Case Study – Boscastle Floods
Floods devastate village.
On 16 August 2004, a devastating flood swept through the small Cornish village of Boscastle.
Very heavy rain fell in storms close to the village, causing two rivers to burst their banks. About two billion litres of water then rushed down the valley straight into Boscastle.
Residents had little time to react. Cars were swept out to sea, buildings were badly damaged and people had to act quickly to survive. Fortunately, nobody died – thanks largely to a huge rescue operation involving helicopters — but there was millions of pounds worth of damage.

Physical Impacts
Responses to the flooding, what happened to cause this event.
Flooding On the day of the flood, about 75mm of rain fell in two hours — the same amount that normally falls in the whole of August. Huge amounts of water from this sudden downpour flowed into two rivers, the Valency and Jordan (which flows into the Valency just above Boscastle). Both overflowed, and this caused a sudden rush of water to speed down the Valency — which runs through the middle of Boscastle.
Destruction of houses, businesses and gardens Floodwater gushed into houses, shops and pubs. Cars, walls and even bridges were washed away. The church was filled with six feet of mud and water. Trees were uprooted and swept into peoples’ gardens. The weight of water eroded river banks, damaged gardens and pavements.
Human Impacts There was a huge financial cost to the floods. This included:
- the rescue operation – involving helicopters, lifeboats, and the fire service.
- the loss of 50 cars
- damage to homes, businesses and land
- a loss of tourism, a major source of income for the area
The flooding also had several other key impacts on Boscastle and its inhabitants. These included:
- environmental damage to local wildlife habitats
- coastal pollution caused as debris and fuel from cars flowed out to sea.
- long-term disruption to the village, as a major rebuild project had to be carried out.
- long-term stress and anxiety to people traumatised by the incident.
- John Prescott, the Deputy Prime Minister, and Prince Charles visited members of the emergency services and the local GP surgery, which acted as the emergency centre, in the days following the disaster.
- Prince Charles, who is the Duke of Cornwall, made a large donation to a fund to help rebuild parts of Boscastle.
- The Environment Agency is responsible for warning people about floods and reducing the likelihood of future floods. The Environment Agency has carried a major project to increase flood defences in Boscastle, with the aim of preventing a similar flood happening again.
- We are investing in new ways of predicting heavy rainfall events on a small scale to produce better warnings.
In Pictures

Weather chart
Radar imagery
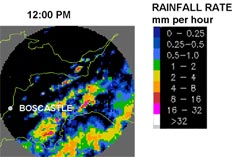
Fig. 2 shows radar pictures at 12 p.m. (midday) on 16 August.
The rainfall rate key shows how the colours in the image relate to the rate the rainfall is falling. For example, the red areas indicate that rain is falling at between eight and 16 mm per hour.
A line of very heavy rain starts at about 1 p.m. on the moors close to Boscastle. It remains over the area for about six hours. Rainfall rates of at least 32 mm per hour are being measured.
There is more about rainfall radar in the weather section of the Met Office website.
Satellite imagery Fig. 3 shows an animation of satellite pictures from 12 p.m. (midday) to 7 p.m. on 16 August.

The thickest cloud is shown by the brightest white areas on the picture. The pictures show cloud forming over Boscastle at about 1 p.m. and staying there for much of the afternoon.
Further information on other websites BBC News website covering the Boscastle flooding BBC News article – Boscastle one year on
Boscastle 16 August 2004 the day of the flood , 2006, Galvin, 61, 29
Web page reproduced with the kind permission of the Met Office
Start exploring
- Search Resources
- All Levels Primary Secondary Geography Secondary Maths Secondary Science
- Choose a topic All Topics Air Masses Anticyclones Carbon Cycle Climate Climate Change Climate Zones Clouds Contour Coriolis Depressions El Nino Extreme Weather Flooding Front Global Atmospheric Circulation Hydrological Cycle Microclimates Past Climate Snow Synoptic Charts Tropical Cyclones Urban Heat Island Water Cycle Weather Weather Forecast Weather Map Weather System
- All Climate Change Adaptation Afforestation Agriculture air quality aircraft Albedo Anthropocene anthropogenic Arctic/ Antarctic Carbon cycle Carbon dioxide removal/ sequestration Carbon footprint Carbon sinks Causes Climate Climate Crisis/ Emergency Climate justice Climate literacy climate stripes/ visualisation Climate zone shift clouds CO2/ carbon dioxide emissions COP Cryosphere Deforestation Desertification Ecosystems Electric vehicles Energy Equity Evidence Extreme weather Feedback loops Fire weather Flood defences Flooding/ flood risk Fossil fuels Fuel security Global energy budget/ balance Green climate fund Greenhouse effect Greenhouse gas concentrations Heatwaves/ extreme heat Hydroelectric power Ice sheets Impacts IPCC Keeling curve Mitigation Modelling Natural variability Nature based solutions Negotiations Net zero Nuclear power Observations Ocean acidification Ocean warming Proxy records Regional climate change Renewable/ non fossil fuel energy Scenarios Schools Strike for Climate Society Solar energy Solutions Storms Temperature/ global warming Tipping points Transport Tropical cyclones Uneven impacts UNFCCC/ governance Urban green infrastructure Urban heat Urbanisation Water cycle Water security Water vapour (H2O) concentrations Weather Wild fires Wind power
- Choose an age range All ages Primary 0 to 7 7 to 11 Secondary 11 to 14 14 to 16 16 to 18
Latest from blog
5 common climate misconceptions, weather and climate: updated teachers’ cpd, new maths lesson with climate context, quality control of climate education resoures, related resources ….
Ecosystem Feedbacks from Carbon and Water Cycle Changes

