

What is Report Writing? Parts, Types, Structure, Process
- Post last modified: 4 June 2023
- Reading time: 30 mins read
- Post category: Business Communication

- What is Report Writing?
Report writing is a formal style of presenting objective facts and information. There can be various types of reports, such as academic reports, science reports, business reports, technical reports, and news reports. A report can be verbal or written. However, a written report is more formal than a verbal report.

Table of Content
- 1 What is Report Writing?
- 2 Report Writing Definition
- 3 Report Writing Advantage
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Background
- 4.3 Findings
- 4.4 Conclusions
- 4.5 Recommendations
- 5.1 Informational reports
- 5.2 Analytical reports
- 5.3 News reports
- 6.2 Remaining details
- 6.3 Informational news report
- 6.4 Analytical news report
- 6.5 Additional details
- 6.6 Concluding sentence
- 7.1 Identify
- 7.2 Research
- 7.3 Organise
- 8 Feasibility Reports
- 9.1 Cover letter
- 9.2 Executive summary
- 9.3 Proposal
- 9.4 Pricing information
- 9.5 Terms and conditions
Report Writing Definition
Report writing is the process of organizing and presenting information in a clear, concise, and objective manner for a specific audience. It involves gathering data, analyzing it, and presenting it in a format that is easy to understand and relevant to the topic at hand. – The University of Wisconsin Writing Center
Report writing is the art of communicating information that has been acquired through research or investigation in a formal, structured manner. It involves synthesizing information, drawing conclusions, and making recommendations based on the findings. – The American Management Association
Report writing is the process of creating a document that provides information, analysis, and recommendations on a particular topic or issue. It requires the ability to organize and present data in a logical and meaningful way, as well as to convey complex ideas in a clear and concise manner. – The International Business Communication Standards (IBCS)
Report Writing Advantage
A written report also provides the following advantages:
- A written report presents a formal record of a transaction, which is not possible in a verbal report.
- A written report conveys a message without any distortion. On the other hand, a message can be easily misrepresented in a verbal report.
- A written report is more convenient for lengthy and distant communication.
- A written report requires a reader to think before responding to a message.
- Facts, figures and statistical data can be better represented graphically in a written report.
However, writing a report is not as easy as drafting a formal e-mail. A report is a brief, precise document. It is written for a specific audience with some specific objective. To write a report, you need to first thoroughly understand the purpose of report writing, then research information from various sources, verify the validity of information, analyse information, and then present findings or results. These findings must be reported objectively without personal biases.
A well-written report must have an effective objective analysis. Based on the analysis, you can recommend possible courses of action for the future. However, it is up to the report reader to accept the recommendations.
Therefore, while report writing, you must pay attention to why you are writing the report and who has asked you to write the report. This will help you investigate the information appropriately.
Parts of a Report
Following are the main sections of a formal report :
Introduction
Conclusions, recommendations.
This section indicates the purpose of the report, who has ordered the report, how the data is collected, and whether any recommendations are provided. In addition, the introduction section may also provide information on who has written the report and the date on which it is submitted.
This section provides the background of a problem or a situation on which the report is written. In case the report is too lengthy, then instead of introduction, an executive summary should be written.
The purpose of an executive summary is to enable top executives and managers to get a quick snapshot of a long report without reading the entire report. Therefore, the executive summary comes before introduction. Of course, then there would be no background section.
This is the longest section of a report, which is written after the investigation is over. This section presents factual information without any interpretation or suggestions.
Each finding is summarised as a conclusion in this section. In the above sample report, there are four conclusions based on the summary of each paragraph in the findings section. These conclusions are listed numerically in the same order as the corresponding findings.
The final section provides a numbered list of recommendations, which are based on the list of the conclusion. Each recommendation uses the verb should. This is because the writer is simply giving suggestions and not making a decision. Therefore, the verb should is used instead of the verb will. However, there are exceptions:
- To give a strong recommendation: Use the verb must. For example, ‘The team managers must ensure that the break hours are not shortened.’
- To give a weak recommendation: Use the verb could. For example, ‘Having a coffee dispenser in the facility could boost the staff morale.’
Types of Reports
Reports exist in our academics and workplaces in so many forms that we may not even be aware of them. For example, a student submits a laboratory report to communicate the methods and results of scientific experiments conducted in a lab.
Academicians and business people use research reports to view scientific studies of an issue or a problem. Policy-makers read field study reports to read about the ground situation from branch offices and manufacturing plants. Similarly, there are progress reports, technical reports, functional reports, case studies, etc.
All these reports share the attributes, principles, and format of report writing, which are described above. These reports can be organised into three groups:
Informational reports
Analytical reports, news reports.
An informational report is used to objectively present information without any analysis. Examples of informational reports include the First Information Report (FIR), annual reports, monthly financial reports, or employee attrition reports. These reports only report the facts as they are.
For example, the police write an FIR to record details about a cognisable offence, such as personal details of the complainant/informant, place, date and time of occurrence, offence, description of the accused, witnesses, and complaint.
Similarly, a company presents an annual report to its shareholders to present details of its business activities and finances of the previous financial year. An informational report presents objective facts without analysing the reasons and conditions behind the reported situation.
For example, if someone wants to study information on a field trip, then he can ask for a site visit report. Similarly, if a manager wants to view the feedback of a training programme, then he can ask for the training feedback report from the trainer. If the head of a department wants to get an update on the different projects in his department, he can ask for progress reports from different project managers.
An analytical report evaluates a problem or an issue and presents the outcomes of analysis to explain the causes of the problem, demonstrate relationships, or make recommendations.
For example, a scientific or market research report studies a problem scientifically by developing a hypothesis, gathering data, analysing data, and presenting findings and conclusions.
Similarly, a feasibility analysis report studies a problem and predicts whether the current solution or alternatives will be practical or will produce the desired outcome. Whenever you need to make a critical decision, then an analytical report is prepared. These reports help the decision-maker(s) analyse the prevailing situation.
For example, a company wants to decide where to open a branch office in a particular area. In this situation, an analytical report can evaluate the details of the property, such as infrastructure, land cost, competitive stores, etc., and then recommend the best site from the available options.
If you are working as or aspire to be a journalist, then you may need to write a press report. A press report is a newsworthy article in a newspaper, magazine or website. It is different from the press release by companies. A press release is an official statement of a company on an important subject or event. A press release generally focuses on one particular subject, such as a milestone, a launch, an anniversary, etc.
On the other hand, a press report discusses the subject in detail. A press release is a marketing tool used by companies to keep the general public and the media updated about its newsworthy occasions. It helps build a company’s visibility in the minds of its customers and community at large.
A press release is generally prepared by a company’s marketing or Public Relations (PR) team, whereas a press report is written by an independent journalist. Therefore, a press report presents more objective information than a press release, which is a company’s promotional mouthpiece. Just like informational and analytical reports, a press report requires considerable research on a subject before it is written credibly.
The author must ask the 5 Ws and 1 H – who, what, where, why, when, and how. Questions arise in the following manner:
- What happened?
- Where did it happen?
- When did it happen?
- Who was involved?
- Why did it happen?
- How did it happen?
After finding the answers, he must note down all the relevant facts that must be mentioned in the news report. These facts can be organised into the following three groups:
- Vital and interesting facts
- Not vital but interesting facts
- Not vital, not interesting, but related facts
By organising information into the above groups, the author will be able to include all the relevant facts into the news report. The facts must be specific. If there are gaps in the story and the related information is not available, then questions can be marked against them so that these can be researched further.
Next, the author must decide the type of news report he wants to write – informational or analytical. The former will provide objective and straightforward information, whereas the latter will also provide the author’s opinion on the subject.
After determining the type of news report to write, the author must create an outline or structure of the report. The most common structure is an inverted triangle, where the most important information is at the top.
A news report must provide the information that the readers want as soon as possible. If the news report is for a newspaper, then the most important news must be above the “fold”. The “fold” is the crease in the newspaper when it is folded in half. All the engaging stories are above the fold. Similarly, on a website, the most important information is at the top of the screen before one has to scroll down.
A news report must be written according to the audience. The author should ask the 5Ws with respect to the audience reaction, such as:
- Who is the audience?
- Where is the audience?
- What does the audience want to read?
- Why do they want to read it?
- When will they read it?
Structure of News Report
Finally, the structure of a news report is as follows:
Remaining details
Informational news report, analytical news report, additional details, concluding sentence.
The leading sentence of a news report is the most important section. It should tell what the news report is all about, why it is important, and what information the rest of the news report provides.
These provide the basic information of what happened, where it happened, when it happened, who was involved, and why it was remarkable.
In this report, the remaining details provide more information about the newsworthy item.
In this report, the remaining details also provide the opinion of the author.
These details help the reader learn more about the newsworthy item, such as additional facts about the subject, contact information, or interview quotes. These details comprise transitional elements that help build the flow of information. In an analytical report, these can also include counter-arguments and their authors.
The news report should end with a concluding sentence, which repeats the leading statement or a statement mentioning future developments.
Report Writing Process
This process will ensure that your report is accurate, clear, comprehensive and credible.
Before writing a report, identify the following parameters:
- Issue or problem : Identify the issue or problem to analyse.
- Audience : Identify who the audience is. Find out their background information. Determine why they would want to read the report.
- Purpose : Determine the purpose for which the report will be used.
- Scope and limitations : Identify the scope of the report. Determine the limitations of report writing.
- Expectations : Determine expectations regarding the format or structure of the report. Identify the models available for report writing. Determine whether there is a style guide and/or a marketing guide.
To research the facts or information for report writing:
- Plan : Make a draft plan on how to analyse the problem and present the objective of the report.
- Collect data: Collect information based on the purpose of the report.
- Analyse : Finally, analyse and evaluate the collected information.
After gathering and analysing the required information, organise it as follows:
- Main points : Identify the main points of the report. These main points should be supported by adequate evidence.
- Additional information : Identify the supporting information that analyses and confirms the main points. This information should be placed in appendices.
- Logical structure : Organise the entire information into a logical structure to help the readers easily navigate to the desired part of the report.
- Write : After deciding the logical structure of the report, fill in the elements of the report, including executive summary, main body, introduction and conclusion.
- Revise : Finally, verify if it is appropriate for the problem, audience, and purpose.
Feasibility Reports
A feasibility report is a written document that analyses the proposed solution and examines whether it is feasible considering various types of constraints such as financial, social, environmental, social, technical, and legal that can make it impossible for a solution to be opted.
Feasibility reports assess the practicality of following a particular course of action for a project. It advises whether it will be feasible to opt for a particular course of action or will this proposal or plan work? These are written internal reports that advise on consolidating departments or to organise a wellness programme for employees or to outsource company’s accounting or social media or to move the manufacturing unit to a new location.
Some companies hire a professional consultant to write feasibility reports in order to investigate a problem. These reports help in deciding whether to proceed or reject the proposed option.
- Overview of the Project
- Objectives of the Project
- The Need for the Project
- Overview of Existing Systems and Technologies
- Scope of the Project
- Deliverables
- Financial Feasibility
- Technical Feasibility
- Resource and Time Feasibility
- Risk Feasibility
- Social/Legal Feasibility
- Considerations
Proposal Writing
A business proposal is defined as a written document from a seller that offers a particular service or product to a prospective buyer. Business proposals are important in scenarios where a buyer might consider multiple prices in a transaction.
A good business proposal considers the buyer’s requirements and puts forth the seller’s proposal in a way that favours the seller’s products and services, and persuades the buyer about the offer. A business proposal is a critical document as it determines the difference between success and failure in a venture. Business proposals can be:
- Solicited : These are requested by clients themselves or submitted in response to an advertisement published by the client. Solicited business proposals generally have a better chance of success since they are tailored to the requirements of the person receiving the proposal.
- Unsolicited : These are submitted to potential clients even though they did not request for one. These are non-specific proposals and have no direct connection to the client’s requirements. Sellers use them to market a product or service to a prospective customer.
Because proposals are time-consuming, it is the best to start with available templates if possible. You will save a lot of time if you start with a proposal template that matches what you need and then customise it according to your requirements.
A business proposal includes various sections which are defined as follows:
Cover letter
Executive summary, pricing information, terms and conditions.
In the other article, you studied writing cover letters for a job application. A business proposal also needs a cover letter because a good cover letter will stimulate interest in the proposal. Make sure to highlight your positives and personalise them to the client to whom you are sending the business proposal.
This is where you give the client a ‘problem statement’ to help him identify the challenges and requirements in his business. This is because in order to persuade the client to do business with you, you first need to make sure that the client realises they have those needs. Then you briefly state how you will be able to help them meet those requirements.
The proposal is the part where you offer a detailed solution to the challenges and needs of the prospective client. This is the main reason for submitting a business proposal so it should be as detailed as possible, addressing all the needs of the client.
You should explain to the client all services that you can provide. You should tailor your list of services to suit the particular client’s needs but include other services that you may provide. Also include an estimated project schedule and time frame.
Most buyers consider the price of services before offering a contract. Thus, getting accurate pricing information is crucial. However, two points must be kept in mind. One it is important to be exact with the pricing and the second is to never negotiate below what you think the project is worth.
For smaller projects, a ‘fee summary’ will do the job. But a ‘fee schedule’ is needed for bigger projects, where payments need to be broken down to specific milestones.
It is in your interest to get legal counsel to review the proposal as this will cover your business against claims.
Business Communication Notes
( Click on Topic to Read )
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
Types of Communication
7 c of communication.
- Barriers To Business Communication
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
- Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
- Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
Organisational communication.
- Horizontal C ommunication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Group Discussion?
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
- Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
- What Is Market Segmentation?
- What Is Marketing Mix?
- Marketing Concept
- Marketing Management Process
- What Is Marketing Environment?
- What Is Consumer Behaviour?
- Business Buyer Behaviour
- Demand Forecasting
- 7 Stages Of New Product Development
- Methods Of Pricing
- What Is Public Relations?
- What Is Marketing Management?
- What Is Sales Promotion?
- Types Of Sales Promotion
- Techniques Of Sales Promotion
- What Is Personal Selling?
- What Is Advertising?
- Market Entry Strategy
- What Is Marketing Planning?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- Brand Building Process
- Kotler Five Product Level Model
- Classification Of Products
- Types Of Logistics
- What Is Consumer Research?
- What Is DAGMAR?
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- What Is Green Marketing?
- What Is Electronic Commerce?
- Agricultural Cooperative Marketing
- What Is Marketing Control?
- What Is Marketing Communication?
- What Is Pricing?
- Models Of Communication
- What is Sales Management?
- Objectives of Sales Management
- Responsibilities and Skills of Sales Manager
- Theories of Personal Selling
- What is Sales Forecasting?
- Methods of Sales Forecasting
- Purpose of Sales Budgeting
- Methods of Sales Budgeting
- Types of Sales Budgeting
- Sales Budgeting Process
- What is Sales Quotas?
- What is Selling by Objectives (SBO) ?
- What is Sales Organisation?
- Types of Sales Force Structure
- Recruiting and Selecting Sales Personnel
- Training and Development of Salesforce
- Compensating the Sales Force
- Time and Territory Management
- What Is Logistics?
- What Is Logistics System?
- Technologies in Logistics
- What Is Distribution Management?
- What Is Marketing Intermediaries?
- Conventional Distribution System
- Functions of Distribution Channels
- What is Channel Design?
- Types of Wholesalers and Retailers
- What is Vertical Marketing Systems?
- What i s Marketing?
- What i s A BCG Matrix?
- 5 M’S Of Advertising
- What i s Direct Marketing?
- Marketing Mix For Services
- What Market Intelligence System?
- What i s Trade Union?
- What Is International Marketing?
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- What i s International Marketing Research?
- What is Exporting?
- What is Licensing?
- What is Franchising?
- What is Joint Venture?
- What is Turnkey Projects?
- What is Management Contracts?
- What is Foreign Direct Investment?
- Factors That Influence Entry Mode Choice In Foreign Markets
- What is Price Escalations?
- What is Transfer Pricing?
- Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC)
- What is Promotion Mix?
- Factors Affecting Promotion Mix
- Functions & Role Of Advertising
- What is Database Marketing?
- What is Advertising Budget?
- What is Advertising Agency?
- What is Market Intelligence?
- What is Industrial Marketing?
- What is Customer Value
- What is Consumer Behaviour?
- What Is Personality?
- What Is Perception?
- What Is Learning?
- What Is Attitude?
- What Is Motivation?
- Consumer Imagery
- Consumer Attitude Formation
- What Is Culture?
- Consumer Decision Making Process
- Applications of Consumer Behaviour in Marketing
- Motivational Research
- Theoretical Approaches to Study of Consumer Behaviour
- Consumer Involvement
- Consumer Lifestyle
- Theories of Personality
- Outlet Selection
- Organizational Buying Behaviour
- Reference Groups
- Consumer Protection Act, 1986
- Diffusion of Innovation
- Opinion Leaders
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India
- What is Brand Management?
- 4 Steps of Strategic Brand Management Process
- Customer Based Brand Equity
- What is Brand Equity?
You Might Also Like
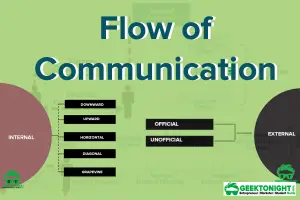
Flow of Communication: Internal and External
What is johari window model.

What is Interview? Types, Questions, Do’s and Don’ts, Preparing

What is Digital Communication? Website, Social Media, Blogging as Tool of Communication

What is Upward Communication? Advantages, Disadvantages

10 Verbal Communication Skills Worth Mastering
What is a presentation objectives, elements, important skills, four ps.
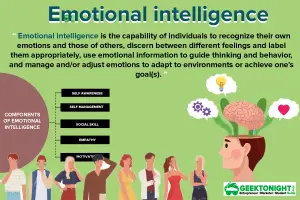
Emotional Intelligence
Leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
World's Best Online Courses at One Place
We’ve spent the time in finding, so you can spend your time in learning
Digital Marketing
Personal growth.

Development

What is Report Writing: Format, Examples, Types & Process
- Table of Contents
Many professionals struggle to create effective reports due to a lack of understanding of the essential elements and organization required. This can lead to frustration and a failure to communicate key information to the intended audience.
In this blog, we’ll explore what is report writing, the types of reports, essential elements, and tips for creating effective reports to help you communicate your message and achieve your goals.
Definition of report writing?
According to Mary Munter and Lynn Hamilton, authors of “Guide to Managerial Communication,” report writing is “the process of selecting, organizing, interpreting, and communicating information to meet a specific objective.”
What is report writing?
Report writing refers to the process of creating a document that represents information in a clear and concise manner. Reports can be written for various purposes, such as providing updates on a project, analyzing data or presenting findings, or making recommendations.
Effective report writing requires careful planning, research, analysis, and organization of information. A well-structured report should be accurate, and objective, and contain a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. It should also be written in a professional and accessible style, with appropriate use of headings, subheadings, tables, graphs, and other visual aids.
Overall, report writing is an important skill for professionals in many fields, as it helps to communicate information and insights in a clear and concise manner.
What is a report?
A report is a formal document that is structured and presented in an organized manner, with the aim of conveying information, analyzing data, and providing recommendations. It is often used to communicate findings and outcomes to a specific audience, such as stakeholders, or managers. Reports can vary in length and format, but they usually contain a clear introduction, body, and conclusion.
Types of report writing
By understanding the different types of report writing, individuals can select the appropriate format and structure to effectively communicate information and achieve their objectives. However, the kind of report used will depend on the purpose, audience, and context of the report.
1/ Informational reports: These reports provide information about a topic, such as a product, service, or process.
Further Reading : What is an information report
2/ Analytical reports: These reports present data or information in a structured and organized manner, often with charts, graphs, or tables, to help the reader understand trends, patterns, or relationships.
3/ Formal Reports: These are detailed and structured reports written for a specific audience, often with a specific objective. In comparison with informal reports , formal reports are typically longer and more complex than other types of reports.
4/ Progress reports: These reports provide updates on a project or initiative, detailing the progress made and any challenges or obstacles encountered.
5/ Technical reports: These reports provide technical information, such as specifications, designs, or performance data, often aimed at a technical audience.
6/ Research reports: These reports present the findings of research conducted on a particular topic or issue, often including a literature review, data analysis, and conclusions.
7/ Feasibility Report: A feasibility report assesses the likelihood of achieving success for a suggested project or initiative.
8/ Business Reports: These reports are used in a business setting to communicate information about a company’s performance, operations, or strategies. Different types of business reports include financial statements, marketing reports, and annual reports.
Structure of report writing
The structure of a report refers to the overall organization and layout of the report, including the sections and subsections that make up the report, their order, and their relationships to each other. A report can we divided into three parts.
Preliminary Parts:
- Acknowledgments (Preface or Foreword)
- List of Tables and Illustrations
- Introduction (clear statement of research objectives, background information, hypotheses, methodology, statistical analysis, scope of study, limitations)
- Statement of findings and recommendations (summarized findings, non-technical language)
- Results (detailed presentation of findings with supporting data in the form of tables and charts, statistical summaries, and reductions of data, presented in a logical sequence)
- Implications of the results (clearly stated implications that flow from the results of the study)
- Summary (brief summary of the research problem, methodology, major findings, and major conclusions)
End Matter:
- Appendices (technical data such as questionnaires, sample information, and mathematical derivations)
- Bibliography of sources consulted.
This structure provides a clear and organized framework for presenting a research report, ensuring that all important information is included and presented in a logical and easy-to-follow manner.
Extra Learnings Role of a report structure in report writing The report structure plays a crucial role in report writing as it provides a clear and organized framework for presenting information in an effective and logical manner. It ensures that the reader can easily understand the purpose and scope of the report, locate and access the relevant information. The preliminary parts of the report, provide an overview of the report and aid navigation. The main text makes it easier for the reader to comprehend and analyze the information. And The end matter provides additional details and sources for reference. An organized report structure also helps the author to communicate their research and ideas effectively to the intended audience.
What is the report writing format?
The format of report writing refers to the structure of a formal document that provides information on a particular topic or issue. The report writing format typically includes the following key components:
8 Essential elements of report writing are:
1/ Title: The title is the first thing that readers will see, and it should be clear and concise. The title should include the report’s subject or topic and the author’s name, date of writing, or who the report is for. Remember to keep the title brief and informative, avoiding vague or ambiguous language.
Example of Business Report Title Page: “Market Analysis and Growth Strategies for XYZ Corporation” Author: Mary Johnson Date: January 2, 2022 Company: Earthcon Corporation Department: Strategy and Planning
In this example, the title page includes the name of the report, ‘Market Analysis 2022,’ the author’s name, ‘John Doe,’ the submission date, ‘January 1, 2024,’ and other details such as the name of the organization, ‘Earthcon Corporation.’
2/ Table of Contents : The table of contents provides an overview of the report’s contents. It should list all sections and subsections with clear headings. It is essential to make the table of contents organized and easy to read, allowing readers to locate specific information quickly.
Example of Table of Contents I. Introduction…… 1 Purpose of the Report…… 2 Methodology Used…… 2 II. Executive Summary…… 3 III. Background and Context…… 3 IV. Analysis and Findings…… 4 Market Trends and Data…… 5 Competitor Analysis…… 6 SWOT Analysis…… 7 V. Recommendations and Conclusion…… 8 VI. References…… 9
3/ Summary : Also known as the executive summary, the summary provides a brief overview of the entire report. It should summarize the report’s main points, including findings, objectives, and recommendations. The summary should be written after the entire report is completed, and it should be concise and summarized in less than one page.
Example of executive summary: The Annual Sales Report for Earthcon Company shows a 10% increase in overall sales compared to the previous year. The report also reveals that the majority of sales came from the Midwest region and the target demographic is primarily males aged 25-40. Based on these findings, recommendations have been made to focus marketing efforts towards this demographic in the upcoming year.
4/ Introduction : The introduction introduces the report’s topic and informs readers what they can expect to find in the report. The introduction should capture readers’ attention and provide relevant background information. It should be clear and concise, including why the report was written and its objectives.
Example of Introduction: This comprehensive report aims to analyze and evaluate the sales performance of EarthCon Corporation throughout 2024. It will look into detailed sales trends observed throughout the year, carefully examining the various factors that have influenced these trends. Additionally, the report will identify and highlight potential areas for growth, offering valuable insights and recommendations to drive future success.
5/ Body: The body is the longest section and includes all the information, data, and analysis. It should present information in an organized manner, often using subheadings and bullet points. The body should include all relevant research findings and data, often accompanied by visuals such as graphs and tables. It is essential to cite all sources correctly and remain objective, avoiding personal opinions or biases.
Example of Background and Context: This report seeks to analyze the influence of technological advancements on business productivity. Previous research has indicated a correlation between the adoption of innovative technologies and increased operational efficiency for Earthcon. The report will examine further into this topic and offer suggestions for maximizing the benefits of these advancements. Example of Analysis and Findings: The market trends and data show a steady increase in demand for innovative products, with a significant rise in sales in the past five years. In comparison, competitor analysis reveals that Earthcon Corporation is well-positioned to take advantage of this trend due to its strong brand reputation and product portfolio. A SWOT analysis also highlights potential areas for improvement and growth.
6/ Conclusion: The conclusion summarizes the findings and conclusions of the report. It should wrap up all the essential information presented in the body and make recommendations based on the report’s findings. The conclusion must be brief and clear, avoiding the introduction of any new information not previously presented in the body.
7/ Recommendations: The recommendation section should provide suggested goals or steps based on the report’s information. It should be realistic and achievable, providing well-crafted solutions. It is often included in the conclusion section.
Example of Recommendations and Conclusion: Based on the analysis, it is recommended that EarthCon Corporation invest in research and development to continue producing innovative products. Additionally, efforts should be made to expand into emerging markets to increase global reach. In conclusion, the Annual Sales Report shows positive outcomes and recommends strategic actions for future growth.
8/ Appendices: The appendices section includes additional technical information or supporting materials, such as research questionnaires or survey data. It should provide supplementary information to the report without disrupting the report’s main content.
It is important to use clear headings and subheadings and to label tables and figures. Also, proofreading and fact-checking are critical before submitting the report. A well-crafted report is concise, informative and free of personal bias or opinions.
What are the features of report writing
There are several key features of effective report writing that can help ensure that the information presented is clear, concise, and useful. Some of these features include:
1/ Clarity: Reports should be written in clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or technical terms that may be confusing to the reader.
2/ Objectivity: A report should be objective, meaning that it should be free from bias or personal opinions. This is particularly important when presenting data or analysis.
3/ Accuracy: Reports should be based on reliable sources and accurate data. Information should be verified and cross-checked to ensure that it is correct and up-to-date.
4/ Structure: A report should be structured in a logical and organized manner, with clear headings, subheadings, and sections.
5/ Visual aids: A report may include visual aids such as charts, tables, and graphs, which can help to illustrate the key points and make the information easier to understand.
6/ Evidence: Reports should include evidence to support any claims or findings, such as statistics, quotes, or references to relevant literature.
7/ Recommendations: Many reports include recommendations or suggestions for future action based on the findings or analysis presented.
Significance of report writing
Report writing is a critical skill that can have a significant impact on individuals, and organizations. In fact, a report by the National Association of Colleges and Employers found that the ability to communicate effectively, including report writing, was the most important skill sought by employers.
- Reports provide decision-makers with the information they need to make informed decisions.
- Effective report writing demonstrates professionalism and attention to detail, which can help to build trust and credibility with clients.
- Reports can inform planning processes by providing data and insights that can be used to develop strategies and allocate resources.
- Reports often include recommendations or suggestions for future action, which can help to improve processes, procedures, or outcomes.
Further Reading: What is the significance of report writing
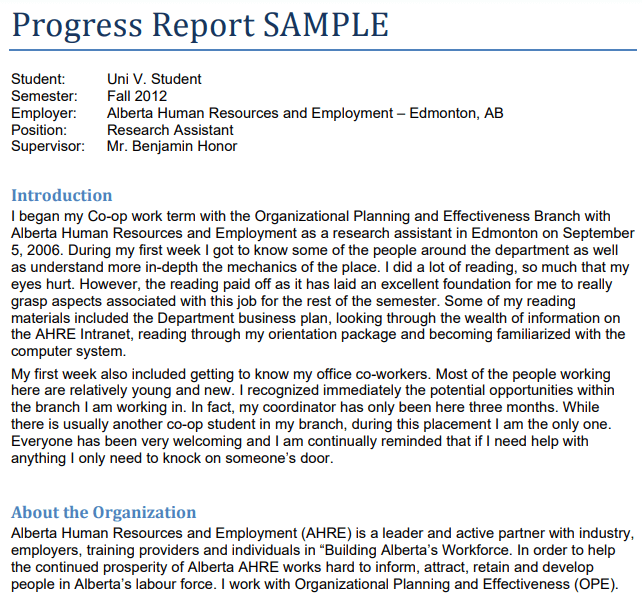
Report writing examples and samples

