- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Phenomenology – Methods, Examples and Guide

Research Methods – Types, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Descriptive Research Design – Types, Methods and...

Correlational Research – Methods, Types and...

Exploratory Research – Types, Methods and...
Qualitative study design: Case Studies
- Qualitative study design
- Phenomenology
- Grounded theory
- Ethnography
- Narrative inquiry
- Action research
Case Studies
- Field research
- Focus groups
- Observation
- Surveys & questionnaires
- Study Designs Home
In depth description of the experience of a single person, a family, a group, a community or an organisation.
An example of a qualitative case study is a life history which is the story of one specific person. A case study may be done to highlight a specific issue by telling a story of one person or one group.
- Oral recording
Ability to explore and describe, in depth, an issue or event.
Develop an understanding of health, illness and health care in context.
Single case can be used to develop or disprove a theory.
Can be used as a model or prototype .
Limitations
Labour intensive and generates large diverse data sets which can be hard to manage.
Case studies are seen by many as a weak methodology because they only look at one person or one specific group and aren’t as broad in their participant selection as other methodologies.
Example questions
This methodology can be used to ask questions about a specific drug or treatment and its effects on an individual.
- Does thalidomide cause birth defects?
- Does exposure to a pesticide lead to cancer?
Example studies
- Choi, T. S. T., Walker, K. Z., & Palermo, C. (2018). Diabetes management in a foreign land: A case study on Chinese Australians. Health & Social Care in the Community, 26(2), e225-e232.
- Reade, I., Rodgers, W., & Spriggs, K. (2008). New Ideas for High Performance Coaches: A Case Study of Knowledge Transfer in Sport Science. International Journal of Sports Science & Coaching , 3(3), 335-354.
- Wingrove, K., Barbour, L., & Palermo, C. (2017). Exploring nutrition capacity in Australia's charitable food sector. Nutrition & Dietetics , 74(5), 495-501.
- Green, J., & Thorogood, N. (2018). Qualitative methods for health research (4th ed.). London: SAGE.
- University of Missouri-St. Louis. Qualitative Research Designs. Retrieved from http://www.umsl.edu/~lindquists/qualdsgn.html
- << Previous: Action research
- Next: Field research >>
- Last Updated: Apr 8, 2024 11:12 AM
- URL: https://deakin.libguides.com/qualitative-study-designs

Research Writing and Analysis
- NVivo Group and Study Sessions
- SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Statistical Analysis Group sessions
- Using Qualtrics
- Dissertation and Data Analysis Group Sessions
- Defense Schedule - Commons Calendar This link opens in a new window
- Research Process Flow Chart
- Research Alignment Chapter 1 This link opens in a new window
- Step 1: Seek Out Evidence
- Step 2: Explain
- Step 3: The Big Picture
- Step 4: Own It
- Step 5: Illustrate
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review This link opens in a new window
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- How to Synthesize and Analyze
- Synthesis and Analysis Practice
- Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Locating Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks This link opens in a new window
- Quantitative Research Questions
- Qualitative Research Questions
- Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data
- Analysis and Coding Example- Qualitative Data
- Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- International Journal of Online Graduate Education (IJOGE) This link opens in a new window
- Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning (JRIT&L) This link opens in a new window
Writing a Case Study

What is a case study?

A Case study is:
- An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology.
- Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research.
- Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event.
- Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
What are the different types of case studies?

Note: These are the primary case studies. As you continue to research and learn
about case studies you will begin to find a robust list of different types.
Who are your case study participants?

What is triangulation ?
Validity and credibility are an essential part of the case study. Therefore, the researcher should include triangulation to ensure trustworthiness while accurately reflecting what the researcher seeks to investigate.

How to write a Case Study?
When developing a case study, there are different ways you could present the information, but remember to include the five parts for your case study.

Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Next: Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS) >>
- Last Updated: May 29, 2024 8:05 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchtools


What Is a Research Design? | Definition, Types & Guide

Introduction
Parts of a research design, types of research methodology in qualitative research, narrative research designs, phenomenological research designs, grounded theory research designs.
- Ethnographic research designs

Case study research design
Important reminders when designing a research study.
A research design in qualitative research is a critical framework that guides the methodological approach to studying complex social phenomena. Qualitative research designs determine how data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted, ensuring that the research captures participants' nuanced and subjective perspectives. Research designs also recognize ethical considerations and involve informed consent, ensuring confidentiality, and handling sensitive topics with the utmost respect and care. These considerations are crucial in qualitative research and other contexts where participants may share personal or sensitive information. A research design should convey coherence as it is essential for producing high-quality qualitative research, often following a recursive and evolving process.

Theoretical concepts and research question
The first step in creating a research design is identifying the main theoretical concepts. To identify these concepts, a researcher should ask which theoretical keywords are implicit in the investigation. The next step is to develop a research question using these theoretical concepts. This can be done by identifying the relationship of interest among the concepts that catch the focus of the investigation. The question should address aspects of the topic that need more knowledge, shed light on new information, and specify which aspects should be prioritized before others. This step is essential in identifying which participants to include or which data collection methods to use. Research questions also put into practice the conceptual framework and make the initial theoretical concepts more explicit. Once the research question has been established, the main objectives of the research can be specified. For example, these objectives may involve identifying shared experiences around a phenomenon or evaluating perceptions of a new treatment.
Methodology
After identifying the theoretical concepts, research question, and objectives, the next step is to determine the methodology that will be implemented. This is the lifeline of a research design and should be coherent with the objectives and questions of the study. The methodology will determine how data is collected, analyzed, and presented. Popular qualitative research methodologies include case studies, ethnography , grounded theory , phenomenology, and narrative research . Each methodology is tailored to specific research questions and facilitates the collection of rich, detailed data. For example, a narrative approach may focus on only one individual and their story, while phenomenology seeks to understand participants' lived common experiences. Qualitative research designs differ significantly from quantitative research, which often involves experimental research, correlational designs, or variance analysis to test hypotheses about relationships between two variables, a dependent variable and an independent variable while controlling for confounding variables.

