

Present Continuous Tense: How to Use It, With Examples
Published by
Olivia Drake
If you are learning English, you will likely come across the present continuous tense. This verb tense is used to describe actions that are happening now or are currently in progress. It is essential to understand how to use the present continuous tense correctly, as it is a fundamental tense in English grammar.
On this page:
Structure of the Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense is formed using the verb “to be” in the present tense and the present participle of the main verb. The structure of a present continuous sentence is as follows:
Subject + am/is/are + verb (present participle)
For example:
- She is cooking dinner.
- They are studying English grammar.
- He is watching TV.
Uses of the Present Continuous Tense
1. Actions Happening Now The present continuous tense is commonly used to describe actions that are happening now or at the present moment. For example:
- I am drinking coffee right now.
- She is talking to her friend on the phone.
- They are playing soccer in the park.
2. Temporary Actions or Situations The present continuous tense can also be used to describe temporary actions or situations. For example:
- She is staying with her sister for a few days.
- They are working on a project together.
- He is living in the city for the summer.
3. Ongoing Actions The present continuous tense is also used to describe actions that are currently in progress and are expected to continue in the near future. For example:
- The company is expanding its operations in Asia.
- She is studying for her final exams.
- They are planning a vacation for next month.
4. Future Plans The present continuous tense can be used to describe future plans, particularly when discussing arrangements or scheduled events. For example:
- I am meeting my friends for dinner tonight.
- They are flying to New York next week.
- She is attending a conference in London next month.
5. Annoying or Repetitive Actions The present continuous tense can also be used to describe annoying or repetitive actions that are currently happening. For example:
- He is always interrupting me when I am speaking.
- They are constantly playing loud music.
- She is forever checking her phone.
When to Use the Present Continuous Tense?
Remember to use “to be” in the present tense (am, is, are) followed by the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
Use the present continuous tense to describe actions happening right now, ongoing actions, future plans, and temporary situations.
When Not to Use the Present Continuous Tense?
The present continuous tense is a verb tense used to describe actions that are happening right now or actions that are ongoing. However, there are certain situations when it is not appropriate to use the present continuous tense.
1. States and Conditions
The present continuous tense should not be used to describe states and conditions that are not temporary. For example, instead of saying “I am believing in myself,” you should say “I believe in myself.” This is because beliefs are not temporary and are ongoing, rather than in the process of happening right now.
Incorrect: I am believing in myself. Correct: I believe in myself.
2. Habits and Routines
The present continuous tense should not be used to describe habits and routines. Instead, use the simple present tense. For example, instead of saying “I am going to the gym every day,” you should say “I go to the gym every day.” This is because going to the gym is a habit or routine that is ongoing, rather than in the process of happening right now.
Incorrect: I am going to the gym every day. Correct: I go to the gym every day.
3. Non-Continuous Verbs
The present continuous tense should not be used with non-continuous verbs, also known as stative verbs. These verbs describe a state or condition, rather than an action. For example, instead of saying “I am understanding the problem,” you should say “I understand the problem.” This is because understanding is a state or condition, rather than an action that is happening right now.
Incorrect: I am understanding the problem. Correct: I understand the problem.
4. Completed Actions
The present continuous tense should not be used to describe completed actions. Instead, use the past simple tense. For example, instead of saying “I am finishing my homework,” you should say “I finished my homework.” This is because finishing the homework is a completed action, rather than an ongoing action.
Incorrect: I am finishing my homework. Correct: I finished my homework.
Present Continuous and Stative Verbs
When it comes to stative verbs, which describe a state of being or a condition that is ongoing rather than an action in progress, the use of the present continuous tense can be a bit tricky.
Stative verbs typically describe things like emotions, mental states, senses, and physical conditions. Examples of stative verbs include “like,” “hate,” “love,” “prefer,” “believe,” “know,” “understand,” “feel,” “see,” “smell,” “taste,” “seem,” “appear,” and “have.”
In general, stative verbs are not typically used in the present continuous tense because they describe a state of being or a condition that is ongoing rather than an action in progress. However, there are some cases where the present continuous tense can be used with stative verbs to describe a temporary change in the state of being.
- “I am feeling sick today.” (describing a temporary physical condition)
- “She is seeming more confident lately.” (describing a temporary change in someone’s demeanor)
- “He is having trouble with the new software.” (describing a temporary difficulty with a task)
In these examples, the present continuous tense is being used to describe a temporary change in the state of being or condition, rather than a permanent or ongoing state. It’s important to note that the use of the present continuous tense with stative verbs is generally less common and should be used with caution. In most cases, it is best to use the simple present tense when describing stative verbs, as this more accurately reflects the ongoing nature of the state of being or condition.
Here are some common stative verbs that do not use the present continuous:
- Like: I like ice cream. (Not: I am liking ice cream.)
- Believe: I believe in aliens. (Not: I am believing in aliens.)
- Understand: I understand the instructions. (Not: I am understanding the instructions.)
- Know: I know the answer. (Not: I am knowing the answer.)
- Want: I want a new car. (Not: I am wanting a new car.)
- Love: I love my family. (Not: I am loving my family.)
- Prefer: I prefer tea to coffee. (Not: I am preferring tea to coffee.)
- Dislike: I dislike horror movies. (Not: I am disliking horror movies.)
- Own: I own a house. (Not: I am owning a house.)
- Belong: This book belongs to me. (Not: This book is belonging to me.)
It’s important to note that while these verbs do not typically use the present continuous tense, there may be some situations where they can be used in this way. For example, “I’m liking this new ice cream flavor” may be acceptable in some dialects or contexts, although it is not considered standard English.
Common Construction in the Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense is a verb tense used to describe actions or processes that are currently in progress or ongoing. It is formed by using the auxiliary verb “to be” in the present tense (am, is, are) and adding the present participle form of the main verb (-ing).
