Home / Guides / Citation Guides / APA Format / APA In-text Citations

APA In-Text Citations
Welcome to our guide on in-text citations! If you’re looking to learn the ins and outs of APA style in-text citations and how to do in-text citations APA, we’ve got you covered in this thorough guide.
The information below follows the 7th edition of the Publication manual of the American Psychological Association .
Here’s a run through of everything this page includes:
- APA Style overview
- In-text citations and why we use them
- Two types of APA in-text citations
- Corresponding entry in reference list
- In-text citations for direct quotes
Paraphrasing in APA
- In-text citations for sources with one author
- In-text citations for sources with multiple authors
- In-text citations for sources with no author or date
- Additional in-text citation examples
If you’re simply looking for a quick guide, check out our APA parenthetical citation guide, which serves as a lite-version of this page.
Let’s get started!
What is APA?
This is a term that you might hear your teacher, professor, or librarian throw around a lot. This abbreviation stands for
P sychological
A ssociation
This association is kind of a big deal. They do a lot of things related to psychology, but they’re also famous for creating one of the most popular citation styles, APA format . There are other big names on campus, such as MLA format , and Chicago, but this particular style is commonly used by individuals who are writing a science-related paper.
Even if your paper doesn’t necessarily fall into a “science” category, many educators ask their students to cite in this style since it’s so commonly used.
If you’re trying to find information about other commonly used styles, there are more styles on EasyBib.com.
What is an APA In-text Citation?
In plain and simple terms, APA in-text citations are found in the text of a project. Get it? In text. The purpose of an in-text citation in APA is to show the reader, while they’re reading your work, that a piece of information in your project was found elsewhere. They’re placed IN the wording or body of a project, not on the last page; the last page has full references. To learn more about those types of references, check out APA citation .
We’ve all heard about the word plagiarism , and you already know what it means. Simply put, including APA in-text citations are one way to prevent plagiarism.
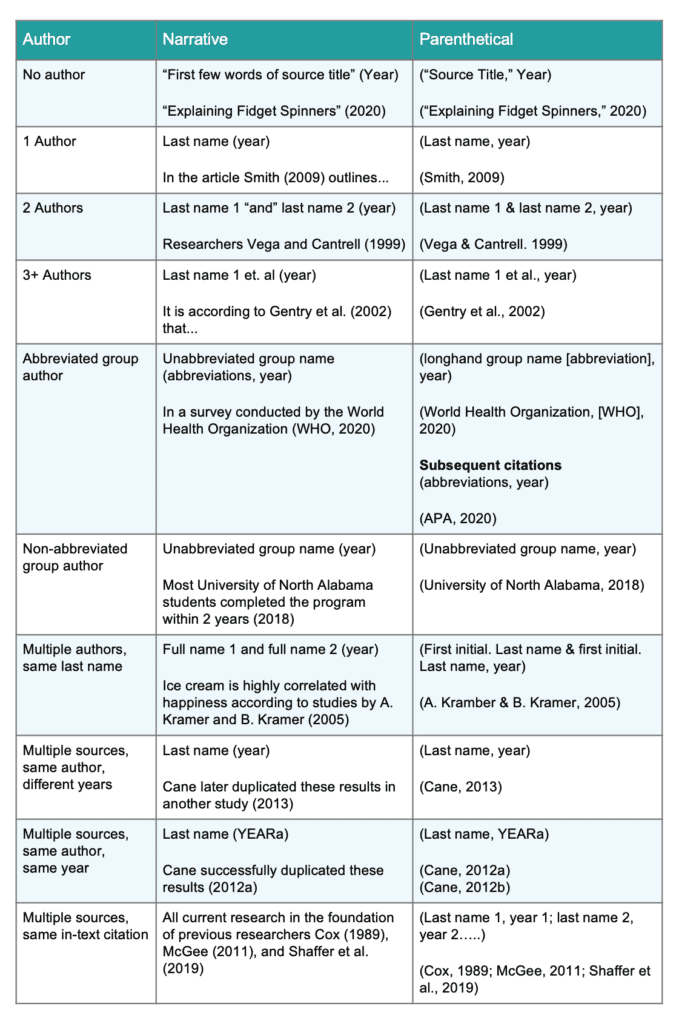
Here’s what’s included in an APA 7th edition in-text citation:
- Last name(s) of the author(s) or Group name
- Year the source was published
- Page number (if available)
Depending on the number of authors and the source type, some in-text citations look different than others. Read on to learn how to structure an in-text citation for APA. In fact, if you’re looking for an easy route, EasyBib.com has an in-text citation APA generator, which does the work for you. Use our automatic generator to create your full references, and you’ll see an option on the final screen to format your APA in-text citations. An APA in-text citation generator and full reference generator all in one. What could beat that?
Why do we use in-text citations?
When you do a research project, you’re probably going to include facts from websites, databases, books, and other sources. When you add those facts into your project, you must show where those facts came from. It’s the responsible thing to do. It prevents plagiarism. You always give credit to the original author. It’s kind of like thanking them for their contribution to your paper.
Here’s the neat thing about in-text citations. Since they’re IN your project, readers get a quick idea as to where the information you included came from. In-text citations APA are not long and lengthy, like the full references on the APA reference page or APA bibliography . In-text citations are cute, little, and give us the perfect amount of information we need to understand where a fact came from. If you want to get the full information about the source, then you can flip to the back page of the paper, where the full reference is listed. The in-text citation APA style provides us with a tidbit of information. Just enough to glance at it and keep on going with reading the paper.
To recap, in-text citations are great because:
- They credit the original author of a work or information
- They let readers quickly see where the information is coming from
- Including helps make you an ethical writer
If you’re looking to learn more about footnotes in Chicago format , MLA in-text & parenthetical citations , or want to learn how to cite websites in MLA , EasyBib.com has the information you need to be a citing superstar.
Types of APA In-text Citations
Just like there are two days in the weekend, two types of peanut butter (creamy and nutty), and two types of foods we crave (salty and sweet), there are (you guessed it) two types of in-text citations.
The in-text citation APA option you include in your paper depends on how you craft your sentences.
Narrative In-Text APA Citations:
In-text citation APA format, in narrative form, is one that shows the author’s name in the sentence itself.
Narrative In-text APA Citation Example:
Tyson, Strauss, and Gott (2016) encourage the use of simplified terms when it comes to discussing and defining the universe. For example, a small white star is simply called a white dwarf. Keep it short and sweet because the universe is confusing enough (p. 22).
Parenthetical Citations:
This is a type of APA in-text citation where the author’s name(s) are in parentheses, usually at the end of the fact or quote.
Parenthetical Citation Example
Use simplified terms when discussing and defining the universe. For example, a small white star is simply called a white dwarf. Keep it short and sweet because the universe is confusing enough (Tyson, Strauss, & Gott, 2016, p. 22).
As you can see, the type of APA in-text citation you include, whether it’s a narrative one or one in parentheses, depends on how you decide to structure your sentences. It doesn’t matter if you use all narrative, all parentheses, or a mix of both.
What is important is that you’re a responsible researcher and you properly cite your sources!
Remember, most facts, quotes, stats, and copied and pasted information NEED an APA in-text citation next to it.
What’s the only type of information you don’t need to create an in-text citation APA for? Anything that’s common knowledge. For example, paper is made from trees. You and most people already knew that. That’s an example of common knowledge. It’s a piece of information that everyone already knows.
Now, before you simply include the author’s name(s), the date, and the page number in your project and think you’ve covered all your bases, you’re not quite done yet. In-text citations APA are only part of the puzzle.
The other piece of the puzzle is found on the last page of the project: the reference page. That’s where all of the full references are found in their entirety. In-text citations only include the author’s name, year published, and the page number.
The reference page, on the other hand, includes the title of each source, the publishers, the website addresses, and other information. Continue reading to learn why in-text citations and references on the reference page are the perfect match.
Before we continue, MLA works cited pages are very similar to the ones in this style. EasyBib.com has resources for many styles, to help you learn the ins and outs of referencing your work. We even have full pages on grammar topics too, to keep your paper in tip-top shape. Brush up on your noun , conjunction , and interjection skills with our easy-to-follow, comprehensive guides.
Corresponding entry in APA reference list
Would you ever put on one shoe and walk around without the other? Of course not. The same goes with in-text citations and full references. You must include both in your paper. Where there’s one there has to be the other.
Each and every in-text citation APA must have a matching full reference on the reference page (American Psychological Association, p. 262 ).
If you’re wondering why, it’s to allow the reader to get that sneak peek about the source while reading your paper (the APA in-text citation), and then learn all about it on the final page (the reference page). If the reader wants to get their hands on a copy of the sources you used, all of the information they need can be found on the reference page.
Remember those APA style in-text citation examples found above? Let’s take a peek at them again.
Here’s the one with the authors’ names in parentheses: Use simplified terms when discussing and defining the universe. For example, a small white star is simply called a white dwarf. Keep it short and sweet because the universe is confusing enough (deGrasse, Strauss, & Gott, 2016, p. 22).
Here’s the full reference, which would be found on the final page of the project:
Tyson, N. D., Strauss, M. A., and Gott, J. R. (2016). Welcome to the universe: An astrophysical tour. Princeton University Press.
Notice that in the above in-text citation APA example, the full title of the book, the place the book was published, and the publisher are displayed. If the reader wants to locate the book themselves, all of the information they need is found in the full reference.
One other important thing we’d like to point out is that the same information from the in-text citation APA (Tyson, Strauss, & Gott) matches the first part of the full reference. This is done to allow the reader to easily find the full reference on the final page.
