Heuristics: Definition, Examples, And How They Work
Benjamin Frimodig
Science Expert
B.A., History and Science, Harvard University
Ben Frimodig is a 2021 graduate of Harvard College, where he studied the History of Science.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
Every day our brains must process and respond to thousands of problems, both large and small, at a moment’s notice. It might even be overwhelming to consider the sheer volume of complex problems we regularly face in need of a quick solution.
While one might wish there was time to methodically and thoughtfully evaluate the fine details of our everyday tasks, the cognitive demands of daily life often make such processing logistically impossible.
Therefore, the brain must develop reliable shortcuts to keep up with the stimulus-rich environments we inhabit. Psychologists refer to these efficient problem-solving techniques as heuristics.

Heuristics can be thought of as general cognitive frameworks humans rely on regularly to reach a solution quickly.
For example, if a student needs to decide what subject she will study at university, her intuition will likely be drawn toward the path that she envisions as most satisfying, practical, and interesting.
She may also think back on her strengths and weaknesses in secondary school or perhaps even write out a pros and cons list to facilitate her choice.
It’s important to note that these heuristics broadly apply to everyday problems, produce sound solutions, and helps simplify otherwise complicated mental tasks. These are the three defining features of a heuristic.
While the concept of heuristics dates back to Ancient Greece (the term is derived from the Greek word for “to discover”), most of the information known today on the subject comes from prominent twentieth-century social scientists.
Herbert Simon’s study of a notion he called “bounded rationality” focused on decision-making under restrictive cognitive conditions, such as limited time and information.
This concept of optimizing an inherently imperfect analysis frames the contemporary study of heuristics and leads many to credit Simon as a foundational figure in the field.

Kahneman’s Theory of Decision Making
The immense contributions of psychologist Daniel Kahneman to our understanding of cognitive problem-solving deserve special attention.
As context for his theory, Kahneman put forward the estimate that an individual makes around 35,000 decisions each day! To reach these resolutions, the mind relies on either “fast” or “slow” thinking.

The fast thinking pathway (system 1) operates mostly unconsciously and aims to reach reliable decisions with as minimal cognitive strain as possible.
While system 1 relies on broad observations and quick evaluative techniques (heuristics!), system 2 (slow thinking) requires conscious, continuous attention to carefully assess the details of a given problem and logically reach a solution.
Given the sheer volume of daily decisions, it’s no surprise that around 98% of problem-solving uses system 1.
Thus, it is crucial that the human mind develops a toolbox of effective, efficient heuristics to support this fast-thinking pathway.
Heuristics vs. Algorithms
Those who’ve studied the psychology of decision-making might notice similarities between heuristics and algorithms. However, remember that these are two distinct modes of cognition.
Heuristics are methods or strategies which often lead to problem solutions but are not guaranteed to succeed.
They can be distinguished from algorithms, which are methods or procedures that will always produce a solution sooner or later.
An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure that can be reliably used to solve a specific problem. While the concept of an algorithm is most commonly used in reference to technology and mathematics, our brains rely on algorithms every day to resolve issues (Kahneman, 2011).
The important thing to remember is that algorithms are a set of mental instructions unique to specific situations, while heuristics are general rules of thumb that can help the mind process and overcome various obstacles.
For example, if you are thoughtfully reading every line of this article, you are using an algorithm.
On the other hand, if you are quickly skimming each section for important information or perhaps focusing only on sections you don’t already understand, you are using a heuristic!
Why Heuristics Are Used
Heuristics usually occurs when one of five conditions is met (Pratkanis, 1989):
- When one is faced with too much information
- When the time to make a decision is limited
- When the decision to be made is unimportant
- When there is access to very little information to use in making the decision
- When an appropriate heuristic happens to come to mind at the same moment
When studying heuristics, keep in mind both the benefits and unavoidable drawbacks of their application. The ubiquity of these techniques in human society makes such weaknesses especially worthy of evaluation.
More specifically, in expediting decision-making processes, heuristics also predispose us to a number of cognitive biases .
A cognitive bias is an incorrect but pervasive judgment derived from an illogical pattern of cognition. In simple terms, a cognitive bias occurs when one internalizes a subjective perception as a reliable and objective truth.
Heuristics are reliable but imperfect; In the application of broad decision-making “shortcuts” to guide one’s response to specific situations, occasional errors are both inevitable and have the potential to catalyze persistent mistakes.
For example, consider the risks of faulty applications of the representative heuristic discussed above. While the technique encourages one to assign situations into broad categories based on superficial characteristics and one’s past experiences for the sake of cognitive expediency, such thinking is also the basis of stereotypes and discrimination.
In practice, these errors result in the disproportionate favoring of one group and/or the oppression of other groups within a given society.
Indeed, the most impactful research relating to heuristics often centers on the connection between them and systematic discrimination.
The tradeoff between thoughtful rationality and cognitive efficiency encompasses both the benefits and pitfalls of heuristics and represents a foundational concept in psychological research.
When learning about heuristics, keep in mind their relevance to all areas of human interaction. After all, the study of social psychology is intrinsically interdisciplinary.
Many of the most important studies on heuristics relate to flawed decision-making processes in high-stakes fields like law, medicine, and politics.
Researchers often draw on a distinct set of already established heuristics in their analysis. While dozens of unique heuristics have been observed, brief descriptions of those most central to the field are included below:
Availability Heuristic
The availability heuristic describes the tendency to make choices based on information that comes to mind readily.
For example, children of divorced parents are more likely to have pessimistic views towards marriage as adults.
Of important note, this heuristic can also involve assigning more importance to more recently learned information, largely due to the easier recall of such information.
Representativeness Heuristic
This technique allows one to quickly assign probabilities to and predict the outcome of new scenarios using psychological prototypes derived from past experiences.
For example, juries are less likely to convict individuals who are well-groomed and wearing formal attire (under the assumption that stylish, well-kempt individuals typically do not commit crimes).
This is one of the most studied heuristics by social psychologists for its relevance to the development of stereotypes.
Scarcity Heuristic
This method of decision-making is predicated on the perception of less abundant, rarer items as inherently more valuable than more abundant items.
We rely on the scarcity heuristic when we must make a fast selection with incomplete information. For example, a student deciding between two universities may be drawn toward the option with the lower acceptance rate, assuming that this exclusivity indicates a more desirable experience.
The concept of scarcity is central to behavioral economists’ study of consumer behavior (a field that evaluates economics through the lens of human psychology).
Trial and Error
This is the most basic and perhaps frequently cited heuristic. Trial and error can be used to solve a problem that possesses a discrete number of possible solutions and involves simply attempting each possible option until the correct solution is identified.
For example, if an individual was putting together a jigsaw puzzle, he or she would try multiple pieces until locating a proper fit.
This technique is commonly taught in introductory psychology courses due to its simple representation of the central purpose of heuristics: the use of reliable problem-solving frameworks to reduce cognitive load.
Anchoring and Adjustment Heuristic
Anchoring refers to the tendency to formulate expectations relating to new scenarios relative to an already ingrained piece of information.