Example of Progress Report
The essential process of report writing
Report writing requires careful planning, organization, and analysis to ensure that the report effectively communicates the intended message to the audience. Here are the general steps involved in the process of report writing:
Plan and prepare:
- Identify the purpose of the report, the target audience, and the scope of the report.
- Collect and examine data from different sources, including research studies, surveys, or interviews.
- Create an outline of the report, including headings and subheadings.
Write the introduction:
- Start with a brief summary of the report and its purpose.
- Provide background information and context for the report.
- Explain the research methodology and approach used.
Write the main body:
- Divide the report into logical sections, each with a clear heading.
- Present the findings and analysis of the research in a clear and organized manner.
- Use appropriate visual aids, such as tables, graphs, or charts to present data and information.
- Utilize a language that is both clear and Brief, and avoid using unnecessary jargon or technical terminology.
- Cite all sources used in the report according to a specified citation style.
Write the conclusion:
- Summarize the main findings and conclusions of the report.
- Restate the purpose of the report and how it was achieved.
- Provide recommendations or suggestions for further action, if applicable.
Edit and revise:
- Review the report for errors in grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Check that all information is accurate and up-to-date.
- Revise and improve the report as necessary.
Format and present:
- Use a professional and appropriate format for the report.
- Include a title page, table of contents, and list of references or citations.
- Incorporate headings, subheadings, and bullet points to enhance the report’s readability and facilitate navigation.
- Use appropriate fonts and sizes, and ensure that the report is well-structured and visually appealing.
Important Principles of report writing
To write an effective report, it is important to follow some basic principles. These principles ensure that your report is clear, concise, accurate, and informative. In this regard, here are some of the key principles that you should keep in mind when writing a report:
1/ Clarity: The report should be clear and easy to understand.
2/ Completeness: The report should cover all the relevant information needed to understand the topic
3/ Conciseness: A report should be concise, presenting only the information that is relevant and necessary to the topic.
4/ Formatting: The report should be properly formatted, with consistent fonts, spacing, and margins
5/ Relevance: The information presented in the report should be relevant to the purpose of the report.
6/ Timeliness: The report should be completed and delivered in a timely manner.
7/ Presentation: The report should be visually appealing and well-presented.
Extra Learnings Styles of report writing When it comes to the style of report writing, it’s important to use hard facts and figures, evidence, and justification. Using efficient language is crucial since lengthy reports with too many words are difficult to read. The most effective reports are easy and quick to read since the writer has comprehended the data and formulated practical recommendations. To achieve this, it’s important to write as you speak, avoid empty words, use descending order of importance, use an active voice, and keep sentences short. The goal should be to write to express and not to impress the reader. It’s also important to get facts 100% right and to be unbiased and open. By following these tips, one can create a well-written report that is easy to understand and provides valuable insights.
Differences between a report and other forms of writing
Reports are a specific form of writing that serves a distinct purpose and have unique characteristics. Unlike other forms of writing, such as essays or fiction, reports are typically focused on presenting factual information and making recommendations based on that information. Below we have differentiated report writing with various other forms of writing.
Essay vs report writing
Project writing vs report writing, research methodology vs report writing, article writing vs report writing, content writing vs report writing, business plan vs report writing, latest topics for report writing in 2024.
The possibilities for report topics may depend on the goals and scope of the report. The key is to choose a topic that is relevant and interesting to your audience, and that you can conduct thorough research on in order to provide meaningful insights and recommendations.
- A market analysis for a new product or service.
- An evaluation of employee satisfaction in a company.
- A review of the state of cybersecurity in a particular industry.
- A study of the prevalence and consequences of workplace discrimination.
- Analysis of the environmental impact of a particular industry or company.
- An assessment of the impact of new technology or innovations on a particular industry or sector.
Report writing skills and techniques
Effective report writing requires a combination of skills and techniques to communicate information and recommendations in a clear, and engaging manner.
From organizing information to tailoring the report to the intended audience, there are many factors to consider when writing a report. By mastering these skills and techniques, you can ensure that your report is well-written, informative, and engaging for your audience. Some of the primary ones are:
1/ Organization and structure: Structure your report in a logical and organized manner with headings and subheadings.
2/ Use of data and evidence: Present objective data and evidence to support your findings and recommendations.
3/ Audience awareness: Tailor your report to the needs and interests of your intended audience.
4/ Effective visuals: Use graphs, charts, or other visuals to communicate complex information in a clear and engaging way.
5/ Editing and proofreading: Carefully edit and proofread your report to ensure it is error-free and professional.
6/ Tone: Use a professional and objective tone to communicate your findings and recommendations.
7/ Time management: Manage your time effectively to ensure you have enough time to research, write, and revise your report.
Tips for effective report writing
- Understand your audience before you start writing.
- Start with an outline and cover all the important points.
- Employ clear and concise language.
- Utilize headings and subheadings to organize your report.
- Incorporate evidence and examples to support your points.
- Thoroughly edit and proofread your report before submission.
- Follow formatting guidelines If your report has specific formatting requirements.
- Use visuals to enhance understanding.
What is the ethical consideration involved in report writing
Ethical considerations play a crucial role in report writing. The accuracy of the information presented in the report is of utmost importance, as it forms the basis for any conclusions or recommendations that may be made. In addition, it is essential to avoid plagiarism by giving credit to the original sources of information and ideas.
Another crucial ethical consideration is confidentiality, particularly when the report contains sensitive or confidential information. It is important to safeguard this information and prevent its disclosure to unauthorized individuals.
Avoiding bias in report writing is also crucial, as it is essential to present information in an objective and unbiased manner. In cases where research or data collection is involved, obtaining informed consent from human subjects is a necessary ethical requirement.
By taking these ethical considerations into account, report writers can ensure that their work is fair, accurate, and respectful to all parties involved.
Common mistakes in report writing
There are several common mistakes that students and report writers make in report writing. By avoiding these common mistakes, students as well as report writers can create effective and impactful reports that are clear, accurate, and objective.
1/ Writing in the first person: Often, students and report writers commit an error by writing in the first person and utilizing words such as “I” or “me. In reports, it is recommended to write impersonally, using the passive voice instead.
2/ Using the wrong format: Reports should use numbered headings and subheadings to structure the content, while essays should have a clear line of argument in their content.
3/ Failing to introduce the content: The introduction of the report should introduce the content of the report, not the subject for discussion. It is important to explain the scope of the report and what is to follow, rather than explaining what a certain concept is.
4/ Missing relevant sections: Students and report writers, often miss out on including relevant sections that were specified in the assignment instructions, such as a bibliography or certain types of information. This can result in poor interpretation.
5/ Poor proofreading: Finally, not spending enough time proofreading the reported work can create unwanted mistakes. Therefore, It is important to proofread and correct errors multiple times before submitting the final report to avoid any mistakes that could have been easily corrected.
By avoiding these common mistakes, students and report writers can improve the quality of their reports.
What are some challenges of report writing and how to overcome them
Report writing can be a challenging task for many reasons. Here are some common challenges of report writing and how to overcome them:
1/ Lack of clarity on the purpose of the report: To overcome this challenge, it is important to clearly define the purpose of the report before starting. This can help to focus the content of the report and ensure that it meets the needs of the intended audience.
2/ Difficulty in organizing ideas: Reports often require a significant amount of information to be organized in a logical and coherent manner. To overcome this challenge, it can be helpful to create an outline or flowchart to organize ideas before beginning to write.
3/ Time management: Writing a report can be time-consuming, and it is important to allow sufficient time to complete the task. To overcome this challenge, it can be helpful to create a timeline or schedule for the various stages of the report-writing process.
4/ Writer’s block: Sometimes writers may experience writer’s block, making it difficult to start or continue writing the report. To overcome this challenge, it can be helpful to take a break, engage in other activities or brainstorming sessions to generate new ideas.
5/ Difficulty in citing sources: It is important to properly cite sources used in the report to avoid plagiarism and maintain credibility. To overcome this challenge, it can be helpful to use citation management tools, such as EndNote or Mendeley, to keep track of sources and ensure accurate referencing.
6/ Review and editing: Reviewing and editing a report can be a challenging task, especially when it is one’s own work. To overcome this challenge, it can be helpful to take a break before reviewing the report and seek feedback from others to gain a fresh perspective.
By being aware of these challenges and taking proactive steps to overcome them, report writers can create effective and impactful reports that meet the needs of their intended audience.
Best Software for writing reports
Report writing software has made it easier for writers to produce professional-looking reports with ease. These software tools offer a range of features and functionalities, including data visualization, collaboration, and customization options. In this section, we will explore some of the best report-writing software available:
1/ Tableau : This tool is great for creating interactive and visually appealing reports, as it allows users to easily create charts, graphs, and other data visualizations. It also supports data blending, which means that you can combine data from multiple sources to create more comprehensive reports.
2/ Zoho reporting : This tool is designed to help users create and share professional-looking reports quickly and easily. It offers a variety of customizable templates, as well as a drag-and-drop interface that makes it easy to add data and create charts and graphs.
3/ Bold Reports by Syncfusion : This tool is designed specifically for creating reports in .NET applications. It offers a wide range of features, including interactive dashboards, real-time data connectivity, and customizable themes and templates.
4/ Fast Reports : This tool is a reporting solution for businesses of all sizes. It allows users to create reports quickly and easily using a drag-and-drop interface and offers a variety of templates and customization options. It also supports a wide range of data sources, including databases, spreadsheets, and web services.
Further Reading : 10+ Best Report Writing Software and Tools in 2024
What is the conclusion of report writing
The conclusion of report writing is the final section of the report that summarizes the main findings, conclusions, and recommendations. It should tie together all the different sections of the report and present a clear and concise summary of the key points.
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEWCASTLE has given an inverted introduction framework that can use used for writing effective conclusions for reports.
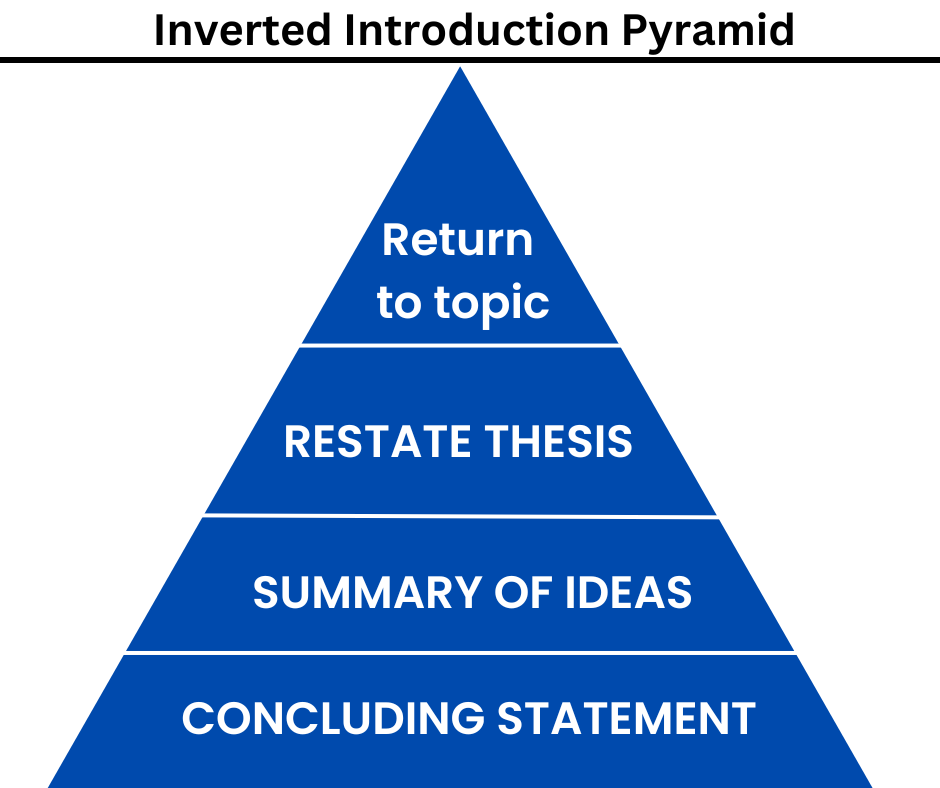
Example of conclusion in report writing:
The implication of the above diagram can be explained with the following example:
1. RETURN TO TOPIC:
Social media has revolutionized the marketing landscape, providing new opportunities for brands to connect with their target audience.
2. RESTATE THESIS:
However, the complexities and limitations of social media mean that it is unlikely to completely replace traditional marketing methods. The role of the marketing professional remains crucial in ensuring that social media strategies align with the company’s overall goals and effectively reach the desired audience.
3. SUMMARY OF IDEAS DISCUSSED:
Automated tools cannot fully account for the nuances of human communication or provide the level of personalization that consumers crave. Therefore, the most effective marketing strategies will likely blend social media tactics with traditional marketing channels.
4. CONCLUDING STATEMENT [restating thesis]:
In conclusion, while social media presents significant opportunities for brands, the expertise of marketing professionals is still essential to creating successful campaigns that achieve desired outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) what is report writing and example.
Ans: Report writing involves preparing a structured document that delivers information to a particular audience in a clear and systematic manner. An example of a report could be a business report analyzing the financial performance of a company and making recommendations for improvement.
Q2) What is report writing and types of reports?
Ans: The act of presenting information in an orderly and structured format is known as report writing. Reports come in different types, such as analytical reports, research reports, financial reports, progress reports, incident reports, feasibility reports, and recommendation reports.
Q3) What are the 5 steps of report writing
The five steps of report writing, are as follows:
- Planning: This involves defining the purpose of the report, determining the audience, and conducting research to gather the necessary information.
- Structuring: This step involves deciding on the structure of the report, such as the sections and subsections, and creating an outline.
- Writing: This is the stage where the actual writing of the report takes place, including drafting and revising the content.
- Reviewing: In this step, the report is reviewed for accuracy, coherence, and effectiveness, and any necessary changes are made.
- Presenting: This final step involves presenting the report in a clear and professional manner, such as through the use of headings, visuals, and a table of contents.
Q4) What is a report in short answer?
Share your read share this content.
- Opens in a new window
Aditya Soni
You might also like.

10 Differences Between Formal & Informal Reports + Examples

24 Types of Business Reports With Samples & Writing Structure

11 Characteristics of a Good Business Report
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
20 Types of Report Writing: A Detailed Guide
A Report is a written record detailing observation, information, actions taken, or investigations conducted. There are various Types of Report Writing. They provide an opportunity to hone a valuable skill that finds widespread use in the professional environment. Learn more about various Types of Report Writing and its characteristics through this blog.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Strategic Planning and Thinking Course
- Creative Writing Course
- Journalism Course
- Academic Writing Course

In the face of various Types of Report Writing, a pressing question arises: When should you use these Reports effectively? How can you position yourself ahead of the competition by harnessing the transformative potential of information? In this blog, we explore 20 Types of Report Writing, such as Formal Reports, Informal Reports, Audit Reports, Marketing Reports, Regular Progress Reports, Trend Reports, and more.
Table of Contents
1) What is Report Writing?
2) Types of Report Writing
a) Formal Report
b) Informal Report
c) Audit Report
d) Marketing Report
e) Regular Progress Report
f) Trend Report
g) Analytical Report
h) Long Reports
i) Short Reports
j) Proposal Reports
3) Conclusion
What is Report Writing?
Report Writing is a structured and systematic method of conveying information, findings, and analysis to a specific audience. Reports are typically used in academic, scientific, business, and professional settings to account for research, experiments, investigations, or other activities.
The primary purpose of a Report is to present data, facts, and recommendations in a clear, organised, and objective manner. A well-crafted Report should include the following characteristics:
1) Strict adherence to the Report brief's stipulations.
2) A thorough analysis of pertinent information.
3) Structuring the content in a coherent and logically ordered manner.
4) Consistent presentation following the guidelines outlined in the Report brief.
5) Drawing sound conclusions substantiated by evidence.

Types of Report Writing
The following are the different Types of Report Writing:

1) Formal Report
Formal Reports are typically characterised by their objective and detailed nature, devoid of personal anecdotes or references. They demand a meticulous structuring approach tailored to the specific style and intended purpose of the organisation.
Key Characteristics:
1) Objective and data driven.
2) Structured with a defined format.
2) Informal Report
Informal Reports represent a departure from the formal Report Writing Format, characterised by their lack of rigid structure, brevity, and the employment of casual language. They prioritise efficient communication over the structuring seen in formal Reports. Various types of informal Reports can be classified within this category, encompassing digital postings, emails, memorandum Reports, and certain internal documents.
1) Brief and to the point.
2) Informal language and style.
Learn everything from assertiveness and self-esteem skills to negotiation and writing skills with our Personal Development Training and stay ahead of the learning curve!
3) Audit Report
Audit Reports are essential in assessing an organisation's financial status and compliance with auditing standards. These Reports provide a snapshot of the financial health of a business, highlighting areas that need attention and improvement. An Audit Report is a structured and official document prepared by an auditor to provide an assessment of an organisation's financial condition. These Reports adhere to the established framework of Generally Accepted Auditing Standards (GAAS).
It's worth noting that the specific format of Audit Reports may exhibit minor variations, contingent upon the unique circumstances of the audit in question.
1) Focus on financial data and compliance.
2) Objective and fact-based.
4) Marketing Report
Marketing Reports are essential tools that provide a deep dive into the world of marketing campaigns. They offer an overview of promotional activities that encompass a wide spectrum, ranging from traditional, on-ground marketing efforts to contemporary social media campaigns.
Marketing Reports play a vital role in the post-campaign analysis. They help marketing professionals and stakeholders understand what worked effectively and what areas require improvement. By presenting detailed data and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), these Reports provide valuable insights that can be used to refine future marketing strategies.
1) Focus on marketing activities and results.
2) Use data and analytics to evaluate performance.
5) Regular Progress Report
Progress Reports, also known as periodic Reports, are crafted and distributed at fixed time intervals to track and communicate the evolution of a project, business, or specific processes. These intervals can span, ranging from daily and weekly updates to monthly, quarterly, and even annual summaries. In some cases, they might align with scheduled calendar dates.
The primary purpose of Progress Reports is to furnish stakeholders with precise and timely insights into the performance and advancement of a particular endeavour. They serve as a vital mechanism for keeping everyone informed about the status of a project, department, or organisation.
6) Trend Report
Referred to as trend analysis Reports, these documents scrutinise routine business activities and juxtapose them against previously projected outcomes. They analyse business operations and compare them to forecasts. These Reports help organisations discover current industry trends and how to leverage them for their benefit.
These Reports are instrumental in aiding businesses in uncovering contemporary trends within their respective industries and discerning how these trends can be leveraged to the advantage of the organisation.
1) Focus on data analysis and comparisons.
2) Explore shifts and patterns in operations.
Acquire skills to recognise emergent approaches to monitoring and evaluation with our Strategic Planning And Thinking Course
7) Analytical Report
Significance of Analytical Reports has seen a significant upsurge, primarily driven by the increasing emphasis on data analysis.
These Reports have become important for organisations as they harness the power of data-driven insights, making them one of the most frequently employed Report types. What sets Analytical Reports apart is their unique ability to extract valuable recommendations aimed at enhancing business operations. By mining and interpreting data insights, they provide a means to scrutinise and assess performance comprehensively.
1) Rely on data analysis and interpretation.
2) Focus on assessing performance.
8) Long Reports
Long Reports, as their name implies, are extensive documents that typically encompass more than ten pages. Their classification as formal Reports is primarily due to their substantial length, and they serve as a medium for conveying detailed and in-depth information.
1) In-depth exploration of a subject.
2) Comprehensive analysis and discussion.
9) Short Reports
Short Reports are concise documents, usually not exceeding one page. They are suitable for announcing new results, conveying brief messages, or informing staff about imminent changes. These concise Reports find their purpose in announcing fresh findings or events. Short Reports can encompass memos or brief messages designed to update staff on imminent changes, making them an integral part of informal Report formats.
1) Highly concise and focused.
2) Usually, one page or less.
10) Proposal Reports
Proposal Reports, alternatively known as problem-solving Reports, come into play when an organisation or company encounters a particular challenge. These Reports are crafted with the explicit goal of identifying solutions to resolve the issue at hand. They typically encompass a comprehensive project overview, proposed solutions, and anticipated outcomes, providing a roadmap for implementing these strategies. They include project overviews, solutions, and anticipated outcomes, making them vital for strategy implementation.
1) Solution-focused.
2) Outline a problem and proposed solutions.
11) Functional Reports
Functional Reports encompass a variety of Report types, such as accounting Reports, fiscal Reports, and marketing Reports. They are instrumental in managing and optimising specific functions within an organisation, offering insights and data for informed decision-making.
1) Functional Reports are tailored to address specific areas or functions within an organisation, such as finance, marketing, or operations.
2) They rely on data, statistics, and performance metrics to provide insights and support decision-making.
Learn how to handle Creative Writing challenges with our Creative Writing Training .
12) Lateral Reports
Lateral Reports prioritise interdepartmental coordination within an organisation. They serve to transmit information, ensuring that the entire team is on the same page when making collective decisions.
1) Lateral Reports focus on enhancing coordination and communication between different departments within an organisation.
2) They serve as a conduit for sharing information horizontally across the organisation, ensuring that teams are aligned and informed.
13) Financial Report
Financial Reports are critical documents that provide an overview of an organisation's financial health. They include income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, offering a snapshot of the company's financial performance.
1) Financial Reports primarily contain data related to an organisation's financial health, including income, expenses, assets, and liabilities.
2) They often follow standard formats, such as income statements and balance sheets, to facilitate comparisons and analysis.
14) Sales Report
Sales Reports are central to tracking and analysing a company's sales performance. They include data on sales volume, revenue, customer acquisition, and market trends, providing insights to refine sales strategies.
1) Sales Reports are packed with performance metrics, including sales volume, revenue, customer acquisition, and market trends.
2) They link sales data to specific goals and objectives, providing a basis for performance evaluation.
15) Management Report
Management Reports are designed for organisational decision-makers, such as executives and managers. These Reports encompass a range of information, from financial and operational data to strategic insights, supporting effective management and strategic planning.
1) Management Reports cover a wide range of information, from financial and operational data to strategic insights and recommendations.
2) They are designed for decision-makers within the organisation, such as executives and managers, providing insights to support effective management and strategic planning.
16) IT Report
IT Reports cover various aspects of information technology, such as system performance, security, and project updates. They are essential for maintaining the efficiency and security of IT infrastructure.
1) IT Reports focus on the performance of an organisation's information technology systems and infrastructure.
2) They often address security, compliance, and potential risks to IT operations.
17) Social Media Report
Social media Reports offer an in-depth analysis of an organisation's social media presence. They include data on engagement, reach, and the effectiveness of social media campaigns, aiding in social media strategy development.
1) Social media Reports contain metrics related to an organisation's social media presence, such as engagement, reach, and user behaviour.
2) They assess the effectiveness of social media campaigns, helping organisations fine-tune their digital marketing strategies.
18) Manufacturing Report
Manufacturing Reports focus on the production process, quality control, and efficiency within a manufacturing facility. They provide valuable data for optimising operations and ensuring product quality.
1) Manufacturing Reports delve into the production process, quality control, and operational efficiency within a manufacturing facility.
2) They rely on data to ensure product quality and manufacturing efficiency.
19) Retail Report
Retail Reports are essential for monitoring sales, inventory management, and customer behaviour in the retail sector. They provide insights for improving store operations and customer satisfaction.
1) Retail Reports focus on monitoring sales, inventory management, and customer behaviour in retail settings.
2) They provide insights into customer preferences, buying behaviour, and trends.
20) Annual Report
Annual Reports are comprehensive documents that summarise an organisation's activities, performance, and financial status over the past year. They are typically intended for shareholders, investors, and other stakeholders, offering transparency and accountability.
1) Annual Reports provide a comprehensive summary of an organisation's activities, performance, and financial status over the past year.
2) They are primarily intended for shareholders, investors, and other stakeholders interested in the organisation's financial and operational performance.
Develop yourself as a skillful writer with our Personal Development Training and stay ahead of the learning curve!
Conclusion
Acquiring the skill of Report Writing is valuable for individuals in various aspects of life. These Reports can serve various purposes, including informing, analysing, or persuading a targeted audience. We hope our blog has answered your queries on the Types of Report Writing and its features.
Get Into Journalism Training to learn the styles of feature writing, sports writing and headlines writing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming business skills resources batches & dates.
Fri 7th Jun 2024
Fri 16th Aug 2024
Fri 4th Oct 2024
Fri 6th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
A Guide To The Top 14 Types Of Reports With Examples Of When To Use Them

Table of Contents
1) What Is The Report Definition?
2) Top 14 Types Of Reports
3) What Does A Report Look Like?
4) What To Look For In A Reporting Tool
Businesses have been producing reports forever. No matter what role or industry you work in, chances are that you have been faced with the task of generating a tedious report to show your progress or performance.
While reporting has been a common practice for many decades, the business world keeps evolving, and with more competitive industries, the need to generate fast and accurate reports becomes critical. This presents a problem for many modern organizations today, as building reports can take from hours to days. In fact, a survey about management reports performed by Deloitte says that 50% of managers are unsatisfied with the speed of delivery and the quality of the reports they receive.
With this issue in mind, several BI tools have been developed to assist businesses in generating interactive reports with just a few clicks, enhancing the way companies make critical decisions and service insights from their most valuable data.
But, with so many types of reports used daily, how can you know when to use them effectively? How can you push yourself ahead of the pack with the power of information? Here, we will explore the 14 most common types of reports in business and provide some examples of when to use them to your brand-boosting advantage. In addition, we will see how online dashboards have overthrown the static nature of classic reports and given way to a much faster, more interactive way of working with data.
Let’s get started with a brief report definition.
What Is The Report Definition?
A report is a document that presents relevant business information in an organized and understandable format. Each report is aimed at a specific audience and business purpose, and it summarizes the development of different activities based on goals and objectives.
That said, there are various types of reports that can be used for different purposes. Whether you want to track the progress of your strategies or stay compliant with financial laws, there is a different report for each task. To help you identify when to use them, we will cover the top 14 most common report formats used for businesses today.
What Are The Different Types Of Reports?

1. Informational Reports
The first in our list of reporting types is informational reports. As their name suggests, this report type aims to give factual insights about a specific topic. This can include performance reports, expense reports, and justification reports, among others. A differentiating characteristic of these reports is their objectivity; they are only meant to inform but not propose solutions or hypotheses. Common informational reports examples are for performance tracking, such as annual, monthly, or weekly reports .
2. Analytical Reports
This report type contains a mix of useful information to facilitate the decision-making process through a mix of qualitative and quantitative insights as well as real-time and historical insights. Unlike informational reports that purely inform users about a topic, this report type also aims to provide recommendations about the next steps and help with problem-solving. With this information in hand, businesses can build strategies based on analytical evidence and not simple intuition. With the use of the right BI reporting tool , businesses can generate various types of analytical reports that include accurate forecasts via predictive analytics technologies. Let's look at it with an analytical report example.
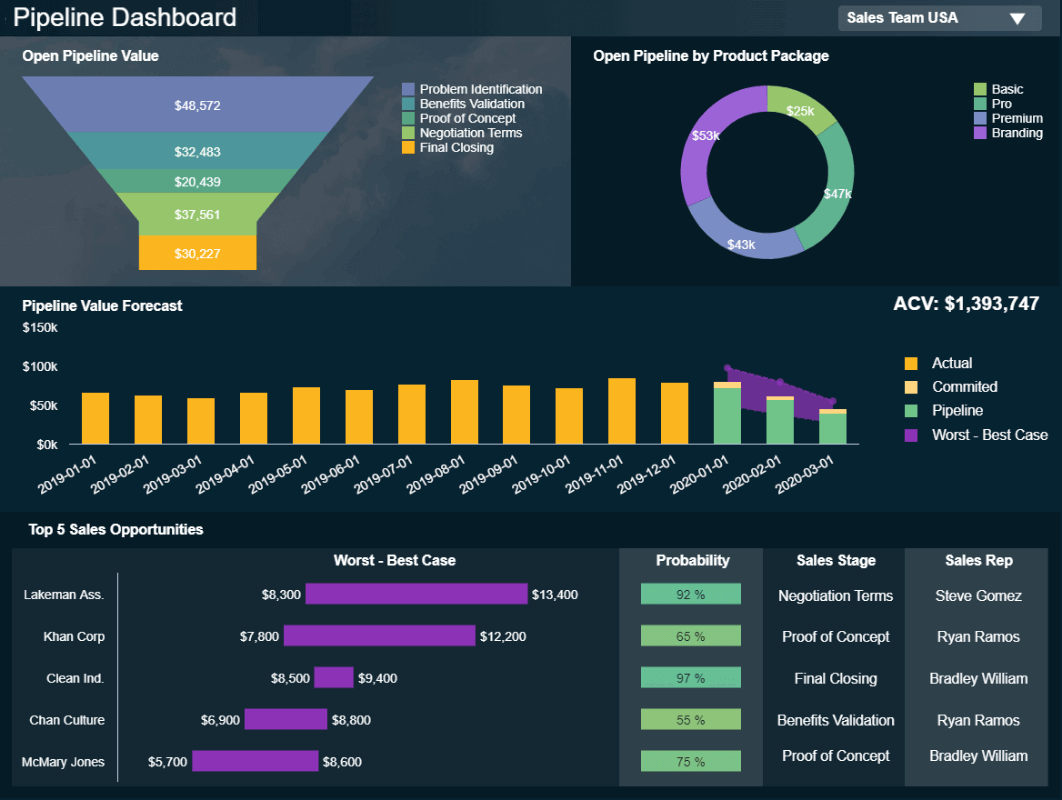
**click to enlarge**
The example above is the perfect representation of how analytical reports can boost a business’s performance. By getting detailed information such as sales opportunities, a probability rate, as well as an accurate pipeline value forecast based on historical data, sales teams can prepare their strategies in advance, tackle any inefficiencies, and make informed decisions for increased efficiency.
3. Operational Reports
These reports track every pertinent detail of the company's operational tasks, such as its production processes. They are typically short-term reports as they aim to paint a picture of the present. Businesses use this type of report to spot any issues and define their solutions or to identify improvement opportunities to optimize their operational efficiency. Operational reports are commonly used in manufacturing, logistics, and retail as they help keep track of inventory, production, and costs, among others.
4. Product Reports
As its name suggests, this report type is used to monitor several aspects related to product development. Businesses often use them to track which of their products or subscriptions are selling the most within a given time period, calculate inventories, or see what kind of product the client values the most. Another common use case of these reports is to research the implementation of new products or develop existing ones. Let’s see it in more detail with a visual example.
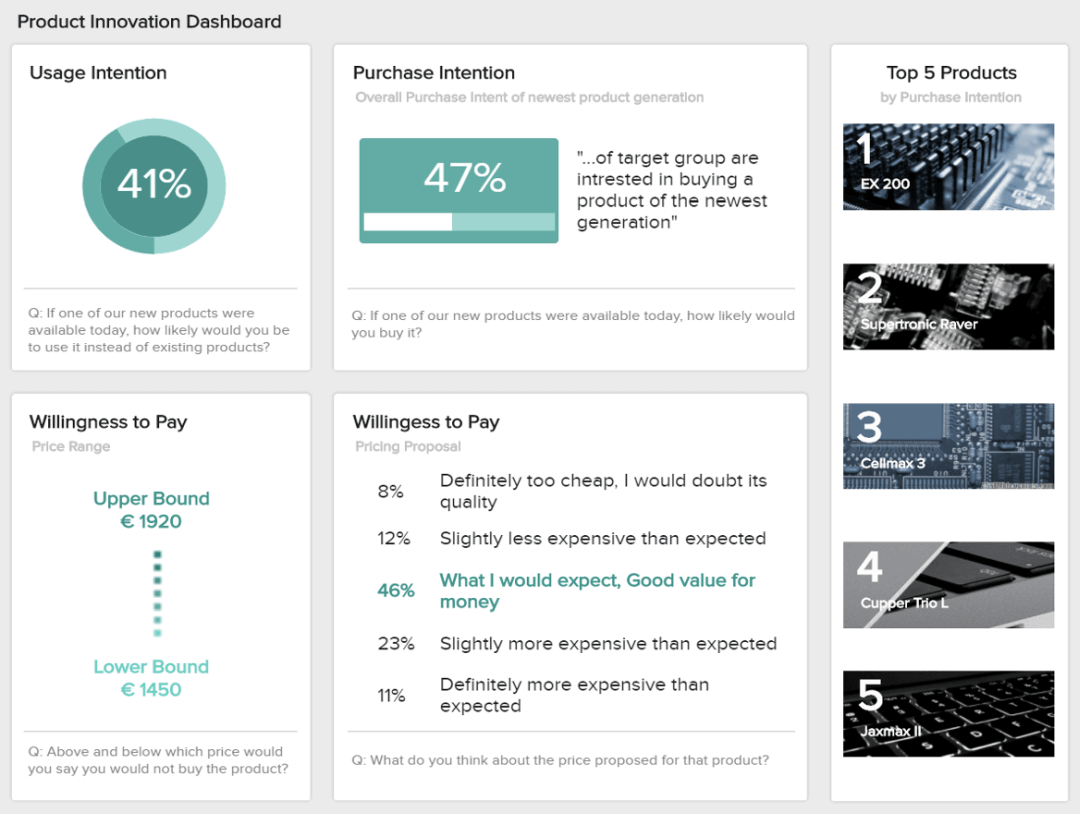
The image above is a product report that shows valuable insights regarding usage intention, purchase intention, willingness to pay, and more. In this case, the report is based on the answers from a survey that aimed to understand how the target customer would receive a new product. Getting this level of insights through this report type is very useful for businesses as it allows them to make smart investments when it comes to new products as well as set realistic pricing based on their client’s willingness to pay.
5. Industry Reports
Next in our list of the most common kinds of reports, we have industry-specific reports. Typically, these reports provide an overview of a particular industry, market, or sector with definitions, key trends, leading companies, and industry size, among others. They are particularly useful for businesses that want to enter a specific industry and want to learn how competitive it is or for companies who are looking to set performance benchmarks based on average industry values.
6. Department Reports
These reports are specific to each department or business function. They serve as a communication tool between managers and team members who must stay connected and work together for common goals. Whether it is the sales department, customer service, logistics, or finances, this specific report type helps track and optimize strategies on a deeper level. Let’s look at it with an example of a team performance report .