Literature review
After the methodology is identified, conducting a thorough literature review is integral to the research design. This review identifies gaps in knowledge, positioning the new study within the larger academic dialogue and underlining its contribution and relevance. Meta-analysis, a form of secondary research, can be particularly useful in synthesizing findings from multiple studies to provide a clear picture of the research landscape.
Data collection
The sampling method in qualitative research is designed to delve deeply into specific phenomena rather than to generalize findings across a broader population. The data collection methods—whether interviews, focus groups, observations, or document analysis—should align with the chosen methodology, ethical considerations, and other factors such as sample size. In some cases, repeated measures may be collected to observe changes over time.
Data analysis
Analysis in qualitative research typically involves methods such as coding and thematic analysis to distill patterns from the collected data. This process delineates how the research results will be systematically derived from the data. It is recommended that the researcher ensures that the final interpretations are coherent with the observations and analyses, making clear connections between the data and the conclusions drawn. Reporting should be narrative-rich, offering a comprehensive view of the context and findings.
Overall, a coherent qualitative research design that incorporates these elements facilitates a study that not only adds theoretical and practical value to the field but also adheres to high quality. This methodological thoroughness is essential for achieving significant, insightful findings. Examples of well-executed research designs can be valuable references for other researchers conducting qualitative or quantitative investigations. An effective research design is critical for producing robust and impactful research outcomes.
Each qualitative research design is unique, diverse, and meticulously tailored to answer specific research questions, meet distinct objectives, and explore the unique nature of the phenomenon under investigation. The methodology is the wider framework that a research design follows. Each methodology in a research design consists of methods, tools, or techniques that compile data and analyze it following a specific approach.
The methods enable researchers to collect data effectively across individuals, different groups, or observations, ensuring they are aligned with the research design. The following list includes the most commonly used methodologies employed in qualitative research designs, highlighting how they serve different purposes and utilize distinct methods to gather and analyze data.

The narrative approach in research focuses on the collection and detailed examination of life stories, personal experiences, or narratives to gain insights into individuals' lives as told from their perspectives. It involves constructing a cohesive story out of the diverse experiences shared by participants, often using chronological accounts. It seeks to understand human experience and social phenomena through the form and content of the stories. These can include spontaneous narrations such as memoirs or diaries from participants or diaries solicited by the researcher. Narration helps construct the identity of an individual or a group and can rationalize, persuade, argue, entertain, confront, or make sense of an event or tragedy. To conduct a narrative investigation, it is recommended that researchers follow these steps:
Identify if the research question fits the narrative approach. Its methods are best employed when a researcher wants to learn about the lifestyle and life experience of a single participant or a small number of individuals.
Select the best-suited participants for the research design and spend time compiling their stories using different methods such as observations, diaries, interviewing their family members, or compiling related secondary sources.
Compile the information related to the stories. Narrative researchers collect data based on participants' stories concerning their personal experiences, for example about their workplace or homes, their racial or ethnic culture, and the historical context in which the stories occur.
Analyze the participant stories and "restore" them within a coherent framework. This involves collecting the stories, analyzing them based on key elements such as time, place, plot, and scene, and then rewriting them in a chronological sequence (Ollerenshaw & Creswell, 2000). The framework may also include elements such as a predicament, conflict, or struggle; a protagonist; and a sequence with implicit causality, where the predicament is somehow resolved (Carter, 1993).
Collaborate with participants by actively involving them in the research. Both the researcher and the participant negotiate the meaning of their stories, adding a credibility check to the analysis (Creswell & Miller, 2000).
A narrative investigation includes collecting a large amount of data from the participants and the researcher needs to understand the context of the individual's life. A keen eye is needed to collect particular stories that capture the individual experiences. Active collaboration with the participant is necessary, and researchers need to discuss and reflect on their own beliefs and backgrounds. Multiple questions could arise in the collection, analysis, and storytelling of individual stories that need to be addressed, such as: Whose story is it? Who can tell it? Who can change it? Which version is compelling? What happens when narratives compete? In a community, what do the stories do among them? (Pinnegar & Daynes, 2006).

Make the most of your data with ATLAS.ti
Powerful tools in an intuitive interface, ready for you with a free trial today.
A research design based on phenomenology aims to understand the essence of the lived experiences of a group of people regarding a particular concept or phenomenon. Researchers gather deep insights from individuals who have experienced the phenomenon, striving to describe "what" they experienced and "how" they experienced it. This approach to a research design typically involves detailed interviews and aims to reach a deep existential understanding. The purpose is to reduce individual experiences to a description of the universal essence or understanding the phenomenon's nature (van Manen, 1990). In phenomenology, the following steps are usually followed:
Identify a phenomenon of interest . For example, the phenomenon might be anger, professionalism in the workplace, or what it means to be a fighter.
Recognize and specify the philosophical assumptions of phenomenology , for example, one could reflect on the nature of objective reality and individual experiences.
Collect data from individuals who have experienced the phenomenon . This typically involves conducting in-depth interviews, including multiple sessions with each participant. Additionally, other forms of data may be collected using several methods, such as observations, diaries, art, poetry, music, recorded conversations, written responses, or other secondary sources.
Ask participants two general questions that encompass the phenomenon and how the participant experienced it (Moustakas, 1994). For example, what have you experienced in this phenomenon? And what contexts or situations have typically influenced your experiences within the phenomenon? Other open-ended questions may also be asked, but these two questions particularly focus on collecting research data that will lead to a textural description and a structural description of the experiences, and ultimately provide an understanding of the common experiences of the participants.
Review data from the questions posed to participants . It is recommended that researchers review the answers and highlight "significant statements," phrases, or quotes that explain how participants experienced the phenomenon. The researcher can then develop meaningful clusters from these significant statements into patterns or key elements shared across participants.
Write a textual description of what the participants experienced based on the answers and themes of the two main questions. The answers are also used to write about the characteristics and describe the context that influenced the way the participants experienced the phenomenon, called imaginative variation or structural description. Researchers should also write about their own experiences and context or situations that influenced them.
Write a composite description from the structural and textural description that presents the "essence" of the phenomenon, called the essential and invariant structure.
A phenomenological approach to a research design includes the strict and careful selection of participants in the study where bracketing personal experiences can be difficult to implement. The researcher decides how and in which way their knowledge will be introduced. It also involves some understanding and identification of the broader philosophical assumptions.

