10 Best Problem-Solving Therapy Worksheets & Activities

Cognitive science tells us that we regularly face not only well-defined problems but, importantly, many that are ill defined (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
Sometimes, we find ourselves unable to overcome our daily problems or the inevitable (though hopefully infrequent) life traumas we face.
Problem-Solving Therapy aims to reduce the incidence and impact of mental health disorders and improve wellbeing by helping clients face life’s difficulties (Dobson, 2011).
This article introduces Problem-Solving Therapy and offers techniques, activities, and worksheets that mental health professionals can use with clients.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free . These science-based exercises explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology, including strengths, values, and self-compassion, and will give you the tools to enhance the wellbeing of your clients, students, or employees.

This Article Contains:
What is problem-solving therapy, 14 steps for problem-solving therapy, 3 best interventions and techniques, 7 activities and worksheets for your session, fascinating books on the topic, resources from positivepsychology.com, a take-home message.
Problem-Solving Therapy assumes that mental disorders arise in response to ineffective or maladaptive coping. By adopting a more realistic and optimistic view of coping, individuals can understand the role of emotions and develop actions to reduce distress and maintain mental wellbeing (Nezu & Nezu, 2009).
“Problem-solving therapy (PST) is a psychosocial intervention, generally considered to be under a cognitive-behavioral umbrella” (Nezu, Nezu, & D’Zurilla, 2013, p. ix). It aims to encourage the client to cope better with day-to-day problems and traumatic events and reduce their impact on mental and physical wellbeing.
Clinical research, counseling, and health psychology have shown PST to be highly effective in clients of all ages, ranging from children to the elderly, across multiple clinical settings, including schizophrenia, stress, and anxiety disorders (Dobson, 2011).
Can it help with depression?
PST appears particularly helpful in treating clients with depression. A recent analysis of 30 studies found that PST was an effective treatment with a similar degree of success as other successful therapies targeting depression (Cuijpers, Wit, Kleiboer, Karyotaki, & Ebert, 2020).
Other studies confirm the value of PST and its effectiveness at treating depression in multiple age groups and its capacity to combine with other therapies, including drug treatments (Dobson, 2011).
The major concepts
Effective coping varies depending on the situation, and treatment typically focuses on improving the environment and reducing emotional distress (Dobson, 2011).
PST is based on two overlapping models:
Social problem-solving model
This model focuses on solving the problem “as it occurs in the natural social environment,” combined with a general coping strategy and a method of self-control (Dobson, 2011, p. 198).
The model includes three central concepts:
- Social problem-solving
- The problem
- The solution
The model is a “self-directed cognitive-behavioral process by which an individual, couple, or group attempts to identify or discover effective solutions for specific problems encountered in everyday living” (Dobson, 2011, p. 199).
Relational problem-solving model
The theory of PST is underpinned by a relational problem-solving model, whereby stress is viewed in terms of the relationships between three factors:
- Stressful life events
- Emotional distress and wellbeing
- Problem-solving coping
Therefore, when a significant adverse life event occurs, it may require “sweeping readjustments in a person’s life” (Dobson, 2011, p. 202).

