Business Analysis Problem Solving Techniques
Why is problem solving important to the business analyst.
The expression problem solving refers to the intellectual process that people go through to uncover, analyse and solve problems. Problem solving is a major discipline within business analysis. You’ll often hear business analysts state that the thing they love about their work is solving problems. This makes sense because as a business analyst, your role is to identify and solve problems in an organisation.

Examples of Business Analysis Problem Solving
Here are some examples of problem-solving scenarios that a business analyst might face:
- Process Improvement: This is about improving a organisation’s manufacturing or operational processes. You would gather data on current processes, identify bottlenecks, and work with the team to design and implement a more efficient workflow.
- Decreasing Sales: You would be determining why a company’s sales have been decreasing. To solve this problem, you would analyse sales data, conduct customer surveys, and review competitors’ strategies to determine the root cause of the issue.
- Customer Retention: This where you would be be tasked with improving customer retention rates. You would conduct surveys to gather feedback, analyse customer data, and work with the marketing team to develop targeted retention strategies.
- Cost Reduction: You are asked to reduce costs for a company by analysing the budget, identifying areas where costs can be reduced without compromising quality, and work with the team to implement cost-saving measures.
- New Product Development: This is where you are asked to assist in developing a new product. You would conduct market research to determine customer needs, develop product specifications, and work with the product development team to ensure that the product meets customer requirements.
These are just a few examples of the types of problems that a business analyst may solve. The key is to approach each problem with a structured, analytical mindset and work collaboratively with stakeholders to find the best solution.
Process Improvement Example
To further expand on this here is an example of how you could could solve a process improvement problem.
Problem : A manufacturing company is experiencing delays in production due to bottlenecks in their production process.
- Define the problem: Gather data on the production process and identify the specific bottlenecks causing the delays.
- Analyse the process: Use process mapping tools to visually map out the production process and identify areas for improvement.
- Identify solutions: Work with the production team to brainstorm solutions to the bottlenecks identified in the process analysis. Possible solutions could include streamlining the process flow, improving the quality of raw materials, or upgrading equipment.
- Evaluate alternatives: Evaluate the potential impact of each solution and determine the most effective solution based on the resources available to the company.
- Implement the solution: Work with the production team to implement the chosen solution and monitor the results to ensure that the bottleneck has been successfully resolved.
- Continuous improvement: Continue to monitor the production process and make adjustments as needed to ensure that the process remains efficient and effective.
By using a structured approach to problem-solving, you can help the manufacturing company to identify and solve bottlenecks in their production process, resulting in improved productivity, reduced costs, and increased customer satisfaction.
Problem Solving Techniques
There are many techniques that you can use to help solve problems in a business environment. Here are some common tools that can be used for problem-solving. These techniques can be used in brainstorming sessions / workshops or as personal thinking tools.
Brainstorming
This tool helps to generate new ideas and solutions to a problem by encouraging open discussion and collaboration.
Process Mapping
This tool helps to visually map out the current process to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement.
Root Cause Analysis
This tool helps to identify the underlying cause of a problem by looking at the relationship between various factors. Root Cause Analysis is another common technique and assumes that systems and events are interrelated. An action in one area triggers an action in another, and another, and so on. By tracing back these actions, you can discover where the problem started and how it grew into the symptom you are now facing. There are three basic causes of problems: physical, human and organisational.
The Five Whys
The Five Whys technique is simply the process of asking “why” enough times that you eventually get to the root cause of a problem. It is an effective way to solving problems that can be used by any business analyst to improve a business process or write better requirements. Learn more about this questioning technique in “Why” is the How of Getting to the Root Cause of a Problem .
Mind Mapping
This visual technique is used to outline information around a central word or phrase. This central concept may form the known issue that may be causing the problem. Learn more about Mind Mapping in How to Explore a Problem Using a Mind Map and 6 Strategic Categories .
Fishbone Diagram
This tool helps to identify the various factors that contribute to a problem by creating a diagram that looks like a fishbone. Like Mind Mapping, Fishbone Analysis is a visual technique for exploring a central problem or concept. This tool is also called the Ishikawa Diagram as it was first used by Dr. Kaoru Ishikawa of the University of Tokyo in 1943. Learn more about this technique in How to Identify the Likely Causes of a Problem with a Fishbone Diagram .
SWOT Analysis
This tool helps to identify the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats facing a business.
Pareto Chart
This tool helps to identify the most important factors contributing to a problem by plotting them in a bar chart.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
This tool helps to evaluate the costs and benefits of different solutions to a problem to determine the most effective option.
Decision Matrix
This tool helps to compare different options by evaluating various criteria and assigning weights to each criterion.
CATWOE can be used as a stand-alone tool or can be combined with other techniques to ensure that the identified problem has been given full consideration, i.e. you don’t have a problem statement that is really a solution instead. CATWOE allows you to look at the issue from a variety of perspectives: customers, actors, transformation process, world view, owner and environmental constraints.
These are just a few examples of the tools and techniques that can be used by a business analyst to solve problems. The key is to select the most appropriate tool for the specific problem at hand and use it to guide the problem-solving process.
The Community
Modern analyst blog, community blog.
- Member Profiles
Networking Opportunities
Community spotlight, business analysis glossary, articles listing, business analyst humor, self assessment.
- Training Courses
- Organizations
- Resume Writing Tips
- Interview Questions
Let Us Help Your Business
Advertise with us, rss feeds & syndication, privacy policy.

Problem Solving for Business Analysts
This article explores the discipline of problem solving. Some might consider problem solving an art, while others might define it as science. The reality is a little in between since part of problem solving involves creativity, which by definition cannot be rationalized as science since we are basically unaware or not conscious of it occurring. Creative formulation of new concepts and ideas is a process lies deep within the sub consciousness and we are only aware of the output of the creative process; a new idea is a good example. We don’t understand how the idea was created, but we know we thought of it.
This article does consider the creative process and instead deems it out of scope. Instead a process for problem solving is proposed that defines a number of phases that can be rationally quantified, executed and basically tested and verified.
Introduction
What does it mean to solve a problem? It relies upon two things occurring in the following order; an issue, or undesirable state that remains to cause angst, disadvantage, some negative consequence, or a limited capability and as a result some drive to overcome this situation through the formulation of some kind of a solution to resolve, nullify, or improve the current state of affairs.
How do we solve problems? Some people would say, by thinking. Thinking about what? The problem, right? Not necessarily. Thinking about the problem may help the situation and provide a starting point, but if thinking about the problem alone is not immediately returning positive inspiration and results then you are probably selling yourself short, being too narrow minded in breath and/or depth or focused on the symptoms rather than the cause. If the solution is not obvious, then there is obviously something missing from the equation.
For languages sake of descriptions, the term ‘problem’ is sometimes used interchangeably with the word ‘issue’. We don’t say ‘issue solving’, only ‘problem solving’. Issue is used since it is a more positive expression of the situation. One might say that there are no problems, only issues.
Practical Context
Undertaking business analysis, business architecture, or enterprise architecture involve the use of a broad spectrum of knowledge and best practice in frameworks and techniques to solve business problems. Apart from information relative to the professional practices, there are other domains such as the specific context in the organisation; the drivers & motivations, constraints, legacies, culture, etc. and issue or problem.
Finding a solution to a problem involves some kind of change within the organisation to be realized and formulated that could include a new product or service, capability, technology improvement, process maturity uplift, etc. All of these examples represent solutions to underling issues/problems that impact capability, and value to shareholders, customers, partners and suppliers.
Solving business problems always involves some kind of starting point, and a finishing point in terms of where in the spectrum one lies with respect to the problem and the solution.

Important Elements of Consideration
There are a number of important elements of problem solving which will be explored in detail later when considering the proposed overall process of problem solving. See below;
· Problem Statement: Describes the nature of the issue at hand
· Scope & Information: Associated information contained within boundaries of consideration
· Association and Relationships: Linkages between information within the scope
· Rationale: The logical deduction within the scope that links the problem to the solution
· Solution: A defined change in the system that nullifies, the problem and/or problem driver
The following are a series of sequential phases that should occur to complete a problem solving exercise, which would result in a solution to the problem statement. The phases can be viewed as a waterfall. If however a phase cannot be completed, it means that a previous stage is incomplete and requires further exploring. Hence each phase has an optional feedback loop.
Problem Statement
The problem itself should be understood as something discrete, defined or quantifiable. It can be represented as question or a statement that describes something. Problems can also be ambiguous in that they are hard to understand or pin down as something concrete. Ambiguous problems require further exploration that can occur from proceeding to the next phase of defining the scope, and then returning to reevaluate the problem statement.
Definition of Scope
The scope of the problem is extremely important and provides the platform to which all other considerations are included and excluded. A good analogy to scope is the expressions of ‘ring fencing’. Picture yourself actually laying a fence around an area to encapsulate something. The goal of building a fence is to keep something in, and to keep something out. Seems obvious but it’s worth thinking about this in terms of information and problem solving. All information that needs to be considered is within the fence line, and everything else is outside.
This is important from a planning perspective since if one knows what information needs to be considered, one must review the information. Because the information is known one can actually plan and put constraints around this; who needs to be consulted, where the information is obtained from, what systems and resource needs to be drawn upon.
Scope itself is a constraint. The output or solution to a problem is directly dependent on the information that went into the problem solving process. Information that is critical to formulating the correct solution is essential to being included in the scope. This can be demonstrated through a mathematical equation.
Take the following equation, which the problem is to find the value of X;
X = Y + 10
Consider for a second that the problem is X, and X cannot be determined. What can be determined is that Y has the value of 5.
Unfortunately, due to poor research Y is not considered, only X. This equation is them impossible to solve and a solution is not found.
If however, you broadened the scope to include Y (Equals 5) then you could add 5 to 10 and have the solution;
This may seem elementary but it highlights that without proper considering and scoping, one’s perspective may not be adequate to see the whole picture.
Quite often in business some information is considered, but not everything due to time constraints and economic pressure guiding a shorter term perspective on the solution. Often when this is done the depth of analysis is limited resulting in shallow or knee jerk reactions and band aid solutions that do not address the underlying cause.
In this sense scoping can be strategic since it takes into account the broader perspective including a broader more considerate base of information that is often not focused on the short term.
Resolving Ambiguity: Ambiguity factors
Resolving ambiguity is very import. When there is confusion or uncertainty statements made become imprecise approximations that fuel a culture of anxiety. People need to have the right knowledge at the right time to solve problems by making sound decisions. It’s important to note that nothing sure footed can really be achieved when there is confusion.
Resolving ambiguity or confusion is present in the following situations. Note that the following does not include any human communication dynamics.
· Missing Information: Information that is not present
· Incorrect information: Information that can be verified by other information to be incorrect
· Conflicting Information: Information in at least two separate places that contradicts
· Duplicate information: Same or similar information that is in more than one place
· Incomplete information: Information that is present but has an unsatisfactory level of detail
How do you know if you’re missing information? Sometimes this is obvious based on the existing information. (You can see the outline of the footprint.). Other times there is no footprint, all your have is your current information, which is the best starting point for further information and traceability.
Traceability
Traceability is the art of defining concepts and their associated connection points. Consider a dot to dot drawing or a mind map; what presents is an interconnected network. This network can be used to explore its boundaries, both its breath of scope and level of scope. This two way exploration can always start with the existing information, considering other related concepts and relationships.
For example, if the word ‘Interface’ was on a mind map, I could also draw other branches with connections that say ‘client’, ‘server’, ‘api’, ‘web service’, ‘xml’, ‘meta-data’, ‘contract’, ‘data flow’ etc. The root of this exploration is the word ‘interface’.
Traceability can be explored within a mind map, or in any other conceptual model where you are connecting information, to other information through some kind of relationships.
Root Cause Analysis
Since the entire scope has now been defined, the process of identifying the problem symptoms and problem causes can begin. The symptoms are obvious effects, outcomes, metrics, sales figures, costs, performance measures; negative qualitative or quantitative measurements.
Asking the question why is the basis for root cause analysis. It considers the result of questions and then traces backwards to underlying causes. If we ask the question why, the result is the answer and potentially the basis to another question. This is an iterative process that is continued until the underlying cause is uncovered. Note, that the underlying cause should also be within the bounds of the scope already defined.
For example, the problem is a person driving a car along the highway breaks down and is stuck on the side of the road. The problem is “Car has broken down”. See below for root cause analysis.
· Question: Why has the car broken down?
· Answer: Engine has overheated.
· Question: Why has the engine overheated?
· Answer: No water in the radiator.
· Question: Why is there no water in the radiator?
· Answer: Didn’t get the car serviced
· Question: Why didn’t the car get serviced?
· Answer: Forgot to get the car serviced.
· Question: Why did you forget to get the car serviced?
· Answer: It was a new car and the owner never had to get the car serviced before.
· Question: What is the servicing requirements of the car?
· Answer: Get it serviced 6 months after purchase, then 12 months thereafter. (Stated in contract.)
· Question: Did the owner read the contract?
· Answer: No. Owner didn’t read the contract and was unaware of car servicing requirements.
· Problem Symptom (Effect) = “Car broken down. Can’t go anywhere. Stranded on highway.”
· Real Problem (Cause) = “Owner didn’t read the contract and had no idea that car needed to be serviced”
Identification and realization to solution
Once the underlying cause is attained through root cause analysis, the solution is often the formulation of a preventative action that is undertaken to resolve the problem symptom from ever occurring. This is usually obvious since it is only a single ‘jump’ to understand the resolution.
In the above example, the solution would be for the owner after they purchased the vehicle to read the contract or ask the sales dealer. That way they would have understood the responsibilities of owner the car and taken it in for service, preventing the breakdown from ever occurring.
A less savvy car owner would have opted for a more reactive solution. In this example, the owner could have just carried a jerrycan of water in the car. When the car breaks down the owner can simply fill the radiator up again with water and restart the car. (Assuming the engine is still working.)
The most challenging aspect to problem solving is having the right information and doing adequate work in scoping the issue. When the right information has been considered, mapping out the context and domain diagrams, the relationships can be defined; the problems and their causal drivers can easily be identified through logical deduction.
It’s also important to point out that sometimes it’s better not to be too focused on the actual problem, since as we have demonstrated here, the problem itself is just a single breadcrumb in the investigation; a mere starting point for exploration. This is what problem solving can be described as, a process of guided exploration within a domain, that has boundaries and has been defined to be within scope. Exploration starts at the symptom and goes backward, forward, underneath and around the problem to provide context and understanding of the bigger picture.
Often it’s the bigger picture that allows us the understanding to see the problem relative to the context and proceed in a process of questioning from a defined starting point to an ending point. This is one way to solve problems that starts by considering the problem statement, examining the scope boundaries and information, conducting logical deductions; asking questions and assessing answers, asking further questions etc, and deriving a solution that addresses the cause or root of the problem. Sometimes root cause analysis is not required, other times there a multiple problems, seemingly interrelated with dependencies - and this is all compounded with complexity and ambiguity of course, not to mention miss communication and misinterpretation related to human factors.
Yes, problem solving can be challenging, but it can be made less so with a methodical and logical approach that works.
Related Articles

Article/Paper Categories
Upcoming live webinars.
ACE THE INTERVIEW
Roles and Titles
- Business Analyst
- Business Process Analyst
- IT Business Analyst
- Requirements Engineer
- Business Systems Analyst
- Systems Analyst
- Data Analyst
Career Resources
- Interview Tips
- Salary Information
- Directory of Links
Community Resources
- Project Members
Advertising Opportunities | Contact Us | Privacy Policy

