Difference Between Report Form and Account Form Balance Sheets
- Small Business
- Accounting & Bookkeeping
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">

How to Add Beneficiaries to a Joint Bank Account
Distributions vs. retained earnings, how to adjust the balance on a profit and loss report.
- Creating a Company Financial Analysis Report
- Business Factors Indicating Liquidity Problems
The balance sheet is one of a company’s most important financial statements, because it gives investors a snapshot of the company’s financial health at any given moment in time. Essentially, it is a company’s account ledger, containing information about assets the company possesses, liabilities and obligations it needs to address, and owner equity in the company.
A balance sheet can be presented in account form and report form, but first, it is important to have a basic understanding of the types of financial statements to prepare and why they are important.
Statements of Financial Position Forms
There are four different statement of financial position forms that a company’s accountant prepares, and they each cover a very important piece of the company’s financial health. Statements of financial position forms provide a snapshot of the performance, overall financial position and cash flows of a business. These documents are reviewed by investors, lenders, creditors and management to evaluate a company.
Each of the documents relies on data from other statements, so they are usually prepared in a certain order.
- Income statement . The income statement is the most important of the financial statements, because it reveals basic truths about the financial performance of a company for a given reporting period. Beginning with sales, it subtracts expenses and arrives at a net profit or loss, and, in the case of publicly reported companies, an earnings-per-share figure for investors.
- Statement of retained earnings. If the income statement is a measure of financial health at any given moment, this document — also known as the statement of owner's equity, an equity statement or a statement of shareholders’ equity — offers the information over time. Management and investors want to know if they are making or losing money, so the statement reconciles the beginning and ending retained earnings for the period (for instance, over a year or so) using information such as net income from the other financial statements.
- Balance sheet. This report shows the financial position of a business as of the report date, and like the income statement, it is a snapshot of financial performance at a given moment because it can change daily or hourly, depending on circumstances. The information is divided into the general classifications of assets, liabilities and equity. As a rule, the total amount of the company's assets is equal to the total amount of its liabilities plus the owners' equity in the company. This equation must always balance, with the same amount on each side of the sheet. Unlike the income statement, however, the balance sheet is much more detailed — it lists specific line items of assets and liabilities.
- Statement of cash flows. This report reveals the cash inflows and outflows experienced by a company during a reporting period. These cash flows are broken down into three classifications: operating activities, investing activities and financing activities.
Account Form and Report Form Balance Sheets
A company’s balance sheet can be presented in one of two ways, account form and report form, depending on the preference of those who will review the document.
The account form balance sheet is presented in a horizontal format, with information in two columns beside each other. The left column of the account form balance sheet lists assets, while the right column lists liabilities and equity. Naturally, the last line in each column lists the total value of all assets and liabilities and equity, respectively. The account form balance sheet can be easier to use when information is being presented for multiple periods, and it allows the reader to verify that the ledger is in balance at a glance.
The report form balance sheet is presented in a vertical orientation, and is essentially one column that spans the entire width of a page. Starting with assets, the report form balance sheet provides a total value at the end of the assets section, followed by liabilities and equity, with the final line of the report form balance sheet providing the total combined value of liabilities and equity.
- My Accounting Course: What is a Report Form Balance Sheet?
- Accounting Tools: Types of Financial Statements
- IgniteSpot Accounting: The Four Basic Financial Statements
- WikiAccounting: 5 Main Elements of Financial Statements
John began his 25-year career in the editorial business as a newspaper journalist in his native Connecticut before moving to Boston in 2012. He started fresh out of college as a weekly newspaper reporter and cut his teeth covering news, politics, police, and even a visit from a waterskiing squirrel. He went on to work in the newsrooms of several busy daily newspapers, and developed a love for detailed storytelling, focusing on the lives and diverse tales that all people have to offer. Moving on to the business arena later in his career, John worked as a managing editor for a healthcare publishing company and a technology software firm. He’s used his background in broadcast journalism as a webinar moderator, voice-over specialist, and podcast narrator. John also holds a master’s degree as an elementary school teacher and spent 10 years working with and tutoring students of various ages and backgrounds, including multilingual students and students with special needs of all ages.
Related Articles
How to change the asset account in quickbooks, how to set up a line of credit account in quicken, how to remove a credit card account & all of its transactions from quickbooks, types of statements in accounting, how to e-sign a name online, how to delete an account in outlook 13, a summary of the accounting cycle, how to find your google accounts, how to build data entry forms & reports for mysql, most popular.
- 1 How to Change the Asset Account in QuickBooks
- 2 How to Set Up a Line of Credit Account in Quicken
- 3 How to Remove a Credit Card Account & All of Its Transactions From QuickBooks
- 4 Types of Statements in Accounting

What is a Report Form Balance Sheet?
Home › Accounting › Financial Statements › What is a Report Form Balance Sheet?
Definition: A report form balance sheet is a balance sheet that presents asset, liability , and equity accounts in a vertical format. In financial reporting , there are two general formats for balance sheets: the account format and the report format.
- What Does Report Form Balance Sheet Mean?
The account format presents the asset accounts on the left side and the liabilities and equity accounts on the right. The report format presents all the accounts vertically. Although both balance sheet formats are acceptable, the report form is much more popular.
As the name implies, the report format looks more like a traditional report and is used more often in the general-purpose financial statements . Here is an example of a report form balance sheet.
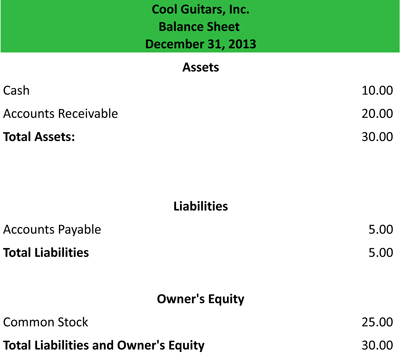
Download this accounting example in excel.
As you can see, all of the accounts are listed in a vertical fashion. The report form has a traditional balance sheet heading with subtotals for each of the asset, liability, and equity accounts. GAAP offers a lot of flexibility with the accounts that can be listed or not listed on the balance sheet. For example, some companies list cash as one account and cash equivalents as another. Other companies combine these accounts into one cash and cash equivalents account.
In some ways the report format is easier to read than the account format because all the account totals are listed on the right side of the report. This is especially true for multiple comparative balance sheets. Although the balance sheet above is only for one year, it could easily be converted into a two-year comparative report by adding another column of numbers for an additional year.

Accounting & CPA Exam Expert
Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career.
Search 2,000+ accounting terms and topics.
- Basic Accounting Course
- Financial Accounting Basics
- Accounting Principles
- Accounting Cycle
- Financial Statements
- Financial Ratio

What is Report Writing: Format, Examples, Types & Process
- Table of Contents
Many professionals struggle to create effective reports due to a lack of understanding of the essential elements and organization required. This can lead to frustration and a failure to communicate key information to the intended audience.
In this blog, we’ll explore what is report writing, the types of reports, essential elements, and tips for creating effective reports to help you communicate your message and achieve your goals.
Definition of report writing?
According to Mary Munter and Lynn Hamilton, authors of “Guide to Managerial Communication,” report writing is “the process of selecting, organizing, interpreting, and communicating information to meet a specific objective.”
What is report writing?
Report writing refers to the process of creating a document that represents information in a clear and concise manner. Reports can be written for various purposes, such as providing updates on a project, analyzing data or presenting findings, or making recommendations.
Effective report writing requires careful planning, research, analysis, and organization of information. A well-structured report should be accurate, and objective, and contain a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. It should also be written in a professional and accessible style, with appropriate use of headings, subheadings, tables, graphs, and other visual aids.
Overall, report writing is an important skill for professionals in many fields, as it helps to communicate information and insights in a clear and concise manner.
What is a report?
A report is a formal document that is structured and presented in an organized manner, with the aim of conveying information, analyzing data, and providing recommendations. It is often used to communicate findings and outcomes to a specific audience, such as stakeholders, or managers. Reports can vary in length and format, but they usually contain a clear introduction, body, and conclusion.
Types of report writing
By understanding the different types of report writing, individuals can select the appropriate format and structure to effectively communicate information and achieve their objectives. However, the kind of report used will depend on the purpose, audience, and context of the report.
1/ Informational reports: These reports provide information about a topic, such as a product, service, or process.
Further Reading : What is an information report
2/ Analytical reports: These reports present data or information in a structured and organized manner, often with charts, graphs, or tables, to help the reader understand trends, patterns, or relationships.
3/ Formal Reports: These are detailed and structured reports written for a specific audience, often with a specific objective. In comparison with informal reports , formal reports are typically longer and more complex than other types of reports.
4/ Progress reports: These reports provide updates on a project or initiative, detailing the progress made and any challenges or obstacles encountered.
5/ Technical reports: These reports provide technical information, such as specifications, designs, or performance data, often aimed at a technical audience.
6/ Research reports: These reports present the findings of research conducted on a particular topic or issue, often including a literature review, data analysis, and conclusions.
7/ Feasibility Report: A feasibility report assesses the likelihood of achieving success for a suggested project or initiative.
8/ Business Reports: These reports are used in a business setting to communicate information about a company’s performance, operations, or strategies. Different types of business reports include financial statements, marketing reports, and annual reports.
Structure of report writing
The structure of a report refers to the overall organization and layout of the report, including the sections and subsections that make up the report, their order, and their relationships to each other. A report can we divided into three parts.
Preliminary Parts:
- Acknowledgments (Preface or Foreword)
- List of Tables and Illustrations
- Introduction (clear statement of research objectives, background information, hypotheses, methodology, statistical analysis, scope of study, limitations)
- Statement of findings and recommendations (summarized findings, non-technical language)
- Results (detailed presentation of findings with supporting data in the form of tables and charts, statistical summaries, and reductions of data, presented in a logical sequence)
- Implications of the results (clearly stated implications that flow from the results of the study)
- Summary (brief summary of the research problem, methodology, major findings, and major conclusions)
End Matter:
- Appendices (technical data such as questionnaires, sample information, and mathematical derivations)
- Bibliography of sources consulted.
This structure provides a clear and organized framework for presenting a research report, ensuring that all important information is included and presented in a logical and easy-to-follow manner.
Extra Learnings Role of a report structure in report writing The report structure plays a crucial role in report writing as it provides a clear and organized framework for presenting information in an effective and logical manner. It ensures that the reader can easily understand the purpose and scope of the report, locate and access the relevant information. The preliminary parts of the report, provide an overview of the report and aid navigation. The main text makes it easier for the reader to comprehend and analyze the information. And The end matter provides additional details and sources for reference. An organized report structure also helps the author to communicate their research and ideas effectively to the intended audience.
What is the report writing format?
The format of report writing refers to the structure of a formal document that provides information on a particular topic or issue. The report writing format typically includes the following key components:
8 Essential elements of report writing are:
1/ Title: The title is the first thing that readers will see, and it should be clear and concise. The title should include the report’s subject or topic and the author’s name, date of writing, or who the report is for. Remember to keep the title brief and informative, avoiding vague or ambiguous language.
Example of Business Report Title Page: “Market Analysis and Growth Strategies for XYZ Corporation” Author: Mary Johnson Date: January 2, 2022 Company: Earthcon Corporation Department: Strategy and Planning
In this example, the title page includes the name of the report, ‘Market Analysis 2022,’ the author’s name, ‘John Doe,’ the submission date, ‘January 1, 2024,’ and other details such as the name of the organization, ‘Earthcon Corporation.’
2/ Table of Contents : The table of contents provides an overview of the report’s contents. It should list all sections and subsections with clear headings. It is essential to make the table of contents organized and easy to read, allowing readers to locate specific information quickly.
Example of Table of Contents I. Introduction…… 1 Purpose of the Report…… 2 Methodology Used…… 2 II. Executive Summary…… 3 III. Background and Context…… 3 IV. Analysis and Findings…… 4 Market Trends and Data…… 5 Competitor Analysis…… 6 SWOT Analysis…… 7 V. Recommendations and Conclusion…… 8 VI. References…… 9
3/ Summary : Also known as the executive summary, the summary provides a brief overview of the entire report. It should summarize the report’s main points, including findings, objectives, and recommendations. The summary should be written after the entire report is completed, and it should be concise and summarized in less than one page.
Example of executive summary: The Annual Sales Report for Earthcon Company shows a 10% increase in overall sales compared to the previous year. The report also reveals that the majority of sales came from the Midwest region and the target demographic is primarily males aged 25-40. Based on these findings, recommendations have been made to focus marketing efforts towards this demographic in the upcoming year.
4/ Introduction : The introduction introduces the report’s topic and informs readers what they can expect to find in the report. The introduction should capture readers’ attention and provide relevant background information. It should be clear and concise, including why the report was written and its objectives.
Example of Introduction: This comprehensive report aims to analyze and evaluate the sales performance of EarthCon Corporation throughout 2024. It will look into detailed sales trends observed throughout the year, carefully examining the various factors that have influenced these trends. Additionally, the report will identify and highlight potential areas for growth, offering valuable insights and recommendations to drive future success.
5/ Body: The body is the longest section and includes all the information, data, and analysis. It should present information in an organized manner, often using subheadings and bullet points. The body should include all relevant research findings and data, often accompanied by visuals such as graphs and tables. It is essential to cite all sources correctly and remain objective, avoiding personal opinions or biases.
Example of Background and Context: This report seeks to analyze the influence of technological advancements on business productivity. Previous research has indicated a correlation between the adoption of innovative technologies and increased operational efficiency for Earthcon. The report will examine further into this topic and offer suggestions for maximizing the benefits of these advancements. Example of Analysis and Findings: The market trends and data show a steady increase in demand for innovative products, with a significant rise in sales in the past five years. In comparison, competitor analysis reveals that Earthcon Corporation is well-positioned to take advantage of this trend due to its strong brand reputation and product portfolio. A SWOT analysis also highlights potential areas for improvement and growth.
6/ Conclusion: The conclusion summarizes the findings and conclusions of the report. It should wrap up all the essential information presented in the body and make recommendations based on the report’s findings. The conclusion must be brief and clear, avoiding the introduction of any new information not previously presented in the body.
7/ Recommendations: The recommendation section should provide suggested goals or steps based on the report’s information. It should be realistic and achievable, providing well-crafted solutions. It is often included in the conclusion section.
Example of Recommendations and Conclusion: Based on the analysis, it is recommended that EarthCon Corporation invest in research and development to continue producing innovative products. Additionally, efforts should be made to expand into emerging markets to increase global reach. In conclusion, the Annual Sales Report shows positive outcomes and recommends strategic actions for future growth.
8/ Appendices: The appendices section includes additional technical information or supporting materials, such as research questionnaires or survey data. It should provide supplementary information to the report without disrupting the report’s main content.
It is important to use clear headings and subheadings and to label tables and figures. Also, proofreading and fact-checking are critical before submitting the report. A well-crafted report is concise, informative and free of personal bias or opinions.
What are the features of report writing
There are several key features of effective report writing that can help ensure that the information presented is clear, concise, and useful. Some of these features include:
1/ Clarity: Reports should be written in clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or technical terms that may be confusing to the reader.
2/ Objectivity: A report should be objective, meaning that it should be free from bias or personal opinions. This is particularly important when presenting data or analysis.
3/ Accuracy: Reports should be based on reliable sources and accurate data. Information should be verified and cross-checked to ensure that it is correct and up-to-date.
4/ Structure: A report should be structured in a logical and organized manner, with clear headings, subheadings, and sections.
5/ Visual aids: A report may include visual aids such as charts, tables, and graphs, which can help to illustrate the key points and make the information easier to understand.
6/ Evidence: Reports should include evidence to support any claims or findings, such as statistics, quotes, or references to relevant literature.
7/ Recommendations: Many reports include recommendations or suggestions for future action based on the findings or analysis presented.
Significance of report writing
Report writing is a critical skill that can have a significant impact on individuals, and organizations. In fact, a report by the National Association of Colleges and Employers found that the ability to communicate effectively, including report writing, was the most important skill sought by employers.
- Reports provide decision-makers with the information they need to make informed decisions.
- Effective report writing demonstrates professionalism and attention to detail, which can help to build trust and credibility with clients.
- Reports can inform planning processes by providing data and insights that can be used to develop strategies and allocate resources.
- Reports often include recommendations or suggestions for future action, which can help to improve processes, procedures, or outcomes.
Further Reading: What is the significance of report writing
Report writing examples and samples

Example of Progress Report
The essential process of report writing
Report writing requires careful planning, organization, and analysis to ensure that the report effectively communicates the intended message to the audience. Here are the general steps involved in the process of report writing:
Plan and prepare:
- Identify the purpose of the report, the target audience, and the scope of the report.
- Collect and examine data from different sources, including research studies, surveys, or interviews.
- Create an outline of the report, including headings and subheadings.
Write the introduction:
- Start with a brief summary of the report and its purpose.
- Provide background information and context for the report.
- Explain the research methodology and approach used.
Write the main body:
- Divide the report into logical sections, each with a clear heading.
- Present the findings and analysis of the research in a clear and organized manner.
- Use appropriate visual aids, such as tables, graphs, or charts to present data and information.
- Utilize a language that is both clear and Brief, and avoid using unnecessary jargon or technical terminology.
- Cite all sources used in the report according to a specified citation style.
Write the conclusion:
- Summarize the main findings and conclusions of the report.
- Restate the purpose of the report and how it was achieved.
- Provide recommendations or suggestions for further action, if applicable.
Edit and revise:
- Review the report for errors in grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Check that all information is accurate and up-to-date.
- Revise and improve the report as necessary.
Format and present:
- Use a professional and appropriate format for the report.
- Include a title page, table of contents, and list of references or citations.
- Incorporate headings, subheadings, and bullet points to enhance the report’s readability and facilitate navigation.
- Use appropriate fonts and sizes, and ensure that the report is well-structured and visually appealing.
Important Principles of report writing
To write an effective report, it is important to follow some basic principles. These principles ensure that your report is clear, concise, accurate, and informative. In this regard, here are some of the key principles that you should keep in mind when writing a report:
1/ Clarity: The report should be clear and easy to understand.
2/ Completeness: The report should cover all the relevant information needed to understand the topic
3/ Conciseness: A report should be concise, presenting only the information that is relevant and necessary to the topic.
4/ Formatting: The report should be properly formatted, with consistent fonts, spacing, and margins
5/ Relevance: The information presented in the report should be relevant to the purpose of the report.
6/ Timeliness: The report should be completed and delivered in a timely manner.
7/ Presentation: The report should be visually appealing and well-presented.
Extra Learnings Styles of report writing When it comes to the style of report writing, it’s important to use hard facts and figures, evidence, and justification. Using efficient language is crucial since lengthy reports with too many words are difficult to read. The most effective reports are easy and quick to read since the writer has comprehended the data and formulated practical recommendations. To achieve this, it’s important to write as you speak, avoid empty words, use descending order of importance, use an active voice, and keep sentences short. The goal should be to write to express and not to impress the reader. It’s also important to get facts 100% right and to be unbiased and open. By following these tips, one can create a well-written report that is easy to understand and provides valuable insights.
Differences between a report and other forms of writing
Reports are a specific form of writing that serves a distinct purpose and have unique characteristics. Unlike other forms of writing, such as essays or fiction, reports are typically focused on presenting factual information and making recommendations based on that information. Below we have differentiated report writing with various other forms of writing.
Essay vs report writing
Project writing vs report writing, research methodology vs report writing, article writing vs report writing, content writing vs report writing, business plan vs report writing, latest topics for report writing in 2024.
The possibilities for report topics may depend on the goals and scope of the report. The key is to choose a topic that is relevant and interesting to your audience, and that you can conduct thorough research on in order to provide meaningful insights and recommendations.
- A market analysis for a new product or service.
- An evaluation of employee satisfaction in a company.
- A review of the state of cybersecurity in a particular industry.
- A study of the prevalence and consequences of workplace discrimination.
- Analysis of the environmental impact of a particular industry or company.
- An assessment of the impact of new technology or innovations on a particular industry or sector.
Report writing skills and techniques
Effective report writing requires a combination of skills and techniques to communicate information and recommendations in a clear, and engaging manner.
From organizing information to tailoring the report to the intended audience, there are many factors to consider when writing a report. By mastering these skills and techniques, you can ensure that your report is well-written, informative, and engaging for your audience. Some of the primary ones are:
1/ Organization and structure: Structure your report in a logical and organized manner with headings and subheadings.
2/ Use of data and evidence: Present objective data and evidence to support your findings and recommendations.
3/ Audience awareness: Tailor your report to the needs and interests of your intended audience.
4/ Effective visuals: Use graphs, charts, or other visuals to communicate complex information in a clear and engaging way.
5/ Editing and proofreading: Carefully edit and proofread your report to ensure it is error-free and professional.
6/ Tone: Use a professional and objective tone to communicate your findings and recommendations.
7/ Time management: Manage your time effectively to ensure you have enough time to research, write, and revise your report.
Tips for effective report writing
- Understand your audience before you start writing.
- Start with an outline and cover all the important points.
- Employ clear and concise language.
- Utilize headings and subheadings to organize your report.
- Incorporate evidence and examples to support your points.
- Thoroughly edit and proofread your report before submission.
- Follow formatting guidelines If your report has specific formatting requirements.
- Use visuals to enhance understanding.
What is the ethical consideration involved in report writing
Ethical considerations play a crucial role in report writing. The accuracy of the information presented in the report is of utmost importance, as it forms the basis for any conclusions or recommendations that may be made. In addition, it is essential to avoid plagiarism by giving credit to the original sources of information and ideas.
Another crucial ethical consideration is confidentiality, particularly when the report contains sensitive or confidential information. It is important to safeguard this information and prevent its disclosure to unauthorized individuals.
Avoiding bias in report writing is also crucial, as it is essential to present information in an objective and unbiased manner. In cases where research or data collection is involved, obtaining informed consent from human subjects is a necessary ethical requirement.
By taking these ethical considerations into account, report writers can ensure that their work is fair, accurate, and respectful to all parties involved.
Common mistakes in report writing
There are several common mistakes that students and report writers make in report writing. By avoiding these common mistakes, students as well as report writers can create effective and impactful reports that are clear, accurate, and objective.
1/ Writing in the first person: Often, students and report writers commit an error by writing in the first person and utilizing words such as “I” or “me. In reports, it is recommended to write impersonally, using the passive voice instead.
2/ Using the wrong format: Reports should use numbered headings and subheadings to structure the content, while essays should have a clear line of argument in their content.
3/ Failing to introduce the content: The introduction of the report should introduce the content of the report, not the subject for discussion. It is important to explain the scope of the report and what is to follow, rather than explaining what a certain concept is.
4/ Missing relevant sections: Students and report writers, often miss out on including relevant sections that were specified in the assignment instructions, such as a bibliography or certain types of information. This can result in poor interpretation.
5/ Poor proofreading: Finally, not spending enough time proofreading the reported work can create unwanted mistakes. Therefore, It is important to proofread and correct errors multiple times before submitting the final report to avoid any mistakes that could have been easily corrected.
By avoiding these common mistakes, students and report writers can improve the quality of their reports.
What are some challenges of report writing and how to overcome them
Report writing can be a challenging task for many reasons. Here are some common challenges of report writing and how to overcome them:
1/ Lack of clarity on the purpose of the report: To overcome this challenge, it is important to clearly define the purpose of the report before starting. This can help to focus the content of the report and ensure that it meets the needs of the intended audience.
2/ Difficulty in organizing ideas: Reports often require a significant amount of information to be organized in a logical and coherent manner. To overcome this challenge, it can be helpful to create an outline or flowchart to organize ideas before beginning to write.
3/ Time management: Writing a report can be time-consuming, and it is important to allow sufficient time to complete the task. To overcome this challenge, it can be helpful to create a timeline or schedule for the various stages of the report-writing process.
4/ Writer’s block: Sometimes writers may experience writer’s block, making it difficult to start or continue writing the report. To overcome this challenge, it can be helpful to take a break, engage in other activities or brainstorming sessions to generate new ideas.
5/ Difficulty in citing sources: It is important to properly cite sources used in the report to avoid plagiarism and maintain credibility. To overcome this challenge, it can be helpful to use citation management tools, such as EndNote or Mendeley, to keep track of sources and ensure accurate referencing.
6/ Review and editing: Reviewing and editing a report can be a challenging task, especially when it is one’s own work. To overcome this challenge, it can be helpful to take a break before reviewing the report and seek feedback from others to gain a fresh perspective.
By being aware of these challenges and taking proactive steps to overcome them, report writers can create effective and impactful reports that meet the needs of their intended audience.
Best Software for writing reports
Report writing software has made it easier for writers to produce professional-looking reports with ease. These software tools offer a range of features and functionalities, including data visualization, collaboration, and customization options. In this section, we will explore some of the best report-writing software available:
1/ Tableau : This tool is great for creating interactive and visually appealing reports, as it allows users to easily create charts, graphs, and other data visualizations. It also supports data blending, which means that you can combine data from multiple sources to create more comprehensive reports.
2/ Zoho reporting : This tool is designed to help users create and share professional-looking reports quickly and easily. It offers a variety of customizable templates, as well as a drag-and-drop interface that makes it easy to add data and create charts and graphs.
3/ Bold Reports by Syncfusion : This tool is designed specifically for creating reports in .NET applications. It offers a wide range of features, including interactive dashboards, real-time data connectivity, and customizable themes and templates.
4/ Fast Reports : This tool is a reporting solution for businesses of all sizes. It allows users to create reports quickly and easily using a drag-and-drop interface and offers a variety of templates and customization options. It also supports a wide range of data sources, including databases, spreadsheets, and web services.
Further Reading : 10+ Best Report Writing Software and Tools in 2024
What is the conclusion of report writing
The conclusion of report writing is the final section of the report that summarizes the main findings, conclusions, and recommendations. It should tie together all the different sections of the report and present a clear and concise summary of the key points.
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEWCASTLE has given an inverted introduction framework that can use used for writing effective conclusions for reports.
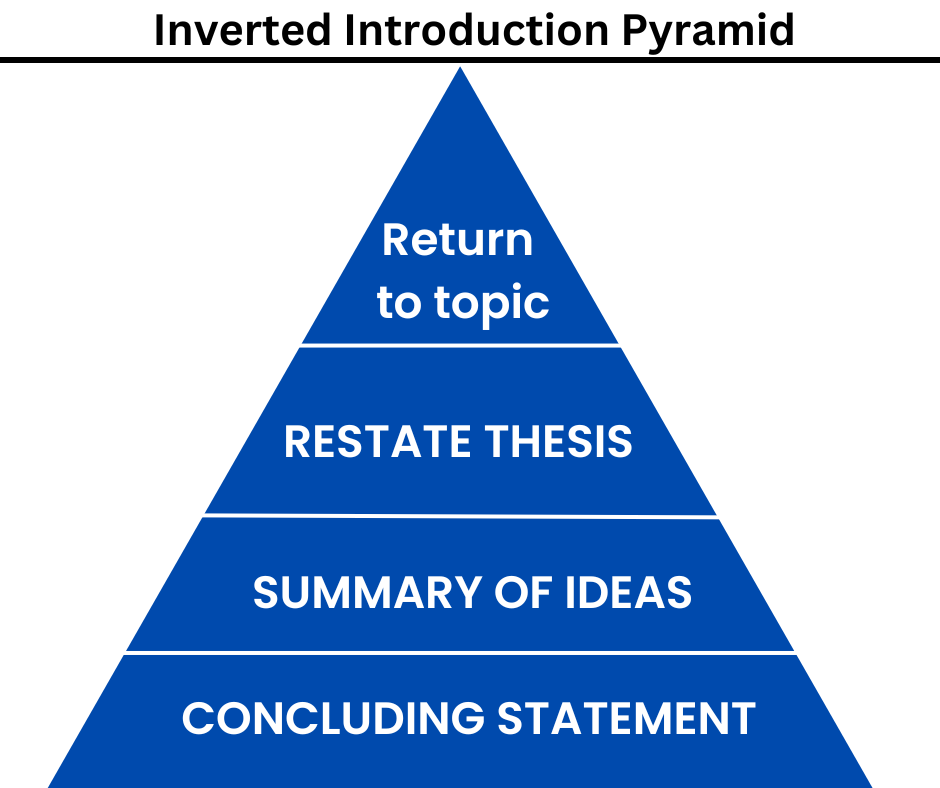
Example of conclusion in report writing:
The implication of the above diagram can be explained with the following example:
1. RETURN TO TOPIC:
Social media has revolutionized the marketing landscape, providing new opportunities for brands to connect with their target audience.
2. RESTATE THESIS:
However, the complexities and limitations of social media mean that it is unlikely to completely replace traditional marketing methods. The role of the marketing professional remains crucial in ensuring that social media strategies align with the company’s overall goals and effectively reach the desired audience.
3. SUMMARY OF IDEAS DISCUSSED:
Automated tools cannot fully account for the nuances of human communication or provide the level of personalization that consumers crave. Therefore, the most effective marketing strategies will likely blend social media tactics with traditional marketing channels.
4. CONCLUDING STATEMENT [restating thesis]:
In conclusion, while social media presents significant opportunities for brands, the expertise of marketing professionals is still essential to creating successful campaigns that achieve desired outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) what is report writing and example.
Ans: Report writing involves preparing a structured document that delivers information to a particular audience in a clear and systematic manner. An example of a report could be a business report analyzing the financial performance of a company and making recommendations for improvement.
Q2) What is report writing and types of reports?
Ans: The act of presenting information in an orderly and structured format is known as report writing. Reports come in different types, such as analytical reports, research reports, financial reports, progress reports, incident reports, feasibility reports, and recommendation reports.
Q3) What are the 5 steps of report writing
The five steps of report writing, are as follows:
- Planning: This involves defining the purpose of the report, determining the audience, and conducting research to gather the necessary information.
- Structuring: This step involves deciding on the structure of the report, such as the sections and subsections, and creating an outline.
- Writing: This is the stage where the actual writing of the report takes place, including drafting and revising the content.
- Reviewing: In this step, the report is reviewed for accuracy, coherence, and effectiveness, and any necessary changes are made.
- Presenting: This final step involves presenting the report in a clear and professional manner, such as through the use of headings, visuals, and a table of contents.
Q4) What is a report in short answer?
Share your read share this content.
- Opens in a new window
Aditya Soni
You might also like.

10 Differences Between Formal & Informal Reports + Examples

24 Types of Business Reports With Samples & Writing Structure

11 Characteristics of a Good Business Report
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

A Guide To The Top 14 Types Of Reports With Examples Of When To Use Them

Table of Contents
1) What Is The Report Definition?
2) Top 14 Types Of Reports
3) What Does A Report Look Like?
4) What To Look For In A Reporting Tool
Businesses have been producing reports forever. No matter what role or industry you work in, chances are that you have been faced with the task of generating a tedious report to show your progress or performance.
While reporting has been a common practice for many decades, the business world keeps evolving, and with more competitive industries, the need to generate fast and accurate reports becomes critical. This presents a problem for many modern organizations today, as building reports can take from hours to days. In fact, a survey about management reports performed by Deloitte says that 50% of managers are unsatisfied with the speed of delivery and the quality of the reports they receive.
With this issue in mind, several BI tools have been developed to assist businesses in generating interactive reports with just a few clicks, enhancing the way companies make critical decisions and service insights from their most valuable data.
But, with so many types of reports used daily, how can you know when to use them effectively? How can you push yourself ahead of the pack with the power of information? Here, we will explore the 14 most common types of reports in business and provide some examples of when to use them to your brand-boosting advantage. In addition, we will see how online dashboards have overthrown the static nature of classic reports and given way to a much faster, more interactive way of working with data.
Let’s get started with a brief report definition.
What Is The Report Definition?
A report is a document that presents relevant business information in an organized and understandable format. Each report is aimed at a specific audience and business purpose, and it summarizes the development of different activities based on goals and objectives.
That said, there are various types of reports that can be used for different purposes. Whether you want to track the progress of your strategies or stay compliant with financial laws, there is a different report for each task. To help you identify when to use them, we will cover the top 14 most common report formats used for businesses today.
What Are The Different Types Of Reports?

1. Informational Reports
The first in our list of reporting types is informational reports. As their name suggests, this report type aims to give factual insights about a specific topic. This can include performance reports, expense reports, and justification reports, among others. A differentiating characteristic of these reports is their objectivity; they are only meant to inform but not propose solutions or hypotheses. Common informational reports examples are for performance tracking, such as annual, monthly, or weekly reports .
2. Analytical Reports
This report type contains a mix of useful information to facilitate the decision-making process through a mix of qualitative and quantitative insights as well as real-time and historical insights. Unlike informational reports that purely inform users about a topic, this report type also aims to provide recommendations about the next steps and help with problem-solving. With this information in hand, businesses can build strategies based on analytical evidence and not simple intuition. With the use of the right BI reporting tool , businesses can generate various types of analytical reports that include accurate forecasts via predictive analytics technologies. Let's look at it with an analytical report example.
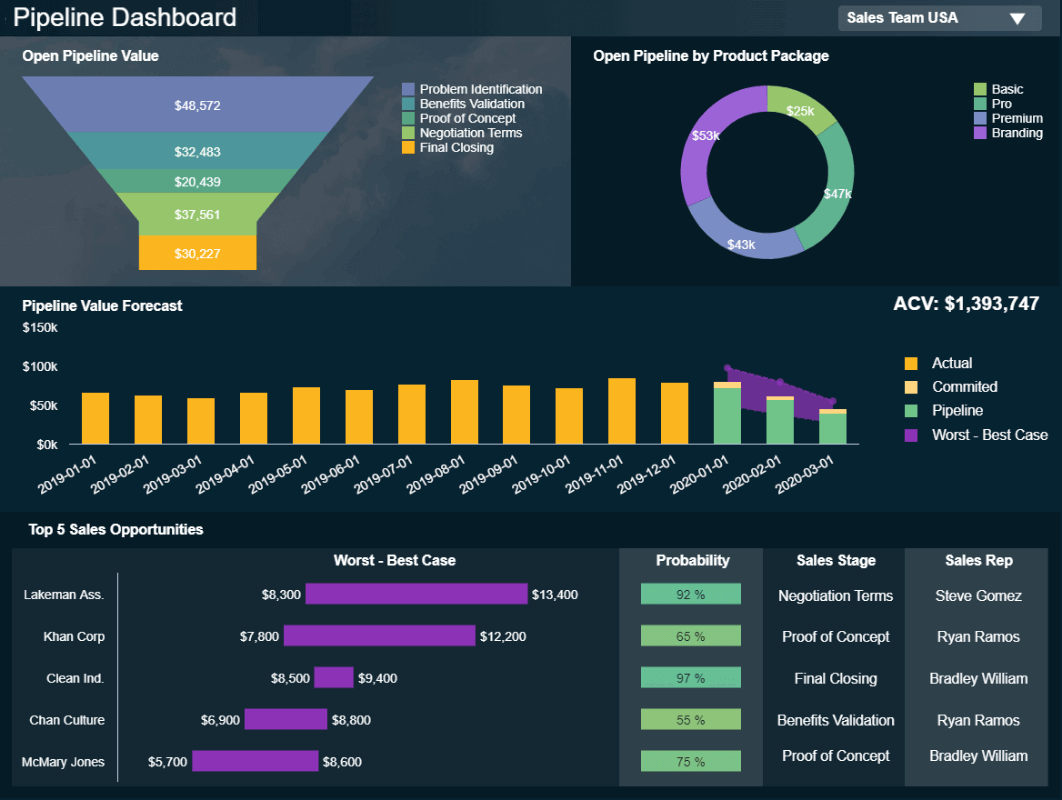
**click to enlarge**
The example above is the perfect representation of how analytical reports can boost a business’s performance. By getting detailed information such as sales opportunities, a probability rate, as well as an accurate pipeline value forecast based on historical data, sales teams can prepare their strategies in advance, tackle any inefficiencies, and make informed decisions for increased efficiency.
3. Operational Reports
These reports track every pertinent detail of the company's operational tasks, such as its production processes. They are typically short-term reports as they aim to paint a picture of the present. Businesses use this type of report to spot any issues and define their solutions or to identify improvement opportunities to optimize their operational efficiency. Operational reports are commonly used in manufacturing, logistics, and retail as they help keep track of inventory, production, and costs, among others.
4. Product Reports
As its name suggests, this report type is used to monitor several aspects related to product development. Businesses often use them to track which of their products or subscriptions are selling the most within a given time period, calculate inventories, or see what kind of product the client values the most. Another common use case of these reports is to research the implementation of new products or develop existing ones. Let’s see it in more detail with a visual example.
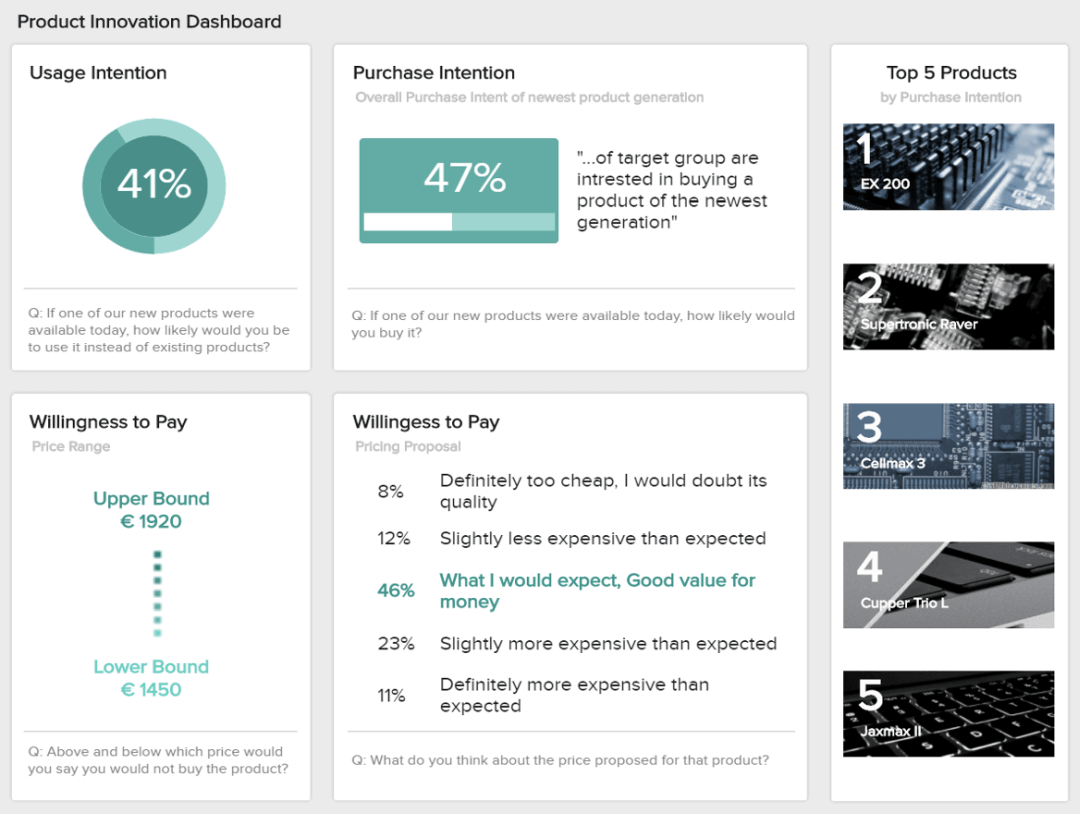
The image above is a product report that shows valuable insights regarding usage intention, purchase intention, willingness to pay, and more. In this case, the report is based on the answers from a survey that aimed to understand how the target customer would receive a new product. Getting this level of insights through this report type is very useful for businesses as it allows them to make smart investments when it comes to new products as well as set realistic pricing based on their client’s willingness to pay.
5. Industry Reports
Next in our list of the most common kinds of reports, we have industry-specific reports. Typically, these reports provide an overview of a particular industry, market, or sector with definitions, key trends, leading companies, and industry size, among others. They are particularly useful for businesses that want to enter a specific industry and want to learn how competitive it is or for companies who are looking to set performance benchmarks based on average industry values.
6. Department Reports
These reports are specific to each department or business function. They serve as a communication tool between managers and team members who must stay connected and work together for common goals. Whether it is the sales department, customer service, logistics, or finances, this specific report type helps track and optimize strategies on a deeper level. Let’s look at it with an example of a team performance report .

