Artificial Intelligence MCQ – Problem-Solving Agents
Here are 25 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) related to Artificial Intelligence, focusing specifically on Problem-Solving Agents. Each question includes four options, the correct answer, and a brief explanation. These MCQ questions cover various aspects of AI problem-solving agents, including algorithms, search strategies, optimization techniques, and problem-solving methods, providing a comprehensive overview of this area in AI.

1. What is the primary objective of a problem-solving agent in AI?
Explanation:.
A problem-solving agent is designed to find a sequence of actions that leads from the initial state to a goal state, solving a specific problem or achieving a set goal.
2. In AI, a heuristic function is used in problem-solving to:
A heuristic function is used to guide the search process by providing an educated guess about the cost to reach the goal from each node, thus helping to efficiently reduce the search space.
3. Which algorithm is commonly used for pathfinding in AI?
The A* Algorithm is widely used for pathfinding and graph traversal. It efficiently finds the shortest path between two nodes in a graph, combining the features of uniform-cost search and greedy best-first search.
4. What is "backtracking" in AI problem-solving?
Backtracking involves going back to previous states and trying different actions when the current path does not lead to a solution, allowing for exploring alternative solutions.
5. The "branch and bound" technique in AI is used to:
Branch and bound is an algorithmic technique used for solving various optimization problems. It systematically enumerates candidate solutions by branching and then uses a bounding function to eliminate suboptimal solutions.
6. Which of the following is a characteristic of a depth-first search algorithm?
Depth-first search explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking, going deep into a search tree before exploring siblings of earlier nodes.
7. In AI, "constraint satisfaction problems" are typically solved using:
Constraint satisfaction problems, where a set of constraints must be met, are commonly solved using backtracking algorithms, which incrementally build candidates to the solutions and abandon candidates as soon as they determine that the candidate cannot possibly be completed to a valid solution.
8. The primary goal of "minimax" algorithm in AI is:
The minimax algorithm is used in decision-making and game theory to minimize the possible loss for a worst-case scenario. When dealing with gains, it seeks to maximize the minimum gain.
9. What is "state space" in AI problem-solving?
The state space in AI problem-solving refers to the set of all possible states that can be reached from the initial state by applying a sequence of actions. It is often represented as a graph.
10. In AI, "pruning" in the context of search algorithms refers to:
Pruning in search algorithms involves eliminating paths that are unlikely to lead to the goal or are less optimal, thus reducing the search space and improving efficiency.
11. The "traveling salesman problem" in AI is an example of:
The traveling salesman problem is a classic optimization problem in AI and computer science, where the goal is to find the shortest possible route that visits a set of locations and returns to the origin.
12. "Greedy best-first search" in AI prioritizes:
Greedy best-first search is a search algorithm that prioritizes nodes that seem to be leading to a solution the quickest, often using a heuristic to estimate the cost from the current node to the goal.
13. In AI, "dynamic programming" is used to:
Dynamic programming is a method for solving complex problems by breaking them down into simpler subproblems. It is used when the subproblems are overlapping and the problem exhibits the properties of optimal substructure.
14. The "Monte Carlo Tree Search" algorithm in AI is widely used in:
Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) is an algorithm used for making decisions in some kinds of game-playing, particularly where it is impractical to search all possible moves due to the complexity of the game.
15. What does an "admissible heuristic" in AI guarantee?
An admissible heuristic is one that never overestimates the cost to reach the goal. In heuristic search algorithms, using an admissible heuristic guarantees finding an optimal solution.
16. The concept of "hill climbing" in AI problem solving is similar to:
Hill climbing in AI is a mathematical optimization technique which belongs to the family of local search. It is used to solve computational problems by continuously moving in the direction of increasing elevation or value.
17. The "no free lunch theorem" in AI implies that:
The "no free lunch" theorem states that no one algorithm works best for every problem. It implies that each problem needs to be approached uniquely and that there's no universally superior method.
18. In AI, "means-ends analysis" is a technique used in:
Means-ends analysis is a problem-solving technique used in AI that involves breaking down the difference between the current state and the goal state into smaller and smaller differences, then achieving those smaller goals.
19. The "Pigeonhole principle" in AI is used to:
In AI and mathematics, the Pigeonhole principle is used to prove that a solution exists under certain conditions. It states that if n items are put into m containers, with n > m, then at least one container must contain more than one item.
20. "Simulated annealing" in AI is inspired by:
Simulated annealing is an optimization algorithm that mimics the process of annealing in metallurgy. It involves heating and controlled cooling of a material to increase the size of its crystals and reduce their defects.
21. In AI, the "Bellman-Ford algorithm" is used for:
The Bellman-Ford algorithm is an algorithm that computes shortest paths from a single source vertex to all of the other vertices in a weighted graph. It's particularly useful for graphs where edge weights may be negative.
22. What is the primary function of "Alpha-Beta pruning" in AI?
Alpha-Beta pruning is a search algorithm that seeks to decrease the number of nodes that are evaluated by the minimax algorithm in its search tree. It is used in game playing to prune away branches that cannot possibly influence the final decision.
23. The "Hungarian algorithm" in AI is best suited for solving:
The Hungarian algorithm, a combinatorial optimization algorithm, is used for solving assignment problems where the goal is to assign resources or tasks to agents in the most effective way.
24. In problem-solving, "depth-limited search" is used to:
Depth-limited search is a modification of depth-first search, where the search is limited to a specific depth. This prevents the algorithm from going down infinitely deep paths and helps manage the use of memory.
25. "Bidirectional search" in AI problem solving is used to:
Bidirectional search is an efficient search strategy that runs two simultaneous searches: one forward from the initial state and the other backward from the goal, stopping when the two meet. This approach can drastically reduce the amount of required exploration.
Related MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) :
Artificial intelligence mcq – agents, artificial intelligence mcq – natural language processing, artificial intelligence mcq – partial order planning, artificial intelligence mcq – expert systems, artificial intelligence mcq – fuzzy logic, artificial intelligence mcq – neural networks, artificial intelligence mcq – robotics, artificial intelligence mcq – rule-based system, artificial intelligence mcq – semantic networks, artificial intelligence mcq – bayesian networks, artificial intelligence mcq – alpha beta pruning, artificial intelligence mcq – text mining, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Artificial Intelligence
Control System
- Interview Q
Intelligent Agent
Problem-solving, adversarial search, knowledge represent, uncertain knowledge r., subsets of ai, artificial intelligence mcq, related tutorials.
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share

Learn Latest Tutorials
Transact-SQL
Reinforcement Learning
R Programming
React Native
Python Design Patterns
Python Pillow
Python Turtle
Preparation

Verbal Ability

Interview Questions

Company Questions

Trending Technologies
Cloud Computing
Data Science
Machine Learning
B.Tech / MCA
Data Structures
Operating System
Computer Network
Compiler Design
Computer Organization
Discrete Mathematics
Ethical Hacking
Computer Graphics
Software Engineering
Web Technology
Cyber Security
C Programming
Data Mining
Data Warehouse

- 10 Tips for Increasing Your Manuscript’s Potential to Captivate Readers
- Top 5 Benefits of French SEO for Global and Regional Reach
- Data Analysts: A Comprehensive Guide to Job Opportunities and Career Paths
- Timing Your Thread Posts: Unveiling the Best Time to Post on Threads
- The AI Advantage: Content Marketing Tools for the Modern Market
- Evolution of Responsive Web Design: A Historical Overview
- 5 Secret Strategies to Optimize Content for Higher Search Engine Ranking
- 7 Best Benefits of Using OCR Tools in 2024
- X (Twitter)

Top 20 MCQ Questions on Problem-Solving in AI

Read Also: Solved MCQ on Artificial Intelligence (AI) Set-1
1. State whether the following statements about defining the problem are True or False. i) A problem will define a state space that contains all the possible configurations of relevant objects. ii) A problem will specify a set of rules that describe the actions available. A. i-True, ii-False B. i-False, ii-True C. i-True, ii-True D. i- False, ii-False
2. … provides the frameworks into which more direct methods for solving sub-parts of a problem, can be embedded. A. Search B. Problem C. State D. State Space
3. A … is a representation of problem elements at a given moment. A. Search B. Problem C. State D. State Space
4. State whether the following statements about the state space are True. i) A state-space forms a graph in which the nodes are states and the arch between nodes are actions. ii) In state space, a path is a sequence of states connected by a sequence of actions. A. i-only B. ii-only C. Both i and ii D. None of the above
5. A production system consists of i) A set of rules. ii) One or more databases. iii) A Control Strategy A. i and ii only B. ii and iii only C. i and iii only D. All i, ii and iii
6. … specifies the order in which the rules will be compared to the database. A. A set of rules B. A control strategy C. One or more knowledge D. A rule applier
7. … is the computational system that implements the control strategy and applies the rules. A. A set of rules B. A control strategy C. One or more knowledge D. A rule applier
8. Which of the following are the benefits of the production system? i) Production systems provide an excellent tool for structuring AI programs. ii) The individual rules can be added, removed, or modified independently. iii) The production rules are expressed in a natural form. A. i and ii only B. ii and iii only C. i and iii only D. All i, ii and iii
9. In… the application of a rule never prevents the later application of another rule. A. monolithic production system B. commutative production system C. fully commutative production system D. bitonic production system
10. … is a production system that is both monotonic and partially commutative. A. monolithic production system B. commutative production system C. fully commutative production system D. bitonic production system
11. … help us to decide which rule to apply next during the process of searching for a solution to a problem. A. Control strategies B. Production system C. Problem D. State space
12. State whether the following statements about the uninformed search control strategy are True or False. i) It does not have additional information about states beyond problem definition. ii) In an uninformed search control strategy, the total search space is looked for a solution. iii) Best first search and problem decomposition are examples of uninformed search control strategies. A. i-True, ii-False, iii-True B. i-False, ii-True, iii-True C. i-True, ii-True, iii-False D. i- False, ii-False, iii-False
13. In… the search generates all nodes a particular level before proceeding to the next level to the tree. A. depth-first search techniques B. breadth-first search techniques C. iterative deepening search techniques D. heuristic search techniques
14. … does not guarantee to find a solution and backtracking is required if the wrong path is selected. A. depth-first search techniques B. breadth-first search techniques C. iterative deepening search techniques D. heuristic search techniques
15. State whether the following statements in the heuristic search techniques are True or False. i) It can be used to limit the search process. ii) Special-purpose heuristics exploit domain-specific knowledge. A. i-True, ii-False B. i-False, ii-True C. i-True, ii-True D. i- False, ii-False
16. … search algorithm is a very simple algorithm that guarantees to find a solution if done systematically and there exists a solution. A. Generate-and-Test B. Simple Hill Climbing C. Steepest-Ascent Hill Climbing D. Simulated Annealing
17. … is often used when a good heuristic function is available for evaluating states but when no useful knowledge is available. A. Generate-and-Test B. Simple Hill Climbing C. Steepest-Ascent Hill Climbing D. Simulated Annealing
18. … algorithm considers all the moves from the current state and selects the best one as the next state. A. Generate-and-Test B. Simple Hill Climbing C. Steepest-Ascent Hill Climbing D. Simulated Annealing
19. Simulated annealing differs from … in that a move is selected at random and then decides whether to accept it. A. Generate-and-Test B. Hill Climbing C. Best First Search D. Simulated Annealing
20. Which of the following are the drawbacks of hill climbing. i) Local maximum ii) Plateau iii) Ridge A. i and ii only B. ii and iii only C. i and iii only D. All i, ii and iii
- C. i-True, ii-True
- C. Both i and ii
- D. All i, ii, and iii
- B. A control strategy
- D. A rule applier
- A. monolithic production system
- B. commutative production system
- A. Control strategies
- C. i-True, ii-True, iii-False
- B. breadth-first search techniques
- A. depth-first search techniques
- A. Generate-and-Test
- B. Simple Hill Climbing
- C. Steepest-Ascent Hill Climbing
- B. Hill Climbing
- D. All i, ii and iii
Read Next: 20 MCQ Questions on Knowledge Representation in AI
Shuseel Baral is a web programmer and the founder of InfoTechSite has over 8 years of experience in software development, internet, SEO, blogging and marketing digital products and services is passionate about exceeding your expectations.

3 Marketing Lessons From the Online Gambling Industry

7 Best Small Business SEO Tips for Time-Strapped Entrepreneurs
Related posts.

10+ Best Tips to Revolutionize IT Operations with Artificial Intelligence

20 Simple MCQs on Microsoft Excel That You Don’t Want to Miss

20 top Multiple Choice Questions on SDLC Set-4

Machine Learning and AI: Identifying Differences and Similarities

Top 10 Advantages and Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence

Artificial Intelligence: Definition, History, Types, and Components
Comments are closed.
- 100’s Best Software Testing Tutorials
- CSS Tutorials
- JavaScript Tutorials
- Programming Tutorials
- Basic IT MCQs
- Data Structure MCQs
- Operating System MCQs
- Computer Networking MCQs
- Software Engineering MCQs
- JavaScript MCQs
- C & C++ MCQs
- Digital Marketing Guides
- Online Earning Guides
- Products & Services Reviews
- Word Counter
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser .
T4Tutorials.com
Problem solving mcqs artificial intelligence.
Problem Solving solved MCQs of Artificial Intelligence (Questions Answers).
1. Which of the following is the main job of a problem-solving agent?
(A). Solve the given problem and reach the goal
(B). To discover which sequence of the job will get it to the goal state
(C). All of these
(D). None of these
MCQ Answer is: c
2. Which of the following is state space?
(A). Expressing your problem with variable and parameter
(B). Your Definition of a problem
(C). Problem you design
(D). The whole problem
MCQ Answer is: d
3. The problem-solving agent with several immediate options of unknown value can determine that what to do by just investigating the various possible sequences of actions that lead to states of known value, and then selecting the best sequence among all. This kind of looking for such a sequence is commonly called Search.
(B). False (C). Partially True
MCQ Answer is: a
4. Which of the following is the input ……….and output………..of the search algorithm?
(A). Input, output
(B). Parameters, sequence of actions
(C). Solution, problem
(D). Problem, solution
MCQ Answer is: b
5. A problem in search space is defined by which one of the following states.
(A). Intermediate state
(B). Last state
(C). Initial state
(D). All of these
MCQ Answer is: C
6. The Set of actions for a problem in state space is formulated by which one of the following?
(A). Successor function, which takes current action and returns next immediate state
(B). Initial state
(C). Intermediate states
MCQ Answer is: A
7. A solution to a problem is a path from the initial state to its goal or aim state. The quality of the solution is calculated by the path cost function, and an optimal solution has the highest path cost as compared to all given solutions.
8. Which of the following is the process of eliminating the detail from a given state representation?
(A). Extraction
(B). data Mining
(C). Information Retrieval
(D). Abstraction
MCQ Answer is: D
9. A problem-solving approach works effectively for which of the following?
(A). Mars Hover (Robot Navigation)
(B). 8-queen problem
(C). Finding an optimal path from a given source to a destination
(D). 8-Puzzle problem
10. Which of the following is a touring problem in which each city must be visited exactly once. The purpose is to search for the shortest tour among all the tours.
(A). Searching the shortest path between a source and a destination
(B). Depth-first search traversal on a given map represented as a graph
(C). Map coloring problem
(D). Travelling Salesman problem
11. What kind of agent is a Web Crawler?
(A). Model-based agent
(B). Problem-solving agent
(C). Simple reflex agent
(D). Intelligent goal-based agent
12. Which of the following is the main component for measuring the performance of problem-solving techniques?
(A). Completeness
(B). Optimality
(C). Time and Space complexity
13. The production rule consists of which of the following?
(A). A set of Rule
(B). A sequence of steps
(C). both a and b
(D). Arbitrary representation to problem
14. Which of the following searching technique takes less memory?
(A). Optimal search
(B). Breadth-First Search
(C). Linear Search
(D). Depth-First Search
15. Which of the following is the ideal method to go for Game playing problems?
(A). Linear approach
(B). An Optimal approach
(C). Random approach
(D). Heuristic approach (Some knowledge is store(D).
More MCQs on the sidebar of Website Agent Architecture MCQs, Alpha Beta Pruning MCQs, Backward Chaining, Forward Chaining MCQs, Bayesian Networks MCQs, Communication, Hidden Markov Model, Image Perception MCQs, Uninformed Search Strategy, Inductive logic programming, Informed Search Strategy, Learning, Object Recognition, Online Search Agent, Uncertain Knowledge and Reasoning MCQs on Artificial Intelligence.
MCQs collection of solved and repeated MCQs with answers for the preparation of competitive exams, admission test and job of PPSC, FPSC, UPSC, AP, APPSC, APSC, BPSC, PSC, GOA, GPSC, HPSC, HP, JKPSC, JPSC, KPSC, KERALAPSC, MPPSC, MPSC, MPSCMANIPUR, MPSC, NPSC, OPSC, RPSC, SPSCSKM, TNPSC, TSPSC, TPSC, UPPSC, UKPSC, SPSC, KPPSC, BPSC, AJKPSC ALPSC, NPSC, LPSC, SCPSC, DPSC, DCPSC, PSC, UPSC, WVPSC, PSCW, and WPSC.
Related Posts:
- Which of the following is the first step in the scientific method of problem solving?
- Critical Section Problem in OS
- Dekker’s Algorithm for Critical Section Problem
- Problem Statement in Research
- Speech about Family Problem [1,2,3 Minutes]
- Letter for water supply problem

- Data Structure
- Coding Problems
- C Interview Programs
- C++ Aptitude
- Java Aptitude
- C# Aptitude
- PHP Aptitude
- Linux Aptitude
- DBMS Aptitude
- Networking Aptitude
- AI Aptitude
- MIS Executive
- Web Technologie MCQs
- CS Subjects MCQs
- Databases MCQs
- Programming MCQs
- Testing Software MCQs
- Digital Mktg Subjects MCQs
- Cloud Computing S/W MCQs
- Engineering Subjects MCQs
- Commerce MCQs
- More MCQs...
- Machine Learning/AI
- Operating System
- Computer Network
- Software Engineering
- Discrete Mathematics
- Digital Electronics
- Data Mining
- Embedded Systems
- Cryptography
- CS Fundamental
- More Tutorials...
- Tech Articles
- Code Examples
- Programmer's Calculator
- XML Sitemap Generator
- Tools & Generators