- Enhance positive problem orientation
- Decrease negative orientation
- Foster ability to apply rational problem-solving skills
- Reduce the tendency to avoid problem-solving
- Minimize the tendency to be careless and impulsive
D’Zurilla’s and Nezu’s model includes (modified from Dobson, 2011):
- Initial structuring Establish a positive therapeutic relationship that encourages optimism and explains the PST approach.
- Assessment Formally and informally assess areas of stress in the client’s life and their problem-solving strengths and weaknesses.
- Obstacles to effective problem-solving Explore typically human challenges to problem-solving, such as multitasking and the negative impact of stress. Introduce tools that can help, such as making lists, visualization, and breaking complex problems down.
- Problem orientation – fostering self-efficacy Introduce the importance of a positive problem orientation, adopting tools, such as visualization, to promote self-efficacy.
- Problem orientation – recognizing problems Help clients recognize issues as they occur and use problem checklists to ‘normalize’ the experience.
- Problem orientation – seeing problems as challenges Encourage clients to break free of harmful and restricted ways of thinking while learning how to argue from another point of view.
- Problem orientation – use and control emotions Help clients understand the role of emotions in problem-solving, including using feelings to inform the process and managing disruptive emotions (such as cognitive reframing and relaxation exercises).
- Problem orientation – stop and think Teach clients how to reduce impulsive and avoidance tendencies (visualizing a stop sign or traffic light).
- Problem definition and formulation Encourage an understanding of the nature of problems and set realistic goals and objectives.
- Generation of alternatives Work with clients to help them recognize the wide range of potential solutions to each problem (for example, brainstorming).
- Decision-making Encourage better decision-making through an improved understanding of the consequences of decisions and the value and likelihood of different outcomes.
- Solution implementation and verification Foster the client’s ability to carry out a solution plan, monitor its outcome, evaluate its effectiveness, and use self-reinforcement to increase the chance of success.
- Guided practice Encourage the application of problem-solving skills across multiple domains and future stressful problems.
- Rapid problem-solving Teach clients how to apply problem-solving questions and guidelines quickly in any given situation.
Success in PST depends on the effectiveness of its implementation; using the right approach is crucial (Dobson, 2011).
Problem-solving therapy – Baycrest
The following interventions and techniques are helpful when implementing more effective problem-solving approaches in client’s lives.
First, it is essential to consider if PST is the best approach for the client, based on the problems they present.
Is PPT appropriate?
It is vital to consider whether PST is appropriate for the client’s situation. Therapists new to the approach may require additional guidance (Nezu et al., 2013).
Therapists should consider the following questions before beginning PST with a client (modified from Nezu et al., 2013):
- Has PST proven effective in the past for the problem? For example, research has shown success with depression, generalized anxiety, back pain, Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, and supporting caregivers (Nezu et al., 2013).
- Is PST acceptable to the client?
- Is the individual experiencing a significant mental or physical health problem?
All affirmative answers suggest that PST would be a helpful technique to apply in this instance.
Five problem-solving steps
The following five steps are valuable when working with clients to help them cope with and manage their environment (modified from Dobson, 2011).
Ask the client to consider the following points (forming the acronym ADAPT) when confronted by a problem:
- Attitude Aim to adopt a positive, optimistic attitude to the problem and problem-solving process.
- Define Obtain all required facts and details of potential obstacles to define the problem.
- Alternatives Identify various alternative solutions and actions to overcome the obstacle and achieve the problem-solving goal.
- Predict Predict each alternative’s positive and negative outcomes and choose the one most likely to achieve the goal and maximize the benefits.
- Try out Once selected, try out the solution and monitor its effectiveness while engaging in self-reinforcement.
If the client is not satisfied with their solution, they can return to step ‘A’ and find a more appropriate solution.

Download 3 Free Positive Psychology Exercises (PDF)
Enhance wellbeing with these free, science-based exercises that draw on the latest insights from positive psychology.
Download 3 Free Positive Psychology Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
Positive self-statements
When dealing with clients facing negative self-beliefs, it can be helpful for them to use positive self-statements.
Use the following (or add new) self-statements to replace harmful, negative thinking (modified from Dobson, 2011):
- I can solve this problem; I’ve tackled similar ones before.
- I can cope with this.
- I just need to take a breath and relax.
- Once I start, it will be easier.
- It’s okay to look out for myself.
- I can get help if needed.
- Other people feel the same way I do.
- I’ll take one piece of the problem at a time.
- I can keep my fears in check.
- I don’t need to please everyone.