Remember, always include both in-text citations AND full references in your projects.
In the body of projects, in-text citations APA serve an important purpose. They give the reader a snippet of understanding as to the origin of information. It’s just enough information to allow the reader to continue reading the paper in a natural and fluid manner, without having to trip over long, clunky references. If the reader wants to get a detailed understanding of a source, they can flip to the back page, the reference page, to scope out all of the nitty gritty details.
In the next two sections of this page, we’re going to switch gears and share how to properly format direct quotes and paraphrases.
If you’re looking for specific source types, check out APA citation website and APA book citation . These two resources will explain how to format those specific types of references. If you’re stuck and not sure how to start, check out Chapter 10 of the Publication manual for some sample citations.
Direct Quotes in APA
As Drake states in his lyrics, “We don’t like to do too much explaining,” so we’re going to keep this one short and to the point.
“Direct quotes” are a fancy term used for any text that has been copied and pasted into your paper. That Drake quote above is a direct quote.
Direct quotes are any words or sentences copied and pasted into your project, but they don’t necessarily have to be a person’s quote. Anytime you copy and paste text into your assignment, you must include an APA in-text citation next to it. This shows the reader that:
- The information came from another source
- You’re being a responsible researcher and clearly documenting the outside source.
Here are some guidelines to keep in mind when it comes to direct quotes:
- Direct quotes are a solid way to show evidence and prove your point, but use them sparingly. Your paper shouldn’t be riddled with copied and pasted text.
- Put quotation marks around the copied and pasted information. (The exception are APA block quotes , which are direct quotes longer than 40 words and are formatted differently.)
- Always include the page number for direct quotes, if one is available. When formatting APA page numbers for an in-text citation, include p. before the number. Use pp. for a page range.
To create a narrative APA in-text citation, include the author’s last name in the sentence like this:
- As Drake (2013) once said “We don’t like to do too much explaining.”
- In the above APA in-text citation example, the Drake quote was taken from the song, “Started From the Bottom,” in 2013. The title of the source would be included in the reference page.
Or, you include the author’s name in parentheses:
- “We don’t like to do too much explaining” (Drake, 2013).
If you are looking for more examples, go to page 272 of the American Psychological Association’s official Publication manual .
We said above that your entire paper shouldn’t have direct quotes everywhere. So, another way to include information from a source is by adding a paraphrase . Simply put, a paraphrase is restated information, but formed using your own words and writing style
APA paraphrases still need an in-text citation since the information was obtained elsewhere. Check out this quote from the song, “For Time,” by Drake:
“I like it when money makes a difference, but don’t make you different.”
To include it in your paper, without using the exact quote, make a paraphrase. Here’s one that would work:
Money has the ability to benefit things in your life, but it’s truly great when it doesn’t cause the person to act differently or change who they are (Drake, 2013).
The above APA in-text citation example is one with Drake’s name in parentheses. If you’d like to include the author’s name narratively, here’s an option:
In Drake’s (2013) lyrics, he shares that money has the ability to benefit things in your life. It’s truly great when it doesn’t cause the person to act differently or change who they are.
It is recommended to include page numbers for paraphrased material, but isn’t required.
Here’s more on paraphrases and direct quotes.
Organizing APA In-text Citations
Ready to learn how to structure your in-text citations? The next section dives deep into developing them and answers “How to do in-text citations APA.” Keep in mind that how each one is formed depends on the number of authors and other factors. All the examples below follow rules laid out in Chapter 8 of the Publication manual.
Even though the structure varies, most in-text citations APA are placed in this manner for narrative in-text citations:
Author’s Last Name (Year) “Quote or Paraphrase” (p. number).
For ones in parentheses, most are placed in this manner:
“Quote” or Paraphrase (Author’s Last Name, Year, p. number).
Notice that whether you choose to include a narrative in-text citation APA or one in parentheses, the author names and the year published are always together. They’re pretty much holding hands. Cute, huh?
Read on to learn the ins and outs of structuring various in-text citations.
Don’t forget, EasyBib.com has an in-text citation APA generator. Wondering what it’s all about? Here’s a quick explanation: We work for you so citing is easy for you. Yep, you read that correctly.
Our tools structure your in-text citations the way they’re supposed to be structured. Use our automatic generator to create your full references, and on the final screen you’ll see the option to create your in-text citations. An APA in-text citation generator that’s easy as pie!
Something else we do for you? We have a plagiarism checker that scans your paper for any instances of accidental copying. We also have tons of grammar pages to keep your page in check. Check out our adverb , preposition , and verb pages.
APA In-Text Citations for Sources with One Author
If your source has one author.
If your source has one author, lucky you! Your in-text citation is pretty simple to structure.
Narrative In-text APA Citation:
Author’s Last Name (Year published) are found in the sentence with a “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
Parenthetical APA Citation:
“Direct quote” or Paraphrase (Author’s Last Name, Year published, p. number).
Citing multiple sources by the same author in the same year
You may have a bunch of case studies, articles, or books that you’re referencing, all by the same author. Let’s say you’re analyzing two works by Sigmund Freud, Jokes and Their Relation to the Unconscious and also Fragment of an Analysis of a Case of Hysteria , both of which were published in 1905. Placing (Freud, 1905) in the text would be confusing for the reader. How would the reader determine which source you’re referencing?
If this is the situation you’re in, there’s a pretty simple fix.
Place a lowercase a next to the year in the first source (Freud, 1905a). Place a lowercase b next to the second source (Freud, 1905b). Include those same lowercase letters in the full references on the reference page, like so:
Freud, S. (1905a). Fragment of an analysis of a case of hysteria . https://staferla.free.fr/Freud/Freud%20complete%20Works.pdf
Freud, S. (1905b). Jokes and their relation to the unconscious . https://staferla.free.fr/Freud/Freud%20complete%20Works.pdf
But there’s a catch. When you do this et al. can’t stand for only one author. After all it literally means “and others.” If you have two sources that are identical except for the last author, then you have to write out all the names every time. For example:
Gunderman, Slack, Rausch, and Smith (2017)
Gunderman, Slack, Rausch, and Johnston (2017)
These references are completely the same except for the very last name so you’d have to write all 4 names every time.
If your source has multiple works by the same author
What if you had 2 sources with the same author(s) and same publication year? Lucky for us the solution here is a lot simpler. Just a letter to the publication year!
Gunderman, Slack, and Rausch (2017)
Gunderman, Slack, and Rausch (2017a)
Gunderman, Slack, and Rausch (2017b)
Just remember to also follow this format in your works cited page even if there is an exact publication date available. See page 267 of your Publication Manual (American Psychological Association, 2020) for a further breakdown.
Need to create an APA in-text citation for a source without an author? How about an APA in-text citation for multiple authors? Continue reading to see the other ways to structure an APA style in-text citation.
APA In-Text Citations for Sources with Multiple Authors
Apa in-text citation for sources with two authors.
If your source has two authors, place them in the order they appear on the source. Do not place them in alphabetical order.
Use the word “and” in between the authors’ names.
1st Author’s Last Name and 2nd Author’s Last Name (Year published) are found somewhere in the sentence with a “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
If you choose to include both authors’ names in parentheses, use an ampersand in between their names.
“Here is the direct quote” or Here is the paraphrase (1st Author’s Last Name & 2nd Author’s Last name, Year, p. number).
APA in-text citation for sources three or more authors
Only include the first author’s last name and then add ‘et al.’ Et al. is a fancy way of saying “and others” in Latin.
1st Author’s Last Name et al. (Year published) are found somewhere in the sentence with a “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
“Here is the direct quote” or Paraphrase (1st Author’s Last Name et al., Year published, p. number).
If you have author of multiple works (with multiple authors)
Now here is where things can get a tad bit tricky. Sometimes authors with multiple works can cause some confusion in your citations. Generally when that happens you can tell the difference by the publication year, but when you can’t, that’s when you have to list as many authors as necessary to clear up the confusion.
Say you had the two sources below:
Gunderman, Slack, Rausch, and Maule (2017)
Gunderman, Byrnes, Oxner, Wigginton, and Draeger (2017)
Normally, they’d be written as:
Gunderman et al. (2017)
If you reduced both sources to Gunderman et al. (2017) you wouldn’t be able to tell which source you’re talking about. Instead cite it this way:
Gunderman, Slack, Rausch et al. (2017)
Gunderman, Byrnes, Oxner et al. (2017)
If you’re looking for more information on structuring journal articles, check out our APA journal page.
If you’re looking for a simple solution to referencing multiple authors, EasyBib.com creates in-text citations APA for you! Whether you need to create a reference for one or two authors, or an APA in-text citation for multiple authors, we’ve got you covered!
APA In-text citation no author or date
It’s common to come across sources without any authors. Movies, brochures, website pages often do not have a visible author’s name.
Citing a source with no author
If you find that the source you’re attempting to reference does not have an author, use the first few words from the reference list entry in the APA in-text citation with no author. Most often, it’s the title of the source.
Place the source name in quotation marks if the source is a:
- website page
Simply italicize the source name if the source is a:
- Or the full reference starts with italicized information
Remember, you do not have to use the entire title in your in-text citation APA no author. You can use only the first few words from the reference list.
“First few words of the webpage, article, or chapter Title” (Year) along with the “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number). OR First few words of book, newspaper, report, or brochure (Year) along with the “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
“Here is the direct quote” or paraphrase (“Web page, Article, or Chapter Title,” Year, p. number). OR “Here is the direct quote” or paraphrase ( Book, Newspaper, Report, or Brochure Title , Year, p. number).