Grounded theory is used in a research design when the goal is to inductively develop a theory "grounded" in data that has been systematically gathered and analyzed. Starting from the data collection, researchers identify characteristics, patterns, themes, and relationships, gradually forming a theoretical framework that explains relevant processes, actions, or interactions grounded in the observed reality. A grounded theory study goes beyond descriptions and its objective is to generate a theory, an abstract analytical scheme of a process. Developing a theory doesn't come "out of nothing" but it is constructed and based on clear data collection. We suggest the following steps to follow a grounded theory approach in a research design:
Determine if grounded theory is the best for your research problem . Grounded theory is a good design when a theory is not already available to explain a process.
Develop questions that aim to understand how individuals experienced or enacted the process (e.g., What was the process? How did it unfold?). Data collection and analysis occur in tandem, so that researchers can ask more detailed questions that shape further analysis, such as: What was the focal point of the process (central phenomenon)? What influenced or caused this phenomenon to occur (causal conditions)? What strategies were employed during the process? What effect did it have (consequences)?
Gather relevant data about the topic in question . Data gathering involves questions that are usually asked in interviews, although other forms of data can also be collected, such as observations, documents, and audio-visual materials from different groups.
Carry out the analysis in stages . Grounded theory analysis begins with open coding, where the researcher forms codes that inductively emerge from the data (rather than preconceived categories). Researchers can thus identify specific properties and dimensions relevant to their research question.
Assemble the data in new ways and proceed to axial coding . Axial coding involves using a coding paradigm or logic diagram, such as a visual model, to systematically analyze the data. Begin by identifying a central phenomenon, which is the main category or focus of the research problem. Next, explore the causal conditions, which are the categories of factors that influence the phenomenon. Specify the strategies, which are the actions or interactions associated with the phenomenon. Then, identify the context and intervening conditions—both narrow and broad factors that affect the strategies. Finally, delineate the consequences, which are the outcomes or results of employing the strategies.
Use selective coding to construct a "storyline" that links the categories together. Alternatively, the researcher may formulate propositions or theory-driven questions that specify predicted relationships among these categories.
Develop and visually present a matrix that clarifies the social, historical, and economic conditions influencing the central phenomenon. This optional step encourages viewing the model from the narrowest to the broadest perspective.
Write a substantive-level theory that is closely related to a specific problem or population. This step is optional but provides a focused theoretical framework that can later be tested with quantitative data to explore its generalizability to a broader sample.
Allow theory to emerge through the memo-writing process, where ideas about the theory evolve continuously throughout the stages of open, axial, and selective coding.
The researcher should initially set aside any preconceived theoretical ideas to allow for the emergence of analytical and substantive theories. This is a systematic research approach, particularly when following the methodological steps outlined by Strauss and Corbin (1990). For those seeking more flexibility in their research process, the approach suggested by Charmaz (2006) might be preferable.
One of the challenges when using this method in a research design is determining when categories are sufficiently saturated and when the theory is detailed enough. To achieve saturation, discriminant sampling may be employed, where additional information is gathered from individuals similar to those initially interviewed to verify the applicability of the theory to these new participants. Ultimately, its goal is to develop a theory that comprehensively describes the central phenomenon, causal conditions, strategies, context, and consequences.