Here are some common constructions in the present continuous tense:
- I am studying for my exam.
- He is playing soccer with his friends.
- They are cooking dinner in the kitchen.
- I am not watching TV right now.
- She is not working on the project at the moment.
- We are not drinking coffee at this time.
- Are you listening to me?
- Is she singing a song?
- Are they playing a game?
- What are you doing?
- Why is he wearing a hat?
- Where are they going?
- No, she isn’t.
- Yes, they are.
- I’m (I am) running late.
- She’s (she is) dancing in the living room.
- They’re (they are) watching a movie.
It is important to note that the present continuous tense can also be used to talk about future plans or arrangements, as in “I am meeting my friend for lunch tomorrow.”
Common Dynamic Verbs that USE the Present Continuous
The present continuous tense is commonly used with dynamic verbs, which express actions or processes that are ongoing or in progress at the time of speaking. Here are some common dynamic verbs that use the present continuous tense:
Work: “I am working on a new project this week.” Run: “She is running in the park every morning to stay fit.” Study: “They are studying for their final exams at the library.” Drive: “He is driving to work in his new car.” Cook: “My mom is cooking dinner for us tonight.” Sing: “The choir is singing a beautiful song at the concert.” Play: “My friends and I are playing basketball in the park.” Write: “She is writing a novel about her life experiences.” Dance: “The couple is dancing gracefully at their wedding reception.” Paint: “He is painting a portrait of his girlfriend in his studio.”
These are just a few examples of dynamic verbs that are commonly used with the present continuous tense. Remember, dynamic verbs express actions or processes that are ongoing or in progress at the time of speaking, and the present continuous tense is the perfect way to describe them.
Related Articles:
- Questions in Present Continuous Tense with Examples
- Difference between Present Simple vs. Present Continuous with example
- Going to and Present Continuous for Future Plans and Arrangements
- Present Continuous Sentences With Examples
- Present Continuous Negative Sentences with Examples
Share this:
Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.

Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education!
Let’s connect
Join the fun!
Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter.
Type your email…
Recent posts
Future perfect continuous sentences with examples, future perfect sentences with examples, future continuous sentences with examples, future simple sentences with examples, past perfect continuous sentences with examples, past perfect simple sentences with examples, discover more from fluent english grammar.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
Learn How to Use the Present Continuous Tense
- Pronunciation & Conversation
- Writing Skills
- Reading Comprehension
- Business English
- Resources for Teachers
- TESOL Diploma, Trinity College London
- M.A., Music Performance, Cologne University of Music
- B.A., Vocal Performance, Eastman School of Music
The present continuous tense, also known as the present progressive, is one of the most commonly used verb tenses in English. It is one that English learners frequently confuse with a similar tense, the present simple.
Present Continuous vs. Present Simple
The present continuous tense expresses something that is happening at the moment of speaking. It is frequently used in conjunction with time expressions such as "right now" or "today" to indicate that an action is occurring at that moment. For instance:
- What are you doing at the moment?
- She's reading in the garden now.
- They're not standing in the rain. They're waiting in the garage.
In contrast, everyday habits and routines are expressed using the present simple tense. It's common to use the present simple with adverbs of frequency such as "usually" or "sometimes." For example:
- I usually drive to work.
- Alice doesn't have to get up early on Saturdays.
- The boys play soccer on Friday evenings.
The present continuous is used only with action verbs. Actions verbs express things that we do. The present continuous is not used with stative verbs that express a feeling, belief, or state of being, such as "hope" or "want."
- Correct : I hope to see him today.
- Incorrect : I am hoping to be seeing him today.
- Correct : I want some ice cream right now.
- Incorrect : I am wanting some ice cream right now.
Using the Present Continuous
In addition to expressing actions that are currently taking place, the present continuous can also express actions that are happening at or around the present moment in time. For example:
- What are you doing tomorrow afternoon?
- She isn't coming on Friday.
- We're working on the Smith account at the moment.
This tense is also used for future plans and arrangements, especially in business.
- Where are you staying in New York?
- She isn't coming to the presentation on Friday.
- I'm flying to Tokyo next week.
Sentence Structure
The present continuous tense can be used with positive, negative, and question sentences. For positive sentences, conjugate the helping verb "be" and add "ing" to the verb's end. For example:
- I'm (I am) working today.
- You're (You are) studying English at the moment.
- He's (He is) working on the report today.
- She's (She is) planning a vacation in Hawaii.
- It's (It is) raining right now.
- We're (We are) playing golf this afternoon.
- You're (You are) not paying attention, are you?
- They're (They are) waiting for the train.
For negative sentences, conjugate the helping verb "be," then add "not" plus "ing" to the verb's end.
- I'm not (I am not) thinking about my vacation right now.
- You aren't (You are not) sleeping at the moment.
- He isn't (He is not) watching the TV.
- She isn't (She is not) doing her homework today.
- It isn't (It is not) snowing today.
- We aren't (We are not) staying in New York.
- You aren't (You are not) playing chess at the moment.
- They aren't (They are not) working this week.
For sentences that ask a question, conjugate "be," followed by subject and a verb ending in "ing."
- What am I thinking?
- What are you doing?
- Where is he sitting?
- When is she coming?
- How is it doing?
- When are we leaving?
- What are you eating for lunch?
- What are they doing this afternoon?
Present Continuous Passive
The present continuous can also be used in the passive voice . Remember that the passive voice conjugates the verb "to be." To construct, a passive sentence, use the passive subject plus the verb "be" plus "ing" and the past participle . For instance:
- Cars are being made in this factory at the moment.
- English is being taught by the teacher now.
- Steak is being eaten by the people at table 12.