Put simply, this anchoring one to form reasonable estimations around uncertainties. For example, if asked to estimate the number of days in a year on Mars, many people would first call to mind the fact the Earth’s year is 365 days (the “anchor”) and adjust accordingly.
This tendency can also help explain the observation that ingrained information often hinders the learning of new information, a concept known as retroactive inhibition.
Familiarity Heuristic
This technique can be used to guide actions in cognitively demanding situations by simply reverting to previous behaviors successfully utilized under similar circumstances.
The familiarity heuristic is most useful in unfamiliar, stressful environments.
For example, a job seeker might recall behavioral standards in other high-stakes situations from her past (perhaps an important presentation at university) to guide her behavior in a job interview.
Many psychologists interpret this technique as a slightly more specific variation of the availability heuristic.
How to Make Better Decisions
Heuristics are ingrained cognitive processes utilized by all humans and can lead to various biases.
Both of these statements are established facts. However, this does not mean that the biases that heuristics produce are unavoidable. As the wide-ranging impacts of such biases on societal institutions have become a popular research topic, psychologists have emphasized techniques for reaching more sound, thoughtful and fair decisions in our daily lives.
Ironically, many of these techniques are themselves heuristics!
To focus on the key details of a given problem, one might create a mental list of explicit goals and values. To clearly identify the impacts of choice, one should imagine its impacts one year in the future and from the perspective of all parties involved.
Most importantly, one must gain a mindful understanding of the problem-solving techniques used by our minds and the common mistakes that result. Mindfulness of these flawed yet persistent pathways allows one to quickly identify and remedy the biases (or otherwise flawed thinking) they tend to create!
Further Information
- Shah, A. K., & Oppenheimer, D. M. (2008). Heuristics made easy: an effort-reduction framework. Psychological bulletin, 134(2), 207.
- Marewski, J. N., & Gigerenzer, G. (2012). Heuristic decision making in medicine. Dialogues in clinical neuroscience, 14(1), 77.
- Del Campo, C., Pauser, S., Steiner, E., & Vetschera, R. (2016). Decision making styles and the use of heuristics in decision making. Journal of Business Economics, 86(4), 389-412.
What is a heuristic in psychology?
A heuristic in psychology is a mental shortcut or rule of thumb that simplifies decision-making and problem-solving. Heuristics often speed up the process of finding a satisfactory solution, but they can also lead to cognitive biases.
Bobadilla-Suarez, S., & Love, B. C. (2017, May 29). Fast or Frugal, but Not Both: Decision Heuristics Under Time Pressure. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition .
Bowes, S. M., Ammirati, R. J., Costello, T. H., Basterfield, C., & Lilienfeld, S. O. (2020). Cognitive biases, heuristics, and logical fallacies in clinical practice: A brief field guide for practicing clinicians and supervisors. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 51 (5), 435–445.
Dietrich, C. (2010). “Decision Making: Factors that Influence Decision Making, Heuristics Used, and Decision Outcomes.” Inquiries Journal/Student Pulse, 2(02).
Groenewegen, A. (2021, September 1). Kahneman Fast and slow thinking: System 1 and 2 explained by Sue. SUE Behavioral Design. Retrieved March 26, 2022, from https://suebehaviouraldesign.com/kahneman-fast-slow-thinking/
Kahneman, D., Lovallo, D., & Sibony, O. (2011). Before you make that big decision .
Kahneman, D. (2011). Thinking, fast and slow . Macmillan.
Pratkanis, A. (1989). The cognitive representation of attitudes. In A. R. Pratkanis, S. J. Breckler, & A. G. Greenwald (Eds.), Attitude structure and function (pp. 71–98). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Simon, H.A., 1956. Rational choice and the structure of the environment. Psychological Review .
Tversky, A., & Kahneman, D. (1974). Judgment under Uncertainty: Heuristics and Biases. Science, 185 (4157), 1124–1131.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Are Heuristics?
These mental shortcuts can help people make decisions more efficiently
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Steven Gans, MD is board-certified in psychiatry and is an active supervisor, teacher, and mentor at Massachusetts General Hospital.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/steven-gans-1000-51582b7f23b6462f8713961deb74959f.jpg)
Verywell / Cindy Chung
- History and Origins
- Heuristics vs. Algorithms
- Heuristics and Bias
How to Make Better Decisions
Heuristics are mental shortcuts that allow people to solve problems and make judgments quickly and efficiently. These rule-of-thumb strategies shorten decision-making time and allow people to function without constantly stopping to think about their next course of action.
However, there are both benefits and drawbacks of heuristics. While heuristics are helpful in many situations, they can also lead to cognitive biases . Becoming aware of this might help you make better and more accurate decisions.
Press Play for Advice On Making Decisions
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares a simple way to make a tough decision. Click below to listen now.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
The History and Origins of Heuristics
Nobel-prize winning economist and cognitive psychologist Herbert Simon originally introduced the concept of heuristics in psychology in the 1950s. He suggested that while people strive to make rational choices, human judgment is subject to cognitive limitations. Purely rational decisions would involve weighing all the potential costs and possible benefits of every alternative.
But people are limited by the amount of time they have to make a choice as well as the amount of information they have at their disposal. Other factors such as overall intelligence and accuracy of perceptions also influence the decision-making process.
During the 1970s, psychologists Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman presented their research on cognitive biases. They proposed that these biases influence how people think and the judgments people make.
As a result of these limitations, we are forced to rely on mental shortcuts to help us make sense of the world. Simon's research demonstrated that humans were limited in their ability to make rational decisions, but it was Tversky and Kahneman's work that introduced the study of heuristics and the specific ways of thinking that people rely on to simplify the decision-making process.
How Heuristics Are Used
Heuristics play important roles in both problem-solving and decision-making , as we often turn to these mental shortcuts when we need a quick solution.
Here are a few different theories from psychologists about why we rely on heuristics.
- Attribute substitution : People substitute simpler but related questions in place of more complex and difficult questions.
- Effort reduction : People use heuristics as a type of cognitive laziness to reduce the mental effort required to make choices and decisions.
- Fast and frugal : People use heuristics because they can be fast and correct in certain contexts. Some theories argue that heuristics are actually more accurate than they are biased.
In order to cope with the tremendous amount of information we encounter and to speed up the decision-making process, our brains rely on these mental strategies to simplify things so we don't have to spend endless amounts of time analyzing every detail.
You probably make hundreds or even thousands of decisions every day. What should you have for breakfast? What should you wear today? Should you drive or take the bus? Fortunately, heuristics allow you to make such decisions with relative ease and without a great deal of agonizing.
There are many heuristics examples in everyday life. When trying to decide if you should drive or ride the bus to work, for instance, you might remember that there is road construction along the bus route. You realize that this might slow the bus and cause you to be late for work. So you leave earlier and drive to work on an alternate route.
Heuristics allow you to think through the possible outcomes quickly and arrive at a solution.
Are Heuristics Good or Bad?
Heuristics aren't inherently good or bad, but there are pros and cons to using them to make decisions. While they can help us figure out a solution to a problem faster, they can also lead to inaccurate judgments about other people or situations.
Types of Heuristics
There are many different kinds of heuristics. While each type plays a role in decision-making, they occur during different contexts. Understanding the types can help you better understand which one you are using and when.
Availability
The availability heuristic involves making decisions based upon how easy it is to bring something to mind. When you are trying to make a decision, you might quickly remember a number of relevant examples. Since these are more readily available in your memory, you will likely judge these outcomes as being more common or frequently occurring.
For example, if you are thinking of flying and suddenly think of a number of recent airline accidents, you might feel like air travel is too dangerous and decide to travel by car instead. Because those examples of air disasters came to mind so easily, the availability heuristic leads you to think that plane crashes are more common than they really are.
Familiarity
The familiarity heuristic refers to how people tend to have more favorable opinions of things, people, or places they've experienced before as opposed to new ones. In fact, given two options, people may choose something they're more familiar with even if the new option provides more benefits.
Representativeness
The representativeness heuristic involves making a decision by comparing the present situation to the most representative mental prototype. When you are trying to decide if someone is trustworthy, you might compare aspects of the individual to other mental examples you hold.
A soft-spoken older woman might remind you of your grandmother, so you might immediately assume that she is kind, gentle, and trustworthy. However, this is an example of a heuristic bias, as you can't know someone trustworthy based on their age alone.
The affect heuristic involves making choices that are influenced by the emotions that an individual is experiencing at that moment. For example, research has shown that people are more likely to see decisions as having benefits and lower risks when they are in a positive mood. Negative emotions, on the other hand, lead people to focus on the potential downsides of a decision rather than the possible benefits.
The anchoring bias involves the tendency to be overly influenced by the first bit of information we hear or learn. This can make it more difficult to consider other factors and lead to poor choices. For example, anchoring bias can influence how much you are willing to pay for something, causing you to jump at the first offer without shopping around for a better deal.
Scarcity is a principle in heuristics in which we view things that are scarce or less available to us as inherently more valuable. The scarcity heuristic is one often used by marketers to influence people to buy certain products. This is why you'll often see signs that advertise "limited time only" or that tell you to "get yours while supplies last."
Trial and Error
Trial and error is another type of heuristic in which people use a number of different strategies to solve something until they find what works. Examples of this type of heuristic are evident in everyday life. People use trial and error when they're playing video games, finding the fastest driving route to work, and learning to ride a bike (or learning any new skill).
Difference Between Heuristics and Algorithms
Though the terms are often confused, heuristics and algorithms are two distinct terms in psychology.
Algorithms are step-by-step instructions that lead to predictable, reliable outcomes; whereas heuristics are mental shortcuts that are basically best guesses. Algorithms always lead to accurate outcomes, whereas, heuristics do not.
Examples of algorithms include instructions for how to put together a piece of furniture or a recipe for cooking a certain dish. Health professionals also create algorithms or processes to follow in order to determine what type of treatment to use on a patient.
How Heuristics Can Lead to Bias
While heuristics can help us solve problems and speed up our decision-making process, they can introduce errors. As in the examples above, heuristics can lead to inaccurate judgments about how commonly things occur and about how representative certain things may be.
Just because something has worked in the past does not mean that it will work again, and relying on a heuristic can make it difficult to see alternative solutions or come up with new ideas.
Heuristics can also contribute to stereotypes and prejudice . Because people use mental shortcuts to classify and categorize people, they often overlook more relevant information and create stereotyped categorizations that are not in tune with reality.
While heuristics can be a useful tool, there are ways you can improve your decision-making and avoid cognitive bias at the same time.
We are more likely to make an error in judgment if we are trying to make a decision quickly or are under pressure to do so. Whenever possible, take a few deep breaths . Do something to distract yourself from the decision at hand. When you return to it, you may find you have a fresh perspective, or notice something you didn't before.
Identify the Goal
We tend to focus automatically on what works for us and make decisions that serve our best interest. But take a moment to know what you're trying to achieve. Are there other people who will be affected by this decision? What's best for them? Is there a common goal that can be achieved that will serve all parties?
Process Your Emotions
Fast decision-making is often influenced by emotions from past experiences that bubble to the surface. Is your decision based on facts or emotions? While emotions can be helpful, they may affect decisions in a negative way if they prevent us from seeing the full picture.
Recognize All-or-Nothing Thinking
When making a decision, it's a common tendency to believe you have to pick a single, well-defined path, and there's no going back. In reality, this often isn't the case.
Sometimes there are compromises involving two choices, or a third or fourth option that we didn't even think of at first. Try to recognize the nuances and possibilities of all choices involved, instead of using all-or-nothing thinking .
Rachlin H. Rational thought and rational behavior: A review of bounded rationality: The adaptive toolbox . J Exp Anal Behav . 2003;79(3):409–412. doi:10.1901/jeab.2003.79-409
Shah AK, Oppenheimer DM. Heuristics made easy: An effort-reduction framework . Psychol Bull. 2008;134(2):207-22. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.134.2.207
Marewski JN, Gigerenzer G. Heuristic decision making in medicine . Dialogues Clin Neurosci . 2012;14(1):77–89. PMID: 22577307
Schwikert SR, Curran T. Familiarity and recollection in heuristic decision making . J Exp Psychol Gen . 2014;143(6):2341-2365. doi:10.1037/xge0000024
Finucane M, Alhakami A, Slovic P, Johnson S. The affect heuristic in judgments of risks and benefits . J Behav Decis Mak . 2000; 13(1):1-17. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1099-0771(200001/03)13:1<1::AID-BDM333>3.0.CO;2-S
Cheung TT, Kroese FM, Fennis BM, De Ridder DT. Put a limit on it: The protective effects of scarcity heuristics when self-control is low . Health Psychol Open . 2015;2(2):2055102915615046. doi:10.1177/2055102915615046
Mohr H, Zwosta K, Markovic D, Bitzer S, Wolfensteller U, Ruge H. Deterministic response strategies in a trial-and-error learning task . Inman C, ed. PLoS Comput Biol. 2018;14(11):e1006621. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006621
Lang JM, Ford JD, Fitzgerald MM. An algorithm for determining use of trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy . Psychotherapy (Chic) . 2010;47(4):554-69. doi:10.1037/a0021184
Bigler RS, Clark C. The inherence heuristic: A key theoretical addition to understanding social stereotyping and prejudice. Behav Brain Sci . 2014;37(5):483-4. doi:10.1017/S0140525X1300366X
del Campo C, Pauser S, Steiner E, et al. Decision making styles and the use of heuristics in decision making . J Bus Econ. 2016;86:389–412. doi:10.1007/s11573-016-0811-y
Marewski JN, Gigerenzer G. Heuristic decision making in medicine . Dialogues Clin Neurosci . 2012;14(1):77-89. doi:10.31887/DCNS.2012.14.1/jmarewski
Zheng Y, Yang Z, Jin C, Qi Y, Liu X. The influence of emotion on fairness-related decision making: A critical review of theories and evidence . Front Psychol . 2017;8:1592. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01592
Bazerman MH. Judgment and decision making. In: Biswas-Diener R, Diener E, eds., Noba Textbook Series: Psychology. DEF Publishers.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

6.2: Problem Solving Strategies
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 54099