Climate Change Schools’ Project Resources

In Depth – Rainfall and Relief
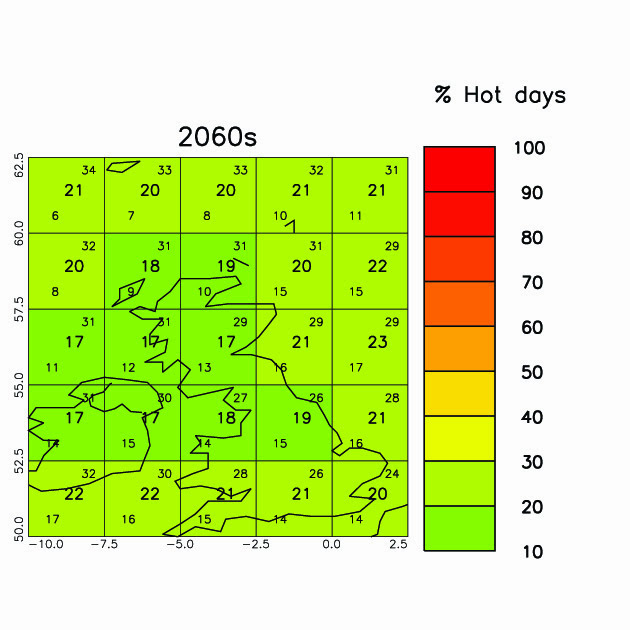
How will the Frequency of Hot Days Change?
Subscribe to metlink updates, weather and climate resources and events for teachers.
© 2024 Royal Meteorological Society RMetS is a registered charity No. 208222
About MetLink Cookies Policy Privacy Policy

- We use cookies on this site to enhance your user experienceBy clicking any link on this page you are giving your consent for us to set cookies. More info
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
By clicking any link on this page you are giving your consent for us to set cookies. More info
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.

Flood Management Scheme – Boscastle
A flood management scheme following the 2004 floods.
Why the Boscastle flood scheme required?
On the 16th August 2004, a devastating flood swept through Boscastle, a small village on the north Cornwall coast.
Very heavy rain fell in storms close to the village, with over 60mm of rainfall in two hours. The ground was already saturated due to above average rainfall during the previous two weeks. Combined with this the drainage basin has many steep slopes and there are areas of impermeable slate that led to rapid run-off. Boscastle is at the confluence (where tributaries meet) of three rivers – Valency, Jordan, and Paradise. About two billion litres of water then rushed down the valley straight into Boscastle within a short space of time causing the rivers to overflow. Additionally, the deluge of water coincided with a high tide.
As the flood happened so quickly local residents had little time to react. Cars were swept out to sea and buildings were badly damaged. Thankfully, no one lost their lives, which is largely due to a huge rescue operation involving helicopters. Million of pounds worth of damage was caused by the flood.