Additional Resources
Want to learn more about the present continuous tense? Check out this teacher's guide for additional exercises and tips.
- Passive Voice Usage and Examples
- Guide to Present Tenses
- Present Continuous Worksheets
- How to Teach the Present Continuous to ESL Students
- Master Verb Tenses With This Sentence Structure Chart
- Example Sentences of the Verb 'To Buy'
- Essential Basic English Lessons
- How to Use the Irregular Verb 'Ride'
- Visual Explanations of Each English Tense
- Parts of Speech: What Are Verbs?
- Understanding and Using the Simple Present Tense
- Example of the Verb 'Meet'
- Example Sentences of the Verb See
- English Tenses Timeline Reference
- Practice English Using This Dialogue With a Famous Actor
- How to Conjugate Verbs
Present Continuous Tense – Uses & Examples
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
The common present continuous tense is also known and used by some as the present progressive tense. This verb tense expresses actions currently happening. I would use this if I were writing something in first person POV with a present tense aka events are currently unfolding.
Discover the uses, rules, and examples of the present continuous tense as I break everything down. Once you learn how to use the present continuous tense, you’ll be able to add liveliness and action to your writing. I promise!
What is the Present Continuous or Present Progressive Tense?
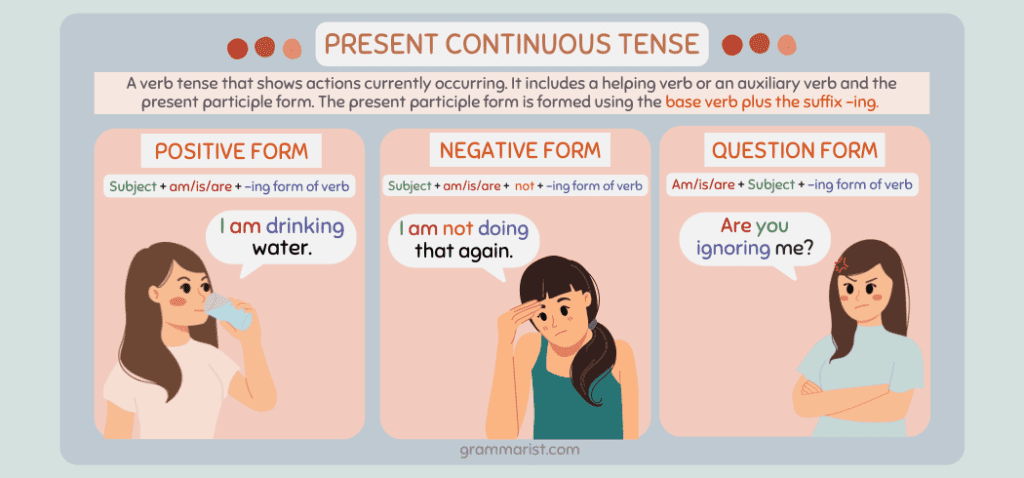
The present continuous tense is a verb tense that shows actions currently occurring. This tense also indicates when the event is temporary.
Like other continuous tenses, present continuous uses the present participle form of a verb. Present continuous verbs include a helping verb or an auxiliary verb and the present participle form.
The present participle form is formed using the base verb plus the suffix -ing. For instance, fix becomes fixing.
Books like All the Light We Cannot See by Anthony Doerr are written in present continuous tense if you want to check them out and get a good feel of it.
The Present Continuous Formula
You can construct a present continuous verb in several ways, depending on the sentence type. Here’s what I would do.
For affirmative sentences, the present continuous form is:
- Subject + am/is/are + -ing form of the verb.
To make the sentence negative, follow this construction:
- Subject + is/am/are + NOT + -ing form of the verb.
If you wish to write question sentences, here is the formula for the question form.
- Am/is/are + subject + -ing form of the verb.
Remember to observe subject-verb agreement when constructing these sentences. Use is for singular subjects and are for plural subjects. The auxiliary verb am is for the subject I.
How to Use the Present Continuous Tense
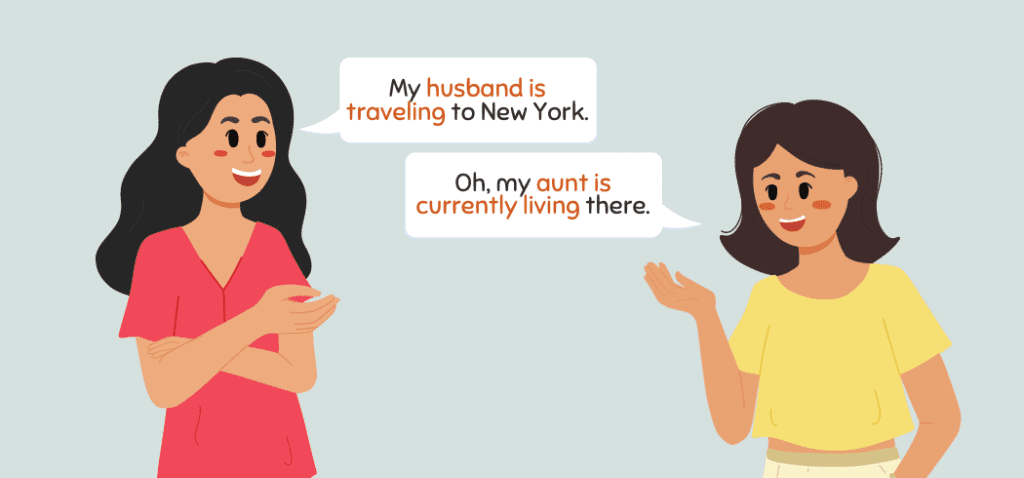
Let’s discuss the different uses of the present continuous tense. I’ll throw in some examples, too.
