
- How to Write Evaluation Reports: Purpose, Structure, Content, Challenges, Tips, and Examples
- Learning Center

This article explores how to write effective evaluation reports, covering their purpose, structure, content, and common challenges. It provides tips for presenting evaluation findings effectively and using evaluation reports to improve programs and policies. Examples of well-written evaluation reports and templates are also included.
Table of Contents

What is an Evaluation Report?
What is the purpose of an evaluation report, importance of evaluation reports in program management, structure of evaluation report, best practices for writing an evaluation report, common challenges in writing an evaluation report, tips for presenting evaluation findings effectively, using evaluation reports to improve programs and policies, example of evaluation report templates, conclusion: making evaluation reports work for you.
An evaluatio n report is a document that presents the findings, conclusions, and recommendations of an evaluation, which is a systematic and objective assessment of the performance, impact, and effectiveness of a program, project, policy, or intervention. The report typically includes a description of the evaluation’s purpose, scope, methodology, and data sources, as well as an analysis of the evaluation findings and conclusions, and specific recommendations for program or project improvement.
Evaluation reports can help to build capacity for monitoring and evaluation within organizations and communities, by promoting a culture of learning and continuous improvement. By providing a structured approach to evaluation and reporting, evaluation reports can help to ensure that evaluations are conducted consistently and rigorously, and that the results are communicated effectively to stakeholders.
Evaluation reports may be read by a wide variety of audiences, including persons working in government agencies, staff members working for donors and partners, students and community organisations, and development professionals working on projects or programmes that are comparable to the ones evaluated.
Related: Difference Between Evaluation Report and M&E Reports .
The purpose of an evaluation report is to provide stakeholders with a comprehensive and objective assessment of a program or project’s performance, achievements, and challenges. The report serves as a tool for decision-making, as it provides evidence-based information on the program or project’s strengths and weaknesses, and recommendations for improvement.
The main objectives of an evaluation report are:
- Accountability: To assess whether the program or project has met its objectives and delivered the intended results, and to hold stakeholders accountable for their actions and decisions.
- Learning : To identify the key lessons learned from the program or project, including best practices, challenges, and opportunities for improvement, and to apply these lessons to future programs or projects.
- Improvement : To provide recommendations for program or project improvement based on the evaluation findings and conclusions, and to support evidence-based decision-making.
- Communication : To communicate the evaluation findings and conclusions to stakeholders , including program staff, funders, policymakers, and the general public, and to promote transparency and stakeholder engagement.
An evaluation report should be clear, concise, and well-organized, and should provide stakeholders with a balanced and objective assessment of the program or project’s performance. The report should also be timely, with recommendations that are actionable and relevant to the current context. Overall, the purpose of an evaluation report is to promote accountability, learning, and improvement in program and project design and implementation.
Evaluation reports play a critical role in program management by providing valuable information about program effectiveness and efficiency. They offer insights into the extent to which programs have achieved their objectives, as well as identifying areas for improvement.
Evaluation reports help program managers and stakeholders to make informed decisions about program design, implementation, and funding. They provide evidence-based information that can be used to improve program outcomes and address challenges.
Moreover, evaluation reports are essential in demonstrating program accountability and transparency to funders, policymakers, and other stakeholders. They serve as a record of program activities and outcomes, allowing stakeholders to assess the program’s impact and sustainability.
In short, evaluation reports are a vital tool for program managers and evaluators. They provide a comprehensive picture of program performance, including strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. By utilizing evaluation reports, program managers can make informed decisions to improve program outcomes and ensure that their programs are effective, efficient, and sustainable over time.

The structure of an evaluation report can vary depending on the requirements and preferences of the stakeholders, but typically it includes the following sections:
- Executive Summary : A brief summary of the evaluation findings, conclusions, and recommendations.
- Introduction: An overview of the evaluation context, scope, purpose, and methodology.
- Background: A summary of the programme or initiative that is being assessed, including its goals, activities, and intended audience(s).
- Evaluation Questions : A list of the evaluation questions that guided the data collection and analysis.
- Methodology: A description of the data collection methods used in the evaluation, including the sampling strategy, data sources, and data analysis techniques.
- Findings: A presentation of the evaluation findings, organized according to the evaluation questions.
- Conclusions : A summary of the main evaluation findings and conclusions, including an assessment of the program or project’s effectiveness, efficiency, and sustainability.
- Recommendations : A list of specific recommendations for program or project improvements based on the evaluation findings and conclusions.
- Lessons Learned : A discussion of the key lessons learned from the evaluation that could be applied to similar programs or projects in the future.
- Limitations : A discussion of the limitations of the evaluation, including any challenges or constraints encountered during the data collection and analysis.
- References: A list of references cited in the evaluation report.
- Appendices : Additional information, such as detailed data tables, graphs, or maps, that support the evaluation findings and conclusions.
The structure of the evaluation report should be clear, logical, and easy to follow, with headings and subheadings used to organize the content and facilitate navigation.
In addition, the presentation of data may be made more engaging and understandable by the use of visual aids such as graphs and charts.
Writing an effective evaluation report requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here are some best practices to consider when writing an evaluation report:
Begin by establishing the report’s purpose, objectives, and target audience. A clear understanding of these elements will help guide the report’s structure and content.
Use clear and concise language throughout the report. Avoid jargon and technical terms that may be difficult for readers to understand.
Use evidence-based findings to support your conclusions and recommendations. Ensure that the findings are clearly presented using data tables, graphs, and charts.
Provide context for the evaluation by including a brief summary of the program being evaluated, its objectives, and intended impact. This will help readers understand the report’s purpose and the findings.
Include limitations and caveats in the report to provide a balanced assessment of the program’s effectiveness. Acknowledge any data limitations or other factors that may have influenced the evaluation’s results.
Organize the report in a logical manner, using headings and subheadings to break up the content. This will make the report easier to read and understand.
Ensure that the report is well-structured and easy to navigate. Use a clear and consistent formatting style throughout the report.
Finally, use the report to make actionable recommendations that will help improve program effectiveness and efficiency. Be specific about the steps that should be taken and the resources required to implement the recommendations.
By following these best practices, you can write an evaluation report that is clear, concise, and actionable, helping program managers and stakeholders to make informed decisions that improve program outcomes.
Catch HR’s eye instantly?
- Resume Review
- Resume Writing
- Resume Optimization
Premier global development resume service since 2012
Stand Out with a Pro Resume
Writing an evaluation report can be a challenging task, even for experienced evaluators. Here are some common challenges that evaluators may encounter when writing an evaluation report:
- Data limitations: One of the biggest challenges in writing an evaluation report is dealing with data limitations. Evaluators may find that the data they collected is incomplete, inaccurate, or difficult to interpret, making it challenging to draw meaningful conclusions.
- Stakeholder disagreements: Another common challenge is stakeholder disagreements over the evaluation’s findings and recommendations. Stakeholders may have different opinions about the program’s effectiveness or the best course of action to improve program outcomes.
- Technical writing skills: Evaluators may struggle with technical writing skills, which are essential for presenting complex evaluation findings in a clear and concise manner. Writing skills are particularly important when presenting statistical data or other technical information.
- Time constraints: Evaluators may face time constraints when writing evaluation reports, particularly if the report is needed quickly or the evaluation involved a large amount of data collection and analysis.
- Communication barriers: Evaluators may encounter communication barriers when working with stakeholders who speak different languages or have different cultural backgrounds. Effective communication is essential for ensuring that the evaluation’s findings are understood and acted upon.
By being aware of these common challenges, evaluators can take steps to address them and produce evaluation reports that are clear, accurate, and actionable. This may involve developing data collection and analysis plans that account for potential data limitations, engaging stakeholders early in the evaluation process to build consensus, and investing time in developing technical writing skills.
Presenting evaluation findings effectively is essential for ensuring that program managers and stakeholders understand the evaluation’s purpose, objectives, and conclusions. Here are some tips for presenting evaluation findings effectively:
- Know your audience: Before presenting evaluation findings, ensure that you have a clear understanding of your audience’s background, interests, and expertise. This will help you tailor your presentation to their needs and interests.
- Use visuals: Visual aids such as graphs, charts, and tables can help convey evaluation findings more effectively than written reports. Use visuals to highlight key data points and trends.
- Be concise: Keep your presentation concise and to the point. Focus on the key findings and conclusions, and avoid getting bogged down in technical details.
- Tell a story: Use the evaluation findings to tell a story about the program’s impact and effectiveness. This can help engage stakeholders and make the findings more memorable.
- Provide context: Provide context for the evaluation findings by explaining the program’s objectives and intended impact. This will help stakeholders understand the significance of the findings.
- Use plain language: Use plain language that is easily understandable by your target audience. Avoid jargon and technical terms that may confuse or alienate stakeholders.
- Engage stakeholders: Engage stakeholders in the presentation by asking for their input and feedback. This can help build consensus and ensure that the evaluation findings are acted upon.
By following these tips, you can present evaluation findings in a way that engages stakeholders, highlights key findings, and ensures that the evaluation’s conclusions are acted upon to improve program outcomes.
Evaluation reports are crucial tools for program managers and policymakers to assess program effectiveness and make informed decisions about program design, implementation, and funding. By analyzing data collected during the evaluation process, evaluation reports provide evidence-based information that can be used to improve program outcomes and impact.
One of the primary ways that evaluation reports can be used to improve programs and policies is by identifying program strengths and weaknesses. By assessing program effectiveness and efficiency, evaluation reports can help identify areas where programs are succeeding and areas where improvements are needed. This information can inform program redesign and improvement efforts, leading to better program outcomes and impact.
Evaluation reports can also be used to make data-driven decisions about program design, implementation, and funding. By providing decision-makers with data-driven information, evaluation reports can help ensure that programs are designed and implemented in a way that maximizes their impact and effectiveness. This information can also be used to allocate resources more effectively, directing funding towards programs that are most effective and efficient.
Another way that evaluation reports can be used to improve programs and policies is by disseminating best practices in program design and implementation. By sharing information about what works and what doesn’t work, evaluation reports can help program managers and policymakers make informed decisions about program design and implementation, leading to better outcomes and impact.
Finally, evaluation reports can inform policy development and improvement efforts by providing evidence about the effectiveness and impact of existing policies. This information can be used to make data-driven decisions about policy development and improvement efforts, ensuring that policies are designed and implemented in a way that maximizes their impact and effectiveness.
In summary, evaluation reports are critical tools for improving programs and policies. By providing evidence-based information about program effectiveness and efficiency, evaluation reports can help program managers and policymakers make informed decisions, allocate resources more effectively, disseminate best practices, and inform policy development and improvement efforts.
There are many different templates available for creating evaluation reports. Here are some examples of template evaluation reports that can be used as a starting point for creating your own report:
- The National Science Foundation Evaluation Report Template – This template provides a structure for evaluating research projects funded by the National Science Foundation. It includes sections on project background, research questions, evaluation methodology, data analysis, and conclusions and recommendations.
- The CDC Program Evaluation Template – This template, created by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, provides a framework for evaluating public health programs. It includes sections on program description, evaluation questions, data sources, data analysis, and conclusions and recommendations.
- The World Bank Evaluation Report Template – This template, created by the World Bank, provides a structure for evaluating development projects. It includes sections on project background, evaluation methodology, data analysis, findings and conclusions, and recommendations.
- The European Commission Evaluation Report Template – This template provides a structure for evaluating European Union projects and programs. It includes sections on project description, evaluation objectives, evaluation methodology, findings, conclusions, and recommendations.
- The UNICEF Evaluation Report Template – This template provides a framework for evaluating UNICEF programs and projects. It includes sections on program description, evaluation questions, evaluation methodology, findings, conclusions, and recommendations.
These templates provide a structure for creating evaluation reports that are well-organized and easy to read. They can be customized to meet the specific needs of your program or project and help ensure that your evaluation report is comprehensive and includes all of the necessary components.
- World Health Organisations Reports
- Checkl ist for Assessing USAID Evaluation Reports
In conclusion, evaluation reports are essential tools for program managers and policymakers to assess program effectiveness and make informed decisions about program design, implementation, and funding. By analyzing data collected during the evaluation process, evaluation reports provide evidence-based information that can be used to improve program outcomes and impact.
To make evaluation reports work for you, it is important to plan ahead and establish clear objectives and target audiences. This will help guide the report’s structure and content and ensure that the report is tailored to the needs of its intended audience.
When writing an evaluation report, it is important to use clear and concise language, provide evidence-based findings, and offer actionable recommendations that can be used to improve program outcomes. Including context for the evaluation findings and acknowledging limitations and caveats will provide a balanced assessment of the program’s effectiveness and help build trust with stakeholders.
Presenting evaluation findings effectively requires knowing your audience, using visuals, being concise, telling a story, providing context, using plain language, and engaging stakeholders. By following these tips, you can present evaluation findings in a way that engages stakeholders, highlights key findings, and ensures that the evaluation’s conclusions are acted upon to improve program outcomes.
Finally, using evaluation reports to improve programs and policies requires identifying program strengths and weaknesses, making data-driven decisions, disseminating best practices, allocating resources effectively, and informing policy development and improvement efforts. By using evaluation reports in these ways, program managers and policymakers can ensure that their programs are effective, efficient, and sustainable over time.
Well understanding, the description of the general evaluation of report are clear with good arrangement and it help students to learn and make practices
Patrick Kapuot
Thankyou for very much for such detail information. Very comprehensively said.
hailemichael
very good explanation, thanks
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.
How strong is my Resume?
Only 2% of resumes land interviews.
Land a better, higher-paying career