Citing source with no date
No date? No problem! An APA in-text citation no date situation is easier to solve than you think. Only include the author’s name and the page number.
APA in-text citation no date example:
(Foster, p. 35).
Additional APA In-Text Citation Examples
Source by a group, organization, company, or government agency.
There are two types of groups: Ones that are abbreviated often and ones that are not abbreviated.
For example, think about these two citation style types: APA and Chicago. One is abbreviated (for the American Psychological Association) and the other is usually written as is (Chicago style).
Abbreviated groups
If the company is often abbreviated, in the first mention in text, display the full name and the abbreviation. In the second and any other subsequent mentions, only use the abbreviation.
1st mention:
Full Company’s Name (Abbreviation, Year) with the “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
2nd mention:
Company Abbrev. (Year) “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
“Direct quote” or paraphrase (Full Company’s Name [Abbreviation], Year, p. number).
“Direct quote” or paraphrase (Abbreviation, Year, p. number).
Non-abbreviated groups
Always include the full group, company, or organization’s name in each and every mention in text.
Full Name of Group (Year) with the “direct quote” or paraphrase (p. number).
“Direct quote” or paraphrase (Full Name of Group, Year, p. number).
Citing sources with different authors with the same last name
We’re not quite sure how the author of The Baby-Sitters Club (Ann M. Martin) could be used in a paper that’s also referencing the author of Game of Thrones (George R. R. Martin), but hey, it could happen! It’s a Martin party! It’s important to show the reader the difference between the two individuals to prevent any confusion. To differentiate between the two authors in the text, include their first initials.
Example of in-text citation APA:
“Here’s a quote” (A. Martin, Year, p. 6). G. Martin (Year) also states “this direct quote” (p. 45).
As always, keep the author names and the dates directly next to each other. They love being together and it’s a best practice.
Citing multiple sources in the same in-text citation
List sources alphabetically and separate with a semicolon.
Be sure to list authors alphabetically.
Johnson (2019), Smith and Adams (2015), and Washington (2017), examined…
“Direct quote” or Paraphrase (Author 1 Last Name, Year published, p. number if needed; Author 2 Last Name, Year published, p. number if needed)
Parenthetical Citation Examples:
(Johnson et al., 2019; Smith & Adams, 2015; Washington, 2017)
(Honda, 2006, p. 107; Sato, 1980)
If you want to emphasize a source because it is particularly important or relevant, add “see also” before the source’s citation. Think of “see also” as synonymous with “for more information see…”
(Johnson et al., 2019; see also Smith & Adams, 2015; Washington, 2017).
Citing a source within a source
Did you stumble upon the perfect quote that’s quoted in another source? It happens all of the time and it can be a little tricky to figure out how to quote a quote.
The American Psychological Association recommends locating the original quote, if possible. Instead of relying on secondary sources, take the time to locate the original source to make sure the quote is accurate. Finding and reading through the original source also provides you with further information on your research topic!
If finding the original source isn’t possible, due to out of print titles, web pages taken down, or other factors, then it’s okay to quote the secondary source. In your writing, use the phrase “as cited in Secondary Author’s Last name, Year.”
On the reference page, include the reference for the secondary source.
As cited in Shapiro’s (2019) article, Carranza stated, “Districts 3 and 15 are showing how we can have the important conversations and take bold action on this issue.”
Carranza stated, “Districts 3 and 15 are showing how we can have the important conversations and take bold action on this issue” (as cited in Shapiro, 2019).
On the reference page, Shapiro’s article would be referenced in its entirety.
Citing audiovisual material
APA in-text citations for YouTube videos , songs, podcasts, television shows, and other audiovisual materials look a bit different than other types of sources. They include an extra piece of information: a time stamp.
Bill Nye (2017) shares that the sun is over four-hundred septillion watts (13:15).
The sun is over four-hundred septillion watts (Bill Nye, 2017, 13:15).
If you’re still scratching your head, and feeling the urge to type “how to do in-text citations APA” into Google, click here for a website that we dig.
If you’re looking for a quick fix to developing your references, EasyBib.com has you covered! Our tools can help you create an APA in-text citation multiple authors, one author, no authors, plus more!
Overview of APA Parenthetical Citations for Websites
Here’s a quick overview of how to create an in-text citation for websites. Notice that since these are for online sources, the in-text citation has no page number.
Once again, if grammar isn’t your thing, and you’re looking for help related to specific parts of speech, check out our adjective , pronoun , and determiner pages, among many, many others!
Follow our EasyBib Twitter feed to find more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.) https:doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
Published May 21, 2019. Updated October 25, 2020.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau . Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and one of the in-house EasyBib librarians. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
APA Formatting Guide
APA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Multiple Authors
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Parenthetical Citations
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all APA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
An in-text citation is a shortened version of the source being referred to in the paper. As the name implies, it appears in the text of the paper. A reference list entry, on the other hand, details the complete information of the source being cited and is listed at the end of the paper after the main text. An example of an in-text citation and the corresponding reference list entry for a journal article with one author is listed below for your understanding:
In-text citation template and example:
Only the author name and the publication year are used in in-text citations to direct the reader to the corresponding reference list entry.
Author Surname (Publication Year)
Elden (2003)
Parenthetical
(Author Surname, Publication Year)
(Elden, 2003)
Reference list entry template and example:
Complete information of the reference is used to guide the reader to locate the source for further reference. In the below template, “F” and “M” are first and middle initials, respectively. #–# denotes the page range.
Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Title of the article: Subtitle. Journal Title, Volume (Issue), #–#. DOI
Elden, S. (2003). Plague, panopticon, police. Surveillance & Society, 1 (3), 240–253. https://doi:10.24908/ss.v1i3.3339
When you use APA style, all sources need to have in-text citations. In-text citations direct a reader to the reference entry to get more information on the source being cited in the text. If an in-text citation is not provided, your reader doesn’t know whether there is a source available in the reference list for the idea or topic being discussed in the text. Even if all the basic elements to cite a source are not available, try to provide an in-text citation with the information you do have. For example, if a source does not have an author, use a shortened version of the title in place of the author in your in-text citation. An example is given below for a parenthetical citation.
Author name available:
(Author Surname, Publication Year, p.# for direct quote)
Author name not available:
(“Title of the Work,” Publication Year, p.# for direct quote)
Therefore, in-text citations are essential to guide a reader to locate the corresponding sources in the reference list for the topics discussed in the text.
APA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Penn State University Libraries
Apa quick citation guide.
- In-text Citation
- Citing Generative AI
- Citing Web Pages and Social Media
- Citing Articles
- Citing Books
- Citing Business Reports
- Other Formats
- APA Style Quiz
Using In-text Citation
Include an in-text citation when you refer to, summarize, paraphrase, or quote from another source. For every in-text citation in your paper, there must be a corresponding entry in your reference list.
APA in-text citation style uses the author's last name and the year of publication, for example: (Field, 2005). For direct quotations, include the page number as well, for example: (Field, 2005, p. 14). For sources such as websites and e-books that have no page numbers , use a paragraph number, for example: (Field, 2005, para. 1). More information on direct quotation of sources without pagination is given on the APA Style and Grammar Guidelines web page.
Example paragraph with in-text citation
A few researchers in the linguistics field have developed training programs designed to improve native speakers' ability to understand accented speech (Derwing et al., 2002; Thomas, 2004). Their training techniques are based on the research described above indicating that comprehension improves with exposure to non-native speech. Derwing et al. (2002) conducted their training with students preparing to be social workers, but note that other professionals who work with non-native speakers could benefit from a similar program.
Derwing, T. M., Rossiter, M. J., & Munro, M. J. (2002). Teaching native speakers to listen to foreign-accented speech. Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development , 23 (4), 245-259.
Thomas, H. K. (2004). Training strategies for improving listeners' comprehension of foreign-accented speech (Doctoral dissertation). University of Colorado, Boulder.
Citing Web Pages In Text
Cite web pages in text as you would any other source, using the author and date if known. Keep in mind that the author may be an organization rather than a person. For sources with no author, use the title in place of an author.
For sources with no date use n.d. (for no date) in place of the year: (Smith, n.d.). For more information on citations for sources with no date or other missing information see the page on missing reference information on the APA Style and Grammar Guidelines web page.
Below are examples of using in-text citation with web pages.
Web page with author:
In-text citation
Heavy social media use can be linked to depression and other mental disorders in teens (Asmelash, 2019).
Reference entry
Asmelash, L. (2019, August 14). Social media use may harm teens' mental health by disrupting positive activities, study says . CNN. https://www.cnn.com/2019/08/13/health/social-media-mental-health-trnd/index.html
Web page with organizational author:
More than 300 million people worldwide are affected by depression (World Health Organization, 2018).
World Health Organization. (2018, March 22). Depression . https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/depression
Web page with no date:
Establishing regular routines, such as exercise, can help survivors of disasters recover from trauma (American Psychological Association [APA], n.d.).
American Psychological Association. (n.d.). Recovering emotionally from disaste r. http://www.apa.org/helpcenter/recovering-disasters.aspx
General Guidelines
In-text references should immediately follow the title, word, or phrase to which they are directly relevant, rather than appearing at the end of long clauses or sentences. In-text references should always precede punctuation marks. Below are examples of using in-text citation.
Author's name in parentheses:
One study found that the most important element in comprehending non-native speech is familiarity with the topic (Gass & Varonis, 1984).