5 Worksheets and workbooks
Problem-solving self-monitoring form.
Answering the questions in the Problem-Solving Self-Monitoring Form provides the therapist with necessary information regarding the client’s overall and specific problem-solving approaches and reactions (Dobson, 2011).
Ask the client to complete the following:
- Describe the problem you are facing.
- What is your goal?
- What have you tried so far to solve the problem?
- What was the outcome?
Reactions to Stress
It can be helpful for the client to recognize their own experiences of stress. Do they react angrily, withdraw, or give up (Dobson, 2011)?
The Reactions to Stress worksheet can be given to the client as homework to capture stressful events and their reactions. By recording how they felt, behaved, and thought, they can recognize repeating patterns.
What Are Your Unique Triggers?
Helping clients capture triggers for their stressful reactions can encourage emotional regulation.
When clients can identify triggers that may lead to a negative response, they can stop the experience or slow down their emotional reaction (Dobson, 2011).
The What Are Your Unique Triggers ? worksheet helps the client identify their triggers (e.g., conflict, relationships, physical environment, etc.).
Problem-Solving worksheet
Imagining an existing or potential problem and working through how to resolve it can be a powerful exercise for the client.
Use the Problem-Solving worksheet to state a problem and goal and consider the obstacles in the way. Then explore options for achieving the goal, along with their pros and cons, to assess the best action plan.
Getting the Facts
Clients can become better equipped to tackle problems and choose the right course of action by recognizing facts versus assumptions and gathering all the necessary information (Dobson, 2011).
Use the Getting the Facts worksheet to answer the following questions clearly and unambiguously:
- Who is involved?
- What did or did not happen, and how did it bother you?
- Where did it happen?
- When did it happen?
- Why did it happen?
- How did you respond?
2 Helpful Group Activities
While therapists can use the worksheets above in group situations, the following two interventions work particularly well with more than one person.
Generating Alternative Solutions and Better Decision-Making
A group setting can provide an ideal opportunity to share a problem and identify potential solutions arising from multiple perspectives.
Use the Generating Alternative Solutions and Better Decision-Making worksheet and ask the client to explain the situation or problem to the group and the obstacles in the way.
Once the approaches are captured and reviewed, the individual can share their decision-making process with the group if they want further feedback.
Visualization
Visualization can be performed with individuals or in a group setting to help clients solve problems in multiple ways, including (Dobson, 2011):
- Clarifying the problem by looking at it from multiple perspectives
- Rehearsing a solution in the mind to improve and get more practice
- Visualizing a ‘safe place’ for relaxation, slowing down, and stress management
Guided imagery is particularly valuable for encouraging the group to take a ‘mental vacation’ and let go of stress.
Ask the group to begin with slow, deep breathing that fills the entire diaphragm. Then ask them to visualize a favorite scene (real or imagined) that makes them feel relaxed, perhaps beside a gently flowing river, a summer meadow, or at the beach.
The more the senses are engaged, the more real the experience. Ask the group to think about what they can hear, see, touch, smell, and even taste.
Encourage them to experience the situation as fully as possible, immersing themselves and enjoying their place of safety.
Such feelings of relaxation may be able to help clients fall asleep, relieve stress, and become more ready to solve problems.
We have included three of our favorite books on the subject of Problem-Solving Therapy below.
1. Problem-Solving Therapy: A Treatment Manual – Arthur Nezu, Christine Maguth Nezu, and Thomas D’Zurilla

This is an incredibly valuable book for anyone wishing to understand the principles and practice behind PST.
Written by the co-developers of PST, the manual provides powerful toolkits to overcome cognitive overload, emotional dysregulation, and the barriers to practical problem-solving.
Find the book on Amazon .
2. Emotion-Centered Problem-Solving Therapy: Treatment Guidelines – Arthur Nezu and Christine Maguth Nezu

Another, more recent, book from the creators of PST, this text includes important advances in neuroscience underpinning the role of emotion in behavioral treatment.
Along with clinical examples, the book also includes crucial toolkits that form part of a stepped model for the application of PST.
3. Handbook of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapies – Keith Dobson and David Dozois

This is the fourth edition of a hugely popular guide to Cognitive-Behavioral Therapies and includes a valuable and insightful section on Problem-Solving Therapy.
This is an important book for students and more experienced therapists wishing to form a high-level and in-depth understanding of the tools and techniques available to Cognitive-Behavioral Therapists.
For even more tools to help strengthen your clients’ problem-solving skills, check out the following free worksheets from our blog.
- Case Formulation Worksheet This worksheet presents a four-step framework to help therapists and their clients come to a shared understanding of the client’s presenting problem.
- Understanding Your Default Problem-Solving Approach This worksheet poses a series of questions helping clients reflect on their typical cognitive, emotional, and behavioral responses to problems.
- Social Problem Solving: Step by Step This worksheet presents a streamlined template to help clients define a problem, generate possible courses of action, and evaluate the effectiveness of an implemented solution.
If you’re looking for more science-based ways to help others enhance their wellbeing, check out this signature collection of 17 validated positive psychology tools for practitioners. Use them to help others flourish and thrive.

