MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Management Case Studies » Case Study: Google’s Recruitment and Selection Process

Case Study: Google’s Recruitment and Selection Process
Google Inc., the world’s largest and most popular search engine company, is also one of the most sought after companies in the world. Due to the popularity of the company caused by its highly attractive compensation and benefits packages for its employees, millions of job applications are constantly received by Google on an annual basis. While other companies envy Google for attracting and acquiring such highly-talented and highly-skilled individuals from all over the world, the company finds it as a serious cause of dilemma.
When Google Inc. topped the ranks for the most popular companies in the world , it could no longer contain the number of applications it receives from thousands of job hunters from all over the globe. And since the company aims to hire only the best employees that fit the organizational culture and standards of Google , the company started thinking of ways to better improve its recruitment and selection process for its would-be employees.
In an article released in New York Times in 2007, Google Inc shared its non-traditional, highly creative and unconventional approach of selecting and hiring employees. Initially, the Google management sought the aid of its highly-competent and well-skilled technical staff in order to find ways to quickly go through and review the millions of applications it stored in its recruitment database.

The Google Inc management also decided to focus on the distinct behavioral characteristics and personality that separates Google employees from any other employees in other known companies. It shifted its focus from academic qualifications and technical experiences to the applicant’s personality , creativity , leadership capacities , innovative and non-conventional ways of thinking and the applicant’s overall exposure to the world. The academic qualifications and the intensive job experience just came in as second priorities of the company in choosing the best candidates for any open positions.
Since then, the Google Inc company not only became known for its outstanding and “luxurious” job compensation and benefits packages it offers its employees, but also in making use of some of the most powerful recruitment assessment tools capable of picking the best employees in the world that fit the standards set by Google.
The Google Recruitment Process
One of the most notable statements of Eric Schmidt , the CEO of Google Inc. is that “Google invests in people.” The main reason why people from different cultures, have been dreaming of being recruited and hired by Google is that the company offers possibly the most outstanding job compensation packages any normal employee could ever enjoy.
In order to attract the best employees, Google draws them by the promise of wealth and luxury, providing their employees with almost everything an employee could possibly need, from absurdly high compensations to extravagant and luxurious benefits like gourmet food, carwash, gym, snacks, exercise classes, dry cleaning services, car services, haircuts, oil changes, massages, checkups and many more, all for free.
Nevertheless, the recruitment process was also far beyond ordinary. Several people who have had experience in the Google recruitment process narrates that the experience was totally nerve-wracking. One applicant who underwent interviews for Google has had five to seven interviews in one day for two to three straight days. That applicant claims that the interviews were really tough with some of the brightest people in the world, conducting the interviews filled with brain teasers, algorithmic problems, and IQ tests.
Another applicant who also have had experiences in the recruitment process of Google claims that his Google experience was one of the most nerve-wracking adventures of his life. The interviewers were looking for extremely bright individuals and so the recruitment method was filled with IQ tests, brain teasers, algorithms, data structures, and a lot of mathematics involved in it.
The Google Selection Process
Google is no doubt the world’s best recruitment leader. Google is known for various unique approaches that it has utilized in order to attract the cream of the crop or the best of the bests. One way is through employment branding. Google has so successfully utilized their brand in order to attract the most talented and highly-competent individuals in the world. Because of their claim of providing the best employee-employer experience supported by the many perks, benefits and high salaries that Google employees get to enjoy, Google became the most desired companies for men and women in the world.
While the work and job responsibilities in Google are not that easy, the stock options benefit is one of the key drivers of retention and continuous acquisition of the best employees for this company. In 2007, employee turn-over at Google was reportedly less than 5% which was simply phenomenal. People didn’t want to leave the company because the amazing provisions and benefits that the company offers its employees. Moreover, the creative approaches of Google when it comes to hiring and retaining employees were simply exceptional. Employees claim that money was never an issue for Google in terms of utilizing it to take care of its employees.
One notable recruitment technique that Google utilized in 2006 was the targeted and unobtrusive approach to sending recruitment messages. Google crafted a simple technique to recruit the best students in certain schools and universities to work for them. They allowed people from these schools to access the search portal of Google wherein the students’ IP address would be identified to see from what organization the person belongs into. The technique was successfully executed using a minimalist and unobtrusive style of recruitment wherein below the search box, the Google system would know whether the targeted student is graduating or not and whether or not they intend to work for Google after graduation. The approach was definitely a successful micro-targeted approach. It was also in the same year when Google opened up to the idea of an Employee Referral Program. In putting up this program, Google made sure that it would deliver them a world-class employee whose personality, qualifications and work ethics reflect the Google standards.
A year passed by and Google’s attempts for recruitment innovations continued to improve. In 2007, Google developed a simple and effective assessment tool to screen its millions of applicants all over the world via an algorithm assessment tool. The algorithm technique effectively separated the top and the best performers from thousands of candidates vying for a position. Moreover, the assessment tool was made sure to successfully predict the best possible candidates from the least and the average and has managed to resolve the issue on the usual assessment tools being used by most companies, relying mainly on the academic qualifications and intensive industry and job experience.
Truly, what separates the Google recruitment process from the typical and the usual recruitment methodologies that other companies employ is its ability to accurately identify the best candidates for the position using a more data-based and scientific approach to the recruitment process. Also, it has significantly reduced the reliability of interviews, which for most companies, serves as the final indicator of how well an employee will perform at work. Furthermore, the algorithm approach which is a common business model that the company employs was effectively used to assess whether potential candidates can indeed perform given the high performance standards of Google.
The secret to be selected as a Google employee is that one has to think a lot like an “engineer”. Apparently, Google expects their employees to be highly quantitative and highly analytical as well as highly capable of dealing with too many data all at the same time. During the interviews, an applicant must also be able to demonstrate his skill or capacity by writing codes, intelligently analyzing case studies and brain teasers and solving algorithmic problems on the spot. Also, Google is searching for applicants who are highly practical and are capable of making something out of nothing that people can make use of.
The Google Interview Process
Since Google is known to be the ultimate recruitment and selection machine, its interview processes are also the most grueling experiences an applicant could ever have. Usually, the interviews begin using the telephone. Once the phone interviews conducted have been successful, the applicant would be scheduled by the recruitment officer and be invited for a series of five to ten interviews in one day with ten different people. For some people who have successfully undergone this process, they described it as the most excruciating employment experience of their lives as a lot of mental gymnastics were necessary to prove your skills.