What was the management strategy?
In 2008 a flood management scheme for Boscastle was completed. The solution included both soft and hard engineering strategies.
The Environment Agency has made a considerable investment in flood defences in Boscastle to help prevent a similar flood happening in the future. Working with professional partners, more than £10 million of improvements were carried out. This included widening and deepening the Valency River, and installing a flood culvert to improve flow in the Jordan River.
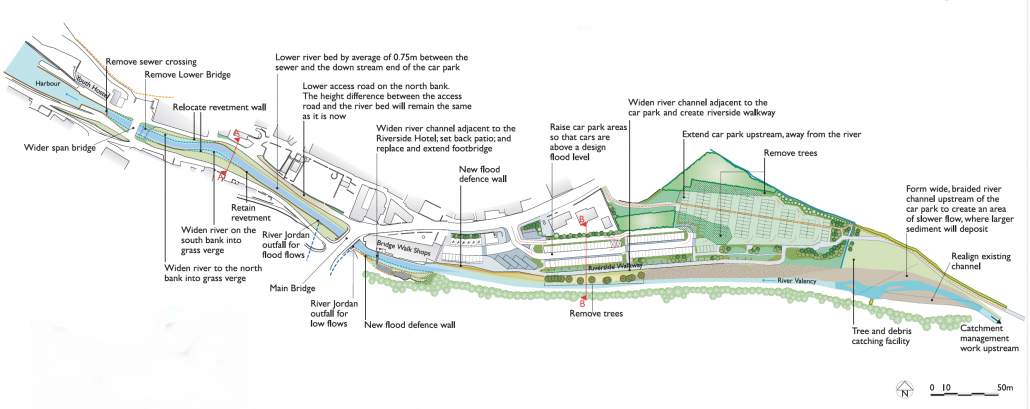
River Valency Flood Management Scheme
The Met Office and Environment Agency have formed the first of several working partnerships, the Flood Forecasting Centre. Combining expertise in weather forecasting and hydrology has helped to prepare communities for flooding during times of extreme weather.
At the time of the floods, the operational forecast model had a resolution of 12 km, which was too large to be able to represent such a small scale collection of thunderstorms. Since 2004 the Boscastle case was re-run with a higher resolution research model which proved able to resolve the line of thunderstorms with much more accuracy and detail.
What are the social, economic and environmental issues?
Social issues.
The rebuilding projects and construction of flood defences took several years which meant the lives of local people were disrupted for sometime. The risk of flooding has been reduced making Boscastle safer. The defences would not protect against a flood the same size as the one in 2004. The new bridge is not popular with local people as it is out of character compared to the rest of the building.
Economic issues
The risk of flooding has been reduced. Therefore, there is less risk of damage to property and businesses. The flood-defence scheme cost over £4 million. However, the scheme could have been significantly better, though some options were too expensive.
Environmental issues
Biodiversity has improved as have the river habitats. Vegetation in the area is now managed.

Premium Resources
Please support internet geography.
If you've found the resources on this page useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
If you've found the resources on this site useful please consider making a secure donation via PayPal to support the development of the site. The site is self-funded and your support is really appreciated.
Search Internet Geography
Top posts and pages.
Latest Blog Entries
Pin It on Pinterest
- Click to share
- Print Friendly
3.13 Case Study - Boscastle Floods (2004)
Flash floods occurred in the valleys of the River Valency and the River Jordan on 16th August 2004.
The village of Boscastle is situated:
in a narrow valley with interlocking spurs which acted like a funnel
in a steep valley which encouraged rapid run-off
on a flat flood plain
in an area where the soil is impermeable clay which does not allow much infiltration
185 mm if rain fell in five hours
The soil was saturated from recent rainfall so no more rain could infiltrate
The collision of winds on a very warm day caused the excessive rainfall (the air mass from the south met the air mass from the south-west and converged on Bodmin which led to towering cumulonimbus clouds. The air was very unstable and the clouds were up to 10 km high).
The natural channel of the river had been walled (for the construction of the B3263 and a pedestrian area) which prevented it from adjusting to a variation in the discharge of the water.
The village had been built on a flat flood plain.
There was no flood control system.
Cars, trees and boulders became stuck under the bridge and created a temporary dam which caused the water to build up behind it.
The sewers and drainage systems were old and small in capacity; they broke and the water that was in the, took an overland route.
50 cars were swept into the harbour.
The bridge was washed away and roads were submerged under 2.75 m of water, making communication difficult.
The sewerage system burst.
For health and safety reasons Boscastle was declared inaccessible.
The Museum of Withcraft lost 50 per cent of its artefacts.
Four buildings were demolished and 58 flooded and the High Street was badly damaged.
The visitors' centre, a clothes shop and two gift shops were badly damaged.
The youth hostel was flooded.
People were in shock and there were concern about hypothermia or being swept away.
There was no power in the village for some time (an emergency generator had to be blown in).
90 per cent of the economy in Boscastle is based on tourism and there were still three weeks of the summer holidays left; twenty accommodation providers were shut.
Visitors whose cars had been washed away were not able to leave.
A speedy, well-co-ordinated and well-resourced rescue operation ensured that remarkably there was no loss of life. Even by the standards of developed countries, this was outstanding and a tribute to Britain's rescue services.
Emergency workers rescued residents and holiday-makers from a 32 km stretch of the north Cornwall coast.
Hundreds were evacuated from homes, rooftops (120 from rooftops), trees and vehicles.
Seven helicopters from the Coastguards, Royal Navy and RAF were used.
People took emergency shelter in The Rectory, which was on high ground.
The village was cordoned off by building inspectors for the clean-up operation.
People dug out guttering and removed rubble so that the water could flow away.
Sandbagging was used as a form of defence.
People came to see the catastrophe.
Prince Charles and the Deputy Prime Minister at the time, John Prescott, came to see the damage.
There was a church service to give thanks that no one had died.
The repairs were very costly and time consuming.
There was a huge fund-raising effort to help rebuild the village.
Insurance is now costlier in Boscastle.
Flood Control and Prevention
The Environment Agency carried out a major investigation.
A £2 million grant was given to Boscastle to help with flood prevention.
No more schools or old people's homes are built in the valley.
The Environment Agency removed debris from upstream, which meant there was more room for the water to flow freely under the new bridge.
A flood defence system (building a flood wall, widening the River Jordan, raising car parks, removing bridges and using relief channels) was planned and is now complete. This also included building a high-arched single-span bridge which would not impeded flood water debris.
Boscastle Floods - 10 Years On
Only watch the first 11.07 minutes of the video.
Click here to return to the Home page.
Flooding Case Study: Consequences of Boscastle
Consequences of the boscastle flash flood in 2004.
There were immediate and long-term consequences of the Boscastle flash flood that happened on 16th August, 2004. These consequences included:

Decreased tourism
- The flood happened during the peak season for tourism.
- People think that the flood cost the town £50 million in damage and lost income.

Flood damage
- 58 properties were flooded. 4 of these were destroyed.
- 150 cars were swept away.
- Roads and bridges were destroyed.
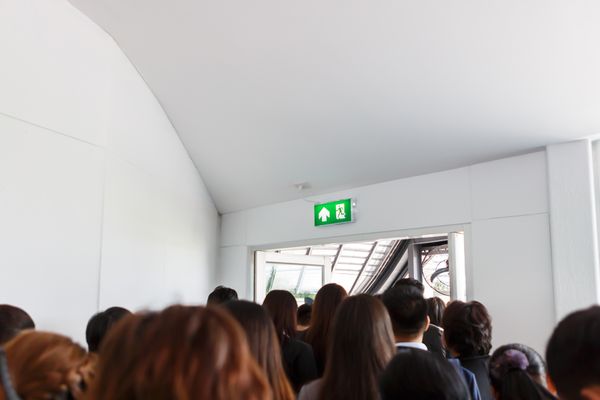

Evacuation was difficult
- Evacuation was difficult because the flooding happened so fast.
- 100 people were airlifted to safety.
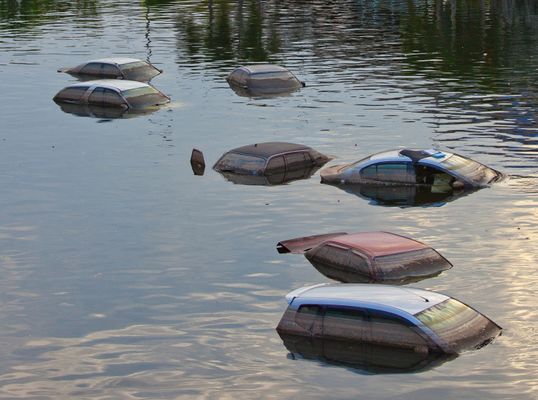

Environmental pollution
- Environmental pollution happened as a result of about 150 cars being transported by the floodwater into the sea. 30 cars were swept out to sea.
- 1,850 tonnes of flood debris were recovered from the surrounding area.