Jobs for You
Chief of party – bosnia and herzegovina.
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
Project Manager I
- United States
Business Development Associate
Director of finance and administration, request for information – collecting information on potential partners for local works evaluation.
- Washington, USA
Principal Field Monitors
Technical expert (health, wash, nutrition, education, child protection, hiv/aids, supplies), survey expert, data analyst, team leader, usaid-bha performance evaluation consultant.
- International Rescue Committee
Manager II, Institutional Support Program Implementation
Senior human resources associate, energy and environment analyst – usaid bureau for latin america and the caribbean, intern- international project and proposal support, ispi, services you might be interested in, useful guides ....
How to Create a Strong Resume
Monitoring And Evaluation Specialist Resume
Resume Length for the International Development Sector
Types of Evaluation
Monitoring, Evaluation, Accountability, and Learning (MEAL)
LAND A JOB REFERRAL IN 2 WEEKS (NO ONLINE APPS!)
Sign Up & To Get My Free Referral Toolkit Now:

How to Write an Evaluation Report
Report generator.

An evaluation is an assessment of certain topics or subjects typically conducted for a specific purpose. An evaluation report, in the simplest sense, is a document which reports the results, findings, interpretations, conclusions, or recommendations derived through an evaluation. An evaluation report primarily gives a executive summary of the points covered by the evaluation. It also presents an overview of the evaluation process.
Importance of an Evaluation Report
An evaluation report is an essential way of presenting an evaluation to a certain audience. It is intended to promote awareness on how the evaluation reached its outcomes and conclusions.
An evaluation report is thus an effective way to disseminate findings of an evaluation to the people concerned. It is essential to report the conclusions derived from a specific evaluation to ensure its transparency, and to be able to properly use such conclusions in the future.
This is also for the people to properly understand the purpose of the evaluation plan , and of course, know the outcomes and the possible effects to the subject or subjects of the evaluation. An evaluation report is also presented to determine if the time and resources allocated for such evaluation were used accordingly.
Key Components of an Evaluation Report
Evaluation formal reports contain an essential parts and processes of an evaluation. It is thus important for one to know what constitutes a good evaluation report. The following are the key components commonly discussed in an evaluation report.
- Title or header. This includes a clear and concise title, the authors’ names, date of preparation, etc.
- Executive summary. This should contain a brief summary of the subject of the report.
- Table of contents. This includes an overview of the contents of the report and their respective pages.
- Introductory remarks. Mainly a short report introduction on the purpose, and target of the evaluation.
- Scope. This discusses the evaluation focus.
- Resources and methods. Materials, equipment, and methods involved in the evaluation.
- Summary. Typically includes findings, conclusions, and interpretations derived in the evaluation.
- Recommendations. This provides an idea on information dissemination and intended use of the evaluation’s findings and conclusions.
- References. This contains the references used by the authors upon report writing the evaluation.
Tips in Writing an Evaluation Report
An evaluation report gives the audience a general idea about the whole evaluation. For it to effectively convey information, it needs to be constructed properly. Consider the following tips in writing an evaluation report.
- Think of a purpose. This creates the foundation of the evaluation business report . One needs to determine the purpose of creating an evaluation report to determine its focus.
- Gather the most important details of the evaluation to be included in the report.
- Know the audience of your report. This includes the people who will view the report, its users, and in most cases, the evaluation’s subjects. Anticipate the questions and concerns they might ask regarding the technical report .
- Divide the report into different sections. This will promote better distribution of ideas and contents of the evaluation itself.
- Write in a clear manner. This will allow your audience to comprehend the ideas you present better.
- Proofread your report. Proofreading is the best way to get rid of the possible errors your report might contain.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate a report on the impact of technology in the classroom on student learning outcomes
Prepare a report analyzing the trends in student participation in sports and arts programs over the last five years at your school.
How to Write an Evaluation Report

Whether you are monitoring or evaluating, at some point or points, there will be a reporting process. This reporting process follows the stages of analyzing information.
You will report to different stakeholders (Board, Management team, Staff, Beneficiaries, and Donors) in different ways, sometimes in written form, sometimes verbally, and, increasingly, making use of tools such as PowerPoint presentations, slides, and videos.
A written evaluation report may be prepared in line with the following format: these are the components of an evaluation report.
- Executive summary.
- Content page.
- Introduction.
- Conclusions.
- Recommendations.
- Appendices.
The executive summary is intended for time-constraint readers but must be attractive to make people curious so that they want to read the entire report.
A preface is a place where you become courteous to thank people and make broad comments about the processes and findings.
The introductory section is designed to deal with the background of the project, the need for the evaluation, and the entire activity in a nutshell.
The findings section will accommodate the results about the efficiency, effectiveness, and impact thereof that have emerged.
The conclusions you draw will follow your findings, while your recommendations will address weaknesses, followed by what needs to be done to strengthen the programs being evaluated.
Include your Terms of References (TOR), a questionnaire used in the evaluation, and any other reference documents in the appendices that you could not accommodate inside the text.
Outline of writing an evaluation report
Here is an example of an outline of writing an evaluation report adapted from the UNICEF Guide “Program Manager’s Planning, Monitoring, and Evaluation Toolkit (2006):
Why is the reporting process essential in monitoring or evaluating?
The reporting process is crucial as it follows the stages of analyzing information, allowing stakeholders to understand the results and implications of the monitoring or evaluation.
What are the different ways to report to stakeholders?
Stakeholders can be reported to in various ways, including written reports, verbal communication , PowerPoint presentations, slides, and videos.
What are the primary components of a written evaluation report?
The main components of a written evaluation report include the Executive summary, Preface, Content page, Introduction, Findings, Conclusions, Recommendations, and Appendices.
What is the purpose of the executive summary in an evaluation report?
The executive summary is designed for time-constraint readers and should be compelling enough to make readers curious about reading the entire report.
How does the introduction section of the evaluation report differ from the preface?
The introduction deals with the background of the project, the need for the evaluation, and summarizes the entire activity. In contrast, the preface is where you thank people and make broad comments about the processes and findings.
What should be included in the findings section of the evaluation report?
The findings section should accommodate results about the efficiency, effectiveness, and impact of the project or program being evaluated.
What is the purpose of the appendices in an evaluation report?
The appendices include the Terms of References (TOR), questionnaires used in the evaluation, and any other reference documents that couldn’t be accommodated within the main text of the report.