The image above is a department report created with an online data analysis tool , and it tracks the performance of a support team. This insightful report displays relevant metrics such as the top-performing agents, net promoter score, and first contact resolution rate, among others. Having this information in hand not only helps each team member to keep track of their individual progress but also allows managers to understand who needs more training and who is performing at their best.
7. Progress Reports
From the brunch of informational reports, progress reports provide critical information about the status of a project. These reports can be produced on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis by employees or managers to track performance and fine-tune tasks for the better development of the project. Progress reports are often used as visual materials to support meetings and discussions. A good example is a KPI scorecard .
8. Internal Reports
A type of report that encompasses many others on this list, internal reports refer to any type of report that is used internally in a business. They convey information between team members and departments to keep communication flowing regarding goals and business objectives.
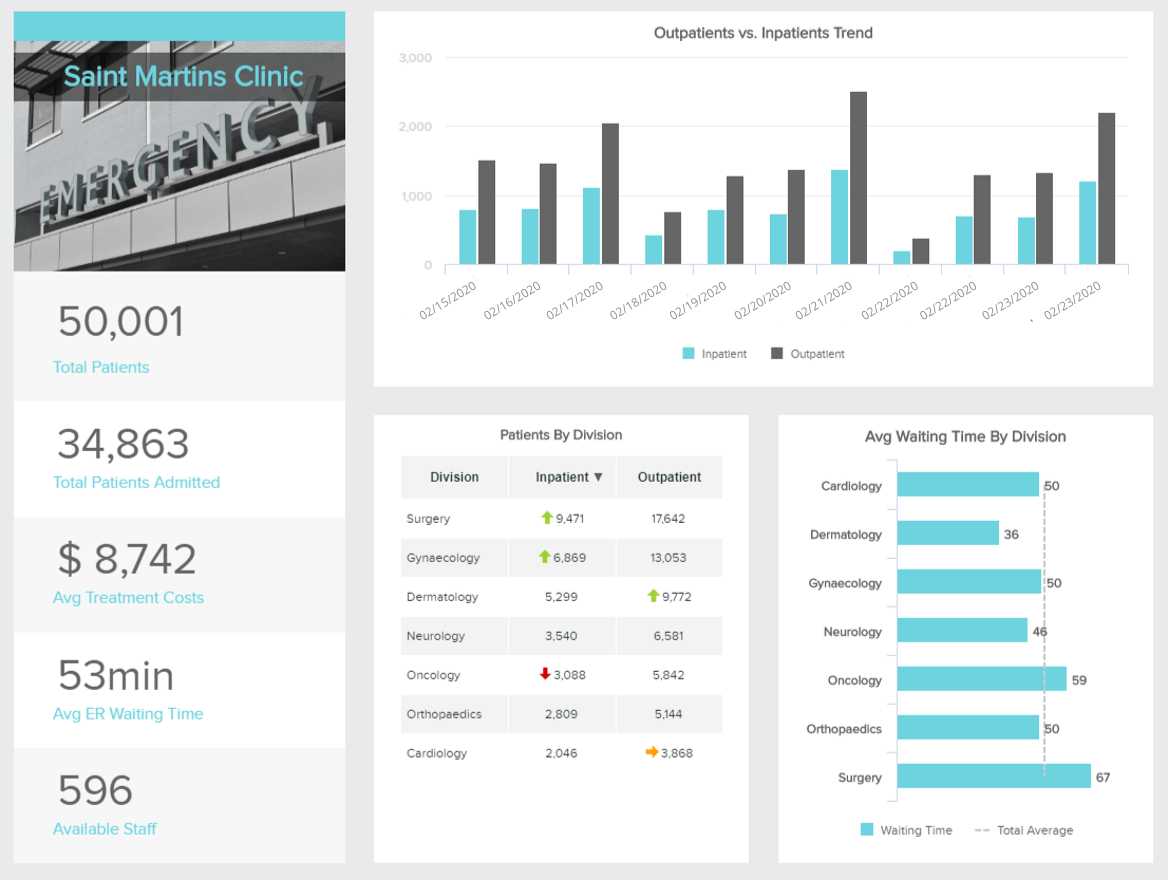
As mentioned above, internal reports are useful communication tools to keep every relevant person in the organization informed and engaged. This healthcare report aims to do just that. By providing insights into the performance of different departments and areas of a hospital, such as in and outpatients, average waiting times, treatment costs, and more, healthcare managers can allocate resources and plan the schedule accurately, as well as monitor any changes or issues in real-time.
9. External Reports
Although most of the reports types listed here are used for internal purposes, not all reporting is meant to be used behind closed doors. External reports are created to share information with external stakeholders such as clients or investors for budget or progress accountability, as well as to governmental bodies to stay compliant with the law requirements.
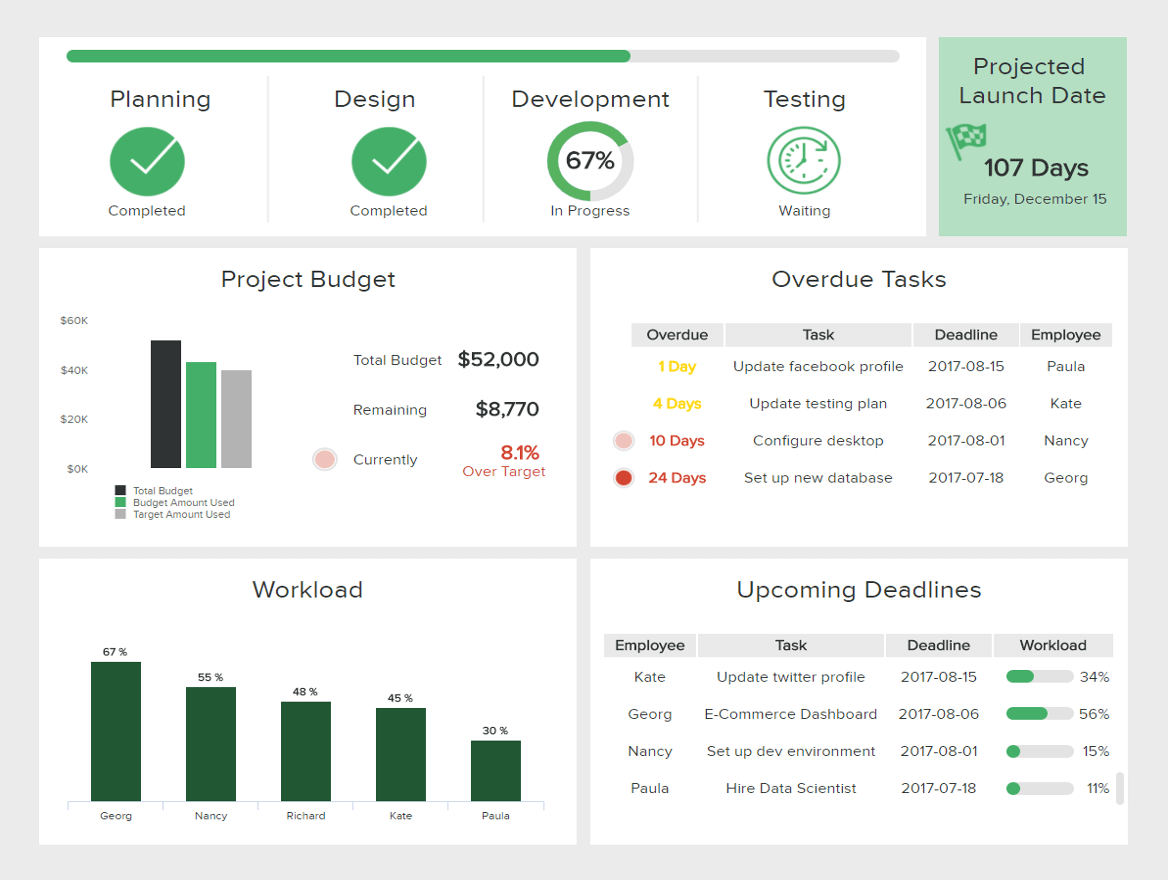
The image above is the perfect example of an external client report from an IT project. This insightful report provides a visual overview of every relevant aspect of the project's development. From deadlines, budget usage, completion stage, and task breakdown, clients can be fully informed and involved in the project.
10. Vertical & Lateral Reports
Next, in our rundown of types of reports, we have vertical and lateral reports. This reporting type refers to the direction in which a report travels. A vertical report is meant to go upward or downward the hierarchy, for example, a management report. A lateral report assists in organization and communication between groups that are at the same level of the hierarchy, such as the financial and marketing departments.
11. Research Reports
Without a doubt, one of the most vital reporting types for any modern business is centered on research. Being able to collect, collate, and drill down into insights based on key pockets of your customer base or industry will give you the tools to drive innovation while meeting your audience’s needs head-on.
The image above is a market research analytics report example for customer demographics. It serves up a balanced blend of metrics that will empower you to boost engagement as well as retention rates. Here, you can drill down into your audience’s behaviors, interests, gender, educational levels, and tech adoption life cycles with a simple glance.
What’s particularly striking about this dashboard is the fact that you can explore key trends in brand innovation with ease, gaining a working insight into how your audience perceives your business. This invaluable type of report will help you get under the skin of your consumers, driving growth and loyalty in the process.
12. Strategic Reports
Strategy is a vital component of every business, big or small. Strategic analytics tools are perhaps the broadest and most universal of all the different types of business reports imaginable.
These particular tools exist to help you understand, meet, and exceed your most pressing organizational goals consistently by serving up top-level metrics on a variety of initiatives or functions.
By working with strategic-style tools, you will:
- Improve internal motivation and engagement
- Refine your plans and strategies for the best possible return on investment (ROI)
- Enhance internal communication and optimize the way your various departments run
- Create more room for innovation and creative thinking
13. Project Reports
Projects are key to keeping a business moving in the right direction while keeping innovation and evolution at the forefront of every plan, communication, or campaign. But without the right management tools, a potentially groundbreaking project can become a resource-sapping disaster.
A project management report serves as a summary of a particular project's status and its various components. It's a visual tool that you can share with partners, colleagues, clients, and stakeholders to showcase your project's progress at multiple stages. Let’s look at our example and dig a little deeper.
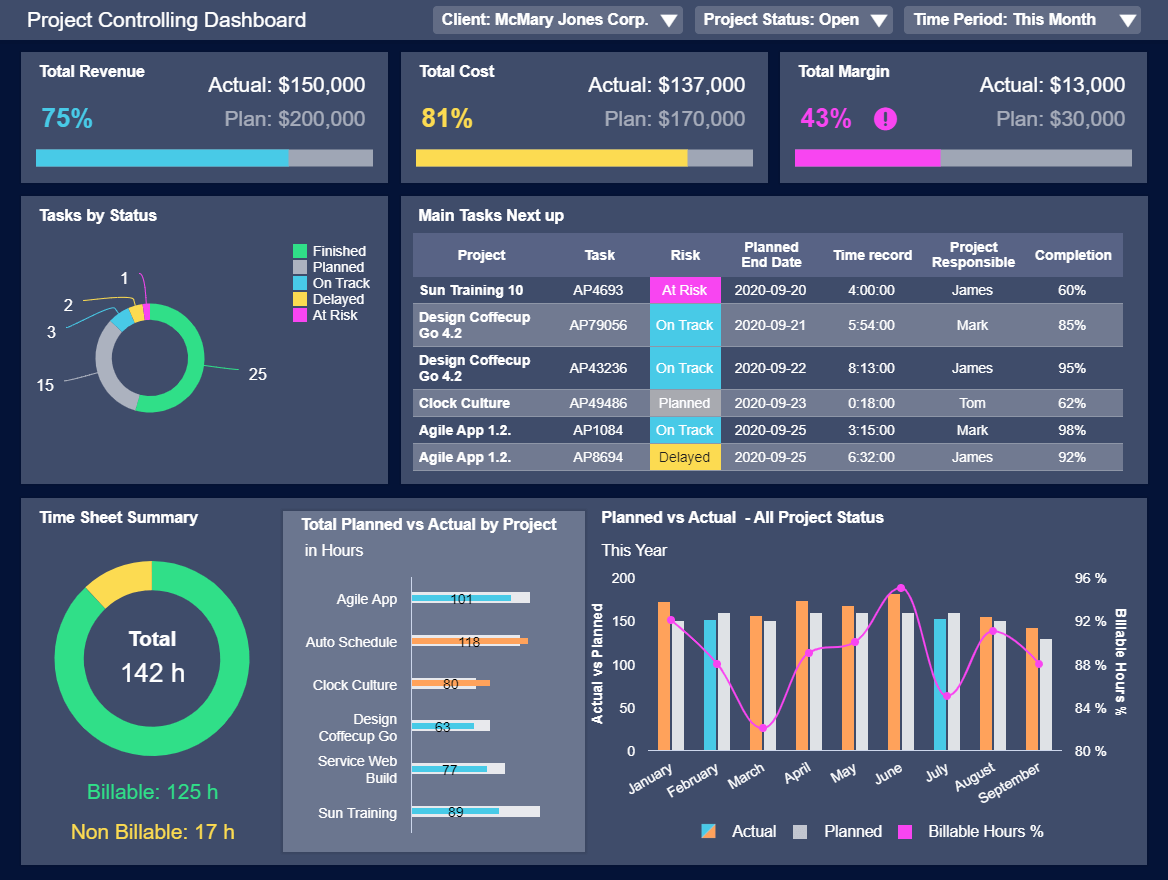
To ensure consistent success across the board, the kinds of reports you must work with are based on project management.
Our example is a project management dashboard equipped with a melting pot of metrics designed to improve the decision-making process while keeping every facet of your company’s most important initiatives under control. Here, you can spot pivotal trends based on costs, task statuses, margins, costs, and overall project revenue. With this cohesive visual information at your fingertips, not only can you ensure the smooth end-to-end running of any key project, but you can also drive increased operational efficiency as you move through every significant milestone.
14. Statutory Reports
It may not seem exciting or glamorous, but keeping your business's statutory affairs in order is vital to your ongoing commercial health and success.
When it comes to submitting such vital financial and non-financial information to official bodies, one small error can result in serious repercussions. As such, working with statutory types of report formats is a water-tight way of keeping track of your affairs and records while significantly reducing the risk of human error.
Armed with interactive insights and dynamic visuals, you will keep your records clean and compliant while gaining the ability to nip any potential errors or issues in the bud.
What Does A Report Look Like?
Now that we’ve covered the most relevant types of reports, we will answer the question: what does a report look like?
As mentioned at the beginning of this insightful guide, static reporting is a thing of the past. With the rise of modern technologies like self-service BI tools , the use of interactive reports in the shape of business dashboards has become more and more popular among companies.
Unlike static reports that take time to be generated and are difficult to understand, modern reporting tools are intuitive. Their visual nature makes them easy to understand for any type of user, and they provide businesses with a central view of their most important performance indicators for an improved decision-making process. Here, we will cover 20 useful dashboard examples from different industries, functions, and platforms to put the value of dashboard reporting into perspective.
1. Financial Report
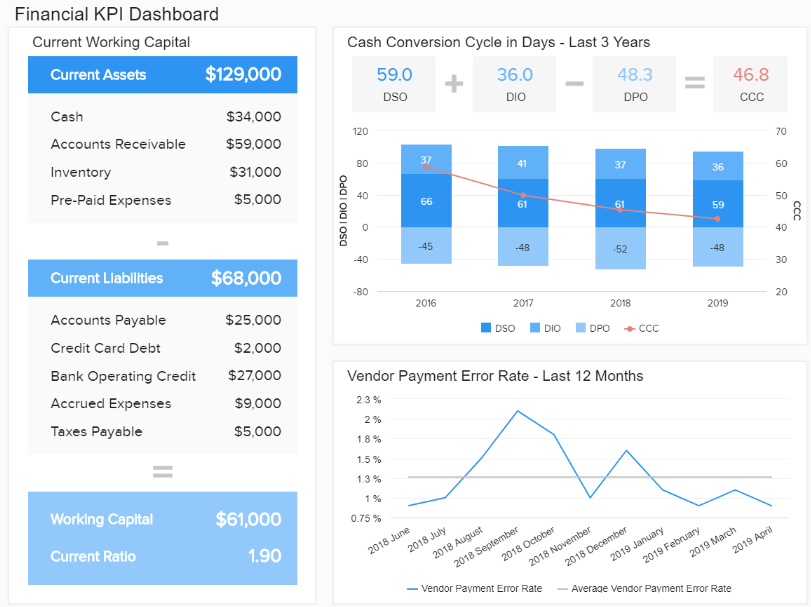
Keeping finances in check is critical for success. This financial report offers an overview of the most important financial metrics that a business needs to monitor its economic activities and answer vital questions to ensure healthy finances.
With insights about liquidity, invoicing, budgeting, and general financial stability, managers can extract long and short-term conclusions to reduce inefficiencies, make accurate forecasts about future performance, and keep the overall financial efficiency of the business flowing. For instance, getting a detailed calculation of the business's working capital can allow you to understand how liquid your company is. If it's higher than expected, it means you have the potential to invest and grow—definitely, one of the most valuable types of finance reports.
2. Marketing Report
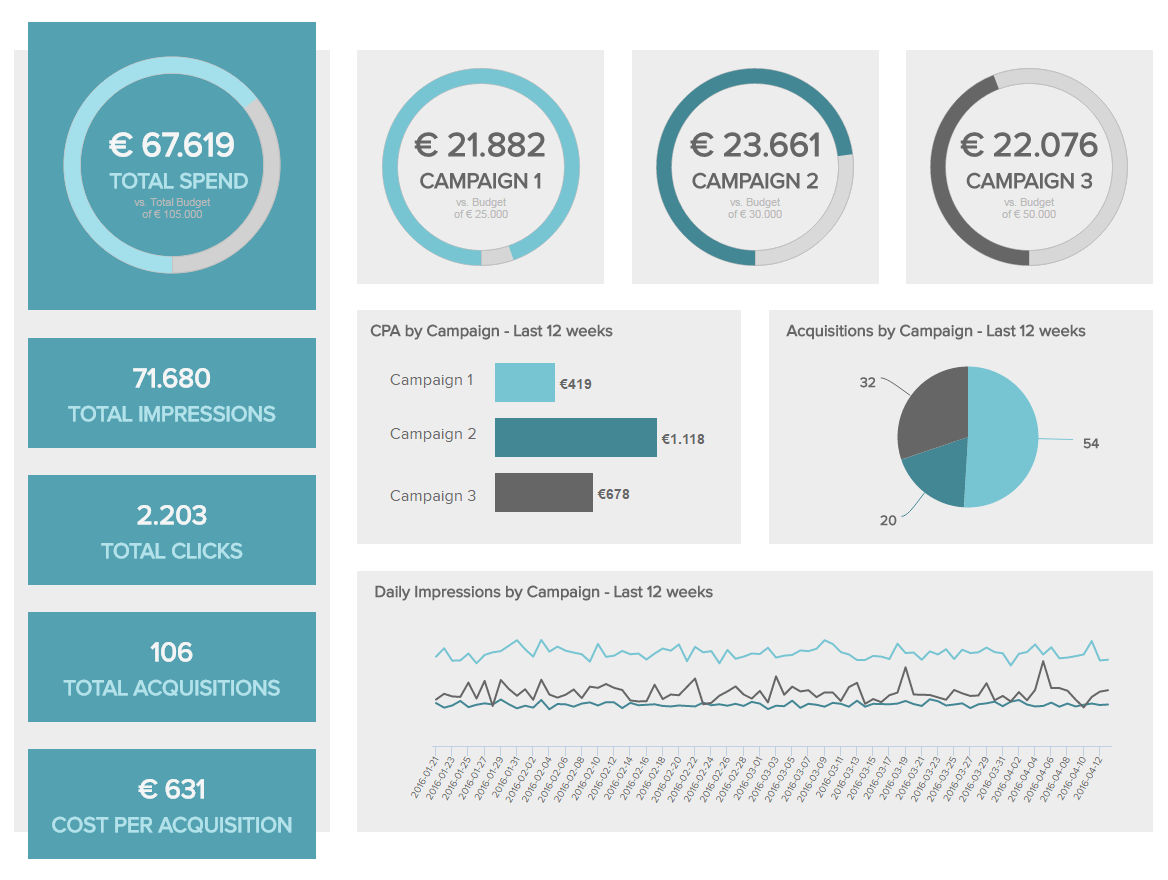
Our following example is a marketing report that ensures a healthy return on investment from your marketing efforts. This type of report offers a detailed overview of campaign performance over the last 12 weeks. Having access to this information enables you to maximize the value of your promotional actions, keeping your audience engaged by providing a targeted experience.
For instance, you can implement different campaign formats as a test and then compare which one is most successful for your business. This is possible thanks to the monitoring of important marketing metrics such as the click-through rate (CTR), cost per click (CPC), cost per acquisition (CPA), and more.
The visual nature of this report makes it easy to understand important insights at a glance. For example, the four gauge charts at the top show the total spending from all campaigns and how much of the total budget of each campaign has been used. In just seconds, you can see if you are on target to meet your marketing budgets for every single campaign.
3. Sales Report