Home » MCQs
- Artificial Intelligence MCQs
Artificial Intelligence MCQs : This section contains multiple-choice questions on Artificial Intelligence . All MCQs have the correct answers and explanations. These MCQs will help students and professionals to test their skills and to enhance their knowledge of Artificial Intelligence .
List of Artificial Intelligence MCQs
1. Which of the following are comprised within AI?
- Machine Learning
- Deep Learning
- Both (A) and (B)
- None of the above
Answer: C) Both (A) and (B)
Explanation:
Both Machine Learning and Deep Learning are the sub-categories of Artificial Intelligence . They are studied differently due to their depth of subject and vast areas of application.
Discuss this Question
2. State whether the following condition is true or false? "Artificial Intelligence means to mimic a human. Hence, if a robot can move from one place to another like a human, then it comes under Artificial Intelligence."
Answer: B) False
AI deals with human behavior rather than human actions. It deals with the way the human mind thinks and causes the body to act in a way in any particular situation. Hence, if a robot just moves like humans through external commands, we cannot say that AI has been implemented for moving that robot.
3. Which of the mentioned human behavior does the AI aim to mimic?
Answer: A) Thinking
The main and foremost aim of Artificial Intelligence is to make the machine think and act like humans.
4. Which of the following is not a goal of AI?
- Thinking humanly
- Adapting to the environment and situations
- To rule over humans
- Real Life Problem Solving
Answer: C) To rule over humans
The goal of AI might be to mimic human behavior and its way of thinking, but its goal is never to make the AI robots rule on humans. If this would happen, it would lead to a serious man-made disaster.
5. "In AI, we study the whole universe by dividing it into two components." What are these two components?
- Sky and Land
- Agent and environment
Answer: B) Agent and environment
In AI, we study the whole universe by dividing it into two components: Agent and Environment. The agent is the system under study and all its surroundings are termed as the environment.
6. Which of the following are the main tasks of an AI agent?
- Movement and Humanly Actions
- Perceiving and acting on the environment
- Input and Output
Answer: B) Perceiving and acting on the environment
The main task of an AI-based agent is to perceive the relevant information and data from its environment and act upon it accordingly.
7. State whether the following condition is true or false? "An Artificial Intelligence-based agent does not require capable of doing tasks on its own without any human intervention for inputs or other commands."
Answer: A) True
An AI-based agent is able to perform the entire tasks on its own. Provided, the agent is following strong AI and not weak AI.
8. Which of the mentioned parts of an agent would you consider to be the most valuable in terms of AI?
- Sensors and Actuators
- Wheels and steering
- Arms and legs
- All of the above
Answer: A) Sensors and Actuators
The sensors and actuators are the most important parts of an AI-based agent. This is because, even if an agent is not doing some manual tasks, still it needs sensors and actuators for perceiving and acting upon the environment.
9. Which of the following is not a goal of an AI agent?
- Perceiving data from the environment
- Acting upon the Environment
- Reversing the previously performed actions
Answer: D) Reversing the previously performed actions
The goal of the AI agent cannot be reversing the previously performed actions because this thing is not possible. If something has been taken place, and it is an irreversible process, then no agent can reverse it to its previous state.
10. "An AI agent is defined though it's PEAS." What does the term PEAS stand for?
- Personal Enhancement Area in Science
- Performance, Environment, Actuators and Sensors
- Performance, Entity, Area, State
Answer: B) Performance, Environment, Actuators and Sensors
Any AI agent is defined through its four factors: Performance, Environment, Actuators and Sensors.
11. Which of the following is a valid AI agent type?
- Simple based Reflex agent
- Model Based Reflex Agent
- Goal Based Agent
Answer: D) All of the above
All the mentioned agents are valid types of AI agents. The simple based reflex agent works only on the current problem and does not consider anything else. The model-based reflex agent works similarly but can also work in a partially observable environment. And the goal-based agent works to meet the goal as soon as possible.
12. State whether the following condition is true or false? "A simple reflex based agent does not care about meeting the utility of the user."
The simple based reflex agent is designed only to respond to the currently occurring problem. I do not bother about the effect its actions will cause on the environments or the utility of the user.
13. Which of the mentioned properties of the Utility-based AI agent differentiates it from the rest of the AI agents?
- Responding and providing solution to the problem
- Meeting the preference of the user
- Meeting the goal
Answer: B) Meeting the preference of the user
The utility-based agent focuses more on the utilities and preferences of the user to satisfy the user's needs. This property of this agent differentiates it from the other types of AI agents.
14. Which of the following does not represent a Goal based agent?
- Reaching the goal in minimal amount of time
- Reaching the goal in minimal cost
- Reaching the initial state again after reaching the goal state
Answer: C) Reaching the initial state again after reaching the goal state
The goal-based agent focuses only on reaching the goal state. Going back to the initial state is not the necessary action for it to take unless necessary.
15. Which of the following is considered as the most powerful AI agent?
- Simple based reflex agent
- Model based reflex agent
- Goal based agent
- Utility based agent
Answer: D) Utility based agent
The utility-based agent is termed as the most powerful agent because it meets all the user needs as well as takes care whether the user is satisfied or not.
16. Which of the following classifications of the environment are valid?
- Deterministic and Non-Deterministic
- Observable and partially-observable
- Static and dynamic
All the mentioned classifications of the environment are valid. The environment for an AI-based system can be classified using any of the mentioned ways. There are two more ways of classification of environments that are not listed. They are: Accessible and Inaccessible; and continuous and Discrete.
17. State whether the following condition is true or false? "The classification of the environment is independent of the type of AI model being used."
The classification of the environment is done only so that it becomes easier for the AI agent to perceive it. In the real, no such classification exists because the environment is vast and more likely unpredictable. Therefore, this classification highly depends upon the type of Agent.
18. Which of the mentioned Environment Classifications determine whether the environment variables are constant or keep changing?
- Deterministic and non- Deterministic
Answer: C) Static and dynamic
The classification of the environment which classifies the environment into two categories: Static and dynamic determines whether the environment variables are static or dynamic. If you want to deal with a continuous or static environment variable, then this type of classification must be chosen.
19. Which of the following does not represent a valid environment type according to AI classification of environments?
- Left sided and right sided
Answer: D) Left sided and right sided
There is no classification of the environment such as left-sided or right-sided. Thus this classification is invalid.
20. Which of the following is considered as the most specific environment classifications in AI?
- Discrete or Continuous
Answer: D) None of the above
None of the classifications can be termed as the most specific. Every classification is important and it solely depends on the type of situation and agent that which classification should be considered.
21. Which of the following definitions correctly defines the State-space in an AI system?
- A state space can be defined as the collection of all the problem states
- A state space is a state which exists in environment which is in outer space
- A state space is the total space available for the agent in the state
Answer: A) A state space can be defined as the collection of all the problem states
All the possible states for an AI system together form the state space. The state-space means the collection of all those states in which the agent can be.
22. State whether the following condition is true or false? "An AI agent cannot be in any other state except for those included in the state space for that particular system."
An AI system can be only in a state that is defined in its state space. This is because the state space is the collection of all the possible states that the system can be in. Hence, there exists no other state except for these in which the system can reside.
23. Which of the mentioned definitions correctly define 'move' for an AI agent?
- When the agent moves from one place to another, then it is called the move of the agent
- When the agent goes from one state to another, it is known as a move
Answer: B) When the agent goes from one state to another, it is known as a move
The "move" of an agent is defined with respect to the state it changes and not with respect to its actual position.
24. "The complete set of rules for defining the valid movements of an AI agent for changing the states" What does the above definition refer to?
- Documentation for an AI agent
- Production rules for an AI agent
- Pseudo Code for an AI agent
Answer: B) Production rules for an AI agent
The production rules for an AI agent are the complete set of rules for defining the valid movements of an AI agent for changing the states.
25. State whether the following condition is true or false? "Fault tolerance of a system can be defined as the ability of a system to sustain failures and continue functioning."
The given statement is true and is the definition of Fault tolerance of the system.
26. Which of the following agents is the best in terms of AI?
- An agent which needs user inputs for solving any problem
- An agent which can solve any problem on its own without any humanintervention
- An agent which needs an exemplary similar problem defined in its knowledge base prior to the actual problem
Answer: B) An agent which can solve any problem on its own without any humanintervention
The main aim of AI is to develop a system that can solve problems on its own without any human commands or inputs. If such a system is developed, then it will be the best kind of AI system.
27. Consider the following steps:
- Gathering knowledge
- Defining problem
- Applying solution
- Forming the state space
What is the correct order for solving an AI problem?
- i. v. ii. iv. iii.
- i. ii. iii. iv. v.
- ii. i. v. iv. iii.
Answer: C) ii. i. v. iv. iii.
The correct order for solving a problem is:
- ii.Defining problem
- i.Gathering knowledge
- v.Forming the state space
- iv.Planning
- iii.Applying solution
28. Which of the mentioned options are a part of 'planning' while solving a problem by an AI agent?
- Deciding which data Structure to choose
- Forming the control strategy
- Inferring for similar problems in the knowledge base
All the mentioned options are a part of 'planning' while solving a problem by an AI agent. Planning includes tasks like deciding the data structure, Forming control strategy, and looking for solutions in the knowledge base, deciding the necessary moves to perform, etc.
29. Consider the following statement, "After all the gathering of knowledge and planning the strategies, the knowledge should be applied and the plans should be executed systematically to reach the goal state most efficiently and fruitfully." What does the above definition refer to?
- Knowledge gathering strategy
- Final step of solving the AI problem, which is applying the strategies
- State space deciding
Answer: B) Final step of solving the AI problem, which is applying the strategies
The given definition is of the final step of solving a problem in AI problem solving, which is applying the strategies.
30. Consider the following statement, "Gathering knowledge is to collect and isolate only that knowledge which is present in the Knowledge base of the agent" State whether the above condition is true or false?
Gathering knowledge means collecting knowledge both from perceiving the environment, form knowledge base and in every way possible.
31. The main Aim of the AI system is to provide a solution for real-life problems by acting and thinking humanly. Whenever an agent is confronted by a problem, what is the first step that it follows towards searching a solution to the problem?
- Searching for relevant data in the surroundings
- Searching into its own knowledge base for solutions
- Seeking for human inputs for approaching towards the solution
Answer: B) Searching into its own knowledge base for solutions
Whenever an AI-based agent is confronted by a problem, it first looks into its database for a solution or similar type of problem. Then it looks at other places like perceiving the environment, applying logic, etc.
32. Which of the following mentioned searches are heuristic searches?
- Random Search
- Depth First Search
- Breadth First Search
- Best First Search
- All i., ii., iii. and iv.
- ii. and iv.
Answer: A) Only iv.
In the best first search, which is also known as the heuristic search, the agent picks up the best node based upon the heuristic value irrespective of where the node is.
33. Which of the mentioned properties of heuristic search differentiates it from other searches?
- It provides solution in a reasonable time frame
- It provides the reasonably accurate direction to a goal
- It considers both actual costs that it took to reach the current state and approximate cost it would take to reach the goal from the current state
All the mentioned options are the properties that differentiate a heuristic search from other searches.
34. Consider the following statement: "The search first begins from the root node and the first one of the child node's sub-tree is completely traversed. That is, first all the one-sided nodes are checked, and then the other sided nodes are checked." Which search algorithm is described in the above definition?
- The Breadth First Search (BFS)
- The Depth First Search (DFS)
- The A* search
Answer: B) The Depth First Search (DFS)
In DFS, the search first begins from the root node and the first one of the child node's sub-tree is completely traversed. That is, first all the one-sided nodes are checked, and then the other sided nodes are checked.
35. Consider the following statement: "In AI search algorithms, we look for a solution which provides us the most optimized way in terms of both time and cost to reach from the current state to the Goal State." State whether the above condition is true or false?
If we want to optimize our algorithm, we must take care of both the time limit as well as the cost that occurred in our searching. The lesser they are, the more efficient our algorithm is.
36. What do the Constraints refer to in a CSP ( Constraint Satisfactory problem )?
- Restrictions
- Regulations
The constraint is the collection of all the restrictions and regulations that are imposed on the agent while solving the problem. The Agent cannot violate or avoid these restrictions while performing any action.
37. Which of the following mentioned problems are CSP (Constraint Satisfactory Problems)?
- N queens Problem
- Crypt- arithmetic problem
- Map coloring problem
Answer: B) All i., ii., iii. and iv.
All the mentioned problems are examples of CSP (Constraint Satisfactory problem) in AI.
38. Which of the mentioned properties of Constraint Satisfactory Problems dare valid?
- Constraints are a set of restrictions and regulations
- While solving a CSP, the agent cannot violate any of the rules and regulations or disobey the restrictions mentioned as the constraints
- It also focuses on reaching to the goal state
All the properties are valid as they are the properties of a CSP (Constraint Satisfactory Problem).
39. Consider the following statement: "While solving a CSP (Constraint Satisfactory Problem), the agent cannot violate any of the rules and regulations or disobey the restrictions mentioned as the constraints." Which of the following problems do not fall under the category of CSP?
- N- Queens Problem
In all the mentioned problems (or games) there are a set of constraints defined and the agent is bounded to follow the rules. Therefore, none of the mentioned problems fall apart from CSV.ache
40. Consider the following statement: "In AI, CSP are mathematical questions defined as a set of the object whose state must satisfy a number constraint or limitation." State whether the above condition is true or false?
The given definition is the actual definition of the Constraint Satisfactory Problem (CSP) and hence is true.
41. Which of the following types does the Cryptarithmetic problem belong to?
- Encryption Problem
- Constraint Satisfactory Problem
- Number problem
The Cryptarithmetic problem belongs to every type of mentioned problem: Encryption problem, Constraint satisfactory problem, as well as Number Problem.
42. Which of the following mentioned properties are valid for a Cryptarithmetic problem?
- A number 0-9 is assigned to a particular alphabet.
- Each different alphabet has a unique number.
- All the same alphabets have the same numbers.
- The numbers should satisfy all the operations that any normal number does.
All the mentioned properties are valid properties for a Cryptarithmetic problem.
43. Which of the mentioned points are not valid with respect to a Cryptarithmetic problem?
- Constraints should be taken care of while solving the problem
- The text is converted from readable format to non-readable format
- If numbers are not sufficient, we can use special symbols like $#@% to encrypt the text
Answer: C) If numbers are not sufficient, we can use special symbols like $#@% to encrypt the text
There is no rule in the Cryptarithmetic problems regarding using the special numbers for encryption. We must encrypt the text using the numbers 0-9. Hence, this encryption method is limited to small length texts only.
44. Consider the following statement: "The Cryptarithmetic problem in Artificial Intelligence is a type of encryption problem in which the written message in an alphabetical form which is easily readable and understandable is converted into a numeric form which is neither easily readable nor understandable." By reading the above statement, what are the places where this technique can be applied?
- To share passwords
- To encode number plates of vehicles
- To encode their names by students while filling the answer sheet
Answer: A) To share passwords
The Cryptarithmetic problem is an efficient way to share passwords. However, the other things mentioned do not require any encryption, so applying this technique there would be a waste of time.
45. Provide the answer for the following Cryptarithmetic problem: "SEND MORE MONEY"
- S=12; E=5; N=6; D=8; M=1; O=0; R=8; Y=2
- S=9; E=5; N=6; D=7; M=1; O=0; R=8; Y=2
- S=5; E=5; N=6; D=7; M=1; O=0; R=8; Y=2
- S=9; E=5; N=9; D=7; M=1; O=0; R=8; Y=2
Answer: B) S=9; E=5; N=6; D=7; M=1; O=0; R=8; Y=2
Cryptarithmetic problems should be solved, but here we can find the answer to this question through the options itself.
- The first option has S=12 which exceeds 0-9 range.
- The third option has the same value for S and E
- The fourth option also has the same values for S and N
- Therefore, the correct option is b.
46. Which of the following statements correctly define knowledge representation in AI?
- It is the way in which facts and information are stored in the storage system of the agent
- It is the way in which we feed the knowledge in machine understandable form
- We modify the knowledge and convert it into the format which is acceptable by the machine
All the mentioned points define the knowledge representation in AI correctly.
47. In AI systems, Knowledge can be represented in two ways. What are these two ways?
- Machine Logic
- Predicate Logic
- Propositional Logic
- Compound Logic
- i. and iii.
- ii. and iii.
- iii. and iv.
Answer: C) ii. and iii.
In an intelligent agent, the knowledge can be represented in two ways:
- Propositional logic and
- Predicate logic
48. Which of the mentioned point are not valid with respect to a Propositional Logic?
- In propositional Logic, each sentence is a declarative sentence
- In propositional logic, the sentence can have answers other than True or False
- Propositional Logic is a type of knowledge representation in AI
Answer: C) Propositional Logic is a type of knowledge representation in AI
In propositional logic, each sentence is a declarative sentence which is a sentence or proposition which is either true or false.
49. Consider the following statement: "In the propositional logic system of knowledge representation, it is assumed that the word contains object, relations, and functions. The Predicate logic is a symbolized reasoning in which we can divide the sentence into a well-defined subject and predicate." By reading the above statement, State whether it is true or false?
The given statement is false because it is not what a propositional Logic is. The given statement holds for Predicate logic.
50. What does a first order predicate logic contain?
- Predicate and a subject
- Predicate and a Preposition
- Subject and an object
Answer: A) Predicate and a subject
The Predicate logic is a symbolized reasoning in which we can divide the sentence into a well-defined subject and predicate. The subject is defined by the predicate. It should be noted that the predicate can only refer to a single subject.
51. Why do we want to implement the concept of Logic in an AI system?
- So that the agent can have decision making capability
- So that the agent can think and act humanly
- So that the agent can apply the logic for finding the solution to any particular problem
All the mentioned points are the valid reason behind- "Why we want to implement logic in an AI system?"
52. In AI systems, Logic can be represented in two types. What are these two types?
- Inductive Logic
- Common Logic
- Deductive Logic
Answer: B) i. and iii.
In artificial intelligence, we deal with two types of logics: Deductive and Inductive.
53. Which of the following statements correctly defines the deductive logic in AI?
- In deductive logic, the complete evidence is provided about the truth of the conclusion made