The 5 Steps in Problem Analysis
One technique that is extremely useful to gain a better understanding of the problems before determining a solution is problem analysis .
Problem analysis is the process of understanding real-world problems and user’s needs and proposing solutions to meet those needs. The goal of problem analysis is to gain a better understanding of the problem being solved before developing a solution.
There are five useful steps that can be taken to gain a better understanding of the problem before developing a solution.
- Gain agreement on the problem definition
- Understand the root-causes – the problem behind the problem
- Identify the stakeholders and the users
- Define the solution boundary
- Identify the constraints to be imposed on the solution
Table of Contents
Gain agreement on the problem definition.
The first step is to gain agreement on the definition of the problem to be solved. One of the simplest ways to gain agreement is to simply write the problem down and see whether everyone agrees.
Business Problem Statement Template
A helpful and standardised format to write the problem definition is as follows:
- The problem of – Describe the problem
- Affects – Identify stakeholders affected by the problem
- The results of which – Describe the impact of this problem on stakeholders and business activity
- Benefits of – Indicate the proposed solution and list a few key benefits
Example Business Problem Statement
There are many problems statement examples that can be found in different business domains and during the discovery when the business analyst is conducting analysis. An example business problem statement is as follows:
The problem of having to manually maintain an accurate single source of truth for finance product data across the business, affects the finance department. The results of which has the impact of not having to have duplicate data, having to do workarounds and difficulty of maintaining finance product data across the business and key channels. A successful solution would have the benefit of providing a single source of truth for finance product data that can be used across the business and channels and provide an audit trail of changes, stewardship and maintain data standards and best practices.
Understand the Root Causes Problem Behind the Problem
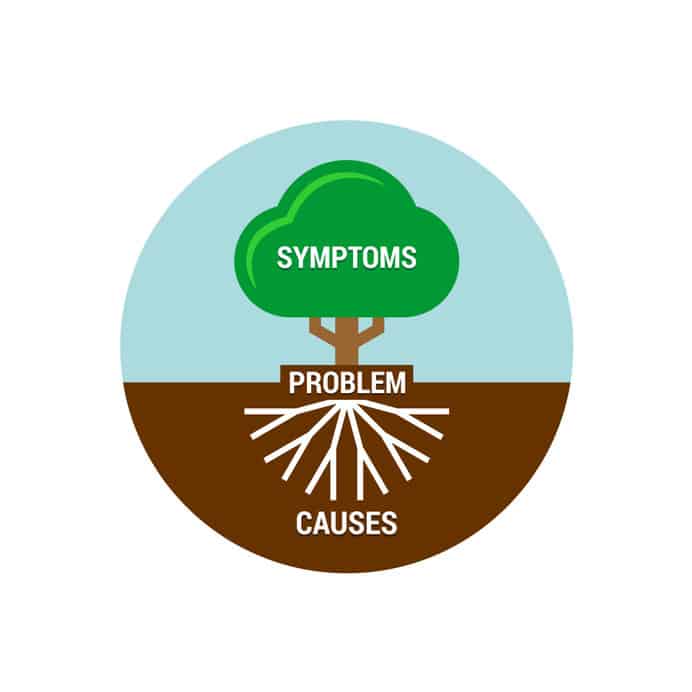
You can use a variety of techniques to gain an understanding of the real problem and its real causes. One such popular technique is root cause analysis, which is a systematic way of uncovering the root or underlying cause of an identified problem or a symptom of a problem.
Root cause analysis helps prevents the development of solutions that are focussed on symptoms alone .
To help identify the root cause, or the problem behind the problem, ask the people directly involved.
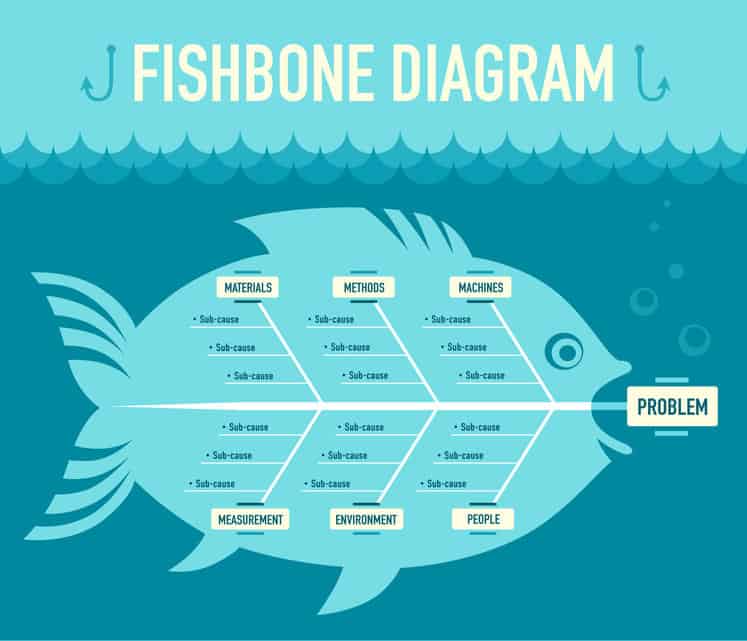
The primary goal of the technique is to determine the root cause of a defect or problem by repeating the question “Why?” . Each answer forms the basis of the next question. The “five” in the name derives from an anecdotal observation on the number of iterations needed to resolve the problem .
Identify the Stakeholders and the Users
Effectively solving any complex problem typically involves satisfying the needs of a diverse group of stakeholders. Stakeholders typically have varying perspectives on the problem and various needs that must be addressed by the solution. So, involving stakeholders will help you to determine the root causes to problems.
Define the Solution Boundary
Once the problem statement is agreed to and the users and stakeholders are identified, we can turn our attention of defining a solution that can be deployed to address the problem.
Identify the Constraints Imposed on Solution
We must consider the constraints that will be imposed on the solution. Each constraint has the potential to severely restrict our ability to deliver a solution as we envision it.
Some example solution constraints and considerations could be:-
- Economic – what financial or budgetary constraints are applicable?
- Environmental – are there environmental or regulatory constraints?
- Technical – are we restricted in our choice of technologies?
- Political – are there internal or external political issues that affect potential solutions?
Conclusion – Problem Analysis
Try the five useful steps for problem solving when your next trying to gain a better understanding of the problem domain on your business analysis project or need to do problem analysis in software engineering.
The problem statement format can be used in businesses and across industries.

Jerry Nicholas
Jerry continues to maintain the site to help aspiring and junior business analysts and taps into the network of experienced professionals to accelerate the professional development of all business analysts. He is a Principal Business Analyst who has over twenty years experience gained in a range of client sizes and sectors including investment banking, retail banking, retail, telecoms and public sector. Jerry has mentored and coached business analyst throughout his career. He is a member of British Computer Society (MBCS), International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA), Business Agility Institute, Project Management Institute (PMI), Disciplined Agile Consortium and Business Architecture Guild. He has contributed and is acknowledged in the book: Choose Your WoW - A Disciplined Agile Delivery Handbook for Optimising Your Way of Working (WoW).
Recent Posts
Introduction to Train the Trainer for a Business Analyst
No matter the industry, modern professionals need to continuously improve themselves and work on up skilling and re-skilling to maintain satisfactory success within their field. This is particularly...
CliftonStrengths for a Business Analyst | Be You
Today, the job of a business analyst is probably more challenging than ever. The already intricate landscape of modern business analysis has recently gone through various shifts, mainly due to the...
Smart. Open. Grounded. Inventive. Read our Ideas Made to Matter.
Which program is right for you?

Through intellectual rigor and experiential learning, this full-time, two-year MBA program develops leaders who make a difference in the world.
A rigorous, hands-on program that prepares adaptive problem solvers for premier finance careers.
A 12-month program focused on applying the tools of modern data science, optimization and machine learning to solve real-world business problems.
Earn your MBA and SM in engineering with this transformative two-year program.
Combine an international MBA with a deep dive into management science. A special opportunity for partner and affiliate schools only.
A doctoral program that produces outstanding scholars who are leading in their fields of research.
Bring a business perspective to your technical and quantitative expertise with a bachelor’s degree in management, business analytics, or finance.
A joint program for mid-career professionals that integrates engineering and systems thinking. Earn your master’s degree in engineering and management.
An interdisciplinary program that combines engineering, management, and design, leading to a master’s degree in engineering and management.
Executive Programs
A full-time MBA program for mid-career leaders eager to dedicate one year of discovery for a lifetime of impact.
This 20-month MBA program equips experienced executives to enhance their impact on their organizations and the world.
Non-degree programs for senior executives and high-potential managers.
A non-degree, customizable program for mid-career professionals.
Meet the 6 new faculty members joining MIT Sloan in 2024
Gensler exec: ‘Amplify your impact as you advance your career’
How can we preserve human ability in the age of machines?
Credit: Mimi Phan / Shutterstock
Ideas Made to Matter
3 business problems data analytics can help solve
Sep 18, 2023
Generative artificial intelligence is booming, the post-COVID economy wobbles on, and the climate crisis is growing. Amid this disruption, what practical problems are global businesses trying to solve in 2023?
Each year, the MIT Sloan Master of Business Analytics Capstone Project partners students with companies that are looking to solve a business problem with data analytics. The program offers unique and up-close insight into what companies were grappling with at the beginning of 2023. This year, students worked on 41 different projects with 33 different companies. The winning projects looked at measuring innovation through patents for Accenture and using artificial intelligence to improve drug safety for Takeda.
“This annual tradition is an insightful pulse check on the ‘data wish list’ of the industry’s top analytics leaders,” said MIT Sloan lecturer Jordan Levine, who leads the Capstone program.
Here are three questions that companies are seeking to answer with analytics.
1. How can data help us identify growth in specific geographic regions?
Businesses looking to open new locations or invest in real estate are using data to find areas that are poised for growth.
Understanding urbanization is important for firms like JPMorgan Chase , which aims to reach new clients and serve existing customers by opening new bank branches in U.S. cities. To get a handle on what areas are likely to grow in the future, the company is using satellite images — including land-cover segmentation from Google — to predict urbanization rates and identify hot spots .
Small and medium-sized businesses account for about 99% of U.S. companies but only 40% of the U.S. economy. Using historic transaction data and U.S. census data, Visa is looking at what parts of the U.S. have the most potential for SMB growth and what levers it can use to help develop those areas, such as helping businesses accept digital transactions.
Asset management firm Columbia Threadneedle wants to identify promising areas for real estate investment in Europe by building a predictive tool for location growth, using factors such as economic drivers, livability, connectivity, and demographics. MBAn students created a tool that predicts long-term growth potential for more than 600 cities and identifies key factors used to make those predictions.
2. How can data help us empower front-line workers?
Employees working directly with customers or in the field often have to make educated guesses and snap decisions. Companies are turning to data analytics to create support tools that will improve efficiency, accuracy, and sales.
Coca-Cola Southwest Beverages is looking to improve how front-line workers assess store inventory and create orders — a process that is now time-consuming and prone to errors. Using demographics, consumption trends, historical sales data, and out-of-stock information, a sales forecast algorithm will improve forecasting, increase sales, and simplify operations.
Handle Global , a health care supply chain technology company, is looking to help hospitals estimate budget allocation and capital expenditures for medical devices, given the churn of assets, variations in types and models, and mergers and acquisitions between manufacturers and hospital systems. The company is looking to develop a decision support tool that uses historic data to make better purchasing decisions.
3. What’s the best way to get the most from large or unwieldy datasets?
While data analytics can produce powerful results, some data is still hard to process, such as unstructured data — data that does not conform to a specific format — or large datasets. Companies are looking for ways to efficiently process and gain insight from this kind of data, which can be time-consuming and inefficient to process.
Related Articles
Health insurance pricing data is now available to competing companies, thanks to a new U.S. government regulation . But this information isn’t easy to access because of the sheer volume of data, insurer noncompliance with disclosure requirements, and data that’s broken into several different categories. Wellmark Blue Cross and Blue Shield is looking to create a coverage rate transparency tool that recommends pricing and areas for negotiation to help it maintain competitive advantage and see optimal profits.
Information services company Wolters Kluwer ’s compliance business unit helps firms meet regulatory requirements while managing risk and increasing efficiency. But verifying government documents, such as vehicle registrations, can be an error-prone and time-consuming process, and the documents have a high rejection rate. The company is looking to create a document classification system using natural language processing and computer vision that makes paperwork that is usually handled manually more accurate and easier to process.
CogniSure AI was created in 2019 to use technology to solve the problem of unstructured data, which makes it difficult to digitize the insurance underwriting industry. The company is looking to build a generic machine learning tool to process documents that are not yet automated , such as loss runs — claims histories of past losses — which have complex and varied formats and structures.
View all of the capstone projects

MBA059: Problem Solving for Business Analysts
by Dave Saboe | Feb 16, 2016 | Podcast , Start | 0 comments

In this episode, Matt Fishbeck shares a six step problem solving framework that can help you to address the right problem and come up with the best solution for your organization and customers.
After listening to this episode, you'll understand:.
- Why the skill of problem is so critical
- How to apply a 6 step problem solving framework
- How to apply problem solving techniques
- Defining the problem statement
- Defining scope
- Elicit information & resolving ambiguity
- Identifying associations and relationships
- Root cause analysis
- Solution proposal
The Problem Solving Process Start by creating the problem statement. The problem statement is a well-defined statement or question to frame the context. After you have a clear and unambiguous problem statement, define the scope of the effort. The scope definition is probably the most important stage since it basically whether or not the problem can be solved satisfactorily. Scope is defined to apply constraints to the domain of consideration. When we have scope we know what to consider and what not to consider. Therefore, all possible solutions are directly dependant on the information within the scope. Once the scope is defined, you can move on to eliciting information & resolving ambiguity. Perform a stakeholder analysis and elicit information from all known stakeholders/sources as a basis for investigation. You can use workshops, focus groups, interviews, document analysis, and other approaches to elicit information. When we elicit information, we try to remove ambiguity as ambiguity represents the unknown, liability, and risk. To reduce ambiguity, we need to consider the taxonomy of ambiguity to provide a frame of reference to how we will resolve it. Ambiguity may be:
- Missing information
- Incorrect information
- Duplicate information
- Conflicting information
- Incomplete information
The above provide a basis to ask questions concerning all information that is within scope, to challenge this information to be reliable and suitable for use. Context diagrams and domain diagram can help resolve ambiguity. Next, we identify associations and relationships to organize the information so we can derive meaning from it. Information needs to be structured, aligned, and associated that provides an additional level of meaning. This is the basis for traceability. The linking of concepts. It’s not just solely used for requirements. Once we thoroughly understand the information, we can move on to performing a root cause analysis. A root cause analysis helps you to understand the underlying cause of the problem so you can address it instead of addressing a symptom of a greater issue. There are many techniques for root cause analysis including 5 Whys and Fishbone diagrams. Now that we understand the real root cause, we can propose solutions that will address that root cause. When identifying proposed solutions, consider the scope, constraints, and relative cost and value of each option. Problem solving is not some illusive black art; it’s an analytical process that can be broken down, quantified, and analyzed to identify the root cause to give rise to a viable solution. Listen to the full episode to hear all of Matt’s examples and tips for problem solving.
Your Homework
- Begin applying Matt’s six-stage problem solving approach. Often, the most difficult part of problem solving is knowing where to start.
- Start learning the root cause analysis techniques in the Guide to the Business Analysis Body of Knowledge (BABOK). The techniques will give you more tools to help in your problem solving efforts.
Links mentioned in this episode:
- Matt’s Problem Solving article on ModernAnalyst.com
Matt Fishbeck
Senior Business Analyst and Writer
Thank you for listening to the program
Trackbacks/pingbacks.
- Think Like a Freak to be a Trusted Advisor - […] BAs solve the right problem with the right solution among multiple possible options. We’re able to see work that…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Exclusive Discount from cPrime Learning

Buy One, Get One Free


Process of Business Analytics (Step-By-Step Guide)

Varun Saharawat is a seasoned professional in the fields of SEO and content writing. With a profound knowledge of the intricate aspects of these disciplines, Varun has established himself as a valuable asset in the world of digital marketing and online content creation.
Process of Business Analytics is explained below in this article. Business analytics is a systematic approach to analyzing vast datasets to uncover trends, patterns, and insights that can inform business decisions and strategies.