When Something is Happening at the Present Time
Use the present continuous tense with normal verbs to express something currently happening. This tense also expresses an action that is not happening right now. Here are some sentences with present continuous verbs.
- Donna is traveling to New York.
- I am reading Ottessa Moshfegh’s novel.
- My sister’s personal trainer is seeing my friend.
Notice how all topics in the examples show ongoing action.
When Something is Happening at the Time of Speaking
Use this grammatical tense for actions currently happening while you are speaking. It can be an action you’re doing or a specific event occurring. For example:
- My aunt is baking cookies now.
- I am eating dinner at the moment.
Regular Unplanned Events
You should use the present continuous with words like always, continually, and constantly to describe regular events that do not entail a firm plan. These events are also typically unwanted or indicative of irritation. For example:
- My husband is always going out late at night.
- I am constantly breaking things in the house.
When Describing a Future Plan
The present continuous form is essential when we want to share what we have planned at a specific time in the future. Remember to use time expressions in these sentences to show a specific period of time for future plans. For example:
- I’m writing him a letter tonight.
- Sasha is starting driving lessons this summer break.
When Indicating a Temporary Event
Use the present continuous tense when a situation is temporary. Take a look at the sentences below.
- I usually read romance fiction, but I’m reading non-fiction tonight.
- Los Angeles looks sunny, but I’m staying in Chicago at the moment.
When Asking Certain Types of Questions
Present continuous questions express questions about actions currently happening. For example:
- Are we buying that house?
Don’t Use It With Stative Verb Categories
Stative verbs are ones that show a state of being. They do not show qualities of change, and they always stay in simple present form. For example:
- Incorrect: I am preferring the brown leather jacket over the knitted cardigan.
Correct: I prefer the brown leather jacket over the knitted cardigan.
Non-continuous verbs/mixed verbs cannot be used in continuous tenses. Meanwhile, dynamic verbs describe actions that begin and end. Some examples of dynamic verbs are run, drive, and eat. These verbs work with the present continuous tense.
You can also use perception verbs with present continuous tense. These are see, hear, feel, taste, and smell.
Present Continuous Examples in Sentences
Below are some examples of present continuous tense sentences.
- The professor is sending the lessons by email this November.
- I am working on a new project.
- Are you asking comprehension questions to your students?
- Lorna’s daughter is studying to be a neurologist.
- The committee is planning to restructure the church.
- I am reading My Year of Rest and Relaxation.
- Are you listening to me?
- You’re constantly twitching when sleeping.
- They are running later.

Final Word on Present Continuous Tense
Now you know the definition, rules, and formula for using the present continuous tense. This verb tense is used for actions that are occurring now, temporary events, planned and unplanned situations, and future plans.
Remember what I said about that the present continuous tense always useing the helping verbs is/are/am and the present participle form of the verb.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
How do you use the present continuous tense to talk about the future in English? - Easy Learning Grammar
- The present continuous tense is used to talk about plans for the future, or specific arrangements that people have made for future events.
- It is often used in questions about future arrangements.
- If there are two verbs in the sentence, it is normal not to repeat the auxiliary before the second and subsequent ones.
Quick word challenge
Quiz Review
Score: 0 / 5


Direct and Indirect of Present Continuous Tense
Learn how to convey a message what someone is saying, feeling or thinking in present continuous tense. Direct and indirect of present continuous tense rules and structures of affirmative, negative, interrogative and negative interrogative sentences along with examples.
For direct and indirect speech complete rules click: Direct and indirect speech complete rules
Tense Change As a rule when you report something someone has said you go back a tense, therefore, when we report what someone is saying in present continuous we go one tense back. Instead we use past continuous tense in reported speech.
Affirmatives
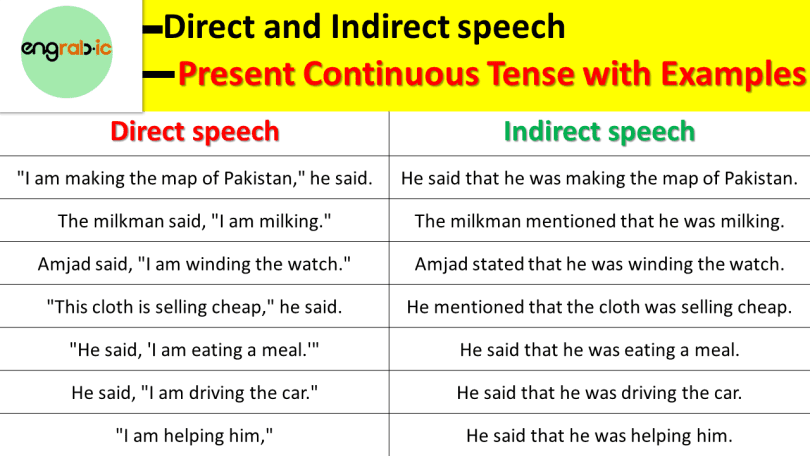
- Direct speech: RP +, + S + be1 + V1ing + ROTS He said, “I am doing my homework.”
- Indirect speech: RP + that + S + be2 + V1ing + ROTS He told me that he was doing his homework.
Interrogatives
- Direct speech: RP +, + be1 + S + V1ing + ROTS He asked, “Are you going to school?”
- Indirect speech: RP + if + S + be2 + V1ing + ROTS He asked me if I was coming/going to school.
- Direct speech: RP +, + S + be1 not + V1ing + ROTS He said, “She is not listening to me.”
- Indirect speech: RP + that + S + be2 not + V1ing + ROTS He said to me that she was not listening to him.
Negative interrogatives
- Direct speech: RP +, + b2 not + S + V1ing + ROTS He asked, “Aren`t they staying with us for tonight?”