Author's name part of narrative:
Gass and Varonis (1984) found that the most important element in comprehending non-native speech is familiarity with the topic.
Group as author: First citation: (American Psychological Association [APA], 2015) Subsequent citation: (APA, 2015)
Multiple works: (separate each work with semi-colons)
Research shows that listening to a particular accent improves comprehension of accented speech in general (Gass & Varonis, 1984; Krech Thomas, 2004).
Direct quote: (include page number and place quotation marks around the direct quote)
One study found that “the listener's familiarity with the topic of discourse greatly facilitates the interpretation of the entire message” (Gass & Varonis, 1984, p. 85).
Gass and Varonis (1984) found that “the listener’s familiarity with the topic of discourse greatly facilitates the interpretation of the entire message” (p. 85).
Note: For direct quotations of more than 40 words , display the quote as an indented block of text without quotation marks and include the authors’ names, year, and page number in parentheses at the end of the quote. For example:
This suggests that familiarity with nonnative speech in general, although it is clearly not as important a variable as topic familiarity, may indeed have some effect. That is, prior experience with nonnative speech, such as that gained by listening to the reading, facilitates comprehension. (Gass & Varonis, 1984, p. 77)
Works by Multiple Authors
APA style has specific rules for citing works by multiple authors. Use the following guidelines to determine how to correctly cite works by multiple authors in text. For more information on citing works by multiple authors see the APA Style and Grammar Guidelines page on in-text citation .
Note: When using multiple authors' names as part of your narrative, rather than in parentheses, always spell out the word and. For multiple authors' names within a parenthetic citation, use &.
One author: (Field, 2005)
Two authors: (Gass & Varonis, 1984)
Three or more authors: (Tremblay et al., 2010)
- << Previous: Overview
- Next: Citing Generative AI >>
- Last Updated: Jul 19, 2023 2:50 PM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/apaquickguide
APA (7th Edition) Referencing Guide
- Information for EndNote Users
- Authors - Numbers, Rules and Formatting
Everything must match!
Types of citations, in-text citations, quoting, summarising and paraphrasing, example text with in-text referencing, slightly tricky in-text citations, organisation as an author, secondary citation (works referred to in other works), what do i do if there are no page numbers.
- Reference List
- Books & eBooks
- Book chapters
- Journal Articles
- Conference Papers
- Newspaper Articles
- Web Pages & Documents
- Specialised Health Databases
- Using Visual Works in Assignments & Class Presentations
- Using Visual Works in Theses and Publications
- Using Tables in Assignments & Class Presentations
- Custom Textbooks & Books of Readings
- ABS AND AIHW
- Videos (YouTube), Podcasts & Webinars
- Blog Posts and Social Media
- First Nations Works
- Dictionary and Encyclopedia Entries
- Personal Communication
- Theses and Dissertations
- Film / TV / DVD
- Miscellaneous (Generic Reference)
- AI software
- APA Format for Assignments
- What If...?
- Other Guides

There are two basic ways to cite someone's work in text.
In narrative citations , the authors are part of the sentence - you are referring to them by name. For example:
Becker (2013) defined gamification as giving the mechanics of principles of a game to other activities.
Cho and Castañeda (2019) noted that game-like activities are frequently used in language classes that adopt mobile and computer technologies.
In parenthetical citations , the authors are not mentioned in the sentence, just the content of their work. Place the citation at the end of the sentence or clause where you have used their information. The author's names are placed in the brackets (parentheses) with the rest of the citation details:
Gamification involves giving the mechanics or principles of a game to another activity (Becker, 2013).
Increasingly, game-like activities are frequently used in language classes that adopt mobile and computer technologies (Cho & Castañeda, 2019).
Using references in text
For APA, you use the authors' surnames only and the year in text. If you are using a direct quote, you will also need to use a page number.
Narrative citations:
If an in-text citation has the authors' names as part of the sentence (that is, outside of brackets) place the year and page numbers in brackets immediately after the name, and use 'and' between the authors' names: Jones and Smith (2020, p. 29)
Parenthetical citations:
If an in-text citation has the authors' names in brackets use "&" between the authors' names : (Jones & Smith, 2020, p. 29).
Note: Some lecturers want page numbers for all citations, while some only want page numbers with direct quotes. Check with your lecturer to see what you need to do for your assignment. If the direct quote starts on one page and finishes on another, include the page range (Jones & Smith, 2020, pp. 29-30).
1 author
Smith (2020) found that "the mice disappeared within minutes" (p. 29).
The author stated "the mice disappeared within minutes" (Smith, 2020, p. 29).
Jones and Smith (2020) found that "the mice disappeared within minutes" (p. 29).
The authors stated "the mice disappeared within minutes" (Jones & Smith, 2020, p. 29).
For 3 or more authors , use the first author and "et al." for all in-text citations
Green et al.'s (2019) findings indicated that the intervention was not based on evidence from clinical trials.
It appears the intervention was not based on evidence from clinical trials (Green et al., 2019).
If you cite more than one work in the same set of brackets in text , your citations will go in the same order in which they will appear in your reference list (i.e. alphabetical order, then oldest to newest for works by the same author) and be separated by a semi-colon. E.g.:
- (Corbin, 2015; James & Waterson, 2017; Smith et al., 2016).
- (Corbin, 2015; 2018)
- (Queensland Health, 2017a; 2017b)
- Use only the surnames of your authors in text (e.g., Smith & Brown, 2014) - however, if you have two authors with the same surname who have published in the same year, then you will need to use their initials to distinguish between the two of them (e.g., K. Smith, 2014; N. Smith, 2014). Otherwise, do not use initials in text .
If your author isn't an "author".
Whoever is in the "author" position of the refence in the references list is treated like an author in text. So, for example, if you had an edited book and the editors of the book were in the "author" position at the beginning of the reference, you would treat them exactly the same way as you would an author - do not include any other information. The same applies for works where the "author" is an illustrator, producer, composer, etc.
- Summarising
- Paraphrasing

It is always a good idea to keep direct quotes to a minimum. Quoting doesn't showcase your writing ability - all it shows is that you can read (plus, lecturers hate reading assignments with a lot of quotes).
You should only use direct quotes if the exact wording is important , otherwise it is better to paraphrase.
If you feel a direct quote is appropriate, try to keep only the most important part of the quote and avoid letting it take up the entire sentence - always start or end the sentence with your own words to tie the quote back into your assignment. Long quotes (more than 40 words) are called "block quotes" and are rarely used in most subject areas (they mostly belong in Literature, History or similar subjects). Each referencing style has rules for setting out a block quote. Check with your style guide .
It has been observed that "pink fairy armadillos seem to be extremely susceptible to stress" (Superina, 2011, p. 6).
NB! Most referencing styles will require a page number to tell readers where to find the original quote.

It is a type of paraphrasing, and you will be using this frequently in your assignments, but note that summarising another person's work or argument isn't showing how you make connections or understand implications. This is preferred to quoting, but where possible try to go beyond simply summarising another person's information without "adding value".
And, remember, the words must be your own words . If you use the exact wording from the original at any time, those words must be treated as a direct quote.
All information must be cited, even if it is in your own words.
Superina (2011) observed a captive pink fairy armadillo, and noticed any variation in its environment could cause great stress.
NB! Some lecturers and citation styles want page numbers for everything you cite, others only want page numbers for direct quotes. Check with your lecturer.
Paraphrasing often involves commenting about the information at the same time, and this is where you can really show your understanding of the topic. You should try to do this within every paragraph in the body of your assignment.
When paraphrasing, it is important to remember that using a thesaurus to change every other word isn't really paraphrasing. It's patchwriting , and it's a kind of plagiarism (as you are not creating original work).
Use your own voice! You sound like you when you write - you have a distinctive style that is all your own, and when your "tone" suddenly changes for a section of your assignment, it looks highly suspicious. Your lecturer starts to wonder if you really wrote that part yourself. Make sure you have genuinely thought about how *you* would write this information, and that the paraphrasing really is in your own words.
Always cite your sources! Even if you have drawn from three different papers to write this one sentence, which is completely in your own words, you still have to cite your sources for that sentence (oh, and excellent work, by the way).
Captive pink fairy armadillos do not respond well to changes in their environment and can be easily stressed (Superina, 2011).
NB! Some lecturers and citation styles want page numbers for all citations, others only want them for direct quotes. Check with your lecturer.
This example paragraph contains mouse-over text. Run your mouse over the paragraph to see notes on formatting.
Excerpt from "The Big Fake Essay"
You can read the entire Big Fake Essay on the Writing Guide. It includes more details about academic writing and the formatting of essays.
- The Big Fake Essay
- Academic Writing Workshop
When you have multiple authors with the same surname who published in the same year:
If your authors have different initials, then include the initials:
As A. Smith (2016) noted...
...which was confirmed by J.G. Smith's (2016) study.
(A. Smith, 2016; J. G. Smith, 2016).
If your authors have the same initials, then include the name:
As Adam Smith noted...
...which was confirmed by Amy Smith's (2016) study.
(Adam Smith, 2016; Amy Smith, 2016).
Note: In your reference list, you would include the author's first name in [square brackets] after their initials:
Smith, A. [Adam]. (2016)...
Smith, A. [Amy]. (2016)...
When you have multiple works by the same author in the same year:
In your reference list, you will have arranged the works alphabetically by title (see the page on Reference Lists for more information). This decides which reference is "a", "b", "c", and so on. You cite them in text accordingly:
Asthma is the most common disease affecting the Queensland population (Queensland Health, 2017b). However, many people do not know how to manage their asthma symptoms (Queensland Health, 2017a).
