- Utility Menu

fa3d988da6f218669ec27d6b6019a0cd
A publication of the harvard college writing program.
Harvard Guide to Using Sources
- The Honor Code
- Bibliography
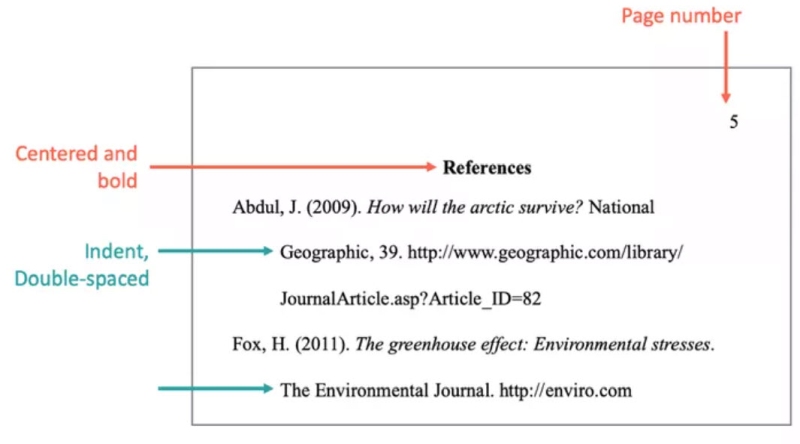
If you are using Chicago style footnotes or endnotes, you should include a bibliography at the end of your paper that provides complete citation information for all of the sources you cite in your paper. Bibliography entries are formatted differently from notes. For bibliography entries, you list the sources alphabetically by last name, so you will list the last name of the author or creator first in each entry. You should single-space within a bibliography entry and double-space between them. When an entry goes longer than one line, use a hanging indent of .5 inches for subsequent lines. Here’s a link to a sample bibliography that shows layout and spacing . You can find a sample of note format here .
Complete note vs. shortened note
Here’s an example of a complete note and a shortened version of a note for a book:
1. Karen Ho, Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street (Durham: Duke University Press, 2009), 27-35.
1. Karen Ho, Liquidated , 27-35.
Note vs. Bibliography entry
The bibliography entry that corresponds with each note is very similar to the longer version of the note, except that the author’s last and first name are reversed in the bibliography entry. To see differences between note and bibliography entries for different types of sources, check this section of the Chicago Manual of Style .
For Liquidated , the bibliography entry would look like this:
Ho, Karen, Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street . Durham: Duke University Press, 2009.
Citing a source with two or three authors
If you are citing a source with two or three authors, list their names in your note in the order they appear in the original source. In the bibliography, invert only the name of the first author and use “and” before the last named author.
1. Melissa Borja and Jacob Gibson, “Internationalism with Evangelical Characteristics: The Case of Evangelical Responses to Southeast Asian Refugees,” The Review of Faith & International Affairs 17, no. 3 (2019): 80-81, https://doi.org/10.1080/15570274.2019.1643983 .
Shortened note:
1. Borja and Gibson, “Internationalism with Evangelical Characteristics,” 80-81.
Bibliography:
Borja, Melissa, and Jacob Gibson. “Internationalism with Evangelical Characteristics: The Case of Evangelical Responses to Southeast Asian Refugees.” The Review of Faith & International Affairs 17. no. 3 (2019): 80–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/15570274.2019.1643983 .
Citing a source with more than three authors
If you are citing a source with more than three authors, include all of them in the bibliography, but only include the first one in the note, followed by et al. ( et al. is the shortened form of the Latin et alia , which means “and others”).
1. Justine M. Nagurney, et al., “Risk Factors for Disability After Emergency Department Discharge in Older Adults,” Academic Emergency Medicine 27, no. 12 (2020): 1271.
Short version of note:
1. Justine M. Nagurney, et al., “Risk Factors for Disability,” 1271.
Nagurney, Justine M., Ling Han, Linda Leo‐Summers, Heather G. Allore, Thomas M. Gill, and Ula Hwang. “Risk Factors for Disability After Emergency Department Discharge in Older Adults.” Academic Emergency Medicine 27, no. 12 (2020): 1270–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/acem.14088 .
Citing a book consulted online
If you are citing a book you consulted online, you should include a URL, DOI, or the name of the database where you found the book.
1. Karen Ho, Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street (Durham: Duke University Press, 2009), 27-35, https://doi-org.ezp-prod1.hul.harvard.edu/10.1215/9780822391371 .
Bibliography entry:
Ho, Karen. Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street . Durham: Duke University Press, 2009. https://doi-org.ezp-prod1.hul.harvard.edu/10.1215/9780822391371 .
Citing an e-book consulted outside of a database
If you are citing an e-book that you accessed outside of a database, you should indicate the format. If you read the book in a format without fixed page numbers (like Kindle, for example), you should not include the page numbers that you saw as you read. Instead, include chapter or section numbers, if possible.
1. Karen Ho, Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street (Durham: Duke University Press, 2009), chap. 2, Kindle.
Ho, Karen. Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street . Durham: Duke University Press, 2009. Kindle.
- Citation Management Tools
- In-Text Citations
- Examples of Commonly Cited Sources
- Frequently Asked Questions about Citing Sources in Chicago Format
- Sample Bibliography
PDFs for This Section
- Citing Sources
- Online Library and Citation Tools
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Bibliography
Last Updated: March 12, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Diane Stubbs . Diane Stubbs is a Secondary English Teacher with over 22 years of experience teaching all high school grade levels and AP courses. She specializes in secondary education, classroom management, and educational technology. Diane earned a Bachelor of Arts in English from the University of Delaware and a Master of Education from Wesley College. There are 14 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 660,646 times.
When you write a paper or a book, it's important to include a bibliography. A bibliography tells your reader what sources you've used. It lists all the books, articles, and other references you cited in or used to inform your work. Bibliographies are typically formatted according to one of three styles: American Psychological Association (APA) for scientific papers, Modern Language Association (MLA) for humanities papers, and Chicago Manual of Style (CMS) for the social sciences. Make sure you always check with your superior - whether a professor or boss - about which style they prefer.
Sample Bibliographies

Writing an APA Bibliography

- For example, if the author's name for a source is "John Adams Smith," you would list him as "Smith, J.A.," before listing the title of his piece.

- For example, if one source has twelve authors, and the seventh author is "Smith, J.A." and the twelfth is "Timothy, S.J.," you would list the first six authors, then write "Smith, J.A. ...Timothy, S.J."

- For example, if you have a World Health Organization Report without an author as one of your sources, you would write, "World Health Organization, "Report on Development Strategies in Developing Nations," July 1996."

- For example, an article citation might look like this: Jensen, O. E. (2012). "African Elephants." Savannah Quarterly , 2(1), 88.
- If the periodical the article comes from always begins with page number 1 (these types of periodicals are called “paginated by issue” periodicals, you should include the full page range of the article.
- If the article was retrieved online, end the citation with the words "Retrieved from" followed by the web address.

- Example: Worden, B. L. (1999). Echoing Eden. New York, New York: One Two Press.
- If the title is more than one word long and doesn’t contain any proper nouns, only the first word should be capitalized. Only the first letter of any subtitle should be capitalized as well.
![bibliography proper way Step 9 [8]...](https://www.wikihow.com/images/thumb/6/65/Write-a-Bibliography-Step-9-Version-3.jpg/v4-460px-Write-a-Bibliography-Step-9-Version-3.jpg)
- For example, a cited website might look like this: Quarry, R. R. (May 23, 2010). Wild Skies. Retrieved from https://wildskies.com.
- If no author is available, just start with the title. If no date is available, write "n.d."

Writing a MLA Bibliography

- You shouldn’t use an author’s title or degrees when listing their names in your bibliography. This is true even if they are listed that way on the source.

- For example, a book citation might look like this: Butler, Olivia. Parable of the Flower. Sacramento: Seed Press, 1996.

- For example, an article published in a scholarly journal might look like this: Green, Marsha. "Life in Costa Rica." Science Magazine vol. 1, no. 4, Mar 2013: 1-2.
- If you’re citing an article in a newspaper, you only need the name of the newspaper, followed by the date it was published, and the page number. A citation for that might look like this: Smith, Jennifer. “Tiny Tim Wins Award.” New York Times, 24 Dec 2017, p. A7.

- For example, a website citation might look like this: Jong, June. "How to Write an Essay." Writing Portal. 2 Aug. 2012. University of California. 23 Feb. 2013. <https://writingportal.com>
- Some websites, particularly academic ones, will have what’s called a DOI (digital object identifier). Write “doi:” in front of this number in place of the website’s url if a DOI is available.

