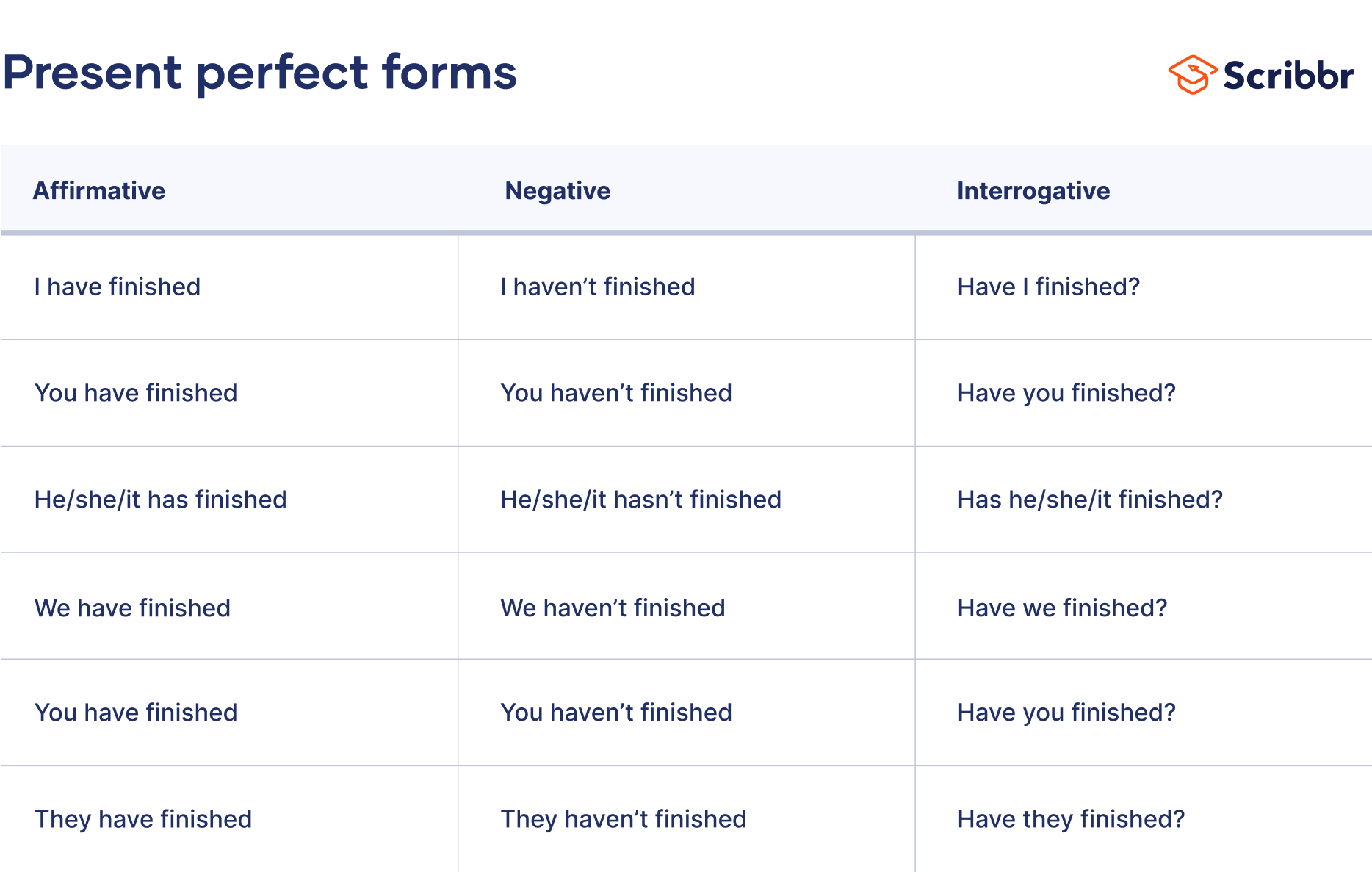
Table of contents
How to use the present perfect, past simple vs. present perfect, present perfect vs. present perfect continuous, how to form negatives, how to form questions, how to form the passive voice, other interesting language articles, frequently asked questions about the present perfect tense.
The present perfect is used to refer to a completed past action that’s relevant to the present or to an action that began in the past and may continue in the present.
It’s used to talk about experience up to now , a change that occurred over time , recent actions (often used with “just”), and unfinished action that is expected to be completed (in the negative, often with “yet”).
The present perfect is formed using the auxiliary verb “have” along with the past participle of the main verb. The only exception is the third person singular form (“he,” “she,” “it,” and singular nouns), which uses “has” instead of “have.”
In affirmative present perfect statements, the subject and auxiliary verb are often contracted (e.g., “ I’ve dreamed”).
The theater group has improved .
Sashi has just brushed his teeth.
The present perfect can also be used along with future simple tense constructions to describe a future action. In these instances, the present perfect clause is usually preceded by a subordinating conjunction (e.g., “when,” “until”).
After Anna has presented the report, we’ll take a short break . Note When the present perfect occurs more than once in a sentence and refers to the same subject, the second verb can be written without the auxiliary verb “have.” If the second instance refers to a different subject, a conjugated form of the auxiliary verb should be included.
- I’ve cleaned the kitchen and cooked dinner.
- Jennifer has left , and Henry has arrived .
Indicating time
As the present perfect refers to an action that occurred at an unspecified time in the past, sentences in the present perfect commonly use adverbs that refer to non-specific time (e.g., “ever,” “never,” “once,” and “so far”).
Expressions that refer to a specific time (e.g., “last week,” “yesterday”) are typically used along with a preposition (e.g., “for,” “since”).
- I’ve worked on this project yesterday .
- I’ve worked on this project since yesterday .
- Sophie has felt ill last week .
- Sophie has felt ill for the last week .
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
Both the present perfect and past simple refer to past action. However, they have different functions:
- The past simple is typically used to refer to an action that occurred at a definite time in the past and will not continue.
- The present perfect is used to refer to an action that occurred in the past and has present consequences or to an action that began in the past and may continue.
I have seen that film before. [I may see it again.]
I went to Toronto last year.
Both the present perfect and the present perfect continuous can be used to refer to the present consequences of a past action or situation (e.g., “I have lived here for two years” and “I have been living here for two years”).
However, they cannot always be used interchangeably:
- The present perfect can be used to refer to a past action or situation that may continue in the present.
- The present perfect continuous refers to actions or situations that began in the past and are definitely continuing in the present.
Aria has been traveling the world. [She is still traveling.] Note Stative verbs (e.g., “know,” “feel,” “want”) can be used in the present perfect to describe states of being that began in the past.
These verbs are typically not used in the present perfect continuous .
- I have been knowing him for years.
- I have known him for years.
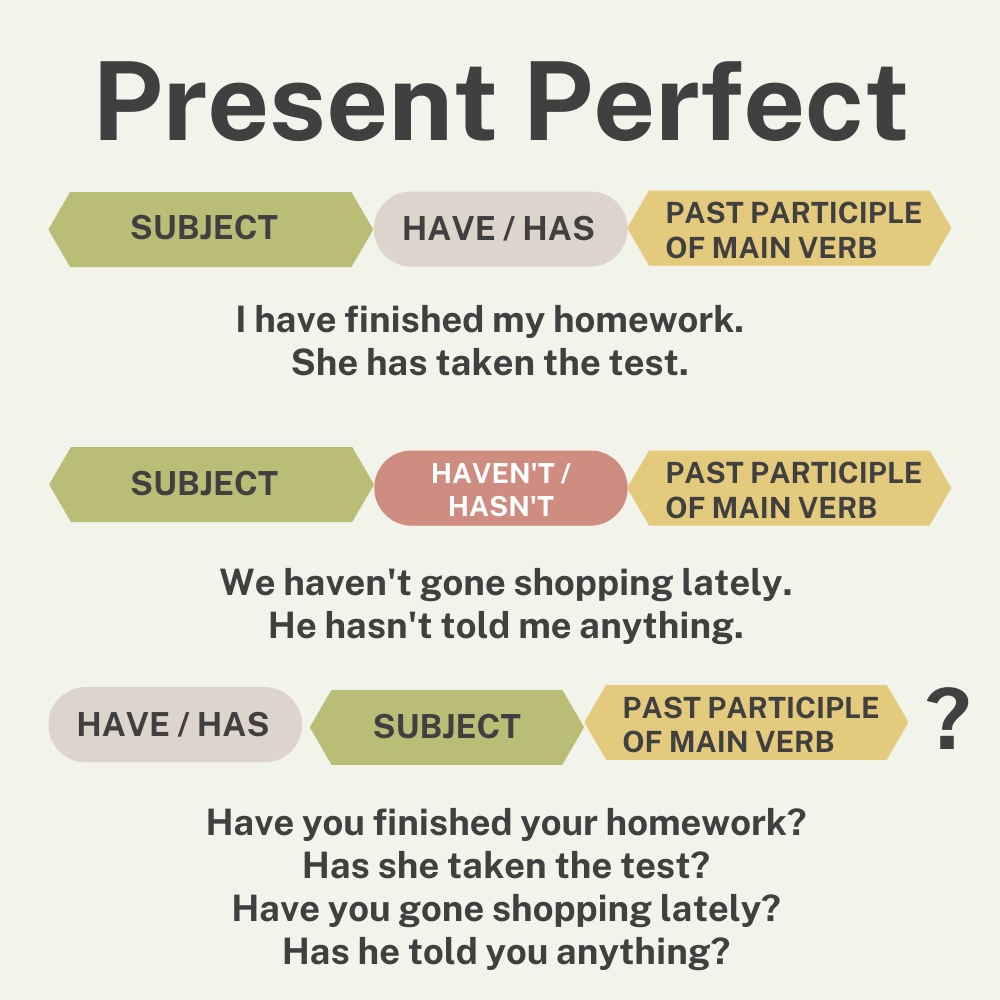
Negatives are formed by adding the adverb “not” between the subject and the main verb . This is the case for all subjects.
To ask a yes–no question in the present perfect, put the auxiliary verb first, followed by the subject and the past participle of the main verb.
To ask a question using a wh-word (an interrogative pronoun like “what” or an interrogative adverb like “when”), place the pronoun or adverb before “have” (or “has” for the third person singular).
What have we done?
In a passive sentence, the subject is acted upon (rather than performing the action). In the present perfect, the passive voice is formed by adding the past participle of the verb “be” (i.e., “been”) between the auxiliary verb and the past participle of the main verb .
The thieves have been followed by the police.
If you want to know more about nouns , pronouns , verbs , and other parts of speech , make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations and examples.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Possessive nouns
- Indefinite pronouns
- Relative pronouns
- Interrogative pronouns
- Simple present
- Modal verbs
- Conditional sentences
- Subjunctive mood
- Imperative mood
- Interjections
- Determiners
- Prepositions
The present perfect tense and the present perfect continuous can both be used to refer to the present consequences of a past action or situation:
- The present perfect can be used to refer to a past action that may continue in the present (e.g., “I have lived here for six months”).
- The present perfect continuous refers to actions or situations that began in the past and are definitely continuing in the present (e.g., “I have been arguing with him constantly”).
- The past simple is typically used to refer to an action that was completed at a definite time in the past (e.g., “I slept in this morning”).
- The present perfect is used to refer to a past action that has present consequences or to an action that began in the past and may continue (e.g., “I have written a book”).
Sources in this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
Ryan, E. (2023, September 25). Present Perfect Tense | Examples & Use. Scribbr. Retrieved July 22, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/verbs/present-perfect/
Aarts, B. (2011). Oxford modern English grammar . Oxford University Press.