There were many instances when the applicants were asked to write codes, brain storm, role play or solve mathematical equations on the spot just to prove that they are highly-skilled and competent. In other instances, the applicants are even tested of their marketing skills even though the position an applicant is applying for is highly technical. The interviewers seem to have control and power over the applicants letting them do everything just to prove that they are worthy for the position. Common questions involved computer network problems, Java programming and algorithms by which Google is known for.
Moreover, other applicants can rate and share comments on another applicant which Google can track and use as another basis for hiring or not hiring an applicant. Overall, the process was a lengthy, tedious and nerve-wracking experience which can possibly traumatize anyone whose dream is to work for one of the most prestigious companies in the world. Nevertheless, the perks and benefits are limitless and are more than enough to compensate for such a tough employment experience.
Related posts:
- Best Practices in Recruitment and Selection
- How to Improve Your Recruitment Process
- Integrity Testing in Employee Selection Process
- How Blockchain Transforms the Recruitment Process?
- Recruitment Process Outsourcing (RPO) – Definition, Benefits and Risks
- Recruitment Process
- Case Study: Restructuring Process of Volkswagen
- Type of tests taken in the selection process
- Types of interview conducted in the selection process
- Selection Process in Human Resource Management
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- About / Contact
- Privacy Policy
- Alphabetical List of Companies
- Business Analysis Topics
- Google (Alphabet) HRM: Recruitment, Selection, Retention

Google’s (Alphabet’s) success is based on its high-quality human resources. The competitive qualities of the company’s employees include smartness and excellence. The information technology company’s human resource management also includes carefully selected strategies, methods, and techniques for recruitment and selection, and for the retention of high-quality workers. Recruitment practices, selection processes, and retention programs ensure an adequate workforce and retain excellent employees, who are the foundation of the business strengths noted in the SWOT analysis of Google (Alphabet) . These programs also attract employees to the firm. The company is now one of the best places to work. Such popularity and positive perception indicate the success of Alphabet’s human resource management in recruitment, selection, and employee retention.
This article is part of a series on Google’s (Alphabet’s) human resource management:
- Google (Alphabet) HRM: HR Planning, Job Analysis & Design
- Google (Alphabet) HRM: Training, Performance Management
- Google (Alphabet) HRM: Compensation, Career Development
Google’s (Alphabet’s) Recruitment Practices
Sources . Google’s human resource management uses a mixture of internal and external recruitment sources to maintain the adequacy of its human resources. The company uses promotions, transfers, and trainees/interns as the main internal recruitment sources for HR needs. On the other hand, the external recruitment sources at Google include educational institutions and respondents to job advertisements. Most of these ads are available through the Careers section of Google’s website. Through these recruitment sources, the company facilitates a continuous influx of qualified workers, while matching these employees’ capabilities with human resource needs.
Methods . Considering the combination of internal and external recruitment sources, Google uses indirect methods and direct methods of recruitment. The indirect methods are more significant to the company. These indirect methods include advertisements on the company’s website. However, Alphabet’s human resource management also uses direct methods in the form of contacts with potential interns and future employees through academic institutions. This combination of direct and indirect recruitment methods is aligned with the mixture of internal and external recruitment sources to satisfy Google’s human resource requirements.
Selection Process at Google (Alphabet)
The most significant criteria used in Google’s human resource management for the selection of applicants are smartness, creativity, drive for excellence, and alignment with the organization. The company does not use work experience as the main criterion for selection. These criteria are based on the goal of maximizing innovation to support Google’s (Alphabet’s) generic competitive strategy and intensive growth strategies . For instance, the company’s human resource selection provides HR support for software engineering, hardware design, and consumer electronics marketing.
There are different processes used for the selection of applicants at Google. However, in general, the company’s selection process involves background checks, preliminary screening, on-the-job tests, and interviews. Google’s human resource management uses different procedures and steps for the various positions in the organization. For instance, on-the-job tests are generally used for positions that are more frequently filled through absorption of interns and trainees.
Retention Programs for Alphabet (Google) Employees
Compensation packages are the main HRM tool that the business uses for retaining high-quality human resources to fulfill the strategies and goals set in Alphabet’s (Google’s) corporate mission statement and corporate vision statement . The company’s compensation packages are competitive and above average. For example, Google provides high salaries and wages. In addition, employees get free meals and other incentives and benefits. The typical design of the company’s offices emphasizes fun and creativity, which attract and retain creative and innovative workers. Alphabet’s human resource management uses coaching and mentoring to retain and develop employees with leadership potential.
- Alphabet Inc. – Building a Sense of Belonging at Google and Beyond .
- Alphabet Inc. – Form 10-K .
- Engelsberger, A., Bartram, T., Cavanagh, J., Halvorsen, B., & Bogers, M. (2023). The role of collaborative human resource management in supporting open innovation: A multi-level model. Human Resource Management Review, 33 (2), 100942.
- Google Careers – How We Hire .
- Gu, M., Zhang, Y., Li, D., & Huo, B. (2023). The effect of high-involvement human resource management practices on supply chain resilience and operational performance. Journal of Management Science and Engineering, 8 (2), 176-190.
- U.S. Department of Commerce – International Trade Administration – Software and Information Technology Industry .
- Copyright by Panmore Institute - All rights reserved.
- This article may not be reproduced, distributed, or mirrored without written permission from Panmore Institute and its author/s.
- Educators, Researchers, and Students: You are permitted to quote or paraphrase parts of this article (not the entire article) for educational or research purposes, as long as the article is properly cited and referenced together with its URL/link.
MBA Knowledge Help
For Business and Management Research and Analysis
Google Recruiting Case Study: A Case Study of Google’s Recruitment and Selection Process

Millions of job applications are sent to Google every year, according to indicative statistics from Wikipedia and Statista.com, but only a very small percentage of these applicants eventually make it through to Google as employee. This Google recruiting case study is a case study of Google’s recruitment and selection process that will help us delineate some important details on methodologies and policies used in Google for talent recruitments into one of the world’s biggest and most competitive workplace of the century.
The entire world is aware of Google’s competitive job opportunities and remuneration structures for its employees. Being one of the biggest tech companies in the world, Google is one of the most popular search engine companies with more than 50% percent of the total shares in the search engine industry. But much more, Google’s influence in the tech world transcends the search engine industry, it has major stakes in AI sector, cloud computing, with the most popular data and analytics franchise. As a result of this prominence and influence, many smart techies and other categories of talented people hope to get a job at Google. But getting a job at Google is more than just a game of hope, it is important to also understand Google’s recruitment and selection process.