Writing a CMS Bibliography

- Example: Skylar Marsh. "Walking on Water." Earth Magazine 4(2001): 23.

- For example, a book entry might look like this: Walter White. Space and Time . New York: London Press, 1982

- Example: University of California. "History of University of California." Last modified April 3, 2013. https://universityofcalifornia.com.
- Unless there is a publication date for the website you’re citing, you don’t need to include an access date. If you do have an access date, it goes at the end of the citation.
Expert Q&A

- Ask your teacher or professor which style they prefer you to use in your paper. Thanks Helpful 6 Not Helpful 2
- Be sure to include each and every source you reference in your work. Thanks Helpful 7 Not Helpful 5
- When writing a bibliography or a reference page, it really comes down to looking at an example and applying it to your own information. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libguides.reading.ac.uk/citing-references/compilingbibliography
- ↑ https://morningside.libguides.com/APA7/references
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/03/
- ↑ Cite articles
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/08/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/560/10/
- ↑ https://www.scribbr.com/mla/works-cited/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/747/05/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_page_basic_format.html
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/747/06/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/747/07/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/717/02/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/717/03/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/717/05/
About This Article

To create an APA bibliography, title a separate page at the end of your paper "References." Then, use the authors' last names to organize your list alphabetically, for example by writing the author John Adam Smith as "Smith, J. A." If a source has more than 7 authors, list the first 7 before adding an ellipses. To cite an article, include the author's name, year of publication, article title, publication title, and page numbers. When citing a book, begin with the author's name, then the date of publication, title in Italics, location of the publisher, and publisher's name. For tips on how to write an MLA or CMS bibliography, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Dec 9, 2023
Did this article help you?

Mar 11, 2023
Mar 12, 2020
Braden White
Oct 21, 2020
Oct 12, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Free printable Mother's Day questionnaire 💐!
How To Write a Bibliography (Three Styles, Plus Examples)
Give credit where credit is due.

Writing a research paper involves a lot of work. Students need to consult a variety of sources to gather reliable information and ensure their points are well supported. Research papers include a bibliography, which can be a little tricky for students. Learn how to write a bibliography in multiple styles and find basic examples below.
IMPORTANT: Each style guide has its own very specific rules, and they often conflict with one another. Additionally, each type of reference material has many possible formats, depending on a variety of factors. The overviews shown here are meant to guide students in writing basic bibliographies, but this information is by no means complete. Students should always refer directly to the preferred style guide to ensure they’re using the most up-to-date formats and styles.
What is a bibliography?
When you’re researching a paper, you’ll likely consult a wide variety of sources. You may quote some of these directly in your work, summarize some of the points they make, or simply use them to further the knowledge you need to write your paper. Since these ideas are not your own, it’s vital to give credit to the authors who originally wrote them. This list of sources, organized alphabetically, is called a bibliography.
A bibliography should include all the materials you consulted in your research, even if you don’t quote directly from them in your paper. These resources could include (but aren’t limited to):
- Books and e-books
- Periodicals like magazines or newspapers
- Online articles or websites
- Primary source documents like letters or official records
Bibliography vs. References
These two terms are sometimes used interchangeably, but they actually have different meanings. As noted above, a bibliography includes all the materials you used while researching your paper, whether or not you quote from them or refer to them directly in your writing.
A list of references only includes the materials you cite throughout your work. You might use direct quotes or summarize the information for the reader. Either way, you must ensure you give credit to the original author or document. This section can be titled “List of Works Cited” or simply “References.”
Your teacher may specify whether you should include a bibliography or a reference list. If they don’t, consider choosing a bibliography, to show all the works you used in researching your paper. This can help the reader see that your points are well supported, and allow them to do further reading on their own if they’re interested.
Bibliography vs. Citations
Citations refer to direct quotations from a text, woven into your own writing. There are a variety of ways to write citations, including footnotes and endnotes. These are generally shorter than the entries in a reference list or bibliography. Learn more about writing citations here.
What does a bibliography entry include?
Depending on the reference material, bibliography entries include a variety of information intended to help a reader locate the material if they want to refer to it themselves. These entries are listed in alphabetical order, and may include:
- Author/s or creator/s
- Publication date
- Volume and issue numbers
- Publisher and publication city
- Website URL
These entries don’t generally need to include specific page numbers or locations within the work (except for print magazine or journal articles). That type of information is usually only needed in a footnote or endnote citation.
What are the different bibliography styles?
In most cases, writers use one of three major style guides: APA (American Psychological Association), MLA (Modern Language Association), or The Chicago Manual of Style . There are many others as well, but these three are the most common choices for K–12 students.
Many teachers will state their preference for one style guide over another. If they don’t, you can choose your own preferred style. However, you should also use that guide for your entire paper, following their recommendations for punctuation, grammar, and more. This will ensure you are consistent throughout.
Below, you’ll learn how to write a simple bibliography using each of the three major style guides. We’ve included details for books and e-books, periodicals, and electronic sources like websites and videos. If the reference material type you need to include isn’t shown here, refer directly to the style guide you’re using.
APA Style Bibliography and Examples
Source: Verywell Mind
Technically, APA style calls for a list of references instead of a bibliography. If your teacher requires you to use the APA style guide , you can limit your reference list only to items you cite throughout your work.
How To Write a Bibliography (References) Using APA Style
Here are some general notes on writing an APA reference list:
- Title your bibliography section “References” and center the title on the top line of the page.
- Do not center your references; they should be left-aligned. For longer items, subsequent lines should use a hanging indent of 1/2 inch.
- Include all types of resources in the same list.
- Alphabetize your list by author or creator, last name first.
- Do not spell out the author/creator’s first or middle name; only use their initials.
- If there are multiple authors/creators, use an ampersand (&) before the final author/creator.
- Place the date in parentheses.
- Capitalize only the first word of the title and subtitle, unless the word would otherwise be capitalized (proper names, etc.).
- Italicize the titles of books, periodicals, or videos.
- For websites, include the full site information, including the http:// or https:// at the beginning.
Books and E-Books APA Bibliography Examples
For books, APA reference list entries use this format (only include the publisher’s website for e-books).
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Publication date). Title with only first word capitalized . Publisher. Publisher’s website
- Wynn, S. (2020). City of London at war 1939–45 . Pen & Sword Military. https://www.pen-and-sword.co.uk/City-of-London-at-War-193945-Paperback/p/17299
Periodical APA Bibliography Examples
For journal or magazine articles, use this format. If you viewed the article online, include the URL at the end of the citation.
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Publication date). Title of article. Magazine or Journal Title (Volume number) Issue number, page numbers. URL
- Bell, A. (2009). Landscapes of fear: Wartime London, 1939–1945. Journal of British Studies (48) 1, 153–175. https://www.jstor.org/stable/25482966
Here’s the format for newspapers. For print editions, include the page number/s. For online articles, include the full URL.
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Year, Month Date) Title of article. Newspaper title. Page number/s. URL
- Blakemore, E. (2022, November 12) Researchers track down two copies of fossil destroyed by the Nazis. The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/science/2022/11/12/ichthyosaur-fossil-images-discovered/
Electronic APA Bibliography Examples
For articles with a specific author on a website, use this format.
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Year, Month Date). Title . Site name. URL
- Wukovits, J. (2023, January 30). A World War II survivor recalls the London Blitz . British Heritage . https://britishheritage.com/history/world-war-ii-survivor-london-blitz
When an online article doesn’t include a specific author or date, list it like this:
Title . (Year, Month Date). Site name. Retrieved Month Date, Year, from URL
- Growing up in the Second World War . (n.d.). Imperial War Museums. Retrieved May 12, 2023, from https://www.iwm.org.uk/history/growing-up-in-the-second-world-war
When you need to list a YouTube video, use the name of the account that uploaded the video, and format it like this:
Name of Account. (Upload year, month day). Title [Video]. YouTube. URL
- War Stories. (2023, January 15). How did London survive the Blitz during WW2? | Cities at war: London | War stories [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/uwY6JlCvbxc
For more information on writing APA bibliographies, see the APA Style Guide website.
APA Bibliography (Reference List) Example Pages

Source: Simply Psychology
More APA example pages:
- Western Australia Library Services APA References Example Page
- Ancilla College APA References Page Example
- Scribbr APA References Page Example
MLA Style Bibliography Examples