Campaigning guidance
Our guidance for charities on campaigning in the lead up to the general election. Learn more
- Writing an evaluation report
Use this page to learn about the process of writing an evaluation report.
Writing an evaluation report helps you share key findings and recommendations with those in your organisation and the people and communities you work with. This is the next step in the evaluation cycle after our guidance on analysing and reporting on your evaluation .
A report can be used to:
- suggest changes to how you work
- communicate your value to funders
- share good practice with other organisations
- share learning with the people and communities you work with.
Once you’ve completed these parts of your project, you’ll be able to write your evaluation report:
- You have data that you've collected and analysed.
- You’ve got the software to help you design your report.
- You have an understanding of the people who'll be reading your report.
- There are helpful colleagues available to read your drafts.
Choose the right software for your report
You have several options for software. Here are some suggestions below to get you started:
The Microsoft suite
- Word has a range of icons, images and smart art you can use - it is probably the most popular choice.
- Slide documents (using PowerPoint) can be helpful for writing briefer reports. You can also create data visualisation within PowerPoint and import it to Microsoft Word if preferred.
- You can create dashboards in Excel and/or import data visualisation graphs to other Microsoft applications.
Other applications
- SurveyMonkey has a dashboard function which can be used for reporting.
- Piktochart, Tablea and Canva are all design software. They have evaluation and impact report templates available.
- If you're producing content for webpages, Google Charts and Datawrapper may prove helpful.
Consider your audience
Think about the people you're reporting to so you can tell them what they need to know. You should consider these points:
- What kind of information they need. For example, whether they need to know more about the difference you’ve made or the way in which you’ve delivered your work.
- How they'd like the information presented. For example, as a traditional evaluation report and/or data visualisation, webpages, or PowerPoint and when.
- Why they need the information and what you want them to do as a result.
- Whether there are any accessibility needs that you need to consider. For example, does the report need to work on a screen reader?
Plan your report
Having a clear structure makes your report easier to read. Before you write, plan your headings and subheadings. Most evaluation reports will include the following sections.
- Executive summary – a summary of your key findings and recommendations.
- Introduction – a brief description of what you're evaluating, the purpose of your evaluation and the methods you've used (for example, surveys and interviews).
- Findings and discussion – information on what you delivered, how you delivered it and what outcomes came out of it.
- Recommendations – actions that need to be taken to respond to the evaluation findings.
What to include in your report
Reports will vary depending on the nature of your work, but you'll probably need to include findings on the following:
- Outcomes – What outcomes have been achieved, for whom and under what circumstances. You should also report on intended outcomes.
- Activities and outputs – What has been delivered, when and to who. You should also report on how satisfied the people and communities you work with were.
- Processes – Information about how you delivered your outputs. You may need this information to explain why something worked particularly well, or why it didn’t work.
Describe and interpret your data
In your report, you should describe your data and interpret it – analysing your data before you start writing will help with this.
Describing means presenting what the data tells you. You might describe, for example, what outcomes were achieved, by whom and in what circumstances.
Interpretation moves beyond description to say what the data means – make sure you word your report clearly so the reader can tell when you're describing data and when you're interpreting it.
To help you interpret data, you could do the following.
- Make connections by looking for trends, patterns and links . For example, if two groups had very different outcomes, what factors might have led to this?
- Put data in a meaningful context . Numbers don’t speak for themselves. Is 70% good or bad? How do you know?
When you interpret your data, you could discuss the following.
- Why outcomes were achieved, or not achieved . Understanding this may help you make decisions about future service planning. Many funders will also want to know about this.
- What worked and what didn’t . Knowing about this will put you in a good position to improve your work. It may also be useful to share with partners or funders to improve practice in the sector.
- Answers to your evaluation questions . When you planned your evaluation , you may have had two or three key questions you wanted it to answer. For example, you may have wanted to know whether your service works equally well for all groups.
Choose how to present your data
A common mistake is to try to present all your data, rather than focusing on what’s most important. It helps to narrow down to what people reading your report need to know.
It’s also important to think about how you'll present your information. You could consider the following points.
Which key numbers do your audience need to know?
- Decide whether to report using percentages, averages or other statistics.
- Think about whether you need to compare numerical data for different groups. You may want to look at whether men were more likely to experience outcomes than women, for instance.
- Read our guide on analysing quantitative data .
Which quotations will help you illustrate your themes?
- Choose quotations that bring your outcomes to life. Don’t choose too many or they'll distract the reader from the point you want to make.
- Have a mixture of typical responses and those that don’t fit easily into your categories.
- Read our guide on analysing qualitative data .
What visual aids will you use?
- Diagrams, graphs or charts should be used to highlight the most important information, rather than information which is less relevant.
- It’s very easy for diagrams to mislead your audience. Here are some examples of misleading charts . If you think a diagram might be misleading, it’s better to leave it out.
As far as possible, present data that has been analysed or summarised rather than raw data, to make it as easy as possible for the reader to follow.
Check anonymity and consent
When you collected your data, respondents will have said whether they wanted to remain anonymous (most do) and whether you should check with them before using a quote or case study in your report. Make sure you do any checking with plenty of time before you need to complete the report.
Depending on the size of your sample and how easy it is to identify individuals, you may have to do more than just change the name to make someone anonymous.
You might have to change their age or other identifying details, or remove references to anything that would allow people to identify them as an individual.
Write accurately and clearly
It’s important to write accurately and clearly so that your report can be easily understood and is not misleading.
Be transparent
Being transparent means being open about what you can and can’t say, and clear about how you reached your conclusions and about the limitations of your data.
Just as it's important to minimise bias when collecting or analysing data, it's equally important to minimise bias when reporting.
- Avoid overclaiming your role in making a difference . Your work may not be solely responsible for the outcomes that have occurred for individuals or organisations you've worked with. Remember to report on evidence of any other contributing factors. For example, support received from other organisations or other sources.
- Choose case studies carefully . Evaluation case studies are not the same as marketing case studies. They should illustrate your learning points, not just the very best of what you do. You won't have a representative group of case studies, but as far as possible, choose case studies – and quotations – that reflect the full range of responses you had.
- Explore alternative interpretations or causal links . Sometimes, data is ambiguous and there could be more than one interpretation. All of us are prone to 'confirmation bias' – paying more attention to data that fits our existing beliefs. It's important to look for and talk about reasonable alternative interpretations or explanations of your data.
- Be clear about the limitations of your data . If there was a group you weren't able to hear from, or your sample over- or under-represents a particular group, say so.
- Be open about your sample size . In general, the smaller your sample, the less able you're to make generalisations about everyone in your target group.
- Report negative findings . If the data shows something isn't working or an outcome hasn't been achieved, don’t ignore it. Reporting negative findings will help your audience to use the evaluation to learn and improve.
Use precise language
Evaluation reports need to be as clear and precise as possible in their wording. Be especially careful about using the word 'proof' or 'prove'.
To prove something requires 100% certainty, which you are very unlikely to have. 'Indicates', 'demonstrates', 'shows', 'suggests' or 'is evidence for' are useful alternative phrases.
Make your report easy to read
Subheadings will make your report clear for your readers. Looking back at your evaluation framework or theory of change can help you think of ideas for subheadings.
It often makes sense to have a subheading for each intended outcome.
Sometimes you'll have collected data about the same outcome from a range of different sources such as questionnaires, interviews, observation or secondary data.
When you analysed your data, you probably looked at each source separately.
In your report, it usually makes sense to write about all the data relating to each outcome together (rather than having separate sections on data from different sources).
Keep your language simple and straightforward. Remember to explain any terminology that might be unfamiliar to your audience.
Develop your recommendations
Your recommendations are likely to be one of the most important parts of your report. Good recommendations will make your evaluation findings more likely to be used.
Recommendations are more likely to be put in place if the following factors are considered.
- Supported by evidence – Be clear about how the recommendations build on the key findings. It can help to structure the recommendations in the same order as the main findings to help readers understand the evidence base for each.
- Specific – Say exactly what action needs to be taken and when within the control of the evaluation.
- Users – Make sure individuals or groups have the authority and capability to take forward what you’re suggesting.
- Realistic and achievable – Recommendations should be feasible. You can categorise them by which ones are easy to implement and which are less so. More ‘difficult’ recommendations might need budget or staff changes. These should still be stated, as well as the impact of it.
- Prioritised – It’s helpful to show some priorities for action. You could, for example, split your recommendations into ‘essential’ versus ‘optional’ or ‘for consideration’ versus ‘for action’. Make sure the number of recommendations you include is achievable.
Involve people in the reporting process
You can involve other internal staff and the poeple and communities you work with at several points. For example, you could share your report drafts and ask them to help you refine the conclusions.
This 'co-production' of findings can be valuable and provide interpretations you may not have thought about.
You can also co-produce recommendations by sharing the findings with those you work with and asking them to suggest and prioritise recommendations.
If you do this, take care to guide people to base their recommendations on the evidence, and not their own interests or preoccupations.
Finishing the report
Allow time for a couple of report drafts and make sure there are people available to review the report for you. It's good to have someone look at it with ‘fresh eyes’.
If the report is being widely shared, you could have someone from outside your sector review the draft to make sure it's clear for external audiences.
To complete the report, leave time for proofreading and editing, checking references, and design and print if needed.
You might include your data collection tools in appendices – this could help other organisations working in your field to improve their evaluation.
Once you’ve completed your report, read our guidance on using your findings to improve your work .

Need information and guidance? We're here to help.
Contact our small charity helpdesk
Share this page
Tell a colleague
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
Last reviewed: 18 September 2023
Analysis and reporting
- Analysing quantitative data for evaluation
- Analysing qualitative data for evaluation
This page was last reviewed for accuracy on 18 September 2023
Reporting and data visualisation
Take a look at this example of reporting and data visualisation
Our evaluation training
See what training courses we have to support you in your evaluation work
Impact round-up: March 2024
Our latest impact and evaluation support, guidance and training
- Impact and evaluation
Impact round-up: December 2023
The latest resources, events and training to help your organisation with its impact and evaluation
Impact round-up: Summer 2023
Senior consultant, Sandy Chidley, runs through some recent work on ethical evaluation and shares useful evaluation events and training opportunities
Impact round-up: Spring 2023
Evaluation consultant Lucy Lernelius takes a deep dive into measuring the impact of volunteering
Key findings from Time Well Spent 2023
New data reveals how much volunteering has transformed over recent years
- Involving volunteers
Insights and reflections
Sign up for emails
Get regular updates on NCVO's help, support and services
tools4dev Practical tools for international development

How to Write a Monitoring and Evaluation Report
Good impact stories require excellent reporting. Having the right mix of quantitative evidence, well visualized and applied; positioning your case-studies, and providing the relevant theoretical background are all part of telling a good impact story.
Start your report when you are designing the M&E framework. As implementation progresses, core things about the way teams understand their work changes too, and capturing these changes is key, particularly in contexts of complex or developmental evaluation. Being clear about precisely how the problem statement was defined, and having a clear and finalized logical framework for how the work initially set about to address this problem as close as possible to the start of the implementation is key for good M&E.
There are a few important aspects to think about as you compile your report:
Present the M&E system clearly at the start of the report. Include a diagram of your theoretical framework, as well as your more specific logical framework. The first should be stated more in the language and results and change, and should include concepts which are linked to and justified by empirical studies which form the basis of your programme rationale. You may draw from international studies, or your own past evaluations, but providing this clear background, not just for the change you hope to see, but why the programme was designed in this way is key for framing the project intention. The second; the Logical Framework should be depicted in the language of indicators, and the direction and quantity of the change you are hoping to measure.
Be sure to outline and describe the context: the beneficiary groups, and the circumstances of their lives. This is a section of the report where the problem statement and the programme rationale align, and it is also the point where you define the very heart of the change, whether you’re providing skills, information to change to mindsets, or whether you’re distributing resources. This is where you define any ongoing measures such as assessments and how this is relevant from the perspective of the beneficiaries, stated in the language of change.
Include a very clear description of the activities of the project. Although there is not space in an impact report to explore the full workings of a project, stating programme activities as the catalyst for change is extremely important. What activities are being undertaken, and why these are expected to create change is key.
Once you have clearly stated the intention of the project, as well as the intention and design of the system for measuring the project’s work, then it is a good idea to clearly state and describe the methods used in the M&E function, and to justify the chosen method. If you are taking a rigorous quantitative approach, for example in public health projects where change can be clearly measured; or if you are working in a complex social space, and have chosen to use a developmental or other realistic evaluation approach; the rest of the report will depend on the method you have chosen. Some methods, such as Social Return on Investment impact analyses include clear guides on how to report; while more qualitative, research oriented studies might be far less quantitatively analytical, but explanatory.
Whichever course your particular work might take, honesty and clarity are key. It is far more useful to reveal a missed milestone, or a goal not achieved (and why) than not to write about it. With the scope and extent of the problems which the communities of the world aim to remedy, there are only more lessons to learn. Including a section on ‘what didn’t work’ shows not only that the M&E has been effective, but also indicates that the organization is reflective and critical. For any project aiming to make serious change, this is the first step to ongoing improvement.
The bulk of the report should focus on the presentation of findings: the achievement of outputs and outcomes, and the project impact. The form this takes will depend largely on the type of work you are doing, and the adopted M&E methodology.
In summary, your report may take the following format:
Introduction
A strong introduction is key. Be sure to state the overall length of time of the project, and the reach, or total beneficiary information.
Background and Context
Include a problem statement as well as the theoretical background, or literature review.
Programme Overview
In this section, describe the programme – the overall vision (or results), the beneficiaries and the programme activities designed to create the change
Programme M&E
In this section, you will bring together the contextual, and the programme design into a visual representation of the overall theoretical framework. Then, include the log frame, and a section on methodology.
Analysis of Outcomes & Impacts
In this section, you may explore the outputs and outcomes against the log frame as you have presented it. This may include graphical visualization of quantitative indicators, or case studies for more observation based, or qualitative change. Include a section on the overall impact, returning to and referencing the programme information outlined in the report, but more importantly defining convergence, challenges and lessons learnt.
Finally, once you have completed your report, take some time on an executive summary. Not only will having this ensure that high-level stakeholders can get the salient information in a short amount of time, but this will also provide the space to be more exploratory in the main body of reporting. If you can summarize your outcomes and impact findings into an infographic, this can also be useful for your communications and fundraising strategies. Be prepared that a good impact report can take months, and to truly capture the complexity of change, M&E teams should take note throughout programme implementation. Unlike an independent, external evaluation, and Impact Report can really be an opportunity to explore and explain the full length and breadth of change as you conduct your work. Whether entirely quantitative, and working within a relatively closed system, or as a record of the iterative growth and learning of your organization as it strives to have an impact, an Impact Report is your biography, your testament.
About Angela Biden
Related Articles