Butterfield, J. (Ed.). (2015). Fowler’s dictionary of modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Garner, B. A. (2022). Garner’s modern English usage (5th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, simple present tense | examples, use & worksheet, the subjunctive mood | definition & examples, verb tenses in academic writing | rules, differences & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Present Perfect Tense in English Grammar
When to use the present perfect simple, conjugation of english present perfect tense, contractions.
- Lingolia Plus English
What is the present perfect?
The present perfect tense connects the past with the present; it expresses completed past actions and experiences that have an influence on or connection to the present.
We use the present perfect when the exact time of the action is not important.
The present perfect is formed using the present tense of the verb have and the past participle of the main verb. Be aware that many languages have a tense that is similar to the present perfect, however, the usage is probably different.
Learn how to conjugate the present perfect and when to use it, then test your skills in the exercises.
Adam: You have been on your phone all day, you should take a break from party planning!
James: I know, but I want everything to be perfect. Lisa has never had a surprise party before.
Adam: She’s going to be delighted.
James: Hopefully! I’ve invited all of her friends and family and now I’m waiting for their replies.
Adam: Has Tony replied yet? I haven’t seen him for ages!
James: Not yet, but Ella has just sent a message. She doesn’t know if she can come.
Adam: That’s annoying, you have reminded her at least seven times!
James: I know, I’m getting worried. I have already ordered food and drinks for thirty people, but so far only ten have said yes!
We use the present perfect simple to express:
- completed actions that have an influence on the present, usually without a specific time marker Example: I’ve invited all her friends and family, now I’m waiting for their replies. we don’t know when the invites were sent
- past experiences with the signal words ever and never Examples: She has never had a surprise party before. Have you ever had a surprise party?
- recently completed actions (usually with the signal word just ) Example: Ella has just sent a message.
- actions that did or did not happen up to the moment of speaking (with already and yet ) Examples: Has Tony replied yet? I have already ordered food and drinks for thirty people.
- how often or how many times up to now Example: You have reminded her at least seven times.
- states and situations that began in the past and continue up to the present (with the signal words for and since ) Example: I haven’t seen him for ages. She has wanted a surprise party for years.
Learn about the difference between the present perfect simple and other tenses in Lingolia’s English Tense Comparison section:
- Present Perfect Simple vs. Present Perfect Progressive
- Simple Past vs. Present Perfect Simple
Signal Words for the Present Perfect Simple
Signal words can help us recognise which tense to use. The typical signal words for the present perfect simple are:
- ever, never
- already, just, not … yet
- so far, until now, up to now …
- for, since (often with stative verbs )
The signal words just, already, ever and never follow the auxiliary:
Other signal words like yet, so far, for, since … come at the end of the phrase:
Remember: already is used in positive sentences whereas yet is used in negative sentences and questions.
Some of the signal words for the present perfect simple are the same as those for the past perfect simple . The difference is whether they refer to a time in the present or the past.
To conjugate the present perfect tense in English we use the present form of the auxiliary verb have and the past participle of the main verb . The table below provides and overview of the conjugation in positive , negative and interrogative sentences.
| positive | negative | question | |
|---|---|---|---|
| I/you/we/they | I play / | I not play / | I play / ? |
| he/she/it | he play / | he not play / | he play / ? |
Past participle – Spelling Rules
The past participle for regular verbs is formed by adding -ed to the base form of the verb. The past participle of irregular verbs is different and should be memorised. However, here are a few exceptions to take note of when conjugating the past participle of regular verbs:
- When a verb ends with -e , we simply add a -d . Example: lov e – lov ed (not: loveed )
- The final consonant is doubled after short stressed vowels. Example: adm it – admi tt ed
- The final consonant -l is always doubled after a vowel in British English but not in American English. Example: trav el – trave ll ed (British), trave l ed (American)
- A -y at the end of the word is replaced by an -i . Example: hurr y – hurr i ed
Learn the difference between the irregular past participles of the verb go with our page on been to/gone to.
been vs. gone
The verb go has two past participle forms: been and gone . The difference depends on where the subject is currently located.
- Use gone for incomplete visits: Example: —Where’s Sarah? I haven’t seen her yet. —She’s just gone to the supermarket, she’ll be back soon. Sarah is still at the supermarket or on her way there at the time of speaking
- Use been for completed visits: Example: —Oh no! Callum has just been to the supermarket, the fridge is already full! Callum is no longer at the supermarket at the time of speaking, this visit is complete
Read more about the difference between been and gone in English grammar.
Contractions are a combination of certain pronouns , verbs and the word not . They are mostly used in spoken and informal written English. The table below provides an overview of contractions in the present perfect tense using the verb have .
| long form | contraction | example |
|---|---|---|
| have | …’ve | they’ve |
| have not | …’ve not/… haven’t | I’ve not/I haven’t |
| has | …’s | she’s |
| has not | …’s not/… hasn’t | he’s not/he hasn’t |
In written English, we usually form contractions with a pronoun and an auxiliary (help verb), but not with a noun and an auxiliary.
However, the contraction of has can be used after nouns as well as pronouns.
Words that end in -s are an exception to this:
How good is your English?
Find out with Lingolia’s free grammar test
Take the test!
Maybe later