17 Top-Rated Positive Psychology Exercises for Practitioners
Expand your arsenal and impact with these 17 Positive Psychology Exercises [PDF] , scientifically designed to promote human flourishing, meaning, and wellbeing.
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
While we are born problem-solvers, facing an incredibly diverse set of challenges daily, we sometimes need support.
Problem-Solving Therapy aims to reduce stress and associated mental health disorders and improve wellbeing by improving our ability to cope. PST is valuable in diverse clinical settings, ranging from depression to schizophrenia, with research suggesting it as a highly effective treatment for teaching coping strategies and reducing emotional distress.
Many PST techniques are available to help improve clients’ positive outlook on obstacles while reducing avoidance of problem situations and the tendency to be careless and impulsive.
The PST model typically assesses the client’s strengths, weaknesses, and coping strategies when facing problems before encouraging a healthy experience of and relationship with problem-solving.
Why not use this article to explore the theory behind PST and try out some of our powerful tools and interventions with your clients to help them with their decision-making, coping, and problem-solving?
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free .
- Cuijpers, P., Wit, L., Kleiboer, A., Karyotaki, E., & Ebert, D. (2020). Problem-solving therapy for adult depression: An updated meta-analysis. European P sychiatry , 48 (1), 27–37.
- Dobson, K. S. (2011). Handbook of cognitive-behavioral therapies (3rd ed.). Guilford Press.
- Dobson, K. S., & Dozois, D. J. A. (2021). Handbook of cognitive-behavioral therapies (4th ed.). Guilford Press.
- Eysenck, M. W., & Keane, M. T. (2015). Cognitive psychology: A student’s handbook . Psychology Press.
- Nezu, A. M., & Nezu, C. M. (2009). Problem-solving therapy DVD . Retrieved September 13, 2021, from https://www.apa.org/pubs/videos/4310852
- Nezu, A. M., & Nezu, C. M. (2018). Emotion-centered problem-solving therapy: Treatment guidelines. Springer.
- Nezu, A. M., Nezu, C. M., & D’Zurilla, T. J. (2013). Problem-solving therapy: A treatment manual . Springer.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
Thanks for your information given, it was helpful for me something new I learned
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles


The Empty Chair Technique: How It Can Help Your Clients
Resolving ‘unfinished business’ is often an essential part of counseling. If left unresolved, it can contribute to depression, anxiety, and mental ill-health while damaging existing [...]

29 Best Group Therapy Activities for Supporting Adults
As humans, we are social creatures with personal histories based on the various groups that make up our lives. Childhood begins with a family of [...]

47 Free Therapy Resources to Help Kick-Start Your New Practice
Setting up a private practice in psychotherapy brings several challenges, including a considerable investment of time and money. You can reduce risks early on by [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (54)
- Coaching & Application (58)
- Compassion (26)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (23)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (27)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (44)
- Motivation & Goals (46)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (30)
- Positive Communication (22)
- Positive Education (48)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (19)
- Positive Parenting (16)
- Positive Psychology (34)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (18)
- Relationships (45)
- Resilience & Coping (39)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (38)
- Strengths & Virtues (32)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)
Problem Solving