Table of Contents
Effective Recruitment and Selection at Google
Effective recruitment and selection process is important for organizations like Google who must carefully select talents who not only have the required technical expertise but also crucial behavioural qualities which align with the strategic direction of such global organizations. Google offers employees very attractive payment, some even call it luxurious salaries, and other benefits such as car wash, gym exercise breaks, exquisite lunches, and other incentive packages. While most other tech companies envy Google’s prominence and the manner in which employees troop to submit job applications, the case is not all positive for Google as the company find it a big challenge to sift through the millions of job applications received yearly just to select and recruit the best of the best.
In case study article by Financial Times in 2010, experts who have investigated deep into Google recruiting case study believe that Google has moved from a traditional approach to hiring that is primary focused on expertise and academic qualifications, to a more personality-oriented recruiting process. In past years, Google was known to prioritize technical and academic competence of potential employees, but now, Google employs more of an unconventional approach to recruiting. But that was not without problem, because it increases the filtering time and prolongs the recruiting process as more care is taken to evaluate candidates’ behavioural characteristics and see how those align with the organizational culture.
To review the millions of applications, Google had looked for innovative database management solutions from its tech talents who were able to develop an application database and system that does the initial evaluation of the millions of applications sent to Google. However, this at best was only able to separate applications that didn’t provide particular information required, when it comes to actually going through the selection process, real humans have to do it.
Google Inc employees are not only known for their mouth-watering paycheck and other benefits that are attached to working at Google, they are also known as a distinct breed of talents. While technical expertise and experience is still an important consideration, Google Inc. has over the years focused more on such behavioural qualities like leadership, creativity, eccentricity, unconventional thinking, ability to think outside of the box, tolerance, empathy, and many other aspects of employee personality that set Google’s employees apart from other employees globally.
However, it is important to say that although these personality qualities are in fact principal considerations in Google recruiting, academic qualifications and highly relevant job experience are also still major considerations, although some experts think they are only just secondary considerations.
The reason for this is not far-fetched, Google is a global organization that depends on the technical expertise on employees to thrive, so it is naturally logical that an employee would need to be very technically qualified to even be considered a spot at Google Inc. The point, however, is that technical knowledge and academic qualifications are not enough.
Why Techies Want to Work at Google
Working at Google is not only job ambition for some, it is a life-long target for many, both techies and non-techies. Apart from being an organization with a global reach, exerting prominence across every nook and cranny of the world, Google is a reputable tech company with only few companies that can boast of the level of influence it has. According to EarthWeb, 5.07 billion use the internet daily, and more than 60% of this number use Google per day. This not only underscores the importance of Google to daily life across the globe, it is a testimony of the tech company’s undebatable prominence.
Google is an example of what we call a fortune company, which is a treasure mine for employees who receive eye-boggling salaries and other attractions. According to the CEO of Google, Eric Schmidt, Google as a company has prioritized investing in its employees, and as a result, since Google offers employees arguably one of the biggest salaries in the world.
Understanding Recruitment and Selection at Google
In order to differentiate between recruitment and selection at Google Inc, we will consider the significance of these two in relation to the need to be strategic about workforce for a global company like Google. Recruitment is the process of bringing in qualified workforce into a company, whether to replace the present ones, fill up vacancies, or expand the present workforce. In most times, Google is only looking at expanding the staff power of the company and also fill up vacancies created by promotions. The recruitment process is accompanied side-by-side by the selection process which involves the process where the exact individuals who can fit the positions of vacancies are selected out of the multitude. In other words, it is how Google selects the cream of the crop from the crowd of prospective employees.
The significance of a well-structured recruitment and selection process has been noted by experts who believe that through these two processes, a company can strategically position itself for long-term success, as in the case of Google Inc. A popular management saying is that “employees are the real competitive advantage for organizations,” indicating that companies are getting more intentional about selection and recruitment as a strategy for growth and development.
Google’s Recruitment Process
Google structures its recruitment process around its recruitment philosophy which highlights Google’s unique corporate culture and values. At Google, recruitment is done with the aim of enriching organizational effectiveness and serving the world better. With this philosophy, it is clear the Google will naturally prioritize recruitment of employees who can add value to organizational effectiveness in terms of leadership, innovativeness and ingenuity, while also having the required skills to tackle emerging problems from a technical point of view.
Some experts, like the author of this blog post at www.mbaknol.com , believe the Google attracts employees by the promises of wealth and affluence, which may be true. But when you say “by promises of wealth”, it challenges what we know global organizations to be known for in terms of remuneration structure for employees. On the other hand, Google attracts employees through what we call employment branding, which means that employees would like to work for a brand because of the perceived value attached to the brand, which could be promises of wealth like the author has said.
Google most times uses a quiet hiring approach which means that most hiring going on is not formally made known to the public. Although there have been ethical questions regarding this approach, it is important to note that Google Inc. does this to ensure there are fewer applications to be sorted through.
Recruitment Strategies at Google
To accomplish its goal of hiring the best candidates for positions out of the millions of interested candidates, Google uses a three-step strategy, which involves, (i) express communication with candidates (ii) Rigorous interview process (iii) team selection approach
Express communication between recruiters and candidates is one of the most Google-known approaches to hiring. This approach cuts across several hiring stages and levels. Having interviewed a couple of persons who have experienced the Google recruitment process, we know that Google is big on communication as a way to make sure prospective employees are relaxed and comfortable through the whole process.
Another strategy is the use of rigorous interview process during the Google hiring process. For a company like Google, people who have worked their way through the interviews note that it was not a walk in the park. In fact, as some present employees note, it was nerve-wracking and highly challenging. While this may seem to scare candidates, it is actually an opportunity to prepare adequately and prove themselves to be capable of being associated with a fortune tech company like Google.
Google Selection Process
The selection process at Google is perhaps the most important part of the recruitment process, as this process involves the screening of applications and multi-stage interviews that eventually lead up to selection. So, what is Google’s selection process like?
Google Inc. makes selection decisions based on multiple factors that are determined by a data-driven assessment of candidates, behavioural interviews and scenario-based assessment, and the use of technical evaluations. After this, a rigorous multi-stage interview is followed where participants are evaluated using different techniques such as IQ tests, algorithm tests, quantitative and qualitative reasoning just to make sure that they are the best candidates to choose.
One of Google’s employees who granted an interview maintained that the interview process is the most challenging part of the recruitment journey for him, saying that he had multiple interviews for days back-to-back.
If the interview process is so challenging, it is important to wonder why many still want to work at Google regardless. The answer is that employees want to enjoy the insanely big salaries, fancy compensation packages, and also working at Google literally makes you the talk of the town, especially such professional websites as LinkedIn.