Present Perfect Tense: Definition, Rules and Useful Examples
Present Perfect Tense! In this section, we are going to be explaining exactly what the present perfect tense and how we can use it, allowing you to be able to speak much more clearly about certain actions and the times they are occurring.
Learn how and when to use the Present Perfect Tense in English with useful grammar rules, example sentences and ESL printable worksheets.
- Present Perfect Tense
What Is the Present Perfect Tense?
The present perfect tense is something which might seem complicated at first glance, but once you understand the basic rules, it becomes much more simple. This tense is used to talk about an action which began in the past but has continued into the present moment and is something that we see often when using the English language.
The present perfect tense is used to describe:
- an action or situation that began sometime in the past and continues into the present time.
- an action performed during a period that has not yet completed.
- a repeated activity in an unspecified time period between the past and the current time period.
- an action that finished in the very recent past, expressed by ‘just’.
- an action when the time is not important.
It is formed with a variant of the verb to have + the present participle (verb form ending in -ed).
The part that may confuse some readers is whether to use this present perfect verb tense (e.g. have walked) or to use the simple past (e.g. walked).
Simple Past
- Used with adverbs that describe a time already past (e.g. I studied for the test on Sunday).
- Used with an adverb that marks a specific point in time (e.g. I have studied today).
Present Perfect
- Used with adverbs describing a time that started in the past and continues right up to the present time (e.g. I have studied every day this week).
- Used when speaking about an event that happened in the recent past (e.g. I have studied night after night for this test).
In the next section are ten examples to demonstrate the various use cases described above. After that are several exercises to provide practice identifying the different forms of the present perfect verb tense. As always, a good way to continually reinforce this information is to try and identify this type of verb while reading and always, always, always keep a dictionary or google search window handy.
Present Perfect Tense Structure
In English grammar, the present perfect is a combination of the present tense and perfect aspect that is used to express a past event that has present consequences.
The structure of the Present Perfect (formula):
- Affirmative Sentence
Subject + have/has + past participle
I have tried sushi before.
- Negative Sentence
Subject + have not (haven’t)/has not (hasn’t) + past participle
I have not tried sushi before.
- Interrogative Sentence
Have/Has + subject + past participle?
Have you tried sushi before?
Examples of the Present Perfect Tense
- My daughter has completed her math and reading homework assignments.
- The gardener has planted all the seeds he is going to for the tomato season.
- We have finished watching Star Wars and now we can start watching The Empire Strikes Back .
- My company has banned remote work-from-home and now we all have to drive into the office every day.
- For the last two weeks, I have read a book a day and reviewed it for my website.
- I have traveled back and forth to Japan once a month for the last year .
- The cat has played with the ribbon for too long and now she just looks silly!
- I have listened to all the PMP podcasts, and now I am ready to take the exam.
- The trick-or-treaters have visited my house three times tonight and I’m not sure I can stay hidden any longer.
- My son has performed the same piano exercises for the last hour and I can’t get the sounds out of my head!
How to Use the Present Perfect Tense?
The present perfect tense usage.
The Present Perfect is used:
- To express things you have done in your life
I’ve been to England.
She has never studied Japanese.
- To express the number of times you have done something
I’ve been to Paris three times.
How many times have you tried to call her?
- To describe recently completed actions which are important now
I have some bad news. I’ve lost my job.
I can’t play football tonight – I’ve hurt my leg.
- To express situations that started in the past and are still true
I’ve known James for 4 or 5 years.
She’s been the director of that company since 2007.
- To describe unfinished actions or situations
I’ve known Julie for ten years. (I met her ten years ago and I still know her)
We have lived here since 2004.
- To express the present result
I’ve lost my keys.
John has missed the bus, so he’ll be late.
Time Adverbs in Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense is commonly used with the indefinite time adverbs (time expressions):
Final thoughts
This article covers a lot of ground relating to one specific verb tenses that describe actions occurring starting in the past that ended already but have some continued effect on the present time. This may be the most difficult to use verb form since it is not actually used to describe actions occurring in the present time. The simple form sometimes gets confused with the present progressive and may require a bit more active concentration to identify when it is appropriate to use which form. It is still fairly common in speech to hear some confusion between the simple form and the present progressive form.
The present progressive is used particularly often; many speakers, however, do not specifically understand when or why to use this form since it was originally learned through habit rather than study. Just as with any other language, whether it is a primary or a secondary tongue, both speaking and writing the words as well as keeping a dictionary and thesaurus handy is imperative to become truly fluent.
Finally, the best way to cement and maintain an understanding of these verb forms is to read much and focus on why specific verb forms are used in the text; not all at once, but one verb form at a time.
Present Perfect Tense Chart | Picture