- Mehgan Andrade and Neil Walker
- College of the Canyons
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
When you are presented with a problem—whether it is a complex mathematical problem or a broken printer, how do you solve it? Before finding a solution to the problem, the problem must first be clearly identified. After that, one of many problem solving strategies can be applied, hopefully resulting in a solution.
A problem-solving strategy is a plan of action used to find a solution. Different strategies have different action plans associated with them ( Table 3 ). For example, a well-known strategy is trial and error. The old adage, “If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again” describes trial and error. In terms of your broken printer, you could try checking the ink levels, and if that doesn’t work, you could check to make sure the paper tray isn’t jammed. Or maybe the printer isn’t actually connected to your laptop. When using trial and error, you would continue to try different solutions until you solved your problem. Although trial and error is not typically one of the most time-efficient strategies, it is a commonly used one.
Table 1. Problem Solving Strategies
Another type of strategy is an algorithm. An algorithm is a problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve a desired outcome (Kahneman, 2011). You can think of an algorithm as a recipe with highly detailed instructions that produce the same result every time they are performed. Algorithms are used frequently in our everyday lives, especially in computer science. When you run a search on the Internet, search engines like Google use algorithms to decide which entries will appear first in your list of results.
Facebook also uses algorithms to decide which posts to display on your newsfeed. Can you identify other situations in which algorithms are used?
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A “rule of thumb” is an example of a heuristic. Such a rule saves the person time and energy when making a decision, but despite its time-saving characteristics, it is not always the best method for making a rational decision. Different types of heuristics are used in different types of situations, but the impulse to use a heuristic occurs when one of five conditions is met (Pratkanis, 1989):
· When one is faced with too much information
· When the time to make a decision is limited
· When the decision to be made is unimportant
· When there is access to very little information to use in making the decision
· When an appropriate heuristic happens to come to mind in the same moment
Working backwards is a useful heuristic in which you begin solving the problem by focusing on the end result. Consider this example: You live in Washington, D.C. and have been invited to a wedding at 4 PM on Saturday in Philadelphia. Knowing that Interstate 95 tends to back up any day of the week, you need to plan your route and time your departure accordingly. If you want to be at the wedding service by 3:30 PM, and it takes 2.5 hours to get to Philadelphia without traffic, what time should you leave your house? You use the working backwards heuristic to plan the events of your day on a regular basis, probably without even thinking about it.
Link to Learning
What problem-solving method could you use to solve Einstein’s famous riddle?
Another useful heuristic is the practice of accomplishing a large goal or task by breaking it into a series of smaller steps. Students often use this common method to complete a large research project or long essay for school. For example, students typically brainstorm, develop a thesis or main topic, research the chosen topic, organize their information into an outline, write a rough draft, revise and edit the rough draft, develop a final draft, organize the references list, and proofread their work before turning in the project. The large task becomes less overwhelming when it is broken down into a series of small steps.
Everyday Connections: Solving Puzzles
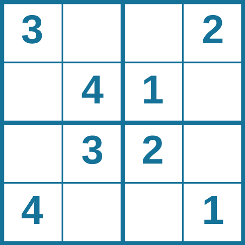
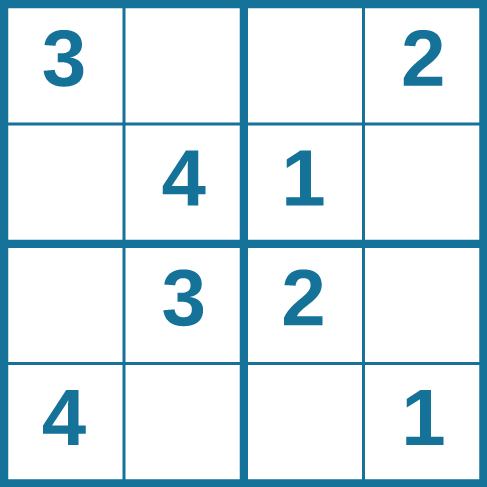
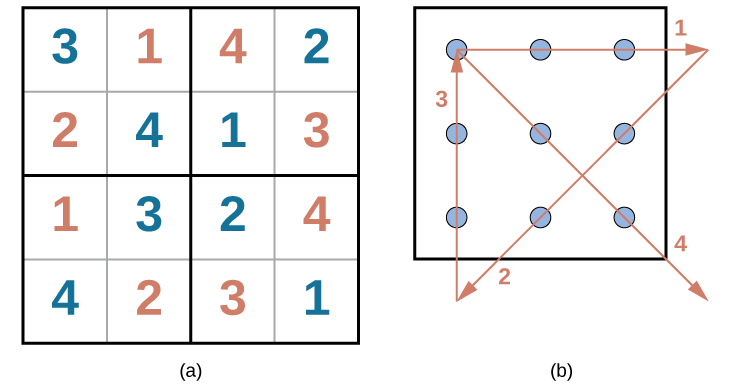
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below is a 4×4 grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: 1, 2, 3, or 4. Here are the rules: The numbers must total 10 in each bolded box, each row, and each column; however, each digit can only appear once in a bolded box, row, and column. Time yourself as you solve this puzzle and compare your time with a classmate.
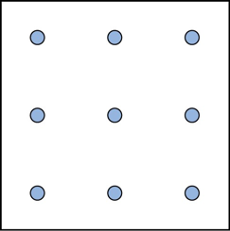
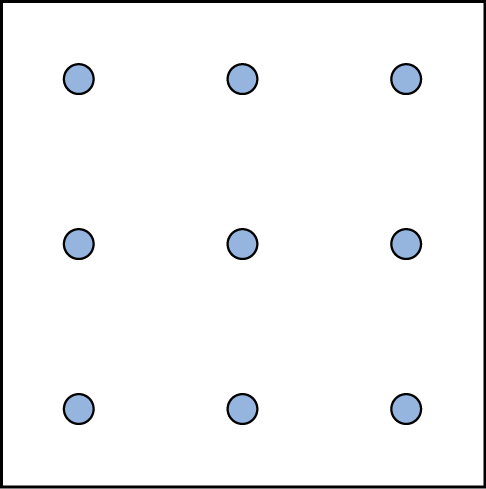
Here is another popular type of puzzle that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper:
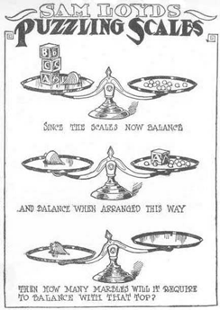
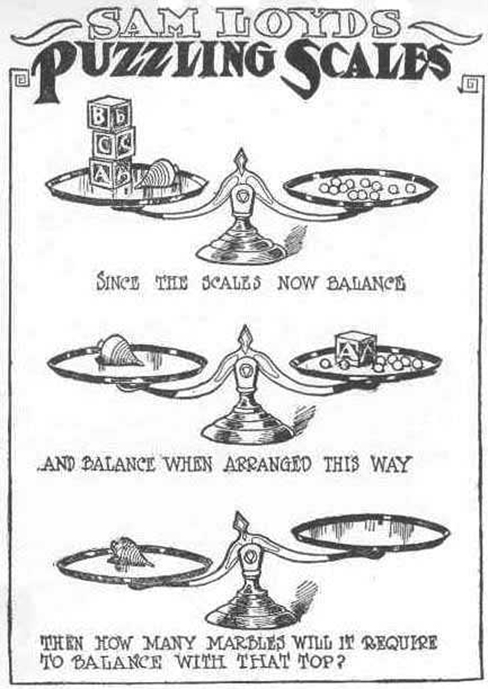
Take a look at the “Puzzling Scales” logic puzzle below. Sam Loyd, a well-known puzzle master, created and refined countless puzzles throughout his lifetime (Cyclopedia of Puzzles, n.d.).
Were you able to determine how many marbles are needed to balance the scales in Figure 3 ? You need nine . Were you able to solve the problems in Figure 1 and Figure 2 ? Here are the answers.
7.3 Problem-Solving
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe problem solving strategies
- Define algorithm and heuristic
- Explain some common roadblocks to effective problem solving
People face problems every day—usually, multiple problems throughout the day. Sometimes these problems are straightforward: To double a recipe for pizza dough, for example, all that is required is that each ingredient in the recipe be doubled. Sometimes, however, the problems we encounter are more complex. For example, say you have a work deadline, and you must mail a printed copy of a report to your supervisor by the end of the business day. The report is time-sensitive and must be sent overnight. You finished the report last night, but your printer will not work today. What should you do? First, you need to identify the problem and then apply a strategy for solving the problem.
The study of human and animal problem solving processes has provided much insight toward the understanding of our conscious experience and led to advancements in computer science and artificial intelligence. Essentially much of cognitive science today represents studies of how we consciously and unconsciously make decisions and solve problems. For instance, when encountered with a large amount of information, how do we go about making decisions about the most efficient way of sorting and analyzing all the information in order to find what you are looking for as in visual search paradigms in cognitive psychology. Or in a situation where a piece of machinery is not working properly, how do we go about organizing how to address the issue and understand what the cause of the problem might be. How do we sort the procedures that will be needed and focus attention on what is important in order to solve problems efficiently. Within this section we will discuss some of these issues and examine processes related to human, animal and computer problem solving.
PROBLEM-SOLVING STRATEGIES
When people are presented with a problem—whether it is a complex mathematical problem or a broken printer, how do you solve it? Before finding a solution to the problem, the problem must first be clearly identified. After that, one of many problem solving strategies can be applied, hopefully resulting in a solution.
Problems themselves can be classified into two different categories known as ill-defined and well-defined problems (Schacter, 2009). Ill-defined problems represent issues that do not have clear goals, solution paths, or expected solutions whereas well-defined problems have specific goals, clearly defined solutions, and clear expected solutions. Problem solving often incorporates pragmatics (logical reasoning) and semantics (interpretation of meanings behind the problem), and also in many cases require abstract thinking and creativity in order to find novel solutions. Within psychology, problem solving refers to a motivational drive for reading a definite “goal” from a present situation or condition that is either not moving toward that goal, is distant from it, or requires more complex logical analysis for finding a missing description of conditions or steps toward that goal. Processes relating to problem solving include problem finding also known as problem analysis, problem shaping where the organization of the problem occurs, generating alternative strategies, implementation of attempted solutions, and verification of the selected solution. Various methods of studying problem solving exist within the field of psychology including introspection, behavior analysis and behaviorism, simulation, computer modeling, and experimentation.
A problem-solving strategy is a plan of action used to find a solution. Different strategies have different action plans associated with them (table below). For example, a well-known strategy is trial and error. The old adage, “If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again” describes trial and error. In terms of your broken printer, you could try checking the ink levels, and if that doesn’t work, you could check to make sure the paper tray isn’t jammed. Or maybe the printer isn’t actually connected to your laptop. When using trial and error, you would continue to try different solutions until you solved your problem. Although trial and error is not typically one of the most time-efficient strategies, it is a commonly used one.
Another type of strategy is an algorithm. An algorithm is a problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve a desired outcome (Kahneman, 2011). You can think of an algorithm as a recipe with highly detailed instructions that produce the same result every time they are performed. Algorithms are used frequently in our everyday lives, especially in computer science. When you run a search on the Internet, search engines like Google use algorithms to decide which entries will appear first in your list of results. Facebook also uses algorithms to decide which posts to display on your newsfeed. Can you identify other situations in which algorithms are used?
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A “rule of thumb” is an example of a heuristic. Such a rule saves the person time and energy when making a decision, but despite its time-saving characteristics, it is not always the best method for making a rational decision. Different types of heuristics are used in different types of situations, but the impulse to use a heuristic occurs when one of five conditions is met (Pratkanis, 1989):
- When one is faced with too much information
- When the time to make a decision is limited
- When the decision to be made is unimportant
- When there is access to very little information to use in making the decision
- When an appropriate heuristic happens to come to mind in the same moment
Working backwards is a useful heuristic in which you begin solving the problem by focusing on the end result. Consider this example: You live in Washington, D.C. and have been invited to a wedding at 4 PM on Saturday in Philadelphia. Knowing that Interstate 95 tends to back up any day of the week, you need to plan your route and time your departure accordingly. If you want to be at the wedding service by 3:30 PM, and it takes 2.5 hours to get to Philadelphia without traffic, what time should you leave your house? You use the working backwards heuristic to plan the events of your day on a regular basis, probably without even thinking about it.
Another useful heuristic is the practice of accomplishing a large goal or task by breaking it into a series of smaller steps. Students often use this common method to complete a large research project or long essay for school. For example, students typically brainstorm, develop a thesis or main topic, research the chosen topic, organize their information into an outline, write a rough draft, revise and edit the rough draft, develop a final draft, organize the references list, and proofread their work before turning in the project. The large task becomes less overwhelming when it is broken down into a series of small steps.
Further problem solving strategies have been identified (listed below) that incorporate flexible and creative thinking in order to reach solutions efficiently.
Additional Problem Solving Strategies :
- Abstraction – refers to solving the problem within a model of the situation before applying it to reality.
- Analogy – is using a solution that solves a similar problem.
- Brainstorming – refers to collecting an analyzing a large amount of solutions, especially within a group of people, to combine the solutions and developing them until an optimal solution is reached.
- Divide and conquer – breaking down large complex problems into smaller more manageable problems.
- Hypothesis testing – method used in experimentation where an assumption about what would happen in response to manipulating an independent variable is made, and analysis of the affects of the manipulation are made and compared to the original hypothesis.
- Lateral thinking – approaching problems indirectly and creatively by viewing the problem in a new and unusual light.
- Means-ends analysis – choosing and analyzing an action at a series of smaller steps to move closer to the goal.
- Method of focal objects – putting seemingly non-matching characteristics of different procedures together to make something new that will get you closer to the goal.
- Morphological analysis – analyzing the outputs of and interactions of many pieces that together make up a whole system.
- Proof – trying to prove that a problem cannot be solved. Where the proof fails becomes the starting point or solving the problem.
- Reduction – adapting the problem to be as similar problems where a solution exists.
- Research – using existing knowledge or solutions to similar problems to solve the problem.
- Root cause analysis – trying to identify the cause of the problem.
The strategies listed above outline a short summary of methods we use in working toward solutions and also demonstrate how the mind works when being faced with barriers preventing goals to be reached.
One example of means-end analysis can be found by using the Tower of Hanoi paradigm . This paradigm can be modeled as a word problems as demonstrated by the Missionary-Cannibal Problem :
Missionary-Cannibal Problem
Three missionaries and three cannibals are on one side of a river and need to cross to the other side. The only means of crossing is a boat, and the boat can only hold two people at a time. Your goal is to devise a set of moves that will transport all six of the people across the river, being in mind the following constraint: The number of cannibals can never exceed the number of missionaries in any location. Remember that someone will have to also row that boat back across each time.
Hint : At one point in your solution, you will have to send more people back to the original side than you just sent to the destination.
The actual Tower of Hanoi problem consists of three rods sitting vertically on a base with a number of disks of different sizes that can slide onto any rod. The puzzle starts with the disks in a neat stack in ascending order of size on one rod, the smallest at the top making a conical shape. The objective of the puzzle is to move the entire stack to another rod obeying the following rules:
- 1. Only one disk can be moved at a time.
- 2. Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the stacks and placing it on top of another stack or on an empty rod.
- 3. No disc may be placed on top of a smaller disk.
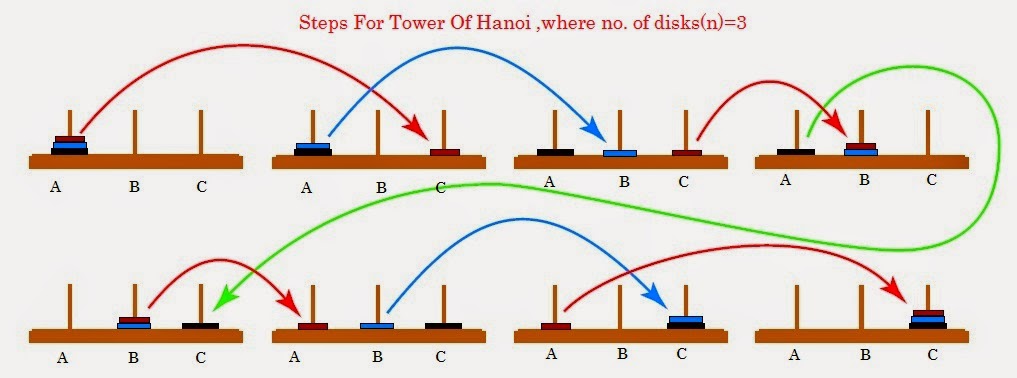
Figure 7.02. Steps for solving the Tower of Hanoi in the minimum number of moves when there are 3 disks.
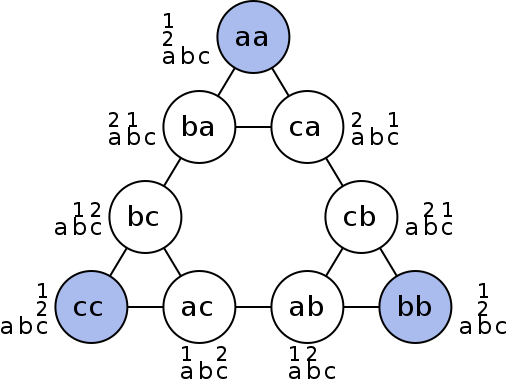
Figure 7.03. Graphical representation of nodes (circles) and moves (lines) of Tower of Hanoi.
The Tower of Hanoi is a frequently used psychological technique to study problem solving and procedure analysis. A variation of the Tower of Hanoi known as the Tower of London has been developed which has been an important tool in the neuropsychological diagnosis of executive function disorders and their treatment.
GESTALT PSYCHOLOGY AND PROBLEM SOLVING
As you may recall from the sensation and perception chapter, Gestalt psychology describes whole patterns, forms and configurations of perception and cognition such as closure, good continuation, and figure-ground. In addition to patterns of perception, Wolfgang Kohler, a German Gestalt psychologist traveled to the Spanish island of Tenerife in order to study animals behavior and problem solving in the anthropoid ape.
As an interesting side note to Kohler’s studies of chimp problem solving, Dr. Ronald Ley, professor of psychology at State University of New York provides evidence in his book A Whisper of Espionage (1990) suggesting that while collecting data for what would later be his book The Mentality of Apes (1925) on Tenerife in the Canary Islands between 1914 and 1920, Kohler was additionally an active spy for the German government alerting Germany to ships that were sailing around the Canary Islands. Ley suggests his investigations in England, Germany and elsewhere in Europe confirm that Kohler had served in the German military by building, maintaining and operating a concealed radio that contributed to Germany’s war effort acting as a strategic outpost in the Canary Islands that could monitor naval military activity approaching the north African coast.
While trapped on the island over the course of World War 1, Kohler applied Gestalt principles to animal perception in order to understand how they solve problems. He recognized that the apes on the islands also perceive relations between stimuli and the environment in Gestalt patterns and understand these patterns as wholes as opposed to pieces that make up a whole. Kohler based his theories of animal intelligence on the ability to understand relations between stimuli, and spent much of his time while trapped on the island investigation what he described as insight , the sudden perception of useful or proper relations. In order to study insight in animals, Kohler would present problems to chimpanzee’s by hanging some banana’s or some kind of food so it was suspended higher than the apes could reach. Within the room, Kohler would arrange a variety of boxes, sticks or other tools the chimpanzees could use by combining in patterns or organizing in a way that would allow them to obtain the food (Kohler & Winter, 1925).
While viewing the chimpanzee’s, Kohler noticed one chimp that was more efficient at solving problems than some of the others. The chimp, named Sultan, was able to use long poles to reach through bars and organize objects in specific patterns to obtain food or other desirables that were originally out of reach. In order to study insight within these chimps, Kohler would remove objects from the room to systematically make the food more difficult to obtain. As the story goes, after removing many of the objects Sultan was used to using to obtain the food, he sat down ad sulked for a while, and then suddenly got up going over to two poles lying on the ground. Without hesitation Sultan put one pole inside the end of the other creating a longer pole that he could use to obtain the food demonstrating an ideal example of what Kohler described as insight. In another situation, Sultan discovered how to stand on a box to reach a banana that was suspended from the rafters illustrating Sultan’s perception of relations and the importance of insight in problem solving.