Illness and injury
- Nobody was seriously injured. Most of the harm was due to stress and mental health.
1 Geography Skills
1.1 Mapping
1.1.1 Map Making
1.1.2 OS Maps
1.1.3 Grid References
1.1.4 Contour Lines
1.1.5 Symbols, Scale and Distance
1.1.6 Directions on Maps
1.1.7 Describing Routes
1.1.8 Map Projections
1.1.9 Aerial & Satellite Images
1.1.10 Using Maps to Make Decisions
1.2 Geographical Information Systems
1.2.1 Geographical Information Systems
1.2.2 How do Geographical Information Systems Work?
1.2.3 Using Geographical Information Systems
1.2.4 End of Topic Test - Geography Skills
2 Geology of the UK
2.1 The UK's Rocks
2.1.1 The UK's Main Rock Types
2.1.2 The UK's Landscape
2.1.3 Using Rocks
2.1.4 Weathering
2.2 Case Study: The Peak District
2.2.1 The Peak District
2.2.2 Limestone Landforms
2.2.3 Quarrying
3 Geography of the World
3.1 Geography of America & Europe
3.1.1 North America
3.1.2 South America
3.1.3 Europe
3.1.4 The European Union
3.1.5 The Continents
3.1.6 The Oceans
3.1.7 Longitude
3.1.8 Latitude
3.1.9 End of Topic Test - Geography of the World
4 Development
4.1 Development
4.1.1 Classifying Development
4.1.3 Evaluation of GDP
4.1.4 The Human Development Index
4.1.5 Population Structure
4.1.6 Developing Countries
4.1.7 Emerging Countries
4.1.8 Developed Countries
4.1.9 Comparing Development
4.2 Uneven Development
4.2.1 Consequences of Uneven Development
4.2.2 Physical Factors Affecting Development
4.2.3 Historic Factors Affecting Development
4.2.4 Human & Social Factors Affecting Development
4.2.5 Breaking Out of the Poverty Cycle
4.3 Case Study: Democratic Republic of Congo
4.3.1 The DRC: An Overview
4.3.2 Political & Social Factors Affecting Development
4.3.3 Environmental Factors Affecting the DRC
4.3.4 The DRC: Aid
4.3.5 The Pros & Cons of Aid in DRC
4.3.6 Top-Down vs Bottom-Up in DRC
4.3.7 The DRC: Comparison with the UK
4.3.8 The DRC: Against Malaria Foundation
4.4 Case Study: Nigeria
4.4.1 The Importance & Development of Nigeria
4.4.2 Nigeria's Relationships with the Rest of the World
4.4.3 Urban Growth in Lagos
4.4.4 Population Growth in Lagos
4.4.5 Factors influencing Nigeria's Growth
4.4.6 Nigeria: Comparison with the UK
5 Weather & Climate
5.1 Weather
5.1.1 Weather & Climate
5.1.2 Components of Weather
5.1.3 Temperature
5.1.4 Sunshine, Humidity & Air Pressure
5.1.5 Cloud Cover
5.1.6 Precipitation
5.1.7 Convectional Precipitation
5.1.8 Frontal Precipitation
5.1.9 Relief or Orographic Precipitation
5.1.10 Wind
5.1.11 Extreme Wind
5.1.12 Recording the Weather
5.1.13 Extreme Weather
5.2 Climate
5.2.1 Climate of the British Isles
5.2.2 Comparing Weather & Climate London
5.2.3 Climate of the Tropical Rainforest
5.2.4 End of Topic Test - Weather & Climate
5.3 Tropical Storms
5.3.1 Formation of Tropical Storms
5.3.2 Features of Tropical Storms
5.3.3 The Structure of Tropical Storms
5.3.4 Tropical Storms Case Study: Katrina Effects
5.3.5 Tropical Storms Case Study: Katrina Responses
6 The World of Work
6.1 Tourism
6.1.1 Landscapes
6.1.2 The Growth of Tourism
6.1.3 Benefits of Tourism
6.1.4 Economic Costs of Tourism
6.1.5 Social, Cultural & Environmental Costs of Tourism
6.1.6 Tourism Case Study: Blackpool
6.1.7 Ecotourism
6.1.8 Tourism Case Study: Kenya
7 Natural Resources
7.1.1 What are Rocks?
7.1.2 Types of Rock
7.1.4 The Rock Cycle - Weathering
7.1.5 The Rock Cycle - Erosion
7.1.6 What is Soil?
7.1.7 Soil Profiles
