Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., how to write a successful book chapter for..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, what is academic writing: tips for students, why traditional editorial process needs an upgrade.
Literature Reviews
- Introduction: What, Who & Why
- Define a topic
- Identify keywords
Identifying keywords
Comprehesive vs precise, using text mining to identify keywords.
- More search tips
- Understand & Analyse
- More resources
- Accessing help
- Systematic Style Reviews Guide
It is important to find all the relevant keywords for the topic to ensure the search is comprehensive by identifying:
- different spellings, tenses and word variants of keywords
- related concepts
- names of people or authors associated with these ideas
There are many ways to locate these terms, including
- recommended readings, textbooks and other review articles that provide an overview of the field of research
- dictionaries, thesauri, handbooks and encyclopedias that provide definitions and general information about topics.
- database thesauri or subject headings that tell you which terms are used in the databases and professional literature.
- text mining tools that allow you to analyse large amounts of text or information and identify commonly used terms in the field.
The process of searching will also help identify more terms that you should be adding to your list.
There needs to be a balance in searching between making the search comprehensive enough to encompass everything on the topic and precise enough to only capture those results that are specifically relevant.
Both approaches have advantages and disadvantages
Increasing the comprehensiveness (or sensitivity) of a search will reduce its precision and will retrieve more non-relevant articles.
Text mining will help identify how often terms come up in the literature and help identify other related terms and subject headings that have not been considered or thought of as being useful.
Text mining is a process used to look at large amounts of text and find relationships in the results by using computer programs designed to extract and analyse this data.
It is used to categorise information and identify trends and patterns which can be done across large documents or multiple sources (or both).
1. Mining for terms Use these tools to find alternate search terms that are related by identifying how often keywords appear and which other terms appear with them by number of occurrences.
2. Mine within the text Locate terms within blocks of text (e.g. an article) to find word patterns and frequency. More frequent words are more likely to be relevant to the topic.
3. Use visualising tools These tools create word clouds related to search terms
These are just some of the tools available for mining text that are available on the web. There is also both commercial and free software that can be downloaded and installed. The web pages linked below have lists of yet more tools.
Further reading:
- EPC Methods: An Exploration of the Use of Text-Mining Software in Systematic Reviews Paynter R., Bañez L. L., Berliner E., Erinoff, E., Lege-Matsuura, J., Potter, S., & Uhl, S. (2016). EPC methods: An exploration of the use of text-mining software in systematic reviews. Retrieved from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK362044/
- << Previous: Search the literature
- Next: More search tips >>
- Last Updated: Apr 26, 2024 10:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.jcu.edu.au/litreview

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.

Literature Reviews
- Steps to Writing a Lit Review
- Topic Selection
Suggested Tutorials
Identifying keywords & search terms, keyword tips, link keywords effectively (boolean searching), what are keywords, resources for instructors.
- Advanced Search Techniques
- Government Information
- Find Images This link opens in a new window
- News & Journalism
- Evaluating Information Sources This link opens in a new window
- Citation Style Help This link opens in a new window
- Citation Management

Email Us
Icons from Font Awesome under CC 4.0 Attribution License
- Identifying Keywords
- Choosing and Using Keywords: Credo Tutorial
Identify Keywords
To identify keywords, first start by writing out your research statement or question. Then follow these steps:
- Start by writing your research question, or thesis statement.
- Example: Are social media users concerned about their personal privacy ?
- NOTE: You can always add in search terms later, so try starting with fewer terms.
- Example synonyms: concern, worry

Searching with keywords
Example search: ( "Social Media" OR "social network") AND (privacy OR "personal privacy") AND (concern OR worry)
· As you search you may find more -or better- keywords & synonyms to use, or different spellings... play around with keywords and different combinations to see what is most useful
· Use AND to link different concepts and keywords together
· Use OR to group synonyms, or similar concepts together in parentheses
· Use quotation marks to search for specific phrases , or key words with two or more words
- Try different search terms
- Go into Advanced Search to search by topic, such as "nuclear power," then create another subject box to add a second term of "history" or other terms that make sense for your interest.
- Most databases will allow you to check various boxes to manipulate your search terms (dates of publication, types of sources, whether or not there are illustrations, etc.).
- Try popular terms such as "fracking"
- See if the catalog leads you to a formal term, such as "hydraulic fracturing."
- If nothing comes up for your term, search a basic database such as Academic Search Complete or look around in Google or even Wikipedia to see if you can find some alternative terms to use.
- Perform an initial search in CatSearch. From the results page, explore subject categories on the right
Boolean operators are words you use to link your search terms together when searching for resources.
Use them to increase or decrease the number of search results to find what you need
Unlike Google and other web searches, databases work best when you enter keywords instead of full phrases or questions.
- Keywords represent the major concepts of your topic
- Learn new vocabulary or keywords from your initial search results
- Try variations of a keyword, or synonyms.
- When you find a worthy source, get additional keywords from the title, abstract, and subject headings.
Identifying main concepts within your research question/topic.
Research Question: How does lack of access to food effect child development?
Main Concepts: lack of access to food, child development (words like how, does, and, to, etc. are not important)
There are a few types of keywords that you can work with, depending on your topic.
- Narrow - can you use a more focused word or idea? (ex. brain development, physical health)
- Broad - what is the big picture idea behind your topic? (ex. Wellness, Health)
- Related - are there concepts that closely relate to your topic? (ex. hunger, nutrition)
- Similar - are there synonyms for your topic/concepts? (ex. hunger, food insecurity, food security, food desert)
- Instructor Resources for Teaching Research Lesson plans, activities, suggested tutorials, and handouts for each part of the research process. Resources are included for both in person, and online asynchronous classes.
- Neurodiversity Teaching Strategies
- << Previous: Topic Selection
- Next: Search for Articles, Books, & More >>
- Last Updated: Mar 19, 2024 8:27 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.montana.edu/literaturereviews