- Indirect speech: RP + that + if + S + be2 not + V1ing + ROTS He asked if they weren`t staying with them for that night.
WH/Information questions
- Direct speech: RP +, + WH + be1 + S + V1ing + ROTS She asked, “What are you buying tomorrow?”
- Indirect speech: RP + that + WH + S + be2 + V1ing + ROTS She wanted to know what I was buying the next day.
More sentences:
Affirmative
- Direct speech: He said,” They are playing football.”
- Indirect speech: He said that they were playing football.
Interrogative
- Direct speech: He asked, “Are they playing football?”
- Indirect speech: He asked me if they were playing football.
- Direct speech: He said, “They are not playing football.”
- Indirect speech: He said that they were not playing football.
Negative interrogative
- Direct speech: He asked,” Aren’t they playing football?”
- Indirect speech: He asked me if they weren’t playing football.
Wh/ Information question
- Direct speech: He asked,” Where are they playing now?”
- Indirect speech: He wanted to know where they are playing now.
Check out Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises With Answers
If you would like to know more about direct or quoted speech, or indirect or reported speech, check out more in the book below.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
Related posts
Common verbal phrases in english, how to use do and make, indirect speech of imperative sentences.
I really like this website please send me your topic in email
Hello Sudais Khattak, Please subscribe and then you will receive all updates through your email address.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
English For Yourself
Present Continuous or Progressive Tense
In this section, you will find information about the different uses of the present continuous / progressive tense with examples.
Uses of the Present Continuous Tense
One of its uses is to talk about situations that are happening at the moment of speaking.
My dad is making a fruit salad now. I am doing my school project at the moment. Fer is playing with her cat.
We use it to talk about situations happening around the moment of speaking.
Amy is learning how to take photographs. Nowadays the Internet is becoming a useful tool. The singer is releasing many songs these days.
Another use is for situations that are temporary.
Our cousin is staying at our house for the time being. Paulina is taking Spanish lessons for now. I am working extra hours this month.
It is also used for planned events taking place in the near future.
My mom and I are having a picnic tomorrow. Steve is visiting his grandparents this weekend. They are releasing a new album next Sunday.
We use it to talk about situations that are changing.
Tablets are becoming more and more popular nowadays. Her singing abilities are improving. More and more people are moving abroad.
You can also use it to express annoyance or irritation towards a repeated action, usually with the adverbs always and constantly.
I hate that you are always taking my laptop without asking. Daniel is constantly complaining. She is always running in the house.
In the following table, you will find information about the structure of the present continuous or progressive tense and positive, negative and interrogative sentences.
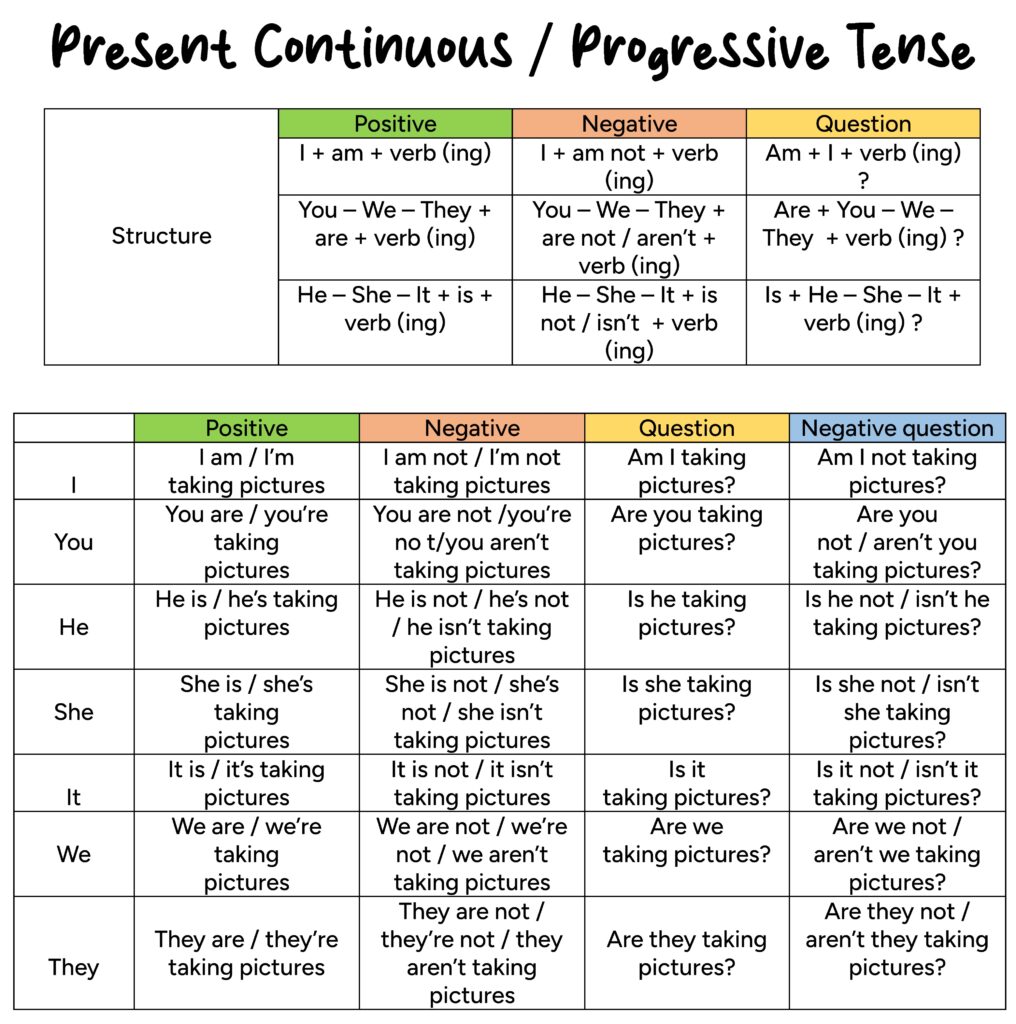
More Information about English verb tenses here .