7.1.8 Water
7.1.9 Global Water Demand
7.2 Fossil Fuels
7.2.1 Introduction to Fossil Fuels
7.2.2 Fossil Fuels
7.2.3 The Global Energy Supply
7.2.5 What is Peak Oil?
7.2.6 End of Topic Test - Natural Resources
8.1 River Processes & Landforms
8.1.1 Overview of Rivers
8.1.2 The Bradshaw Model
8.1.3 Erosion
8.1.4 Sediment Transport
8.1.5 River Deposition
8.1.6 River Profiles: Long Profiles
8.1.7 River Profiles: Cross Profiles
8.1.8 Waterfalls & Gorges
8.1.9 Interlocking Spurs
8.1.10 Meanders
8.1.11 Floodplains
8.1.12 Levees
8.1.13 Case Study: River Tees
8.2 Rivers & Flooding
8.2.1 Flood Risk Factors
8.2.2 Flood Management: Hard Engineering
8.2.3 Flood Management: Soft Engineering
8.2.4 Flooding Case Study: Boscastle
8.2.5 Flooding Case Study: Consequences of Boscastle
8.2.6 Flooding Case Study: Responses to Boscastle
8.2.7 Flooding Case Study: Bangladesh
8.2.8 End of Topic Test - Rivers
8.2.9 Rivers Case Study: The Nile
8.2.10 Rivers Case Study: The Mississippi
9.1 Formation of Coastal Landforms
9.1.1 Weathering
9.1.2 Erosion
9.1.3 Headlands & Bays
9.1.4 Caves, Arches & Stacks
9.1.5 Wave-Cut Platforms & Cliffs
9.1.6 Waves
9.1.7 Longshore Drift
9.1.8 Coastal Deposition
9.1.9 Spits, Bars & Sand Dunes
9.2 Coast Management
9.2.1 Management Strategies for Coastal Erosion
9.2.2 Case Study: The Holderness Coast
9.2.3 Case Study: Lyme Regis
9.2.4 End of Topic Test - Coasts
10 Glaciers
10.1 Overview of Glaciers & How They Work
10.1.1 Distribution of Glaciers
10.1.2 Types of Glaciers
10.1.3 The Last Ice Age
10.1.4 Formation & Movement of Glaciers
10.1.5 Shaping of Landscapes by Glaciers
10.1.6 Glacial Landforms Created by Erosion
10.1.7 Glacial Till & Outwash Plain
10.1.8 Moraines
10.1.9 Drumlins & Erratics
10.1.10 End of Topic Tests - Glaciers
10.1.11 Tourism in Glacial Landscapes
10.1.12 Strategies for Coping with Tourists
10.1.13 Case Study - Lake District: Tourism
10.1.14 Case Study - Lake District: Management
11 Tectonics
11.1 Continental Drift & Plate Tectonics
11.1.1 The Theory of Plate Tectonics
11.1.2 The Structure of the Earth
11.1.3 Tectonic Plates
11.1.4 Plate Margins
11.2 Volcanoes
11.2.1 Volcanoes & Their Products
11.2.2 The Development of Volcanoes
11.2.3 Living Near Volcanoes
11.3 Earthquakes
11.3.1 Overview of Earthquakes
11.3.2 Consequences of Earthquakes
11.3.3 Case Study: Christchurch, New Zealand Earthquake
11.4 Tsunamis
11.4.1 Formation of Tsunamis
11.4.2 Case Study: Japan 2010 Tsunami
11.5 Managing the Risk of Volcanoes & Earthquakes
11.5.1 Coping With Earthquakes & Volcanoes
11.5.2 End of Topic Test - Tectonics
12 Climate Change
12.1 The Causes & Consequences of Climate Change
12.1.1 Evidence for Climate Change
12.1.2 Natural Causes of Climate Change
12.1.3 Human Causes of Climate Change
12.1.4 The Greenhouse Effect
12.1.5 Effects of Climate Change on the Environment
12.1.6 Effects of Climate Change on People
12.1.7 Climate Change Predictions
12.1.8 Uncertainty About Future Climate Change
12.1.9 Mitigating Against Climate Change
12.1.10 Adapting to Climate Change
12.1.11 Case Study: Bangladesh
13 Global Population & Inequality
13.1 Global Populations
13.1.1 World Population
13.1.2 Population Structure
13.1.3 Ageing Populations
13.1.4 Youthful Populations
13.1.5 Population Control
13.1.6 Mexico to USA Migration
13.1.7 End of Topic Test - Development & Population
14 Urbanisation
14.1 Urbanisation
14.1.1 Rural Characterisitcs