Process of Business Analytics : One way to conceptualize business analysis is as a research field that assists in determining business needs and problem-solving strategies. The creation of software or system components, process enhancements, organizational modifications, or the creation of strategic plans and policies are a few examples of these solutions. Business analysis’s goal is to find solutions that address the requirement for development.
The business analysis process provides ideas and perceptions on how every project’s first framework is developed. It has the secret to directing project participants who carry out business modeling in a systematic way.
Learning is a continuous process and there is always more to explore in the field of business analytics. That’s why we would highly recommend checking out Physics Wallah’s Data Analytics course . And just for being a reader of this blog post, use the coupon code “READER” to get a special discount on the course.
So take action now and start your journey towards becoming a skilled and successful business analyst.
Table of Contents
Process of Business Analytics With Examples
Business analytics is a systematic approach to analyzing data and deriving actionable insights to drive informed decision-making, optimize processes, and achieve strategic objectives. Below is a step-by-step explanation of the business analytics process, illustrated with examples for better understanding.
1) Define Objectives and Scope:
- Example : A retail company aims to increase sales and improve customer satisfaction. The objective is to analyze customer purchasing behavior, identify trends, and develop targeted marketing strategies to enhance customer engagement and loyalty.
2) Data Collection and Integration:
- Example : The retail company collects data from various sources, including point-of-sale (POS) systems, customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, online transactions, and social media channels. Data integration tools like Talend or Apache Kafka are used to consolidate and unify data from these disparate sources into a centralized data repository.
3) Data Exploration and Preparation:
- Example : Data analysts explore the collected data to identify patterns, trends, and correlations related to customer preferences, purchasing behavior, and product preferences. They clean, preprocess, and transform the data using tools like Python or R, addressing missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies to ensure data quality and readiness for analysis.
4) Data Analysis and Modeling:
- Example : Data scientists apply statistical analysis and machine learning algorithms to analyze customer data, develop predictive models, and identify factors influencing sales and customer satisfaction. They use tools like IBM SPSS or SAS to perform regression analysis, clustering, and classification to uncover insights, forecast trends, and make data-driven recommendations.
5) Data Visualization and Reporting:
- Example : The data insights are visualized using interactive dashboards and reports created with tools like Tableau or Microsoft Power BI. The dashboards display key metrics, KPIs, and visualizations such as sales trends, customer segmentation, and product performance, enabling stakeholders to explore data, identify patterns, and make informed decisions.
6) Insight Interpretation and Action Planning:
- Example : Based on the insights derived from the data analysis and visualization, the retail company develops actionable strategies and initiatives to enhance customer engagement, optimize product offerings, and improve sales performance. For instance, they launch targeted marketing campaigns, introduce personalized promotions, and enhance product recommendations to drive customer satisfaction and loyalty.
7) Implementation and Monitoring:
- Example : The retail company implements the recommended strategies and initiatives, closely monitoring their effectiveness, impact, and ROI. They track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales growth, customer retention rates, and marketing campaign performance, using tools like Google Analytics or Adobe Analytics to measure, evaluate, and optimize their efforts continuously.
Process of business analytics with Diagram
With below conceptual diagram description, you can create a visual representation of the process of business analytics that illustrates the sequential flow, key stages, and interconnected tasks involved in transforming raw data into actionable insights, driving informed decision-making, and achieving strategic objectives in today’s data-driven business landscape.
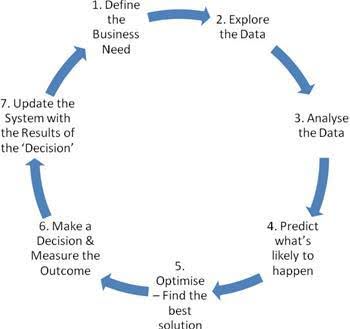
Steps in Business Analytics Process
The business analytics process is a systematic approach that enables organizations to harness the power of data to make informed decisions, drive strategic initiatives, and achieve competitive advantage. Below, we delve into a detailed exploration of the seven critical steps involved in this transformative process.
Step 1: Define Business Needs
The journey begins with a clear understanding of the organization’s objectives and challenges. Stakeholders, business users, and analysts collaborate to define specific business goals and identify the relevant data required to achieve them. Essential questions regarding data availability, usability, and sufficiency are addressed to lay a solid foundation for subsequent stages.
Step 2: Data Exploration and Preparation
Once the objectives are defined, the focus shifts to data exploration and preparation. This phase involves rigorous data cleaning, handling missing values, outlier detection, and variable transformation to ensure data integrity and reliability. Visual exploratory techniques, such as scatter plots and time series graphs, are employed to uncover patterns, correlations, and anomalies, thereby providing insights into the underlying data structure and quality.
Step 3: Data Analysis
In this stage, sophisticated statistical analysis techniques, including correlation analysis, hypothesis testing, and regression analysis, are utilized to explore relationships between variables and identify significant factors influencing the target outcome. The data is meticulously analyzed, sliced, and diced to derive actionable insights, enabling organizations to understand trends, patterns, and key drivers that impact business performance.
Step 4: Predictive Modeling
Armed with insights from the analysis phase, predictive modeling techniques, such as decision trees, neural networks, and logistic regression, are employed to forecast future trends, behaviors, and outcomes. Multiple models are evaluated based on accuracy, performance metrics, and alignment with organizational goals to select the most robust and reliable predictive model.
Step 5: Solution Optimization
The optimization stage involves leveraging the predictive model to evaluate various ‘what-if’ scenarios, simulate outcomes, and identify the optimal solution that aligns with organizational objectives, constraints, and strategic goals. By fine-tuning model parameters and evaluating alternative scenarios, organizations can make informed decisions that maximize efficiency, effectiveness, and return on investment.
Step 6: Decision Making and Outcome Measurement
With a comprehensive understanding of the insights derived from the analytics process, organizations make informed decisions, implement strategic initiatives, and take actionable steps to achieve desired outcomes. Post-implementation, the effectiveness of decisions and actions is systematically measured against predefined metrics, KPIs, and performance indicators to assess impact, identify areas for improvement, and refine strategies as needed.
Step 7: Systematic Update and Continuous Improvement
The final step in the business analytics process involves systematically updating the organizational database with insights, outcomes, and lessons learned from the decision-making process. By continuously monitoring performance, evaluating results, and integrating new insights into the database, organizations create a dynamic, evolving analytics ecosystem that fosters innovation, drives continuous improvement, and enables agile decision-making in an ever-changing business landscape.
Business analytics process is a holistic, data-driven approach that empowers organizations to transform raw data into actionable insights, informed decisions, and strategic initiatives that drive business growth, enhance competitiveness, and unlock new opportunities for innovation and success. By systematically navigating through these seven steps, organizations can harness the full potential of data analytics to achieve sustainable growth, mitigate risks, and create value for stakeholders across the enterprise.
Also Read: Graph Analytics – What Is it and Why Does It Matter?
Benefits of Business Analytics
Business analytics has emerged as a pivotal tool for organizations across industries, enabling them to transform raw data into actionable insights, informed decisions, and strategic advantages. Below are some of the key benefits associated with leveraging business analytics:
- Business analytics provides organizations with the necessary insights and information to make data-driven decisions. By analyzing historical data, current trends, and predictive analytics, decision-makers can evaluate various scenarios, assess risks, and identify opportunities, leading to more informed and effective decision-making processes.
- Business analytics enables organizations to gain a deeper understanding of customer behavior, preferences, and needs. By analyzing customer data, organizations can segment their customer base, personalize marketing strategies, improve customer engagement, and enhance overall customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- By analyzing operational data and processes, business analytics helps organizations identify inefficiencies, streamline operations, optimize resource allocation, and reduce costs. Through process optimization and performance monitoring, organizations can enhance productivity, profitability, and competitiveness in the marketplace.
- Business analytics empowers organizations to gain a competitive edge by identifying market trends, consumer preferences, and emerging opportunities. By analyzing market data, competitor performance, and industry trends, organizations can develop innovative products, services, and strategies that differentiate them from competitors and position them for success in the marketplace.
- Business analytics enables organizations to proactively identify, assess, and mitigate risks by analyzing historical data, trends, and predictive analytics. By identifying potential risks, organizations can develop strategies to minimize exposure, protect assets, and ensure business continuity, thereby enhancing resilience and sustainability in an increasingly complex and uncertain business environment.
- By leveraging business analytics to optimize sales and marketing strategies, organizations can identify new market opportunities, target high-value customers, and maximize revenue growth. Through data-driven insights, organizations can tailor their products, services, and marketing efforts to meet customer needs, drive sales, and achieve revenue targets.
- Business analytics enables organizations to develop and implement strategic plans based on data-driven insights, market trends, and predictive analytics. By analyzing internal and external data, organizations can identify opportunities, assess market dynamics, and develop strategic initiatives that align with their long-term goals and objectives.
- Business analytics provides organizations with the tools and insights to effectively communicate with stakeholders, including employees, customers, investors, and partners. By analyzing stakeholder data and feedback, organizations can identify opportunities to enhance engagement, build trust, and foster collaboration, ultimately driving organizational success and stakeholder satisfaction.
Also Check: What is the difference between big data analysis and analytics?
Process of Business Analytics Notes
Business analytics is a systematic approach to transforming raw data into actionable insights that drive informed decision-making, optimize processes, and achieve strategic objectives. The process of business analytics involves several key stages, methodologies, and techniques to extract value from data. Here are some key notes outlining the process of business analytics:
1) Define Objectives and Scope :
- Clearly articulate the business objectives, goals, and scope of the analytics project.
- Identify key stakeholders, data sources, and relevant metrics to align analytics efforts with organizational priorities and requirements.
2) Data Collection and Integration :
- Gather relevant data from various internal and external sources, including databases, CRM systems, ERP systems, web analytics tools, and third-party sources.
- Integrate and consolidate data to create a unified view of the business, ensuring data quality, consistency, and reliability.
3) Data Exploration and Preparation :
- Explore and analyze data to identify patterns, trends, correlations, and outliers.
- Cleanse, transform, and preprocess data to address missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies, ensuring data integrity and readiness for analysis.
4) Data Analysis and Modeling :
- Apply statistical analysis, machine learning, and predictive modeling techniques to derive insights, forecast trends, and uncover relationships within the data.
- Develop and evaluate predictive models, hypothesis tests, and statistical models to identify patterns, make predictions, and validate assumptions.
5) Data Visualization and Reporting :
- Visualize insights, findings, and recommendations using interactive dashboards, charts, graphs, and reports.
- Communicate complex data and insights effectively to stakeholders, decision-makers, and other relevant parties using visualization tools and storytelling techniques.
6) Insight Interpretation and Action Planning :
- Interpret findings, insights, and recommendations in the context of business objectives, goals, and challenges.
- Collaborate with stakeholders to develop actionable strategies, initiatives, and solutions based on data-driven insights and analysis.
7) Implementation and Monitoring :
- Implement recommended strategies, initiatives, and solutions to address business challenges, optimize processes, and achieve desired outcomes.
- Monitor, evaluate, and measure the impact, effectiveness, and ROI of implemented solutions using key performance indicators (KPIs), metrics, and performance analytics.
8) Continuous Improvement and Optimization :
- Continuously refine, optimize, and iterate analytics processes, methodologies, and techniques to adapt to changing business requirements, technologies, and market dynamics.
- Foster a culture of data-driven decision-making, innovation, and continuous improvement across the organization to drive growth, efficiency, and competitiveness.
5 Stages of Business Analytics Application Advancement
The application of business analytics within organizations evolves through distinct stages as companies mature in their data-driven decision-making capabilities. Understanding these stages can help organizations identify where they currently stand and what steps they need to take to advance their analytics capabilities further. Here are the five stages of business analytics application advancement:
Stage 1: Descriptive Analytics (What Happened?)
The initial stage of business analytics focuses on descriptive analytics, which involves analyzing historical data to understand past performance and trends. Organizations at this stage use basic reporting tools and techniques to summarize data, generate dashboards, and visualize key metrics and KPIs.
Descriptive analytics provides insights into what happened, allowing organizations to monitor performance, track key metrics, and gain a foundational understanding of their business operations.
Stage 2: Diagnostic Analytics (Why Did It Happen?)
As organizations progress, they move to the diagnostic analytics stage, which involves exploring data to identify patterns, correlations, and relationships to understand why specific events occurred.
At this stage, organizations leverage advanced analytics tools and techniques, such as data mining, statistical analysis, and exploratory data analysis, to uncover insights into the root causes of performance trends, anomalies, and issues. Diagnostic analytics enables organizations to diagnose problems, identify opportunities for improvement, and make data-driven decisions based on a deeper understanding of underlying factors and relationships.
Stage 3: Predictive Analytics (What Will Happen?)
In the predictive analytics stage, organizations use statistical, machine learning, and predictive modeling techniques to forecast future trends, behaviors, and outcomes based on historical data and existing patterns. By analyzing historical data, identifying predictive variables, and developing predictive models, organizations can anticipate customer behavior, market trends, operational risks, and other critical factors that impact business performance.
Predictive analytics enables organizations to proactively address challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and make informed decisions to drive growth, efficiency, and competitive advantage.
Stage 4: Prescriptive Analytics (How Can We Make It Happen?)
As organizations advance, they move to the prescriptive analytics stage, which involves leveraging advanced analytics techniques, optimization algorithms, and decision-making models to recommend actions, strategies, and solutions to achieve specific objectives and outcomes.
By combining insights from descriptive, diagnostic, and predictive analytics, prescriptive analytics enables organizations to identify the most effective courses of action, optimize decision-making processes, and align strategies with business goals. Prescriptive analytics empowers organizations to make informed decisions, optimize resources, and drive continuous improvement by providing actionable recommendations based on data-driven insights and analysis.
Stage 5: Cognitive Analytics (Automated Decision Making and Learning)
The most advanced stage of business analytics application advancement is cognitive analytics, which involves leveraging artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics capabilities to automate decision-making processes, enable real-time insights, and facilitate continuous learning and adaptation.
Cognitive analytics enables organizations to automate routine tasks, analyze complex data sets, identify hidden patterns, and make intelligent decisions based on real-time insights and analysis. By harnessing the power of cognitive computing and advanced analytics technologies, organizations can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, innovation, and agility, driving sustainable growth and competitive advantage in today’s rapidly evolving business landscape.
Also Read: What Is Big Data Analytics? Definition, Benefits, and More
Tools of Business Analytics
Business analytics tools play a crucial role in transforming raw data into actionable insights, enabling organizations to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and achieve strategic objectives. Here’s an overview of some of the key categories and examples of tools commonly used in business analytics:
1) Data Collection and Integration Tools:
- Apache Kafka : A distributed streaming platform used for building real-time data pipelines and streaming applications.
- Talend : An open-source data integration platform that enables organizations to connect, access, and manage data from various sources, ensuring data quality and consistency.
2) Data Storage and Management Tools:
- Amazon Redshift : A fully managed data warehouse service that enables organizations to analyze large datasets using SQL and BI tools.
- Google BigQuery : A serverless, highly scalable cloud data warehouse that enables real-time analytics and insights from large datasets without the need for infrastructure management.
3) Data Processing and Transformation Tools:
- Apache Spark : An open-source distributed computing system that provides in-memory processing capabilities for large-scale data processing, analytics, and machine learning tasks.
- Informatica : A data integration platform that enables organizations to transform, cleanse, and prepare data for analytics, ensuring data quality, consistency, and reliability.
4) Data Visualization and Reporting Tools:
- Tableau : A leading data visualization and business intelligence tool that enables organizations to create interactive dashboards, reports, and visualizations to explore and communicate insights from data.
- Microsoft Power BI : A business analytics service that enables organizations to visualize data, share insights across the organization, and make data-driven decisions using interactive dashboards, reports, and analytics tools.
5) Statistical Analysis and Modeling Tools:
- R : An open-source programming language and software environment specifically designed for statistical computing, data analysis, and visualization.
- Python : A versatile programming language widely used for data analysis, machine learning, and statistical modeling, with libraries such as Pandas, NumPy, and SciPy providing extensive capabilities for data manipulation, analysis, and visualization.
6) Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning Tools:
- IBM SPSS : A comprehensive statistical analysis software that enables organizations to analyze data, predict future trends, and make data-driven decisions using advanced statistical models and machine learning algorithms.
- SAS : A powerful analytics platform that provides a wide range of tools and solutions for data management, advanced analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, enabling organizations to derive insights, automate processes, and drive innovation.
7) Business Intelligence Platforms:
- Sisense : A business intelligence platform that enables organizations to simplify complex data analysis, visualize insights, and share interactive dashboards and reports across the organization.
- QlikView/Qlik Sense : Business intelligence and data visualization platforms that enable organizations to create interactive dashboards, reports, and visualizations, and make data-driven decisions using self-service analytics tools.
And for those wanting to delve even deeper into this field or enhance their skills, we
highly recommend checking out the Data Analytics Course by Physics Wallah . With their comprehensive syllabus and expert instructors, you can learn everything you need to know about business analytics in one place. Don’t forget to use the coupon code ‘ READER ‘ at checkout for a special discount!
For Latest Tech Related Information, Join Our Official Free Telegram Group : PW Skills Telegram Group
Process of Business Analytics FAQs
What is the process in business analytics.
The process in business analytics refers to a systematic approach or methodology used to analyze data, derive insights, and make informed decisions to drive organisational success.
What is the 5 step business analytics process model?
The 5-step business analytics process model typically includes stages such as data collection, data processing and preparation, data analysis, interpretation of results, and implementation of insights to achieve business objectives.
What are the stages of business analytics?
The stages of business analytics encompass data collection, data processing and preparation, exploratory data analysis, statistical analysis and modeling, interpretation of results, implementation of insights, and continuous monitoring and optimization.
What are the 7 steps to analysis?
The 7 steps to analysis generally involve defining the problem, gathering relevant data, analyzing the data, interpreting the results, validating the findings, implementing recommendations, and monitoring outcomes to ensure effectiveness and drive continuous improvement.