Privacy Policy - Terms and Conditions
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Future: present continuous to talk about the future ( I’m working tomorrow )
The present continuous can refer to the future. It shows that we have already decided something and usually that we have already made a plan or arrangements:
[talking about plans for a tour by a rock music group]
The band is visiting Denmark next May.
I am taking the train to Paris tomorrow.
We don’t use the present continuous when we predict something. Instead, we use going to or will :
It ’s going to rain again soon.
Not: It’s raining again soon .
Present continuous ( I am working )
Future: be going to ( I am going to work )

Word of the Day
on top of the world
extremely happy

Keeping up appearances (Talking about how things seem)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- English Grammar
- English Tenses
- Present Tense
- Present Continuous Tense
Present Continuous Tense - Meaning, Definition, Formula, Uses, Structure with Examples
Are you wondering how the present continuous tense can be used? Well, fret no more. You just came across a sentence with the present continuous tense. In this article, you will learn all that you need to know about what the present continuous tense is, its definition, uses, structure and rules of usage. Along with these, with the examples and practice questions, you will surely be able to use the frame sentences using the present continuous tense accurately.

Table of Contents
Definition of the present continuous tense, structure of the present continuous tense, rules and points to remember when using the present continuous tense, uses of the present continuous tense, 10 sentences using the present continuous tense, test your understanding of the present continuous tense, frequently asked questions on present continuous tense, understanding the present continuous tense.
The present continuous tense, as the name suggests, is the form of tense that is used to denote an action that is ongoing or occurring in that current moment. It is also referred to as the present progressive tense as they represent the action that is progressing in the present. Let us now take a look at the definitions provided by various dictionaries about the present continuous tense.
The Cambridge Dictionary defines the ‘present continuous tense’ as “the verb form used for actions or events that are happening or developing now.” According to the Collins Dictionary, the present continuous tense is defined as “a verb form consisting of an auxiliary be in the present tense followed by a present participle and used especially to indicate that a present action or event is in progress, being repeated, or of a temporary nature or to express the future.” The present continuous tense is “the tense used to talk about actions or behaviour that are in progress now or planned for the future”, according to the Macmillan Dictionary.
There is definitely just one formula to mastering the present continuous tense and this is how it goes.
However, there is something more you should pay attention to. You should also learn how the sentences with the present continuous tense form of the verb are structured when they are positive, negative, interrogative and negative interrogative.
Have a look at the table given below to have a deeper understanding of the structure of the present continuous tense.
When using the present continuous tense, make sure you follow the sentence structure exactly.
- Always start with the subject when it is a positive or negative sentence and with the helping verb when it is in the interrogative format.
- A sentence with the present continuous tense consists of a helping verb (‘to be’ form of verbs) and a main verb . The helping verbs can be ‘am’ for the pronoun ‘I’, ‘is’ for singular subject and ‘are’ for a plural subject.
- Just note that like the other pronouns, the pronoun ‘am’ cannot be used in the negative form in an interrogative sentence. Instead of ‘amn’t’, ‘aren’t’ is used.
For example:
- Amn’t I reading a newspaper? Wrong
- Aren’t I reading a newspaper? Correct
- The present continuous tense can never be used with stative verbs .
Like the simple present tense , the present continuous tense is also generally used to talk about an action that is taking place in the present. The only difference is that it denotes an action that is continuing to happen or progressing at the current moment.
Take a look at the following points that elaborate on the more specific uses of the present continuous tense.
- It is used to represent an action that is happening or progressing in the moment that the speaker is speaking.
- My son is working on his science project.
- Santana is singing Don’t Rain on my Parade.
- It is used to depict a future event or arrangement.
- What are you planning to do tomorrow?
- I heard that Rachel is moving to Paris next month.
- It is used to denote an action that is going on or continuing at the time of speaking.
- Is she still working at the National Institute of Medical Sciences?
- I am currently taking guitar lessons so that I could play for your wedding.
Examples of Present Continuous Tense
Going through more and more examples can only make you an expert in the particular subject or topic. So , here you go. Check out the examples of sentences using the present continuous tense given below.
- My mom is cooking dinner.
- The band is playing all the classics.
- Monica and Rachel are going on a trip tomorrow.
- Sheethal is not practising for the final audition.
- I am trying out something new.
- They are not travelling to London next week.
- Are you watching a movie tonight?
- Is your phone working properly now?
- The children are loving the new park.
- Diana is playing the main role in the play.
Having gone through all the given examples, you should have understood really well. Check your understanding of the present continuous tense by filling in the blanks in the following sentence with the right form of tense using the verbs given in the brackets.
1. ______ the clock ________ (work)?
2. The teachers ___________ (plan) to dance to all the latest songs on Childrens Day.
3. ______ she ___________ (play – negative) the piano anymore?
4. The dog __________ (run) all around the garden.
5. We ____________ (go – negative) to the party tomorrow.
6. The Bellas ___________ (perform) the songs of the 80s.
7. Will, Smith and Sherlock ___________ (dance) well.
8. _______ I __________ (look) good today?
9. Trinita and Vinitha ____________ (ride) on their new cat.
10. _____ he still ________ (stand) there?
Ready to see if you got it all right. Check out the answers given below.
1. Is the clock working ?
2. The teachers are planning to dance to all the latest songs on Childrens Day.
3. Is she not playing the piano anymore?
4. The dog is running all around the garden.
5. We are not going to the party tomorrow.
6. The Bellas are performing the songs of the 80s.
7. Will, Smith and Sherlock are dancing well.
8. Am I looking good today?
9. Trinita and Vinitha are riding on their new cat.
10. Is he still standing there?
What is the present continuous tense?