The image above is a department report created with an online data analysis tool , and it tracks the performance of a support team. This insightful report displays relevant metrics such as the top-performing agents, net promoter score, and first contact resolution rate, among others. Having this information in hand not only helps each team member to keep track of their individual progress but also allows managers to understand who needs more training and who is performing at their best.
7. Progress Reports
From the brunch of informational reports, progress reports provide critical information about the status of a project. These reports can be produced on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis by employees or managers to track performance and fine-tune tasks for the better development of the project. Progress reports are often used as visual materials to support meetings and discussions. A good example is a KPI scorecard .
8. Internal Reports
A type of report that encompasses many others on this list, internal reports refer to any type of report that is used internally in a business. They convey information between team members and departments to keep communication flowing regarding goals and business objectives.
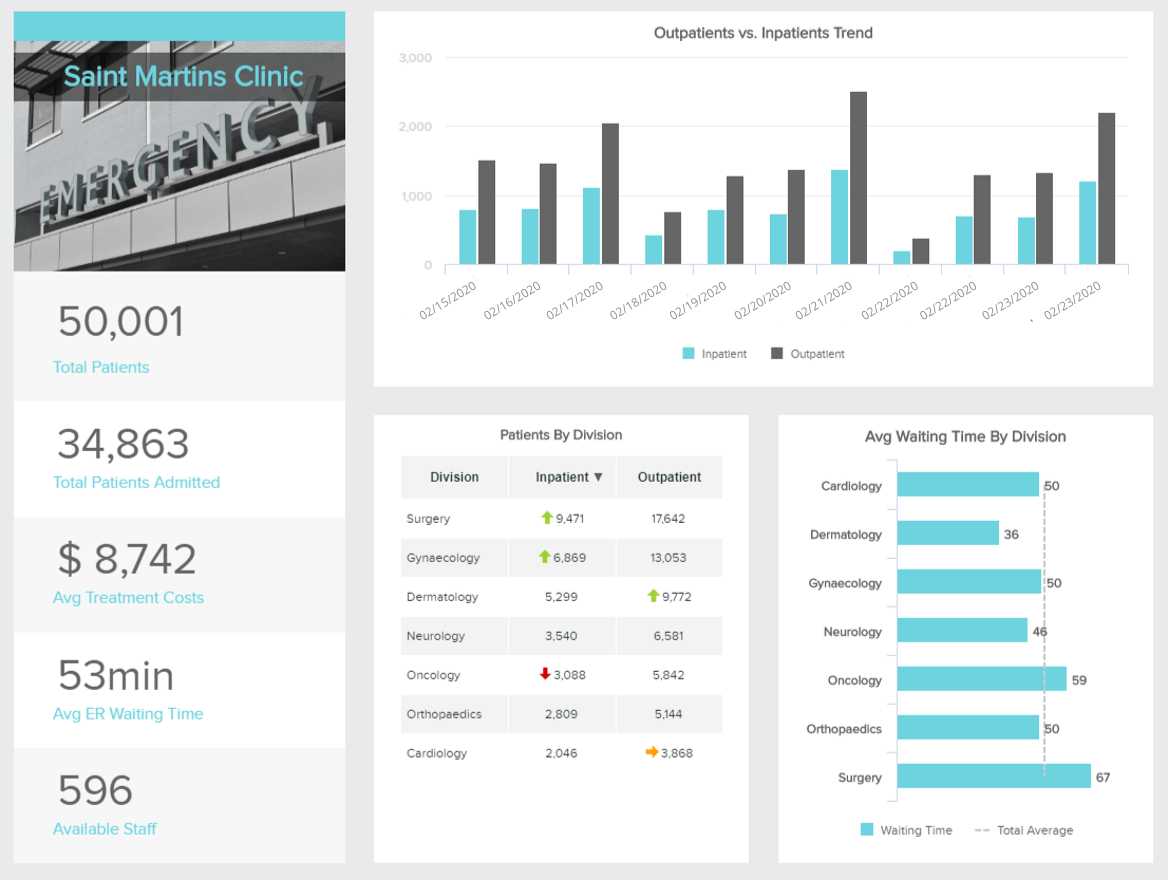
As mentioned above, internal reports are useful communication tools to keep every relevant person in the organization informed and engaged. This healthcare report aims to do just that. By providing insights into the performance of different departments and areas of a hospital, such as in and outpatients, average waiting times, treatment costs, and more, healthcare managers can allocate resources and plan the schedule accurately, as well as monitor any changes or issues in real-time.
9. External Reports
Although most of the reports types listed here are used for internal purposes, not all reporting is meant to be used behind closed doors. External reports are created to share information with external stakeholders such as clients or investors for budget or progress accountability, as well as to governmental bodies to stay compliant with the law requirements.
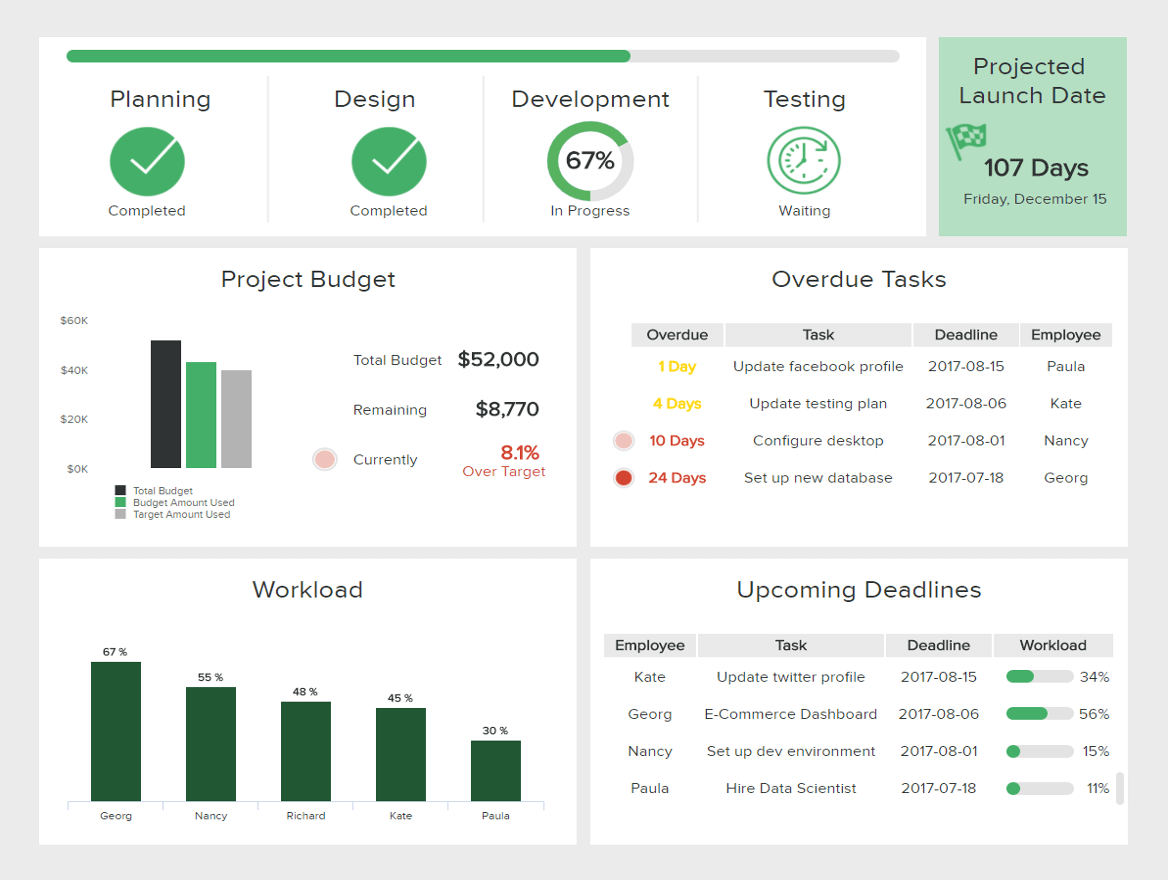
The image above is the perfect example of an external client report from an IT project. This insightful report provides a visual overview of every relevant aspect of the project's development. From deadlines, budget usage, completion stage, and task breakdown, clients can be fully informed and involved in the project.
10. Vertical & Lateral Reports
Next, in our rundown of types of reports, we have vertical and lateral reports. This reporting type refers to the direction in which a report travels. A vertical report is meant to go upward or downward the hierarchy, for example, a management report. A lateral report assists in organization and communication between groups that are at the same level of the hierarchy, such as the financial and marketing departments.
11. Research Reports
Without a doubt, one of the most vital reporting types for any modern business is centered on research. Being able to collect, collate, and drill down into insights based on key pockets of your customer base or industry will give you the tools to drive innovation while meeting your audience’s needs head-on.
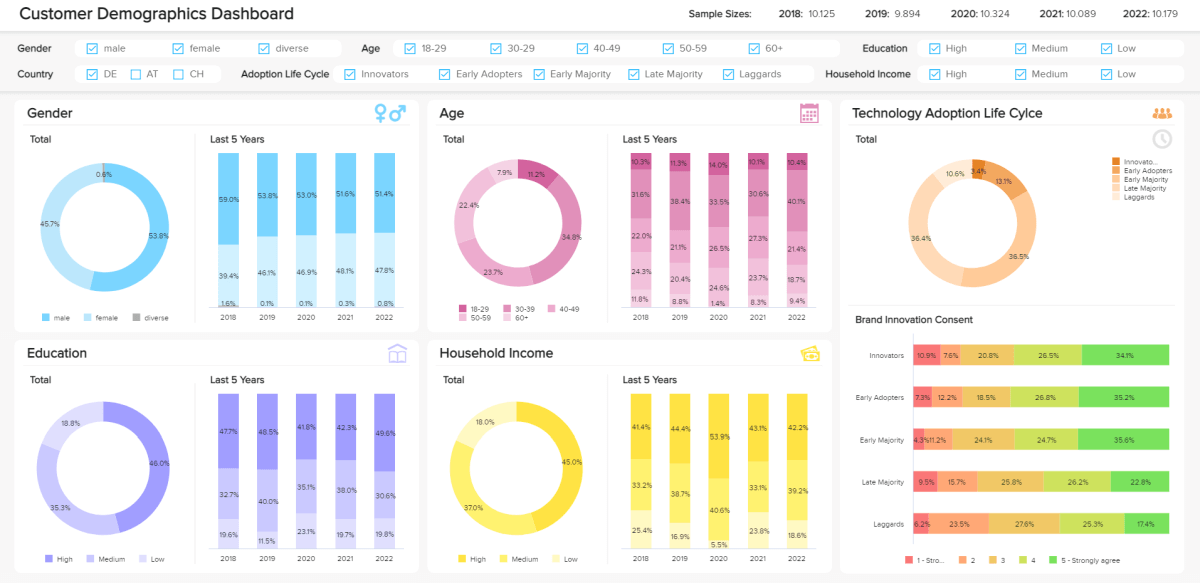
The image above is a market research analytics report example for customer demographics. It serves up a balanced blend of metrics that will empower you to boost engagement as well as retention rates. Here, you can drill down into your audience’s behaviors, interests, gender, educational levels, and tech adoption life cycles with a simple glance.
What’s particularly striking about this dashboard is the fact that you can explore key trends in brand innovation with ease, gaining a working insight into how your audience perceives your business. This invaluable type of report will help you get under the skin of your consumers, driving growth and loyalty in the process.
12. Strategic Reports
Strategy is a vital component of every business, big or small. Strategic analytics tools are perhaps the broadest and most universal of all the different types of business reports imaginable.
These particular tools exist to help you understand, meet, and exceed your most pressing organizational goals consistently by serving up top-level metrics on a variety of initiatives or functions.
By working with strategic-style tools, you will:
- Improve internal motivation and engagement
- Refine your plans and strategies for the best possible return on investment (ROI)
- Enhance internal communication and optimize the way your various departments run
- Create more room for innovation and creative thinking
13. Project Reports
Projects are key to keeping a business moving in the right direction while keeping innovation and evolution at the forefront of every plan, communication, or campaign. But without the right management tools, a potentially groundbreaking project can become a resource-sapping disaster.
A project management report serves as a summary of a particular project's status and its various components. It's a visual tool that you can share with partners, colleagues, clients, and stakeholders to showcase your project's progress at multiple stages. Let’s look at our example and dig a little deeper.
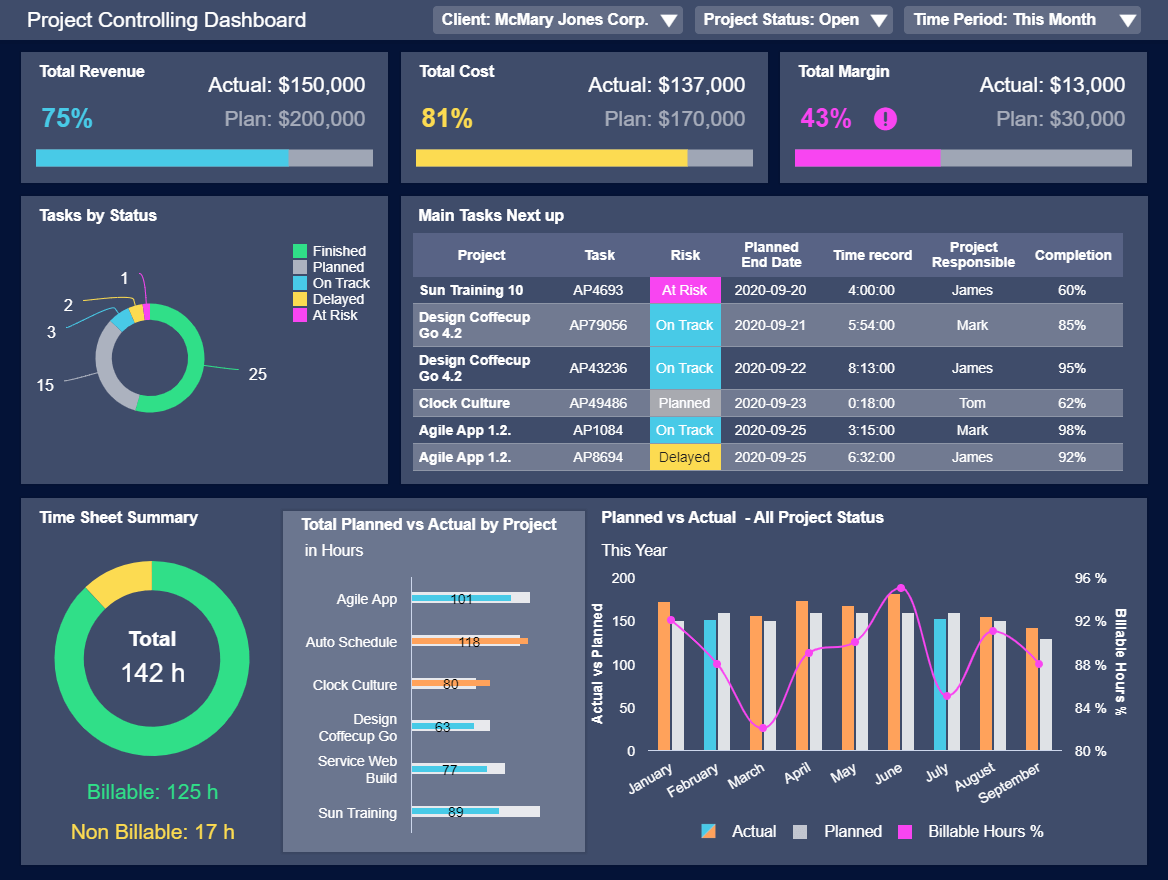
To ensure consistent success across the board, the kinds of reports you must work with are based on project management.
Our example is a project management dashboard equipped with a melting pot of metrics designed to improve the decision-making process while keeping every facet of your company’s most important initiatives under control. Here, you can spot pivotal trends based on costs, task statuses, margins, costs, and overall project revenue. With this cohesive visual information at your fingertips, not only can you ensure the smooth end-to-end running of any key project, but you can also drive increased operational efficiency as you move through every significant milestone.
14. Statutory Reports
It may not seem exciting or glamorous, but keeping your business's statutory affairs in order is vital to your ongoing commercial health and success.
When it comes to submitting such vital financial and non-financial information to official bodies, one small error can result in serious repercussions. As such, working with statutory types of report formats is a water-tight way of keeping track of your affairs and records while significantly reducing the risk of human error.
Armed with interactive insights and dynamic visuals, you will keep your records clean and compliant while gaining the ability to nip any potential errors or issues in the bud.
What Does A Report Look Like?
Now that we’ve covered the most relevant types of reports, we will answer the question: what does a report look like?
As mentioned at the beginning of this insightful guide, static reporting is a thing of the past. With the rise of modern technologies like self-service BI tools , the use of interactive reports in the shape of business dashboards has become more and more popular among companies.
Unlike static reports that take time to be generated and are difficult to understand, modern reporting tools are intuitive. Their visual nature makes them easy to understand for any type of user, and they provide businesses with a central view of their most important performance indicators for an improved decision-making process. Here, we will cover 20 useful dashboard examples from different industries, functions, and platforms to put the value of dashboard reporting into perspective.
1. Financial Report
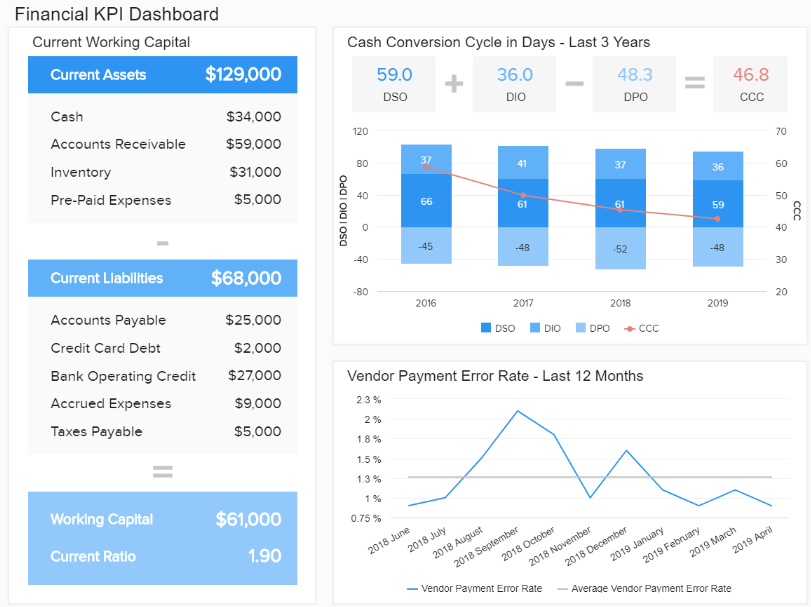
Keeping finances in check is critical for success. This financial report offers an overview of the most important financial metrics that a business needs to monitor its economic activities and answer vital questions to ensure healthy finances.
With insights about liquidity, invoicing, budgeting, and general financial stability, managers can extract long and short-term conclusions to reduce inefficiencies, make accurate forecasts about future performance, and keep the overall financial efficiency of the business flowing. For instance, getting a detailed calculation of the business's working capital can allow you to understand how liquid your company is. If it's higher than expected, it means you have the potential to invest and grow—definitely, one of the most valuable types of finance reports.
2. Marketing Report
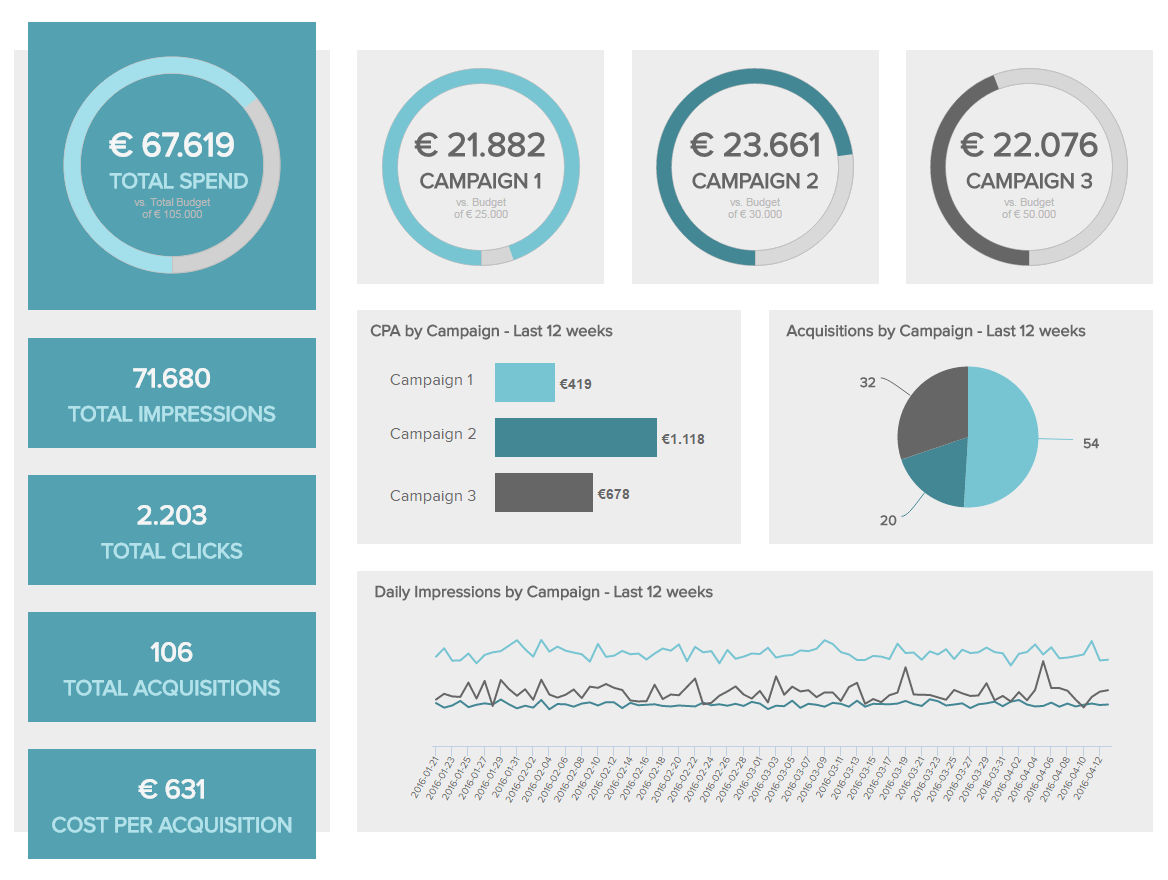
Our following example is a marketing report that ensures a healthy return on investment from your marketing efforts. This type of report offers a detailed overview of campaign performance over the last 12 weeks. Having access to this information enables you to maximize the value of your promotional actions, keeping your audience engaged by providing a targeted experience.
For instance, you can implement different campaign formats as a test and then compare which one is most successful for your business. This is possible thanks to the monitoring of important marketing metrics such as the click-through rate (CTR), cost per click (CPC), cost per acquisition (CPA), and more.
The visual nature of this report makes it easy to understand important insights at a glance. For example, the four gauge charts at the top show the total spending from all campaigns and how much of the total budget of each campaign has been used. In just seconds, you can see if you are on target to meet your marketing budgets for every single campaign.
3. Sales Report