- Data Analytics Internships – What Does A Data Analyst Intern Do?

Data analytics internships involve working with data to identify trends, create visualizations, and generate reports. Data Analytics Internships learn to…
- Best Courses For Data Analytics: Top 10 Courses For Your Career in Trend

Best courses for data analytics: If you are looking for the best courses for data analytics, then go through this…
- Best BI Tool: Top 15 Business Intelligence Tools (BI Tools)

Discover the ultimate Business Intelligence Tools (Best BI Tools) for data-driven decision-making. Compare features, benefits, and pricing to find your…

Related Articles
- Data Analysis Techniques in Research – Methods, Tools & Examples
- 5 BI Business Intelligence Tools You Must Know in 2024
- Python for Data Analysis
- What is OLAP (Online Analytical Processing)?
- Best Data Analyst Class Online
- What Is Business Analytics Business Intelligence?
- Difference Between Data Analysis and Data Analytics: Primary Differences


The Functional BA
Unraveling the world of business analysis
Problem solving in business analysis

Problem solving is one of the core competencies of an effective business analyst.
They describe and solve problems to ensure that the root cause of a problem is well understood by all stakeholders and resolved by the solution.
Describing the problem involves ensuring that the type of problem and any underlying issues connected to the problem are clearly understood by all stakeholders.
In order to do this the stakeholders viewpoints need to be understood and well communicated to avoid any conflicts between the goals and objectives of the different stakeholders groups.
Assumptions also need to be recognized and confirmed.
The goals and objectives which are to be met by the solution needs to be explicitly stated, and alternative solutions need to be considered and possibly developed.
There are some performance measures of effective problem solving which include the following:
1. The confidence of the stakeholders in the problem solving process.
2. The selected solutions must meet the defined enterprise objectives and solve the root cause of the problem.
3. The new solution options must be effectively evaluated effectively using the problem solving process which avoids making decisions based on invalidated assumptions, preconceived notions, or other traps that may cause the wrong solution to be selected.
Share this:
Privacy overview.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Business Analytics: What It Is & Why It's Important

- 16 Jul 2019
Business analytics is a powerful tool in today’s marketplace that can be used to make decisions and craft business strategies. Across industries, organizations generate vast amounts of data which, in turn, has heightened the need for professionals who are data literate and know how to interpret and analyze that information.
According to a study by MicroStrategy , companies worldwide are using data to:
- Improve efficiency and productivity (64 percent)
- Achieve more effective decision-making (56 percent)
- Drive better financial performance (51 percent)
The research also shows that 65 percent of global enterprises plan to increase analytics spending.
In light of these market trends, gaining an in-depth understanding of business analytics can be a way to advance your career and make better decisions in the workplace.
“Using data analytics is a very effective way to have influence in an organization,” said Harvard Business School Professor Jan Hammond, who teaches the online course Business Analytics , in a previous interview . “If you’re able to go into a meeting and other people have opinions, but you have data to support your arguments and your recommendations, you’re going to be influential.”
Before diving into the benefits of data analysis, it’s important to understand what the term “business analytics” means.
Check out our video on business analytics below, and subscribe to our YouTube channel for more explainer content!
What Is Business Analytics?
Business analytics is the process of using quantitative methods to derive meaning from data to make informed business decisions.
There are four primary methods of business analysis:
- Descriptive : The interpretation of historical data to identify trends and patterns
- Diagnostic : The interpretation of historical data to determine why something has happened
- Predictive : The use of statistics to forecast future outcomes
- Prescriptive : The application of testing and other techniques to determine which outcome will yield the best result in a given scenario
These four types of business analytics methods can be used individually or in tandem to analyze past efforts and improve future business performance.
Business Analytics vs. Data Science
To understand what business analytics is, it’s also important to distinguish it from data science. While both processes analyze data to solve business problems, the difference between business analytics and data science lies in how data is used.
Business analytics is concerned with extracting meaningful insights from and visualizing data to facilitate the decision-making process , whereas data science is focused on making sense of raw data using algorithms, statistical models, and computer programming. Despite their differences, both business analytics and data science glean insights from data to inform business decisions.
To better understand how data insights can drive organizational performance, here are some of the ways firms have benefitted from using business analytics.
The Benefits of Business Analytics
1. more informed decision-making.
Business analytics can be a valuable resource when approaching an important strategic decision.
When ride-hailing company Uber upgraded its Customer Obsession Ticket Assistant (COTA) in early 2018—a tool that uses machine learning and natural language processing to help agents improve speed and accuracy when responding to support tickets—it used prescriptive analytics to examine whether the product’s new iteration would be more effective than its initial version.
Through A/B testing —a method of comparing the outcomes of two different choices—the company determined that the updated product led to faster service, more accurate resolution recommendations, and higher customer satisfaction scores. These insights not only streamlined Uber’s ticket resolution process, but saved the company millions of dollars.
2. Greater Revenue
Companies that embrace data and analytics initiatives can experience significant financial returns.
Research by McKinsey shows organizations that invest in big data yield a six percent average increase in profits, which jumps to nine percent for investments spanning five years.
Echoing this trend, a recent study by BARC found that businesses able to quantify their gains from analyzing data report an average eight percent increase in revenues and a 10 percent reduction in costs.
These findings illustrate the clear financial payoff that can come from a robust business analysis strategy—one that many firms can stand to benefit from as the big data and analytics market grows.
Related: 5 Business Analytics Skills for Professionals
3. Improved Operational Efficiency
Beyond financial gains, analytics can be used to fine-tune business processes and operations.
In a recent KPMG report on emerging trends in infrastructure, it was found that many firms now use predictive analytics to anticipate maintenance and operational issues before they become larger problems.
A mobile network operator surveyed noted that it leverages data to foresee outages seven days before they occur. Armed with this information, the firm can prevent outages by more effectively timing maintenance, enabling it to not only save on operational costs, but ensure it keeps assets at optimal performance levels.

Why Study Business Analytics?
Taking a data-driven approach to business can come with tremendous upside, but many companies report that the number of skilled employees in analytics roles are in short supply .
LinkedIn lists business analysis as one of the skills companies need most in 2020 , and the Bureau of Labor Statistics projects operations research analyst jobs to grow by 23 percent through 2031—a rate much faster than the average for all occupations.
“A lot of people can crunch numbers, but I think they’ll be in very limited positions unless they can help interpret those analyses in the context in which the business is competing,” said Hammond in a previous interview .
Skills Business Analysts Need
Success as a business analyst goes beyond knowing how to crunch numbers. In addition to collecting data and using statistics to analyze it, it’s crucial to have critical thinking skills to interpret the results. Strong communication skills are also necessary for effectively relaying insights to those who aren’t familiar with advanced analytics. An effective data analyst has both the technical and soft skills to ensure an organization is making the best use of its data.

Improving Your Business Analytics Skills
If you’re interested in capitalizing on the need for data-minded professionals, taking an online business analytics course is one way to broaden your analytical skill set and take your career to the next level
Through learning how to recognize trends, test hypotheses , and draw conclusions from population samples, you can build an analytical framework that can be applied in your everyday decision-making and help your organization thrive.
“If you don’t use the data, you’re going to fall behind,” Hammond said . “People that have those capabilities—as well as an understanding of business contexts—are going to be the ones that will add the most value and have the greatest impact.”
Do you want to leverage the power of data within your organization? Explore our eight-week online course Business Analytics to learn how to use data analysis to solve business problems.
This post was updated on November 14, 2022. It was originally published on July 16, 2019.

About the Author

What is business analytics and why is it important?
In today’s data-driven world, your business’s success hinges on your ability to extract valuable insights from vast amounts of information. Enter business analytics, the transformative discipline that empowers organizations to make informed decisions, drive growth, and gain a competitive edge. In this article, we delve into the fundamentals of business analytics, explore its key components, and, most importantly, discuss why it has become an indispensable tool for thriving in the modern marketplace.
- What is business analytics?
6 ways business analytics can help your organization
What are the types of business analytics.
- How business analytics works in different industries?
What are some tools and tricks of the trade?
- What challenges come with business analytics?
How can you advance your organization and career with business analytics?
What is business analytics .
It’s the systematic exploration, interpretation, and analysis of data to extract actionable insights that drive informed decision-making and improve organizational performance. It involves various statistical and quantitative techniques, data modeling, predictive analytics, and data visualization to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships within complex datasets.
Leveraging business analytics allows you to gain a comprehensive understanding of your business operations, customer behavior, market trends, and internal processes. This helps you identify opportunities, optimize business strategies, mitigate risks, and enhance your organization’s overall efficiency and profitability.
Business analytics methods, and how they work
- Forecasting : Since the aim of business analytics is to make data-driven decisions, business analysts use predictive modeling to analyze trends, predict outcomes, and inform business decisions. For example, you can use past sales data to predict future sales and decide how much inventory to stock for a particular season.
- Data visualization : In data visualization, insights gleaned from data sets are contextualized and communicated through visual reports, such as charts, graphs, models, and data dashboards. Analysts use data visualization techniques to make complex data easier for an audience to digest.
- Data mining: In data mining, the goal is to use machine learning, information technology, and statistical methods to discover patterns within data sets. It aims to uncover valuable information for decision-making, strategic planning, and gaining a competitive advantage.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): Because it’s impossible for humans to manage and interpret big data on our own, we use AI to automatically aggregate and identify patterns within datasets . It uses algorithms and machine learning techniques to identify patterns, trends, and correlations and generate insights and predictions.
- Optimization : This involves using mathematical algorithms and models to maximize profits, minimize costs, or optimize resource allocation. It helps organizations make informed decisions by identifying the best course of action aligned with their goals, constraints, and available data.
- Simulation: Business analysts can create a virtual representation of a real-world system or process to analyze and understand its behavior under different scenarios. Organizations can run simulations and experiment with various inputs to gain insights into potential outcomes, assess risks, and make informed decisions that optimize performance and mitigate uncertainty.
Business analytics is all about modeling quantitative data to identify the best business decisions backed by empirical information. In the world of business analytics, there’s no room for decision-making based on gut feelings.
What do business analysts do?
Because of the constant influx of data for organizations to deal with, data management and data analytics play an increasingly important role in every industry. Data analysts have a hand in an organization’s problem-solving and strategic decisions. Their actionable insights are valuable in all departments of an organization, from human resources and operations to marketing and finance.
A business analyst’s job is to gain insights from business data to solve business problems and do things like evaluate a company’s performance, run predictive analytics on customer behavior, and model marketing analytics.
Beyond data analysis, they also create data visualizations that explain the findings they glean from data sets using a wide range of communication skills and visualization tools. These help clarify the reasoning behind their actionable insights. After all, understanding the best strategic decision is one thing. Convincing key stakeholders to take that course of action is another.
Business analytics can do a lot, but what can it do for you? Here are the top six benefits:
1. Increase day-to-day operational efficiency
Business analytics helps organizations streamline their operations by identifying inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. Businesses can use data-driven analysis to optimize processes, allocate resources more effectively, and enhance productivity, ultimately driving operational efficiency to new heights.
2. Provide insights into customer behavior and habits
Organizations can delve deep into customer data to uncover valuable insights about preferences, purchasing patterns, and behaviors. This can help them personalize their marketing strategies, tailor their product offerings, and improve customer experiences to foster long-term loyalty and boost customer satisfaction.
3. Predict the impact of company initiatives
With business analytics, organizations can create data-driven forecasts that shed light on potential outcomes, allowing for proactive decision-making and risk mitigation. Analyzing historical data, market trends, and customer insights helps businesses anticipate the market response to new product launches, marketing campaigns, or strategic investments so they can allocate resources effectively.
4. Promote success through strategic and well-informed business decisions
With access to comprehensive data analysis, organizations can make strategic decisions based on insights rather than relying solely on intuition. Business analytics creates a solid foundation for informed decision-making so they can identify emerging trends, market opportunities, and potential risks. This results in more effective strategies that drive success and reduce uncertainties.
5. Evaluate and measure performance
Business analysts can monitor and measure key performance indicators (KPIs) to gauge their progress and success. Tracking these metrics and analyzing trends lets them assess the effectiveness of business strategies, identify areas for improvement, and align performance with broader company objectives as needed.
6. Leverage patterns and trends for a competitive advantage
Organizations can use advanced data analysis to uncover valuable data patterns, correlations, and trends. These insights help businesses anticipate customer demands and seize opportunities that can position them ahead of the competition.
Here are the three main types of business analytics and how each one works:
Descriptive analytics
This branch of business analytics focuses on analyzing historical data to provide insights into past events and trends. It involves summarizing and visualizing data to understand what has happened and how certain variables are related. Descriptive analytics enables organizations to uncover data patterns, trends, and anomalies, providing a foundation for making informed decisions and identifying areas for improvement.
A real-world example of descriptive analytics is tracking sales across a designated time frame, such as a business quarter or multiple years, to understand how these fluctuations resulted in the current sales figures.
Predictive analytics
Where descriptive analytics looks at the past, predictive analytics looks at the future. It uses historical data, statistical modeling, and machine learning techniques to predict future outcomes. This involves analyzing data patterns and relationships to generate forecasts and probabilities. Predictive analytics enables organizations to anticipate trends, identify potential risks and opportunities, and make proactive decisions to optimize outcomes.
For example, a company can apply predictive analytics to its finances to anticipate future cash flow and profits.
Prescriptive analytics
Prescriptive analytics goes beyond studying past data to make predictions – it uses it to create targeted solutions to business problems. It leverages advanced techniques like optimization and simulation to determine the best course of action in complex decision-making scenarios. Prescriptive analytics considers various constraints, objectives, and potential outcomes to help organizations make data-driven decisions that optimize resources, minimize risks, and maximize desired outcomes.
Prescriptive analytics in action could look like studying the results of past investments to influence future decision-making about which investments a company should (or shouldn’t) make.
How business analytics works in different industries
Because virtually every field involves some level of data management, business analytics has a hand in many industries’ decision-making processes. Here’s how it works in a few different applications:
- Health care : With predictive modeling, data analysts can anticipate future clinical, financial, and operational needs. These forecasts can apply to things like operational costs, staffing, and resource allocation, and it can also help anticipate patient outcomes.
- Marketing: Marketing companies can use business analytics to gain insight into customer behavior. This enables data-driven decision-making and lets them target their strategies and measure their marketing campaigns’ effectiveness.
- Finance: Business analytics allows finance professionals to harness vast amounts of data to predict investment performance, assess risk, and evaluate potential return on investment (ROI) to make informed decisions and optimize their investment strategies.
- Supply chain logistics: Using historical data to predict consumer demand is essential for inventory management. Business analytics can also help optimize shipping routes, vehicle performance, and delivery logistics.
- Human resources (HR): Tracking certain KPIs and employee-related data enables HR to make better-informed decisions about recruitment and organizational structure. Businesses can gain insight into their staffing needs by analyzing workforce productivity KPIs, turnover rates, and business demands.
Finding data-driven applications to business problems using big data often requires investing in the right data management and data visualization tools. Let’s take a look at some of the most commonly used business analytics tools on the market:
- Knime Analytics Platform: This user-friendly platform lets users perform machine learning, data pipelining, and advanced analytics tasks.
- Dundas Business Intelligence : This tool is known for its comprehensive features, including automatic trend forecasting, and helps organizations gain valuable insights into future patterns to make data-informed decisions.
- QlikView: This tool excels in data visualization and text analysis, helping users explore and analyze their data through intuitive visualizations and interactive dashboards.
- Sisense: This software is renowned for its data warehousing capabilities, allowing organizations to efficiently store, manage, and analyze large volumes of data.
- Splunk: Data visualization is one key feature of this tool, but it also offers powerful data search and analysis capabilities. This helps organizations gain deep insights from machine-generated data, detect anomalies, and troubleshoot issues in real time.
- Tableau: Tableau goes beyond traditional data visualization by incorporating natural language processing and text analysis.
- Tibco Spotfire: If you’re looking to do statistical and text analysis, this is the tool for you. It comes with everything you need to perform advanced statistical modeling, explore patterns and correlations, and gain insights from unstructured text data.
Before investing in a business analytics tool, consider what type of data you’re analyzing and its source. This will tell you what type of usability, functions, and statistical methods you’ll need to get the insights you want. Also, decide which dashboards will be most helpful in visualizing your data depending on the unique business problems you may face.
What challenges come with business analytics ?
Common challenges that may arise when implementing business analytics include:
- Too much data from different sources: Scattered data set sources can make it difficult to synthesize the information. Your data might also be formatted as different file types, which can further complicate the data analytics process.
- Hiring the right business analyst : While it’s hard to know which software and tools to invest in, it might be even more difficult to bring in the right talent for the job. Ensure you understand the type of data analytics your business needs so you can find the right person to handle it.
- Data storage: Storing and managing vast amounts of data requires robust infrastructure, efficient data architectures, and scalable storage solutions to ensure data accessibility, security, and optimal performance for analytics processes.
An overwhelming amount of big data drives today’s decision-making, and it’s only getting larger. Data science tools like predictive modeling and forecasting allow you to identify business decisions, initiatives, and actionable insights that can lead to sustainable success for your organization.
And with valuable benefits like improved operational efficiency and data-driven decision-making, investing in business analytics is a wise investment that can help you in the long-run. However, it’s important to weigh the costs and benefits of the tools and labor needed to do it right based on your unique needs.
If you’re inspired to leverage the power of business intelligence in your company, look no further than IMD’s Business Analytics for Leaders online program. This learning experience will equip you with a digital analytics roadmap to your company’s future success.
Subscribe for more great digital transformation content 💌
Subscribe now for exclusive content from imd.