The Present Continuous Tense, as the name suggests, is the form of tense that is used to denote the action that is ongoing or occuring in that current moment. It is also referred to as the present progressive tense as they represent the action that is progressing in the present.
What is the definition of the present continuous tense?
What is the formula to be followed when using the present continuous tense.
The formula to be kept in mind and used when writing or speaking a sentence in the present continuous tense is as follows: Subject + am/is/are + present participle (verb+ing) + the rest of the sentence
Give some examples of the present continuous tense.
Here are a few examples to show you how the present continuous tense is used.
What are the uses of the present continuous tense?
The present continuous tense can be used to talk about an action that
- is happening or progressing in the moment that the speaker is speaking.
- depicts a future event or arrangement.
- is going on or continuing at the time of speaking.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Reported speech – Present Progressive – Sentences – Exercise
Task no. 2337.
Finish the sentences using Reported speech. Always change the tense, although it is sometimes not necessary.
Joe, "I'm drawing a picture." Joe said (that)
Joe said (that) he was drawing a picture .
Do you need help?
Reported speech
- Jenny, "I'm coming down." Jenny said (that) .
- Tim, "Jack is having breakfast." Tim said (that) .
- Jamy, "She's telling a joke." Jamy told me (that) .
- Mavis, "The dog is running after the cat." Mavis remarked (that) .
- Peter, "I'm playing the piano." Peter said (that) .
- Zack, "You're drinking tea." Zack mentioned (that) .
- Ella, "It's not raining." Ella remarked (that) .
- Jacob, "Riley is checking the computer." Jacob said (that) .
- Owen, "They aren't watching TV." Owen told me (that) .
- Nora, "He is learning Spanish words." Nora said (that) .
- You are here:
- Grammar Exercises
- Reported Speech

Direct and Indirect of Present Continuous Tense
English is a flexible language that helps us talk about things happening now or near now. We call one of the ways to do this the “present continuous tense.” It helps us explain actions as they are happening. In this article, we’ll learn how to use this tense when someone is talking directly or telling us what someone else said. We’ll make it simple with clear examples to understand better.
Understanding the Present Continuous Tense:
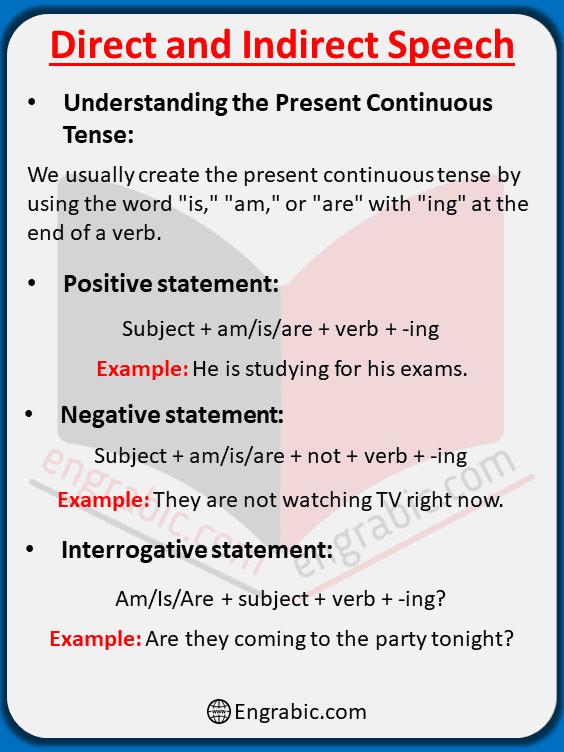
Present Continuous Tense Overview
Before we go to learn direct and indirect speech, let’s quickly go over how we make and use the present continuous tense. We usually create the present continuous tense by using the word “is,” “am,” or “are” with “ing” at the end of a verb.
Important Note : You can Download FREE PDF at the bottom
Positive statement: Subject + am/is/are + verb + -ing
Example: He is studying for his exams.
Negative statement: Subject + am/is/are + not + verb + -ing
Example: They are not watching TV right now.
Interrogative statement: Am/Is/Are + subject + verb + -ing?
Example: Are they coming to the party tonight?
Present Continuous Tense in Direct Speech:
Direct speech means we repeat exactly what someone said. When we tell others what someone is saying right now using the present continuous tense, we can put quotation marks around those words. Here are some examples:
Original Statement: Uzair said, “I am reading a great book.”
Direct Speech: Uzair said, “I am reading a great book.”
Original Statement: “We are going to the market,” they announced.
Direct Speech: “We are going to the market,” they announced.
Change the pronoun in the reporting verb: When changing the pronouns in sentences with the present continuous tense from direct speech to reported speech:
Direct Speech: “I am working on a project,” she said.
Reported Speech: She mentioned that she was working on a project.
To make a sentence from someone talking into a present continuous one, you change the words to fit what’s happening now or when you want to talk about. Here are some examples of how you can do that:
Change time expression:
Original Direct Speech: “I am studying for the exam.”
- Present Time: “He says, ‘I am studying for the exam right now.”
- Past Time: “He said, ‘I was studying for the exam yesterday.”
- Future Time: “He will say, ‘I am studying for the exam tomorrow.'”
Present Continuous Tense in Indirect Speech:
Indirect speech, which is also called reported speech, helps us share what someone said without repeating their words exactly.
Here are the rules for changing what someone said in the present continuous tense from direct speech to indirect speech:
Change the Verb Tense: In indirect speech, we usually talk about what someone said in a slightly different way. The words like “am,” “is,” or “are” change to “was” or “were,” but the action word with “ing” stays the same.