An intuitive sales dashboard like the one above is the perfect analytical tool to monitor and optimize sales performance. Armed with powerful high-level metrics, this report type is especially interesting for managers, executives, and sales VPs as it provides relevant information to ensure strategic and operational success.
The value of this sales report lies in the fact that it offers a complete and comprehensive overview of relevant insights needed to make smart sales decisions. For instance, at the top of an analysis tool, you get important metrics such as the number of sales, revenue, profit, and costs, all compared to a set target and to the previous time period. The use of historical data is fundamental when building successful sales strategies as they provide a picture of what could happen in the future. Being able to filter the key metrics all in one screen is a key benefit of modern reporting.
4. HR Report
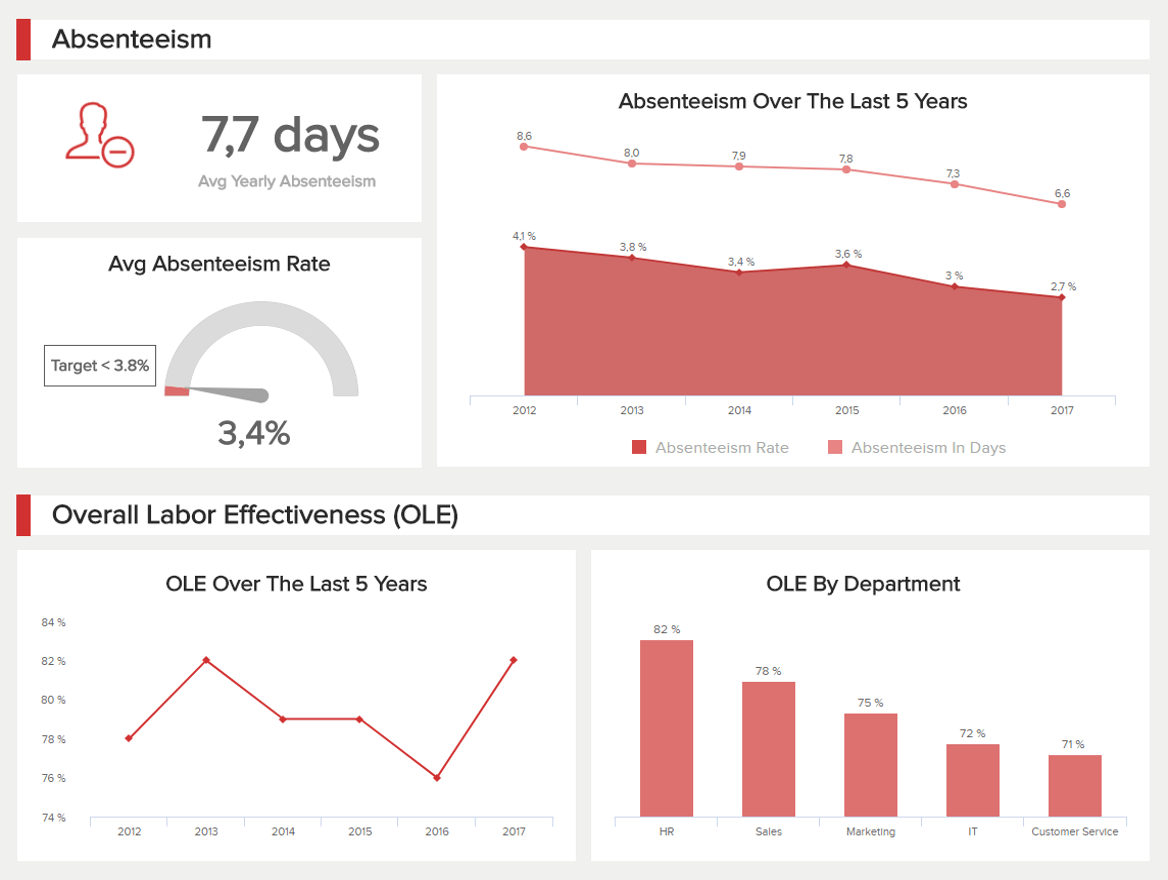
Our next example of a report is about human resources analytics . The HR department needs to track various KPIs for employee performance and effectiveness. But overall, they have to ensure that employees are happy and working in a healthy environment since an unhappy workforce can significantly damage an organization. This is all possible with the help of this intuitive dashboard.
Providing a comprehensive mix of metrics, this employee-centric report drills down into every major element needed to ensure successful workforce management. For example, the top portion of the dashboard covers absenteeism in 3 different ways: yearly average, absenteeism rate with a target of 3.8%, and absenteeism over the last five years. Tracking absenteeism rates in detail is helpful as it can tell you if your employees are skipping work days. If the rate is over the expected target, then you have to dig deeper into the reasons and find sustainable solutions.
On the other hand, the second part of the dashboard covers the overall labor effectiveness (OLE). This can be tracked based on specific criteria that HR predefined, and it helps them understand if workers are achieving their targets or if they need extra training or help.
5. Management Report
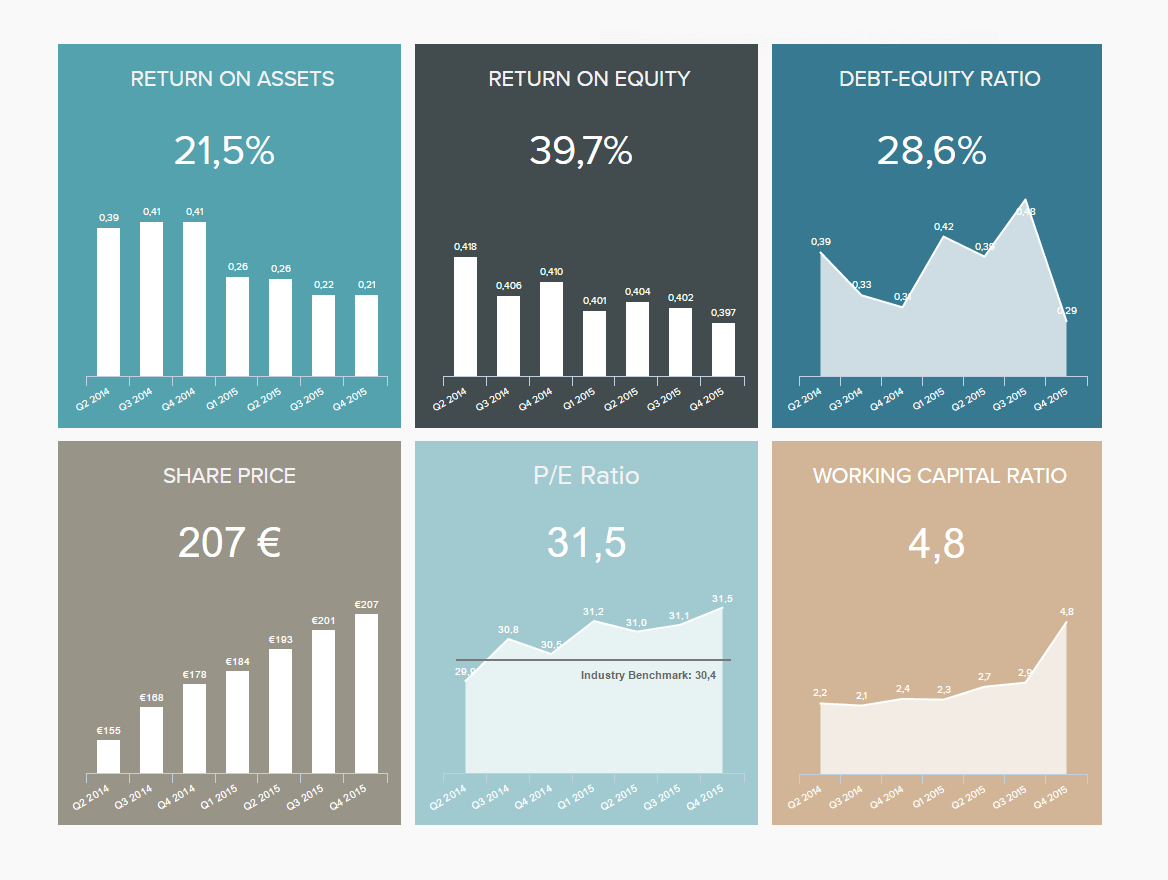
Managers must monitor big amounts of information to ensure that the business is running smoothly. One of them being investor relationships. This management dashboard focuses on high-level metrics that shareholders need to look at before investing, such as the return on assets, return on equity, debt-equity ratio, and share price, among others.
By getting an overview of these important metrics, investors can easily extract the needed information to make an informed decision regarding an investment in your business. For instance, the return on assets measures how efficiently are the company's assets being used to generate profit. With this information, investors can understand how effectively your company deploys available resources compared to others in the market. Another great indicator is the share price; the higher the increase in your share price, the more money your shareholders are making from their investment.
6. IT Report
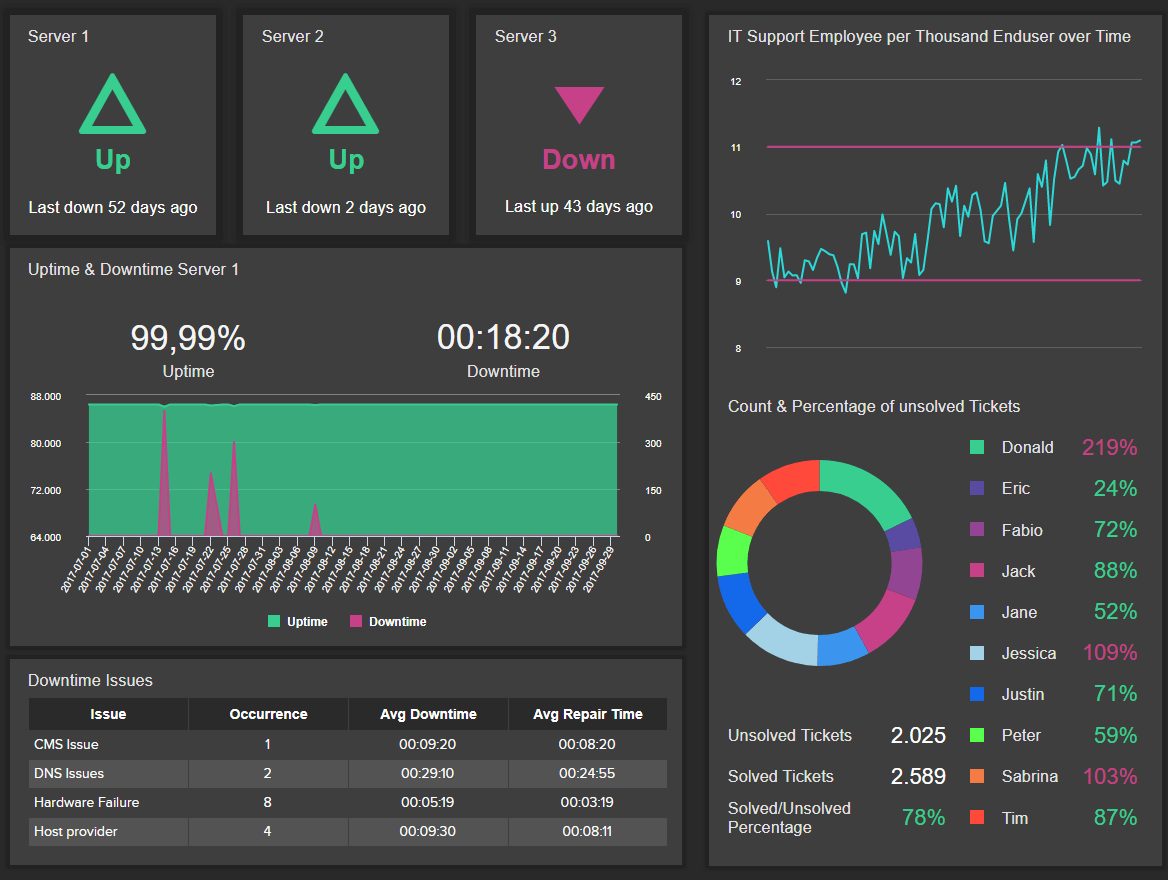
Just like all the other departments and sections covered in this list, the IT department is one that can especially benefit from these types of reports. With so many technical issues to solve, the need for a visual tool to help IT specialists stay on track with their workload becomes critical.
As seen in the image above, this IT dashboard offers detailed information about different system indicators. For starters, we get a visual overview of the status of each server, followed by a detailed graph displaying the uptime & downtime of each week. This is complemented by the most common downtown issues and some ticket management information. Getting this level of insight helps your IT staff to know what is happening and when it is happening and find proper solutions to prevent these issues from repeating themselves. Keeping constant track of these metrics will ensure robust system performance.
7. Procurement Report
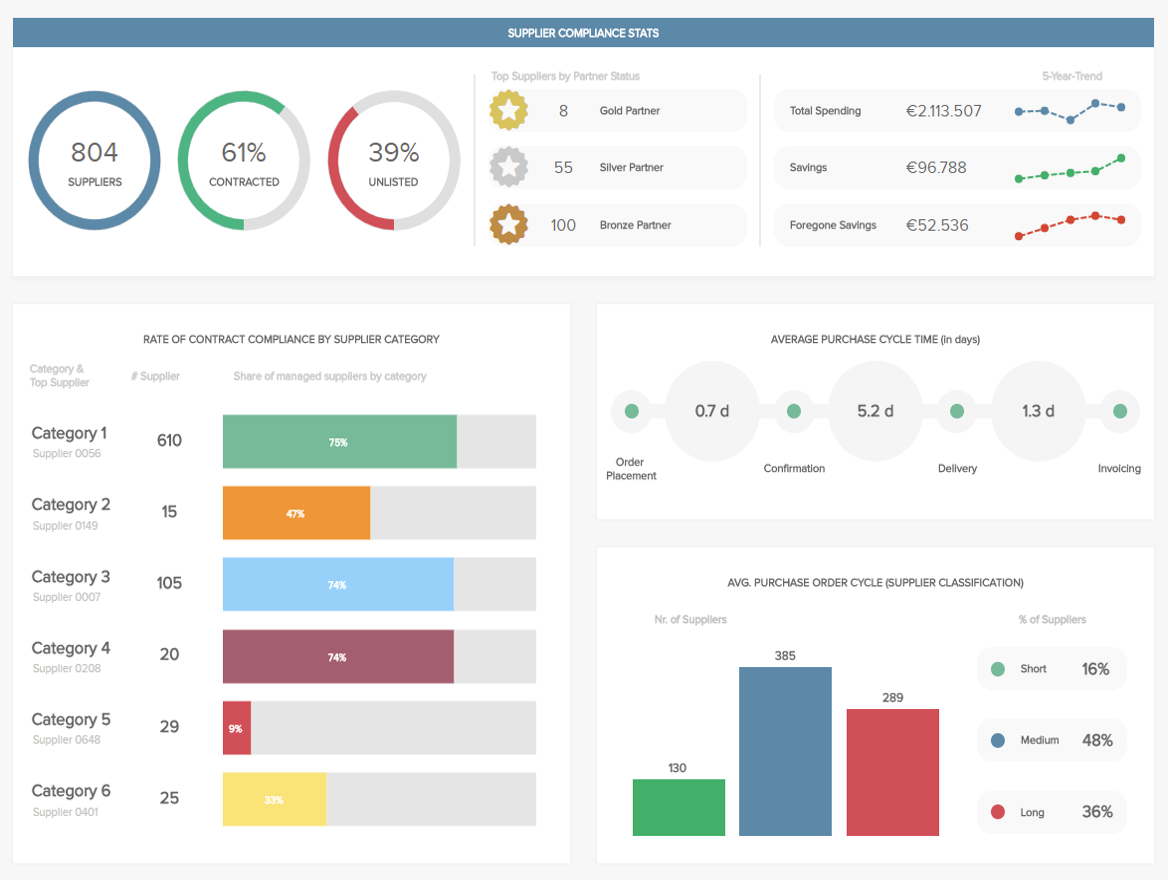
The following example of a report was built with intuitive procurement analytics software , and it gives a general view of various metrics that the procurement department needs to work with regularly.
With the possibility to filter, drill down, and interact with KPIs, this intuitive procurement dashboard offers key information to ensure a healthy supplier relationship. With metrics such as compliance rate, the number of suppliers, or the purchase order cycle time, the procurement team can classify the different suppliers, define the relationship each of them has with the company, and optimize processes to ensure it stays profitable.
8. Customer Service Report
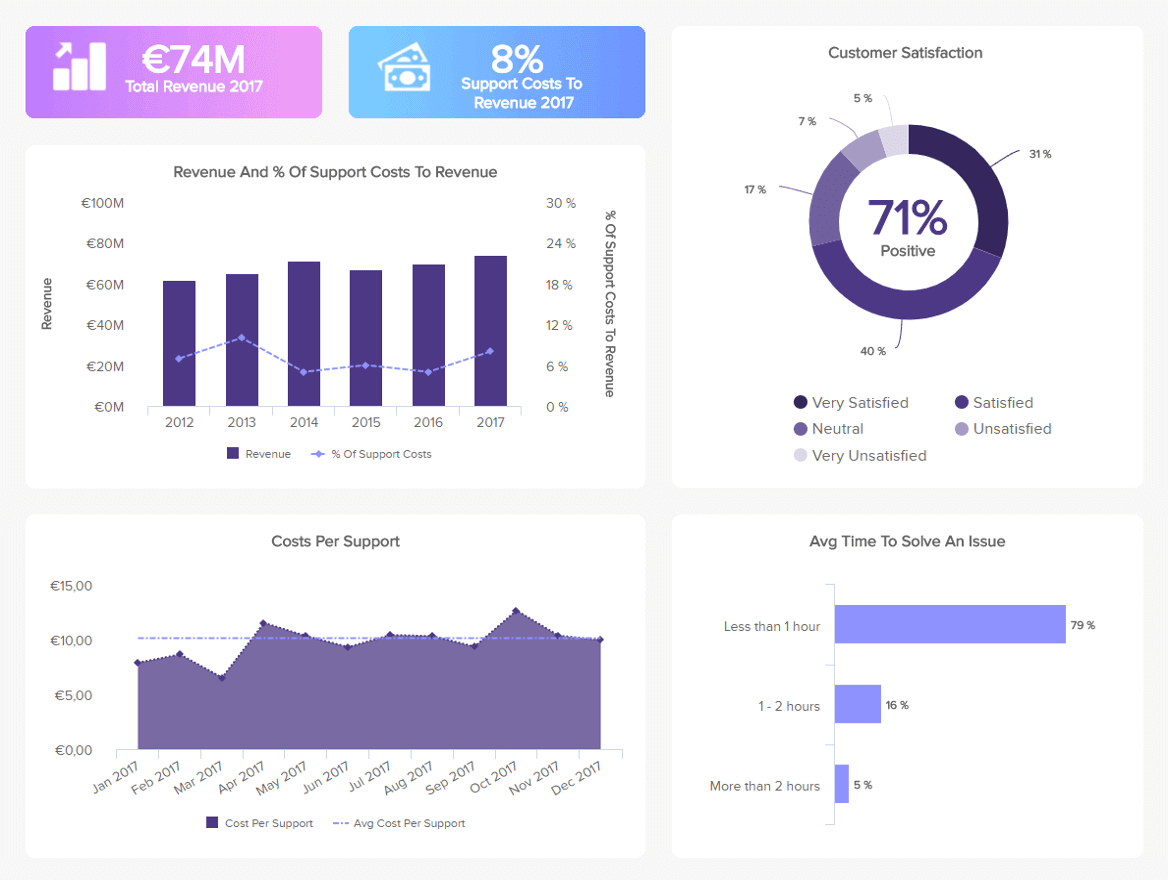
Following our list of examples of reports is one from the support area. Armed with powerful customer service KPIs , this dashboard is a useful tool to monitor performance, spot trends, identify strengths and weaknesses, and improve the overall effectiveness of the customer support department.
Covering aspects such as revenue and costs from customer support as well as customer satisfaction, this complete analysis tool is the perfect tool for managers who have to keep an eye on every little detail from a performance and operational perspective. For example, by monitoring your customer service costs and comparing them to the revenue, you can understand if you are investing the right amount into your support processes. This can be directly related to your agent’s average time to solve issues; the longer it takes to solve a support ticket, the more money it will cost and the less revenue it will bring. If you see that your agents are taking too long to solve an issue, you can think of some training instances to help them reduce this number.
9. Market Research Report
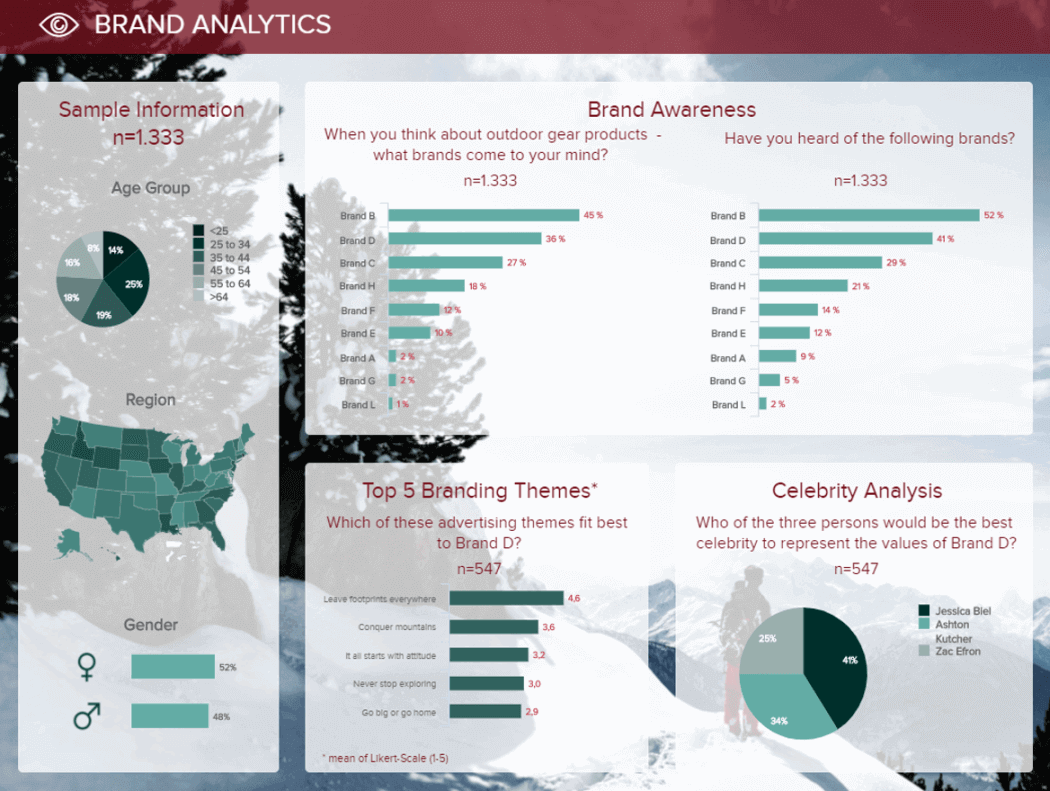
This list of report types examples would not be complete without a market research report . Market research agencies deal with a large amount of information coming from surveys and other research sources. Taking all this into account, the need for reports that can be filtered for deeper interaction becomes more necessary for this industry than any other.
The image above is a brand analytics dashboard that displays the survey results about how the public perceives a brand. This savvy tool contains different charts that make it easy to understand the information visually. For instance, the map chart with the different colors lets you quickly understand in which regions each age range is located. The charts can be filtered further to see the detailed answers from each group for a deeper analysis.
10. Social Media Report
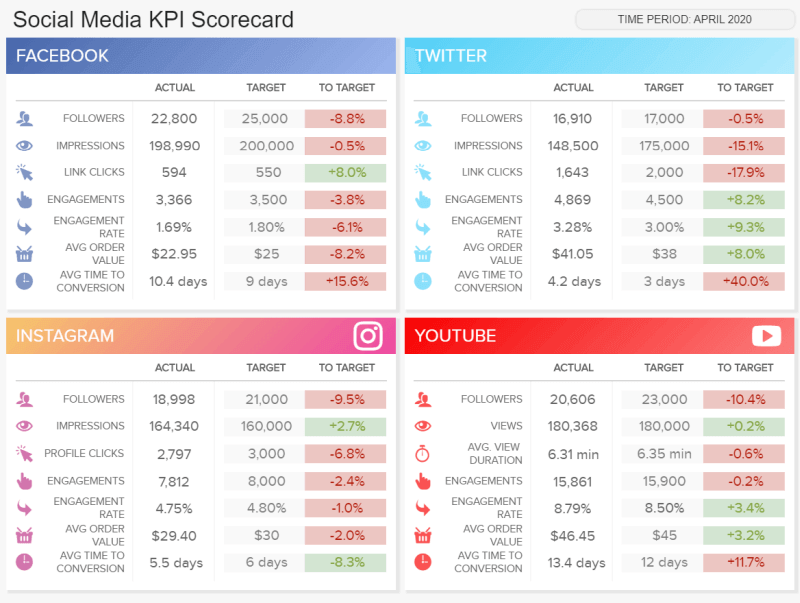
Last but not least, we have a social media report . This scorecard format dashboard monitors the performance of 4 main social media channels: Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and YouTube, and it serves as a perfect visual overview to track the performance of different social media efforts and achievements.
Tracking relevant metrics such as followers, impressions, clicks, engagement rates, and conversions, this report type serves as a perfect progress report to show to managers or clients who need to see the status of their social channels. Each metric is shown in its actual value and compared to a set target. The colors green and red from the fourth column let you quickly understand if a metric is over or under its expected target.
11. Logistics Report
Logistics are the cornerstone of an operationally fluent and progressive business. If you deal with large quantities of goods and tangible items, in particular, maintaining a solid logistical strategy is vital to ensuring you maintain your brand reputation while keeping things flowing in the right direction.
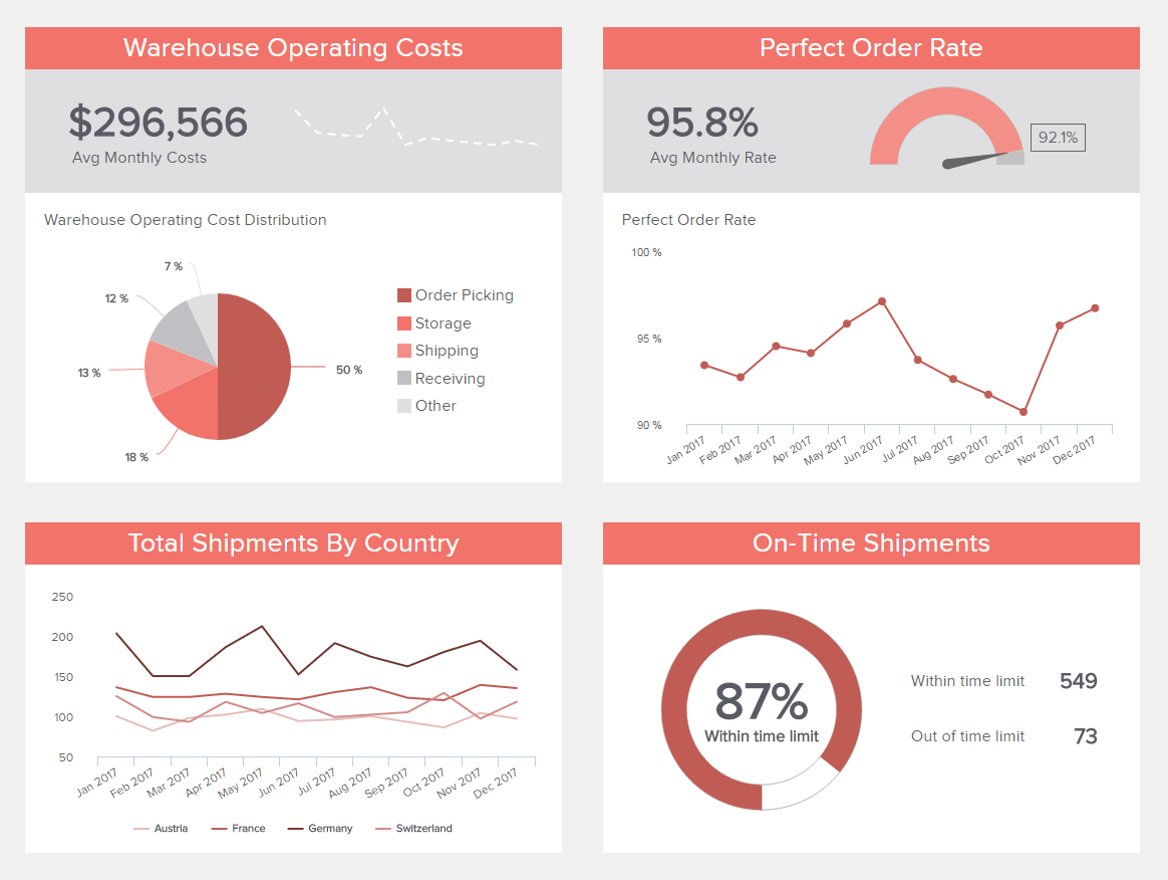
A prime example of the types of data reporting tool designed to improve logistical management, our warehouse KPI dashboard is equipped with metrics required to maintain strategic movement while eliminating any unnecessary costs or redundant processes. Here, you can dig into your shipping success rates across regions while accessing warehouse costs and perfect order rates in real-time. If you spot any potential inefficiencies, you can track them here and take the correct course of action to refine your strategy. This is an essential tool for any business with a busy or scaling warehouse.
12. Manufacturing Report
Next, in our essential types of business reports examples, we’re looking at tools made to improve your business’s various manufacturing processes.
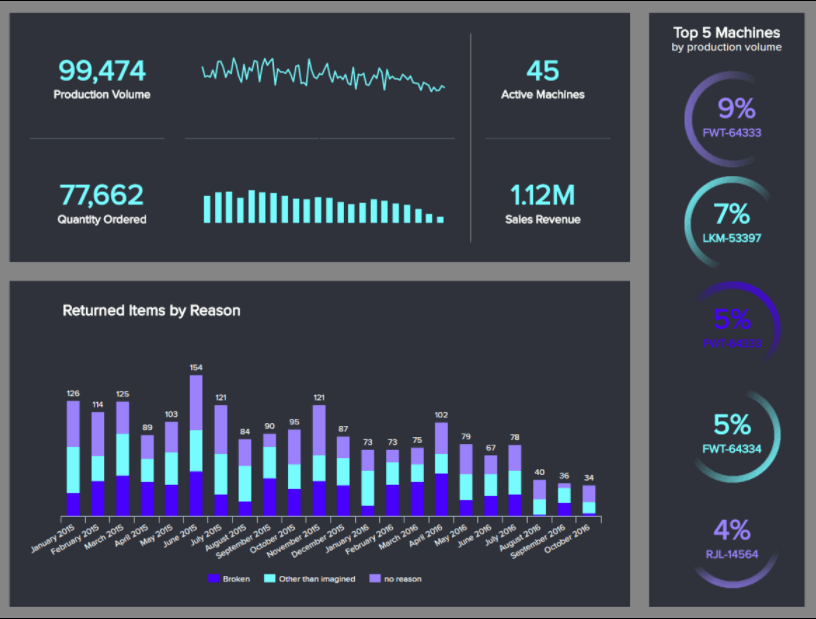
Our clean and concise production tool is a sight to behold and serves up key manufacturing KPIs that improve the decision-making process regarding costs, volume, and machinery.
Here, you can hone in on historical patterns and trends while connecting with priceless real-time insights that will not only help you make the right calls concerning your manufacturing process at the moment but will also help you formulate predictive strategies that will ultimately save money, boost productivity, and result in top-quality products across the board.
13. Retail Report
As a retailer with so many channels to consider and so many important choices to make, working with the right metrics and visuals is absolutely essential. Fortunately, we live in an age where there are different types of reporting designed for this very reason.
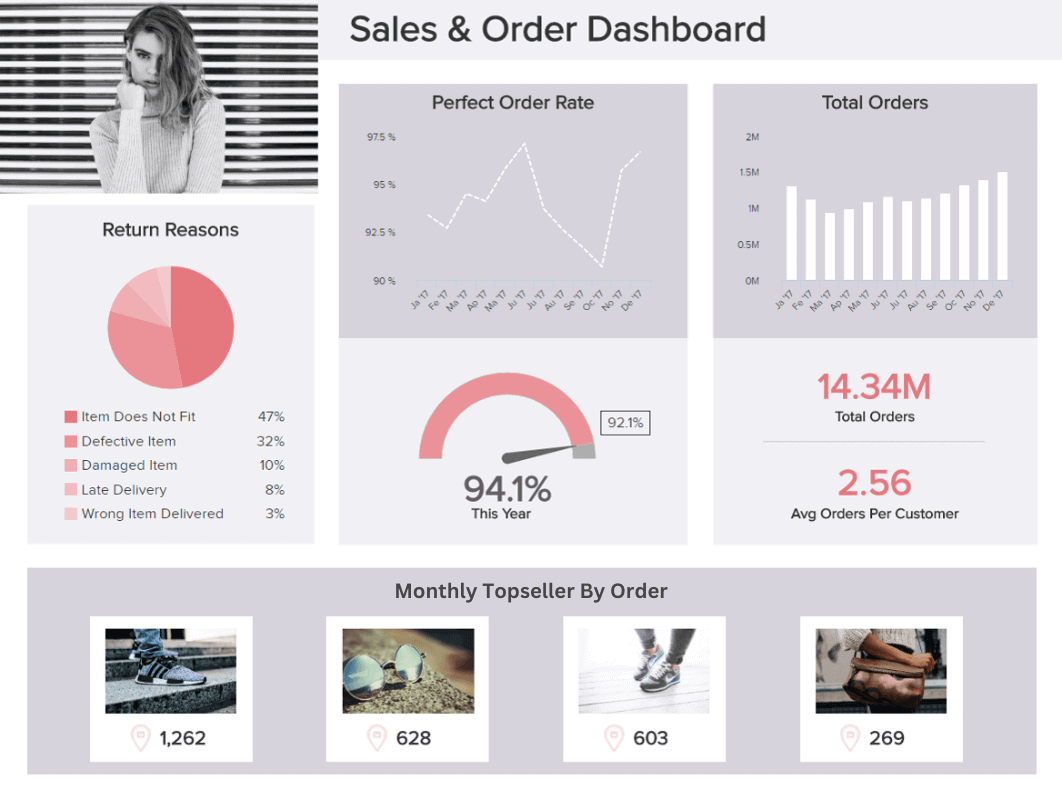
Our sales and order example, generated with retail analytics software , is a dream come true for retailers as it offers the visual insights needed to understand your product range in greater detail while keeping a firm grip on your order volumes, perfect order rates, and reasons for returns.
Gaining access to these invaluable insights in one visually presentable space will allow you to track increases or decreases in orders over a set timeframe (and understand whether you’re doing the right things to drive engagement) while plowing your promotional resources into the products that are likely to offer the best returns.
Plus, by gaining an accurate overview of why people are returning your products, you can omit problem items or processes from your retail strategy, improving your brand reputation as well as revenue in the process.
14. Digital Media Report
The content and communications you publish are critical to your ongoing success, regardless of your sector, niche, or specialty. Without putting out communications that speak directly to the right segments of your audience at the right times in their journey, your brand will swiftly fade into the background.
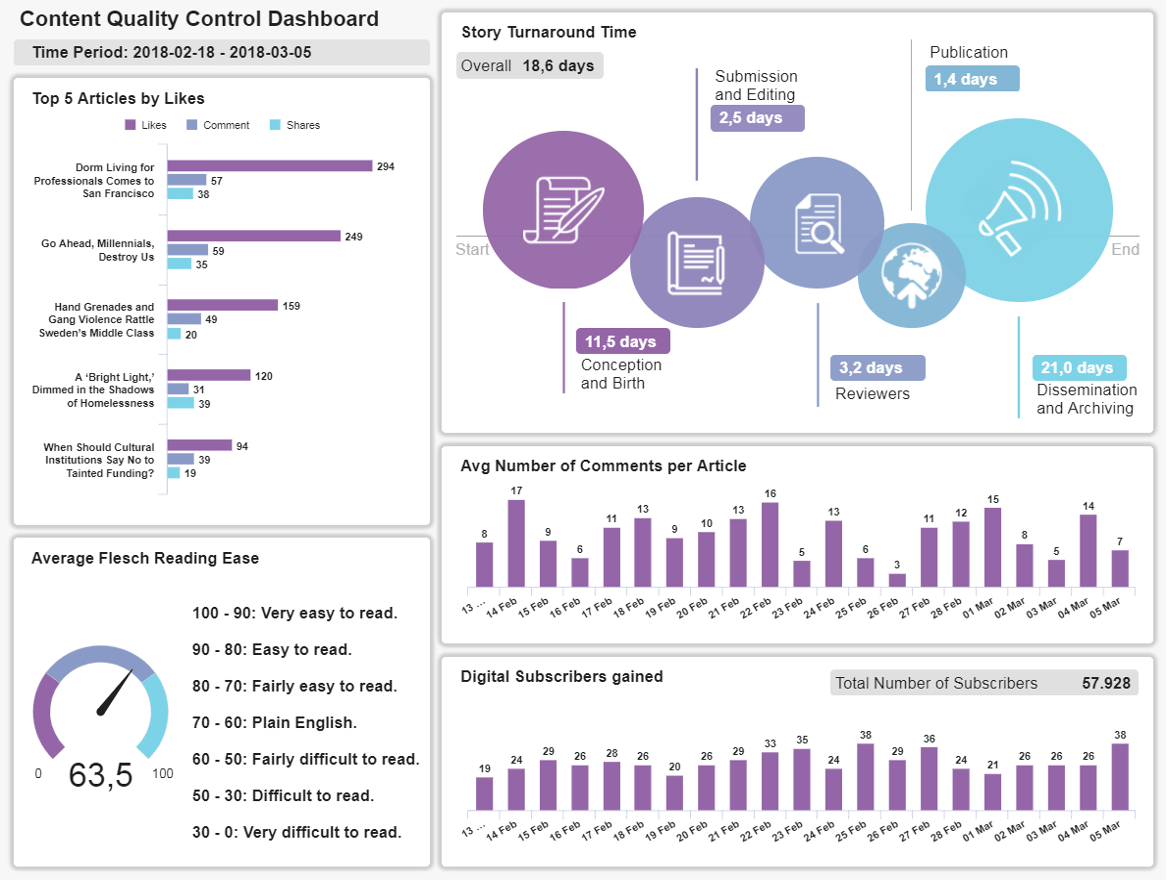
To ensure your brand remains inspiring, engaging, and thought-leading across channels, working with media types of a business report is essential. You must ensure your communications cut through the noise and scream ‘quality’ from start to finish—no ifs, no buts, no exceptions.
Our content quality control tool is designed with a logical hierarchy that will tell you if your content sparks readership, if the language you’re using is inclusive and conversational, and how much engagement-specific communications earn. You can also check your most engaged articles with a quick glance to understand what your users value most. Armed with this information, you can keep creating content that your audience loves and ultimately drives true value to the business.
15. Energy Report
In the age of sustainability and in the face of international fuel hikes, managing the energy your business uses effectively is paramount. Here, there is little room for excess or error, and as such, working with the right metrics is the only way to ensure successful energy regulation.
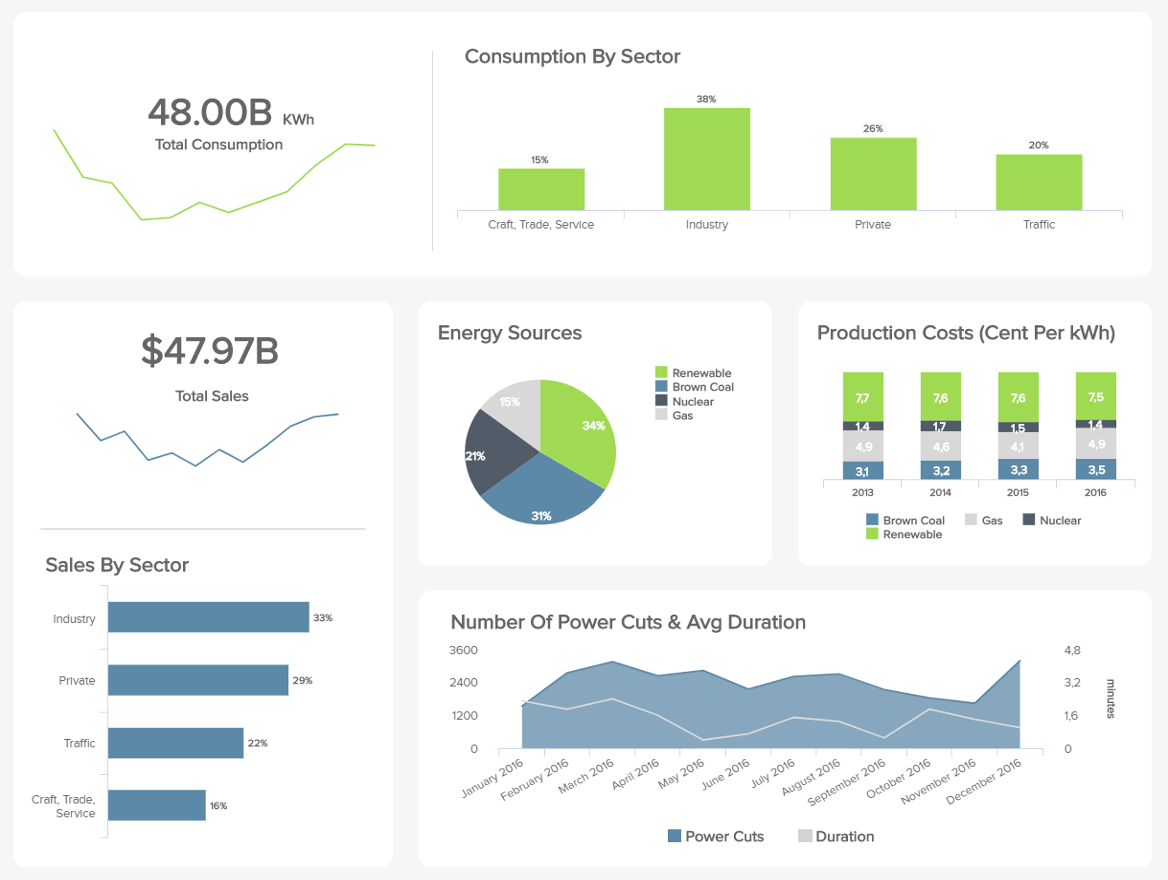
If your company has a big HQ or multiple sites that require power, our energy management analytics tool will help you take the stress out of managing your resources. One of the most striking features of this dashboard is the fact that it empowers you to compare your company’s energy usage against those from other sectors and set an accurate benchmark.
Here, you can also get a digestible breakdown of your various production costs regarding energy consumption and the main sources you use to keep your organization running. Regularly consulting these metrics will not only help you save colossal chunks of your budget, but it will also give you the intelligence to become more sustainable as an organization. This, in turn, is good for the planet and your brand reputation—a real win-win-win.
16. FMCG Report
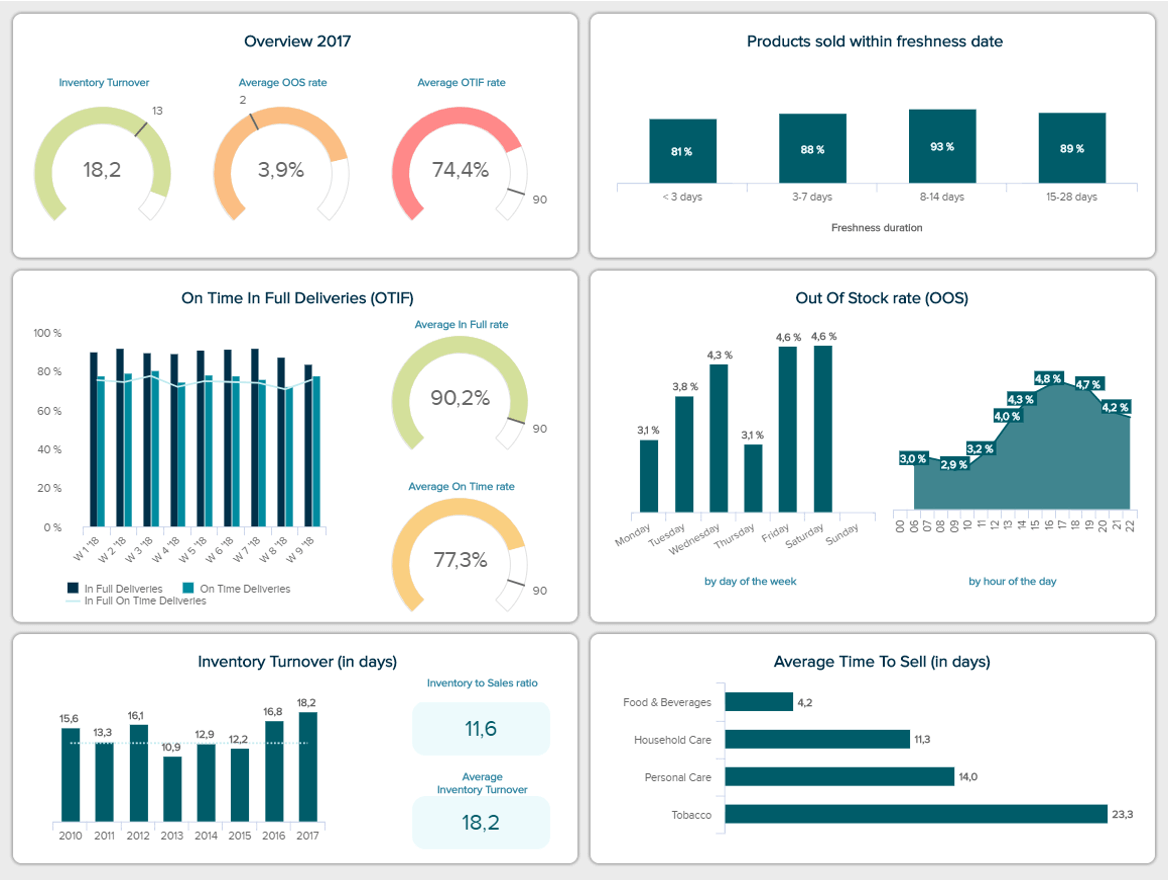
The fast-moving consuming goods (FMCG) industry can highly benefit from a powerful report containing real-time insights. This is because the products handled in this sector which are often food and beverages, don’t last very long. Therefore, having a live overview of all the latest developments can help decision-makers optimize the supply chain to ensure everything runs smoothly and no major issues happen.
Our report format example above aims to do just that by providing an overview of critical performance indicators, such as the percentage of products sold within freshness date, the out-of-stock rate, on-time in full deliveries, inventory turnover, and more. What makes this template so valuable is the fact that it provides a range of periods to get a more recent view of events but also a longer yearly view to extract deeper insights.
The FMCG dashboard also offers an overview of the main KPIs to help users understand if they are on the right track to meet their goals. There, we can observe that the OTIF is far from its target of 90%. Therefore, it should be looked at in more detail to optimize it and prevent it from affecting the entire supply chain.
17. Google Analytics Report

Regardless of the industry you are in, if you have a website then you probably require a Google Analytics report. This powerful tool helps you understand how your audience interacts with your website while helping you reach more people through the Google search engine. The issue is that the reports the tool provides are more or less basic and don’t give you the dynamic and agile view you need to stay on top of your data and competitors.
For that reason, at datapine, we generated a range of Google Analytics dashboards that take your experience one step further by allowing you to explore your most important KPIs in real-time. That way, you’ll be able to spot any potential issues or opportunities to improve as soon as they occur, allowing you to act on them on the spot.
Among some of the most valuable metrics you can find in this sample are the sessions and their daily, weekly, and monthly development, the average session duration, the bounce rate by channel and by top 5 countries, among others.
18. YouTube Report
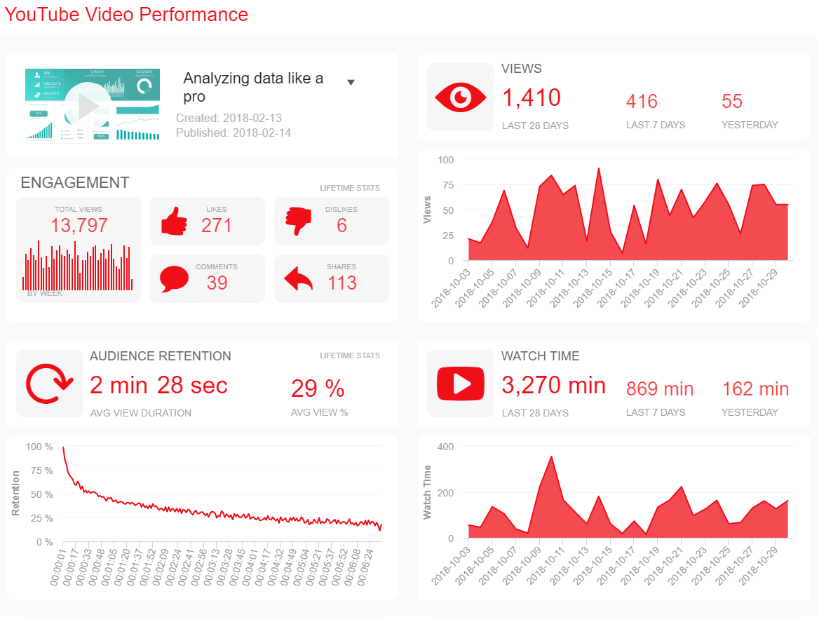
So far, we’ve covered examples for various industries and sectors. Now, we will dive a bit deeper into some templates related to popular platforms businesses use in their daily operations. With the rise in video-related content, we could not leave YouTube outside of the list. This popular platform hides some valuable insights that can help you improve your content for your current audience but also reach new audiences that can be interested in your products or services.
This highly visual and dynamic sample offers an interactive view of relevant KPIs to help you understand every aspect of your video performance. The template can be filtered for different videos to help you understand how each type of content performs. For instance, you get an overview of engagement metrics, such as likes, dislikes, comments, and shares, that way, you can understand how your audience interacts with your content.
Additionally, you also get more detailed charts about the number of views, the average watch time per day, and audience retention. These indicators can help you understand if something needs to be changed. For instance, audience retention goes down a lot after one minute and a half. Therefore you either need to make sure you are making the rest of the video a bit more interesting or offering your product or service or any other relevant information in the first minute.
19. LinkedIn Report
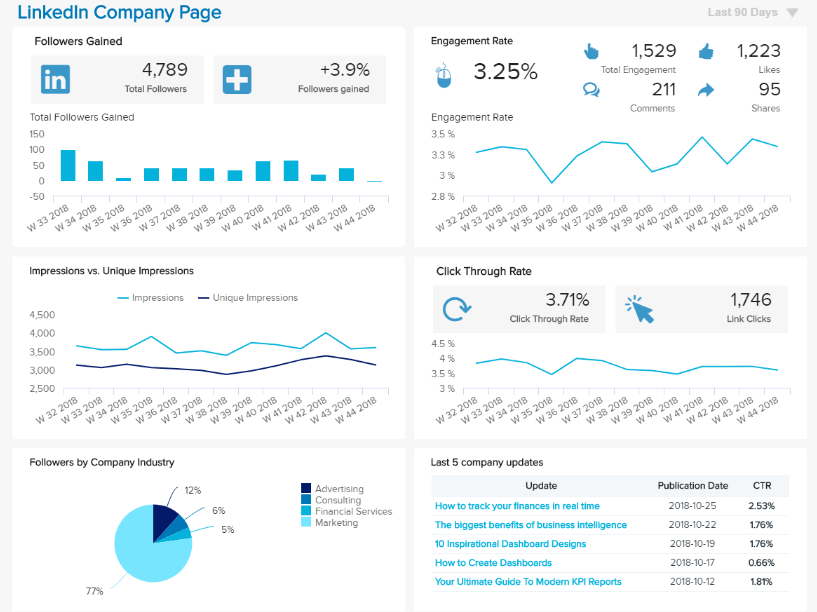
Another very important platform that companies use, no matter their size or industry, is LinkedIn. This platform is the place where companies develop and showcase their corporate image, network with other companies, and tell their clients and audience about the different initiatives they are developing to grow and be better. Some organizations also use LinkedIn to showcase their charity or sustainability initiatives.
The truth is LinkedIn has become an increasingly relevant platform, and just like we discussed with YouTube, organizations need to analyze data to ensure their strategies are on the right path to success.
The template above offers a 360-degree view of a company page's performance. With metrics such as the followers gained, engagement rate, impressions vs unique impressions, CTR, and more. Decision-makers can dive deeper into the performance of their content and understand what their audience enjoys the most. For instance, by looking at the CTR of the last 5 company updates, you can start to get a sense of what topics and content format your audience on the platforms interact with the most. That way, you’ll avoid wasting time and resources producing content without interaction.
20. Healthcare Report

Moving on from platform-related examples, we have one last monthly report template from a very relevant sector, the healthcare industry. For decades now, hospitals and healthcare professionals have benefited from data to develop new treatments and analyze unknown diseases. But, data can also help to ensure daily patient care is of top quality.
Our sample above is a healthcare dashboard report that tracks patient satisfaction stats for a clinic named Saint Martins Clinic. The template provides insights into various aspects of patient care that can affect their satisfaction levels to help spot any weak areas.
Just by looking at the report in a bit more detail, we can already see that the average waiting time for arrival to a bed and time to see a doctor are on the higher side. This is something that needs to be looked into immediately, as waiting times are the most important success factors for patients. Additionally, we can see those lab test turnarounds are also above target. This is another aspect that should be optimized to prevent satisfaction levels from going down.
If you feel inspired by this list and want to see some of the best uses for business reports, then we recommend you take a look at our dashboard examples library, where you will find over 80+ templates from different industries, functions, and platforms for extra inspiration!
What You Should Look For In A Reporting Tool
As you learned from our extensive list of examples, different types of reports are widely used across industries and sectors. Now, you might wonder, how do I get my hands on one of these reports? The answer is a professional online reporting tool. With the right software in hand, you can generate stunning reports to extract the maximum potential out of your data and boost business growth in the process.
But, with so many options in the market, how do make sure you choose the best tool for your needs? Below we cover some of the most relevant features and capabilities you should look for to make the most out of the process.
- Pre-made reporting templates
To ensure successful operations, a business will most likely need to use many types of reports for its internal and external strategies. Manually generating these reports can become a time-consuming task that burdens the business. That is why professional reporting software should offer pre-made reporting templates. At datapine, we offer an extensive template library that allows users to generate reports in a matter of seconds—allowing them to use their time on actually analyzing the information and extracting powerful insights from it.
- Multiple visualization options
If you look for report templates on Google you might run into multiple posts about written ones. This is not a surprise, as written reports have been the norm for decades. That being said, a modern approach to reporting has developed in the past years where visuals have taken over text. The value of visuals lies in the fact that they make the information easier to understand, especially for users who have no technical knowledge. But most importantly, they make the information easier to explore by telling a compelling story. For that reason, the tool you choose to invest in should provide you with multiple visualization options to have the flexibility to tell your data story in the most successful way possible.
- Customization
While pre-made templates are fundamental to generating agile reports, being able to customize them to meet your needs is also of utmost importance. At datapine, we offer our users the possibility to customize their reports to fit their most important KPIs, as well as their logo, business colors, and font. This is an especially valuable feature for external reports that must be shown to clients or other relevant stakeholders, giving your reports a more professional look. Customization can also help from an internal perspective to provide employees who are uncomfortable with data with a familiar environment to work in.
- Real-time insights
In the fast-paced world we live in today, having static reports is not enough. Businesses need to have real-time access to the latest developments in their data to spot any issues or opportunities as soon as they occur and act on them to ensure their resources are spent smartly and their strategies are running as expected. Doing so will allow for agile and efficient decision-making, giving the company a huge competitive advantage.
- Sharing capabilities
Communication and collaboration are the basis of a successful reporting process. Today, team members and departments need to be connected to ensure everyone is on the right path to achieve general company goals. That is why the tool you invest in should offer flexible sharing capabilities to ensure every user can access the reports. For instance, at datapine, we offer our users the possibility to share reports through automated emails or password-protected URLs with viewing or editing rights depending on what data the specific user can see and manipulate. A great way to keep everyone connected and boost collaboration.
Types Of Reporting For Every Business & Purpose
As we’ve seen throughout our journey, different report formats are used by businesses for diverse purposes in their everyday activities. Whether you’re talking about types of reports in research, types of reports in management, or anything in between, these dynamic tools will get you where you need to be (and beyond).
In this post, we covered the top 14 most common ones and explored key examples of how different report types are changing the way businesses are leveraging their most critical insights for internal efficiency and, ultimately, external success.
With modern tools and solutions, reporting doesn’t have to be a tedious task. Anyone in your organization can rely on data for their decision-making process without needing technical skills. Rather, you want to keep your team connected or show progress to investors or clients. There is a report type for the job. To keep your mind fresh, here are the top 14 types of data reports covered in this post:
- Informational reports
- Analytical reports
- Operational reports
- Product reports
- Industry reports
- Department reports
- Progress reports
- Internal reports
- External reports
- Vertical and lateral reports
- Strategic reports
- Research reports
- Project reports
- Statutory reports
Now, over to you. Are you ready? If you want to start building your own types of reports and get ahead of the pack today, then you should try our BI reporting software for 14 days for free !
Balance Sheet - Report Form:
Definition and explanation:.
Balance sheet shows the financial position or condition of an organization at a particular point in time. In fact, it is sometimes referred to as a position statement or statement of condition.
It shows the economic resources (properties, possessions) of an organization, referred to as assets, and the claims that creditors and owners have against the assets. Economic obligations of an organization (amount owed to creditors) are called liabilities, and owners, claims are referred to as owner's equity, or capital.
A common arrangement of the balance sheet is to list assets on the left side and liabilities and owner's equity on the right. This balance arrangement, with assets and equities (liabilities) side by side, is sometimes referred to as the account form of balance sheet, because it resembles the traditional T-form of an account.
An alternative arrangement, sometimes called the report form of balance sheet , centers the asset section under the heading, with the equity claims shown below the asset. The report form frequently fits on a standard sheet of paper better than the account form.
Assets are normally reported on balance sheet in the order of their relative nearness to cash. For example, the account receivable (sundry debtors) account usually follows the cash account because the accounts receivable are likely to turn into cash very soon. On the other hand, assets like land and buildings are normally listed towards the end, because they are expected to be around a long time. So, the balance sheet that divides its accounts into subgroups within the major sections of the statement is called a classified balance sheet . Generally assets are divided into two groups, current and non-current assets are cash and other assets that are relatively close to being cash. In practice, an asset is classified as current if it can meet any of the following conditions within the year:
If it can reasonably be expected to turn into cash.
If it can easily be converted to cash by the managers of the entity.
If it can take the place of cash (as with prepaid expenses).
When assets are divided into current and non-current groups, It is common practice to classify liabilities in a similar way. Current liabilities are liabilities that cash reasonably be expected to be paid within one year. Naturally, the liabilities that are not expected to be paid within one year are transferred to as non-current liabilities:
Format/Example of Report Form Balance Sheet:
The format of a balance sheet in report form is given below:
Name of the Business Balance Sheet December 31, 2005
Relevant Articles:
👀 Turn any prompt into captivating visuals in seconds with our AI-powered design generator ✨ Try Piktochart AI!
- Piktochart Visual
- Video Editor
- AI Design Generator
- Infographic Maker
- Banner Maker
- Brochure Maker
- Diagram Maker
- Flowchart Maker
- Flyer Maker
- Graph Maker
- Invitation Maker
- Pitch Deck Creator
- Poster Maker
- Presentation Maker
- Report Maker
- Resume Maker
- Social Media Graphic Maker
- Timeline Maker
- Venn Diagram Maker
- Screen Recorder
- Social Media Video Maker
- Video Cropper
- Video to Text Converter
- Video Views Calculator
- AI Brochure Maker
- AI Document Generator
- AI Flyer Generator
- AI Image Generator
- AI Infographic
- AI Instagram Post Generator
- AI Newsletter Generator
- AI Report Generator
- AI Timeline Generator
- For Communications
- For Education
- For eLearning
- For Financial Services
- For Healthcare
- For Human Resources
- For Marketing
- For Nonprofits
- Brochure Templates
- Flyer Templates
- Infographic Templates
- Newsletter Templates
- Presentation Templates
- Resume Templates
- Business Infographics
- Business Proposals
- Education Templates
- Health Posters
- HR Templates
- Sales Presentations
- Community Template
- Explore all free templates on Piktochart
- Course: What is Visual Storytelling?
- The Business Storyteller Podcast
- User Stories
- Video Tutorials
- Need help? Check out our Help Center
- Earn money as a Piktochart Affiliate Partner
- Compare prices and features across Free, Pro, and Enterprise plans.
- For professionals and small teams looking for better brand management.
- For organizations seeking enterprise-grade onboarding, support, and SSO.
- Discounted plan for students, teachers, and education staff.
- Great causes deserve great pricing. Registered nonprofits pay less.
How to Write a Report (2023 Guide & Free Templates)

You have a report due in a few days, but you’re still procrastinating like a pro.
Sounds familiar?
If you’ve been staring at a blank page, wondering how to write a report the best way possible, you’re not alone. For many, writing a report, especially for the first time, can feel like rolling a giant boulder uphill.
The good news is that from a first draft to creating reports that people love to read is a skill you can develop and polish over time.
Whether you’re a student, a professional, or someone who wants to up their report-writing game, keep reading for a 2023 guide and step-by-step instructions on how to write a report. Plus, learn about the basic report format.
You’ll also get access to report templates that you can edit and customize immediately and learn about a tool to make reports online (no need to download software!). You can also jump right into customizing templates by creating a free account .
What is report writing?
Report writing is a way of communicating information, data, insight, or analysis. It’s an essential skill that will come in handy in various settings, from academic research or diving into historical events to business meetings.
But creating a report can be a bit intimidating at first.
In its simplest form, report writing starts with researching and gathering all the information, analyzing your findings, and presenting it in a way that’s easy for your audience to understand.
Sounds easy enough, right?
Well, there’s a bit more to it than that. We’ll guide you through every step of the process to write an entire report from a rough draft and data in the next section.
But first, let’s get to know the different types of reports.
Types of reports
Reports come in all shapes and sizes, and the type of report you write will depend on your specific goals and audience. Each type of report has its unique purpose, format, and style.