Download or send
Choose your language, professional version.
A PDF of the resource, theoretical background, suggested therapist questions and prompts.
Premium Feature
Client version.
A PDF of the resource plus client-friendly instructions where appropriate.
Fillable version (PDF)
A fillable version of the resource. This can be edited and saved in Adobe Acrobat, or other PDF editing software.
Editable version (PPT)
An editable Microsoft PowerPoint version of the resource.
Translation Template
Are you a qualified therapist who would like to help with our translation project?
Languages this resource is available in
- Chinese (Simplified)
- Chinese (Traditional)
- English (GB)
- English (US)
- Spanish (International)
Mechanisms associated with this resource
- Skills deficit
Introduction & Theoretical Background
Problem Solving is a helpful intervention whenever clients present with difficulties, dilemmas, and conundrums, or when they experience repetitive thought such as rumination or worry. Effective problem solving is an essential life skill and this Problem Solving worksheet is designed to guide adults through steps which will help them to generate solutions to ‘stuck’ situations in their lives. It follows the qualities of effective problem solving outlined by Nezu, Nezu & D’Zurilla (2013), namely: clearly defining a problem; generation of alternative solutions; deliberative decision making; and the implementation of the chosen solution.
The therapist’s stance during problem solving should be one of collaborative curiosity. It is not for the therapist to pass judgment or to impose their preferred solution. Instead it is the clinician’s role to sit alongside clients and to help them examine the advantages and disadvantages of their options and, if the client is ‘stuck’ in rumination or worry, to help motivate them to take action to become unstuck – constructive rumination asks “How can I…?” questions instead of “Why…?” questions.
In their description of problem solving therapy Nezu, Nezu & D’Zurilla (2013) describe how it is helpful to elicit a positive orientation towards the problem which involves: being willing to appraise problems as challenges; remain optimistic that problems are solvable; remember that successful problem solving involves time and effort.
Therapist Guidance
- What is the nature of the problem?
- What are my goals?
- What is getting the way of me reaching my goals?
- “Can you think of any ways that you could make this problem not be a problem any more?”
- “What’s keeping this problem as a problem? What could you do to target that part of the problem?”
- “If your friend was bothered by a problem like this what might be something that you recommend they try?”
- “What would be some of the worst ways of solving a problem like this? And the best?”
- “How would Batman solve a problem like this?”
- Consider short term and long-term implications of each strategy
- Implications may relate to: emotional well-being, choices & opportunities, relationships, self-growth
- The next step is to consider which of the available options is the best solution. If you do not feel positive about any solutions, the choice becomes “Which is the least-worst?”. Remember that “even not-making-a-choice is a form of choice”.
- The last step of problem solving is putting a plan into action. Rumination, worry, and being in the horns of a dilemma are ‘stuck’ states which require a behavioral ‘nudge’ to become unstuck. Once you have put your plan into action it is important to monitor the outcome and to evaluate whether the actual outcome was consistent with the anticipated outcome.
References And Further Reading
- Beck, A.T., Rush, A.J., Shaw, B.F., & Emery, G. (1979). Cognitive therapy of depression . New York: Guilford. Nezu, A. M., Nezu, C. M., D’Zurilla, T. J. (2013). Problem-solving therapy: a treatment manual . New York: Springer.
- For clinicians
- For students
- Resources at your fingertips
- Designed for effectiveness
- Resources by problem
- Translation Project
- Help center
- Try us for free
- Terms & conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
Your browser is outdated. To ensure the best experience, update to the latest version of your preferred browser. Update
Problem Solving Packet
Guide your clients and groups through the problem solving process with the help of the Problem Solving Packet . Each page covers one of five problem solving steps with a rationale, tips, and questions. The steps include defining the problem, generating solutions, choosing one solution, implementing the solution, and reviewing the process.
Be sure to talk to your clients about how the five problem solving steps can be useful in day-to-day life. Are there any steps that they usually skip? What questions or steps helped them work through their problem?
Download Fillable Worksheet
Instructions.
PDF reading software is required to use fillable worksheets. This software is pre-installed on many devices. However, if it is not on your device, it can be downloaded for free. We recommend Adobe Acrobat Reader or Foxit Reader .
Notice: Opening a fillable worksheet directly within an internet browser (e.g. Internet Explorer, Chrome, or Safari) may prevent work from being saved. Instead, the file should be saved to your device and opened with a PDF reader.
To learn more or share these instructions, visit the Fillable Worksheet Instructions .
Download Customizable Worksheet
Use custom worksheets for the purpose of education and treatment.
Download, print, and share unlimited copies of custom worksheets.
Do not remove or alter copyright information.
Do not redistribute on a website, or as a part of a database or library.
Do not sell or sublicense custom worksheets.
Read our complete Terms and Conditions of Use .
PREVIEW - Page of

Download Options
Related Tools
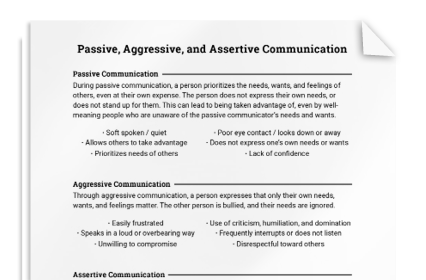
Passive, Aggressive, and Assertive Communication