An intuitive sales dashboard like the one above is the perfect analytical tool to monitor and optimize sales performance. Armed with powerful high-level metrics, this report type is especially interesting for managers, executives, and sales VPs as it provides relevant information to ensure strategic and operational success.
The value of this sales report lies in the fact that it offers a complete and comprehensive overview of relevant insights needed to make smart sales decisions. For instance, at the top of an analysis tool, you get important metrics such as the number of sales, revenue, profit, and costs, all compared to a set target and to the previous time period. The use of historical data is fundamental when building successful sales strategies as they provide a picture of what could happen in the future. Being able to filter the key metrics all in one screen is a key benefit of modern reporting.
4. HR Report
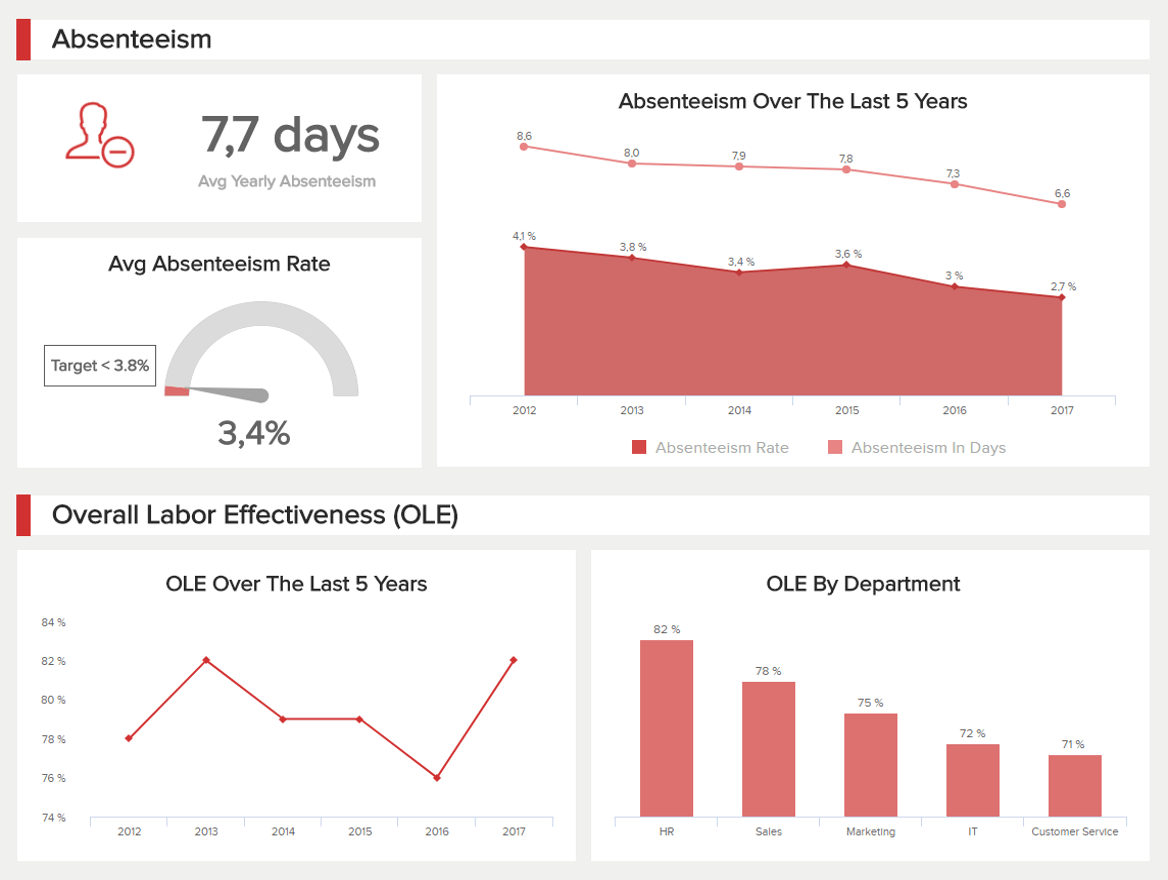
Our next example of a report is about human resources analytics . The HR department needs to track various KPIs for employee performance and effectiveness. But overall, they have to ensure that employees are happy and working in a healthy environment since an unhappy workforce can significantly damage an organization. This is all possible with the help of this intuitive dashboard.
Providing a comprehensive mix of metrics, this employee-centric report drills down into every major element needed to ensure successful workforce management. For example, the top portion of the dashboard covers absenteeism in 3 different ways: yearly average, absenteeism rate with a target of 3.8%, and absenteeism over the last five years. Tracking absenteeism rates in detail is helpful as it can tell you if your employees are skipping work days. If the rate is over the expected target, then you have to dig deeper into the reasons and find sustainable solutions.
On the other hand, the second part of the dashboard covers the overall labor effectiveness (OLE). This can be tracked based on specific criteria that HR predefined, and it helps them understand if workers are achieving their targets or if they need extra training or help.
5. Management Report
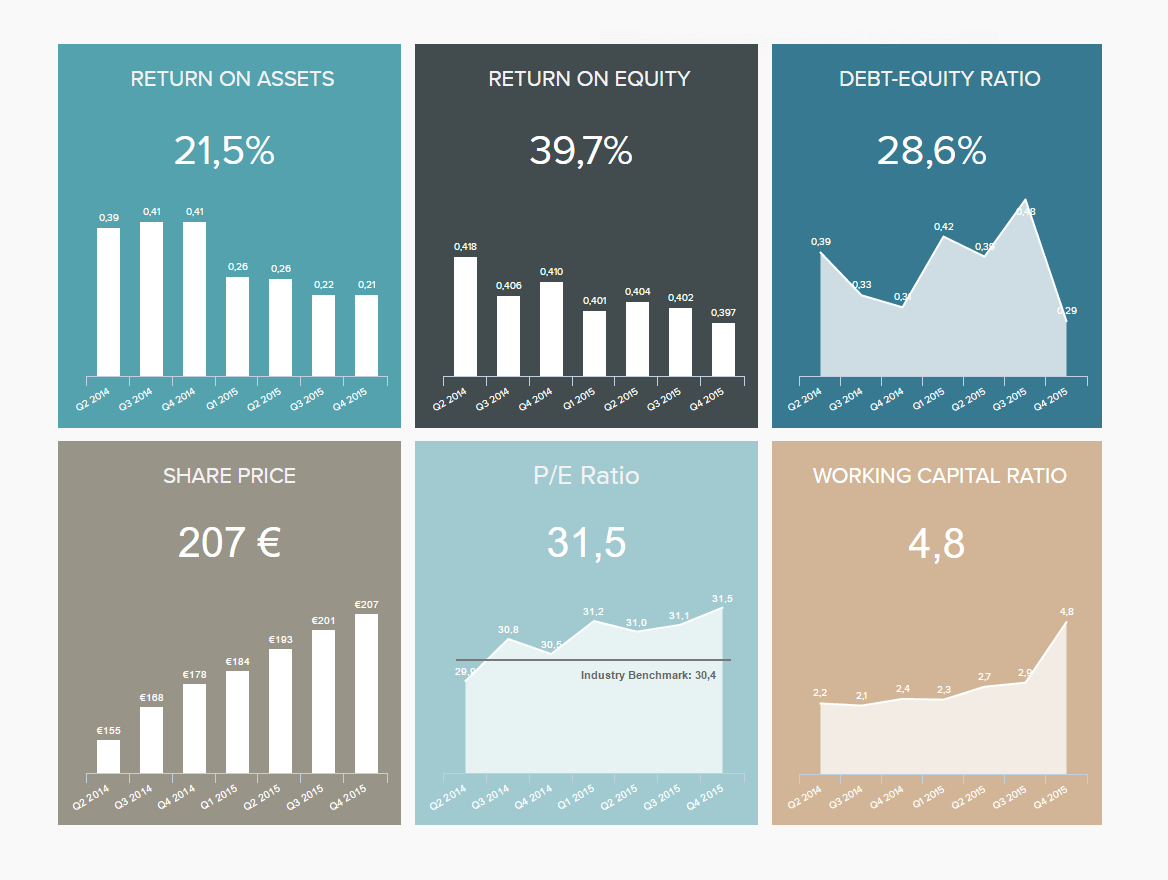
Managers must monitor big amounts of information to ensure that the business is running smoothly. One of them being investor relationships. This management dashboard focuses on high-level metrics that shareholders need to look at before investing, such as the return on assets, return on equity, debt-equity ratio, and share price, among others.
By getting an overview of these important metrics, investors can easily extract the needed information to make an informed decision regarding an investment in your business. For instance, the return on assets measures how efficiently are the company's assets being used to generate profit. With this information, investors can understand how effectively your company deploys available resources compared to others in the market. Another great indicator is the share price; the higher the increase in your share price, the more money your shareholders are making from their investment.
6. IT Report
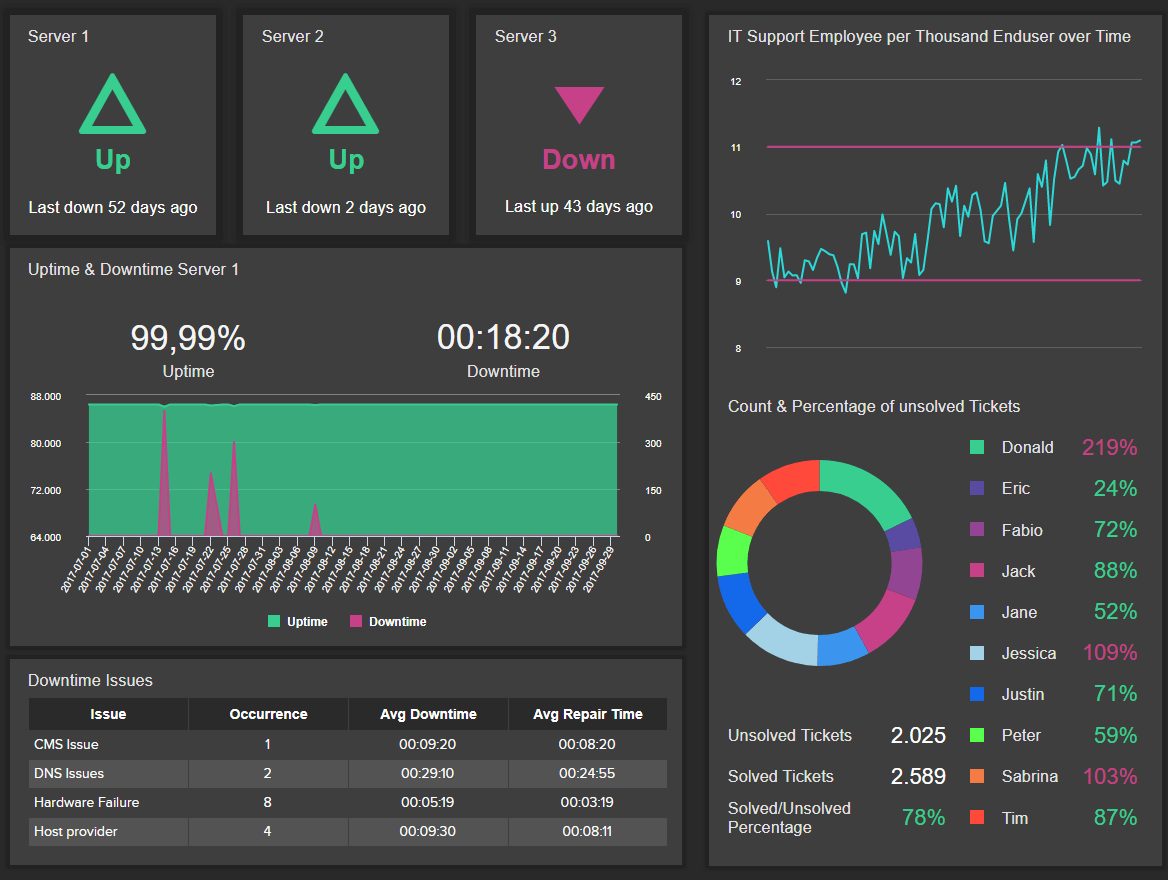
Just like all the other departments and sections covered in this list, the IT department is one that can especially benefit from these types of reports. With so many technical issues to solve, the need for a visual tool to help IT specialists stay on track with their workload becomes critical.
As seen in the image above, this IT dashboard offers detailed information about different system indicators. For starters, we get a visual overview of the status of each server, followed by a detailed graph displaying the uptime & downtime of each week. This is complemented by the most common downtown issues and some ticket management information. Getting this level of insight helps your IT staff to know what is happening and when it is happening and find proper solutions to prevent these issues from repeating themselves. Keeping constant track of these metrics will ensure robust system performance.
7. Procurement Report
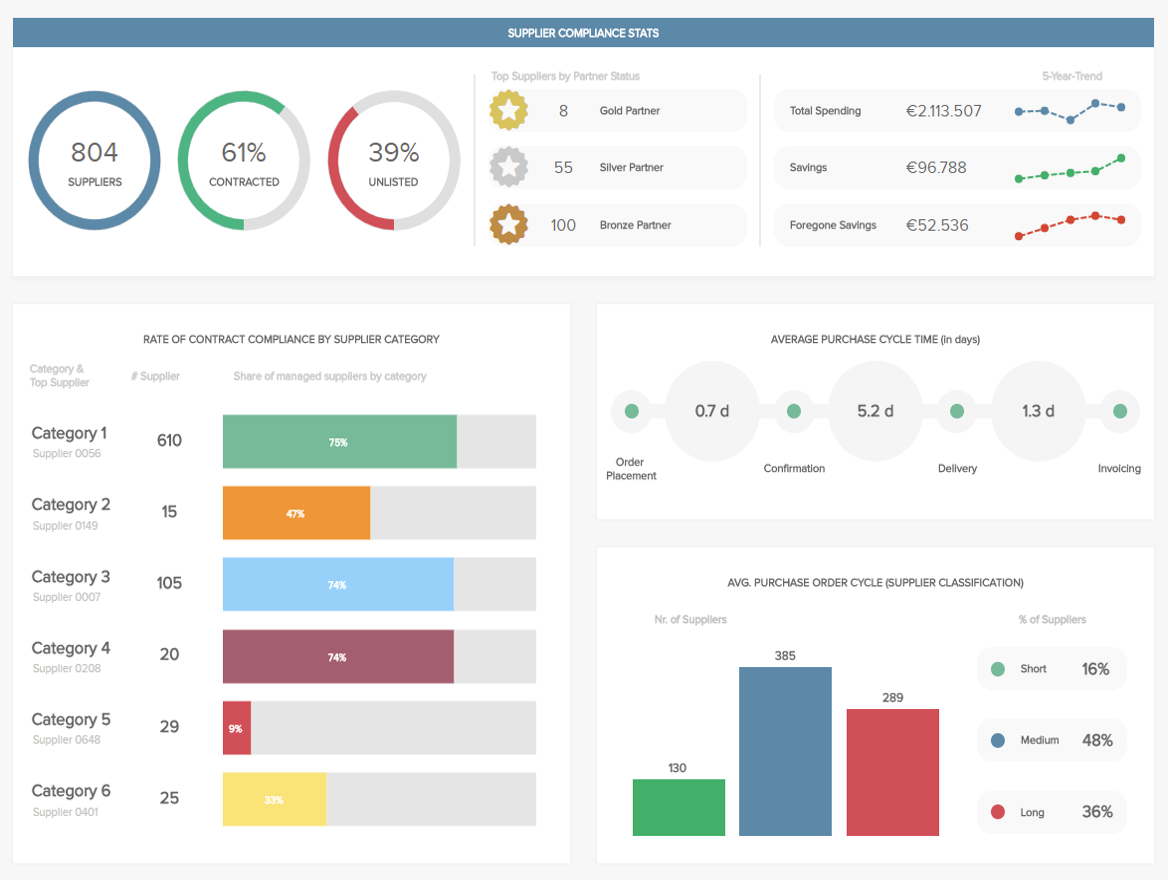
The following example of a report was built with intuitive procurement analytics software , and it gives a general view of various metrics that the procurement department needs to work with regularly.
With the possibility to filter, drill down, and interact with KPIs, this intuitive procurement dashboard offers key information to ensure a healthy supplier relationship. With metrics such as compliance rate, the number of suppliers, or the purchase order cycle time, the procurement team can classify the different suppliers, define the relationship each of them has with the company, and optimize processes to ensure it stays profitable.
8. Customer Service Report
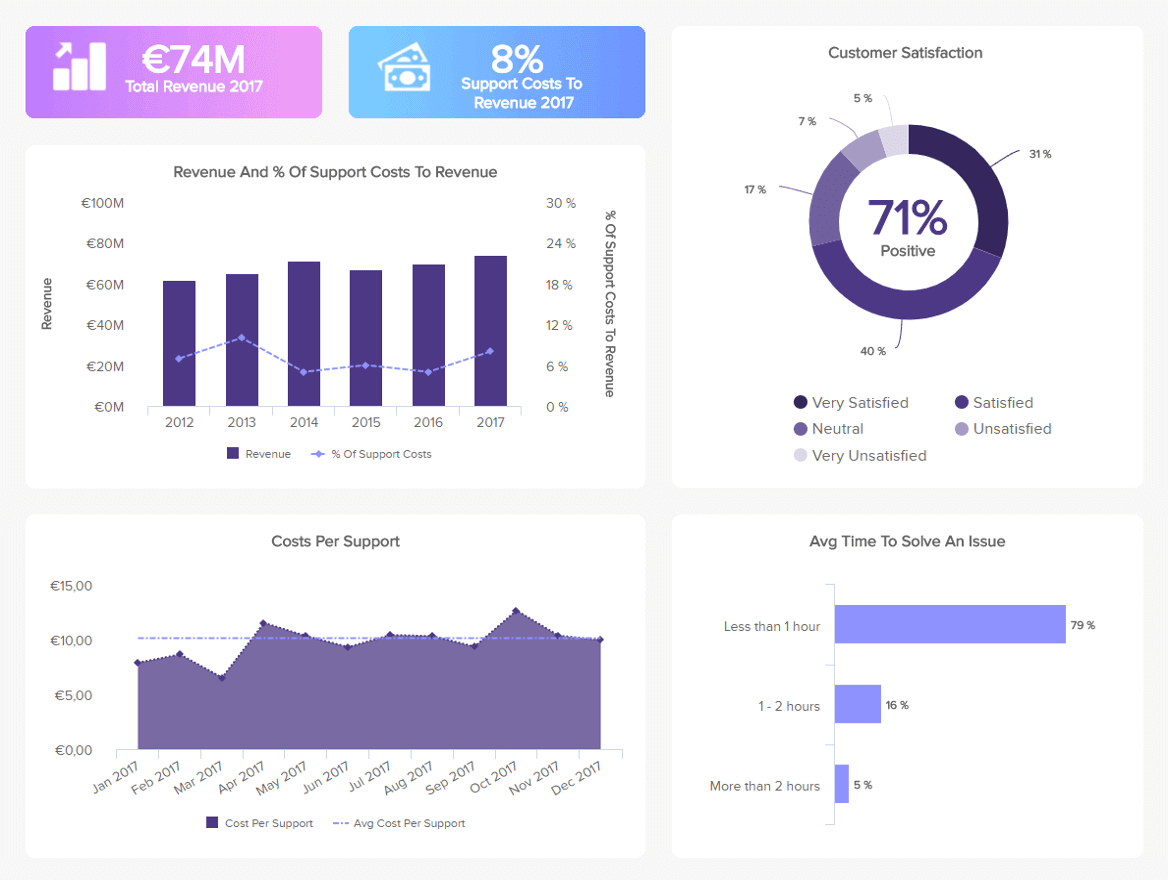
Following our list of examples of reports is one from the support area. Armed with powerful customer service KPIs , this dashboard is a useful tool to monitor performance, spot trends, identify strengths and weaknesses, and improve the overall effectiveness of the customer support department.
Covering aspects such as revenue and costs from customer support as well as customer satisfaction, this complete analysis tool is the perfect tool for managers who have to keep an eye on every little detail from a performance and operational perspective. For example, by monitoring your customer service costs and comparing them to the revenue, you can understand if you are investing the right amount into your support processes. This can be directly related to your agent’s average time to solve issues; the longer it takes to solve a support ticket, the more money it will cost and the less revenue it will bring. If you see that your agents are taking too long to solve an issue, you can think of some training instances to help them reduce this number.
9. Market Research Report
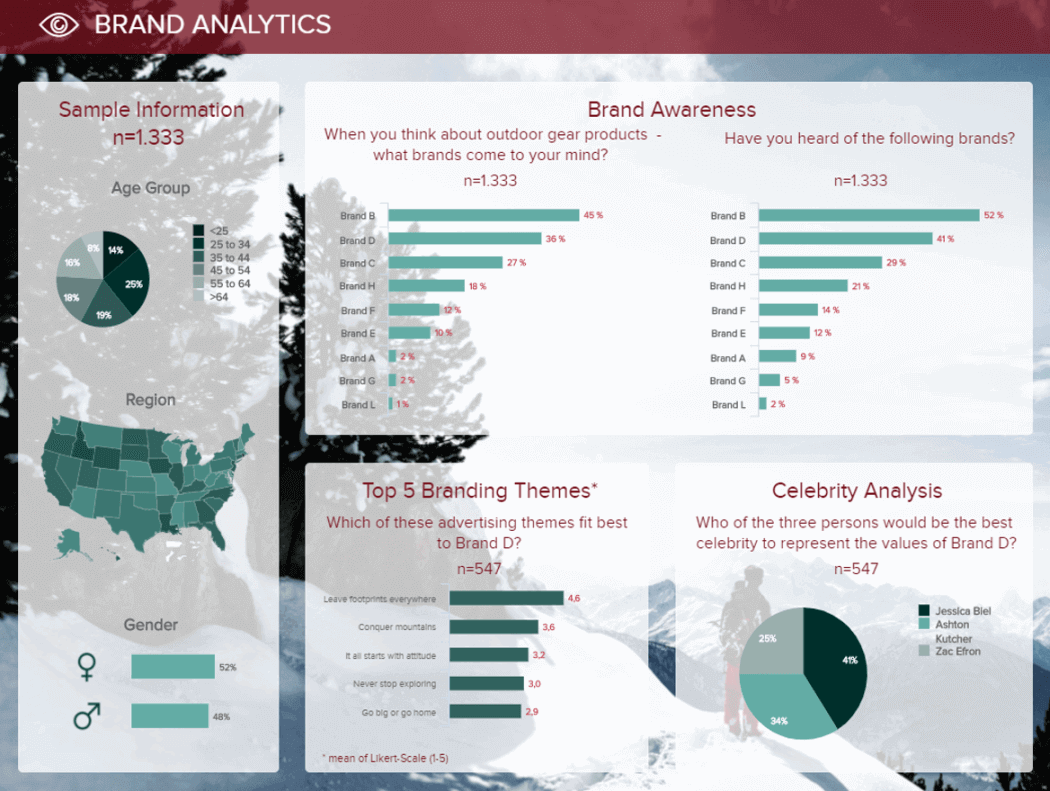
This list of report types examples would not be complete without a market research report . Market research agencies deal with a large amount of information coming from surveys and other research sources. Taking all this into account, the need for reports that can be filtered for deeper interaction becomes more necessary for this industry than any other.
The image above is a brand analytics dashboard that displays the survey results about how the public perceives a brand. This savvy tool contains different charts that make it easy to understand the information visually. For instance, the map chart with the different colors lets you quickly understand in which regions each age range is located. The charts can be filtered further to see the detailed answers from each group for a deeper analysis.
10. Social Media Report
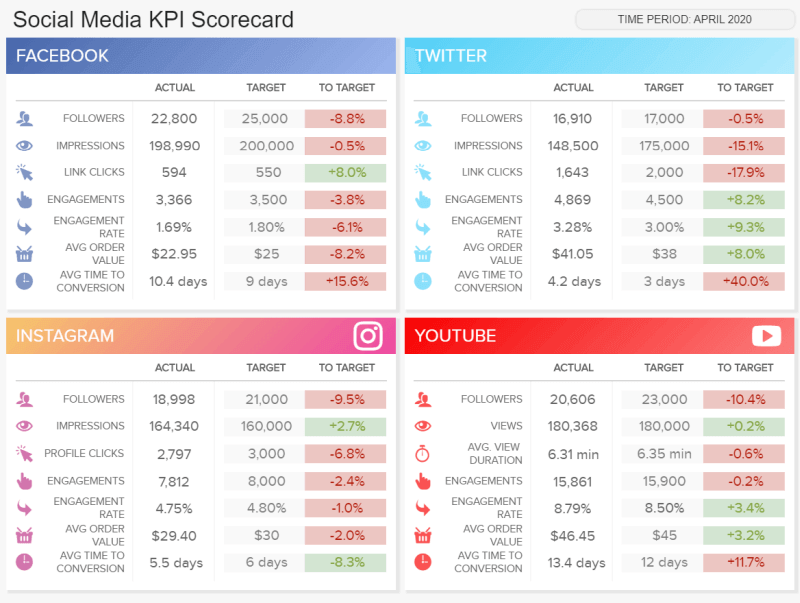
Last but not least, we have a social media report . This scorecard format dashboard monitors the performance of 4 main social media channels: Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and YouTube, and it serves as a perfect visual overview to track the performance of different social media efforts and achievements.
Tracking relevant metrics such as followers, impressions, clicks, engagement rates, and conversions, this report type serves as a perfect progress report to show to managers or clients who need to see the status of their social channels. Each metric is shown in its actual value and compared to a set target. The colors green and red from the fourth column let you quickly understand if a metric is over or under its expected target.
11. Logistics Report
Logistics are the cornerstone of an operationally fluent and progressive business. If you deal with large quantities of goods and tangible items, in particular, maintaining a solid logistical strategy is vital to ensuring you maintain your brand reputation while keeping things flowing in the right direction.
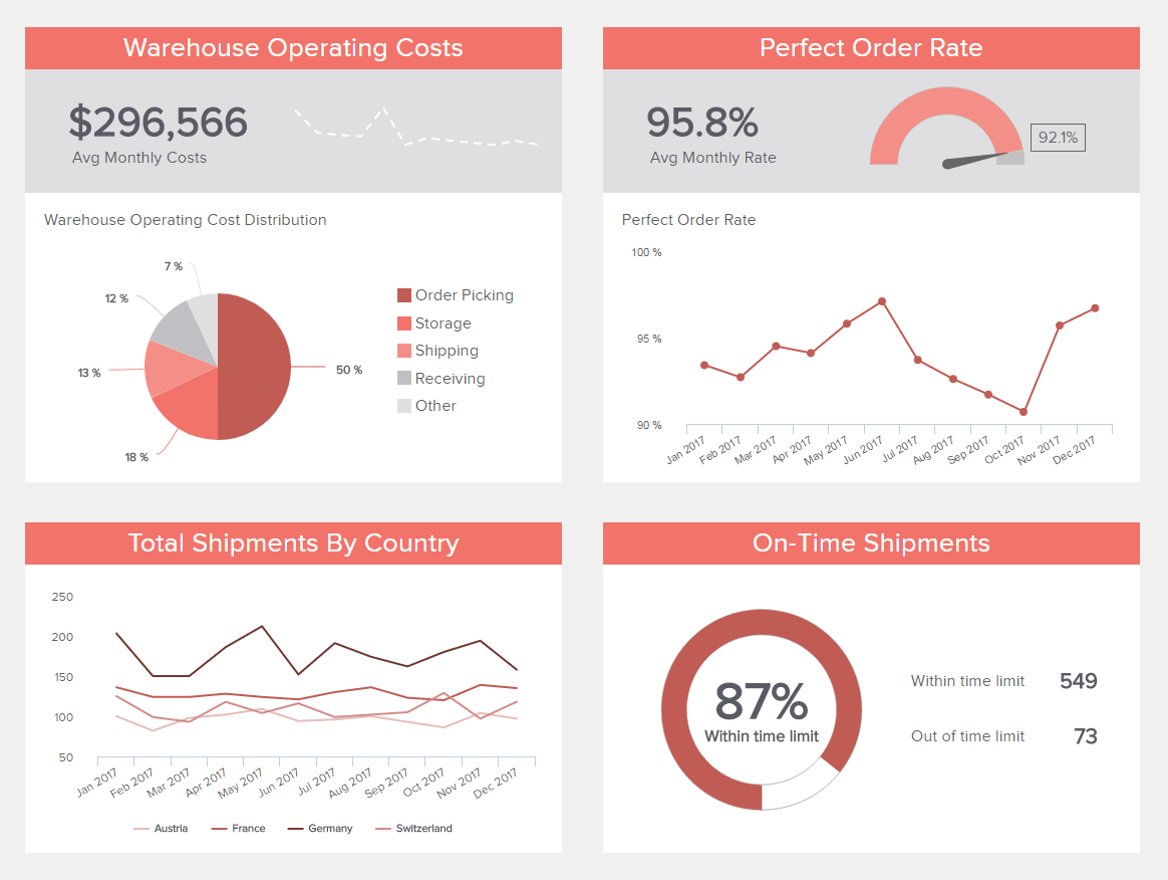
A prime example of the types of data reporting tool designed to improve logistical management, our warehouse KPI dashboard is equipped with metrics required to maintain strategic movement while eliminating any unnecessary costs or redundant processes. Here, you can dig into your shipping success rates across regions while accessing warehouse costs and perfect order rates in real-time. If you spot any potential inefficiencies, you can track them here and take the correct course of action to refine your strategy. This is an essential tool for any business with a busy or scaling warehouse.
12. Manufacturing Report
Next, in our essential types of business reports examples, we’re looking at tools made to improve your business’s various manufacturing processes.
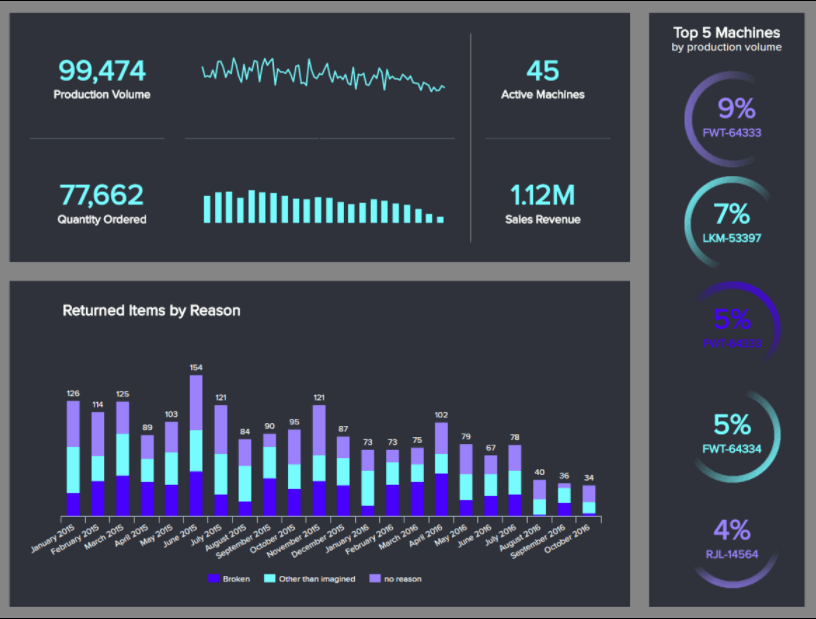
Our clean and concise production tool is a sight to behold and serves up key manufacturing KPIs that improve the decision-making process regarding costs, volume, and machinery.
Here, you can hone in on historical patterns and trends while connecting with priceless real-time insights that will not only help you make the right calls concerning your manufacturing process at the moment but will also help you formulate predictive strategies that will ultimately save money, boost productivity, and result in top-quality products across the board.
13. Retail Report
As a retailer with so many channels to consider and so many important choices to make, working with the right metrics and visuals is absolutely essential. Fortunately, we live in an age where there are different types of reporting designed for this very reason.
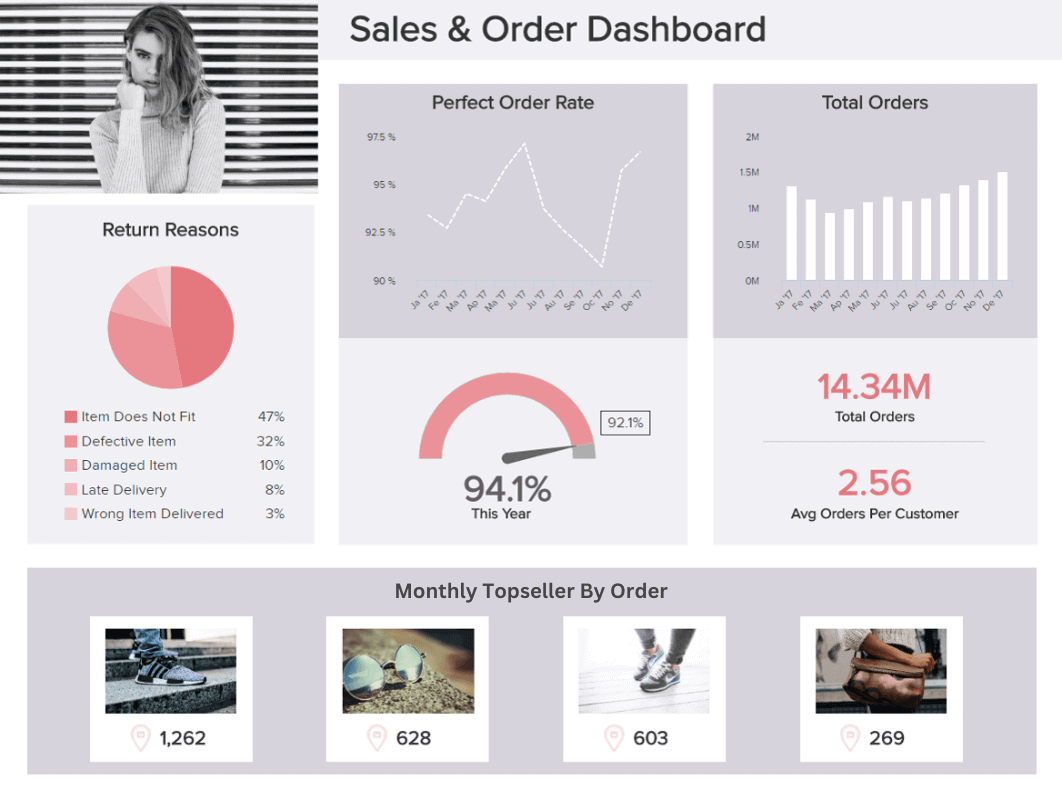
Our sales and order example, generated with retail analytics software , is a dream come true for retailers as it offers the visual insights needed to understand your product range in greater detail while keeping a firm grip on your order volumes, perfect order rates, and reasons for returns.
Gaining access to these invaluable insights in one visually presentable space will allow you to track increases or decreases in orders over a set timeframe (and understand whether you’re doing the right things to drive engagement) while plowing your promotional resources into the products that are likely to offer the best returns.
Plus, by gaining an accurate overview of why people are returning your products, you can omit problem items or processes from your retail strategy, improving your brand reputation as well as revenue in the process.
14. Digital Media Report
The content and communications you publish are critical to your ongoing success, regardless of your sector, niche, or specialty. Without putting out communications that speak directly to the right segments of your audience at the right times in their journey, your brand will swiftly fade into the background.
To ensure your brand remains inspiring, engaging, and thought-leading across channels, working with media types of a business report is essential. You must ensure your communications cut through the noise and scream ‘quality’ from start to finish—no ifs, no buts, no exceptions.
Our content quality control tool is designed with a logical hierarchy that will tell you if your content sparks readership, if the language you’re using is inclusive and conversational, and how much engagement-specific communications earn. You can also check your most engaged articles with a quick glance to understand what your users value most. Armed with this information, you can keep creating content that your audience loves and ultimately drives true value to the business.
15. Energy Report
In the age of sustainability and in the face of international fuel hikes, managing the energy your business uses effectively is paramount. Here, there is little room for excess or error, and as such, working with the right metrics is the only way to ensure successful energy regulation.
If your company has a big HQ or multiple sites that require power, our energy management analytics tool will help you take the stress out of managing your resources. One of the most striking features of this dashboard is the fact that it empowers you to compare your company’s energy usage against those from other sectors and set an accurate benchmark.
Here, you can also get a digestible breakdown of your various production costs regarding energy consumption and the main sources you use to keep your organization running. Regularly consulting these metrics will not only help you save colossal chunks of your budget, but it will also give you the intelligence to become more sustainable as an organization. This, in turn, is good for the planet and your brand reputation—a real win-win-win.
16. FMCG Report
The fast-moving consuming goods (FMCG) industry can highly benefit from a powerful report containing real-time insights. This is because the products handled in this sector which are often food and beverages, don’t last very long. Therefore, having a live overview of all the latest developments can help decision-makers optimize the supply chain to ensure everything runs smoothly and no major issues happen.
Our report format example above aims to do just that by providing an overview of critical performance indicators, such as the percentage of products sold within freshness date, the out-of-stock rate, on-time in full deliveries, inventory turnover, and more. What makes this template so valuable is the fact that it provides a range of periods to get a more recent view of events but also a longer yearly view to extract deeper insights.
The FMCG dashboard also offers an overview of the main KPIs to help users understand if they are on the right track to meet their goals. There, we can observe that the OTIF is far from its target of 90%. Therefore, it should be looked at in more detail to optimize it and prevent it from affecting the entire supply chain.
17. Google Analytics Report