Present Perfect Tense Exercises
Instructions : Each question will present a sentence with one or more empty spaces. The correct form of the verb or verbs must be selected from the answers given (A, B, C, D).
[h5p id=”3″]
All Tenses in English
Learn all (12) tenses in English with useful grammar rules, examples and ESL worksheets.
Verb Tenses Chart
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Continuous Tense
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Perfect Continuous Tense
- Simple Future Tense
- Future Continuous Tense
- Future Perfect Tense
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Latest Posts
- Active vs. Passive Voice Exercises – Active vs. Passive Voice Worksheet - December 25, 2023
- Phrase Exercises – Phrase Worksheet - December 23, 2023
- Sentence Exercises – Sentence Worksheet - December 23, 2023

Present Perfect Tense in English: How to use it + examples

The present perfect tense is one of the most common English verb tenses , and it’s used in several different ways. This lesson will teach you everything you ever wanted to know about the present perfect – try the four quizzes with grammar exercises in each section!

Download lesson PDF + audio
Table of contents:
- What is the present perfect tense & when do we use it?
- How to form the present perfect: Positive, Negative, Questions
What is the past participle?
- Present perfect with ever/never
- Present perfect with already, yet, recently, lately, just
- Present perfect with for and since
- Present perfect active voice and passive voice
- Present perfect simple vs. Present perfect continuous

What is the present perfect tense and when do we use it?
The present perfect is formed by subject + have/has + past participle of the main verb, for example:
- I = subject, have = auxiliary verb, bought = past participle of the main verb “buy”
- She = subject, has = auxiliary verb, visited = past participle of the main verb “visit”
We use the present perfect for unfinished time (a period of time that continues to the present moment), differently from the simple past tense which describes finished time:
- Present Perfect: We have lived in New York since 2002. (and we still live in New York)
- Simple Past: We lived in New York from 2002-2006. (and we do not still live in New York)
We also use the present perfect tense for unspecified time (when we don’t know or don’t say exactly when), differently from the simple past tense which describes specific time:
- Present Perfect: I ‘ve seen that movie. (I don’t say exactly when)
- Simple Past: I saw that movie a year ago.
- Present Perfect: He has sold his house recently. (it happened recently, but I don’t know exactly when)
- Simple past: He sold his house last week.
More examples of present perfect vs. past simple

How to form the Present Perfect
Present perfect positive.
| I / you / we / they | have | written |
| he / she / it | has | written |
Note: In spoken English, it’s common to use the contraction for the auxiliary verb have or has:
- I ’ve written three books.
- We ’ve already seen that movie
- Barbara ’s forgotten her cell phone.
- He ’s just woken up.
In this case, he’s, she’s, Barbara’s, etc. mean he has, she has , and Barbara has, not he is, she is, or Barbara is.
Present Perfect Negative
| I / you / we / they | haven’t | seen |
| he / she / it | hasn’t | seen |
Example sentences:
- I haven’t seen John this week.
- Mary hasn’t come to class for the past two days.
Present Perfect Questions
| Have | I / you / we / they | finished? |
| Has | he / she / it | finished? |
- Have you finished the project yet?
- Has George ever been to New York?
How to answer present perfect questions:
We can create a “short answer” using the auxiliary verb have/has, or their negative forms haven’t/hasn’t:
- Have you been to London? Yes, I have. / No, I haven’t.
- Has Alex met Miriam yet? Yes, he has. / No, he hasn’t.
- Have the results of the election been announced? Yes, they have. / No, they haven’t.