Grande (another chimp in the group studied by Kohler) builds a three-box structure to reach the bananas, while Sultan watches from the ground. Insight , sometimes referred to as an “Ah-ha” experience, was the term Kohler used for the sudden perception of useful relations among objects during problem solving (Kohler, 1927; Radvansky & Ashcraft, 2013).
Solving puzzles.
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below (see figure) is a 4×4 grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: 1, 2, 3, or 4. Here are the rules: The numbers must total 10 in each bolded box, each row, and each column; however, each digit can only appear once in a bolded box, row, and column. Time yourself as you solve this puzzle and compare your time with a classmate.
How long did it take you to solve this sudoku puzzle? (You can see the answer at the end of this section.)
Here is another popular type of puzzle (figure below) that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper:
Did you figure it out? (The answer is at the end of this section.) Once you understand how to crack this puzzle, you won’t forget.
Take a look at the “Puzzling Scales” logic puzzle below (figure below). Sam Loyd, a well-known puzzle master, created and refined countless puzzles throughout his lifetime (Cyclopedia of Puzzles, n.d.).

What steps did you take to solve this puzzle? You can read the solution at the end of this section.
Pitfalls to problem solving.
Not all problems are successfully solved, however. What challenges stop us from successfully solving a problem? Albert Einstein once said, “Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result.” Imagine a person in a room that has four doorways. One doorway that has always been open in the past is now locked. The person, accustomed to exiting the room by that particular doorway, keeps trying to get out through the same doorway even though the other three doorways are open. The person is stuck—but she just needs to go to another doorway, instead of trying to get out through the locked doorway. A mental set is where you persist in approaching a problem in a way that has worked in the past but is clearly not working now.
Functional fixedness is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for. During the Apollo 13 mission to the moon, NASA engineers at Mission Control had to overcome functional fixedness to save the lives of the astronauts aboard the spacecraft. An explosion in a module of the spacecraft damaged multiple systems. The astronauts were in danger of being poisoned by rising levels of carbon dioxide because of problems with the carbon dioxide filters. The engineers found a way for the astronauts to use spare plastic bags, tape, and air hoses to create a makeshift air filter, which saved the lives of the astronauts.
Researchers have investigated whether functional fixedness is affected by culture. In one experiment, individuals from the Shuar group in Ecuador were asked to use an object for a purpose other than that for which the object was originally intended. For example, the participants were told a story about a bear and a rabbit that were separated by a river and asked to select among various objects, including a spoon, a cup, erasers, and so on, to help the animals. The spoon was the only object long enough to span the imaginary river, but if the spoon was presented in a way that reflected its normal usage, it took participants longer to choose the spoon to solve the problem. (German & Barrett, 2005). The researchers wanted to know if exposure to highly specialized tools, as occurs with individuals in industrialized nations, affects their ability to transcend functional fixedness. It was determined that functional fixedness is experienced in both industrialized and nonindustrialized cultures (German & Barrett, 2005).
In order to make good decisions, we use our knowledge and our reasoning. Often, this knowledge and reasoning is sound and solid. Sometimes, however, we are swayed by biases or by others manipulating a situation. For example, let’s say you and three friends wanted to rent a house and had a combined target budget of $1,600. The realtor shows you only very run-down houses for $1,600 and then shows you a very nice house for $2,000. Might you ask each person to pay more in rent to get the $2,000 home? Why would the realtor show you the run-down houses and the nice house? The realtor may be challenging your anchoring bias. An anchoring bias occurs when you focus on one piece of information when making a decision or solving a problem. In this case, you’re so focused on the amount of money you are willing to spend that you may not recognize what kinds of houses are available at that price point.
The confirmation bias is the tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs. For example, if you think that your professor is not very nice, you notice all of the instances of rude behavior exhibited by the professor while ignoring the countless pleasant interactions he is involved in on a daily basis. Hindsight bias leads you to believe that the event you just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t. In other words, you knew all along that things would turn out the way they did. Representative bias describes a faulty way of thinking, in which you unintentionally stereotype someone or something; for example, you may assume that your professors spend their free time reading books and engaging in intellectual conversation, because the idea of them spending their time playing volleyball or visiting an amusement park does not fit in with your stereotypes of professors.
Finally, the availability heuristic is a heuristic in which you make a decision based on an example, information, or recent experience that is that readily available to you, even though it may not be the best example to inform your decision . Biases tend to “preserve that which is already established—to maintain our preexisting knowledge, beliefs, attitudes, and hypotheses” (Aronson, 1995; Kahneman, 2011). These biases are summarized in the table below.
Were you able to determine how many marbles are needed to balance the scales in the figure below? You need nine. Were you able to solve the problems in the figures above? Here are the answers.