The most common types of reports are:
- Academic report – These include school reports, book reports, thesis reports, or analytical reports between two opposing ideas.
- Business report – Business reports range from annual reports to SWOT analyses . The goal of business reports is to communicate ideas, information, or insights in a business setting.
- Research report – Research reports are often more scientific or methodological in nature. They can take the form of case studies or research papers.
Learn more : 20 Types of Reports and When to Use Them (Plus Templates)
How to write a report without feeling overwhelmed
Breaking down the report writing process into three stages can make it much more manageable for you, especially if it’s your first time to create one.
These three stages are:
- Pre-writing stage
- Writing stage
- Post-writing stage
Let’s take a look at the steps for each stage and how to write a good report in 2023 that you can be proud of.
Stage 1: Pre-writing
The pre-writing stage is all about preparation. Take some time to gather your thoughts and organize your main idea. Write a summary first.
Here are important steps to help you deal with the overwhelm of creating an insightful report.
Understand the purpose of your report
Knowing your purpose will help you focus and stay on track throughout the process. Dig into the why of your report through these questions:
- Who is your intended reader? Are you familiar with your audience’s language and how they think?
- What are you trying to achieve with your report? Are you trying to inform, persuade, or recommend a course of action to the reader?
Research your topic
It’s time to gather as much information as you can about your topic. This might involve reading books, articles, and other reports. You might also need to conduct interviews with subject matter experts.
Pro tip on how to write a report : Pick reputable sources like research papers, recently-published books, and case studies by trustworthy authors.
Make a report outline
An outline is a roadmap for your report. It covers your title, introduction, thesis statement, main points, and conclusion. Organizing your thoughts this way will help you keep focus and ensure you cover all the necessary information.
While you can create a report without creating an outline, you could write a better report with an outline. An outline helps you organize your facts and important points on paper.
Stage 2: Writing
Once you have completed the pre-writing stage, it’s time to write your report.
Follow the proper report writing format
You will feel a lot of resistance at this point because this is where most of the tedious work of report writing happens. However, the process can be a breeze if you follow a proper structure and report writing format.
The structure of your report can vary depending on the type of report you’re creating, but the report writing format below can serve as a guide for anyone.
- Title page. This is the first page of your report and should include the report’s title, the author’s name, the date of presentation or submission, and any other relevant information, such as your name or the organization’s name.
- Table of Contents (TOC ). This section contains subsections of your report and their corresponding page numbering. A well-written TOC will help readers navigate your report easily and find the information they need.
- Brief summary . This part provides an overview of the report’s particular purpose, subject, methodology, key findings, and recommendations. This section is often called the executive summary in corporate reports.
- Introduction . The introduction should provide background information about the topic and explain why the report was written. It should also state the aims and objectives of your report and give an overview of the methodology used to gather and analyze the data. Make sure you include a powerful topic sentence.
- Main body. The main body of the report should be divided into subsections, each dealing with a specific aspect of the topic. These sections should be clearly labeled and organized in a logical order. In most reports, this is also the part where you explain and present your findings, analysis, and recommendations.
- Conclusion. Summarize the main points of your report and provide a final summary, thought, or suggestions. Review your thesis statement. The conclusion also includes any limitations of the study and areas for further research or future action.
- References . This section should include a list of all the sources cited in the report, like books, journal articles, websites, and any other sources used to gather information on your subject.
- Appendices . In the appendices section, you should include any additional information relevant to the report but not in the article’s main body. This might consist of raw data, event details, graphs, charts, or tables.
With all these key report elements, your readers can look forward to an informative, well-organized, and easy-to-read report.
Pro tips: Remember to use clear and concise language in your essay. It is also required to follow a specific type of formatting set by your organization or instructor.
Plus, use the active voice when you can because it helps improve clarity. To write a report essay in a passive voice makes it sound less concise.
Reports should usually be written in the third person.
Edit and proofread the article
Once you have completed your first essay draft, take some time to edit and proofread your work. Look for spelling mistakes and grammar errors, as well as any areas where the flow of your article could be improved. Review your topic sentence.
If hiring a professional editor isn’t possible, have a colleague or someone else read your rough draft and provide feedback. You can also use tools like Grammarly and the Hemingway App .
Stage 3: Post-writing
You’re almost there! This stage is about finalizing your report and ensuring it is ready to be shared.
Format your report
Ensure your report is formatted correctly, with clear and easy-to-read fonts, headings, and subheadings.
Incorporate visuals
Adding visuals to your report article is another great way to help your audience understand complex information more easily.
From charts to illustrations, the right visual can help highlight and explain key points, events, trends, and patterns in your data, making it easier for the reader to interpret the information.

Want to check out more templates? Get access to the template gallery today .
However, it’s important to use visuals sparingly and ensure they are relevant and effectively support the texts. You will learn more about effectively incorporating visuals into your report as you scroll down below to the next sections.
Share your report
Once your report is complete, share it with your audience. This might involve submitting it to your boss, presenting it to a group, or sharing it online.
A final note for this section: Remember to take your time, stay organized, and most importantly, have fun! Writing a report can be a rewarding experience, especially if you get positive feedback when you present.
How to add visuals to your report
Adding visuals to your report is more than just putting a graph or chart for every piece of information.
There are no hard and fast rules but use the pointers below as guidelines:
- Each visual in your report should have a purpose. Don’t just add a pie chart or bar graph for the sake of adding one. Your visual of choice should offer clarity to readers that’s impossible to achieve with words alone. Piktochart’s report maker lets you search for free stock images and illustrations to add to any page with drag and drop.
- Add captions, legends, or arrows to your visuals when possible. For more technical reports, graphics are either Tables or Figures. Number them in order of appearance (Figure 1, Figure 2, Table 1, etc.) and give each a descriptive title.
- Place the visual close to the relevant text on the page.
- Document the source of the visual, citing it in both the caption and references section if necessary.
- Make the graphic stand out with colors, borders, boxes, spacing, and frames.
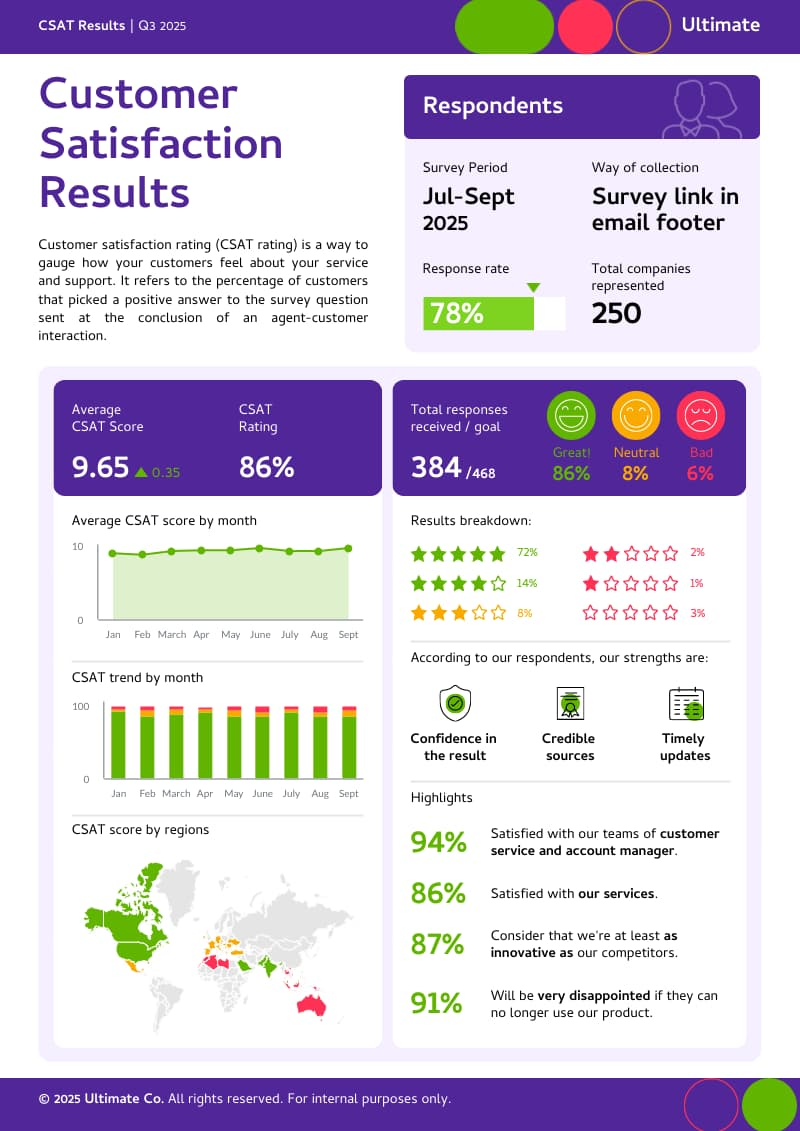
Learn more : How to Improve Your Data Visualization Design in 6 Steps
Write reports like a pro with Piktochart’s easy-to-edit report templates
Creating reports from scratch can be time-consuming. The great news is you don’t have to make reports from scratch like how it used to be in the 90s and early 2000s. Organizations of all shapes and sizes now understand that you can also create the perfect report with the help of templates.
For example, Piktochart offers a variety of fully customizable templates, allowing you to easily add your branding, colors, and text within the online editor. You can visualize your thesis statement and first draft in less than an hour. It’s also possible to start writing directly in the tool, adding graphics page by page.
These templates range from reports for school presentations to sales reports. By editing them, you can create professional-looking reports without the hassle of formatting and design.
Here are some examples of Piktochart’s professionally-designed templates. If you can’t pick one that matches your report writing format and needs, create a free Piktochart account to get access to more templates.
Survey report template
This survey report template includes clear visualizations, making your report findings easier to understand. From customer surveys to employee satisfaction reports, this template is quite versatile.
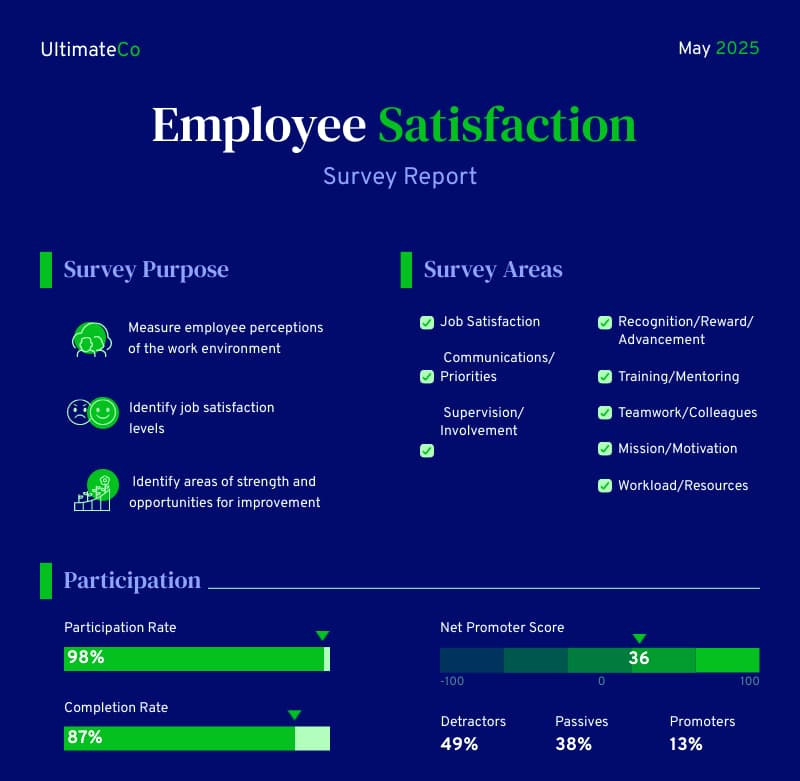
Research report template
This research report template is perfect for anyone looking to create a thorough and professional research report. The template includes all the necessary sections to help you easily organize your research and present your findings in a concise document.

Corporate report template
Looking for a corporate report template example with an editable table of contents and foreword? This template is the perfect fit!
Whether you’re presenting to investors or sharing information with your team, this corporate report template will help you create a polished and informative executive summary for any corporate organization.

Case study report template
Whether you’re conducting a business case study or an academic case study, this case study report template can help you earn your readers’ trust. This template is specifically designed with fashion as its main theme, but you can edit the photos and details to make it more on-brand with your niche.

Marketing report template
Use this template to create comprehensive marketing reports. The template includes editable sections for social media, data from search engines, email marketing, and paid ads.

Financial report template
With this customizable finance report template, you don’t need to make a financial report from scratch. Once you’ve written your content, save your report in PDF or PNG formats.
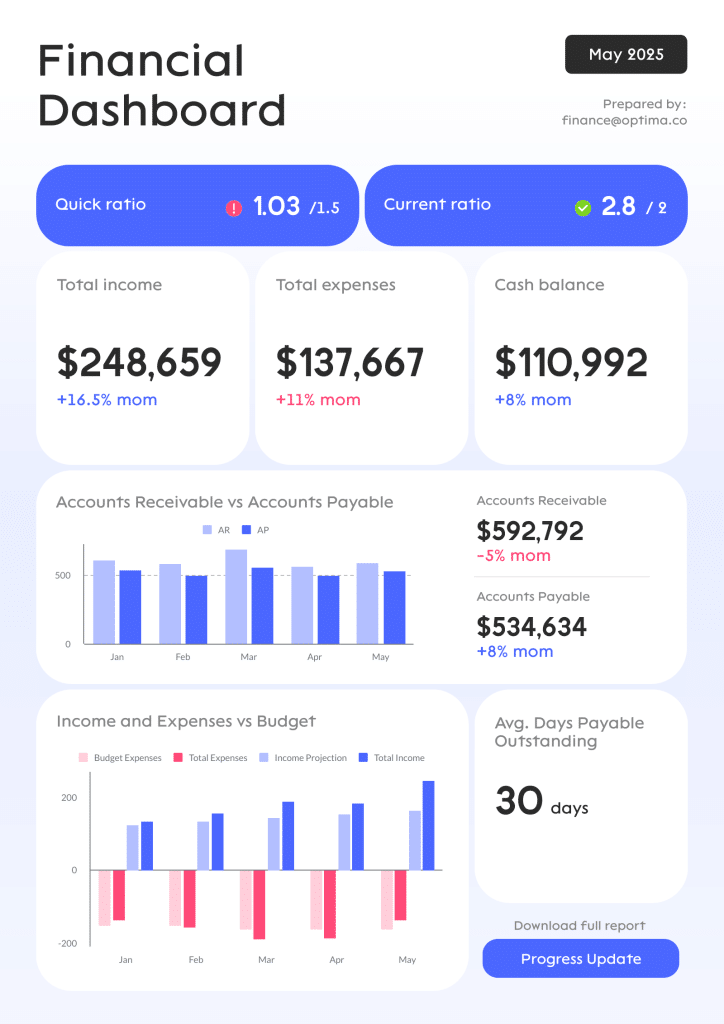
Annual report template
This annual report template is the right template for creating a professional and informative executive summary of your organization’s performance over the past year. This template was designed for HR annual reports, but you can also repurpose it for other types of yearly reports.

See more report templates by creating a free Piktochart account .
Quick checklist for better report writing
Before you submit or present your report, use the quick checklist below to help ensure that your report is well-structured, accurate, clear, and properly cited. Most of all, you must ensure that your report meets your audience’s expectations and has all the information and details they need.
Purpose and audience
- Does the report address its purpose and meet the needs of the intended audience?
Structure and organization
- Is the material appropriately arranged in sections?
- Have irrelevant details been removed?
Accuracy and analysis
- Has all the material been checked for accuracy?
- Are graphs and tables clearly labeled? Check the page numbers too.
- Is the data in graphs or tables analyzed and explained in words?
- Does the discussion or conclusion show how the results relate to the objectives mentioned in the introduction?
- Have the results been compared with existing research from the literature survey?
Writing style and clarity
- Is the report written in a tone that’s indicated in the brand style guide (for corporate reports)? Does it avoid colloquialisms or contractions?
- Does it follow the organization’s specific guidelines for writing style?
- Is it jargon-free and clearly written? Have you translated technical terms into simpler words?
- Use the active voice when you can because it helps improve clarity. A written report in a passive voice may make it sound less concise.
Acknowledgment and citation
- Have all ideas and event data taken from or inspired by someone else’s work been acknowledged with a reference?
- Have all illustrations and figures taken from someone else’s work been cited correctly?
Proofreading
- Has the report been carefully proofread for typos, spelling errors, and grammatical mistakes?
Make engaging and effective reports quickly with Piktochart
Writing a report is a must-have skill for anyone looking to communicate more effectively in their personal and professional lives.
With the steps we’ve provided in this guide, anyone can learn how to write a report that is informative, engaging, and comprehensive.
Plus, the free templates we highlighted are valuable for individuals looking to create reports quickly and efficiently. They can also be used to transform a longer report filled with texts into something more engaging and easy to digest.
Sign up for a free Piktochart account today, and look forward to writing reports with its library of modern, customizable report templates.
Piktochart offers professionally designed templates for all your visual communication needs. It is your one-stop shop for presentations , posters , logos , email signatures , infographics , and more. Customize all templates according to your brand assets in seconds. Get started for free today.

Other Posts
10 Best Sales Report Templates for Tracking Revenue, KPIs & Growth

10 Types of HR Reports (With Templates and Examples)

7 Captivating Report Design Ideas And Tips (With Templates and Examples)
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Perspect Clin Res
- v.5(4); Oct-Dec 2014
Basics of case report form designing in clinical research
Shantala bellary.
Global Medical Affairs, Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd., Hyderabad, India
Binny Krishnankutty
1 Clinical Research, USV Limited, Mumbai, India
M. S. Latha
Case report form (CRF) is a specialized document in clinical research. It should be study protocol driven, robust in content and have material to collect the study specific data. Though paper CRFs are still used largely, use of electronic CRFs (eCRFS) are gaining popularity due to the advantages they offer such as improved data quality, online discrepancy management and faster database lock etc. Main objectives behind CRF development are preserving and maintaining quality and integrity of data. CRF design should be standardized to address the needs of all users such as investigator, site coordinator, study monitor, data entry personnel, medical coder and statistician. Data should be organized in a format that facilitates and simplifies data analysis. Collection of large amount of data will result in wasted resources in collecting and processing it and in many circumstances, will not be utilized for analysis. Apart from that, standard guidelines should be followed while designing the CRF. CRF completion manual should be provided to the site personnel to promote accurate data entry by them. These measures will result in reduced query generations and improved data integrity. It is recommended to establish and maintain a library of templates of standard CRF modules as they are time saving and cost-effective. This article is an attempt to describe the methods of CRF designing in clinical research and discusses the challenges encountered in this process.
INTRODUCTION
A case report form (CRF) is designed to collect the patient data in a clinical trial; its development represents a significant part of the clinical trial and can affect study success.[ 1 ] Site personnel capture the subject's data on the CRF, which is collected during their participation in a clinical trial. The International Conference on Harmonization Guidelines for Good Clinical Practice define the CRF as: A printed, optical or electronic document designed to record all of the protocol – required information to be reported to the sponsor on each trial subject.[ 2 ]
Case report form designing requires enormous planning and attention to minute detail. Designing a CRF is crucial in a clinical trial as it will aid in assessing the safety and efficacy of the medicinal product accurately. CRF should be designed for optimal collection of data in accordance with the study protocol compliance, regulatory requirements and shall enable the researcher test the hypothesis or answer the trial related questions.
A well-designed CRF should represent the essential contents of the study protocol and in an ideal situation, CRF is designed once the study protocol is finalized. It can be prepared either concurrently along with the protocol development, but may result in many versions, and hence needs to be version controlled. Timing of the design process will also play an important role as both the approaches have pros and cons.
It is increasingly recognized that the design of the CRF (paper form/electronic form) is a key quality step in ensuring the data required by the protocol, regulatory compliance and/or safety needs/comments, study-specific hypothesis attributes, site work flow, and cross-checking of data items within a form or across different forms are addressed.[ 3 ] The CRF used in clinical research reduces messy clinical realities to round integers and categorical answers.[ 4 ]
This article is an attempt to describe the methods of CRF designing in clinical research, discusses the challenges encountered and measures to be taken to prevent the occurrence of issues in its development.
PAPER CASE REPORT FORM VERSUS ELECTRONIC CASE REPORT FORM
There are two types of CRFs used in clinical research, that is, traditional paper CRF and improvised electronic CRF (eCRF). Paper CRF is the traditional way of data capture and a better option if studies are small or vary in design, whereas eCRFs are considered if studies are large with similar designs.[ 5 ]
In the current global scenario, eCRFs are preferred over paper CRFs as they are less time-consuming, and also encourage the sponsor/pharmaceutical company to carry out large multicentric studies at the same time due to the ease of administration. It is designed in such a way that data entry can be done with zero/minimal errors. Moreover, the regulatory authorities are readily accepting submissions in which validated electronic data capture (EDC) systems are used.[ 6 ]
While designing an eCRF, repetitive data such as protocol ID, site code, subject ID, and patient initials will be generated by the system automatically from the first page to all others, thus ensuring no duplication of CRF pages.
In eCRF, linking the data between two related pages of CRFs becomes easy and quick. They have built-in edit checks tagged to each data field as well as to the CRF as a whole. Therefore, majority of data cleaning activities will take place during the completion of the eCRFs, thus reducing the time and effort required by data management personnel. Instant query resolution reduces the time spent on obtaining the clarification from the site/investigator and hence, clean data is obtained much quickly, resulting in timely database lock, faster regulatory submission, and subsequent approval.
Designing a paper CRF is a tedious job that could result in data errors and wrong conclusions, requiring meticulous attention to minimize duplication of CRF pages. Chances of error during data transfer from the source document to paper CRF are common. Moreover, for studies with large sample size if traditional method of data collection through paper CRFs is opted, then manual data cleaning may be a major concern. However, this method may not require user training and system validation as in the case of EDC systems, where such things are essential before implementing it. Despite their many advantages, eCRFs have not been accepted widely. Main reasons behind this are lack of available on-site technology, investigators’ lack of motivation, complexity of installation, and maintenance of the software and high investment cost.
STANDARD CASE REPORT FORM DESIGN
Designing a CRF is an art that should to be based on scientific practices and the design should be implemented keeping the end-user (the one who enters data in the CRF) in mind. While designing, all important sections of the CRF should be included with care; always it is worth to remember that insufficient/inaccurate data collection would prove expensive during analysis. Hence, it is advisable to have a standard operating procedure for CRF preparation and to follow best practices of CRF designing.
Primary objective of CRF designing is to gather complete and accurate data by avoiding duplication and facilitating transcription of data from source documents onto the CRF. CRF should be designed with the primary safety and efficacy endpoints as the main goal of data collection.[ 6 ] Ideally, it should be well-structured, easy to complete without much assistance and should collect data of the highest quality. Always minimum amount of data needed to answer the study hypotheses should be collected avoiding collection of elaborate, unimportant information. For ordinal data, to ensure uniformity and clarity among raters, adequate explanation should be provided adjacent to the CRF fields. Capturing the same piece of data in more than one place (duplication) on the CRF should also be avoided. In other words, CRF should collect data in sufficient detail without ambiguity and at the same time, should avoid redundancy and avoid capture of unwanted details. Hence, striking the perfect chords to ensure balance between effective data collection and structuring the CRF to support accurate data entry is essential. Collecting the data in the coded form whenever possible is ideal as it facilitates data entry (at CRF and at the database levels) and helps the statistician in data interpretation and analysis.
Important part of the CRF is an informative header and footer, which can be customized.[ 7 ] In general, the header includes protocol ID, site code, subject ID, and patient initials. Whereas, the footer includes investigator's signature, date of signature, version number, and page number.
In order to enhance easy reading/understanding and accurate data entry, an uncrowded CRF layout should be preferred. Placing too many details on the same page, makes the CRF look cluttered and makes data entry difficult, which eventually leads to increase in data discrepancies.
Case report form design should be standardized to address the needs of all those who handle the data such as investigator, data manager, biostatistician, clinical research monitor/coordinator, database developer/programmer and data entry personnel etc. An effective CRF design would always be user friendly. Moreover, it should capture legible, consistent and valid data, thereby, reducing query generations.[ 7 ] While designing the CRFs, design standards should be adhered to for improving the quality of data collected. Hence, data should be organized in a format that facilitates data analysis and makes it simplified.
The following points are to be borne in mind while designing a CRF:
- Use of consistent formats, font style and font sizes throughout the CRF booklet
- Selection of portrait versus landscape versus combination layouts
- Use of clear and concise questions, prompts, and instructions
- Visual cues, such as boxes that clearly indicate place and format of data to be recorded should be provided to the person recording the data as much as possible
- Using the option of “circling of answers” should be limited as it's hard to interpret; instead check boxes would be appropriate
- Clear guidance about skip patterns like what to skip and what not to skip should be mentioned at appropriate places
- Skips (are instructions provided in the CRF page to maintain the connectivity between pages) should be kept to a minimum by the placement of questions to avoid confusions
- Provide boxes or separate lines to hold the answers. This indirectly informs the data recorder where to write/enter the response and helps to differentiate it visually from the entry fields for other questions
- Separate the columns with thick lines
- Provide bold and italicized instructions
- Minimize free text responses
- Position only specified density of questions on each page
- Page numbering if necessary, should be consistent throughout
- Avoid using “check all that apply” as it forces assumptions about the clinical data
- Specify the unit of measurement
- Indicate the number of decimal places to be recorded
- Use standard data format (e.g., dd/mm/yyyy) throughout the CRF
- Use precoded answer sets such as yes/no, male/female, method of administration of medicine, and severity of adverse event (AE) (mild/moderate/severe) wherever possible
- Not to split modules/sections (a set of one or more related groups of questions that pertain to a single clinical study visit) like, for example, AE section should not be split and laid across pages such that information related to a single AE will have to be collected from different pages
- Use “no carbon required (NCR)” copies to ensure exact replica of CRF

A sample case report form (CRF) page. An adverse event page of CRF is depicted showing codes, and skips questions
WELL DESIGNED CASE REPORT FORM VERSUS POORLY DESIGNED CASE REPORT FORM
Table 1 provides the comparison between well-designed and poorly designed CRF. In case of poorly designed CRF, by placing a single line for required response results in variations in the investigator's responses from site to site. On the other hand, separate lines and boxes are provided in the well-designed form, which gives the visual cues about what is expected as a response and thereby, reduces the unnecessary queries. Usually, boxes are used for entering dates and the date format (i.e., dd/mm/yyyy) should be consistent on all pages of CRF. Units and decimal points should be displayed for vital sign records, which clarify the user about the expected values and also facilitates the data interpretation and reduces manipulation during analysis procedures. Figures Figures2 2 and and3 3 are examples of poorly designed CRFs. Poor CRF design results in frequent database modification thus affecting the study timelines. Data need to be collected in a way that does not introduce bias or errors. Collection of a large amount of data will result in wasted resources in collecting and processing it. Questions in the CRF should be clear and unambiguous to avoid unnecessary confusions.[ 8 ]
Illustrating a well-designed and poorly designed data fields imparting the significance of visual cues to help the site personnel to understand the format

Example of a poorly designed case report form

Illustrating the missing indicator question
In some circumstances, data can be obtained using derivation procedures; collection of derived data again on the CRF should be avoided to minimize calculation errors. For example, age can be calculated using date of birth. Body mass index can be calculated using height and weight of the subject, only the latter two should be captured.
In conditions where same parameters are to be recorded at multiple visits, it is recommended to use the same CRF module for each visit to reduce the number of query generation. For example, vital Signs and body systems in the physical examination (PE) module can be collected in the same order each time.
In some places, answers are coded in order to simplify the data collection. When codes are used to obtain an answer for a question, consistency in codes should be maintained throughout the CRF booklet and there should not be any variation in the answer for the same question.
For example, yes/no answers are coded as 1 = yes and 2 = no (preferred coding) as shown in Figure 4 . If the codes are assigned in this order, the same order should be practiced throughout the CRF. Nowhere in the same CRF “1” should be coded for “no” and “2” should be coded for “yes”.

Coding on the case report form module
Even the location of these codes on the CRF should be consistent; same is shown in Figure 4 . Clear instructions should be provided to the user where ever necessary; otherwise, it will have a significant impact on the data management activities like database designing, data cleaning, data validation, and data extraction due to poor understanding of the site personnel about the expected responses. It is advisable to use indicator questions wherever needed to avoid assumptions about the data. Use indicator questions in connection to a set of other questions, and the response to the indicator question would decide on whether the associated set of questions needs to be answered or not. For example, in an AE question group, an indicator question could be, “Did any AE occur after the last visit?”
If the response is “yes”, the remaining questions pertaining to the details of the AE(s) (such as severity, seriousness, causality, date of onset, date of resolution, and action taken) require responses. If the response is “no”, the rest of the question group is not answered. Incorporation of an indicator question and skips are shown in Figure 1 . Ideally, CRF booklet should have a chart reflecting the expected list of assessments as per schedule specified in the protocol.
STANDARD CASE REPORT FORM TEMPLATES
Some of the data requirements such as demography, PE, AEs are same across studies, so standard CRF templates should be developed which can be customized accordingly. These templates are of great help while conducting multiple studies in the same research area. These templates will have the same design principles that help the user to enter data with ease since the design is familiar to them; there is no need for special training on these modules of CRFs.
A “library” of standard templates should be established and maintained by the sponsor/contract research organizations, pharmaceutical companies in order to maintain uniformity in the CRF design and to save time. Most commonly used standard CRF templates are inclusion criteria, exclusion criteria, demography, medical history, PE, AE, concomitant medication and study outcome modules, whereas, the modules which captures efficacy data are not unique. Their design varies from study to study depending on the protocol specifications.
CASE REPORT FORM CONNECTIVITY/WELL REFERENCED CASE REPORT FORMS
Linking of CRF (paper CRF and eCRF) pages wherever necessary is known as CRF connectivity. Each CRF booklet is assigned with unique subject ID and it is the duty of site personnel to make sure that same ID is entered on all pages of CRF booklet. Consistently entered subject ID will help in tracking the missing CRF pages. The fields such as protocol ID, site code, subject ID, and patient initials make database designing easier and helps linking CRF pages to the study database. The fields like protocol ID and visit labels are informative features as they provide brief descriptions of the study and the schedule of assessments, respectively. The CRF version number is a critical field that prevents an incorrect CRF page being used. All pages of the CRF booklet should be numbered in sequential order, which will help in identifying queries through data validation procedures and manual reviews. Page numbering not only provides the site personnel with a quick reference to specific pages, but also helps to design the database in a structured manner. Especially, in case of eCRF, retrieving of CRFs becomes challenging if proper programming is not carried out. CRF connectivity is crucial when statistical analysis plan (SAP) is complex and these fields will be of help in statistical analysis.
CHALLENGES IN CASE REPORT FORM DESIGNING
Commonly encountered challenges in CRF designing are consistency in the design, collection of precise data and user-friendliness. These challenges can be overcome by proper planning by a team of data management personnel, biostatisticians, clinicians, and medical writers. Objectives should be defined clearly before designing. Consistent design is a crucial aspect as it reduces the number of mistakes in data entry. It is of great advantage when using them across various studies. Maintaining standard CRF templates would resolve this issue. Collection of extraneous data is another issue and measures should be taken to avoid it, as processing this becomes tedious. In such instances, ensuring accuracy and quality become major challenges. Attention should be paid to avoid duplication. Design the CRF to avoid referential and redundant data collection. For example, collecting calculated fields/derivable data should be avoided and to ensure that data collection is cost-effective. Designing user-friendly CRF to reduce data entry errors is again a challenge. Simple/standard designs should be incorporated wherever possible.
User feedback mechanism should be built into the CRF design and maintenance process. Best practices should be applied to improve the data quality and save time with CRF design. Providing CRF completion guideline aids in minimizing the challenges in data capture and data entry.
CASE REPORT FORM COMPLETION GUIDELINES
A CRF completion guideline is a document to assist the investigator to complete the CRF in a step by step manner and is drafted concurrently in line with the CRF and protocol. Figure 5 shows sample page of CRF completion guideline. There is no standard template for CRF completion guidelines as it is study specific. It should be prepared in such a way that it enables the site personnel to complete the CRFs with ease and legibility. CRF completion manual should provide clear instructions to site personnel for accurate completion of CRFs along with clear expectations including proper instructions on handling unknown data. For example, if exact date is unknown, then use a preferred notation in the place of missing value (i.e., UK/UNK/2012). The language used should be simple with clear instructions, concise, and easy to understand.

Sample page of case report form completion guideline
Case report form completion guidelines document, while bridging the gap between the study protocol and the data collection process, explains the activities involved in CRF completion, correction, signing, and data handling.[ 7 ] It provides unambiguous instructions on CRF completion in all practical scenarios. For example, if data were wrongly entered and the site personnel wants to correct it, the instruction provided would be to strike-through the incorrect data with a single line, put the initials (of the person who makes the change) with date and to write the correct entry in the margin against the corresponding line. Similarly, instructions will be provided for each data entry field on each page in the CRF booklet. This helps to ensure completion of all required data fields and enhances the data flow.[ 7 ] CRF completion guidelines could be a separate document or could be a part of the CRF booklet giving page by page instructions. If it is included as part of the CRF, it is advisable to print instructions on the page facing the CRF page (back side of the previous page) as the investigator can easily take instructions and simultaneously fill the CRF page. CRF completion guidelines document should have version control and amendments should be done as and when required.
Case report form design is the initial step in translating the protocol into standard questionnaires and is paramount to a successful clinical trial. Standard CRF should be designed in such a way that it helps the collection of consistent and valid data, ultimately resulting in submission of data to regulatory authorities and its acceptance. Regardless of the time and effort spent conducting the trial, the correct data points (response to a CRF question/data is entered) must be collected; otherwise, a meaningful analysis may not be possible. Therefore, a sound SAP should be used as a tool to develop and judge the adequacy of the CRF, which should be available to guide on what data points need to be captured on the CRF. To avoid future amendments, it is important to have design principles in mind well in advance before CRF designing is initiated. These standard guidelines will contribute in preparing a well-designed CRF for data acquisition.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We would like to acknowledge the technical support offered by Mr. Vinoth T. and Mr. Sagi Subbaraju that has helped us during the preparation of this article.
Source of Support: Nil.
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Cookie consent
We use our own and third-party cookies to show you more relevant content based on your browsing and navigation history. Please accept or manage your cookie settings below. Here's our cookie policy

- Form Builder Signups and orders
- Survey maker Research and feedback
- Quiz Maker Trivia and product match
- Find Customers Generate more leads
- Get Feedback Discover ways to improve
- Do research Uncover trends and ideas
- Marketers Forms for marketing teams
- Product Forms for product teams
- HR Forms for HR teams
- Customer success Forms for customer success teams
- Business Forms for general business
- Form templates
- Survey templates
- Quiz templates
- Poll templates
- Order forms
- Feedback forms
- Satisfaction surveys
- Application forms
- Feedback surveys
- Evaluation forms
- Request forms
- Signup forms
- Business surveys
- Marketing surveys
- Report forms
- Customer feedback form
- Registration form
- Branding questionnaire
- 360 feedback
- Lead generation
- Contact form
- Signup sheet
- Help center Find quick answers
- Contact us Speak to someone
- Our blog Get inspired
- Our community Share and learn
- Our guides Tips and how-to
- Updates News and announcements
- Brand Our guidelines
- Partners Browse or join
- Careers Join our team

Report form templates

Project Completion Form Template

Travel Expenses Form Template

Sales Call Log Form Template

School Report Form Template

Property Condition Report Form Template

Damage report form Template

School Incident Report Form Template

Construction Daily Report Form Template
Police Incident Report Form Template

Service Report Form Template

Daily Report Form Template

Inspection Form Template

Hazard Report Form Template

Maintenance Report Form Template

Workplace Accident Report Form Template
Incident Report Form Template

Expense Reimbursement Form Template
Personal Expense Tracker Template

Online Activity Log Template
- All templates
- → Report forms
Footer Section

Yearly paid plans are up to 65% off for the spring sale. Limited time only! 🌸
- Form Builder
- Survey Maker
- AI Form Generator
- AI Survey Tool
- AI Quiz Maker
- Store Builder
- WordPress Plugin
HubSpot CRM
Google Sheets
Google Analytics
Microsoft Excel
- Popular Forms
- Job Application Form Template
- Rental Application Form Template
- Hotel Accommodation Form Template
- Online Registration Form Template
- Employment Application Form Template
- Application Forms
- Booking Forms
- Consent Forms
- Contact Forms
- Donation Forms
- Customer Satisfaction Surveys
- Employee Satisfaction Surveys
- Evaluation Surveys
- Feedback Surveys
- Market Research Surveys
- Personality Quiz Template
- Geography Quiz Template
- Math Quiz Template
- Science Quiz Template
- Vocabulary Quiz Template
Try without registration Quick Start
Read engaging stories, how-to guides, learn about forms.app features.
Inspirational ready-to-use templates for getting started fast and powerful.
Spot-on guides on how to use forms.app and make the most out of it.
See the technical measures we take and learn how we keep your data safe and secure.
- Integrations
- Help Center
- Sign In Sign Up Free
Free Online Report Form Templates
Create a report form and easily keep track of incidents, accidents, complaints, and many more subjects that need reporting. You can simplify these processes by starting with an online template to collect the information you need.