Apply now: Master of Science in Engineering, Sustainability and Health
15 May 2024

Top 10 Websites to find Monitoring and Evaluation Jobs
12 August 2023

Monitoring and Evaluation Tools for NGOs
6 August 2023
How to write a good monitoring and evaluation report - guidelines and best practices
July 27, 2021.
Reporting is an integral part of any monitoring and evaluation plan or framework. Good reporting enables organisations to communicate the value of their work and their impact while allowing them to demonstrate aid effectiveness and enhance performance, collaboration, learning and adaptation within their organisation and throughout the entire project cycle.
In this article, we will explain what monitoring and evaluation reporting is, how it’s done and how your organisation can benefit from periodic reporting. Plus, stay with us as we walk you through some of the best practices of M&E reporting – M&E report formats and frequency, what to include in your M&E report and some top guidelines from experts to help you streamline your reporting process and write reports that are credible and constructive.
What is monitoring and evaluation (M&E) reporting and how is it done?
Reporting is the documentation and communication of M&E results to appropriate audiences at specified times. The key purpose of reporting may be to account for funds expended, to provide rich data for the decision-making process or to improve targeting and coordination of investments and on-ground actions. Reporting can be done at a project or program level. Most M&E reports include financial summary of a project as well as updates on its progress and achievements, activities undertaken, inputs supplied, money disbursed, key findings, results, impacts, plus, conclusions and recommendations from the interventions that have been compiled from various monitoring and evaluation activities and data sources.
The goal of reporting is to present these collected and analyzed data as information or evidence to key stakeholders and investors to utilize and to increase their confidence in the project and the implementing team.

Benefits of periodic monitoring and evaluation (M&E) reporting
Periodic reporting on M&E data helps internal staff and management teams to assess and communicate their transparency and accountability to their stakeholders, partners, funders, beneficiaries and others. It enables them to identify and interpret the progress their interventions have made against their set targets and indicators and its impact in the community of interest and its people.
M&E reports also help the team to test the effectiveness of their underlying assumptions, project activities, design, strategy and suggest ways for future adaptation and improvements. Moreover, M&E reports allow the team to identify and share challenges they have encountered, unexpected changes that have emerged in the process, along with underlying reasons for under-performance or shortcomings of existing management and monitoring systems and their proposed recommendations and action plans for improvements of subsequent work plans and sustainability of their results.
M&E reports help the stakeholders, partners, donors and others involved in the project to grasp a clear picture of the performance of the project and its real impact on the ground, helping them make evidence-based decisions to improve the current intervention and design better projects in the future. These reports also help the higher-up management teams to make adjustments to their internal operations and make recommendations for the state or country level policy amendments. Moreover, the evidence from such reports also help the donors to direct aid and funding to where it’s needed most – to address the most critical issues and help the most vulnerable communities in need.
Monitoring and Evaluation (M&E) reports - frequency and formats
Each organisation is different and so are its projects, hence every organisation has its own unique reporting system. M&E reports can be produced and distributed on a weekly, bi-weekly, monthly, quarterly, bi-annually or on an annual basis. Weekly and bi-weekly reports are usually concise and shared with the internal team and some external stakeholders to keep them up to date on the project progress against their targets, budget, any changes made to the project or the implementing team etc. However, monthly, quarterly bi-annual or annual reports are much more comprehensive and include more details and evidence on the progress of the intervention, project inputs, activities, outputs, outcomes, lessons learned, recommendations etc. These are shared with a wider audience, including partners, donors and other stakeholders.
Many organisations report on their M&E data in a traditional narrative format in the form of paper reports. However, with the emergence of digital technology and approaches, many others are adopting new and innovative mediums to report, such as videos, recorded audio, interactive media, mapping, data visualization, interactive dashboards, online presentations and more. How often and in which format reports are produced and distributed depends on the organisation and its reporting system. The frequency and format also depend on the nature of the project, its M&E plan and log frames, the resources available, the requirements of the donors and the audience of the report – how and by whom reporting data will be utilized etc.
Note that many organisations report on their monitoring and evaluation activities together, however, there are exceptions. In some organisations, monitoring and evaluation reporting is done separately. Monitoring is done by implementing staff members and it’s undertaken more frequently than evaluation. Evaluation on the other hand could be undertaken by internal staff or external consultants.
See how TolaData’s configurable dashboards can add value to your organisation’s reporting processes.
Some key points to keep in mind before writing your M&E report
- Have you identified indicators for each project activity? Indicators must be relevant and easy to track, measure and report. Here’s how to create indicators that make sense.
- Have you identified key monitoring and evaluation questions and determined what data will need to be collected and which tools and methods will be used to collect them?
- How will you collect, consolidate and analyse your data and distil insights from it? Here’s how you can integrate data from multiple sources and tools.
- How will you compile and consolidate the findings and results and include them in your report?
- How frequently will you send out your report and in what format?
- Be mindful of the audience and timing of your report. M&E reports are effective only when they are submitted to the right people at the right time and facilitates corrective decision making.
What goes into an M&E report?
Please note that this list includes some common elements included in an M&E report. As mentioned above, every organisation and every project is different and so is their reporting system. Therefore, you will have to adjust this list according to the nature of your project, the requirements of your donors and stakeholders and the audience of your report.

This list has been adapted from the Evaluation Report Checklist by USAID .
Guidelines for writing credible and constructive monitoring and evaluation (M&E) reports.
The following guidelines have been adapted from the document – Monitoring and Evaluation Guidelines from the UN World Food Programme.
- To help ensure efficiency, the purpose of reporting should be clearly defined. Be sure to include a section in the introduction describing the need to produce this report and its anticipated use.
- Make sure the i nformation you are providing is accurate, complete, reliable, timely, relevant and easy to understand.
- Be clear who your audience is and ensure that the information is meaningful and useful to them. If needed, tailor the content, format and timing of the report to suit the audiences’ needs. Information is of little value if it is too late or infrequent for its intended purpose.
- Consistency is key. Reporting should adopt units and formats that allow comparison over time, enabling progress to be tracked against indicators, targets and other agreed-upon milestones.
- Make sure your report is concise and the layout clean and consistent.
- Focus on results and accomplishments and link the use of resources allocated to their delivery and use.
- Be sure to include a section describing the data sources and data collection methods used so that your findings are objectively verifiable.
- Write in plain language that can be understood by the target audience. Avoid complex jargons and details if possible and be consistent in your use of terminology, definitions and descriptions of partners, activities and places. Be sure to define any technical terms or acronyms in the annex section.
- Make use of graphs and charts to communicate your findings. Present complex data with the help of figures, summary tables, maps, photographs, and graphs that are easier to understand.
- Include references for sources and authorities.
- Include a table of contents for reports over 5 pages in length.
- Make sure your reporting system is cost effective. Avoid excessive, unnecessary reporting. Information overload is costly and can burden information flow and the potential of using other more relevant information.
- Be open to feedback. Make sure to include an email address, a physical address or a telephone number for the recipients to send their feedback on the report.
As we can see, there are many benefits of good and timely reporting and it should be a part of every development project and its monitoring and evaluation system. However, many organisations continue to report on their progress only as a part of the donor requirement, without giving much heed to the huge prospect of collaboration, learning, adaptation and improvement. Therefore, a good reporting system should have a balance of all these elements, plus quality project management and good coordination and communication flow within the team.
We hope you found our article helpful. If you have any comments or suggestions on how we can improve it, please leave a comment below.
Key References
- Monitoring and evaluation guidelines, UN World Food Programme
- Reporting, INTRAC
- Evaluation report checklist, USAID
By Chandani Lopez Peralta, Content Marketing Manager at TolaData.
22 thoughts on “How to write a good M&E report – guidelines & best practices”
Thank you very much for the useful information
Our pleasure, Hassani. So glad to hear that you found our article helpful. Do check our Blog section for more resources on M&E — https://www.toladata.com/blog/
thank you so much just checked it out, you guys are doing a great job and now you have made my job much easier. Jackpot here!
I like the simplicity of explanations and clarity on topics. Best wishes
Thank you for your lovely comment, Benedicta!
This document is quite enriching and had greatly enhanced my reporting skills. From now henceforth my reports will be much more improved and quite concise.
Glad to be of help, Mercy! In case you are looking for more insightful resources on M&E related topics, do check out our blog section – https://www.toladata.com/blog/
Thank you very much. I have found your articles very enlightening. Do you have any on how to budget for M&E? Also is M&E reported separately from the report produced by project officers or both are merged
Thank you for your feedback, Amina! To answer your question, it depends on your donor’s reporting requirements. Some choose to report on M&E activities separately while others merge them with their project reports. We do not have a separate article on budgeting for M&E yet but we will definitely add that to our list.
Thanks a lot. I realized how M&E is important and how useful for us.
Glad to hear that, Thein Zaw!
This was helpful and enlightening Thanks
I really love this write-ups. Thank you so much.
I realized that M&E report is the best Thanks alot
When evaluating project management software, it is important to consider the compatibility of the software with your current project management process.
very helpful
Thank you so much, content is so informative
thanks its very intersting
I have an inquiry, for the report conclusion, do we need to support this section with numbers or percentages or no need!!
Thank so much for the resources it actually help a lot
thank you for your assistance it has helped me alot
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Data Collection
- Data Management
- Indicator Tracking
- Indicator Aggregation
- Custom Solutions
- IATI Reporting
- TolaData Partners
- Client Testimonials
- Help Center
- Quick Start Guide
- Knowledge Base
- Release Notes
- Case Studies
- Feature Focus
© TolaData 2024

The TolaBrief Newsletter
A monthly round-up of news and useful links on the digitisation of the sustainable development sector, from the team at TolaData

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Evaluation Report Examples With Templates and Samples