Google’s emphasis on data-driven candidate assessment is an important part of this selection process, as employees data are processed and based on this, selection decisions are made. Candidates submit important personal and experience data to the Google recruitment database. It is this database that process information that helps aid reasoning and decision making regarding who might be the best or who might be better. Although machine do that data-driven processing, the selection has to be done by humans.
Role of online coding tests and technical evaluations is also noted as important since employees have to compulsorily go through online coding tests and technical evaluations in order to be selected. Coding tests and technical evaluations often depend on the role being applied to, but generally it is common knowledge that these tests are not an easy nut to crack, because if it was easy everyone would be working at Google. Talking about technical evaluations, candidates are expected to be able to work through algorithm assessments, figure out solutions to complex problems, and provide insights into scenarios in as little time as possible. This is to make sure that best performers are separated from the other categories of applicants who may have struggled through the tests. This assessment technique also echoes Google’s commitment to favour technical knowledge over academic qualifications, which has been a recruitment issue in most companies.
Behavioral interviews and scenario-based assessments also form a pillar in the selection process at Google. Candidates have to take behaviour-oriented assessments because Google’s standards believe that beyond technical skills, employees must have the required skills to deal with issues in a multi-cultural working environment. As a result, scenario-based assessments that test leadership skills, empathy, communication, teamplaying and other organizational-oriented qualities are compulsory passes candidates must make.
Finally, Google uses a more data-driven recruitment methodology that sets it aloft of other recruitment methodologies used in other companies. This progressively-improving scientific approach to hiring helps Google identify top candidates who are most likely more apt to perform on the job than other candidates. With this data-based strategy, Google can augment interviews with data-based insights that helps it employ top candidates
Google Interview Process
Being renowned as the ultimate talent acquisition and curation engine, Google’s interview procedures also encompass the most demanding encounters an aspirant could possibly undergo. Candidates have been known to go through five to ten interviews per day, where they are asked several questions regarding their skills, leadership experience, and motivation for applying to Google. Assessment tests also include anything from IQ tests to coding and algorithm interviews where candidates have to figure out solutions to questions within short periods.
Related Posts:
- Case Study: Complete Johnson & Johnson Company Analysis
- Impact of Operations Management on Organizational Direction…
- Case Study: Coca Cola's Share a Coke Campaign Case Study and…
- Case Study: Analysis of Dove’s Campaign for Real Beauty
- Case Study: Analysis of Corporate Governance Failure at…
- Social Work Ethos: Development and Relevance for Social…
No related posts.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Interesting piece. I really enjoyed reading it.
A Case Study of Google Recruiting, Part 2
- Advertising & Marketing
As part of my continuing series of case studies and analyses of truly world-class recruiting functions, I am highlighting the key features of Google, the world’s first recruiting culture and the only “corporate recruiting machine.” Google recruiting has made an incredible breakthrough in that they have convinced senior management to literally “change the work” so that every employee has time to work on his or her own projects and is continually challenged, stimulated, and learning. There is no better attraction and retention tool then exciting work and Google has made it the centerpiece of their company. In Part 2 of this case study, I’ll highlight the remaining elements of Google’s recruiting approach and point out some areas where they can improve.
Recruiting Structure
Google has plans to nearly double its workforce, growing from approximately 5,000 employees to 10,000 employees in the near future. The recruiting structure that they have designed to enable such growth is, like most successful recruiting organizations, primarily a centralized operations model. The basic reason why firms use a centralized a recruiting function is to ensure that most of the recruiting is done by recruiting professionals, as opposed to generalists, who for the most part don’t have the skills or the attitude to be great recruiters. Centralization also makes it easier to share top applicants between business units, a key activity which seldom occurs when decentralized generalists execute recruiting.
The recruiting function is headed by Arnnon Geshuri. A key tenet of any excellent recruiting function is that the function has the capability to handle in-house the most important and visible positions, i.e. executive search. At Google, recruiting is responsible for filling both executive leadership and top-level technical positions. The executive group is notably headed up by Mike Strong, one of the best recruiting leaders I have ever met. Because Google believes wholeheartedly in sourcing the best talent that is ferociously sought after by competitors, every element of the recruiting function is abundantly staffed with highly focused professionals. They realize that the volume and caliber of talent they desire is not going to be mined from a job board, resume bank, or general recruitment advertising (something Google consciously avoids.) To ensure that the company has the capability to recruit talent at the capacity needed, the recruiting model has been broken up into very distinct roles, each requiring specialized expertise. These activities, carried out in a highly choreographed manner by teams tied to divisions and business units, include:
- Recruiting research analysts
- Candidate developers (sourcers)
- Process coordinators
- Candidate screeners
- Specialized recruiters for college
- Specialized recruiters for technical and leadership executive search
- Specialized international recruiters to be located in Asia and Europe
- Recruiting program managers
- Recruiting project managers
Such specialization enables the function to be managed in a way similar to a supply chain. The specialized positions allow Google to manage a high volume of resumes, estimated to exceed half a million each year. without degrading either the candidate or hiring manager experience. Some outside consultants have argued that such a large number of recruiters and specialized positions is an indication of inefficiency, but I have not found that to be true. Like all things in business, obtaining a specific level of efficiency requires that one make tradeoffs between output quality and input cost, and at this point in time Google values the quality over the cost. The willingness to fund this recruiting model is a clear indication that talent more than any other input is the most critical at Google, a notion many pay lip service to but few actually execute. Since, however, Google’s recruiting and HR metrics are “underdeveloped,” for lack of a better word, it’s difficult to make an accurate assessment as to whether their approach is producing new hires with exceptional on-the-job performance. All that can be said to quality of hire at this point is that Google managers believe they are getting it, a perception few other organizations seem to be able to develop.
Like many young firms experiencing rapid growth, Google has been slow in forming its international recruiting unit, but with the appointment of Jason Dellinger, an up-and-coming star, it looks like it will develop into one of the best global recruiting functions in the world. Mr. Dellinger is currently implementing an ambitious plan to attract the very best recruiters simultaneously in both Asia and Europe. His plan provides for the needed degree of consistency in recruiting around the globe while simultaneously allowing a reasonable amount of local flexibility to meet unique market needs.