Report Forms
- Agreement Forms
- Attendance Forms
- Cancellation Forms
- Clothing Order Forms
- Complaint Forms
- Consultation Forms
- Contest Registration Forms
- Customer Registration Forms
- Customer Service Forms
- Employment Forms
- Estimate Forms
- Evaluation Forms
- Event Booking Forms
- Event Registration Forms
- Feedback Forms
- File Upload Forms
- Food Order Forms
- Hotel Booking Forms
- Informed Consent Forms
- Inquiry Forms
- Inspection Forms
- Insurance Forms
- Intake Forms
- Job Application Forms
- Medical Consent Forms
- Medical Forms
- Medical History Forms
- Membership Application Forms
- Membership Forms
- Membership Registration Forms
- Order Forms
- Pastry Order Forms
- Payment Forms
- Personal Forms
- Petition Forms
- Pre-Order Forms
- Product Order Forms
- Quote Forms
- Real Estate Forms
- Recommendation Forms
- Referral Forms
- Registration Forms
- Release Forms
- Rental Application Forms
- Request Forms
- Reservation Forms
- School Application Forms
- School Registration Forms
- Self-evaluation Forms
- Service Booking Forms
- Sign-up Forms
- Sponsorship Forms
- Subscription Forms
- Tracking Forms
- Virtual Event Forms
- Volunteer Forms
- Voting Forms
- Web Design Forms
- Work Order Forms
- Marketing Surveys
- Product Surveys
- Relationship Surveys
- Research Surveys
- School Surveys
- Polls & Questionnaires
Daily Report Form Template

Sales Call Report Form Template
Employee End Of Day Report Form Template

Traffic Accident Report Form Template
Daily Sales Report Form Template

Incident Report Form Template
Police Report Form Template
Suspicious Activity Report Form Template
Safety Inspection Form Template

Vehicle Inspection Form Template
Bug Report Form Template
Discord Report Form Template
Weekly Activity Report
Maintenance Report Form
Report an Issue Form
Non Conformity Report Form
Copyright Infringement Form
Animal Cruelty Report Form
Bullying Incident Report Form
Customer Accident Report Form
What is a report form template.
To simplify your data collection procedures, you can find various report form templates on forms.app. You can choose the one that suits your preferences and needs among various online report form templates. Reports are the writings that notify examination results about any subject or event. Reports can be about an issue that needs to be examined or work that requires accurate, certain, and reliable information.
How to create an online report form?
You can start to create your form by choosing a template and clicking on the ‘use template’ button. With free and customizable templates that forms.app provides you; it is easy to gather specific information according to your needs.
For instance, you can create an accident report form. You can specify what type of incident occurred, which people were involved, the nature of the incident, or the details of the incident by means of forms.app. You don’t have to deal with detailed and complicated work to report incidents anymore!
There are numerous report form templates , including incident report forms, accident report forms, request forms, insurance claims, and many more. It is up to you to use one of the ready-made templates or create your own form by customizing it. You can add extra form fields and change form design as well as colors and themes as you see fit.
What is the importance of report forms?
There are a variety of report forms that can vary according to the incidents encountered. For example, to document an event that caused injury, illness, or property damage, you will need an incident report form template. More specifically, to write up a comprehensive report about an event that happened at school, you can create a school incident report form on the forms.app.
Report forms essentials
Different incidents require to be documented differently, and there are some significant matters in order to create an accurate and useful report form.
Pay attention to obtaining necessary information — knowing what information you need to include in your report is an important step to gathering data efficiently. Be careful about the details you would like to add to your report when creating a report form.
Be attentive to collecting accurate and factual data — report forms are the documentation of actual incidents, accidents, and complaints, and they indicate true information. Hence, giving the truest information is the foremost responsibility of the reporter.
Do not skip over the details — you should ask the right questions to get the right answers. It is important to add essential details to your form according to what type of incident you would like to report.
Share your forms online
After you chose one of the ready-made templates we provide or created your own form by adding the required fields and essential details, now it is time to share your report form online. There are various social media platforms, such as WhatsApp, Facebook, and Twitter, where you can directly share your form with. If you are looking for more options, you can also convey your form to a lot of people via email or URL.
Create online forms
By using forms.app’s easy and extensive form builder user interface, you can create online forms, surveys, and exams with less effort than anything else! You can quickly start with a ready-made template and customize it according to your needs or you can start from scratch and build your form with many different types of form fields and customization options.
Powerful features:
- Conditional logic
- Create forms with ease
- Calculator for exams and quote forms
- Geolocation restriction
- Real-time data
- Detailed design customization
Automate the work that you don’t like
Automations between the tools you use are vital as it saves time and deducts tons of workload. Imagine that you would need to transmit data from your form responses to another tool manually. That would be boring and time-consuming distracting you from your real work.
forms.app integrates with +500 third-party applications such as Asana, Slack, and Pipedrive via Zapier. Thus, you can automate your workflows and focus more on enriching your business.
Ease your work with +1000 templates
Let our templates do errands for you and let you focus more on critical parts of your forms and surveys such as form fields, questions, and design customization. With over 100 templates, forms.app enables you to create a form that you need and customize it according to your needs by using our form creator.
Share or embed your form
You can share your forms in any way you like. If you want to share your form and collect responses through your form’s unique link, you can simply adjust privacy settings and copy paste your form link anywhere. And if you would like to embed your form in your website, you can easily copy and paste embed code in your website HTML.
Create eye-pleasing free online forms
On forms.app, you can customize your form’s theme and design elements in depth. Once you switch to the ‘Design’ tab after getting your form done, you will see many different design customization options. You can change your form theme by choosing your own colors or picking one of many ready-made themes.
Skip to Content
Massey University
- Search OWLL
- Handouts (Printable)
- Pre-reading Service
- StudyUp Recordings
- StudyUp Postgraduate
- Academic writing
- Intro to academic writing
- What is academic writing?
- Writing objectively
- Writing concisely
- 1st vs. 3rd person
- Inclusive language
- Te Reo Māori
- Assignment planning
- Assignment planning calculator
- Interpreting the assignment question
- Command words
- Organising points
- Researching
- Identifying academic sources
- Evaluating source quality
- Editing & proofreading
- Apostrophes
- Other punctuation
- Active voice
- American vs. British spelling
- Conditionals
- Prepositions
- Pronoun Reference
- Sentence fragments
- Sentence Structure
- Subject-verb agreement
- Formatting and layout
- Word limits and assignment length
- Commonly confused words
- How assignments are marked
- Marking guides
- Getting an A
- Levels of assessment
- Using feedback
- Professional emails
- Forum posts
- Forum netiquette guidelines
- Sharing personal information
- Writing about personal experiences
- Assignment types
- What is an essay?
- Essay planning and structure
- Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Body paragraphs
- Essay revision
- Essay writing resources
What is a report?
- Report structure
- Analysing issues for a report
- Business report
- What is a business report?
- Business report structure
- Inductive vs. deductive reports
- Other kinds of business communication
- Business report format and layout
- What is a lab report?
- Lab report structure
- Science lab report writing resources
- Psychology lab report writing resources
- Lab report body paragraphs
- Literature review
- What is a literature review?
- Writing a literature review
- Literature review structure
- Literature review writing resources
- Research proposal
- Writing a research proposal
- Research proposal structure
- Other types
- Article critique
- Book review
- Annotated bibliography
- Reflective writing
- Oral presentation
- Thesis / dissertation
- Article / conference paper
- Shorter responses
- PhD confirmation report
- Computer skills
- Microsoft Word
- Basic formatting
- Images, tables, & figures
- Long documents
- Microsoft Excel
- Basic spreadsheets
- Navigating & printing spreadsheets
- Charts / graphs & formulas
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Basic skills
- Advanced skills
- Distance study
- Getting started
- How to study
- Online study techniques
- Distance support
- Reading & writing
- Reading strategies
- Writing strategies
- Grammar resources
- Listening & speaking
- Listening strategies
- Speaking strategies
- Maths & statistics
- Trigonometry
- Finance formulas
- Postgraduate study
- Intro to postgrad study
- Planning postgrad study
- Postgrad resources
- Postgrad assignment types
- Referencing
- Intro to referencing
- What is referencing?
- Why reference?
- Common knowledge
- Referencing styles
- What type of source is this?
- Reference list vs. bibliography
- Referencing software
- Quoting & paraphrasing
- Paraphrasing & summarising
- Paraphrasing techniques
- APA Interactive
- In-text citation
- Reference list
- Online material
- Other material
- Headings in APA
- Tables and Figures
- Referencing elements
- 5th vs. 6th edition
- 6th vs. 7th edition
- Chicago style
- Chicago Interactive
- About notes system
- Notes referencing elements
- Quoting and paraphrasing
- Author-date system
- MLA Interactive
- Abbreviations
- List of works cited
- Captions for images
- 8th vs 9th edition
- Oxford style
- Other styles
- Harvard style
- Vancouver style
- Legal citations
- Visual material
- Sample assignments
- Sample essay 1
- Sample essay 2
- Sample annotated bibliography
- Sample book review
- Study skills
- Time management
- Intro to time management
- Procrastination & perfectionism
- Goals & motivation
- Time management for internal students
- Time management for distance students
- Memory skills
- Principles of good memory
- Memory strategies
- Note-taking
- Note-taking methods
- Note-taking in lectures
- Note-taking while reading
- Digital note-taking
- Reading styles
- In-depth reading
- Reading comprehension
- Reading academic material
- Reading a journal article
- Reading an academic book
- Critical thinking
- What is critical thinking?
- Constructing an argument
- Critical reading
- Logical fallacies
- Tests & exams
- Exam & test study
- Planning exam study
- Gathering & sorting information
- Reviewing past exams
- Phases of revision
- Last-minute study strategies
- Question types
- Short answer
- Multi-choice
- Problem / computational
- Case-study / scenario
- Open book exam
- Open web exam or test
- Take home test
- In the exam
- Online exam
- Physical exam
A report is a specific form of writing that is organised around concisely identifying and examining issues, events, or findings that have happened in a physical sense, such as events that have occurred within an organisation, or findings from a research investigation.
These events can also pertain to events or issues identified within a body of literature. A report informs the reader simply and objectively about all relevant issues. There are three features that characterise report writing at a very basic level: a pre-defined structure, independent sections, and reaching unbiased conclusions.
Pre-defined structure
Report structures vary widely. So, check your guidelines to ensure that you are following the structure that has been specified.
At a very basic level, a report can be distinguished from an essay by headings which are used to organise information.
Headings typically indicate sections within a report, such as an introduction, discussion, and conclusion.
Within the discussion section, which usually makes up the main body of a report, you can often add sub-sections according to the literature you have sourced, your development of ideas, and the assigned task. The difference between main sections and sub-sections may be indicated through numbering and/or heading font style. You will need to check the assignment instructions to see whether this is appropriate.
1. Introduction 2. Discussion 2.1 Technological benefits 2.1.1 Efficiency 2.1.2 Access to monitoring 2.2 Technological weaknesses 2.2.1 Disconnections 2.2.2 Lack of face-to-face support 3. Conclusion 4. References
You may find that you do not need linking sentences as the headings provide a link between sections, although including a linking sentence from time-to-time may assist the reader's understanding.
Overall, a report is a highly structured piece of work and typically, the course co-ordinator or lecturer identifies the main sections required or indicates that you should follow a standard structure (such as a business report structure ). You are often given more guidance on how to write the assignment, with respect to its structure and section, compared to an essay where you decide the order of information in the essay body.
While you may have more freedom in structuring an essay, it may be more difficult to decide how to order information within your essay. In contrast, a report provides you with that structure before you begin to answer the question, while still allowing you some flexibility and freedom in deciding on the organisation of sub-sections.
Unbiased conclusions
Another element of report writing (in fact, all academic writing ) is that it is an unbiased and objective form of writing.
However, while essays put forward a particular position or argument at the very beginning, summarised in the thesis statement and then backed up in the body, a report's focus is slightly different.
A report sways more towards the process of identifying and reviewing the range of issues in the body of the report, and then reaching an objective conclusion or position at the end, sometimes with recommendations based on the discussion and conclusions.
Of course, you can always have in mind a particular point of view when you begin your report, but try to give the impression that you have come to your conclusion via an objective and methodical review of the issues involved.
Sometimes you will need to briefly summarise the report's findings in your introduction. Alternatively, sometimes you might need to provide an overview of your report in an executive summary or abstract . Report structures vary so this is something you need to check with your assignment instructions or course coordinator. Nevertheless, try to ensure that the conclusion is where you give emphasis to your findings and the recommendations or decisions you have arrived at after a careful analysis of all the issues. It should be clear to the reader that your conclusion is reasoned logically from the discussion of the issues and the evidence you have presented in the body of the report.
Page authorised by Director - Centre for Learner Success Last updated on 11 June, 2019
- Academic Q+A
Have a study or assignment writing question? Ask an expert at Academic Q+A
Live online workshops
- StudyUp (undergraduate)
- Campus workshops
- Albany (undergraduate)
- Albany (postgraduate)
- Albany (distance)
- Manawatu (undergraduate)
- Manawatu (postgraduate)
Upcoming events
- All upcoming events
- Academic writing and learning support
- 0800 MASSEY | (+64 6 350 5701)
- [email protected]
- Online form
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
Registration Statements
Proxy statement, forms 3, 4, and 5, schedule 13d, foreign investment disclosures, sec filings faqs, the bottom line.
- Securities Registration Forms
SEC Filings: Forms You Need To Know
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) requires public companies, certain company insiders, and broker-dealers to file periodic financial statements and other disclosures. Finance professionals and investors rely on SEC filings to make informed decisions when evaluating whether to invest in a company. SEC filings can be accessed for free at EDGAR , the commission's online database .
The SEC was created through the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 , which was signed into law by President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The act was intended to help restore investor confidence following the stock market crash of 1929 . The SEC is an independent government agency tasked with protecting investors, maintaining a fair and orderly market, and facilitating capital formation.
The SEC selectively reviews the information it receives to monitor and enhance compliance. Investors study these filings to form a view of a company's performance and activities. Here are some of the most common forms that companies are required to submit to the SEC. Understanding how to read SEC filings can be beneficial to investors as they perform their due diligence. In this article, we’ll discuss these filings in greater detail.
Key Takeaways
- SEC filings are important regulatory documents required of all public companies to provide key information to investors or potential investors.
- The public can review SEC filings by visiting the commission's online database, EDGAR.
- Registration statements are required when a company initially sells shares to the public.
- Among the most common SEC filings are: Form 10-K, Form 10-Q, Form 8-K, the proxy statement, Forms 3,4, and 5, Schedule 13, Form 114, and Foreign Investment Disclosures.
- The annual 10-K report, for instance, provides a comprehensive summary of a company's financial performance. Proxy statements are presented prior to a shareholder meeting and before voting on the election of directors and other corporate actions.
Registration statements provide information about the securities being offered by a company as well as its financial condition. A company preparing to offer securities to the public will file a Form S-1 registration statement with the SEC. The statement consists of two parts:
- Prospectus : This mandatory document must be given to any person who is offered to buy the company's securities. The prospectus must provide details about the company's management, business operations, financial health, operational results, risk factors, and other pertinent information. The Securities Act of 1933 mandates that all companies seeking to raise capital for new publicly offered products in the U.S. must file a prospectus with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Financial statements such as the company's income statement must be audited by an independent certified public accountant (CPA).
- Additional information : The company may provide any relevant additional information, for example, recent sales of unregistered securities.
Why Registration Statements Are Important to Investors
Registration statements help investors and analysts understand the nature of newly issued shares or bonds that will come to market. The type of information conveyed in these filings includes a description of the issuer's business and assets, a description of the security being offered, the names and bios of the company's key management, and an independently certified copy of the issuer's latest financial statements .
Investors look especially to the prospectus, which contains all of the information a potential investor would need to make a quantitative evaluation of a new security's prospects. It will also often contain important qualitative information that can be interpreted by investors as potential red flags. Because the prospectus is a legal declaration and must meet transparency standards, most companies include certain facts and statements to ensure investors aren't misled in any way, although they may choose careful or clever wording to disguise overt red flags. For instance, if the company faces substantial risks, its prospectus might state " risks for the company include, but are not limited to, an evolving and unpredictable business model and the management of growth" or, " there can be no assurance that the company will be successful in addressing its risks; failure to do so could have a material adverse effect on the company's business, prospects, financial condition and results of operations."
Reading an issuer's registration statements will often be met with flowery legal prose and lengthy cautionary statements that serve to protect the company more than the investor. Yet, it is also the legal nature of these documents that provides investors with candid information about a prospective investment's risks, opportunities, and competitive landscape. When reading a prospectus, make particular note of company-specific or unique information as opposed to broad or blanket statements that could apply to any publicly traded company.
Forward-looking statements in the prospectus are only projections. Therefore, while they use a company's honest and latest estimates, there is no guarantee the company will meet all or even any of its targets for sales and profits.
Form 10-K is an annual report that provides a comprehensive analysis of the company's financial condition. Though the Form 10-K contains information that overlaps with the company's annual report , the two documents are not the same . Companies must submit this lengthy annual filing within 60 to 90 days of the close of their fiscal year.
The Form 10-K is comprised of several parts. These include:
- Business summary : This describes the company's operations. It would include information about business segments , products and services, subsidiaries, markets, regulatory issues, research and development , competition, and employees, among other details.
- Management Discussion and Analysis : This section allows the company to explain its operations and financial results for the past year.
- Financial statements : The financial statements would include the company's balance sheet , income statement , and cash flow statement .
- Additional sections : Additional sections may discuss the company's management team and legal proceedings.
Why Form 10-K Is Important to Investors
The SEC mandates that all public companies file regular 10-Ks to keep investors aware of a company's financial condition and to allow them to have enough information before they buy or sell securities issued by that company. The 10-K can appear overly complex at first glance, complete with tables full of data and figures. However, it is because it is so comprehensive that this filing is key for investors to get a handle on a company's financial position and prospects.
A company will file both an annual report and a 10-K report with the SEC. The annual report is a shorter version that often comes with illustrations, glossy pages, a letter from the chair or CEO, and a summary overview of the financials. The 10-K is a longer, more thorough technical document that will have all of the company's financial statements available for fundamental analysis. Fundamental analysis is a common way to evaluate a firm by constructing ratios and other metrics by extracting information from the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows. For stocks, fundamental analysis looks to revenues, earnings, future growth, return on equity (ROE), profit margins, and equity multiples to determine a company's underlying value and potential for future growth. For corporate bonds, liquidity, leverage, and solvency ratios would be appropriate.
In addition to the quantitative approach to fundamental analysis, readers of a 10-K should also pay attention to its "Item 1", which explains what the company does, who its customers are, and the primary industry in which it operates. Then, look for risk factors such as legal proceedings or statements indicating future charges or volatility.
Also, pay attention to any footnotes that are included in the report. These notes will tell you which accounting method a company uses and how it compares to the generally accepted accounting method and industry standards. This information can flag potentially shady accounting practices. Other details mentioned in the footnotes include errors in previous accounting statements, looming legal cases in which the company is involved, and details of any synthetic leases . These disclosures found in the footnotes are of the utmost importance to investors with an interest in the company's operations.
Read the Footnotes
As an investor, pay special attention to any footnotes in Form 10-K, as they can help you flag any questionable accounting practices in the company you are considering.
Form 10-Q is a truncated version of Form 10-K that is filed quarterly. The form provides a view of the company's ongoing financial condition throughout the year. The Form 10-Q must be filed for the first three quarters of the company's fiscal year . The deadline to file is within 40 days from the end of the quarter. Unlike Form 10-K, the financial statements in Form 10-Q are unaudited, and the information required is less detailed.
Why Form 10-Q Is Important to Investors
The 10-Q is important since it is updated quarterly, while the more comprehensive 10-K is only filed once a year. This allows investors to update their valuation metrics and financial ratios without as much of a lag. Investors can use the 10-Q to observe any changes that may be taking place within the corporation even before it files its annual report.
Some areas of interest to investors that are commonly visible in the 10-Q include changes to working capital and/or accounts receivables, factors affecting a company's inventory, share buybacks, and even any legal risks that a company faces. You can use a close competitor's 10-Q as a comparison company to put side-by-side the company you are considering to see how it's performing on a relative basis. This will give you a broader idea of whether your investment is a strong choice, where its weaknesses are, and how it could stand to improve.
The Form 8-K is what a company uses to disclose major developments that occur between filings of the Form 10-K or Form 10-Q. Major company events that would necessitate the filing of a Form 8-K include bankruptcies or receiverships , material impairments , completion of acquisition or disposition of assets, or departures or appointments of executives.
Why Form 8-K Is Important to Investors
Form 8-K provides investors with timely notification of significant changes at a company. Many of these changes are defined explicitly by the SEC (such as a merger or acquisition), while others are simply events that firms consider to be sufficiently noteworthy for its shareholders (such as a new product release or upgrade). Either way, the 8-K provides a way for firms to communicate directly with investors in a way that is not filtered or altered by media organizations or sell-side analysts.
Form 8-K also provides a valuable record for financial research and analysis. For example, an analyst may wonder what influence certain corporate events have on stock prices. It is possible to estimate the impact of these events using statistical techniques like regressions , but researchers need reliable data. Because 8-K disclosures are legally standardized and must be honest and accurate, they provide a complete record and prevent sample selection bias .
In the proxy statement , investors can view the salaries of the management of a company and any other perks that a company's management is eligible for. The proxy statement is presented prior to the shareholder meeting and must be filed with the SEC before soliciting a shareholder vote on the election of directors and approval of other corporate actions .
Why a Proxy Statement is Important to Investors
Public companies hold annual meetings where shareholders convene to vote on various corporate actions or for new members to the board of directors . Owning common stock in a company gives you a vote (usually one vote per share), but it is not typically feasible to attend the annual meeting. The proxy statement allows you to cast your votes using a designated person, who will aggregate votes and cast them on your behalf. This person is known as a proxy and will cast a proxy vote in line with the shareholder's directions as written on their proxy card. Proxy votes may be cast by mail, phone, or online before the cutoff time. This deadline is usually 24 hours before the shareholder meeting commences. Vote responses will typically include "For," "Against," "Abstain," or "Not Voted."
The proxy statement will therefore present the items that will be voted on and allow you to return a form to the company to inform your proxy how your votes should be cast.
Corporate insiders must file Forms 3, 4, and 5. The SEC defines a corporate insider as "a company's officers and directors, and any beneficial owners of more than ten percent of a class of the company's equity securities registered under Section 12 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934." These forms are meant to reveal more information about the securities that company insiders own.
- Form 3 is the initial filing and discloses ownership amounts.
- Form 4 identifies changes in ownership.
- Form 5 is an annual summary of Form 4 and includes any information that should have been reported.
Why Forms 3, 4, and 5 Are Important to Investors
If you're an investor, it pays to know what the company's owners and most important shareholders (i.e., insiders) are doing. By watching the trading activity of corporate insiders and large institutional investors , it's easier to get a sense of a stock's prospects. While insider or institutional ownership on its own is not necessarily a buy or sell signal, it certainly offers a handy first screen in the search for a good investment. Since insider ownership and trading can impact share prices, Forms 3, 4, and 5 are useful disclosures
By paying close attention to what insiders do with their company shares, savvy investors can make the reasonable assumption they know a lot more about their company's prospects than the rest of us outsiders. So, if insiders are buying shares in their own companies, they might know something that normal investors do not. The insider might buy because they see great potential, the possibility for merger or acquisition in the future, or simply because they think their stock is undervalued.
One of the greatest investors of all time, Peter Lynch , once said, "insiders might sell their shares for any number of reasons, but they buy them for only one: they think the price will rise." Note that insiders are usually prevented from buying and selling their company stock within a six-month period following a corporate event or new issue; therefore, insiders tend to buy stocks when they feel the company will perform well over the long-term.
You can also have too much insider ownership. When insiders gain corporate control, management may not feel responsible to shareholders and instead try to enrich only themselves.
The Schedule 13D is also known as the "beneficial ownership report" and is required when any owner acquires 5% or more of the voting shares in a company. The report must be filed within 10 days of reaching the 5% threshold. It provides the following information:
- The acquirer's name, address, and other background information
- Type of relationship this owner has with the company
- Whether the person has been convicted of a crime in the past five years
- An explanation of why the transaction is taking place
- The type and class of the security
- The origin of funds used for purchases
Why Schedule 13D is Important to Investors
Section 13D was added to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as part of a 1968 amendment known as the Williams Act . This addition responded to the increasing use of tender offers as part of corporate takeovers . Schedule 13D was designed to give individual investors warning of impending changes to corporate control that could impact the future of the company, which would result from the consolidation of voting power by corporate raiders .
Investors use Schedule 13D to both detect red flags in the consolidation of insider ownership that can be potentially harmful to individual shareholders, but also as a possible harbinger of a company being acquired or bought out, which could benefit shareholders.
Form 144 is required when corporate insiders want to dispose of company stock. Form 144 is a notice of the intent to sell restricted stock, typically acquired by insiders or affiliates in a transaction not involving a public offering . The stock is restricted because it must meet certain conditions before becoming transferable. The transaction, or at least part of it, is made within 90 days of filing. Form 144 is required when the amount sold during any three-month period exceeds 5,000 shares or $50,000.
Why Form 144 Is Important to Investors
While investors can look to Forms 3, 4, and 5 for changes in insider ownership, Form 144 is useful for knowing how many potential shares will be offered for sale on the open market after the lock-up period for a new issue, such as an IPO, expires. Form 144 can indicate how much a stock price might suffer if a flood of new sale orders enter the market when the lock-up ends.
Underwriters and regulators require that a company's executives, managers, employees, and early investors (such as venture capitalists ) sign lock-up agreements surrounding a company’s initial public offering (IPO) to encourage an element of stability in the stock's price in the first few months of trading. The lock-up agreement is a legally binding contract between company underwriters and insiders that prohibits insiders from selling any shares of stock for a specified period of time. Lock-up periods typically last 180 days but can on occasion last for as little as 120 days or as long as 365 days.
In 2008, the SEC updated disclosure requirements for foreign companies offering securities in the U.S. market. For foreign companies without SEC-registered securities, the rules eliminated the requirement that they submit paper disclosures to the SEC, in favor of allowing them to post disclosures in English on the internet. In addition, the deadline for foreign companies to submit annual reports was shortened from six months to four months.
Why Foreign Investment Disclosures Are Important to Investors
Many investors today seek to diversify their portfolios geographically by including holdings of securities issued by non-U.S. companies. These can include shares or bonds issued by companies in the developed world to emerging market economies. Shares of foreign companies can be acquired on U.S. exchanges in the form of American Depositary Receipts , or ADRs. ADRs offer U.S. investors a way to purchase stock in overseas companies that would not be available otherwise. Foreign firms also benefit, as ADRs enable them to attract American investors and capital without the hassle and expense of listing on U.S. stock exchanges.
Foreign issuers must file forms with the SEC in a similar fashion to domestic companies to provide investors with accurate and up-to-date information. Form F-6 , for instance, is a regulatory document that all investment firms must register with the SEC if they wish to offer ADRs, while Form F-4 supports the registration of securities involving foreign private issuers in connection with exchange offers and business combinations.
What Are SEC Filings?
SEC Filings are regulatory documents that companies and issuers of securities must submit to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) on a regular basis. The purpose is to provide transparency and information to investors, analysts, and regulators.
How Do I Look Up SEC Filings?
SEC forms are filed through a system known as EDGAR (Electronic Data Gathering, Analysis, and Retrieval system). EDGAR performs automated collection, validation, indexing, acceptance, and forwarding of submissions by companies and others required by law to file forms with the SEC. Information on EDGAR can be found on the SEC's website , where you can search through forms as well as familiarize yourself with the system using its EDGAR tutorial .
You may also be able to find SEC filings using your online brokerage platform or a financial portal such as Google Finance.
How Do I Print out SEC Filings?
Filings pulled from EDGAR can be printed directly from your web browser.
Are SEC Filings Public Information?
Yes, SEC filings are public information and can be retrieved for free via the EDGAR system online. Companies may also host their own copies on their corporate websites and would be available from their investor relations department.
Note that in special circumstances, a company may request that certain information be redacted from their otherwise public filings. A confidential treatment application or confidential treatment request (CTR) is a form filled out in accordance with a company's SEC Forms 8-K, 10-Q, or 10-K report. It allows for information in the SEC filing to be kept secret or redacted on public documents, if leaking such information could cause material or financial harm to the company or a business partner.
SEC filings provide transparency and crucial information for individual and institutional investors, for analysts & researchers, and for regulators. Ultimately, the SEC wants the public to know the facts so they can make well-informed decisions about when to buy, sell, or hold a company's securities. Obtaining the available material and interpreting it correctly can provide any investor with valuable guidance when making investment decisions.
Understanding the information submitted by companies through SEC filings involves reading between the lines . Review several SEC documents together to better understand the overall picture, especially with financial forms, and read them in a way that maximizes efficiency . Financial ratios are often used to identify a company's short- and long-term financial strength. Red flags are often revealed in a company's footnotes. Red flags include a very confusing section(s) in a 10-K or 10-Q, sudden one-time or special charges, or a large degree of insider selling.
Securities and Exchange Commission Historical Society. " 431 Days: Joseph P. Kennedy and the Creation of the SEC (1934-35) ."
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " What We Do ."
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " Filing Review Process ."
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " What is a registration statement? "
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " Form 10-K ."
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " Proxy Statement ."
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " How to Read a 10-K ."
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " Form 10-K General Instructions ," Pages 8-11.
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " Form 10-Q ."
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " Form 8-K ."
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " Forms 3, 4, 5 ."
Legal Information Institute, Cornell Law School. " 17 CFR Sec. 240.13d-101 - Schedule 13D - Information to be included in statements filed pursuant to Sec. 240.13d-1(a) and amendments thereto filed pursuant to Sec. 240.13d-2(a) ."
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " Form 144 ."
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " SEC Votes to Modernize Disclosure Requirements to Help U.S. Investors in Foreign Companies ."
Securities and Exchange Commission. " About EDGAR ."
Securities and Exchange Commission. " How Do I Use EDGAR? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/10-K--f7185a10d5d342c68235646bd3ceefcd.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
- Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
Advertisement
[ ri- pawrt , - pohrt ]
a report on the peace conference;
a medical report on the patient.
Synonyms: story , description
Synonyms: dispatch , bulletin
- a widely circulated statement or item of news; rumor; gossip.
- an account of a speech, debate, meeting, etc., especially as taken down for publication.
the report of a distant cannon.
Synonyms: detonation , shot
- a statement of a student's grades, level of achievement, or academic standing for or during a prescribed period of time.
- Computers. output, especially printed, containing organized information.
- a statement of a judicial opinion or decision, or of a case argued and determined in a court of justice.
- reports, Law. a collection of adjudications.
a man of bad report.
verb (used with object)
Synonyms: relay
to report a deficit.
The committee reported out the bill.
I intend to report him to the dean for cheating.
Synonyms: accuse
to report a ship missing.
- to present (oneself ) to a person in authority, as in accordance with requirements.
- to take down (a speech, lecture, etc.) in writing.
- to write an account of (an event, situation, etc.), as for publication in a newspaper.
Synonyms: repeat , detail , describe , recount , rehearse , narrate
verb (used without object)
- to prepare, make, or submit a report of something observed, investigated, or the like.
- to serve or work as a reporter , as for a newspaper.
to report sick.
to report to Room 101.
/ rɪˈpɔːt /
- an account prepared for the benefit of others, esp one that provides information obtained through investigation and published in a newspaper or broadcast
according to report, he is not dead
a report of parliamentary proceedings
- a statement on the progress, academic achievement, etc, of each child in a school, written by teachers and sent to the parents or guardian annually or each term
- a written account of a case decided at law, giving the main points of the argument on each side, the court's findings, and the decision reached
he is of good report here
- a sharp loud noise, esp one made by a gun
- to give an account (of); describe
to report on housing conditions
- (of a committee, legislative body, etc) to make a formal report on (a bill)
I'll report you to the teacher
- tr to reveal information about (a fugitive, escaped prisoner, etc) esp concerning his whereabouts
report to the manager's office
to report fit
the plant manager reports to the production controller
- intr to act as a reporter for a newspaper or for radio or television
- law to take down in writing details of (the proceedings of a court of law) as a record or for publication
Discover More
Derived forms.
- reˈportable , adjective
Other Words From
- re·porta·ble adjective
- nonre·porta·ble adjective
- nonre·ported adjective
- over·re·port verb
- prere·port noun verb
- quasi-re·ported adjective
- subre·port noun
- unre·porta·ble adjective
- unre·ported adjective
- well-re·ported adjective
Word History and Origins
Origin of report 1
Idioms and Phrases
- on report , Military. (of personnel) under restriction pending disciplinary action.
Example Sentences
Developing and manufacturing vaccines, which are significant challenges in their own right, “won’t end the pandemic quickly unless we also deliver them equitably,” the report notes.
Separately, Yelp released a new local economic impact report this week.
He based his report on information from NSA leaker Edward Snowden.
More importantly, notice that more than 70% of my impression volume comes from search terms that are not in the search query performance report.
Of the report’s 11 recommendations, the first highlighted safety.
Then add in all bored people, as well as people whose job it is to report on celebrities.
Despite the strong language, however, the neither the JPO nor Lockheed could dispute a single fact in either Daily Beast report.
Did he go to the authorities to file a report against the Guerreros Unidos drug cartel?
The Amazon biography for an author named Papa Faal mentions both Gambia and lists a military record that matches the FBI report.
Similarly, a recent NPR report covered the challenges many police departments are having recruiting officers of color.
Most of my observations are in keeping with Skutch's detailed report of the species in Central America.
Aguinaldo withheld his decision until Paterno could report to him the definite opinions of his generals.
William has thus been happily able to report to the society the approaching conversion of M'Bongo and his imminent civilization.
At last the report of several rifles from the island of trees gave us a clue to the mystery.
Mrs. Charmington hastened to spread the report that his Royal Highness was seriously smitten.
Related Words
- account for
More About Report
What is a basic definition of report .
A report is a detailed account of something based on observation and research. Report is also used to mean to relay information or to appear at a destination as ordered. The word report has many other senses as a noun and a verb.
A report is a paper, article, announcement, or similar account that contains detailed information that someone has gathered through observation, study, or other research. Sometimes, another noun is used with report to specify what the report is about. For example, students often write book reports in school in which they analyze books they have read.
- Real-life examples : Businesses often create budget reports so they can figure out how much money they have to spend. Scientists compile scientific reports in which they present the results of experiments. Sports journalists often compile injury reports that list all of the players who will miss games due to injuries.
- Used in a sentence : I listened to the weather report on the news to see if I needed to bring an umbrella.
As a verb, report means to repeat or relay information that a person has heard from another source or has gathered themselves. People who report things (such as at a news agency) are called reporters .
- Real-life examples : A journalist’s job is to report information to the public. A spy’s job is to gather secret information and report it to their boss. Scientists will report things they have learned to scientific journals or to the news media.
- Used in a sentence : The tabloid magazine reported sightings of Bigfoot in the woods.
Report is also used to mean to go to a specific place because you were ordered to.
- Used in a sentence : General Harris ordered the recruits to report to basic training in the morning.
Where does report come from?
The first records of the verb report come from around 1325. It ultimately comes from the Latin reportāre , meaning to carry. The first records of the noun report come from around 1425. It comes from the Middle French report .
Did you know ... ?
What are some other forms related to report ?
- reporter (noun)
- reportable (adjective)
- nonreportable (adjective)
- nonreported (adjective)
- overreport (verb)
- prereport (verb, noun)
- quasi-reported (adjective)
- subreport (noun)
- unreportable (adjective)
- unreported (adjective)
- well-reported (adjective)
What are some synonyms for report ?
What are some words that share a root or word element with report ?
- report card
What are some words that often get used in discussing report ?
How is report used in real life?
Report is a very common word that often means a detailed account or to disclose information.
In a new report, the International Criminal Court confirmed a reasonable basis to believe that crimes against humanity have been committed in the Philippines under President Rodrigo Duterte’s merciless war on drugs https://t.co/MgWt69WUIm — New York Times World (@nytimesworld) December 15, 2020
Over 500 people have been hospitalized and at least one person killed by an unidentified illness in southern India. People have suddenly started to convulse. Nausea and loss of consciousness have been reported. Experts are still baffled by the cause. https://t.co/nmJ2XwPmNZ — The Associated Press (@AP) December 8, 2020
After today, I'll be awaiting the call to report to basic training! — Jake Wetherell (@Wetherell4cast) February 2, 2014
Try using report !
Which of the following is NOT a synonym of report ?
A. detail B. broadcast C. hide D. disclose
Definitions and idiom definitions from Dictionary.com Unabridged, based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, © Random House, Inc. 2023
Idioms from The American Heritage® Idioms Dictionary copyright © 2002, 2001, 1995 by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Official Writing
- Report Writing
How to Write a Report
Last Updated: March 15, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA and by wikiHow staff writer, Amy Bobinger . Emily Listmann is a private tutor in San Carlos, California. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. There are 22 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 8,736,889 times.
When you’re assigned to write a report, it can seem like an intimidating process. Fortunately, if you pay close attention to the report prompt, choose a subject you like, and give yourself plenty of time to research your topic, you might actually find that it’s not so bad. After you gather your research and organize it into an outline, all that’s left is to write out your paragraphs and proofread your paper before you hand it in!
Easy Steps to Write a Report
- Choose an interesting topic and narrow it down to a specific idea.
- Take notes as you research your topic. Come up with a thesis, or main theme of your report, based on your research.
- Outline the main ideas you’ll cover in your report. Then, write the first draft.
Sample Reports

Selecting Your Topic

- The guidelines will also typically tell you the requirements for the structure and format of your report.
- If you have any questions about the assignment, speak up as soon as possible. That way, you don’t start working on the report, only to find out you have to start over because you misunderstood the report prompt.

- For instance, if your report is supposed to be on a historical figure, you might choose someone you find really interesting, like the first woman to be governor of a state in the U.S., or the man who invented Silly Putty.
- If your report is about information technology , you could gather information about the use of computers to store, retrieve, transmit, and manipulate data or information.
- Even if you don’t have the option to choose your topic, you can often find something in your research that you find interesting. If your assignment is to give a report on the historical events of the 1960s in America, for example, you could focus your report on the way popular music reflected the events that occurred during that time.
Tip: Always get approval from your teacher or boss on the topic you choose before you start working on the report!

- If you’re not sure what to write about at first, pick a larger topic, then narrow it down as you start researching.
- For instance, if you wanted to do your report on World Fairs, then you realize that there are way too many of them to talk about, you might choose one specific world fair, such as the Panama-Pacific International Exposition, to focus on.
- However, you wouldn’t necessarily want to narrow it down to something too specific, like “Food at the Panama-Pacific International Exposition,” since it could be hard to find sources on the subject without just listing a lot of recipes.
Researching the Report

- If you don’t have guidelines on how many sources to use, try to find 1-2 reputable sources for each page of the report.
- Sources can be divided into primary sources, like original written works, court records, and interviews, and secondary sources, like reference books and reviews.
- Databases, abstracts, and indexes are considered tertiary sources, and can be used to help you find primary and secondary sources for your report. [5] X Research source
- If you’re writing a business report , you may be given some supplementary materials, such as market research or sales reports, or you may need to compile this information yourself. [6] X Research source

- Librarians are an excellent resource when you're working on a report. They can help you find books, articles, and other credible sources.
- Often, a teacher will limit how many online sources you can use. If you find most of the information you need in the library, you can then use your online sources for details that you couldn’t find anywhere else.
Tip: Writing a report can take longer than you think! Don't put off your research until the last minute , or it will be obvious that you didn't put much effort into the assignment.

- Examples of authoritative online sources include government websites, articles written by known experts, and publications in peer-reviewed journals that have been published online.

- If you’re using a book as one of your sources, check the very back few pages. That’s often where an author will list the sources they used for their book.

- Remember to number each page of your notes, so you don’t get confused later about what information came from which source!
- Remember, you’ll need to cite any information that you use in your report; however, exactly how you do this will depend on the format that was assigned to you.

- For most reports, your thesis statement should not contain your own opinions. However, if you're writing a persuasive report, the thesis should contain an argument that you will have to prove in the body of the essay.
- An example of a straightforward report thesis (Thesis 1) would be: “The three main halls of the Panama-Pacific International Exposition were filled with modern creations of the day and were an excellent representation of the innovative spirit of the Progressive era.”
- A thesis for a persuasive report (Thesis 2) might say: “The Panama-Pacific International Exposition was intended as a celebration of the Progressive spirit, but actually harbored a deep racism and principle of white supremacy that most visitors chose to ignore or celebrate.”

- The purpose of an outline is to help you to visualize how your essay will look. You can create a straightforward list or make a concept map , depending on what makes the most sense to you.
- Try to organize the information from your notes so it flows together logically. For instance, it can be helpful to try to group together related items, like important events from a person’s childhood, education, and career, if you’re writing a biographical report.
- Example main ideas for Thesis 1: Exhibits at the Court of the Universe, Exhibits at the Court of the Four Seasons, Exhibits at the Court of Abundance.
Tip: It can help to create your outline on a computer in case you change your mind as you’re moving information around.
Writing the First Draft

- Try to follow any formatting instructions to the letter. If there aren't any, opt for something classic, like 12-point Times New Roman or Arial font, double-spaced lines, and 1 in (2.5 cm) margins all around.
- You'll usually need to include a bibliography at the end of the report that lists any sources you used. You may also need a title page , which should include the title of the report, your name, the date, and the person who requested the report.
- For some types of reports, you may also need to include a table of contents and an abstract or summary that briefly sums up what you’ve written. It’s typically easier to write these after you’ve finished your first draft. [14] X Research source

- Example Intro for Thesis 1: “The Panama-Pacific International Exposition (PPIE) of 1915 was intended to celebrate both the creation of the Panama Canal, and the technological advancements achieved at the turn of the century. The three main halls of the PPIE were filled with modern creations of the day and were an excellent representation of the innovative spirit of the Progressive era.”

- Typically, you should present the most important or compelling information first.
- Example topic sentence for Thesis 1: At the PPIE, the Court of the Universe was the heart of the exposition and represented the greatest achievements of man, as well as the meeting of the East and the West.
Tip: Assume that your reader knows little to nothing about the subject. Support your facts with plenty of details and include definitions if you use technical terms or jargon in the paper.

- Paraphrasing means restating the original author's ideas in your own words. On the other hand, a direct quote means using the exact words from the original source in quotation marks, with the author cited.
- For the topic sentence listed above about the Court of the Universe, the body paragraph should go on to list the different exhibits found at the exhibit, as well as proving how the Court represented the meeting of the East and West.
- Use your sources to support your topic, but don't plagiarize . Always restate the information in your own words. In most cases, you'll get in serious trouble if you just copy from your sources word-for-word. Also, be sure to cite each source as you use it, according to the formatting guidelines you were given. [18] X Research source

- Your commentary needs to be at least 1-2 sentences long. For a longer report, you may write more sentences for each piece of commentary.

- Avoid presenting any new information in the conclusion. You don’t want this to be a “Gotcha!” moment. Instead, it should be a strong summary of everything you’ve already told the reader.
Revising Your Report

- A good question to ask yourself is, “If I were someone reading this report for the first time, would I feel like I understood the topic after I finished reading?
Tip: If you have time before the deadline, set the report aside for a few days . Then, come back and read it again. This can help you catch errors you might otherwise have missed.

- Try reading the report to yourself out loud. Hearing the words can help you catch awkward language or run-on sentences you might not catch by reading it silently.

- This is a great trick to find spelling errors or grammatical mistakes that your eye would otherwise just scan over.

- Ask your helper questions like, “Do you understand what I am saying in my report?” “Is there anything you think I should take out or add?” And “Is there anything you would change?”