When you have multiple works by the same author in different years:
Asthma is the most common disease affecting the Queensland population (Queensland Health, 2017, 2018).
When you do not have an author, and your reference list entry begins with the title:
Use the title in place of the author's name, and place it in "quotation marks" if it is the title of an article or book chapter, or in italics if the title would go in italics in your reference list:
During the 2017 presidential inauguration, there were some moments of awkwardness ("Mrs. Obama Says ‘Lovely Frame’", 2018).
Note: You do not need to use the entire title, but a reasonable portion so that it does not end too abruptly - "Mrs. Obama Says" would be too abrupt, but the full title "Mrs. Obama Says 'Lovely Frame' in Box During Awkward Handoff" is unecessarily long. You should also use title case for titles when referring to them in the text of your work.
If there are no page numbers, you can include any of the following in the in-text citation:
- "On Australia Day 1938 William Cooper ... joined forces with Jack Patten and William Ferguson ... to hold a Day of Mourning to draw attention to the losses suffered by Aboriginal people at the hands of the whiteman" (National Museum of Australia, n.d., para. 4).
- "in 1957 news of a report by the Western Australian government provided the catalyst for a reform movement" (National Museum of Australia, n.d., The catalyst for change section, para. 1)
- "By the end of this year of intense activity over 100,000 signatures had been collected" (National Museum of Australia, n.d., "petition gathering", para. 1).
When you are citing a classical work, like the Bible or the Quran:
References to works of scripture or other classical works are treated differently to regular citations. See the APA Blog's entry for more details:
Happy Holiday Citing: Citation of Classical Works . (Please note, this document is from the 6th edition of APA).
In text citation:
If the name of the organisation first appears in a narrative citation, include the abbreviation before the year in brackets, separated with a comma. Use the official acronym/abreviation if you can find it. Otherwise check with your lecturer for permission to create your own acronyms.
Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS, 2013) shows that...
The Queensland Department of Education (DoE, 2020) encourages students to... (please note, Queensland isn't part of the department's name, it is used in the sentence to provide clarity)
If the name of the organisation first appears in a citation in brackets, include the abbreviation in square brackets.
(Australian Bureau of Statistics [ABS], 2013)
(Department of Education [DoE], 2020)
In the second and subsequent citations, only include the abbreviation or acronym
ABS (2013) found that ...
DoE (2020) instructs teachers to...
This is disputed ( ABS , 2013).
Resources are designed to support "emotional learning pedagogy" (DoE, 2020)
In the reference list:
Use the full name of the organisation in the reference list.
Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. (2017). Australia's welfare 2017 . https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/australias-welfare/australias-welfare-2017/contents/table-of-contents
Department of Education. (2020, April 22). Respectful relationships education program . Queensland Government. https://education.qld.gov.au/curriculum/stages-of-schooling/respectful-relationships
Academically, it is better to find the original source and reference that.
If you do have to quote a secondary source:
- In the text you must cite the original author of the quote and the year the original quote was written as well as the source you read it in. If you do not know the year the original citation was written, omit the year.
- In the reference list you only list the source that you actually read.
Wembley (1997, as cited in Olsen, 1999) argues that impending fuel shortages ...
Wembley claimed that "fuel shortages are likely" (1997, as cited in Olsen, 1999, pp. 10-12).
Some have noted that fuel shortages are probable in the future (Wembley, 1997, as cited in Olsen, 1999).
Olsen, M. (1999). My career. Gallimard.
- << Previous: Dates
- Next: Reference List >>
- Last Updated: May 13, 2024 5:20 PM
- URL: https://libguides.jcu.edu.au/apa

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Referencing
- APA Referencing (7th Ed.) Quick Guide | In-text Citations & References
APA Referencing (7th Ed.) Quick Guide | In-text Citations & References
Published on 18 January 2021 by Raimo Streefkerk . Revised on 17 January 2024.

This citation guide outlines the most important citation guidelines from the 7th edition APA Publication Manual (2020). Scribbr also offers free guides for the older APA 6th edition , MLA Style , and Chicago Style .
Generate accurate APA citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.


Table of contents
Apa in-text citations, apa references, formatting the apa reference page, free lecture slides.
In-text citations are brief references in the running text that direct readers to the reference entry at the end of the paper. You include them every time you quote or paraphrase someone else’s ideas or words.
An APA in-text citation consists of the author’s last name and the year of publication (also known as the author-date system). If you’re citing a specific part of a source, you should also include a locator such as a page number or timestamp. For example: (Smith, 2020, p. 170) .
Parenthetical vs. narrative citation
The in-text citation can take two forms: parenthetical and narrative. Both types are generated automatically when citing a source with Scribbr’s APA Citation Generator.
- Parenthetical citation: According to new research … (Smith, 2020) .
- Narrative citation: Smith (2020) notes that …
Multiple authors and corporate authors
The in-text citation changes slightly when a source has multiple authors or an organization as an author. Pay attention to punctuation and the use of the ampersand (&) symbol.
Missing information
When the author, publication date or locator is unknown, take the steps outlined below.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
APA references generally include information about the author , publication date , title , and source . Depending on the type of source, you may have to include extra information that helps your reader locate the source.
Reference examples
Citing a source starts with choosing the correct reference format. Use Scribbr’s Citation Example Generator to learn more about the format for the most common source types. Pay close attention to punctuation, capitalization, and italicization.
Generate APA citations for free
It is not uncommon for certain information to be unknown or missing, especially with sources found online. In these cases, the reference is slightly adjusted.
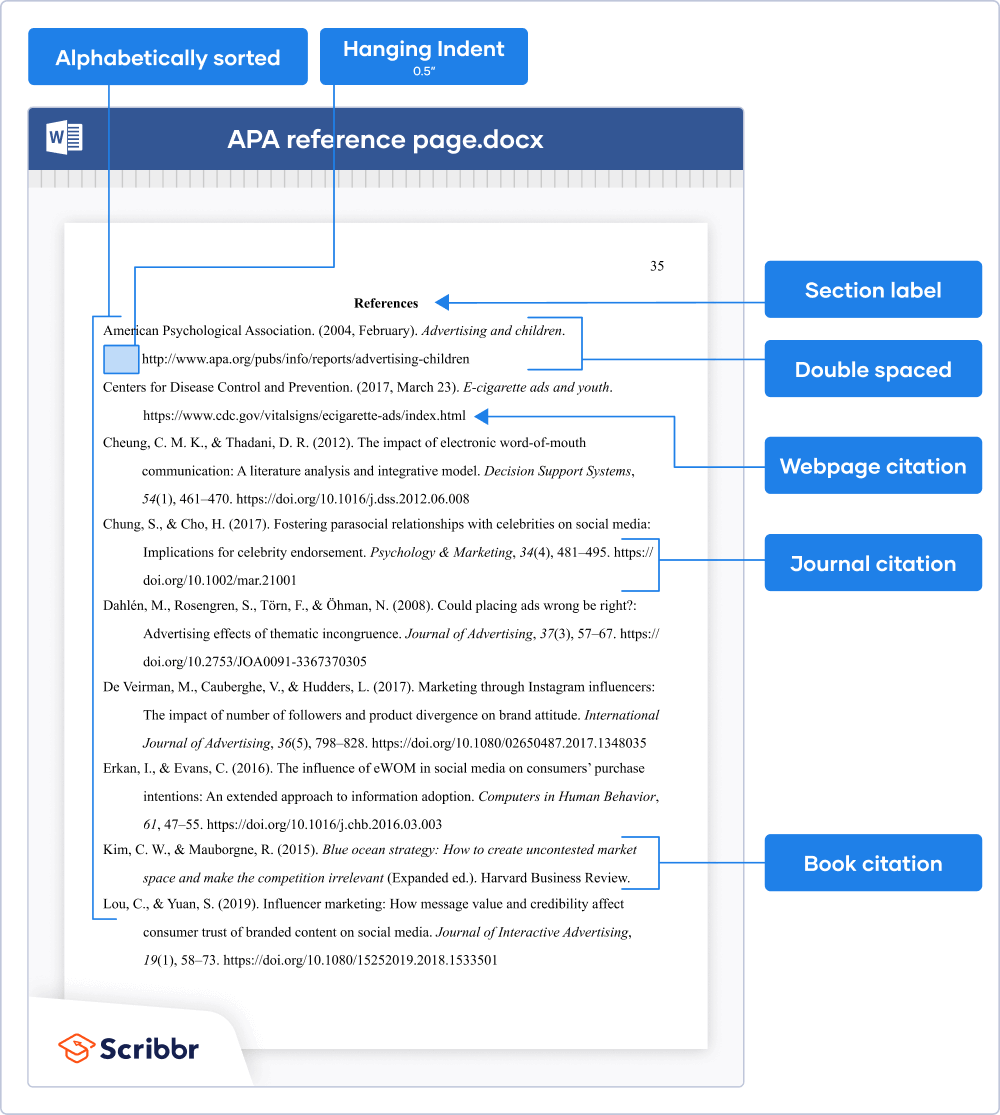
On the first line of the page, write the section label “References” (in bold and centred). On the second line, start listing your references in alphabetical order .
Apply these formatting guidelines to the APA reference page:
- Double spacing (within and between references)
- Hanging indent of ½ inch
- Legible font (e.g. Times New Roman 12 or Arial 11)
- Page number in the top-right header
Which sources to include
On the reference page, you only include sources that you have cited in the text (with an in-text citation ). You should not include references to personal communications that your reader can’t access (e.g. emails, phone conversations or private online material).