Source: PressBooks
MLA style calls for a Works Cited section, which includes all materials quoted or referred to in your paper. You may also include a Works Consulted section, including other reference sources you reviewed but didn’t directly cite. Together, these constitute a bibliography. If your teacher requests an MLA Style Guide bibliography, ask if you should include Works Consulted as well as Works Cited.
How To Write a Bibliography (Works Cited and Works Consulted) in MLA Style
For both MLA Works Cited and Works Consulted sections, use these general guidelines:
- Start your Works Cited list on a new page. If you include a Works Consulted list, start that on its own new page after the Works Cited section.
- Center the title (Works Cited or Works Consulted) in the middle of the line at the top of the page.
- Align the start of each source to the left margin, and use a hanging indent (1/2 inch) for the following lines of each source.
- Alphabetize your sources using the first word of the citation, usually the author’s last name.
- Include the author’s full name as listed, last name first.
- Capitalize titles using the standard MLA format.
- Leave off the http:// or https:// at the beginning of a URL.
Books and E-Books MLA Bibliography Examples
For books, MLA reference list entries use this format. Add the URL at the end for e-books.
Last Name, First Name Middle Name. Title . Publisher, Date. URL
- Wynn, Stephen. City of London at War 1939–45 . Pen & Sword Military, 2020. www.pen-and-sword.co.uk/City-of-London-at-War-193945-Paperback/p/17299
Periodical MLA Bibliography Examples
Here’s the style format for magazines, journals, and newspapers. For online articles, add the URL at the end of the listing.
For magazines and journals:
Last Name, First Name. “Title: Subtitle.” Name of Journal , volume number, issue number, Date of Publication, First Page Number–Last Page Number.
- Bell, Amy. “Landscapes of Fear: Wartime London, 1939–1945.” Journal of British Studies , vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 153–175. www.jstor.org/stable/25482966
When citing newspapers, include the page number/s for print editions or the URL for online articles.
Last Name, First Name. “Title of article.” Newspaper title. Page number/s. Year, month day. Page number or URL
- Blakemore, Erin. “Researchers Track Down Two Copies of Fossil Destroyed by the Nazis.” The Washington Post. 2022, Nov. 12. www.washingtonpost.com/science/2022/11/12/ichthyosaur-fossil-images-discovered/
Electronic MLA Bibliography Examples
Last Name, First Name. Year. “Title.” Month Day, Year published. URL
- Wukovits, John. 2023. “A World War II Survivor Recalls the London Blitz.” January 30, 2023. https://britishheritage.com/history/world-war-ii-survivor-london-blitz
Website. n.d. “Title.” Accessed Day Month Year. URL.
- Imperial War Museum. n.d. “Growing Up in the Second World War.” Accessed May 9, 2023. https://www.iwm.org.uk/history/growing-up-in-the-second-world-war.
Here’s how to list YouTube and other online videos.
Creator, if available. “Title of Video.” Website. Uploaded by Username, Day Month Year. URL.
- “How did London survive the Blitz during WW2? | Cities at war: London | War stories.” YouTube . Uploaded by War Stories, 15 Jan. 2023. youtu.be/uwY6JlCvbxc.
For more information on writing MLA style bibliographies, see the MLA Style website.
MLA Bibliography (Works Cited) Example Pages

Source: The Visual Communication Guy
More MLA example pages:
- Writing Commons Sample Works Cited Page
- Scribbr MLA Works Cited Sample Page
- Montana State University MLA Works Cited Page
Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
The Chicago Manual of Style (sometimes called “Turabian”) actually has two options for citing reference material : Notes and Bibliography and Author-Date. Regardless of which you use, you’ll need a complete detailed list of reference items at the end of your paper. The examples below demonstrate how to write that list.
How To Write a Bibliography Using The Chicago Manual of Style

Source: South Texas College
Here are some general notes on writing a Chicago -style bibliography:
- You may title it “Bibliography” or “References.” Center this title at the top of the page and add two blank lines before the first entry.
- Left-align each entry, with a hanging half-inch indent for subsequent lines of each entry.
- Single-space each entry, with a blank line between entries.
- Include the “http://” or “https://” at the beginning of URLs.
Books and E-Books Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
For books, Chicago -style reference list entries use this format. (For print books, leave off the information about how the book was accessed.)
Last Name, First Name Middle Name. Title . City of Publication: Publisher, Date. How e-book was accessed.
- Wynn, Stephen. City of London at War 1939–45 . Yorkshire: Pen & Sword Military, 2020. Kindle edition.
Periodical Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
For journal and magazine articles, use this format.
Last Name, First Name. Year of Publication. “Title: Subtitle.” Name of Journal , Volume Number, issue number, First Page Number–Last Page Number. URL.
- Bell, Amy. 2009. “Landscapes of Fear: Wartime London, 1939–1945.” Journal of British Studies, 48 no. 1, 153–175. https://www.jstor.org/stable/25482966.
When citing newspapers, include the URL for online articles.
Last Name, First Name. Year of Publication. “Title: Subtitle.” Name of Newspaper , Month day, year. URL.
- Blakemore, Erin. 2022. “Researchers Track Down Two Copies of Fossil Destroyed by the Nazis.” The Washington Post , November 12, 2022. https://www.washingtonpost.com/science/2022/11/12/ichthyosaur-fossil-images-discovered/.
Electronic Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
Last Name, First Name Middle Name. “Title.” Site Name . Year, Month Day. URL.
- Wukovits, John. “A World War II Survivor Recalls the London Blitz.” British Heritage. 2023, Jan. 30. britishheritage.com/history/world-war-ii-survivor-london-blitz.
“Title.” Site Name . URL. Accessed Day Month Year.
- “Growing Up in the Second World War.” Imperial War Museums . www.iwm.org.uk/history/growing-up-in-the-second-world-war. Accessed May 9, 2023.
Creator or Username. “Title of Video.” Website video, length. Month Day, Year. URL.
- War Stories. “How Did London Survive the Blitz During WW2? | Cities at War: London | War Stories.” YouTube video, 51:25. January 15, 2023. https://youtu.be/uwY6JlCvbxc.
For more information on writing Chicago -style bibliographies, see the Chicago Manual of Style website.
Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Example Pages

Source: Chicago Manual of Style
More Chicago example pages:
- Scribbr Chicago Style Bibliography Example
- Purdue Online Writing Lab CMOS Bibliography Page
- Bibcitation Sample Chicago Bibliography
Now that you know how to write a bibliography, take a look at the Best Websites for Teaching & Learning Writing .
Plus, get all the latest teaching tips and ideas when you sign up for our free newsletters .

You Might Also Like

30 Tips for Setting Up an Inspired, Organized Classroom Library
Keep kids reading from day one. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Referencing
A Quick Guide to Referencing | Cite Your Sources Correctly
Referencing means acknowledging the sources you have used in your writing. Including references helps you support your claims and ensures that you avoid plagiarism .
There are many referencing styles, but they usually consist of two things:
- A citation wherever you refer to a source in your text.
- A reference list or bibliography at the end listing full details of all your sources.
The most common method of referencing in UK universities is Harvard style , which uses author-date citations in the text. Our free Harvard Reference Generator automatically creates accurate references in this style.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Referencing styles, citing your sources with in-text citations, creating your reference list or bibliography, harvard referencing examples, frequently asked questions about referencing.
Each referencing style has different rules for presenting source information. For in-text citations, some use footnotes or endnotes , while others include the author’s surname and date of publication in brackets in the text.
The reference list or bibliography is presented differently in each style, with different rules for things like capitalisation, italics, and quotation marks in references.
Your university will usually tell you which referencing style to use; they may even have their own unique style. Always follow your university’s guidelines, and ask your tutor if you are unsure. The most common styles are summarised below.
Harvard referencing, the most commonly used style at UK universities, uses author–date in-text citations corresponding to an alphabetical bibliography or reference list at the end.
Harvard Referencing Guide
Vancouver referencing, used in biomedicine and other sciences, uses reference numbers in the text corresponding to a numbered reference list at the end.
Vancouver Referencing Guide
APA referencing, used in the social and behavioural sciences, uses author–date in-text citations corresponding to an alphabetical reference list at the end.
APA Referencing Guide APA Reference Generator
MHRA referencing, used in the humanities, uses footnotes in the text with source information, in addition to an alphabetised bibliography at the end.
MHRA Referencing Guide
OSCOLA referencing, used in law, uses footnotes in the text with source information, and an alphabetical bibliography at the end in longer texts.
OSCOLA Referencing Guide
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
In-text citations should be used whenever you quote, paraphrase, or refer to information from a source (e.g. a book, article, image, website, or video).
Quoting and paraphrasing
Quoting is when you directly copy some text from a source and enclose it in quotation marks to indicate that it is not your own writing.
Paraphrasing is when you rephrase the original source into your own words. In this case, you don’t use quotation marks, but you still need to include a citation.
In most referencing styles, page numbers are included when you’re quoting or paraphrasing a particular passage. If you are referring to the text as a whole, no page number is needed.
In-text citations
In-text citations are quick references to your sources. In Harvard referencing, you use the author’s surname and the date of publication in brackets.
Up to three authors are included in a Harvard in-text citation. If the source has more than three authors, include the first author followed by ‘ et al. ‘
The point of these citations is to direct your reader to the alphabetised reference list, where you give full information about each source. For example, to find the source cited above, the reader would look under ‘J’ in your reference list to find the title and publication details of the source.
Placement of in-text citations
In-text citations should be placed directly after the quotation or information they refer to, usually before a comma or full stop. If a sentence is supported by multiple sources, you can combine them in one set of brackets, separated by a semicolon.
If you mention the author’s name in the text already, you don’t include it in the citation, and you can place the citation immediately after the name.
- Another researcher warns that the results of this method are ‘inconsistent’ (Singh, 2018, p. 13) .
- Previous research has frequently illustrated the pitfalls of this method (Singh, 2018; Jones, 2016) .
- Singh (2018, p. 13) warns that the results of this method are ‘inconsistent’.
The terms ‘bibliography’ and ‘reference list’ are sometimes used interchangeably. Both refer to a list that contains full information on all the sources cited in your text. Sometimes ‘bibliography’ is used to mean a more extensive list, also containing sources that you consulted but did not cite in the text.
A reference list or bibliography is usually mandatory, since in-text citations typically don’t provide full source information. For styles that already include full source information in footnotes (e.g. OSCOLA and Chicago Style ), the bibliography is optional, although your university may still require you to include one.
Format of the reference list
Reference lists are usually alphabetised by authors’ last names. Each entry in the list appears on a new line, and a hanging indent is applied if an entry extends onto multiple lines.