In the present perfect, it’s possible to say “have had” and “has had” when “have” is BOTH the auxiliary verb (helping verb) AND the main verb in the sentence, for example:
- I ‘ve had a lot of computer problems lately. (I have had)
- She’ s had three children in the past five years. (She has had)
- We haven’t had time to visit our relatives.
- He hasn’t had a haircut for months.
Click here to learn more about HAVE HAD and HAD HAD
Click here to learn about the present perfect vs. past perfect
The past participle form of the verb describes a completed action or state.
For regular verbs, the past participle is the same as the past simple tense:
- I worked (simple past) all day yesterday.
- I’ve worked (past participle) here since August.
This is also the case for many irregular verbs:
- He sold (simple past) his car last week.
- He’s sold (past participle) 200 books so far.
However, some irregular verbs’ past participles are different from their simple past form:
- We wrote (simple past) an article for the newspaper.
- We’ve written (past participle) for many famous publications.
Many of these irregular past participles end in –n:
| be | was / were | been |
| break | broke | broken |
| choose | chose | chosen |
| do | did | done |
| drive | drove | driven |
| eat | ate | eaten |
| fall | fell | fallen |
| fly | flew | flown |
| forget | forgot | forgotten |
| give | gave | given |
| go | went | gone |
| know | knew | known |
| see | saw | seen |
| show | showed | shown |
| speak | spoke | spoken |
| steal | stole | stolen |
| take | took | taken |
| wear | wore | worn |
| write | wrote | written |
Other irregular past participles have a change in the vowel:
| become | became | become |
| begin | began | begun |
| come | came | come |
| drink | drank | drunk |
| ring | rang | rung |
| run | ran | run |
| sing | sang | sung |
| swim | swam | swum |
Present Perfect Quiz
Present Perfect tense with unfinished time
Present perfect with ever / never.
The present perfect is used with ever and never to talk about actions done at any time in a person’s life, or at any time in history until now.
- Have you ever been to Japan?
- Has she ever seen Titanic?
- Have they ever ridden a motorcycle?
- Has Jason ever failed a test?
Use ever in questions only – NOT in statements.
- “I’ve ever been to Japan.”
- “I’ve been to Japan.”
Use never in statements – but only with have/has, not with haven’t/hasn’t:
- “My sister hasn’t never seen Titanic.”
- “My sister has never seen Titanic.”
- “My sister hasn’t seen Titanic.”
Present Perfect with already, yet, recently, lately, and just
The words already, yet, recently, lately, and just all refer to a recent and non-specific time period. (A specific time would be “yesterday” or “three hours ago” or last Friday,” and in these cases we would use the simple past).
Already and yet
Already can be used in positive statements and questions.
- “I’ve already read today’s newspaper.”
- “Have you already paid the electric bill?”
- “She’s finished the test already.”
Note: Already can go in between “have/has” and the past participle (as in the first two examples) or at the end of the sentence.
Yet can be used in negative statements and questions.
- “We haven’t cleaned the house yet.”
- “Has he told you the good news yet?”
- “Have they booked their tickets yet?”
Note: Yet usually goes at the end of the sentence or phrase.
Recently, lately, and just
Recently and lately can be used in positive statements, negative statements, or questions:
- “He’s recently lost some weight.”
- “I haven’t seen her recently.”
- “Have you spoken to Beth recently?”
- “I’ve gotten a lot of spam e-mails lately.”
- “Adam and Jessica haven’t been to church lately.”
- “Have you seen any good movies lately?”
Just (usually means very recent) is typically only used in positive statements and questions:
- “Don’t touch the walls – I’ve just painted them and they’re still wet.”
- “What book have you just finished reading?”
Spoken American English often uses the simple past with already, yet, and just:
- “Did you book the tickets yet?”
- “I already replied to the e-mail.”
- “We just got back from the gym.”
Quiz: Present Perfect with ever, never, already, recently, lately, and just
Present Perfect with for and since
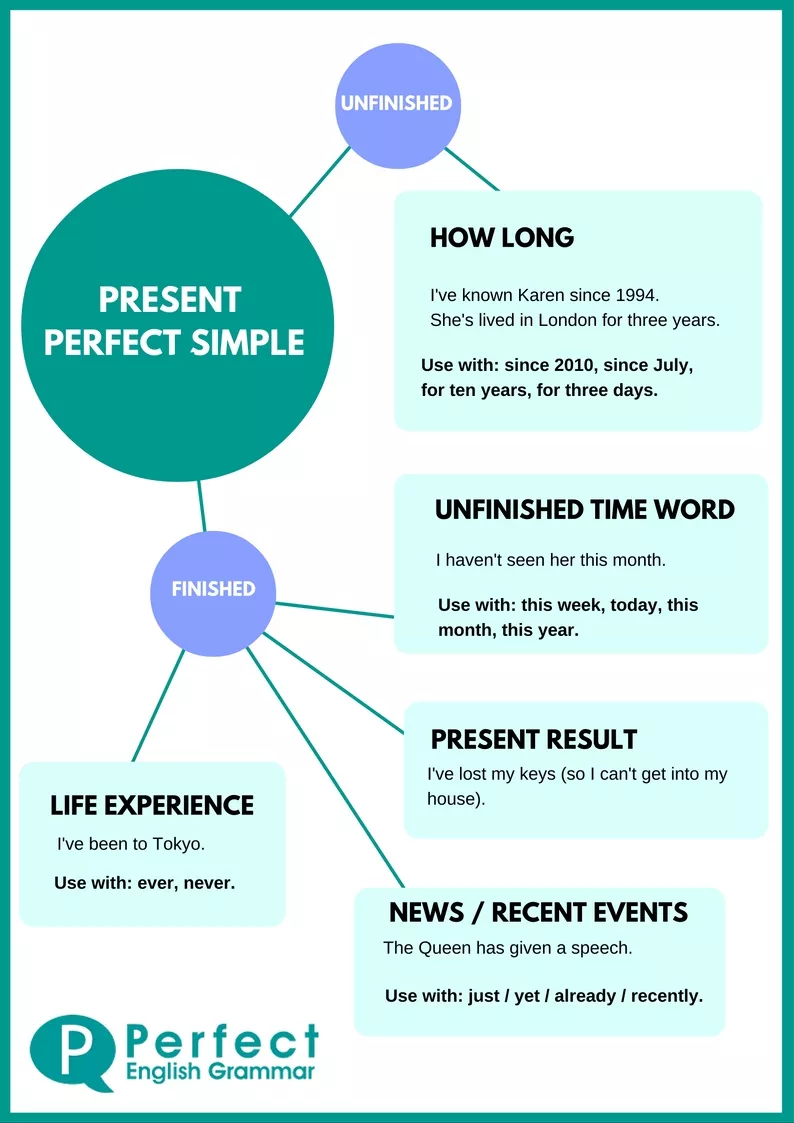
The present perfect is also used with for and since to talk about actions that began in the past and continue to the present.
- “I’ve lived here since 2004.”
- “I’ve lived here for 8 years.”
Since is used with a point in time , and means “from that point in time until the present.” Use since with dates (2011, January, Tuesday, etc.), times (6:15, noon, this morning, etc.), and past events (I was a child, he graduated from college, etc).
Since is always used with the present perfect, and not the simple past:
- “I’ve gone to the beach every year since I was a child.” (repeated action that continues until today)
- “I went to the beach when I was a child.” (finished action at a specific time in the past; I don’t go to the beach today)
For is used with a time period, and means “for that period of time until the present.” Use for with time periods of any length (five seconds, eight hours, two days, six weeks, nine months, ten years, a decade, centuries, etc.)
Be careful with for, because using the present perfect or the simple past can change the meaning:
- “ We’ve lived in Berlin for 6 months.” (and we live in Berlin now)
- “ We lived in Berlin for 6 months.” (and we don’t live in Berlin now)
Quiz: Present perfect with FOR and SINCE

Present Perfect Active Voice & Passive Voice
We can also form passive voice sentences with the present perfect tense! Here’s how to do it:
- Active voice: I have sent the packages.
- Passive voice: The packages have been sent.
- Active voice: He has fixed the car.
- Passive voice: The car has been fixed.
The passive voice of the present perfect tense needs two auxiliary verbs: have/has + been + main verb.
Note that whether we use “have” or “has” depends on the new subject of the passive sentence (the receiver of the action):
- Active voice: I have sent the letter.
- Passive voice: The letter has been sent.
- Active voice: He has fixed the wheels.
- Passive voice: The wheels have been fixed.
Present Perfect Simple vs. Present Perfect Continuous
How to form the present perfect continuous:, positive and negative statements:.
| SUBJECT | AUXILIARY VERB | BEEN | -ING FORM |
| I | have | been | working here since 1992. |
| He | hasn’t | been | sleeping well lately. |
| AUXILIARY VERB | SUBJECT | BEEN | -ING FORM | |
| How long | have | you | been | studying English? |
| How long | has | she | been | playing tennis? |
In some cases, the present perfect simple and the present perfect continuous are the same:
- “I’ve worked here since 1992.” = “I’ve been working here since 1992.”
However, we often use the present perfect continuous to emphasize the action, and the present perfect simple to emphasize the result:
- “ I’ve been working on this report for three weeks.” (emphasizes the action of working)
- “ I’ve finished the project.” (emphasizes that the project is done)
- “ We’ve been cleaning the house all afternoon.” (emphasizes the action of cleaning)
- “ We’ve cleaned the bathroom and the kitchen.” (emphasizes the fact that the bathroom and kitchen are done)
Be careful: Remember that stative verbs (describing the status of something) are never used in the present perfect continuous:
- “I’ve been knowing my best friend since elementary school.”
- “I’ve known my best friend since elementary school.”
- “She’s been understanding everything in the advanced class so far.”
- “She’s understood everything in the advanced class so far.”
In spoken English, we often use the present perfect continuous to talk about w ays you have spent your time recently:
“Hi, Joanna! What have you been up to lately?”
“ I’ve been training for a karate competition.”
“Wow – good luck! And how is your son?”
“He’s good. He’s been studying a lot lately because finals are coming up next week.”
Quiz: Present Perfect Continuous / Present Perfect Simple
Now you know all about the present perfect tense in English!
Click here to learn about more English verb tenses .
Make sure to put it into practice by writing your own example sentences with this verb tense.
What’s next for learning English grammar? Join my Advanced English Grammar Course to learn in detail about verb tenses, advanced sentence structure, nouns, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, and much more.
The lessons will help you not only understand English grammar rules, but also put grammar in use in your own English. You can even send in your written English for correction.
Master the details of English grammar:

You might also like...

24 Examples of Adjective + Preposition Combinations

Relative Clauses + Exercises

Advanced English Prepositions Quiz

Hi, I’m Shayna. I create courses helping English as a Second Language learners become more fluent in just a few minutes a day – so they can speak English naturally and confidently in work and daily life.