- If you have any questions about the assignment requirements, ask your instructor. It's important to know how they'll be grading your assignment.
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libguides.reading.ac.uk/reports/writing-up
- ↑ https://emory.libanswers.com/faq/44525
- ↑ https://opentextbc.ca/writingforsuccess/chapter/chapter-7-sources-choosing-the-right-ones/
- ↑ https://libguides.merrimack.edu/research_help/Sources
- ↑ https://www.wgtn.ac.nz/__data/assets/pdf_file/0010/1779625/VBS-Report-Writing-Guide-2017.pdf
- ↑ https://www.library.illinois.edu/hpnl/tutorials/primary-sources/
- ↑ https://libguides.scu.edu.au/harvard/secondary-sources
- ↑ https://learningcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/taking-notes-while-reading/
- ↑ https://wts.indiana.edu/writing-guides/how-to-write-a-thesis-statement.html
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/outline
- ↑ https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/engl250oer/chapter/10-4-table-of-contents/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/thesis-statements/
- ↑ https://www.yourdictionary.com/articles/report-writing-format
- ↑ https://www.monash.edu/rlo/assignment-samples/assignment-types/writing-an-essay/writing-body-paragraphs
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/5-most-effective-methods-for-avoiding-plagiarism/
- ↑ https://wts.indiana.edu/writing-guides/using-evidence.html
- ↑ https://www.student.unsw.edu.au/writing-report
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/revising-drafts/
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/grammarpunct/proofreading/
- ↑ https://opentextbc.ca/writingforsuccess/chapter/chapter-12-peer-review-and-final-revisions/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

It can seem really hard to write a report, but it will be easier if you choose an original topic that you're passionate about. Once you've got your topic, do some research on it at the library and online, using reputable sources like encyclopedias, scholarly journals, and government websites. Use your research write a thesis statement that sums up the focus of your paper, then organize your notes into an outline that supports that thesis statement. Finally, expand that outline into paragraph form. Read on for tips from our Education co-author on how to format your report! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
NIYONSENGA J.
Did this article help you?
Bella McKinnon
Mar 10, 2018
Manasseh M.
Mar 20, 2023