Regardless of the industry you are in, if you have a website then you probably require a Google Analytics report. This powerful tool helps you understand how your audience interacts with your website while helping you reach more people through the Google search engine. The issue is that the reports the tool provides are more or less basic and don’t give you the dynamic and agile view you need to stay on top of your data and competitors.
For that reason, at datapine, we generated a range of Google Analytics dashboards that take your experience one step further by allowing you to explore your most important KPIs in real-time. That way, you’ll be able to spot any potential issues or opportunities to improve as soon as they occur, allowing you to act on them on the spot.
Among some of the most valuable metrics you can find in this sample are the sessions and their daily, weekly, and monthly development, the average session duration, the bounce rate by channel and by top 5 countries, among others.
18. YouTube Report
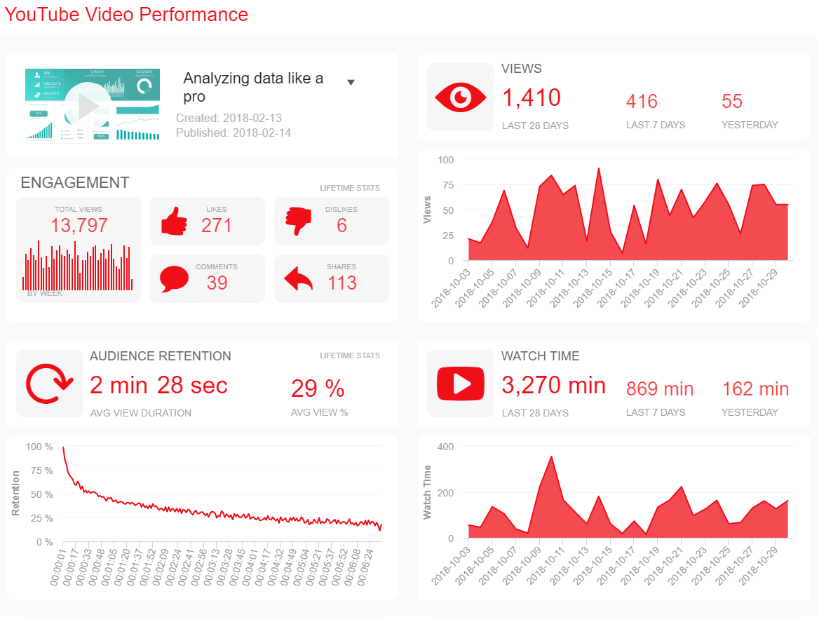
So far, we’ve covered examples for various industries and sectors. Now, we will dive a bit deeper into some templates related to popular platforms businesses use in their daily operations. With the rise in video-related content, we could not leave YouTube outside of the list. This popular platform hides some valuable insights that can help you improve your content for your current audience but also reach new audiences that can be interested in your products or services.
This highly visual and dynamic sample offers an interactive view of relevant KPIs to help you understand every aspect of your video performance. The template can be filtered for different videos to help you understand how each type of content performs. For instance, you get an overview of engagement metrics, such as likes, dislikes, comments, and shares, that way, you can understand how your audience interacts with your content.
Additionally, you also get more detailed charts about the number of views, the average watch time per day, and audience retention. These indicators can help you understand if something needs to be changed. For instance, audience retention goes down a lot after one minute and a half. Therefore you either need to make sure you are making the rest of the video a bit more interesting or offering your product or service or any other relevant information in the first minute.
19. LinkedIn Report
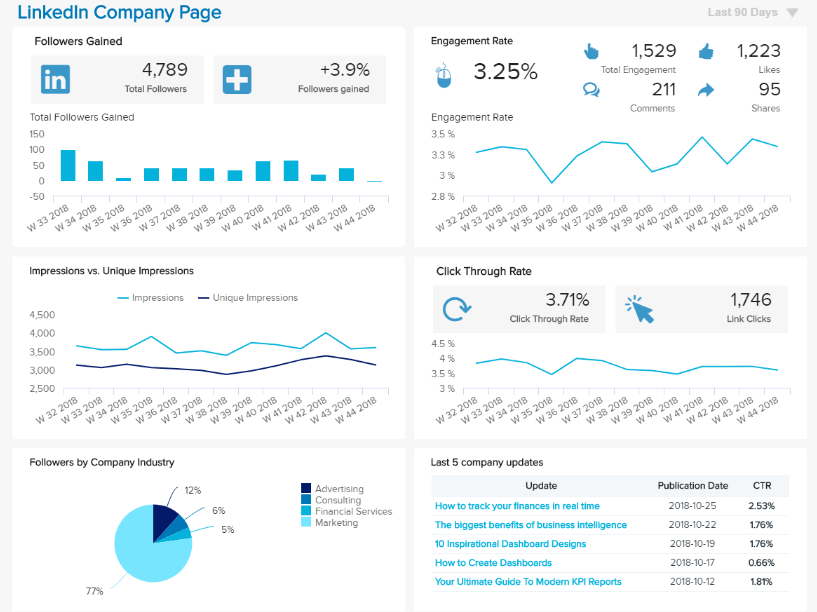
Another very important platform that companies use, no matter their size or industry, is LinkedIn. This platform is the place where companies develop and showcase their corporate image, network with other companies, and tell their clients and audience about the different initiatives they are developing to grow and be better. Some organizations also use LinkedIn to showcase their charity or sustainability initiatives.
The truth is LinkedIn has become an increasingly relevant platform, and just like we discussed with YouTube, organizations need to analyze data to ensure their strategies are on the right path to success.
The template above offers a 360-degree view of a company page's performance. With metrics such as the followers gained, engagement rate, impressions vs unique impressions, CTR, and more. Decision-makers can dive deeper into the performance of their content and understand what their audience enjoys the most. For instance, by looking at the CTR of the last 5 company updates, you can start to get a sense of what topics and content format your audience on the platforms interact with the most. That way, you’ll avoid wasting time and resources producing content without interaction.
20. Healthcare Report

Moving on from platform-related examples, we have one last monthly report template from a very relevant sector, the healthcare industry. For decades now, hospitals and healthcare professionals have benefited from data to develop new treatments and analyze unknown diseases. But, data can also help to ensure daily patient care is of top quality.
Our sample above is a healthcare dashboard report that tracks patient satisfaction stats for a clinic named Saint Martins Clinic. The template provides insights into various aspects of patient care that can affect their satisfaction levels to help spot any weak areas.
Just by looking at the report in a bit more detail, we can already see that the average waiting time for arrival to a bed and time to see a doctor are on the higher side. This is something that needs to be looked into immediately, as waiting times are the most important success factors for patients. Additionally, we can see those lab test turnarounds are also above target. This is another aspect that should be optimized to prevent satisfaction levels from going down.
If you feel inspired by this list and want to see some of the best uses for business reports, then we recommend you take a look at our dashboard examples library, where you will find over 80+ templates from different industries, functions, and platforms for extra inspiration!
What You Should Look For In A Reporting Tool
As you learned from our extensive list of examples, different types of reports are widely used across industries and sectors. Now, you might wonder, how do I get my hands on one of these reports? The answer is a professional online reporting tool. With the right software in hand, you can generate stunning reports to extract the maximum potential out of your data and boost business growth in the process.
But, with so many options in the market, how do make sure you choose the best tool for your needs? Below we cover some of the most relevant features and capabilities you should look for to make the most out of the process.
- Pre-made reporting templates
To ensure successful operations, a business will most likely need to use many types of reports for its internal and external strategies. Manually generating these reports can become a time-consuming task that burdens the business. That is why professional reporting software should offer pre-made reporting templates. At datapine, we offer an extensive template library that allows users to generate reports in a matter of seconds—allowing them to use their time on actually analyzing the information and extracting powerful insights from it.
- Multiple visualization options
If you look for report templates on Google you might run into multiple posts about written ones. This is not a surprise, as written reports have been the norm for decades. That being said, a modern approach to reporting has developed in the past years where visuals have taken over text. The value of visuals lies in the fact that they make the information easier to understand, especially for users who have no technical knowledge. But most importantly, they make the information easier to explore by telling a compelling story. For that reason, the tool you choose to invest in should provide you with multiple visualization options to have the flexibility to tell your data story in the most successful way possible.
- Customization
While pre-made templates are fundamental to generating agile reports, being able to customize them to meet your needs is also of utmost importance. At datapine, we offer our users the possibility to customize their reports to fit their most important KPIs, as well as their logo, business colors, and font. This is an especially valuable feature for external reports that must be shown to clients or other relevant stakeholders, giving your reports a more professional look. Customization can also help from an internal perspective to provide employees who are uncomfortable with data with a familiar environment to work in.
- Real-time insights
In the fast-paced world we live in today, having static reports is not enough. Businesses need to have real-time access to the latest developments in their data to spot any issues or opportunities as soon as they occur and act on them to ensure their resources are spent smartly and their strategies are running as expected. Doing so will allow for agile and efficient decision-making, giving the company a huge competitive advantage.
- Sharing capabilities
Communication and collaboration are the basis of a successful reporting process. Today, team members and departments need to be connected to ensure everyone is on the right path to achieve general company goals. That is why the tool you invest in should offer flexible sharing capabilities to ensure every user can access the reports. For instance, at datapine, we offer our users the possibility to share reports through automated emails or password-protected URLs with viewing or editing rights depending on what data the specific user can see and manipulate. A great way to keep everyone connected and boost collaboration.
Types Of Reporting For Every Business & Purpose
As we’ve seen throughout our journey, different report formats are used by businesses for diverse purposes in their everyday activities. Whether you’re talking about types of reports in research, types of reports in management, or anything in between, these dynamic tools will get you where you need to be (and beyond).
In this post, we covered the top 14 most common ones and explored key examples of how different report types are changing the way businesses are leveraging their most critical insights for internal efficiency and, ultimately, external success.
With modern tools and solutions, reporting doesn’t have to be a tedious task. Anyone in your organization can rely on data for their decision-making process without needing technical skills. Rather, you want to keep your team connected or show progress to investors or clients. There is a report type for the job. To keep your mind fresh, here are the top 14 types of data reports covered in this post:
- Informational reports
- Analytical reports
- Operational reports
- Product reports
- Industry reports
- Department reports
- Progress reports
- Internal reports
- External reports
- Vertical and lateral reports
- Strategic reports
- Research reports
- Project reports
- Statutory reports
Now, over to you. Are you ready? If you want to start building your own types of reports and get ahead of the pack today, then you should try our BI reporting software for 14 days for free !

- WRITING SKILLS
- Business Writing
How to Write a Report
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Writing Skills:
- A - Z List of Writing Skills
The Essentials of Writing
- Common Mistakes in Writing
- Improving Your Grammar
- Active and Passive Voice
- Using Plain English
- Writing in UK and US English
- Clarity in Writing
- Writing Concisely
- Coherence in Writing
- The Importance of Structure
- Know Your Audience
- Know Your Medium
- Business Writing Tips
- How to Write a To-Do List
- How to Write a Business Case
- How to Write a Press Release
- Writing a Marketing Strategy
- Writing Marketing Copy
- Copywriting
- How to Write an Executive Summary
- Taking Minutes and the Role of the Secretary
- How to Write a Letter
- Writing Effective Emails
- Good Email Etiquette
- Write Emails that Convince, Influence and Persuade
- Storytelling in Business
- Using LinkedIn Effectively
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Some academic assignments ask for a ‘report’, rather than an essay, and students are often confused about what that really means.
Likewise, in business, confronted with a request for a ‘report’ to a senior manager, many people struggle to know what to write.
Confusion often arises about the writing style, what to include, the language to use, the length of the document and other factors.
This page aims to disentangle some of these elements, and provide you with some advice designed to help you to write a good report.
What is a Report?
In academia there is some overlap between reports and essays, and the two words are sometimes used interchangeably, but reports are more likely to be needed for business, scientific and technical subjects, and in the workplace.
Whereas an essay presents arguments and reasoning, a report concentrates on facts.
Essentially, a report is a short, sharp, concise document which is written for a particular purpose and audience. It generally sets outs and analyses a situation or problem, often making recommendations for future action. It is a factual paper, and needs to be clear and well-structured.
Requirements for the precise form and content of a report will vary between organisation and departments and in study between courses, from tutor to tutor, as well as between subjects, so it’s worth finding out if there are any specific guidelines before you start.
Reports may contain some or all of the following elements:
- A description of a sequence of events or a situation;
- Some interpretation of the significance of these events or situation, whether solely your own analysis or informed by the views of others, always carefully referenced of course (see our page on Academic Referencing for more information);
- An evaluation of the facts or the results of your research;
- Discussion of the likely outcomes of future courses of action;
- Your recommendations as to a course of action; and
- Conclusions.
Not all of these elements will be essential in every report.
If you’re writing a report in the workplace, check whether there are any standard guidelines or structure that you need to use.
For example, in the UK many government departments have outline structures for reports to ministers that must be followed exactly.
Sections and Numbering
A report is designed to lead people through the information in a structured way, but also to enable them to find the information that they want quickly and easily.
Reports usually, therefore, have numbered sections and subsections, and a clear and full contents page listing each heading. It follows that page numbering is important.
Modern word processors have features to add tables of contents (ToC) and page numbers as well as styled headings; you should take advantage of these as they update automatically as you edit your report, moving, adding or deleting sections.
Report Writing
Getting started: prior preparation and planning.
The structure of a report is very important to lead the reader through your thinking to a course of action and/or decision. It’s worth taking a bit of time to plan it out beforehand.
Step 1: Know your brief
You will usually receive a clear brief for a report, including what you are studying and for whom the report should be prepared.
First of all, consider your brief very carefully and make sure that you are clear who the report is for (if you're a student then not just your tutor, but who it is supposed to be written for), and why you are writing it, as well as what you want the reader to do at the end of reading: make a decision or agree a recommendation, perhaps.
Step 2: Keep your brief in mind at all times
During your planning and writing, make sure that you keep your brief in mind: who are you writing for, and why are you writing?
All your thinking needs to be focused on that, which may require you to be ruthless in your reading and thinking. Anything irrelevant should be discarded.
As you read and research, try to organise your work into sections by theme, a bit like writing a Literature Review .
Make sure that you keep track of your references, especially for academic work. Although referencing is perhaps less important in the workplace, it’s also important that you can substantiate any assertions that you make so it’s helpful to keep track of your sources of information.
The Structure of a Report
Like the precise content, requirements for structure vary, so do check what’s set out in any guidance.
However, as a rough guide, you should plan to include at the very least an executive summary, introduction, the main body of your report, and a section containing your conclusions and any recommendations.
Executive Summary
The executive summary or abstract , for a scientific report, is a brief summary of the contents. It’s worth writing this last, when you know the key points to draw out. It should be no more than half a page to a page in length.
Remember the executive summary is designed to give busy 'executives' a quick summary of the contents of the report.
Introduction
The introduction sets out what you plan to say and provides a brief summary of the problem under discussion. It should also touch briefly on your conclusions.
Report Main Body
The main body of the report should be carefully structured in a way that leads the reader through the issue.
You should split it into sections using numbered sub-headings relating to themes or areas for consideration. For each theme, you should aim to set out clearly and concisely the main issue under discussion and any areas of difficulty or disagreement. It may also include experimental results. All the information that you present should be related back to the brief and the precise subject under discussion.
If it’s not relevant, leave it out.
Conclusions and Recommendations
The conclusion sets out what inferences you draw from the information, including any experimental results. It may include recommendations, or these may be included in a separate section.
Recommendations suggest how you think the situation could be improved, and should be specific, achievable and measurable. If your recommendations have financial implications, you should set these out clearly, with estimated costs if possible.
A Word on Writing Style
When writing a report, your aim should be to be absolutely clear. Above all, it should be easy to read and understand, even to someone with little knowledge of the subject area.
You should therefore aim for crisp, precise text, using plain English, and shorter words rather than longer, with short sentences.
You should also avoid jargon. If you have to use specialist language, you should explain each word as you use it. If you find that you’ve had to explain more than about five words, you’re probably using too much jargon, and need to replace some of it with simpler words.
Consider your audience. If the report is designed to be written for a particular person, check whether you should be writing it to ‘you’ or perhaps in the third person to a job role: ‘The Chief Executive may like to consider…’, or ‘The minister is recommended to agree…’, for example.
A Final Warning
As with any academic assignment or formal piece of writing, your work will benefit from being read over again and edited ruthlessly for sense and style.
Pay particular attention to whether all the information that you have included is relevant. Also remember to check tenses, which person you have written in, grammar and spelling. It’s also worth one last check against any requirements on structure.
For an academic assignment, make sure that you have referenced fully and correctly. As always, check that you have not inadvertently or deliberately plagiarised or copied anything without acknowledging it.
Finally, ask yourself:
“Does my report fulfil its purpose?”
Only if the answer is a resounding ‘yes’ should you send it off to its intended recipient.
Continue to: How to Write a Business Case Planning an Essay
See also: Business Writing Tips Study Skills Writing a Dissertation or Thesis

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

12.4: Types of Reports
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 83670

- Arley Cruthers
- Kwantlen Polytechnic University
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Reports vary by function, style, and tradition. Within your organization, you may need to address specific expectations. This section discusses reports in general terms, focusing on common elements and points of distinction. Reference to similar documents at your workplace may serve you well as you prepare your own report. As shown in Table 11.1, there are many types of reports.
Progress report
A progress report is used to give management an update on the status of a project. It is generated at timed intervals (for example, once a month) or on completion of key stages. It records accomplishments to date and identifies any challenges or concerns. It is usually written by the project lead and is one to two pages long.
When you write a progress report, begin by stating why you are writing the report:
- Identify what you’ve accomplished
- List any problems you have encountered
- Outline what work still remains
- Conclude by providing an overview of the project’s status and what should be done next.
It’s helpful to think about a report not just in terms of what should be included, but why certain elements are included. Most reports have a persuasive element, so when reporting your progress you are trying to:
- Demonstrate that you have taken appropriate, competent action so far.
- Assure the reader that they can trust you to finish the remainder of the work effectively and that your plan remains a good one.
- Convince the reader that the project has been successful so far.
- If the project hasn’t been successful, then you will want to explain why and suggest ways to improve. Never downplay or lie about challenges you are experiencing. Not only will this damage your reputation when the truth comes out, but you’ll also be defeating the purpose of the progress report: which is to evaluate the project and address issues as they happen.
Understanding your persuasive strategy will help you organize and write your progress report.
Recommendation report
A recommendation report is used to help management make decisions. The goal of this report is to identify a solution to a problem or suggest a course of action. In it, the writer might suggest that a procedure be adopted or rejected, assess an unsatisfactory situation, or persuade decision makers to make a change that will benefit the organization. For example, the report might suggest ways to enhance the quality of a product, increase profit, reduce cost, or improve workplace conditions. The intention of a recommendation report is not to assign blame or be overly critical, but to suggest improvements in a positive manner.
The persuasive goals of most recommendation reports are:
- That a problem or opportunity exists and the organization should take it seriously. Why should your organization devote its resources to this issue? Why now?
- That you have done the necessary research and have the expertise to solve the problem.
- That your research and expertise has led you to a solution, which is the best of all possible solutions.
- That your solution offers benefits to the company and has minimal risks. If there are risks, you are aware of them and have a plan to mitigate them.
The importance and expense of what you’re recommending will dictate the form, amount of detail, length and use of visual aids like charts and graphs. It will also dictate how you lay out your argument.
In Chapter 10 , we explored how to craft an argument. This section will be useful to you as you craft the persuasive strategy for your recommendation report. Let’s take another look at the example of an argument we studied in Chapter 10.
A Very Short Report
To: Ralph Niblet, CEO From: Hannah Vuong, Communications Manager Subject: Migrating to MailChimp Date: Sept. 1st, 2018
Last week, you asked me to research whether we should switch our email marketing software from Constant Contact to MailChimp. I think that we should go with MailChimp for the following reasons:
- MailChimp is free for a business of our size, while Constant Contact costs us $57 a month.
- MailChimp integrates with Salesforce and would allow us to use our database more effectively. I spoke to Sam Cho, who currently administers our Salesforce account, and he shared many exciting ways that we could integrate the two platforms without much effort. He also offered to host a webinar to train our staff.
- MailChimp allows us segment audiences more effectively. I’ve included some links to a few blog posts that illustrate what we could do. A lot of our current unsubscribes happen because we can’t target emails to specific groups of customers effectively. Our email marketing report from last quarter showed that 70% unsubscribed because of emails that were “not relevant.”
Some colleagues have voiced the objection that they already know how to use Constant Contact and they find MailChimp less intuitive. We will also have to migrate our existing data and clean it. I believe, however, that these barriers can easily be overcome with employee training and good data migration practices.
I am happy to show you a demo of MailChimp this week if you are free.
If Hannah wanted to turn this email into a report, she would likely find that the major elements are there. She’s done some research, she has used that research to come up with a solution, and she’s anticipated some potential risks or downsides to her plan. As you read about the parts of the report, think about how Hannah might turn her email into a recommendation report.
Summary Report
A summary report is used to give management information. For example, if you work in the marketing department, your boss might ask you to find out about your competitors’ online activities so that your company can effectively compete with them. To do this, you would research your competitors’ websites, social media profiles, digital advertising campaigns, and so on. You would then distill what you find down to the key points so that your boss can get the essential information in a short time, and then decide how to act on it. Unlike the recommendation report, the summary report focuses on the facts, leaving it to management to decide on a course of action.
In general, the main persuasive point that you are making in summary reports is that you have done enough research and have used appropriate sources, and that you have organized this information in a logical and useful manner. Because summary reports give a general overview, it’s important to think about how your reader can skim through the document. Remember: your goal is to save your audience time, so part of the challenge of the report is determining what information your audience needs, and what is irrelevant. You will also have to condense material.

30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.