Ethnographic research design
An ethnographic approach in research design involves the extended observation and data collection of a group or community. The researcher immerses themselves in the setting, often living within the community for long periods. During this time, they collect data by observing and recording behaviours, conversations, and rituals to understand the group's social dynamics and cultural norms. We suggest following these steps for ethnographic methods in a research design:
Assess whether ethnography is the best approach for the research design and questions. It's suitable if the goal is to describe how a cultural group functions and to delve into their beliefs, language, behaviours, and issues like power, resistance, and domination, particularly if there is limited literature due to the group’s marginal status or unfamiliarity to mainstream society.
Identify and select a cultural group for your research design. Choose one that has a long history together, forming distinct languages, behaviours, and attitudes. This group often might be marginalized within society.
Choose cultural themes or issues to examine within the group. Analyze interactions in everyday settings to identify pervasive patterns such as life cycles, events, and overarching cultural themes. Culture is inferred from the group members' words, actions, and the tension between their actual and expected behaviours, as well as the artifacts they use.
Conduct fieldwork to gather detailed information about the group’s living and working environments. Visit the site, respect the daily lives of the members, and collect a diverse range of materials, considering ethical aspects such as respect and reciprocity.
Compile and analyze cultural data to develop a set of descriptive and thematic insights. Begin with a detailed description of the group based on observations of specific events or activities over time. Then, conduct a thematic analysis to identify patterns or themes that illustrate how the group functions and lives. The final output should be a comprehensive cultural portrait that integrates both the participants (emic) and the researcher’s (etic) perspectives, potentially advocating for the group’s needs or suggesting societal changes to better accommodate them.
Researchers engaging in ethnography need a solid understanding of cultural anthropology and the dynamics of sociocultural systems, which are commonly explored in ethnographic research. The data collection phase is notably extensive, requiring prolonged periods in the field. Ethnographers often employ a literary, quasi-narrative style in their narratives, which can pose challenges for those accustomed to more conventional social science writing methods.
Another potential issue is the risk of researchers "going native," where they become overly assimilated into the community under study, potentially jeopardizing the objectivity and completion of their research. It's crucial for researchers to be aware of their impact on the communities and environments they are studying.
The case study approach in a research design focuses on a detailed examination of a single case or a small number of cases. Cases can be individuals, groups, organizations, or events. Case studies are particularly useful for research designs that aim to understand complex issues in real-life contexts. The aim is to provide a thorough description and contextual analysis of the cases under investigation. We suggest following these steps in a case study design:
Assess if a case study approach suits your research questions . This approach works well when you have distinct cases with defined boundaries and aim to deeply understand these cases or compare multiple cases.
Choose your case or cases. These could involve individuals, groups, programs, events, or activities. Decide whether an individual or collective, multi-site or single-site case study is most appropriate, focusing on specific cases or themes (Stake, 1995; Yin, 2003).
Gather data extensively from diverse sources . Collect information through archival records, interviews, direct and participant observations, and physical artifacts (Yin, 2003).
Analyze the data holistically or in focused segments . Provide a comprehensive overview of the entire case or concentrate on specific aspects. Start with a detailed description including the history of the case and its chronological events then narrow down to key themes. The aim is to delve into the case's complexity rather than generalize findings.
Interpret and report the significance of the case in the final phase . Explain what insights were gained, whether about the subject of the case in an instrumental study or an unusual situation in an intrinsic study (Lincoln & Guba, 1985).
The investigator must carefully select the case or cases to study, recognizing that multiple potential cases could illustrate a chosen topic or issue. This selection process involves deciding whether to focus on a single case for deeper analysis or multiple cases, which may provide broader insights but less depth per case. Each choice requires a well-justified rationale for the selected cases. Researchers face the challenge of defining the boundaries of a case, such as its temporal scope and the events and processes involved. This decision in a research design is crucial as it affects the depth and value of the information presented in the study, and therefore should be planned to ensure a comprehensive portrayal of the case.

Qualitative and quantitative research designs are distinct in their approach to data collection and data analysis. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research prioritizes understanding the depth and richness of human experiences, behaviours, and interactions.
Qualitative methods in a research design have to have internal coherence, meaning that all elements of the research project—research question, data collection, data analysis, findings, and theory—are well-aligned and consistent with each other. This coherence in the research study is especially crucial in inductive qualitative research, where the research process often follows a recursive and evolving path. Ensuring that each component of the research design fits seamlessly with the others enhances the clarity and impact of the study, making the research findings more robust and compelling. Whether it is a descriptive research design, explanatory research design, diagnostic research design, or correlational research design coherence is an important element in both qualitative and quantitative research.
Finally, a good research design ensures that the research is conducted ethically and considers the well-being and rights of participants when managing collected data. The research design guides researchers in providing a clear rationale for their methodologies, which is crucial for justifying the research objectives to the scientific community. A thorough research design also contributes to the body of knowledge, enabling researchers to build upon past research studies and explore new dimensions within their fields. At the core of the design, there is a clear articulation of the research objectives. These objectives should be aligned with the underlying concepts being investigated, offering a concise method to answer the research questions and guiding the direction of the study with proper qualitative methods.
Carter, K. (1993). The place of a story in the study of teaching and teacher education. Educational Researcher, 22(1), 5-12, 18.
Charmaz, K. (2006). Constructing grounded theory. London: Sage.
Creswell, J. W., & Miller, D. L. (2000). Determining validity in qualitative inquiry. Theory Into Practice, 39(3), 124-130.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1985). Naturalistic inquiry. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Moustakas, C. (1994). Phenomenological research methods. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Ollerenshaw, J. A., & Creswell, J. W. (2000, April). Data analysis in narrative research: A comparison of two “restoring” approaches. Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New Orleans, LA.
Stake, R. E. (1995). The art of case study research. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Strauss, A., & Corbin, J. (1990). Basics of qualitative research: Grounded theory procedures and techniques. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
van Manen, M. (1990). Researching lived experience: Human science for an action sensitive pedagogy. Ontario, Canada: University of Western Ontario.
Yin, R. K. (2003). Case study research: Design and methods (3rd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage

Whatever your research objectives, make it happen with ATLAS.ti!
Download a free trial today.