87% of digital transformation initiatives fail. The imperative for capable digital and AI leadership is more pronounced than ever. As disruption continues to reshape the global economy, digitalization now stands as a fundamental cornerstone for organizational resilience and growth. Consumer giants like Adidas and Lego exemplify a blueprint for success, having woven digital and AI […]

In an era where data is the new currency, mastering business analytics has become crucial for leaders aiming to steer their organizations toward unprecedented growth and success. This guide is tailored for you, the business leader, to harness the power of data science and analytics in decision-making. Here, we delve into the fundamentals of business […]

Today, data is the cornerstone of decision-making and the key to business success. This puts data science and data analytics at the heart of our data-driven world, where every click, preference, and even the temperature setting of your fridge is a valuable data point. Target, a leading retail giant used data analytics to predict with […]

Businesses in the 21st century are navigating an ever-growing sea of data. In our digital era, data mining has become the driving force behind many of our advancements. We produce staggering volumes of data daily, surpassing amounts previously generated over entire decades within just a few years. Data science has emerged as the lighthouse in […]
5 Reasons Why Data Analytics is Important in Problem Solving
Data analytics is important in problem solving and it is a key sub-branch of data science. Even though there are endless data analytics applications in a business, one of the most crucial roles it plays is problem-solving.
Whether you’re fresh out of university graduate or a professional who works for an organization, having top-notch problem-solving skills is a necessity and always comes in handy.
Everybody keeps facing new kinds of complex problems every day, and a lot of time is invested in overcoming these obstacles. Moreover, much valuable time is lost while trying to find solutions to unexpected problems, and your plans also get disrupted often.
This is where data analytics comes in. It lets you find and analyze the relevant data without too much of human-support. It’s a real time-saver and has become a necessity in problem-solving nowadays. So if you don’t already use data analytics in solving these problems, you’re probably missing out on a lot!
As the saying goes from the chief analytics officer of TIBCO,
“Think analytically, rigorously, and systematically about a business problem and come up with a solution that leverages the available data .”
– Michael O’Connell.
In this article, I will explain the importance of data analytics in problem-solving and go through the top 5 reasons why it cannot be ignored. So, let’s dive into it right away.
Highly Recommended Articles:
13 Reasons Why Data Analytics is Important in Decision Making
This is Why Business Analytics is Vital in Every Business
What is Data Analytics?
Why is data analytics important in problem solving.
Problem-solving and data analytics often proceed hand in hand. When a particular problem is faced, everybody’s first instinct is to look for supporting data. Data analytics plays a pivotal role in finding this data and analyzing it to be used for tackling that specific problem.
Also, you come up with a more informed solution, not leaving anything out of the equation.
Having strong analytical skills help you dig deeper into the problem and get all the insights you need. Once you have extracted enough relevant knowledge, you can proceed with solving the problem.
Let’s see a very straightforward daily life example to examine the importance of data analytics in problem-solving; what would you do if a question appears on your exam, but it doesn’t have enough data provided for you to solve the question?
Obviously, you won’t be able to solve that problem. You need a certain level of facts and figures about the situation first, or you’ll be wandering in the dark.
5 Reasons Why Data Analytics Is Important in Problem Solving
Now that we’ve established a general idea of how strongly connected analytical skills and problem-solving are, let’s dig deeper into the top 5 reasons why data analytics is important in problem-solving .
1. Uncover Hidden Details
Data analytics is great at putting the minor details out in the spotlight. Sometimes, even the most qualified data scientists might not be able to spot tiny details existing in the data used to solve a certain problem. However, computers don’t miss. This enhances your ability to solve problems, and you might be able to come up with solutions a lot quicker.
2. Automated Models
Automation is the future. Businesses don’t have enough time nor the budget to let manual workforces go through tons of data to solve business problems.
Instead, what they do is hire a data analyst who automates problem-solving processes, and once that’s done, problem-solving becomes completely independent of any human intervention.
The tools can collect, combine, clean, and transform the relevant data all by themselves and finally using it to predict the solutions. Pretty impressive, right?
However, there might be some complex problems appearing now and then, which cannot be handled by algorithms since they’re completely new and nothing similar has come up before. But a lot of the work is still done using the algorithms, and it’s only once in a blue moon that they face something that rare.
However, there’s one thing to note here; the process of automation by designing complex analytical and ML algorithms might initially be a bit challenging. Many factors need to be kept in mind, and a lot of different scenarios may occur. But once it goes up and running, you’ll be saving a significant amount of manpower as well as resources.
3. Explore Similar Problems
Once you’re there, the process gets a lot smoother because you get references to how such problems were tackled in the past.
Such data is available all over the internet and is automatically extracted by the data analytics tools according to the current problems. People run into difficulties all over the world, and there’s no harm if you follow the guidelines of someone who has gone through a similar situation before.
4. Predict Future Problems
While we have already gone through the fact that data analytics tools let you analyze the data available from the past and use it to predict the solutions to the problems you’re facing in the present, it also goes the other way around.
Whenever you use data analytics to solve any present problem, the tools you’re using store the data related to the problem and saves it in the form of variables forever. This way, similar problems faced in the future don’t need to be analyzed again. Instead, you can reuse the previous solutions you have, or the algorithms can predict the solutions for you even if the problems have evolved a bit.
5. Faster Data Extraction
However, with the latest tools, the data extraction is greatly reduced, and everything is done automatically with no human intervention whatsoever.
When businesses come across a problem, around 70%-80% is their time is consumed while gathering the relevant data and transforming it into usable forms. So, you can estimate how quick the process could get if the data analytics tools automate all this process.
Even though many of the tools are open-source, if you’re a bigger organization that can spend a bit on paid tools, problem-solving could get even better. The paid tools are literal workhorses, and in addition to generating the data, they could also develop the models to your solutions, unless it’s a very complex one, without needing any support of data analysts.
What problems can data analytics solve? 3 Real-World Examples
Employee performance problems .
By Analyzing data sets of employee attendance, productivity, and issues that tend to delay in resolution. Through that, preparing refresher training plans, and mentorship plans according to key weak areas identified.
Sales Efficiency Problems
Imagine a Business that is spread out across multiple cities or regions
Business Investment Decisions Problems
By analyzing the number of subscribers, sales, the trends in usage, the demographics, you can decide which peace of software has a better Return on Investment over the long term.
Throughout the article, we’ve seen various reasons why data analytics is very important for problem-solving.
Many different problems that may seem very complex in the start are made seamless using data analytics, and there are hundreds of analytical tools that can help us solve problems in our everyday lives.
As an IT Engineer, who is passionate about learning and sharing. I have worked and learned quite a bit from Data Engineers, Data Analysts, Business Analysts, and Key Decision Makers almost for the past 5 years. Interested in learning more about Data Science and How to leverage it for better decision-making in my business and hopefully help you do the same in yours.
Recent Posts
In today’s fast-paced business landscape, it is crucial to make informed decisions to stay in the competition which makes it important to understand the concept of the different characteristics and...
- Conferences
- Discussions
- Claim PDU/CDU
- Project Management
- Whitepapers
- Advertise with BA Times
- Contribute to BA Times