“Wow” Recruiting Tools
As you might expect, Google employs a variety of impressive recruiting tools that certainly “wowed” me while I was performing this case study:
- AdWords as a recruiting tool. Google’s first “wow” approach is its use of its own Google search tool to find “passive” candidates. Because Google is recognized as the “master of search,” it’s not surprising that they utilize their own search tool to find top candidates without active resumes. In addition, they attract top performers by placing their own job ads that appear when certain keywords are typed into a search (in a fashion just like the sponsored product ads that we’re all familiar with). Anyone can do this by “buying keywords” (AdWords technology). For example, if someone types in a search that includes the words nurse and Phoenix, it’s highly likely that the person doing the search is either a recruiter looking for a nurse in Phoenix or a nurse professional that is looking for nursing position in Phoenix. Smart companies can thus buy keywords in order to identify and recruit smart recruiters or to find nurse candidates for the Phoenix area. These types of searches are even more effective if you place your job opening announcements around searches that include words like “becoming a great nurse” or “awards for nursing excellence” because these types of searches are indications of a professional that is striving to become one of the best. Google has also placed position announcements on searches that include the name of top Google scientists and engineers.
- Contests as recruiting tools. A second “wow” aspect of Google recruiting is its use of a contest to identify and attract top software engineers. The Google Code Jam, as they call it, is a global online software writing contest that can attract over 7,500 people each year. The top 25 finalists are invited to the Mountain View campus to compete for $50,000 in prizes as well as a chance to work at Google. The contest is powered by TopCoder, a vendor that helps manage the contest and score the winners. The concept itself is just brilliant. What better way to assess potential hires than to have them write code that is relevant to your firm’s problems? In addition to being a great recruiting tool, the publicity related to the contest helps further strengthen the employment brand of being innovative and creative. Another interesting aspect of the contest is that it demonstrates that the winners seldom come from noted U.S. universities. The information gathered on participant education can be used to better refine the college recruiting model so that it also includes lesser-known European and international schools that have a proven ability to produce graduates capable of producing simulated on-the-job performance.
- Brain teasers as recruiting tools. The third “wow” aspect of Google’s recruiting is its creative use of roadside billboards and “math tests” placed in magazines to garner the attention of math and programming wizards. Google has placed “brain teaser” billboards in the Silicon Valley and by Harvard Square. The math puzzles on these billboards challenge math-oriented people and get them thinking. Although they do not specifically mention Google, the billboard puzzle does eventually lead interested participants to the Google site. In addition, Google has placed math and problem solving tests in magazines read by mathematicians as well as Linux and open-source programmers. Not only do the tests create a buzz (again, Google does not focus on traditional advertising) among Google’s target community, but it also results in direct hires.
- “Friends of Google.” The final “wow” recruiting tool is the “friends of Google” system. This tool creates an electronic email network of people that are interested in Google and its products but not necessarily interested in working for the company. By signing up these individuals and then periodically sending them emails about the firm’s products and events, Google can build a relationship among thousands of people that like the firm. After building and maintaining relationships with these individuals over time, recruiters eventually begin to utilize the membership list as a source for referrals and potential hires.
Standard Recruiting Tools
In addition to the “wow” recruiting approaches above, Google also has successfully implemented many of the standard best practice tools found at other companies:
- Employee referral. Google’s referral program is without any industry leading features, but the company’s strong brand coupled with its highly enthusiastic workforce makes up for weaknesses in the program.
- College recruiting. Google hires a large number of PhDs on the premise that they enjoy exploring areas that no one else has explored. To accomplish this, they have developed a network of direct relationships with over 350 professors at major schools. In addition, Google has an outstanding internship program that has a very high conversion rate to permanent hires. (Internship conversions typically have one of the highest success rates of any hiring source, according to my own research.)
- Professional networking. Google also effectively uses networking groups like Linkedin and other live professional events to recruit top performers.
- Recruiter training. Google is one of only a handful of companies that requires most newly hired recruiters to go through extensive recruiter training prior to starting. Most of the training at Google is handled by the exceptional group headed by James Duran, whom I call “the godfather of recruiting.”
Some Weaknesses in the Google Approach
Google’s primary strength in recruiting comes from the fact that they “change the work” and that they have and continue to make an outstanding business case to fund the recruiting organization at an unparalleled level. But it’s equally important to point out that Google recruiting is not without weaknesses. Some of the current and potential issues facing Google recruiting are outlined below. Given the relative youth of the company, none of these weaknesses even reach the level of being considered a threat, but in a company whose slogan is “great isn’t good enough,” it’s critical that HR and recruiting management spend some time and resources in the following areas:
- Employment branding. Although Google is clearly well known as a great employer, it is clear that much of that recognition has come as a result of programs and ideas that originated outside of HR. The only long-term recruiting tool that is available to any firm is employment branding. It is critical that HR and recruiting devote resources to developing a formal employment brand strategy and execution plan.
- Metrics. At a technology company driven by mathematics and staffed largely with mathematicians, it’s almost unbelievable how both the HR and the recruiting function have dragged their feet on developing metrics. In particular, Google’s inability to track the on-the-job performance of new hires is inexcusable. everyone in recruiting must be more cynical and learn to make decisions based on data, not intuition. In a company whose slogan is “great is not good enough,” the use of metrics is an absolute requirement.
- Recruiting strategy. Although Google recruiting obviously does great things, those things seem to occur “at random” and in spite of the fact that there is no formal, well-communicated recruitment strategy. Whether you talk to recruiters or hiring managers at Google, no one seems to be able to clearly articulate the strategy and how it differentiates Google from its talent competitors. Having a written recruiting plan and a superior strategy that focuses on building and maintaining a competitive advantage is essential.
- Speed. Almost everyone that has been a candidate at Google comments on how slow the screening, recruiting, and interview process is. The fact that some stock option grants and all new professional hires must be approved by senior management (an activity limited to one day a week) is “industry leading” in a way that hurts the recruiting effort. Excessive approvals at the top and the related time to fill issues must be addressed as the company becomes larger and more global.
- Contingent labor. The number of temps and contractors in the recruiting function at Google is high. The unwillingness to give permanent jobs immediately to recruiters may reduce Google’s ability to get seasoned recruiters, who have mortgages and car payments like the rest of and require a certain level of stability. One of the net results of this policy seems to be a disproportionately large number of “rookie” recruiters who learn as they go.
- Emphasis on youth. Google’s emphasis on “youth culture” might hurt its ability to attract more senior and experienced personnel. I heard concerns related to their emphasis on “youth” from more than one employee, and at least one former worker has accused them of age discrimination.