Relationship Conflict Resolution
Therapy Goals
Become a Member!
- Customizable Worksheets
- Interactive Therapy Tools
- No More Ads
- Support Therapist Aid
Your account has been created.
Would you like to explore more features?
Recommended
Professional
Customizable and fillable worksheets.
Unlimited access to interactive therapy tools.
Support the creation of new tools for the entire mental health community.
Ad-free browsing.
Mindfulness
Distress Tolerance
Emotion Regulation
Interpersonal Effectiveness
Miscellaneous
Problem Solving
Emotion Regulation is the Dialectical Behavioral Therapy module that teaches how emotions work. It provides skills to help manage emotions instead of being managed by them, reduce vulnerability to negative emotions, and build positive emotional experiences.
When you find yourself experiencing a challenging emotion, you are faced with the choice between changing the emotion or changing the situation. Often this decision depends on whether your emotion is justified or not, which you can determine by using the skill Check the Facts. If your emotion and its intensity are justified, consider changing the situation by Problem Solving. This skill will help you find a solution to the problem situation and put it into action. There is also a handy flow chart to help you figure out whether Problem Solving or Opposite Action is the right skill to use.
There are 7 steps to Problem Solving that can help you figure out what to do next.
1. What is the problem? Describe the situation
2. Use Check the Facts to ensure you’re describing it accurately
3. Figure out your goal in solving the problem
What needs to happen so you can feel okay?
Keep it simple and realistically attainable
4. Brainstorm as many solutions as you can
Ask for suggestions from people you trust
Practice willingness – don’t be critical of any ideas at first
5. Choose a solution that fits the goal and is likely to work
If you’re having trouble choosing one, pick two
Do a Pro-Con 4-Square to compare them, then pick the best to try first
6. Take it step by stepTry the solution
7. Did it work? If not, go back to step 5 and choose another solution to tryEvaluate the results
Opposite to Emotion Action
Pleasant activities, check the facts, increasing positive emotions, letting go of painful emotions, managing extreme emotions, additional resources, mental health resources.
We aren't the only mental health resource out there. Check out these books, websites, social media accounts, and more for additional support. Read More
DBT Flashcards
Making DBT skills second nature takes practice. Use these flashcards on their page, download your own to print out, or purchase our pre-made set from our shop. Read More
DBT Encyclopedia
DBT has its own lingo which can be hard to understand for beginners. Visit our homemade DBT Encyclopedia to figure out what a term means. Read More
Mindfulness Exercises
Mindfulness practice is key to DBT. You don't have to meditate in silence everyday, though. Try these Mindfulness exercises to guide you. Read More
Diary Cards
Diary cards help track your emotions, urges, behaviors, and skill use. They help you see patterns. Learn how to use them and get samples. Read More