10 Common Problems Business Analysts Help Solve
Written by Esta Lessing on July 27, 2022 . Posted in Articles .
Often Business Analysts are swept up by the hustle and bustle of project life and simply do what is needed to get to the end goal. Business Analysts focus on delivering a valuable solution to business stakeholders and they forget just how much value they add by help solving many problems along the way.
This short article outlines 10 of the common problems that Business Analysts help solve in the organization and especially when helping to deliver progressive change initiatives for the organization.
In no specific order of importance, find out more about these common problems that Business Analysts help solve and see if you can recognize some as familiar problems you often help solve too:
#1 Unclear or conflicting stakeholder expectations
Stakeholders may have unclear or conflicting expectations of what a project will deliver which hampers progress and can lead to disappointment.
Business analysts can help mitigate this problem is to ensure that all stakeholders have a shared understanding of what is achievable and what the project will deliver.
A Business Analyst helps to solve this problem by facilitating workshops with stakeholders to reach agreement on project outcomes, and by creating clear documentation of requirements that can be referred to throughout the project.
#2 Inadequate resources
Many projects also suffer from inadequate resources these days, which can lead to delays and frustration. Experienced Business Analysts can help identify which skillsets are needed to help deliver a project during the planning stages of the project to ensure resources are request early during the project set up stages.
Some more ways that a Business Analyst helps to solve this problem is by monitoring project progress and highlighting to the Project Manager where risks of resource shortages may occur. Where possible Business Analysts also help to create mitigating actions to avoid potential project delays due to resource constraints.
#3 Poor communication
Poor communication is often a root cause of many problems that occur during a project. Miscommunication can lead to misunderstandings, errors, and delays.
A Business Analyst can help to improve communication by facilitating communication between stakeholders, creating clear and concise documentation, and holding regular meetings to update everyone on the project status.
#4 Unclear or changing requirements
Unclear or changing requirements are one of the most common problems faced by Business Analysts. This can cause confusion amongst team members, as well as delays in completing the project.
One way that a business analyst can help solve or minimize this problem within a project is to ensure that requirements are well-defined and agreed upon by all stakeholders before work begins, whether they are working in Waterfall projects or Agile based iterations. This can be done through creating a requirements document which outlines all the requirements for the project and getting sign-off from relevant stakeholders.
In an Agile environment, the Business Analyst can help manage this issue by ensuring that user stories are well-defined and understood by all team members before work begins on them.
#5 Lack of engagement from stakeholder
Another common problem faced by Business Analysts is lack of engagement from stakeholders. This can be due to several reasons, such as stakeholders being too busy, or not feeling invested in the project or even mistrust of the business analyst.
The Business Analyst can solve this by ensuring a clear stakeholder engagement plan is a key activity within the project. The Business Analyst can also work to build relationships with stakeholders and ensure that they are kept updated on the project status and progress.
#6 Ineffective or missing processes
Ineffective or missing processes can lead to a number of problems within a project, such as errors, delays and duplication of work. This is often due to a lack of understanding of current processes being followed within the area the project is trying to solve for.
A way that the Business Analyst can help to solve this problem is by conducting a business process analysis to understand the current processes in place and identify areas for improvement. The Business Analyst can also work with the relevant stakeholders to develop new or improved processes where needed.
#7 Lack of understanding of user needs
A very common problem that a Business Analyst face is a lack of understanding of user needs. This is not because the Business Analyst is ineffective when engaging stakeholders necessarily, it can be due to several reasons including unavailability of key stakeholders and time or resource constraints that exist within the organization.
If there is a lack of understanding of user needs, it can lead to the development of a solution that does not meet the needs of the users, and ultimately will not be successful.
The Business Analyst can help to solve this problem by conducting user research and requirements elicitation to understand the needs of the users that will be using the solution. This can be done through a few methods such as interviews, focus groups, workshops or surveys.
#8 Lack of understanding of business goals
Many business analysts also find that there is a lack of understanding of business goals within an organization. This can make it difficult to align projects with organizational objectives and ensure that the right solutions are delivered. Often a Business Analyst will be assigned the task of developing a business case for a potential solution without having clear alignment of business objectives.
A way the Business Analyst can help to establish a clear understanding of the business goals is to work with stakeholders to document the business goals and objectives for the project. This can be done through workshops or interviews to understand the pain points that the organization is experiencing, and what they are looking to achieve by undertaking the project.
#9 Change fatigue
Another common yet less tangible problem faced in organizations is change fatigue. This is when staff members become resistant to change because change happens so frequently within the organizational area. This situation can make it difficult for Business Analysts who has to introduce new changes to business stakeholders and it becomes hard for Business Analysts to achieve their requirement outcomes.
One strategy a Business Analyst can follow to help manage the change fatigue of their stakeholders is to ensure that they keep them updated and engaged at the appropriate level throughout the project. They should at the same time aim to champion the benefits of the change to stakeholders and try to avoid asking stakeholders to repeat requirements or information that may have been articulated in the recent past by other Business Analysts. This is where it is very useful if Business Analysts can research similar project information to avoid rehashing the same content with fatigued stakeholders.
#10 Lack of governance
Finally, another common problem faced by Business Analysts is a lack of governance around requirements management. This can lead to several issues such as scope creep, requirements changes being made without consent or approval, and a general lack of control over the requirements. This can be a particular problem on larger projects where there are many stakeholders involved and the Business Analyst is not the only person working on gathering and documenting requirements.
A way to help solve this problem is for the Business Analyst to put in place a requirements management governance framework. This should include processes and procedures for how requirements will be managed, approved, and changed throughout the project. It is also important to ensure that all stakeholders are aware of and agree to the governance framework prior to the start of the project.
These are some of the top problems I could think of that Business Analysts often face and help solve. Some projects have multiple of these challenges happening at the same time which makes the role of the Business analyst very valuable as problem solver.
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
Esta Lessing
Register for more free business analyst resources.
Get Access to Live and On-Demand Webinars, Templates, Claim PDU/CDUs, and Many More!
- Coaching Skills Training
- Coaching TIPS²™
- Continuous Improvement Coaching
- Courageous Conversations Workshop
- Executive Coaching Program
- Feedback 360
- Safety Coaching
- Sales Coaching Training Program
- Free Consultation
- Applied Strategic Thinking®
- Strategic Leadership Course
- Strategic Teaming
- Strategy Development Processes and Services
- Communication Training for Managers
- Conflict and Collaboration
- Confronting Racism Workshop
- Delegation & Accountability
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Workshop
- Flexible Leadership
- Leading Change
- Leading Groups to Solutions
- Leading Innovation
- Mid-Level Management Training
- Qualities of Leadership
- Bottom Line Leadership
- Customized Leadership Development Programs
- Leadership Development Program Design
- Mini-MBA & Operational Finance
- Problem Solving and Decision Making in the Workplace
- Transition to Leadership
- Virtual Leadership
- High-Performance Teamwork
- Leadership Team Alignment Workshop
- Orienteering
- Corporate Outdoor Training and Team Building
- Retreats for Teams
- Innovation Skills Training
- Personal Impact Workshop
- Supervisor Training Programs
- Customization of CMOE’s Learning Library
- Full Curriculum Development and Design
- Learning & Development Advisory Services
- Bottom Line Leadership Training
- Consulting Services
- Leadership Retreats
- Learning and Development Consulting Services
- Needs Analysis and Organization Assessments
- Transformation & Change Solutions
- Facilitator Training Workshop
- Empathic Leadership
- Supervisor Development Series
- All Courses
- Digital Learning
- Books and Publications
- Assessments and Surveys
- Clients Served
- History and Experience
- Meet the CMOE Team
- Testimonials
- Articles & Tools
- Scenario Templates
- Certified Partners
- Event Resources
- Industry Insights
- Resource Library
- Video Library
- News and Events
- Professional Accreditation and Continuing Education Units
- Surveys & Assessments
- Problem Solving in Business
- 360-Degree Leadership Assessment
- Adaptive Communication
- Adaptive Leadership
- Authentic Leadership Style
- Boundary Spanning Leadership
- Business Change Strategies
- Business-Strategy Principles
- Capacity Building
- Cascading Strategy
- Change Management
- Charismatic Leadership
- Coaching Framework
- Coaching in the Workplace
- Coaching Leadership Style
- Collaborative Coaching
- Competency Assessment
- Conflict Resolution in the Workplace
- Core Competence
- Corporate Strategic Planning
- Crisis Leadership
- Critical Success Factors
- DEI in the Workplace
- Directive Leader
- Empathetic Leadership Definition
- Horizontal Leadership
- Inclusive Leadership
- Innovation Strategy
- Leadership Assessment
- Leadership Competency Framework
- Leadership Model
- Management Succession Planning
- Operational Excellence
- Organizational Alignment
- Participative Leadership Style
- Performance Deficiency Coaching
- Persuasive Leadership Style
- Servant Leadership Style
- Strategic Agility
- Strategic Alignment
- Strategic Audit
- Strategic Framework
- Strategic Initiatives: Examples and Development
- Strategic Management
- Strategic Mindset Competency
- Strategic Thinking
- Strategy Committee
- Strategy Issues
- Strategy Maps
- Supportive Leadership Style: Definition and Qualities
- Team Building Interventions
- Team Environment
- Team Performance Assessment
- Teamwork Atmosphere
- Total Employee Involvement
- Training Needs Analysis (TNA) Definition
- Transformational Leadership
- Visionary Leadership Style
What Is Problem Solving in Business?
Problem-solving in business is defined as implementing processes that reduce or remove obstacles that are preventing you or others from accomplishing operational and strategic business goals.
In business, a problem is a situation that creates a gap between the desired and actual outcomes. In addition, a true problem typically does not have an immediately obvious resolution.
Business problem-solving works best when it is approached through a consistent system in which individuals:
- Identify and define the problem
- Prioritize the problem based on size, potential impact, and urgency
- Complete a root-cause analysis
- Develop a variety of possible solutions
- Evaluate possible solutions and decide which is most effective
- Plan and implement the solution
Why Is Problem-Solving Important in Business?
Understanding the importance of problem-solving skills in the workplace will help you develop as a leader. Problem-solving skills will help you resolve critical issues and conflicts that you come across. Problem-solving is a valued skill in the workplace because it allows you to:
- Apply a standard problem-solving system to all challenges
- Find the root causes of problems
- Quickly deal with short-term business interruptions
- Form plans to deal with long-term problems and improve the organization
- See challenges as opportunities
- Keep your cool during challenges
How Do You Solve Business Problems Effectively?
There are many different problem-solving strategies, but most can be broken into general steps. Here is a six-step method for business problem solving:
1) Identify the Details of the Problem: Gather enough information to accurately define the problem. This can include data on procedures being used, employee actions, relevant workplace rules, and so on. Write down the specific outcome that is needed, but don’t assume what the solution should be.
- Use the Five Whys: When assessing a problem, a common strategy is to ask “why” five times. First, ask why the problem occurred. Then, take the answer and ask “why” again, and so on. The intention is to help you get down to the root cause of the problem so you can directly target that core issue with your solution.
2) Creatively Brainstorm Solutions: State every solution you can think of. Write them down. Seek input from those who possess in-depth knowledge of or experience with the problem you’re trying to solve. These insights will provide you with valuable perspectives you can transform into tangible and impactful solutions.
3) Evaluate Solutions and Make a Decision: Assess the feasibility of each solution. Is the deadline realistic? Are there readily available resources you can leverage to successfully implement the solution? What is the return on investment of each solution? If necessary, come up with alternative solutions or adjust the initial ones you brainstormed in step 2.
4) Make a Decision: Finally, make a firm decision on one solution. This final solution should clearly address the root cause of the problem.
- Perform a SWOT Analysis: You can use a SWOT analysis to help you decide on the best solution. A SWOT analysis involves identifying the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats linked to a specific decision. With this framework, your team can assess a decision from various angles, thereby gaining a holistic view of it.
5) Take Action: Write up a detailed plan. This involves developing a comprehensive roadmap that outlines the steps required to implement your solution. The steps should specify milestones, deadlines, roles, and how to obtain the necessary approvals. To ensure accountability, your entire team should have access to this action plan. Each team member should be able to track and share their progress with the group.
6) Gather and Share Feedback: Problem-solving is not a “set it and forget it” process. It’s a dynamic journey that necessitates ongoing attention, deliberation, and refinement to achieve optimal results. Thus, periodic feedback is critical in validating whether the chosen solution creates the desired impact. It allows key stakeholders to check in and make any necessary changes.
What Are Problem-Solving Skills?
Problem-solving skills are specific procedures that can be used to complete one or more of the six general steps of problem-solving (discussed above). Here are five important examples:
Using Emotional Intelligence: You’ll solve problems more calmly when you learn to recognize your own emotional patterns and to empathize with and guide the emotions of others. Avoid knee-jerk responses and making assumptions.
Researching Problems: An effective solution requires an accurate description of the problem. Define simple problems using quick research methods such as asking, “What? Where? When? and How much?.” Difficult problems require more in-depth research, such as data exploration, surveys, and interviews.
Creative Brainstorming: When brainstorming with a group, encourage idea creation by listening attentively to everyone, and recognizing everyone’s unique contributions.
Logical Reasoning: Develop standard logical steps for analyzing possible solutions to problems. Study and apply ideas about logical fallacies, deductive reasoning, and other areas of analytical thought.
Decisiveness: Use an agreed-upon system for choosing a solution, which can include assigning pros and cons to solutions, identifying mandatory results, getting feedback about solutions, choosing the decision-maker(s), and finishing or repeating the process.
How Can You Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills?
Learning how to solve business problems takes time and effort. Though some people appear to have been born with superior problem-solving skills, great problem-solvers usually have taken the time to refine their abilities. You can develop high-level skills for solving problems too, through the following methods:
Ask and Listen: Don’t expect to solve every problem alone. Ask for advice, and listen to it carefully.
Practice Curiosity: Any time you’re involved in solving a problem, practice researching and defining the problem just a little longer than you would naturally.
Break Down Problems: Whenever possible, break large problems into their smallest units. Then, search for solutions to one unit at a time.
Don’t Label Yourself Negatively: Don’t allow a problem to mean something negative about you personally. Separate yourself from it. Look at it objectively and be part of the solution.
Enhance Your Problem-Solving Skills with CMOE
Problem-solving skills in business are not developed overnight. Developing then takes ongoing practice and the right guidance to get right. We encourage you to leverage CMOE’s Problem-Solving and Decision Making in the Workplace workshop to further develop your skills. We’ll help you identify new ways to solve problems methodically so you can create greater impact.
Clients We’ve Worked With
Contact form.
Need More Information? Please fill out the following form and we will be in contact with you with more information.
" * " indicates required fields
As Featured In:
The Better Business Bureau has determined that CMOE meets accreditation standards. These standards verify that CMOE’s product quality and competence enhance customer trust and confidence.
©2024 Center for Management & Organization Effectiveness. All rights reserved.
Leveraging Data, Statistics, and Probability in Business Analytics: A Modern Approach for Transforming Information into Actionable Insights
Nilimesh Halder, PhD
Analyst’s corner
In the age of information, businesses have access to more data than ever before. Whether it’s customer purchasing patterns, supply chain logistics, marketing campaign effectiveness, or employee performance, companies are inundated with data. This overwhelming abundance of data is where statistics and probability come into play, providing the tools necessary to interpret, analyze, and make use of this wealth of information. In the context of business analytics, data, statistics, and probability work together to create a framework for decision-making, risk management, and strategic planning. Let’s explore this intriguing intersection and how it shapes modern business practices.
Data: The Foundation of Insight
Data is at the core of business analytics, representing the raw facts and figures collected from various sources. It might be the number of products sold, the time spent on a website, customer demographics, or sales across different regions.
Example: Customer Purchase Data
An online retailer gathers data on customer purchases, including what products were bought, when they were bought, the price, and the location of the buyer. This data is the starting point for understanding customer behavior and preferences.
Statistics: Making Sense of the Data
Statistics is the science of collecting, analyzing, interpreting, presenting, and organizing data. It helps businesses understand trends, patterns, and relationships within the data.
Example: Analyzing Sales Trends
Using the customer purchase data, statistical methods can be applied to identify trends over time. Seasonal variations, growth patterns, and correlations with external factors like holidays or economic conditions can be understood and visualized.
Probability: Assessing the Likelihood
Probability deals with the measure of how likely an event is to occur. In business analytics, it’s used to predict future occurrences based on historical data, assessing risks, and making informed decisions.
Example: Predicting Future Sales
Using the sales trend analysis, probability can predict future sales based on the observed patterns. This prediction can guide inventory management, marketing efforts, and strategic planning.
Data Processing and Cleaning
Before diving into statistical analysis, data often needs to be cleaned and processed. Incomplete, inaccurate, or irrelevant parts of the data must be modified or removed.
Example: Removing Outliers
In the customer purchase data, an abnormally high or low purchase might skew the analysis. Identifying and handling these outliers ensures a more accurate understanding of typical customer behavior.
Descriptive and Inferential Statistics
In business analytics, statistics is usually divided into two categories:
Descriptive Statistics: These provide a summary of the main aspects of the data, such as mean, median, mode, and standard deviation.
Inferential Statistics: This goes beyond the data available and makes inferences about a population based on a sample of that population.
Example: Market Segmentation
Descriptive statistics might reveal that a majority of customers fall within a particular age range. Inferential statistics could then be used to make predictions about the purchasing behavior of that age group in the entire population.
Probability Distributions and Risk Assessment
Different probability distributions like the Normal distribution, Binomial distribution, and Poisson distribution are used to model various business scenarios.
Example: Stock Inventory Management
A Poisson distribution might model the number of customers arriving at a store. This distribution can help in understanding the inventory levels required to meet customer demand without overstocking.
Predictive Analytics and Machine Learning
Modern business analytics often incorporates predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms. These use statistical and probability models to predict future events, classify data, and even make recommendations.
Example: Customer Recommendations
An online retailer might use machine learning algorithms to analyze past purchase behavior and browsing history. This data, analyzed through statistical methods, allows the system to make personalized product recommendations.
Conclusion: The Confluence of Data, Statistics, and Probability in Business
The collaboration of data, statistics, and probability in business analytics offers a robust framework for decision-making, planning, and optimization. By understanding the past and present, businesses can make educated predictions about the future. They can identify opportunities, minimize risks, and create strategies tailored to their specific goals and challenges.
In the dynamic and complex business environment of 2023, these tools are not just optional; they are essential. They empower businesses to navigate uncertainty, adapt to changing market conditions, and maintain a competitive edge. From understanding customer preferences to optimizing supply chains, the integration of data, statistics, and probability continues to be a driving force in the successful operation and growth of modern businesses.
Find more … …
Harnessing the power of chatgpt: a comprehensive exploration of language ai in the modern world, articles, blogs and tutorials harnessing the power of chatgpt: a comprehensive exploration of language ai in the modern….
setscholars.net
AI Risk Management: A Deep Dive into Safeguarding Artificial Intelligence Implementations
Articles, blogs and tutorials ai risk management: a deep dive into safeguarding artificial intelligence implementations, decoding time series data: insights, implications, and advanced analytical techniques, articles, blogs and tutorials - decoding time series data: insights, implications, and advanced analytical techniques.