6 Qualitative data examples for thorough market researchers
Types of qualitative data in market research, 6 qualitative data examples, get nuanced insights from qualitative market research.
There are plenty of ways to gather consumer insights for fresh campaigns and better products, but qualitative research is up there with the best sources of insight.
This guide is packed with examples of how to turn qualitative data into actionable insights, to spark your creativity and sharpen your research strategy. You’ll see how qualitative data, especially through surveys, opens doors to deeper understanding by inviting consumers to share their experiences and thoughts freely, in their own words — and how qualitative data can transform your brand.
Before we dig into some examples of how qualitative data can empower your teams to make focused, confident and quick decisions on anything from product to marketing, let’s go back to basics. We can categorize qualitative data into roughly three categories: binary, nominal and ordinal data. Here’s how each of them is used in qualitative data analysis.
Binary data
Binary data represents a choice between two distinct options, like ‘yes’ or ‘no’. In market research, this type of qualitative data is useful for filtering responses or making clear distinctions in consumer preferences.
Binary data in qualitative research is great for straightforward insights, but has its limits. Here’s a quick guide on when to use it and when to opt for qualitative data that is more detailed:
Binary data is great for:
- Quick Yes/No questions : like “Have you used our app? Yes or No.”
- Initial screening : to quickly sort participants for further studies.
- Clear-cut answers : absolute factors, such as ownership or usage.
Avoid binary data for:
- Understanding motivations : it lacks the depth to explore why behind actions.
- Measuring intensity : can’t show how much someone likes or uses something.
- Detail needed for product development : misses the nuanced feedback necessary for innovations.

Nominal data
Nominal data categorizes responses without implying any order. For example, when survey respondents choose their favorite brand from a list, the data collected is nominal, offering insights into brand preferences among different demographics.
Some other examples of qualitative data that can be qualified as nominal are asking participants to name their primary information source about products in categories like social media, friends, or online reviews. Or in focus groups, discussing brand perceptions could classify brands into categories such as luxury, budget-friendly, or eco-conscious, based on participant descriptions.
Nominal data is great for:
- Categorizing responses : such as types of consumer complaints (product quality, customer service, delivery issues).
- Identifying preferences : like favorite product categories (beverages, electronics, apparel).
- Segmentation : grouping participants based on attributes (first-time buyers, loyal customers).
Nominal data is not for:
- Measuring quantities : it can’t quantify how much more one category is preferred over another.
- Ordering or ranking responses : it doesn’t indicate which category is higher or lower in any hierarchy.
- Detailed behavioral analysis : While it can group behaviors, it doesn’t delve into the frequency or intensity of those behaviors.

Ordinal data
Ordinal data introduces a sense of order, ranking preferences or satisfaction levels. In qualitative analysis, it’s particularly useful for understanding how consumers prioritize features or products, giving researchers a clearer picture of market trends.
Other examples of qualitative data analyses that use ordinal data, are for instance a study on consumer preferences for coffee flavors, participants might rank flavors in order of preference, providing insights into flavor trends. You can also get ordinal data from focus groups on things like customer satisfaction surveys or app usability, by asking users to rate their ease of use or happiness on an ordinal scale.
Ordinal data is great for:
- Ranking preferences : asking participants to rank product features from most to least important.
- Measuring satisfaction levels : using scales like “very satisfied,” “satisfied,” “neutral,” “dissatisfied,” “very dissatisfied.”
- Assessing Agreement : with statements on a scale from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree.”
Ordinal data is not for:
- Quantifying differences : it doesn’t show how much more one rank is preferred over another, just the order.
- Precise measurements : can’t specify the exact degree of satisfaction or agreement, only relative positions.

This mix of qualitative and quantitative data will give you a well-rounded view of participant attitudes and preferences.
The things you can do with qualitative data are endless. But this article shouldn’t turn into a work of literature, so we’ll highlight six ways to collect qualitative data and give you examples of how to use these qualitative research methods to get actionable results.