For information on how to make the present perfect, click here. Download this explanation in PDF here.
- I've known Karen since 1994.
- She's lived in London for three years.
- I've worked here for six months.
- I've known Sam since 1992.
- I've liked chocolate since I was a child.
- She's been here since 2pm.
- I've known Julie for ten years.
- I've been hungry for hours.
- She's had a cold for a week.
- I have been to Tokyo.
- They have visited Paris three times.
- We have never seen that film.
- I haven't seen her this month.
- She's drunk three cups of coffee today.
- I've already moved house twice this year!
- NOT: I've seen him yesterday.
- I've lost my keys (so I can't get into my house).
- She's hurt her leg (so she can't play tennis today).
- They've missed the bus (so they will be late).
- The Queen has given a speech.
- I've just seen Lucy.
- The Mayor has announced a new plan for the railways.
- I've been to Paris (in my life, but now I'm in London, where I live).
- She has been to school today (but now she's back at home).
- They have never been to California.
- Where's John? He's gone to the shops (he's at the shops now).
- Julie has gone to Mexico (now she's in Mexico).
- They've gone to Japan for three weeks (now they're in Japan).

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
- Present Perfect Tense in English
Affirmative Sentences
- I have finished the report.
This is a sentence in the present perfect tense . We know it is in the present perfect tense because it has the auxiliary verb HAVE (or HAS ) followed by a PAST PARTICIPLE .
Look at the structure for affirmative sentences in the present perfect tense. The word order is: subject + have / has + past participle
Past Participles
The past participle can be regular or irregular. Let’s look at the present perfect tense with regular past participles.
Regular past participles end in ED. Some example sentences:
- We have opened all of the windows.
- She has lived in Germany for ten years.
- He has called his mother twice today.
Notice how the past participle of these regular verbs is the same as the past simple tense form. But some past participles are IRREGULAR. For example:
- I have been very busy this week. ( Been is the past participle of TO BE)
- We have done our homework. ( Done is the past participle of TO DO)
- She has spoken to a large audience many times. ( Spoken is the past participle of TO SPEAK)
- Rob Woodward has taught English since 1997. ( Taught is the past participle of TO TEACH)
Notice how the past participle of these irregular verbs is different from their past tense form. I recommend our lesson about 101 Irregular Past Participles with example sentences in English .

Present Perfect Tense Contractions – Affirmative Sentences
In spoken English, we almost always use contractions with the present perfect tense. We contract the subject and the auxiliary have / has .
For example: I have
We contract the subject I with the auxiliary HAVE which becomes I’VE … and then you can add the past participle.
Here is the list of present perfect tense contractions:
- I have ➡️ I’ve
- You have ➡️ You’ve
- He has ➡️ He’s
- She has ➡️ She’s
- It has ➡️ It’s
- We have ➡️ We’ve
- They have ➡️ They’ve
Let’s look at some example sentences. Can you change these present perfect sentences to contain a contraction?
- We have done our homework.
- She has lived in Italy for six years.
- John has been here before.
Here are the answers:
- I have finished the report. ➡️ I’ ve finished the report.
- We have done our homework. ➡️ We ’ve done our homework.
- She has lived in Italy for six years. ➡️ She ’s lived in Italy for six years.
- John has been here before. ➡️ John ’s been here before.

Now, let’s look at how to make negative sentences in the present perfect tense.
Present Perfect Tense – Negative sentences
Look at this affirmative sentence:
There is the auxiliary HAVE and the past participle FINISHED . How can we make this negative?
To create a negative sentence in the present perfect tense, we just add NOT between the auxiliary HAVE or HAS and the past participle .
- I have finished the report. (This is an affirmative sentence)
- I have not finished the report. (This is a negative sentence)
However, it is much more common to use a contraction in negative sentences. You will normally hear:
- I haven’t finished the report.
- She has seen the movie.
How can we make this negative?
- She has seen the movie. (This is an affirmative sentence)
- She has not seen the movie (This is a negative sentence)
- She hasn’t seen the movie.
Let’s look at some more examples of negative sentences in the present perfect tense:
- I haven’t cleaned the kitchen today.
- We haven’t finished our meal yet.
- It hasn’t rained this week.
- He hasn’t seen the movie.
Here is the summary chart to make negatives sentences in the present perfect tense. We have the subject + negative auxiliary (haven’t/hasn’t) + past participle

Present Perfect Tense – Questions
- They have studied for the test.
It has the subject THEY, the auxiliary HAVE and the past participle STUDIED.
How can we change this into a question?
To make a question in the present perfect tense, we change the order of the subject with HAVE / HAS .
- They have studied for the test. … becomes …
- Have they studied for the test?
- She has arrived early.
How can we make this a question? We change the order of the subject and the auxiliary . The question becomes…
- Has she arrived early?
Let’s look at some more examples of present perfect questions:
- Have you taken your medicine today?
- Have we finished for the day?
- Has the game started ?
- Has she read the report? (Remember READ is the past participle of READ – yes, they have the same spelling but the pronunciation is different)

Present Perfect Tense – Short Answers
We can also give short answers to present perfect tense questions. Look at these questions:
- Have you done your homework?
- Has he told the truth?
- Has Mary called today?
Obviously, you can reply with just YES or NO, but in reality, we almost always give a short answer. Present perfect short answers use HAVE or HAVEN’T in them.
Let’s look at the first question:
Since this question is HAVE YOU…?
The short answers would be: Yes, I have. … or … No I haven’t.
- Have you done your homework? Yes, I have. … or … No, I haven’t .
What would the short answers be for the next two questions?
You could say:
- Has he told the truth? Yes, he has. … or … No, he hasn’t .
- Has Mary called today? Yes, she has. … or … No, she hasn’t .
Present Perfect Tense with Questions Words
We can also use question words (what, where, why, etc.) at the beginning of the question. For example:
- What have you done?
- Where has he gone?
- Why have they stopped?
- How has she felt today?
Present Perfect Tense Summary Chart
In the next lesson we are going to look at WHEN to use the present perfect tense in English .
I hope you found this lesson about the present perfect tense useful. If you did, please let other people know about it.
- 934k Followers
- 214k Followers
- 104k Followers
English Course
Perfect tense.
- When to use the Present Perfect Tense
- Adverbs with the Present Perfect Tense
- Still - Yet - Already
- Been To vs. Gone To
- Do - Does - Did - Done
- 101 Irregular Past Participles in English
Pin It on Pinterest
Present Perfect Simple
Exercises on present perfect.
The present perfect simple expresses an action that is still going on or that stopped recently, but has an influence on the present. It puts emphasis on the result.
Form of Present Perfect
| Positive | Negative | Question | |
|---|---|---|---|
| I have spoken. | I have not spoken. | Have I spoken? | |
| He has spoken. | He has not spoken. | Has he spoken? |
For irregular verbs, use the participle form (see list of irregular verbs , 3rd column). For regular verbs, just add “ ed ” .
Exceptions in Spelling when Adding ‘ ed ’
| Exceptions in spelling when adding | Example |
|---|---|
| after a final only add | love – loved |
| final consonant after a short, stressed vowel or as final consonant after a vowel is doubled | admit – admitted travel – travelled |
| final after a consonant becomes | hurry – hurried |
Use of Present Perfect
Example: She has written five letters.
Example: School has not started yet.
Example: She has cooked dinner.
Example: I have lost my key.
Example: I have never been to Australia.
Signal Words of Present Perfect
- already, ever, just, never, not yet, so far, till now, up to now
- Exceptions in Spelling when adding ‘ ed ’
- have or has
- Positive Sentences in Present Perfect Simple
- Negative Sentences in Present Perfect Simple
- Sentences with ‘ never ’ in Present Perfect Simple
- Questions in Present Perfect Simple
- Questions with Interrogative Particles in Present Perfect Simple
- Mixed Exercise on Present Perfect Simple
- Exercise on the text “ Loch Ness ”
- Irregular Verbs
Tests on Present Perfect
- Present Perfect: Level 1 , Level 2 , Level 3
Grammar in Texts
English For Yourself
Present Perfect Tense
In this section you will learn information about the different uses of the present perfect tense with examples.
Uses of the Present Perfect Tense
For actions that happened in the past when the time they happened is not relevant. The action is more important.
I have changed the bedsheets. They have mended the bike. She has been to Albania.
For past events that have an effect in the present.
Laura has broken the TV. He has forgotten the present. I have broken my nose.
For actions that finished recently. The adverb ‘just’ is usually used.
John has just finished his school assignment. I have sent the email to my teacher. He has just finished breakfast.
For actions/states which began in the past and are still happening in the present. Stative verbs are usually used.
Sandra has lived in Mexico for twenty years. I have been in bed since Monday. He has worked in the local cinema for two years.
For events which happened in a specific time and that are incomplete at the time of speaking. Some time expressions can be used, such as: today, ever, never, this week/morning/month/year.
They have had five meetings this week. I have never been to Japan. She has read ten books this year.
To talk about personal experiences.
I have never dyed my hair. Jennie has been to many concerts. We have won the soccer match five times in a row.
In the following table, you will find information about the structure of the present perfect tense and positive, negative and interrogative sentences.