Different source information is included for different source types. Each style provides detailed guidelines for exactly what information should be included and how it should be presented.
Below are some examples of reference list entries for common source types in Harvard style.
- Chapter of a book
- Journal article
Your university should tell you which referencing style to follow. If you’re unsure, check with a supervisor. Commonly used styles include:
- Harvard referencing , the most commonly used style in UK universities.
- MHRA , used in humanities subjects.
- APA , used in the social sciences.
- Vancouver , used in biomedicine.
- OSCOLA , used in law.
Your university may have its own referencing style guide.
If you are allowed to choose which style to follow, we recommend Harvard referencing, as it is a straightforward and widely used style.
References should be included in your text whenever you use words, ideas, or information from a source. A source can be anything from a book or journal article to a website or YouTube video.
If you don’t acknowledge your sources, you can get in trouble for plagiarism .
To avoid plagiarism , always include a reference when you use words, ideas or information from a source. This shows that you are not trying to pass the work of others off as your own.
You must also properly quote or paraphrase the source. If you’re not sure whether you’ve done this correctly, you can use the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker to find and correct any mistakes.
Harvard referencing uses an author–date system. Sources are cited by the author’s last name and the publication year in brackets. Each Harvard in-text citation corresponds to an entry in the alphabetised reference list at the end of the paper.
Vancouver referencing uses a numerical system. Sources are cited by a number in parentheses or superscript. Each number corresponds to a full reference at the end of the paper.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- A Quick Guide to Harvard Referencing | Citation Examples
- APA Referencing (7th Ed.) Quick Guide | In-text Citations & References
How to Avoid Plagiarism | Tips on Citing Sources
More interesting articles.
- A Quick Guide to OSCOLA Referencing | Rules & Examples
- Harvard In-Text Citation | A Complete Guide & Examples
- Harvard Referencing for Journal Articles | Templates & Examples
- Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples
- MHRA Referencing | A Quick Guide & Citation Examples
- Reference a Website in Harvard Style | Templates & Examples
- Referencing Books in Harvard Style | Templates & Examples
- Vancouver Referencing | A Quick Guide & Reference Examples
Scribbr APA Citation Checker
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!

- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Bibliography in APA Format
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
- APA Bibliography
- How to Create One
- Why You Need It
Sample Bibliography
An APA format bibliography lists all of the sources that might be used in a paper. A bibliography can be a great tool to help you keep track of information during the research and writing process. In some cases, your instructor may require you to include a bibliography as part of your assignment.
At a Glance
A well-written APA format bibliography can help you keep track of information and sources as you research and write your psychology paper. To create a bibliography, gather up all of the sources that you might use in your paper. Create an APA format reference for each source and then write a brief annotation. Your annotation should be a brief summary of what each reference is about. You can quickly refer to these annotations When writing your paper and determine which to include.
What Is an APA Format Bibliography?
An APA format bibliography is an alphabetical listing of all sources that might be used to write an academic paper, essay, article, or research paper—particularly work that is covering psychology or psychology-related topics. APA format is the official style of the American Psychological Association (APA). This format is used by many psychology professors, students, and researchers.
Even if it is not a required part of your assignment, writing a bibliography can help you keep track of your sources and make it much easier to create your final reference page in proper APA format.
Creating an APA Bibliography
A bibliography is similar in many ways to a reference section , but there are some important differences. While a reference section includes every source that was actually used in your paper, a bibliography may include sources that you considered using but may have dismissed because they were irrelevant or outdated.
Bibliographies can be a great way to keep track of information you might want to use in your paper and to organize the information that you find in different sources. The following are four steps you can follow to create your APA format bibliography.
Start on a New Page
Your working bibliography should be kept separate from the rest of your paper. Start it on a new page, with the title "Bibliography" centered at the top and in bold text. Some people use the title "References" instead, so it's best to check with your professor or instructor about which they prefer you to use.

Gather Your Sources
Compile all the sources you might possibly use in your paper. While you might not use all of these sources in your paper, having a complete list will make it easier later on when you prepare your reference section.
Gathering your sources can be particularly helpful when outlining and writing your paper.
By quickly glancing through your working bibliography, you will be able to get a better idea of which sources will be the most appropriate to support your thesis and main points.
Reference Each Source
Your references should be listed alphabetically by the author’s last name, and they should be double-spaced. The first line of each reference should be flush left, while each additional line of a single reference should be a few spaces to the right of the left margin, which is known as a hanging indent.
The format of each source is as follows for academic journals:
- Last name of first author (followed by their first initial)
- The year the source was published in parentheses
- The title of the source
- The journal that published the source (in italics)
- The volume number, if applicable (in italics)
- The issue number, if applicable
- Page numbers (in parentheses)
- The URL or "doi" in lowercase letters followed by a colon and the doi number, if applicable
The following examples are scholarly articles in academic journals, cited in APA format:
- Kulacaoglu, F., & Kose, S. (2018). Borderline personality disorder (BPD): In the midst of vulnerability, chaos, and awe. Brain sciences , 8 (11), 201. doi:10.3390/brainsci8110201
- Cattane, N., Rossi, R., & Lanfredi, M. (2017). Borderline personality disorder and childhood trauma: exploring the affected biological systems and mechanisms. BMC Psychiatry, 18 (221). doi:10.1186/s12888-017-1383-2
Visit the American Psychological Association's website for more information on citing other types of sources including online media, audiovisual media, and more.
Create an Annotation for Each Source
Normally a bibliography contains only references' information, but in some cases you might decide to create an annotated bibliography. An annotation is a summary or evaluation of the source.
An annotation is a brief description of approximately 150 words describing the information in the source, your evaluation of its credibility, and how it pertains to your topic. Writing one of these for each piece of research will make your writing process faster and easier.
This step helpful in determining which sources to ultimately use in your paper. Your instructor may also require it as part of the assignment so they can assess your thought process and understanding of your topic.
Reasons to Write a Bibliography
One of the biggest reasons to create an APA format bibliography is simply to make the research and writing process easier.
If you do not have a comprehensive list of all of your references, you might find yourself scrambling to figure out where you found certain bits of information that you included in your paper.
A bibliography is also an important tool that your readers can use to access your sources.
While writing an annotated bibliography might not be required for your assignment, it can be a very useful step. The process of writing an annotation helps you learn more about your topic, develop a deeper understanding of the subject, and become better at evaluating various sources of information.
The following is an example of an APA format bibliography by the website EasyBib:
There are many online resources that demonstrate different formats of bibliographies, including the American Psychological Association website . Purdue University's Online Writing Lab also has examples of formatting an APA format bibliography.
Check out this video on their YouTube channel which provides detailed instructions on formatting an APA style bibliography in Microsoft Word.
You can check out the Purdue site for more information on writing an annotated APA bibliography as well.
What This Means For You
If you are taking a psychology class, you may be asked to create a bibliography as part of the research paper writing process. Even if your instructor does not expressly require a bibliography, creating one can be a helpful way to help structure your research and make the writing process more manageable.
For psychology majors , it can be helpful to save any bibliographies you have written throughout your studies so that you can refer back to them later when studying for exams or writing papers for other psychology courses.
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . 7th Edition. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 2020.
Masic I. The importance of proper citation of references in biomedical articles. Acta Inform Med . 2013;21(3):148–155. doi:10.5455/aim.2013.21.148-155
American Psychological Association. How do you format a bibliography in APA Style?
Cornell University Library. How to prepare an annotated bibliography: The annotated bibliography .
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Cite Sources
Create citations for free.
Website Book Journal Other
You’ve probably heard your teacher or professor talk about the importance of including citations in your research papers. But what exactly are citations? Why are they so important, and what are the different types? Read on for citation basics.
Here’s a table of contents for this guide:
What is a Citation?
Citation examples, why do we have citations.
- Where Do We Have Citations?
- When Do I Make Citations?
Common Mistakes
5 tips for making the perfect citation, troubleshooting.
To begin, let’s examine what a citation actually is. A citation is how you let your readers know that you used information from outside sources in your work. It also describes those sources, and provides information that allows the reader to track them down. This information could be the author’s name, the publication date, or page numbers. The exact information included in the citation depends on the citation style you are using. Please see the citation manual for your chosen style for more specifics on how to make your citations in that style. Popular styles include MLA formatting , Chicago style, and APA style.
- How to Cite Google Images
- How to Cite Netflix
- How to Cite a PDF
- How to Cite Statistics
- How to Cite a Song
- How to Cite a Poem
- How to Cite a YouTube Video
- How to Cite a Podcast
- How to Cite a Book
- How to Cite an Inscription
- How to Cite a Quote
Having to write citations may seem like another boring step in the paper writing process. However, correctly citing sources in your research projects will ensure that you receive a better grade and create something that uniquely contributes to the subject area you are studying.
It doesn’t matter if you use MLA formatting , APA formatting, or any other citation style. Citing sources is something you should always do.
Here are just a few reasons why it is important for you to cite sources in your work:
Citations Provide Hard Evidence of Your Thesis/Ideas
Citing sources that back up your claim, otherwise known as your thesis statement, creates credibility for you as a researcher. It also opens up room for fact-checking and further research.
- Bonus points : If you can, find a way to cite a few sources that have the converse opinion or idea, and then demonstrate to the reader why you believe that viewpoint is wrong while backing up your claim up with sources. If you can do this, you are well on their way to winning over the reader to your side.
- Pro tip: Having many citations from a wide variety of sources related to your thesis indicates to your professor that you are working on a well-researched and respected subject.
Citations Give Credit to the Right People
Citing sources ensures that your reader or teacher can differentiate your original thoughts from the ideas in your sources and of other researchers in your subject area. This ensures that the sources you use receive proper credit for the author’s work, and that as the student, you receive deserved recognition for your unique contributions to the topic. Citations serve as a natural way to place your work within in the broader context of a subject area, and are an easy way for your teacher or professor to gauge your commitment to the project at hand. Going above and beyond in your work is always a good idea!
Citations Promote Originality and Prevent Plagiarism
The point of research projects is not to regurgitate information that can already be found elsewhere. We have Google for that! What your project should aim to do is promote an original idea or put a spin on an existing idea, and use credible sources to promote that idea. Copying or directly referencing a source without proper citations can lead to not only a poor grade, but accusations of academic dishonesty. By backing up your ideas with credible sources, you can easily avoid the trap of plagiarism, and promote further research on their topic. To help people find your unique perspective on your topic and create consistency throughout your work, it is always a good idea to use a specific, standardized citation style, such as APA format or MLA format.
Where Do We Have Citations, and What are the Types of Citations?
Citations typically can be found in two places: at the end of a paper in a bibliography or reference list, and within the text. The latter, sometimes called “in-text” citations, usually consist of a few details about the source, and are generally written in parenthesis at the end of the sentence where you referenced the source.
When Scout meets Boo Radley in To Kill a Mockingbird, she realizes that his reputation does not match his true character (Lee 85).
The citation in the reference list or bibliography corresponds with the in-text citation, and provides more holistic information about the source that you are citing. Publication information is included, as well as a list of all contributors to the source.
Lee, Harper. To Kill a Mockingbird. Perennial Modern Classics, 2006.
Note that each citation style has its own formatting rules regarding in-text and bibliographic citations. An APA citation will have similar information but look different from an MLA citation . Consult the style manual of your chosen citation style for more information.
When Should I Make Citations?
You should make a citation for a source whenever you:
● Directly quote a source ● Paraphrase information from a source ● Use an idea that is expressed in another source ● Make a specific reference to the work of another person
Let’s have a moment of silence for anyone out there who just received a graded paper filled with those dreaded red marks. Ugh. Nothing is worse than spending hours and hours pouring your heart and soul into a research paper, only to receive a failing grade or an accusation of plagiarism (gasp!) due to incorrect citations. It’s tough enough finding quality resources, analyzing them, and writing a high quality paper, but to receive marks off for incorrect citing totally crushes the soul.
We know there are so many rules to follow when it comes to citing sources. We’re here to highlight some of the most common citation mistakes students and scholars make when developing their research projects. Check out our top 5 below. Perhaps you’ll recognize a mistake or two you’ve been making in your own work.
If you’re looking for some extra help or guidance, check out the Citation Machine plagiarism and grammar checker. Write your paper, pop it into our “smart proofreader” and watch the magic happen. We’ll provide suggestions for citations and grammar edits so you can worry less about those dreaded red marks and more on your learning. Try it out now!
1. Forgetting to include in-text and parenthetical citations
You’ve found the perfect piece of information to include in your paper. Cool! As you’ve learned throughout school, you need to include a citation for that source in your bibliography or works cited list. Don’t forget to also include an in-text or parenthetical citation in the body of your project.
>Remember, every time outside information is added into a paper, you need to provide the reader with a glimpse as to where that information came from. You can do this with an in-text or parenthetical citation, which includes the author’s name in the sentence or directly after it, in parentheses. Depending on the citation style, you may also need to include the page number or year the source was published.
Here’s an example of how an MLA in-text citation could look in an assignment:
Stockett describes Celia as, “probably ten or fifteen years younger than me, twenty-two, twenty-three, and she’s real pretty” (37).
This excerpt is taken from page 37 in Kathryn Stockett’s book, The Help . In the works cited page at the end of the paper, the reader is provided with a full citation that shares the title of the book, the publisher, the year it was published, and possibly some other key pieces of information, depending on the citation style.
Every piece of information added into a paper needs two citations: a brief one in the body of the project and the full citation on the final page. Bam!
2. Period placement gone wrong
Inside? Outside? Outside and inside? It can be tricky to determine where to place those pesky little periods when including parenthetical citations.
For the majority of citation styles, the period is placed on the outside of the parentheses. Here’s a visual to help you out:
“It’s just that sometimes, our future is dictated by what we are, as opposed to what we want” (Sparks 59).
3. In-text and parenthetical citation overload
If you’re using the same reference over and over in one paragraph, it isn’t necessary to include an in-text or parenthetical citation after each sentence. Instead, save it for the end. The reader will be able to ascertain that all of the information from that single paragraph pertains to the individual in-text or parenthetical citation you’ve included.
4. Using the incorrect citation style or switching between two
Even though there are thousands (yes, thousands!) of citation styles available on Citation Machine, make sure to choose just one style for your project. Not sure whether to choose MLA formatting , APA , Chicago style format or another? Check to see if it’s included in the the assignment’s guidelines. Still not sure? Ask your teacher or school librarian. Whichever style you choose to roll with, make sure it’s consistent throughout the entire project. Remember, citations are included to help readers understand where information originated. If you choose to use various citation styles, it could cause some major confusion.
5. Problems with paraphrasing
A proper paraphrase involves taking someone else’s idea and rewriting it using your own words, in your own writing style. What it’s not is taking someone else’s idea and replacing the words with synonyms. Don’t be a synonym swapper. That’s plagiarism!
If you’re having a tough time trying to paraphrase another author’s words, try this out: Carefully read the text again. When you’re through, put it to the side, and think about what you just read. What was the author’s message? Now, rewrite it, using your own words and writing style. Remember to add an in-text or parenthetical citation at the end of the paraphrase and include the full citation in the works cited or reference page.
When you’re in a rush to meet a deadline and hand in your paper ASAP, it can be all too easy to make a mistake that can cost you big time. Citations are an often-overlooked component of a research paper that, when done correctly, can help you get your best grade yet. So how can you be sure that your citations are helping you achieve success? Here are some tips to take your research paper to the next level.
1. Include In-text or Parenthetical Citations When Paraphrasing
It can be tempting to just re-write a sentence from a source to include in your paper. But neglecting inclusion of a parenthetical, or in-text citation can lead to accusations of plagiarism. Being accused of committing plagiarism can not only impact your grade, but can put your enrollment in jeopardy as well. To avoid making this error, be sure to paraphrase carefully, and include a parenthetical or in-text citation in your paper each time you reference an outside source.
2. Periods (Almost) Always Go After the Parenthesis
Something as minor as an incorrectly placed period after a reference can lead to losing major points on your paper. In nearly every citation style with parenthetical citations, the period comes after the parenthesis, not before. Here is an example of a correctly placed period after a reference in APA format :
(Smith, 2005).
3. Be Consistent with Your Citation Style
Some classes require you use MLA format , while others require APA, while still others require Chicago Manual of Style . These specifications can be difficult to keep track of, but being consistent with your style is perhaps the easiest thing you can do to make sure you have well written citations. Double-checking your citations at the end of your paper before handing it in can lead to good last minute improvements.
4. All In-text and Parenthetical Citations Should Correspond with a Reference List Entry
In-text and parenthetical citations can be done while you are writing your paper, and are included each time you include information from an outside source. It is important to remember, however, that each time you do this, you should bear in mind that at the end of your paper in the works cited, bibliography, reference list, etc., there should be a corresponding longer reference to that same source that matches the in-text or parenthetical reference. When you are finished making your in-text and parenthetical references, use them to make a list of full citations you will need to include at the end of your paper.
5. Cite Properly, Not in Excess
While it is important to include citations in your paper, you shouldn’t be including them after each and every sentence you write. The important thing to remember is to cite only if you are including information from an outside source. This information should only be included if you feel that it backs up your claim effectively enough to the point where another researcher could potentially find that source and identify it as being related to your argument. If all the information in one paragraph you write refers to the same source, you only need to include one in-text or parenthetical citation in that paragraph, not after each individual sentence.
Solution #1: Identifying where to place a period in an in-text citation
1. If the in-text citation is at the end of the sentence or quotation, place a period after the citation (outside the parenthesis).
APA examples:
The results of Singh’s (2021) experiment were inconclusive (p. 42).
“The origin of the two variables could not be determined” (Singh, 2021, p. 42).
MLA examples:
The results of Singh’s experiment were inconclusive (42).
“The origin of the two variables could not be determined” (Singh 42).
2. Always use periods after the phrase “et al.”.
As Gregory Cheffsworth, et al. (2021) suggest, “sour cream can be used as a milk substitute whenever one is low on ingredients and willingness to go to the store” (p. 12).
“Sour cream can be used as a milk substitute whenever one is low on ingredients and willingness to go to the store” (Cheffsworth et al., 2021, p. 12).
As Gregory Cheffsworth, et al. suggest, “sour cream can be used as a milk substitute whenever one is low on ingredients and willingness to go to the store” (p. 12).
“Sour cream can be used as a milk substitute whenever one is low on ingredients and willingness to go to the store” (Cheffsworth et al. 12).
3. Block quotations in APA and MLA place the citation after the period.
A block quotation in APA is a quotation that is longer than forty words. The entire block quotations are indented by 0.5-inches.
I wanted to make a casserole, but I soon realized that I did not have milk. However, as Gregory Cheffsworth, et al. (2021) suggest,
“Sour cream can be used as a milk substitute whenever one is low on ingredients and willingness to go to the store but, when one encounters this situation, they must be prepared to adapt to the differences in flavor profiles by incorporating new spices.” (p. 12)
In MLA, if the quotation is longer than four lines, use a block quotation by indenting the entire paragraph 0.5-inches.
MLA example:
I wanted to make a casserole, but I soon realized that I did not have milk. However, as Gregory Cheffsworth, et al. suggest,
Sour cream can be used as a milk substitute whenever one is low on ingredients and willingness to go to the store but, when one encounters this situation, they must be prepared to adapt to the differences in flavor profiles by incorporating new spices. Depending on the selections, the sour cream’s natural taste can be emphasized or completely neutralized. As a result, one should not be afraid of the “sour” in sour cream. (12)
Solution #2: How to choose which citation style to use
- First, consult your syllabus, rubric, or writing guidelines. Most often, the expected citation style will be listed. If it is not, ask your teacher or the publication if they have a style preference.
- Use MLA style if you are writing within the humanities. This includes English literature, language, history, religion, and the arts.
- Use APA style if you are writing on the sciences, which includes subjects such as geology, education, or psychology.
- Use Chicago style if you are writing for business, history, or the fine arts.
- Note that some scientific genres require their own specific citation guide outside of these three widely used guides. For example, computer science frequently uses the IEEE citation guide.
- Look at sample papers or journal articles to see what is typically used.
- If all else fails, go to a library or your school’s writing center and ask for help.
Solution #3 When and how to create a direct quote versus a paraphrased citation
- For example, if you chose to directly quote information because the wittiness of an original excerpt is meaningful to your paper and is altered as a paraphrase.
- For example, when the quoted material is short compared to the rest of the sentence and does not add a significant amount of information. Use a paraphrase instead.
- Be aware that writing a direct quote without explaining it or further relating it to your topic can give the impression that you do not understand the information and are simply regurgitating the information.
- Avoid overusing direct quotes. Ideally, a paper is mostly written using your own words and thoughts.
- Use a paraphrase if you truly understand the idea/information and you can effectively relay the message in your own words.
- A paraphrase is also useful if you’re trying to synthesize a long quote or passage into a shorter passage.
- Before or after the paraphrase, you will need to discuss the information’s significance to your argument or paper.
- If you find that your paragraph is following the same word structure as the original statement, consider using a direct quote or consider rephrasing the sentence.
- One more reminder: Include an in-text citation to indicate that the original idea comes from another source.
Example of a direct quote:
I wanted to make a casserole, but I soon realized that I did not have milk. However, as Gregory Cheffsworth (2021) suggests, “sour cream can be used as a milk substitute whenever one is low on ingredients and willingness to go to the store” (p. 47).
Example of a paraphrased citation:
I wanted to make a casserole, but I soon realized that I did not have milk. However, I may be able to use sour cream instead of milk (Cheffsworth, 2021).
Finished with your citations and paper? Check out Citation Machine’s handy paper checker ! It can help you spot errors and polish your paper. There’s also a free grammar guides library where you can learn what is a verb , an adjective definition , relative pronoun examples , and other grammar-related topics.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?

Generate formatted bibliographies, citations, and works cited automatically
What is mybib.
MyBib is a free bibliography and citation generator that makes accurate citations for you to copy straight into your academic assignments and papers.
If you're a student, academic, or teacher, and you're tired of the other bibliography and citation tools out there, then you're going to love MyBib. MyBib creates accurate citations automatically for books, journals, websites, and videos just by searching for a title or identifier (such as a URL or ISBN).
Plus, we're using the same citation formatting engine as professional-grade reference managers such as Zotero and Mendeley, so you can be sure our bibliographies are perfectly accurate in over 9,000 styles -- including APA 6 & 7, Chicago, Harvard, and MLA 7 & 8.
Quick features:
Help | Advanced Search
Economics > Econometrics
Title: fused extended two-way fixed effects for difference-in-differences with staggered adoptions.
Abstract: To address the bias of the canonical two-way fixed effects estimator for difference-in-differences under staggered adoptions, Wooldridge (2021) proposed the extended two-way fixed effects estimator, which adds many parameters. However, this reduces efficiency. Restricting some of these parameters to be equal (for example, subsequent treatment effects within a cohort) helps, but ad hoc restrictions may reintroduce bias. We propose a machine learning estimator with a single tuning parameter, fused extended two-way fixed effects (FETWFE), that enables automatic data-driven selection of these restrictions. We prove that under an appropriate sparsity assumption FETWFE identifies the correct restrictions with probability tending to one, which improves efficiency. We also prove the consistency, oracle property, and asymptotic normality of FETWFE for several classes of heterogeneous marginal treatment effect estimators under either conditional or marginal parallel trends, and we prove the same results for conditional average treatment effects under conditional parallel trends. We demonstrate FETWFE in simulation studies and an empirical application.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
- Plagiarism and grammar
- School access
The best papers start with EasyBib®
Powered by chegg.
Start a new citation or manage your existing projects.
Scan your paper for plagiarism and grammar errors.
Check your paper for grammar and plagiarism
Catch plagiarism and grammar mistakes with our paper checker
Wipe out writing errors with EasyBib® Plus
Double check for plagiarism mistakes and advanced grammar errors before you turn in your paper.
- expert check
Know you're citing correctly
No matter what citation style you're using (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) we'll help you create the right bibliography
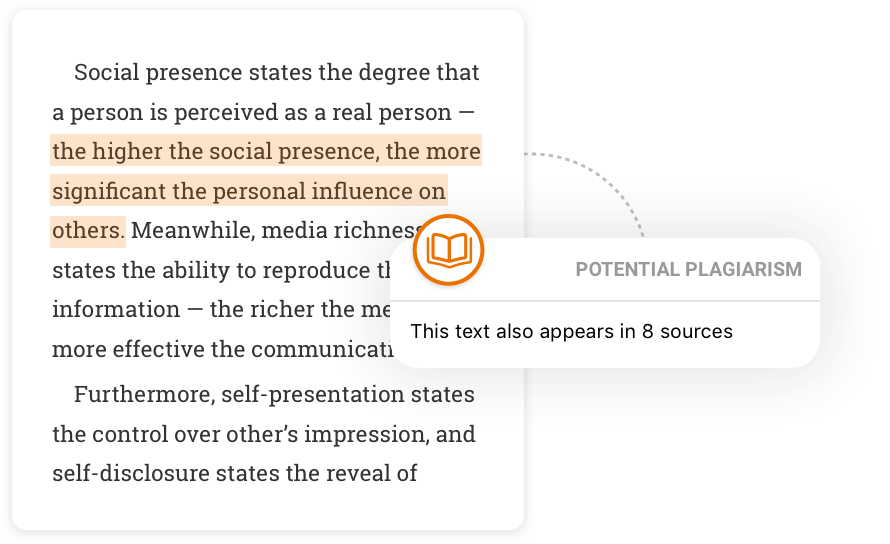
Check for unintentional plagiarism
Scan your paper the way your teacher would to catch unintentional plagiarism. Then, easily add the right citation
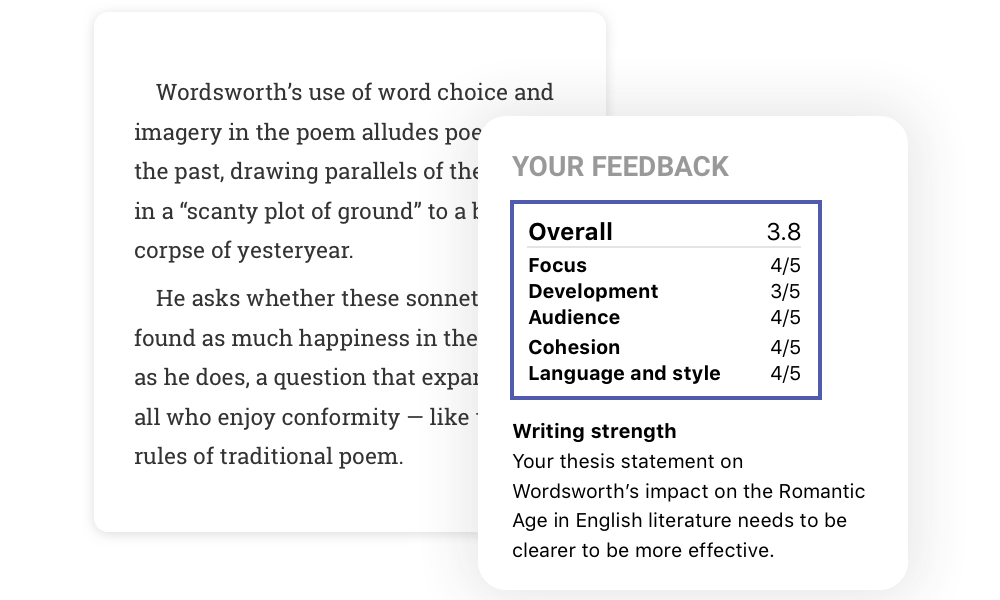
Strengthen your writing
Give your paper an in-depth check. Receive feedback within 24 hours from writing experts on your paper's main idea, structure, conclusion, and more.