Written by Nilimesh Halder, PhD
Principal Analytics Specialist - AI, Analytics & Data Science ( https://nilimesh.substack.com/ ). Find my PDF articles at https://nilimesh.gumroad.com/l/bkmdgt
Text to speech

- Web App Development
- Mobile App Development
- React Native Development
- Java Development Services
- .NET Development Services
- PHP Development Services
- Laravel Development Services
- Cloud App Development
- Testing & QA Services
- IT Infrastructure Services
- Software Support & Maintenance
- Power BI Consulting
- DevOps Consulting
- DevSecOps Consulting
- PowerApps Consulting
- Microservices Consulting
- Site Reliability Engineering
- Legacy App Modernization
- Full Stack Developers
- Testing Engineers
- .NET Developers
- Python Developers
- Java Developers
- NodeJS Developers
- PHP Developers
- Laravel Developers
- AngularJS Developers
- React.Js Developers
- Vue.JS Developers
- CakePHP Developers
- Flutter Developers
- React Native Developers
- Xamarin Developers
- iOS Developers
- Android Developers
- Shopify Developers
- NopCommerce Developers
- Fintech Developers
- DevOps Engineers
- Azure Developers
- WordPress Developers
- Joomla Developers
- Drupal Developers
- Power BI Developers
- Tableau Developers
- More Developers
- vEMPLOYEE TM
- WIN WITH AI
- Case Studies
- Whitepapers
- Infographics
- Testimonials
- About Clarion
- Partner with us

Solve Common Business Problem with Analytics Solutions

Several successful companies today whether they’re based on online or brick and mortar have started to utilize some sort of technologies to support their key business functions like storing customer details, tracking sales and marketing activities; and handling entire finances. They recognized that investing in technology could drive better business results. Especially, technology is most commonly used to solve some complex business problems associated with management, advertising, customer support, and decision-making. In addition, enterprises are turning towards advanced tools for help. Data analytics is one such technology and the analytics tools are significantly used by businesses to diagnose and address business problems. This article highlights the problems that can be solved with the analytical solutions.
Analytics make businesses understand what they are doing right and what they are doing wrong. In addition, it displays what is working and what is not working on all sides of marketing, including content, social media, and email marketing. The action of measuring instead of guessing enables businesses to attain almost a sure thing. For instances, analytics allow discovering content that the audience really likes and shares. Spending devoted time on social media activities usually provides a net benefit, but in several cases, spending some of those hours on analysis will lead to a large benefit. That offers the knowledge to streamline business activities and results in better outcome from those activities.
Why Use Analytics Tools to Solve the Business Problem?
Businesses often forget that the most complex business issues can be solved using analytics by involving the latest data analytics tools. It is important to realize that around 70% - 80 % of the analyst’s time is spent on generating the analytical files. Only the remaining 20% -30% is spent on building a solution. Here, the approach to solution development involves predictive models or straightforward business rules. With analytics tools, a business can extract the simple structured data and reduce its effort in extracting unstructured and semi-structured information. The analytics tools used in problem-solving have two criteria:
1. Ease in the generation of analytic files 2. A simple business algorithm in the formation of a solution
The rapid demand for an analytical solution has forced the enterprises to invest in analytics tools that can enable the business users and employees across the enterprise to obtain answers to, what they require. With these powerful tools, businesses can allow them to do advanced analytics without demanding any programming support of data scientists. Thereby enterprises will find a new competitive advantage and power to uncover previously unseen trends that project them into an influential position.
7 Common Problems Solved with Data Analytics Solution
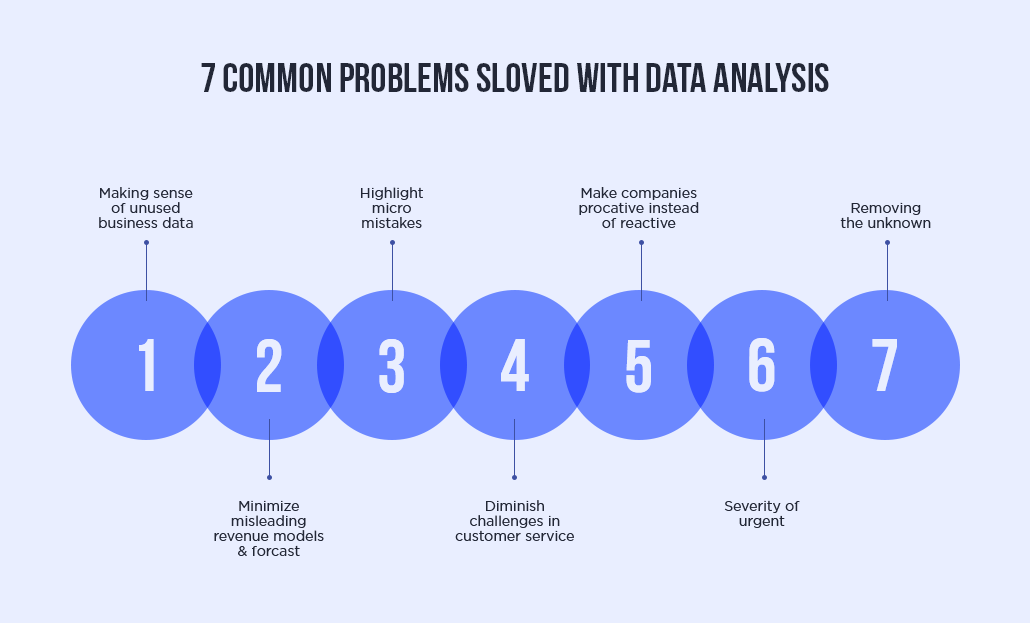
- Making Sense of Unused Business Data
With the reducing cost of cloud storage, enterprises today are accumulating more data. There is no in data collection, but the reality is that enterprises only use about 1% of their stored data to make valuable business decisions. It is because they cannot find the appropriate data. The competency to search and retrieve data is the most vital action for enhancing business and realizing the power of big data. In addition, the search technology should be fast, and contextual to read complex information so it is usable for employees across the entire levels of an organization. This is where the analytical solution steps in. It streamlines data to be accessible and consumable to everyone.
- Minimize Misleading Revenue Models and Forecast
Businesses frequently anticipate revenue with rough models. In addition, these models always point out a single part of the estimate for every month going forward. A real fact is revenues can fluctuate disorderly and companies have excessive uncertainty about next month, next quarter or year.
Data analytics solve this challenge by properly accounting for certain mechanisms by which businesses generate revenue and the improbability in sales. Therefore, in addition to the best revenue estimate, a business can gain transparency into the inconsistency if there are varied revenue results.
- Highlight Micro Mistakes
Often business analysts are caught up in solving relatively large issues with predictive analysis. However, focusing on the small decisions that are made several times tends to provide better results. This includes what checkbox to pre-check, what part of the website a customer is most likely to use or what item they’re more likely to purchase. Even though improving these things can yield a considerably smaller percentage of gain, the total improvement can be great as they occur so frequently.
- Diminish Challenges in Customer Service
The analytics software can be used to offer better customer services and deepen their relationships. Analytics can play a vital role in decreasing and eliminating customer problems before they occur. Just imagine a customer receiving a call from a company with a solution for a product recall, before he or she encounters the issue. By creating data from multiple sources, analytics can be employed to be proactive. It helps to realize what is lagging and address it before a customer awakes. This technique can support any enterprise to convert mountains of data into useful insights that strengthen customer relationships.
- Make Companies Proactive instead of Reactive
With the advent of new channels and regulations in the global economy, there are countless changes in the way companies doing business. Companies require upholding awareness – be proactive instead of reactive to these changes. Analytics can support companies in the following ways:
- Support to remain relevant to the customers
- Offer insight into trends influencing the industry
- Alert of macroeconomic influence that may cause local operations
- Priority of Urgent
Most of the business executives and owners virtually spend all of their time and effort on critical things. They don't even consider spending on activities that are both critical and urgent. The primary reason is that the most businesses are not functioning based on a strategic plan. While urgent tasks come with any business, relying on a strategic plan can guarantee that at least some time is allotted to the acute success factors. Analytics software gives business a valuable insight about an issue that could be brewing.
- Removing the Unknown
Uncertainty is one of the huge issues business leaders are facing today. Whether it is over their customer retention, workforce or service – uncertainty possesses its own way of routing decision paralysis. Analytics can encourage companies to make a decision in line with insight, not on hindsight. Changing decisions based on existing data will solve a plenty of business unknowns. Data analytics tools support them to build a customer profile, determine exit triggers, and offer a kind of customized marketing strategy that makes the customer stay for a long period.
Data analytics help enterprises to solve these complex issues and make enterprises confident in moving forward with the best analytical reports. Data is now competent enough to improve any business process, whether it is optimizing the communication in the supply chain or enhancing the relevance and quality of business offerings.

Mistakes to Avoid while considering DevOps transformation
Complete guide to building microservices with node.js, best practices for security testing in healthcare applications, building secure banking applications with .net, power bi developer: roles and responsibilities, skills, scope and more, top emerging technology trends to watch in 2024, best web development technologies to use in 2024, 20 scenarios for testing login pages & search functionalities, talk to our experts, related blogs.

How is Analytics Transforming Businesses Today?

Top 10 Guaranteed Big Data Software Features

Top 15 Jira Service Desk Features to Scale your Customer Support
More From Forbes
Five business problems you can solve with bi tools.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Business intelligence (BI) tools merge data from marketing, finance and sales into one system to produce reports based on real values from the company’s CRM and sales data (including data on returns and delivery performance). Moreover, BI tools automate routine marketing activities and optimize ad expenses.
Here are some practices that can make setting up your BI tool easy:
• Behavioral website data is collected correctly and in compliance with all rules for data merging.
• Ad campaigns are marked with UTM tags, and ad cost data is constantly collected.
• Managers save data on online and offline purchases in a CRM and use a call tracking system.
• Offline customers have unique identifiers for tracking online and offline purchases.
You should compare the cost of implementing a BI tool with the cost of leaving everything as is. In most cases, sometimes doing nothing is the more expensive option. Below are the top business challenges that you can overcome with a BI tool:
1. You have a poor data ecosystem resulting in a lack of control over business processes.
A BI tool, in general, sets a high standard for collecting, cleaning, merging and storing your marketing and business data. Business intelligence can’t be built on fragmented or dispersed data, so you’ll have to start by collecting all your data, including:
• Website data.
• Ad data from all advertising services.
• CRM data on contacts, sales and requests.
• Call tracking and offline data.
An audit of channels and sources will help you create a whole picture of your company’s data flow. To conquer an inefficient data ecosystem, you’ll need to audit your channels and sources, choose a central storage system, merge and clean your data, and set up automated data updates. After doing this, you can be sure your data is reliable.
2. The evaluations of online and offline marketing data differ from your revenue data.
When you invest in various advertising campaigns with platforms such as Google Ads, Facebook, YouTube and banner and CPA networks, you get a bunch of colorful reports from your marketing (or outsourcing) agency showing that everything has performed great. But why should you believe these reports when you can see for yourself?
To know what marketing efforts bring the most and the least profit to your company, you should build an individual attribution model that reflects the real sequence of funnel steps for your company and includes real revenue and ad cost data in calculations.
With this model, you can find which channels generate leads and revenue, engage your audience, or just drain your budget. The more data your attribution model has, the more precise your channel estimates will be.
By combining a BI tool with a fitting attribution model, you can:
• Include all data in your calculations, considering ad costs and revenue generated from ads.
• Calculate your model based on data for real purchases.
• Include offline data.
Thus, you don’t have to sift through thousands of separate reports to understand what happens with your channels.
3. Ad campaigns are managed in separate ad services, and you can’t compare campaigns.
With a BI tool, you can analyze how your ad channels influence each other — not just how they perform. This is useful for debugging your marketing funnel, creating a smoother customer experience, achieving precise targeting, spending less on advertising and analyzing your cross-channel audiences.
You can switch the focus of your ad campaign analysis to purchases, not leads, to see the most active customers and what channels are influencing them.
Also, identifying dependencies between your ad channels is one of the best ways to test your creative visuals and marketing hypotheses. If you can set up minimal testing automation, you’ll likely spend your ad budget smarter.
4. Your reports aren’t timely, or they lack the quality required for decision-making.
What are the main distinctions between manual reporting and BI reporting?
• Time needed to build reports: Simple reports can be built fast either automatically or by hand. But it takes a lot of time to manually build complex reports, with a few channels, long periods and lots of data. With a BI system, any kind of report can be built fast.
• Potential for error: If you set up your BI tool correctly, there’s a limited chance for errors in your reports.
• Relevance: Thanks to the speed of building reports with a BI tool, actionable reports will always be available in real time. Complex manual reports typically take so long to create that they lose their relevance.
• Diversity of reports: Some reports are almost impossible for one person to create (like attribution reports). For a BI system, all reports are realistic.
With a BI tool, you can build reports that you couldn’t previously build due to incomplete data, and those reports contain actual values that fit your financial reporting. Thus, management can see the efficiency of the whole department, not separate activities.
5. Your company can’t grow any more by doing the same old thing, and increasing the ad budget doesn’t help.
A BI system gives enough valuable insights for management to make the right decisions. This is what it means to be data-driven — not needing to recall what you did last time or what your competitors are doing. Just get revenue and expense data from an analytics system and use it to form your action plan. A BI tool can even predict the results of implementing that plan.
BI is just the first step.
Implementing a BI tool is only the first step in building an analytics system that covers the whole business. Building such a system demands the determination to continue when nothing’s going as it should. But this struggle will lead to a data-driven mindset and prove that relevant analytics is the best gift you could give your company.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
7 Business Analytics Examples From Top Companies (+Use Cases)

Data-driven companies are 58% more likely to hit revenue goals. This shows how important business analytics is for your product .
Business analytics gives insights that help you make better decisions to improve your product. This article will show seven examples of business analytics to highlight its positive impact.
- Business analytics uses data to find trends and boost performance. It helps companies make smart decisions and optimize operations.
- Tracking customer behavior improves marketing, enhances user experience , and boosts customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Business analytics has four types: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive , and prescriptive. These analyze past trends , identify causes , forecast future events, and recommend actions.
- Segment customers by demographics and usage to personalize experiences . This boosts satisfaction and retention with tailored messages and offers.
- Map the user journey to find key touchpoints. Use path analysis to optimize the experience , remove friction, and improve outcomes.
- Use feature heatmaps to analyze user behavior. This helps optimize in-app engagement , promote key features, and boost satisfaction and retention.
- Improve product usability by analyzing data to find issues through funnel analysis and session recordings. Then, make targeted improvements.
- Find upselling opportunities by analyzing usage patterns. Target the right segments , features, and timing for tailored upsell messages.
- Use predictive analytics on user data to forecast churn . Monitor with a churn prevention dashboard to improve retention.
- Cuvama used Userpilot for path analysis to find and fix user-specific errors. This enhanced customer experience through direct communication.
- ClearCalcs improved user activation rates with Userpilot by addressing user needs through cohort analysis and personalized onboarding flows.
- RecruitNow used Userpilot to create and analyze onboarding surveys. This improved their training process and saved over 1,000 hours of customer training.
- DocuSign boosted freemium-to-paid conversions by 5% using funnel analytics. They offered free users select premium features, enhancing user experience.
- Netflix’s 93% retention rate comes from using user behavior analytics and personalization . This offers tailored recommendations and content, boosting engagement.
- Amazon drives 35% of sales through personalized recommendations and dynamic pricing. Prices adjust based on user behavior and market factors.
- Uber Eats uses taxi business data to model delivery times and coordinate pick-ups. They also employ meteorologists to ensure efficient, timely deliveries.
- If you want to segment your product, understand user behavior, and predict churn, book a demo now to see how Userpilot can help!
Try Userpilot and Take Your Product Experience to the Next Level
- 14 Day Trial
- No Credit Card Required

What are business analytics?
Business analytics is the use of data to make better business decisions. It involves gathering and examining data to find trends and patterns that can improve a company’s performance.
With user analytics, businesses can learn about what their customers like and how they behave. This approach helps companies make smart decisions, improve how they work, and get better results.
Why is it important to track customer behavior analytics?
Tracking customer behavior analytics is essential for business analytics for several reasons:
- Optimize marketing campaigns based on customer preferences : By understanding what your customers like and dislike, you can tailor your marketing campaigns to match their interests. This makes your marketing efforts more effective and engaging , leading to better results.
- Identify friction points : Analyzing user behavior can help you spot areas where customers face difficulties. Addressing these issues can make the user experience smoother and more enjoyable.
- Increase customer satisfaction and loyalty : Using data to understand and meet your customers’ needs makes them happier and more likely to stick with your brand. Satisfied customers are more loyal and can become advocates for your business.
What are the four types of business analytics?
Business analytics can be divided into four main types. Each serves a unique purpose in helping you analyze data to improve performance.
A business analyst plays a role in leveraging these analytics to drive success:
- Descriptive analytics : This type of analytics examines historical data to understand past trends and performance. By analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs), business analysts can identify patterns that inform future strategies. Descriptive analytics helps you make sense of past events for future planning and decision-making .
- Diagnostic analytics : This type of analytics investigates the reasons behind past outcomes. By drilling into the data, business analysts can uncover the root causes of specific results to understand why certain things happened. Diagnostic analytics provides deeper insights into the factors that influenced past performance.
- Predictive analytics : Predictive analytics : This type uses models to forecast future trends and behaviors. Using machine learning and historical data, predictive analytics can help businesses predict future events. This allows them to prepare and plan.
- Prescriptive analytics : This type provides recommendations for decision-making to achieve desired outcomes. By analyzing raw data and predicting future trends, prescriptive analytics offers actionable advice on the best steps to meet business goals. Business analysts use these recommendations to guide organizations in making informed decisions.
How to leverage customer data for actionable insights?
Understanding how to use customer data can change your business. Use this data through analytics to find valuable insights. These insights drive key decisions and improve customer experiences. Here’s how to turn customer data into useful insights.
Create personalized experiences for different segments
To create personalized experiences , segment your customers by different factors. These can include age, gender, and product usage. Using business analytics, gain deeper insights into these segments.
By understanding these segments, you can send personalized messages. Tailor suggestions and offers to each group’s needs. This focused approach improves customer experience. It helps boost satisfaction and retention .