Kanica Sharma
What is the business value this product or service offers my customers? This fundamental question, on the minds of top CEOs, deserves an evaluation report. Have you ever been tasked with providing one, be it for any area of business? Why is an evaluation report even necessary, you ask?
Here’s the answer: Evaluation reports help you evaluate your company's success and prepare a report for the same on a regular basis based on pre-set goals. Evaluations not only keep you up to date on your current situation, but they also warn you of potential threats that could ambush your business.
As part of your evaluation, you will need to combine everything together in the form of a report.
Looking for more clarity? We’ve got you!
An Evaluation Report is a document that evaluates the strengths, weaknesses, results, quality, and effectiveness of a product or service using some relevant criteria and standards.
An evaluation report’s sole purpose is to provide decision-makers with information that will assist them in making informed decisions about a product, service, program, or policy. That is exactly what we at SlideTeam, strive for as well!
SlideTeam has curated a collection of Evaluation Report PPT Templates that are objective and balanced and are also based on empirical evidence. The 100% customizable nature of these templates gives you the desired flexibility to edit your presentations. The content-ready slides provide the necessary structure.
With these content-ready designs in hand, decision-makers can be informed about what is working well and what could be improved. Now is the time to develop the habit of evaluating reports and going through organizational data to decide on things.
Let’s take a tour.
Template 1: Customer Evaluation Report PPT Template
With our PPT Template, you can summarize the effectiveness of a product or service in line with the applicable procedures and standards. Also, have a general understanding of the evaluation process to help you along the way. Download now!
Download this template
Template 2: Evaluation Report Form To Review Employee Performance
An evaluation report form is a performance review tool that covers information about an employee's basic details, qualities, and comments. With our free Employee Evaluation Forms, you can collect responses to assess what your employees are doing well and where they need to improve. Use this to highlight 11 parameters on which you can rate your employees on a 4-point subjective scale of ‘Unsatisfactory to Excellent.’ Download now!
Template 3: Post-Event Evaluation Report with Detailed Description
Committing to post-event reflection and evaluation is just as important as planning. Our PPT Template enables you and your group to learn from the event and make decisions about other events that your group will host. Have every minute detail of the event ready for close scrutiny. Use this presentation template to invite recommendations as well. Get this design right away!
Template 4: Post-Business Meeting Event Evaluation Report
We all know that the end of an event means there are a lot of loose ends to tie up and things to handle that are time-consuming and tedious but important. One of the most difficult tasks is compiling and writing the post-event report. Our PPT Design simplifies this task for you, reducing it to a five-minute job. Our template will be useful because it will incorporate your valuable input to improve future events. Considering all the future possibilities, this template is a must-have. Download now!
Template 5: Agency Performance Evaluation Report
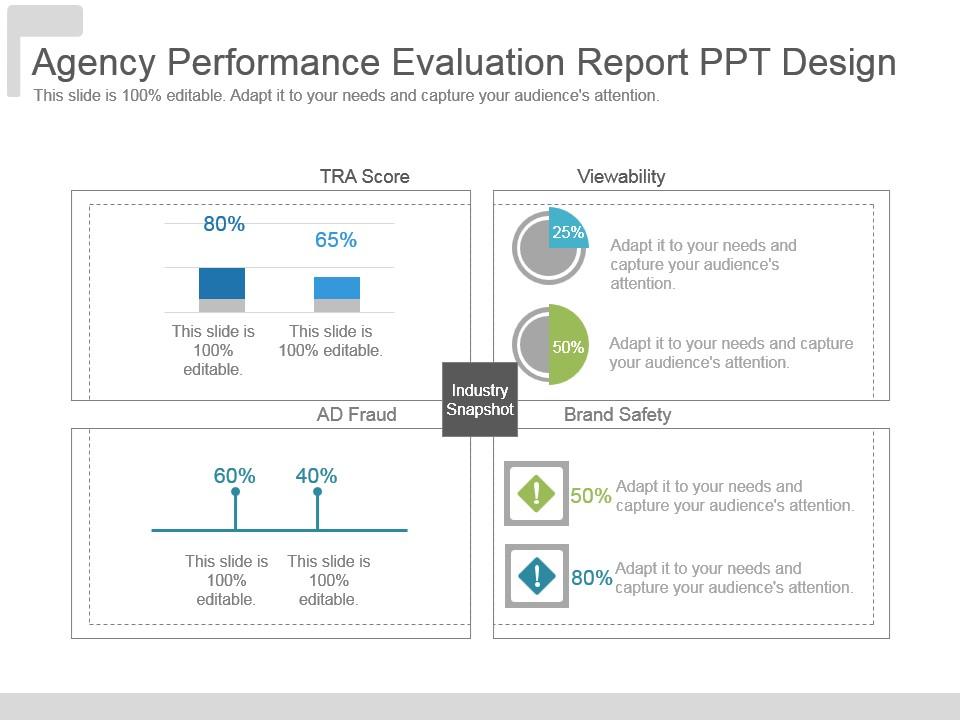
Our Agency Performance Evaluation Report PPT Template represents critical business performance measures. Keep track of the Technology Ready Assessment (TRA) score, viewability, brand, safety, and fraud for better performance. Use our design and report the evaluation of your workplace, and present it in the most professional way. Get it now!
Template 6: Project Management Plan With Evaluation Report
Managing a project with a lot of moving parts can be difficult, to say the least, but the project evaluation report is intended to make the process easier to understand. You can assist project managers in creating an evaluation report for the project management plan by incorporating our PPT Template. It also includes evaluation parameters such as scope, schedule, and budget. Download now!