- A top-down approach is followed
- The agent uses specific and accurate premises that lead to a specific conclusion
All the mentioned statements correctly defined the deductive logic in AI .
54. Consider the following statement: "While taking any decision, the agent must provide specific reasons based on which the decision was taken. And this reasoning can be done by the agent only if the agent has the capability of understanding the logic." Among which of the following situations will the agent use and apply logic for solving the problem?
- To solve real life problems
- To play a game against a human in the same way as a human would do
- To understand the environment variables
In all the mentioned situations, the agent will have to apply logic to solve the problem humanly.
55. In AI, the Logic is classified into two types: deductive and inductive. Which of the following approaches is followed up by the Inductive logic?
- Top-down approach
- Bottom-up approach
- No specific approach
- According to precedence
Answer: B) Bottom-up approach
In Inductive logic, the reasoning is done through a 'bottom-up' approach. What this means is that the agent here takes specific information and them generalizes it for the sake of complete understanding.
56. How many types of quantifiers are there that are used to represent knowledge?
- User can define as many quantifiers he wants
Answer: B) 2 types
There are two types of quantifiers: Universal Quantifier and Existential Quantifier.
57. There are two types of quantifiers used to quantify the statement in the knowledge representation in AI. What are these two types of quantifiers?
- Universal Quantifiers
- Subjective Quantifiers
- Existential Quantifiers
- Selective Quantifier
There are two types of quantifiers that are used to quantify the statement in an AI system: Universal Quantifier and Existential Quantifier.
58. Which of the mentioned point correctly defines a quantifier in AI?
- Quantifiers are numbers ranging from 0-9.
- Quantifiers are the quantity defining terms which are used with the predicates.
- Quantifiers quantize the term between 0 and 1.
Answer: B) Quantifiers are the quantity defining terms which are used with the predicates.
Quantifiers are the quantity defining terms that are used with the predicates. There are two types of quantifiers that are used to quantify the statement in an AI system: Universal Quantifier and Existential Quantifier.
59. Consider the following statement: "The universal quantifier is used to define the whole subject population under the predicate." By reading the above statement, what are the phrases for which the universal quantifier can be applied?
The universal quantifier is used to define the whole subject population under the predicate. It can be used anywhere where the phrases like: 'for all', 'for each', 'for every' are used.
60. Consider the following statement: "The Existential Quantifier is used at the places where only some part of the subject's population is to be defined under the predicate." By reading the above statement, what are the phrases for which the existential quantifier can be applied?
Answer: B) For some
The Existential Quantifier is used at the places where only some part of the subject's population is to be defined under the predicate. It can be used at all the places where the following phrases are used: 'There exist', 'For some', 'For at least', etc.
61. Using how many levels can a knowledge-based agent be defined?
Answer: B) Java
The knowledge-based agent can be described using three levels. These are,
- Knowledge level
- Logical level
- Implementation level
62. There are various knowledge-based agent levels in AI. What are these levels?
- Knowledge Level
- Logical Level
- Common Sense Level
- Implementation Level
- i., ii. and iii.
Answer: B) i., ii. and iii
The knowledge-based agent can be described using three levels. These are:
63. Which of the levels in a knowledge-based agent is the most abstract level?
- Can't be determined
Answer: A) Knowledge Level
The Knowledge Level is the basic and the most abstract in a knowledge-based agent. This level describes the agent by what it knows, i.e. through its knowledge base. In this level, the information that the agent has, its goals and the utility are defined.
64. Consider the following statement: "The knowledge-based agent can be described using three levels. These are: Knowledge level, Logical level, and Implementation level" In which of these levels, is the raw and discrete information encoded into sentences?
Answer: B) Logical Level
In the logical level, the raw and discrete information which is present in the knowledge level is encoded into sentences. In simple words, the agent at this level derives the logic out of the knowledge base according to the problem.
65. Consider the following statement: "The knowledge-based agent can be described using three levels. These are: Knowledge level, Logical level, and Implementation level" Which of the following layers deals with the physical representation of the sentences?
Answer: C) Implementation Level
The Implementation level is the final layer of the knowledge-based agent. In the implementation level, the logic which the agent has derived in the logical level is brought to implementation. This layer deals with the physical representation of the sentences.
66. Which of the following is true with respect to uncertainty in AI systems?
- Uncertainty arises when we are not 100 percent confident in our decisions
- Whenever uncertainty arises, there is needs to be an estimation taken fo getting to any conclusion
- The AI agent should take certain decisions even in the situations of uncertainty
All the mentioned points are true and valid with respect to uncertainty in AI systems. Also, each point is very important while dealing with uncertainty in AI agents.
67. Which of the following mentioned statements are uncertain?
- The number occurred on rolling a die.
- What will the temperature tomorrow?
- What card will be get on picking a card from a fair deck of 52 cards?
- What output will we get on tossing a coin?
We cannot be 100% sure about the output we get on tossing a die, coin or picking a card, or the upcoming day's temperature as it depends on various factors which are almost impossible to monitor accurately. Hence we have uncertainty there.
68. Which of the mentioned points are valid reasons for uncertainty in the nature?
- Partially observable environment
- Dynamic nature of the environment
- Inaccessible area in the environment
All the mentioned reasons are valid as they are responsible for causing uncertainty in the environment.
69. Consider the following statement: "When we talk about perceiving information from the environment, then the main problem that arises is that there is always some uncertainty is our observations. This is because the world is an enormous entity and the surroundings that we take under study are not always well defined. So, there is needs to be an estimation taken for getting to any conclusion." Which among the following takes the best decisions in a situation with uncertainty?
- AI based agents
Answer: B) Humans
Human being face this uncertainty daily that too many times. But still, they manage to make successful decisions. This is because humans have strong estimating and decision making power and their brains function in such a way that every time such a situation arises, the alternative with the maximum positive output is chosen.
70. State whether the following condition is true or false? "The cases of uncertainty mostly happen in those cases where the conditions are neither completely true nor completely false."
Uncertainty arises when we are not 100 percent sure about the outcome of the decisions. This mostly happens in those cases where the conditions are neither completely true nor completely false.
71. Which of the following correctly defines the use of probabilistic reasoning in AI systems?
- In situations of uncertainty, probabilistic theory can help us give an estimate of how much an event is likely to occur or happen.
- It helps to find the probability whether the agent should do the task or not.
- It does not help at all.
- None of the above.
Answer: A) In situations of uncertainty, probabilistic theory can help us give an estimate of how much an event is likely to occur or happen.
The only option (A) is the valid reason which correctly defines the use of probabilistic reasoning in AI systems.
72. On which of the mentioned points does the Probabilistic Reasoning depend?
- Observations
All the mentioned reasons are valid as the Probabilistic reasoning depends upon all of them.
73. The results that we get after we apply probabilistic reasoning to a problem are,
- 100% accurate
- Estimated values
- Wrong values
Answer: B) Estimated values
Probabilistic theory helps us to derive an estimate about how much an event is likely to occur or happen.
74. State whether the following condition is true or false? "The sum of all these probabilities for an experiment is always 1 because all these events/alternatives can happen only within this experiment."
It is the basic and most important law of probability that the sum of probabilities for an experiment is always 1.
75. Which of the following points are valid with respect to conditional probability?
- Conditional Probability gives 100% accurate results.
- Conditional Probability can be applied to a single event.
- Conditional Probability has no effect or relevance or independent events.
Answer: C) Conditional Probability has no effect or relevance or independent events.
Independent events are those events that neither cause any effect nor are affected by the occurrence of some other event. Hence, the Conditional Probability has no effect or relevance on the independent events.
76. Among which of the following mentioned statements will the conditional probability be applied?
- The number occurred on rolling a die one time.
- What card will get on picking a card from a fair deck of 52 cards?
- What output will we get on tossing a coin once?
Answer: D) Only ii.
The upcoming day's temperature as it depends on various factors such as wind speed, current temperature, and humidity level, etc. So, the future weather conditions are dependent upon these factors and thus it is a dependent event and hence conditional property can be applied to it.
77. On which of the mentioned points does the Conditional Probability reasonable to apply?
- Dependent Events
- Independent Events
- Neither a. nor b.
- Both a. and b.
Answer: A) Dependent Events
78. The results that we get after we apply conditional probability to a problem are,
Like all other probabilistic theory methods, conditional probability also helps us to derive an estimate about how much an event is likely to occur or happen.
79. State whether the following condition is true or false? "The independent events are affected by the happening of some other events which may occur simultaneously or have occurred before it."
The given statement is false because dependent events are affected by the happening of some other events which may occur simultaneously or have occurred before it, not the independent events.
80. Bayesian Theorem was named after its inventor. Who invented the Bayesian theorem?
- Reverend Thomas Bayes
- Stuart Bayes Hamilton
- Bayes Canney
Answer: A) Reverend Thomas Bayes
Bayes' theorem was given by Reverend Thomas Bayes and thus named after him.
81. Among which of the following mentioned statements can the Bayesian probability be applied?
- In the cases, where we have one event
- In the cases, where we have two events
- In the cases, where we have three events
- In the cases, where we have more than three events
Bayes' Theorem is applicable only in those experiments where we have only two events. It does not apply to the cases where the number of events is more than two.
82. On which of the mentioned points is the Bayesian theorem reasonable to apply?
The Bayesian theorem is used to find the conditional probability. As the Conditional Probability has no effect or relevance on the independent events and is relevant only for dependent events, the Bayesian theorem also applies for the same.
83. The results that we get after we apply Bayesian Theorem to a problem are,
Like all other probabilistic theory methods like conditional probability, the Bayesian theorem also helps us to derive an estimate about how much an event is likely to occur or happen.
84. State whether the following condition is true or false? "In Bayesian theorem, it is important to find the probability of both the events occurring simultaneously."
It should be noted that in the Bayesian equation, we need not find the probability of both the events occurring simultaneously, i.e. P(A^B). We can calculate the same using the below Bayesian equation,
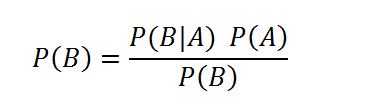
85. Which of the following statements correctly define the concept of Inference in AI?
- When we conclude the facts and figures to reach a particular decision, that is called inference
- All of the above.
Answer: B) When we conclude the facts and figures to reach a particular decision, that is called inference
Inference means finding a conclusion based on facts, information, and evidences. In simple words, when we conclude the facts and figures to reach a particular decision, that is called inference.
86. Which of the following are valid inference rules that are used in Inference?
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
Answer: A) Only i.
The addition is a valid inference rule. Apart from these, there are further many inference rules such as simplification, modus ponens, modus tollens, etc.
87. Which of the mentioned rules are valid Inference rules?
- Modus Ponens
- Backward Chaining
All the mentioned rules are valid inference rules. Apart from these, there are further many inference rules such as simplification, Addition, forward chaining, modus tollens, etc.
88. Consider the following statement: "In the reasoning by resolution, we are given the goal condition and available facts and statements. Using these facts and statements, we have to decide whether the goal condition is true or not." By reading the above statement, state whether it is true or false?
The above statement is True.
89. Which of the following are a deductive type of Inference rule?
- Forward Chaining
- Both A. and B.
Answer: C) Both A. and B.
Both forward chaining and backward chaining are types of deductive inference rules.
90. Which of the following statements define the certainty factor accurately?
- The certainty factor is same as the probability of any event
- The Certainty Factor (CF) is a numeric value that tells us about how likely an event or a statement is supposed to be true
- The Certainty Factor (CF) is a numeric value that tells us about how certain we are about performing a particular task
Answer: B) The Certainty Factor (CF) is a numeric value that tells us about how likely an event or a statement is supposed to be true
The statement (B) define the certainty factor accurately.
91. "The Certainty Factor (CF) is a numeric value which tells us about how likely an event or a statement is supposed to be true." What is the range of this numeric value, i.e. Certainty Factor?
- Between 0 to 1 (Both inclusive)
- Between 0 to 1 (Both exclusive)
- Between -1 to +1
Answer: C) Between -1 to +1
The value of the Certainty factor lies between -1.0 to +1.0, where the negative 1.0 value suggests that the statement can never be true in any situation, and the positive 1.0 value defines that the statement can never be false.
92. Consider the following statement: "The value of the Certainty factor lies between -1.0 to +1.0, where the negative 1.0 value suggests that the statement can never be true in any situation, and the positive 1.0 value defines that the statement can never be false." What does the value 0 denote for CF?
- Half true Half False
- Somewhat true but not entirely false
- Agent has no information about the event
Answer: C) Agent has no information about the event
The value 0 suggests that the agent has no information about the event or the situation.
93. What is the minimum Certainty factor which decided whether the value is true or false?
- Is decided in prior to every problem
Answer: D) Is decided in prior to every problem
A minimum Certainty factor is decided for every case through which the agent decides whether the statement is true or false.
94. State whether the following condition is true or false: "The value of the Certainty factor lies between -1.0 to +1.0, where the negative 1.0 value suggests that the statement can never be true in any situation, and the positive 1.0 value defines that the statement can never be false."
The given condition is True.
95. Which of the mentioned statements are true with respect to Fuzzy logic in AI?
- Fuzzy Logic (FL) is a method by which any expert system or any agent based on Artificial Intelligence performs reasoning under uncertain conditions.
- In this method, the reasoning is done in almost the same way as it is done in humans.
- In this method, all the possibilities between 0 and 1 are drawn.
All the mentioned statements are true and valid with respect to Fuzzy Logic in AI systems.
96. Which of the following hold in the Fuzzy Logic System? Choose from the following options?
- Well defined inference making model
- Complex Decision making can be easily performed
- It is easily understandable
- All i, ii. and iii.
Answer: D) All i, ii. and iii.
All the mentioned points are valid and hold true for a fuzzy Logic AI system.
97. Which of the following are a part of Fuzzy Logic System? Choose from the following options?
- Knowledge base
- Fuzzification Module
- Inference Engine
- Defuzzification Module
- All i, ii. and iii. and iv.
Answer: D) All i, ii. and iii. and iv.
If we take a look at the architecture of the Fuzzy Logic system, then we find that it is composed of following four major parts:
- Knowledge Base
98. Consider the following statement: "Through the Fuzzy Logic, The Agent can handle situations like incomplete data, imprecise knowledge, etc." By reading the above statement, State whether it is true or false?
In the Fuzzy Set Theory, the inference-making process and other concluding methods are well defined using algorithms that the agent or any computer system can easily understand. Thus the Agent in this method can handle situations like incomplete data, imprecise knowledge, etc.
99. Fuzzy Logic is a convenient way of representing which of the following situations?
- Partially True and Partially False
- Completely True and Completely False
Answer: A) Partially True and Partially False
Fuzzy Logic is an effective and convenient way for representing the situation where the results are partially true or partially false instead of being completely true or completely false.
100. Which of the following mentioned statements are the valid reasons for implementing the learning part in the systems in AI?
- To implement humanly behavior.
- To deal with unknown environment.
- To improve the reasoning capability of the agent.
All the mentioned statements are true and valid reasons for implementing the learning part in the AI systems.
101. Which of the following streams of AI deal with the learning part of the machine (AI systems)? Choose from the following options?
- Cloud computing
- Humanly Learning
The stream of AI that deals with the learning part of the machine (AI systems) is Machine Learning.
102. How many types of learning are there for an AI system?
Answer: B) 3 types
The Learning process in the AI agent is broadly classified into three types. They are:
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
- Reinforcement Learning (or semi supervised learning)
103. Consider the following statement: "Semi-supervised learning is a type of learning which falls between supervised and unsupervised learning." By reading the above statement, Choose from the following?
- Yes, the given statement is true
- No, the given statement is false as there is nothing such as semi-supervised learning
Answer: A) Yes, the given statement is true
The given statement: "Semi-supervised learning is a type of learning which falls between supervised and unsupervised learning" is true.
104. How does the agent learn through its surroundings?
- By perceiving the environment through sensors
- By human's sensory organs
Answer: A) By perceiving the environment through sensors
The agent implements the learning part from its surroundings through its sensors, like the camera, audio input devices, temperature sensors etc.
105. What is the major problem for AI systems while solving the real world problems?
- Uncertainty in Environment
- Poor battery life of the system
- Improper training time
Answer: A) Uncertainty in Environment
Uncertainty in environment is the biggest problem for AI systems while solving the real-world problems.
106. Which of the following are valid methods used for decision making by an AI agent in situations of uncertainty? Choose from the following options?
- Probabilistic theory
- Fuzzy logic
- Truth Maintenance
The following three are among the basic and widely used methods to perform decision making while handling the uncertainty:
- Probabilistic Theory
- Fuzzy Logic
107. Which among the following does fuzzy logic refer to the most?
- Probability
- Heuristic Search
Answer: A) Probability
Fuzzy Logic is also somewhat similar to Probability theory. In fuzzy logic also, all the possible values between the range 0 to 1 are considered and the system produces a real number lying between this range which determines the possibility of the event.
108. Consider the following statement: "In most of the cases, the conditions appear to be partially true. So, their representation was not possible in the Boolean knowledge representation. Hence other methods to deal with this were invented so that uncertainty situations can be dealt with" By reading the above statement, Choose from the following?
The given statement is True.
109. The Maintenance system in the Truth maintenance method stores what?
- Only valid data
- Only invalid data
- Both valid and invalid data
Answer: A) Only valid data
Maintenance System keeps a record of the data which is valid till now. The data which becomes invalid is either moved to trash or is stored in some other file.
Comments and Discussions!
Load comments ↻
- Marketing MCQs
- Blockchain MCQs
- Data Analytics & Visualization MCQs
- Python MCQs
- C++ Programs
- Python Programs
- Java Programs
- D.S. Programs
- Golang Programs
- C# Programs
- JavaScript Examples
- jQuery Examples
- CSS Examples
- C++ Tutorial
- Python Tutorial
- ML/AI Tutorial
- MIS Tutorial
- Software Engineering Tutorial
- Scala Tutorial
- Privacy policy
- Certificates
- Content Writers of the Month
Copyright © 2024 www.includehelp.com. All rights reserved.
Download our App for Study Materials and Placement Preparation 📝✅ | Click Here