Many different strategies exist for solving problems. Typical strategies include trial and error, applying algorithms, and using heuristics. To solve a large, complicated problem, it often helps to break the problem into smaller steps that can be accomplished individually, leading to an overall solution. Roadblocks to problem solving include a mental set, functional fixedness, and various biases that can cloud decision making skills.
References:
Openstax Psychology text by Kathryn Dumper, William Jenkins, Arlene Lacombe, Marilyn Lovett and Marion Perlmutter licensed under CC BY v4.0. https://openstax.org/details/books/psychology
Review Questions:
1. A specific formula for solving a problem is called ________.
a. an algorithm
b. a heuristic
c. a mental set
d. trial and error
2. Solving the Tower of Hanoi problem tends to utilize a ________ strategy of problem solving.
a. divide and conquer
b. means-end analysis
d. experiment
3. A mental shortcut in the form of a general problem-solving framework is called ________.
4. Which type of bias involves becoming fixated on a single trait of a problem?
a. anchoring bias
b. confirmation bias
c. representative bias
d. availability bias
5. Which type of bias involves relying on a false stereotype to make a decision?
6. Wolfgang Kohler analyzed behavior of chimpanzees by applying Gestalt principles to describe ________.
a. social adjustment
b. student load payment options
c. emotional learning
d. insight learning
7. ________ is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for.
a. functional fixedness
c. working memory
Critical Thinking Questions:
1. What is functional fixedness and how can overcoming it help you solve problems?
2. How does an algorithm save you time and energy when solving a problem?
Personal Application Question:
1. Which type of bias do you recognize in your own decision making processes? How has this bias affected how you’ve made decisions in the past and how can you use your awareness of it to improve your decisions making skills in the future?
anchoring bias
availability heuristic
confirmation bias
functional fixedness
hindsight bias
problem-solving strategy
representative bias
trial and error
working backwards
Answers to Exercises
algorithm: problem-solving strategy characterized by a specific set of instructions
anchoring bias: faulty heuristic in which you fixate on a single aspect of a problem to find a solution
availability heuristic: faulty heuristic in which you make a decision based on information readily available to you
confirmation bias: faulty heuristic in which you focus on information that confirms your beliefs
functional fixedness: inability to see an object as useful for any other use other than the one for which it was intended
heuristic: mental shortcut that saves time when solving a problem
hindsight bias: belief that the event just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t
mental set: continually using an old solution to a problem without results
problem-solving strategy: method for solving problems
representative bias: faulty heuristic in which you stereotype someone or something without a valid basis for your judgment
trial and error: problem-solving strategy in which multiple solutions are attempted until the correct one is found
working backwards: heuristic in which you begin to solve a problem by focusing on the end result

Share This Book
- Increase Font Size
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Thinking and Intelligence
Problem Solving
OpenStaxCollege
[latexpage]
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe problem solving strategies
- Define algorithm and heuristic
- Explain some common roadblocks to effective problem solving
People face problems every day—usually, multiple problems throughout the day. Sometimes these problems are straightforward: To double a recipe for pizza dough, for example, all that is required is that each ingredient in the recipe be doubled. Sometimes, however, the problems we encounter are more complex. For example, say you have a work deadline, and you must mail a printed copy of a report to your supervisor by the end of the business day. The report is time-sensitive and must be sent overnight. You finished the report last night, but your printer will not work today. What should you do? First, you need to identify the problem and then apply a strategy for solving the problem.
PROBLEM-SOLVING STRATEGIES
When you are presented with a problem—whether it is a complex mathematical problem or a broken printer, how do you solve it? Before finding a solution to the problem, the problem must first be clearly identified. After that, one of many problem solving strategies can be applied, hopefully resulting in a solution.
A problem-solving strategy is a plan of action used to find a solution. Different strategies have different action plans associated with them ( [link] ). For example, a well-known strategy is trial and error . The old adage, “If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again” describes trial and error. In terms of your broken printer, you could try checking the ink levels, and if that doesn’t work, you could check to make sure the paper tray isn’t jammed. Or maybe the printer isn’t actually connected to your laptop. When using trial and error, you would continue to try different solutions until you solved your problem. Although trial and error is not typically one of the most time-efficient strategies, it is a commonly used one.
Another type of strategy is an algorithm. An algorithm is a problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve a desired outcome (Kahneman, 2011). You can think of an algorithm as a recipe with highly detailed instructions that produce the same result every time they are performed. Algorithms are used frequently in our everyday lives, especially in computer science. When you run a search on the Internet, search engines like Google use algorithms to decide which entries will appear first in your list of results. Facebook also uses algorithms to decide which posts to display on your newsfeed. Can you identify other situations in which algorithms are used?
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A “rule of thumb” is an example of a heuristic. Such a rule saves the person time and energy when making a decision, but despite its time-saving characteristics, it is not always the best method for making a rational decision. Different types of heuristics are used in different types of situations, but the impulse to use a heuristic occurs when one of five conditions is met (Pratkanis, 1989):
- When one is faced with too much information
- When the time to make a decision is limited
- When the decision to be made is unimportant
- When there is access to very little information to use in making the decision
- When an appropriate heuristic happens to come to mind in the same moment
Working backwards is a useful heuristic in which you begin solving the problem by focusing on the end result. Consider this example: You live in Washington, D.C. and have been invited to a wedding at 4 PM on Saturday in Philadelphia. Knowing that Interstate 95 tends to back up any day of the week, you need to plan your route and time your departure accordingly. If you want to be at the wedding service by 3:30 PM, and it takes 2.5 hours to get to Philadelphia without traffic, what time should you leave your house? You use the working backwards heuristic to plan the events of your day on a regular basis, probably without even thinking about it.
Another useful heuristic is the practice of accomplishing a large goal or task by breaking it into a series of smaller steps. Students often use this common method to complete a large research project or long essay for school. For example, students typically brainstorm, develop a thesis or main topic, research the chosen topic, organize their information into an outline, write a rough draft, revise and edit the rough draft, develop a final draft, organize the references list, and proofread their work before turning in the project. The large task becomes less overwhelming when it is broken down into a series of small steps.
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below ( [link] ) is a 4×4 grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: 1, 2, 3, or 4. Here are the rules: The numbers must total 10 in each bolded box, each row, and each column; however, each digit can only appear once in a bolded box, row, and column. Time yourself as you solve this puzzle and compare your time with a classmate.
Here is another popular type of puzzle ( [link] ) that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper:
Take a look at the “Puzzling Scales” logic puzzle below ( [link] ). Sam Loyd, a well-known puzzle master, created and refined countless puzzles throughout his lifetime (Cyclopedia of Puzzles, n.d.).
PITFALLS TO PROBLEM SOLVING
Not all problems are successfully solved, however. What challenges stop us from successfully solving a problem? Albert Einstein once said, “Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result.” Imagine a person in a room that has four doorways. One doorway that has always been open in the past is now locked. The person, accustomed to exiting the room by that particular doorway, keeps trying to get out through the same doorway even though the other three doorways are open. The person is stuck—but she just needs to go to another doorway, instead of trying to get out through the locked doorway. A mental set is where you persist in approaching a problem in a way that has worked in the past but is clearly not working now.
Functional fixedness is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for. During the Apollo 13 mission to the moon, NASA engineers at Mission Control had to overcome functional fixedness to save the lives of the astronauts aboard the spacecraft. An explosion in a module of the spacecraft damaged multiple systems. The astronauts were in danger of being poisoned by rising levels of carbon dioxide because of problems with the carbon dioxide filters. The engineers found a way for the astronauts to use spare plastic bags, tape, and air hoses to create a makeshift air filter, which saved the lives of the astronauts.

Check out this Apollo 13 scene where the group of NASA engineers are given the task of overcoming functional fixedness.
Researchers have investigated whether functional fixedness is affected by culture. In one experiment, individuals from the Shuar group in Ecuador were asked to use an object for a purpose other than that for which the object was originally intended. For example, the participants were told a story about a bear and a rabbit that were separated by a river and asked to select among various objects, including a spoon, a cup, erasers, and so on, to help the animals. The spoon was the only object long enough to span the imaginary river, but if the spoon was presented in a way that reflected its normal usage, it took participants longer to choose the spoon to solve the problem. (German & Barrett, 2005). The researchers wanted to know if exposure to highly specialized tools, as occurs with individuals in industrialized nations, affects their ability to transcend functional fixedness. It was determined that functional fixedness is experienced in both industrialized and nonindustrialized cultures (German & Barrett, 2005).
In order to make good decisions, we use our knowledge and our reasoning. Often, this knowledge and reasoning is sound and solid. Sometimes, however, we are swayed by biases or by others manipulating a situation. For example, let’s say you and three friends wanted to rent a house and had a combined target budget of $1,600. The realtor shows you only very run-down houses for $1,600 and then shows you a very nice house for $2,000. Might you ask each person to pay more in rent to get the $2,000 home? Why would the realtor show you the run-down houses and the nice house? The realtor may be challenging your anchoring bias. An anchoring bias occurs when you focus on one piece of information when making a decision or solving a problem. In this case, you’re so focused on the amount of money you are willing to spend that you may not recognize what kinds of houses are available at that price point.
The confirmation bias is the tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs. For example, if you think that your professor is not very nice, you notice all of the instances of rude behavior exhibited by the professor while ignoring the countless pleasant interactions he is involved in on a daily basis. Hindsight bias leads you to believe that the event you just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t. In other words, you knew all along that things would turn out the way they did. Representative bias describes a faulty way of thinking, in which you unintentionally stereotype someone or something; for example, you may assume that your professors spend their free time reading books and engaging in intellectual conversation, because the idea of them spending their time playing volleyball or visiting an amusement park does not fit in with your stereotypes of professors.
Finally, the availability heuristic is a heuristic in which you make a decision based on an example, information, or recent experience that is that readily available to you, even though it may not be the best example to inform your decision . Biases tend to “preserve that which is already established—to maintain our preexisting knowledge, beliefs, attitudes, and hypotheses” (Aronson, 1995; Kahneman, 2011). These biases are summarized in [link] .
Please visit this site to see a clever music video that a high school teacher made to explain these and other cognitive biases to his AP psychology students.
Were you able to determine how many marbles are needed to balance the scales in [link] ? You need nine. Were you able to solve the problems in [link] and [link] ? Here are the answers ( [link] ).
Many different strategies exist for solving problems. Typical strategies include trial and error, applying algorithms, and using heuristics. To solve a large, complicated problem, it often helps to break the problem into smaller steps that can be accomplished individually, leading to an overall solution. Roadblocks to problem solving include a mental set, functional fixedness, and various biases that can cloud decision making skills.
Review Questions
A specific formula for solving a problem is called ________.
- an algorithm
- a heuristic
- a mental set
- trial and error
A mental shortcut in the form of a general problem-solving framework is called ________.
Which type of bias involves becoming fixated on a single trait of a problem?
- anchoring bias
- confirmation bias
- representative bias
- availability bias
Which type of bias involves relying on a false stereotype to make a decision?
Critical Thinking Questions
What is functional fixedness and how can overcoming it help you solve problems?
Functional fixedness occurs when you cannot see a use for an object other than the use for which it was intended. For example, if you need something to hold up a tarp in the rain, but only have a pitchfork, you must overcome your expectation that a pitchfork can only be used for garden chores before you realize that you could stick it in the ground and drape the tarp on top of it to hold it up.
How does an algorithm save you time and energy when solving a problem?
An algorithm is a proven formula for achieving a desired outcome. It saves time because if you follow it exactly, you will solve the problem without having to figure out how to solve the problem. It is a bit like not reinventing the wheel.
Personal Application Question
Which type of bias do you recognize in your own decision making processes? How has this bias affected how you’ve made decisions in the past and how can you use your awareness of it to improve your decisions making skills in the future?
Problem Solving Copyright © 2014 by OpenStaxCollege is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Heuristic Problem Solving: A comprehensive guide with 5 Examples
What are heuristics, advantages of using heuristic problem solving, disadvantages of using heuristic problem solving, heuristic problem solving examples, frequently asked questions.
- Speed: Heuristics are designed to find solutions quickly, saving time in problem solving tasks. Rather than spending a lot of time analyzing every possible solution, heuristics help to narrow down the options and focus on the most promising ones.
- Flexibility: Heuristics are not rigid, step-by-step procedures. They allow for flexibility and creativity in problem solving, leading to innovative solutions. They encourage thinking outside the box and can generate unexpected and valuable ideas.
- Simplicity: Heuristics are often easy to understand and apply, making them accessible to anyone regardless of their expertise or background. They don’t require specialized knowledge or training, which means they can be used in various contexts and by different people.
- Cost-effective: Because heuristics are simple and efficient, they can save time, money, and effort in finding solutions. They also don’t require expensive software or equipment, making them a cost-effective approach to problem solving.
- Real-world applicability: Heuristics are often based on practical experience and knowledge, making them relevant to real-world situations. They can help solve complex, messy, or ill-defined problems where other problem solving methods may not be practical.
- Potential for errors: Heuristic problem solving relies on generalizations and assumptions, which may lead to errors or incorrect conclusions. This is especially true if the heuristic is not based on a solid understanding of the problem or the underlying principles.
- Limited scope: Heuristic problem solving may only consider a limited number of potential solutions and may not identify the most optimal or effective solution.
- Lack of creativity: Heuristic problem solving may rely on pre-existing solutions or approaches, limiting creativity and innovation in problem-solving.
- Over-reliance: Heuristic problem solving may lead to over-reliance on a specific approach or heuristic, which can be problematic if the heuristic is flawed or ineffective.
- Lack of transparency: Heuristic problem solving may not be transparent or explainable, as the decision-making process may not be explicitly articulated or understood.
- Trial and error: This heuristic involves trying different solutions to a problem and learning from mistakes until a successful solution is found. A software developer encountering a bug in their code may try other solutions and test each one until they find the one that solves the issue.
- Working backward: This heuristic involves starting at the goal and then figuring out what steps are needed to reach that goal. For example, a project manager may begin by setting a project deadline and then work backward to determine the necessary steps and deadlines for each team member to ensure the project is completed on time.
- Breaking a problem into smaller parts: This heuristic involves breaking down a complex problem into smaller, more manageable pieces that can be tackled individually. For example, an HR manager tasked with implementing a new employee benefits program may break the project into smaller parts, such as researching options, getting quotes from vendors, and communicating the unique benefits to employees.
- Using analogies: This heuristic involves finding similarities between a current problem and a similar problem that has been solved before and using the solution to the previous issue to help solve the current one. For example, a salesperson struggling to close a deal may use an analogy to a successful sales pitch they made to help guide their approach to the current pitch.
- Simplifying the problem: This heuristic involves simplifying a complex problem by ignoring details that are not necessary for solving it. This allows the problem solver to focus on the most critical aspects of the problem. For example, a customer service representative dealing with a complex issue may simplify it by breaking it down into smaller components and addressing them individually rather than simultaneously trying to solve the entire problem.
Test your problem-solving skills for free in just a few minutes.
The free problem-solving skills for managers and team leaders helps you understand mistakes that hold you back.
What are the three types of heuristics?
What are the four stages of heuristics in problem solving.
Other Related Blogs