Find and fix grammar errors
Don't give up sweet paper points for small mistakes. Our algorithms flag grammar and writing issues and provide smart suggestions
Choose your online writing help
Easybib® guides & resources, mla format guide.
This is the total package when it comes to MLA format. Our easy to read guides come complete with examples and step-by-step instructions to format your full and in-text citations, paper, and works cited in MLA style. There’s even information on annotated bibliographies.
Works Cited | In-Text Citations | Bibliography | Annotated Bibliography | Website | Book | Journal | YouTube | View all MLA Citation Examples
APA Format Guide
Get the facts on citing and writing in APA format with our comprehensive guides. Formatting instructions, in-text citation and reference examples, and sample papers provide you with the tools you need to style your paper in APA.
Reference Page | In-Text Citations | Annotated Bibliography | Website | Books | Journal | YouTube | View all APA citation Examples
Chicago Format Guide
Looking to format your paper in Chicago style and not sure where to start? Our guide provides everything you need! Learn the basics and fundamentals to creating references and footnotes in Chicago format. With numerous examples and visuals, you’ll be citing in Chicago style in no time.
Footnotes | Website | Book | Journal
Harvard Referencing Guide
Learn the requirements to properly reference your paper in Harvard style. The guides we have provide the basics and fundamentals to give credit to the sources used in your work.
In-Text Citations | Books | Article | YouTube | View all Harvard Referencing Examples
Check Your Paper
Avoid common grammar mistakes and unintentional plagiarism with our essay checker. Receive personalized feedback to help identify citations that may be missing, and help improve your sentence structure, punctuation, and more to turn in an error-free paper.
Grammar Check | Plagiarism Checker | Spell Check
Learn From Our Innovative Blog
Our blog features current and innovative topics to keep you up to speed on citing and writing. Whether you’re an educator, student, or someone who lives and breathes citations (it’s not as uncommon as you might think!), our blog features new and exciting articles to discover and learn from.
Looking for Other Tools and Resources?
Our Writing Center is jam-packed with tons of exciting resources. Videos, infographics, research guides, and many other citation-related resources are found here. Check it out to find what you need to succeed!
- EasyBib® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style Format
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO

Algorithms help people see and correct their biases, study shows
Professor of Marketing and Everett W. Lord Distinguished Faculty Scholar, Boston University
Disclosure statement
Carey K. Morewedge does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Boston University provides funding as a founding partner of The Conversation US.
View all partners
Algorithms are a staple of modern life. People rely on algorithmic recommendations to wade through deep catalogs and find the best movies, routes, information, products, people and investments. Because people train algorithms on their decisions – for example, algorithms that make recommendations on e-commerce and social media sites – algorithms learn and codify human biases .
Algorithmic recommendations exhibit bias toward popular choices and information that evokes outrage, such as partisan news . At a societal level, algorithmic biases perpetuate and amplify structural racial bias in the judicial system , gender bias in the people companies hire , and wealth inequality in urban development .
Algorithmic bias can also be used to reduce human bias. Algorithms can reveal hidden structural biases in organizations. In a paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, my colleagues and I found that algorithmic bias can help people better recognize and correct biases in themselves .
The bias in the mirror
In nine experiments, Begum Celikitutan , Romain Cadario and I had research participants rate Uber drivers or Airbnb listings on their driving skill, trustworthiness or the likelihood that they would rent the listing. We gave participants relevant details, like the number of trips they’d driven, a description of the property, or a star rating. We also included an irrelevant biasing piece of information: a photograph revealed the age, gender and attractiveness of drivers, or a name that implied that listing hosts were white or Black.
After participants made their ratings, we showed them one of two ratings summaries: one showing their own ratings, or one showing the ratings of an algorithm that was trained on their ratings. We told participants about the biasing feature that might have influenced these ratings; for example, that Airbnb guests are less likely to rent from hosts with distinctly African American names. We then asked them to judge how much influence the bias had on the ratings in the summaries.
Whether participants assessed the biasing influence of race, age, gender or attractiveness, they saw more bias in ratings made by algorithms than themselves. This algorithmic mirror effect held whether participants judged the ratings of real algorithms or we showed participants their own ratings and deceptively told them that an algorithm made those ratings.
Participants saw more bias in the decisions of algorithms than in their own decisions, even when we gave participants a cash bonus if their bias judgments matched the judgments made by a different participant who saw the same decisions. The algorithmic mirror effect held even if participants were in the marginalized category – for example, by identifying as a woman or as Black.
Research participants were as able to see biases in algorithms trained on their own decisions as they were able to see biases in the decisions of other people. Also, participants were more likely to see the influence of racial bias in the decisions of algorithms than in their own decisions, but they were equally likely to see the influence of defensible features, like star ratings, on the decisions of algorithms and on their own decisions.
Bias blind spot
People see more of their biases in algorithms because the algorithms remove people’s bias blind spots . It is easier to see biases in others’ decisions than in your own because you use different evidence to evaluate them.
When examining your decisions for bias, you search for evidence of conscious bias – whether you thought about race, gender, age, status or other unwarranted features when deciding. You overlook and excuse bias in your decisions because you lack access to the associative machinery that drives your intuitive judgments, where bias often plays out. You might think, “I didn’t think of their race or gender when I hired them. I hired them on merit alone.”
When examining others’ decisions for bias, you lack access to the processes they used to make the decisions. So you examine their decisions for bias, where bias is evident and harder to excuse. You might see, for example, that they only hired white men.
Algorithms remove the bias blind spot because you see algorithms more like you see other people than yourself. The decision-making processes of algorithms are a black box , similar to how other people’s thoughts are inaccessible to you.
Participants in our study who were most likely to demonstrate the bias blind spot were most likely to see more bias in the decisions of algorithms than in their own decisions.
People also externalize bias in algorithms. Seeing bias in algorithms is less threatening than seeing bias in yourself, even when algorithms are trained on your choices. People put the blame on algorithms. Algorithms are trained on human decisions, yet people call the reflected bias “ algorithmic bias .”
Corrective lens
Our experiments show that people are also more likely to correct their biases when they are reflected in algorithms. In a final experiment, we gave participants a chance to correct the ratings they evaluated. We showed each participant their own ratings, which we attributed either to the participant or to an algorithm trained on their decisions.
Participants were more likely to correct the ratings when they were attributed to an algorithm because they believed the ratings were more biased. As a result, the final corrected ratings were less biased when they were attributed to an algorithm.
Algorithmic biases that have pernicious effects have been well documented . Our findings show that algorithmic bias can be leveraged for good. The first step to correct bias is to recognize its influence and direction. As mirrors revealing our biases, algorithms may improve our decision-making.
- Algorithmic bias
- Algorithmic harm