More information about English verb tenses here .
Privacy Policy - Terms and Conditions
- English Grammar
- English Tenses
- Present Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
Present Perfect Tense - Meaning, Definition, Formula, Structure and Uses with Examples
The present perfect tense is indeed simple and easy if you try to understand and use it the right way. It seems to be confusing to some though the tense has a very simple structure. However, anything can be learnt, and so this article on present perfect tense is here to help your learning process. In this article, the meaning, definition, formula, structure and uses will be explained along with examples to help you understand better.

Table of Contents
Definition of the present perfect tense, structure and formula of the present perfect tense.
- Rules to Be Followed When Using the Present Perfect Tense
Uses of the Present Perfect Tense
Examples of the present perfect tense, check your understanding of the present perfect tense, frequently asked questions on the present perfect tense, what is the present perfect tense.
The present perfect tense is employed in a sentence to represent an action that just happened in the recent past and still has its effect in the present or an action that represents an indefinite time in the past. To have a clearer idea of the tense, let us look at how different dictionaries define the tense.
The Oxford Learner’s Dictionary defines the present perfect tense as “the form of a verb that expresses an action done in a time period up to the present, formed in English with the present tense of ‘have’ and the ‘past participle’ of the verb, as in I have eaten .” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, the present perfect tense is defined as “the form of the verb used for actions or events that have been completed or have happened in a period of time up to now.”
A much more elaborate definition is given by the Collins Dictionary and according to it, “the present perfect tenses of a verb are the ones used to talk about things which happened before the time you are speaking or writing but are relevant to the present situation, or things that began in the past and are still happening.” The Merriam-Webster Dictionary defines the present perfect tense as one “relating to, or constituting a verb tense that is traditionally formed in English with have and a past participle and that expresses an action or state begun in the past and completed at the time of speaking (as in “I have finished”) or continuing in the present (as in “We have lived here for several years”).
The general formula of the present perfect tense is as described below:
| Subject + + the rest of the sentence |
The structure of the present perfect tense can be analysed with reference to positive, negative, interrogative and negative interrogative types of sentences. Have a look at the table given below for a closer look at the same.
| Subject + + the rest of the sentence | Subject + + the rest of the sentence | subject + + the rest of the sentence | subject + + the rest of the sentence (or) subject + the rest of the sentence |
| Examples: my work. your work. his work. her work. their work. | Examples: my work. your work. his work. her work. their work. | Examples: I my work? you your work? he his work? she her work? they their work? | Examples: I my work? you your work? he his work? she her work? they their work? you your work? she her work? he his work? they their work? |
Rules to be Followed When Using the Present Perfect Tense
The very first thing that you will have to learn before you start using present perfect tense is how past participles are formed. In the English language , a past participle is formed by adding an ‘ed’ to the base form of the verb in most cases. However, there are a number of irregular verbs that have different spellings and do not, in any way, follow the concept of adding ‘ed’ to the base form like regular verbs . You can take a look at the extensive list of irregular verbs to analyse how these verbs are in their past participle form.
The next point to remember is that a sentence with the past perfect form of the verb uses two verbs – a helping verb and a main verb . ‘Have’ and ‘has’ are the two helping verbs that are used. ‘Have’ is used when the pronouns ‘I’, ‘you’, ‘they’ or plural nouns act as the subject in a sentence. ‘Has’ is used when the pronouns ‘he’, ‘she’, ‘it’ or singular nouns act as the subject.
The present perfect tense can be used
- To denote an action or event that happened or started in the past and still has its impact or some connection to the subject in the present.
- To indicate an action that happened in the past and continues to occur in the present.
- To connect the events of the present to the events that happened in the past.
Learn how to use the present perfect tense effectively by going through the examples given below.
| I | I as a teacher for two years. |
| You | You as a teacher for two years. |
| We | We as teachers for two years. |
| He | He as a teacher for two years. |
| She | She as a teacher for two years. |
| They | They as teachers for two years. |
| It | It here the whole time. |
| Singular noun | Michael as a teacher for two years. |
| Plural noun | Devika and Priscilla as teachers for two years. |
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate form of the present perfect tense in the following sentences:
1. We ___________ (find – negative) it yet.
2. Venu and Parvati ____________ (invited) all their friends for today’s party.
3. Shashi _________ (sleep – negative) all night.
4. ________ he _________ (finish) his work?
5. It ___________ (be – negative) the same ever since you left.
6. They __________ (buy) a 2BHK flat.
7. You ___________ (come) to the right place.
8. _______ you ever ________ (be) to Malaysia?
9. Do you know why she __________ (like – negative) it?
10. ________ you _________ (hear) about the new education policies?
Check if you have used the right form of the tense from the following sentences.
1. We have not found it yet.
2. Venu and Parvati have invited all their friends for today’s party.
3. Shashi has not slept all night.
4. Has he finished his work?
5. It has not been the same ever since you left.
6. They have bought a 2BHK flat.
7. You have come to the right place.
8. Have you ever been to Malaysia?
9. Do you know why she has not liked it?
10. Have you heard about the new education policies?
What is the present perfect tense?
The present perfect tense is employed in a sentence to represent an action that just happened in the recent past and still has its effect in the present or an action that represents an indefinite time in the past.
What is the definition of the present perfect tense?
What is the formula of the present perfect tense.
The general formula of the present perfect tense is as described below: Subject + have/has + past participle + the rest of the sentence
What are the rules to be followed when using the present perfect tense?
The point that you should keep in mind when using the present perfect tense is that it has two verbs – a helping verb and a main verb. ‘Have’ and ‘has’ are the two helping verbs that are used. This is followed by the main verb which appears in its past participle form.
Give some examples of the present perfect tense form.
Given below are a few examples of sentences using the present perfect form of the verb.
- Veena has not reached home yet.
- All the children have finished their assignments.
- Rinita has eaten all the mangoes.
- I have not watched the movie yet.
- Has she still not gone to the hospital?
What are the uses of the present perfect tense?
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Present perfect - 1
Present perfect - 2
Worksheets - handouts
Affirmative, negative, questions
- Present perfect simple - exercises
- Present perfect exercises
- Present perfect: have / has
- Present perfect - multiple choice
- Present perfect - write
- Negative / questions - write
- Present perfect - exercises
- Questions - present perfect
- Present perfect – form and use
- Past simple or present perfect?
- Present perfect - game