Top 15 Tips for Effective Conflict Mediation at Work
Top 10 games for negotiation skills to make you a better leader, manager effectiveness: a complete guide for managers in 2024, 5 proven ways managers can build collaboration in a team.

Reviewed by Psychology Today Staff
A heuristic is a mental shortcut that allows an individual to make a decision, pass judgment, or solve a problem quickly and with minimal mental effort. While heuristics can reduce the burden of decision-making and free up limited cognitive resources, they can also be costly when they lead individuals to miss critical information or act on unjust biases.
- Understanding Heuristics
- Different Heuristics
- Problems with Heuristics

As humans move throughout the world, they must process large amounts of information and make many choices with limited amounts of time. When information is missing, or an immediate decision is necessary, heuristics act as “rules of thumb” that guide behavior down the most efficient pathway.
Heuristics are not unique to humans; animals use heuristics that, though less complex, also serve to simplify decision-making and reduce cognitive load.
Generally, yes. Navigating day-to-day life requires everyone to make countless small decisions within a limited timeframe. Heuristics can help individuals save time and mental energy, freeing up cognitive resources for more complex planning and problem-solving endeavors.
The human brain and all its processes—including heuristics— developed over millions of years of evolution . Since mental shortcuts save both cognitive energy and time, they likely provided an advantage to those who relied on them.
Heuristics that were helpful to early humans may not be universally beneficial today . The familiarity heuristic, for example—in which the familiar is preferred over the unknown—could steer early humans toward foods or people that were safe, but may trigger anxiety or unfair biases in modern times.

The study of heuristics was developed by renowned psychologists Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky. Starting in the 1970s, Kahneman and Tversky identified several different kinds of heuristics, most notably the availability heuristic and the anchoring heuristic.
Since then, researchers have continued their work and identified many different kinds of heuristics, including:
Familiarity heuristic
Fundamental attribution error
Representativeness heuristic
Satisficing
The anchoring heuristic, or anchoring bias , occurs when someone relies more heavily on the first piece of information learned when making a choice, even if it's not the most relevant. In such cases, anchoring is likely to steer individuals wrong .
The availability heuristic describes the mental shortcut in which someone estimates whether something is likely to occur based on how readily examples come to mind . People tend to overestimate the probability of plane crashes, homicides, and shark attacks, for instance, because examples of such events are easily remembered.
People who make use of the representativeness heuristic categorize objects (or other people) based on how similar they are to known entities —assuming someone described as "quiet" is more likely to be a librarian than a politician, for instance.
Satisficing is a decision-making strategy in which the first option that satisfies certain criteria is selected , even if other, better options may exist.

Heuristics, while useful, are imperfect; if relied on too heavily, they can result in incorrect judgments or cognitive biases. Some are more likely to steer people wrong than others.
Assuming, for example, that child abductions are common because they’re frequently reported on the news—an example of the availability heuristic—may trigger unnecessary fear or overprotective parenting practices. Understanding commonly unhelpful heuristics, and identifying situations where they could affect behavior, may help individuals avoid such mental pitfalls.
Sometimes called the attribution effect or correspondence bias, the term describes a tendency to attribute others’ behavior primarily to internal factors—like personality or character— while attributing one’s own behavior more to external or situational factors .
If one person steps on the foot of another in a crowded elevator, the victim may attribute it to carelessness. If, on the other hand, they themselves step on another’s foot, they may be more likely to attribute the mistake to being jostled by someone else .
Listen to your gut, but don’t rely on it . Think through major problems methodically—by making a list of pros and cons, for instance, or consulting with people you trust. Make extra time to think through tasks where snap decisions could cause significant problems, such as catching an important flight.

Artificial intelligence already plays a role in deciding who’s getting hired. The way to improve AI is very similar to how we fight human biases.

Think you are avoiding the motherhood penalty by not having children? Think again. Simply being a woman of childbearing age can trigger discrimination.

Psychological experiments on human judgment under uncertainty showed that people often stray from presumptions about rational economic agents.

Psychology, like other disciplines, uses the scientific method to acquire knowledge and uncover truths—but we still ask experts for information and rely on intuition. Here's why.

We all experience these 3 cognitive blind spots at work, frequently unaware of their costs in terms of productivity and misunderstanding. Try these strategies to work around them.

Have you ever fallen for fake news? This toolkit can help you easily evaluate whether a claim is real or phony.

An insidious form of prejudice occurs when a more powerful group ignores groups with less power and keeps them out of the minds of society.
We can never know everything and yet unconscious biases often convince us that we do. Being alert to your own ignorance is crucial for more efficient thinking in daily life.
Chatbot designers engage in dishonest anthropomorphism by designing features to exploit our heuristic processing and dupe us into overtrusting and assigning moral responsibility.

How do social media influencers convert a scroll into a like, follow, and sale? Here are the psychological principles used by digital influencers.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8.2 Problem-Solving: Heuristics and Algorithms
Learning objectives.
- Describe the differences between heuristics and algorithms in information processing.
When faced with a problem to solve, should you go with intuition or with more measured, logical reasoning? Obviously, we use both of these approaches. Some of the decisions we make are rapid, emotional, and automatic. Daniel Kahneman (2011) calls this “fast” thinking. By definition, fast thinking saves time. For example, you may quickly decide to buy something because it is on sale; your fast brain has perceived a bargain, and you go for it quickly. On the other hand, “slow” thinking requires more effort; applying this in the same scenario might cause us not to buy the item because we have reasoned that we don’t really need it, that it is still too expensive, and so on. Using slow and fast thinking does not guarantee good decision-making if they are employed at the wrong time. Sometimes it is not clear which is called for, because many decisions have a level of uncertainty built into them. In this section, we will explore some of the applications of these tendencies to think fast or slow.
We will look further into our thought processes, more specifically, into some of the problem-solving strategies that we use. Heuristics are information-processing strategies that are useful in many cases but may lead to errors when misapplied. A heuristic is a principle with broad application, essentially an educated guess about something. We use heuristics all the time, for example, when deciding what groceries to buy from the supermarket, when looking for a library book, when choosing the best route to drive through town to avoid traffic congestion, and so on. Heuristics can be thought of as aids to decision making; they allow us to reach a solution without a lot of cognitive effort or time.
The benefit of heuristics in helping us reach decisions fairly easily is also the potential downfall: the solution provided by the use of heuristics is not necessarily the best one. Let’s consider some of the most frequently applied, and misapplied, heuristics in the table below.
In many cases, we base our judgments on information that seems to represent, or match, what we expect will happen, while ignoring other potentially more relevant statistical information. When we do so, we are using the representativeness heuristic . Consider, for instance, the data presented in the table below. Let’s say that you went to a hospital, and you checked the records of the babies that were born on that given day. Which pattern of births do you think you are most likely to find?
Most people think that list B is more likely, probably because list B looks more random, and matches — or is “representative of” — our ideas about randomness, but statisticians know that any pattern of four girls and four boys is mathematically equally likely. Whether a boy or girl is born first has no bearing on what sex will be born second; these are independent events, each with a 50:50 chance of being a boy or a girl. The problem is that we have a schema of what randomness should be like, which does not always match what is mathematically the case. Similarly, people who see a flipped coin come up “heads” five times in a row will frequently predict, and perhaps even wager money, that “tails” will be next. This behaviour is known as the gambler’s fallacy . Mathematically, the gambler’s fallacy is an error: the likelihood of any single coin flip being “tails” is always 50%, regardless of how many times it has come up “heads” in the past.
The representativeness heuristic may explain why we judge people on the basis of appearance. Suppose you meet your new next-door neighbour, who drives a loud motorcycle, has many tattoos, wears leather, and has long hair. Later, you try to guess their occupation. What comes to mind most readily? Are they a teacher? Insurance salesman? IT specialist? Librarian? Drug dealer? The representativeness heuristic will lead you to compare your neighbour to the prototypes you have for these occupations and choose the one that they seem to represent the best. Thus, your judgment is affected by how much your neibour seems to resemble each of these groups. Sometimes these judgments are accurate, but they often fail because they do not account for base rates , which is the actual frequency with which these groups exist. In this case, the group with the lowest base rate is probably drug dealer.
Our judgments can also be influenced by how easy it is to retrieve a memory. The tendency to make judgments of the frequency or likelihood that an event occurs on the basis of the ease with which it can be retrieved from memory is known as the availability heuristic (MacLeod & Campbell, 1992; Tversky & Kahneman, 1973). Imagine, for instance, that I asked you to indicate whether there are more words in the English language that begin with the letter “R” or that have the letter “R” as the third letter. You would probably answer this question by trying to think of words that have each of the characteristics, thinking of all the words you know that begin with “R” and all that have “R” in the third position. Because it is much easier to retrieve words by their first letter than by their third, we may incorrectly guess that there are more words that begin with “R,” even though there are in fact more words that have “R” as the third letter.
The availability heuristic may explain why we tend to overestimate the likelihood of crimes or disasters; those that are reported widely in the news are more readily imaginable, and therefore, we tend to overestimate how often they occur. Things that we find easy to imagine, or to remember from watching the news, are estimated to occur frequently. Anything that gets a lot of news coverage is easy to imagine. Availability bias does not just affect our thinking. It can change behaviour. For example, homicides are usually widely reported in the news, leading people to make inaccurate assumptions about the frequency of murder. In Canada, the murder rate has dropped steadily since the 1970s (Statistics Canada, 2018), but this information tends not to be reported, leading people to overestimate the probability of being affected by violent crime. In another example, doctors who recently treated patients suffering from a particular condition were more likely to diagnose the condition in subsequent patients because they overestimated the prevalence of the condition (Poses & Anthony, 1991).
The anchoring and adjustment heuristic is another example of how fast thinking can lead to a decision that might not be optimal. Anchoring and adjustment is easily seen when we are faced with buying something that does not have a fixed price. For example, if you are interested in a used car, and the asking price is $10,000, what price do you think you might offer? Using $10,000 as an anchor, you are likely to adjust your offer from there, and perhaps offer $9000 or $9500. Never mind that $10,000 may not be a reasonable anchoring price. Anchoring and adjustment does not just happen when we’re buying something. It can also be used in any situation that calls for judgment under uncertainty, such as sentencing decisions in criminal cases (Bennett, 2014), and it applies to groups as well as individuals (Rutledge, 1993).
In contrast to heuristics, which can be thought of as problem-solving strategies based on educated guesses, algorithms are problem-solving strategies that use rules. Algorithms are generally a logical set of steps that, if applied correctly, should be accurate. For example, you could make a cake using heuristics — relying on your previous baking experience and guessing at the number and amount of ingredients, baking time, and so on — or using an algorithm. The latter would require a recipe which would provide step-by-step instructions; the recipe is the algorithm. Unless you are an extremely accomplished baker, the algorithm should provide you with a better cake than using heuristics would. While heuristics offer a solution that might be correct, a correctly applied algorithm is guaranteed to provide a correct solution. Of course, not all problems can be solved by algorithms.
As with heuristics, the use of algorithmic processing interacts with behaviour and emotion. Understanding what strategy might provide the best solution requires knowledge and experience. As we will see in the next section, we are prone to a number of cognitive biases that persist despite knowledge and experience.
Key Takeaways
- We use a variety of shortcuts in our information processing, such as the representativeness, availability, and anchoring and adjustment heuristics. These help us to make fast judgments but may lead to errors.
- Algorithms are problem-solving strategies that are based on rules rather than guesses. Algorithms, if applied correctly, are far less likely to result in errors or incorrect solutions than heuristics. Algorithms are based on logic.
Bennett, M. W. (2014). Confronting cognitive ‘anchoring effect’ and ‘blind spot’ biases in federal sentencing: A modest solution for reforming and fundamental flaw. Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology , 104 (3), 489-534.
Kahneman, D. (2011). Thinking, fast and slow. New York, NY: Farrar, Straus and Giroux.
MacLeod, C., & Campbell, L. (1992). Memory accessibility and probability judgments: An experimental evaluation of the availability heuristic. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 63 (6), 890–902.
Poses, R. M., & Anthony, M. (1991). Availability, wishful thinking, and physicians’ diagnostic judgments for patients with suspected bacteremia. Medical Decision Making, 11 , 159-68.
Rutledge, R. W. (1993). The effects of group decisions and group-shifts on use of the anchoring and adjustment heuristic. Social Behavior and Personality, 21 (3), 215-226.
Statistics Canada. (2018). Ho micide in Canada, 2017 . Retrieved from https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/en/daily-quotidien/181121/dq181121a-eng.pdf
Tversky, A., & Kahneman, D. (1973). Availability: A heuristic for judging frequency and probability. Cognitive Psychology, 5 , 207–232.
Psychology - 1st Canadian Edition Copyright © 2020 by Sally Walters is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Cite this chapter