Are you a teacher or professor looking to introduce your students to APA Style? Download our free introductory lecture slides, available for Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2024, January 17). APA Referencing (7th Ed.) Quick Guide | In-text Citations & References. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/referencing/apa-style/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk
Other students also liked, a quick guide to harvard referencing | citation examples, mhra referencing | a quick guide & citation examples, how to avoid plagiarism | tips on citing sources, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!

APA Style 7th Edition: Citing Your Sources
- Basics of APA Formatting
Purpose and Overview of In-text Citations
Citations for direct quotes, one work, one author, two or more authors, group authors, etcetera, multiple works by the same author(s) in the same year, citing indirect sources.
- In Text Quick View
- Block Quotes
- Books & eBooks
- Thesis/Dissertation
- Audiovisual
- Conference Presentations
- Social Media
- Legal References
- Reports and Gray Literature
- Academic Integrity and Plagiarism
Additional Resources
- Reference Page
- Annotated Sample Student Paper Here's a sample paper provided by APA. For every style rule, there is a comment highlighted in the paper that tells you where to find the discussion of the rule in the APA Style Manual.
APA follows an author and date of publication model for citing sources in your research paper and are presented as either narrative or parenthetical citations. The formatting does not vary due to format type, however it may deviate from the norm due to factors such as: number of authors, organization instead of individual author, lack of author, or lack of date. By providing the standard author and date within your paper, the reader will be able to link the information presented easily to the full citation provided in the reference list.
View examples and explanations on this page or visit the In Text Quick View for more examples.
APA encourages paraphrasing over using direct quotes. Use direct quotes when:
- Reproducing an exact definition
- Author has said something memorably or succinctly
- When you want to respond to exact wording
When creating a citation for a direct quote, provide author, year and page number for both narrative and parenthetical citations.
Ex. University of Southern California (2020) "direct quote from author" (p. 4) OR "direct quote from author" (University of Southern California, 2020, p. 4).
How to cite specific parts of a source:
Author named in text:
Social historian Richard Sennett (1980) names the tendency to come to terms with difficult experiences a "purification process" whereby "threatening or painful dissonances are warded off to preserve intact a clear and articulated image of oneself and one's place in the world" (p. 11).
Author named in parentheses:
The tendency to come to terms with difficult experiences is referred to as a "purification process" whereby "threatening or painful dissonances are warded off to preserve intact a clear and articulated image of oneself and one's place in the world" (Sennett, 1980, p. 11).
These examples © Duke University Libraries http://library.duke.edu/research/citing/within/apa.html
More than one way to cite:
Flynn (1999) stated in her treatise In a recent treatise on services (Flynn, 1999) In a 1999 treatise, Flynn stated
Subsequent references to same study in same paragraph:
In her treatise on services, Flynn (1999) stated her evaluative methods…Flynn also described
One work, multiple authors
When a work has two authors, always cite both authors' names in your text:
Significant findings in a study of Los Angeles (McCroskey & O'Keefe, 2000)
When a citation has 3 or more authors, include the last name of the first author, followed by et al. (not italicized), and the year.
(Nishimoto et al., 1998)
For narrative citations, use the word "and" to separate authors, for parenthetical citations, use an ampersand:
McCroskey and O'Keefe (2000) studied Los Angeles... (McCroskey & O'Keefe, 2000)
Groups as authors
First narrative citation: National Association of Social Workers (NASW, 1987)
Subsequent narrative citation: NASW (1987)
First text citation: (National Association of Social Workers [NASW], 1987)
Subsequent text citation: (NASW, 1987)
Works with no authors
Cite the work in your text using the first few words of the reference list entry (usually the title). Put double quotation marks around the title of an article or chapter, and italicize the title of a periodical, book, brochure or report:
The policy stated in the article (“Services for Disabled Children,” 1992)
The policy stated in the book Access to Services for Children (1995)
Specific parts of a source
Indicate the page, chapter, figure, table, or equation at the appropriate point in your text. Give page numbers for quotations, and use the abbreviations for the words page and chapter:
(Aranda & Knight, 1997, p. 344)
(Ell & Castaneda, 1998, chap. 5)
Personal communications
This format applies to emails, messages from nonarchived discussion groups, electronic bulletin boards, personal interviews, telephone conversations, etc. Do not list personal communications in your reference list as they are not recoverable by your reader. In your text, provide initials and surname of communicator and as exact a date as possible.
(M. Flynn, personal communication, September 20, 1999)
Sometimes you'll have multiple works by the same author in the same year. For instance, you may reference a number of tax documents from the same year, which would all be cited with (Internal Revenue Service, 2012). So how do you differentiate?
In those instances, differentiate sources with a letter after the year. From the example above, the 990 form might be (Internal Revenue Service, 2012a) and the 1040 form would be (Internal Revenue Service, 2012b). Just make sure the letters stay consistent in your reference list!
Sometimes, you will use a source that you didn't yourself read. In those cases, the original source came from a secondary source you did read. APA states that you should use secondary sources sparingly and may occur when "the original work is out of print, unavailable, or available only in a language that you do not understand."
When using secondary sources, indicate it by included "as cited in" as part of your in-text citation
- << Previous: Basics of APA Formatting
- Next: In Text Quick View >>
- Last Updated: Apr 22, 2024 9:37 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/APA7th

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

16.2: Citing and Referencing Techniques
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 251726

\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Apply American Psychological Association (APA) style formatting guidelines for citations.
This section covers the nitty-gritty details of in-text citations. You will learn how to format citations for different types of source materials, whether you are citing brief quotations, paraphrasing ideas, or quoting longer passages. You will also learn techniques you can use to introduce quoted and paraphrased material effectively. Keep this section handy as a reference to consult while writing the body of your paper.
Formatting Cited Material: The Basics
As noted in previous sections of this book, in-text citations usually provide the name of the author(s) and the year the source was published. For direct quotations, the page number must also be included. Use past-tense verbs when introducing a quote—“Smith found…” and not “Smith finds.…”
Formatting Brief Quotations
For brief quotations—fewer than forty words—use quotation marks to indicate where the quoted material begins and ends, and cite the name of the author(s), the year of publication, and the page number where the quotation appears in your source. Remember to include commas to separate elements within the parenthetical citation. Also, avoid redundancy. If you name the author(s) in your sentence, do not repeat the name(s) in your parenthetical citation. Review following the examples of different ways to cite direct quotations.
- Chang (2008) emphasized that “engaging in weight-bearing exercise consistently is one of the single best things women can do to maintain good health” (p. 49).
The author’s name can be included in the body of the sentence or in the parenthetical citation. Note that when a parenthetical citation appears at the end of the sentence, it comes after the closing quotation marks and before the period. The elements within parentheses are separated by commas.
- Weight Training for Women (Chang, 2008) claimed that “engaging in weight-bearing exercise consistently is one of the single best things women can do to maintain good health” (p. 49).
- Weight Training for Women claimed that “engaging in weight-bearing exercise consistently is one of the single best things women can do to maintain good health” (Chang, 2008, p. 49).
Including the title of a source is optional.
In Chang’s 2008 text Weight Training for Women , she asserts, “Engaging in weight-bearing exercise is one of the single best things women can do to maintain good health” (p. 49).
The author’s name, the date, and the title may appear in the body of the text. Include the page number in the parenthetical citation. Also, notice the use of the verb asserts to introduce the direct quotation.
“Engaging in weight-bearing exercise,” Chang asserts, “is one of the single best things women can do to maintain good health” (2008, p. 49).
You may begin a sentence with the direct quotation and add the author’s name and a strong verb before continuing the quotation.
Formatting Paraphrased and Summarized Material
When you paraphrase or summarize ideas from a source, you follow the same guidelines previously provided, except that you are not required to provide the page number where the ideas are located. If you are summing up the main findings of a research article, simply providing the author’s name and publication year may suffice, but if you are paraphrasing a more specific idea, consider including the page number.
Read the following examples.
- Chang (2008) pointed out that weight-bearing exercise has many potential benefits for women.
Here, the writer is summarizing a major idea that recurs throughout the source material. No page reference is needed.
Chang (2008) found that weight-bearing exercise could help women maintain or even increase bone density through middle age and beyond, reducing the likelihood that they will develop osteoporosis in later life (p. 86).
Although the writer is not directly quoting the source, this passage paraphrases a specific detail, so the writer chose to include the page number where the information is located.
Although APA style guidelines do not require writers to provide page numbers for material that is not directly quoted, your instructor may wish you to do so when possible.
Check with your instructor about his or her preferences.
Formatting Longer Quotations
When you quote a longer passage from a source—forty words or more—use a different format to set off the quoted material. Instead of using quotation marks, create a block quotation by starting the quotation on a new line and indented five spaces from the margin. Note that in this case, the parenthetical citation comes after the period that ends the sentence. Here is an example:
In recent years, many writers within the fitness industry have emphasized the ways in which women can benefit from weight-bearing exercise, such as weightlifting, karate, dancing, stair climbing, hiking, and jogging. Chang (2008) found that engaging in weight-bearing exercise regularly significantly reduces women’s risk of developing osteoporosis. Additionally, these exercises help women maintain muscle mass and overall strength, and many common forms of weight-bearing exercise, such as brisk walking or stair climbing, also provide noticeable cardiovascular benefits. (p. 93)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Review the places in your paper where you cited, quoted, and paraphrased material from a source with a single author. Edit your citations to ensure that
- each citation includes the author’s name, the date of publication, and, where appropriate, a page reference;
- parenthetical citations are correctly formatted;
- longer quotations use the block-quotation format.