Perhaps the most surprising area in need of significant attention is Google’s corporate careers site. Don’t get me wrong, it does have features that many sites don’t have, including streaming video of the headquarters site and a few narrative personal profiles. But for one of the world’s leading technology companies, it gives the impression that HR is exempt from utilizing the latest in Web technology. The passion and excitement of the employees and the campus just don’t come through on the job site. Position descriptions are dull. Even the information on Google’s record-breaking benefits is static, with no opportunity to actually get more information about them. There is no personalization on the site.
- Applications
Paper Information
- Previous Paper
- Paper Submission
Journal Information
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Current Issue
- Author Guidelines
p-ISSN: 2162-9374 e-ISSN: 2162-8416
2014; 4(4): 98-101
doi:10.5923/j.mm.20140404.03

A Evaluation of Google’s Organisational & Recruitment Culture
Yusuf Ali Kausar Rushdi 1 , Asma Nasir Kamal 2
1 Kensington College of Business, University of Wales, Glasgow, UK
2 General Practice, Glasgow, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2014 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
“A new idea to prepare a universal search engine which could connect with other websites around the globe” - Google. Google is the world leader in recruiting culture and has the world’s largest recruiting budget. Its organisational culture is people centred & knowledge driven with a 7- 20 -10 framework. This culture has many benefits for its employees like flexible hours, free meals etc. Google’s culture has been structured with two main dimensions that are a ‘physical object’ and a ‘behaviour pattern’. But due to the informal culture it adoptsit is noticed that there is an absence of a clear management structure, poor employee relations and work ethics.
Keywords: Organisational culture, Business model, Framework, Assumptions, Recruitment
Cite this paper: Yusuf Ali Kausar Rushdi, Asma Nasir Kamal, A Evaluation of Google’s Organisational & Recruitment Culture, Management , Vol. 4 No. 4, 2014, pp. 98-101. doi: 10.5923/j.mm.20140404.03.
Article Outline
1. introduction, 2. main body, 2.1. factors governing recruitment, 2.2. strategic “disruptive recruiting”, 2.3. recruiting culture, 2.4. “20% time”, 2.5. google’s interviewing criteria (li 2008), 2.6. google's recruitment strategy revealed, 3. conclusions.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Reengineering the Recruitment Process

The skills needed in many roles are continually changing—and sources of talent are too.
The Covid-19 pandemic has upended many traditional business practices. When it comes to recruiting, the crisis has not so much disrupted as accelerated shifts in the talent landscape that were already under way, leaving many companies poorly served by their current hiring practices. In a period of steep unemployment, it might seem that companies looking to add workers would be in the driver’s seat. But job openings have also been rising in recent months, meaning that competition for top talent remains keen—and in uncertain times, bringing on the right people is more important than ever.
Partner Center
- Guidelines to Write Experiences
- Write Interview Experience
- Write Work Experience
- Write Admission Experience
- Write Campus Experience
- Write Engineering Experience
- Write Coaching Experience
- Write Professional Degree Experience
- Write Govt. Exam Experiences
Google Recruitment Process
- Olam Recruitment Process
- GreyOrange Recruitment Process
- Adobe Recruitment Process
- GS Lab Recruitment Process
- InfoEdge Recruitment Process
- Newgen Recruitment Process
- Lowe's Recruitment Process
- GlobalLogic Recruitment Process
- GenPact Recruitment Process
- Genpact Recruitment Process
- Oracle Recruitment Process
- Groupon Recruitment Process
- Eze Recruitment Process
- Chegg Recruitment Process
- Accolite Recruitment Process
- enStage Recruitment Process
- Nagarro Recruitment Process
- PhonePe Recruitment Process
- Evive Recruitment Process
This article will give you information about the company, their recruitment process, sample questions that have been asked previously, lots of experiences shared by other aspirants, and the portal where you can apply.

About the Company:
Google is an American multinational technology firm with an emphasis on consumer electronics, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, and search engine technology. Due to its market dominance, data collection, and technological advantages in the field of artificial intelligence, it has been referred to as the most powerful firm in the world and one of the most valuable brands in the world.
Recruitment Process:
- Online Assessment
- Technical Phone Screen
- Coding Rounds 4-5
- Behavioral (Googleyness)
Google Eligibility Criteria:
- Bachelor’s degree or equivalent practical experience.
Online Assessment: 2 Coding Questions on Data Structures and Algorithms Medium – Hard Level
Technical Phone Screen: Google’s interview process begins with a technical phone interview for experienced software engineers. During this stage, tech leads conduct interviews via Google Meet or Hangouts.
Coding Rounds: Check Problem Solving Skills and System Design Questions and Computer Science Concepts and Discussion on Projects.
Behavioral Rounds Check your Personality and Attitude, soft skills, etc.
Interview Experience: It is always beneficial if you know what it is to be there at that moment. So, to give you an advantage, we provide you with Interview Experiences of candidates who have been in your situation earlier. Make the most of it. To check all types of interview experiences please go through Google .
Questions asked in Google
- Number of subarrays having a sum exactly equal to k
- How to replace a substring of a string
- Find length of loop in linked list
- Find the row with maximum number of 1s
- ZigZag Tree Traversal
We have resources for you from which you can prepare the programming questions that tech companies will ask you in the interview.
- Google SDE Sheet: Interview Questions and Answers
Where to apply
- Google LinkedIn
- Google Career Page
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Experiences
- Interview Experiences
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Evaluation of online job portals for HR recruitment selection using AHP in two wheeler automotive industry: a case study
- ORIGINAL ARTICLE
- Published: 12 May 2024
Cite this article

- S. M. Vadivel ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5287-3693 1 &
- Rohan Sunny ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0002-2347-3081 2
Automotive companies are booming worldwide in the economy. In order to sustain in the highly competitive world, every organization tries to create itself a trademark in the market. In our research, we looked at how two wheelers automotive company's selection enhances an organizational performance, which ensures the company's future growth. In today's fast-paced, globally integrated world, human resources are one of the most important production variables. It is critical to preserve and improve economic competitiveness by properly selecting and developing these resources. The main aim of this study is to identify the best online job portal website for recruitment at Two Wheeler Company and to suggest an HR strategy which resonates company’s values and culture. In this study, we have selected 6 criteria and 6 online popular job portals for recruitment with a sample of 15 candidates have been selected. Findings reveal that, AHP method has significant results on the selection of best employer, which helps HR Manager to finalize the decision making process/strategies. Towards the managerial implications section, the researcher aims to design an functional and effective HR strategy that can grasp, engage and retain the top talent in the organization.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Availability of data and material
'Not applicable' in this section.