Report Writing

- Updated on
- Nov 4, 2023

The term “report” refers to a nonfiction work that presents and/or paraphrases the facts on a specific occasion, subject, or problem. The notion is that a good report will contain all the information that someone who is not familiar with the subject needs to know. Reports make it simple to bring someone up to speed on a subject, but actually writing a report is far from simple. This blog will walk you through the fundamentals of report writing, including the structure and practice themes.
This Blog Includes:
What is a report, reporting formats, newspaper or magazine reports, business reports, technical reports, what is report writing, report writing: things to keep in mind, structure of report writing, magazine vs newspaper report writing format, report writing format for class 10th to 12th, report writing example, report writing for school students: practice questions, report writing slideshare.
- Report Writing in 7 steps
Also Read: Message Writing
A report is a short document written for a particular purpose or audience. It usually sets out and analyses a problem often recommended for future purposes. Requirements for the precise form of the report depend on the department and organization. Technically, a report is defined as “any account, verbal or written, of the matters pertaining to a given topic.” This could be used to describe anything, from a witness’s evidence in court to a student’s book report.
Actually, when people use the word “report,” they usually mean official documents that lay out the details of a subject. These documents are typically written by an authority on the subject or someone who has been tasked with conducting research on it. Although there are other forms of reports, which are discussed in the following section, they primarily fulfil this definition.
What information does reporting contain? All facts are appreciated, but reports, in particular, frequently contain the following kinds of information:
- Information about a circumstance or event
- The aftereffects or ongoing impact of an incident or occurrence
- Analytical or statistical data evaluation
- Interpretations based on the report’s data
- Based on the report’s information, make predictions or suggestions
- Relationships between the information and other reports or events
Although there are some fundamental differences, producing reports and essays share many similarities. Both rely on facts, but essays also include the author’s personal viewpoints and justifications. Reports normally stick to the facts only, however, they could include some of the author’s interpretation in the conclusion.
Reports are also quite well ordered, frequently with tables of contents of headers and subheadings. This makes it simpler for readers to quickly scan reports for the data they need. Essays, on the other hand, should be read from beginning to end rather than being perused for particular information.
Depending on the objective and audience for your report, there are a few distinct types of reports. The most typical report types are listed briefly below:
- Academic report: Examines a student’s knowledge of the subject; examples include book reports, historical event reports, and biographies.
- Identifies data from company reports, such as marketing reports, internal memoranda, SWOT analyses, and feasibility reports, that is useful in corporate planning.
- Shares research findings in the form of case studies and research articles, usually in scientific publications.
Depending on how they are written, reports can be further categorised. A report, for instance, could be professional or casual, brief or lengthy, and internal or external. A lateral report is for persons on the author’s level but in separate departments, whereas a vertical report is for those on the author’s level but with different levels of the hierarchy (i.e., people who work above you and below you).
Report formats can be as varied as writing styles, but in this manual, we’ll concentrate on academic reports, which are often formal and informational.
Also Read: How to Write a Leave Application?
Major Types of Reports
While the most common type of reports corresponds to the ones we read in newspapers and magazines, there are other kinds of reports that are curated for business or research purposes. Here are the major forms of report writing that you must know about:
The main purpose of newspaper or magazine reports is to cover a particular event or happening. They generally elaborate upon the 4Ws and 1H, i.e. What, Where, When, Why, and How. The key elements of newspaper or magazine report writing are as follows:
- Headline (Title)
- Report’s Name, Place, and Date
- Conclusion (Citation of sources)
Here is an example of a news report:
Credit: Pinterest
Business reports aim to analyze a situation or case study by implementing business theories and suggest improvements accordingly. In business report writing, you must adhere to a formal style of writing and these reports are usually lengthier than news reports since they aim to assess a particular issue in detail and provide solutions. The basic structure of business reports includes:
- Table of Contents
- Executive summary
- Findings/Recommendations
The main purpose of the technical report is to provide an empirical explanation of research-based material. Technical report writing is generally carried out by a researcher for scientific journals or product development and presentation, etc. A technical report mainly contains
- Introduction
- Experimental details
- Results and discussions
- Body (elaborating upon the findings)
Must Read: IELTS Writing Tips
A report is a written record of what you’ve seen, heard, done, or looked into. It is a well-organized and methodical presentation of facts and results from an event that has already occurred. Reports are a sort of written assessment that is used to determine what you have learned through your reading, study, or experience, as well as to provide you with hands-on experience with a crucial skill that is often used in the business.
Before writing a report, there are certain things you must know to ensure that you draft a precise and structured report, and these points to remember are listed below:
- Write a concise and clear title of the report.
- Always use the past tense.
- Don’t explain the issue in the first person, i.e. ‘I’ or ‘Me’. Always write in the third person.
- Put the date, name of the place as well as the reporter’s name after the heading.
- Structure the report by dividing it into paragraphs.
- Stick to the facts and keep it descriptive.
Must Read: IELTS Sample Letters
The format of a report is determined by the kind of report it is and the assignment’s requirements. While reports can have their own particular format, the majority use the following general framework:
- Executive summary: A stand-alone section that highlights the findings in your report so that readers will know what to expect, much like an abstract in an academic paper. These are more frequently used for official reports than for academic ones.
- Introduction: Your introduction introduces the main subject you’re going to explore in the report, along with your thesis statement and any previous knowledge that is necessary before you get into your own results.
- Body: Using headings and subheadings, the report’s body discusses all of your significant findings. The majority of the report is made up of the body; in contrast to the introduction and conclusion, which are each only a few paragraphs long, the body can span many pages.
- In the conclusion, you should summarize all the data in your report and offer a clear interpretation or conclusion. Usually, the author inserts their own personal judgments or inferences here.
Report Writing Formats
It is quintessential to follow a proper format in report writing to provide it with a compact structure. Business reports and technical reports don’t have a uniform structure and are generally based on the topic or content they are elaborating on. Let’s have a look at the proper format of report writing generally for news and magazines and the key elements you must add to a news report:
To Read: How to Learn Spoken English?
The report writing structure for students in grades 10 and 12 is as follows.
- Heading : A title that expresses the contents of the report in a descriptive manner.
- Byline : The name of the person who is responsible for drafting the report. It’s usually included in the query. Remember that you are not allowed to include any personal information in your response.
- (introduction) : The ‘5 Ws,’ or WHAT, WHY, WHEN, and WHERE, as well as WHO was invited as the main guest, might be included.
- The account of the event in detail : The order in which events occurred, as well as their descriptions. It is the primary paragraph, and if necessary, it can be divided into two smaller paragraphs.
- Conclusion : This will give a summary of the event’s conclusion. It might include quotes from the Chief Guest’s address or a summary of the event’s outcome.
Credit: sampletemplates.com
Credit: SlideShare
Now that you are familiar with all the formats of report writing, here are some questions that you can practice to understand the structure and style of writing a report.
- You are a student of Delhi Public School Srinagar handling a campus magazine in an editorial role. On the increasing level of global warming, write a report on the event for your school magazine.
- On the Jammu-Srinagar highway, a mishap took place, where a driver lost his control and skidded off into a deep gorge. Write a report on it and include all the necessary details and eyewitness accounts.
- As a reporter for the Delhi Times, you are assigned to report on the influx of migrants coming from other states of the country. Take an official statement to justify your report.
- There is a cultural program in Central Park Rajiv Chowk New Delhi. The home minister of India is supposed to attend the event apart from other delegates. Report the event within the 150-200 word limit.
- Write today’s trend of COVID-19 cases in India. As per the official statement. include all the necessary details and factual information. Mention the state with a higher number of cases so far.
- In Jawaharlal Nehru Stadium in New Delhi, a table tennis tournament was held between Delhi Public School New Delhi and DPS Punjab. Report the event in 250-300 words.
Also Read: Formal Letter Format, Types & Samples
Credits: Slideshare
Report Writ ing in 7 steps
- Choose a topic based on the assignment
- Conduct research
- Write a thesis statement
- Prepare an outline
- Write a rough draft
- Revise and edit your report
- Proofread and check for mistakes
Make sure that every piece of information you have supplied is pertinent. Remember to double-check your grammar, spelling, tenses, and the person you are writing in. A final inspection against any structural criteria is also important. You have appropriately and completely referenced academic work. Check to make sure you haven’t unintentionally, purposefully, or both duplicated something without giving credit.
Related Articles
Any business professional’s toolkit must include business reports. Therefore, how can you create a thorough business report? You must first confirm that you are familiar with the responses to the following three questions.
Every company report starts with an issue that needs to be fixed. This could be something straightforward, like figuring out a better way to organise procuring office supplies, or it could be a more challenging issue, like putting in place a brand-new, multimillion-dollar computer system.
You must therefore compile the data you intend to include in your report. How do you do this? If you’ve never conducted in-depth research before, it can be quite a daunting task, so discovering the most efficient techniques is a real plus.
Hopefully, this blog has helped you with a comprehensive understanding of report writing and its essential components. Aiming to pursue a degree in Writing? Sign up for an e-meeting with our study abroad experts and we will help you in selecting the best course and university as well as sorting the admission process to ensure that you get successfully shortlisted.
Ankita Mishra
A writer with more than 10 years of experience, including 5 years in a newsroom, Ankita takes great pleasure in helping students via study abroad news updates about universities and visa policies. When not busy working you can find her creating memes and discussing social issues with her colleagues.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
30,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
- Directories
Report writing
Report writing is common in a number of disciplines. A report is a specific form of writing, written concisely and clearly and typically organised around identifying and examining issues, events, or findings from a research investigation.
Reports often involve investigating and analysing a problem and coming up with a solution. This means that you need to take a position or provide a solution and you need clear reasons for your solution.
A key, central message is a vital part of the report and will help to make it clear and persuasive.
A report might involve
- an analysis of existing data and literature
- conducting analysis and problem solving
- results of an investigation
Whatever the type of report, they are expected to be well written, clearly structured and expressed in a way that suits the particular audience. Results and analysis should be accurate, clear and objective. Report structures can vary between disciplines and audiences but the structure needs to support the key message.
Reports differ from essays in a number of ways. Consider the following:
Report writing process
It can be helpful to think of writing your report as a process and to break it down into the various tasks that you need to complete.
What goes on when you are writing a report? What are the various tasks you need to do to complete it?
There are three main phases:
The preparation phase where you analyse exactly what you are being asked to do and if you are working in a group, agree on the group communication plan.
The analysis phase where you gather all your evidence, conduct research, undertake investigations, complete coding, calculations etc
The analysis phase will enable you to come up with your key message - your answer to the question/solution to the problem. This key message will then determine the structure of your report and enable you to complete the writing phase of the report.
A note on group work
Reports are often written in groups, which present both rewards and challenges. The key to effective group work is effective communication and good planning. See our advice on group work for useful strategies to ensure a productive and fair group project.
Understanding the task >>
Understanding the task
Analysis and research
Writing the report
- ANU Library Academic Skills
- +61 2 6125 2972
👀 Turn any prompt into captivating visuals in seconds with our AI-powered design generator ✨ Try Piktochart AI!
- Piktochart Visual
- Video Editor
- AI Design Generator
- Infographic Maker
- Banner Maker
- Brochure Maker
- Diagram Maker
- Flowchart Maker
- Flyer Maker
- Graph Maker
- Invitation Maker
- Pitch Deck Creator
- Poster Maker
- Presentation Maker
- Report Maker
- Resume Maker
- Social Media Graphic Maker
- Timeline Maker
- Venn Diagram Maker
- Screen Recorder
- Social Media Video Maker
- Video Cropper
- Video to Text Converter
- Video Views Calculator
- AI Brochure Maker
- AI Document Generator
- AI Flyer Generator
- AI Infographic
- AI Instagram Post Generator
- AI Newsletter Generator
- AI Report Generator
- AI Timeline Generator
- For Communications
- For Education
- For eLearning
- For Financial Services
- For Healthcare
- For Human Resources
- For Marketing
- For Nonprofits
- Brochure Templates
- Flyer Templates
- Infographic Templates
- Newsletter Templates
- Presentation Templates
- Resume Templates
- Business Infographics
- Business Proposals
- Education Templates
- Health Posters
- HR Templates
- Sales Presentations
- Community Template
- Explore all free templates on Piktochart
- Course: What is Visual Storytelling?
- The Business Storyteller Podcast
- User Stories
- Video Tutorials
- Need help? Check out our Help Center
- Earn money as a Piktochart Affiliate Partner
- Compare prices and features across Free, Pro, and Enterprise plans.
- For professionals and small teams looking for better brand management.
- For organizations seeking enterprise-grade onboarding, support, and SSO.
- Discounted plan for students, teachers, and education staff.
- Great causes deserve great pricing. Registered nonprofits pay less.
20 Types of Reports and When to Use Them (Plus Templates)

If the many types of business reports make you want to scream, you’re not alone.
It can get overwhelming – from internal reports about sales activities to reports you must submit for external collaborators.
However, the reality of modern business is that they require several business report types to achieve success.
A Unito report revealed that over 75% of respondents said reports provide valuable insights almost every time.
The chances are high that you’ve had to write certain types of reports, whether you realize it or not. Irrespective of your role, you’ll likely need to write reports, whether occasionally or once in a while.
And to ensure you’re writing the appropriate report for specific situations, you need to recognize the different types of reports and how to write them.
Below, you’ll discover an exhaustive list of business report types, what they do, and when you need them, plus examples and templates.
Let’s get into it.
Table of contents
- What is report writing?
1. Formal report
2. informal report , 3. audit report, 4. marketing report, 5. progress or periodic report, 6. trend report, 7. analytical report, 8. evaluation report, 9. client report, 10. sales report, 11. proposal report, 12. survey report , 13. research report, 14. financial report, 15. incident report, 16. project report, 17. annual report, 18. lateral report.
- 19. Vertical report
20. Event report
Make beautiful, engaging reports with Piktochart. Try it for free .
What is report writing?
Do you remember those report cards you received at the end of every school session? The details of how well you perform academic and extracurricular activities during the year.
This is what reports do.
Reports are documents detailing the results or findings from a process, project, or investigation. They can also refer to a well-detailed analysis of specific data sets or situations.
In business communications, report writing is the process of preparing formal documents that elaborate on a specific topic. Report writing often uses facts, tables, graphs , charts, diagrams , etc., to explain its findings for easy comprehension.
Since any report aims to educate and inform through scientific research, preparing the perfect report focusing on the target audience is crucial. Some reports also present available options and recommendations based on their findings.
20 types of reports, examples, and templates
While businesses use numerous types of reports, these are the most common ones we’ve seen used almost daily.
Formal reports often carry objective information that is in-depth and straight to the point without personal references. These reports require careful structuring based on the organization’s style and purpose.
Formal report classification includes accounting reports, functional reports, and other lengthy reports.
Informal reports are the opposite of a formal reports. It lacks strict structuring, contains short messages, and uses casual language. Businesses intending to pass quick critical information often use informal reports. Informal reports pay more attention to fast and effective communication than formal structuring.
Again, other types of informal reports fall into this category, including digital postings, emails, memo reports, and some forms of internal reports.

An audit report is a formal report created by an auditor about the financial status of an organization. Audit reports are written using generally accepted auditing standards.
However, these formats may vary slightly depending on the audit’s circumstances. An example is an end-of-the-year audit report for an organization.

Marketing reports give detailed information about marketing campaigns, from on-ground to social media campaigning . They are used for monitoring marketing activities and informing about marketing strategies that work or require improvements.

Progress reports , or periodic reports, are generated at specific intervals. Depending on the needs for the performance reports, they could be daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, and annual reports or they may even use regularly scheduled dates.
Progress reports are used to supply progress or performance information. Other business report types could also qualify as periodic reports if they are made available at intervals.
Examples of progress reports include analytical reports, Google analytics reports, and inventory reports.

Sometimes called trend analysis reports, trend reports analyze everyday business operations and compare them to forecasts.
This report helps businesses discover recent industry trends and how they can benefit organizations. They also reveal important details about marketing campaigns and tell you the reach of your messages and their influences on marketing.
Examples include Google Analytics reports, surveys, and statistical reports.

Analytical reports have gained prominence in recent years due to the growing importance of business data analysis.
The last few years have seen data analysis ingrained as part of standard business practices, and the industry expects to reach $68 billion in annual revenue by 2025.
Organizations leverage data-driven insights that make analytical reports one of the most common reports used. Analytical reports can suggest recommendations to improve businesses by leveraging data insights to evaluate performance.
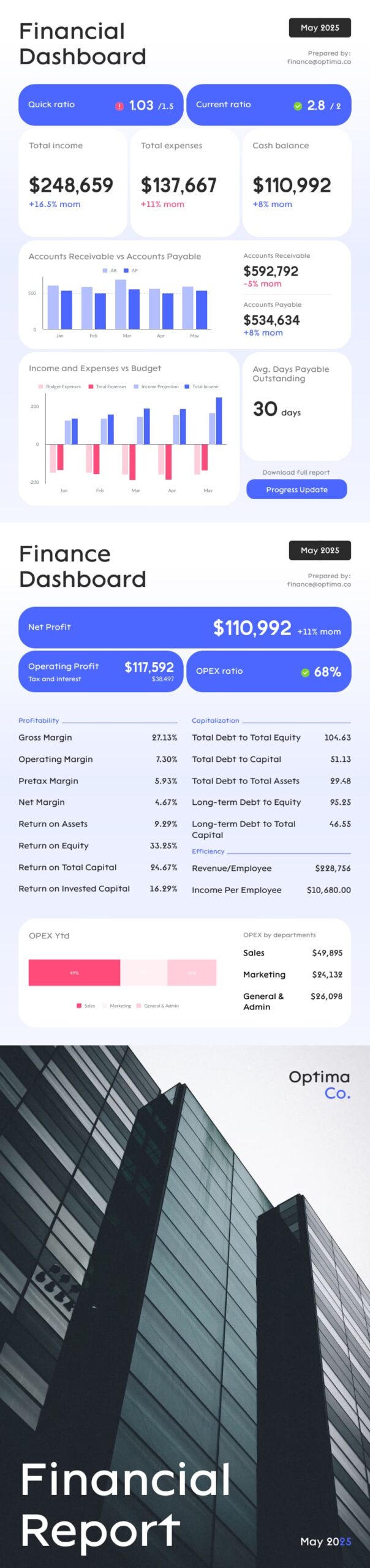
When an organization rolls out products, services, campaigns, or processes, it must evaluate the success periodically or after the program.
An evaluation report documents a product’s effectiveness if a service meets expectations or if a campaign is successful.
Evaluation reports also highlight findings and make recommendations based on the performance. It is a formal, in-depth report, sometimes including background information, definitions, results, forecasts, and recommendations.
This report can assist with the decision-making process and show transparency to stakeholders.

Since businesses deal with clients, they need a client report detailing their relationship with each client and their work activities. Client reports clarify projects’ progress and help the business make management decisions.
Client reports are created and delivered according to the agreed time frame. For example, it could be weekly, monthly, quarterly, etc. This makes the report a periodic report.
Meetings and discussions with clients could also accompany it to explain the content. As a result, client reporting helps a business build trust.

The sales department reports a business’ sales performance to executives and the board through the sales reports. Members of the sales team could also make a sales report for other group members or the team manager.
A sales report details the performance of a business for a specified period. They can also reveal happenings on the field to inform decisions.
This type of report highlights sales volume, revenue from the sales, leads, etc. They may be used to set key performance indicators or formulate an entire business target.
Examples of sales reports include periodic reports that track sales performance for the specified period. For instance, a weekly or monthly sales report will detail sales, revenue, leads, and other metrics for the specified time periods.
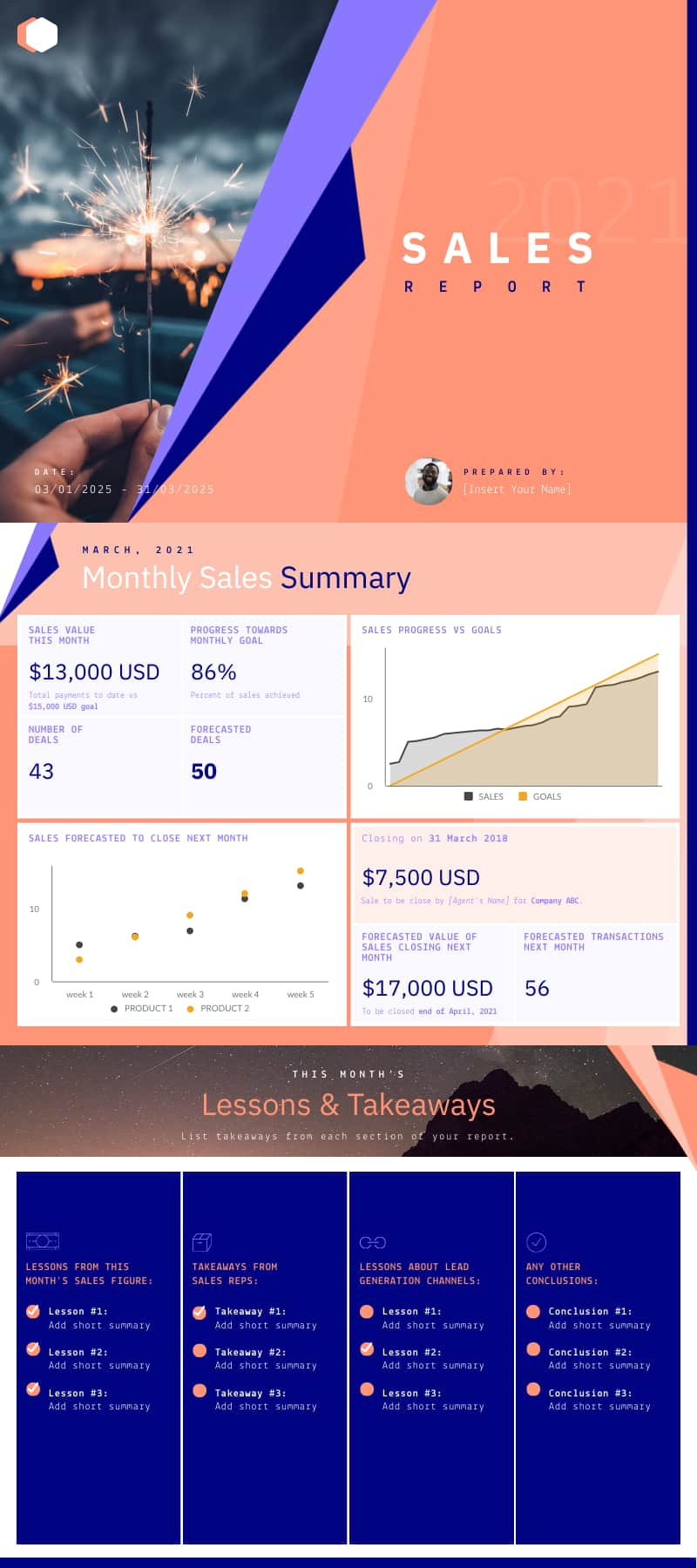
Businesses go into partnerships and other forms of business relationships. But before this happens, they establish the specifics of the relationship through a proposal report.
Proposal reports are official documents highlighting how a business intends to help another.
Proposal reports are sent in response to a Request for Proposal or RFP. They contain specific steps the business will undertake to assist the recipient business.
Since a company usually receives business proposals from many businesses, aim for thorough and precise proposal reports.

Survey reports are documents that help a business highlight the findings from a survey. It does its best to summarize the responses of a survey and objectively present the information while using visuals like tables, graphs, charts, and infographics to make reports easy to read .

Research reports are documents created to communicate the findings from the research – whether business or scientific – related to the company. Experts in the field usually do it. Sometimes, a research report can uncover information requiring urgent attention.
The content in a research report includes the research process, findings, conclusions, recommendations, and limitations.
It will inform a business about essential market needs they need to attend to and how their products or service affects the public. For example, some social media platforms are looking into how they influence young people.

Financial reports and budget reports are often used interchangeably, but they are not necessarily the same.
Production and finance departments are typically in charge of these reports. Financial reports are formal documents that explain a business’s financial status and performance. Examples of budget reports include weekly or monthly financial reports that detail the economic activities for the period specified.
On the other hand, budget reports are concerned with the pre-set budget conditions and how they compare with the company’s financial situation. They help businesses make proper financial decisions and can be used to compare milestones over a specific period.

Although businesses put measures to prevent accidents and other undesirable incidents, they can still happen in the workplace. And when these incidents occur, additional steps may be required to avoid a reoccurrence. An incident report is an informational report that details the facts of an incident.
Incident reports may also reveal unusual occurrences, safety and health issues, security breaches, near misses, damage, etc.
It highlights the cause, exact occurrence, and ways to prevent incidents in the future. Specific industries like insurance companies and security agencies may also require them.

Also known as a project health report, project reports help the organization give information about specific projects.
Businesses generally embark on projects, and making reports about each allows them to track progress and assess performance effectively.
Project reports contain the objectives, which can help ensure compliance from everyone overseeing the project. Such reports also make it easy for stakeholders to give feedback, edit, assess financial requirements, and implement necessary actions.

Annual reports are comprehensive longer reports that give in-depth details about a business in the preceding year. It details the financial statements and achievements for the specific year.
They could qualify as external reports since many organizations release their annual reports to the public. In some instances, releasing annual reports may be a mandate for some businesses.
However, companies mainly design annual reports to review the company’s business during the year. They help stakeholders become aware of the performance and inform shareholders and others about the financial performance.

Vertical and lateral reports are terms used when referring to the direction of a report. Compared to other reports, lateral reports describe those that move between members at the same organizational level.
Examples of these types of reports are informational reports exchanged between team managers, short reports between members of a team, or comprehensive reports between departments.

19. Vertical report
Vertical reports comprise a document prepared in a report form shared between different organizational hierarchies. It could be from a higher level to a lower level or vice versa.
Examples include business reports from employees members of an executive team or managers to their team members.

Businesses organize many events, and event reports analyze each event’s success.
Event managers prepare these short reports and work by comparing event results to the set goals. It determines an event’s success and serves as a blueprint for future events.

Make beautiful, engaging, and different types of reports with Piktochart
Understanding the different types of reports is crucial to using them for the growth and organization of your business.
Not only report vital, but they can also help a business identify pain points and forecast future occurrences when appropriately used.
However, this isn’t always the case because many business report types often confuse employees and owners.
The way out is to use report-writing tools like Piktochart. Piktochart is an all-in-one business communication tool that helps businesses create reports, presentations, infographics, and various other business designs.
Pick a template, input your data, and watch your report come alive. Writing reports will be a breeze once you work from professional templates. Create a free Piktochart account to get started now!