How to get qual insights with Attest
You can get to the heart of what your target customers think, with reliable qualitative insights from Attest Video Responses
1. Highlighting brand loyalty drivers with open-ended surveys and questionnaires
Open-ended surveys and questionnaires are great at finding out what makes customers choose and stick with a brand. Here’s why this qualitative data analysis tool is so good for gathering qualitative data on things like brand loyalty and customer experience:
Straight from the source
Open-ended survey responses show the actual thoughts and feelings of your target audience in their own words, while still giving you structure in your data analysis.
Understanding ‘why’
Numbers can show us how many customers are loyal; open-ended survey responses explain why they are. You can also easily add thematic analysis to the mix by counting certain keywords or phrases.
Guiding decisions
The insights from these surveys can help a brand decide where to focus its efforts, from making sure their marketing highlights what customers love most to improving parts of their product.
Surveys are one of the most versatile and efficient qualitative data collection methods out there. We want to bring the power of qualitative data analysis to every business and make it easy to gather qualitative data from the people who matter most to your brand. Check out our survey templates to hit the ground running. And you’re not limited to textual data as your only data source — we also enable you to gather video responses to get additional context from non verbal cues and more.
2. Trend identification with observation notes
Observation notes are a powerful qualitative data analysis tool for spotting trends as they naturally unfold in real-world settings. Here’s why they’re particularly valuable insights and effective for identifying new trends:
Real behavior
Observing people directly shows us how they actually interact with products or services, not just how they say they do. This can highlight emerging trends in consumer behavior or preferences before people can even put into words what they are doing and why.
Immediate insights
By watching how people engage with different products, we can quickly spot patterns or changes in behavior. This immediate feedback is invaluable for catching trends as they start.
Context matters
Observations give you context. You can see not just what people do, but where and how they do it. This context can be key to understanding why a trend is taking off.
Unprompted reactions
Since people don’t know they’re being observed for these purposes, their actions are genuine. This leads to authentic insights about what’s really catching on.
3. Understanding consumer sentiments through semi-structured interviews
Semi-structured interviews for qualitative data analysis are an effective method for data analysts to get a deep understanding of consumer sentiments. It provides a structured yet flexible approach to gather in-depth insights. Here’s why they’re particularly useful for this type of research question:
Personal connection
These interviews create a space for a real conversation, allowing consumers to share their feelings, experiences, and opinions about a brand or product in a more personal setting.
Flexibility
The format lets the interviewer explore interesting points that come up during the conversation, diving deeper into unexpected areas of discussion. This flexibility uncovers richer insights than strictly structured interviews.
Depth of understanding
By engaging in detailed discussions, brands can understand not just what consumers think but why they think that way and what stations their train of thought passes by.
Structure and surprise
Semi-structured interviews can be tailored to explore specific areas of interest while still allowing for new insights to emerge.
4. Using focus groups for informing market entry strategies
Using a focus group to inform market entry strategies provides a dynamic way to discover your potential customers’ needs, preferences, and perceptions before launching a product or entering a new market. Here’s how focus groups can be particularly effective for this kind of research goal:
Real conversations
Focus groups allow for real-time, interactive discussions, giving you a front-row seat to hear what your potential customers think and feel about your product or service idea.
Diverse Perspectives
By bringing together people from various backgrounds, a focus group can offer a wide range of views and insights, highlighting different consumer needs and contextual information that you might miss out on in a survey.
Spotting opportunities and challenges
The dynamic nature of focus groups can help uncover unique market opportunities or potential challenges that might not be evident through other research methods, like cultural nuances.
Testing ideas
A focus group is a great way to test and compare reactions to different market entry strategies, from pricing models to distribution channels, providing clear direction on what approach might work best.
5. Case studies to gain a nuanced understanding of consumers on a broad level
Case studies in qualitative research zoom in on specific stories from customers or groups using a product or service, great for gaining a nuanced understanding of consumers at a broad level. Here’s why case studies are a particularly effective qualitative data analysis tool for this type of research goal:
In-depth analysis
Case studies can provide a 360-degree look at the consumer experience, from initial awareness to post-purchase feelings.
This depth of insight reveals not just what consumers do, but why they do it, uncovering motivations, influences, and decision-making processes.
Longitudinal insight
Case studies can track changes in consumer behavior or satisfaction over time, offering a dynamic view of how perceptions evolve.
This longitudinal perspective is crucial for giving context to the lifecycle of consumer engagement with a brand.
Storytelling power
The narrative nature of case studies — when done right — makes them powerful tools for communicating complex consumer insights in an accessible and engaging way, which can be especially useful for internal strategy discussions or external marketing communications.
6. Driving product development with diary studies
Diary studies are a unique qualitative research method that involves participants recording their thoughts, experiences, or behaviors over a period of time, related to using a product or service. This qualitative data analysis method is especially valuable for driving product development for several reasons:
Real-time insights
Diary studies capture real-time user experiences and feedback as they interact with a product in their daily lives.
This ongoing documentation provides a raw, unfiltered view of how a product fits into the user’s routine, highlighting usability issues or unmet needs that might not be captured in a one-time survey or interview.
Realistic user journey mapping
By analyzing diary entries, you can map out the entire user journey, identifying critical touch points where users feel delighted, frustrated, or indifferent.
This then enables you to implement targeted improvements and innovations at the moments that matter most.
Identifying patterns
Over the course of a diary study, patterns in behavior, preferences, and challenges can emerge, which is great for thematic analysis.
It can guide product developers to prioritize features or fixes that will have the most significant impact on user satisfaction, which is especially great if they don’t know what areas to focus on first.
Qualitative research brings your consumers’ voices directly to your strategy table. The examples we’ve explored show how qualitative data analysis methods like surveys, interviews, and case studies illuminate the ‘why’ behind consumer choices, guiding more informed decisions. Using these insights means crafting products and messages that resonate deeply, ensuring your brand not only meets but exceeds consumer expectations.

Customer Research Manager
Related articles
Making it personal – using tech to build connections with consumers | diageo, panel discussion – future-proofing your brand with consumer insights, attest product release: multi-market | attest’s alyssa stringer, subscribe to our newsletter.
Fill in your email and we’ll drop fresh insights and events info into your inbox each week.
* I agree to receive communications from Attest. Privacy Policy .
You're now subscribed to our mailing list to receive exciting news, reports, and other updates!
An update to the technology education teaching framework: factors that support and hinder technology education teachers in Canada
- Published: 03 June 2024
Cite this article