Accessibility Statement
Literature review: your definitive guide

Joanna Wilkinson
This is our ultimate guide on how to write a narrative literature review. It forms part of our Research Smarter series .
How do you write a narrative literature review?
Researchers worldwide are increasingly reliant on literature reviews. That’s because review articles provide you with a broad picture of the field, and help to synthesize published research that’s expanding at a rapid pace .
In some academic fields, researchers publish more literature reviews than original research papers. The graph below shows the substantial growth of narrative literature reviews in the Web of Science™, alongside the percentage increase of reviews when compared to all document types.
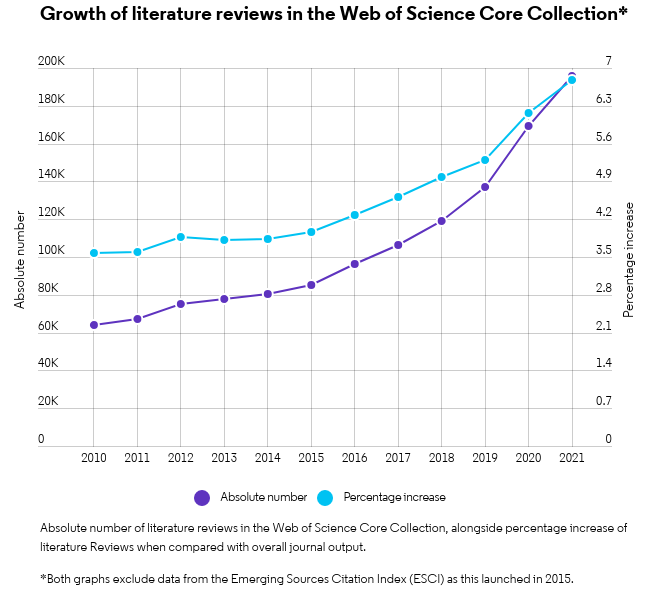
It’s critical that researchers across all career levels understand how to produce an objective, critical summary of published research. This is no easy feat, but a necessary one. Professionally constructed literature reviews – whether written by a student in class or an experienced researcher for publication – should aim to add to the literature rather than detract from it.
To help you write a narrative literature review, we’ve put together some top tips in this blog post.
Best practice tips to write a narrative literature review:
- Don’t miss a paper: tips for a thorough topic search
- Identify key papers (and know how to use them)
- Tips for working with co-authors
- Find the right journal for your literature review using actual data
- Discover literature review examples and templates
We’ll also provide an overview of all the products helpful for your next narrative review, including the Web of Science, EndNote™ and Journal Citation Reports™.
1. Don’t miss a paper: tips for a thorough topic search
Once you’ve settled on your research question, coming up with a good set of keywords to find papers on your topic can be daunting. This isn’t surprising. Put simply, if you fail to include a relevant paper when you write a narrative literature review, the omission will probably get picked up by your professor or peer reviewers. The end result will likely be a low mark or an unpublished manuscript, neither of which will do justice to your many months of hard work.
Research databases and search engines are an integral part of any literature search. It’s important you utilize as many options available through your library as possible. This will help you search an entire discipline (as well as across disciplines) for a thorough narrative review.
We provide a short summary of the various databases and search engines in an earlier Research Smarter blog . These include the Web of Science , Science.gov and the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ).
Like what you see? Share it with others on Twitter:
[bctt tweet=”Writing a #LiteratureReview? Check out the latest @clarivateAG blog for top tips (from topic searches to working with coauthors), examples, templates and more”]
Searching the Web of Science
The Web of Science is a multidisciplinary research engine that contains over 170 million papers from more than 250 academic disciplines. All of the papers in the database are interconnected via citations. That means once you get started with your keyword search, you can follow the trail of cited and citing papers to efficiently find all the relevant literature. This is a great way to ensure you’re not missing anything important when you write a narrative literature review.
We recommend starting your search in the Web of Science Core Collection™. This database covers more than 21,000 carefully selected journals. It is a trusted source to find research papers, and discover top authors and journals (read more about its coverage here ).
Learn more about exploring the Core Collection in our blog, How to find research papers: five tips every researcher should know . Our blog covers various tips, including how to:
- Perform a topic search (and select your keywords)
- Explore the citation network
- Refine your results (refining your search results by reviews, for example, will help you avoid duplication of work, as well as identify trends and gaps in the literature)
- Save your search and set up email alerts
Try our tips on the Web of Science now.
2. Identify key papers (and know how to use them)
As you explore the Web of Science, you may notice that certain papers are marked as “Highly Cited.” These papers can play a significant role when you write a narrative literature review.
Highly Cited papers are recently published papers getting the most attention in your field right now. They form the top 1% of papers based on the number of citations received, compared to other papers published in the same field in the same year.
You will want to identify Highly Cited research as a group of papers. This group will help guide your analysis of the future of the field and opportunities for future research. This is an important component of your conclusion.
Writing reviews is hard work…[it] not only organizes published papers, but also positions t hem in the academic process and presents the future direction. Prof. Susumu Kitagawa, Highly Cited Researcher, Kyoto University
3. Tips for working with co-authors
Writing a narrative review on your own is hard, but it can be even more challenging if you’re collaborating with a team, especially if your coauthors are working across multiple locations. Luckily, reference management software can improve the coordination between you and your co-authors—both around the department and around the world.
We’ve written about how to use EndNote’s Cite While You Write feature, which will help you save hundreds of hours when writing research . Here, we discuss the features that give you greater ease and control when collaborating with your colleagues.
Use EndNote for narrative reviews
Sharing references is essential for successful collaboration. With EndNote, you can store and share as many references, documents and files as you need with up to 100 people using the software.
You can share simultaneous access to one reference library, regardless of your colleague’s location or organization. You can also choose the type of access each user has on an individual basis. For example, Read-Write access means a select colleague can add and delete references, annotate PDF articles and create custom groups. They’ll also be able to see up to 500 of the team’s most recent changes to the reference library. Read-only is also an option for individuals who don’t need that level of access.
EndNote helps you overcome research limitations by synchronizing library changes every 15 minutes. That means your team can stay up-to-date at any time of the day, supporting an easier, more successful collaboration.
Start your free EndNote trial today .
4.Finding a journal for your literature review
Finding the right journal for your literature review can be a particular pain point for those of you who want to publish. The expansion of scholarly journals has made the task extremely difficult, and can potentially delay the publication of your work by many months.
We’ve written a blog about how you can find the right journal for your manuscript using a rich array of data. You can read our blog here , or head straight to Endnote’s Manuscript Matcher or Journal Citation Report s to try out the best tools for the job.
5. Discover literature review examples and templates
There are a few tips we haven’t covered in this blog, including how to decide on an area of research, develop an interesting storyline, and highlight gaps in the literature. We’ve listed a few blogs here that might help you with this, alongside some literature review examples and outlines to get you started.
Literature Review examples:
- Aggregation-induced emission
- Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering
- Object based image analysis for remote sensing
(Make sure you download the free EndNote™ Click browser plugin to access the full-text PDFs).
Templates and outlines:
- Learn how to write a review of literature , Univ. of Wisconsin – Madison
- Structuring a literature review , Australian National University
- Matrix Method for Literature Review: The Review Matrix , Duquesne University
Additional resources:
- Ten simple rules for writing a literature review , Editor, PLoS Computational Biology
- Video: How to write a literature review , UC San Diego Psychology
Related posts
Reimagining research impact: introducing web of science research intelligence.