If you are quoting a passage that continues into a second paragraph, indent five spaces again in the first line of the second paragraph. Here is an example:
In recent years, many writers within the fitness industry have emphasized the ways in which women can benefit from weight-bearing exercise, such as weightlifting, karate, dancing, stair climbing, hiking, and jogging. Chang (2008) found that engaging in weight-bearing exercise regularly significantly reduces women’s risk of developing osteoporosis. Additionally, these exercises help women maintain muscle mass and overall strength, and many common forms of weight-bearing exercise, such as brisk walking or stair climbing, also provide noticeable cardiovascular benefits.
It is important to note that swimming cannot be considered a weight-bearing exercise, since the water supports and cushions the swimmer. That doesn’t mean swimming isn’t great exercise, but it should be considered one part of an integrated fitness program. (p. 93)
Be wary of quoting from sources at length. Remember, your ideas should drive the paper, and quotations should be used to support and enhance your points. Make sure any lengthy quotations that you include serve a clear purpose. Generally, no more than 10–15 percent of a paper should consist of quoted material.
Introducing Cited Material Effectively
Including an introductory phrase in your text, such as “Jackson wrote” or “Copeland found,” often helps you integrate source material smoothly. This citation technique also helps convey that you are actively engaged with your source material. Unfortunately, during the process of writing your research paper, it is easy to fall into a rut and use the same few dull verbs repeatedly, such as “Jones said,” “Smith stated,” and so on.
Punch up your writing by using strong verbs that help your reader understand how the source material presents ideas. There is a world of difference between an author who “suggests” and one who “claims,” one who “questions” and one who “criticizes.” You do not need to consult your thesaurus every time you cite a source, but do think about which verbs will accurately represent the ideas and make your writing more engaging. The following chart shows some possibilities.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Review the citations in your paper once again. This time, look for places where you introduced source material using a signal phrase in your sentence.
- Highlight the verbs used in your signal phrases, and make note of any that seem to be overused throughout the paper.
- Identify at least three places where a stronger verb could be used.
- Make the edits to your draft.
writing at work
It is important to accurately represent a colleague’s ideas or communications in the workplace. When writing professional or academic papers, be mindful of how the words you use to describe someone’s tone or ideas carry certain connotations. Do not say a source argues a particular point unless an argument is, in fact, presented. Use lively language, but avoid language that is emotionally charged. Doing so will ensure you have represented your colleague’s words in an authentic and accurate way.
Formatting In-Text Citations for Other Source Types
These sections discuss the correct format for various types of in-text citations. Read them through quickly to get a sense of what is covered, and then refer to them again as needed.
Print Sources
This section covers books, articles, and other print sources with one or more authors.
A Work by One Author
For a print work with one author, follow the guidelines provided in Section 13.1 . Always include the author’s name and year of publication. Include a page reference whenever you quote a source directly. (See also the guidelines presented earlier in this chapter about when to include a page reference for paraphrased material.)
Two or More Works by the Same Author
At times, your research may include multiple works by the same author. If the works were published in different years, a standard in-text citation will serve to distinguish them. If you are citing multiple works by the same author published in the same year, include a lowercase letter immediately after the year. Rank the sources in the order they appear in your references section. The source listed first includes an a after the year, the source listed second includes a b , and so on.
Rodriguez (2009a) criticized the nutrition-supplement industry for making unsubstantiated and sometimes misleading claims about the benefits of taking supplements. Additionally, he warned that consumers frequently do not realize the potential harmful effects of some popular supplements (Rodriguez, 2009b).
If you have not yet created your references section, you may not be sure which source will appear first. See Section 13.3 for guidelines—or assign each source a temporary code and highlight the in-text citations so you remember to double-check them later on.
Works by Authors with the Same Last Name
If you are citing works by different authors with the same last name, include each author’s initials in your citation, whether you mention them in the text or in parentheses. Do so even if the publication years are different.
- J. S. Williams (2007) believes nutritional supplements can be a useful part of some diet and fitness regimens. C. D. Williams (2008), however, believes these supplements are overrated.
- According to two leading researchers, the rate of childhood obesity exceeds the rate of adult obesity (K. Connelley, 2010; O. Connelley, 2010).
- Studies from both A. Wright (2007) and C. A. Wright (2008) confirm the benefits of diet and exercise on weight loss.
A Work by Two Authors
When two authors are listed for a given work, include both authors’ names each time you cite the work. If you are citing their names in parentheses, use an ampersand (&) between them. (Use the word and , however, if the names appear in your sentence.)
- As Garrison and Gould (2010) pointed out, “It is never too late to quit smoking. The health risks associated with this habit begin to decrease soon after a smoker quits” (p. 101).
- As doctors continue to point out, “It is never too late to quit smoking. The health risks associated with this habit begin to decrease soon after a smoker quits” (Garrison & Gould, 2010, p. 101).
A Work by Three to Five Authors
If the work you are citing has three to five authors, list all the authors’ names the first time you cite the source. In subsequent citations, use the first author’s name followed by the abbreviation et al. ( Et al. is short for et alia , the Latin phrase for “and others.”)
- Henderson, Davidian, and Degler (2010) surveyed 350 smokers aged 18 to 30.
- One survey, conducted among 350 smokers aged 18 to 30, included a detailed questionnaire about participants’ motivations for smoking (Henderson, Davidian, & Degler, 2010).
Note that these examples follow the same ampersand conventions as sources with two authors. Again, use the ampersand only when listing authors’ names in parentheses.
- As Henderson et al. (2010) found, some young people, particularly young women, use smoking as a means of appetite suppression.
- Disturbingly, some young women use smoking as a means of appetite suppression (Henderson et al., 2010).
Note how the phrase et al. is punctuated. No period comes after et , but al. gets a period because it is an abbreviation for a longer Latin word. In parenthetical references, include a comma after et al. but not before. Remember this rule by mentally translating the citation to English: “Henderson and others, 2010.”
A Work by Six or More Authors
If the work you are citing has six or more authors, list only the first author’s name, followed by et al. , in your in-text citations. The other authors’ names will be listed in your references section.
Researchers have found that outreach work with young people has helped reduce tobacco use in some communities (Costello et al., 2007).
A Work Authored by an Organization
When citing a work that has no individual author(s) but is published by an organization, use the organization’s name in place of the author’s name. Lengthy organization names with well-known abbreviations can be abbreviated. In your first citation, use the full name, followed by the abbreviation in square brackets. Subsequent citations may use the abbreviation only.
- It is possible for a patient to have a small stroke without even realizing it (American Heart Association [AHA], 2010).
- Another cause for concern is that even if patients realize that they have had a stroke and need medical attention, they may not know which nearby facilities are best equipped to treat them (AHA, 2010).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\)
- Review the places in your paper where you cited material from a source with multiple authors or with an organization as the author. Edit your citations to ensure that each citation follows APA guidelines for the inclusion of the authors’ names, the use of ampersands and et al. , the date of publication, and, where appropriate, a page reference.
- Mark any additional citations within your paper that you are not sure how to format based on the guidelines provided so far. You will revisit these citations after reading the next few sections.
A Work with No Listed Author
If no author is listed and the source cannot be attributed to an organization, use the title in place of the author’s name. You may use the full title in your sentence or use the first few words—enough to convey the key ideas—in a parenthetical reference. Follow standard conventions for using italics or quotations marks with titles:
- Use italics for titles of books or reports.
- Use quotation marks for titles of articles or chapters.
- “Living With Diabetes: Managing Your Health” (2009) recommends regular exercise for patients with diabetes.
- Regular exercise can benefit patients with diabetes (“Living with Diabetes,” 2009).
- Rosenhan (1973) had mentally healthy study participants claim to be experiencing hallucinations so they would be admitted to psychiatric hospitals.
A Work Cited within Another Work
To cite a source that is referred to within another secondary source, name the first source in your sentence. Then, in parentheses, use the phrase as cited in and the name of the second source author.
Rosenhan’s study “On Being Sane in Insane Places” (as cited in Spitzer, 1975) found that psychiatrists diagnosed schizophrenia in people who claimed to be experiencing hallucinations and sought treatment—even though these patients were, in fact, imposters.
Two or More Works Cited in One Reference
At times, you may provide more than one citation in a parenthetical reference, such as when you are discussing related works or studies with similar results. List the citations in the same order they appear in your references section, and separate the citations with a semicolon.
Some researchers have found serious flaws in the way Rosenhan’s study was conducted (Dawes, 2001; Spitzer, 1975).
Both of these researchers authored works that support the point being made in this sentence, so it makes sense to include both in the same citation.
A Famous Text Published in Multiple Editions
In some cases, you may need to cite an extremely well-known work that has been repeatedly republished or translated. Many works of literature and sacred texts, as well as some classic nonfiction texts, fall into this category. For these works, the original date of publication may be unavailable. If so, include the year of publication or translation for your edition. Refer to specific parts or chapters if you need to cite a specific section. Discuss with your instructor whether he or she would like you to cite page numbers in this particular instance.
In New Introductory Lectures on Psycho-Analysis , Freud explains that the “manifest content” of a dream—what literally takes place—is separate from its “latent content,” or hidden meaning (trans. 1965, lecture XXIX).