- David D. Gill ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4731-1466 1
This research paper presents the second in a series of case studies on teaching technology education within a Canadian context. Specifically, this paper will discuss what is helping and hindering the teaching of technology education and skilled trades at the secondary level (grades 10–12) in relation to a previous intermediate level (grades 7–9) case study.
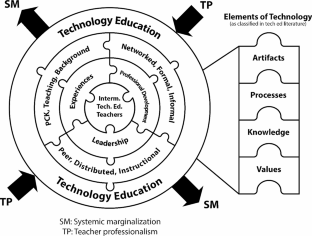
In the previous research intermediate technology education was found to be marginalized in relation to other areas of the general curriculum within the Canadian context. As such, this research study sought to understand if marginalization and other related themes were present at the secondary level. The Technology Education Teaching Framework (TETF) which emphasises the role of teacher experience, professional development, and leadership was used as the primary lens of inquiry.
A qualitative case study methodology framed this study. Data were collected via an online questionnaire, semi-structured interviews, and classroom observations from a purposeful typical case sample of Canadian technology education and skilled trades teachers. Two cycle coding was used in conjunction with thematic analysis to analyze and interpret the data.
Secondary technology education and skilled trades teachers share similar beliefs and pedagogical practices as their intermediate counterparts. Themes of professionalism and systemic marginalization emerged as helping and hindering teachers’ efforts. However, at this level there was an identified tension between the values associated with the technology education and skilled trades curricula. Moving forward, raising the profile of technology education is framed within the potential transferability of local strategies and solutions to other jurisdictions with similar circumstances.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Atkinson, S. (2023). Design and technology education in England. The Bloomsbury Handbook of Technology Education (pp. 28–41). Bloomsbury Academic.
Baxter, P., & Jack, S. (2008). Qualitative case study methodology: Study design and implementation for novice researchers. The Qualitative Report , 13 (4), 544–559. Academic OneFile.
Google Scholar
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3 (2), 77–101. https://doi.org/10.1191/1478088706qp063oa .
Article Google Scholar
Buckley, J. (2023). Historical and philosophical origins of technology education. The Bloomsbury Handbook of Technology Education (pp. 14–27). Bloomsbury Academic.
Cheek, D. W. (2000). Marginalization of technology within the STS movement in American K-12 education. Science, Technology, and Society: A sourcebook on research and practice (pp. 167–192). Kluwer Academic/Plenum.
Clarke, V., & Braun, V. (2013). Teaching thematic analysis: Overcoming challenges and developing strategies for effective learning. The Psychologist , 26 (2), 120–123.
Copeland, L. L. J., & Gray, R. C. (2002). Developing Maryland’s technology education leaders for the 21st century: Technology education leadership project (TELP). Journal of Industrial Teacher Education , 39 (3), 104–121.
Darling-Hammond, L., Hyler, M. E., & Gardner, M. (2017). Effective teacher professional development . Learning Policy Institute.
de Vries, M. J. (2016). Teaching about technology: An introduction to the philosophy of technology for non-philosophers (2nd ed.). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-32945-1 .
Department of Education, Government of Newfoundland, & Labrador, L. (2021, May 17). Minister Osborne Announces High Schools Chosen for First Year of Technology Career Pathway Pilot Program . News Releases. https://www.gov.nl.ca/releases/2021/education/0517n02/ .
Fasso, W., & Knight, B. A. (2019). Identity development in school makerspaces: Intentional design. International Journal of Technology and Design Education . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-019-09501-z .
Foster, P. N. (1994). Technology education: AKA industrial arts. Journal of Technology Education , 5 (2).
Fox-Turnbull, W. (2017). Implementing digital technology in the New Zealand curriculum. In N. Seery, J. Buckley, D. Canty, & J. Phelan (Eds.), Research and practice in technology education: Perspectives on human capacity and development (pp. 441–467). Athlone Institute of Technology.
Gill, D. (2018). A technology education teaching framework: Factors that support and hinder intermediate technology education teachers. International Journal of Technology and Design Education . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-018-9465-0 .
Haché, G. J. (2007). Revitalizing technology education with apprenticeship studies. In J. R. Dakers, W. J. Dow, & de M. J. Vries (Eds.), Teaching and learning technological literacy in the classroom (pp. 347–352). Faculty of Education University of Glasgow. http://www.iteea.org/File.aspx?id=39541&v=cbfe53da .
Hill, A. M. (1997). Reconstructionism in technology education . Springer. http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-94-011-5598-4_11 .
Irving-Bell, D. (2022). The formation of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics teacher identities: Pre-service teacher’s perceptions. In P. J. Williams & B. von Mengersen (Eds.), Applications of Research in Technology Education (pp. 31–46). Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7885-1_3 .
ITEA (2007). Standards for technological literacy: Content for the study of technology . International Technology Education Association . https://www.iteea.org/File.aspx?id=67767&v=691d2353
Jones, A., Buntting, C., & de Vries, M. J. (2013). The developing field of technology education: A review to look forward. International Journal of Technology and Design Education , 23 (2), 191–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-011-9174-4 .
Jones, L., McDermott, H. J., Tyrer, J. R., & Zanker, N. P. (2019). The effect of teacher’s confidence on technology and engineering curriculum provision. International Journal of Technology and Design Education . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-019-09542-4 .
Merriam, S. B., & Tisdell, E. J. (2016). Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation (Fourth Edition). Jossey-Bass.
Mitcham, C. (1994). Thinking through technology: The path between engineering and philosophy . University of Chicago Press.
Morrison-Love, D. (2023). Doing: Skills, knowledge, and understanding in conceptual, theoretical, and practical contexts. The Bloomsbury Handbook of Technology Education (pp. 122–135). Bloomsbury Academic.
Snyder, M. (2018). A Century of perspectives that influenced the consideration of technology as a critical component of STEM Education in the United States. The Journal of Technology Studies , 44 (2), 42–56. https://doi.org/10.21061/jots.v44i2.a.1 .
Snyder, J. F., & Hales, J. A. (Eds.). (1981). Jackson’s mill industrial arts curriculum theory . Dept. of Education.
Strimel, G. (2023). Technology education’s place in STEM: The relationship and role of technology in STEM education, using the United States as a case study. The Bloomsbury Handbook of Technology Education (pp. 76–94). Bloomsbury Academic.
Technology education gets a big boost . (2006). [News Release]. https://www.releases.gov.nl.ca/releases/2006/edu/0324n04.htm .
Tucker, M., & Maxwell, P. (1995). Directions for change: A consultation paper on the senior high school program . Government of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Tuff, J., & Gill, D. (2023). Decentralized technology education curricula development. The Bloomsbury Handbook of Technology Education (pp. 60–75). Bloomsbury Academic.
Wells, J. G. (2008). STEM education: The potential of technology education. 95th Mississippi Valley Technology Teacher Education Conference, St. Louis, MO , 41 . http://www.mississippivalley.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/Wells_2008_MississippiValleyConference_STEM-ED_TE-Potential.pdf .
Download references
For this research project was provided by the Newfoundland and Labrador Teachers’ Association’s (NLTA) Centennial Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Education , Memorial University of Newfoundland, G. A. Hickman Building, St. John’s, NL, A1B 3X8, Canada
David D. Gill