Abbreviations
Analytic hierarchy process
Artificial intelligence
Analysis of variance
Chief Human Resources Officer
Consistency index
Curriculum vitae
Consistency ratio
Decision making
Faculty Development Programme
Hierarchical linear modelling
Human resources
Research and Development
Randomized index
Structural equation modelling
Search engine optimization
Triple bottom line
Technique for order preference by similarity
Maximum Eigen value
The normalized value of ith criterion for the jth alternative
The normalized value of jth criterion for the ith alternative
The number of alternatives for a certain MCDM problem
The number of criteria for a certain MCDM problem
Avinash Kapse S, Vishal Patil S, Nikhil PV (2021) E-Recruitment. Int J Eng Adv Technol (IJEAT) 1(4):82–86
Google Scholar
Chahar B, Jain SR, Hatwal V (2021) Mediating role of employee motivation for training, commitment, retention, and performance in higher education institutions. Probl Perspect Manag 19(3):95
Chauhan P (2019) Impact of training and development programs on motivation of employees in “A” graded commercial bank of Nepal. Int J Res Anal Rev 6(3):850–857
Elsafty A, Oraby M (2022) The impact of training on employee retention: an empirical research on the Private Sector in Egypt. Int J Bus Manage 17(5):58–74
Article Google Scholar
Habibie M, Mustika I (2020) The effect of training on work motivation and its impact on employee performance (Case Study at BPJS Ketenagakerjaan Headquarters). Int J Innovat Sci Res Technol 5(7):51–57
Haryono S, Supardi S, Udin U (2020) The effect of training and job promotion on work motivation and its implications on job performance: evidence from Indonesia. Manage Sci Lett 10(9):2107–2112
Horodyski P (2023a) Recruiter’s perception of artificial intelligence (AI)-based tools in recruitment. Comp Human Behav Reports 10:100298
Horodyski P (2023b) Applicants’ perception of artificial intelligence in the recruitment process. Comp Human Behav Reports 11:100303
Jack Walker H, Feild HS, Giles WF, Bernerth JB, Short JC (2011) ‘so what do you think of the organization? a contextual priming explanation for recruitment web site characteristics as antecedents of job seekers’ organizational image perceptions. Organ Behav Human Decis Process 2(2011):165–178
Khan N (2018) Does training & employee commitment predict employee retention. In: International Conference on Management and Information Systems (Vol. 21, pp. 120–124)
Lee I (2005) The evolution of E-Recruiting. A content analysis of Fortune 100 Career Websites. J Electronic Commerce Organ 3(3):57–68
Lievens F, Harris MM (2003) Research on Internet recruiting and testing: current status and future directions. Int Rev Ind Organ Psychol 16:131–165
Lin CY, Huang CK (2021) Employee turnover intentions and job performance from a planned change: the effects of an organizational learning culture and job satisfaction. Int J Manpow 42(3):409–423
Martins D, Diaconescu LM (2014) Expatriates recruitment and selection for long-term international assignments in Portuguese companies. Tékhne 12:48–57
RoyChowdhury T, Srimannarayana M (2013) Applicants’ perceptions on online recruitment procedures. Manage Labour Stud 38(3):185–199
Ryu G, Moon SG (2019) The effect of actual workplace learning on job satisfaction and organizational commitment: The moderating role of intrinsic learning motive. J Workplace Learn 31(8):481–497
Saaty TL (1990) How to make a decision: the analytic hierarchy process. Eur J Oper Res 48(1):9–26
Sengazhani Murugesan V, Sequeira AH, Shetty DS, Jauhar SK (2020) Enhancement of mail operational performance of India post facility layout using AHP. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manage 11(2):261–273
Sigalingging H, Pakpahan ME (2021) The Effect of training and work environment on employee performance with motivation as an intervening variable At PT Intraco Agroindustry. South East Asia Journal of Contemporary Business. Econ Law 24(6):130–139.
Sharawat K, Dubey SK (2018) An approach to vendor selection on usability basis by AHP and fuzzy topsis method. In: Soft computing: theories and applications: proceedings of SoCTA 2016, vol 2. Springer, Singapore, pp 595–604
Steil AV, de Cuffa D, Iwaya GH, Pacheco RCDS (2020) Perceived learning opportunities, behavioral intentions and employee retention in technology organizations. J Work Learn 32(2):147–159
Sugiarti E (2022) The influence of training, work environment and career development on work motivation that has an impact on employee performance at PT. Suryamas Elsindo Primatama In West Jakarta. Int J Artif Intell Res 6(1.2).
Sumrit D (2020) Supplier selection for vendor-managed inventory in healthcare using fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making approach. Decis Sci Lett 9(2):233–256
Thompson LF, Braddy PW, Wuensch KL (2008) E-recruitment and the benefits of organizational web appeal. Comp Human Behav 24(5):2384–2398
Turan FK, Scala NM, Sacre MB, Needy KL (2009) An Analytic Network Process (ANP) approach to the project portfolio management for Organizational Sustainability. In: Proceedings of the Industrial Engineering Research Conference. Institute of Industrial Engineers.
Wadhawan S, Sinha S (2018) Factors Influencing Young Job Seekers Perception towards Job Portals. AIMS Int J Manage 12(3).
Weerarathna RS, Somawardana WSD (2021) Impact on training and employee motivation in an electricity company. Future Work, 497.
Zusman R, Landis R (2002) Applicant preferences for Web-based versus traditional job postings. Comput Hum Behav 18(3):285–329
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to two wheeler Automotive Industries in Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India, for their invaluable assistance and cooperation. We greatly acknowledge Ms. Ruchi Mishra, Research scholar from NIT Karnataka, for editing this manuscript in better form.
There is no funding provided in this research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Operations Management Division, Vellore Institute of Technology Chennai, Vandalur-Kelambakkam Road, Chennai, 600127, India
S. M. Vadivel
Vellore Institute of Technology Chennai, Vandalur-Kelambakkam Road, Chennai, 600127, India
Rohan Sunny
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
S M Vadivel: Methodology, Writing—review & editing, Supervision. Rohan Sunny: Data Curation, Writing—original draft preparation.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to S. M. Vadivel .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This manuscript has a research study involves human participants (Interview Candidates) for studying job portal evaluations in Indian two wheeler company running in Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
Consent for publication
‘ Not applicable’ in this section.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Vadivel, S.M., Sunny, R. Evaluation of online job portals for HR recruitment selection using AHP in two wheeler automotive industry: a case study. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-024-02358-z
Download citation
Received : 04 December 2023
Revised : 07 April 2024
Accepted : 25 April 2024
Published : 12 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-024-02358-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Analytical hierarchy process (AHP)
- Online job portals
- Automobile two wheeler industries
- Artificial intelligence (AI)
- HR recruitment
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case Study: Google's Recruitment and Selection Process. Google Inc., the world's largest and most popular search engine company, is also one of the most sought after companies in the world. Due to the popularity of the company caused by its highly attractive compensation and benefits packages for its employees, millions of job applications ...