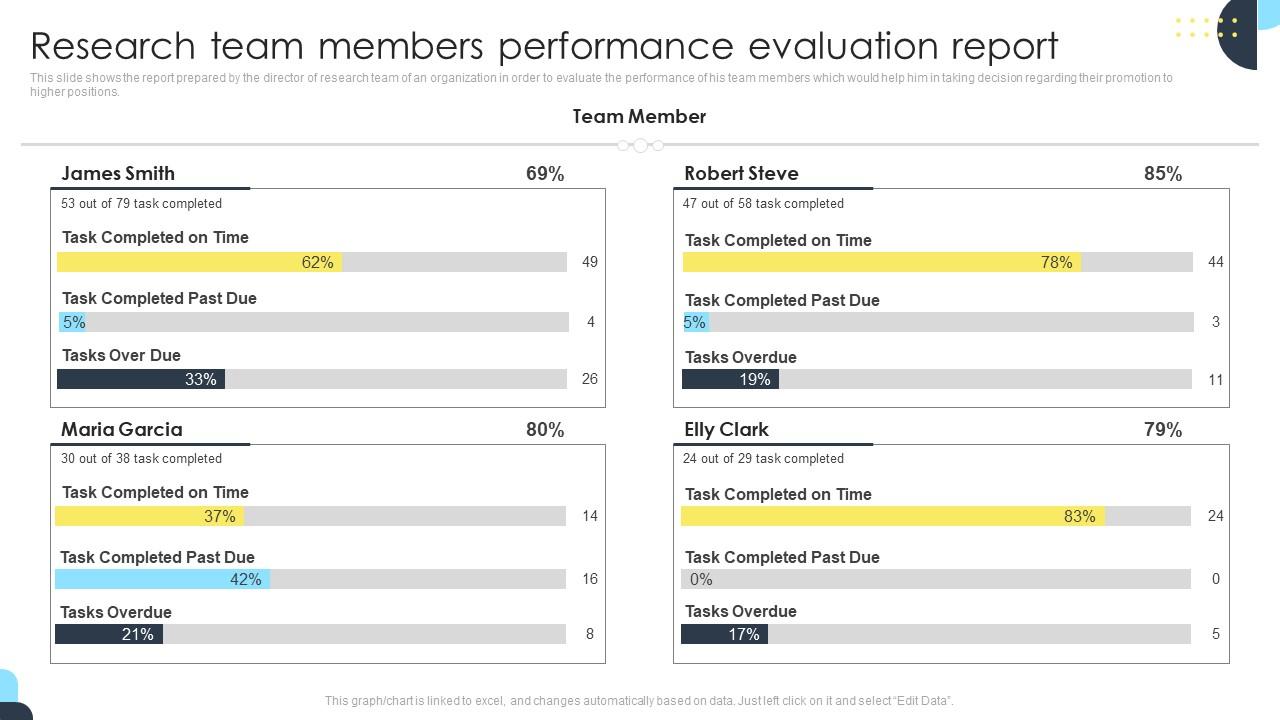
Template 7: Research Team Members Performance Evaluation Report
Employee performance must be evaluated on a regular basis. Every day worked and every assignment completed allows the supervisor to assess how well duties are carried out. Our PPT Layout assists them in making decisions about their promotion to higher positions and is intended to help the supervisor in forming these evaluations as objectively as possible. Download your design now!
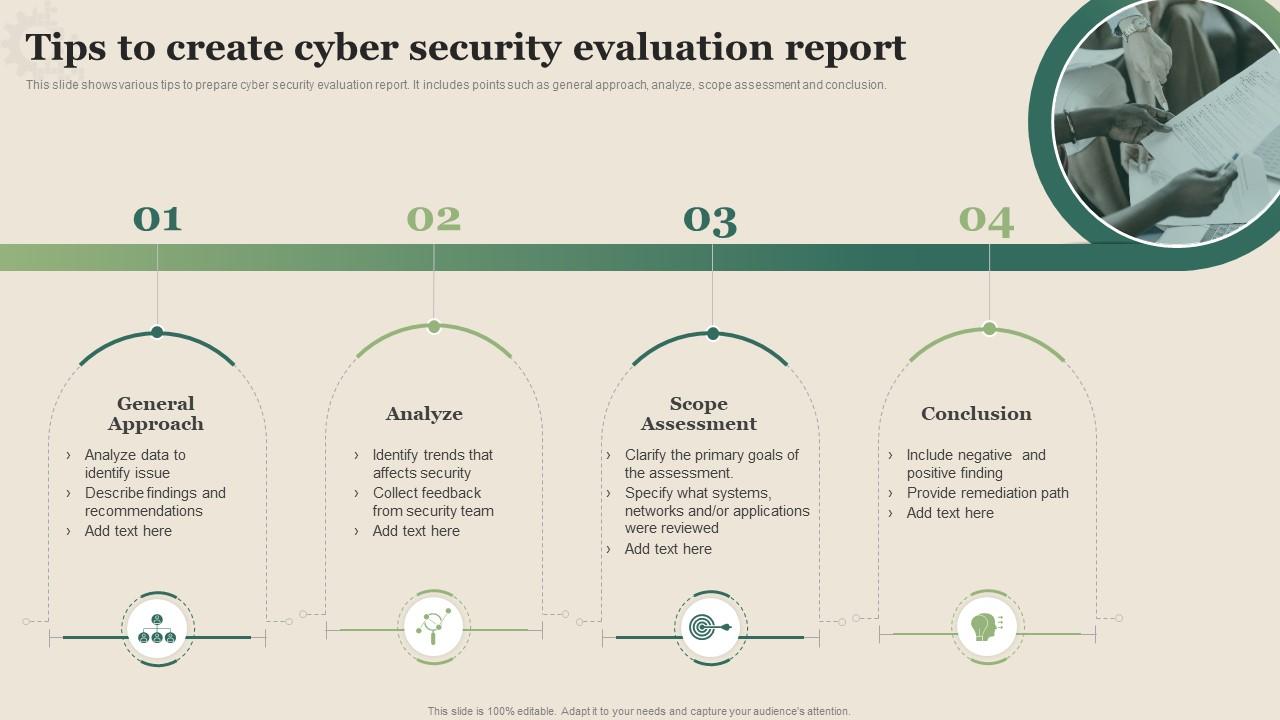
Template 8: Tips To Create Cyber Security Evaluation Report
Tackling hackers and other intruders attempting to gain access to your systems and cause disruption and loss is a constant challenge for business cybersecurity. The best way to protect yourself is to learn how to write a cyber security evaluation report. Security assessment reports, when done correctly, reduce risk and allow businesses to decide where to improve their cyber defenses. A security assessment report, in essence, contains conclusions and recommendations. It is about flaws in an IT environment. Get yours now!
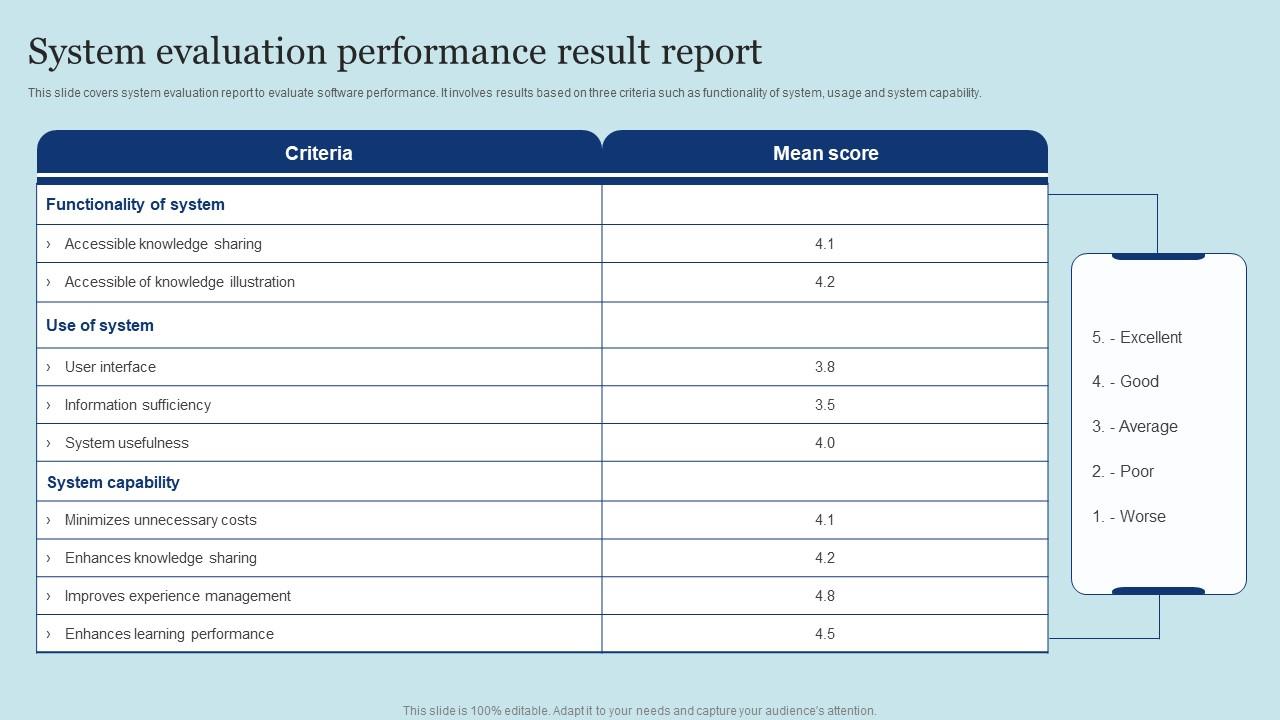
Template 9: System Evaluation Performance Result Report
Deploy our PPT Template, which examines how a specific system performs on a daily basis and chronicles what slows down performance and causes errors. . It includes outcomes based on three criteria: system functionality, usage, and system capability. Monitoring and reporting performance on a regular basis can save a lot of time and trouble. Download now!
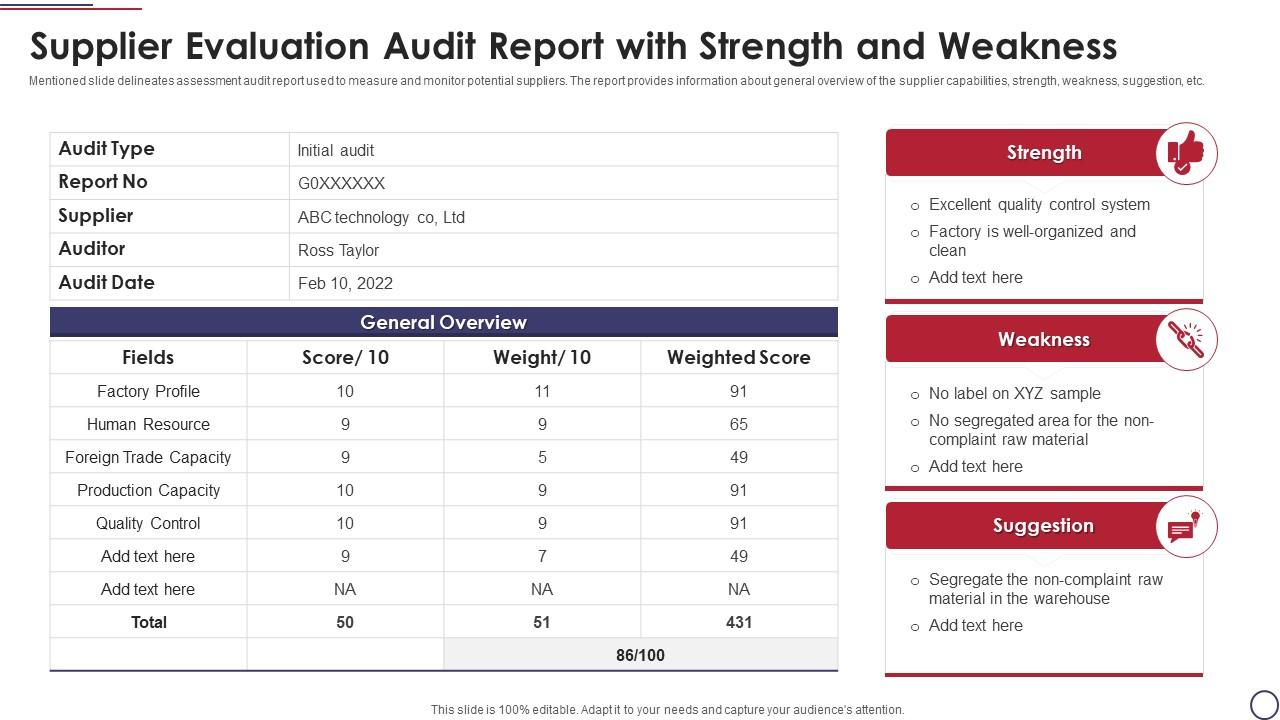
Template 10: Supplier Evaluation Audit Report With Strength And Weakness
Suppliers can have a significant impact on quality costs. Our PPT Design walks you through the assessment audit report, which is used to assess and monitor potential suppliers. The report provides an overview of the supplier's capabilities, strengths, weaknesses, suggestions, and so on. Get an in-depth analysis of supply chain performance to identify winners and losers. Download now!
Over To You!
Creating an effective evaluation report can be challenging, but with the right tools, it can be a breeze. Our PPT templates for evaluation reports are designed to help you present your data and findings in a clear and professional manner, leaving a lasting impression on your audience.
Not only do our templates save you time and effort in the creation process, but they also have been designed to increase audience retention and engagement, making your report more effective.
Don't waste any more time creating your report from scratch. Download our templates today and see the difference for yourself.
P.S.- With our content-ready templates , you can now have an exhaustive and in-depth look at different sales KPIs and map them out visually to see the trends and fluctuations.
FAQs on Evaluation Report
How do you write an evaluation report.
An evaluation report is a document that summarizes the results and findings of an evaluation project. Here are the steps on how to write an evaluation report:
Define the purpose and scope of the evaluation: Clearly state the goals and objectives of the evaluation, as well as the program being evaluated.
Describe the evaluation methods used: Include information about data collection techniques and the sample size, as well as the methods used for data analysis.
Present the findings: Summarize the results of the evaluation, including both quantitative and qualitative data, and present them in a clear and logical manner.
Interpret the findings: Discuss the implications of the findings and provide a clear explanation of what the results mean in the context of the evaluation.
Provide recommendations: Based on the findings, provide specific recommendations for improvement and/or continuation of the program or population being evaluated.
Conclude the report: Summarize the main findings and recommendations of the evaluation report.
Appendices and references: Include any additional materials that support the report, such as data tables, questionnaires, and interview transcripts, as well as any relevant references cited in the report.
Review and edit: Review the report for grammar, punctuation, and formatting errors, and make any necessary revisions.
What are the 5 Ps in evaluation procedures?
The 5 Ps in evaluation procedures are:
Purpose: Defining the overall aim of the evaluation and its specific goals and objectives.
Participants: Identifying the individuals or groups who will be involved in the evaluation.
Procedures: Outline the specific methods and techniques that will be used to collect and analyze data.
Products: Identifying what outputs will be produced as a result of the evaluation, such as a report or set of recommendations.
Performance: Monitoring and assessing the implementation of the evaluation and making adjustments as needed.
These five elements are the key components of a comprehensive evaluation plan that should be taken into account during the evaluation process.
What are the three parts of evaluation?
There are three main parts of an evaluation: planning, implementation, and dissemination.
Planning: Establishing clear goals, determining methods, and developing a plan for data collection and analysis.
Implementation: Conducting the evaluation using systematic and rigorous methods, following the plan.
Dissemination: Sharing the results with stakeholders and creating a report, making recommendations for action.
Related posts:
- Top 30 Digital Marketing Templates to Track your Campaigns
- Maximize your ROI with these Top 25 Marketing Deck PowerPoint Templates
- [Updated 2023] 50 Best Company Presentation Templates To Ace The Corporate Ladder
- Top 25 Food & Agriculture PowerPoint Templates to Create Delicious Looking Presentations
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Analytics Report Templates with Samples and Examples

Top 5 Call Report Templates To Optimize Your Sales Calling Process!

Project Conclusion Report: 6 Project Report Templates To Get Started

Create the Perfect Annual Report Presentation with Annual Report Template
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format


How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
53 performance review examples to boost growth

Jump to section
The importance of performance reviews
53 performance review examples, 3 tips for delivering a performance review to an underperformer, a performance review is an opportunity to foster growth.
Even the most well-intentioned criticism can be hard to hear.
If you need to give feedback to a peer or employee, you might feel nervous. After all, you can probably empathize — most of us have been in their position. You want the person to know where they excel and how to improve, but you don’t want to come off as harsh or lose your authority. It’s a delicate balance.
When sharing professional feedback, you need to achieve that perfect equilibrium to motivate your team to continue doing their best work. Perfect your delivery by studying these 53 performance review examples.
A performance review -– also known as a performance appraisal — evaluates how well an employee is tracking toward goals and upholding the company vision and values . This formal assessment documents strengths and weaknesses , expectations for improvement , and other relevant employee feedback , like kudos for a standout performance.
Performance reviews are essential because they provide managers (or employees assessing their peers) with a set time and structure for delivering in-depth, example-driven feedback. It’s also an opportunity for the reviewer to set metrics-based expectations so the reviewee knows how to improve for next time.
Plus, performance reviews are an excellent opportunity to open lines of communication between peers or a manager and their direct reports. Both sides can clarify questions or concerns about performance, and the reviewer may use this time to motivate the reviewee. These types of workplace conversations build more trusting, engaged, and caring professional relationships.
Unfortunately, typical performance reviews only inspire 14% of employees . In other words, reviewers need to step up their own performance if they want to make an impression during these meetings.
Effective performance reviews are level-headed and honest. They aren’t excuses to scold an employee for a mistake or poor performance . They make time to offer constructive criticism, praise what the team member is doing well, and provide suggested areas for improvement.
To keep the conversation as productive as possible, study our list of performance evaluation examples that provide focused feedback and maintain an upbeat, inspiring tone that doesn’t undermine the seriousness of the commentary.
Here are 53 employee evaluation examples for various scenarios.
Communication
Good workplace communication helps teams clearly express ideas and work through problems effectively. Respectful communication also fosters healthy social relationships between peers, which are essential for a positive work culture.
When you assess a colleague on this interpersonal skill , focus on the politeness of their interactions, the coherence of how they present information, and their ability to listen to others actively .
Use performance evaluation comments like the following when a colleague has done an exceptional job of clearly and respectfully communicating:
1. “I’ve noticed how clearly you communicate complex concepts to clients. I really admire this ability.”
2. “You’re excellent at solving conflicts . Thank you for taking on this responsibility.”
3. “Several of your teammates have told me how pleasant it is to work with you. Thank you for being such a respectful communicator.”
4. “I’ve been observing your standout negotiation skills and will continue to look for opportunities for you to use them.”
5. “I’d like to congratulate you on your clear and easy-to-follow presentations. Would you consider giving a workshop for your teammates?”
Improvement suggestions
Poor communication leads to confusion and fraught interactions. Plus, muddled instructions or explanations can cause project errors, and negative delivery can harm team and stakeholder relationships . It’s important for each team member to have this skill.
Here’s how to cite communication that needs improving:
6. “I’ve noticed that you sometimes miss part of an explanation. I have helpful materials on active listening I recommend taking a look at.”
7. “Clients have noted that your explanations are difficult to understand. You have a strong grasp of complex concepts, but let’s work together on ways to break them down for an unfamiliar audience.”
8. “I’d appreciate it if you could communicate when there’s an issue on a project or you have a question. I’ve seen delays and errors due to a lack of updates.”
9. “Some of your emails to clients have had spelling and grammar errors. Could you make an extra effort to check your work so that we keep our company communication as polished as possible?”
10. “Your teammates have cited rude interactions with you. We must keep communication respectful. Is something going on that’s causing you frustration or prompting these interactions?”
Innovation and creativity
Innovative solutions and creativity allow organizations to generate new products and services, build a more resonant brand image, and connect successfully with their target audience. When giving a performance review, provide positive feedback on how the person contributes to the team or company’s growth.
Teammates who offer fresh ideas for projects or ways to improve company processes to boost efficiency deserve a proverbial pat on the back. Here are five performance appraisal examples that show how to give it:
11. “Last quarter, you saved our team 50 hours of administrative work with your solution for streamlining databases. Thank you for this invaluable idea.”
12. “The marketing campaign you created to target younger audiences has been one of our most successful. Everyone on our team has something to learn from you.”
13. “You’ve been integral to launching one of the most innovative apps on the market. You should be proud of yourself. You’re helping a lot of end users.”
14. “I admire the way you creatively approach complex problems . You resolved a tricky supply chain issue that kept our deliveries on track.”
15. “You deeply understand the brand image and voice. All of your marketing copy and designs represent us well.”

Improvement suggestions
Team members in creativity- and innovation-driven roles may stagnate. Your organization might have a performance review template you can follow to zero on in how to improve in these areas. You can also use the following feedback pieces to push them in the right direction:
16. "You’re one of our most valued graphic designers. However, I’ve noticed that your recent designs have been similar. Let’s talk about ways to innovate.”
17. “Since you’re in a leadership role, I would like it if you took more initiative to offer creative solutions to problems . I have some reading to guide you.”
18. “I’ve noticed that your copy lacks that fresh voice we admire. Have you also tracked this change, and what solutions do you have to liven up the writing?”
19. “You’ve offered some of the most innovative development ideas our company’s seen. But you’ve been quiet in brainstorming sessions lately. Let’s talk about what may be going on.”
20. “Your latest product innovation had flaws resulting from rushed work and a lack of attention to detail. Does that resonate?”
Everyone can be a leader — regardless of their rank at an organization. Team members set examples for their peers, and managers guide reports toward success. Whether you’re giving a performance review for a veteran or an entry-level employee, address their leadership skills where you can.
When an employee exceeds expectations by mentoring others, taking charge of problems, and upholding organizational values , recognize their outstanding work with phrases like the following:
21. “Your positive attitude , willingness to take on more responsibility, and ability to explain concepts to your peers makes you an example to all.”
22. “I appreciate your advances in developing better leadership skills, like clear communication and excellent negotiation tactics. Kudos.”
23. “I know you started here recently, but many people already look up to you. You take initiative, aren’t afraid to share ideas, and treat your peers respectfully.”
24. “Since you’ve become a project manager, the development team consistently delivers quality outputs on time. You’re doing a great job guiding the group.”
25. “When there was a conflict with a client last month, you stepped in to manage it. You have the makings of a great leader.”
If an employee like a project manager or team lead isn’t mentoring others as well as they could, a performance review is the perfect moment to tackle the issue. And if you have a stellar employee who isn’t showing the leadership and initiative required to earn them a promotion, they might need some encouragement to strengthen these skills. Use the following examples as a guide for wording your feedback:
26. “You’ve consistently been an excellent leader, but teammates have reported a lack of mentorship on recent projects, leading to confusion and poor results. What can we do to improve the clarity of your communication and guidance?”
27. “I’ve noticed that you’re stepping back from public speaking opportunities. You’re a strong leader already, but giving talks is an inevitable part of your role. Here’s information on a speaking course I took that could help.”
28. “Some of your teammates have said you’re difficult to approach with a problem. Let’s work to improve your communication skills to make others comfortable asking you for help.”
29. “Your communication and mentorship skills are unmatched, but you still have to improve your time management skills. Several projects have run late, impacting client deliveries.”
30. “You form excellent social relationships with your team, but you may be getting too close. I’m concerned you could lose your authority if you continue to act more like a peer than a mentor.”
Collaboration and teamwork
Teams must work well together — it’s synergy that allows them to accomplish more than they’d be able to alone. Collaboration drives better organizational results and fosters a communicative, innovative work environment. Here’s how to tackle this topic in a performance appraisal.
Certain team members go above and beyond to help peers, manage conflicts, and share their knowledge. Reward them with statements like the following:
31. “You’re an excellent resource for new team members. Thank you for being willing to share what you know.”
32. “Your ability to adapt when obstacles arise and encourage your teammates to do the same has saved us from late deliveries several times. Congratulations, and thank you.”
33. “You didn’t have to navigate that conflict between your peers last week, but you stepped up. I think everyone in your group learned something from you that day.”
34. “I know you’d like to be doing more on projects, but I appreciate that you’re splitting the work with newer teammates so they can learn. Exciting opportunities are coming your way soon.”
35. “Your team traditionally had trouble working together. Thank you for identifying their strengths and guiding them as a leader to use them in harmony.”
Employees resisting participation in a team or creating conflicts must change behaviors to help their peers thrive. Here are a few ways to suggest improvements:
36. “I’ve noticed that you’ve been canceling team meetings and avoiding social events. Let’s talk about what’s going on.”
37. “It’s great to challenge your peers' ideas, but I’ve repeatedly observed you push contrary thoughts when the rest of the team has reached a consensus. This can hold up projects, so I’d like to ask you to be more flexible.”
38. “I know you’ve been very busy, but could you take more time to share your skills with others? There are new team members who could learn from you.”
39. “You’re sometimes quick to nix others’ ideas. Try listening to their suggestions with a more open mind to be a better team player.”
40. “You’re an involved leader, and that’s an excellent trait. But sometimes, you get too close to a project, and your guidance borders on micromanaging . I’d encourage you to try taking a step back when the team is working well together.”
Work ethic and organization
Punctuality, time management , and planning keep work flowing. In performance reviews, ensure all team members understand how their work ethics contribute to overall success.
Show your appreciation to those employees who keep administrative tasks running smoothly. Here are some examples:
41. “Thank you for changing our customer relationship management system. Now everyone can access data more easily, and it’s improved our workflow.”
42. “Your persistence in implementing the Agile project management framework has paid off. We’re delivering better, more timely products to clients.”
43. “You’re never late and sometimes even early. I appreciate your dedication to punctuality. It helps meetings run on time, and the day gets off to a strong start.”
44. “You always answer clients’ emails promptly. Thank you for your dedication to excellent customer service.”
45. “As a project manager, you do a great job resolving teammate’s blockers efficiently. This allows them to perform tasks confidently and keeps projects on track.”
Improvement suggestion
Employees who consistently arrive late or have trouble organizing tasks and following company processes negatively impact others’ ability to work well — not to mention their own. Here are constructive employee review examples for those cases:
46. “You’re often tardy to meetings, which causes your teammates and clients to wait. This can be frustrating for stakeholders. I’d like to share some tips for time management.”
47. “I’ve noticed you consistently turn in work late. I’m concerned you may have too much on your plate. Let’s assess your workload.”
48. “Client emails are falling through the cracks, making us look like we don’t care. Here’s a system I use to ensure I respond to every email quickly.”
49. “I understand the new customer relationship management system is tricky, but we need everyone to get on board. Would it be helpful if I set up an additional training session to walk you through the software?”
50. “You didn’t meet your goals this quarter, so I’m modifying them for the upcoming one. Please let me know if you need tools, skills, or support to make achieving these goals possible.”
Performance review summary examples
Wrap up your review by revisiting what the employee has done well and highlighting the improvements they should make. Here are three examples you can model your performance review summary on:
51. “You’ve improved your communication and public speaking skills this quarter, making you a stronger leader. But you can still work on your task and time management skills by implementing better organizational practices.”
52. “Your first few months at the company have been a success. You’ve learned to use our tools and processes, and your teammates enjoy working with you. Next quarter, I’d like you to take more initiative in brainstorming sessions.”
53. “You’re a long-time valued employee, and you have a unique talent as a graphic designer. Your social media campaign last quarter was top-notch, but others have been stagnant. I know you can tap into your talents and do more innovative work.”

You’re a compassionate leader and never want to hurt anyone’s feelings. But in a performance review , you may have to deliver tricky constructive criticism . You’re giving this feedback with the best intentions, but doing so might make the other person defensive. Keep the conversation productive and focus on framing improvement as a positive with these three tips:
- Start and end on a high note: Open the conversation with what the employee has done well and circle back to this point after giving criticism. This will remind the employee of their value.
- Use metrics: Don’t run a performance review on “gut feelings.” Quantifiable metrics and clear feedback allow you to identify areas of improvement. You must demonstrate specific examples and measurable figures to back up your claims. Otherwise, your criticism can seem unfounded.
- Offer suggestions: An employee may not know how to interpret feedback and translate it into action items. And they might have some concluding performance review questions about how to improve. Offer help and a professional development plan so the person feels inspired, capable, and supported in making the changes you suggest.
Many fear receiving and giving sub-optimal feedback. However, in performance reviews, colleagues inevitably highlight negative aspects of a person’s work.
But if you establish a healthy balance between recognizing an employee’s strengths and offering constructive feedback for improvement (like in our performance review examples), these sessions turn into growth opportunities. Your colleagues take on new challenges, acquire better skills, and become more understanding teammates thanks to criticism.
And guess what? The next performance review will be less nerve-wracking for everyone involved.
Lead with confidence and authenticity
Develop your leadership and strategic management skills with the help of an expert Coach.
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
What is financial coaching, and why do you need it?
How to coach your team to success: 5 key tips for managers, 7 types of employee coaching (and why you can’t afford to miss out), coaching during crisis: new betterup research shows coaching helps employees navigate change and uncertainty, how coaching drove $10m in additional sales, how professional coaching can be a force multiplier for the military, innovations in coaching: growth through connection for an evolving world of work, language analysis reveals how coaching has evolved over the last 3 years, what to get coaching on here’s what managers are saying, similar articles, 31 examples of problem solving performance review phrases, 17 positive feedback examples to develop a winning team, leverage love languages at work to improve your office culture, 10 performance review tips to drastically move the needle, how to give positive comments to your boss, 5 ways to recognize employees, how to praise someone professionally on their work (with examples), 25 performance review questions (and how to use them), 16 constructive feedback examples — and tips for how to use them, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
Post-Surgery Center for Lymphatic Drainage and Fibrosis
Photos & videos.
See all 32 photos

Services Offered
Verified by Business
Lymphatic Drainage
Virtual Consultations
You Might Also Consider

Ultra Cryo & Recovery
14.1 miles away from this business
Introducing Ultra Cryo & Recovery's newest destination for wellness in Davenport, FL! Are you tired of invasive and surgical treatments? Look no further, as our non-invasive, non-surgical wellness therapies have arrived in your… read more
in Cryotherapy, Body Contouring, Iv Hydration

Lotus Blossom Spa
Tam L. said "Oh my goodness, I just got out of this massage and I just have to write a review right away to steer as many Yelpers here as possible. Ok so I arrived around 6:30 after 2 long days at Universal Studios, I NEEDED this massage. But I…" read more
in Acupuncture, Massage Therapy, Skin Care

Aesthetic District Medspa
Our Medical Professionals specialize in you. Aesthetic District MedSpa offers premium Injectables, Botox, Fillers, Skincare, Hydrafacials, Facials, Laser hair removal, Medical Weight Loss, and more in Lake Nona, FL. Browse through… read more
in Aestheticians, Laser Hair Removal
About the Business
We are the creator of 2 USA Patented techniques to prevent and treat fibrosis after liposuction. 30 + YEARS of experience in this field. More than 700+ before and after photos on Instagram @mariansotelopaz and more than 100+ customer testimonies. Check our YouTube Channel. …
Location & Hours
Suggest an edit
Ask the Community
Ask a question
Yelp users haven’t asked any questions yet about Post-Surgery Center for Lymphatic Drainage and Fibrosis .
People also searched for
lymphatic drainage
virtual consultations
health & medical
Recommended Reviews
- 1 star rating Not good
- 2 star rating Could’ve been better
- 3 star rating OK
- 4 star rating Good
- 5 star rating Great
Select your rating
Overall rating

This is THE ONLY Fibrosis treatment I've ever gotten done that has actually WORKED. Many fibrosis places will show you only 1 or 2 before and after photos of treatment but Mariam has a plethora of happy patients that you can clearly see the difference and resolution. Her team does an excellent job setting realistic expectations based upon your case. There is no one size fits all when it comes to this treatment. She truly is an expert and professional. From entering the facility to leaving it's always the best customer service and experience. I can't thank her and her team enough for truly changing my life for the better.
After a week of having my lipo 360 done, I reached to Marian's hands and it was the best thing that happened to me. I was very traumatized with the previous massages and with Marian it was completely different. She is very professional. I felt very confident from the beginning. Thank you Marian for helping me.
I went to this place with my wife after her lipo surgery, we got the therapeutic plan of 10 sessions. They sell this treatment to prevent fibrosis. Let me just start off by telling everybody this nothing but the best limphatic drainage treatment, not only because my wife feels very happy with the results but also because she was treated like family. Marian did a video conference with my wife and right immediately she realized my wife was the perfect candidate for the treatment to obtain great results. Dont go and waste your time and hard earned money anywhere else, this is the place.
This woman is a fraud ! She takes your money for a virtual appointment and then says you are not a candidate. She is working off the notion that your body gets swollen as she works on it from her aggressive techniques. When the swelling goes away the fibrosis would clearly still be there. If you are a medical professional she will just take ur money and will fail to provide u any valid verifiable evidence that what she does works!
2 other reviews that are not currently recommended

Rejuvenate Wellness Center
4.4 miles away from this business
Rejuvenate Wellness Center specializes in personalized IV infusions, delivering a broad spectrum of health benefits tailored to individual needs. Our certified medical professionals provide treatments that optimize cellular repair,… read more
in Weight Loss Centers, Iv Hydration, Body Contouring

Panda Spa & Massage
5.2 miles away from this business
✨Couples free $10 🌟 Experience ultimate relaxation at our newly opened massage shop! 🌟 Indulge in the soothing touch of our expert therapists with a range of massage options to suit your needs. Whether you're craving a full-body… read more
in Massage Therapy, Massage, Reflexology
People Also Viewed

Massage by M.E

Dragon Phoenix Acupuncture

Michele Rodriguez, LMT, MLD/C - E.N.J Massage

Joan LMT Massage Therapy

Michelle Boone Aesthetics

FIRM Cosmetic and Wellness Center

Beautiful Orlando Medical Spa & Cosmetic Surgery

Enlighten Skin & Body Medspa

Orlando Resorts Spine And Body

Lisa Hartman Massage Therapy
Browse Nearby
Things to Do
Other Places Nearby
Find more Body Contouring near Post-Surgery Center for Lymphatic Drainage and Fibrosis
Find more Massage Therapy near Post-Surgery Center for Lymphatic Drainage and Fibrosis
People found Post-Surgery Center for Lymphatic Drainage and Fibrosis by searching for…
Best Fibrosis Post Surgery in Kissimmee
Service Offerings in Kissimmee

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Writing an evaluation report can be a challenging task, even for experienced evaluators. Here are some common challenges that evaluators may encounter when writing an evaluation report: Data limitations: One of the biggest challenges in writing an evaluation report is dealing with data limitations. Evaluators may find that the data they ...
Learn the key components and tips for writing an evaluation report, a document that summarizes the results, findings, and conclusions of an assessment. Find out the importance of an evaluation report and how to present it to your audience.
Name of the organization to which the report is submitted. Names and affiliations of the evaluators. Identify the chapters and major sections along with the page numbers. List of tables, graphs, and charts by page numbers. Identify those who contributed to the evaluation. A self-contained paper of 1-3 pages.
A guide from USAID that offers tips and a suggested outline for writing evaluation reports. It covers common problems, reader-friendly style, and other key sections of the report.
Learn the definition, purpose, and structure of evaluation reports. This lesson covers the six main sections of an evaluation report and the importance of evaluation reports for decision-making.
A good evaluation report contains these basic components: An executive summary containing a condensed version of the most important aspects of the evaluation (see previous point). A summary of the evaluation's focus, with a discussion of the purpose, objectives and questions used to direct the evaluation. A summary of the evaluation plan.
Learn how to write an evaluation report for your organisation or project, including choosing the right software, planning your report, describing and interpreting your data, and involving people in the reporting process. This guide from NCVO covers the key steps and tips for effective evaluation reporting.
Learn how to write effective evaluation reports with this tool and resource from Better Evaluation. Find out what elements to highlight, how to balance narrative and data, and what program managers look for in evaluation reports.
Learn how to write a clear, concise and complete evaluation report for a project of any kind. Follow the guide on report format, structure, content and methodology, with examples and templates.
These elements are to (1) collaboratively develop the report with a stakeholder workgroup; (2) write the report clearly and succinctly with its intended audience in mind; (3) interpret the data in a meaningful way; and (4) include recommendations for program improvement.
Present the M&E system clearly at the start of the report. Include a diagram of your theoretical framework, as well as your more specific logical framework. The first should be stated more in the language and results and change, and should include concepts which are linked to and justified by empirical studies which form the basis of your ...
STEPS IN THE PROCESS. 1. Define Report Requirements in the Evaluation Statement of Work and Final Work Plan. All evaluation statements of work (SOW) should clearly define requirements and expectations for the final evaluation report. All of the items in Table 1 must be included as requirements for the final report.
As part of your evaluation, you will need to pull everything together in a report. By this stage, you will have your evaluation framework in place and developed some data collection tools e.g. you may have interviewed people, observed them or surveyed them etc. The data is in and you've spent some time analysing and trying to make sense of it ...
How to write a good monitoring and evaluation report - guidelines and best practices. July 27, 2021. Reporting is an integral part of any monitoring and evaluation plan or framework. Good reporting enables organisations to communicate the value of their work and their impact while allowing them to demonstrate aid effectiveness and enhance ...
Learn how to write an evaluation report for health or wellbeing initiatives, including purpose, format, headings and questions. Find tips on data collection, analysis, discussion, conclusion and recommendations.
Template 4: Post-Business Meeting Event Evaluation Report. We all know that the end of an event means there are a lot of loose ends to tie up and things to handle that are time-consuming and tedious but important. One of the most difficult tasks is compiling and writing the post-event report.
This guide addresses the issue of ensuring that evaluation findings are used by stakeholders. It guides readers through the process of creating effective evaluation reports, focusing on the key considerations that need to be taken into account, the essential elements of reports, the importance of dissemination, and offers tools and resources to help with this task. Although created with assist ...
Evaluation reports consist of an executive summary, introduction, evaluation objectives & methods, evaluation findings, discussion and recommendations. Understanding this overall structure helps to plan headings and subheadings. The executive summary presents the key findings and recommendations in brief. The introduction provides a background ...
Make sure that you enter data into the correct box. Once you finish entering data, your analysis is ready to report. The Excel file provides you two evaluation summaries instantly. Summary of results is available in table form on sheet 2. Summary of results is available in chart form on sheet 3. When you are at this stage, your data analysis is ...
The evaluation should provide an assessment of the level of achievement of programme results. First, the evaluation should describe the programme's planned activities, outputs and outcomes. Based on these, the evaluation should assess the programme's actual achievements using sound indicators and other data sources.
The report should address all evaluation questions. It should be based on the best methods of appropriate rigor. It should be independent, objective, and unbiased in measuring and reporting. It should adequately capture the situations and experiences of both males and females.
Pade, Wright and other clinicians provide more guidance on how to take your reports to the next level. Verify that your report relies on solid data. Before the report writing even begins, make sure that the tests you will be citing in the report are backed by the latest research and were used appropriately, Wright says.
Community health practitioners and services put a lot of effort into evaluation but it seldom gets written up in a way that services and others can use. This template provides you with a framework to produce credible reports that will reflect well on your organisation. It will also help others to learn from your evaluation.
Use performance evaluation comments like the following when a colleague has done an exceptional job of clearly and respectfully communicating: 1. "I've noticed how clearly you communicate complex concepts to clients. I really admire this ability." 2. "You're excellent at solving conflicts. Thank you for taking on this responsibility ...
Company Reports and Employee Orientation If you need to present data about the company's performance or share important metrics with colleagues, a one-pager can easily convey this information. By using visuals, charts and graphs , you can present complex stats in an easy-to-understand way.
That's why getting a police report is crucial. A police report is meant to provide an objective view of the facts of an incident. Generally, a responding officer is not there to take sides. The information they record is often deemed more reliable than those personally involved. That's why a police report is a valuable piece of evidence.
6 reviews and 32 photos of POST-SURGERY CENTER FOR LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AND FIBROSIS "I felt the need to write here my first review as I truly think is necessary to outweigh the untruthful comment of Lydia G. ... Well the first impression was great and after the consultation I and a day or two after the virtual evaluation, I had a report with a ...