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to David D. Gill .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Gill, D.D. An update to the technology education teaching framework: factors that support and hinder technology education teachers in Canada. Int J Technol Des Educ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-024-09907-4
Download citation
Accepted : 23 May 2024
Published : 03 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-024-09907-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Technology education
- Curricular marginalization
- Teacher professionalism
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
McMaster University, West Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. Qualitative case study methodology prov ides tools for researchers to study. complex phenomena within their contexts. When the approach is ...
28) calls case study research design a 'craftwork'. This is rightly so, because how rigorous and sharp the design is constructed ultimately determines the efficacy, reliability and validity 3 of the final case study outcome. Research design is the key that unlocks before the both the researcher and the audience all the primary elements of ...
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
key elements for designing and implementing qualitative case study research projects. An overview of the types of case study designs is ... According to Yin (2003) a case study design should be considered when: (a) the focus of the study is to answer "how" ... Developing Case Study Research Questions. Case Examples The Research Questions 1 ...
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
The purpose of case study research is twofold: (1) to provide descriptive information and (2) to suggest theoretical relevance. Rich description enables an in-depth or sharpened understanding of the case. It is unique given one characteristic: case studies draw from more than one data source. Case studies are inherently multimodal or mixed ...
Qualitative study design; Case Studies; Qualitative study design. Qualitative study design ... An example of a qualitative case study is a life history which is the story of one specific person. ... Qualitative methods for health research (4th ed.). London: SAGE. University of Missouri-St. Louis. Qualitative Research Designs. Retrieved from ...
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
1. Case study is a research strategy, and not just a method/technique/process of data collection. 2. A case study involves a detailed study of the concerned unit of analysis within its natural setting. A de-contextualised study has no relevance in a case study research. 3. Since an in-depth study is conducted, a case study research allows the
I follow this description with methods considerations, including case study design, research questions, sample size, data collection, and data analysis. Note that there are many approaches and styles to case study research. This chapter focuses primarily on case studies that rely on qualitative methods; more advanced readings are listed at the ...
Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research. Qualitative Inquiry, 12(2), 219-245. ... observation data are positioned as the central component of the research design. Case study observational research offers a promising approach for researchers in a wide range of health care settings seeking more complete understandings of complex topics ...
According to the book Understanding Case Study Research, case studies are "small scale research with meaning" that generally involve the following: The study of a particular case, or a number of cases. That the case will be complex and bounded. That it will be studied in its context. That the analysis undertaken will seek to be holistic.
The qualitative researcher today faces a baffling array of options for con-ducting qualitative research. Numerous inquiry strategies (Denzin & Lincoln, 2005), inquiry traditions (Creswell, 1998), qualitative approaches (Miller & Crabtree, 1992), and design types (Creswell, 2007) are available for selec-tion. What criteria should govern whether ...
Case study research has experienced growing recognition during the past 30 years, evidenced by its more frequent application in published research and increased avail-ability of reference works (e.g., Thomas, 2015; Yin, 2014). Encouraging the use of case study research is an expressed goal of the editors of the recent . Encyclopedia of Case Study
qualitative research professor. I was positive that I would design a quantitative research study but the qualitative courses in the program highlighted the merits of qualitative research. Dr. Cozza and Ms. Rosaria Cimino, thanks for the advisement support. To all the Ed.D. candidates that I encountered on my academic journey, especially my
The field of qualitative research there are a number of research designs (also referred to as "traditions" or "genres"), including case study, phenomenology, narrative inquiry, action research, ethnography, grounded theory, as well as a number of critical genres including Feminist theory, indigenous research, critical race theory and cultural studies.
The sample size for a case study depends on th e research question and the epistemological . ... the paper includes components of a qualitative research design: research paradigm, methodological ...
Although case studies have been discussed extensively in the literature, little has been written about the specific steps one may use to conduct case study research effectively (Gagnon, 2010; Hancock & Algozzine, 2016).Baskarada (2014) also emphasized the need to have a succinct guideline that can be practically followed as it is actually tough to execute a case study well in practice.
Abstract. This article presents the case study as a type of qualitative research. Its aim is to give a detailed description of a case study - its definition, some classifications, and several ...
Qualitative research example If you want to generate new ideas for online teaching strategies, a qualitative approach would make the most sense. You can use this type of research to explore exactly what teachers and students struggle with in remote classes. ... Type of design Purpose and characteristics; Case study: Detailed study of a specific ...
A Case study is: An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology. Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research. Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event. Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
Kekeya, qualitative case study research design: the commonalities and differences between collective, intrinsic and instrumental case studies. ... via notetaking or digitally, for example, using a video recorder (Cohen et al., 2011; Johnson & Christensen, 2012). A video camera can be used as non-participant observer because the "video ...
Introduction. A research design in qualitative research is a critical framework that guides the methodological approach to studying complex social phenomena. Qualitative research designs determine how data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted, ensuring that the research captures participants' nuanced and subjective perspectives.
Themes should be far away from the description of any facet of the context. Themes should be closer to explaining the endogenous constructs of a research. Further, often the contribution of a qualitative case study research (QCSR) emerges from the 'extension of a theory' or 'developing deeper understanding—fresh meaning of a phenomenon'.
Get nuanced insights from qualitative market research. Qualitative research brings your consumers' voices directly to your strategy table. The examples we've explored show how qualitative data analysis methods like surveys, interviews, and case studies illuminate the 'why' behind consumer choices, guiding more informed decisions.
This research paper presents the second in a series of case studies on teaching technology education within a Canadian context. Specifically, this paper will discuss what is helping and hindering the teaching of technology education and skilled trades at the secondary level (grades 10-12) in relation to a previous intermediate level (grades 7-9) case study.In the previous research ...