14.1.2 Urban Characteristics
14.1.3 Urbanisation Growth
14.1.4 The Land Use Model
14.1.5 Rural-Urban Pull Factors
14.1.6 Rural-Urban Push Factors
14.1.7 The Impacts of Migration
14.1.8 Challenges of Urban Areas in Developed Countries
14.1.9 Challenges of Urban Areas in Developing Countries
14.1.10 Urban Sustainability
14.1.11 Case Study: China's Urbanisation
14.1.12 Major UK Cities
14.1.13 Urbanisation in the UK
14.1.14 End of Topic Test- Urbanisation
14.1.15 End of Topic Test - Urban Issues
15 Ecosystems
15.1 The Major Biomes
15.1.1 Distribution of Major Biomes
15.1.2 What Affects the Distribution of Biomes?
15.1.3 Biome Features: Tropical Forests
15.1.4 Biome Features: Temperate Forests
15.1.5 Biome Features: Tundra
15.1.6 Biome Features: Deserts
15.1.7 Biome Features: Tropical Grasslands
15.1.8 Biome Features: Temperate Grasslands
15.2 Case Study: The Amazon Rainforest
15.2.1 Interdependence of Rainforest Ecosystems
15.2.2 Nutrient Cycling in Tropical Rainforests
15.2.3 Deforestation in the Amazon
15.2.4 Impacts of Deforestation in the Amazon
15.2.5 Protecting the Amazon
15.2.6 Adaptations of Plants to Rainforests
15.2.7 Adaptations of Animals to Rainforests
16 Life in an Emerging Country
16.1 Case Studies
16.1.1 Mumbai: Opportunities
16.1.2 Mumbai: Challenges
17 Analysis of Africa
17.1 Africa
17.1.1 Desert Biomes in Africa
17.1.2 The Semi-Desert Biome
17.1.3 The Savanna Biome
17.1.4 Overview of Tropical Rainforests
17.1.5 Colonisation History
17.1.6 Population Distribution in Africa
17.1.7 Economic Resources in Africa
17.1.8 Urbanisation in Africa
17.1.9 Africa's Location
17.1.10 Physical Geography of Africa
17.1.11 Desertification in Africa
17.1.12 Reducing the Risk of Desertification
17.1.13 Case Study: The Sahara Desert - Opportunities
17.1.14 Case Study: The Sahara Desert - Development
18 Analysis of India
18.1 India - Physical Geography
18.1.1 Geographical Location of India
18.1.2 Physical Geography of India
18.1.3 India's Climate
18.1.4 Natural Disasters in India
18.1.5 Case Study: The Thar Desert
18.1.6 Case Study: The Thar Desert - Challenges
18.2 India - Human Geography
18.2.1 Population Distribution in India
18.2.2 Urabinsation in India
18.2.3 The History of India
18.2.4 Economic Resources in India
19 Analysis of the Middle East
19.1 The Middle East
19.1.1 Physical Geography of the Middle East
19.1.2 Human Geography of the Middle East
19.1.3 Climate Zones in the Middle East
19.1.4 Climate Comparison with the UK
19.1.5 Oil & Natural Gas in the Middle East
19.1.6 Water in the Middle East
19.1.7 Population of the Middle East
19.1.8 Development Case Studies: The UAE
19.1.9 Development Case Studies: Yemen
19.1.10 Supporting Development in Yemen
19.1.11 Connection to the UK
19.1.12 Importance of Oil
19.1.13 Oil & Tourism in the UAE
20 Analysis of Bangladesh
20.1 Bangladesh Physical Geography
20.1.1 Location of Bangladesh
20.1.2 Climate of Bangladesh
20.1.3 Rivers in Bangladesh
20.1.4 Flooding in Bangladesh
20.2 Bangladesh Human Geography
20.2.1 Population Structure in Bangladesh
20.2.2 Urbanisation in Bangladesh
20.2.3 Bangladesh's Economy
20.2.4 Energy & Sustainability in Bangladesh
21 Analysis of Russia
21.1 Russia's Physical Geography
21.1.1 Russia's Climate
21.1.2 Russia's Landscape
21.2 Russia's Human Geography
21.2.1 Population of Russia
21.2.2 Russia's Economy
21.2.3 Energy & Sustainability in Russia
Jump to other topics