Identify the shortest path to value to help users achieve future outcomes
Mapping the user journey is key to finding important touchpoints. Use path analysis to improve the user experience. Understand these critical moments with business analytics.
Remove friction points and streamline the path to value. Ensure users reach their goals more efficiently. Focus on these improvements to boost the customer experience. This will drive better results for your business.
Optimize in-app engagement
To optimize in-app engagement , start by analyzing user behavior. Use business analytics to understand what drives engagement.
Feature heatmaps are an effective tool for this purpose. They visually show how users interact with different parts of the app. These heatmaps reveal which features are most and least used. This helps identify areas for improvement.
Use this information to promote key features. Target in-app messages to highlight important features. Encourage users to engage more with your app. This leads to better user satisfaction and retention.

Improve product usability for a better user experience
To improve product use and enhance the user experience, start by using business analytics to find and fix problems.
Spot these issues through funnel analysis drop-offs. This shows where users leave a process or feature. Use session recordings (coming soon in Userpilot) to see where users have trouble.
By knowing where and why users struggle, you can make targeted fixes. This ensures a smoother and more satisfying user experience. This proactive approach helps keep users and boosts overall happiness.

Identify the right opportunities for upselling
To find upselling chances, analyze customer usage with business analytics. This helps you pinpoint:
- The right segments to upsell : Find which customer groups are most engaged. Target these users with tailored upsell messages. Segments might include frequent users or those using certain features a lot.
- The right features to upsell : See which features are popular. Offer upgrades or extra features that match their usage. Users of a particular feature might want an upgraded version or added functionality.
- The right time to upsell : Timing is key. Look at when users are most active or reach app milestones. After using a feature often or completing a task, they might welcome an upsell offer for better capabilities or more services.
By analyzing these patterns with business analytics, you can create effective upsell campaigns. This increases revenue and customer satisfaction.

Predict customer churn to increase retention
Creating predictive models using user behavior data can help forecast churn . Use business analytics to find patterns showing a customer might leave.
To manage these insights, create a churn prevention dashboard . This tool helps you monitor churn levels and act quickly. By fixing issues that lead to churn, you can improve retention rates. This keeps your customers happy and engaged.
7 business analytics examples from leading companies
This section will explore how top companies use business analytics to succeed. These examples will show how businesses use data to improve operations, enhance customer experiences, and boost performance.
Cuvama successfully used business intelligence, data analytics, and Userpilot. They used path analysis to find an error message affecting certain users. By accessing profile information through Userpilot, they could click on names in the paths report and contact those users directly to resolve the error.
Leyre Iniguez, Customer Experience Lead at Cuvama, praised the user profile feature: “I love this. I can come here and see who my user is having those problems, so I can directly contact the person and check out what’s happening.” This proactive approach allowed Cuvama to enhance its customer experience significantly.

2. ClearCalcs
ClearCalcs , a structural design software, significantly improved user activation rates using Userpilot. They identified customers delaying activation by using business analytics and cohort analysis . This analysis helped them understand user behavior and address specific needs.
Using Userpilot, ClearCalcs implemented personalized onboarding flows. This played a crucial role in improving user activation and delivering value faster. These tailored onboarding experiences ensured new users quickly found and used the calculators they needed, enhancing their initial interaction with the product.

3. RecruitNow
RecruitNow used Userpilot to train its growing customer base effectively. They used business analytics and Userpilot to create an onboarding survey to monitor their onboarding flow.
RecruitNow tracked survey completions, satisfaction levels, and customer feedback through survey analytics. This data-driven approach allowed them to improve their training process and ensure high customer satisfaction.
Using these insights, RecruitNow saved over 1,000 hours in customer training. This made their onboarding process more efficient and impactful.

4. DocuSign
DocuSign, a leading e-signature platform, aimed to boost its freemium-to-paid conversion rates. They used business and data analytics to give free users access to select premium features.
Using funnel analytics, they identified which features would drive upgrades. This strategy resulted in a 5% improvement in conversions, a significant increase given their 130,000 new users daily. By leveraging data insights, DocuSign successfully enhanced its conversion rates and overall user experience.
With nearly 270 million subscribers, Netflix is the world’s largest streaming service, boasting a 93% retention rate. This success is driven by using business analytics and personalization.
Netflix analyzes viewing patterns, including what users watch, when, and for how long. These insights allow them to offer personalized recommendations, AI-generated trailers, and develop original content that matches their audience’s tastes.
This data-driven approach boosts retention and helps Netflix compete with traditional media giants, as shown by their Golden Globe and Oscars wins.

Amazon, the largest e-commerce business, attributes 35% of its sales to personalized recommendations. By analyzing user behavior—such as viewed items, added to the cart, or purchases—they create tailored suggestions for each user.
Amazon also uses dynamic pricing, adjusting prices up to 2.5 million times daily based on shopping patterns, competitor prices, and product demand. This use of big data and analysis enhances the customer experience and drives significant sales, demonstrating Amazon’s effective data-driven strategies to maintain its market leadership.
7. Uber Eats
Uber Eats used its extensive data from the taxi business to excel in the competitive food delivery market. To ensure timely and warm deliveries, Uber Eats used business analytics and natural language processing to model the physical world and predict delivery times accurately.
They collected data on meal preparation times to coordinate precise pick-ups, allowing drivers to deliver multiple orders efficiently per trip with incentives. Their innovative approach includes employing meteorologists to anticipate weather impacts. Uber Eats shows how Big Data and analysis can expand services, gain a competitive edge, and predict customer needs .
It’s clear that data is crucial for all types of business analytics and can produce fantastic results for your business. With business analytics, you understand how your product is performing.
Getting started with business analytics can be daunting, but Userpilot makes it easy. Userpilot helps you segment users to create personalized experiences, measure in-app engagement, and understand product usage to improve the customer experience. For examples of business analytics in action, Userpilot can show you how it works. If you want to know more, book a demo now .
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth,Management & Trends.
The coolest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends. Delivered fresh to your inbox, weekly.
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
You might also be interested in ...
A/b testing analytics: definition, process, and examples, the ultimate guide to usability testing: types, methods, and steps.
Aazar Ali Shad

Scranton is a private Catholic and Jesuit institution that delivers a transformative education, grounded in the liberal arts.
- About Us - Overview
- Office of the President
- Facts About Scranton
- Outcomes & National Recognition
- Our Location
- Value of a Scranton Education
- Equity, Diversity & Inclusion
- Strategic Plan
- Community Relations
- Campus Health and Safety

At The University of Scranton, our rigorous, in-depth education provides the field-specific knowledge and competencies needed for professional success.
- Academics - Overview
- Undergraduate Programs
- All Graduate Programs
- Online Graduate Programs
- Colleges & Departments
- Graduate Education
- Academic Calendars
- Office of the Provost
- Pre-Med / Pre-Health
- Menu Item #1
- Menu Item #3
- Menu Item #4
- Menu Item #5

Become a Royal! Scranton offers the perfect combination of academic environment, social experience, and personal support our students need to build successful lives and careers.
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Transfer Students
- International Students
- Financial Aid
- Join Our Contact List
- Schedule a Visit
- Apply to Scranton
- Graduate Admissions
- Request Information

Student Life is vibrant and varied, from ministries-based programs and leadership initiatives to student-run activities, clubs and organizations.
- Student Life - Overview
- Residence Life
- Clubs & Organizations
- Career Development
- Campus Ministry
- Center for Service & Social Justice
- Current Students

With more than 51,000 Scranton graduates out there, connecting with fellow alumni couldn't be easier, and we're here to help!
- Alumni - Overview
- University Advancement
- Make a Gift
- Calendar of Events
- Alumni Board
- Networking Opportunities
- Reunion Weekend
- Scranton Journal
- Recreation and Intramurals

Operations and Analytics Department
- About the Department
- Business Analytics major
- Operations Management major
- Business Analytics minor
- Operations Management minor
- MBA - Business Analytics specialization
- MBA - Operations Management specialization
- MS - Business Analytics
- Graduate Certificate - Business Analytics
- Faculty & Staff Directory
- Internships
- Operations and Analytics Club
- Six Sigma Certification
- Faculty Research
Contact Us:
- Nabil Tamimi, Ph.D., Professor and Chair
- Kania School of Management
- Brennan Hall, Room 437
- Scranton, PA 18510
- The University of Scranton
- Phone: (570) 941-4288
- [email protected]
Supply Chain Management Major
Program overview.
How do you effectively transform materials and labor into goods and services? Then, how do you deliver high quality goods and services to customers as efficiently as possible? How can big data and analytics be leveraged to better manage supply chains? These are just some of the questions addressed by the major in operations management.
Supply Chain Management is one of the core areas of business. It has a significant impact on a company’s long run survival and success. Given rapid advances in technology, ever increasing global competition, and a constantly changing business environment, companies must provide products and services of superior quality at affordable prices.
Supply Chain management teaches students the analytic, problem-solving and technical skills needed to apply a systems perspective to managing processes that can achieve and sustain performance excellence. Besides face-to-face classroom instruction, students have ample opportunity for:
- Experiential learning that includes hands-on computer applications with various software, such as Excel, statistical and simulation packages
- On-site visits to companies in the region, such as Walmart Distribution Center and Flowserve Corporation
- Networking with professionals through the OIM student club and NEPA chapter of APICS
- Paid internships with local organizations like the Tobyhanna Army Depot.
- Gaining the foundational knowledge to prepare them for various certifications (e.g., CPIM, CSCP and CLTD) in the field. To learn more about professional certifications, visit the American Production and Inventory Control Society.
The following three courses are required:
- OIM 363 Quality Management
- OIM 366 Supply Chain Management
- OIM 470 Production Planning and Control
Three of the following elective courses may be selected:
- OIM 353 Business Process Overview
- OIM 462 Project Management in Organizations
- OIM 472 Electronic Business and Entrepreneurship
- OIM 444 Business Forecasting Models
- OIM 463 Data Mining
VIEW THE CURRICULUM
Career Outcomes
Since supply chain management is a core function of every business, our seniors have many options as they begin their job searches. The median annual salary for operations managers in May 2018 was $100,930, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
© 2024 University of Scranton
Business Analytics Internship
About the internship, skill(s) required, who can apply.
Only those candidates can apply who:
1. are available for full time (in-office) internship
2. can start the internship between 8th Jul'24 and 12th Aug'24
3. are available for duration of 3 months
4. have relevant skills and interests
Number of openings
About webknot technologies private limited.
- Tuesday, July 09, 2024

© 2023 - Businessday NG. All Rights Reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The expression problem solving refers to the intellectual process that people go through to uncover, analyse and solve problems. Problem solving is a major discipline within business analysis. You'll often hear business analysts state that the thing they love about their work is solving problems. This makes sense because as a business analyst ...
The following stages are commonly used by Business Analysts when problem solving is required. 1) Problem Definition. Τhe first step in the approach is the problem definition. Gathering information, ascertaining its validity against other sources of information, and analyzing the available information are key at this stage. The way a problem is ...
Here's the 8 step Business Analyst way to solve the problem: 1. Identify the problem — 'What's going on?'. This basic question will help the BA get an idea about problems being faced in ...
Information that is critical to formulating the correct solution is essential to being included in the scope. This can be demonstrated through a mathematical equation. Take the following equation, which the problem is to find the value of X; X = Y + 10. Consider for a second that the problem is X, and X cannot be determined.
A helpful and standardised format to write the problem definition is as follows: The problem of - Describe the problem. Affects - Identify stakeholders affected by the problem. The results of which - Describe the impact of this problem on stakeholders and business activity. Benefits of - Indicate the proposed solution and list a few key ...
Each year, the MIT Sloan Master of Business Analytics Capstone Project partners students with companies that are looking to solve a business problem with data analytics. The program offers unique and up-close insight into what companies were grappling with at the beginning of 2023. This year, students worked on 41 different projects with 33 ...
Matt's Recommended 6 Stage Problem Solving Approach The problem solving approach that Matt uses is a simple six stage process. The staged do not need to be completed sequentially; the individual stages may repeat and be completed in iterations. The stages consist of: Defining the problem statement. Defining scope.
How to Translate Business Problems into Analytical Problems. Photo by Zdeněk Macháček on Unsplash This article is the first of a series focusing on solving common business problems using analytics.
Business Analytics Examples. According to a recent survey by McKinsey, an increasing share of organizations report using analytics to generate growth. Here's a look at how four companies are aligning with that trend and applying data insights to their decision-making processes. 1. Improving Productivity and Collaboration at Microsoft.
In business analytics, problem-solving typically involves the following steps: Defining the problem: This involves understanding the issue or challenge facing the business and identifying the key ...
Identifying Opportunities and Threats. Business can sometimes feel like a battlefield, with competitors and market dynamics ever-changing. Here, data analytics acts as your strategic reconnaissance team. It helps you identify opportunities to seize and threats to mitigate. By analyzing market trends, tracking competitor movements, and gauging ...
Process of Business Analytics: One way to conceptualize business analysis is as a research field that assists in determining business needs and problem-solving strategies.The creation of software or system components, process enhancements, organizational modifications, or the creation of strategic plans and policies are a few examples of these solutions.
Problem solving is one of the core competencies of an effective business analyst. They describe and solve problems to ensure that the root cause of a problem is well understood by all stakeholders and resolved by the solution. Describing the problem involves ensuring that the type of problem and any underlying issues connected to the problem ...
Email. Business analytics is a powerful tool in today's marketplace that can be used to make decisions and craft business strategies. Across industries, organizations generate vast amounts of data which, in turn, has heightened the need for professionals who are data literate and know how to interpret and analyze that information.
Business analytics helps organizations streamline their operations by identifying inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. Businesses can use data-driven analysis to optimize processes, allocate resources more effectively, and enhance productivity, ultimately driving operational efficiency to new heights. 2.
Now that we've established a general idea of how strongly connected analytical skills and problem-solving are, let's dig deeper into the top 5 reasons why data analytics is important in problem-solving. 1. Uncover Hidden Details. Data analytics is great at putting the minor details out in the spotlight.
A way that the Business Analyst can help to solve this problem is by conducting a business process analysis to understand the current processes in place and identify areas for improvement. The Business Analyst can also work with the relevant stakeholders to develop new or improved processes where needed. #7 Lack of understanding of user needs
Problem-solving in business is defined as implementing processes that reduce or remove obstacles that are preventing you or others from accomplishing operational and strategic business goals. In business, a problem is a situation that creates a gap between the desired and actual outcomes. In addition, a true problem typically does not have an ...
In business analytics, statistics is usually divided into two categories: Descriptive Statistics: These provide a summary of the main aspects of the data, such as mean, median, mode, and standard ...
With analytics tools, a business can extract the simple structured data and reduce its effort in extracting unstructured and semi-structured information. The analytics tools used in problem-solving have two criteria: 1. Ease in the generation of analytic files. 2.
Below are the top business challenges that you can overcome with a BI tool: 1. You have a poor data ecosystem resulting in a lack of control over business processes. A BI tool, in general, sets a ...
This shows how important business analytics is for your product. Business analytics gives insights that help you make better decisions to improve your product. This article will show seven examples of business analytics to highlight its positive impact. TL;DR. Business analytics uses data to find trends and boost performance. It helps companies ...
The Supply Chain Management major at The University of Scranton teaches students analytic, problem-solving and technical skills. Supply Chain Management is one of the core areas of business. Apply Apply: Undergraduate Apply: Graduate Give to Scranton Contact My.Scranton
Business Analytics internship in Bangalore by Webknot Technologies Private Limited. ... Understanding of business processes Ability to gather and document business requirements Attention to detail and problem-solving abilities Ability to work independently and as part of a team Experience with relevant software tools and technologies is a plus ...
S&P Global, an International financial analytics corporation, has described the 650,000 barrels per day (bpd) Dangote Oil Refinery and Petrochemicals company as capable of resolving Nigeria's foreign exchange (forex) issue and its huge pressure on the local Naira currency, while also catalysing the country's economic development.