Other Posts
10 Best Sales Report Templates for Tracking Revenue, KPIs & Growth

10 Types of HR Reports (With Templates and Examples)

7 Captivating Report Design Ideas And Tips (With Templates and Examples)

Report Writing: Format, Topics, and Examples

Learn the essentials of report writing with this comprehensive guide. Explore the proper format, find inspiring topics, and discover real-world examples to enhance your report writing skills.
What is Report Writing?
A Report Writing is a written account that helps us to know about an event, situation, or occurrence in detail that has already taken place.
Report Writing is a narrative of Events described in an impartial approach. Rules and Format of Report Writing are necessary to know for English report writing. Examples of Report Writing help us in doing this easily.
The Power of Effective Report Writing
Report writing is a skill that transcends industries and disciplines, playing a vital role in conveying information, analyzing data, and making informed decisions.
Whether you are a student, a researcher, a business professional, or someone looking to improve your communication abilities, mastering the art of report writing is essential for success.
This article will provide you with insights into the format, topics, and real-world examples of report writing to help you become a proficient report writer.
Understanding the Format of a Report
A well-structured report not only facilitates easy comprehension but also leaves a lasting impact on the reader. Understanding the proper format is the foundation of creating an effective report. In crafting a comprehensive and impactful report, one must carefully consider and include the following crucial elements. :
1. Title Page
The title page should include the report’s title, the name of the author or organization, the date of submission, and any relevant affiliations.
2. Abstract or Executive Summary
The abstract or executive summary is a concise overview of the report’s main points, providing the reader with a snapshot of the entire report’s content.
3. Table of Contents
The table of contents outlines the report’s structure, listing the headings and subheadings with corresponding page numbers.
4. Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the report, providing context, stating the purpose, and highlighting the significance of the topic.
5. Methodology
In research-oriented reports, the methodology section explains the approach taken to gather data, conduct experiments, or perform studies.
6. Findings
The findings section presents the data collected or the results of the research in a clear and organized manner, often using tables, graphs, or charts.
7. Discussion
The discussion section interprets the findings, provides insights, and offers explanations for observed patterns or trends.
8. Conclusion
The conclusion summarizes the main points, draws conclusions based on the findings, and may include recommendations for future actions.
9. Recommendations
In reports with actionable outcomes, the recommendations section suggests specific steps or strategies based on the findings.
10. References
The references section lists all the sources cited in the report, ensuring proper acknowledgment of external work and adding credibility.
Writing Tips for an Effective Sample Report
Creating a compelling report requires not just proper structure but also excellent writing skills. Here are some valuable tips to enhance your report writing:
1. Know Your Audience
Understanding your target audience is crucial when writing a report. Tailor your language, tone, and content to suit the reader’s level of expertise and interest.
2. Use Clear and Concise Language
Keep your writing clear, straightforward, and to the point. Avoid jargon and unnecessary technical terms that may confuse readers.
3. Organize Information Logically
Present information in a logical sequence, ensuring that each section flows smoothly into the next. Use headings and subheadings to provide a clear structure.
4. Support Claims with Evidence
Back up your statements with credible evidence and data. This adds credibility to your report and strengthens your arguments.
5. Edit and Proofread Thoroughly
Always review your report for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. A well-edited report shows professionalism and attention to detail.
6. Seek Feedback
Before finalizing your report, seek feedback from colleagues or peers. Fresh perspectives can help identify areas of improvement.
Selecting Engaging Report Writing Topics
Choosing the right topic is essential for crafting a compelling report. Whether it’s for academic, business, or research purposes, an engaging topic will capture the reader’s interest and keep them invested in your report. Here are some inspiring report writing topics:
1. The Impact of Technology on Modern Workplace s
Explore how technology has transformed traditional workplaces, affecting productivity, communication, and employee satisfaction.
2. Environmental Sustainability in Urban Cities
Examine the efforts made by urban cities to promote environmental sustainability, including green initiatives and waste reduction strategies.
3. The Rise of E-Learning: A Comprehensive Analysis
Analyze the growth of e-learning platforms, their effectiveness in education, and their potential to revolutionize the traditional learning system.
4. Cybersecurity Threats and Mitigation Strategies for Businesses
Investigate the latest cybersecurity threats faced by businesses and outline effective strategies to safeguard sensitive data and prevent cyber attacks.
5. Mental Health in the Workplace: Strategies for Employee Well-Being
Discuss the importance of addressing mental health issues in the workplace and propose strategies to support employee well-being.
Real-World Examples of Impactful Reports
To gain a deeper understanding of report writing’s practical applications, let’s explore some real-world examples:
1. World Health Organization (WHO) – Global Health Report
The WHO publishes comprehensive reports on global health issues, providing data on disease outbreaks, vaccination rates, and healthcare access worldwide. These reports play a crucial role in shaping global health policies and initiatives.
2. McKinsey & Company – Industry Research Reports
Management consulting firm McKinsey & Company produces insightful industry research reports that analyze market trends, consumer behavior, and business strategies. These reports serve as valuable resources for executives and decision-makers.
3. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) – Climate Assessment Reports
The IPCC releases periodic reports on climate change, assessing its impacts, causes, and potential solutions. These reports are instrumental in guiding environmental policies and international climate agreements.
A Sample Report Writing Format on A Bank Robbery.
The following points will make it easy to write a report easily shown below.
( Heading) DARING BANK ROBBERY
( Who Reported ) By a Special Correspondent
Where, When, What: Kolkata, August 14 (Introduction): A daring (CART) robbery took place today at 3 p.m. at the United Bank of India, Gariahat Branch, Kolkata.
How, why, Casualty: According to the Branch Manager, three men armed with pistols overpowered the security staff and locked the gate from the inside. One of the miscreants (710) herded the customers and the staff into one corner of the bank and kept them silent at gunpoint. The other two miscreants snatched the keys from the Manager.
Condition: Then they unlocked the vault and bagged cash and jewelry worth Rs. 40 lacks. They came out of the bank hurling bombs, jumped into a black Maruti Van, and sped away.
Reaction & Measures Taken (Conclusion): The police arrived within half an hour. No one has been arrested yet. Investigations are on, as the Deputy Commissioner of Police told the media.
People may also like
Report writing types in english:.
Basically, Report writing in English is of three types .
- General Report Writing: These reports give an account of a person’s experience of an event or an incident.
- Newspaper Report Writing: Newspaper reports are based on true incidents or accidents meant to express some information to the public.
- Business Report Writing: Business reports are made on orders based on observation, investigation, and analysis.
General Report Writing Examples
Example 1: Business Report – Market Analysis
Title: Market Analysis for XYZ Company’s Product Expansion
Executive Summary: The market analysis report assesses the potential of XYZ Company to expand its product line into a new market segment.
Introduction: This report aims to investigate the feasibility and potential challenges associated with XYZ Company’s entry into the youth-oriented consumer electronics market.
Methodology: Data was collected through a combination of surveys, focus groups, and secondary research from reputable industry reports.
Findings: The youth-oriented consumer electronics market is growing rapidly, with an annual growth rate of 12% over the past three years.
XYZ Company’s brand recognition is relatively low among the target audience.
The price sensitivity of the target market is a significant factor to consider.
- Analysis: The findings suggest that while there is a lucrative opportunity for XYZ Company to enter the market, it will require a focused marketing campaign and competitive pricing strategies to overcome initial brand awareness challenges.
- Discussion: By leveraging social media and influencers, XYZ Company can effectively reach the target audience and build brand loyalty. Additionally, offering a competitive pricing model will attract price-conscious customers.
- Recommendations:
- Collaborate with popular influencers to gain credibility and reach a wider audience.
Offer attractive introductory pricing and discounts to entice price-sensitive customers.
Conclusion: Entering the youth-oriented consumer electronics market presents a promising opportunity for XYZ Company. By implementing the recommended strategies, the company can capitalize on this potential growth and expand its product line successfully.
Remember that the specific format and content of a report may vary based on the requirements set by your institution, organization, or supervisor. Always check for any specific guidelines before starting your report writing.
Write a newspaper report on the “Annual Prize Distribution Ceremony in your school”
Annual Prize Distribution Ceremony in your school
By Staff Reporter
[City, Date]: The air was abuzz with excitement and anticipation as [Your School Name] hosted its grand Annual Prize Distribution Ceremony yesterday. The event, held in the school auditorium, was a momentous occasion that celebrated the academic excellence and achievements of the students.
Distinguished guests, parents, and faculty members graced the ceremony with their presence. The school principal, in his opening address, emphasized the significance of recognizing and applauding students’ efforts beyond academics.
The highlight of the event was the distribution of prizes to the meritorious students, acknowledging their outstanding performance in academics, sports, and extracurricular activities. The audience erupted with applause as the achievers walked up the stage to receive their awards.
The melodious music, vibrant dances, and thought-provoking skits captivated the audience.
The Annual Prize Distribution Ceremony concluded on a high note, leaving everyone inspired and motivated. It served as a testament to the school’s commitment to nurturing holistic development among its students.
[Your School Name] once again proved that it is not only a center of academic excellence but also a platform for nurturing well-rounded individuals.
By [Your Name]
Write a newspaper repot on “A terrible fire broke out in Kolkata”
Terrible fire breaks out in kolkata, causing extensive damage.
Kolkata, Date: A devastating fire broke out in a commercial area of Kolkata yesterday, causing widespread destruction and panic among residents and businesses. The incident occurred in the bustling market district, engulfing several multi-story buildings.
Eyewitnesses reported that the fire started in one of the shops due to an electrical short circuit and quickly spread to nearby establishments. Despite the immediate response from firefighters, the blaze proved challenging to control, as narrow streets hindered their access.
Local authorities and emergency services rushed to the scene, evacuating people from nearby buildings and providing medical assistance to those affected. Tragically, a few individuals sustained minor injuries in the process.
The fire caused extensive damage to properties, resulting in significant financial losses for business owners. The full extent of the damage is yet to be assessed.
Investigations into the incident are underway to determine the exact cause and potential safety lapses. As the city mourns the loss of properties and livelihoods, efforts are being made to extend relief and support to the affected residents.
1. Write a report for a newspaper about A Terrible Train Accident.
Odisha Train Accident / Coromandel Express Train Accident
Balasore, 3rd June 2023: At around 7 pm, 2nd June on Friday evening 10-12 coaches of the Shalimar-Chennai Coromandel Express derailed near Baleswar and fell on the opposite track. After some time, another train from Yeswanthpur to Howrah dashed into those derailed coaches resulting in the derailment of its 3-4 coaches. The train crash involving two passenger trains and a goods train in Odisha’s Balasore on Friday is said to be one of the deadliest rail accidents in India. More than 230 people have lost their lives in the accident and 900 have been injured. NDRF, ODRAF, and Fire Services are still working to cut the bogie and try to recover the living or the dead. Local people were seen helping the teams responsible for rescue and relief operations and they queued up to donate blood for the injured in Balasore. As a result, Local people became able to rescue 200-300 injured people A high-level committee has been declared to conduct an inquiry into the train accident. The Centre has announced an ex-gratia compensation of Rs 10 Lakh each to the kin of the deceased and Rs 2 Lakh to grievous and Rs 50,000 for minor injuries, Union Railways Minister Ashwini Vaishnav said.
2. Write a report for a newspaper about A Magic Show .
By Anik Dutta
On Friday, November 18: our school authority invited a magician to surprise the students of the school with a magic show. The magic show was a gift to the students from the school’s authoritative body as the school won the award for Best Disciplined School in Kolkata for the year 2015. The magic show was organized on the school’s open-air stage. The show went on for 2 hours, from 12 to 2 pm. The first magic shown by the great magician was pulling out of a rabbit from his hat which was absolutely empty when he wore it. The spectators were pleasantly surprised. He showed exciting magic tricks one after the other and ended the show with a message to the awestruck students, ‘Practice maths well, and you can do magic too as it is nothing but a game of calculation’. The show was immensely appreciated by all.
3. Write a report for a newspaper about Health Issues of the people of your District .
Health Issues of the People of Your District
By Ravi Yogi
On 20 May 2021: a health awareness campaign camp was organized in the Howrah district by the World Health Organisation. Some volunteers were chosen, who from then on, visit each house every month to remind people to get their children vaccinated. People now follow their instructions and keep their surroundings clean to avoid certain diseases. The volunteers distributed water purifiers at a cheap rate so that people could use them to get pure water. The mosquito-repellant sprays are used every month and mosquito nets are now used to keep mosquitoes away. If the volunteers arrange a blood donation camp every month it could help the people in need. Also, a free health checkup camp could be arranged for further health improvement of the people of the locality.
4. Write a report for a newspaper about the Annual sports Event of Your School .
Annual Sports Event of Your School
By Anwesha Das
The annual sports day of our school (St. Agnes H.S. School) was held on February 15 for the junior students at the school grounds. The event for the junior students started at 9:30 in the morning with a relay race. The next race they had was a tricycle race and the last one the junior students had was a treat to watch. The junior ones’ had to run wearing long gowns and they had to run the track without falling even once.
The juniors enjoyed the fun sporting events a lot, while the visitors’ race involving the parents remained the highlight of the day. At the end of the program Chief Guest Sourav Ganguly gave away the awards to the winners and the class teacher of each class distributed a box containing candies, a chocolate pastry, an orange, and two vanilla cream-filled wafer biscuits to every pupil of her class. The event turned out to be a joyful one with a smile on everyone’s face.
Newspaper Report Writing : Format, Topics, Examples
5. write a newspaper report on the first downpour of the season ..
FIRST DOWNPOUR OF THE SEASON
Kolkata, June 13: Today Kolkata experienced its first downpour during the season. The showers were brought about by a deep depression over the Gangetic West Bengal. There was incessant (WESO) rainfall accompanied by thunder and lightning. In Kolkata, it rained throughout the day with occasional breaks. The weather office at Alipore has recorded a rainfall of 20 cm. Many low-lying areas went underwater. Some of the major roads were waterlogged for several hours. There were traffic jams on many roads. The hand-pulled rickshaws had stopped. Train and air services were disrupted. There were cable faults in many parts of the city. Two persons were electrocuted. But they have not yet been identified, said the police officials.
6. As a Reporter for an English daily, write a report about A violent cyclonic storm .
A VIOLENT CYCLONIC STORM
By a Special Correspondent
Katak, August 12: A violent cyclonic storm ravaged the coastal areas of Odisha today. The cyclone started at about 6.45 p.m. It was said to have rushed at a speed of 80 km per hour. The worst-affected areas include Puri, Baleswar, and Paradip. The cyclone raised the sea to an alarming height. The high tidal waves submerged the low-lying coastal areas. It caused incalculable damage to life and property. More than 10,000 people were rendered homeless. Train services were totally disrupted. The State Government sent its rescue team along with central paramilitary forces to tackle the situation. A sum of Rs. 3 crores has been sanctioned for the relief and rehabilitation of the cyclone-hit people.
7. Write a report for a newspaper about A Serious Road Accident
A Serious Road Accident
Kolkata, January 18: As many as 20 persons including two women and a child were injured in an accident at about 8 pm, on M, G, Road yesterday. The accident took place when a speeding minibus, in a bid to overtake a private bus, skidded off the road. The vehicle carrying 45 passengers went straight into a shopping mall, after breaking the roadside railing, Persons inside the mall and the bus suffered serious injuries Local people started the rescue operation. The injured were taken to the nearest hospital. Locals got agitated and blocked the road causing the suspension of traffic for more than 3 hours. However, the police came and brought the situation under control.
8. Write a report within 100 words for an English daily about Cyclone hitting Coastal West Bengal .
Cyclone hits Coastal West Bengal
-By a Staff Reporter
Kolkata, June 12, 2013: A severe cyclone with a speed of 80 km. per hour hit the coastal areas of West Bengal yesterday evening at about 6-45 p.m. Caused by a deep depression in the Bay of Bengal, the cyclone ripped through the state resulting in huge damage to life and property. 60 persons have died and thousands have been rendered homeless. Train services have been disrupted leaving a number of people stranded. The state government has taken immediate steps to provide relief to the victims. More than 5000 people have been evacuated to temporary relief shelters. The Chief Minister has reviewed the situation and assured the people of all help.
9. Write a newspaper report on a road accident within 100 words .
BRAKE FAILURE BUS COLLIDES WITH A TRUCK
By a Staff Reporter
Kolkata, October 1, 2015: Yesterday at around 10:30 am an accident took place at Sinthi More when an Esplanade bound bus, of route no 78/1, suddenly collided with a truck. The report says the brake failure of the bus was the cause of this mishap. Five passengers were injured including a child and a woman. According to passengers, the ill-fated bus was moving at a great speed. Near Sinthi More the driver lost control and banged behind a truck. Local people rushed in, and took the injured to the nearest hospital where they were released after first aid. Traffic got disrupted. Cops reached the spot quickly, intervened, and normalcy was restored within an hour.
10. Write a report on a Railway accident.
A MAN DIED IN A RAILWAY ACCIDENT
By Kishore Ganguli
Kolkata, April 25: A man died after he had been hit by a Sealdah bound train close to Barrackpore station around 5.40 am today when the victim was returning home from a regular morning walk. According to an eyewitness, the man was trying to cross the tracks, got confused, and ended up on the track on which the train was coming on. Being hit on his head, he was hospitalized immediately. But the doctors declared him dead. The locals made a blockade on the railway tracks. The police came, dispersed the irate mob and the train service was restored. The railway authorities announced an exgratia payment of Rs 2 lakh to the next of kin of the deceased. The situation is tense till now.
FAQs about Report Writing
Q: what is the ideal length for a report.
Reports can vary in length depending on their purpose and complexity. However, a concise report of 10-20 pages is often preferred to keep the reader engaged.
Q: Can I use bullet points in my report?
Yes, using bullet points can enhance readability and make key information stand out. However, use them sparingly and only when appropriate.
Q: Should I include visuals in my report?
Yes, incorporating relevant visuals like graphs, charts, and images can make complex data easier to understand.
Q: Can I include my opinion in the report?
While reports should be objective and fact-based, there might be instances where your expert opinion is valuable. If so, clearly distinguish between facts and opinions.
Q: How can I make my executive summary compelling?
The executive summary should be concise yet informative. Highlight the most important findings and recommendations to pique the reader’s interest.
Q: Is it necessary to follow a specific report writing style?
Different organizations or fields may have their preferred report writing style. Always follow the guidelines provided by your institution or industry standards.
Q: What is the main purpose of a report?
A: The main purpose of a report is to present information, findings, and recommendations in a structured and organized manner.
A: Yes, bullet points can help present information concisely and improve readability.
Q: How long should an executive summary be?
A: An executive summary should be concise, typically ranging from one to two pages.
Q: Is it necessary to include visuals in a report?
A: Including visuals such as charts, graphs, and images can enhance the reader’s understanding of complex data.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid in report writing?
A: Common mistakes to avoid include using overly technical language, neglecting to cite sources properly, and lacking a clear structure.
Q: How can I make my report more engaging?
A: To make your report engaging, use real-life examples, incorporate visuals, and use a conversational tone when appropriate.
- I nfographics
- Show AWL words
- Subscribe to newsletter
- What is academic writing?
- Academic Style
- What is the writing process?
- Understanding the title
- Brainstorming
- Researching
- First draft
- Proofreading
- Report writing
- Compare & contrast
- Cause & effect
- Problem-solution
- Classification
- Essay structure
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Book review
- Research proposal
- Thesis/dissertation
- What is cohesion?
- Cohesion vs coherence
- Transition signals
- What are references?
- In-text citations
- Reference sections
- Reporting verbs
- Band descriptors
Show AWL words on this page.
Levels 1-5: grey Levels 6-10: orange
Show sorted lists of these words.
Any words you don't know? Look them up in the website's built-in dictionary .
Choose a dictionary . Wordnet OPTED both
Report writing An overview and comparison with essays
There are many forms of writing which you may have to undertake at university, from reflective journals to extended researched assignments. The two most common forms of writing are reports and essays . This page describes what a report is , outlines the main types of report you may need to write, and summarises the differences between reports and essays .
What is a report?

For another look at the same content, check out the video on YouTube (also available on Youku ).
A report is a clearly structured form of writing which presents and analyses information clearly and briefly for a particular audience. The information is usually the result of an experiment, investigation, or some other form of primary research such as a questionnaire or survey. It will contain headings and sub-headings, as well as graphics such as graphs, charts and tables. Reports often use the information they contain to present recommendations for future action. They are common not only at university, but also in industry and government. For more information on what a report is, see the section below which compares reports to essays .
Types of report
There are many different types of reports which can be written, though the type you will write at university depends very much on your course of study. Each report will have a different format and writing conventions, though the structure and language used are broadly similar for all reports. The following are some of the main reports written at university.
- Laboratory report . This type of report explains and analyses the results of an experiment. It may also be called lab report , experimental report , or science report .
- Business report . This analyses a situation and uses business theory to provide solutions or recommendations. It includes many types, e.g. market research report , marketing report , and financial report .
- Case study report . This examines a real-world situation (the 'case') and analyses it using appropriate theory (the 'study').
- project report . This reports on project work which has been conducted.
- Research report . This gives the results of research which has been conducted, for example through surveys (via questionnaires or interviews).
- progress report . This informs a supervisor about progress on a project over a certain period of time.
- Design report . This report describes and evaluates a design used to solve a particular problem.
- Field report . This combines theory and practice by describing an observed person, place or event and analysing the observation.
Other types of report are possible, such as a systems analysis report , a maths report , a feasibility study and a client case work report . Some disciplines, especially business, may require you to write an essay with headings. This is not a report, since all the other features, aside from the headings, are the same as a conventional essay.
Reports vs. essays
Although many of the writing skills required for essays also apply to reports, such as use of topic sentences , cohesion and citations , reports are quite unlike essays in several regards. The table below summarises the main differences. These are divided into three categories: general areas, structure, and content.
Charles Darwin University (2013) Report . Available from http://learnline.cdu.edu.au/studyskills/studyskills/reports.html (Access date 19 July, 2015).
Massey University (2012) Business Report . Available from http://owll.massey.ac.nz/assignment-types/business-report.php (Access date 20 July, 2015).
Monash University (2015) Report Writing . Available from http://www.monash.edu.au/lls/llonline/writing/general/report/index.xml (Access date 20 July, 2015).
Purdue University (2015) Purposes and Types of Report Format . Available from https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/726/02/ (Access date 20 July, 2015).
Queensland University of Technology (2014) Writing a report Available from http://www.citewrite.qut.edu.au/write/report.jsp (Access date 19 July, 2015).
RMIT University (2007) Differences between Essays, Reports and Journals . Available from https://www.dlsweb.rmit.edu.au/lsu/content/2_assessmenttasks/assess_pdf/diffbet_reportsessays.pdf (Access date 19 July, 2015).
Unilearning (2000) Comparison: reports and essays . Available from http://unilearning.uow.edu.au/report/1b.html (Access date 19 July, 2015).
University of Queensland (2015) Types of assignment . Available from http://www.uq.edu.au/student-services/learning/types-of-assignments (Access date 20 July, 2015).

GET FREE EBOOK
Like the website? Try the books. Enter your email to receive a free sample from Academic Writing Genres .
Next section
Find out about report structure in the next section.
Previous section
Read the previous article about the writing process .

Author: Sheldon Smith ‖ Last modified: 01 February 2022.
Sheldon Smith is the founder and editor of EAPFoundation.com. He has been teaching English for Academic Purposes since 2004. Find out more about him in the about section and connect with him on Twitter , Facebook and LinkedIn .
Compare & contrast essays examine the similarities of two or more objects, and the differences.
Cause & effect essays consider the reasons (or causes) for something, then discuss the results (or effects).
Discussion essays require you to examine both sides of a situation and to conclude by saying which side you favour.
Problem-solution essays are a sub-type of SPSE essays (Situation, Problem, Solution, Evaluation).
Transition signals are useful in achieving good cohesion and coherence in your writing.
Reporting verbs are used to link your in-text citations to the information cited.
Report Purposes & Types
Reports are key communication tools in business; they often become part of an organization’s archives so that current and future employees can see the research, information, and reasoning underlying certain issues, actions, and decisions. Reports may be formal or informal, informative or analytical. They may be intended to provide updates, influence action, provide information, and/or offer different perspectives important in an organization’s discussion of an issue. At some point in your career, you most likely will need to write a report related to some aspect of your work.
The following video provides a good introduction to professional reports.
Report Purposes
Reports have two main purposes:
Informative Reports
An informative report explains or instructs and presents details of events, activities, individuals, or conditions. It provides background and explanation without analysis or evaluation. For example, a progress report is a standard informative report intended to explain the completion of a project at certain key points within that project’s timeline. You might review the project’s purpose, explain what phase the project is in at this particular point in time, identify project accomplishments to date, and/or discuss anticipated next steps within the project timeline. You would not evaluate, analyze, or recommend, but would simply present relevant information to inform stakeholders about how the project is progressing.

Analytical Reports
An analytical report often provides some of the same information as an informative report along with evaluation of that information. Analytical reports may solve problems, demonstrate relationships, or make recommendations. For example, in addition to informing, you may also have an analytical purpose in a progress report, especially if the project has not progressed as planned. You might analyze situations that derailed the project from the intended timeline, and/or recommend ways to catch up and get the project back onto the original timeline. Another example of an analytical report is a field report by a Center for Disease Control (CDC) employee from the site of an outbreak of the H1N1 virus, noting symptoms, disease progression, steps taken to arrest the spread of the disease, and recommendations on the quarantine of subjects.
The following video clearly introduces and illustrates the nature of an analytical report. Note that the report sections mentioned will vary depending on your own writing context and situational analysis.
Report Types
There are two main types of report:
Informal Reports
Employees in most organizations create and use informal reports, many of which are for internal use. Some institutions have prescribed formats for certain types of informal reports (e.g., expense reports, mileage reimbursement), but allow you, as a writer, the freedom to structure other types of informal reports, such as status updates, recommendation reports, conference reports, or others.
The main characteristic of an informal report is that it tends to be relatively short, with fewer sections than a formal report. Overall, informal reports typically include the following structure:
- Introduction or background – the “why” of the report
- Information and/or analysis – your facts, findings, data, analysis, explanatory details, and/or recommendations
- Summary – restatement of main ideas
Informal reports may be in memo, email, letter, video, powerpoint, or written report format. An informal report usually has specific topics grouped in paragraphs, and these topics tend to have simple headings. Note that while informal reports do not require headings, you may decide to use them, especially if the report is a page or two, since headings may help your reader better understand and retain your main ideas.
A QUICK COMPARISON: USING HEADINGS
Look at the two brief samples to compare how you read and react to the same information in an informal report without headings and with headings. Which one is easier for you to read, understand, and find information?
Formal Reports
Formal reports may be written because of many different situations, for example, to provide information and research on the psychological effects on employees as a result of moving from offices to cubicles, to analyze the results of moving from offices to cubicles in terms of employee productivity, or to make recommendations on the financial feasibility of moving employees from offices to cubicles. The hallmark of a formal report is its length; format reports delve into a subject much more deeply than informal reports. Formal reports synthesize main ideas related to your subject, drawing from your information, analysis, and/or research, to fulfill your purpose. Formal reports are not simply compilations of large quantities of data around a topic, with no purpose or reasoned presentation.
Like informal reports, formal reports also have an overall structure of introduction, information/analysis, and summary. But because they investigate a concept or issue deeply, formal reports usually have many sections within the body of the report, which definitely require headings and subheadings. Formal reports also contain standard front and back matter. You can read more fully about Report Sections in the next page of this text.
Formal reports are usually written documents, because of their quantity of information. However, formal written reports are often presented and/or accompanied by powerpoint presentations, explanatory videos, or other professional communications that condense and introduce concepts offered in the formal report.
The following video compares and reviews informal and formal reports.
Importance of Reports in Organizations

Report purposes and types may be combined in many different ways; reports on the same topic may be informative or analytical in different situations, just as they may be informal or formal in different situations.
For example, if a group of workers in a particular department is experimenting with working remotely a few days a week, you could potentially write:
- an informal, informative, compliance report to your supervisor letting her know that this is occurring and providing a short description of, and question about, company policy on telecommuting
- an informal, analytical, feasibility report to your supervisor evaluating evidence gathered through discussions with the department head and workers who are part of the experiment
- a formal, informative, research report citing evidence that worker flexibility in work location can boost productivity
- a formal, analytical, recommendation report to your supervisor building upon your research and proposing the need to implement this option in your department
- any number of additional types of reports, depending on your purpose and role
It’s up to you, as a communicator, to decide on the best approach for each particular report you need to create, based on your purpose and comprehensive analysis of the communication situation.
Examples of some common reports include the following:
- Status updates may be internal to a company in addressing a business situation, or external in providing the status of a project to another organization. Status reports are usually to-the-point, tightly focused, brief informational reports.
- Project reports are lengthier documents which may cover many different aspects of a project at various stages, for various stakeholders in the project. They may be informative or analytical, depending on your purpose and situation.
- Feasibility reports analyze a situation and propose a direction to take. They are often written to explore a new idea or process, or to evaluate a current situation and make recommendations, as a way to explore a change before making major investments of time or money. For example, a feasibility report may be a first step toward doing a full business plan, since it can be developed in much less time and still provides direction for decision makers.
- Business plans are often informative reports about what an individual or organization plans to do over an upcoming period of time. A business plan can be informative but may be more analytical if it’s intended for potential investors. In some cases, a business plan may include a request for funds; in those cases, the writing is more persuasive and may, in fact, turn into a formal proposal.
- Proposals analyze a problem or situation, research possible solutions, and propose a specific solution or action, as a result of the evidence presented. They often include action plans, timelines, costs, and other appropriate information. Proposals may be informal or formal, internal to a company or external to an outside audience, depending on the situation.
- Recommendation reports often result from a business problem that an individual or team has been asked to solve; these reports are usually analytical and internal to an organization. Reports that deal with needs assessment are one type of recommendation report.
- Research reports gather and explain data; these reports are usually informative.
- Compliance reports may be informative or analytical as they deal with how well a department, division, or the whole organization is addressing a set of standards.
- Financial reports may be informative or analytical as they deal with use of funds in certain contexts. Financial reports may be internal or external to the organization.
- Trip or conference reports summarize and transmit information learned, therefore increasing the value of the trip by disseminating information through the organization. They are usually informative.
- Meeting minutes are informative reports that summarize concepts and topics discussed at a meeting.
From the list above, which is by no means exhaustive, you can see the pervasiveness of reports in professional situations.
No matter what type of report you create, all reports need to contain accurate information, clear writing, logical organization of information, and professional layout. These characteristics affect the report’s reliability and validity, as well as your reader’s comprehension of your information. Use simple, clear language and organization. Make key report concepts easy to grasp for the widest audience. Remember that a report may be retained for a long time and may be viewed by many readers.
Guadalupe is the manager for meats and seafoods for a rapidly-expanding grocery chain, Valuetown. Valuetown’s expansion has happened mostly by buying up individually-owned stores or small chains in the region. One of the issues Guadalupe has faced is that the display and storage units in these stores are not in great shape, and often meats can’t be displayed. Valuetown is also spending a lot on repairs. Guadalupe has done an analysis of what the old refrigeration units are costing in terms of repairs and lost revenue. Her manager told her to write a report to present to the Valuetown board requesting new units. How should she proceed?
She should write a formal report with her conclusions at the front, a summary of her analysis in the middle, and back matter that includes the raw data on costs and lost revenue as well as estimated costs to replace the units. This report should be thoroughly edited and proofread so it is both stylistically perfect and in line with the needs of her audience.
Is this a good option? Check here.
She should write an informal report that briefly summarizes what she wants to do, gives highlights of her analysis, and then leaves most of the data in the back matter. Her goal should be to get this report out as quickly as possible, even if it has a few errors.
She should ask for time to give a presentation at the next board meeting and then take questions. She’s more persuasive in person than on paper.
- Report Purposes & Types, original information and information adapted from pages on Business, Informal, and Formal Reports from Business Communication Skills for Managers, and page 9.4 Report from Business Communication for Success; attributions below. Authored by : Susan Oaks. Project : Communications for Professionals. License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- Business Reports. Authored by : Susan Kendall. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wmopen-businesscommunicationmgrs/chapter/business-reports/ . Project : Business Communication Skills for Managers. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Informal Reports. Authored by : Susan Kendall. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wmopen-businesscommunicationmgrs/chapter/informal-reports/ . Project : Business Communication Skills for Managers. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Formal Reports. Authored by : Susan Kendall. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wmopen-businesscommunicationmgrs/chapter/formal-reports/ . Project : Business Communication Skills for Managers. License : CC BY: Attribution
- 9.4 Report. Provided by : University of Minnesota Libraries. Located at : https://open.lib.umn.edu/businesscommunication/chapter/9-4-report/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- image of professional reading a report on a tablet. Authored by : rawpixel. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/photos/paper-business-document-analysis-3249919/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- video How to write a business report. Provided by : USC: University of the Sunshine Coast. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V8uF1EoIneE . License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video
- video Formal Reports vs. Informal Reports. Provided by : Penn State Harrisburg . Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aqeeh353NR8 . Project : Penn State Harrisburg English 202 Online Videos. License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video
- image of businesswoman reading report on a tablet. Authored by : rawpixel. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/photos/pill-laptop-technology-business-3203069/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved

Privacy Policy
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Table of Contents