Direct Speech: He said, “I am studying for my exams.”
Indirect Speech: He said that she was studying for her exams.
Direct and Indirect of Present Continuous Tense Examples

Present Continuous Tense in Direct Speech Exercises with PDF

Present Continuous Tense in Direct Speech Exercise
Download FREE PDF Here
You may also like to read:
Direct and Indirect Narration with Rules and Examples
Direct and Indirect of Simple Present Tense
Active and Passive Voice with Rules and Examples
You may also like
Interjections – Definition, Rules and Examples
Interjection is one of the Parts of Speech, which is used to express sudden emotions, strong...
Future Indefinite Tense | Structures, Examples & Rules
The simple future tense is a fundamental aspect of English grammar that is used to talk about...

Parts of Speech | The 8 Parts of Speech with Examples and Rules
Parts of speech are fundamental categories that classify words based on their grammatical...
Participles | What Are Participles? | Definition and Examples
English Grammar has many branches and Important topics like Tenses, Direct Indirect Narration...
Leave a Comment X

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The present continuous tense is formed using the verb "to be" in the present tense and the present participle of the main verb. The structure of a present continuous sentence is as follows: Subject + am/is/are + verb (present participle) For example: She is cooking dinner. They are studying English grammar. He is watching TV.
The present continuous (also called present progressive) is a verb tense which is used to show that an ongoing action is happening now, either at the moment of speech or now in a larger sense. The present continuous can also be used to show that an action is going to take place in the near future. Read on for detailed descriptions, examples ...
Present continuous ( I am working ) - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
The present continuous tense normally requires a dynamic verb. Verbs that instead describe a state of being such as emotion, belief, perception, or possession are called stative verbs. Some examples include "prefer," "appear," "exist," and "own.". Stative verbs should not be used in the present continuous tense.
How to Use the Present Continuous. The present progressive is used: 1. To describe something which is happening at the exact moment of speech. Example: Jim is watching television at the moment. 2. To describe an action that is taking place now but not at the exact moment of speech. Example:
The Present Continuous Tense (also called Present Progressive) is used to indicate that an ongoing action or condition is happening now, either at the moment of speech or now in a larger sense. The present continuous can also be used to show that an action is going to take place in the near future. Examples. I am playing cricket. They are dancing.
The present continuous tense can be used with positive, negative, and question sentences. For positive sentences, conjugate the helping verb "be" and add "ing" to the verb's end. For example: I'm (I am) working today. You're (You are) studying English at the moment. He's (He is) working on the report today. She's (She is) planning a vacation in ...
Learn how to use the present continuous verb tense in English. You can see different meanings of the present continuous and how to use them in English. Pract...
The present continuous tense is a verb tense that shows actions currently occurring. This tense also indicates when the event is temporary. Like other continuous tenses, present continuous uses the present participle form of a verb. Present continuous verbs include a helping verb or an auxiliary verb and the present participle form.
The present continuous tense is used to talk about plans for the future, or specific arrangements that people have made for future events. The school is having a sale next week; I 'm running the bookstall.
Direct speech: RP +, + WH + be1 + S + V1ing + ROTS She asked, "What are you buying tomorrow?" Indirect speech: RP + that + WH + S + be2 + V1ing + ROTS She wanted to know what I was buying the next day. More sentences: Affirmative. Direct speech: He said," They are playing football." Indirect speech: He said that they were playing football. ...
Uses of the Present Continuous Tense. One of its uses is to talk about situations that are happening at the moment of speaking. My dad is making a fruit salad now. I am doing my school project at the moment. Fer is playing with her cat. We use it to talk about situations happening around the moment of speaking.
The Present Continuous. 5/10/2022. "The present continuous (also called present progressive) is a verb tense which is used to show that an ongoing action is happening now, either at the moment of speech or now in a larger sense. The present continuous can also be used to show that an action is going to take place in the near future.
ESL Present Continuous Game - Grammar and Speaking: Drawing, Asking and Answering Questions, Guessing, Controlled and Freer - Group and Pair Work - Pre-intermediate (A2) - 35 minutes. Here is an entertaining present continuous drawing game to help students practice present continuous yes/no questions and short answers.
Future: present continuous to talk about the future ( I'm working tomorrow ) - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
Definition of the Present Continuous Tense. The Cambridge Dictionary defines the 'present continuous tense' as "the verb form used for actions or events that are happening or developing now." According to the Collins Dictionary, the present continuous tense is defined as "a verb form consisting of an auxiliary be in the present tense followed by a present participle and used ...
The present continuous, also called the present progressive or present imperfect, is a verb form used in modern English that combines the present tense with the continuous aspect. It is formed by the present tense form of be and the present participle of a verb. The present continuous is generally used to describe something that is taking place at the present moment and can be employed in both ...
Ella, "It's not raining." Ella remarked (that) . Jacob, "Riley is checking the computer." Jacob said (that) . Owen, "They aren't watching TV." Owen told me (that) . Nora, "He is learning Spanish words." Nora said (that) . Sentences in Reported speech in the Present Progressive in English in an Online Exercise.
Original Direct Speech: "I am studying for the exam.". Present Time: "He says, 'I am studying for the exam right now.". Past Time: "He said, 'I was studying for the exam yesterday.". Future Time: "He will say, 'I am studying for the exam tomorrow.'". Present Continuous Tense in Indirect Speech: Indirect speech, which is ...
This impaired tracking could potentially affect the processing and learning of words as well as continuous speech. The present results offer an explanation for the problems in language comprehension and acquisition in DLD. In developmental language disorder (DLD), learning to comprehend and express oneself with spoken language is impaired, but ...
Preparatory for Early College Graduation 2024 at Joe R. Sanchez Stadium