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

- Submit Post
- Union Budget 2024
FAQs on Reporting Portal, Form 61A, Form 61B, Form 60 & Form 61
Page Contents
1.1 Reporting Obligation
1.2 forms overview, 1.3 project insight, 1.4 reporting portal, 2.1 registration overview, 2.2 reporting entity users, 2.3 details submission, 2.4 itdrein, 3.1 reporting portal login, 3.2 forgot password, 4.1 adding/deactivating user, 4.2 updating profile details, 4.3 digital signature, 4.4 preliminary response, 4.5 changing password, 5.1 sft reporting obligation, 5.2 sft reporting format, 5.3 preparation of sft using report generation utility, 5.4 preparation of deletion statement, 5.5 validation of sft using report generation utility, 5.6 generation of sft using report generation utility, 5.7 upload of sft through submission utility, 5.8 upload of sft on reporting portal, 5.9 data quality report (dqr), 6.1 sra reporting obligation, 6.2 sra reporting format, 6.3 preparation of sra using report generation utility, 6.4 validation of sra using report generation utility, 6.5 generation of sra using report generation utility, 6.6 upload of sra through submission utility, 6.7 upload of sra on reporting portal, 6.8 data quality report (dqr), 7.1 reporting obligation, 7.2 reporting format, 7.3 preparation of form 61 using report generation utility, 7.4 validation of form 61 using report generation utility, 7.5 generation of form 61 using report generation utility, 7.6 upload of form 61 through submission utility, 7.7 upload of form 61 on reporting portal, 7.8 data quality report (dqr), 8.1 quick reference guides, 8.2 user guides, 8.3 schema guides, 8.4 training tool kit, 9.1 my query/problem is not listed here, 1. overview.
1. Who is a Reporting Entity?
Reporting Entity or Reporting Person is an entity which is required to furnish a Statement of Financial Transaction (in Form 61 A) or Statement of Reportable Account (in Form 61B) with the Income tax Department as per the provisions of section 285BA of the Income-tax Act 1961. Also, Under Rule 114D of IT rules 1962, any entity/person receiving Form 60 is required to report details of Form 60 in Form 61.
2. What are the Reporting Obligations u/s 285BA of the IT Act?
Under the Annual Information Return (AIR) Scheme, which was introduced w.e.f. 01-04-2004, specified entities were required to report notified transactions to ITD. Section 285BA of the IT Act was amended w.e.f. 01-04-2015, and it now requires specified persons to furnish Statement of Financial Transaction or reportable account. Under Rule 114D of IT rules 1962, details of Form 60 are required to be reported in Form 61. Rule 114E mentions the nature and value of transactions which are required to be reported. Rules 114F, 114G and 114H deal with due diligence procedure for identification and reporting of reportable accounts.
3. Is it Mandatory to file NIL Statement?
No. However it is advisable to submit ‘SFT Preliminary Response’.
1. What are different forms relating to third party reporting u/s 285BA?
There are three forms namely Form 61, 61A and 61B.
Form61: Details of Form 60 submitted by transacting parties not having PAN
Form 61A: Statement of financial transactions (SFT)
Form61B: Statement of reportable accounts (SRA)
2. What is Form 61?
As per rule 114B of IT rules 1962, an entity is required to obtain PAN of the transacting party. In case transacting party does not have a PAN, form 60 is to be filled by transacting party. Details of these Forms are to be reported in form 61 for the period 1st October to 31st March by 30th of April and for the period 1st April to 30th of September by 31st of October.
3. What is Form 61A?
As per rule 114E of the IT rules 1962, a Reporting Entity is required to file statement of financial transaction in form 61A. A Reporting Entity has to report in specified SFT reportable transaction of the nature specified in this rule for the relevant financial year on or before 31st of May immediately following the financial year.
4. What is Form 61B?
Requirement of filing form 61B arises for implementation of FATCA (Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act) and CRS (Common Reporting Standard). For this purpose rule 114F, 114G and 114H are to be referred. Briefly, these rules provide for due diligence procedure for identification of reportable accounts. Once a Reporting Entity identifies reportable accounts, information about such accounts is to be filed in form 61B for the calendar year by 31st of May following the end of the calendar year
1. What is Project Insight?
Income tax Department has initiated Project Insight to focus on three goals namely (i) to promote voluntary compliance and deter noncompliance; (ii) to impart confidence that all eligible persons pay appropriate tax; and (iii) to promote fair and judicious tax administration. Under this project, an integrated data warehousing and business intelligence platform is being rolled out in a phased manner. The project also operationalizes two new centres namely Income Tax Transaction Analysis Centre (INTRAC) and Compliance Management Centralized Processing Centre (CMCPC).
2. What is INTRAC?
The Income Tax Transaction Analysis Centre (INTRAC) is the new centre operationalized under Project Insight. INTRAC leverages data analytics for tax administration and performs tasks related to data integration, data processing, data quality monitoring, data warehousing, master data management, data analytics, web/text mining, alert generation, compliance management, enterprise reporting and research support.
3. What is CMCPC?
The Compliance Management Centralized Processing Centre (CMCPC) is the third CPC of Income tax Department operationalized under Project Insight. The Compliance Management Centralized Processing Centre (CMCPC) uses campaign management approach (consisting of emails, SMS, reminders, outbound calls, letters) to support voluntary compliance and resolution of compliance issues of tax payers, tax deductors & reporting entities.
1. What is Reporting Portal?
Reporting Portal is an online facility made available to Reporting entities to register with the Income Tax Department and consequently submit the statements in prescribed format.
2. What are the enhancements in the Reporting Portal over e-filing portal?
The Reporting Portal provides enhancements (over present functionalities on the e-filing portal) in the following aspects:
i. Seamless data processing & quality monitoring
ii. Data encryption for enhanced security
iii. Seamless information exchange with reporting entities
iv. Comprehensive resources module for capacity building
v. Seamless Reporting Entity compliance management
vi. Dedicated helpdesk support
3. How can Reporting Portal be accessed?
Step 1: Enter Reporting Portal URL in web browser: https://report.insight.gov.in
Step 2: Enter valid credentials provided by Income Tax Department
Step 3: Click on Submit
4. What are the basic features of Reporting Portal?
Following are the basic features of Reporting Portal:
i. Registration – Reporting Entities can register with Reporting Portal & can generate ITDREIN.
ii. Addition and Deactivation of Users – Reporting Entity can add/deactivate users from profile section of Reporting Portal.
iii. Reporting Entity Profile Update – Reporting Entity profile can be updated from profile section of Reporting Portal.
iv. Statement Upload – Reporting Entity can upload statements which have been generated and validated against prescribed format through utilities.
v. View Uploaded Statements – Reporting Entity can view uploaded statements.
vi. Correction Statement Upload – Reporting Entity can also upload the correction statements generated as per Data Quality Report.
vii. Preliminary Response Submission – Reporting Entity can submit preliminary response for different SFTs.
viii. Resources – Reporting Entity can download utilities, user guides and training material.
Other functionalities of the Reporting Portal will be rolled out in a phased manner.
5. Who can access the Reporting Portal?
Access to the various web services at Reporting Portal is role based. Principal Officer of the Reporting Entity and others who have been authorized by the principal officer can access the portal and they will be provided a user id and password for login to the Reporting Portal.
2. Registration
1. What is the need to register on Reporting Portal?
Reporting Portal is one of the main components of Project Insight platform to provide a comprehensive interface between Reporting Entities and the Income-tax Department. The Reporting Portal will enable the Reporting Entity to avail the various web services provided by the ITD and also keep track of the status of the various statements uploaded and processed.
2. What are the different categories for Reporting Entities?
There are two set of categories for reporting entities depending upon the form type.
For 61,61A:
M – Mutual Fund
N – NBFC/Nidhi
P – Post Office
R – Reserve Bank of India
S – Securities Market Intermediary
I – Insurer
G – Government
O – Others
C – Co-operative Bank
B – Banking Company
D – Depository
S – Specified Insurance Company
I – Investment Entity
C – Custodial Institution
D – Depository Institution
3. How can a Reporting Entity initiate the registration?
The Principal Contact of the Reporting Entity on e-filing portal will initiate the registration by accessing the Reporting Portal link at e-filing Portal under “My Account” tab. Principal Contact will be redirected to the Reporting Portal for registration. Principal Contact will identify the authorised persons i.e. Principal Officer and Designated Director and enter the basic information required. User ids and passwords will be provided to respective users. They will be able to login on the Reporting Portal using the communicated User id and password.
4. What are the steps in registration?
Step 1: Principal Contact of Reporting Entity logs in to e-filing portal
Step 2: Clicks on Reporting Portal link under “My Account” tab.
Step 3: Select “Form Type” & “Reporting Entity” category
Step 4: Enter Reporting Entity & Other users details
Step 5: Submit the details
For more details refer “Reporting Portal User Guide” in Resources section of Reporting Portal.
5. Can Reporting Entity be registered using both PAN and TAN?
Except Post offices and Property registrar (which do not have a PAN), all other Reporting Entities must register using their PAN. Post offices & Registrar can register using TAN.
6. What is the use of the ‘Manage Principal Officer’ section which appears while logging through e-filing portal?
Manage principal officer section is required in following scenarios –
- In case reporting entity does not have a principal officer, and the principal contact wishes to add a new principal officer.
- In case current principal officer has left the organization and principal contact wishes to change the existing principal officer.
1. Who are the Reporting Entity users?
Principal Officer, Designated director, Nodal officer, Alternate Nodal Officer and other users.
2. Who is the Designated Director and Principal Officer?
As per Explanation 1 to Rule 114E of the Income-Tax Rules, a “Designated Director” means a person designated by the reporting person to ensure overall compliance with the obligations imposed under section 285BA and rules 114B to 114E and includes— (i) the Managing Director or a whole-time Director duly authorised by the Board of Directors if the reporting person is a company; (ii) the managing partner if the reporting person is a partnership firm; (iii)the proprietor if the reporting person is a proprietorship concern; (iv)the managing trustee if the reporting person is a trust; (v) a person or individual, who controls and manages the affairs of the Reporting Entity if the reporting person is, an unincorporated association or, a body of individuals or, any other person. The Designated Director only has the privilege to upload the statement.
“ Principal Officer ” means an officer designated as such by the reporting person.
3. Can Designated Director and Principal Officer be the same person?
Yes. The Principal Contact of the Reporting Entity can assign the role of the Designated Director and Principal Officer to the same person.
4. Who can add/remove users to Reporting Entity?
Only principal officer of reporting entity can add, remove or change other users using the links available in profile section on reporting portal.
5. Are there different roles and privileges for different Reporting Entity users?
Yes. The Roles and privileges will determine the kind of access that will be available to the user.
6. Does reporting entity need to access e-filing portal every time?
Reporting entity need to access e-filing portal only for new registration, managing principal officer and submit preliminary response (in case entity is not registered). Once registration is complete, reporting entity users can directly login to reporting portal.
1. Whether the Reporting Entity details and Reporting Entity users’ details needs to be submitted separately?
No. It is all part of a single registration process.
2. Is it necessary to provide details of all the users at the time of registration?
No. Only Reporting Entity details and Principal Officer details are mandatory at the time of registration to obtain ITDREIN. Other users can be added from the profile section at Reporting Portal later.
1. What is ITDREIN?
ITDREIN is an identification number allotted by the Income Tax Department to a Reporting Entity for reporting on reportable transaction of a specified type. A Reporting Entity may have more than one ITDREIN for each type of reporting obligation.
2. What is the format of ITDREIN?
The ITDREIN is a system generated 16-character identification number in the format XXXXXXXXXX.YZNNN where
XXXXXXXXXX → PAN or TAN of the Reporting Entity
Y → Code of Form Code
Z → Code of Reporting Entity Category for the Form Code
NNN → Sequence number.
3. How many ITDREINs can a Reporting Entity obtain?
For each unique combination of Form Type and reporting entity category, a unique ITDREIN could be generated.
4. How to obtain ITDREIN?
Once the registration application for a particular form type and Reporting Entity category is processed and accepted by the Income-tax Department, the system will generate the ITDREIN and communicate the same to the Reporting Entity.
1. Who can log into Reporting Portal?
Users who have been registered as Reporting Entity Users and have obtained a user ID and password after registration can log into the Reporting Portal with the login details.
2. What are the credentials required to login to Reporting Portal?
The User ID required is the PAN of the registered user who is logging into the reporting portal. Please note that the user cannot log in using PAN of a reporting entity. The PAN of the individual user must be entered while logging in.
1. How can user retrieve forgotten password?
User can retrieve password by following methods:
1. OTP Based
a. Over Email
b. Over SMS
2. Answer Security Question
For details, please refer “Reporting Portal User Guide.”
4. Reporting Entity & User Profile
1. Who can add/deactivate Reporting Entity users?
Principal Officer can Add or Deactivate other users.
2. How can users be added to Reporting Entity?
Step 1: Login to Reporting Portal
Step 2: Go to “Profile” Section
Step 3: Select “Manage Users”
Step 4: Click on “Add Users”
Step 5: Enter User details
Step 6: Click on Submit
3. How to deactivate any user?
Step 4: Select the check box corresponding to the sub-user to be deactivated.
Step 5: Click on deactivate user button.
It is mandatory to have at least one active user (Principal Officer) in Reporting Entity. However, for uploading statements, existence of Designated Director is mandatory.
For more details, refer “Reporting Portal User Guide” in Resources section of Reporting Portal.
4. Can “Principal Officer” be deactivated?
There has to be one active member at least with the Reporting Entity. Principal Officer can deactivate other members. However to change the Principal officer, the Principal Contact of Reporting Entity will need to:
Step 1: Log in to e-filing portal
Step 2: Go to “My Account” tab and click on “Reporting Portal” link
Step 3: User will be redirected to “Reporting Portal”
Step 4: Select “Manage Principal Officer” option and click on “Continue”.
1. Can principal officer update profile of all the users?
No. The Principal Officer cannot update the profile of other users. However, Principal Officer will approve the profile change request by other users.
2. Who can update the Reporting Entity details?
Principal officer can update the Reporting Entity details (Address & Contact Details). However information under the basic details tab cannot be changed.
3. Will Reporting Entity users’ profile change go for verification to income tax Department?
No. These changes need to be approved by Principal Officer only.
4. How can principal officer approve the changes made by other users?
Step 1: Reporting Entity User logs in to Reporting Portal
Step 2: User selects “Profile” section
Step 3: User selects “Manage Approval” section
Step 4: User will have list view of pending request for approval
Step 5: User can do bulk approval by providing comments in text box given
Step 6: User clicks on “Status” button to view the request detail page
Step 7: User can approve/reject request by providing reason in given text box.
1. What is Digital Signature?
As per Explanation to sub-rule 4(a) of Rule 114E, “Digital Signature” means a digital signature issued by any Certifying Authority authorised to issue such certificates by the Controller of Certifying Authorities. Please refer section “Upload of SFT through Submission Utility” for more details on digital certificate.
2. Whose digital signature is required to sign the XML?
The form is required to be submitted using a Digital Signature Certificate of the Designated Director who will register it from profile section of Reporting Portal upon successful registration.
1. What is Preliminary Response and how is it relevant to Reporting Entities?
Preliminary response can be submitted by the reporting entities to indicate whether they have liability to file SFTs for current financial year. Reporting Entity may select any of the following option for each SFT code:
– Yes (Liable to file statement and having reportable transactions)
– Nil Transactions (No transaction to report)
– Not Applicable (Not liable to file statement)
2. Can both types of Reporting Entities, registered & unregistered submit Preliminary Response?
3. How can Reporting Entities submit Preliminary Response?
Following Steps to be followed to submit Preliminary Response (In case entity is not registered):
1. Login to e-filing portal
2. Select “My Account”
3. Go to “Reporting Portal”
4. Select “Submit Preliminary Response” from option displayed
5. Select relevant response from drop down in front of each SFT
Registered Reporting Entities need to submit Preliminary Response through “Profile” section of Reporting Portal.
Please refer “Reporting Portal User Guide” for more details.
4. For which reporting period, reporting entities can submit preliminary response?
Reporting entities can submit the preliminary response for last financial year. For example currently reporting entity need to submit preliminary response for financial year 2017-18.
1. Does a user require different passwords for different ITDREIN?
No. There would be a single user id (PAN of that user) and password for a user for different ITDREIN. At the time of login user will be asked for which ITDREIN it wishes to proceed.
2. If a user changes the password for one profile, will it be automatically changed for other profiles for the same entity but different ITDREINs?
3. What are the steps to change the password?
Step 2: Selects “Profile” section
Step 3: Selects “Change Password” section
Step 4: Enters current password
Step 5: Enters new password
Step 6: Confirms new password
Step 7: Submits the details
5. Statement of Financial Transactions (Form 61A)
1. What is the legal framework for reporting Statement of Financial Transactions (SFT)?
Section 285BA of the Income Tax requires specified reporting persons to furnish statement of financial transaction. Rule 114E of the Income Tax Rules, 1962 specifies that the statement of financial transaction required to be furnished under sub-section (1) of section 285BA of the Act shall be furnished in Form No. 61A.
2. Who is required to file Statement of Financial Transactions (SFT)?
As per Rule 114E, following persons are required to furnish statement of financial transactions registered or recorded or maintained by them during a financial year to the prescribed authority.
- Any person who is liable for audit under section 44AB of the Income –tax Act
- A Banking Company
- A Co-operative Bank
- Post Master General of Post office
- A Nidhi referred to in sec 406 of the Companies Act 2013
- A Non-banking Financial Company (NBFC)
- Any Institution issuing Credit Card
- A Company or Institution issuing bonds or debentures
- A Company issuing shares
- A company listed on a recognised stock exchange purchasing its own securities
- A Trustee of a Mutual Fund or such other person authorized by the trustee
- Authorized Dealer, Money Changer, Off-shore Banking Unit or any other person defined in FEMA, 1999
- Inspector-General or Sub-Registrar appointed under Registration Act, 1908
3. What is the periodicity and due date of furnishing statement of financial transaction?
The statement of financial transactions (online return in Form No. 61A with digital signature) shall be furnished on or before 31st of May, immediately following the financial year in which the transaction is registered or recorded. Section 285BA (5) empower the tax authorities to issue a notice to a person who is required to furnish a statement as above and who has not filed the statement within prescribed time, requiring person to furnish the statement within a period not exceeding 30 days from the date of service of such notice and in such case, the person shall furnish the statement within the time as specified in the notice.
4. How can an entity comply with reporting obligation?
To comply with reporting obligation, the statements need to be filed by all reporting entities in a prescribed format and within prescribed timeline.
5. Who needs to file SFT – 013?
Any person whether proprietary concern (Individual) or any other entity liable for Audit Under section 44AB need to file SFT – 013 (Cash payment for goods and services). Please note that No Aggregation of transactions is to be done.
6. What are the consequences of not furnishing statement of financial transactions or reportable accounts?
Failure to furnish statement of financial transaction or reportable account will attract a penalty under section 271FA at the rate of one hundred rupees for every day during which such failure continues.
As per provisions of section 285BA(5), the prescribed Income-tax authorities may issue a notice to a person who is required to furnish such statement and has not furnished the same in the prescribed time, directing person to file the statement within a period not exceeding 30 days from the date of service of such notice and in such case, the person shall furnish the statement within the time specified in the notice.
If such person fails to file the statement within the specified time then a penalty of Rs. 500 for every day for which the failure continues, may be levied from the day immediately following the day on which the time specified in such notice for furnishing the statement expires.
7. What are the consequences of Failure to correct Inaccurate or defective statement of financial transaction or reportable account filed?
As per section 271FAA of the Income-tax Act, if a person who is required to furnish statement of financial transaction or reportable account, provides inaccurate information in the statement, and where:
(a) the inaccuracy is due to a failure to comply with the due diligence requirement prescribed under section 285BA(7) or is deliberate on the part of that person;
(b) the person knows of the inaccuracy at the time of furnishing the statement but does not inform the prescribed income-tax authority or such other authority or agency;
(c) the person discovers the inaccuracy after the statement is furnished and fails to inform and furnish correct information within a period of 10 days as specified under section 285BA(6),
Then, the prescribed income-tax authority may direct that such person shall pay, by way of penalty, a sum of fifty thousand rupees.
1. What is prescribed format for statement of financial transaction (SFT)?
All statements uploaded to the Reporting Portal should be in the XML format consistent with the prescribed schema published by the Income-tax Department. The Reporting entities may use the utilities provided by the Income-tax Department or third party utilities for preparation of XML file. For more details refer “Report Generation Utility User Guides” available in “Resources” section of Reporting Portal.
2. What is a Statement?
A Statement is the file which contains many reports containing details of financial transactions (SFT) (Form 61A). A statement may contain multiple reports.
3. How to identify reportable transactions under SFT?
The first step in preparation of Statement of Financial Transactions (SFT) is to identify transactions/persons/accounts which are reportable under Rule 114E. In the second step, the reporting person/entity is required to submit details of transactions/persons/accounts which are determined as reportable.
4. What is aggregation rule?
Aggregation rule needs to be applied for specified transaction types to identify transactions/persons/accounts which are reportable. Rule 114E specifies that the reporting person shall, while aggregating the amounts for determining the threshold amount for reporting in respect of any person –
(a) take into account all the accounts of the same nature maintained in respect of that person during the financial year;
(b) aggregate all the transactions of the same nature recorded in respect of that person during the financial year;
(c) attribute the entire value of the transaction or the aggregated value of all the transactions to all the persons, in a case where the account is maintained or transaction is recorded in the name of more than one person;
The aggregation rule is applicable for all transaction types except SFT- 012 (Purchase or sale of immovable property) and SFT- 013 (Cash payment for goods and services).
5. What are different parts of Form 61A?
Form 61A has two parts. Part A which contains statement level information is common to all transaction types. The report level information has to be reported in one of the following parts (depending of the transaction type):
- Part B (Person Based Reporting)
- Part C (Account Based Reporting)
- Part D (Immovable Property Transaction Reporting)
6. What is Person Based Reporting (Part B)?
Part B shall be used for person based reporting which is relevant to following transactions:
- SFT- 001: Purchase of bank drafts or pay orders in cash
- SFT- 002: Purchase of pre-paid instruments in cash
- SFT- 005: Time deposit
- SFT- 006: Payment for credit card
- SFT- 007: Purchase of debentures
- SFT- 008: Purchase of shares
- SFT- 009: Buy back of shares
- SFT- 010: Purchase of mutual fund units
- SFT- 011: Purchase of foreign currency
- SFT- 013: Cash payment for goods and services
For determining reportable persons and transactions, the reporting person/entity is required to aggregate all the transactions of the same nature recorded in respect of the person during the financial year (refer to the applicability of aggregation rule). In a case, where the transaction is recorded in the name of more than one person, the reporting person/entity should attribute the entire value of the transaction or the aggregated value of all the transactions to all the persons.
The reporting person/entity is required to submit details of persons and transactions which are determined as reportable. The reporting format also enables reporting person/entity to furnish information relating to each individual product within a product type. E.g: if a person has multiple credit cards and the aggregate value of the transactions in all credit cards exceeds the threshold value, the aggregate transaction value will be reported in section B3 of form 61 A and the transactions pertaining to individual credit cards can be reported in section B4 of form 61 A.
7. What is Account Based Reporting (Part C)
Part C shall be used for account based reporting which is relevant to following transactions:
- SFT- 003: Cash deposit in current account
- SFT- 004: Cash deposit in account other than current account
- SFT- 014: Cash deposits during specified period (9th Nov to 30th Dec, 2016).
For determining reportable persons and accounts, the reporting person/entity is required to take into account all the accounts of the same nature maintained in respect of that person during the financial year and aggregate all the transactions of the same nature recorded in respect of the person during the financial year (refer to the applicability of aggregation rule). In a case where the account is maintained in the name of more than one person, the reporting person/entity should attribute the entire value of the transaction or the aggregated value of all the transactions to all the persons. In case of SFT- 003 (Cash deposit or withdrawals in current account), the threshold limit has to be applied separately to deposits and withdrawals in respect of transactions. After identification of reportable persons and accounts, the reporting person/entity is required to submit details of accounts which are determined as reportable. Part C3 of the form 61 A has details of the accounts that need to be reported along with the aggregate transaction values. Aggregation of transaction has the same definition as explained in person based accounting.
8. What is Immovable Property Transaction Reporting (Part D)?
Part D shall be used for reporting of purchase or sale of immovable property (SFT- 012). The reportable immovable property transactions have to be determined by applying the threshold limit. The reporting person/entity is required to submit specified details of immovable property transactions which are determined as reportable.
9. What are different Statement types?
One Statement can contain only one type of Statement. Permissible values for type of Statement are:
- NB – New Statement containing new information
- CB – Correction Statement containing corrections for previously submitted information
- DB – Deletion Statement for deletion of previously submitted information
- ND – No Data to report
10. What is the difference between Statement Number and Statement ID?
Statement Number is a free text field capturing the sender’s unique identifying number (created by the sender) that identifies the particular Statement being sent. The identifier allows both the sender and receiver to identify the specific Statement later if questions or corrections arise. After successful submission of the Statement to ITD, a new unique Statement ID will be allotted for future reference. The reporting person/entity should maintain the linkage between the Statement Number and Statement ID. In case the correction statement is filed, statement ID of the original Statement which is being corrected should be mentioned in the element ‘Original Statement ID’. In case the Statement is new and unrelated to any previous Statement, ‘0’ will be mentioned in the element ‘Original Statement ID’.
11. What is original statement Id?
Statement ID of the original Statement which is being replaced deleted or referred by reports in the current Statement. In case the Statement is new and unrelated to any previous Statement, mention ‘0’ here.
12. What is Report Serial Number?
The Report Serial Number uniquely represents a report within a Statement. The Report Serial Number should be unique within the Statement. This number along with Statement ID will uniquely identify any report received by ITD. In case of correction, the complete report has to be resubmitted. The Report Serial Number of the original report that has to be replaced or deleted should be mentioned in the element ‘Original Report Serial Number’. This number along with Original Statement ID will uniquely identify the report which is being corrected. In case there is no correction of any report, ‘0’ will be mentioned in the element ‘Original Report Serial Number’.
13. What is Original Report Serial Number?
The Report Serial Number of the original report that has to be replaced or deleted. This number along with Original Statement ID will uniquely identify the report which is being corrected. In case there is no correction of any report, mention ‘0’ here.
14. What needs to be captured in Form 61 Acknowledgement No.?
If reporting person/entity has received declarations in Form 60 in respect of transactions listed in Rule 114E, Form 61 is required to be furnished to ITD. As mentioned in Chapter I, on successful loading of Form 61 (containing the particulars of Form 60), an Acknowledgement No. would be generated which has to be mentioned at the time of filling Form 61A. Hence, unless Form 61 has been furnished, Reporting person/entity may face difficulty in filling Form 61A. Accordingly, it is to be ensured that Form 61 is furnished to the Department before Form 61A is filled.
1. What is a Report Generation Utility?
Report Generation Utility is a desktop utility based on java. The utility enables user to generate and validate XML file which is to be submitted to Income-tax Department.
2. How to download and install the Report Generation Utility on a windows platform?
The Report Generation Utility can be downloaded from “Resources” section of the Reporting Portal. The downloaded zip file has to be extracted using WinZip or Win RAR tools.
3. Is any other software required to be installed to use Report Generation Utility?
Yes. Report Generation Utility requires JRE to run on Windows based operating system. Download and install JRE version 1.8 Update 101 or later.
4. How to run the Report Generation Utility?
Step 1: Unzip the downloaded utility
Step 2: Click on Form61A.jar file to run the utility.
5. How to Export CSV from the Utility?
Steps to import CSV are:
1. Open 61A utility
2. Select relevant SFT Code
3. Go to Reports Details or Account Details
4. Export CSV and Save
For any further assistance please refer to the “Report Generation Utility Guide-61A” under “Resources” section of reporting portal.
6. How to prepare a statement using Report Generation Utility?
Step 1: Go to Reporting Portal at https://report.insight.gov.in
Step 2: Download Report Generation Utility from “Resources” section
Step 3: Select the Transaction Type (for Form 61A) on Instructions window
Step 4: Capture Statement Details and other relevant details depending upon the form type
For more details refer “Report Generation Utility User Guides” in Resources section of Reporting Portal.
7. How to capture data in the Report Generation Utility?
Data can be captured either by data entry or by importing CSV.
8. How to load an existing XML file?
9. Select the saved XML file using the Open button from the tool bar.
10. What date format should be used while filling CSV?
User should use DD-MM-YYYY format while entering data in CSV. If date is entered in incorrect format, the CSV will not be imported successfully.
11. Can data be saved before generating the XML file in Report Generation Utility?
Yes. User can save the data using the “Save” button in the tool bar. The data is saved with a draft extension. To retrieve the saved data in the utility, use the “Open” button from the tool bar.
12. How to capture information for an account with more than one account holder?
For an account with more than one account holder, a user needs to enter multiple record rows, where account details (including “Report Serial Number”) will be repeated for each account holder. The utility will automatically create reports with unique Report Serial Number.
13. How to view information after importing CSV?
After successful CSV import, data is visible in the relevant tabs of the utility.
14. If corrections have to be made only to a statement, keeping reports unchanged, should the reports also be submitted along with the corrected statement?
No, if there are issues in Part A of the Statement, you do not need to submit the reports. In this case, the Number of Reports field will be set to 0.
15. Form 61A was uploaded with Statement type “ND” and a DQR issue was reported on it afterwards. But some reportable data pertaining to this statement was received later. What should be the status of the already issued DQR in this case?
The DQR issued on ND will be closed. However, a new DQR can be generated on the data received later.
16. If the Reporting Entity wants to delete/correct the statement or report details that were wrongly reported, what is the corrective procedure?
Separate facility to delete any report is not provided in the purview of Form 61A reporting. If Reporting Entities wants to correct any statement or report uploaded earlier, they must select “CB” as the Statement type and submit the modified/ updated statement/ report.
1. What is deletion statement? Why it is required?
Reporting entities has been provided with a facility to delete previously submitted reports due to any of the following reasons:
- Deleting Reports as they were not required to be reported
- Deleting Reports as they are already reported in other / same statement (Duplicate reporting)
Reporting entities need to prepare a deletion statement which will consist of the reports to be deleted in original statement.
2. Which statement to be referred while deleting reports?
Original Statement should be referred while deleting the reports.
3. What are the steps to prepare deletion statement in report generation utility?
Step by step process to prepare deletion statement (DB) is as follows:
1. Click on “Open” button to populate original statement XML in the utility.
2. Click the Statement (Part A) tab.
3. From the Statement Type drop-down list, select DB – Deletion Statement for deletion of Mention the statement ID of the original Statement in the Original Statement ID field from which the reports are being deleted.
4. Mention the statement ID of the original Statement in the Original Statement ID field from which the reports are being deleted.
5. Deletion statement should contain only those reports which are to be deleted from original statement. Reports which are not to be deleted from original statement should be removed from populated XML in utility.
6. Select row and click on “Delete Row” to remove report from the utility.
7. Copy the “Report Serial Number” and paste it in “Original Report Serial Number” field for all the reports to be deleted.
8. As the final step, click Generate XML on the toolbar to generate the deletion statement’s XML.
4. Whether Data Quality Report (DQR) will be generated on Deletion Reports also?
System will reject the reports in deletion statement if the attributes provided in the deletion report do not match with the original reports’ attributes. Same shall be communicated to reporting entity in data quality report. Reporting entities need to file a new deletion statement for rejected reports as mentioned in DQR.
5. Is partial deletion allowed for already submitted reports?
Yes, Partial deletion is allowed for already submitted reports. Deletion statement should contain only those reports which are to be deleted from original statement. Reports which are not to be deleted from original statement should be removed from populated XML in utility.
1. What is the purpose of Statement Validation?
Validation is a process of applying the data input rules to ensure that the data is in the prescribed format. Errors in data entry will be highlighted during the process of validation.
2. How can a statement be validated?
Step 1: Click on “Validate” button on the tool bar
Step 2: Utility will display validation errors on “Validation” Tab
Step 3: Click on Validation row to see details of Validation errors on the right window pane of screen
Step 4: Click on any particular validation error from list, utility will show the field highlighted in red, where corrections can be made
Step 5: Fix the errors and then click on Validate button again
Step 6: If there are no validation errors, “Validation Successful” dialog box is displayed to the user. In addition, certain validations will be applied by the Income Tax Department at their end.
3. Is it mandatory to validate the statement?
Yes. Otherwise, statements with validation errors will be rejected in data quality check.
4. What are various types of validation errors?
The errors have been classified as mandatory errors, defects and exceptions.
5. What are mandatory errors?
Mandatory errors need to be resolved by user for successful generation of XML report. These are generally schema level errors. For resolving these type of errors, the data filled should be as per the Form 61A schema validation.
6. What are defects?
Defects can be Statement level defects or Report level Defects. Statement Defects are those which render the Statement (Part A) defective. Such Statements will be rejected and the Reporting Entity needs to resubmit the statement. Report defects are those which render a particular report(s) (Part B/C/D) as defective in the statement. A statement may have multiple reports and only reports with defects would be rejected. The Reporting Entity needs to correct and submit the reports again in the corrected statement.
7. What are exceptions?
Exceptions do not result in the statement/report being rejected. The exceptions should be reviewed by the reporting person/entities and if any information is available, the Reporting Entity may provide the information.
8. How to identify validation errors?
When user clicks on the validate button, validation summary is displayed in the Validation Error tab. On selecting a particular row on the validation error screen, error details are displayed on the section on the right side. On selecting the error, user is directed towards the erroneous field on the screen.
9. How to rectify validation errors?
User can navigate to erroneous fields via Validation Error Details section on the right side of the screen. Erroneous fields are highlighted in Red and are editable for user to correct.
1. How to generate and save the statements?
Step 1: Click on Generate XML button on the toolbar.
Step 2: If there are no validation errors, user needs to provide the path to save generated XML.
2. What is the extension of generated XML file?
Generated XML file should have ‘.xml’ extension.
1. How to download submission utility?
The submission utility can be downloaded from “Resources” section of the Reporting Portal. The downloaded zip file has to be extracted using WinZip or WinRAR tools.
2. Is any other software required to be installed to use Report Generation Utility?
Yes. Submission utility requires JRE to run on Windows based operating system. Download and install JRE version 1.8 Update 101 or later.
3. How to run submission utility?
Step 2: Click on Submission_Utility.jar file to run the utility.
4. What is digital signature?
A digital signature is an electronic form of a signature that helps in authenticating the identity of the sender of a message or the signer of a document. It also ensures that the message being sent is not modified by an unauthorized party. Digital signatures are easily transportable and cannot be imitated by someone else.
5. How to view and save the digital signature certificate?
To view and save a digital signature certificate, perform the following steps:
Step 1: Open Internet Explorer
Step 2: Go to Settings >> Internet Options
Step 3: On the Internet Options pop-up, select the tab Content and then click the button Certificates
Step 4: A list of certificates is displayed on a new pop-up. Select the required certificate and click the Export button . Select the location where you want to save the certificate.
Step 5: The Certificate export wizard opens. Click Next to continue on the subsequent screens.
Step 6: On completing the wizard, Export Successful message is displayed.
Step 7: To sign a statement using the exported certificate, use the Submission Utility.
6. What are the steps to digitally sign the generated XML using submission utility?
Step 1. Go to “Secure XML” tab in submission utility
Step 2. Browse statement XML
Step 3. Click on “Generate Package” button (DSC should be connected to the system through USB while generating package)
Step 4. Select the certificate displayed in insight signer window
Step 5. Click on “Sign”
Step 6. Enter the password
Step 7. Save the package
7. What is the extension of digitally signed package?
Digitally signed package shall be saved as “.tar.gz” extension.
8. Can digital signature certificate be copied?
A Digital Signature Certificate cannot be used without having a private key. The private key should always be password-protected and not to be shared over a network.
9. If a reporting entity does not have a digital signature, does this mean it cannot file the statement?
It is mandatory to digitally sign the XML else at the time of upload system will throw an error.
10. Who is the signatory authority for signing the statement XML? Statement XML has to be signed by designated director’s DSC.
11. Which class of DSC should be used while signing the XML?
DSC should be of Class II or III only, issued by CCA approved certifying agencies in India.
12. Is it mandatory to sign the statement XML with the same digital certificate which has been registered with ITD?
Yes, Registered digital certificate and the certificate with which statement XML is being signed should be same otherwise system will throw an error at the time of statement upload.
13. What are the steps to submit the statement through submission utility?
Step 1: Go to “Statement >> Statement Upload” tab in submission utility
Step 2: Enter user name and password
Step 3: Select the form type to be uploaded and enter “ITDREIN”
Step 4: Select SFT code (Only for form type 61A), “Reporting Period Ending On” & “Type of Filing”
Step 5: Enter original statement id (only in case correction statement is being filed)
Step 6: Attach the report and Click on “Validate”
Step 7: If no manifest error displayed, “Upload” button will be displayed.
Step 8: Click on “Upload”
14. Can DQR be downloaded through submission utility?
Yes, DQR can be downloaded through submission utility
1. What are the steps to submit a Form 61A statement at reporting portal?
Step 1: Once statement XML is generated, sign and encrypt the XML using the Submission utility and prepare secure statement package to be uploaded (Refer submission utility user guide).
Step 2: Go to “Upload Statement” section under “Statement” tab
Step 3: Fill out the “Upload Statement” form (Depending upon Form 61, 61A, or 61B; the fields may differ)
Step 4: Select the “Filing Type” from drop down
Step 7: If no manifest error is shown, Click on displayed “Upload” button
Step 8: Upon successful submission, an email with “Acknowledgment Number” will be sent to the registered email id.
For more details, refer “Report Generation User Guide-61A”, “Reporting Portal User Guide” in Resources section of Reporting Portal.
2. Who can submit the statement?
Only Designated Director of Reporting Entity can submit the statement.
3. What are the different manifest level errors which should be taken care of at the time of statement upload?
Following manifest level errors should be checked and rectified at the time of statement upload:
1. ITDREIN should be valid and must be in correct format.
2. Selected form type should match with the actually prepared form (61,61A or 61B).
3. Reporting Period mentioned in statement XML should match with reporting period as selected in upload form.
4. Filing type selected in upload form should match with filing type prepared statement.
5. In case correction statement is being filed, reference of the “Original Statement Id” must be provided.
6. In case statement type is “ND”, value of “Number of Reports” field should be 0.
7. In case statement type is “NB”, value of “Number of Reports” field should not be 0.
Please refer “Report Generation Utility User Guide” for more details about manifest, file and record level validations errors.
4. What are the different file level errors which should be taken care of at the time of statement upload?
Following file level errors should be checked and rectified at the time of statement upload:
1. XML file should be properly decrypted using digital certificate
2. XML file must be signed by valid digital signature which should be registered with ITD
3. XML file should be free of any threats
4. XML file should be free from any viruses
5. XML file should be as per the form 61A schema guide (refer Schema validation section)
1. What is Data Quality Report (DQR)?
The Data Quality Report contains details of the data quality errors present in the statement submitted by the Reporting Entity. DQR helps Reporting Entity(s) in identifying the errors in data submitted.
2. Why is Data Quality Report (DQR) required?
The report cannot be considered accurate if there are data quality errors. It is mandatory for Reporting Entities to file accurate reports in the prescribed formats as per law. Failure to comply with the provisions of law may attract penal provisions.
3. What should be Reporting Entity’s next course of action after receiving DQR?
Step 1: Download the DQR from Reporting Portal.
Step 2: Correct the statement for removal of Data quality errors using the offline utility as mentioned in DQR
Step 3: Validate and submit the correction statement.
Step 4: Upon successful submission, an email with “Acknowledgment Number” will be sent to the registered email id.
Step 5: Download the data quality report, if any.
Step 6: Repeat steps 1 to 5 till there are no more data quality errors.
Kindly refer “SFT Report Generation User Guide-Form-61A” for detail process of generating correction statement.
4. What is RRC?
RRC stands for Report Requiring Correction. It is a field that will display the number of reports which are yet to be rectified in original statement. RRC field and count can be viewed under “Statements Pending for Correction” tab on reporting portal. Reporting entity need to ensure to reduce RRC (Report Requiring Correction) count to zero by rectifying all the defective reports.
5. What is Incorrect ITDREIN (40010)?
Issue Description – Incorrect ITDREIN (40010) is the issue raised when ITDREIN in the statement does not match with the ITDREIN mentioned while uploading the statement.
Action required – Please submit the statement using the correct ITDREIN.
6. What is Incorrect Form Name (40020)?
Issue Description – Incorrect Form Name (40020) is the issue raised when Incorrect Form name is entered while uploading the statement.
Action required – Please submit the statement with Form Name as Form 61A.
7. What is Incorrect Original Statement ID for CB (40030)?
Issue Description – Incorrect Original Statement ID for CB (40030) is the issue raised when the original statement ID mentioned in the correction statement (CB) does not match with the statement ID of original statement (NB).
Action required – Please submit the statement with correct original statement ID
8. What is Incorrect Original Statement ID for DB (40031)?
This issue is raised when The original statement ID mentioned in the Deletion statement (DB) does not match with the statement ID of original statement (NB).
9. What is Inconsistent Statement Type ND for submitted reports (40040)?
This issue is raised when Statement type is “ND” for a statement where number of reports is greater than 0
10. What is Inconsistent Statement Type NB for nil reports (40041)?
This issue is raised when Statement type is “NB” for a statement where number of reports is 0
11. What is Inconsistent Statement Type (40042)?
This issue is raised when the statement type selected while uploading the statement does not match with the statement type mentioned in the statement.
12. What is Inconsistent Original Statement ID for new statement (40050)?
This issue is raised when Original statement ID is not 0 for a new statement (NB).
13. What is Inconsistent Original Statement ID for No Data statement (40051)?
This issue is raised when Original statement ID is not 0 for a new statement with no data to report (ND).
14. What is Inconsistent Reason for correction for NB (40060)?
This issue is raised when Reason for correction is other than “N” (Not applicable) for the Statement type “NB”
15. What is Inconsistent Reason for correction for ND (40061)?
This issue is raised when Reason for correction is other than “N” (Not applicable) for the Statement type “ND”
16. What is Inconsistent Reason for correction for CB (40062)?
This issue is raised when Reason for correction is “N” (Not applicable) for the Statement type “CB”
17. What is Inconsistent Reason for correction for DB (40063)?
This issue is raised when Reason for correction is other than “N” (Not applicable) for the Statement type “DB”
18. What is Inconsistent Reporting Period for NB & ND (40070)?
This issue is raised when The Reporting Period mentioned in statement does not relate to Reporting Period selected on Portal while uploading the statement.
19. What is Inconsistent Reporting Period for CB (40071)?
This issue is raised when the reporting period in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement) does not match with the reporting period of the original statement (Statement Type “NB”).
20. What is Inconsistent Reporting Period for DB (40073)?
This issue is raised when the reporting period in Deletion statement (DB) does not match with the reporting period of the original statement (NB).
21. What is Inconsistent SFT code for CB (40080)?
This issue is raised when the SFT Code in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement) does not match with the SFT Code of the original statement (Statement Type “NB”).
22. What is Inconsistent SFT code for DB (40081)?
This issue is raised when the SFT Code in Statement Type “DB” (Deletion statement) does not match with the SFT Code of the original statement (Statement Type “NB”).
23. What is Inconsistent SFT code (40082)?
This issue is raised when the SFT Code selected while uploading the statement does not match with the SFT code mentioned in the statement.
24. What is Inconsistent Report type – AF (40090)?
This issue is raised when the Report type “AF” does not match with the SFT code of the submitted statement.
25. What is Inconsistent Report type – BA (40091)?
This issue is raised when the Report type “BA” does not match with the SFT code of the submitted statement.
26. What is Inconsistent Report type – IM (40092)?
This issue is raised when the Report type “IM” does not match with the SFT code of the submitted statement
27. What is Failed Decryption (50002)?
The file received from reporting portal is decrypted
28. What is Failed Decompression (50003)
Decompressing the received file to its original form.
29. What is Failed Signature Check (50004)?
The digital signature on the received file is validated.
30. What is Failed Threat Scan (50005)?
The received file should be free of any threats
31. What is Failed Virus scan (50006)?
The received file should be free from any viruses.
32. What is Failed Schema Validation (50007)?
The received file should be as per the form 61A schema guide (refer Schema validation section).
33. What is Signature not Uploaded (50021)?
The user has not uploaded the digital signature certificate file on the Reporting portal.
34. What is Signature Expired (50022)?
The digital signature certificate has been expired.
35. What is Failed Original Report Serial Number in CB (61A_98000)?
Failed Original Report Serial Number in CB (61A_98000) is the issue raised when Original Report Serial Number for Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement) does not match with the report serial number as mentioned in the Original Statement (Statement Type “NB”) submitted earlier.
36. What is Failed Original Report Serial Number in DB (61A_98002)?
This issue is raised when Original Report Serial Number for Statement Type “DB” (Deletion Statement) does not match with the report serial number as mentioned in the Original Statement (Statement Type “NB”) submitted earlier.
37. What is Failed Original Report Serial Number in CB after Deletion (61A_98003)?
This issue is raised when Original Report Serial Number mentioned in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement) corresponds to the report already deleted.
38. What is Blank Customer ID (61A_98010)?
This issue is raised when Customer ID is not provided for reports filed under SFT-003, SFT-004, SFT-005, SFT-006, SFT-010, SFT-011 and SFT-014. It may be provided, if available.
39. What is Blank Father’s Name for individual without PAN (61A_98020)?
This issue is raised when Father’s Name is blank and PAN is not provided. Father’s Name is mandatory if PAN is not provided.
40. What is No PAN (61A_98030)?
This issue is raised when PAN not provided for person who has neither submitted Form 60 or who is exempted under Rule 114B. This defect can be resolved by either providing PAN or selecting person type as IE, HE, LE or GO (as applicable) or by providing the Form 60 acknowledgement number.
41. What is Invalid PAN (61A_98031)?
This issue is raised when there is Invalid PAN (not in valid format/ does not match with the PAN database)
PAN should be of format: CCCCCNNNNC; where C denotes the alphabets and N is numeric.
This defect can be resolved by either providing correct PAN or selecting person type as IE, HE, LE or GO (as applicable) or by providing Form 60 acknowledgement number.
42. What is Modified PAN (61A_98032)?
This issue is raised when Valid PAN/ PAN(s) has been changed (added/deleted) in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement). The modification in PAN may be verified and if it was not intended, correction statement may be filed again.
43. What is Duplicate PAN in person based reporting (61A_98033)?
This issue is raised when details for same PAN (B.2.6) is reported more than once in same statement. As “Part B” relates to Person based reporting, the information has to be aggregated at PAN level. Presence of duplicate PAN in Part B is considered as duplicate reporting.
44. What is Invalid Aadhaar Number (61A_98040)?
This issue is raised when there is Invalid Aadhaar Number format (12 digits).
45. What is Wrong Aadhaar Number ((61A_98041)?
This issue is raised when Wrong Aadhaar Number is provided
46. What is Failed Form 60 Acknowledgment Number for no PAN case (61A_98050)?
This issue is raised when Form 60 acknowledgement number is not provided for the cases where Person Type is selected as “IE” (Individual without PAN which has submitted Form 60 or who is exempted under Rule 114B) or “HE” (HUF without PAN which has submitted Form 60).
47. What is Failed Identification Type for no PAN case (61A_98060)?
This issue is raised when Identification type is not provided and PAN is also not provided.
48. What is Failed Identification Number for no PAN case (61A_98061)?
This issue is raised when Identification number is not provided and PAN is also not provided.
49. What is Failed DOB/DOI for no PAN case (61A_98070)?
This issue is raised when Date of birth/ incorporation is blank and PAN is not provided.
50. What is Failed Date of Birth Range (61A_98072)?
This issue is raised when Date of birth is not in valid range (for individual) and PAN is not provided/ Invalid PAN provided.
Valid date of birth range = from 01.01.1900 to end of reporting period.
51. What is Failed Address type (61A_98090)?
This issue is raised when No value/ incorrect value is reported in “Address Type”.
52. What is Invalid Postal code – India (61A_98092)?
This issue is raised when Invalid postal code is provided when country selected is India.
53. What is Wrong Postal code – India (61A_98093)?
This issue is raised when Wrong postal code is provided when country selected is India. Pin code provided should be linked to state and locality.
54. What is Insufficient Address (61A_98094)?
This issue is raised when Address appears to be Insufficient /incomplete.
55. What is Failed Mobile No – India (61A_98100)?
This issue is raised when Incorrect mobile number format is provided when country selected is India. It should be 10 digit mobile Number and should start from 5, 6, 7, 8 or 9
56. What is Failed Mobile No – Outside India (61A_98101)?
This issue is raised when Incorrect mobile number format is provided when country selected is outside India. Maximum 15 digits are allowed.
57. What is Failed Contact details (61A_98102)?
This issue is raised when No Contact details are provided
58. What is Failed Product type (61A_98110)?
This issue is raised when Details related to Product type are not provided.
59. What is Inconsistent Product type (61A_98111)?
Product type is not consistent with the SFT Code.
BD – Bonds or Debentures (SFT-007)
CC- Credit Card (SFT-006)
DD – Bank draft or pay order or banker’s cheque (SFT-001)
PI – Prepaid Instrument (SFT-002)
FC – Foreign Currency sale (SFT-011)
MF – Mutual Fund (SFT-010)
SI – Shares issued (SFT-008)
SB – Shares bought back (SFT-009)
TD – Time Deposit (SFT-005)
ZZ – Others (SFT-013)
XX – Unspecified (SFT-013)
60. What is Failed reporting of aggregate gross amount received from the person (61A_98120)?
This issue is raised when No data is reported for the field “Aggregate gross amount received from the person”.
61. What is Aggregate gross amount received is less than amount received in cash (61A_98121)?
This issue is raised when Aggregate gross amount received from the person (B.3.2) is less than Aggregate gross amount received from the person in cash (B.3.3).
62. What is Aggregate gross amount received is less than product level aggregation (61A_98122)?
This issue is raised when “Aggregate gross amount received from the person” (B.3.2) is less than the sum of “Aggregate gross amount received from the person” (B.4.3).
63. What is Exceptional gross amount received from the person (61A_98123)?
This issue is raised when Amount reported is greater than 100 crores
64. What is Modification in aggregate gross amount received from the person (61A_98124)?
This issue is raised when “Aggregate gross amount received from the person” has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement).
65. What is Failed reporting of aggregate gross amount received from the person in cash (61A_98130)?
This issue is raised when No data is reported for the field “Aggregate gross amount received from the person in cash”.
66. What is Aggregate gross amount received in cash is less than product level aggregation (61A_98131)?
This issue is raised when “Aggregate gross amount received from the person in cash” (B.3.3) is less than the sum of “Aggregate gross amount received from the person in cash” (B.4.4).
67. What is Exceptional gross amount received from the person in cash (61A_98132)?
This issue is raised when Amount reported is greater than 100 crores.
68. What is Modification in aggregate gross amount received from the person in cash (61A_98133)?
This issue is raised when “Aggregate gross amount received from the person in cash” has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement).
69. What is Aggregate gross amount paid is less than product level aggregation (61A_98140)?
This issue is raised when “Aggregate gross amount paid to the person” (B.3.4) is less than the sum of “Aggregate gross amount paid to the person (B.4.5)”
70. What is Exceptional gross amount paid to the person (61A_98141)?
71. What is Modification in aggregate gross amount paid to the person (61A_98142)?
This issue is raised when “Aggregate gross amount paid to the person” has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement).
72. What is Truncated Account Number (61A_98160)?
This issue is raised when Account Number is less than 4 digits
73. What is Invalid Account Number (61A_98161)?
This issue is raised when Account Number contains invalid character (‘E+’)
74. What is Modification in Account Number (61A_98162)?
This issue is raised when Account number has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (correction statement).
75. What is Duplicate Account Reporting (Part C) (61A_98170)?
This issue is raised when Details for same account (Same Branch Reference Number (C.2.5) + Account Number (C.2.2)) is reported more than once in same statement. This indicates duplicate reporting of account
76. What is Failed Branch Address (61A_98180)?
This issue is raised when Branch Address is not provided.
77. What is Failed aggregate gross amount credited to the account in cash (61A_98190)?
This issue is raised when No data reported for the field “Aggregate gross amount credited to the account in cash”.
78. What is Aggregate gross amount credited to the account in cash is less than part period amount (61A_98191)?
This issue is raised when Aggregate gross amount credited to the account in cash (C.3.1) is less than Total of Aggregate gross amount credited to the account in cash from 1st day of April, 2016 to 8th November, 2016 (C.3.3) and Aggregate gross amount credited to the account in cash from 9th day of November, 2016 to 30th day of December, 2016 (C.3.4).
79. What is Exceptional aggregate amount credited in cash – Current account (61A_98192)?
This issue is raised when Amount reported is greater than 1000 crore for Account type “BC” (Current Account).
80. What is Exceptional aggregate amount credited in cash- Other than current account (61A_98193)?
This issue is raised when Amount reported is greater than 100 crore for Account type other than “BC” (Current Account).
81. What is Modification of gross amount credited to the account in cash (61A_98194)?
This issue is raised when Aggregate gross amount credited to the account in cash has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement).
82. What is Exceptional aggregate amount debited in cash – Current account (61A_98200)?
83. What is Exceptional aggregate amount debited in cash – Other than current account (61A_98201)?
84. What is Exceptional aggregate amount credited pre demonetization – Current account (61A_98210)?
85. What is Exceptional aggregate amount credited pre demonetization – Other than current account (61A_98211)?
86. What is Exceptional aggregate amount credited post demonetization – Current account (61A_98220)?
87. What is Exceptional aggregate amount credited post demonetization – Other than current account (61A_98221)?
This issue is raised when Amount reported is greater than 100 crore (Account type is other than “BC” (Current Account).
88. What is No First/Sole Account Holder (61A_98230)?
This issue is raised when No person reported as “F” – (First/Sole Account Holder) under account relationship (C.4.1).
89. What is Nil Transaction Amount (61A_98250)?
This issue is raised when Transaction Amount (D.2.4) is NIL.
90. What is Low Transaction Amount (61A_98251)?
This issue is raised when Maximum of Transaction Amount (D.2.4) & Stamp Value (D.2.12) is less than 30 lakh.
91. What is Exceptional Transaction Amount (61 A_98252)?
This issue is raised when Transaction Amount (D.2.4) is more than 1000 crore.
92. What is Inconsistent Aggregated Transaction Amount – Seller (61A_98253)?
This issue is raised when Transaction Amount (D.2.4) is not equal to the sum of Transaction Amount related to the person (D.3.2) for Transaction Relation “S” (Seller/Transferor).
93. What is Inconsistent Aggregated Transaction Amount – Buyer (61A_98254)?
This issue is raised when Transaction Amount (D.2.4) is not equal to the sum of Transaction Amount related to the person (D.3.2) for Transaction Relation “B” (Buyer/Transferee).
94. What is Modified Transaction Amount (61A_98255)?
This issue is raised when Transaction Amount (D.2.4) has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (correction statement).
95. What is Blank Property address (61A_98260)?
This issue is raised when Property address is not provided
96. What is Insufficient Property address (61A_98261)?
This issue is raised when Property address appears to be insufficient.
97. What is Failed Seller/Transferor Transaction relation (61A_98270)?
This issue is raised when No person reported with Transaction relation “S” (Seller/Transferor) under transaction relation (D.3.1).
98. What is No Buyer/Transferee (61A_98280)?
This issue is raised when No person reported with Transaction relation “B” – (Buyer/Transferee) under transaction relation (D.3.1).
99. What is Nil transaction amount related to seller (61A_98290)?
This issue is raised when Nil Transaction Amount related to the person (D.3.2) where transaction relation is “S” (Seller/Transferor).
100. What is Nil transaction amount related to Buyer (61A_98291)?
This issue is raised when Nil Transaction Amount related to the person (D.3.2) where transaction relation is “B” (Buyer/Transferee).
6. Statement of Reportable Accounts (SRA) (Form 61B)
1. What is FATCA?
In 2010, USA enacted a law known as “Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act” (FATCA) with the objective of tackling tax evasion through obtaining information in respect of offshore financial accounts maintained by USA Residents and citizens The provisions of FATCA essentially provide for 30% withholding tax on US source payments made to Foreign Financial Institutions unless they enter into an agreement with the Internal Revenue Service (US IRS) to provide information about the accounts held with them by US persons or entities (Companies/ Firms/ Trusts) controlled by US persons.
2. What is Inter Governmental Agreement (IGA) between India and US?
The IGA between India and USA was signed on 9th July, 2015. It provides that the Indian Financial Institutions will provide necessary information to the Indian tax authorities, which will then be transmitted to USA periodically. USA will also provide substantial information about Indians having assets in USA.
3. What are new Global Standards (Common Reporting Standards, CRS) on Automatic Exchange of Information?
To combat the problem of offshore tax evasion and avoidance and stashing of unaccounted money abroad, the G20 and OECD countries worked together to develop a Common Reporting Standard (CRS) on Automatic Exchange of Information (AEOI). The CRS on AEOI requires the financial institutions of the “source” jurisdiction to collect and report information to their tax authorities about account holders “resident” in other countries. The reporting needs to be done for a wide range of financial products, by a wide variety of financial institutions including banks, depository institutions, collective investment vehicles and insurance companies. Such information is to be transmitted automatically on yearly basis.
4. What is the legal framework for reporting Statement of Reportable Accounts (61B)?
With a view to implement the CRS on AEOI and also the IGA with USA, and with a view to provide information to other countries, necessary legislative changes have been made by amending section 285BA of the Income-tax Act, 1961. Income-tax Rules, 1962 were amended by inserting Rules 114F to 114H and Form 61B to provide a legal basis for the Reporting Financial Institutions (RFIs) for maintaining and reporting information about the Reportable Accounts.
5. Who is required to file Statement of Reportable Accounts (61B)?
An entity needs to find out whether it is a reporting financial institution. Thereafter, reporting financial institution needs to review financial accounts held with it by applying due diligence procedure to identify whether any financial account is a reportable account. If any account is identified as a reportable account, the reporting financial institution shall report the relevant information in Form 61B in respect of the identified reportable accounts. For further details, please refer to Third Party Reporting Handbook.
6. Who is a Reporting Financial Institution?
RFI is defined in rule 114F (7) to mean:
- A financial institution which is resident in India, but excludes any branch of such institution that is located outside India, and
- Any branch of financial Institution (other than a non-reporting financial institution) which is not resident in India, if that branch is located in India.
Financial Institutions will not include Non-reporting Financial Institutions even though they satisfy the above conditions.
7. What are the different Financial Institution Categories?
FI Categories: The definition of Financial Institution in rule 114(F) 3 classifies FIs in four different category:
- Custodial Institutions – “Custodial Institution” means any Entity that holds, as a substantial portion of its business, Financial Assets for the account of others. Entities such as central securities depositors (CSDL & NSDL), custodian banks and depositary participants would generally be considered as custodial institutions.
- Depository Institutions – A depository institution is a financial institution (such as a savings bank, commercial bank, savings and loan associations, or credit unions) that is legally allowed to accept monetary deposits from consumers in the ordinary course of a banking or similar business.
- Investment Entities – Entity’s primary business consists of trading in money market instruments, foreign exchange, exchange, interest rate & index instruments, transferable securities or individual & collective portfolio management, investing, administering or managing financial asset or money for or on behalf of a customer’.
- Specified Insurance Companies – “Specified Insurance Company” means any Entity that is an insurance company (or the holding company of an insurance company) that issues, or is obligated to make payments with respect to, a Cash Value Insurance Contract or an Annuity Contract.
- Others – A Financial Institution not falling under any of the category as mentioned above.
8. What are the Reporting Financial Accounts?
A financial account is an account maintained by a financial institution and includes specific categories of accounts as discussed in Rule 114F(1). There are broadly five types of financial accounts:
Depository Accounts: “Depository Account” includes any commercial, checking, savings, time, or thrift account, or an account that is evidenced by a certificate of deposit, thrift certificate, investment certificate, certificate of indebtedness, or other similar instrument maintained by a Financial Institution in the ordinary course of a banking or similar business.
Custodial Accounts: The term custodial account means an arrangement for holding a financial instrument, contract, or investment (including, but not limited to, a share of stock in a corporation, a note, bond, debenture, or other evidence of indebtedness, a currency or commodity transaction, a credit default swap, a swap based upon a nonfinancial index, a notional principal contract as defined an insurance or annuity contract, and any option or other derivative instrument) for the benefit of another person.
Equity and Debt Interest: Equity and debt interests are financial accounts if they are interests in an investment entity e.g. a capital or profits interest in a firm and any interest held by any person treated as a settlor or beneficiary of all or a portion of the trust. Where an entity is an investment entity solely because it acts on behalf of a customer by investing, managing or administering Financial Assets in the name of the customer, the debt and equity interest in the investment entity are not Financial Assets provided it renders only investment advice to, or manages portfolios for, the customer.
Cash Value Insurance Contracts: Insurance contract means a contract under which issuer agrees to pay an amount upon the occurrence of a Specified contingency involving mortality, morbidity, accident, liability, or property risk. The term “Cash Value Insurance Contract” means an Insurance Contract (other than an indemnity reinsurance contract between two insurance companies) that has a Cash Value greater than US $50,000 at any time during the calendar year.
Annuity Contracts: Annuity contract means a contract under which the issuer agrees to make payments for a period of time determined in whole or in part by reference to the life expectancy of one or more individuals.
9. What is a Reportable Account?
A reportable accounts means an account which has been identified pursuant to the due diligence procedure, as held by:
- A reportable person
- An entity, not based in USA, with one or more controlling person that is a specified controlling person.
- A passive non-financial entity with one or more controlling persons that is a person described in sub-clause (b) of clause (8) of the rule 114F.
10. Who is a reportable person?
Reportable person has been defined in the Rule 114F(8) and means:-
- One or more specified US persons; or
- A corporation the stock of which is regularly traded on one or more established securities markets;
- Any corporation that is a related entity of a corporation described in item (i);
- A Governmental entity;
- An International organization;
- A Central Bank; or
- A financial institution
That is resident of any country or territory outside India (except United States of America) under the tax laws of such country or territory or an estate of a dependent that was a resident of any country or territory outside India (except US) under the tax laws of such country or territory.
Thus, generally speaking, there are two types of reportable persons. First one has been defined specifically for USA. Second one is for other countries.
11. Who is a US person?
US person means,
a) An individual, being a citizen or resident of USA
b) A partnership or corporation organized in the USA or under the laws of the USA or any state thereof;
c) A trust if;
a. A court within the USA would have authority to render orders or judgments on issues regarding administration of the trust; or
b. One or more US persons have the authority to control all substantial decisions of the trust; or
d) An estate of a descendent who was a citizen or resident of the USA.
12. What is the due diligence procedure?
The RFIs need to identify the reportable accounts for reporting in form 61B by carrying out due diligence procedures. There are different due diligence procedures for the accounts held by individuals and accounts held by entities.
For more details please refer separate document “Guidance-Note-For-FATCA-and-CRS-31.12.2015.pdf, Page 28”.
13. Whether any aggregation rules are applicable while identifying reportable accounts?
For the purpose of determining the aggregate balance or value of financial accounts held by an individual or entity, a reporting financial institution shall be required to take into account all financial accounts which are maintained by it, or by a related entity, but only to the extent that the computerized systems of that reporting financial institution links the financial accounts by reference to a data element such as client number or taxpayer identification number and allows account balances or values to be aggregated.
For the purpose of determining the aggregate balance or value of financial accounts held by a person to determine whether a financial account is a high value account, a reporting FI shall also be required, in the case of any financial accounts that a relationship manager knows, or has reason to know, are directly or indirectly owned, controlled or established by the same person, to aggregate all such accounts.
14. How are joint accounts to be reported?
Where a Financial Account is jointly held, the balance or value to be reported in respect of the Reportable Person is the entire balance or value of the account. The entire balance or value should be attributed to each holder of the account.
15. Who is a related entity?
Related entity is defined in Explanation (E) to section 114F(6). An entity is a “related entity” of another entity if either entity controls the other entity, or the two entities are under common control.
16. How can an entity comply with reporting obligation?
After the RFI has identified the reportable accounts, RFI needs to report specific information in respect of each reportable account as prescribed in Form 61B.
17. Whether trusts are also required to fulfil reporting obligations?
In the case of trusts, two situations may arise:-
- When trust itself is a reporting financial institution; or
- When trust is an NFE that maintains a financial account with a reporting financial institution.
18. What are the consequences of not furnishing statement of financial Accounts?
19. What are the consequences of Failure to correct Inaccurate or defective statement of financial account filed?
(d) the inaccuracy is due to a failure to comply with the due diligence requirement prescribed under section 285BA(7) or is deliberate on the part of that person;
(e) the person knows of the inaccuracy at the time of furnishing the statement but does not inform the prescribed income-tax authority or such other authority or agency;
(f) the person discovers the inaccuracy after the statement is furnished and fails to inform and furnish correct information within a period of 10 days as specified under section 285BA(6),
1. What is prescribed format for Statement of Reportable Accounts (61B)??
2. What is ITDREIN?
3. What is the format of ITDREIN?
The ITDREIN is a 16-character identification number in the format XXXXXXXXXX.YZNNN where XXXXXXXXXX – PAN or TAN of the Reporting Entity
Y → Code of Form Code
NNN →- Sequence number.
4. How many ITDREINs can a Reporting Entity obtain?
A Reporting Entity needs to have separate ITDREIN for each Form Type. Hence to furnish Form 61, 61A & 61B, Reporting Entity would need to obtain three separate ITDREINs.
5. How can ITDREIN be received?
ITDREIN is a system generated number. Once the registration application is processed and accepted by the Income-tax Department, the system will generate the ITDREIN and communicate the same to the Reporting Entity.
6. What is a Statement?
A Statement is the file which contains many reports containing details of reportable accounts (Form 61B). A statement may contain multiple reports.
7. What are different parts of Form 61B?
Form 61B has two parts. Part A which contains statement level details and Part B which contains Report Details. Part B report details should be provided for each Account being reported.
8. What are different Statement types?
9. What is the difference between Statement Number and Statement ID?
10. What is original statement Id?
11. What is Report Serial Number?
12. What is Original Report Serial Number?
The Report Generation Utility can be downloaded from “Resources” section of the Reporting Portal. The downloaded zip file has to be extracted using WinZip or WinRAR tools.
Step 2: Click on Form61B.jar file to run the utility.
5. How to prepare a statement using Report Generation Utility?
Step 3: Capture Statement Details and other relevant details depending upon the form type
6. How to capture data in the Report Generation Utility?
7. How to load an existing XML file?
8. Select the saved XML file using the Open button from the tool bar.
9. What date format should be used while filling CSV?
10. Can data be saved before generating the XML file in Report Generation Utility?
11. How to capture information for an account with more than one account holder?
12. How to view information after importing CSV?
13. If corrections have to be made only to a statement, keeping reports unchanged, should the reports also be submitted along with the corrected statement?
14. Form 61B was uploaded with Statement type “ND” and a DQR issue was reported on it afterwards. But some reportable data pertaining to this statement was received later. What should be the status of the already issued DQR in this case?
15. If the Reporting Entity wants to delete/correct the statement or report details that were wrongly reported, what is the corrective procedure?
Separate facility to delete any report is not provided in the purview of Form 61B reporting. If Reporting Entities wants to correct any statement or report uploaded earlier, they must select “CB” as the Statement type and submit the modified/ updated statement/ report.
Mandatory errors need to be resolved by user for successful generation of XML report. These are generally schema level errors. For resolving these type of errors, the data filled should be as per the Form 61B schema validation.
Defects can be Statement level defects or Report level Defects. Statement Defects are those which render the Statement (Part A) defective. Such Statements will be rejected and the Reporting Entity needs to resubmit the statement. Report defects are those which render a particular report(s) as defective in the statement. A statement may have multiple reports and only reports with defects would be rejected. The Reporting Entity needs to correct and submit the reports again in the corrected statement.
Exceptions do not result in the statement/report being rejected. The exceptions should be reviewed by the reporting person/entities and if any information is available, the Reporting Entity may provide the information. If any defect is noticed, the Reporting Entity needs to rectify the defect by submitting a correction statement.
9. How to rectify validation errors?
10. Is Global Intermediary Identification Number (GIIN) mandatory for filing of form 61B?
The GIIN is not mandatory at the time of registration of reporting entity, However, it is mandatorily required to be furnished in Part A of the report generation utility for form 61B.
1. How to download submission utility?
Step 4: A list of certificates is displayed on a new pop-up. Select the required certificate and click the Export button. Select the location where you want to save the certificate.
10. Who is the signatory authority for signing the statement XML?
Statement XML has to be signed by designated director’s DSC.
Step 4: “Reporting Period Ending On” & “Type of Filing”
14. Can DQR be downloaded through submission utility?
1. What are the steps to submit a Form 61B statement?
Step 1: Once statement XML is generated, sign and encrypt the XML using the Submission utility and prepare package to be uploaded (Refer submission utility user guide).
For more details, refer “Report Generation Utility User Guide-61B”, “Reporting Portal User Guide” in Resources section of Reporting Portal.
1. ITDREIN should be valid and must be in correct format
2. Selected form type should match with the actually prepared form (61,61A or 61B)
3. Reporting Period mentioned in statement XML should match with reporting period as selected in upload form
4. Filing type selected in upload form should match with filing type prepared statement
5. In case correction statement is being filed, reference of the “Original Statement Id” must be provided
5. XML file should be as per the form 61B schema guide (refer Schema validation section)
Please refer “Report Generation Utility User Guide-61B” for more details about manifest, file and record level validations errors.
5. What should be entered in the fields “Original Statement ID” and “Original Report Serial Number” when filing a Correction Statement?
If you are filing a Correction Statement (either because of a DQ issue raised or suo motu correction), the Original Statement ID and Original Report Serial Number corresponding to the original statement (filed as NB) should be mentioned in the respective fields.
6. What is Incorrect ITDREIN (40010)?
Issue Description – Incorrect ITDREIN (40010) is the issue raised when ITDREIN in the statement does not match with the ITDREIN mentioned on Portal while uploading the statement.
Action Required – Please submit the statement using the correct ITDREIN.
7. What is Incorrect Form Name (40020)?
Issue Description – Incorrect Form Name (40020) is the issue raised when Incorrect Form name entered while uploading the statement.
Action Required – Please submit the statement with Form Name as Form 61B.
8. What is Incorrect Original Statement ID for CB (40030)?
Issue Description- Incorrect Original Statement ID for CB (40030) is the issue raised The original statement ID mentioned in the Statement Type “CB” (Correction statement) does not match with the statement ID of Original Statement (Statement Type “NB”).
Action Required – Please submit the statement with correct original statement ID.
9. What is Incorrect Original Statement ID for DB (40031)?
Issue Description – This issue is raised when the original statement ID mentioned in the Deletion Statement (Statement Type “DB”) does not match with the statement ID of Original Statement (Statement Type “NB”).
10. What is Inconsistent Statement Type ND for submitted reports (40040)?
Issue Description – This issue is raised when Statement type is “ND” (No Data to Report) for a statement where number of reports is greater than 0.
11. What is Inconsistent Statement Type NB for nil reports (40041)?
This issue is raised when Statement Type is “NB” (New Statement) for a statement where number of reports is 0.
12. What is Inconsistent Statement Type (40042)?
This issue is raised when the Statement Type selected while uploading the statement does not match with the Statement Type mentioned in the statement.
13. What is Inconsistent Original Statement ID for new statement (40050)?
This issue is raised when Original statement ID is not 0 for Statement Type “NB” (New Statement).
14. What is Inconsistent Original Statement ID for No Data statement (40051)?
Issue Description – This issue is raised when Original statement ID is not 0 for Statement Type “ND” (No data to report).
15. What is Inconsistent Reason for correction for NB (40060)?
Issue Description – This issue is raised when Reason for correction is other than “N” (Not Applicable) for the Statement type “NB” (New Statement).
16. What is Inconsistent Reason for correction for ND (40061)?
Issue Description – This issue is raised when Reason for correction is other than “N” (Not applicable) for the Statement type “ND” (No Data to Report).
17. What is Inconsistent Reason for correction for CB (40062)?
Issue Description – This issue is raised when Reason for correction is “N” (Not applicable) for the Statement type “CB” (Correction Statement).
18. What is Inconsistent Reason for correction for DB (40063)?
Issue Description – This issue is raised when Reason for correction is other than “N” (Not applicable) for the Statement type “DB” (Deletion Statement).
19. What is Inconsistent Reporting Period for NB (40070)?
Issue Description – This issue is raised when the reporting period mentioned in statement does not relate to the Reporting Period selected on Portal while uploading the statement.
20. What is Inconsistent Reporting Period for CB (40071)?
Issue Description – This issue is raised when the reporting period in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement) does not match with the reporting period of the original statement (Statement Type “NB”).
21. What is Inconsistent Reporting Period for DB (40073)?
Issue Description – This issue is raised when the reporting period in Statement Type “DB” (Deletion Statement) does not match with the reporting period of the original statement (Statement Type “NB”).
22. What is Failed Decryption (50002)?
Validation Description – The file received from reporting portal is decrypted. Action required – Please encrypt the file with a valid key and resubmit the file
23. What is Failed Decompression (50003)?
Validation Description – Decompressing the received file to its original form Action required – Please compress and resubmit the file.
24. What is Failed Signature Check (50004)?
Validation Description – The digital signature on the received file is validated
Action required – Please re-sign the file with the Digital Signature of the Designated Director.
25. What is Failed Threat Scan (50005)?
Validation Description – The received file should be free of any threats.
Action required – Please scan the file for threats and viruses. Remove all detected threats and viruses prior to encryption.
26. What is Failed Virus scan ((50006)?
Validation Description – The received file should be free from any viruses.
Action required – Please scan the file for threats and viruses. Remove all detected threats and viruses prior to encryption
27. What is Failed Schema Validation (50007)?
Validation Description – The received file should be as per the form 61B schema guide (refer Schema validation section).
Action required – Please re-validate the file against the XML Schema, resolve any validation errors.
28. What is Signature not Uploaded (50021)?
Validation Description – The user has not uploaded the digital signature certificate file on the Reporting portal.
Action required – Please upload the digital signature certificate file on the Reporting portal.
29. What is Signature Expired (50022)?
Validation Description – The digital signature certificate has been expired
Action required – Please upload the updated digital signature certificate on the Reporting portal as the existing certificate is expired
30. What is Failed Original Report Serial Number in CB (61B_98000)?
This issue is raised when Original Report Serial Number for Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement) does not match with the report serial number as mentioned in the Original Statement (Statement Type “NB”) submitted earlier.
31. What is Failed Original Report Serial Number in DB (61B_98002)?
This issue is raised when Original Report Serial Number for Statement Type “DB” (Deletion Statement) does not match with the report serial number as mentioned in the Original Statement (Statement Type “NB”) submitted earlier
32. What is Failed Original Report Serial Number in CB after Deletion (61B_98003)?
Original Report Serial Number mentioned in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement) corresponds to the report already deleted
33. What is Truncated Account Number (61B_98160)?
Account Number is less than 4 digits.
34. What is Invalid Account Number (61B_98161)?
Account Number contains invalid character (‘E+’).
35. What is Modification in Account Number (61B_98162)?
Account number has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (correction statement).
36. What is Failed Account structure (61B_60001)?
The Account number mentioned does not follow ISIN Structure. Account number should be in ISIN format when Account Number Type is selected as “03” (International Securities Information Number).
ISIN Format: 12-character alpha-numerical code:
- 2 alphabetic characters, which are the ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code for the issuing country,
- 9 alpha-numeric characters (the National Securities Identifying Number, or NSIN, which identifies the security, padded as necessary with leading zeros), and 1 numerical check digit.
37. What is Impermissible Account Number type (61B_98300)?
Impermissible Account number type “01” (International Bank Account Number) selected by Reporting Entity.
Indian Banks to use “02” (Other Bank Account number) as an option as IBAN is not applicable in case of India.
38. What is Failed Date of closure (61B_98310)?
This issue is raised when Account closure date is not provided when Account Status is “C” (Closed).
39. What is Invalid Postal code – India (61B_98092)?
This issue is raised when Invalid postal code provided when country selected is India.
40. What is Insufficient Address (61B_98094)?
41. What is Invalid Country Code (61B_98095)?
This issue is raised when Country selected in “Branch Details” is other than India.
42. What is Failed Mobile No India (61B_98100)?
This issue is raised when Incorrect mobile number format provided when country selected is India. It should be 10 digit mobile Number and should start from 5, 6, 7, 8 or 9.
43. What is Failed Mobile No – Outside India (61B_98101)?
This issue is raised when Incorrect mobile number format provided when country selected is outside India.
44. What is Failed Branch Contact details (61B_98104)?
This issue is raised when Branch contact details not provided.
45. What is Failed Account balance (61B_60002)?
This issue is raised when “Account balance or value at the end of reporting period” is less than zero.
46. What is Incorrect Account balance (61B_60003)?
This issue is raised when Account balance is other than zero with Account Status is “C” (Closed). Account balance should be zero as
Account is reported as closed.
47. What is Exceptional Account balance (61B_98330)?
48. What is Modification in Account balance (61B_98331)?
This issue is raised when “Account balance or value at the end of reporting period” has been changed in Statement type “CB” (Correction Statement).
49. What is Mismatch in Account Balance (61B_98332)?
This issue is raised when Account balance is not equal to the difference of (Aggregate gross amount credited (B.3.6) and Aggregate gross amount debited (B.3.7)).
50. What is Failed Aggregate gross Interest paid or Credited (61B_98340)?
This issue is raised when “Aggregate gross Interest paid or credited” not reported for Account Category “DA” (Depository Account) or “CA” (Custodial Account).
51. What is Exceptional gross Interest paid or credited (61B_98341)?
52. What is Modification in gross Interest paid or credited (61B_98342)?
This issue is raised when “Aggregate gross Interest paid or credited” has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement).
53. What is Failed Aggregate gross dividend paid or credited (61B_98350)?
This issue is raised when “Aggregate gross dividend paid or credited” not reported for Account category “CA” (Custodial Account).
54. What is Exceptional gross dividend paid or credited (61B_98351)?
55. What is Modification in gross dividend paid or credited (61B_98352)?
This issue is raised when “Aggregate gross dividend paid or credited” has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement).
56. What is Failed Gross proceeds from the sale of property (61B_98360)?
This issue is raised when “Gross proceeds from the sale of property” is not reported for Account category “CA” (Custodial Account).
57. What is Exceptional Gross proceeds from the sale of property (61B_98361)?
58. What is Modification in Gross proceeds from the sale of property (61B_98362)?
This issue is raised when “Gross proceeds from the sale of property” has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement).
59. What is Failed Aggregate gross amount of all other income paid or credited to the account (61B_98370)?
This issue is raised when “Aggregate gross amount of all other income paid or credited to the account” not reported for Account category “CA” (Custodial Account).
60. What is Exceptional gross amount of all other income paid or credited (61B_98371)?
61. What is Modification in gross amount of all other income paid or credited (61B_98372)?
This issue is raised when “Aggregate gross amount of all other income paid or credited to the account” has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement).
62. What is Exceptional gross amount credited (61B_98380)?
63. What is Modification in gross amount credited (61B_98381)?
This issue is raised when “Aggregate gross amount credited” has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement).
64. What is Mismatch in gross amount credited (61B_98382)?
This issue is raised when Aggregate gross amount credited is less than sum of (gross interest paid, (B.3.2) gross dividend paid (B.3.3), gross proceeds from sale of property (B.3.4) and gross amount of all other income (B.3.5)).
65. What is Exceptional gross amount debited (61B_98390)?
66. What is Modification in gross amount debited (61B_98391)?
This issue is raised when “Aggregate gross amount debited” has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement).
67. What is Blank First Name Individual (61B_70002)?
This issue is raised when First Name not provided for Individual Account Holder. Reporting entity can mention “NFN” if it does not have a complete First Name.
68. What is Blank Last Name Individual (61B_70003)?
This issue is raised when Last Name not provided for Individual Account Holder.Reporting entity can mention the full name if it does not have a Last Name
69. What is Incorrect Name Type (61B_60004)?
This issue is raised when Name Type should not be “N1” (SMFAliasOrOther) when Report Type is “02” (Report of other reportable accounts under Rule 114G).
70. What is Blank Father’s Name for individual without PAN (61B_98020)?
71. What is No PAN (61B_98034) ?
This issue is raised when PAN not provided.
72. What is Invalid PAN (61B_98031)?
This issue is raised when Invalid PAN (not in valid format/ does not match with the PAN database) PAN should be of format:
CCCCCNNNNC; where C denotes the alphabets and N is numeric.
73. What is Modified PAN (61B_98032)?
This issue is raised when Valid PAN/PAN(s) has been changed (added/deleted) in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement). The modification in PAN may be verified and if it was not intended, correction statement may be filed again.
74. What is Invalid Aadhaar Number (61B_98040)?
This issue is raised when Invalid Aadhaar Number format (12 digits).
75. What is Wrong Aadhaar Number (61B_98041)?
This issue is raised when Wrong Aadhaar Number.
76. What is Failed Identification Number for no PAN case (61B_70011)?
This issue is raised when Identification number not provided
77. What is Failed DOB/DOI for no PAN case (61B_98070)?
78. What is Failed Date of Birth Range (61B_60014)?
This issue is raised when Date of birth is not in valid year range Valid date of birth range = from 01.01.1900 to end of reporting period.
79. What is Failed Country of Residence (61B_98400)?
This issue is raised when Incorrect country code provided. Country code should not be “XX”.
80. What is Blank Place of Birth/ Incorporation (61B_98401)?
This issue is raised when Place of Birth/ Incorporation not provided.
81. What is Blank Country of birth/ Incorporation (61B_98402)?
This issue is raised when Country of Birth not provided. This information is mandatory for foreign national (other than India) or non-resident.
82. What is Blank Foreign TIN – Individual (61B_70001)?
This issue is raised when Tax Identification Number (TIN) allotted by tax resident country (other than India) not provided.
This information is mandatory for foreign national (other than India) or non-resident.
83. What is Blank TIN country (61B_98410)?
This issue is raised when Details of TIN Issuing country (other than India) not provided. This information is mandatory for foreign national (other than India) or non-resident.
84. What is Failed Contact details (61B_98103)?
This issue is raised when Contact details not provided.
85. What is Incorrect Controlling person details (61B_60005)?
This issue is raised when Controlling person details provided when “Account Holder Type for Other Reportable Person” is “C2” (other reportable person) or “C3” (Passive Non-Financial Entity that is a CRS Reportable) with Report Type “02” (Report of other reportable accounts under Rule 114G).
Controlling person details should be provided only when “Account Holder Type for Other Reportable Person” is “C1” (Passive Non-Financial Entity with one or more controlling person that is Reportable Person) with Report Type “02” (Report of other reportable accounts under Rule 114G).
86. What is Missing Controlling Person details (61B_60006)?
This issue is raised when Controlling person details not provided when “Account Holder Type for Other Reportable Person” is “C1” (Passive Non-Financial Entity with one or more controlling person that is Reportable Person) with Report Type “02” (Report of other reportable accounts under Rule 114G).
87. What is Inconsistent Account Holder type for US reportable Person – Report Type 01 (61B_98420)?
This issue is raised when Account Holder Type for US Reportable Person is “XX” when the Report Type is “01”.
88. What is Inconsistent Account Holder type for US reportable Person – Report Type 02 (61B_98421)?
This issue is raised when Account Holder Type for US Reportable Person is not “XX” when the Report Type is “02”.
89. What is Inconsistent Account Holder type for Other reportable Person – Report Type 01 (61B_98422)?
This issue is raised when Account Holder Type for other Reportable Person is not “XX” when the report type is “01”.
90. What is Inconsistent Account Holder type for Other reportable Person – Report Type 02 (61B_98423)?
This issue is raised when Account Holder Type for other Reportable Person is “XX” when the report type is “02”.
91. What is Blank Nature of business (61B_98430)?
This issue is raised when Nature of Business not provided.
92. What is Blank First Name Controlling Person (61B_70007)?
This issue is raised when First Name not provided for Controlling Person.Reporting entity can mention “NFN” if it does not have a complete First Name.
93. What is Blank Last Name Controlling Person (61B_70008)?
This issue is raised when Last Name not provided for Controlling Person.Reporting entity can mention the full name if it does not have a Last Name.
94. What is Blank Foreign TIN – Controlling Person (61B_70006)?
This issue is raised when Tax Identification Number (TIN) allotted by tax resident country (other than India) not provided. This information is mandatory for foreign national (refer Nationality field) or nonresident.
7. Statement containing particulars of declaration received in Form 60 (Form 61)
1. What is Form 61?
Rule 114B specifies certain transactions for which quoting of PAN is mandatory. In case a person (other than a company or a firm) does not have a PAN and who enters any such transaction is required to file a declaration in Form 60. Every entity who receives such Form 60 is required to file a statement in Form 61 containing particulars of declarations received in such Form 60.
2. Who is required to submit Form 61?
Every person who has received any declaration in Form 60, on or after the 1st day of January, 2016, in relation to a transaction specified in rule 114B has to submit Form 61.
3. What are these transactions?
Rule 114B specifies the following transactions-
- Sale or purchase of a motor vehicle or vehicle other than two wheeled vehicles.
- Opening an account [other than a time-deposit referred to at Sl. No.12 and a Basic Savings Bank Deposit Account]
- For issue of a credit or debit card.
- Opening of a demat account with a depository, participant, custodian of securities or any other person
- Payment to a hotel or restaurant against a bill or bills at any one time in cash of amount exceeding Rs. 50,000/-.
- Payment in connection with travel to any foreign country or payment for purchase of any foreign currency at any one time in cash of amount exceeding Rs. 50,000/-.
- Payment to a Mutual Fund for purchase of its units of amount exceeding Rs. 50,000/-
- Payment to a company or an institution for acquiring debentures or bonds issued by it of amount exceeding Rs. 50,000/-.
- Payment to the Reserve Bank of India of amount exceeding Rs. 50,000/-.
- Cash Deposits exceeding fifty thousand rupees during any one day or aggregating to more than two lakh fifty thousand rupees during the period 09th November, 2016 to 30th December, 2016 with any bank or post office.
- Purchase of bank drafts or pay orders or banker’s cheques in cash for an amount exceeding fifty thousand rupees during any one day.
- A time deposit with a bank, post office, Nidhi or NBFC Amount exceeding fifty thousand rupees or aggregating to more than five lakh rupees during a financial year.
- Payment for one or more pre-paid payment instruments in cash or by way of a bank draft or pay order or banker’s cheque of an amount aggregating to more than fifty thousand rupees in a financial year.
- Payment as life insurance premium of amount aggregating to more than fifty thousand rupees in a financial year.
- A contract for sale or purchase of securities (other than shares) of amount exceeding one lakh rupees per transaction.
- Sale or purchase, by any person, of shares of a company not listed in a recognised stock exchange of amount exceeding one lakh rupees per transaction.
- Sale or purchase of any immovable property of amount exceeding ten lakh rupees or valued by stamp valuation authority referred to in section 50C of the Act at an amount exceeding ten lakh rupees.
- Sale or purchase, by any person, of goods or services of any nature other than those specified above, if any of amount exceeding two lakh rupees per transaction.
4. What is the due date of furnishing the Form 61?
Form 61 shall be filed twice a year –
H1 – where the declarations in Form 60 are received from 01st of April to 30th September, be furnished by 31st of October immediately following, and
H2 – where such declarations are received from 01st of October to 31st March, be furnished by 30th of April immediately following.
5. How can an entity submit Form 61?
The form can be submitted online by logging to the portal https://report.insight.gov.in. For detailed steps refer section upload of form 61 on reporting portal.
6. What are the consequences of not furnishing Form 61?
Statement of Financial Transactions is required to be filed in Form 61A for the financial year by 31st of May immediately following. If any transactions are there for which PAN has not been taken by an entity, acknowledge no. of filing of Form 61 is required to be mentioned in Form 61A. Therefore, an entity is required to file Form 61 before it can file Form 61A.
1. What are the different parts of Form 61?
Form 61 has two parts. Part A contains particulars of the reporting person and whether the statement is original or revised.
Part B contains details of the transacting person and details of financial transactions undertaken.
2. What are different statement types?
3. What is the difference between Statement Number and Statement ID?
Statement Number is a free text field capturing the sender’s unique identifying number (created by the sender) that identifies the particular Statement being sent. The identifier allows both the sender and receiver to identify the specific Statement later if questions or corrections arise. After successful submission of the Statement to ITD, a new unique Statement ID will be allotted for future reference.
The reporting person/entity should maintain the linkage between the Statement Number and Statement ID. In case the correction statement is filed, statement ID of the original Statement which is being corrected should be mentioned in the element ‘Original Statement ID’. In case the Statement is new and unrelated to any previous Statement, ‘0’ will be mentioned in the element ‘Original Statement ID’.
4. What is original statement ID?
5. What is Report Serial Number?
6. What is Original Report Serial Number?
Step 2: Click on Form61.jar file to run the utility.
Step 3: Select the Transaction Type (for Form 61) on Instructions window.
Select the saved XML file using the Open button from the tool bar.
8. What date format should be used while filling CSV?
9. Can data be saved before generating the XML file in Report Generation Utility?
10. How to capture information for an account with more than one account holder?
11. How to view information after importing CSV?
12. If corrections have to be made only to a statement, keeping reports unchanged, should the reports also be submitted along with the corrected statement?
13. In case form 61 was uploaded with Statement type “ND” and a DQR issue was reported on it afterwards. But some reportable data pertaining to this statement was received later. What should be the status of the already issued DQR in this case?
14. If the Reporting Entity wants to delete/correct the statement or report details that were wrongly reported, what is the corrective procedure?
Separate facility to delete any report is not provided in the purview of Form 61 reporting. If Reporting Entities wants to correct any statement or report uploaded earlier, they must select “CB” as the Statement type and submit the modified/ updated statement/ report.
Defects can be Statement level defects or Report level Defects. Statement Defects are those which render the Statement (Part A) defective. Such Statements will be rejected and the Reporting Entity needs to resubmit the statement. Report defects are those which render a particular report(s) (Part B) as defective in the statement. A statement may have multiple reports and only reports with defects would be rejected. The Reporting Entity needs to correct and submit the reports again in the corrected statement.
10. Which class of DSC should be used while signing the XML?
11. Is it mandatory to sign the statement XML with the same digital certificate which has been registered with ITD?
12. What are the steps to submit the statement through submission utility?
13. Can DQR be downloaded through submission utility?
1. What are the steps to submit a Form 61 statement?
For more details, refer “Report Generation User Guide-61”, “Reporting Portal User Guide” in Resources section of Reporting Portal.
2. Who can submit the Form 61 statement?
In case of Form 61, only the principal officer of reporting entity can submit the statement.
1. ITDREIN should be valid and must be in correct format
5. XML file should be as per the form 61 schema guide (refer Schema validation section)
The Data Quality Report contains details of the data quality errors present in the statement submitted by the Reporting Entity. DQR helps Reporting Entity(s) in identifying and rectifying the errors in data submitted.
2. Why is Data Quality Report (DQR) required?
Issue Description – Incorrect ITDREIN (40010) is the issue raised when ITDREIN in the statement does not match with the ITDREIN mentioned while uploading the statement/ is not a valid ITDREIN.
Action Required – Please submit the statement with Form Name as Form 61.
Issue Description – Incorrect Original Statement ID for CB (40030) is the issue raised when the original statement ID mentioned in the Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement) does not match with the statement ID of original statement “NB” (New Statement).
8. What is Incorrect Original Statement ID for DB (40031)?
Issue Description – Incorrect Original Statement ID for DB (40031) is the issue raised when the original statement ID mentioned in the Deletion statement (Statement Type “DB”) does not match with the statement ID of Original Statement (Statement Type “NB”).
Issue Description – Inconsistent Statement Type ND for submitted reports (40040) is the issue raised when Statement type is “ND” (No Data to Report) for a statement where number of reports is greater than 0.
Action Required – The inconsistency in the statement type has been ignored and statement is considered as “NB” (New Statement).In case Statement Type is not “NB” (New Statement), kindly use the deletion functionality (Statement Type as “DB”) to delete the statement and file a new original statement.
Issue Description – Inconsistent Statement Type NB for nil reports (40041) is the issue raised when Statement type is “NB” (New Statement) for a statement where number of reports is 0.
Action Required – The inconsistency in the statement type has been ignored and statement is considered as “ND” (No Data to Report). In case Statement Type is not “ND” (No Data to Report), kindly file a new original statement (Statement Type as “NB”) with reports.
11. What is Inconsistent Statement Type (40042)?
Issue Description – Inconsistent Statement Type (40042) is the issue raised when the Statement Type selected while uploading the statement does not match with the Statement Type mentioned in the statement.
12. What is Inconsistent Original Statement ID for new statement (40050)?
Issue Description – Inconsistent Original Statement ID for new statement (40050) is the issue raised when Original statement ID is not 0 for Statement Type “NB” (New Statement).
Action Required – The inconsistency in the original statement ID has been ignored and original statement ID is considered as 0. In case the statement type is not “NB” (New Statement), kindly use the deletion functionality (Statement Type as “DB”) to delete the statement and file a new original statement.
13. What is Inconsistent Original Statement ID for No Data statement (40051)?
Issue Description – Inconsistent Original Statement ID for No Data statement (40051) is the issue raised when Original statement ID is not 0 for a Statement Type “ND” (No Data to Report).
Action Required – The inconsistency in the original statement ID has been ignored and original statement ID is considered as 0. In case Statement Type is not “ND” (No data to Report), kindly use the deletion functionality (Statement Type as “DB”) to delete the statement and file a new original statement.
Issue Description – Inconsistent Reason for correction for NB (40060) is the issue raised when Reason for correction is other than “N” (Not applicable) for the Statement Type “NB” (New Statement).
Action Required – The inconsistency in the reason for correction has been ignored and reason for correction is considered as “N” (Not Applicable).
In case reason for correction is not “N”, kindly use the deletion functionality (Statement Type as “DB”) to delete the statement and file a new original statement.
Issue Description – Inconsistent Reason for correction for ND (40061 is the issue raised when Reason for correction is other than “N” (Not applicable) for the Statement Type “ND” (No Data to Report).
Action Required – The inconsistency in the reason for correction has been ignored and reason for correction is considered as “N” (Not Applicable). In case reason for correction is not “N”, kindly use the deletion functionality (Statement Type as “DB”) to delete the statement and file a new original statement.
Issue Description – Inconsistent Reason for correction for CB (40062) is the issue raised when Reason for correction is “N” (Not applicable) for the Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement).
Issue Description – Inconsistent Reason for correction for DB (40063) is the issue raised when Reason for correction is other than “N” (Not applicable) for the Statement Type “DB” (Deletion Statement).
18. What is Inconsistent Reporting Period for CB (40071)?
Issue Description – Inconsistent Reporting Period for CB (40071) is the issue raised when the reporting period in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement) does not match with the reporting period of the original statement (Statement Type “NB”).
Action Required – The inconsistency in the reporting period of correction statement has been ignored and the reporting period of the original statement has been maintained. In case the reporting period in the original statement was incorrect, kindly use the deletion functionality to delete the statement and file a new original statement
19. What is Inconsistent Reporting Period/ Half Year (40072)?
Issue Description – Inconsistent Reporting Period/ Half Year (40072) is the issue raised when the period selected in the field “Reporting Period” & “Half Year” while submitting Form 61, on reporting portal, does not match with the “Reporting Period” mentioned in statement.
Issue Description – Inconsistent Reporting Period for DB (40073) is the issue raised when the reporting period in Statement Type “DB” (Deletion Statement) does not match with the reporting period of the original statement (Statement Type “NB”).
21. What is Inconsistent Number of Reports (40100)
Inconsistent Number of Reports (40100) is raised when Number of reports mentioned in Part A does not match with the actual number of reports.
Action Required – The inconsistency in the field “number of reports” has been ignored and actual number of reports is considered as “number of reports.” In case the actual number of reports is not to be considered, kindly use the deletion functionality to delete the statement and file a new original statement
22. What is Failed Original Report Serial Number in CB (61_98000)?
Failed Original Report Serial Number in CB (61_98000) is the issue raised when Original Report Serial Number for Statement Type ”CB” (Correction Statement) does not match with the report serial number as mentioned in the Original Statement (Statement Type “NB”) submitted earlier.
23. What is Failed Original Report Serial Number in DB (61_98002)?
Failed Original Report Serial Number in DB (61_98002) is the issue raised when Original Report Serial Number for Statement Type “DB” (Deletion Statement) does not match with the report serial number as mentioned in Original Statement (Statement Type “NB”) submitted earlier.
24. What is Failed Original Report Serial Number in CB after Deletion (61_98003)?
Failed Original Report Serial Number in CB after Deletion (61_98003) is the issue raised when Original Report Serial Number mentioned in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement) corresponds to the report already deleted.
25. What is Failed Date of Birth Range (61_98071)?
Failed Date of Birth Range (61_98071) is the issue raised when Date of birth is not in valid year range (for individual) i.e., not before 01.01.1900 and not after the end of reporting period.
26. What is Invalid PAN Acknowledgment Number format (61_98440)?
Invalid PAN Acknowledgment Number format (61_98440) is the issue raised when Invalid format of PAN Acknowledgement number (15 digits) is entered.
27. What is Wrong PAN Acknowledgement Number (61_98441)?
Wrong PAN Acknowledgement Number (61_98441) is the issue raised when Wrong PAN Acknowledgement number is entered.
28. What is Invalid Aadhaar Number (61_98040)?
Invalid Aadhaar Number (61_98040) is the issue raised when Invalid Aadhaar Number format (12 digits) is entered.
29. What is Wrong Aadhaar Number (61_98041)?
Wrong Aadhaar Number (61_98041) is the issue raised when Wrong Aadhaar Number is entered
30. What is Invalid Postal code – India (61_98092)?
Invalid Postal code – India (61_98092) is the issue raised when Invalid postal code is provided when country selected is India.
31. What is Wrong Postal code – India (61_98093)?
Wrong Postal code – India (61_98093) is the issue raised when Wrong postal code is provided when country selected is India. Pin code provided should be linked to state and locality.
32. What is Insufficient Address (61_98094)?
Insufficient Address (61_98094) is the issue raised when Address appears to be Insufficient /incomplete
33. What is Failed Mobile No – India (61_98100)?
Failed Mobile No – India (61_98100) is the issue raised when Incorrect mobile number format is provided when country selected is India. It should be a 10 digit mobile number and should start from 5, 6, 7, 8 or 9.
34. What is Failed Mobile No – Outside India (61_98101)?
Failed Mobile No – Outside India (61_98101) is the issue raised when Incorrect mobile number format is provided when country selected is outside India.Maximum 15 digits are allowed.
35. What is Exceptional estimated agricultural Income (61_ 98450)?
Exceptional estimated agricultural Income (61_ 98450) is the issue raised when Amount reported is greater than 1 crore.
36. What is Modification in estimated agricultural Income (61_ 98451)?
Modification in estimated agricultural Income (61_ 98451) is the issue raised when “Estimated Agricultural Income” has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement).
37. What is Exceptional estimated non- agricultural Income (61_ 98460)?
Exceptional estimated non- agricultural Income (61_ 98460) is the issue raised when Amount reported is greater than 1 crore.
38. What is Modification in estimated non-agricultural Income (61_ 98461)?
Modification in estimated non-agricultural Income (61_ 98461) is the issue raised when “Estimated Non-Agricultural Income” has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement).
39. What is Exceptional Transaction Amount (61_98252)?
Exceptional Transaction Amount (61_98252) is the issue raised when Transaction Amount is more than 1 crore.
40. What is Modified Transaction Amount (61_98255)?
Modified Transaction Amount (61_98255) is the issue raised when Transaction Amount has been changed in Statement Type “CB” (Correction Statement).
8. Resources
1. What is a quick reference guide? How can user access/download it?
Quick reference guide provides a concise & targeted course of action for performing the tasks. It can be downloaded from the resources section of Reporting Portal.
1. How can one download detailed guides?
User guides can be downloaded from the resources section of Reporting Portal.
1. What are the schema guides and how can they be useful?
Schema guides are meant to assist in creation of xml files in the format acceptable to the Income tax Department. The acceptable schema guides are published from time to time for each type of statement to be submitted by the Reporting Entity and these guides must be adhered to for submission of error free statements by the entity.
2. How can one download the schema guides?
Schema guides can be downloaded from the “Resources” section of Reporting Portal.
1. What is a training tool kit?
Training Toolkit contains multiple documents intended to give assistance to Reporting Entity users in using the Reporting Portal and reporting utility.
2. How can one access the training tool kit?
Step 1: Log in to the Reporting Portal
Step 2: Navigate to the “Resources” tab and click on “Training Tool kit”
1. What should a user do if its query/problem is not listed in FAQs?
Step 1: Click on the “Help” icon on the Reporting Portal
Step 2: Click on “Contact us” button
Step 3: Select the issue category and sub-category
Step 4: Enter details if user is not logged in/registered
Step 5: Click on “Email Us” and describe the problem being faced and click on “Submit”
Source- Directorate of Income Tax (Systems), Reporting Portal Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Version 2.0 (April 2018)
- « Previous Article
- Next Article »