Research Report
Definition:
Research Report is a written document that presents the results of a research project or study, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions, in a clear and objective manner.
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the findings of the research to the intended audience, which could be other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public.
Components of Research Report
Components of Research Report are as follows:
Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the research report and provides a brief overview of the research question or problem being investigated. It should include a clear statement of the purpose of the study and its significance or relevance to the field of research. It may also provide background information or a literature review to help contextualize the research.
Literature Review
The literature review provides a critical analysis and synthesis of the existing research and scholarship relevant to the research question or problem. It should identify the gaps, inconsistencies, and contradictions in the literature and show how the current study addresses these issues. The literature review also establishes the theoretical framework or conceptual model that guides the research.
Methodology
The methodology section describes the research design, methods, and procedures used to collect and analyze data. It should include information on the sample or participants, data collection instruments, data collection procedures, and data analysis techniques. The methodology should be clear and detailed enough to allow other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the study in a clear and objective manner. It should provide a detailed description of the data and statistics used to answer the research question or test the hypothesis. Tables, graphs, and figures may be included to help visualize the data and illustrate the key findings.
The discussion section interprets the results of the study and explains their significance or relevance to the research question or problem. It should also compare the current findings with those of previous studies and identify the implications for future research or practice. The discussion should be based on the results presented in the previous section and should avoid speculation or unfounded conclusions.
The conclusion summarizes the key findings of the study and restates the main argument or thesis presented in the introduction. It should also provide a brief overview of the contributions of the study to the field of research and the implications for practice or policy.
The references section lists all the sources cited in the research report, following a specific citation style, such as APA or MLA.
The appendices section includes any additional material, such as data tables, figures, or instruments used in the study, that could not be included in the main text due to space limitations.
Types of Research Report
Types of Research Report are as follows:
Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master’s or Doctoral degree, although it can also be written by researchers or scholars in other fields.
Research Paper
Research paper is a type of research report. A research paper is a document that presents the results of a research study or investigation. Research papers can be written in a variety of fields, including science, social science, humanities, and business. They typically follow a standard format that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion sections.
Technical Report
A technical report is a detailed report that provides information about a specific technical or scientific problem or project. Technical reports are often used in engineering, science, and other technical fields to document research and development work.
Progress Report
A progress report provides an update on the progress of a research project or program over a specific period of time. Progress reports are typically used to communicate the status of a project to stakeholders, funders, or project managers.
Feasibility Report
A feasibility report assesses the feasibility of a proposed project or plan, providing an analysis of the potential risks, benefits, and costs associated with the project. Feasibility reports are often used in business, engineering, and other fields to determine the viability of a project before it is undertaken.
Field Report
A field report documents observations and findings from fieldwork, which is research conducted in the natural environment or setting. Field reports are often used in anthropology, ecology, and other social and natural sciences.
Experimental Report
An experimental report documents the results of a scientific experiment, including the hypothesis, methods, results, and conclusions. Experimental reports are often used in biology, chemistry, and other sciences to communicate the results of laboratory experiments.
Case Study Report
A case study report provides an in-depth analysis of a specific case or situation, often used in psychology, social work, and other fields to document and understand complex cases or phenomena.
Literature Review Report
A literature review report synthesizes and summarizes existing research on a specific topic, providing an overview of the current state of knowledge on the subject. Literature review reports are often used in social sciences, education, and other fields to identify gaps in the literature and guide future research.
Research Report Example
Following is a Research Report Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance among High School Students
This study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students. The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The findings indicate that there is a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students. The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers, as they highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities.
Introduction:
Social media has become an integral part of the lives of high school students. With the widespread use of social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Snapchat, students can connect with friends, share photos and videos, and engage in discussions on a range of topics. While social media offers many benefits, concerns have been raised about its impact on academic performance. Many studies have found a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance among high school students (Kirschner & Karpinski, 2010; Paul, Baker, & Cochran, 2012).
Given the growing importance of social media in the lives of high school students, it is important to investigate its impact on academic performance. This study aims to address this gap by examining the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students.
Methodology:
The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The questionnaire was developed based on previous studies and was designed to measure the frequency and duration of social media use, as well as academic performance.
The participants were selected using a convenience sampling technique, and the survey questionnaire was distributed in the classroom during regular school hours. The data collected were analyzed using descriptive statistics and correlation analysis.
The findings indicate that the majority of high school students use social media platforms on a daily basis, with Facebook being the most popular platform. The results also show a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students.
Discussion:
The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. The negative correlation between social media use and academic performance suggests that strategies should be put in place to help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. For example, educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, this study provides evidence of the negative impact of social media on academic performance among high school students. The findings highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. Further research is needed to explore the specific mechanisms by which social media use affects academic performance and to develop effective strategies for addressing this issue.
Limitations:
One limitation of this study is the use of convenience sampling, which limits the generalizability of the findings to other populations. Future studies should use random sampling techniques to increase the representativeness of the sample. Another limitation is the use of self-reported measures, which may be subject to social desirability bias. Future studies could use objective measures of social media use and academic performance, such as tracking software and school records.
Implications:
The findings of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. Educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. For example, teachers could use social media platforms to share relevant educational resources and facilitate online discussions. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. They could also engage in open communication with their children to understand their social media use and its impact on their academic performance. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students. For example, schools could implement social media policies that restrict access during class time and encourage responsible use.
References:
- Kirschner, P. A., & Karpinski, A. C. (2010). Facebook® and academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6), 1237-1245.
- Paul, J. A., Baker, H. M., & Cochran, J. D. (2012). Effect of online social networking on student academic performance. Journal of the Research Center for Educational Technology, 8(1), 1-19.
- Pantic, I. (2014). Online social networking and mental health. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 17(10), 652-657.
- Rosen, L. D., Carrier, L. M., & Cheever, N. A. (2013). Facebook and texting made me do it: Media-induced task-switching while studying. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(3), 948-958.
Note*: Above mention, Example is just a sample for the students’ guide. Do not directly copy and paste as your College or University assignment. Kindly do some research and Write your own.
Applications of Research Report
Research reports have many applications, including:
- Communicating research findings: The primary application of a research report is to communicate the results of a study to other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public. The report serves as a way to share new knowledge, insights, and discoveries with others in the field.
- Informing policy and practice : Research reports can inform policy and practice by providing evidence-based recommendations for decision-makers. For example, a research report on the effectiveness of a new drug could inform regulatory agencies in their decision-making process.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research in a particular area. Other researchers may use the findings and methodology of a report to develop new research questions or to build on existing research.
- Evaluating programs and interventions : Research reports can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and interventions in achieving their intended outcomes. For example, a research report on a new educational program could provide evidence of its impact on student performance.
- Demonstrating impact : Research reports can be used to demonstrate the impact of research funding or to evaluate the success of research projects. By presenting the findings and outcomes of a study, research reports can show the value of research to funders and stakeholders.
- Enhancing professional development : Research reports can be used to enhance professional development by providing a source of information and learning for researchers and practitioners in a particular field. For example, a research report on a new teaching methodology could provide insights and ideas for educators to incorporate into their own practice.
How to write Research Report
Here are some steps you can follow to write a research report:
- Identify the research question: The first step in writing a research report is to identify your research question. This will help you focus your research and organize your findings.
- Conduct research : Once you have identified your research question, you will need to conduct research to gather relevant data and information. This can involve conducting experiments, reviewing literature, or analyzing data.
- Organize your findings: Once you have gathered all of your data, you will need to organize your findings in a way that is clear and understandable. This can involve creating tables, graphs, or charts to illustrate your results.
- Write the report: Once you have organized your findings, you can begin writing the report. Start with an introduction that provides background information and explains the purpose of your research. Next, provide a detailed description of your research methods and findings. Finally, summarize your results and draw conclusions based on your findings.
- Proofread and edit: After you have written your report, be sure to proofread and edit it carefully. Check for grammar and spelling errors, and make sure that your report is well-organized and easy to read.
- Include a reference list: Be sure to include a list of references that you used in your research. This will give credit to your sources and allow readers to further explore the topic if they choose.
- Format your report: Finally, format your report according to the guidelines provided by your instructor or organization. This may include formatting requirements for headings, margins, fonts, and spacing.
Purpose of Research Report
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the results of a research study to a specific audience, such as peers in the same field, stakeholders, or the general public. The report provides a detailed description of the research methods, findings, and conclusions.
Some common purposes of a research report include:
- Sharing knowledge: A research report allows researchers to share their findings and knowledge with others in their field. This helps to advance the field and improve the understanding of a particular topic.
- Identifying trends: A research report can identify trends and patterns in data, which can help guide future research and inform decision-making.
- Addressing problems: A research report can provide insights into problems or issues and suggest solutions or recommendations for addressing them.
- Evaluating programs or interventions : A research report can evaluate the effectiveness of programs or interventions, which can inform decision-making about whether to continue, modify, or discontinue them.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies.
When to Write Research Report
A research report should be written after completing the research study. This includes collecting data, analyzing the results, and drawing conclusions based on the findings. Once the research is complete, the report should be written in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
In academic settings, research reports are often required as part of coursework or as part of a thesis or dissertation. In this case, the report should be written according to the guidelines provided by the instructor or institution.
In other settings, such as in industry or government, research reports may be required to inform decision-making or to comply with regulatory requirements. In these cases, the report should be written as soon as possible after the research is completed in order to inform decision-making in a timely manner.
Overall, the timing of when to write a research report depends on the purpose of the research, the expectations of the audience, and any regulatory requirements that need to be met. However, it is important to complete the report in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
Characteristics of Research Report
There are several characteristics of a research report that distinguish it from other types of writing. These characteristics include:
- Objective: A research report should be written in an objective and unbiased manner. It should present the facts and findings of the research study without any personal opinions or biases.
- Systematic: A research report should be written in a systematic manner. It should follow a clear and logical structure, and the information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand and follow.
- Detailed: A research report should be detailed and comprehensive. It should provide a thorough description of the research methods, results, and conclusions.
- Accurate : A research report should be accurate and based on sound research methods. The findings and conclusions should be supported by data and evidence.
- Organized: A research report should be well-organized. It should include headings and subheadings to help the reader navigate the report and understand the main points.
- Clear and concise: A research report should be written in clear and concise language. The information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand, and unnecessary jargon should be avoided.
- Citations and references: A research report should include citations and references to support the findings and conclusions. This helps to give credit to other researchers and to provide readers with the opportunity to further explore the topic.
Advantages of Research Report
Research reports have several advantages, including:
- Communicating research findings: Research reports allow researchers to communicate their findings to a wider audience, including other researchers, stakeholders, and the general public. This helps to disseminate knowledge and advance the understanding of a particular topic.
- Providing evidence for decision-making : Research reports can provide evidence to inform decision-making, such as in the case of policy-making, program planning, or product development. The findings and conclusions can help guide decisions and improve outcomes.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research on a particular topic. Other researchers can build on the findings and conclusions of the report, which can lead to further discoveries and advancements in the field.
- Demonstrating expertise: Research reports can demonstrate the expertise of the researchers and their ability to conduct rigorous and high-quality research. This can be important for securing funding, promotions, and other professional opportunities.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies. Producing a high-quality research report can help ensure compliance with these requirements.
Limitations of Research Report
Despite their advantages, research reports also have some limitations, including:
- Time-consuming: Conducting research and writing a report can be a time-consuming process, particularly for large-scale studies. This can limit the frequency and speed of producing research reports.
- Expensive: Conducting research and producing a report can be expensive, particularly for studies that require specialized equipment, personnel, or data. This can limit the scope and feasibility of some research studies.
- Limited generalizability: Research studies often focus on a specific population or context, which can limit the generalizability of the findings to other populations or contexts.
- Potential bias : Researchers may have biases or conflicts of interest that can influence the findings and conclusions of the research study. Additionally, participants may also have biases or may not be representative of the larger population, which can limit the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Accessibility: Research reports may be written in technical or academic language, which can limit their accessibility to a wider audience. Additionally, some research may be behind paywalls or require specialized access, which can limit the ability of others to read and use the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Why writing by hand beats typing for thinking and learning
Jonathan Lambert

If you're like many digitally savvy Americans, it has likely been a while since you've spent much time writing by hand.
The laborious process of tracing out our thoughts, letter by letter, on the page is becoming a relic of the past in our screen-dominated world, where text messages and thumb-typed grocery lists have replaced handwritten letters and sticky notes. Electronic keyboards offer obvious efficiency benefits that have undoubtedly boosted our productivity — imagine having to write all your emails longhand.
To keep up, many schools are introducing computers as early as preschool, meaning some kids may learn the basics of typing before writing by hand.
But giving up this slower, more tactile way of expressing ourselves may come at a significant cost, according to a growing body of research that's uncovering the surprising cognitive benefits of taking pen to paper, or even stylus to iPad — for both children and adults.
Is this some kind of joke? A school facing shortages starts teaching standup comedy
In kids, studies show that tracing out ABCs, as opposed to typing them, leads to better and longer-lasting recognition and understanding of letters. Writing by hand also improves memory and recall of words, laying down the foundations of literacy and learning. In adults, taking notes by hand during a lecture, instead of typing, can lead to better conceptual understanding of material.
"There's actually some very important things going on during the embodied experience of writing by hand," says Ramesh Balasubramaniam , a neuroscientist at the University of California, Merced. "It has important cognitive benefits."
While those benefits have long been recognized by some (for instance, many authors, including Jennifer Egan and Neil Gaiman , draft their stories by hand to stoke creativity), scientists have only recently started investigating why writing by hand has these effects.
A slew of recent brain imaging research suggests handwriting's power stems from the relative complexity of the process and how it forces different brain systems to work together to reproduce the shapes of letters in our heads onto the page.
Your brain on handwriting
Both handwriting and typing involve moving our hands and fingers to create words on a page. But handwriting, it turns out, requires a lot more fine-tuned coordination between the motor and visual systems. This seems to more deeply engage the brain in ways that support learning.

Shots - Health News
Feeling artsy here's how making art helps your brain.
"Handwriting is probably among the most complex motor skills that the brain is capable of," says Marieke Longcamp , a cognitive neuroscientist at Aix-Marseille Université.
Gripping a pen nimbly enough to write is a complicated task, as it requires your brain to continuously monitor the pressure that each finger exerts on the pen. Then, your motor system has to delicately modify that pressure to re-create each letter of the words in your head on the page.
"Your fingers have to each do something different to produce a recognizable letter," says Sophia Vinci-Booher , an educational neuroscientist at Vanderbilt University. Adding to the complexity, your visual system must continuously process that letter as it's formed. With each stroke, your brain compares the unfolding script with mental models of the letters and words, making adjustments to fingers in real time to create the letters' shapes, says Vinci-Booher.
That's not true for typing.
To type "tap" your fingers don't have to trace out the form of the letters — they just make three relatively simple and uniform movements. In comparison, it takes a lot more brainpower, as well as cross-talk between brain areas, to write than type.
Recent brain imaging studies bolster this idea. A study published in January found that when students write by hand, brain areas involved in motor and visual information processing " sync up " with areas crucial to memory formation, firing at frequencies associated with learning.
"We don't see that [synchronized activity] in typewriting at all," says Audrey van der Meer , a psychologist and study co-author at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. She suggests that writing by hand is a neurobiologically richer process and that this richness may confer some cognitive benefits.
Other experts agree. "There seems to be something fundamental about engaging your body to produce these shapes," says Robert Wiley , a cognitive psychologist at the University of North Carolina, Greensboro. "It lets you make associations between your body and what you're seeing and hearing," he says, which might give the mind more footholds for accessing a given concept or idea.
Those extra footholds are especially important for learning in kids, but they may give adults a leg up too. Wiley and others worry that ditching handwriting for typing could have serious consequences for how we all learn and think.
What might be lost as handwriting wanes
The clearest consequence of screens and keyboards replacing pen and paper might be on kids' ability to learn the building blocks of literacy — letters.
"Letter recognition in early childhood is actually one of the best predictors of later reading and math attainment," says Vinci-Booher. Her work suggests the process of learning to write letters by hand is crucial for learning to read them.
"When kids write letters, they're just messy," she says. As kids practice writing "A," each iteration is different, and that variability helps solidify their conceptual understanding of the letter.
Research suggests kids learn to recognize letters better when seeing variable handwritten examples, compared with uniform typed examples.
This helps develop areas of the brain used during reading in older children and adults, Vinci-Booher found.
"This could be one of the ways that early experiences actually translate to long-term life outcomes," she says. "These visually demanding, fine motor actions bake in neural communication patterns that are really important for learning later on."
Ditching handwriting instruction could mean that those skills don't get developed as well, which could impair kids' ability to learn down the road.
"If young children are not receiving any handwriting training, which is very good brain stimulation, then their brains simply won't reach their full potential," says van der Meer. "It's scary to think of the potential consequences."
Many states are trying to avoid these risks by mandating cursive instruction. This year, California started requiring elementary school students to learn cursive , and similar bills are moving through state legislatures in several states, including Indiana, Kentucky, South Carolina and Wisconsin. (So far, evidence suggests that it's the writing by hand that matters, not whether it's print or cursive.)
Slowing down and processing information
For adults, one of the main benefits of writing by hand is that it simply forces us to slow down.
During a meeting or lecture, it's possible to type what you're hearing verbatim. But often, "you're not actually processing that information — you're just typing in the blind," says van der Meer. "If you take notes by hand, you can't write everything down," she says.
The relative slowness of the medium forces you to process the information, writing key words or phrases and using drawing or arrows to work through ideas, she says. "You make the information your own," she says, which helps it stick in the brain.
Such connections and integration are still possible when typing, but they need to be made more intentionally. And sometimes, efficiency wins out. "When you're writing a long essay, it's obviously much more practical to use a keyboard," says van der Meer.
Still, given our long history of using our hands to mark meaning in the world, some scientists worry about the more diffuse consequences of offloading our thinking to computers.
"We're foisting a lot of our knowledge, extending our cognition, to other devices, so it's only natural that we've started using these other agents to do our writing for us," says Balasubramaniam.
It's possible that this might free up our minds to do other kinds of hard thinking, he says. Or we might be sacrificing a fundamental process that's crucial for the kinds of immersive cognitive experiences that enable us to learn and think at our full potential.
Balasubramaniam stresses, however, that we don't have to ditch digital tools to harness the power of handwriting. So far, research suggests that scribbling with a stylus on a screen activates the same brain pathways as etching ink on paper. It's the movement that counts, he says, not its final form.
Jonathan Lambert is a Washington, D.C.-based freelance journalist who covers science, health and policy.
- handwriting

China Builds World’s First Dedicated Drone Carrier
China has built the world's first dedicated drone carrier. the ship has not been reported however and many of the circumstances surrounding it remain a mystery..
H I Sutton 15 May 2024
Hidden away in a shipyard on the Yangtze, far upriver from the major yards at Shanghai, is a new aircraft carrier. It’s China’s fourth, a ship whose mere existence has not been reported before. Only China can build an aircraft carrier in relative secrecy.
This ship, launched in December 2022 but not reported until now, is surrounded by mystery. Naval News, together with J. Michael Dahm, Senior Resident Fellow at the Mitchell Institute , have been analyzing it.
Mysterious Drone Carrier
The world knows about China’s first three carriers; the largest and most capable, the Type-003 Fujian, is currently undergoing sea trials . This new carrier is very different. Its claim to fame will not be that it is larger. Instead, we are confident that this ship is the world’s first dedicated fixed-wing drone carrier.
The design is smaller than the regular aircraft carriers, with a flight deck approximately one third the length and half the width of a U.S. Navy or Chinese Navy (PLAN) super carrier. For comparison, it is slightly shorter but wider than a World War Two escort carriers. It would be possible to operate fixed wing aircraft from it, but its straight deck arrangement would be anachronistic, not allowing aircraft to take off and land at the same time. Additionally there doesn’t appear to be space for a typical aircraft hangar, so the number of aircraft would be greatly limited. It does make sense as a drone carrier however.
Drones are an increasing part of naval warfare. Leading navies are already trialing them from regular aircraft carriers. And some navies, notably Iran and Turkey, are working on plans for ‘drone carriers’. But this space is still in its infancy.
Analysis of the ship
It is immediately apparent that it is, in general arrangement, an aircraft carrier of some sort. It has a marked runaway running along the port (left side) with an island superstructure on the starboard (right) side.
Beyond this, it is unusual in every respect. The hull is a widely spaced catamaran. While catamarans are often featured in aircraft carrier concepts because they allow a large deck area, no one has actually built one before. Additionally, analysis of satellite imagery shows that the flight deck is very low. It appears unlikely there is a hangar deck below the flight deck. If there is, its ceiling is very low. Therefore, it does not appear designed to support high tempo or prolonged flight operations.
The flight deck is wide enough to comfortably operate aircraft or drones with a wingspan of around 20 meters (65 feet) such as Chinese equivalents of the Predator drone.
However, the mere existence of a flight deck suggests that aircraft intend to land on it. A catapult or launch rail of some form would be sufficient for launch if recovery wasn’t necessary.
Potential roles for this ship
J. Michael Dahm notes that the shipyard where it is being built, Jiangsu Dayang Marine, has previously built simulated enemy ships for the PLAN. China has an extensive program of simulating Western and Western-leaning navies’ ships in its weapon testing program. Its anti-ship ballistic missiles are tested on full-size outlines of U.S. Navy aircraft carriers .
Several high-tech target barges and two large dr one motherships have already been built at this shipyard. All these perform as opposing forces in training, a role known as ‘Electronic Blue Force’. So it is possible that this ship too is designed to support that mission.
Whether it is intended for Blue Force simulation or purely research and development remains to be seen. Similarly, we question whether it is an official PLAN program or a speculative commercial project. The new drone carrier remains something of a mystery. Watch this space.
Related Articles

Chinese Experimental Corvette Starts Sea Trials

France Orders First Long Lead Items for PANG Aircraft Carrier Program

Chinese Aircraft Carrier Fujian Prepares For First Sea Trial (Updated)
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Documentary filmmaker Morgan Spurlock, who skewered fast food industry, dies at 53
From AP’s archives: “Super Size Me” filmmaker Morgan Spurlock talks about the dangers of eating fast food. The Oscar-nominee who famously ate only at McDonald’s for a month to illustrate the dangers of a fast-food diet, has died. He was 53.
FILE - Filmmaker Morgan Spurlock participate in the BUILD Speaker Series to discuss the film, “Go North”, at AOL Studios on Wednesday, Jan. 4, 2017, in New York. Spurlock, an Oscar-nominee who made food and American diets his life’s work, famously eating only at McDonald’s for a month to illustrate the dangers of a fast-food diet, has died. He was 53. (Photo by Evan Agostini/Invision/AP, File)
- Copy Link copied
FILE - Morgan Spurlock poses at the Los Angeles premiere of his film “Super Size Me,” Thursday night, April 22, 2004, in the Hollywood section of Los Angeles. Spurlock, an Oscar-nominee who made food and American diets his life’s work, famously eating only at McDonald’s for a month to illustrate the dangers of a fast-food diet, has died. He was 53. (AP Photo/Mark J. Terrill)
FILE - Filmmaker Morgan Spurlock arrives at the premiere of “Pom Wonderful Presents: The Greatest Movie Ever Sold” in Los Angeles on Wednesday, April 20, 2011. Spurlock, an Oscar-nominee who made food and American diets his life’s work, famously eating only at McDonald’s for a month to illustrate the dangers of a fast-food diet, has died. He was 53. (AP Photo/Matt Sayles, File)
FILE - Director Morgan Spurlock from the film “Focus Forward” poses for a portrait during the 2013 Sundance Film Festival at the Fender Music Lodge on Jan. 21, 2013 in Park City, Utah. Spurlock, an Oscar-nominee who made food and American diets his life’s work, famously eating only at McDonald’s for a month to illustrate the dangers of a fast-food diet, has died. He was 53. (Photo by Victoria Will/Invision/AP, File)
FILE - Morgan Spurlock of the CNN series “Inside Man” poses at the CNN Worldwide All-Star Party, on Friday, Jan. 10, 2014, in Pasadena, Calif. Spurlock, an Oscar-nominee who made food and American diets his life’s work, famously eating only at McDonald’s for a month to illustrate the dangers of a fast-food diet, has died. He was 53. (Photo by Chris Pizzello/Invision/AP, File)

NEW YORK (AP) — Documentary filmmaker Morgan Spurlock, an Oscar nominee whose most famous works skewered America’s food industry and who notably ate only at McDonald’s for a month to illustrate the dangers of a fast-food diet, has died. He was 53.
Spurlock died Thursday in New York from complications of cancer, according to a statement issued Friday by his family.
“It was a sad day, as we said goodbye to my brother Morgan,” Craig Spurlock, who worked with him on several projects, said in the statement. “Morgan gave so much through his art, ideas, and generosity. The world has lost a true creative genius and a special man. I am so proud to have worked together with him.”
Spurlock made a splash in 2004 with his groundbreaking film “Super Size Me,” which was nominated for an Academy Award. The film chronicled the detrimental physical and psychological effects of Spurlock eating only McDonald’s food for 30 days. He gained about 25 pounds, saw a spike in his cholesterol and lost his sex drive.
“Everything’s bigger in America,” he said in the film. “We’ve got the biggest cars, the biggest houses, the biggest companies, the biggest food, and finally: the biggest people.”
In one scene, Spurlock showed kids a photo of George Washington and none recognized the Founding Father. But they all instantly knew the mascots for Wendy’s and McDonald’s.
The film grossed more than $22 million on a $65,000 budget and preceded the release of Eric Schlosser’s influential “Fast Food Nation,” which accused the industry of being bad for the environment and rife with labor issues.
Spurlock returned in 2017 with “Super Size Me 2: Holy Chicken!” — a sober look at an industry that processes 9 billion animals a year in America. He focused on two issues: chicken farmers stuck in a peculiar financial system and the attempt by fast-food chains to deceive customers into thinking they’re eating healthier.
“We’re at an amazing moment in history from a consumer standpoint where consumers are starting to have more and more power,” he told The Associated Press in 2019. “It’s not about return for the shareholders. It’s about return for the consumers.”
Spurlock was a gonzo-like filmmaker who leaned into the bizarre and ridiculous. His stylistic touches included zippy graphics and amusing music, blending a Michael Moore-ish camera-in-your-face style with his own sense of humor and pathos.
“I wanted to be able to lean into the serious moments. I wanted to be able to breathe in the moments of levity. We want to give you permission to laugh in the places where it’s really hard to laugh,” he told the AP.
After he exposed the fast-food and chicken industries, there was an explosion in restaurants stressing freshness, artisanal methods, farm-to-table goodness and ethically sourced ingredients. But nutritionally not much had changed.
“There has been this massive shift and people say to me, ‘So has the food gotten healthier?’ And I say, ‘Well, the marketing sure has,’” he said.
Not all his work dealt with food. Spurlock made documentaries about the boy band One Direction and the geeks and fanboys at Comic-Con. One of his films looked at life behind bars at the Henrico County Jail in Virginia.
With 2008’s “Where in the World is Osama bin Laden?” Spurlock went on a global search to find the al-Qaida leader, who was killed in 2011. In “POM Wonderful Presents: The Greatest Movie Ever Sold,” Spurlock tackled questions of product placement, marketing and advertising.
“Being aware is half the battle, I think. Literally knowing all the time when you’re being marketed to is a great thing,” Spurlock told AP at the time. “A lot of people don’t realize it. They can’t see the forest for the trees.”
“Super Size Me 2: Holy Chicken!” was to premiere at the Sundance Film Festival in 2017 but it was shelved at the height of the #MeToo movement when Spurlock came forward to detail his own history of sexual misconduct.
He confessed that he had been accused of rape while in college and had settled a sexual harassment case with a female assistant. He also admitted to cheating on numerous partners. “I am part of the problem,” he wrote.
“For me, there was a moment of kind of realization — as somebody who is a truth-teller and somebody who has made it a point of trying to do what’s right — of recognizing that I could do better in my own life. We should be able to admit we were wrong,” he told the AP.
Spurlock grew up in Beckley, West Virginia. His mother was an English teacher who he remembered would correct his work with a red pen. He graduated with a BFA in film from New York University in 1993.
He is survived by two sons — Laken and Kallen; his mother Phyllis Spurlock; father Ben; brothers Craig and Barry; and former spouses Alexandra Jamieson and Sara Bernstein, the mothers of his children.
Mark Kennedy is at http://twitter.com/KennedyTwits


COMMENTS
What is Report Writing? Report writing is a formal style of presenting objective facts and information. There can be various types of reports, such as academic reports, science reports, business reports, technical reports, and news reports. A report can be verbal or written.
Ans: The act of presenting information in an orderly and structured format is known as report writing. Reports come in different types, such as analytical reports, research reports, financial reports, progress reports, incident reports, feasibility reports, and recommendation reports.
Report Writing is the process of presenting information in a structured and organised way. It serves as a means of communicating facts, findings, or recommendations to a specific audience, typically in a written format. This type of writing is used in various fields, including academics, business, science, and government, to convey important ...
Types of Report Writing . The following are the different Types of Report Writing: 1) Formal Report . Formal Reports are typically characterised by their objective and detailed nature, devoid of personal anecdotes or references. They demand a meticulous structuring approach tailored to the specific style and intended purpose of the organisation.
Focus on the data rather than the structure of the report. Share critical information internally. Share information to change operational decisions quickly. Annual budget reports, monthly financial reports, scientific research and employee appraisals are some of the examples of informal reports.
10. Vertical & Lateral Reports. Next, in our rundown of types of reports, we have vertical and lateral reports. This reporting type refers to the direction in which a report travels. A vertical report is meant to go upward or downward the hierarchy, for example, a management report.
2. Follow the Right Report Writing Format: Adhere to a structured format, including a clear title, table of contents, summary, introduction, body, conclusion, recommendations, and appendices. This ensures clarity and coherence. Follow the format suggestions in this article to start off on the right foot. 3.
Essentially, a report is a short, sharp, concise document which is written for a particular purpose and audience. It generally sets outs and analyses a situation or problem, often making recommendations for future action. It is a factual paper, and needs to be clear and well-structured. Requirements for the precise form and content of a report ...
There are three main forms of reports: factual, instructional and persuasive; each has a different purpose and will require different arguments and evidence to achieve that purpose. It will help you write good reports if you know what you are trying to achieve before you start your report. Factual. Instructional. Persuasive.
Description. Progress report. Monitor and control production, sales, shipping, service, or related business process. Recommendation report. Make recommendations to management and provide tools to solve problems or make decisions. Summary report. Present summaries of the information available on a given subject.
Report Writing Format for Class 10th to 12th. The report writing structure for students in grades 10 and 12 is as follows. Heading : A title that expresses the contents of the report in a descriptive manner. Byline: The name of the person who is responsible for drafting the report. It's usually included in the query.
Report writing is common in a number of disciplines. A report is a specific form of writing, written concisely and clearly and typically organised around identifying and examining issues, events, or findings from a research investigation.Reports often involve investigating and analysing a problem and coming up with a solution. This means that you need to take a position or provide a solution ...
A report is a type of writing that represents information, data, and research findings on a specific topic. The writer is expected to deliver a well-structured, credible, and informative text that dives into the small details of a certain topic, discussing its benefits and challenges.
12. Survey report. Survey reports are documents that help a business highlight the findings from a survey. It does its best to summarize the responses of a survey and objectively present the information while using visuals like tables, graphs, charts, and infographics to make reports easy to read.
Report Writing Types in English: Basically, Report writing in English is of three types. Example: General Report Writing: These reports give an account of a person's experience of an event or an incident. Newspaper Report Writing: Newspaper reports are based on true incidents or accidents meant to express some information to the public.
There are different types of reports, for example, feasibility studies, informational reports, or analytical reports. 3. Case studies are a type of report that exemplify a particular point. A case study may relate to a person, organisation, phenomenon, or a specific event. 1. Analyse the assignment task 2. Establish the purpose and scope of the ...
Report writing. There are many forms of writing which you may have to undertake at university, from reflective journals to extended researched assignments. The two most common forms of writing are reports and essays. This page describes what a report is, outlines the main types of report you may need to write, and summarises the differences ...
Here are the various types of reports that are generally used: Long and short reports: As the names suggest, these reports are characterized based on their lengths. A two-page report or memorandum is a short report, while a 30-page report is certainly long. The longer reports are among the types of report writing that have a formal style.
Report Purposes & Types. Reports are key communication tools in business; they often become part of an organization's archives so that current and future employees can see the research, information, and reasoning underlying certain issues, actions, and decisions. Reports may be formal or informal, informative or analytical.
Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master's or Doctoral degree, although it can also ...
Abstract and Figures. Writing reports is often seen as a time consuming and pointless exercise. However, by sharing information, reports can help develop common purposes and aims, spread ...
•The informal report functions to inform, analyze, and recommend. •It usually takes the form of a memo, letter or a very short international document like a monthly financial report, monthly activities report, research and development report, etc. •This report differs from the formal report in length and formality.
A capstone project is a comprehensive, culminating academic endeavor undertaken by students typically in their final year of study. It synthesizes their learning experiences, requiring students to apply the knowledge, skills, and competencies gained throughout their academic journey. A capstone project aims to address a real-world problem or ...
The six major types of project proposals include: solicited, unsolicited, informal, renewal, continuation and supplemental project proposal. Six steps to writing a project proposal: write the executive summary, explain the project background, present a solution, and define the project deliverables and resources needed.
Writing by hand also improves memory and recall of words, laying down the foundations of literacy and learning. In adults, taking notes by hand during a lecture, instead of typing, can lead to ...
The findings were the same for per-word rates. Of the freelancers who charged between $0.01 and $0.10 per word, 32% were beginner writers, while only 0.8% were experts. And of the writers who charged more than a dollar per word, 54% were experts, while only 5% were beginners. More on pay rates and quality.
Marriage fraud is a serious crime that occurs when two people enter into a marriage for the purpose of helping one of them obtain status as a U.S. citizen. This type of fraud is common, since ...
China has built the world's first dedicated drone carrier. The ship has not been reported however and many of the circumstances surrounding it remain a mystery. Hidden away in a shipyard on the Yangtze, far upriver from the major yards at Shanghai, is a new aircraft carrier. It's China's fourth, a ship whose mere existence has not been ...
Our team uses an eligibility criteria on when the checkmark is given to ensure we maintain the integrity of the platform. Your account must meet the following criteria to receive or retain the blue checkmark: Complete: Your account must have a display name and profile photo. Active use: Your account must be active in the past 30 days to ...
He was 53. Spurlock died Thursday in New York from complications of cancer, according to a statement issued Friday by his family. "It was a sad day, as we said goodbye to my brother Morgan," Craig Spurlock, who worked with him on several projects, said in the statement.