- Loren C. Larson 4
Part of the book series: Problem Books in Mathematics ((PBM))
2744 Accesses
Strategy or tactics in problem-solving is called heuristics . In this chapter we will be concerned with the heuristics of solving mathematical problems. Those who have thought about heuristics have described a number of basic ideas that are typically useful. The five classics on problem-solving by George Polya are masterpieces devoted entirely to the practical study of heuristics in mathematics. Among the ideas developed in these books, we shall focus on the following:
Search for a pattern.
Draw a figure.
Formulate an equivalent problem.
Modify the problem.
Choose effective notation.
Exploit symmetry.
Divide into cases.
Work backward.
Argue by contradiction.
Pursue parity.
Consider extreme cases.
Generalize.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Mathematics, St. Olaf College, Northfield, MN, 55027, USA
Loren C. Larson
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 1983 Springer-Verlag New York Inc.
About this chapter
Larson, L.C. (1983). Heuristics. In: Problem-Solving Through Problems. Problem Books in Mathematics. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-5498-0_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-5498-0_1
Publisher Name : Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN : 978-0-387-96171-2
Online ISBN : 978-1-4612-5498-0
eBook Packages : Springer Book Archive
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Thinking and Intelligence
Solving problems, learning objectives.
- Describe problem solving strategies, including algorithms and heuristics
People face problems every day—usually, multiple problems throughout the day. Sometimes these problems are straightforward: To double a recipe for pizza dough, for example, all that is required is that each ingredient in the recipe be doubled. Sometimes, however, the problems we encounter are more complex. For example, say you have a work deadline, and you must mail a printed copy of a report to your supervisor by the end of the business day. The report is time-sensitive and must be sent overnight. You finished the report last night, but your printer will not work today. What should you do? First, you need to identify the problem and then apply a strategy for solving the problem.
Problem-Solving Strategies
When you are presented with a problem—whether it is a complex mathematical problem or a broken printer, how do you solve it? Before finding a solution to the problem, the problem must first be clearly identified. After that, one of many problem solving strategies can be applied, hopefully resulting in a solution.
A problem-solving strategy is a plan of action used to find a solution. Different strategies have different action plans associated with them. For example, a well-known strategy is trial and error . The old adage, “If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again” describes trial and error. In terms of your broken printer, you could try checking the ink levels, and if that doesn’t work, you could check to make sure the paper tray isn’t jammed. Or maybe the printer isn’t actually connected to your laptop. When using trial and error, you would continue to try different solutions until you solved your problem. Although trial and error is not typically one of the most time-efficient strategies, it is a commonly used one.
Another type of strategy is an algorithm. An algorithm is a problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve a desired outcome (Kahneman, 2011). You can think of an algorithm as a recipe with highly detailed instructions that produce the same result every time they are performed. Algorithms are used frequently in our everyday lives, especially in computer science. When you run a search on the Internet, search engines like Google use algorithms to decide which entries will appear first in your list of results. Facebook also uses algorithms to decide which posts to display on your newsfeed. Can you identify other situations in which algorithms are used?
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A “rule of thumb” is an example of a heuristic. Such a rule saves the person time and energy when making a decision, but despite its time-saving characteristics, it is not always the best method for making a rational decision. Different types of heuristics are used in different types of situations, but the impulse to use a heuristic occurs when one of five conditions is met (Pratkanis, 1989):
- When one is faced with too much information
- When the time to make a decision is limited
- When the decision to be made is unimportant
- When there is access to very little information to use in making the decision
- When an appropriate heuristic happens to come to mind in the same moment
Working backwards is a useful heuristic in which you begin solving the problem by focusing on the end result. Consider this example: You live in Washington, D.C. and have been invited to a wedding at 4 PM on Saturday in Philadelphia. Knowing that Interstate 95 tends to back up any day of the week, you need to plan your route and time your departure accordingly. If you want to be at the wedding service by 3:30 PM, and it takes 2.5 hours to get to Philadelphia without traffic, what time should you leave your house? You use the working backwards heuristic to plan the events of your day on a regular basis, probably without even thinking about it.
You can view the transcript for “Can you solve “Einstein’s Riddle”? – Dan Van der Vieren” here (opens in new window) .
Another useful heuristic is the practice of accomplishing a large goal or task by breaking it into a series of smaller steps. Students often use this common method to complete a large research project or long essay for school. For example, students typically brainstorm, develop a thesis or main topic, research the chosen topic, organize their information into an outline, write a rough draft, revise and edit the rough draft, develop a final draft, organize the references list, and proofread their work before turning in the project. The large task becomes less overwhelming when it is broken down into a series of small steps.
Everyday Connections: Solving Puzzles
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below (Figure 1) is a 4×4 grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: 1, 2, 3, or 4. Here are the rules: The numbers must total 10 in each bolded box, each row, and each column; however, each digit can only appear once in a bolded box, row, and column. Time yourself as you solve this puzzle and compare your time with a classmate.
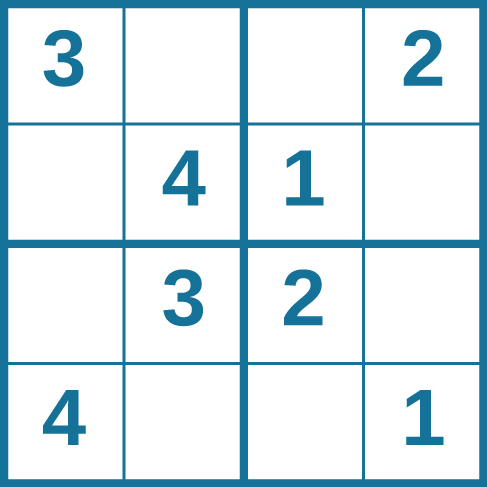
Figure 1 . How long did it take you to solve this sudoku puzzle? (You can see the answer at the end of this section.)
Here is another popular type of puzzle that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper:
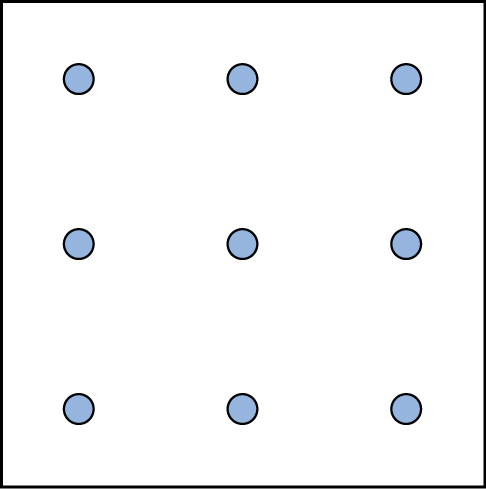
Figure 2 . Did you figure it out? (The answer is at the end of this section.) Once you understand how to crack this puzzle, you won’t forget.
Take a look at the “Puzzling Scales” logic puzzle below (Figure 3). Sam Loyd, a well-known puzzle master, created and refined countless puzzles throughout his lifetime (Cyclopedia of Puzzles, n.d.).
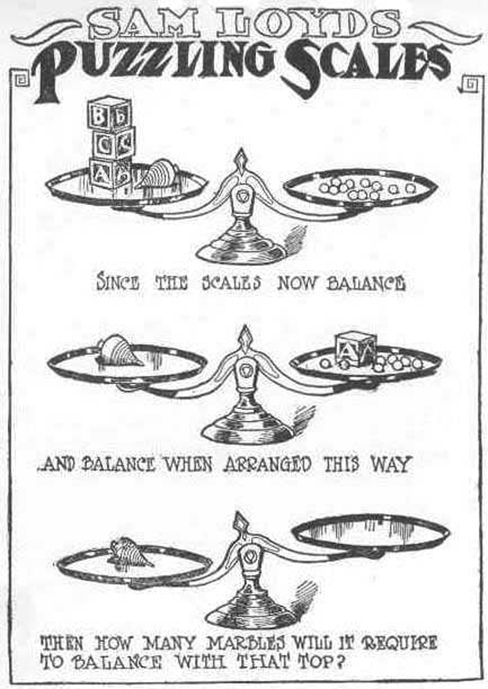
Figure 3 . The puzzle reads, “Since the scales now balance…and balance when arranged this way, then how many marbles will it require to balance with that top?
Were you able to determine how many marbles are needed to balance the scales in the Puzzling Scales? You need nine. Were you able to solve the other problems above? Here are the answers:
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- Modification and adaptation. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Problem-Solving. Authored by : OpenStax College. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/7-3-problem-solving . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Can you solve Einsteinu2019s Riddle? . Authored by : Dan Van der Vieren. Provided by : Ted-Ed. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1rDVz_Fb6HQ&index=3&list=PLUmyCeox8XCwB8FrEfDQtQZmCc2qYMS5a . License : Other . License Terms : Standard YouTube License