Get Latest Exam Updates, Free Study materials and Tips
Your Branch Computer Engineering IT Engineering EXTC Engineering Mechanical Engineering Civil Engineering Others.. Year Of Engineering First Year Second Year Third Year Final Year
Clear Your Aptitude In Very First Attempt!
What's Included!
What's included, 6+ exercise.

[MCQ’s] Artificial Intelligence
Introduction to intelligent systems and intelligent agents, search techniques, knowledge and reasoning, uncertain knowledge and reasoning, natural language processing.
1. What is the main task of a problem-solving agent? A. Solve the given problem and reach to goal B. To find out which sequence of action will get it to the goal state C. Both A and B D. None of the Above Ans : C Explanation: The problem-solving agents are one of the goal-based agents
2. What is Initial state + Goal state in Search Terminology? A. Problem Space B. Problem Instance C. Problem Space Graph D. Admissibility Ans : B Explanation: Problem Instance : It is Initial state + Goal state.
3. What is Time Complexity of Breadth First search algorithm? A. b B. b^d C. b^2 D. b^b Ans : B Explanation: Time Complexity of Breadth First search algorithm is b^d.
4. Depth-First Search is implemented in recursion with _______ data structure. A. LIFO B. LILO C. FIFO D. FILO Ans : A Explanation: Depth-First Search implemented in recursion with LIFO stack data structure.
5. How many types are available in uninformed search method? A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 5 Ans : D Explanation: The five types of uninformed search method are Breadth-first, Uniform-cost, Depth-first, Depth-limited and Bidirectional search.
6. Which data structure conveniently used to implement BFS? A. Stacks B. Queues C. Priority Queues D. None of the Above Ans : B Explanation: Queue is the most convenient data structure, but memory used to store nodes can be reduced by using circular queues.
7. How many types of informed search method are in artificial intelligence? A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 5 Ans : C Explanation: The four types of informed search method are best-first search, Greedy best-first search, A* search and memory bounded heuristic search.
8. Greedy search strategy chooses the node for expansion in ___________ A. Shallowest B. Deepest C. The one closest to the goal node D. Minimum heuristic cost Ans : C Explanation: Sometimes minimum heuristics can be used, sometimes maximum heuristics function can be used. It depends upon the application on which the algorithm is applied.
9. What is disadvantage of Greedy Best First Search? A. This algorithm is neither complete, nor optimal. B. It can get stuck in loops. It is not optimal. C. There can be multiple long paths with the cost ≤ C* D. may not terminate and go on infinitely on one path Ans : B Explanation: The disadvantage of Greedy Best First Search is that it can get stuck in loops. It is not optimal.
10. Searching using query on Internet is, use of ___________ type of agent. A. Offline agent B. Online Agent C. Goal Based D. Both B and C Ans : D Explanation: Refer to the definitions of both the type of agent.
11. An AI system is composed of? A. agent B. environment C. Both A and B D. None of the Above Ans : C Explanation: An AI system is composed of an agent and its environment.
12. Which instruments are used for perceiving and acting upon the environment? A. Sensors and Actuators B. Sensors C. Perceiver D. Perceiver and Sensor Ans : A Explanation: An agent is anything that can be viewed as perceiving and acting upon the environment through the sensors and actuators.
13. Which of the following is not a type of agents in artificial intelligence? A. Model based B. Utility based C. Simple reflex D. target based Ans : D Explanation: The four types of agents are Simple reflex, Model based, Goal based and Utility based agents.
14. Which is used to improve the agents performance? A. Perceiving B. Observing C. Learning D. Sequence Ans : C Explanation: An agent can improve its performance by storing its previous actions.
15. Rationality of an agent does not depends on? A. performance measures B. Percept Sequence C. reaction D. actions Ans : C Explanation: Rationality of an agent does not depends on reaction
16. Agent’s structure can be viewed as ? A. Architecture B. Agent Program C. Architecture + Agent Program D. None of the Above Ans : C Explanation: Agent’s structure can be viewed as – Agent = Architecture + Agent Program
17. What is the action of task environment in artificial intelligence? A. Problem B. Solution C. Agent D. Observation Ans : A Explanation: Task environments will pose a problem and rational agent will find the solution for the posed problem.
18. What kind of environment is crossword puzzle? A. Dynamic B. Static C. Semi Dynamic D. Continuous Ans : B Explanation: As the problem in crossword puzzle are posed at beginning itself, So it is static.
19. What could possibly be the environment of a Satellite Image Analysis System? A. Computers in space and earth B. Image categorization techniques C. Statistical data on image pixel intensity value and histograms D. All of the above Ans : D Explanation: An environment is something which agent stays in.
20. Which kind of agent architecture should an agent an use? A. Relaxed B. Relational C. Both A and B D. None of the AboveAns : C Explanation: Because an agent may experience any kind of situation, So that an agent should use all kinds of architecture.
21. Which depends on the percepts and actions available to the agent? a) Agent b) Sensor c) Design problem d) None of the mentioned Answer: c Explanation: The design problem depends on the percepts and actions available to the agent, the goals that the agent’s behavior should satisfy.
22. Which were built in such a way that humans had to supply the inputs and interpret the outputs? a) Agents b) AI system c) Sensor d) Actuators Answer: b Explanation: AI systems were built in such a way that humans had to supply the inputs and interpret the outputs.
23. Which technology uses miniaturized accelerometers and gyroscopes? a) Sensors b) Actuators c) MEMS d) None of the mentioned Answer: c Explanation: Micro ElectroMechanical System uses miniaturized accelerometers and gyroscopes and is used to produce actuators.
24. What is used for tracking uncertain events? a) Filtering algorithm b) Sensors c) Actuators d) None of the mentioned Answer: a Explanation: Filtering algorithm is used for tracking uncertain events because in this the real perception is involved.
25. What is not represented by using propositional logic? a) Objects b) Relations c) Both Objects & Relations d) None of the mentioned Answer: c Explanation: Objects and relations are not represented by using propositional logic explicitly.
26. Which functions are used as preferences over state history? a) Award b) Reward c) Explicit d) Implicit Answer: b Explanation: Reward functions may be that preferences over states are really compared from preferences over state histories.
27. Which kind of agent architecture should an agent an use? a) Relaxed b) Logic c) Relational d) All of the mentioned Answer: d Explanation: Because an agent may experience any kind of situation, So that an agent should use all kinds of architecture.
28. Specify the agent architecture name that is used to capture all kinds of actions. a) Complex b) Relational c) Hybrid d) None of the mentioned Answer: c Explanation: A complete agent must be able to do anything by using hybrid architecture.
29. Which agent enables the deliberation about the computational entities and actions? a) Hybrid b) Reflective c) Relational d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Because it enables the agent to capture within itself.
30. What can operate over the joint state space? a) Decision-making algorithm b) Learning algorithm c) Complex algorithm d) Both Decision-making & Learning algorithm
31. What is the action of task environment in artificial intelligence? a) Problem b) Solution c) Agent d) Observation Answer: a Explanation: Task environments will pose a problem and rational agent will find the solution for the posed problem.
32. What is the expansion if PEAS in task environment? a) Peer, Environment, Actuators, Sense b) Perceiving, Environment, Actuators, Sensors c) Performance, Environment, Actuators, Sensors d) None of the mentioned Answer: c Explanation: Task environment will contain PEAS which is used to perform the action independently.
33. What kind of observing environments are present in artificial intelligence? a) Partial b) Fully c) Learning d) Both Partial & Fully Answer: d Explanation: Partial and fully observable environments are present in artificial intelligence.
34. What kind of environment is strategic in artificial intelligence? a) Deterministic b) Rational c) Partial d) Stochastic Answer: a Explanation: If the environment is deterministic except for the action of other agent is called deterministic.
35. What kind of environment is crossword puzzle? a) Static b) Dynamic c) Semi Dynamic d) None of the mentioned Answer: a Explanation: As the problem in crossword puzzle are posed at beginning itself, So it is static.
36. What kind of behavior does the stochastic environment posses? a) Local b) Deterministic c) Rational d) Primary Answer: a Explanation: Stochastic behavior are rational because it avoids the pitfall of predictability.
37. Which is used to select the particular environment to run the agent? a) Environment creator b) Environment Generator c) Both Environment creator & Generator d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: None.
38. Which environment is called as semi dynamic? a) Environment does not change with the passage of time b) Agent performance changes c) Environment will be changed d) Environment does not change with the passage of time, but Agent performance changes Answer: d Explanation: If the environment does not change with the passage of time, but the agent performance changes by time.
39. Where does the performance measure is included? a) Rational agent b) Task environment c) Actuators d) Sensor Answer: b Explanation: In PEAS, Where P stands for performance measure which is always included in task environment.
1. Which search strategy is also called as blind search? a) Uninformed search b) Informed search c) Simple reflex search d) All of the mentioned Answer: a Explanation: In blind search, We can search the states without having any additional information. So uninformed search method is blind search.
2. How many types are available in uninformed search method? a) 3 b) 4 c) 5 d) 6 Answer: c Explanation: The five types of uninformed search method are Breadth-first, Uniform-cost, Depth-first, Depth-limited and Bidirectional search.
3. Which search is implemented with an empty first-in-first-out queue? a) Depth-first search b) Breadth-first search c) Bidirectional search d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Because of FIFO queue, it will assure that the nodes that are visited first will be expanded first.
4. When is breadth-first search is optimal? a) When there is less number of nodes b) When all step costs are equal c) When all step costs are unequal d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Because it always expands the shallowest unexpanded node.
5. How many successors are generated in backtracking search? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 Answer: a Explanation: Each partially expanded node remembers which successor to generate next because of these conditions, it uses less memory.
6. What is the space complexity of Depth-first search? a) O(b) b) O(bl) c) O(m) d) O(bm) Answer: d Explanation: O(bm) is the space complexity where b is the branching factor and m is the maximum depth of the search tree.
7. How many parts does a problem consists of? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 Answer: d Explanation: The four parts of the problem are initial state, set of actions, goal test and path cost.
8. Which algorithm is used to solve any kind of problem? a) Breadth-first algorithm b) Tree algorithm c) Bidirectional search algorithm d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Tree algorithm is used because specific variants of the algorithm embed different strategies.
9. Which search algorithm imposes a fixed depth limit on nodes? a) Depth-limited search b) Depth-first search c) Iterative deepening search d) Bidirectional search Answer: a Explanation: None.
10. Which search implements stack operation for searching the states? a) Depth-limited search b) Depth-first search c) Breadth-first search d) None of the mentioned Answer: b
11. What is the other name of informed search strategy? a) Simple search b) Heuristic search c) Online search d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: A key point of informed search strategy is heuristic function, So it is called as heuristic function.
12. How many types of informed search method are in artificial intelligence? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 Answer: d Explanation: The four types of informed search method are best-first search, Greedy best-first search, A* search and memory bounded heuristic search.
13. Which search uses the problem specific knowledge beyond the definition of the problem? a) Informed search b) Depth-first search c) Breadth-first search d) Uninformed search Answer: a Explanation: Informed search can solve the problem beyond the function definition, So does it can find the solution more efficiently.
14. Which function will select the lowest expansion node at first for evaluation? a) Greedy best-first search b) Best-first search c) Depth-first search d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: The lowest expansion node is selected because the evaluation measures distance to the goal.
15. What is the heuristic function of greedy best-first search? a) f(n) != h(n) b) f(n) < h(n) c) f(n) = h(n) d) f(n) > h(n) Answer: c Explanation: None.
16. Which search uses only the linear space for searching? a) Best-first search b) Recursive best-first search c) Depth-first search d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Recursive best-first search will mimic the operation of standard best-first search, but using only the linear space.
17. Which method is used to search better by learning? a) Best-first search b) Depth-first search c) Metalevel state space d) None of the mentioned Answer: c Explanation: This search strategy will help to problem solving efficiency by using learning.
18. Which search is complete and optimal when h(n) is consistent? a) Best-first search b) Depth-first search c) Both Best-first & Depth-first search d) A* search Answer: d Explanation: None.
19. Which is used to improve the performance of heuristic search? a) Quality of nodes b) Quality of heuristic function c) Simple form of nodes d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Good heuristic can be constructed by relaxing the problem, So the performance of heuristic search can be improved.
20. Which search method will expand the node that is closest to the goal? a) Best-first search b) Greedy best-first search c) A* search d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Because of using greedy best-first search, It will quickly lead to the solution of the problem.
21. In many problems the path to goal is irrelevant, this class of problems can be solved using ____________ a) Informed Search Techniques b) Uninformed Search Techniques c) Local Search Techniques d) Informed & Uninformed Search Techniques Answer: c Explanation: If the path to the goal does not matter, we might consider a different class of algorithms, ones that do not worry about paths at all. Local search algorithms operate using a single current state (rather than multiple paths) and generally move only to neighbors of that state.
22. Though local search algorithms are not systematic, key advantages would include __________ a) Less memory b) More time c) Finds a solution in large infinite space d) Less memory & Finds a solution in large infinite space Answer: d Explanation: Two advantages: (1) they use very little memory-usually a constant amount; and (2) they can often find reasonable solutions in large or infinite (continuous) state spaces for which systematic algorithms are unsuitable.
23. A complete, local search algorithm always finds goal if one exists, an optimal algorithm always finds a global minimum/maximum. a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: An algorithm is complete if it finds a solution if exists and optimal if finds optimal goal (minimum or maximum).
24. _______________ Is an algorithm, a loop that continually moves in the direction of increasing value – that is uphill. a) Up-Hill Search b) Hill-Climbing c) Hill algorithm d) Reverse-Down-Hill search Answer: b Explanation: Refer the definition of Hill-Climbing approach.
25. When will Hill-Climbing algorithm terminate? a) Stopping criterion met b) Global Min/Max is achieved c) No neighbor has higher value d) All of the mentioned Answer: c Explanation: When no neighbor is having higher value, algorithm terminates fetching local min/max.
26. What are the main cons of hill-climbing search? a) Terminates at local optimum & Does not find optimum solution b) Terminates at global optimum & Does not find optimum solution c) Does not find optimum solution & Fail to find a solution d) Fail to find a solution View Answer Answer: a Explanation: Algorithm terminates at local optimum values, hence fails to find optimum solution.
27. Stochastic hill climbing chooses at random from among the uphill moves; the probability of selection can vary with the steepness of the uphil1 move. a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: Refer to the definition of variants of hill-climbing search.
28. Hill climbing sometimes called ____________ because it grabs a good neighbor state without thinking ahead about where to go next. a) Needy local search b) Heuristic local search c) Greedy local search d) Optimal local search Answer: c Explanation: None.
29. Hill-Climbing approach stuck for which of the following reasons? a) Local maxima b) Ridges c) Plateaux d) All of the mentioned Answer: d Explanation: Local maxima: a local maximum is a peak that is higher than each of its neighboring states, but lower than the global maximum. Ridges: Ridges result in a sequence of local maxima that is very difficult for greedy algorithms to navigate. Plateaux: a plateau is an area of the state space landscape where the evaluation function is flat.
30. ___________ algorithm keeps track of k states rather than just one. a) Hill-Climbing search b) Local Beam search c) Stochastic hill-climbing search d) Random restart hill-climbing search Answer: b Explanation: Refer to the definition of Local Beam Search algorithm.
31. A genetic algorithm (or GA) is a variant of stochastic beam search in which successor states are generated by combining two parent states, rather than by modifying a single state. a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: Stochastic beam search, analogous to stochastic hill climbing, helps to alleviate this problem. Instead of choosing the best k from the pool of candidate successors, stochastic beam search chooses k successors at random, with the probability of choosing a given successor being an increasing function of its value.
32. What are the two main features of Genetic Algorithm? a) Fitness function & Crossover techniques b) Crossover techniques & Random mutation c) Individuals among the population & Random mutation d) Random mutation & Fitness function Answer: a Explanation: Fitness function helps choosing individuals from the population and Crossover techniques defines the offspring generated.
33. Searching using query on Internet is, use of ___________ type of agent. a) Offline agent b) Online agent c) Both Offline & Online agent d) Goal Based & Online agent Answer: d Explanation: Refer to the definitions of both the type of agent.
34. In how many directions do queens attack each other? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
Answer: c Explanation: Queens attack each other in three directions- vertical, horizontal and diagonal.
35. Placing n-queens so that no two queens attack each other is called? a) n-queen’s problem b) 8-queen’s problem c) Hamiltonian circuit problem d) subset sum problem
Answer: a Explanation: Placing n queens so that no two queens attack each other is n-queens problem. If n=8, it is called as 8-queens problem.
36. Where is the n-queens problem implemented? a) carom b) chess c) ludo d) cards
Answer: b Explanation: N-queens problem occurs in chess. It is the problem of placing n- queens in a n*n chess board.
37. Not more than 2 queens can occur in an n-queens problem. a) true b) false
Answer: b Explanation: Unlike a real chess game, n-queens occur in a n-queen problem since it is the problem of dealing with n-queens.
38. In n-queen problem, how many values of n does not provide an optimal solution? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
Answer: b Explanation: N-queen problem does not provide an optimal solution of only three values of n (i.e.) n=2,3.
39. Which of the following methods can be used to solve n-queen’s problem? a) greedy algorithm b) divide and conquer c) iterative improvement d) backtracking
Answer: d Explanation: Of the following given approaches, n-queens problem can be solved using backtracking. It can also be solved using branch and bound.
40. Of the following given options, which one of the following is a correct option that provides an optimal solution for 4-queens problem? a) (3,1,4,2) b) (2,3,1,4) c) (4,3,2,1) d) (4,2,3,1)
Answer: a Explanation: Of the following given options for optimal solutions of 4-queens problem, (3, 1, 4, 2) is the right option.
41. How many possible solutions exist for an 8-queen problem? a) 100 b) 98 c) 92 d) 88
Answer: c Explanation: For an 8-queen problem, there are 92 possible combinations of optimal solutions.
42. How many possible solutions occur for a 10-queen problem? a) 850 b) 742 c) 842 d) 724
Answer: d Explanation: For a 10-queen problem, 724 possible combinations of optimal solutions are available.
43. If n=1, an imaginary solution for the problem exists. a) true b) false
44. What is the domination number for 8-queen’s problem? a) 8 b) 7 c) 6 d) 5
Answer: d Explanation: The minimum number of queens needed to occupy every square in n-queens problem is called domination number. While n=8, the domination number is 5.
45. Of the following given options, which one of the following does not provides an optimal solution for 8-queens problem? a) (5,3,8,4,7,1,6,2) b) (1,6,3,8,3,2,4,7) c) (4,1,5,8,6,3,7,2) d) (6,2,7,1,4,8,5,3)
Answer: b Explanation: The following given options for optimal solutions of 8-queens problem, (1,6,3,8,3,2,4,7) does not provide an optimal solution.
46. General games involves ____________ a) Single-agent b) Multi-agent c) Neither Single-agent nor Multi-agent d) Only Single-agent and M0ulti-agent
Answer: d Explanation: Depending upon games it could be single agent (Sudoku) or multi-agent (Chess).
47. Adversarial search problems uses ____________ a) Competitive Environment b) Cooperative Environment c) Neither Competitive nor Cooperative Environment d) Only Competitive and Cooperative Environment
Answer: a Explanation: Since in cooperative environment agents’ goals are I conflicts. They compete for goal.
48. Mathematical game theory, a branch of economics, views any multi-agent environment as a game provided that the impact of each agent on the others is “significant,” regardless of whether the agents are cooperative or competitive. a) True b) False
Answer: a Explanation: None.
49. Zero sum games are the one in which there are two agents whose actions must alternate and in which the utility values at the end of the game are always the same. a) True b) False
Answer: b Explanation: Utility values are always same and opposite.
50. Zero sum game has to be a ______ game. a) Single player b) Two player c) Multiplayer d) Three player
Answer: c Explanation: Zero sum games could be multiplayer games as long as the condition for zero sum game is satisfied.
51. A game can be formally defined as a kind of search problem with the following components. a) Initial State b) Successor Function c) Terminal Test d) All of the mentioned
Answer: d Explanation: The initial state includes the board position and identifies the player to move. A successor function returns a list of (move, state) pairs, each indicating a legal move and the resulting state. A terminal test determines when the game is over. States where the game has ended are called terminal states. A utility function (also called an objective function or payoff function), which gives a numeric value for the terminal states. In chess, the outcome is a win, lose, or draw, with values +1, -1, or 0.
52. The initial state and the legal moves for each side define the __________ for the game. a) Search Tree b) Game Tree c) State Space Search d) Forest
Answer: b Explanation: An example of game tree for Tic-Tac-Toe game.
53. General algorithm applied on game tree for making decision of win/lose is ____________ a) DFS/BFS Search Algorithms b) Heuristic Search Algorithms c) Greedy Search Algorithms d) MIN/MAX Algorithms
Answer: d Explanation: Given a game tree, the optimal strategy can be determined by examining the min/max value of each node, which we write as MINIMAX- VALUE(n). The min/max value of a node is the utility (for MAX) of being in the corresponding state, assuming that both players play optimally from there to the end of the game. Obviously, the min/max value of a terminal state is just its utility. Furthermore, given a choice, MAX will prefer to move to a state of maximum value, whereas MIN prefers a state of minimum value.
54. The minimax algorithm computes the minimax decision from the current state. It uses a simple recursive computation of the minimax values of each successor state, directly implementing the defining equations. The recursion proceeds all the way down to the leaves of the tree, and then the minimax values are backed up through the tree as the recursion unwinds. a) True b) False
Answer: a Explanation: Refer definition of minimax algorithm.
55. What is the complexity of minimax algorithm? a) Same as of DFS b) Space – bm and time – bm c) Time – bm and space – bm d) Same as BFS
Answer: a Explanation: Same as DFS.
56. Which search is equal to minimax search but eliminates the branches that can’t influence the final decision? a) Depth-first search b) Breadth-first search c) Alpha-beta pruning d) None of the mentioned
Answer: c Explanation: The alpha-beta search computes the same optimal moves as minimax, but eliminates the branches that can’t influence the final decision.
57. Which values are independant in minimax search algorithm? a) Pruned leaves x and y b) Every states are dependant c) Root is independant d) None of the mentioned
Answer: a Explanation: The minimax decision are independant of the values of the pruned values x and y because of the root values.
58. To which depth does the alpha-beta pruning can be applied? a) 10 states b) 8 States c) 6 States d) Any depth
Answer: d Explanation: Alpha–beta pruning can be applied to trees of any depth and it is possible to prune entire subtree rather than leaves.
59. Which search is similar to minimax search? a) Hill-climbing search b) Depth-first search c) Breadth-first search d) All of the mentioned
Answer: b Explanation: The minimax search is depth-first search, So at one time we just have to consider the nodes along a single path in the tree.
60. Which value is assigned to alpha and beta in the alpha-beta pruning? a) Alpha = max b) Beta = min c) Beta = max d) Both Alpha = max & Beta = min
Answer: d Explanation: Alpha and beta are the values of the best choice we have found so far at any choice point along the path for MAX and MIN.
61. Where does the values of alpha-beta search get updated? a) Along the path of search b) Initial state itself c) At the end d) None of the mentioned
Answer: a Explanation: Alpha-beta search updates the value of alpha and beta as it gets along and prunes the remaining branches at node.
62. How the effectiveness of the alpha-beta pruning gets increased? a) Depends on the nodes b) Depends on the order in which they are executed c) All of the mentioned d) None of the mentioned
63. What is called as transposition table? a) Hash table of next seen positions b) Hash table of previously seen positions c) Next value in the search d) None of the mentioned
Answer: b Explanation: Transposition is the occurrence of repeated states frequently in the search.
64. Which is identical to the closed list in Graph search? a) Hill climbing search algorithm b) Depth-first search c) Transposition table d) None of the mentioned
65. Which function is used to calculate the feasibility of whole game tree? a) Evaluation function b) Transposition c) Alpha-beta pruning d) All of the mentioned
Answer: a Explanation: Because we need to cut the search off at some point and apply an evaluation function that gives an estimate of the utility of the state.
1. There exist only two types of quantifiers, Universal Quantification and Existential Quantification. a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: None.
2. Translate the following statement into FOL. “For every a, if a is a philosopher, then a is a scholar” a) ∀ a philosopher(a) scholar(a) b) ∃ a philosopher(a) scholar(a) c) All of the mentioned d) None of the mentioned Answer: a Explanation: None.
3. A _________ is used to demonstrate, on a purely syntactic basis, that one formula is a logical consequence of another formula. a) Deductive Systems b) Inductive Systems c) Reasoning with Knowledge Based Systems d) Search Based Systems Answer: a Explanation: Refer the definition of Deductive based systems.
4. The statement comprising the limitations of FOL is/are ____________ a) Expressiveness b) Formalizing Natural Languages c) Many-sorted Logic d) All of the mentioned Answer: d Explanation: The Löwenheim–Skolem theorem shows that if a first-order theory has any infinite model, then it has infinite models of every cardinality. In particular, no first-order theory with an infinite model can be categorical. Thus there is no first-order theory whose only model has the set of natural numbers as its domain, or whose only model has the set of real numbers as its domain. Many extensions of first-order logic, including infinitely logics and higher-order logics, are more expressive in the sense that they do permit categorical axiomatizations of the natural numbers or real numbers. This expressiveness comes at a meta-logical cost, however: by Lindström’s theorem, the compactness theorem and the downward Löwenheim–Skolem theorem cannot hold in any logic stronger than first-order. Formalizing Natural Languages : First-order logic is able to formalize many simple quantifier constructions in natural language, such as “every person who lives in Perth lives in Australia”. But there are many more complicated features of natural language that cannot be expressed in (single-sorted) first-order logic. Many-sorted Logic: Ordinary first-order interpretations have a single domain of discourse over which all quantifiers range. Many-sorted first-order logic allows variables to have different sorts, which have different domains.
5. A common convention is: • is evaluated first • and are evaluated next • Quantifiers are evaluated next • is evaluated last. a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: None.
6. A Term is either an individual constant (a 0-ary function), or a variable, or an n-ary function applied to n terms: F(t1 t2 ..tn). a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: Definition of term in FOL.
7. First Order Logic is also known as ___________ a) First Order Predicate Calculus b) Quantification Theory c) Lower Order Calculus d) All of the mentioned Answer: d Explanation: None.
8. The adjective “first-order” distinguishes first-order logic from ___________ in which there are predicates having predicates or functions as arguments, or in which one or both of predicate quantifiers or function quantifiers are permitted. a) Representational Verification b) Representational Adequacy c) Higher Order Logic d) Inferential Efficiency Answer: c Explanation: None.
9. Which is created by using single propositional symbol? a) Complex sentences b) Atomic sentences c) Composition sentences d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Atomic sentences are indivisible syntactic elements consisting of single propositional symbol.
10. Which is used to construct the complex sentences? a) Symbols b) Connectives c) Logical connectives d) All of the mentioned Answer: c Explanation: None.
11. How many proposition symbols are there in artificial intelligence? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 Answer: b Explanation: The two proposition symbols are true and false.
12. How many logical connectives are there in artificial intelligence? a) 2 b) 3 c) 4 d) 5 Answer: d Explanation: The five logical symbols are negation, conjunction, disjunction, implication and biconditional.
13. Which is used to compute the truth of any sentence? a) Semantics of propositional logic b) Alpha-beta pruning c) First-order logic d) Both Semantics of propositional logic & Alpha-beta pruning Answer: a Explanation: Because the meaning of the sentences is really needed to compute the truth.
14. Which are needed to compute the logical inference algorithm? a) Logical equivalence b) Validity c) Satisfiability d) All of the mentioned Answer: d Explanation: Logical inference algorithm can be solved be using logical equivalence, Validity and satisfiability.
15. From which rule does the modus ponens are derived? a) Inference rule b) Module rule c) Both Inference & Module rule d) None of the mentioned Answer: a Explanation: Inference rule contains the standard pattern that leads to desired goal. The best form of inference rule is modus ponens.
16. Which is also called single inference rule? a) Reference b) Resolution c) Reform d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Because resolution yields a complete inference rule when coupled with any search algorithm.
17. Which form is called as a conjunction of disjunction of literals? a) Conjunctive normal form b) Disjunctive normal form c) Normal form d) All of the mentioned Answer: a Explanation: None.
18. What can be viewed as a single lateral of disjunction? a) Multiple clause b) Combine clause c) Unit clause d) None of the mentioned Answer: c Explanation: A single literal can be viewed as a disjunction or one literal also, called a unit clause.
19. Which is a refutation complete inference procedure for propositional logic? a) Clauses b) Variables c) Propositional resolution d) Proposition Answer: c Explanation: Propositional resolution is a refutation complete inference procedure for propositional logic.
20. What kind of clauses are available in Conjunctive Normal Form? a) Disjunction of literals b) Disjunction of variables c) Conjunction of literals d) Conjunction of variables Answer: a Explanation: First-order resolution requires the clause to be in disjunction of literals in Conjunctive Normal Form.
21. What is the condition of literals in variables? a) Existentially quantified b) Universally quantified c) Quantified d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Literals that contain variables are assumed to be universally quantified.
22. Which can be converted to inferred equivalent CNF sentence? a) Every sentence of propositional logic b) Every sentence of inference c) Every sentence of first-order logic d) All of the mentioned Answer: c Explanation: Every sentence of first-order logic can be converted to inferred equivalent CNF sentence.
23. Which sentence will be unsatisfiable if the CNF sentence is unsatisfiable? a) Search statement b) Reading statement c) Replaced statement d) Original statement Answer: d Explanation: The CNF statement will be unsatisfiable just when the original sentence is unsatisfiable.
24. Which rule is equal to the resolution rule of first-order clauses? a) Propositional resolution rule b) Inference rule c) Resolution rule d) None of the mentioned Answer: a Explanation: The resolution rule for first-order clauses is simply a lifted version of the propositional resolution rule.
25. At which state does the propositional literals are complementary? a) If one variable is less b) If one is the negation of the other c) All of the mentioned d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Propositional literals are complementary if one is the negation of the other.
26. What is meant by factoring? a) Removal of redundant variable b) Removal of redundant literal c) Addition of redundant literal d) Addition of redundant variable Answer: b Explanation: None.
27. What will happen if two literals are identical? a) Remains the same b) Added as three c) Reduced to one d) None of the mentioned Answer: c Explanation: Propositional factoring reduces two literals to one if they are identical.
28. When the resolution is called as refutation-complete? a) Sentence is satisfiable b) Sentence is unsatisfiable c) Sentence remains the same d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Resolution is refutation-complete, if a set of sentence is unsatisfiable, then resolution will always be able to derive a contradiction.
29. Which condition is used to cease the growth of forward chaining? a) Atomic sentences b) Complex sentences c) No further inference d) All of the mentioned Answer: c Explanation: Forward chain can grow by adding new atomic sentences until no further inference is made.
30. Which closely resembles propositional definite clause? a) Resolution b) Inference c) Conjunction d) First-order definite clauses Answer: d Explanation: Because they are disjunction of literals of which exactly one is positive.
31. What is the condition of variables in first-order literals? a) Existentially quantified b) Universally quantified c) Both Existentially & Universally quantified d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: First-order literals will accept variables only if they are universally quantified.
32. Which are more suitable normal form to be used with definite clause? a) Positive literal b) Negative literal c) Generalized modus ponens d) Neutral literal Answer: c Explanation: Definite clauses are a suitable normal form for use with generalized modus ponen.
33. Which will be the instance of the class datalog knowledge bases? a) Variables b) No function symbols c) First-order definite clauses d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: If the knowledge base contains no function symbols means, it is an instance of the class datalog knowledge base.
34. Which knowledge base is called as fixed point? a) First-order definite clause are similar to propositional forward chaining b) First-order definite clause are mismatch to propositional forward chaining c) All of the mentioned d) None of the mentioned Answer: a Explanation: Fixed point reached by forward chaining with first-order definiteclause are similar to those for propositional forward chaining.
35. How to eliminate the redundant rule matching attempts in the forward chaining? a) Decremental forward chaining b) Incremental forward chaining c) Data complexity d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: We can eliminate the redundant rule matching attempts in the forward chaining by using incremental forward chaining.
36. From where did the new fact inferred on new iteration is derived? a) Old fact b) Narrow fact c) New fact d) All of the mentioned Answer: c Explanation: None.
37. Which will solve the conjuncts of the rule so that the total cost is minimized? a) Constraint variable b) Conjunct ordering c) Data complexity d) All of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Conjunct ordering will find an ordering to solve the conjuncts of the rule premise so that the total cost is minimized.
38. How many possible sources of complexity are there in forward chaining? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4 Answer: c Explanation: The three possible sources of complexity are an inner loop, algorithm rechecks every rule on every iteration, algorithm might generate many facts irrelevant to the goal.
39. Which algorithm will work backward from the goal to solve a problem? a) Forward chaining b) Backward chaining c) Hill-climb algorithm d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Backward chaining algorithm will work backward from the goal and it will chain the known facts that support the proof.
40. Which is mainly used for automated reasoning? a) Backward chaining b) Forward chaining c) Logic programming d) Parallel programming Answer: c Explanation: Logic programming is mainly used to check the working process of the system.
41. What will backward chaining algorithm will return? a) Additional statements b) Substitutes matching the query c) Logical statement d) All of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: It will contains the list of goals containing a single element and returns the set of all substitutions satisfying the query.
42. How can be the goal is thought of in backward chaining algorithm? a) Queue b) List c) Vector d) Stack View Answer Answer: d Explanation: The goals can be thought of as stack and if all of them us satisfied means, then current branch of proof succeeds.
43. What is used in backward chaining algorithm? a) Conjuncts b) Substitution c) Composition of substitution d) None of the mentioned Answer: c Explanation: None.
44. Which algorithm are in more similar to backward chaining algorithm? a) Depth-first search algorithm b) Breadth-first search algorithm c) Hill-climbing search algorithm d) All of the mentioned Answer: a Explanation: It is depth-first search algorithm because its space requirements are linear in the size of the proof.
45. Which problem can frequently occur in backward chaining algorithm? a) Repeated states b) Incompleteness c) Complexity d) Both Repeated states & Incompleteness Answer: d Explanation: If there is any loop in the chain means, It will lead to incompleteness and repeated states.
46. How the logic programming can be constructed? a) Variables b) Expressing knowledge in a formal language c) Graph d) All of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Logic programming can be constructed by expressing knowledge in a formal expression and the problem can be solved by running inference process.
47. What form of negation does the prolog allows? a) Negation as failure b) Proposition c) Substitution d) Negation as success Answer: a Explanation: None.
48. Which is omitted in prolog unification algorithm? a) Variable check b) Occur check c) Proposition check d) Both Occur & Proposition check Answer: b Explanation: Occur check is omitted in prolog unification algorithm because of unsound inferences.
49. Knowledge and reasoning also play a crucial role in dealing with __________________ environment. a) Completely Observable b) Partially Observable c) Neither Completely nor Partially Observable d) Only Completely and Partially Observable Answer: b Explanation: Knowledge and reasoning could aid to reveal other factors that could complete environment.
50. Treatment chosen by doctor for a patient for a disease is based on _____________ a) Only current symptoms b) Current symptoms plus some knowledge from the textbooks c) Current symptoms plus some knowledge from the textbooks plus experience d) All of the mentioned Answer: c Explanation: None.
51. A knowledge-based agent can combine general knowledge with current percepts to infer hidden aspects of the current state prior to selecting actions. a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: Refer definition of Knowledge based agents.
52. A) Knowledge base (KB) is consists of set of statements. B) Inference is deriving a new sentence from the KB. Choose the correct option. a) A is true, B is true b) A is false, B is false c) A is true, B is false d) A is false, B is true Answer: a Explanation: None.
53. Wumpus World is a classic problem, best example of _______ a) Single player Game b) Two player Game c) Reasoning with Knowledge d) Knowledge based Game Answer: c Explanation: Refer the definition of Wumpus World Problem.
54. ‘α |= β ‘(to mean that the sentence α entails the sentence β) if and only if, in every model in which α is _____ β is also _____ a) True, true b) True, false c) False, true d) False, false Answer: a Explanation: Refer the definition of law of entailment.
55. Which is not a property of representation of knowledge? a) Representational Verification b) Representational Adequacy c) Inferential Adequacy d) Inferential Efficiency Answer: a Explanation: None.
56. Which is not Familiar Connectives in First Order Logic? a) and b) iff c) or d) not Answer: d Explanation: “not” is coming under propositional logic and is therefore not a connective.
57. Inference algorithm is complete only if _____________ a) It can derive any sentence b) It can derive any sentence that is an entailed version c) It is truth preserving d) It can derive any sentence that is an entailed version & It is truth preserving
58. An inference algorithm that derives only entailed sentences is called sound or truth-preserving. a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: None.
59. The rule of Universal Instantiation (UI for short) says that we can infer any sentence obtained by substituting a ground term (a term without variables) for the variable. a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: Rule of universal instantiation.
60. The corresponding Existential Instantiation rule: for the existential quantifier is slightly more complicated. For any sentence a, variable v, and constant symbol k that does not appear elsewhere in the knowledge base. a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: Rule of existential instantiation.
61. What among the following could the universal instantiation of ___________ For all x King(x) ^ Greedy(x) => Evil(x) a) King(John) ^ Greedy(John) => Evil(John) b) King(y) ^ Greedy(y) => Evil(y) c) King(Richard) ^ Greedy(Richard) => Evil(Richard) d) All of the mentioned Answer: d Explanation: Refer the definition if universal instantiation.
62. Lifted inference rules require finding substitutions that make different logical expressions looks identical. a) Existential Instantiation b) Universal Instantiation c) Unification d) Modus Ponen Answer: c Explanation: None.
63. Which of the following is not the style of inference? a) Forward Chaining b) Backward Chaining c) Resolution Refutation d) Modus Ponen Answer: d Explanation: Modus ponen is a rule for an inference.
64. In order to utilize generalized Modus Ponens, all sentences in the KB must be in the form of Horn sentences. a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: None.
65. For resolution to apply, all sentences must be in conjunctive normal form, a conjunction of disjunctions of literals. a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: None.
66. What are the two basic types of inferences? a) Reduction to propositional logic, Manipulate rules directly b) Reduction to propositional logic, Apply modus ponen c) Apply modus ponen, Manipulate rules directly d) Convert every rule to Horn Clause, Reduction to propositional logic Answer: a Explanation: None.
67. Which among the following could the Existential instantiation of ∃x Crown(x) ^ OnHead(x, Johnny)? a) Crown(John) ^ OnHead(John, Jonny) b) Crown(y) ^ OnHead(y, y, x) c) Crown(x) ^ OnHead(x, Jonny) d) None of the mentioned Answer: a Explanation: None.
68. Translate the following statement into FOL. “For every a, if a is a PhD student, then a has a master degree” a) ∀ a PhD(a) -> Master(a) b) ∃ a PhD(a) -> Master(a) c) A is true, B is true d) A is false, B is false Answer: a Explanation: None
69. The rule of Universal Instantiation (UI for short) says that we can infer any sentence obtained by substituting a ground term (a term without variables) for the variable. a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: Rule of universal instantiation.
70. The corresponding Existential Instantiation rule: for the existential quantifier is slightly more complicated. For any sentence a, variable v, and constant symbol k that does not appear elsewhere in the knowledge base. a) True b) False Answer: a Explanation: Rule of existential instantiation.
1. Which is the most straightforward approach for planning algorithm? a) Best-first search b) State-space search c) Depth-first search d) Hill-climbing search
Answer: b Explanation: The straightforward approach for planning algorithm is state space search because it takes into account of everything for finding a solution.
2. What are taken into account of state-space search? a) Postconditions b) Preconditions c) Effects d) Both Preconditions & Effects
Answer: d Explanation: The state-space search takes both precondition and effects into account for solving a problem.
3. How many ways are available to solve the state-space search? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
Answer: b Explanation: There are two ways available to solve the state-space search. They are forward from the initial state and backward from the goal.
4. What is the other name for forward state-space search? a) Progression planning b) Regression planning c) Test planning d) None of the mentioned
Answer: a Explanation: It is sometimes called as progression planning, because it moves in the forward direction.
5. How many states are available in state-space search? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
Answer: d Explanation: There are four states available in state-space search. They are initial state, actions, goal test and step cost.
6. What is the main advantage of backward state-space search? a) Cost b) Actions c) Relevant actions d) All of the mentioned
Answer: c Explanation: The main advantage of backward search will allow us to consider only relevant actions.
7. What is the other name of the backward state-space search? a) Regression planning b) Progression planning c) State planning d) Test planning
Answer: a Explanation: Backward state-space search will find the solution from goal to the action, So it is called as Regression planning.
8. What is meant by consistent in state-space search? a) Change in the desired literals b) Not any change in the literals c) No change in goal state d) None of the mentioned
Answer: b Explanation: Consistent means that the completed actions will not undo any desired literals.
9. What will happen if a predecessor description is generated that is satisfied by the initial state of the planning problem? a) Success b) Error c) Compilation d) Termination
Answer: d Explanation: None.
10. Which approach is to pretend that a pure divide and conquer algorithm will work? a) Goal independence b) Subgoal independence c) Both Goal & Subgoal independence d) None of the mentioned
Answer: b Explanation: Subgoal independence approach is to pretend that a pure divide and conquer algorithm will work for admissible heuristics.
11. The process by which the brain incrementally orders actions needed to complete a specific task is referred as ______________ a) Planning problem b) Partial order planning c) Total order planning d) Both Planning problem & Partial order planning
Answer: b Explanation: Definition of partial order planning.
12. To complete any task, the brain needs to plan out the sequence by which to execute the behavior. One way the brain does this is with a partial-order plan. a) True b) False
13. In partial order plan. A. Relationships between the actions of the behavior are set prior to the actions B. Relationships between the actions of the behavior are not set until absolutely necessary Choose the correct option. a) A is true b) B is true c) Either A or B can be true depending upon situation d) Neither A nor B is true
Answer: a Explanation: Relationship between behavior and actions is established dynamically.
14. Partial-order planning exhibits the Principle of Least Commitment, which contributes to the efficiency of this planning system as a whole. a) True b) False
15. Following is/are the components of the partial order planning. a) Bindings b) Goal c) Causal Links d) All of the mentioned
Answer: d Explanation: Bindings: The bindings of the algorithm are the connections between specific variables in the action. Bindings, as ordering, only occur when it is absolutely necessary. Causal Links: Causal links in the algorithm are those that categorically order actions. They are not the specific order (1,2,3) of the actions, rather the general order as in Action 2 must come somewhere after Action 1, but before Action 2. Plan Space: The plan space of the algorithm is constrained between its start and finish. The algorithm starts, producing the initial state and finishes when all parts of the goal is been achieved.
16. Partial-order planning is the opposite of total-order planning. a) True b) False
Answer: a Explanation: Partial-order planning is the opposite of total-order planning, in which actions are sequenced all at once and for the entirety of the task at hand.
17. Sussman Anomaly can be easily and efficiently solved by partial order planning. a) True b) False
Answer: a Explanation: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sussman_Anomaly.
18. Sussman Anomaly illustrates a weakness of interleaved planning algorithm. a) True b) False
Answer: b Explanation: Sussman Anomaly illustrates a weakness of non interleaved planning algorithm.
19. One the main drawback of this type of planning system is that it requires a lot of computational powers at each node. a) True b) False
20. What are you predicating by the logic: ۷x: €y: loyalto(x, y). a) Everyone is loyal to someone b) Everyone is loyal to all c) Everyone is not loyal to someone d) Everyone is loyal
Answer: a Explanation: ۷x denotes Everyone or all, and €y someone and loyal to is the proposition logic making map x to y.
21. A plan that describe how to take actions in levels of increasing refinement and specificity is ____________ a) Problem solving b) Planning c) Non-hierarchical plan d) Hierarchical plan
Answer: d Explanation: A plan that describes how to take actions in levels of increasing refinement and specificity is Hierarchical (e.g., “Do something” becomes the more specific “Go to work,” “Do work,” “Go home.”) Most plans are hierarchical in nature.
22. A constructive approach in which no commitment is made unless it is necessary to do so, is ____________ a) Least commitment approach b) Most commitment approach c) Nonlinear planning d) Opportunistic planning
Answer: a Explanation: Because we are not sure about the outcome.
23. Uncertainty arises in the Wumpus world because the agent’s sensors give only ____________ a) Full & Global information b) Partial & Global Information c) Partial & local Information d) Full & local information
Answer: c Explanation: The Wumpus world is a grid of squares surrounded by walls, where each square can contain agents and objects. The agent (you) always starts in the lower left corner, a square that will be labeled [1, 1]. The agent’s task is to find the gold, return to [1, 1] and climb out of the cave. Therefore, uncertainty is there as the agent gives partial and local information only. Global variable are not goal specific problem solving.
24. Which of the following search belongs to totally ordered plan search? a) Forward state-space search b) Hill-climbing search c) Depth-first search d) Breadth-first search
Answer: a Explanation: Forward and backward state-space search are particular forms of totally ordered plan search.
25. Which cannot be taken as advantage for totally ordered plan search? a) Composition b) State search c) Problem decomposition d) None of the mentioned
Answer: c Explanation: As the search explore only linear sequences of actions, So they cannot take advantage of problem decomposition.
26. What is the advantage of totally ordered plan in constructing the plan? a) Reliability b) Flexibility c) Easy to use d) All of the mentioned
Answer: b Explanation: Totally ordered plan has the advantage of flexibility in the order in which it constructs the plan.
27. Which strategy is used for delaying a choice during search? a) First commitment b) Least commitment c) Both First & Least commitment d) None of the mentioned
Answer: b Explanation: The general strategy of delaying a choice during search is called the least commitment strategy.
28. Which algorithm places two actions into a plan without specifying which should come first? a) Full-order planner b) Total-order planner c) Semi-order planner d) Partial-order planner
Answer: d Explanation: Any planning algorithm that can place two actions into a plan without specifying which should come first is called partial-order planner.
29. How many possible plans are available in partial-order solution? a) 3 b) 4 c) 5 d) 6
Answer: d Explanation: The partial-order solution corresponds to six possible total-order plans.
30. What is the other name of each and every total-order plans? a) Polarization b) Linearization c) Solarization d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Each and every total order plan is also called as linearization of the partial-order plan.
31. What are present in the empty plan? a) Start b) Finish c) Modest d) Both Start & Finish View Answer
32. What are not present in start actions? a) Preconditions b) Effect c) Finish d) None of the mentioned Answer: a Explanation: Start has no precondition and has as its effects all the literals in the initial state of the planning problem.
33. What are not present in finish actions? a) Preconditions b) Effect c) Finish d) None of the mentioned Answer: b Explanation: Finish has no effects and has as its preconditions the goal literals of the planning algorithm.
34. Which can be adapted for planning algorithms? a) Most-constrained variable b) Most-constrained literal c) Constrained d) None of the mentioned Answer: a Explanation: The most-constrained variable heuristic from CSPs can be adapted for planning algorithm and seems to work well.
1. Using logic to represent and reason we can represent knowledge about the world with facts and rules. a) True b) False
2. Uncertainty arises in the wumpus world because the agent’s sensors give only ___________ a) Full & Global information b) Partial & Global Information c) Partial & local Information d) Full & local information
Answer: c Explanation: The Wumpus world is a grid of squares surrounded by walls, where each square can contain agents and objects. The agent (you) always starts in the lower left corner, a square that will be labeled [1, 1]. The agent’s task is to find the gold, return to [1, 1] and climb out of the cave. So uncertainty is there as the agent gives partial and local information only. Global variable are not goal specific problem solving.
3. A Hybrid Bayesian network contains ___________ a) Both discrete and continuous variables b) Only Discrete variables c) Only Discontinuous variable d) Both Discrete and Discontinuous variable
Answer: a Explanation: To specify a Hybrid network, we have to specify two new kinds of distributions: the conditional distribution for continuous variables given discrete or continuous parents, and the conditional distribution for a discrete variable given continuous parents.
4. How is Fuzzy Logic different from conventional control methods? a) IF and THEN Approach b) FOR Approach c) WHILE Approach d) DO Approach
Answer: a Explanation: FL incorporates a simple, rule-based IF X AND Y THEN Z approach to a solving control problem rather than attempting to model a system mathematically.
5. If a hypothesis says it should be positive, but in fact it is negative, we call it ___________ a) A consistent hypothesis b) A false negative hypothesis c) A false positive hypothesis d) A specialized hypothesis
Answer: c Explanation: Consistent hypothesis go with examples, If the hypothesis says it should be negative but in fact it is positive, it is false negative. If a hypothesis says it should be positive, but in fact it is negative, it is false positive. In a specialized hypothesis we need to have certain restrict or special conditions.
6. The primitives in probabilistic reasoning are random variables. a) True b) False
Answer: a Explanation: The primitives in probabilistic reasoning are random variables. Just like primitives in Propositional Logic are propositions. A random variable is not in fact a variable, but a function from a sample space S to another space, often the real numbers.
7. Which is true for Decision theory? a) Decision Theory = Probability theory + utility theory b) Decision Theory = Inference theory + utility theory c) Decision Theory = Uncertainty + utility theory d) Decision Theory = Probability theory + preference
8. A constructive approach in which no commitment is made unless it is necessary to do so is ___________ a) Least commitment approach b) Most commitment approach c) Nonlinear planning d) Opportunistic planning
9. What is the extraction of the meaning of utterance? a) Syntactic b) Semantic c) Pragmatic d) None of the mentioned
Answer: b Explanation: Semantic analysis is used to extract the meaning from the group of sentences.
10. What is the process of associating a FOL expression with a phrase? a) Interpretation b) Augmented reality c) Semantic interpretation d) Augmented interpretation
Answer: c Explanation: Semantic interpretation is the process of associating a FOL expression with a phrase.
11. What is meant by compositional semantics? a) Determining the meaning b) Logical connectives c) Semantics d) None of the mentioned
Answer: a Explanation: Compositional semantics is the process of determining the meaning of P*Q from P, Q and *.
12. What is used to augment a grammar for arithmetic expression with semantics? a) Notation b) DCG notation c) Constituent d) All of the mentioned
Answer: b Explanation: DCG notation is used to augment a grammar for arithmetic expression with semantics and it is used to build a parse tree.
13. What can’t be done in the semantic interpretation? a) Logical term b) Complete logical sentence c) Both Logical term & Complete logical sentence d) None of the mentioned
Answer: c Explanation: Some kind of sentence in the semantic interpretation can’t be logical term nor a complete logical sentence.
14. How many verb tenses are there in the English language? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
Answer: c Explanation: There are three types of tenses available in english language are past, present and future.
15. Which is used to mediate between syntax and semantics? a) Form b) Intermediate form c) Grammer d) All of the mentioned
16. What is meant by quasi-logical form? a) Sits between syntactic and logical form b) Logical connectives c) All of the mentioned d) None of the mentioned
Answer: a Explanation: It can be translated into a regular first-order logical sentence, So that it Sits between syntactic and logical form.
17. How many types of quantification are available in artificial intelligence? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
Answer: b Explanation: There are two types of quantification available. They are universal and existential.
18. What kind of interpretation is done by adding context-dependant information? a) Semantic b) Syntactic c) Pragmatic d) None of the mentioned
19. How many issues are available in describing degree of belief? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
Answer: b Explanation: The main issues for degree of belief are nature of the sentences and the dependance of degree of the belief.
20. What is used for probability theory sentences? a) Conditional logic b) Logic c) Extension of propositional logic d) None of the mentioned
Answer: c Explanation: The version of probability theory we present uses an extension of propositional logic for its sentences.
21. Where does the dependance of experience is reflected in prior probability sentences? a) Syntactic distinction b) Semantic distinction c) Both Syntactic & Semantic distinction d) None of the mentioned
Answer: a Explanation: The dependance on experience is reflected in the syntactic distinction between prior probability statements.
22. Where does the degree of belief is applied? a) Propositions b) Literals c) Variables d) Statements
23. How many formal languages are used for stating propositions? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
Answer: b Explanation: The two formal languages used for stating propositions are propositional logic and first-order logic.
24. What is the basic element of a language? a) Literal b) Variable c) Random variable d) All of the mentioned
Answer: c Explanation: The basic element for a language is the random variable, which can be thought as a part of world and its status is initially unknown.
25. How many types of random variables are available? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
Answer: c Explanation: The three types of random variables are boolean, discrete and continuous.
26. Which is the complete specification of the state of the world? a) Atomic event b) Complex event c) Simple event d) None of the mentioned
Answer: a Explanation: An atomic event is the complete specification of the state of the world about which the event is uncertain.
27. Which variable cannot be written in entire distribution as a table? a) Discrete b) Continuous c) Both Discrete & Continuous d) None of the mentioned
Answer: b Explanation: For continuous variables, it is not possible to write out the entire distribution as a table.
28. What is meant by probability density function? a) Probability distributions b) Continuous variable c) Discrete variable d) Probability distributions for Continuous variables
29. How many terms are required for building a bayes model? a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
Answer: c Explanation: The three required terms are a conditional probability and two unconditional probability.
30. What is needed to make probabilistic systems feasible in the world? a) Reliability b) Crucial robustness c) Feasibility d) None of the mentioned
Answer: b Explanation: On a model-based knowledge provides the crucial robustness needed to make probabilistic system feasible in the real world.
31. Where does the bayes rule can be used? a) Solving queries b) Increasing complexity c) Decreasing complexity d) Answering probabilistic query
Answer: d Explanation: Bayes rule can be used to answer the probabilistic queries conditioned on one piece of evidence.
32. What does the bayesian network provides? a) Complete description of the domain b) Partial description of the domain c) Complete description of the problem d) None of the mentioned
Answer: a Explanation: A Bayesian network provides a complete description of the domain.
33. How the entries in the full joint probability distribution can be calculated? a) Using variables b) Using information c) Both Using variables & information d) None of the mentioned
Answer: b Explanation: Every entry in the full joint probability distribution can be calculated from the information in the network.
34. How the bayesian network can be used to answer any query? a) Full distribution b) Joint distribution c) Partial distribution d) All of the mentioned
Answer: b Explanation: If a bayesian network is a representation of the joint distribution, then it can solve any query, by summing all the relevant joint entries.
35. How the compactness of the bayesian network can be described? a) Locally structured b) Fully structured c) Partial structure d) All of the mentioned
Answer: a Explanation: The compactness of the bayesian network is an example of a very general property of a locally structured system.
36. To which does the local structure is associated? a) Hybrid b) Dependant c) Linear d) None of the mentioned
Answer: c Explanation: Local structure is usually associated with linear rather than exponential growth in complexity.
37. Which condition is used to influence a variable directly by all the others? a) Partially connected b) Fully connected c) Local connected d) None of the mentioned
38. What is the consequence between a node and its predecessors while creating bayesian network? a) Functionally dependent b) Dependant c) Conditionally independent d) Both Conditionally dependant & Dependant
1. What is the field of Natural Language Processing (NLP)? a) Computer Science b) Artificial Intelligence c) Linguistics d) All of the mentioned
2. NLP is concerned with the interactions between computers and human (natural) languages. a) True b) False
Answer: a Explanation: NLP has its focus on understanding the human spoken/written language and converts that interpretation into machine understandable language.
3. What is the main challenge/s of NLP? a) Handling Ambiguity of Sentences b) Handling Tokenization c) Handling POS-Tagging d) All of the mentioned
Answer: a Explanation: There are enormous ambiguity exists when processing natural language.
4. Modern NLP algorithms are based on machine learning, especially statistical machine learning. a) True b) False
5. Choose form the following areas where NLP can be useful. a) Automatic Text Summarization b) Automatic Question-Answering Systems c) Information Retrieval d) All of the mentioned
6. Which of the following includes major tasks of NLP? a) Automatic Summarization b) Discourse Analysis c) Machine Translation d) All of the mentioned
Answer: d Explanation: There is even bigger list of tasks of NLP. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Natural_language_processing#Major_tasks_in_NLP.
7. What is Coreference Resolution? a) Anaphora Resolution b) Given a sentence or larger chunk of text, determine which words (“mentions”) refer to the same objects (“entities”) c) All of the mentioned d) None of the mentioned
Answer: b Explanation: Anaphora resolution is a specific type of coreference resolution.
8. What is Machine Translation? a) Converts one human language to another b) Converts human language to machine language c) Converts any human language to English d) Converts Machine language to human language
Answer: a Explanation: The best known example of machine translation is google translator.
9. The more general task of coreference resolution also includes identifying so-called “bridging relationships” involving referring expressions. a) True b) False
Answer: a Explanation: Refer the definition of Coreference Resolution.
10. What is Morphological Segmentation? a) Does Discourse Analysis b) Separate words into individual morphemes and identify the class of the morphemes c) Is an extension of propositional logic d) None of the mentioned
11. Given a stream of text, Named Entity Recognition determines which pronoun maps to which noun. a) False b) True
Answer: a Explanation: Given a stream of text, Named Entity Recognition determines which items in the text maps to proper names.
12. Natural Language generation is the main task of Natural language processing. a) True b) False
Answer: a Explanation: Natural Language Generation is to Convert information from computer databases into readable human language.
13. OCR (Optical Character Recognition) uses NLP. a) True b) False
Answer: a Explanation: Given an image representing printed text, determines the corresponding text.
14. Parts-of-Speech tagging determines ___________ a) part-of-speech for each word dynamically as per meaning of the sentence b) part-of-speech for each word dynamically as per sentence structure c) all part-of-speech for a specific word given as input d) all of the mentioned
Answer: d Explanation: A Bayesian network provides a complete description of the domain.
15. Parsing determines Parse Trees (Grammatical Analysis) for a given sentence. a) True b) False
Answer: a Explanation: Determine the parse tree (grammatical analysis) of a given sentence. The grammar for natural languages is ambiguous and typical sentences have multiple possible analyses. In fact, perhaps surprisingly, for a typical sentence there may be thousands of potential parses (most of which will seem completely nonsensical to a human).
16. IR (information Retrieval) and IE (Information Extraction) are the two same thing. a) True b) False
Answer: b Explanation: Information retrieval (IR) – This is concerned with storing, searching and retrieving information. It is a separate field within computer science (closer to databases), but IR relies on some NLP methods (for example, stemming). Some current research and applications seek to bridge the gap between IR and NLP. Information extraction (IE) – This is concerned in general with the extraction of semantic information from text. This covers tasks such as named entity recognition, Coreference resolution, relationship extraction, etc.
17. Many words have more than one meaning; we have to select the meaning which makes the most sense in context. This can be resolved by ____________ a) Fuzzy Logic b) Word Sense Disambiguation c) Shallow Semantic Analysis d) All of the mentioned
Answer: b Explanation: Shallow Semantic Analysis doesn’t cover word sense disambiguation.
18. Given a sound clip of a person or people speaking, determine the textual representation of the speech. a) Text-to-speech b) Speech-to-text c) All of the mentioned d) None of the mentioned
Answer: b Explanation: NLP is required to linguistic analysis.
19. Speech Segmentation is a subtask of Speech Recognition. a) True b) False
/ Youtube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCGFNZxMqKLsqWERX_N2f08Q
Follow For Latest Updates, Study Tips & More Content!
Login with your site account
Remember Me
Not a member yet? Register now
Register a new account
Are you a member? Login now
100+ Solved Artificial Intelligence MCQs Questions & Answers
Artificial Intelligence MCQs On AI introduction, What is AI, Foundations of AI, History of AI, Problem Solving, Searching for Solutions, Types of Search Strategies, Uninformed Search, Breadth-First Search, Depth-First Search, Iterative Deepening, Functions, Local Search Algorithms and Optimization Problems, Adversarial Search: Minmax Algo, Alpha Beta Pruning, Introduction to Reasoning and Knowledge Representation, Propositional Logic, Rules of Inferences, First Order logic.
Syntax and semantics, Inference in first-order logic, Forward and Backward chaining, Resolution, Uncertainty, and Reasoning Bayes’ Theorem, Decision Making, Decision Network, Supervised and Unsupervised, Classification, Clustering, Decision Tree, Introduction to Prolog
Artificial Intelligence MCQs
1. Who is the father of AI? A. Karl Peason B. John Mccarthy C. Mark D. James Gosling View Answer Answer: B
2. Artificial Intelligence Introduce In? A. 1956 B. 1965 C. 1962 D. 1955 View Answer Answer: A
3. Machine Learning Is Introduced In? A. 1959 B. 1956 C. 1969 D. 1965 View Answer Answer: A
4. Formula Of A* Algorithm Is. A. F(N)=G(N) + H(N) B. F(N)=G(N) – H(N) C. F(N)=G(N) / H(N) D. F(N)=G(N) * H(N) View Answer Answer: A
5. 8- Puzzle Problem Without Heuristic Vales Are Also Called? A. Uninformed Search B. Informed Search C. Bubble Sort D. Binary Search View Answer Answer: A
6. 8- Puzzle Problem With Heuristic Vales Are Also Called? A. Uninformed Search B. Informed Search C. Bubble Sort D. Binary Search View Answer Answer: B
7. The Science And Engineering Of Making Intelligent Machines Called? A. Ai B. Machine Learning C. Deep Learning D. Data Mining View Answer Answer: A
8. Python Developed In ? A. 1989 B. 1998 C. 1997 D. 1979 View Answer Answer: A
9. Google Recommendations Are Called? A. Ai B. Machine Learning C. Data Mining D. Data Where Housing View Answer Answer: A
10. Python Was Created By? A. Guido Rossum B. Arthur Samuel C. John Mccarthy D. James Gosling View Answer Answer: A
11. Encounter Some Missing Values, Corrupted Data, And Remove Unnecessary Data Called? A. Data Mining B. Data Cleaning C. Redundancy Control D. Data Where Housing View Answer Answer: B
12. Clustering Is A Problem Of? A. Regression B. Classification C. Un-Supervised Learning D. Reinforcement View Answer Answer: C
13. Whose Machine Learning Type Is Based On Reward? A. Supervised Learning B. Reinforcement C. A & B Both D. Un-Supervised Learning View Answer Answer: B
14. Robot’s “Arm” Is Called? A. Actuator B. Effector C. Manipulator D. Sensors View Answer Answer: A
15. The Conference That Launches The Ai Revolution Was Held In? A. Harvard B. Dartmouth C. New York D. London View Answer Answer: B
16. What Is Ai ? A. Playing Games B. Programming With Your Own Intelligence C. Making Machines Intelligent D. Solve Problems View Answer Answer: C
17. Algorithm Is A Supervised Learning Method For Multilayer Perceptron? A. Back Propagation B. Classification C. Clustering D. Grouping View Answer Answer: A
18. The Process Of Deriving Meaningful Information From A Lot of Data Is Called? A. Extraction B. Data Mining C. Data Where Housing D. Abstraction View Answer Answer: B
19. NLP Stands For? A. Neural Language Processing B. Natural Language Processing C. Network Language Processing D. None Linear Problem View Answer Answer: B
20. The Process Of Splitting The Whole Data Into Smaller Chunks Called? A. Splitting B. Tokenization C. Sorting D. Division View Answer Answer: B
21. Normalize Words Into Its Base Form Or Root Form? A. Spanning B. Stemming C. Sorting D. Normalization View Answer Answer: B
22. To Overcome The Limitation Of Stemming —— Is Used ? A. Lemmatization B. Normalization C. Erosion D. Spanning View Answer Answer: A
23. A Set Of Commonly Used Words In Any Language, Not Just English ? A. Higher Language B. Stop Words C. Predefine Words D. Common Words View Answer Answer: B
24. In Which Conference John Mccarthy First Coined The Term “Artificial Intelligence” In 1956 ? A. Dartmouth Conference. B. Acm Conference C. Aaai Conference D. Aaai Conference View Answer Answer: A
25. Which Programming Language Is Best Choice For Development Of Ai ? A. Python B. Java C. Dot .Net D. Mat-Lab View Answer Answer: A
27. There Are How Many Steps In Machine Learning To Solve A Problem ? A. 3 Steps B. 5 Steps C. 7 Steps D. 9 Steps View Answer Answer: C
28. In Supervised Learning There Is Given ? A. Both Inputs & Outputs B. Only Inputs C. Only Outputs D. None View Answer Answer: A
29. In Unsupervised Learning There Is Given. A. Both Inputs & Outputs B. Only Inputs C. Only Outputs D. None View Answer Answer: B
30. In Supervised Learning Type Of Data Is. A. Labeled Data B. Unlabeled Data C. Both D. None View Answer Answer: A
31. In Unsupervised Learning Type Of Data Is. A. Labeled Data B. Unlabeled Data C. Both D. None View Answer Answer: B
32. Which Algorithm Is Example Of Supervised Learning ? A. K-Nearest Neighbors B. K-Means C. Both D. None View Answer Answer: A
33. Which Algorithm Is Example Of Unsupervised Learning ? A. K-Means B. K-Nearest Neighbors C. Both D. None View Answer Answer: A
34. What Is Date The Birth Of Ai ? A. 1958 B. 1965 C. 1956 D. 1959 View Answer Answer: C
35. What Is The Name Of First Research Lab For Ai ? A. Allen Institute Of Ai B. Robotics Laboratory C. First Al Laboratory D. Turing Institute View Answer Answer: C
36. In Which Year First Ai Research Lab Developed ? A. 1956 B. 1959 C. 1965 D. 1960 View Answer Answer: B
37. First Robot Was Introduced To General Motors Assembly Line In ? A. 1960 B. 1959 C. 1965 D. 1956 View Answer Answer: A
38. First Robot Was Introduced In 1960 To Which Assembly Line ? A. Ai Laboratory B. General Motor’s Assembly Line C. Allen Institute Of Ai D. Turing Institute View Answer Answer: B
39. The First Al Chat-Bot Name Which Introduced In 1961 ? A. Alexa B. Siri C. Eliza D. Cortana View Answer Answer: C
40. Who Won 2005 Darpa Grand Challenge ? A. Stanford Team B. Red Team C. Team Gray D. Team Terramax View Answer Answer: A
41. When Was Developed Ibm Watson ? A. 2017 B. 2011 C. 2015 D. 2019 View Answer Answer: B
42. What Is The Purpose Of Ibm Watson ? A. Computer Hardware B. Making Games C. Chatbot D. Question Answer System View Answer Answer: D
43. On Which Platform Alexa Assistant Is Working ? A. Pixabay B. Amazon C. Google D. Yahoo View Answer Answer: B
44. Why We Need Ai Those Days ? A. Massive Amount Of Data B. To Develop Machines C. Decrease Population D. Increase Population View Answer Answer: A
45. Which Algorithm Is Example Of Reinforcement Learning ? A. Supervised Learning B. Q-Learning C. Unsupervised Learning D. Semi Supervised Learning View Answer Answer: B
46. Unsupervised Learning Solves Which Type Of Problems ? A. Clustering B. Regression C. Classification D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: A
47. Supervised Learning Solves Which Type Of Problems ? A. Clustering B. Regression C. Classification D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: C
48. Reinforcement Learning Solve Which Type Of Problems ? A. Clustering B.Reward Based C. Regression D. Classification View Answer Answer: B
Read Also >> Computer Organization – Assembly Language MCQs
49. In Reinforcement Learning Type Of Data Is. A. Labeled Data B. Unlabeled Data C. No Pre-Defined Data D. Both A & B View Answer Answer: C
50. In Supervised Learning Training Is Under. A. External Supervision B. Internal Supervision C. No Supervision D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: A
51. In Unsupervised Learning Training Is Under. A. External Supervision B. Internal Supervision C. No Supervision D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: C
52. In Reinforcement Learning Training Is Under. A. External Supervision B. Internal Supervision C. No Supervision D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: C
53. In Supervised Learning Output Is. A. Known B. Unknown C. Both A & B D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: A
54. In Unsupervised Learning Output Is. A. Known B. Unknown C. Both A & B D. Understand Patterns And Discover Output View Answer Answer: D
55. In Reinforcement Learning Output Is. A. Understand Patterns And Discover Output B. Known C. Follow Trail And Error Method D. Unknown View Answer Answer: C
56. What Is Example Of Regression ? A. Predict Stock Market Price B. Spam And Non-Spam Emails C. Transactions That Are Fraud In Nature D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: A
57. What Is Example Of Classification ? A. Predict Stock Market Price B. Spam And Non-Spam Emails C. Transactions That Are Fraud In Nature D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: B
58. What Is Example Of Clustering ? A. Predict Stock Market Price B. Spam And Non-Spam Emails C. Transactions That Are Fraud In Nature D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: C
59. Which Is Regression Algorithm. A. Linear Regression B. Logistic Regression C. Both A & B D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: A
60. Which Is Classification Algorithm. A. Linear Regression B. Logistic Regression C. Both A & B D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: B
61. Output Of Regression Model Is. A. Categorical Quantity B.Continuous Quantity C. Both A & B D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: B
62. Output Of Classification Model Is. A. Categorical Quantity B.Continuous Quantity C. Both A & B D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: A
63. Decision Tree Is Which Type Of Machine Learning Algorithm. A. Supervised Learning B. Q-Learning C. Unsupervised Learning D. Semi Supervised Learning View Answer Answer: A
64. In Decision Tree Root Node Represent. A. Input B. Output C. Predictor Variable D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: C
65. In Decision Tree Each Leaf Node Represent. A. Input B. Output C. Predictor Variable D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: B
66. Multiple Decision Tree Combine To Make A. A. K-Means B. Cnn C. Random Forest D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: C
67. If You Want To Avoid Over-Fitting You Use. A. K-Means B. Random Forest C. Cnn D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: B
68. The Sample Dataset That Does Not Include In Bootstrapped Dataset Is Called. A. Bag Of Words B. Tfidf C. Out-Of-Bag (Oob)Dataset D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: C
69. In Real World, How Much Data Is Not Included In Bootstrap Dataset ? A. 1/3rd B. 2/3rd C. 0/3rd D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: A
70. Naive Bayes Solve Which Type Of Problems. A. Classification B. Regression C. Both A & B D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: A
71. The Approach That Is Used By Naive Bayes To Solve A Problem. A. Realistic Approach B. Probabilistic Approach C. Both A & B D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: B
72. Which Variable Or Which Feature Best Splits The Data. A. Information Gain B. Entropy C. Both A & B D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: C
73. Why Random Forest ? A. More Accuracy B. Avoid Over-Fitting C. Bagging D. All Of Them View Answer Answer: D
74. Which Algorithm Is Used To Classify Data Into Different Classes ? A. Random Forest B. Knn C. Svm D. Linear Regression View Answer Answer: C
75. Box-Plot Is Mainly Used In ? A. Data Distribution B. Data Gathering C. Exploratory Data Analysis D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: C
76. Which Concept Deep Learning Used To Solve Complex Problems. A. Svm B. Neural Networks C. Knn D. Cnn View Answer Answer: B
77. Limitation Of Machine Learning is. A. To Handle High Dimensional Data B. To Give Accurate Output C. To Handle Low Dimensional Data D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: A
78. Deep Learning Is One Of The Only Method By Which We Can Overcome The Challenges Of. A. Prediction B. Feature Extraction C. Training Model D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: B
79. The First Layer Of Deep Learning Is Known As. A. Input Layer B. Output Layer C. Hidden Layer D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: A
80. A Single Layer Perceptron is. A. Linear Classifier B. Binary Classifier C. Both A & B D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: C
81. Multilayer Perceptron Contain One Or More Hidden Layer That’s Why It Considers. A. Neural Network B. Deep Neural Network C. Svm D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: B
82. A Very Important Concept Of The Multiple Layer Perceptron Is. A. Feature Extraction B. Data Processing C. Back Propagation D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: C
83. Training A Neural Network Is All About. A. Inputs B. Back Propagation C. Desired Outputs D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: B
84. Which Method Is Used To Reduced The Error / Loss In The Network. A. Gradient Descent B. Gbm C. Svm D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: A
85. For Scaling Which Method Is Used. A. Scaling B. Minmaxscaler C. Measuring D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: B
86. Breaking A Complex Sentences Into Words Is Called. A. Stemming B. Lemmatization C. Tokenization D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: C
87. Normalizing Words Into Its Base Form Is Known As. A. Stemming B. Lemmatization C. Tokenization D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: A
88. The Morphological Analysis Of Words Is Done By. A. Stemming B. Lemmatization C. Tokenization D. None Of Them View Answer Answer: B
89. The Intelligence Displayed By Humans And Other Animals Is Termed. A. Constance B. Ability C. Natural Intelligence D. Cognition View Answer Answer: C
90. An Evolved Definition Of Artificial Intelligence Led To A Phenomenon Known As The A. Formulation B. Data Processing C. Ai Effect D. Machination View Answer Answer: C
91. The Nodes That Have No Child Is Called____? A. Dead Node B. Root Node C. Both Of Them D. None Of These View Answer Answer: A
92. If A Machine Answers Ambiguous Questions, Then It Is Called. A. Machine B. Intelligent Machine C. Local Machine D. Fast Machine View Answer Answer: B
93. A Systematic Approach H To Solve A Problem Is Called . A. Problem Space B. Line Space C. Tree Space D. None Of These View Answer Answer: A
94. The Graphical Representation Of Solution Space Can Also Be Done With___? A. Node B. Tree C. Table D. None Of These View Answer Answer: B
95. The Node Which Has No Parent Is Called___. A. Leaf Node B. Decision Node C. Both A And B D. Root Node View Answer Answer: D
96. After Finding All The Child Of A Node, Then A Node Is Said To Be ? A. Open Node B. Closed Node C. Child Node D. Middle Node View Answer Answer: B
97. A Node That Has One Or More Link Between Parent And Itself Is Called____. A. Decendant B. Ancestor C. Root D. None Of These View Answer Answer: A
98. Blind Search Is Also Known As. A. Informed Search B. Heuristic Search C. Uninformed Search D. Simple Search View Answer Answer: A
99. Number Of Nodes Expending From A Node To Calculate An Average Is Called. A. Height Of Tree B. Depth Of Tree C. Level Of Tree D. Branching Factor View Answer Answer: D
100. The Lowest Leaf Of A Tree. A. Height Of A Tree B. Length Of A Tree C. Level Of A Tree D. None Of A Tree View Answer Answer: A
101. Category Of Information That Control A Search . A. Dfs B. Bfs C. Linear Search D. Heuristic Search View Answer Answer: D
102. The Search That Stops Instantly After Finding The Solution. A. Optimal Search B. Non-Optimal Search C. Informed Search D. Depth First Search View Answer Answer: B
103. The Major Problem With Breath First Search Is. A. Space B. Time C. Resources View Answer Answer: A
104. Deeping Progression Emulates Two Techniques. A. Dfs & Beam Search B. Bfs & Beam Search C. Dfs & Bfs View Answer Answer: C
105. Brute Force Search Is Used When We Have___. A. Finite Node B. Infinite Node C. Primary Node D. None Of These View Answer Answer: A
Read More >> Artificial Intelligence Quiz
Share this:
Related posts.
[…] 8. Artificial Intelligence MCQs […]
- Artificial Intelligence MCQs
- Intelligent Agents
- Natural Language Processing
- Problem Solving Agents
- Partial Order Planning
- Expert System
- Fuzzy Logics
- Neural Networks
- Rule Based Systems
- Semantic Networks
- Bayesian Networks
- Alpha Beta Pruning
- Text Mining
- Reinforcement Learning
- Human Computer Interaction
- AI Reference
- AI Tutorials
- Top 5 AI Courses
- Other Reference
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Learn Machine Learning
- Best Python Books
Artificial Intelligence Agents MCQ
Intelligent Agents MCQs : This section focuses on "Agents" in Artificial Intelligence. These Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) should be practiced to improve the AI skills required for various interviews (campus interviews, walk-in interviews, company interviews), placements, entrance exams and other competitive examinations.
A. agent B. environment C. Both A and B D. None of the Above
Explanation: An AI system is composed of an agent and its environment.
A. An agent is anything that can perceive its environment through sensors B. An agent is anything that can change its environment through sensors C. An agent is anything that can control its environment through sensors D. None of the Above
Explanation: An agent is anything that can perceive its environment through sensors and acts upon that environment through effectors
A. Sensors and Actuators B. Sensors C. Perceiver D. Perceiver and Sensor
Explanation: An agent is anything that can be viewed as perceiving and acting upon the environment through the sensors and actuators.
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
Explanation: There are 4 types of agents in artificial intelligence
A. Model based B. Utility based C. Simple reflex D. target based
Explanation: The four types of agents are Simple reflex, Model based, Goal based and Utility based agents.
A. Behavior of Agent B. Percept C. Percept Sequence D. Agent Function
Explanation: Percept is agent's perceptual inputs at a given instance.
A. Perceiving B. Observing C. Learning D. Sequence
Explanation: An agent can improve its performance by storing its previous actions.
A. being reasonable B. being sensible C. having good sense of judgment. D. All of the above
Explanation: Rationality is nothing but status of being reasonable, sensible, and having good sense of judgment.
A. performance measures B. Percept Sequence C. reaction D. actions
Explanation: Rationality of an agent does not depends on reaction
A. Perceptual Measure, Environment, Actuators, and Sensors B. Performance Measure, Environment, Actuators, and Sensors C. Performance Measure, Entity, Actuators, and Sensors D. Performance Measure, Environment, Agent Function, and Sensors
Explanation: The problem the agent solves is characterized by Performance Measure, Environment, Actuators, and Sensors (PEAS).
A. Architecture B. Agent Program C. Architecture + Agent Program D. None of the Above
Explanation: Agent's structure can be viewed as - Agent = Architecture + Agent Program
A. Discrete / Continuous B. Static / Dynamic C. Deterministic / Non-deterministic D. No agent / Multiple agents
Explanation: No agent / Multiple agents is not Properties of Environment.
A. Problem B. Solution C. Agent D. Observation
Explanation: Task environments will pose a problem and rational agent will find the solution for the posed problem.
A. Discrete B. Continuous C. Episodic D. Non-deterministic
Explanation: chess is example of Discrete Properties of Environment
A. Dynamic B. Static C. Semi Dynamic D. Continuous
Explanation: As the problem in crossword puzzle are posed at beginning itself, So it is static.
A. Environment does not change with the passage of time B. Agent performance changes C. Environment does not change with the passage of time, but Agent performance changes D. Environment will be changed
Explanation: If the environment does not change with the passage of time, but the agent performance changes by time.
A. Computers in space and earth B. Image categorization techniques C. Statistical data on image pixel intensity value and histograms D. All of the above
Explanation: An environment is something which agent stays in.
A. Sensors B. MEMS C. Actuators D. Agent Function
Explanation: Micro ElectroMechanical System uses miniaturized accelerometers and gyroscopes and is used to produce actuators.
A. Relaxed B. Relational C. Both A and B D. None of the Above
Explanation: Because an agent may experience any kind of situation, So that an agent should use all kinds of architecture.
A. Decision-making algorithm B. conditional algortihm C. Complex algorithm D. None of the Above
Explanation: Decision-making and learning algorithms can operate over the joint state space and thereby serve to implement and used to improve the computational activities.
Also check :
- PHP Exception Handling MCQ
* You must be logged in to add comment.
- AI MCQ Topics
Have an account?