Unlock your full potential with GoStudent tutoring
Affordable 1:1 tutoring from the comfort of your home
Tutors are matched to your specific learning needs
30+ school subjects covered
Flooding Case Study: Boscastle
Flooding Case Study: Responses to Boscastle

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Boscastle Case Study GCSE. On the 16th of August 2004 Boscastle was hit by a flash flood due to extreme rainfall - 200mm of rain fell in 24 hours.
Floods Devastate Village. On 16 August 2004, a devastating flood swept through the small Cornish village of Boscastle. Very heavy rain fell in storms close to the village, causing two rivers to burst their banks. About two billion litres of water then rushed down the valley straight into Boscastle.
Causes. Approximately 200 mm of rain fell in 24 hours. The ground was saturated from previous rain storms i.e. a short lag time. The drainage basin has steep slopes. The drainage basin has areas of impermeable rock. Boscastle is at the confluence of three rivers. The flooding coincided with a high tide.
Floods Case Study Boscastle Basic Facts and Figures Flood event began at 5.00pm on Monday 16th August 2004 185mm rain fell over a period of 8 hours over the 20 sq km (7.7sq miles) catchment area. Remnants of Hurricane Alex. Rain fell on ground already saturated reducing infiltration The Rivers Valency and Jordon meet in Boscastle and these rose ...
We used this study to advise North Cornwall District ... case the powers lie with North Cornwall District Council. Environment Agency The floods in Boscastle and North Cornwall August 2004 05. ... A contemporary account details the Boscastle flood of 28 October 1827: 'The whole street was filled with a ...
The first rainfall was recorded above Boscastle at about 12.30 p.m., with heavy rainfall over a concentrated area falling for the next hours. It is estimated that 1,422 million litres of rain fell in just two hours, with some areas in North Cornwall recording 200+ mm of rainfall between 11.00 a.m. and 6.00 p.m.
case today. Boscastle, too, will be restored, with some essential adjustments, largely within a few months of the flood event itself. The settlement of Boscastle Boscastle is a small village on the north Cornish coast (Figure 1). Lying at the mouth of the River Valency, it is surrounded by fairly steep, often wooded slopes. Just upstream from the
The 2004 Boscastle flood ... Boscastle flood study findings (Environment Agency, 12 January 2005) Boscastle Flood Rescue operation helis.com database operations page; UK Floods-Case studies of causes and effects and flooding policies, Boscastle Flood- 16 August 2004 (subscription required)
On the day of the flood, about 75mm of rain fell in two hours - the same amount that normally falls in the whole of August. Huge amounts of water from this sudden downpour flowed into two rivers, the Valency and Jordan (which flows into the Valency just above Boscastle). Both overflowed, and this caused a sudden rush of water to speed down the ...
The 2004 Boscastle flash flood, in the U.K. was selected as a typical case study. Firstly, the appropriateness of the " simplification strategy " was investigated, as a flood risk assessment tool ...
Extra notes for teachers supporting teaching of the Boscastle case study The Boscastle flood carries an important lesson - human societies should expect that unexpected things will sometimes happen. Rounding off teaching of this first part of the Unit, encourage students to think about reasons why, as a society, we can't always
The Boscastle flood: Meteorological analysis of the conditions leading to flooding on 16 August 2004. Brian Golding, Corresponding Author. Brian Golding ... PDF. Tools. Request permission; Export citation; Add to favorites; Track citation; Share Share. Give access. Share full text access.
Boscastle Flood - On the 16th August 2004, a devastating flood swept through Boscastle, a small village on the north Cornwall coast. Very heavy rain fell in storms close to the village, with over 60mm of rainfall in two hours. ... The Great Floods of 2000; Kerala flood case study; Rocks, Resources and Scenery. Geological time is on a different ...
Boscastle Flood Case Study - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
Boscastle is a small coastal settlement in the south west of England. It flooded in August 2004, washing cars and buildings into the sea and putting peoples' lives in danger. £4.5 million has ...
This paper reflects on the implications of the findings of the studies for dam engineers. Whilst the floods affected both the Valency/Jordan and Crackington catchments, this paper concentrates on the Valency/Jordan catchment only. THE CATCHMENT Figure 1 shows the geographical location of the Valency river and its tributaries above Boscastle ...
Effects. 50 cars were swept into the harbour. The bridge was washed away and roads were submerged under 2.75 m of water, making communication difficult. The sewerage system burst. For health and safety reasons Boscastle was declared inaccessible. The Museum of Withcraft lost 50 per cent of its artefacts.
Boscastle. Boscastle 2004 MEDC Floods. Geography case study. 1. BOSCASTLE MEDC FLOODING- CAUSES/EFFECTS AND MANAGEMENT STRAGIES Causes:Physical -Stormy weather up to flood meant saturated ground -Steep saturated sides of Valency Valley meant increased surface run off and therefore discharge volume -Impermeable rock at Bodmin moor prevented ...
The flood management scheme cost over £4 million, but the scheme isn't as good as it could be -some options were still considered too expensive. The new defences have made Boscastle a safer place to live in. The defences will only protect against a 1 in 75 year flood -they won't prevent flooding of the same size as the 2004 flood. The
The boscastle flood (August 2004) - case study. The document summarizes information about the 2004 Boscastle flood in Cornwall, England. Heavy rainfall of 185mm in 5 hours caused the rivers Valency and Jordan to flood the village. The steep sides and lack of floodplains meant surface runoff rapidly increased.
Boscastle Case Study - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
Illness and injury. Nobody was seriously injured. Most of the harm was due to stress and mental health. There were immediate and long-term consequences of the Boscastle flash flood that happened on 16th August, 2004. These consequences included:
The flood on 16 August 2004 in Boscastle in Cornwall was the worst in local memory and an Environment Agency report concluded that it was among the most extreme ever experienced in Britain. There was a combination of human and physical causes contributing to a series of effects and impacts. The responses to the flood were both short and long term.