Join Taxguru’s Network for Latest updates on Income Tax, GST, Company Law, Corporate Laws and other related subjects.
- Join Our whatsApp Group
- Join Our Telegram Group

Need updation for the change in the entity name if the GIIN is showing the old name.
Please mail me all this At my email Id
Error code is “Product type is not consistent with the SFT Code”. We have checked all information but did not find solutions to the error. It may be bugs in the Form 61A report generation utility provided by the dept. Any resolution ?
Leave a Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post Comment

Subscribe to Our Daily Newsletter
Latest posts.

Modification of SION E-125 for export of Shea Stearine

Notification under 10(46A) in case of Mathura Vrindavan Development Authority

Ensuring Input Tax Credit (ITC) Compliance for Exports: A Case Study on Third-Party Exporter Documentation

Know How to Surrender or Cancel Your TAN Number

Corporate Taxes in the United Arab Emirates (UAE): Analysis

Master Circular on IRDAI (Insurance Products) Regulations 2024- Health Insurance

TRAI Guidelines on Unsolicited Commercial Communications for Insurers – IRDAI Circular

Redefining ‘Person’ Under Consumer Protection Act, 1986: SC’s New Take on Long Standing Corporate Claims

Link Your PAN with Aadhaar Today as Non-compliance Costs More

CBDT excludes RBI from definition of specified person under Sec. 206AB & 206CCA of Income Tax Act, 1961
Featured posts.

GSTN Advisory: Portal Enhancements, Pan Masala/Tobacco Manufacturer Info & E-way Bill 2 Portal Launch

Seeking Cancellation of GST Registration is Not Easy

Advisory on launch of E-Way Bill 2 Portal

Importance of Annual Information Statement while filing Income Tax Return!!
CBDT exempts RBI from Section 206CCA provisions (TCS Collection at higher rate)

CBDT exempt RBI from Higher TDS deduction under Section 206AB
CBDT notifies Cost Inflation Index for Financial Year 2024-25

GST Case Law Compendium – May 2024 Edition

Supreme Court Upholds ICAI’s Limit of 60 Tax Audits per CA: Analysis

LinkedIn India Penalized for Companies Act Section 89 & 90 Violations
Popular posts.

Cost Inflation Index – Meaning & Index from 1981-82 to 2024-25

Due Date Compliance Calendar May 2024

Corporate Compliance Calendar for May, 2024

Empanelment of Concurrent Auditors With Canara Bank
May, 2024 Tax Compliance Tracker: Income Tax & GST Deadlines

Empanelment with Punjab & Sind Bank for Concurrent Audit: Last Date 08/06/2024

GST compliance calendar for May 2024
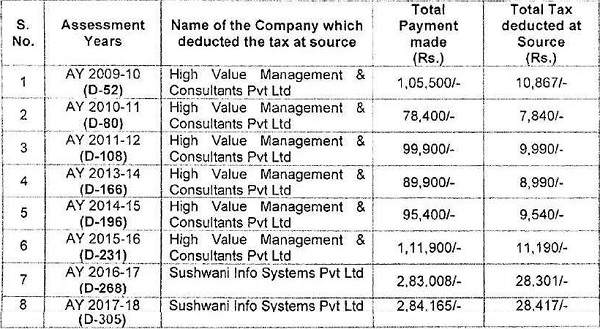
ICAI penalises CA in Practice for involvement in other business without prior permission

Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs) – Tax and It’s Reporting In ITR

Submitting a Bias Report
The University considers bias incidents antithetical to the Penn State Values . The online bias incident report form provides the Penn State community a mechanism for reporting incidents involving acts of bias due to:
- actual or perceived age
- race or color
- ancestry or national origin
- sexual orientation
- gender identity
- physical or mental disability
- religion or creed
- veteran status or service in the uniformed services (as defined in state and federal law)
- marital or family status,
- pregnancy or pregnancy-related conditions
- genetic information
- political ideas
Considerations
Students may use the form to report any act of bias that they have experienced themselves or observed directed against anyone else.
Faculty and staff should only use the form to report acts they observe that are directed against students. If no student is involved, faculty and staff should contact the Office of Equal Opportunity and Access at 814-863-0471 .
You may submit this report anonymously. However, please be advised that, without your contact information, we are unable to follow up with you. Additionally, anonymous submissions may limit our ability to address the reported incident.
Report a Bias Incident
What to expect after submitting a bias incident report
- Immediately upon submission, you will receive an auto-confirmation from the secure online system notifying you that your report was received.
- Within 1-2 working days, you will receive an email from the Bias Response Coordinator to let you know when the Bias Response Network will review your report and to provide any needed resources.
- The Bias Response Network will review your report and determine the appropriate referral.
- The Bias Response Coordinator will refer your report to the appropriate party.
- The Bias Response Coordinator will email you to let you know to whom your report was referred.
- If you requested a meeting to discuss the reported incident, the person to whom your report was referred will contact you to ensure that your perspective is heard, gather any additional details you may wish to provide, and provide additional resources if appropriate.
An official website of the United States Government
- Kreyòl ayisyen
- Search Toggle search Search Include Historical Content - Any - No Include Historical Content - Any - No Search
- Menu Toggle menu
- INFORMATION FOR…
- Individuals
- Business & Self Employed
- Charities and Nonprofits
- International Taxpayers
- Federal State and Local Governments
- Indian Tribal Governments
- Tax Exempt Bonds
- FILING FOR INDIVIDUALS
- How to File
- When to File
- Where to File
- Update Your Information
- Get Your Tax Record
- Apply for an Employer ID Number (EIN)
- Check Your Amended Return Status
- Get an Identity Protection PIN (IP PIN)
- File Your Taxes for Free
- Bank Account (Direct Pay)
- Payment Plan (Installment Agreement)
- Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS)
- Your Online Account
- Tax Withholding Estimator
- Estimated Taxes
- Where's My Refund
- What to Expect
- Direct Deposit
- Reduced Refunds
- Amend Return
Credits & Deductions
- INFORMATION FOR...
- Businesses & Self-Employed
- Earned Income Credit (EITC)
- Child Tax Credit
- Clean Energy and Vehicle Credits
- Standard Deduction
- Retirement Plans
Forms & Instructions
- POPULAR FORMS & INSTRUCTIONS
- Form 1040 Instructions
- Form 4506-T
- POPULAR FOR TAX PROS
- Form 1040-X
- Circular 230
About Form 4797, Sales of Business Property
More in forms and instructions.
- Current Year
- Browser Friendly
- Mobile Friendly Forms
- Post Release Changes to Forms
- Order Forms and Pubs
- Help with Forms and Instructions
- Comment on Tax Forms and Publications
Use Form 4797 to report:
- The sale or exchange of property.
- The involuntary conversion of property and capital assets.
- The disposition of noncapital assets.
- The disposition of capital assets not reported on Schedule D.
- The gain or loss for partners and S corporation shareholders from certain section 179 property dispositions by partnerships and S corporations.
- The computation of recapture amounts under sections 179 and 280F(b)(2) when the business use of section 179 or listed property decreases to 50% or less.
- Gains or losses treated as ordinary gains or losses, if you are a trader in securities or commodities and made a mark-to-market election under Internal Revenue Code section 475(f).
Current revision
Form 4797 PDF
Instructions for Form 4797 ( Print version PDF )
Recent developments
None at this time.
Other items you may find useful
All Form 4797 Revisions
About Form 706, United States Estate (and Generation-Skipping Transfer) Tax Return
About Form 4255, Recapture of Investment Credit
About Form 4684, Casualties and Thefts
About Form 6198, At-Risk Limitations
Other current products
Related publications
Select Committee on Birth Trauma chair disappointed by lack of support for consideration of 'gendered violence'
The head of a New South Wales parliamentary inquiry has expressed her disappointment at the lack of support for birth trauma to be considered a form of "gendered violence".
The Select Committee on Birth Trauma has released its report with five findings and 43 recommendations to try to ensure more people do not suffer trauma during their pregnancies and childbirth.
The findings state that a number of individuals have suffered preventable birth trauma in NSW, that their experiences are "distressing and unacceptable", and that urgent efforts must be made to address this.
"Our hope is that the evidence documented in this report will not only inform the NSW government's consideration of these matters, but more importantly, prompt action across Australia and the world with the hope that every birth is met with dignity, respect and compassion," committee chair and MP Emma Hurst said in the report.
The inquiry's priority in its 43 recommendations is for the NSW government to ensure that all women have access to continuity of carer models with a known provider.
However, it stopped short of recommending universal access to the Midwifery Group Practice, something advocates had been calling for.
Ms Hurst said she was disappointed by this outcome.
"This report doesn't go far enough. I think that we needed to be much stronger in our recommendations around Midwifery Group Practice," she said.
The inquiry also recommended the need for comprehensive antenatal education, a review of laws around informed consent, and a requirement for maternity health practitioners to undergo formal training in this area.
It also asked for greater investment in mental health support and postpartum services, and the adoption of trauma-informed care practices in maternity care.
After testimony from several mothers who experienced stillbirth and miscarriages, the report also recommended specific spaces for women experiencing maternity loss in public hospitals.
This included waiting rooms separated from pregnant women and babies, as well as additional state-funded psychological support for parents who experience loss.
One of the recommendations was also directed at health practitioners who provide individualised maternity care to ensure their patients' birthing decisions and preferences are "supported and respected".
The inquiry has asked the NSW government to undertake consultation to consider whether legislative change was needed to protect these staff.
Missing midwives
Mother Kate Finch said her experience of birth improved dramatically after she gained access to the Midwifery Group Program, which pairs a woman with a known midwife before, during and after birth, for her second baby Cooper.
"I don't want anyone to have to go through the trauma and loneliness of that hospital delivery I had in my first birth," she said.
"I want Health Minister Ryan Park to make sure that every woman in NSW can access this midwife continuity of care."
Doctor Amanda Cohn was a committee member who opposed restricting the continuity of care recommendation to midwives only.
She said allowing an open-ended recommendation allowed for regional and rural women to access GP and obstetrician-led continuity care, which sometimes could be the only option available.
Consumer group Better Birth Illawarra agreed elements such as the lack of universal Midwifery Group Practice was disappointing, but said the report was a good first step.
"This is a once-in-a-generation opportunity for the NSW Health Minister Ryan Park and the NSW government to embed a woman's right to access an empowered birth in maternity health systems," founder Sharon Settecasse said.
Call for 'gendered violence' inclusion
Chair Emma Hurst included a dissenting statement in the report, outlining recommendations which were either "watered or voted down" by other committee members.
She had wanted a finding that some cases of birth trauma should be considered a form of gendered violence, and for a recommendation that the NSW government investigate the possibility of legislative changes to recognise obstetric violence.
"This fails to recognise the power imbalance between birthing parents and health practitioners, and the systemic issues that were clearly presented to the committee regarding the presence of obstetric violence in maternity care systems globally," the chair stated in the report.
"Failure to even consider legislative changes to protect birthing parents from obstetric violence is unacceptable."
NSW government MPs also disagreed with a recommendation that was included in the report.
Recommendation 31 asked the NSW government to appoint a Chief Midwifery Officer.
"We do not believe the inquiry sufficiently established a case to support appointing an additional high-paid executive in NSW as the best use of resources," Labor MP Emily Suvval stated in the report.
"And equally, we believe a fiscally responsible approach would include a review of the progress already achieved to strengthen senior midwifery representation in the NSW government."
8,000 mothers surveyed
The inquiry was set up following a mass complaint launched by mothers against the Wagga Wagga Base Maternity Ward and on the heels of research by the University of Western Sydney.
A survey of 8,000 mothers found one in three experienced birth trauma in Australia, and one in eight experienced obstetric violence — defined as preventable harm in maternity care.
The inquiry received a record 4,000 submissions and held six hearings across the state.
It heard from women who reported inadequate and disrespectful care, mothers who were denied pain relief, bullied, coerced, and given medical procedures without consent in NSW hospitals.
It also heard of experiences of racism and discrimination during pregnancy and birth.
Medical professionals gave evidence of extreme understaffing, a lack of trauma-informed training, and defended life-saving decisions made under emergency scenarios.
Mr Park welcomed the report, and praised the efforts of birthing advocates and the mothers who gave testimony.
"I'm very pleased that the report was handed down," he said.
"We as a system now will carefully and methodically work through this and respond."
He said work had begun to improve the system, with a state birthing and maternity blueprint underway, and an expert advisory group and a consumer group in place.
The NSW government has three months to respond to the inquiry's report.
- X (formerly Twitter)
Related Stories
Harrowing evidence from former teenage mums at nsw birth trauma inquiry's final hearing.
After Liz gave birth, a nurse asked her if she planned to take baby Mary home
Stories of forced procedures and threats from medical staff told at birth trauma inquiry
- Doctors and Medical Professionals
- Pregnancy and Childbirth
- State and Territory Government
- Wagga Wagga
'AI demand train running at full speed': Here's what Wall Street expects from Nvidia's first-quarter earnings
- Nvidia is set to report its first-quarter earnings results after the market close on Wednesday.
- Wall Street expects more sales of Nvidia's AI chip before its next-gen Blackwell release.
- Here's what Wall Street is eyeing ahead of the chipmaker's quarterly earnings report.

Nvidia has a lot to prove when it reports its first-quarter earnings results after the market close on Wednesday.
That's because its stock has surged 91% year to date, is up about 200% over the past year, and is up nearly 500% since the launch of ChatGPT in November 2022 .
Here are the estimates for Nvidia's first-quarter earnings report:
- Revenue: $24.69 billion
- Earnings per share: $5.34
- EBITDA: $16.74 billion
With Nvidia's next-generation Blackwell AI chipset set to be released later this year, analysts will be trying to gauge whether a slowdown in sales of its current-generation H100 chips is on the horizon. Also top of mind for investors will be updated guidance and views on the supply-demand dynamic for its AI-enabling chips.
Here's what Wall Street expects from Nvidia's upcoming earnings report.
Wells Fargo: 'Improving H100 GPU Lead Times + H200 Ramp = Data Center Upside'
Wells Fargo raised its Nvidia price target to $1,150 in a note last week, saying that "improving H100 GPU lead times + H200 ramp = data center upside."
"We are positive on the setup into F1Q25 print and see intra-qtr data points supporting Data Center revenue upside into $23-$24B+ range," a Wells Fargo analyst, Aaron Rakers, said.
Rakers said recent demand data points from Super Micro Computer and Taiwan Semiconductor boded well for Nvidia, in addition to recent commentary from megacap tech companies regarding their planned cloud capital expenditures.
Wells Fargo rated Nvidia as "overweight" with a $1,150 price target.
Bank of America: Expect a beat but increased stock volatility as well
Vivek Arya, a Bank of America analyst, said that while he still thought Nvidia was a "top pick" and expected the company to beat earnings estimates, four factors could increase the stock's volatility following the earnings report.
The first is the potential for quarterly revenue deceleration ahead of Nvidia's launch of the Blackwell chip. This highlights that the July quarter could see Nvidia deliver less than 10% quarter-over-quarter revenue growth as customers pause their purchases until the chip's release.
The three other factors, Arya said, are: "2) Greater China dependence for 2H: start of H20 shipments helps 2H growth pre Blackwell, but also raises China restriction risks, 3) Limited update to '40% inference mix' metric — recall this is what helped the stock on last call, 4) Upcoming Computex perhaps less newsworthy than last quarter's GTC anticipation."
Arya added that Nvidia could report more "normalized" gross margins in the mid-70s vs. its consistent expansion to 77% over the past six quarters.
Bank of America rated Nvidia as "buy" with a $1,100 price target.
Deutsche Bank: 'AI leadership to continue'
Deutsche Bank said it fully expected Nvidia to deliver "healthy multi-billion dollar beats/raises on still healthy demand for AI compute."
"While on the margin some may be paring back orders ahead of the launch of Blackwell, we still expect aggregate demand trends to remain healthy," Deutsche Bank said. "Overall, we remain impressed by NVDAs best-in-class technology roadmap and believe AI fervor by its customers is likely to be sustained (see still strong capex commentary from META, MSFT), yielding yet another strong quarter/guide."
However, the bank sees much of that strength already priced into the stock, leading the firm to believe that Nvidia stock is "fully valued," it said.
Deutsche Bank rated Nvidia as "hold" with a $850 price target.
Bloomberg Intelligence: 'Nvidia has more levers to attack the market'
Kunjan Sobhani, a Bloomberg Intelligence semiconductor analyst, said in a recent note he expected Nvidia to report "a solid beat and raise" on Wednesday, saying that "Nvidia's AI demand train running at full speed."
"During 1Q, we saw multiple demand signals, namely rising cloud capital-spending outlook, AI upside by TSMC and accelerating AI investments from sovereign entities, highlighting continued momentum," Sobhani said. "With H100 lead times falling and H200 and GB200 products now in the mix (with higher average selling prices), Nvidia has more levers to attack the market."
- Main content

COMMENTS
The report form balance sheet is presented in a vertical orientation, and is essentially one column that spans the entire width of a page. Starting with assets, the report form balance sheet ...
The report format presents all the accounts vertically. Although both balance sheet formats are acceptable, the report form is much more popular. Example. As the name implies, the report format looks more like a traditional report and is used more often in the general-purpose financial statements. Here is an example of a report form balance sheet.
Ans: The act of presenting information in an orderly and structured format is known as report writing. Reports come in different types, such as analytical reports, research reports, financial reports, progress reports, incident reports, feasibility reports, and recommendation reports.
10. Vertical & Lateral Reports. Next, in our rundown of types of reports, we have vertical and lateral reports. This reporting type refers to the direction in which a report travels. A vertical report is meant to go upward or downward the hierarchy, for example, a management report.
The report form frequently fits on a standard sheet of paper better than the account form. Assets are normally reported on balance sheet in the order of their relative nearness to cash. For example, the account receivable (sundry debtors) account usually follows the cash account because the accounts receivable are likely to turn into cash very ...
2. Follow the Right Report Writing Format: Adhere to a structured format, including a clear title, table of contents, summary, introduction, body, conclusion, recommendations, and appendices. This ensures clarity and coherence. Follow the format suggestions in this article to start off on the right foot. 3.
Knowing how to write a successful report can make you a valuable asset in your current workplace or an appealing candidate for new employers. Here are some steps to follow when writing a report: 1. Decide on terms of reference. Many formal reports include a section that details the document's "terms of reference" (or ToR).
Business report - Business reports range from annual reports to SWOT analyses. The goal of business reports is to communicate ideas, information, or insights in a business setting. Research report - Research reports are often more scientific or methodological in nature. They can take the form of case studies or research papers.
A case report form (CRF) is designed to collect the patient data in a clinical trial; its development represents a significant part of the clinical trial and can affect study success. [ 1] Site personnel capture the subject's data on the CRF, which is collected during their participation in a clinical trial.
Form Link. FFIEC 002s. Report of Assets and Liabilities of a Non-U.S. Branch that is Managed or Controlled by a U.S. Branch or Agency of a Foreign (Non-U.S.) Bank. Form Link. FFIEC 004. Report on Indebtedness of Executive Officers and Principal Shareholders and their Related Interests to Correspondent Banks.
Simplify the process using our report form templates. Keeping track of incidents and complaints has never been easier. Plus, all the data can be stored in one place so it's quick to find. Take a look at our report form designs or check out our form builder to start from scratch. Link up your report forms with our integrations and let take ...
Report. A report is a document or a statement that presents information in an organized format for a specific audience and purpose. Although summaries of reports may be delivered orally, complete reports are usually given in the form of written documents. [1] [2] Typically reports relay information that was found or observed. [2]
There are numerous report form templates, including incident report forms, accident report forms, request forms, insurance claims, and many more. It is up to you to use one of the ready-made templates or create your own form by customizing it. You can add extra form fields and change form design as well as colors and themes as you see fit.
You can claim the Employee Retention Credit for 2020 on the 4th quarter Form 941 -- 22-JAN-2021. Form W-2 reporting of employee Social Security tax deferred under Notice 2020-65 -- 29-OCT-2020. Changes to reporting tax liabilities if you claim certain nonrefundable credits -- 16-SEP-2020. Failure to deposit penalties on some employers claiming ...
A report is a specific form of writing that is organised around concisely identifying and examining issues, events, or findings that have happened in a physical sense, such as events that have occurred within an organisation, or findings from a research investigation. These events can also pertain to events or issues identified within a body of ...
SEC Form U-13-1: An application that doubles as both a request for approval by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) for any mutual service company, or a declaration of organization and ...
Report definition: an account or statement describing in detail an event, situation, or the like, usually as the result of observation, inquiry, etc.. See examples of REPORT used in a sentence.
1. Scan the report to make sure everything is included and makes sense. Read the report from beginning to end, trying to imagine that you're a reader that has never heard this information before. Pay attention to whether the report is easy to follow, and whether the point you're making comes across clearly.
Using the scenario above, the first section of your report would begin to look something like this: Incident Report Sample fig. 1. In our incident report example, we took advantage of adding photo evidence to better illustrate the environment where the incident took place. Notice that the photo attached had an annotation.
Introduction. Your lab report introduction should set the scene for your experiment. One way to write your introduction is with a funnel (an inverted triangle) structure: Start with the broad, general research topic. Narrow your topic down your specific study focus. End with a clear research question.
A case report form (or CRF) is a paper or electronic questionnaire specifically used in clinical trial research. [1] The case report form is the tool used by the sponsor of the clinical trial to collect data from each participating patient. All data on each patient participating in a clinical trial are held and/or documented in the CRF ...
This report, developed in March 1975, was initially collected on a monthly basis to help identify transactions between the bank and nonbank portions of a bank holding company and its subsidiaries. Effective September 1975, the report was changed to a quarterly report and expanded to collect additional information.
1. Overview 1.1 Reporting Obligation. 1. Who is a Reporting Entity? Reporting Entity or Reporting Person is an entity which is required to furnish a Statement of Financial Transaction (in Form 61 A) or Statement of Reportable Account (in Form 61B) with the Income tax Department as per the provisions of section 285BA of the Income-tax Act 1961.
Students, faculty, staff, alumni, and guests with a Penn State User ID may use the bias incident report form to report acts of bias they observe at Penn State. The University considers bias incidents antithetical to the Penn State Values .
Information about Form 4797, Sales of Business Property, including recent updates, related forms and instructions on how to file. Form 4797 is used to report the details of gains and losses from the sale, exchange, involuntary conversion, or disposition of certain business property and assets.
Gun control groups celebrated the passage of the bill. Moms Demand Action referred to it as a "lifesaving measure." VICTORY! A lifesaving measure that will help cut off the flow of unserialized, untraceable "ghost guns" into Vermont and will also prohibit firearms at polling places passed both chambers of the Vermont legislature with bipartisan support.
If you, or someone you know, needs help: Lifeline on 13 11 14; Stillbirth Foundation (research and education to prevent stillbirth) on 02 9557 9070; Red Nose 24/7 grief and loss support line on ...
Nvidia is set to report its first-quarter earnings results after the market close on Wednesday. Wall Street expects more sales of Nvidia's AI chip before its next-gen Blackwell release.
Once a child is found, the report is closed and the case is updated in NCIC. The Ohio Missing Children Clearinghouse then receives statistics on missing persons within the state that have been entered into NCIC and issues an annual report to raise awareness about the issue of missing children. Additional training, assistance and resources are ...
Draft Reporting Form for Call Report Revisions Effective Beginning with the June 30, 2024, Report Date The following draft reporting form, which is subject to change, presents the pages from the FFIEC 051 Call Report as they are proposed to be revised, subject to final approval by the U.S. Office of Management and Budget.