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 1. Identify the Problem Break it down into smaller steps and decide what you need to action first. Step 2. Brainstorm and write down as many ideas as you can that might help solve the problem, no matter how silly they seem - don't dismiss any possible solutions. Step 3. Consider the pros and cons of each possible solution, using a ...
Problem Solving. Step 1. Identify the Problem. Break it down into smaller steps and decide what you need to action first. Step 2. Brainstorm and write down as many ideas as you can that might help solve the problem, no matter how silly they seem - don't dismiss any possible solutions. Step 3.
We have included three of our favorite books on the subject of Problem-Solving Therapy below. 1. Problem-Solving Therapy: A Treatment Manual - Arthur Nezu, Christine Maguth Nezu, and Thomas D'Zurilla. This is an incredibly valuable book for anyone wishing to understand the principles and practice behind PST.
FACE: Problem SolvingF. Overcome problems by using FACE: Find and identify your target problem - what you need to face and solve Action - decide on the steps you need to take. ategies and resourcesEvalu. how did it go?FINDIdentify what problem you would like to be able to FACE and sol.
This self-help guide is intended for people with mild-to-moderate mental health issues. If you're feeling distressed, in a state of despair, suicidal or in need of emotional support you can phone NHS 24 on 111. For an emergency ambulance phone 999. It's easy to feel overwhelmed by problems, particularly if you're experiencing mental health ...
Problem solving in six steps. − Step 1. Identify your problem. Try to be clear and concise. − Step 2. Brainstorm solutions. List as many options as you can think of regardless of how silly they may seem. − Step 3. Evaluate your options. Choose your top three solutions from Step 2 and draw up a list of the main advantages and disadvantages ...
Problem Solving is a helpful intervention whenever clients present with difficulties, dilemmas, and conundrums, or when they experience repetitive thought such as rumination or worry. Effective problem solving is an essential life skill and this Problem Solving worksheet is designed to guide adults through steps which will help them to generate ...
Step 3: Decide which solution is most effective. Go back to the solutions list and cross out any that are "obviously" ineffective. Re-write the "top" 3-5 below and note several positive and negative consequences (personal, social, short-term, long-term) for each.
worksheet. Guide your clients and groups through the problem solving process with the help of the Problem Solving Packet. Each page covers one of five problem solving steps with a rationale, tips, and questions. The steps include defining the problem, generating solutions, choosing one solution, implementing the solution, and reviewing the process.
solving problems. It is also for people who dislike problem solving or who feel intimidated by problems. And it is for people who want to help others solve problems. For example, many parents may find this book useful for helping their children perform better in school. Business lead
CBT Information Leaflets & Self Help Guides (free downloads). This page: Worksheets ... PDF & PPT. Card pack: 56 cards for self help; ... FACE: Problem Solving. Feared Situation Hierarchy. Finding Meaning in Life. Food Diary. Food Diary 2. GAD: Worry Thought Record Sheet.
Get Started: Problem Solving. Self-check. How do you feel about your problem-solving skills? Write an "x" beside the box that feels like you. How I feel about my problem-solving skills X I have good problem-solving skills. I can solve most problems in my life. I have some problem-solving skills. I need to practice solving big problems.
2. Identifying problems 3. Types of problem - Activity 1 4. Recognising there's a problem 5. Barriers to problem- solving 6. Activity 2 — writing your problem list 7. Activity 3 - focusing on one problem 8. Activity 4 - pros and cons Section 1 of 12 1. Introduction Urgent help This self-help guide is intended for people with mild to-moderate ...
Identify your problem. Try to be clear and concise. − Step 2. Brainstorm solutions. List as many options as you can think of regardless of how silly they may seem. − Step 3. Evaluate your options. Choose your top three solutions from Step 2 and draw up a list of the main advantages and disadvantages of each option. − Step 4.
We end up feeling frustrated, stressed or maybe even depressed and hopeless. Problem-solving may have a number of benefits, including: • Beter functioning at work or school. • More satisfying relationships with friends, family and co-workers. • Higher self-esteem. • Higher life satisfaction. WELLNESS MODULE 4.
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy (CBT) has been proven to help mental health problems. This website provides CBT self help and therapy resources, including worksheets and information sheets, plus videos and self help mp3s. We provide a range of resources to help you get started immediately.
2. Use Check the Facts to ensure you're describing it accurately. 3. Figure out your goal in solving the problem. What needs to happen so you can feel okay? Keep it simple and realistically attainable. 4. Brainstorm as many solutions as you can. Ask for suggestions from people you trust.
Contents of this self help guide. Understanding more about anger. Learning how to challenge your unhelpful thoughts and see things in a more realistic light. Learning how you can feel more relaxed, both physically and mentally. Improving your problem solving skills. Consider making positive changes to your lifestyle.
Self Help Strategies for GAD. SELF-HELP STRATEGIES FOR GAD. STEP 1: Learning about anxiety and GAD. No matter what type of anxiety problem you are struggling with, it is important that you understand certain facts about anxiety. FACT 1: Anxiety is a normal and adaptive system in the body that tells us when we are in danger.
Problem solving self-help guide Introduction This self-help guide is intended for people with mild-to-moderate mental health issues. If you're feeling distressed, in a state of despair, suicidal or need emotional support you can phone Samaritans for free on 116 123. If you're ill and feel it can't wait until your GP practice reopens you can phone
ADHD (Adult) Anger. Anorexia. Anxiety. Attention Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder ( Adult) Avoidance. Breathe : Mindful breathing. Bulimia & Binge Eating. Christian Mental Health.
Adult Problem Solving Adult problem solving is really important to understand. In this article I will address how adults can do effective problem solving in relationships and in life in general. Problem-solving for adults can seem more complicated than problem-solving for children but actually the key principles are the same.
Worry is the main problem, but there are other specific aspects to the anxiety that occur with GAD: Worry about current problems and hypothetical situations, worry about worry, intolerance of uncertainty, cognitive avoidance and lack of problem solving skills. WORRY There are two main types of worry. Type 1 worries relate to feared future ...