Recruitment practices, selection processes, and retention programs ensure an adequate workforce and retain excellent employees, who are the foundation of the business strengths noted in the SWOT analysis of Google (Alphabet). These programs also attract employees to the firm. The company is now one of the best places to work.
CASE STUDY #1: Case Study: Google's Recruitment and Selection Process - MBA Knowledge Base (mbaknol) RECRUITMENT AND SELECTION AT GOOGLE. Google is consistently ranked by Fortune magazine as one of the best places to work. It provides employees with excellent pay and a series of perks that are unheard of at most corporations.
Dec 4, 2005. As part of my continuing series of case studies and analyses of truly world-class recruiting functions, I will highlight some of the key features at Google, the world's only corporate "recruiting machine.". In the past few months, I have spent a good deal of time researching Google and communicating with Google managers and ...
This Google recruiting case study is a case study of Google's recruitment and selection process that will help us delineate some important details on methodologies and policies used in Google for talent recruitments into one of the world's biggest and most competitive workplace of the century.
Empirical Economics Letters, 21 (1): (June 2022) Recruit, Train and Evaluate Human Capital : A case study. in Google. Navaratnam Vejaratnam 1, Tan Say Peng 2, Habibah@Artini Ramlie 3, Norshahrul ...
Google is a company known for its innovative products, unique company culture and unusual, data-driven hiring process. The hiring process refers to the multi-step procedure for selecting a job ...
In Part 2 of this case study, I'll highlight the remaining elements of Google's recruiting approach and point out some areas where they can improve. Recruiting Structure. Google has plans to nearly double its workforce, growing from approximately 5,000 employees to 10,000 employees in the near future.
Google apps. Main menu. We know hiring processes can seem overwhelming, but we don't want you to feel overwhelmed at Google. We want all candidates - from entry level to leadership ...
The following sections analyse Google's recruitment and selection policies. 2.2. Strategic "Disruptive Recruiting" ... "A Case Study of Google Recruiting" ERE Media, Inc. [8] Logan, G. (2008). "Google hiring policy is key to its success as best place to work in UK." Personnel Today. [9] Sinha, B. K. (2009). "Trends and Issues in ...
To be selected by Google each interviewer must be in agreement. Candidates are assessed on 4 dimensions: Cognitive ability, Leadership skills, Googliness and Role related skills. Given that Google ...
CASE STUDY RECRUITMENT AND SELECTION AT GOOGLE. Google is consistently ranked by Fortune magazine as one of the best places to work. It provides employees with excellent pay and a series of perks that are unheard of at most corporations.
Case Study: Google's Recruitment and Selection. Any organization's recruitment and selection process is critical because it must maintain its ability and keep a competitive edge over other businesses in the market[ CITATION PAH21 \l 1033 ]. ... Case Study: Google's recruitment and selection process. Retrieved from MBA Knowledge Base: mbaknol ...
Recruitment and selection is a characterized procedure organizations use to discover and. ... Sullivan, D. and Sullivan, A. (2005). A Case Study of Google Recruiting. [online]
Case Study #1 - Recruitment and Selection at Google. Uploaded by BailiffMagpie3244 on coursehero.com. Google's elaborate strategies for recruiting and selecting future Googlers show how the organization invests in them as its major asset. They use internal and external sources for recruiting future employees. Some examples of internal sourcing ...
Reengineering the Recruitment Process. The Covid-19 pandemic has upended many traditional business practices. When it comes to recruiting, the crisis has not so much disrupted as accelerated ...
Very few would disagree that the discipline of work and organizational psychology started with the study of recruitment and selection (Ployhart et al., Citation 2017).For over 100 years, scholars and practitioners have aimed to determine how to generate recruitment pools of highly qualified applicants and how to select the most suitable ones for available jobs (Nikolaou & Oostrom, Citation ...
Please duplicate only the number of copies needed, one for each student in the class. For more information, please contact: SHRM Academic Initiatives 1800 Duke Street, Alexandria, VA 22314, USA ...
8. Recruitment and Selection JBCN International School The process of getting a job at Google 1. Recruiter Screen- the recruiter checks every resume for technical requirements, education and experience to make sure there is a potential fit. It is estimated that every year Google receives 1 million resumes. 2.
Google's detailed recruitment and selection system is justified because it opts for the best possible ways to recruit talented employees and provide the number of outstanding benefits and pay. In addition to that company focus on selecting the most capable person as they shortlist the most eligible candidates out of many applications.
Recruitment Process: Google Eligibility Criteria: Bachelor's degree or equivalent practical experience. Online Assessment: 2 Coding Questions on Data Structures and Algorithms Medium - Hard Level. Technical Phone Screen: Google's interview process begins with a technical phone interview for experienced software engineers.
The recruitment and selection process is a dynamic, complex and an important part of human resource management in organisations [].All the more critically, those in charge of selecting the successful applicant ought to have sufficient data whereupon to base their choices [].Due to these characteristic features listed above, it has caught the attention of both practitioners and researchers over ...
Case Study RECRUITMENT AND SELECTION AT GOOGLE Google is consistently ranked by Fortune magazine as one of the best places to work. It provides employees with excellent pay and a series of perks that are unheard of at most corporations. Some of these perks are flex hours; bringing your dog to work; casual dress; on-site free massage and yoga; free snacks, drinks, and meals; and a child care ...
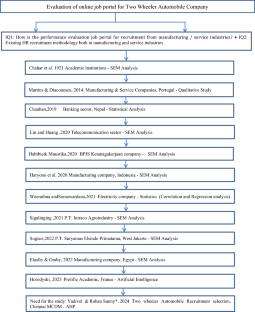
Recruitment and Selection: The HR department is responsible for sourcing, selecting, and hiring the best talent for the company. ... The case study of Two Wheeler Automobile Company, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, South India is then discussed. The paper summarises the results analysis and concludes with research directions. ... Google Scholar Chauhan P ...
Results . We observed a significant difference in the PACIC after 6, 12, and 18 months (18 months: 0.388 points; 95%CI: 0.089-0.687; p = 0.011) for the total group and after 6 and 12 months for type 2 diabetes.After 18 months, we observed a significant difference in the PAM for the total group but not at 6 and 12 months, and not for type 2 diabetes.