Present Perfect Quiz
You can do this grammar quiz online or print it on paper. It tests what you learned on the Present Perfect page.
1. Lindsay _____ not been to France.
2. _____ you finished your homework?
3. They___ gone to a rock concert.
4. _____ you been to Japan?
5. We _____ never eaten Mexican food.
6. Andrea has _____ her umbrella.
7. _____ the sun come up?
8. The children ________ the lost puppy.
9. Wiwi's been a vegetarian _____ three years.
10. I haven't worked _____ last December.
Your score is:
Correct answers:
Back to 12 English Tenses page
Grammar Quizzes
Grammar Games

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Present Perfect ережесі қазақша қазіргі шақтың бір түрін белгілейді. Бұл шақ мына екі жағдайда қолданылады: 1) казіргі мезетке дейін аяқталған іс-әрекеттер болғанда, мысалы I have played - мен ойнадым; 2 ...
The present perfect tense is an English verb tense used to describe an action that began in the past (despite being a present tense). For example: John has taken Sarah's advice. They have fixed the fence. The present perfect tense is formed liked this: [subject] +. "has" or "have". +.
Connection with past: the situation started in the past. Connection with present: the situation continues in the present. For and Since with Present Perfect tense. We often use for and since with perfect tenses:. We use for to talk about a period of time: five minutes, two weeks, six years; We use since to talk about a point in past time: 9 o'clock, 1st January, Monday
To make the positive present perfect tense, use: 'have' / 'has' + the past participle. Make the past participle by adding 'ed' to regular verbs (for example, 'play' becomes 'played') There are a few verbs that change their spelling when you add 'ed' (for example, 'study' becomes 'studied') We also have some completely irregular verbs.
As the present perfect refers to an action that occurred at an unspecified time in the past, sentences in the present perfect commonly use adverbs that refer to non-specific time (e.g., "ever," "never," "once," and "so far"). Examples: Present perfect and adverbs. Joseph has never lived in South Africa. Laura has eaten at this ...
The present perfect tense connects the past with the present; it expresses completed past actions and experiences that have an influence on or connection to the present. We use the present perfect when the exact time of the action is not important. The present perfect is formed using the present tense of the verb have and the past participle of ...
The present perfect tense is used to describe: an action or situation that began sometime in the past and continues into the present time. an action performed during a period that has not yet completed. a repeated activity in an unspecified time period between the past and the current time period. an action that finished in the very recent past ...
The present perfect is a verb tense which is used to show that an action has taken place once or many times before now. The present perfect is most frequently used to talk about experiences or changes that have taken place, but there are other less common uses as well. Read on for detailed descriptions, examples, and present perfect exercises.
Present Perfect with for and since The present perfect is also used with for and since to talk about actions that began in the past and continue to the present. "I've lived here since 2004." "I've lived here for 8 years." Since is used with a point in time, and means "from that point in time until the present."Use since with dates (2011, January, Tuesday, etc.), times (6:15 ...
For irregular verbs, it's the form in the 3rd column. Present perfect - Use. We normally use the present perfect to talk about past events that have a connection with the present, for example, news or past experiences. We can also use the present perfect to talk about situations that started in the past but which are still true in the present.
4: A finished action with a result in the present (focus on result). We often use the present perfect to talk about something that happened in the recent past, but that is still true or important now. Sometimes we can use the past simple here, especially in US English. I've lost my keys (so I can't get into my house).
The present perfect is a grammatical combination of the present tense and perfect aspect that is used to express a past event that has present consequences. The term is used particularly in the context of English grammar to refer to forms like "I have finished". The forms are present because they use the present tense of the auxiliary verb have, and perfect because they use that auxiliary in ...
For example: I have. We contract the subject I with the auxiliary HAVE which becomes I'VE … and then you can add the past participle. Here is the list of present perfect tense contractions: I have ️ I've. You have ️ You've. He has ️ He's. She has ️ She's. It has ️ It's. We have ️ We've.
Use of Present Perfect. puts emphasis on the result. Example: She has written five letters. action that is still going on. Example: School has not started yet. action that stopped recently. Example: She has cooked dinner. finished action that has an influence on the present. Example: I have lost my key.
Present perfect simple tense. 75 Present perfect simple tense English ESL powerpoints. SORT BY. Most popular. TIME PERIOD. All-time. angkosm. present perfect simp. This is a powerpoint. 59453 uses. loveteaching. PRESENT PERFECT game. Students need to cli. 42879 uses. guorkhan. Present Perfect Tens. Grammatical rules pr. 18396 uses.
Uses of the Present Perfect Tense. For actions that happened in the past when the time they happened is not relevant. The action is more important. I have changed the bedsheets. They have mended the bike. She has been to Albania. For past events that have an effect in the present. Laura has broken the TV. He has forgotten the present.
Definition of the Present Perfect Tense. The Oxford Learner's Dictionary defines the present perfect tense as "the form of a verb that expresses an action done in a time period up to the present, formed in English with the present tense of 'have' and the 'past participle' of the verb, as in I have eaten."According to the Cambridge Dictionary, the present perfect tense is defined ...
QUIZ: The Present Perfect Verb Tense. Now, test your knowledge of what you learned in the lesson by trying this quiz. You can get help with some questions if you press 'Hint'. You will get your score at the end, when you can click on 'View Questions' to see all the correct answers. 1. Question.
Video: present perfect. Present perfect - 1. Present perfect - 2. Worksheets - handouts. Content
Present perfect exercises. Present perfect: have / has. Present perfect - multiple choice. Present perfect - write. Negative / questions - write. Present perfect - exercises. Questions - present perfect. Present perfect - form and use. Past simple or present perfect?
The children ________ the lost puppy. 9. Wiwi's been a vegetarian _____ three years. 10. I haven't worked _____ last December. Online quiz to test your understanding of the Present Perfect tense in English. This is a free multiple-choice quiz that you can do online or print out. For ESL learners.
With President Joe Biden's support unleashing a flood of endorsements from nearly every prominent Democrat in the country, Kamala Harris has emerged as the odds-on favorite to take his place as ...