Here, the student is citing a classic work of psychology, originally written in German and later translated to English. Since the book is a collection of Freud’s lectures, the student cites the lecture number rather than a page number.
An Introduction, Foreword, Preface, or Afterword
To cite an introduction, foreword, preface, or afterword, cite the author of the material and the year, following the same format used for other print materials.
Electronic Sources
Whenever possible, cite electronic sources as you would print sources, using the author, the date, and where appropriate, a page number. For some types of electronic sources—for instance, many online articles—this information is easily available. Other times, however, you will need to vary the format to reflect the differences in online media.
Online Sources without Page Numbers
If an online source has no page numbers but you want to refer to a specific portion of the source, try to locate other information you can use to direct your reader to the information cited. Some websites number paragraphs within published articles; if so, include the paragraph number in your citation. Precede the paragraph number with the abbreviation for the word paragraph and the number of the paragraph (e.g., para. 4).
As researchers have explained, “Incorporating fresh fruits and vegetables into one’s diet can be a challenge for residents of areas where there are few or no easily accessible supermarkets” (Smith & Jones, 2006, para. 4).
Even if a source does not have numbered paragraphs, it is likely to have headings that organize the content. In your citation, name the section where your cited information appears, followed by a paragraph number.
The American Lung Association (2010) noted, “After smoking, radon exposure is the second most common cause of lung cancer” (What Causes Lung Cancer? section, para. 2).
This student cited the appropriate section heading within the website and then counted to find the specific paragraph where the cited information was located.
If an online source has no listed author and no date, use the source title and the abbreviation n.d. in your parenthetical reference.
It has been suggested that electromagnetic radiation from cellular telephones may pose a risk for developing certain cancers (“Cell Phones and Cancer,” n.d.).
Personal Communication
For personal communications, such as interviews, letters, and e-mails, cite the name of the person involved, clarify that the material is from a personal communication, and provide the specific date the communication took place. Note that while in-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, personal communications are an exception to this rule. They are cited only in the body text of your paper.
J. H. Yardley, M.D., believes that available information on the relationship between cell phone use and cancer is inconclusive (personal communication, May 1, 2009).
At work, you may sometimes share information resources with your colleagues by photocopying an interesting article or forwarding the URL of a useful website. Your goal in these situations and in formal research citations is the same. The goal is to provide enough information to help your professional peers locate and follow up on potentially useful information. Provide as much specific information as possible to achieve that goal, and consult with your professor as to what specific style he or she may prefer.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Revisit the problem citations you identified in Exercise 3—for instance, sources with no listed author or other oddities. Review the guidelines provided in this section and edit your citations for these kinds of sources according to APA guidelines.
Key Takeaways
- In APA papers, in-text citations include the name of the author(s) and the year of publication whenever possible.
- Page numbers are always included when citing quotations. It is optional to include page numbers when citing paraphrased material; however, this should be done when citing a specific portion of a work.
- When citing online sources, provide the same information used for print sources if it is available.
- When a source does not provide information that usually appears in a citation, in-text citations should provide readers with alternative information that would help them locate the source material. This may include the title of the source, section headings and paragraph numbers for websites, and so forth.
- When writing a paper, discuss with your professor what particular standards he or she would like you to follow.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
APA Citation Basics. When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
In-text citations briefly identify the source of information in the body text. They correspond to a full reference entry at the end of your paper. APA in-text citations consist of the author's last name and publication year. When citing a specific part of a source, also include a page number or range, for example (Parker, 2020, p.
In-text citations are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Chapter 8 and the Concise Guide Chapter 8. Date created: September 2019. APA Style provides guidelines to help writers determine the appropriate level of citation and how to avoid plagiarism and self-plagiarism. We also provide specific guidance for ...
The in-text citation APA style provides us with a tidbit of information. Just enough to glance at it and keep on going with reading the paper. To recap, in-text citations are great because: They credit the original author of a work or information. They let readers quickly see where the information is coming from.
Using In-text Citation. Include an in-text citation when you refer to, summarize, paraphrase, or quote from another source. For every in-text citation in your paper, there must be a corresponding entry in your reference list. APA in-text citation style uses the author's last name and the year of publication, for example: (Field, 2005).
In-text citations. Using references in text. For APA, you use the authors' surnames only and the year in text. If you are using a direct quote, you will also need to use a page number. Narrative citations: If an in-text citation has the authors' names as part of the sentence (that is, outside of brackets) place the year and page numbers in ...
On the first line of the page, write the section label "References" (in bold and centered). On the second line, start listing your references in alphabetical order. Apply these formatting guidelines to the APA reference page: Double spacing (within and between references) Hanging indent of ½ inch.
APA in-text citations The basics. In-text citations are brief references in the running text that direct readers to the reference entry at the end of the paper. You include them every time you quote or paraphrase someone else's ideas or words.. An APA in-text citation consists of the author's last name and the year of publication (also known as the author-date system).
APA follows an author and date of publication model for citing sources in your research paper and are presented as either narrative or parenthetical citations. The formatting does not vary due to format type, however it may deviate from the norm due to factors such as: number of authors, organization instead of individual author, lack of author, or lack of date.
The examples here are in sixth edition APA Style. by Chelsea Lee. The basic citation for a government report follows the author - date - title - source format of APA Style references. Here is a template: Reference list: Government Author. (year). Title of report: Subtitle of report if applicable (Report No. 123).
It points the reader to the source so they can see where you got your information. In-text citations most commonly take the form of short parenthetical statements indicating the author and publication year of the source, as well as the page number if relevant. Example: APA Style in-text citation (Jackson, 2005, p. 16)
Title of Book or "Title of Article". n.d. Note. Titles of books and reports are italicized in in-text citations, and titles of articles and other documents are put in quotation marks. Capitalize the important words (see section 4.15 in the 6th ed. Publication Manual , pp. 101 - 102) in titles in the text. Important Tips and Further Reading.
Resources on using in-text citations in APA style. The Basics General guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay Author/Authors How to refer to authors in-text, including single and multiple authors, unknown authors, organizations, etc. Reference List. Resources on writing an APA style reference list, including citation formats
Use the author-date citation system to cite references in the text in APA Style. In this system, each work used in a paper has two parts: an in-text citation and a corresponding reference list entry. In-text citations may be parenthetical or narrative. In parenthetical citations, use an ampersand (&) between names for a work with two authors ...
The short answer is that in most cases no, you do not put the URL in the text of the paper. In fact, the only time you would put a URL in the text would be to simply mention a website in passing. Because you're citing specific information, you will need to write a regular APA Style author-date citation. Luckily, writing the in-text citation ...
Include a comma between "et al." and the publication date (e.g. Taylor et al., 2018). There should be no punctuation between "et al." and the author's name preceding it. The period ending the sentence always comes after the citation (even when quoting). Never use an ampersand symbol ("&") in the running text.
In APA Style, if you use multiple sources from the same author that have different publication years, the different publication years are sufficient to distinguish the citations. To cite multiple sources with the same publication year in an APA in-text citation , include the author name and date as usual, and add a lowercase letter to the end ...
In Text Format: (Book Title, Publication Year, Page Number) Examples Parenthetical citation: (Merriam-Webster's, 2005, p. 3) & (The Complete Encyclopaedia of Garden Flowers, 2003, p. 19) Narrative citation: The Complete Encyclopedia of Garden Flowers (2003) depicts ... (p. 19). Reference Format: Book title: Subtitle. (Year). Publisher. DOI (if ...
when reproducing an exact definition (see Section 6.22 of the Publication Manual ), when an author has said something memorably or succinctly, or. when you want to respond to exact wording (e.g., something someone said). Instructors, programs, editors, and publishers may establish limits on the use of direct quotations.
APA citation basics. When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, for example, (Jones, 1998), and a complete reference should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
Each time you use any information from a source, include a 1) reference entry and 2) parenthetical citation (sometimes called "in-text"). STEP 1: REFERENCES PAGE (see example on reverse) As you find each source you want to use, create a citation. Note: don't wait to cite; do so early! Those citations you've created will then be placed ...
Throughout your paper, you need to apply the following APA format guidelines: Set page margins to 1 inch on all sides. Double-space all text, including headings. Indent the first line of every paragraph 0.5 inches. Use an accessible font (e.g., Times New Roman 12pt., Arial 11pt., or Georgia 11pt.).
APA (American Psychological Association) style is most commonly used to cite sources within the social sciences. This resource, revised according to the 6th edition, second printing of the APA manual, offers examples for the general format of APA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the reference page. For more information, please consult the Publication Manual of the ...
The citation of interviews depends on the nature of the interview. Third-party interviews: If the interview is in a form that is recoverable (e.g., a recording, transcript, published Q&A), use the reference format appropriate for the source in which the interview is available. Informational interviews: If you have interviewed someone for information about your topic and that person has agreed ...
In APA papers, in-text citations include the name of the author(s) and the year of publication whenever possible. Page numbers are always included when citing quotations. It is optional to include page numbers when citing paraphrased material; however, this should be done when citing a specific portion of a work.
Basic book citation format. The in-text citation for a book includes the author's last name, the year, and (if relevant) a page number. In the reference list, start with the author's last name and initials, followed by the year.The book title is written in sentence case (only capitalize the first word and any proper nouns).Include any other contributors (e.g. editors and translators) and ...
Revised on January 17, 2024. APA website citations usually include the author, the publication date, the title of the page or article, the website name, and the URL. If there is no author, start the citation with the title of the article. If the page is likely to change over time, add a retrieval date. If you are citing an online version of a ...
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.