7.3 Problem Solving
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe problem solving strategies
- Define algorithm and heuristic
- Explain some common roadblocks to effective problem solving and decision making
People face problems every day—usually, multiple problems throughout the day. Sometimes these problems are straightforward: To double a recipe for pizza dough, for example, all that is required is that each ingredient in the recipe be doubled. Sometimes, however, the problems we encounter are more complex. For example, say you have a work deadline, and you must mail a printed copy of a report to your supervisor by the end of the business day. The report is time-sensitive and must be sent overnight. You finished the report last night, but your printer will not work today. What should you do? First, you need to identify the problem and then apply a strategy for solving the problem.
Problem-Solving Strategies
When you are presented with a problem—whether it is a complex mathematical problem or a broken printer, how do you solve it? Before finding a solution to the problem, the problem must first be clearly identified. After that, one of many problem solving strategies can be applied, hopefully resulting in a solution.
A problem-solving strategy is a plan of action used to find a solution. Different strategies have different action plans associated with them ( Table 7.2 ). For example, a well-known strategy is trial and error . The old adage, “If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again” describes trial and error. In terms of your broken printer, you could try checking the ink levels, and if that doesn’t work, you could check to make sure the paper tray isn’t jammed. Or maybe the printer isn’t actually connected to your laptop. When using trial and error, you would continue to try different solutions until you solved your problem. Although trial and error is not typically one of the most time-efficient strategies, it is a commonly used one.
Another type of strategy is an algorithm. An algorithm is a problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve a desired outcome (Kahneman, 2011). You can think of an algorithm as a recipe with highly detailed instructions that produce the same result every time they are performed. Algorithms are used frequently in our everyday lives, especially in computer science. When you run a search on the Internet, search engines like Google use algorithms to decide which entries will appear first in your list of results. Facebook also uses algorithms to decide which posts to display on your newsfeed. Can you identify other situations in which algorithms are used?
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A “rule of thumb” is an example of a heuristic. Such a rule saves the person time and energy when making a decision, but despite its time-saving characteristics, it is not always the best method for making a rational decision. Different types of heuristics are used in different types of situations, but the impulse to use a heuristic occurs when one of five conditions is met (Pratkanis, 1989):
- When one is faced with too much information
- When the time to make a decision is limited
- When the decision to be made is unimportant
- When there is access to very little information to use in making the decision
- When an appropriate heuristic happens to come to mind in the same moment
Working backwards is a useful heuristic in which you begin solving the problem by focusing on the end result. Consider this example: You live in Washington, D.C. and have been invited to a wedding at 4 PM on Saturday in Philadelphia. Knowing that Interstate 95 tends to back up any day of the week, you need to plan your route and time your departure accordingly. If you want to be at the wedding service by 3:30 PM, and it takes 2.5 hours to get to Philadelphia without traffic, what time should you leave your house? You use the working backwards heuristic to plan the events of your day on a regular basis, probably without even thinking about it.
Another useful heuristic is the practice of accomplishing a large goal or task by breaking it into a series of smaller steps. Students often use this common method to complete a large research project or long essay for school. For example, students typically brainstorm, develop a thesis or main topic, research the chosen topic, organize their information into an outline, write a rough draft, revise and edit the rough draft, develop a final draft, organize the references list, and proofread their work before turning in the project. The large task becomes less overwhelming when it is broken down into a series of small steps.
Everyday Connection
Solving puzzles.
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below ( Figure 7.7 ) is a 4×4 grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: 1, 2, 3, or 4. Here are the rules: The numbers must total 10 in each bolded box, each row, and each column; however, each digit can only appear once in a bolded box, row, and column. Time yourself as you solve this puzzle and compare your time with a classmate.
Here is another popular type of puzzle ( Figure 7.8 ) that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper:
Take a look at the “Puzzling Scales” logic puzzle below ( Figure 7.9 ). Sam Loyd, a well-known puzzle master, created and refined countless puzzles throughout his lifetime (Cyclopedia of Puzzles, n.d.).
Pitfalls to Problem Solving
Not all problems are successfully solved, however. What challenges stop us from successfully solving a problem? Imagine a person in a room that has four doorways. One doorway that has always been open in the past is now locked. The person, accustomed to exiting the room by that particular doorway, keeps trying to get out through the same doorway even though the other three doorways are open. The person is stuck—but they just need to go to another doorway, instead of trying to get out through the locked doorway. A mental set is where you persist in approaching a problem in a way that has worked in the past but is clearly not working now.
Functional fixedness is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for. Duncker (1945) conducted foundational research on functional fixedness. He created an experiment in which participants were given a candle, a book of matches, and a box of thumbtacks. They were instructed to use those items to attach the candle to the wall so that it did not drip wax onto the table below. Participants had to use functional fixedness to overcome the problem ( Figure 7.10 ). During the Apollo 13 mission to the moon, NASA engineers at Mission Control had to overcome functional fixedness to save the lives of the astronauts aboard the spacecraft. An explosion in a module of the spacecraft damaged multiple systems. The astronauts were in danger of being poisoned by rising levels of carbon dioxide because of problems with the carbon dioxide filters. The engineers found a way for the astronauts to use spare plastic bags, tape, and air hoses to create a makeshift air filter, which saved the lives of the astronauts.
Link to Learning
Check out this Apollo 13 scene about NASA engineers overcoming functional fixedness to learn more.
Researchers have investigated whether functional fixedness is affected by culture. In one experiment, individuals from the Shuar group in Ecuador were asked to use an object for a purpose other than that for which the object was originally intended. For example, the participants were told a story about a bear and a rabbit that were separated by a river and asked to select among various objects, including a spoon, a cup, erasers, and so on, to help the animals. The spoon was the only object long enough to span the imaginary river, but if the spoon was presented in a way that reflected its normal usage, it took participants longer to choose the spoon to solve the problem. (German & Barrett, 2005). The researchers wanted to know if exposure to highly specialized tools, as occurs with individuals in industrialized nations, affects their ability to transcend functional fixedness. It was determined that functional fixedness is experienced in both industrialized and nonindustrialized cultures (German & Barrett, 2005).
In order to make good decisions, we use our knowledge and our reasoning. Often, this knowledge and reasoning is sound and solid. Sometimes, however, we are swayed by biases or by others manipulating a situation. For example, let’s say you and three friends wanted to rent a house and had a combined target budget of $1,600. The realtor shows you only very run-down houses for $1,600 and then shows you a very nice house for $2,000. Might you ask each person to pay more in rent to get the $2,000 home? Why would the realtor show you the run-down houses and the nice house? The realtor may be challenging your anchoring bias. An anchoring bias occurs when you focus on one piece of information when making a decision or solving a problem. In this case, you’re so focused on the amount of money you are willing to spend that you may not recognize what kinds of houses are available at that price point.
The confirmation bias is the tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs. For example, if you think that your professor is not very nice, you notice all of the instances of rude behavior exhibited by the professor while ignoring the countless pleasant interactions he is involved in on a daily basis. Hindsight bias leads you to believe that the event you just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t. In other words, you knew all along that things would turn out the way they did. Representative bias describes a faulty way of thinking, in which you unintentionally stereotype someone or something; for example, you may assume that your professors spend their free time reading books and engaging in intellectual conversation, because the idea of them spending their time playing volleyball or visiting an amusement park does not fit in with your stereotypes of professors.
Finally, the availability heuristic is a heuristic in which you make a decision based on an example, information, or recent experience that is that readily available to you, even though it may not be the best example to inform your decision . Biases tend to “preserve that which is already established—to maintain our preexisting knowledge, beliefs, attitudes, and hypotheses” (Aronson, 1995; Kahneman, 2011). These biases are summarized in Table 7.3 .
Watch this teacher-made music video about cognitive biases to learn more.
Were you able to determine how many marbles are needed to balance the scales in Figure 7.9 ? You need nine. Were you able to solve the problems in Figure 7.7 and Figure 7.8 ? Here are the answers ( Figure 7.11 ).
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Rose M. Spielman, William J. Jenkins, Marilyn D. Lovett
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Psychology 2e
- Publication date: Apr 22, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/7-3-problem-solving
© Jan 6, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Psychologists refer to these efficient problem-solving techniques as heuristics. A heuristic in psychology is a mental shortcut or rule of thumb that simplifies decision-making and problem-solving. Heuristics often speed up the process of finding a satisfactory solution, but they can also lead to cognitive biases.
Heuristics are mental shortcuts that allow people to solve problems and make judgments quickly and efficiently. These rule-of-thumb strategies shorten decision-making time and allow people to function without constantly stopping to think about their next course of action. However, there are both benefits and drawbacks of heuristics.
However, the list of heuristics included in Table 1 is not at all limitative, and in How to solve it Polya himself mentions and illustrates also other useful strategies, such as working backwards from the intended goal situation or solution, and decomposing a problem in subgoals.. Although the focus of his work relating to heuristics is on mathematical problem solving, Polya also stressed that ...
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A "rule of thumb" is an example of a heuristic.
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A "rule of thumb" is an example of a heuristic.
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems.
Problem-solving skills are essential in our daily lives. The video explains different problem-solving methods, including trial and error, algorithm strategy, and heuristics. It also discusses concepts like means-end analysis, working backwards, fixation, and insight. These techniques help us tackle both well-defined and ill-defined problems ...
The four stages of heuristics in problem solving are as follows: 1. Understanding the problem: Identifying and defining the problem is the first step in the problem-solving process. 2. Generating solutions: The second step is to generate as many solutions as possible.
A heuristic (/ h j ʊ ˈ r ɪ s t ɪ k /; from Ancient Greek εὑρίσκω (heurískō) 'method of discovery', or heuristic technique (problem solving, mental shortcut, rule of thumb) is any approach to problem solving that employs a pragmatic method that is not fully optimized, perfected, or rationalized, but is nevertheless "good enough" as an approximation or attribute substitution.
2. Next. A heuristic is a mental shortcut that allows an individual to make a decision, pass judgment, or solve a problem quickly and with minimal mental effort. While heuristics can reduce the ...
A heuristic is a word from the Greek meaning 'to discover'. It is an approach to problem-solving that takes one's personal experience into account. Heuristics provide strategies to scrutinize a limited number of signals and/or alternative choices in decision-making. Heuristics diminish the work of retrieving and storing information in ...
Algorithms. In contrast to heuristics, which can be thought of as problem-solving strategies based on educated guesses, algorithms are problem-solving strategies that use rules. Algorithms are generally a logical set of steps that, if applied correctly, should be accurate. For example, you could make a cake using heuristics — relying on your ...
Thus, a combination of methods (strategies) rather than one specific method [69] (e.g., heuristics, problem solving, group discussions, giving frequent exercises, etc.) can be applied to minimize ...
Heuristics are strategies that allow individuals to reach a conclusion for themselves or to fill a gap when information is not available. In the past 25 years or so, the empirical study of heuristics showed that these strategies are ingrained in the functioning of the human brain and central to processes like problem-solving and judgment and decision-making.
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems.
Chapter 1. Heuristics Strategy or tactics in problem-solving is called heuristics. In this chapter we will be concerned with the heuristics of solving mathematical problems. Those who have thought about heuristics have described a number of basic ideas that are typically useful. The five classics on problem-solving by George
Keywords: Problem solving; strategies; heuristics; biases; means-ends analysis; cognition. Introduction Problem solving is an important mental activity, and a classic research area in cognitive psychology. Problem solving has received less attention recently, and is still largely dominated by the information processing
In insight problem-solving, the cognitive processes that help you solve a problem happen outside your conscious awareness. 4. Working backward. Working backward is a problem-solving approach often ...
Successful problem solving is a function of how efficiently, rather than how strenuously, a problem solver. 53 works (Anokhin and others, 1996), and heuristics enhance efficiency regardless of ...
A problem-solving heuristic is an informal, intuitive, speculative procedure that leads to a solution in some cases but not in others. The fact that the outcome of applying a heuristic is unpredictable means that the strategy can be either more or less effective than using an algorithm.
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A "rule of thumb" is an example of a heuristic.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like As one type of problem-solving strategy, heuristics:, Carl is giving a presentation to his mathematics class regarding algorithms. He states, "Algorithms _____.", Social media is a perfect environment for fake news, which gets reinforced by the _____ due to algorithms that the social media companies use to show users information ...
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems.