The Perfect Employee Evaluation Form: Templates + How-To
Download 9 handpicked employee evaluation forms ready to be used in your next performance review + find out best practices and legal considerations.
Last Updated
March 20 2024

There have been debates around employee evaluations and some say it’s time to put an end to it. But, while big companies like Adobe have abolished the traditional rating-based performance reviews, 49% of companies still conduct annual or semi-annual employee evaluation in one form or another. Moreover, the majority of employees want to keep some form of performance ratings in place as it at least allows them to understand their standings within a company.
To make sure we’re on the same page—employee evaluation is the assessment and review of a worker’s job performance. Most companies conduct performance evaluations at specific time intervals (usually once or twice a year).
Whether you choose to give and receive employee feedback via email, paper or a one-on-one conversation, you will still need to prepare employee evaluation forms. The format and content may vary greatly, depending on your particular situation and intentions.
In this article, we’ll explore the main considerations and best practices in preparing forms for performance appraisals. If you want to, you can skip directly to the employee review templates .

Why Use Employee Evaluation Forms?
- Remind workers what their managers expect in the workplace
- Provide useful feedback about job performance
- Inform employment decisions such as promotions, pay raises, and layoffs
- Understand employee strengths and weaknesses
- Plan employee training and development programs
- Set performance goals and standards
- Understand what tools employees need to achieve their job responsibilities
- Inform recognition and reward
- Identify highly proficient workers with leadership potential
What to Include in an Employee Evaluation Form?
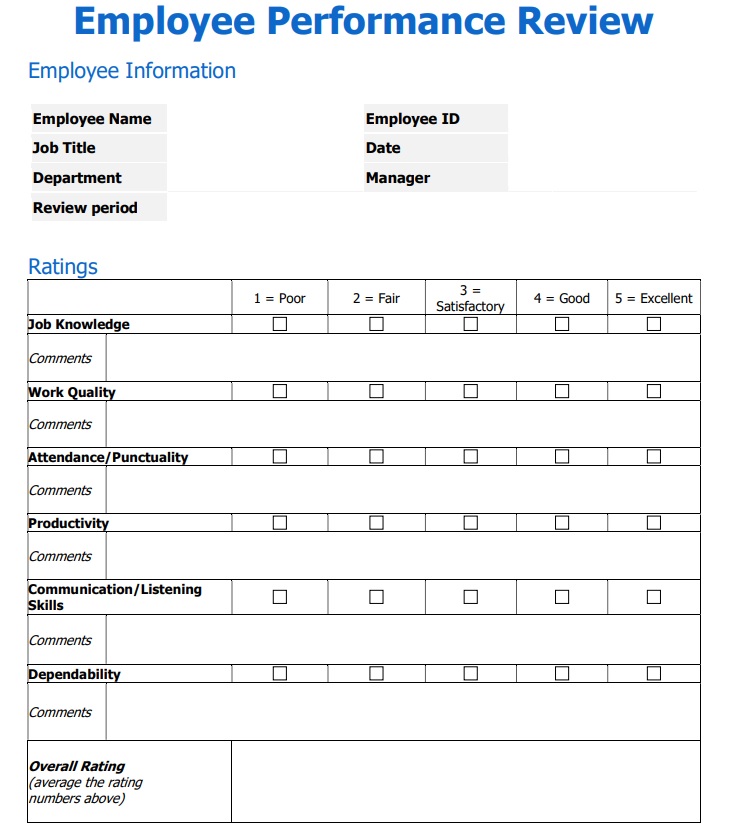
Employee and reviewer information.
The form must have basic information about both parties involved. This includes but not limited to:
- Employee Name
- Department
- Employee ID
- Position Held
- Reviewer Name
- Reviewer Title
Review period
Employee review forms should specify the review period and the date the evaluation was held. This is to determine the progress of the employee since the last time he or she has been assessed.
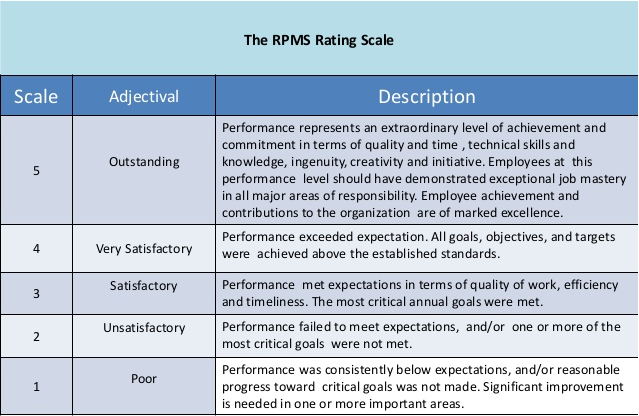
An easy-to-understand rating system
It’s important to clarify your rating system so that employees understand why they are receiving a specific grade. Commonly used performance rating systems include 1 to 10 and “unsatisfactory” to “excellent”.
Evaluation points
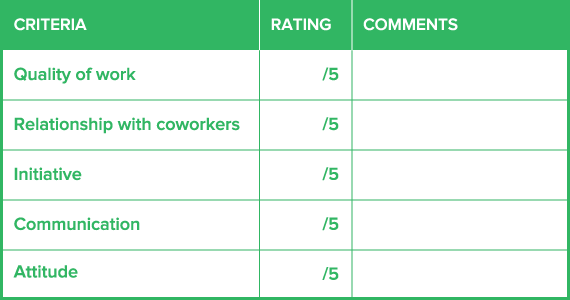
If you’re assessing specific skills or aspects of the job, you can list them in a table where they can be rated easily.
In order for performance evaluation forms to be effective, they have to inform employees of their progress and future goals. This ensures they understand the performance standards they have to meet.
Extra space for comments
Comments include additional information, allowing you to share your honest suggestions to improve performance. The comment section could also serve as a place to encourage the employee or note individual challenges and accomplishments.
Signatures
Signatures are required to ensure that both the reviewer and the employee understand the evaluation process and the contents of the evaluation form.
Best Practices For Creating Effective Employee Evaluation Forms
HBR recently reported that 65% of employees believe performance evaluations are not relevant to their jobs. The article titled “ People Don’t Want to Be Compared with Others in Performance Reviews. They Want to Be Compared with Themselves ”, goes on to say:
“ Employees perceive the fairness of evaluation processes when they feel included and respected. They also consider it fair when their evaluations are accurate and are conducted based on ethical and moral principles .”
Certainly, evaluations can easily become subjective so management has to tread lightly. Here are a few tips on how to approach your performance review process without ambiguity.
- Gather information intentionally : Get clear about the purpose(s) of your appraisal process and ensure you are gathering the right information with your staff evaluation form.
- Stay focused : Don't try to do too much in a single performance review or a single employee review form. Run several evaluation sessions if you have to.
- Customize forms for each position : List the right core and leadership competencies for the job so that, when filled out, your employee review form will reflect performance for a specific role.
- Provide clear descriptions : Describe the job responsibilities, goals and rating system in great detail.
- Choose your rating method wisely : Some roles may be better suited to numerical ratings of competencies while others may need descriptive ratings or even multi-rater feedback.
- Set S.M.A.R.T. goals : Provide specific, relevant descriptions of the goals the worker has to achieve. Define the measurements for success and the expected completion dates.
- Address development : One of the main goals of an employee performance evaluation form is to inspire personal and professional development. Allow space for identifying and establishing training goals.
- Provide detailed feedback : Make sure employees understand what they need to do to develop and improve.
- Be objective : Use specific numbers where possible and avoid subjective or ambiguous language.
There are two main formats used in employee evaluation forms.
This type of employee review form uses a quantitative approach. The appraiser lists job duties and personal characteristics, rating the employee's performance in various categories. This format has to be accompanied by comments to avoid ambiguity and make sure the rating is justified.
As we already mentioned, it’s very important to choose a consistent rating scale that is clearly explained. Both managers and employees should understand the meaning of the score.
This employee performance evaluation format contains open-ended questions that enable managers to do a qualitative appraisal. In some cases, the employee answers some of the questions which helps spark a two-way conversation.
For example, the reviewer may answer a question like, “What are the 3 areas where employee X can improve?” and the employee may answer a question like, “What are your 3 biggest accomplishments this year?”
In practice, the employee evaluation forms that most companies use are a combination of narrative and scorecard. This enables reviewers to gather both quantitative and qualitative information and understand what drives both outstanding and unsatisfactory results.
Legal considerations
Your employee evaluation forms have to be consistent and your process has to be objective because, otherwise, your employees can raise legal concerns. Here’s what to consider when designing your forms:
- Reviews can be used as evidence in court. According to Jeffrey Horton Thomas , of Thomas Employment Law Advocates in West Hollywood, Calif, reviews become key evidence if a former employee alleges that an action taken by the employer was done for an illegal reason.
- Discrimination claims. If you use two different performance appraisal forms for two different groups of employees, you leave yourself open to discrimination claims .
- Retaliation. Be careful when you downgrade an employee’s performance, especially if he or she has complained of harassment, safety violations, wage and hour issues. If you state, for example, that such an employee “is not a team player”, you risk retaliation claims.
Employee Evaluation Templates
Below are nine of the most commonly used employee evaluation forms in PDF, Word and Excel formats.
1. General Employee Performance Evaluation Template
This is a formal review of an employee’s overall performance which can be conducted monthly, quarterly, or annually. It has questions answerable by yes or no with a general comment section at the end.
2. Essay Employee Review Template
This performance review template follows the narrative format. However, the potential downside is that the essay can be biased and contain personal grudges or incidents not directly related to performance.

Word | PDF
3. Numerical Scale Form
This employee performance review template uses an ordered set of numbers where respondents get to rate a statement on a scale of 1 to 10. This detailed form can easily become your annual review template because it can gather a lot of information.
Word | PDF
4. Peer Review Form
Peer review is commonly used in academic and professional fields but it can also be applied in other areas. The premise is simple: Co-workers and managers assess the employee’s behavior and professional qualities.
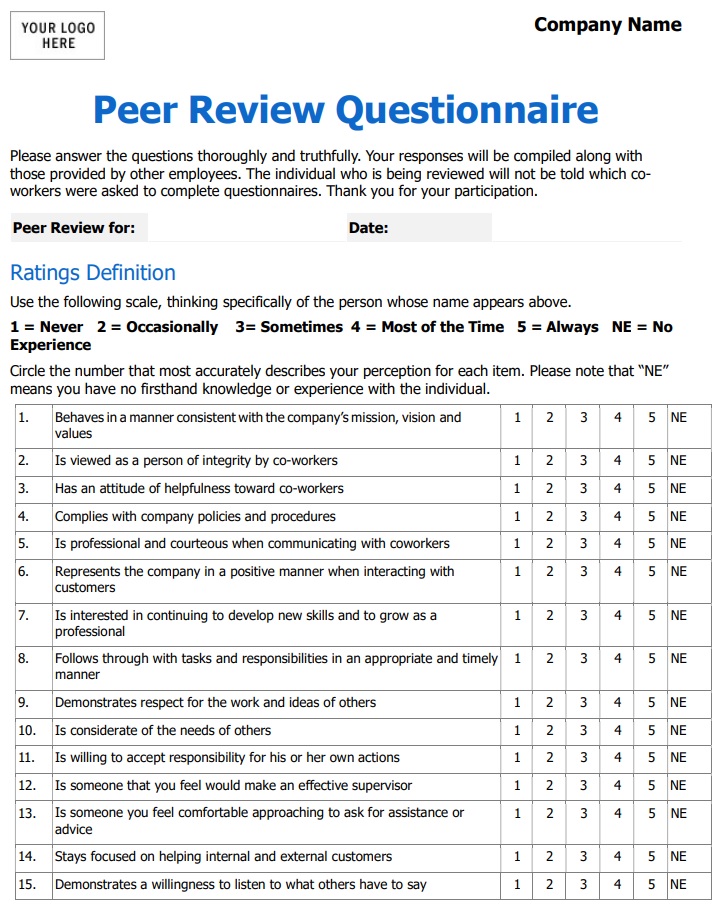
5. Group Evaluation Form
This job evaluation form can help understand team performance at scale. It uses a numerical scale to rate results, communication, adherence to deadlines and other key factors.
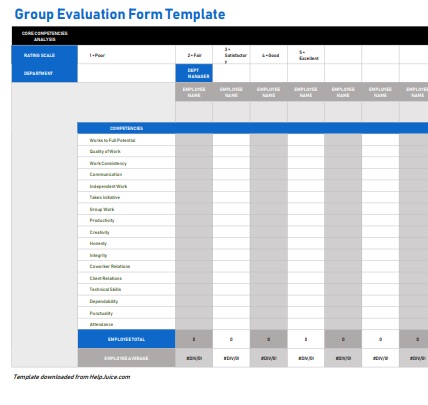
Excel | PDF
6. Employee Self-Evaluation Form
This self-assessment form is sometimes used in conjunction with an annual performance review template filled by the manager. The goal is to gain a better, unbiased overview of the employee’s abilities, actions, and quality of work.
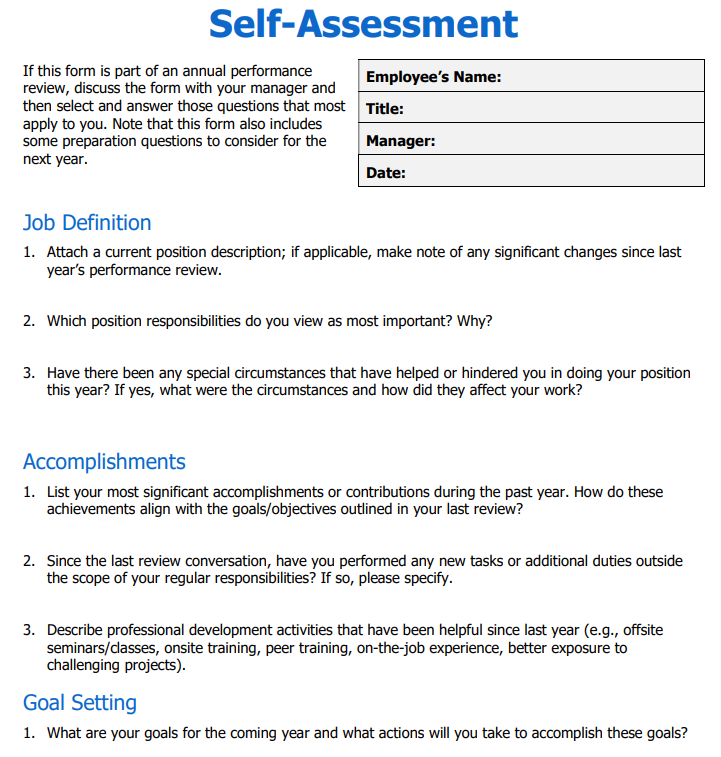
Word | PDF
7. Introductory Period Performance Review Template
After employee onboarding is complete, this evaluation template can help determine if the new hire is a good fit for his or her current position as well as the company.
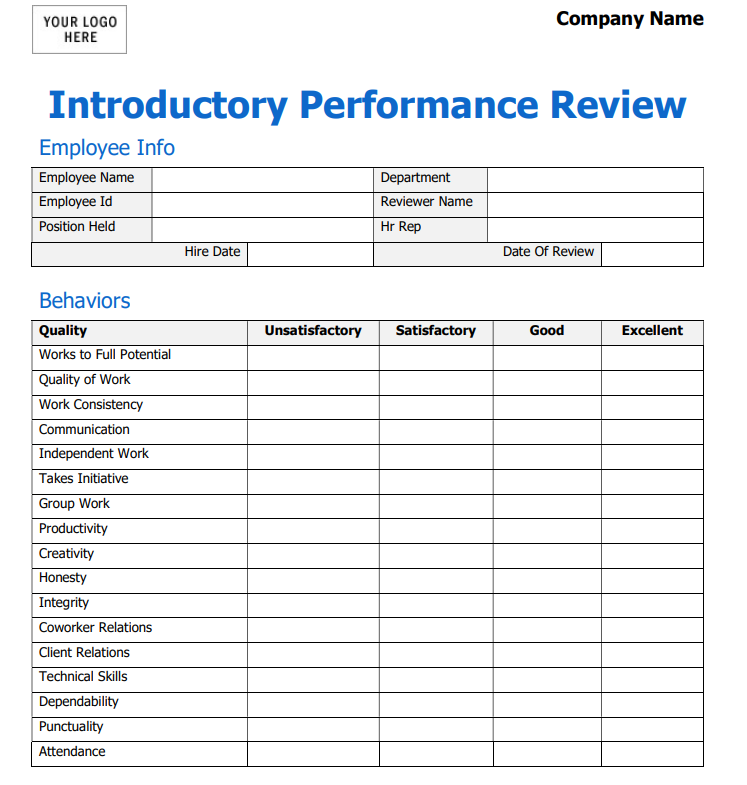
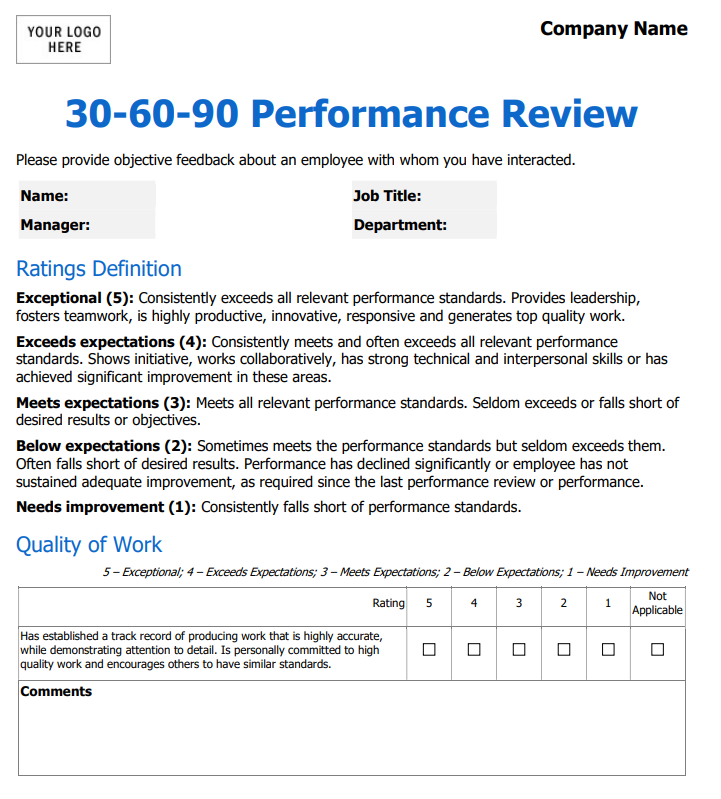
8. 30-60-90 Review Template
A 30-60-90 day template is an employee evaluation form that focuses on the employee's performance during the first 90 days of their employment. The purpose of a 30-60-90 day plan is to set clear expectations and goals for the new employee, provide them with a roadmap for success, and evaluate their progress during their first few months on the job. This evaluation form is commonly used for new hires or employees who are transitioning into a new role.
The template typically includes sections for the employee to set goals and objectives for their first 30, 60, and 90 days on the job. The employee outlines specific actions they plan to take during each phase, including tasks to complete, skills to learn, and relationships to build. The template also includes sections for the employee to reflect on their progress towards these goals and for the manager to provide feedback and guidance.
9. 360 Degree Feedback Form
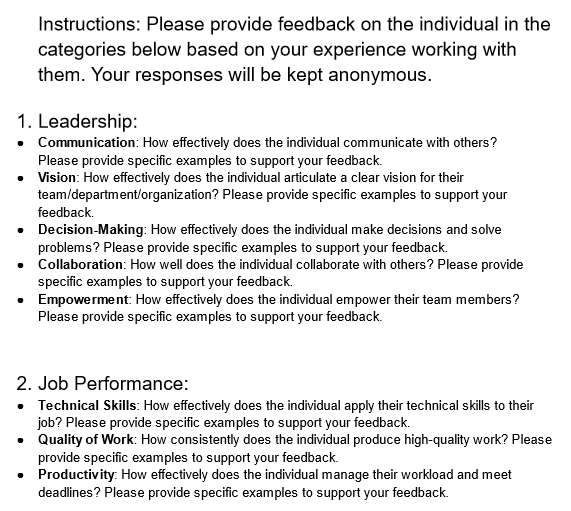
A 360-degree feedback form is an employee evaluation form that gathers feedback from a variety of sources. This feedback may include input from the employee's supervisor, peers, direct reports, and even external stakeholders such as clients or customers. The goal of a 360-degree feedback form is to provide the employee with a more complete understanding of their strengths and weaknesses, as well as areas for improvement.
The 360-degree feedback form typically includes questions about the employee's job performance, communication skills, leadership abilities, and other relevant competencies. The questions may be open-ended or use a rating scale, and respondents are typically asked to provide specific examples to support their feedback. The feedback is collected anonymously to encourage honesty and candor.
The use of a 360-degree feedback form can be a valuable tool for organizations looking to improve employee performance and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
When should an employee evaluation form be used?
Use these forms to document the results of annual or semi-annual performance reviews or at any other time when you need to rate an employee’s performance. You can utilize one form or a combination of several forms, e.g. General form + Self-assessment + Peer review.
Do employee performance evaluation forms make sense for small businesses?
Yes, small businesses also need to assess employee performance on a regular basis. If you use a predefined form or a set of forms, the process will be much easier and more predictable for you. You won’t have to come up with evaluation criteria every time.
How do you prepare employee performance reports?
It will be easier if you prepare well in advance. Here’s what you need:
- Be sure to keep an up-to-date file for each employee by documenting the feedback he or she received during the year
- Give the employee the ability to do a self-assessment
- Collaborate with HRs to improve discipline and incident reporting
- Before the appraisal, review the employee’s file
- After the appraisal, review all documents and evaluation forms to create a report
What should I write in an employee performance evaluation?
It depends on the position but, in most cases, you’ll want to cover quality and accuracy of work, communication and collaboration skills, problem-solving skills, adherence to deadlines, initiative, and reliability.
Even though employee evaluation may have a bad reputation, it’s still a must-have for organizations of all sizes. As Peter Drucker, famously said, “If you can’t measure it, you can’t improve it.” Employee evaluation forms, digital or on paper, are still the most widely used method to measure performance across all positions in your company.
To make sure your employee evaluation form is effective, focus on providing objective and honest rating. Include both numeric scales and open-ended questions to collect quantitative and qualitative data. Most importantly, make it a two-way conversation—engage employees in the evaluation and be the mentor who wants to help them improve.
More Blog Posts
Enjoyed this article? Check out our favorites

Effective Team Management Strategies to Boost Productivity
Customer Service Performance Reviews: Processes + Template
Crafting a Growth-Focused Performance Review
.jpg)
How to Create a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
Case Studies
Our Case Studies
Some of the best case studies to improve your knowledge base

From Support Tickets to Satisfaction: The Incredible Transformation at Sign ...

Discover the Secret to Obbi's 30% Decrease in Support Tickets!...

How Helpjuice Cut Article Creation Time by 8x...
Start your 14-day free trial.
Join over 1000+ companies already growing with Helpjuice.
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Inspire & Impact Collection |
- Performance evaluation template, with e ...
Performance evaluation template, with examples and tips

A performance evaluation is a formal check-in process used to evaluate team members progress. Though evaluations can be stressful, a performance evaluation template can help standardize the process. When your team member knows exactly what you’ll be discussing, they’re able to prepare and have a more productive conversation. Plus, if you pair evaluations with goal-setting, you can focus the conversation not just on current impact but also on future goals. In this article, learn how a performance evaluation template can simplify and improve the feedback process.
Performance evaluations can bring up memories of when you were a new team member in the hot seat. The anticipation before each 1:1 meeting was likely stressful if you didn't know what the format would look like or what you'd talk about. But now that you’re a manager, you can see things from a different perspective and create a more positive experience.
What is a performance evaluation?
A performance evaluation is a formal check-in process used to evaluate team members based on their past work and to give feedback for future success. Sometimes called a performance review, performance evaluations usually occur in quarterly, bi-annual, or annual cycles.
During a performance evaluation, you’ll review each team member's overall performance and break down the competencies they aim to master. You and your employee will walk through specific examples of things your team member did well and areas where they have room for improvement. Some companies use virtual performance evaluation software, but you can also go through the process without using a dedicated HR management tool.
Performance evaluations as self-assessments
Performance evaluations are an opportunity for growth. They’re a chance to have a conversation about each team member’s impact and how they can move forward in their role.
Oftentimes, performance evaluation templates will have a self-assessment component. This gives your team member a chance to drive their own career by sharing their successes and future goals. You can then start the performance evaluation conversation by asking them to share what they think they're doing well and the areas in which they think they need improvement. This can make the evaluation feel less scrutinizing and more like a dialogue.
How do you write a performance evaluation?
A performance evaluation template can help you prepare for the evaluation process by giving you a standardized format to follow. Though you should tailor this template to your team's goals, make sure your team members see the template in advance so they know what the conversation will be about. This allows them to prepare and encourages conversation on how to move forward. A collaborative approach will feel less daunting than a traditional, one-sided performance evaluation form.
![how to write evaluation form [inline illustration] 8 steps to prepare a performance evaluation template (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/9866ad88-939c-4e87-9d51-e7dc7326756a/inline-leadership-performance-evaluation-template-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
1. Identify core competencies
Although you want your performance evaluation template to meet the needs of your team members, it’s also important to standardize your template to provide a fair assessment across the board. This means considering what competencies make the most sense for your entire department.
Core competencies that can measure performance in various team roles include:
Knowledge of job skills
Quality/quantity of work
Customer service skills
Inclusiveness
In addition to these categories, you can include an area in the evaluation form for specific goal-setting and further discussion. This will allow you to get more personal with each team member when you meet with them individually.
Tip: You can add sub-competencies below each category to make your performance evaluation more detailed. For example, under the “quality/quantity of work” competency, add things like: looks for ways to improve quality; performs a full range of duties; achieves goals; and meets deadlines.
2. Choose a rating scale
Once you’ve chosen the competencies for your performance evaluation template, choose how you want to rate your team members. There are two main values of a rating scale:
Provides a shared language to discuss successes and strengths versus areas of opportunity.
Provides something to look back to and see team members career growth.
However, avoid a numerical scale if possible. That way, team members focus less on their “grade” and more on their competencies. The key to your rating scale is to make sure it’s clear to everyone.
Rating scale example:
Exceeds expectations
Often exceeds expectations
Consistently meets expectations
Needs development
Make sure you align your team with what the rating scale means. For example, two people might mentally define "consistently meets expectations" differently, so keeping everyone on the same page can set the stage for a healthy and productive evaluation conversation.
3. Set an evaluation cycle
Setting your evaluation cycle will let you and your team members know how much time you have to prepare between sessions. Common review cycles are quarterly, bi-annually, and annually, and your company may pre-determine these. But if you have a choice, you may choose based on the nature of your workplace. For example, if your work culture is hands-off, you can hold monthly performance evaluations to ensure team members get frequent feedback. If your work culture is highly collaborative, your team may not need frequent reviews.
Some review periods are better for short-term goals while others focus on long-term goals . For example, quarterly review periods provide enough time between evaluations for your team members to take past feedback into consideration and work on any goals you’ve set together. Once you’ve set your evaluation cycle, it’s important to stick to it so everyone knows what to expect moving forward.
Tip: You can also take advantage of the time you have between evaluation cycles to observe job performance in action and offer opportunities for professional development . Helping your team members meet their performance goals benefits the entire team.
4. Prepare a list of questions
Now that you’ve nailed down the basics of your performance evaluation template, you can prepare for the individual meetings you’ll have with your team members. In these meetings, you’ll want to have a list of questions to ask that can move the conversation forward. Some questions you can ask include:
What is something from this quarter that you’re proud of?
Which goals did you meet? Which goals fell short?
What are two or three things you can focus on next quarter to help you grow professionally?
To ease the pressure of the evaluation meeting, standardize these questions for all team members.
Tip: Make sure you choose questions that get team members thinking about their work progress and goals. While the rating system on the performance evaluation is useful for long-term comparisons, the conversation is where your team members can verbalize issues and feel good about their accomplishments.
5. Share questions in advance
The best thing you can do to prepare team members for a performance evaluation meeting is to let them know up front that it's happening and exactly what they can expect. Sharing the questions you’ve prepared in advance can give everyone time to think about them and process them. This reduces nerves and makes it a more collaborative and constructive conversation.
You can also share the format of the review with them so they can get an idea of how the conversation will go. For example, will you expect them to share first or will you lead?
Tip: Aside from sharing the questions with your team members, you can let them know what to expect by asking them about their accomplishments during the interim between evaluation cycles.
6. Have the conversation
Set aside dedicated time outside of your traditional meetings to have your performance evaluation meetings. Plan to meet individually with each team member for between 30 and 45 minutes. If possible, give your team members about a week’s notice so they can plan for them.
Tip: Don’t forget to ask team members for their opinions during the conversation. Aside from the standard questions about past performance and future goals, ask for feedback about your management style or the company culture . You can also ask where or if they hope to grow in the company over the long term.
7. Create a goal-setting framework
The questions you ask team members during evaluations should flow into goal-setting sessions. When you end the performance review process with a set goal, team members have a clear idea of what they need to work on between evaluations. Two goal-setting options include SMART goals and OKRs :
SMART goals:
Objective 1
Key result 1
Key result 2
Key result 3
After you give team members a framework to follow, let them be the visionaries of their goals while you facilitate.
Tip: When you take a backseat in the goal-setting process, your team members will feel more in control of their future growth. It can also make evaluations more enjoyable because they become less bureaucratic.
8. Be open to feedback
You should always ask team members about your performance as a manager so you can continue to meet their needs. Sometimes, team members won’t feel comfortable providing honest feedback in a 1:1 meeting. So if you want genuine responses, consider asking for feedback anonymously. You can:
Send an anonymous survey
Set up a physical or virtual comment box
Hold a team feedback meeting
Emphasize that you’re open to any feedback your team members have for you, whether it’s positive or constructive. You can use their feedback to become a better manager and improve your future performance evaluations.
Tip: If you’re having trouble thinking of ways to get team feedback, ask your co-workers what methods they use. Other managers may have strategies to share and ideas for evaluation templates as well. If you see areas that overlap between your departments, you can borrow ideas for your performance review form.
Performance evaluation template and example
Below, you’ll see a filled-out example of what a performance evaluation template may look like. You can offer this template as a self-assessment for team members, which should spark meaningful discussion about their work progress and future goals.
You can download a blank version of this performance evaluation template below to customize it for your company and department.
![how to write evaluation form [inline illustration] team member performance review template (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/b5e5b7aa-8db6-4609-9a80-0751b382f1b8/inline-leadership-performance-evaluation-template-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
You can download a blank version of this performance evaluation template below to customize for your company and department.
Types of employee performance review templates
The process of conducting employee performance reviews is pivotal for both employee growth and the continuous improvement of your organization. By using a variety of employee performance evaluation templates, you can ensure that these assessments are both comprehensive and effective.
Below, we'll explore different types of employee performance evaluations that help human resources departments offer constructive feedback, improve team performance, and increase employee engagement.
Simple performance review template
A simple performance review is an essential tool for any human resources professional or team leader. It's designed to streamline the evaluation process by focusing on key performance indicators (KPIs) and core competencies.
This template is particularly useful for routine assessments and is a great starting point for those new to performance evaluations. It simplifies how to do a performance review by providing a clear, concise framework for feedback.
Example: A sales associate, for example, might be evaluated on specific KPIs such as sales volume and customer satisfaction, providing clear metrics for assessment and discussion.
Self-evaluation form
The self-evaluation form , which encourages employees to engage in self-reflection, is an important part of the performance review process. This form allows individuals to assess their own performance, highlighting their achievements and identifying areas of improvement.
Example : A software developer could use the form to reflect on their completed projects, coding proficiency improvements, and teamwork contributions. This helps the team member identify their strengths and areas for further professional development.
By integrating self-assessments into your performance evaluation form, you can foster a culture of self-awareness and continuous development.
Peer review template
The peer review template fosters a collaborative review process in which employees can provide feedback on their coworkers' performance. Peer reviews complement traditional performance evaluation forms by adding depth to the understanding of an employee's impact within the team.
This form provides a thorough perspective that might not be apparent to supervisors alone and aids in understanding how peers perceive an employee's progress.
Example: For instance, a graphic designer might receive feedback from their peers on their creativity, ability to meet deadlines, and collaboration on team projects, offering a comprehensive view of their performance from those who work closely with them.
30-60-90 review template
Designed for new hires, the 30-60-90 review template sets clear milestones for the first 90 days of employment. It's a dynamic tool that helps managers and employees establish mutual performance expectations and goals, making new employee onboarding a success.
Example : Consider, a new marketing specialist who is expected to learn the company's marketing strategy in the first 30 days, contribute to a campaign by the 60th day, and lead a small project by day 90.
The 30-60-90 review focuses on the quality of work and alignment with the job description and incorporates a career development plan that includes mentoring. This ensures the new hire is effectively integrated into the team, with clear expectations for their initial months.
360-degree feedback template
The 360-degree feedback template is a comprehensive approach to performance evaluation, incorporating feedback from supervisors, peers, subordinates, and sometimes even clients.
This holistic view provides a well-rounded perspective on employee strengths and any areas that need improvement.
Example: Consider a team leader whose 360-degree feedback reveals a lower performance rating in communication skills compared to other areas. Based on this feedback, the leader is placed on a performance improvement plan specifically designed to enhance their communication skills. The plan includes targeted workshops, mentoring sessions with a communication coach, and regular feedback sessions to monitor progress. This approach ensures that the leader receives the support needed to develop their abilities and positively impact their team's performance.
One-on-one meetings
Performance evaluation templates can be helpful for jotting down notes during face-to-face meetings, but with many teams moving to remote work , online software is more useful than ever. Virtual one-on-one meeting agendas clarify that you're here for your team members and are always willing to chat. They're a great place for casual feedback and to build psychological safety and trust. By developing this relationship with your direct report, you can set yourself up for success when you have a bigger performance review conversation.
![how to write evaluation form [List view] Meeting agenda template in Asana, spreadsheet-style view](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/a073ff73-8c95-4796-819f-717ffa6daf64/inline-project-planning-sales-and-operation-planning-6-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Even if you work in person, you can use one-on-one meeting agendas to stay connected with team members throughout the year.
A one-on-one project also gives team members the chance to choose what they want to talk about with you. Think of the one-on-one as their time. You've set 30 minutes aside for them to use in whatever way is most beneficial for them. Sometimes, they might want to talk about their favorite TV show because they need some time to unwind. Other times, you may get into some serious brainstorming or problem-solving together.
Quarterly performance review template
Focusing on short-term goals and achievements, the quarterly performance review template allows for more frequent assessments of an employee's progress. This performance appraisal is beneficial for tracking progress towards annual goals and adjusting objectives as needed. Quarterly reviews are an excellent way to keep employees motivated and aligned with the company's strategic direction.
Example : For instance, a project manager might be reviewed on their ability to meet project milestones, with adjustments made to their next quarter goals based on the latest project outcomes and feedback.
Annual performance review template
The annual performance review template provides a comprehensive overview of an employee's performance over the year. It's an opportunity to reflect on long-term achievements, set future goals, and discuss career development opportunities.
Incorporating feedback from this template into the next performance review ensures continuous improvement and effective performance management. Additionally, it sets the stage for meaningful one-on-one discussions, allowing managers and employees to follow up on progress and celebrate wins.
Example : For example, imagine an employee who has consistently met their sales targets throughout the year. The annual review not only acknowledges this achievement but also explores areas for further growth. This might involve setting higher targets for the upcoming year, discussing new responsibilities, or identifying training opportunities.
Why performance evaluations are important
Performance evaluations are important for both managers and team members because, when work gets hectic, communication can fall short. A “good job” here and there can go a long way, but team members need scheduled facetime for individual feedback in order to stay on track and grow.
![how to write evaluation form [inline illustration] benefits of performance evaluations (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/6e39edc6-be9b-47a4-b01f-9014764530e7/inline-leadership-performance-evaluation-template-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Performance evaluations can provide the following benefits:
For managers:
Informs hiring practices
Offers feedback on management style
Provides updates on team member wellbeing
For team members:
Improves communication with leadership
Provides a safe space to address concerns
Offers feedback on individual performance
While performance evaluations can feel nerve-wracking, they’re also motivating and give team members clarity on how to improve. Over time, thoughtful performance evaluations build trust and show your team members that you support them and their career paths.
Enhance performance evaluations with goal-setting software
With Asana’s goal-setting software, your team can receive more frequent updates on how they’re doing, which lessens the pressure on everyone when performance evaluations roll around.
Goal-setting enhances the performance evaluation process by focusing more on future progress. When your team can watch their progress in action, they’ll feel more invested in doing their best work.
Related resources

Unmasking impostor syndrome: 15 ways to overcome it at work

How to accomplish big things with long-term goals

Fix these common onboarding challenges to boost productivity
30-60-90 day plan: How to onboard new hires with ease
How to Write a Self Evaluation (With Examples)
First step, be honest about your hits and misses.
Self evaluations are performance assessments that bring you and your manager together to rate your performance over a given time span (quarterly, semi-annually, annually) either using a scale (one to 10 or one to five) or by answering open-ended questions. You complete the evaluation and so does your manager. During the performance review , the two of you compare notes to arrive at a final evaluation.
What Is a Self Evaluation?
Self evaluations are performance assessments that both employees and managers complete. They can be done quarterly, semi-annually or annually, and range from open-ended questions discussed to ratings given on a numeric scale.
Writing about yourself, especially if those words are going to be part of your permanent work record, can be daunting. But it doesn’t have to be. In fact, self evaluations give you a voice in your performance review , and they’re opportunities to outline your career goals and get help in reaching them.
Below, we’ll examine self evaluation benefits, tips and examples, plus how both employees and managers can complete them successfully.
More on Self Evaluations Self-Evaluations Make Stronger Leaders. Here’s How to Write One.
Benefits of Self Evaluations
1. help employees and managers prepare for performance reviews.
Completing a self evaluation can help guide the eventual performance-review conversation in a structured, but meaningful, way. It also helps both parties get an idea of what needs to be discussed during a performance review, so neither feels caught off guard by the conversation.
2. Give Employees an Opportunity to Reflect on Their Progress
Since self evaluations are inherently reflective, they allow employees to identify and examine their strengths and weaknesses. This helps employees both know their worth to an organization and what they still have left to learn.
“Self evaluations enable employees to see their work in its entirety,” Jill Bowman, director of people at fintech company Octane , said. “They ensure that employees reflect on their high points throughout the entire year and to assess their progress towards achieving predetermined objectives and goals.”
3. Help Managers Track Employee Accomplishments
Employee self assessments help managers more accurately remember each employee’s accomplishments. “As many managers often have numerous direct reports, it provides a useful summary of the achievements of each member,” Bowman said.
4. Improve Employee Satisfaction
Academic literature indicates that employees are more satisfied with evaluations that involve two-way communication and encourage a conversation between manager and employee, according to Thomas Begley, professor of management at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute .
The thing is, employees have to trust that the process is fair, Begley added. If they believe it is, and they’re treated fairly and respectfully during the process, employees react positively to self evaluations.
5. Can Decrease Employee Turnover
Some companies see tangible results from self evaluations. For example, Smarty , an address-verification company, enjoys low staff turnover, said Rob Green, chief revenue officer. The self-evaluation method, coupled with a strong focus on a communication-based corporate culture, has resulted in a 97 percent retention rate, Green told Built In.
Related 6 Ways to Be More Confident in Performance Reviews
How to Write a Self Evaluation
The ability to write a self evaluation is a critical career skill.
“Self evaluations give you a platform to influence your manager and in many cases, reframe the nature of the relationship with your manager,” Richard Hawkes, CEO and founder of Growth River , a leadership and management consulting company, said. “And all results in business happen in the context of relationships.”
Below are some tips on how to complete a self evaluation.
1. Track Your Work and Accomplishments
Daily or weekly tracking of your work can help you keep track of your progress and also prevent last-minute “what on earth did I do the last six months?” panic at performance evaluation time, said Peter Griscom, CEO at Tradefluence . “Strip down the questions to two or three, and just ask yourself, ‘How well did I communicate today?’ ‘How well did I solve problems today?’ ‘What have I achieved today?’” Griscom said. “Get in the habit of writing those things out and keeping track and over time.”
2. Answer Honestly
For his first self evaluation, Griscom remembers wondering how to best answer the questions. After he asked his manager for guidance, Griscom answered the questions as accurately as he could. “What came out of it was really valuable, because it gave me a chance to reflect on my own achievements and think about where I can improve,” he said. “It forced me to do the thinking instead of just accepting feedback.”
3. Highlight Your Achievements
If your boss has a handful of direct reports, chances are good they haven’t noticed each of your shining moments during a review period. This is your chance to spotlight yourself. Quotas exceeded, projects finished ahead of schedule, fruitful mentoring relationships, processes streamlined — whatever you’ve done, share it, and don’t be shy about it, said Alexandra Phillips , a leadership and management coach. Women, especially, tend not to share achievements and accomplishments as loudly or often as they should. “Make sure your manager has a good sense of where you’ve had those wins, large and small, because sometimes they can fly under the radar,” Phillips added.
4. Admit Weaknesses and How You Have Grown
If you’ve made a whopper mistake since your past review, mention it — and be sure to discuss what you’ve learned from it. Chances are good your manager knows you made a mistake, and bringing it up gives you the opportunity to provide more context to the situation.
5. Acknowledge Areas of Improvement
Be prepared for your manager to point out a few areas for improvement. This is where career growth happens. “If you want something,” whether it’s a promotion or move to another department, “you need to know how to get there,” said Phillips.
Related What Are Short-Term Career Goals? (With 12 Examples)
Self Evaluation Examples and Templates Answers
Still not sure what to do when you put pen to paper? Here are six open-ended self evaluation sample questions from the Society for Human Resource Management, as well as example answers you can use to prepare for your own self evaluation.
1. Job Performance Examples
List your most significant accomplishments or contributions since last year. How do these achievements align with the goals/objectives outlined in your last review?
How to answer with positive results: In the past year, I successfully led our team in finishing [project A]. I was instrumental in finding solutions to several project challenges, among them [X, Y and Z]. When Tom left the company unexpectedly, I was able to cover his basic tasks until a replacement was hired, thus keeping our team on track to meet KPIs.
I feel the above accomplishments demonstrate that I have taken more of a leadership role in our department, a move that we discussed during my last performance review.
How to answer with ways to improve: Although I didn’t meet all of my goals in the last year, I am working on improving this by changing my workflow and holding myself accountable. I am currently working to meet my goals by doing [X, Y and Z] and I plan to have [project A] completed by [steps here]. I believe that I will be able to correct my performance through these actionable steps.
Describe areas you feel require improvement in terms of your professional capabilities. List the steps you plan to take and/or the resources you need to accomplish this.
I feel I could do better at moving projects off my desk and on to the next person without overthinking them or sweating details that are not mine to sweat; in this regard I could trust my teammates more. I plan to enlist your help with this and ask for a weekly 15-minute one-on-one meeting to do so.
Identify two career goals for the coming year and indicate how you plan to accomplish them.
One is a promotion to senior project manager, which I plan to reach by continuing to show leadership skills on the team. Another is that I’d like to be seen as a real resource for the organization, and plan to volunteer for the committee to update the standards and practices handbook.
2. Leadership Examples
Since the last appraisal period, have you successfully performed any new tasks or additional duties outside the scope of your regular responsibilities? If so, please specify.
How to answer with positive results: Yes. I have established mentoring relationships with one of the younger members of our team, as well as with a more seasoned person in another department. I have also successfully taken over the monthly all-hands meeting in our team, trimming meeting time to 30 minutes from an hour and establishing clear agendas and expectations for each meeting. Again, I feel these align with my goal to become more of a leader.
How to answer with ways to improve: Since the last review period, I focused my efforts on improving my communication with our team, meeting my goals consistently and fostering relationships with leaders in other departments. Over the next six months, I plan on breaking out of my comfort zone by accomplishing [X, Y and Z].
What activities have you initiated, or actively participated in, to encourage camaraderie and teamwork within your group and/or office? What was the result?
How to answer with positive results: I launched the “No More Panicked Mondays” program to help on-site and remote colleagues make Mondays more productive. The initiative includes segmenting the day into 25-minute parts to answer emails, get caught up on direct messages, sketch out to-do lists and otherwise plan for the week ahead. NMPM also includes a 15-minute “Weekend Update” around lunch time, during which staff shares weekend activities. Attendance was slow at first but has picked up to nearly 90 percent participation. The result overall for the initiative is more of the team signs on to direct messages earlier in the day, on average 9:15 a.m. instead of the previous 10 a.m., and anecdotally, the team seems more enthusiastic about the week. I plan to conduct a survey later this month to get team input on how we can change up the initiative.
How to answer with ways to improve: Although I haven’t had the chance to lead any new initiatives since I got hired, I recently had an idea for [A] and wanted to run it by you. Do you think this would be beneficial to our team? I would love to take charge of a program like this.
3. Professional Development Examples
Describe your professional development activities since last year, such as offsite seminars/classes (specify if self-directed or required by your supervisor), onsite training, peer training, management coaching or mentoring, on-the-job experience, exposure to challenging projects, other—please describe.
How to answer with positive results: I completed a class on SEO best practices and shared what I learned from the seminar during a lunch-and-learn with my teammates. I took on a pro-bono website development project for a local nonprofit, which gave me a new look at website challenges for different types of organizations. I also, as mentioned above, started two new mentoring relationships.
How to answer with ways to improve: This is something I have been thinking about but would like a little guidance with. I would love to hear what others have done in the past to help me find my footing. I am eager to learn more about [A] and [B] and would like to hear your thoughts on which courses or seminars you might recommend.
Related How to Find the Right Mentor — and How to Be One
Types of Self Evaluations
Self evaluations can include rating scale questions, open-ended questions or a hybrid of both. Each approach has its own set of pros and cons to consider.
1. Rating Self Evaluation
Rating scale self evaluations give a list of statements where employees are asked to rate themselves on a scale of one to five or one to ten (generally the higher the number, the more favorable the rating).
For example, in Smarty’s self evaluations, it uses a tool called 3A+. This one calls for employees and managers to sit down and complete the evaluation together, at the same time. Employees rate themselves from 3, 2 or 1 (three being the best) on their capability in their role; A, B or C on their helpfulness to others, and plus or minus on their “diligence and focus” in their role. Managers rate the employees using the same scale. A “perfect” score would be 3A+, while an underperforming employee would rate 2B-.
At the performance evaluation meeting, managers and employees compare their ratings, and employees ask for feedback on how they can improve.
But rating systems can have their challenges that are often rooted in bias . For example, women are more likely to rate themselves lower than men. People from individualistic cultures, which emphasize individuals over community, will rate themselves higher than people from collectivist cultures, which place a premium on the group rather than the individual.
2. Open-Ended Question Self Evaluation
Open-ended questions ask employees to list their accomplishments, setbacks and goals in writing. The goal of open-ended questions is to get employees thinking deeply about their work and where they need to improve.
Open-ended questions allow employees a true voice in the process, whereas “self ratings” can sometimes be unfair , Fresia Jackson, lead research people scientist at Culture Amp , said.
With open-ended questions, employees tend to be more forgiving with themselves, which can be both good and bad. Whatever result open ended questions bring about, they typically offer more fodder for discussion between employees and managers.
3. Hybrid Self Evaluation
Hybrid self evaluations combine both rating questions and open-ended questions, where employees assess their skills and accomplishments by using a number scale and by answering in writing. This type of self evaluation lets employees provide quantitative and qualitative answers for a more holistic reflection.
Self-Evaluation Questions for Performance Reviews
If you’ve never done a self evaluation, or if you just need a refresher before your next performance review, looking over some examples of self evaluation questions — like the ones below — can be a helpful starting point.
Common Self-Evaluation Questions for Performance Reviews
- What are you most proud of?
- What would you do differently?
- How have you carried out the company’s mission statement?
- Where would you like to be a year from now?
- List your skills and positive attributes.
- List your accomplishments, especially those that impacted others or moved you toward goals.
- Think about your mistakes and what you’ve learned from them.
- What are your opportunities to grow through advancement and/or learning?
- How do the above tie to your professional goals?
Self-Evaluation Questions for Career Planning and Growth
- What are you interested in working on?
- What are you working on now?
- What do you want to learn more about?
- How can I as your manager better support you?
- What can the company do to support your journey?
- How can the immediate team support you?
- What can you do to better support the team and the company?
Self-Evaluation Questions for Performance and Career Goals
- How did you perform in relation to your goals?
- What level of positive impact did your performance have on the team?
- Did your performance have a positive impact on the business?
- What was your level of collaboration with other departments?
- What corporate value do you bring to life?
- What corporate value do you most struggle to align with?
- Summarize your strengths.
- Summarize your development areas.
- Summarize your performance/achievements during this year.
- How would you rate your overall performance this year?
Related How to Set Professional Goals
How Should Managers Approach Self Evaluations?
It’s clear here that self evaluations, as a type of performance review, are more employee- than manager-driven. That said, managers are a key ingredient in this process, and the way managers handle self evaluations determines much about how useful they are and how well employees respond to them. To make sure they’re as effective as possible, consider these suggestions.
Train Managers on How to Use Evaluations
“If you don’t, there’s no point in doing them, because the manager is going to be the one driving the conversations,” Elisabeth Duncan, vice president of human resources at Evive, said. “Without training, the [evaluations] will be a checkbox and not meaningful.”
Don’t Use Ratings Formulaically
The results of self evaluations that employ a scale (say, one to five) can vary wildly, as one manager’s three is another manager’s five. Use the scale to identify and address discrepancies between the manager’s and employee’s answers, not to decide on raises or promotions across the company.
Hold Self Evaluations Often
They work best as career-development tools if they’re held semi-annually, quarterly or even more often. “It’s about an ongoing, consistent conversation,” Duncan said.
Tailor Them For Each Department
Competencies in sales very likely differ from competencies in tech, marketing and other departments. Competencies for junior-level employees probably differ wildly from those for senior managers. Self evaluations tailored to different employee populations will be more effective, and fairer.
Stress That the Rating Is Just the Start
The rating or the open-ended questions are the beginning of the evaluation process; they are not the process itself. “These are tools to trigger a conversation,” Duncan said.
Overall, think of self evaluations as a way to engage with your manager and your work in a way that furthers your career. Embrace the self evaluation and get good at writing them. In no time at all, you’ll find that they can be a productive way to reflect on yourself and your skillset.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a self evaluation.
A self evaluation is a personal assessment used for employees to reflect on their strengths, weaknesses, accomplishments and overall progress during an allotted time on the job.
Self evaluations are often completed quarterly, semi-annually or annually, and can include numbered rating questions or open-ended written questions.
How do you write a good self evaluation?
An effective self evaluation is one where you highlight your achievements and instances of growth as well as areas for improvement during your given period of time at work. Tracking specific accomplishments and metrics can be especially helpful for writing a good self evaluation.
Jessica Powers contributed reporting to this story.
Recent Career Development Articles

Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
- Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
Employee evaluation forms explained (with free survey template)
Updated August 19, 2022
Ready to formalize and standardize your employee performance management process? Use our tips to build and customize an employee evaluation form that works for the company's performance management process.
Help your employees understand what’s expected at their employee performance reviews, by providing employee evaluation forms that help judge their performance in a fair and consistent way.
If you’re not sure where to begin, let's take a closer look at the role employee performance evaluation forms play in employee performance reviews , the benefits of using an evaluation form, how often to evaluate your employees, and what to include on your own form. Plus, we’ve included a sample template to help you get started.
What is an employee evaluation form?
Typically, an employee performance evaluation form contains the objectives, goals, and behaviors expected of an employee. As part of the performance review process, an employee evaluation form is filled out by both employee and reviewer, and then this is used as a tool to have a performance review conversation(s) to assess an employee’s performance.
It is used in performance evaluations to ensure fair and consistent criteria and scoring and establishes a two-way conversation about performance expectations and deliverables between an employee and his or her leader.
“Leaders that proactively think about how to support employees and help them grow not only benefit the individual employee, but also the company.” Rebekah Bastian , author of Blaze Your Own Trail
For example, by completing and reviewing the employee evaluation form, leaders can identify and discuss a person’s strengths and weaknesses, offer constructive feedback for skills development, and assist with goal setting.
(If you’d like more information on employee performance review template tips, please see our guide to employee performance reviews .)
Why are employee evaluation forms important?
Some of the benefits of using an employee evaluation form include:
- Aligning individual roles to business goals. An employee evaluation form underlines the organization’s vision and goals and illustrates to employees how their individual performance drives organizational performance.
- Establishing a clear understanding of job roles. Clearly defined goals and metrics empower employees to understand their specific job duties. Documenting (and discussing) said goals and metrics on an employee evaluation form eliminates ambiguities and helps to hold employees accountable for their designated work and responsibilities.
- Providing regular feedback about performance. Employee evaluation forms help identify an individual’s strengths and weaknesses, and most importantly, give employees a better understanding of the expectations that they are being held to.
- Discussing career development. A complete employee evaluation form should also contain a section to discuss and plan for an employee’s career. Career development and aspiration discussions help leaders better understand and champion employees’ desires for training and mentoring.
- Informing recognition and rewards. The employee evaluation form documents the outcomes and scores related to an employee’s job performance – two factors often used to inform annual bonus decisions, as well as other recognition and awards .
How often should employees be formally evaluated?
The performance review process varies from one organization to the next, but as a rule of thumb, employees should have formal evaluation discussions with their leaders at least once a year. Organizations may have an annual performance review template for this or may wish to repurpose an existing one.
One common approach to the annual performance appraisal, or the annual performance review, is the 360-degree feedback review . With this evaluation process, employees receive feedback not only from their managers, but also from their peers and junior team members. Employees often review themselves, as well, resulting in a 360-degree view of their strengths and accomplishments.
Some organizations believe in reviewing job performance more frequently. These organizations employ continuous feedback methods, preferring to share feedback with employees on a continual, ad hoc basis.
Falling somewhere between the once-annual performance review and the continual feedback approach, an employee pulse review is a smaller-scale employee review that’s conducted on a regular schedule, such as monthly or quarterly.
Pulse feedback is most commonly associated with employee engagement surveys, but pulses also work well for sharing feedback as they offer clear measures and are quick and easy to complete.
Learn how to give exceptional feedback in this comprehensive guide.
How do you write an employee evaluation form?
What should be included on an employee evaluation form.
Just like company culture , an employee evaluation form will be unique and specific to your organization’s values, goals, and purpose. However, there are a number of baseline components that every employee evaluation form should include:
- Employee and reviewer information , such as names, employee IDs, job titles, and signatures.
- The review period to determine the progress of an employee’s performance over time. This should include the time period being assessed, as well as the date of the review itself.
- A rating system that’s easy to understand.
- Goals should be established by both the manager and the employee. To maximize effectiveness, they should be SMART (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, time-based) goals and tracked regularly. Clearly defined metrics help employees work towards goal achievement.
- A comments section allows both the employee and the leader to add verbatim comments regarding performance. The comments section also serves as a place to provide feedback or encouragement, as well as document individual challenges and accomplishments.
- Signatures from both parties establish that the employee and manager acknowledge the contents of the employee evaluation form.
Get started with our free sample template
Employee evaluation forms don’t need to be lengthy to be effective. First, look at the employee’s goals and make a section for each that collects qualitative and quantitative data , by using open and closed questions .
Then, with the employee’s job in mind, add or take away questions to fit your organization and team.
Here’s a quick template that can act as the foundation for your evaluation form:
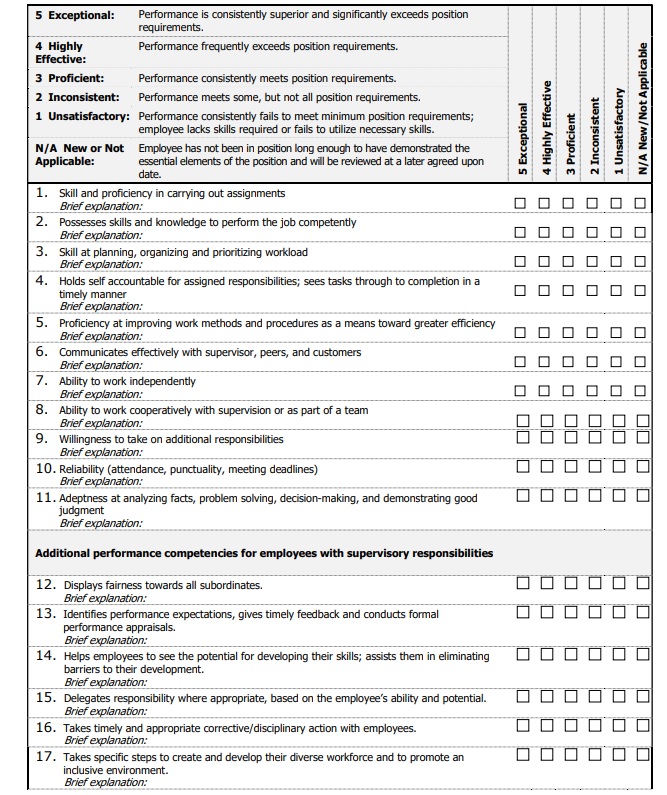
Q1 Overall how do you rate this individual's performance based on your expectations for the role?
Design note - Use a rating scale of 1-5: 1 Significantly below expectations, 2 Below expectations, 3 Meets expectations, 4 Above expectations, 5 Significantly above expectations
This can be used to ask about the employee’s performance in key areas, like:
- Functional expertise. Performs his or her assigned duties with competence; achieves his/her objectives even when faced with obstacles and challenges.
- Communication style. Actively listens to others; tailors his/her communication to the needs of the audience; communicates clearly and concisely.
- Customer focus. Prioritizes his/her work based on the needs of the organization and its customers.
- Adaptability. Demonstrates flexibility to changing priorities and situations.
- Problem-solving . Works through work-related problems, taking a variety of perspectives and solutions into consideration before executing.
- Teamwork . Collaborates effectively with other team members; gives constructive and helpful feedback to others; treats others with respect.
- Leadership. Takes team members’ ideas and opinions into account when making decisions; helps team members resolve work-related problems; holds team members accountable for achieving their objectives.
Design note - Use open text/verbatim comment boxes for Q2 - Q5 to encourage detail
Q2 Indicate the competency in which this individual most excels at, providing examples and an explanation as to why.
Q3 What can this individual do to continue to grow?
Q4 What has this individual accomplished this year that has had the biggest impact on team and organizational success?
Q5 What areas of improvement exist for this individual? (Include any training that would help with career development and growth.)
What should I write in an employee performance evaluation?
When it’s your turn to write, always be honest and fair on the employee’s performance review, as this will be a document that continues to be used time and time again in the future. In extreme cases, they may be used in legal court or claim cases as evidence.
Your input into the performance evaluation form should follow the STAR mnemonic (Situation, Task, Action, and Result). For example, when providing an example of negative performance, be clear about what was asked, the context, what actually happened, and what the result of that was.
This way, when it comes to your discussion with the employee, you can draw on the details. (And, remember not to ‘blame’ them — instead understand things from the employee’s perspective and suggest possible future options to try for next time.)
Performance management – and in its own right, the employee evaluation form – can be a motivational tool, encouraging employees not only to feel more satisfied in their work but to go beyond what’s expected.
How do you evaluate employee performance examples?
Provide feedback.
Providing feedback with clear, positive language is the key to keeping the review goal-focused and productive. Writing performance reviews requires managers (and other raters) to be specific with their feedback, stay constructive, and provide solutions to help the employee grow.
“Despite the power and use of employee feedback for growth, development, and to improve performance, it can sometimes be challenging to provide it. Too often feedback is given a negative connotation, when at its core it’s simply about giving and receiving information.” Marcus Wolf, Principal EX Consultant at Qualtrics
If you’re not sure about giving feedback across any of these types of performance reviews, use our guide covering employee feedback examples using formal, informal, and constructive techniques .
Monitor progress
As performance reviews are crucial to an employee’s development and historical service record, companies are obligated to keep good records that can be audited and checked at a moment’s notice.
The results of the performance review also form the dataset that your future performance reviews will be compared against to see if there has been any improvement.
If you don’t want to do this manually, use an integrated, smart technology system like Qualtrics Employee Experience Management (EMX) to help you to:
- Track when a performance review is coming up
- Automatically send out and collect back the answers to your employee evaluation form
- Gives you quick and automated insights based on the employee’s performance data
Take your employee evaluations to the next level with our ultimate guide to performance review
Amanda Wowk
Amanda Wowk is a freelance writer, founder of Amanda Wowk Creative—a content writing services company—and contributor to the Qualtrics blog. She creates content for clients in a variety of industries, including travel, tech startup, healthcare, and consumer products. Prior to freelancing, she spent 9+ years in human resources and HR communications.
Related Articles
March 27, 2024
A timeline of the gender pay gap in the United States
February 21, 2024
6 effective employee engagement programs
January 11, 2024
Top 7 recruitment strategies for 2024
December 11, 2023
How to be a better manager
November 3, 2023
UNLEASH World: Unveiling what’s next in the world of HR
October 31, 2023
Forrester’s employee listening solutions landscape 2023 – Top three takeaways
October 24, 2023
The 5 employee experience trends redefining work in 2024
October 12, 2023
Psychological safety in the workplace
Stay up to date with the latest xm thought leadership, tips and news., request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Access to 13 certificate programs, courses and all future releases
Personal Coaching and Career Guidance
Community and live events
Resource and template library

- Employee Evaluation Template & Comprehensive...
Employee Evaluation Template & Comprehensive Guide [+ Free Download]

What is an employee evaluation?

Employee performance is tied to employee evaluations
Why implement employee evaluations .
- Performance improvement : Regular evaluations help employees understand their performance levels, identify gaps, and receive improvement guidance. This leads to increased productivity and effectiveness in their roles.
- Goal alignment: A shared understanding of priorities and expectations is achieved when employee goals are aligned with the organization’s overall objectives.
- Employee engagement: Research shows that employees who receive regular feedback and recognition are more engaged and motivated, contributing to higher job satisfaction and retention.
- Professional development: Evaluations provide opportunities for employees to discuss their career aspirations, identify skills they need to develop, and create a plan for growth and advancement.
- Informed decision-making: As an HR professional, you are able to collect and collate valuable performance data through evaluations, which in turn can be used to inform decisions related to promotions, compensation adjustments, and resource allocation.
HR tip The best performing organizations in the world are built on cultures of continuous improvement, employee engagement, and professional development. Employee evaluations are a crucial component of effective HR management.
The different methods of evaluating employees
1. the job performance scale, the pros of using a job performance scale.
- A standardized scale helps ensure performance evaluations are consistent and fair.
- Clear and objective criteria can be applied across employees and roles.
- Offers a structured approach to assessing performance, making it easier for managers to provide specific feedback.
- Employees understand their strengths and areas for improvement.
- Employee performance can be compared across different roles and departments.
- Leaders can make data-driven decisions about promotions, compensation adjustments, and talent management.
- Can be used as a basis for setting performance goals and expectations.
The cons of using a job performance scale
- Evaluators may still be influenced by personal biases or subjective opinions, leading to inconsistencies and unfair assessments.
- A rigid focus on quantifiable performance metrics may not capture the full scope of an employee’s contributions, particularly soft skills like creativity, leadership qualities, or emotional intelligence.
- May not adequately address the unique aspects of specific job roles or individual employees.
- Numerical ratings could limit the depth and usefulness of feedback.
HR tip Even though we know any feedback is better than no feedback, it’s important that employees feel motivated. Don’t reduce an employee to a number. Ensure all feedback is meaningful.

2. The job behavior scale
The pros of using a job behavior scale.
- When used with a job performance scale, assessing job behaviors can provide a more comprehensive understanding of an employee’s overall contribution to the organization.
- The importance of soft skills is understood and measured.
- HR professionals can evaluate whether employees align with the organization’s culture and values.
- Promotes a positive and cohesive work environment.
- Can be used to provide targeted feedback and support for personal and professional growth.
The cons of using a job behavior scale
- Can be highly subjective compared to assessing task-based performance.
- This can lead to inconsistencies and unfair assessments influenced by personal biases or opinions.
- Defining and measuring behaviors can be challenging, as they are often abstract and difficult to quantify.
- Results can be ambiguous, leaving employees who do not understand how to improve.
- Is more time-consuming and labor-intensive than evaluating task-based performance.
HR tip Don’t let a strong focus on job behaviors lead to underestimating the importance of technical skills or task-based performance. A holistic view is crucial for an employee’s overall effectiveness.
3. Competency-based behavioral assessment
The pros of using a competency-based behavioral assessment.
- The importance of both technical and soft skills is emphasized, providing a more comprehensive evaluation of an employee’s overall effectiveness.
- Employees gain a clear understanding of what is expected of them and how they can improve.
- Personalized development is supported because areas, where employees need further training or support are identified.
- Predefined competencies ensure a consistent and fair assessment process across the organization.
- Employees are better positioned to contribute to the business’s overall success.
The cons of using a competency-based behavioral assessment
- Assessing soft skills and behaviors can be subjective and prone to personal biases, leading to inconsistencies and unfair evaluations.
- May not be flexible enough to account for individual differences, unique job responsibilities, or evolving organizational needs.
- May overlook other valuable skills or contributions an employee brings to the organization.
- May not provide enough qualitative feedback, which could limit the depth and usefulness of the evaluations.
HR tip Successfully defining and measuring the competencies that align with organizational objectives requires a thorough understanding of job requirements and the skills needed for success in various roles. As an HR professional, you are well-positioned to add tangible value to your organization.

4. Psychological appraisals
The pros of using psychological appraisals.
- Highly personalized and uncover an individual’s personality traits, preferences, and behavioral tendencies.
- Problem-solving, reasoning, and decision-making abilities can be measured and compared to actual job roles.
- Can be highly beneficial in determining the management style an employee will respond to.
- Can help determine an employee’s intrinsic and extrinsic motivational factors and how these influence job performance.
- Can measure an individual’s ability to cope with stress and maintain emotional well-being in the workplace, potentially helping HR professionals to avoid burn-outs in their organizations.
The cons of using psychological appraisals
- May delve into personal aspects of an employee’s life, raising concerns about privacy and the potential misuse of sensitive information.
- The interpretation of results can be subjective, leading to potential biases and inconsistencies.
- May not always accurately predict job performance or success in a specific role.
- Employees might feel stigmatized or unfairly judged based on the results of psychological appraisals.
- May raise ethical questions about employee autonomy, consent, and the potential for discrimination based on mental health or personality traits.
- Conducting psychological appraisals can be time-consuming and costly, particularly if they require specialized assessments or the involvement of trained professionals.
HR tip Ensure that psychological assessments are conducted with transparency, respect for employee privacy, and in compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
5. 360-degree appraisals
The pros of using 360-degree appraisals.
- By gathering input from various sources, 360-degree appraisals provide a more accurate and holistic view of an employee’s performance, strengths, and areas for improvement.
- Incorporating multiple perspectives helps to counterbalance potential biases or personal opinions, leading to a fairer and more objective evaluation.
- Feedback from different sources can help employees identify specific areas where they can improve and grow, supporting their personal and professional development.
- The process encourages open dialogue and promotes a culture of constructive feedback within the organization.
- By including self-assessment as part of the process, employees can develop a better understanding of their own strengths and weaknesses and become more proactive in addressing them.
The cons of using 360-degree appraisals
- Can be time-consuming for both the participants and the person responsible for compiling and analyzing the results.
- Coordinating and managing a 360-degree appraisal process can be complex, particularly in larger organizations where multiple evaluations need to be conducted simultaneously.
- Receiving feedback from multiple sources can sometimes be overwhelming or confusing for employees, particularly if the feedback is inconsistent or contradictory.
- If not handled carefully, 360-degree appraisals can lead to resentment, mistrust, or damaged relationships among team members.
HR tip 360-degree appraisals can be the best performance tool at your disposal if handled correctly. Ensure no feedback is misinterpreted or taken out of context. Instead, ensure that feedback participants communicate clearly and constructively.
Types of employee evaluations
1. general employee evaluation .

2. 30-60-90 day review
3. peer review , 4. objective-based evaluation, 5. employee self-evaluation.

Checklist: Best practices for creating and implementing employee evaluations
- Have you clearly communicated evaluation criteria? All evaluation assessments are more successful when employees and managers understand the purpose and expectations of the evaluation process.
- Is there fairness and transparency throughout the evaluation process? It’s important to foster trust, encourage open communication, and ensure that employees feel valued and supported in their development.
- Have you included clear expectations? Assessments are far more successful in directing future employee behavior when an employee understands what is expected of them.
- Have you developed a structured system that allows for consistent performance reviews? The goal is to promote consistency through regular feedback, enabling better comparisons and tracking of employee progress over time.
- Does feedback emphasize strengths and areas for improvement? Employees can only improve their performance if they understand where their strengths lie (and how these support business objectives) as well as where there are areas of improvement. Emphasizing strengths also boosts morale.
- Do employees provide input into the evaluation process? Evaluations are far more meaningful when an employee is empowered and encouraged to engage with the process. This ensures a more comprehensive understanding of their performance and development needs.
- Is feedback from previous evaluations analyzed? Regularly review the feedback on previous assessments to identify areas for improvement.
- Are evaluations tied to career development? Tying evaluations to career development motivates employees to improve, aligns their goals with organizational objectives, and helps retain top talent by promoting growth opportunities.
- Are evaluations used to identify learning and development opportunities? Learning and development goals will be far more targeted and successful if they are tied to assessments.
- Is data used to monitor employees’ performance over time? Using data enables objective assessment, tracks progress, identifies trends, and informs targeted development efforts to enhance performance.
- Are evaluations kept confidential? Not only is it important to protect employee privacy and ensure legal compliance with local regulations, but confidentiality fosters trust and maintains a respectful work environment.
HR tips to help managers conduct an effective employee evaluation
- Use evaluations for performance improvement: Promote career development and employee engagement: Help managers to use employee evaluations as a tool for performance improvement rather than just a formality.
- Promote career development and employee engagement : Discuss future goals and development opportunities that align with the employee’s interests and the organization’s objectives.
- Keep things fair and consistent: Help managers overcome bias in employee evaluations and ensure they avoid making comparisons between employees. It is also important to focus on behavior, not personality, when discussing performance issues.
- Make assessment valuable: Guide managers to provide comprehensive, actionable feedback.
- Come prepared: Encourage managers to prepare thoroughly by reviewing the employee’s job description, past evaluations, and recent accomplishments.
- Set a positive tone: Assessments and feedback sessions should be set in an environment that promotes open and honest dialogue. Managers can also encourage two-way communication by asking open-ended questions and actively listening.
- Be specific: When managers use specific examples to illustrate points and avoid generalizations, employees can understand how the feedback they are receiving relates to their performance, job expectations and career development.
- Balance criticism with recognition of achievements and strengths: Offer constructive feedback and actionable suggestions for improvement while recognizing the value an employee brings to the organization.
- Formalize the process: Document key points from the evaluation to track progress and maintain accountability.
- Be consistent: Follow up regularly to monitor progress, provide ongoing support, and address any concerns that arise.
To conclude
Weekly update.
Stay up-to-date with the latest news, trends, and resources in HR

Nadine von Moltke
Related articles.

How To Write a Professional Rejection Letter (+ FREE Samples)

Time Off Request Form Template + How-To Guide

Your All-in-One Guide to Vacation Request Forms [+ Free Template]
New articles.

5 Success Criteria for Effective HR Business Partnering

Job Enrichment: A Practical Guide + 13 Examples

How Much Does HR Make? Your 2024 Salary Guide
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter, are you ready for the future of hr.
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online

| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
Performance Review Template & Examples (2024)

Updated: Apr 30, 2024, 10:41pm

Table of Contents
What is a performance review, how to prepare for a performance review, what to write in a performance review, after the performance review: follow up, free performance review template, performance review do's and don'ts, when to use performance review software, frequently asked questions (faqs).
Performance review: these two words evoke mixed feelings in managers and employees alike. Some might be excited. Others become intimidated. But most managers feel stressed, because giving constructive performance feedback is a tough task.
You have to walk the fine line between coaching and criticizing. It’s easy to slip into the wrong territory. You can avoid this scenario with our tips, examples and a downloadable performance review template.
Featured Partners
$35/month plus $8 PEPM

On Rippling's Website
$40 per month + $6 per user

On OnPay's Website
Paychex Flex
$39-plus per month, depending on company size and needs (6 month free offer)

On Paychex's Website
$40 per month plus $6 per user

On Gusto's Website
Performance review is a systematic process of evaluating the employee’s past performance and articulating future expectations for the job. The purpose of reviews is twofold: Give constructive feedback and suggest the next steps for personal and professional development:
- Managers use performance feedback to motivate employees, prioritize career development opportunities and clarify responsibilities and accountability.
- Employees use performance feedback as a beacon. It helps them reorient their effort toward the right goals and moderate their behaviors accordingly.
Numerous psychological studies suggest that regular, fair and diverse feedback leads to substantial improvements in employee performance. Separately, workplace research suggests that meaningful feedback improves employee engagement levels and prevents talent attrition. But to capture these benefits, you must schedule regular performance reviews for each team member (typically once or twice per year ).
Performance review is a dialogue between the feedback recipient and the giver. To have an impactful conversation, both parties should take the time to prepare their assessments, examples and commentary.
Without the lead-up work, a performance review session will lack substance and fail to deliver on its core objective—promote desired employee behaviors.
As a Manager
- Review the past goals and track key performance indicators (KPIs): Use available metrics to make an objective evaluation of the employee’s work.
- Analyze outcomes, not outputs: Focus on the employee’s positive contributions to the company rather than how many hours or efforts they have put in.
- Talk to colleagues: Request additional feedback from the recipient’s peers or other line managers who they’ve interacted with if you have doubts.
- Set personal biases aside: Try to cleanse your judgment from common unconscious biases, such as the “halo effect,” “conformity bias,” “affinity bias” and possible -isms.
As an Employee
- Collect and prepare evidence of your performance: These can include notable accomplishments, aggregated KPIs, feedback and praise from colleagues and superiors.
- Think about your career goals: What would you like to accomplish next? Which career development paths sound appealing to you? Do consider both vertical and horizontal career growth opportunities .
- Prepare to provide feedback too: Your employer would be interested in hearing what else the company can do to support your performance.
- Complete the provided self-assessment form: Answer the questions honestly. Avoid inflating your personal ratings as this would put you in an awkward position.
Performance review offers an opportunity to speak about the person’s strengths and weaknesses candidly. There’s a fine line between being helpful and overly critical. Less than 20% of United States employees agree that they’ve received meaningful feedback in the last week.
Performance reviews include an evaluation of an employee’s accomplishments, along with a data-based assessment of their strengths, weaknesses and areas for improvement. Effective feedback doesn’t condemn. It guides the employer toward doing better next time.
To provide feedback in a growth-encouraging way, try to phrase your statements in the following way.
Tie your improvement suggestion to past action. Instead of telling the employee to fully change their behavior, indicate how they improve upon past actions. For example:
| Don't | Do |
|---|---|
Put fallout into context. To better articulate the need for change, explain the downstream effects of the employee’s behavior on the team, company and their own career prospects.
Use positive reinforcement. Promote repeat behaviors through appraisal. Acknowledge the person’s strengths and explain how to succeed further—not just avoid failure.
When writing your review feedback, think like a coach—and talk like a mentor.
Performance review is a corrective tool. However, to result in meaningful change, it should be paired with supplementary action on goal-setting and progress tracking. Design an accountability mechanism to promote continuous improvements.
Research on performance management suggests that people set higher goals under the condition of accountability. They’re also more likely to perform better when held publicly accountable, such as the goals known by the manager.
Instead of merely expressing praise and constructive criticism, set up a process for follow-up action. It can be documented either as an employee development plan or a performance improvement plan (PIP).
- Employee Development Plan
An employee development plan―also called an employee growth plan―provides workers with a sequential list of tasks they must complete to improve skills and acquire knowledge for new roles.
Show the employee what actions they should take in the future to accomplish a certain goal—get a raise, advance to a new role, secure new responsibilities, and more. Doing so helps retain ambitious talent, improve overall employee engagement rates and perform succession planning.
Here’s what to include in an employee development plan:
- Career development prospects: Outline the possible paths and actions required to move to a C-level position.
- Extra training and upskilling: Include a list of suggested programs, certifications or educational courses needed to advance in their role or get considered for a promotion.
- New responsibilities and duties: Suggest how an employee can make a bigger contribution to the company by taking ownership of new initiatives, such as new enterprise resource planning (ERP) system rollout, or allocating extra time to new duties like mentorship).
A full employee development plan sits at the nexus of your company’s organizational needs and employees’ strong sides.
Performance Improvement Plan
A performance improvement plan (PIP) documents the employee’s current shortcomings and outlines corrective steps. A PIP can comment on poor performance ratings, address skill gaps, draw attention to inappropriate past actions—and suggest mandatory follow-up steps.
Unlike an employee development plan, a PIP is designed to address past failures or problematic on-the-job behaviors rather than set the backdrop for future successes. What to include in a performance improvement plan:
- Acceptable performance criteria: Outline general expectations around the employee’s on-the-job performance with examples of positive/negative actions.
- Specific KPIs: Present a baseline set of quantifiable goals an employer must meet within the stated period.
- Support resources: Explain how your organization will help them address current shortcomings, such as mandatory training, mentorship and counseling.
- Check-in schedule: State how often you’ll provide feedback and set up recurring meetings.
- Consequences: Describe what will happen if the employee doesn’t comply with the proposed plan.
If an employee fails to follow the PIP, punitive action may be taken, such as transfer, demotion or termination.
Use this performance review template to create an evidence-based approach for evaluating employee competencies and on-the-job behaviors.

The ultimate goal of the performance review is to guide, not admonish, your team members. Your feedback should help the receiver practice the right actions and make them feel recognized for their achievements.
To ensure your feedback achieves the above goals, use the following techniques:
| Instead of: | Try this: |
|---|---|
Performance review software offers a consolidated set of tools and storage for governing employee evaluation processes. Such platforms help you create standardized performance evaluation forms, process feedback and manage review schedules with the managers.
Best-in-class performance review software also promotes a good governance model by making the review process standardized, transparent and cross-attributable. A strong methodology, paired with data traceability, prevents personal biases from affecting evaluations—and protects your organization against discriminatory accusations.
Bottom Line
Regular feedback and coaching are crucial for nurturing an engaged workforce. A documented performance review process is your first step toward creating a more productive work environment where A-level work is regularly acknowledged and temporary performance slips get resolved fast.
How often should you conduct a performance review?
Conducting performance reviews every 6-12 months is the standard practice. Initiate performance for new and entry-level candidates sooner, such as after three and six months, as part of their onboarding. Schedule reviews of other team members less regularly (unless there are issues with their performance).
What should I say in a performance review?
An easy way to figure out what to say in a performance review is to mentally divide your speech into three parts:
- Recognition of the person’s efforts and accomplishments.
- Constructive feedback on the person’s actions and behaviors.
- Outcomes and follow-up steps after the performance review.
Ensure the receiver understands what’s going to happen next and has clear takeaways from the conversation.
What are the 5 performance ratings?
Most managers use a five-point grading system for evaluating employees’ performance across set criteria. The standard 5 performance ratings are:
- 5 (Outstanding)
- 4 (Exceeds Expectations)
- 3 (Meets Expectations)
- 2 (Needs Improvement)
- 1 (Unacceptable)
What are the components of a performance review?
The main parts of a performance review are:
- Performance review form or scoreboard for managers
- Self-assessment form for employees
- 1:1 conversation with the direct supervisor
- Employee development plan
- Performance improvement plan
- Best HR Software
- Best HCM Software
- Best HRIS Systems
- Best Employee Management Software
- Best Onboarding Software
- Best Talent Management Software
- Best HR Outsourcing Services
- Best Workforce Management Software
- Best Time And Attendance Software
- Best Employee Scheduling Software
- Best Employee Time Tracking Apps
- Best Free Time Tracking Apps
- Best Employee Training Software
- Best Employee Monitoring Software
- Best Enterprise Learning Management Systems
- Best Time Clock Software
- Best ERP Systems
- Zenefits Review
- Oracle HCM Review
- UKG Pro Review
- IntelliHR Review
- ADP Workforce Now Review
- ADP TotalSource Review
- SuccessFactors Review
- Connecteam Review
- What is Human Resources?
- Employee Benefits Guide
- What is Workforce Management?
- What is a PEO?
- What is Human Capital Management?
- HR Compliance Guide
- Strategic Human Resource Management
- Onboarding Checklist
- Benefits Administration Guide
- What Is Employee Training?
- 30-60-90 Day Plan Guide
- How To Calculate Overtime
- What Is Outplacement?
- New Hire Orientation Checklist
- HR Analytics Guide
Next Up In Business
- Best Payroll Services For Small Business
- How To Do Payroll
- ADP Run Review: Features, Pricing & More
- Deluxe Review: Features, Pricing & More
- Wave Payroll Review
- SurePayroll Review: Plans, Pricing And Features
- Deprovisioning: Definition & Best Practices
- PerformYard Review

How To Start A Print On Demand Business In 2024
HR For Small Businesses: The Ultimate Guide
How One Company Is Using AI To Transform Manufacturing
Not-For-Profit Vs. Nonprofit: What’s The Difference?
How To Develop an SEO Strategy in 2024
How To Make Money On Social Media in 2024
Tomas Laurinavicius is a writer and designer. He's a co-founder of Best Writing, an all-in-one platform connecting writers with businesses. He has built multiple online businesses and helps startups and enterprises scale their content marketing operations. He worked with TIME, Observer, HuffPost, Adobe, Webflow, Envato, InVision, and BigCommerce.

- How to Write Evaluation Reports: Purpose, Structure, Content, Challenges, Tips, and Examples
- Learning Center

This article explores how to write effective evaluation reports, covering their purpose, structure, content, and common challenges. It provides tips for presenting evaluation findings effectively and using evaluation reports to improve programs and policies. Examples of well-written evaluation reports and templates are also included.
Table of Contents
What is an Evaluation Report?
What is the purpose of an evaluation report, importance of evaluation reports in program management, structure of evaluation report, best practices for writing an evaluation report, common challenges in writing an evaluation report, tips for presenting evaluation findings effectively, using evaluation reports to improve programs and policies, example of evaluation report templates, conclusion: making evaluation reports work for you.
An evaluatio n report is a document that presents the findings, conclusions, and recommendations of an evaluation, which is a systematic and objective assessment of the performance, impact, and effectiveness of a program, project, policy, or intervention. The report typically includes a description of the evaluation’s purpose, scope, methodology, and data sources, as well as an analysis of the evaluation findings and conclusions, and specific recommendations for program or project improvement.
Evaluation reports can help to build capacity for monitoring and evaluation within organizations and communities, by promoting a culture of learning and continuous improvement. By providing a structured approach to evaluation and reporting, evaluation reports can help to ensure that evaluations are conducted consistently and rigorously, and that the results are communicated effectively to stakeholders.
Evaluation reports may be read by a wide variety of audiences, including persons working in government agencies, staff members working for donors and partners, students and community organisations, and development professionals working on projects or programmes that are comparable to the ones evaluated.
Related: Difference Between Evaluation Report and M&E Reports .
The purpose of an evaluation report is to provide stakeholders with a comprehensive and objective assessment of a program or project’s performance, achievements, and challenges. The report serves as a tool for decision-making, as it provides evidence-based information on the program or project’s strengths and weaknesses, and recommendations for improvement.
The main objectives of an evaluation report are:
- Accountability: To assess whether the program or project has met its objectives and delivered the intended results, and to hold stakeholders accountable for their actions and decisions.
- Learning : To identify the key lessons learned from the program or project, including best practices, challenges, and opportunities for improvement, and to apply these lessons to future programs or projects.
- Improvement : To provide recommendations for program or project improvement based on the evaluation findings and conclusions, and to support evidence-based decision-making.
- Communication : To communicate the evaluation findings and conclusions to stakeholders , including program staff, funders, policymakers, and the general public, and to promote transparency and stakeholder engagement.
An evaluation report should be clear, concise, and well-organized, and should provide stakeholders with a balanced and objective assessment of the program or project’s performance. The report should also be timely, with recommendations that are actionable and relevant to the current context. Overall, the purpose of an evaluation report is to promote accountability, learning, and improvement in program and project design and implementation.
Evaluation reports play a critical role in program management by providing valuable information about program effectiveness and efficiency. They offer insights into the extent to which programs have achieved their objectives, as well as identifying areas for improvement.
Evaluation reports help program managers and stakeholders to make informed decisions about program design, implementation, and funding. They provide evidence-based information that can be used to improve program outcomes and address challenges.
Moreover, evaluation reports are essential in demonstrating program accountability and transparency to funders, policymakers, and other stakeholders. They serve as a record of program activities and outcomes, allowing stakeholders to assess the program’s impact and sustainability.
In short, evaluation reports are a vital tool for program managers and evaluators. They provide a comprehensive picture of program performance, including strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. By utilizing evaluation reports, program managers can make informed decisions to improve program outcomes and ensure that their programs are effective, efficient, and sustainable over time.

The structure of an evaluation report can vary depending on the requirements and preferences of the stakeholders, but typically it includes the following sections:
- Executive Summary : A brief summary of the evaluation findings, conclusions, and recommendations.
- Introduction: An overview of the evaluation context, scope, purpose, and methodology.
- Background: A summary of the programme or initiative that is being assessed, including its goals, activities, and intended audience(s).
- Evaluation Questions : A list of the evaluation questions that guided the data collection and analysis.
- Methodology: A description of the data collection methods used in the evaluation, including the sampling strategy, data sources, and data analysis techniques.
- Findings: A presentation of the evaluation findings, organized according to the evaluation questions.
- Conclusions : A summary of the main evaluation findings and conclusions, including an assessment of the program or project’s effectiveness, efficiency, and sustainability.
- Recommendations : A list of specific recommendations for program or project improvements based on the evaluation findings and conclusions.
- Lessons Learned : A discussion of the key lessons learned from the evaluation that could be applied to similar programs or projects in the future.
- Limitations : A discussion of the limitations of the evaluation, including any challenges or constraints encountered during the data collection and analysis.
- References: A list of references cited in the evaluation report.
- Appendices : Additional information, such as detailed data tables, graphs, or maps, that support the evaluation findings and conclusions.
The structure of the evaluation report should be clear, logical, and easy to follow, with headings and subheadings used to organize the content and facilitate navigation.
In addition, the presentation of data may be made more engaging and understandable by the use of visual aids such as graphs and charts.
Writing an effective evaluation report requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here are some best practices to consider when writing an evaluation report:
Begin by establishing the report’s purpose, objectives, and target audience. A clear understanding of these elements will help guide the report’s structure and content.
Use clear and concise language throughout the report. Avoid jargon and technical terms that may be difficult for readers to understand.
Use evidence-based findings to support your conclusions and recommendations. Ensure that the findings are clearly presented using data tables, graphs, and charts.
Provide context for the evaluation by including a brief summary of the program being evaluated, its objectives, and intended impact. This will help readers understand the report’s purpose and the findings.
Include limitations and caveats in the report to provide a balanced assessment of the program’s effectiveness. Acknowledge any data limitations or other factors that may have influenced the evaluation’s results.
Organize the report in a logical manner, using headings and subheadings to break up the content. This will make the report easier to read and understand.
Ensure that the report is well-structured and easy to navigate. Use a clear and consistent formatting style throughout the report.
Finally, use the report to make actionable recommendations that will help improve program effectiveness and efficiency. Be specific about the steps that should be taken and the resources required to implement the recommendations.
By following these best practices, you can write an evaluation report that is clear, concise, and actionable, helping program managers and stakeholders to make informed decisions that improve program outcomes.
Catch HR’s eye instantly?
- Resume Review
- Resume Writing
- Resume Optimization
Premier global development resume service since 2012
Stand Out with a Pro Resume
Writing an evaluation report can be a challenging task, even for experienced evaluators. Here are some common challenges that evaluators may encounter when writing an evaluation report:
- Data limitations: One of the biggest challenges in writing an evaluation report is dealing with data limitations. Evaluators may find that the data they collected is incomplete, inaccurate, or difficult to interpret, making it challenging to draw meaningful conclusions.
- Stakeholder disagreements: Another common challenge is stakeholder disagreements over the evaluation’s findings and recommendations. Stakeholders may have different opinions about the program’s effectiveness or the best course of action to improve program outcomes.
- Technical writing skills: Evaluators may struggle with technical writing skills, which are essential for presenting complex evaluation findings in a clear and concise manner. Writing skills are particularly important when presenting statistical data or other technical information.
- Time constraints: Evaluators may face time constraints when writing evaluation reports, particularly if the report is needed quickly or the evaluation involved a large amount of data collection and analysis.
- Communication barriers: Evaluators may encounter communication barriers when working with stakeholders who speak different languages or have different cultural backgrounds. Effective communication is essential for ensuring that the evaluation’s findings are understood and acted upon.
By being aware of these common challenges, evaluators can take steps to address them and produce evaluation reports that are clear, accurate, and actionable. This may involve developing data collection and analysis plans that account for potential data limitations, engaging stakeholders early in the evaluation process to build consensus, and investing time in developing technical writing skills.
Presenting evaluation findings effectively is essential for ensuring that program managers and stakeholders understand the evaluation’s purpose, objectives, and conclusions. Here are some tips for presenting evaluation findings effectively:
- Know your audience: Before presenting evaluation findings, ensure that you have a clear understanding of your audience’s background, interests, and expertise. This will help you tailor your presentation to their needs and interests.
- Use visuals: Visual aids such as graphs, charts, and tables can help convey evaluation findings more effectively than written reports. Use visuals to highlight key data points and trends.
- Be concise: Keep your presentation concise and to the point. Focus on the key findings and conclusions, and avoid getting bogged down in technical details.
- Tell a story: Use the evaluation findings to tell a story about the program’s impact and effectiveness. This can help engage stakeholders and make the findings more memorable.
- Provide context: Provide context for the evaluation findings by explaining the program’s objectives and intended impact. This will help stakeholders understand the significance of the findings.
- Use plain language: Use plain language that is easily understandable by your target audience. Avoid jargon and technical terms that may confuse or alienate stakeholders.
- Engage stakeholders: Engage stakeholders in the presentation by asking for their input and feedback. This can help build consensus and ensure that the evaluation findings are acted upon.
By following these tips, you can present evaluation findings in a way that engages stakeholders, highlights key findings, and ensures that the evaluation’s conclusions are acted upon to improve program outcomes.
Evaluation reports are crucial tools for program managers and policymakers to assess program effectiveness and make informed decisions about program design, implementation, and funding. By analyzing data collected during the evaluation process, evaluation reports provide evidence-based information that can be used to improve program outcomes and impact.
One of the primary ways that evaluation reports can be used to improve programs and policies is by identifying program strengths and weaknesses. By assessing program effectiveness and efficiency, evaluation reports can help identify areas where programs are succeeding and areas where improvements are needed. This information can inform program redesign and improvement efforts, leading to better program outcomes and impact.
Evaluation reports can also be used to make data-driven decisions about program design, implementation, and funding. By providing decision-makers with data-driven information, evaluation reports can help ensure that programs are designed and implemented in a way that maximizes their impact and effectiveness. This information can also be used to allocate resources more effectively, directing funding towards programs that are most effective and efficient.
Another way that evaluation reports can be used to improve programs and policies is by disseminating best practices in program design and implementation. By sharing information about what works and what doesn’t work, evaluation reports can help program managers and policymakers make informed decisions about program design and implementation, leading to better outcomes and impact.
Finally, evaluation reports can inform policy development and improvement efforts by providing evidence about the effectiveness and impact of existing policies. This information can be used to make data-driven decisions about policy development and improvement efforts, ensuring that policies are designed and implemented in a way that maximizes their impact and effectiveness.
In summary, evaluation reports are critical tools for improving programs and policies. By providing evidence-based information about program effectiveness and efficiency, evaluation reports can help program managers and policymakers make informed decisions, allocate resources more effectively, disseminate best practices, and inform policy development and improvement efforts.
There are many different templates available for creating evaluation reports. Here are some examples of template evaluation reports that can be used as a starting point for creating your own report:
- The National Science Foundation Evaluation Report Template – This template provides a structure for evaluating research projects funded by the National Science Foundation. It includes sections on project background, research questions, evaluation methodology, data analysis, and conclusions and recommendations.
- The CDC Program Evaluation Template – This template, created by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, provides a framework for evaluating public health programs. It includes sections on program description, evaluation questions, data sources, data analysis, and conclusions and recommendations.
- The World Bank Evaluation Report Template – This template, created by the World Bank, provides a structure for evaluating development projects. It includes sections on project background, evaluation methodology, data analysis, findings and conclusions, and recommendations.
- The European Commission Evaluation Report Template – This template provides a structure for evaluating European Union projects and programs. It includes sections on project description, evaluation objectives, evaluation methodology, findings, conclusions, and recommendations.
- The UNICEF Evaluation Report Template – This template provides a framework for evaluating UNICEF programs and projects. It includes sections on program description, evaluation questions, evaluation methodology, findings, conclusions, and recommendations.
These templates provide a structure for creating evaluation reports that are well-organized and easy to read. They can be customized to meet the specific needs of your program or project and help ensure that your evaluation report is comprehensive and includes all of the necessary components.
- World Health Organisations Reports
- Checkl ist for Assessing USAID Evaluation Reports
In conclusion, evaluation reports are essential tools for program managers and policymakers to assess program effectiveness and make informed decisions about program design, implementation, and funding. By analyzing data collected during the evaluation process, evaluation reports provide evidence-based information that can be used to improve program outcomes and impact.
To make evaluation reports work for you, it is important to plan ahead and establish clear objectives and target audiences. This will help guide the report’s structure and content and ensure that the report is tailored to the needs of its intended audience.
When writing an evaluation report, it is important to use clear and concise language, provide evidence-based findings, and offer actionable recommendations that can be used to improve program outcomes. Including context for the evaluation findings and acknowledging limitations and caveats will provide a balanced assessment of the program’s effectiveness and help build trust with stakeholders.
Presenting evaluation findings effectively requires knowing your audience, using visuals, being concise, telling a story, providing context, using plain language, and engaging stakeholders. By following these tips, you can present evaluation findings in a way that engages stakeholders, highlights key findings, and ensures that the evaluation’s conclusions are acted upon to improve program outcomes.
Finally, using evaluation reports to improve programs and policies requires identifying program strengths and weaknesses, making data-driven decisions, disseminating best practices, allocating resources effectively, and informing policy development and improvement efforts. By using evaluation reports in these ways, program managers and policymakers can ensure that their programs are effective, efficient, and sustainable over time.
Well understanding, the description of the general evaluation of report are clear with good arrangement and it help students to learn and make practices
Patrick Kapuot
Thankyou for very much for such detail information. Very comprehensively said.
hailemichael
very good explanation, thanks
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.
How strong is my Resume?
Only 2% of resumes land interviews.
Land a better, higher-paying career

Jobs for You
Consultant mel (georgia and armenia).
- Solidarity Center
Intern – Pricing and Accounting
- United States
Manager I, Institutional Support Program Implementation
Energy/environment analyst, senior environmental programs advisor, manager, impact and financial management.
- Emergent Climate
Information Coordinator – USAID Guatemala Planning and Program Support Office
- United States (Remote)
Director of Market Influence
- Atlanta, GA, USA
- Habitat for Humanity International
CLA Coordinator/Report Officer
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
Director of Collaborating, Learning, and Adapting (CLA) – Bosnia and Herzegovina
Senior transition and closeout consultant, global health technical and mission support (gh-tams), intern – pricing and budget, research technical advisor.
- South Bend, IN, USA (Remote)
- University of Notre Dame
YMELP II Short-Term Technical Assistance (STTA)
Water, sanitation and hygiene advisor (wash) – usaid/drc.
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
Services you might be interested in
Useful guides ....
How to Create a Strong Resume
Monitoring And Evaluation Specialist Resume
Resume Length for the International Development Sector
Types of Evaluation
Monitoring, Evaluation, Accountability, and Learning (MEAL)
LAND A JOB REFERRAL IN 2 WEEKS (NO ONLINE APPS!)
Sign Up & To Get My Free Referral Toolkit Now:

Tips for Writing a Strong Self-Evaluation (With Examples)

It’s no secret that nobody really loves the self-assessment performance review process. Singing our own praises may make our toes curl — and acknowledging where we’ve made mistakes in the past can feel uncomfortable or embarrassing.
So it seems like little wonder, then, that according to 2019 research by Gallup , 86% of employees say that they don’t find performance reviews helpful for driving improvement. Getting this part of the performance review right requires introspection, a non-judgmental attitude, and asking yourself the right questions to guide self-evaluation.
To get things started, use our tips in this article to help guide your reflection process. Then, follow up with our Self-Evaluation Template to help you structure your written evaluation.
Key Takeaways:
- Your self-assessment is a chance to be your own advocate.
- Track achievements year round to make the process easier.
- Include specific examples of any skills learned or goals met.
- If you’re stuck on what to write, consult manager and peer feedback.
What is a Self-Assessment Performance Review?
The self-assessment performance review is a key part of the performance management process. It’s a chance for self-reflection on your job performance, including your core strengths and areas for improvement. It also paints a picture for your manager of how you view yourself in relation to your team and the company as a whole, and surfaces any career aspirations or growth needs.
Self-assessment performance appraisals help employees see how their work contributes to the organization and their overall career aspirations, making them far more motivated to do their best work. They’re linked to increased employee performance, higher levels of job satisfaction, and improved employee engagement.
Benefits of employee self-evaluation include:
- Set goals more effectively: A 2020 study on managerial feedback found that focusing on future actions, rather than dwelling on past events, leads to better performance. When we evaluate our overall performance in the context of our professional development and progression, it helps us pinpoint the skill sets we need in the future.
- Eliminate performance review bias: A 2019 study on 30 years of performance management research found that when employees participate in the performance management process, it leads to greater satisfaction in the outcome. Employees were more likely to say the process felt fair and unbiased, because their participation created a two-way, collaborative process.
- Improve employee confidence: Our self-efficacy — or beliefs about how likely we are to succeed in a particular topic or learning opportunity — play an important role in how we perform. A 2021 study based on classroom learning found that when students reviewed their own performance, it boosted their confidence.
- Increase team alignment: Viewing your own performance in the context of how it contributes to your team’s overall goals helps highlight areas of misalignment in terms of processes or communication — meaning you can improve how your team works together.
What to Reflect On Before Writing an Employee Self-Assessment
Jumping into a self-evaluation might feel a little daunting. Taking a moment to do an informal review of your performance, progress, and goals can help you collect your thoughts when it’s time to write the real thing.
In the spirit of continuous feedback and the performance review process , consider your metrics of success for your own performance — whether that’s a quantitative measure like KPIs and OKRs, or more qualitative, such as your emotions and feelings about the last year.
Make sure you write down specific examples of any skills learned, goals met, or targets hit, so that you’re well-prepared for the next performance review cycle.
Here are our five best practices to get this process right.
1. Identify how you really feel.
Start by figuring out how you actually feel about your overall performance without the pressure of presenting these thoughts in a professional context.
Try taking some notes or consulting a trusted friend or peer about how you feel you’ve performed over the last quarter or year. Acknowledge the full spectrum of your experiences, including any specific examples you might feel hesitant to highlight in your formal performance review.
Coming up with an unfiltered version will help you understand how your perspective comes across, and you can always make edits once you start writing.
2. Review your goals.
Setting goals — and feeling motivated to achieve them — is the cornerstone of doing your best work. Review how you performed against your most recent goals. Did you meet, exceed, or struggle to meet expectations?
For each goal, evaluate yourself based on the following questions:
- Why did you meet — or struggle to meet — this goal?
- When you didn’t meet a goal, what blockers made progress difficult?
- Was this goal clear, specific, and challenging enough? Why?
- Thinking about the goals you struggled to meet, what could you improve on to meet goals like this in future?
- Thinking about the goals you achieved, how can you build on this success to set a new goal?
As you reflect on goal progress, use your objectives and key results (OKRs) to provide a framework for your self-assessment, adding details and examples from the past year that contextualize your progress or challenges.
3. Review your manager’s feedback.
Your performance review is an opportunity to check in with your manager about your progress and have a dialogue on what’s next. But it’s also an opportunity for you to provide additional context on anything that might have improved or hindered your performance and goal accomplishment.
Look at recent one-on-ones or manager feedback from previous check-ins for guidance. What did your manager highlight or praise? Was there any constructive feedback on your performance?
Make sure you reference your accomplishments in your review and highlight what you did well. For areas that need improvement, provide additional context for any questions you think your manager might ask, and share any details about how you approached a project or situation that shed light on its outcome. Reflect on how you grew, and your plans to continue improving.
4. Review notes from peers and coworkers.
Peer feedback isn’t just great for professional development and surfacing new performance perspectives — it’s also vital for fostering the environment needed for great teamwork. In fact, one 2015 study on employee recognition found that praise from team members can have twice the impact on your wellbeing at work compared with manager feedback.
Evaluating feedback from peers can help you see how you’ve supported your team’s overall goals, as well as highlighting your progress on any non-technical skills — like problem-solving or communication — that build a more complete picture of your progress in the last year. Look through any past performance reviews, emails, personal messages, team meeting slide decks, or your company’s Praise Wall to collate a balanced view of how your peers see you.
Evaluate your progress by considering the following questions:
- How have you helped team members and peers deliver on their goals?
- Were there any specific instances or projects where team members praised your contributions?
- How have you followed through on team expectations?
- How would you rate your teamwork and collaboration skills?
Find more question examples in our Peer Review Template .
Writing Your Performance Review Self-Assessment
Once you’re ready to write your self-appraisal, you’ll want to collate everything you’ve noted during the reflection process, and start crafting your highlight reel that outlines all of your accomplishments since your last review.
To get started, use your job description as a guide. Evaluate how you meet each of the core competencies and skill sets, pointing to specific examples when you demonstrated each. While you write, work through the following topics:
- Role in the wider team: How does your work connect to the bigger picture? What kind of teammate are you?
- Unique selling point: What do you contribute that sets you apart? How is your team unable to function without you?
- Key results: Review any OKRs. What key results did or didn’t you achieve? Why or why not?
- Areas for improvement: Things can change for the better after a performance evaluation. What does that look like for you?
Examples of How to Talk about Your Accomplishments in Your Self-Assessment
Many folks worry about sounding braggy in a self-review. And while it might feel uncomfortable to sing your own praises, try writing it like you’re advocating for someone else to show what you’re capable of.
Talk about the cause and effect of your actions on projects, and make sure to reference praise you’ve gotten from others. Include business outcomes, quotes from happy customers, and any tangible data. Talk assertively about your accomplishments like they’re facts.
Try using these self-evaluation examples to help you guide your review.
Goal Accomplishment
- “I set an OKR this year to grow our social channels 20%, but I exceeded that goal by growing them 40%.”
- “My contribution to project X has helped increase customer NPS 10x.”
- “Project Y has streamlined our process and saved time across teams.”
- “Project Z will bring in more and better-qualified leads.”
- “I accomplished a personal developmental goal to learn a new skill by working alongside peers in a different department.”
Project Management
- “I demonstrate strong time management skills when hitting project deadlines.”
- “I communicate project updates with all team members and relevant stakeholders in a timely manner.”
- “When running project X, I was effective at delegating tasks and following up on work to make sure our team stayed on deadline.”
- “I am effective at taking ownership of new projects and managing their successful completion.”
Team Support and Enablement
- “I always review my team member’s work within 24 hours of being asked.”
- “Because of my feedback on this project, XYZ was completed faster.”
- “I supported the success of our customer conference by being a speaker, and received praise from our VP of Marketing.”
- “I go above and beyond to make sure our team operates at its best, and I regularly provide help and support to team members when working on a collective goal.”
Non-Technical Skills
- “My problem-solving skills helped overcome a key strategic challenge in a recent project.”
- “Because of my effective decision-making skills, we were able to complete project XYZ in a timely manner.”
- “I regularly contribute my ideas and perspectives in team meetings to help boost our team’s output and goal accomplishment.”
- “I’m successful at staying on top of my to-do list, and regularly communicate progress with team members on shared projects.”
Ongoing Contributions
- “I maintain and moderate a critical daily community discussion channel.”
- “I reach out to prospects early in the morning, since they’re in a different time zone than I am.”
- “I send out a weekly update to the entire organization about my project or function.”
- “I helped launch and manage a new Employee Resource Group that supports our LGBTQ+ employees.”
Examples of How to Talk About Areas of Improvement
It can be hard to talk about your mistakes or recognize room for improvement in aspects of your work. For this reason, tone is particularly important when it comes to this portion of your self-assessment.
When talking about any areas for improvement, focus on honesty, and try not to be defensive, minimize errors, or blame others in your self-evaluation. Remember that everything you say is from your own perspective, so it’s a good practice to phrase things accordingly, such as “I found out I benefit from x”, or “I found I work best in x conditions”.
Reflecting on where you need to improve can also be a perfect opportunity to talk about how you want to grow in your career or improve in your job. When talking about mistakes or known problems during the review period, stay positive and emphasize the solution and next steps. You want to position yourself as a problem-solver with self-awareness.
For example, perhaps you weren’t prepared to take on a task because you weren’t trained. Propose enrolling in a class to help you step up your career development and take on more responsibilities.
When reflecting on your areas for improvement, try emulating the following examples:
- “I can sometimes struggle to take the lead in project management scenarios. I’d really like to take on some leadership skills classes to help me develop.”
- “I find it hard to share my ideas with team members on how to approach a project or piece of work, because I get overwhelmed when talking in a larger group. This year, I’d really like to learn how to develop my confidence with some mentoring.”
- “I made a scheduling mistake that contributed to a delay on our team’s recent project. I learned better time management skills as a result and have a plan to manage these situations better in future.”
- “I struggle with my presentation skills in front of a large audience. Is there someone in our wider team I can learn from?”
Crafting a Roadmap for Future Progression
Your self-assessment is a chance to be your own biggest advocate. As you work through the review process, try not to look at it as exposing your weaknesses, past failures, or mistakes. Instead, look at it as an opportunity, with your manager’s help, to take ownership of your career path, celebrate your wins, and unravel any niggling issues.
Working through this collaborative process should feel like a conversation with your manager that gives you a roadmap to help you perform at your very best in the future. For more support, download our Self-Evaluation Template .
Related content

How to Customize Your Performance Review Cycles with HR Tech
.webp)
Questions to Ask During Mid-Year Performance Reviews

5 Best Practices to Increase Your Performance Review Participation Rates

Your Performance Review Is Next Week. Here's What to Do.
7 Steps for How to Write an Evaluation Essay (Example & Template)
In this ultimate guide, I will explain to you exactly how to write an evaluation essay.
1. What is an Evaluation Essay?
An evaluation essay should provide a critical analysis of something.
You’re literally ‘evaluating’ the thing you’re looking up.
Here’s a couple of quick definitions of what we mean by ‘evaluate’:
- Merriam-Webster defines evaluation as: “to determine the significance, worth, or condition of usually by careful appraisal and study”
- Collins Dictionary says: “If you evaluate something or someone, you consider them in order to make a judgment about them, for example about how good or bad they are.”
Here’s some synonyms for ‘evaluate’:
So, we could say that an evaluation essay should carefully examine the ‘thing’ and provide an overall judgement of it.
Here’s some common things you may be asked to write an evaluation essay on:
This is by no means an exhaustive list. Really, you can evaluate just about anything!
Get a Pdf of this article for class
Enjoy subscriber-only access to this article’s pdf
2. How to write an Evaluation Essay
There are two secrets to writing a strong evaluation essay. The first is to aim for objective analysis before forming an opinion. The second is to use an evaluation criteria.
Aim to Appear Objective before giving an Evaluation Argument
Your evaluation will eventually need an argument.
The evaluation argument will show your reader what you have decided is the final value of the ‘thing’ you’re evaluating.
But in order to convince your reader that your evaluative argument is sound, you need to do some leg work.
The aim will be to show that you have provided a balanced and fair assessment before coming to your conclusion.
In order to appear balanced you should:
- Discuss both the pros and cons of the thing
- Discuss both the strengths and weaknesses of the thing
- Look at the thing from multiple different perspectives
- Be both positive and critical. Don’t make it look like you’re biased towards one perspective.
In other words, give every perspective a fair hearing.
You don’t want to sound like a propagandist. You want to be seen as a fair and balanced adjudicator.
Use an Evaluation Criteria
One way to appear balanced is to use an evaluation criteria.
An evaluation criteria helps to show that you have assessed the ‘thing’ based on an objective measure.
Here’s some examples of evaluation criteria:
- Strength under pressure
- Longevity (ability to survive for a long time)
- Ease of use
- Ability to get the job done
- Friendliness
- Punctuality
- Ability to predict my needs
- Calmness under pressure
- Attentiveness
A Bed and Breakfast
- Breakfast options
- Taste of food
- Comfort of bed
- Local attractions
- Service from owner
- Cleanliness
We can use evaluation criteria to frame out ability to conduct the analysis fairly.
This is especially true for if you have to evaluate multiple different ‘things’. For example, if you’re evaluating three novels, you want to be able to show that you applied the same ‘test’ on all three books!
This will show that you gave each ‘thing’ a fair chance and looked at the same elements for each.
3. How to come up with an Evaluation Argument
After you have:
- Looked at both good and bad elements of the ‘thing’, and
- Used an evaluation criteria
You’ll then need to develop an evaluative argument. This argument shows your own overall perspective on the ‘thing’.
Remember, you will need to show your final evaluative argument is backed by objective analysis. You need to do it in order!
Analyze first. Evaluate second.
Here’s an example.
Let’s say you’re evaluating the quality of a meal.
You might say:
- A strength of the meal was its presentation. It was well presented and looked enticing to eat.
- A weakness of the meal was that it was overcooked. This decreased its flavor.
- The meal was given a low rating on ‘cost’ because it was more expensive than the other comparative meals on the menu.
- The meal was given a high rating on ‘creativity’. It was a meal that involved a thoughtful and inventive mix of ingredients.
Now that you’ve looked at some pros and cons and measured the meal based on a few criteria points (like cost and creativity), you’ll be able to come up with a final argument:
- Overall, the meal was good enough for a middle-tier restaurant but would not be considered a high-class meal. There is a lot of room for improvement if the chef wants to win any local cooking awards.
Evaluative terms that you might want to use for this final evaluation argument might include:
- All things considered
- With all key points in mind
4. Evaluation Essay Outline (with Examples)
Okay, so now you know what to do, let’s have a go at creating an outline for your evaluation essay!
Here’s what I recommend:
4.1 How to Write your Introduction
In the introduction, feel free to use my 5-Step INTRO method . It’ll be an introduction just like any other essay introduction .
And yes, feel free to explain what the final evaluation will be.
So, here it is laid out nice and simple.
Write one sentence for each point to make a 5-sentence introduction:
- Interest: Make a statement about the ‘thing’ you’re evaluating that you think will be of interest to the reader. Make it a catchy, engaging point that draws the reader in!
- Notify: Notify the reader of any background info on the thing you’re evaluating. This is your chance to show your depth of knowledge. What is a historical fact about the ‘thing’?
- Translate: Re-state the essay question. For an evaluative essay, you can re-state it something like: “This essay evaluates the book/ product/ article/ etc. by looking at its strengths and weaknesses and compares it against a marking criteria”.
- Report: Say what your final evaluation will be. For example you can say “While there are some weaknesses in this book, overall this evaluative essay will show that it helps progress knowledge about Dinosaurs.”
- Outline: Simply give a clear overview of what will be discussed. For example, you can say: “Firstly, the essay will evaluate the product based on an objective criteria. This criteria will include its value for money, fit for purpose and ease of use. Next, the essay will show the main strengths and weaknesses of the product. Lastly, the essay will provide a final evaluative statement about the product’s overall value and worth.”
If you want more depth on how to use the INTRO method, you’ll need to go and check out our blog post on writing quality introductions.
4.2 Example Introduction
This example introduction is for the essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society.
“Facebook is the third most visited website in the world. It was founded in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg in his college dorm. This essay evaluates the impact of Facebook on society and makes an objective judgement on its value. The essay will argue that Facebook has changed the world both for the better and worse. Firstly, it will give an overview of what Facebook is and its history. Then, it will examine Facebook on the criteria of: impact on social interactions, impact on the media landscape, and impact on politics.”
You’ll notice that each sentence in this introduction follows my 5-Step INTRO formula to create a clear, coherent 5-Step introduction.
4.3 How to Write your Body Paragraphs
The first body paragraph should give an overview of the ‘thing’ being evaluated.
Then, you should evaluate the pros and cons of the ‘thing’ being evaluated based upon the criteria you have developed for evaluating it.
Let’s take a look below.
4.4 First Body Paragraph: Overview of your Subject
This first paragraph should provide objective overview of your subject’s properties and history. You should not be doing any evaluating just yet.
The goal for this first paragraph is to ensure your reader knows what it is you’re evaluating. Secondarily, it should show your marker that you have developed some good knowledge about it.
If you need to use more than one paragraph to give an overview of the subject, that’s fine.
Similarly, if your essay word length needs to be quite long, feel free to spend several paragraphs exploring the subject’s background and objective details to show off your depth of knowledge for the marker.
4.5 First Body Paragraph Example
Sticking with the essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society , this might be your paragraph:
“Facebook has been one of the most successful websites of all time. It is the website that dominated the ‘Web 2.0’ revolution, which was characterized by user two-way interaction with the web. Facebook allowed users to create their own personal profiles and invite their friends to follow along. Since 2004, Facebook has attracted more than one billion people to create profiles in order to share their opinions and keep in touch with their friends.”
Notice here that I haven’t yet made any evaluations of Facebook’s merits?
This first paragraph (or, if need be, several of them) should be all about showing the reader exactly what your subject is – no more, no less.
4.6 Evaluation Paragraphs: Second, Third, Forth and Fifth Body Paragraphs
Once you’re confident your reader will know what the subject that you’re evaluating is, you’ll need to move on to the actual evaluation.
For this step, you’ll need to dig up that evaluation criteria we talked about in Point 2.
For example, let’s say you’re evaluating a President of the United States.
Your evaluation criteria might be:
- Impact on world history
- Ability to pass legislation
- Popularity with voters
- Morals and ethics
- Ability to change lives for the better
Really, you could make up any evaluation criteria you want!
Once you’ve made up the evaluation criteria, you’ve got your evaluation paragraph ideas!
Simply turn each point in your evaluation criteria into a full paragraph.
How do you do this?
Well, start with a topic sentence.
For the criteria point ‘Impact on world history’ you can say something like: “Barack Obama’s impact on world history is mixed.”
This topic sentence will show that you’ll evaluate both pros and cons of Obama’s impact on world history in the paragraph.
Then, follow it up with explanations.
“While Obama campaigned to withdraw troops from Iraq and Afghanistan, he was unable to completely achieve this objective. This is an obvious negative for his impact on the world. However, as the first black man to lead the most powerful nation on earth, he will forever be remembered as a living milestone for civil rights and progress.”
Keep going, turning each evaluation criteria into a full paragraph.
4.7 Evaluation Paragraph Example
Let’s go back to our essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society .
I’ve decided to use the evaluation criteria below:
- impact on social interactions;
- impact on the media landscape;
- impact on politics
Naturally, I’m going to write one paragraph for each point.
If you’re expected to write a longer piece, you could write two paragraphs on each point (one for pros and one for cons).
Here’s what my first evaluation paragraph might look like:
“Facebook has had a profound impact on social interactions. It has helped people to stay in touch with one another from long distances and after they have left school and college. This is obviously a great positive. However, it can also be seen as having a negative impact. For example, people may be less likely to interact face-to-face because they are ‘hanging out’ online instead. This can have negative impact on genuine one-to-one relationships.”
You might notice that this paragraph has a topic sentence, explanations and examples. It follows my perfect paragraph formula which you’re more than welcome to check out!
4.8 How to write your Conclusion
To conclude, you’ll need to come up with one final evaluative argument.
This evaluation argument provides an overall assessment. You can start with “Overall, Facebook has been…” and continue by saying that (all things considered) he was a good or bad president!
Remember, you can only come up with an overall evaluation after you’ve looked at the subject’s pros and cons based upon your evaluation criteria.
In the example below, I’m going to use my 5 C’s conclusion paragraph method . This will make sure my conclusion covers all the things a good conclusion should cover!
Like the INTRO method, the 5 C’s conclusion method should have one sentence for each point to create a 5 sentence conclusion paragraph.
The 5 C’s conclusion method is:
- Close the loop: Return to a statement you made in the introduction.
- Conclude: Show what your final position is.
- Clarify: Clarify how your final position is relevant to the Essay Question.
- Concern: Explain who should be concerned by your findings.
- Consequences: End by noting in one final, engaging sentence why this topic is of such importance. The ‘concern’ and ‘consequences’ sentences can be combined
4.9 Concluding Argument Example Paragraph
Here’s a possible concluding argument for our essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society .
“The introduction of this essay highlighted that Facebook has had a profound impact on society. This evaluation essay has shown that this impact has been both positive and negative. Thus, it is too soon to say whether Facebook has been an overall positive or negative for society. However, people should pay close attention to this issue because it is possible that Facebook is contributing to the undermining of truth in media and positive interpersonal relationships.”
Note here that I’ve followed the 5 C’s conclusion method for my concluding evaluative argument paragraph.
5. Evaluation Essay Example Template
Below is a template you can use for your evaluation essay , based upon the advice I gave in Section 4:
| Introduction | Use the to write an introduction. This introduction should clearly state what you are evaluating, the criteria that you will be using to evaluate it, and what will be. |
| Body Paragraph 1: Outline of the Subject | Before evaluating the subject or ‘thing’, make sure you use a paragraph or two to clearly explain what it is to the reader. This is your chance to show your depth of knowledge about the topic. |
Body Paragraphs 2 – 5: Evaluate the Subject | Use the evaluation criteria you have decided upon to evaluate the subject. For each element of the criteria, write one paragraph looking at the pros and cons of the subject. You might want to use my to write your paragraphs. |
Conclusion | Use my to write a 5-sentence conclusion. Make sure you show your final evaluative argument in the conclusion so your reader knows your final position on the issue. |
6. 23+ Good Evaluation Essay Topics
Okay now that you know how to write an evaluation essay, let’s look at a few examples.
For each example I’m going to give you an evaluation essay title idea, plus a list of criteria you might want to use in your evaluation essay.
6.1 Evaluation of Impact
- Evaluate the impact of global warming on the great barrier reef. Recommended evaluation criteria: Level of bleaching; Impact on tourism; Economic impact; Impact on lifestyles; Impact on sealife
- Evaluate the impact of the Global Financial Crisis on poverty. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on jobs; Impact on childhood poverty; Impact on mental health rates; Impact on economic growth; Impact on the wealthy; Global impact
- Evaluate the impact of having children on your lifestyle. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on spare time; Impact on finances; Impact on happiness; Impact on sense of wellbeing
- Evaluate the impact of the internet on the world. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on connectedness; Impact on dating; Impact on business integration; Impact on globalization; Impact on media
- Evaluate the impact of public transportation on cities. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on cost of living; Impact on congestion; Impact on quality of life; Impact on health; Impact on economy
- Evaluate the impact of universal healthcare on quality of life. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on reducing disease rates; Impact on the poorest in society; Impact on life expectancy; Impact on happiness
- Evaluate the impact of getting a college degree on a person’s life. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on debt levels; Impact on career prospects; Impact on life perspectives; Impact on relationships
6.2 Evaluation of a Scholarly Text or Theory
- Evaluate a Textbook. Recommended evaluation criteria: clarity of explanations; relevance to a course; value for money; practical advice; depth and detail; breadth of information
- Evaluate a Lecture Series, Podcast or Guest Lecture. Recommended evaluation criteria: clarity of speaker; engagement of attendees; appropriateness of content; value for monet
- Evaluate a journal article. Recommended evaluation criteria: length; clarity; quality of methodology; quality of literature review ; relevance of findings for real life
- Evaluate a Famous Scientists. Recommended evaluation criteria: contribution to scientific knowledge; impact on health and prosperity of humankind; controversies and disagreements with other scientists.
- Evaluate a Theory. Recommended evaluation criteria: contribution to knowledge; reliability or accuracy; impact on the lives of ordinary people; controversies and contradictions with other theories.
6.3 Evaluation of Art and Literature
- Evaluate a Novel. Recommended evaluation criteria: plot complexity; moral or social value of the message; character development; relevance to modern life
- Evaluate a Play. Recommended evaluation criteria: plot complexity; quality of acting; moral or social value of the message; character development; relevance to modern life
- Evaluate a Film. Recommended evaluation criteria: plot complexity; quality of acting; moral or social value of the message; character development; relevance to modern life
- Evaluate an Artwork. Recommended evaluation criteria: impact on art theory; moral or social message; complexity or quality of composition
6.4 Evaluation of a Product or Service
- Evaluate a Hotel or Bed and Breakfast. Recommended evaluation criteria: quality of service; flexibility of check-in and check-out times; cleanliness; location; value for money; wi-fi strength; noise levels at night; quality of meals; value for money
- Evaluate a Restaurant. Recommended evaluation criteria: quality of service; menu choices; cleanliness; atmosphere; taste; value for money.
- Evaluate a Car. Recommended evaluation criteria: fuel efficiency; value for money; build quality; likelihood to break down; comfort.
- Evaluate a House. Recommended evaluation criteria: value for money; build quality; roominess; location; access to public transport; quality of neighbourhood
- Evaluate a Doctor. Recommended evaluation criteria: Quality of service; knowledge; quality of equipment; reputation; value for money.
- Evaluate a Course. Recommended evaluation criteria: value for money; practical advice; quality of teaching; quality of resources provided.
7. Concluding Advice

Evaluation essays are common in high school, college and university.
The trick for getting good marks in an evaluation essay is to show you have looked at both the pros and cons before making a final evaluation analysis statement.
You don’t want to look biased.
That’s why it’s a good idea to use an objective evaluation criteria, and to be generous in looking at both positives and negatives of your subject.
Read Also: 39 Better Ways to Write ‘In Conclusion’ in an Essay
I recommend you use the evaluation template provided in this post to write your evaluation essay. However, if your teacher has given you a template, of course use theirs instead! You always want to follow your teacher’s advice because they’re the person who will be marking your work.
Good luck with your evaluation essay!

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Self-Actualization Examples (Maslow's Hierarchy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Forest Schools Philosophy & Curriculum, Explained!
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Montessori's 4 Planes of Development, Explained!
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Montessori vs Reggio Emilia vs Steiner-Waldorf vs Froebel
2 thoughts on “7 Steps for How to Write an Evaluation Essay (Example & Template)”
What an amazing article. I am returning to studying after several years and was struggling with how to present an evaluative essay. This article has simplified the process and provided me with the confidence to tackle my subject (theoretical approaches to development and management of teams).
I just wanted to ask whether the evaluation criteria has to be supported by evidence or can it just be a list of criteria that you think of yourself to objectively measure?
Many many thanks for writing this!

Usually we would want to see evidence, but ask your teacher for what they’re looking for as they may allow you, depending on the situation.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Add anything here here or just remove it..
- Professional Services
- Request A Form

- Create an Evaluation Form
- Performance Appraisal Phrases
- Performance Management System
- 360 Degree Feedback
- Performance Appraisal Examples
- Performance Review Examples
- Sample Evaluation Forms
- Sample Lecture Evaluation Form
- Sample Workshop Evaluation Form
- Performance
- Professional
No products in the cart.
Return to shop
An employee evaluation form is an extremely effective tool in helping both employees and supervisors recognize an employee’s areas of strength and weakness. A good evaluation form provides plenty of space for supervisor comments and suggestions and will include an easily understandable rating system. When you create an evaluation form , they can be as simple or complex as you would like. The length of your company’s evaluation form will depend on the type of work performed by employees and the complexity of their tasks.
Create an Evaluation Form: Basics

Include a description of the numerical rating system to be used when you create an evaluation form . For example, you may decide to use the number one for an unsatisfactory rating, a two to indicate that improvement is needed, a three for satisfactory progress, a four for exceeding expectations and a five for superior work.
Create an Evaluation Form: Categories and Sections
Start an evaluation section for a general assessment of the employee’s skills. Include such categories as attendance, team effort, adherence to procedures, communication skills with coworkers and the public, initiative and work ethic. Include a space to write the rating number for each category, and allow several blank lines for comments after each category.
Add a section for skills that may be specific to your industry. If you work in a factory, you will want to include sections that examine such things as the employee’s skill at operating machinery, output and efficiency. If your employees are sales representatives, you will need to include a section rating the ability to meet quotas and bring in new business.
Create a separate section for evaluation of management skills, if applicable. Include spaces for organization, planning, delegation and meeting goals.
Include sections for the evaluation of the employee’s weaknesses and strengths. Follow this section with an overall rating and an area on setting goals for the upcoming year.
Write a paragraph that says that the review has been discussed with the employee and that the employee’s signature indicates only that he has been presented with the review and does not necessarily mean that he agrees with the review. Include several blank lines for the employee to make any comments.
Provide signature lines for the employee and supervisor. Include a space for the date for each line.
- Search for:
- Project Management Methodologies
- Project Management Metrics
- Project Portfolio Management
- Proof of Concept Templates
- Punch List Templates
- Requirement Gathering Process
- Requirements Traceability Matrix
- Resource Scheduling
- Roles and Responsibilities Template
- Setting Sprint Goals
- Stakeholder Engagement Model
- Stakeholder Identification
- Stakeholder Mapping
- Stakeholder-theory
- Team Alignment Map
- Team Charter
- Templates for Managers
- What is Project Baseline
- Work Log Templates
- Workback Schedule
- Workload Management
- Assumption Mapping
- Work Breakdown Structures
- Agile Team Structure
- Avoding Scope Creep
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts
- Precision VS Accuracy
- Scrum-Spike
- User Story Guide
- Creating Project Charters
- Guide to Team Communication
- How to Prioritize Tasks
- Mastering RAID Logs
- Overcoming Analysis Paralysis
- Understanding RACI Model
- Achieving Big Hairy Audacious Goals
- Critical Success Factors
- Deadline Management
- Eisenhower Matrix Guide
- Guide to Multi Project Management
- Procure-to-Pay Best Practices
- Procurement Management Plan Template to Boost Project Success
- Project Execution and Change Management
- Project Management Success Factors
- Project Plan and Schedule Templates
- Resource Planning Templates for Smooth Project Execution
- Risk Management and Quality Management Plan Templates
- Risk Management in Software Engineering
- Setting and Achieving Stretch Goals
- Stage Gate Process
- Stakeholder Management Planning
- Understanding the S-Curve
- Visualizing Your To-Do List
- 30-60-90 Day Plan
- Work Plan Template
- Weekly Planner Template
- Task Analysis Examples
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts for Planning
- Inventory Management Tecniques
- Inventory Templates
- Six Sigma DMAIC Method
- Visual Process Improvement
- Value Stream Mapping
- Creating a Workflow
- Fibonacci Scale Template
- Supply Chain Diagram
- Kaizen Method
- Procurement Process Flow Chart
- Guide to State Diagrams
- UML Activity Diagrams
- Class Diagrams & their Relationships
- Visualize flowcharts for software
- Wire-Frame Benefits
- Applications of UML
- Selecting UML Diagrams
- Create Sequence Diagrams Online
- Activity Diagram Tool
- Archimate Tool
- Class Diagram Tool
- Graphic Organizers
- Social Work Assessment Tools
- Using KWL Charts to Boost Learning
- Editable Timeline Templates
- Kinship Diagram Guide
- Power of Visual Documentation
- Graphic Organizers for Teachers & Students
- Visual Documentation Techniques
- Visual Tool for Visual Documentation
- Concept Maps in Science
- Conducting a Thematic Analysis
- Visualizing a Dichotomous Key
- 5 W's Chart
- Circular Flow Diagram Maker
- Cladogram Maker
- Comic Strip Maker
- Course Design Template
- AI Buyer Persona
- AI Data Visualization
- AI Diagrams
- AI Project Management
- AI SWOT Analysis
- Best AI Templates
- Brainstorming AI
- Pros & Cons of AI
- AI for Business Strategy
- Using AI for Business Plan
- AI for HR Teams
- BPMN Symbols
- BPMN vs UML
- Business Process Analysis
- Business Process Modeling
- Capacity Planning Guide
- Case Management Process
- How to Avoid Bottlenecks in Processes
- Innovation Management Process
- Project vs Process
- Solve Customer Problems
- Spaghetti Diagram
- Startup Templates
- Streamline Purchase Order Process
- What is BPMN
- Approval Process
- Employee Exit Process
- Iterative Process
- Process Documentation
- Process Improvement Ideas
- Risk Assessment Process
- Tiger Teams
- Work Instruction Templates
- Workflow Vs. Process
- Process Mapping
- Business Process Reengineering
- Meddic Sales Process
- SIPOC Diagram
- What is Business Process Management
- Process Mapping Software
- Business Analysis Tool
- Business Capability Map
- Decision Making Tools and Techniques
- Operating Model Canvas
- Mobile App Planning
- Product Development Guide
- Product Roadmap
- Timeline Diagrams
- Visualize User Flow
- Sequence Diagrams
- Flowchart Maker
- Online Class Diagram Tool
- Organizational Chart Maker
- Mind Map Maker
- Retro Software
- Agile Project Charter
- Critical Path Software
- Brainstorming Guide
- Brainstorming Tools
- Concept Map Note Taking
- Visual Tools for Brainstorming
- Brainstorming Content Ideas
- Brainstorming in Business
- Brainstorming Questions
- Brainstorming Rules
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Brainstorming Workshop
- Design Thinking and Brainstorming
- Divergent vs Convergent Thinking
- Group Brainstorming Strategies
- Group Creativity
- How to Make Virtual Brainstorming Fun and Effective
- Ideation Techniques
- Improving Brainstorming
- Marketing Brainstorming
- Plot Diagrams
- Rapid Brainstorming
- Reverse Brainstorming Challenges
- Reverse vs. Traditional Brainstorming
- What Comes After Brainstorming
- Flowchart Guide
- Spider Diagram Guide
- 5 Whys Template
- Assumption Grid Template
- Brainstorming Templates
- Brainwriting Template
- Innovation Techniques
- 50 Business Diagrams
- Business Model Canvas
- Change Control Process
- Change Management Process
- Macro Environmental Analysis
- NOISE Analysis
- Profit & Loss Templates
- Scenario Planning
- What are Tree Diagrams
- Winning Brand Strategy
- Work Management Systems
- Balanced Scorecard
- Developing Action Plans
- Guide to setting OKRS
- How to Write a Memo
- Improve Productivity & Efficiency
- Mastering Task Analysis
- Mastering Task Batching
- Monthly Budget Templates
- Program Planning
- Top Down Vs. Bottom Up
- Weekly Schedule Templates
- Cash Cow Matrix
- Kaizen Principles
- Opportunity Mapping
- Strategic-Goals
- Strategy Mapping
- Strategy vs Tactics
- T Chart Guide
- Business Continuity Plan
- Developing Your MVP
- Incident Management
- Needs Assessment Process
- Product Development From Ideation to Launch
- Value-Proposition-Canvas
- Visualizing Competitive Landscape
- Communication Plan
- Graphic Organizer Creator
- Fault Tree Software
- Bowman's Strategy Clock Template
- Decision Matrix Template
- Communities of Practice
- Goal Setting for 2024
- Meeting Templates
- Meetings Participation
- Microsoft Teams Brainstorming
- Retrospective Guide
- Skip Level Meetings
- Visual Documentation Guide
- Visual Note Taking
- Weekly Meetings
- Affinity Diagrams
- Business Plan Presentation
- Post-Mortem Meetings
- Team Building Activities
- WBS Templates
- Online Whiteboard Tool
- Communications Plan Template
- Idea Board Online
- Meeting Minutes Template
- Genograms in Social Work Practice
- Conceptual Framework
- How to Conduct a Genogram Interview
- How to Make a Genogram
- Genogram Questions
- Genograms in Client Counseling
- Understanding Ecomaps
- Visual Research Data Analysis Methods
- House of Quality Template
- Customer Problem Statement Template
- Competitive Analysis Template
- Creating Operations Manual
- Knowledge Base
- Folder Structure Diagram
- Online Checklist Maker
- Lean Canvas Template
- Instructional Design Examples
- Genogram Maker
- Work From Home Guide
- Strategic Planning
- Employee Engagement Action Plan
- Huddle Board
- One-on-One Meeting Template
- Story Map Graphic Organizers
- Introduction to Your Workspace
- Managing Workspaces and Folders
- Adding Text
- Collaborative Content Management
- Creating and Editing Tables
- Adding Notes
- Introduction to Diagramming
- Using Shapes
- Using Freehand Tool
- Adding Images to the Canvas
- Accessing the Contextual Toolbar
- Using Connectors
- Working with Tables
- Working with Templates
- Working with Frames
- Using Notes
- Access Controls
- Exporting a Workspace
- Real-Time Collaboration
- Notifications
- Using Creately VIZ
- Meet Creately VIZ
- Unleashing the Power of Collaborative Brainstorming
- Uncovering the potential of Retros for all teams
- Collaborative Apps in Microsoft Teams
- Hiring a Great Fit for Your Team
- Project Management Made Easy
- Cross-Corporate Information Radiators
- Creately 4.0 - Product Walkthrough
- What's New
What is Project Evaluation? The Complete Guide with Templates
Project evaluation is an important part of determining the success or failure of a project. Properly evaluating a project helps you understand what worked well and what could be improved for future projects. This blog post will provide an overview of key components of project evaluation and how to conduct effective evaluations.
What is Project Evaluation?
Project evaluation is a key part of assessing the success, progress and areas for improvement of a project. It involves determining how well a project is meeting its goals and objectives. Evaluation helps determine if a project is worth continuing, needs adjustments, or should be discontinued.
A good evaluation plan is developed at the start of a project. It outlines the criteria that will be used to judge the project’s performance and success. Evaluation criteria can include things like:
- Meeting timelines and budgets - Were milestones and deadlines met? Was the project completed within budget?
- Delivering expected outputs and outcomes - Were the intended products, results and benefits achieved?
- Satisfying stakeholder needs - Were customers, users and other stakeholders satisfied with the project results?
- Achieving quality standards - Were quality metrics and standards defined and met?
- Demonstrating effectiveness - Did the project accomplish its intended purpose?
Project evaluation provides valuable insights that can be applied to the current project and future projects. It helps organizations learn from their projects and continuously improve their processes and outcomes.
Project Evaluation Templates
These templates will help you evaluate your project by providing a clear structure to assess how it was planned, carried out, and what it achieved. Whether you’re managing the project, part of the team, or a stakeholder, these template assist in gathering information systematically for a thorough evaluation.
Project Evaluation Template 1
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

Project Evaluation Template 2
Project Evaluation Methods
Project evaluation involves using various methods to assess the performance and impact of a project. The choice of methods depends on the nature of the project, its objectives, and the available resources. Here are some common project evaluation methods:
Pre-project evaluation
Pre-project evaluations are done before a project begins. This involves evaluating the project plan, scope, objectives, resources, and budget. This helps determine if the project is feasible and identifies any potential issues or risks upfront. It establishes a baseline for later evaluations.
Ongoing evaluation
Ongoing evaluations happen during the project lifecycle. Regular status reports track progress against the project plan, budget, and deadlines. Any deviations or issues are identified and corrective actions can be taken promptly. This allows projects to stay on track and make adjustments as needed.
Post-project evaluation
Post-project evaluations occur after a project is complete. This final assessment determines if the project objectives were achieved and customer requirements were met. Key metrics like timeliness, budget, and quality are examined. Lessons learned are documented to improve processes for future projects. Stakeholder feedback is gathered through surveys, interviews, or focus groups .
Project Evaluation Steps
When evaluating a project, there are several key steps you should follow. These steps will help you determine if the project was successful and identify areas for improvement in future initiatives.
Step 1: Set clear goals
The first step is establishing clear goals and objectives for the project before it begins. Make sure these objectives are SMART: specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound. Having clear goals from the outset provides a benchmark for measuring success later on.
Step 2: Monitor progress
Once the project is underway, the next step is monitoring progress. Check in regularly with your team to see if you’re on track to meet your objectives and deadlines. Identify and address any issues as early as possible before they become major roadblocks. Monitoring progress also allows you to course correct if needed.
Step 3: Collect data
After the project is complete, collect all relevant data and metrics. This includes both quantitative data like budget information, timelines and deliverables, as well customer feedback and qualitative data from surveys or interviews. Analyzing this data will show you how well the project performed against your original objectives.
Step 4: Analyze and interpret
Identify what worked well and what didn’t during the project. Highlight best practices to replicate and lessons learned to improve future initiatives. Get feedback from all stakeholders involved, including project team members, customers and management.
Step 5: Develop an action plan
Develop an action plan to apply what you’ve learned for the next project. Update processes, procedures and resource allocations based on your evaluation. Communicate changes across your organization and train employees on any new best practices. Implementing these changes will help you avoid similar issues the next time around.
Benefits of Project Evaluation
Project evaluation is a valuable tool for organizations, helping them learn, adapt, and improve their project outcomes over time. Here are some benefits of project evaluation.
- Helps in making informed decisions by providing a clear understanding of the project’s strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
- Holds the project team accountable for meeting goals and using resources effectively, fostering a sense of responsibility.
- Facilitates organizational learning by capturing valuable insights and lessons from both successful and challenging aspects of the project.
- Allows for the efficient allocation of resources by identifying areas where adjustments or reallocations may be needed.
- Provides evidence of the project’s value by assessing its impact, cost-effectiveness, and alignment with organizational objectives.
- Involves stakeholders in the evaluation process, fostering collaboration, and ensuring that diverse perspectives are considered.
Project Evaluation Best Practices
Follow these best practices to do a more effective and meaningful project evaluation, leading to better project outcomes and organizational learning.
- Clear objectives : Clearly define the goals and questions you want the evaluation to answer.
- Involve stakeholders : Include the perspectives of key stakeholders to ensure a comprehensive evaluation.
- Use appropriate methods : Choose evaluation methods that suit your objectives and available resources.
- Timely data collection : Collect data at relevant points in the project timeline to ensure accuracy and relevance.
- Thorough analysis : Analyze the collected data thoroughly to draw meaningful conclusions and insights.
- Actionable recommendations : Provide practical recommendations that can lead to tangible improvements in future projects.
- Learn and adapt : Use evaluation findings to learn from both successes and challenges, adapting practices for continuous improvement.
- Document lessons : Document lessons learned from the evaluation process for organizational knowledge and future reference.
How to Use Creately to Evaluate Your Projects
Use Creately’s visual collaboration platform to evaluate your project and improve communication, streamline collaboration, and provide a visual representation of project data effectively.
Task tracking and assignment
Use the built-in project management tools to create, assign, and track tasks right on the canvas. Assign responsibilities, set due dates, and monitor progress with Agile Kanban boards, Gantt charts, timelines and more. Create task cards containing detailed information, descriptions, due dates, and assigned responsibilities.
Notes and attachments
Record additional details and attach documents, files, and screenshots related to your tasks and projects with per item integrated notes panel and custom data fields. Or easily embed files and attachments right on the workspace to centralize project information. Work together on project evaluation with teammates with full multiplayer text and visual collaboration.
Real-time collaboration
Get any number of participants on the same workspace and track their additions to the progress report in real-time. Collaborate with others in the project seamlessly with true multi-user collaboration features including synced previews and comments and discussion threads. Use Creately’s Microsoft Teams integration to brainstorm, plan, run projects during meetings.
Pre-made templates
Get a head start with ready-to-use progress evaluation templates and other project documentation templates available right inside the app. Explore 1000s more templates and examples for various scenarios in the community.
In summary, project evaluation is like a compass for projects, helping teams understand what worked well and what can be improved. It’s a tool that guides organizations to make better decisions and succeed in future projects. By learning from the past and continuously improving, project evaluation becomes a key factor in the ongoing journey of project management, ensuring teams stay on the path of excellence and growth.
More project management related guides
- 8 Essential Metrics to Measure Project Success
- How to Manage Your Project Portfolio Like a Pro
- What is Project Baseline in Project Management?
- How to Create a Winning Project Charter: Your Blueprint for Success
- Your Comprehensive Guide to Creating Effective Workback Schedules
- What is a Work Breakdown Structure? and How To Create a WBS?
- The Practical Guide to Creating a Team Charter
- Your Guide to Multi-Project Management
- How AI Is Transforming Project Management
- A Practical Guide to Resource Scheduling in Project Management
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
Amanda Athuraliya is the communication specialist/content writer at Creately, online diagramming and collaboration tool. She is an avid reader, a budding writer and a passionate researcher who loves to write about all kinds of topics.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
A Robot Walks into a Bar: Can Language Models Serve as Creativity Support Tools for Comedy? An Evaluation of LLMs' Humour Alignment with Comedians
- Wojciech Mirowski, Piotr
- Love, Juliette
- Mathewson, Kory W.
- Mohamed, Shakir
We interviewed twenty professional comedians who perform live shows in front of audiences and who use artificial intelligence in their artistic process as part of 3-hour workshops on ``AI x Comedy'' conducted at the Edinburgh Festival Fringe in August 2023 and online. The workshop consisted of a comedy writing session with large language models (LLMs), a human-computer interaction questionnaire to assess the Creativity Support Index of AI as a writing tool, and a focus group interrogating the comedians' motivations for and processes of using AI, as well as their ethical concerns about bias, censorship and copyright. Participants noted that existing moderation strategies used in safety filtering and instruction-tuned LLMs reinforced hegemonic viewpoints by erasing minority groups and their perspectives, and qualified this as a form of censorship. At the same time, most participants felt the LLMs did not succeed as a creativity support tool, by producing bland and biased comedy tropes, akin to ``cruise ship comedy material from the 1950s, but a bit less racist''. Our work extends scholarship about the subtle difference between, one the one hand, harmful speech, and on the other hand, ``offensive'' language as a practice of resistance, satire and ``punching up''. We also interrogate the global value alignment behind such language models, and discuss the importance of community-based value alignment and data ownership to build AI tools that better suit artists' needs.
- Computer Science - Artificial Intelligence;
- Computer Science - Computation and Language

COMMENTS
A 360-degree feedback form is an employee evaluation form that gathers feedback from a variety of sources. This feedback may include input from the employee's supervisor, peers, direct reports, and even external stakeholders such as clients or customers. The goal of a 360-degree feedback form is to provide the employee with a more complete ...
How to write an employee evaluation. Writing employee performance evaluation forms involves a standardized process or procedure. Use the following steps to effectively write a performance review: 1. Gather employee information. Gather required information related to the employee to get the full picture of their value to the company.
Summary. A performance evaluation is a formal check-in process used to evaluate team members progress. Though evaluations can be stressful, a performance evaluation template can help standardize the process. When your team member knows exactly what you'll be discussing, they're able to prepare and have a more productive conversation.
Leadership. "You are fair and treat everyone in the office as an equal.". "You lead by example. Your approach of embracing change and adapting to changing work situations encourages others to do the same." "Your team consistently meets their goals often exceeding expectations.".
Here are six open-ended self evaluation sample questions from the Society for Human Resource Management, as well as example answers you can use to prepare for your own self evaluation. 1. Job Performance Examples. List your most significant accomplishments or contributions since last year.
2. Highlight areas of improvement. If you've worked with a team member for more than one review cycle, find last year's evaluations. Reread each one carefully to remind yourself about how your team members have performed in the past. Make note of issues they needed to address and areas where you suggested improvement.
6. Come up with a clear form layout. Employee evaluation forms aren't complicated as long as you come up with a clear form layout. Employee information usually comes first, with things like Name, Department, Position, Date, Reviewer name, and Review period needing to get filled in.
Employee evaluation forms don't need to be lengthy to be effective. First, look at the employee's goals and make a section for each that collects qualitative and quantitative data, by using open and closed questions. Then, with the employee's job in mind, add or take away questions to fit your organization and team.
Use the following steps when writing performance reviews: 1. Gather employee information. Gather the necessary information about the employee to get the full picture of their value to the company. This may include previous reviews, one-on-one meeting notes, raises and promotions, potential issues, and accomplishments.
Employee Evaluation Template & Comprehensive Guide [+ Free Download] Employee evaluation templates are an indispensable tool that allows HR professionals to develop a structured approach to assessing an individual employee's performance, growth, and potential within an organization. Employee evaluation forms support a culture of continuous ...
What To Write in a Performance Review. Performance review offers an opportunity to speak about the person's strengths and weaknesses candidly. There's a fine line between being helpful and ...
Writing an evaluation report can be a challenging task, even for experienced evaluators. Here are some common challenges that evaluators may encounter when writing an evaluation report: Data limitations: One of the biggest challenges in writing an evaluation report is dealing with data limitations. Evaluators may find that the data they ...
Acknowledge the full spectrum of your experiences, including any specific examples you might feel hesitant to highlight in your formal performance review. Coming up with an unfiltered version will help you understand how your perspective comes across, and you can always make edits once you start writing.. 2. Review your goals.
How to write an Evaluation Essay. There are two secrets to writing a strong evaluation essay. The first is to aim for objective analysis before forming an opinion. The second is to use an evaluation criteria. Aim to Appear Objective before giving an Evaluation Argument. Your evaluation will eventually need an argument.
Begin to create an evaluation form by typing sections for the employee's name, department, date of hire, date of the current review, date of the previous review and supervisor's name. Make blank lines after each heading long enough to accommodate long or hyphenated names. Include a description of the numerical rating system to be used when ...
feedback you have discussed, to use whe n writing your summary evaluation. • Complete your written evaluations promptly, within a week of working with the student. • Describe specific behaviors and concrete examples in your evaluation. • Discuss midpoint feedback using competency-based language.
Project evaluation is a key part of assessing the success, progress and areas for improvement of a project. It involves determining how well a project is meeting its goals and objectives. Evaluation helps determine if a project is worth continuing, needs adjustments, or should be discontinued. A good evaluation plan is developed at the start of ...
An evaluation form is a tool you can use to give feedback about people. They can make the feedback process faster since the questions in the form are standard questions and the evaluator provides feedback from similar aspects. Managers usually use the results of the form to gauge team productivity and to understand how their employees are doing ...
An appraisal form is a document that managers and human resources staff use to evaluate the performance of employees. The form often includes ratings and room for comments on performance. On an appraisal form, managers keep track of employees' achievements and contributions during a specific period. They also indicate the employees' areas ...
There is no point in writing what you think are great questions if they don't meet stakeholders' needs. Group writing is hard—in your evaluation planning session, don't worry about getting every word perfect. Make sure you understand the concept that is important, then finesse the language on your own. Stay open.
Make sure that you enter data into the correct box. Once you finish entering data, your analysis is ready to report. The Excel file provides you two evaluation summaries instantly. Summary of results is available in table form on sheet 2. Summary of results is available in chart form on sheet 3. When you are at this stage, your data analysis is ...
Outline. 2. •Purpose of Evaluations: Identify our Army's best performers and those with the greatest potential - Selection and Separation Boards and assignment managers are theaudience - Requires candor and courage; frank and accurateassessment - Leaders must guard against "word inflation"…words mattermost - Allows for field ...
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out ...
The workshop consisted of a comedy writing session with large language models (LLMs), a human-computer interaction questionnaire to assess the Creativity Support Index of AI as a writing tool, and a focus group interrogating the comedians' motivations for and processes of using AI, as well as their ethical concerns about bias, censorship and ...
The best interview feedback is easy-to-read and approachable. Here is an example of a constructive comment: "Showed strong command of Java and C++ languages and answered problem questions easily and completely. However, they struggled a bit longer with Python question, which is a must-have on the skills list.".