Lecturer / Senior Lecturer - Marketing

Communications and Engagement Officer, Corporate Finance Property and Sustainability

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health

Lecturer/Senior Lecturer, Earth System Science (School of Science)
What EU Sanctions on Russian LNG Would Mean for Global Gas (2)
By Anna Shiryaevskaya and Ewa Krukowska

Since the start of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, Europe and its allies have looked for ways to curb Moscow’s fossil fuel revenues without inflicting higher energy costs on their own citizens. The latest plan: ban use of European Union ports for re-exporting liquefied natural gas.
Russian producer Novatek PJSC relies on stopovers in the EU to move Arctic fuel from ice-class ships onto conventional tankers. While choking off its access won’t prevent cargoes from reaching Europe — where LNG imports from Russia have actually increased in the aftermath of the war — it will make it harder to send them ...
Learn more about Bloomberg Law or Log In to keep reading:
Learn about bloomberg law.
AI-powered legal analytics, workflow tools and premium legal & business news.
Already a subscriber?
Log in to keep reading or access research tools.

COMMENTS
The free Scribbr Citation Generator is the quickest way to cite sources in these styles. Simply enter the URL, DOI, or title, and we'll generate an accurate, correctly formatted citation. Generate accurate citations with Scribbr. Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes ...
6 Interesting Citation Facts. The world of citations may seem cut and dry, but there's more to them than just specific capitalization rules, MLA in-text citations, and other formatting specifications.Citations have been helping researches document their sources for hundreds of years, and are a great way to learn more about a particular subject area.
Formatting a Harvard style bibliography. Sources are alphabetised by author last name. The heading 'Reference list' or 'Bibliography' appears at the top. Each new source appears on a new line, and when an entry for a single source extends onto a second line, a hanging indent is used: Harvard bibliography example.
APA Style is widely used by students, researchers, and professionals in the social and behavioral sciences. Scribbr's APA Citation Generator automatically generates accurate references and in-text citations for free.. This citation guide outlines the most important citation guidelines from the 7th edition APA Publication Manual (2020). Scribbr also offers free guides for the older APA 6th ...
When it is time to turn in your Bibliography, type all of your sources into a list. Use the examples in MLA Format Examples or APA Format Examples as a template to insure that each source is formatted correctly. List the sources in alphabetical order using the author's last name.
For bibliography entries, you list the sources alphabetically by last name, so you will list the last name of the author or creator first in each entry. You should single-space within a bibliography entry and double-space between them. When an entry goes longer than one line, use a hanging indent of .5 inches for subsequent lines.
Each work cited must appear in the reference list, and each work in the reference list must be cited in the text (or in a table, figure, footnote, or appendix). Both paraphrasesand quotationsrequire citations. The following are guidelines to follow when writing in-text citations: Ensure that the spelling of author names and the publication ...
6. Cite books. Include the author's last name and first name, separated by a comma and ending with a period. Then the book title comes in italics with a period at the end of the title. The place of publication and the name of the publishing company are separated by a colon, and then a comma and the publication date.
Here are some general notes on writing an APA reference list: Title your bibliography section "References" and center the title on the top line of the page. Do not center your references; they should be left-aligned. For longer items, subsequent lines should use a hanging indent of 1/2 inch.
APA referencing, used in the social and behavioural sciences, uses author-date in-text citations corresponding to an alphabetical reference list at the end. In-text citation. Sources should always be cited properly (Pears & Shields, 2019). Reference list. Pears, R., & Shields, G. (2019). Cite them right: The essential referencing guide (11th ...
The references in a bibliography are formatted in the same way as they would be in a Works Cited page. However, a bibliography refers to all works that you have consulted in your research, even if you did not use their information directly in your paper. ... When you use the correct MLA bibliography format, it shows the reader what sources you ...
To create a bibliography, gather up all of the sources that you might use in your paper. Create an APA format reference for each source and then write a brief annotation. Your annotation should be a brief summary of what each reference is about. You can quickly refer to these annotations When writing your paper and determine which to include.
How to write a bibliography using APA Reference List Format with examples and tips. Jump to main content ... The exceptions to this rule would be periodical titles and proper names in a title which should still be capitalized. ... When printing this document, you may NOT modify it in any way. For any other use, please contact Science Buddies ...
The way that you create your bibliography will depend on the specific style that you are using. There are several different styles available. MLA: This style is designed for creating liberal arts or humanities essays. APA: Use this style for creating in the education or science fields. Chicago:
Solution #2: How to choose which citation style to use. First, consult your syllabus, rubric, or writing guidelines. Most often, the expected citation style will be listed. If it is not, ask your teacher or the publication if they have a style preference.
In this situation the original author and date should be stated first followed by 'as cited in' followed by the author and date of the secondary source. For example: Lorde (1980) as cited in Mitchell (2017) Or (Lorde, 1980, as cited in Mitchell, 2017) Back to top. 3. How to Cite Different Source Types.
APA 7, released in October 2019, has some new updates. Here is a brief description of the updates made in APA 7. Different types of papers and best practices are given in detail in Chapter 1. How to format a student title page is explained in Chapter 2. Examples of a professional paper and a student paper are included.
MyBib is a free bibliography and citation generator that makes accurate citations for you to copy straight into your academic assignments and papers. If you're a student, academic, or teacher, and you're tired of the other bibliography and citation tools out there, then you're going to love MyBib. MyBib creates accurate citations automatically ...
To cite a book chapter, first give the author and title (in quotation marks) of the chapter cited, then information about the book as a whole and the page range of the specific chapter. The in-text citation lists the author of the chapter and the page number of the relevant passage. MLA format. Author last name, First name.
To address the bias of the canonical two-way fixed effects estimator for difference-in-differences under staggered adoptions, Wooldridge (2021) proposed the extended two-way fixed effects estimator, which adds many parameters. However, this reduces efficiency. Restricting some of these parameters to be equal (for example, subsequent treatment effects within a cohort) helps, but ad hoc ...
This is the total package when it comes to MLA format. Our easy to read guides come complete with examples and step-by-step instructions to format your full and in-text citations, paper, and works cited in MLA style. There's even information on annotated bibliographies.
Algorithms are a staple of modern life. People rely on algorithmic recommendations to wade through deep catalogs and find the best movies, routes, information, products, people and investments.
MSN
Citing a website in MLA Style. An MLA Works Cited entry for a webpage lists the author's name, the title of the page (in quotation marks), the name of the site (in italics), the date of publication, and the URL. The in-text citation usually just lists the author's name. For a long page, you may specify a (shortened) section heading to ...
Asian buyers, European companies with contracts seen affected. Since the start of Russia's invasion of Ukraine, Europe and its allies have looked for ways to curb Moscow's fossil fuel revenues without inflicting higher energy costs on their own citizens. The latest plan: ban use of European Union ports for re-exporting liquefied natural gas.