problem solving by searching

34 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
1. What is the main task of a problem-solving agent?
a) Solve the given problem and reach to goal
b) To find out which sequence of action will get it to the goal state
c) All of the mentioned
d) None of the mentioned
2. What is state space?
a) The whole problem
b) Your Definition to a problem
c) Problem you design
d) Representing your problem with variable and parameter
3. The problem-solving agent with several immediate options of unknown value can decide what to do by just examining different possible sequences of actions that lead to states of known value, and then choosing the best sequence. This process of looking for such a sequence is called Search.
4. A search algorithm takes _________ as an input and returns ________ as an output.
a) Input, output
b) Problem, solution
c) Solution, problem
d) Parameters, sequence of actions
5. A problem in a search space is defined by one of these state.
a) Initial state
b) Last state
c) Intermediate state
d) All of the mentioned
6. The Set of actions for a problem in a state space is formulated by a ___________
a) Intermediate states
b) Initial state
c) Successor function, which takes current action and returns next immediate state
7. A solution to a problem is a path from the initial state to a goal state. Solution quality is measured by the path cost function, and an optimal solution has the highest path cost among all solutions.
8. What is the major component/components for measuring the performance of problem solving?
a) Completeness
b) Optimality
c) Time and Space complexity
9.Which is the best way to go for Game playing problem?
a) Linear approach
b) Heuristic approach (Some knowledge is stored)
c) Random approach
d) An Optimal approach
10.Which search strategy is also called as blind search?
a) Uninformed search
b) Informed search
c) Simple reflex search
How many types are available in uninformed search method?
Which search is implemented with an empty first-in-first-out queue?
a) Depth-first search
b) Breadth-first search
c) Bidirectional search
When is breadth-first search is optimal?
a) When there is less number of nodes
b) When all step costs are equal
c) When all step costs are unequal
What is the space complexity of Depth-first search?
How many parts does a problem consists of?
Which search algorithm imposes a fixed depth limit on nodes?
a) Depth-limited search
b) Depth-first search
c) Iterative deepening search
d) Bidirectional search
Which search implements stack operation for searching the states?
c) Breadth-first search
What is the other name of informed search strategy?
a) Simple search
b) Heuristic search
c) Online search
How many types of informed search method are in artificial intelligence?
Which search uses the problem specific knowledge beyond the definition of the problem?
a) Informed search
d) Uninformed search
Which function will select the lowest expansion node at first for evaluation?
a) Greedy best-first search
b) Best-first search
c) Depth-first search
What is the heuristic function of greedy best-first search?
a) f(n) != h(n
b) f(n) < h(n)
c) f(n) = h(n)
d) f(n) > h(n)
Which search is complete and optimal when h(n) is consistent?
a) Best-first search
c) Both Best-first & Depth-first search
d) A* search
Which is used to improve the performance of heuristic search?
a) Quality of nodes
b) Quality of heuristic function
c) Simple form of nodes
Which search method will expand the node that is closest to the goal?
b) Greedy best-first search
c) A* search
A heuristic is a way of trying ___________
a) To discover something or an idea embedded in a program
b) To search and measure how far a node in a search tree seems to be from a goal
c) To compare two nodes in a search tree to see if one is better than another
A* algorithm is based on ___________
a) Breadth-First-Search
b) Depth-First –Search
c) Best-First-Search
d) Hill climbing
A* is optimal if h(n) is an admissible heuristic-that is, provided that h(n) never underestimates the cost to reach the goal.
What is the evaluation function in A* approach?
a) Heuristic function
b) Path cost from start node to current node
c) Path cost from start node to current node + Heuristic cost
d) Average of Path cost from start node to current node and Heuristic cost
What is the space complexity of Greedy search?
Heuristic function h(n) is ________
a) Lowest path cost
b) Cheapest path from root to goal node
c) Estimated cost of cheapest path from root to goal node
d) Average path cost
The name “best-first search” is a venerable but inaccurate one. After all, if we could really expand the best node first, it would not be a search at all; it would be a straight march to the goal. All we can do is choose the node that appears to be best according to the evaluation function.
Best-First search is a type of informed search, which uses ________________ to choose the best next node for expansion.
a) Evaluation function returning lowest evaluation
b) Evaluation function returning highest evaluation
c) Evaluation function returning lowest & highest evaluation
d) None of them is applicable
Best-First search can be implemented using the following data structure.
c) Priority Queue
d) Circular Queue
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone

- Switch skin
Problem Solving Techniques MCQs with Answers
Welcome to the Problem Solving Techniques MCQs with Answers . In this post, we have shared Problem Solving Techniques Online Test for different competitive exams. Find practice Problem Solving Techniques Practice Questions with answers in Aptitude Test exams here. Each question offers a chance to enhance your knowledge regarding Problem Solving Techniques.
Problem-solving entails several steps, including defining the issue, pinpointing its underlying cause, prioritizing and evaluating potential solutions, and finally implementing the chosen resolution. It’s important to note that there isn’t a universal problem-solving approach that applies to all situations.
Problem Solving Techniques Online Quiz
By presenting 3 options to choose from, Problem Solving Techniques Quiz which cover a wide range of topics and levels of difficulty, making them adaptable to various learning objectives and preferences. Whether you’re a student looking to reinforce your understanding our Student MCQs Online Quiz platform has something for you. You will have to read all the given answers of Problem Solving Techniques Questions and Answers and click over the correct answer.
- Test Name: Problem Solving Techniques MCQ Quiz Practice
- Type: MCQ’s
- Total Questions: 40
- Total Marks: 40
- Time: 40 minutes
Note: Questions will be shuffled each time you start the test. Any question you have not answered will be marked incorrect. Once you are finished, click the View Results button. You will encounter Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) related to Problem Solving Techniques , where three options will be provided. You’ll choose the most appropriate answer and move on to the next question without using the allotted time.
Wrong shortcode initialized
Download Problem Solving Techniques Multiple Choice Questions with Answers Free PDF
You can also download Problem Solving Techniques Questions with Answers free PDF from the link provided below. To Download file in PDF click on the arrow sign at the top right corner.
If you are interested to enhance your knowledge regarding English, Physics , Chemistry , Computer , and Biology please click on the link of each category, you will be redirected to dedicated website for each category.
World Economic Integration Agreements MCQs with Answers
World famous programming languages mcqs with answers, related articles.

Direction Sense MCQs with Answers
Logical games and puzzles mcqs with answers, surds and indices mcqs with answers, data sufficiency mcqs with answers, logical games and riddles mcqs with answers, problem solving and decision making mcqs with answers, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
These MCQ questions cover various aspects of AI problem-solving agents, including algorithms, search strategies, optimization techniques, and problem-solving methods, providing a comprehensive overview of this area in AI. 1. What is the primary objective of a problem-solving agent in AI? a) To find the most cost-effective solution.
This set of Artificial Intelligence Multiple Choice Questions & Answers (MCQs) focuses on "Problem Solving". 1. What is the main task of a problem-solving agent? a) Solve the given problem and reach to goal b) To find out which sequence of action will get it to the goal state c) All of the mentioned d) None of the mentioned View Answer
Artificial Intelligence MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) with Tutorial, Introduction, History of Artificial Intelligence, AI, AI Overview, types of agents, intelligent agent, agent environment etc. ... Explanation: Problem-solving agents are the goal-based agents that use different search strategies and algorithms to solve a given problem. 37 ...
These Multiple Choice Questions (mcq) should be practiced to improve the AI skills required for various interviews (campus interviews, walk-in interviews, company interviews), placements, entrance exams and other competitive examinations. 1. What is the main task of a problem-solving agent? A. Solve the given problem and reach to goal B.
Artificial Intelligence Questions & Answers - Agents. This set of Artificial Intelligence Multiple Choice Questions & Answers (MCQs) focuses on "Agents". 1. Which instruments are used for perceiving and acting upon the environment? a) Sensors and Actuators. b) Sensors. c) Perceiver. d) None of the mentioned. View Answer.
1000+ Artificial Intelligence MCQ are arranged chapter wise! Start practicing now for exams, online tests, quizzes, and interviews! AI MCQ PDF covers topics like AI Basics, AI Agents, Problem Solving, Knowledge & Reasoning, AI Application, Fuzzy Logic, NLP, Strong & Weak AI, AI Robots & Subfields
Chapter 3 Solving Problems by Searching . When the correct action to take is not immediately obvious, an agent may need to plan ahead: to consider a sequence of actions that form a path to a goal state. Such an agent is called a problem-solving agent, and the computational process it undertakes is called search.. Problem-solving agents use atomic representations, that is, states of the world ...
A. Search B. Problem C. State D. State Space. 3. A … is a representation of problem elements at a given moment. A. Search B. Problem C. State D. State Space. 4. State whether the following statements about the state space are True. i) A state-space forms a graph in which the nodes are states and the arch between nodes are actions.
The problem solving agent chooses a cost function that reflects its own performance measure. The solution to the problem is an action sequence that leads from initial state to goal state and the ...
MCQ Answer is: d. 3. The problem-solving agent with several immediate options of unknown value can determine that what to do by just investigating the various possible sequences of actions that lead to states of known value, and then selecting the best sequence among all. This kind of looking for such a sequence is commonly called Search.
An agent which needs user inputs for solving any problem; An agent which can solve any problem on its own without any humanintervention; An agent which needs an exemplary similar problem defined in its knowledge base prior to the actual problem; All of the above; Answer: B) An agent which can solve any problem on its own without any ...
1. What is the main task of a problem-solving agent? A. Solve the given problem and reach to goal B. To find out which sequence of action will get it to the goal state C. Both A and B D. None of the Above Ans : C Explanation: The problem-solving agents are one of the goal-based agents. 2. What is Initial state + Goal state in Search Terminology ...
The first example we will examine is the vacuum world. This can be formulated as a problem as follows: States: The agent is in one of two locations, each of which might or might not contain dirt. Thus there are 2 x 2^2 = 8 possible world states. Initial state: Any state can be designated as the initial state.
The problem-solving agent performs precisely by defining problems and several solutions. So we can say that problem solving is a part of artificial intelligence that encompasses a number of techniques such as a tree, B-tree, heuristic algorithms to solve a problem. We can also say that a problem-solving agent is a result-driven agent and always ...
Uninformed Search Algorithms. Goal Formulation. Problem Formulation. Unknown Environment. Observable Environment. Discrete Environment. Known Environment. Deterministic Environment. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Reflex Agents, Problem Solving Agents, Uninformed Search Algorithms and more.
Artificial Intelligence MCQs On AI introduction, What is AI, Foundations of AI, History of AI, Problem Solving, Searching for Solutions, Types of Search Strategies, Uninformed Search, Breadth-First Search, Depth-First Search, Iterative Deepening, Functions, Local Search Algorithms and Optimization Problems, Adversarial Search: Minmax Algo, Alpha Beta Pruning, Introduction to Reasoning and ...
Artificial Intelligence Agents MCQ. Intelligent Agents MCQs : This section focuses on "Agents" in Artificial Intelligence. These Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) should be practiced to improve the AI skills required for various interviews (campus interviews, walk-in interviews, company interviews), placements, entrance exams and other competitive examinations.
a) A goal state is unreachable from any state. b) A goal state is denied access. c) A goal state is reachable from every state. d) None of the mentioned. View Answer. 5. In which state spaces does the online-dfs-agent will work? a) Irreversible state spaces. b) Reversible state spaces.
3. Multiple Choice. 3. The problem-solving agent with several immediate options of unknown value can decide what to do by just examining different possible sequences of actions that lead to states of known value, and then choosing the best sequence. This process of looking for such a sequence is called Search.
Problem Solving Question 1: Arrange the stages of the problem-solving process in the correct order: A. Identifying the problem. B. Generating potential solutions. C. Implementing the chosen solution. D. Evaluating the outcomes. E. Analyzing the available information.
a) Solve the given problem and reach to goal b) To find out which sequence of action will get it to the goal state c) All of the mentioned d) None of the mentioned The problem-solving agent with several immediate options of unknown value can decide what to do by just examining different possible sequences of actions that lead to states of known ...
Test Name: Problem Solving Techniques MCQ Quiz Practice. Type: MCQ's. Total Questions: 40. Total Marks: 40. Time: 40 minutes. Note: Questions will be shuffled each time you start the test. Any question you have not answered will be marked incorrect. Once you are finished, click the View Results button. You will encounter Multiple Choice ...
Computational thinking skill is a new framework that belongs to the hybrid modes of thinking. This study aims to explore the effect of the problem-solving laboratory and gender in practicing computational thinking skills. Learning media is pursued by designing experimental-based learning using smartphone sensors. A smartphone sensor was used to facilitate students to measure physical ...
Reshape the agent-client relationship by prioritizing clear communication and exceptional results. ... Problem-solving. Real estate transactions rarely run perfectly smoothly. Your ability to ...
Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) has shown strong advantages in urban multi-intersection traffic signal control, but it also suffers from the problems of non-smooth environment and inter-agent coordination. However, most of the existing research on MARL traffic signal control has focused on designing efficient communication to solve the environment non-smoothness problem, while ...