Beyond discovery: AI and the future of the Web of Science

Clarivate welcomes the Barcelona Declaration on Open Research Information

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
- Subject guides
- Researching for your literature review
- Develop a search strategy
Researching for your literature review: Develop a search strategy
- Literature reviews
- Literature sources
- Before you start
- Keyword search activity
- Subject search activity
- Combined keyword and subject searching
- Online tutorials
- Apply search limits
- Run a search in different databases
- Supplementary searching
- Save your searches
- Manage results
Identify key terms and concepts
Start developing a search strategy by identifying the key words and concepts within your research question.
For example: How do s t udents view inclusive educational practices in schools ?
Treat each component as a separate concept (there are usually between 2-4 concepts).
For each concept list the key words derived from your research question, as well as any other relevant terms or synonyms that you have found in your preliminary searches. Also consider singular and plural forms of words, variant spellings, acronyms and relevant index terms (subject headings).
As part of the process of developing a search strategy, it is recommended that you keep a master list of search terms for each key concept. This will make it easier when it comes to translating your search strategy across multiple database platforms.
Concept map template for documenting search terms
Combine search terms and concepts
Boolean operators are used to combine the different concepts in your topic to form a search strategy. The main operators used to connect your terms are AND and OR . See an explanation below:
- Link keywords related to a single concept with OR
- Linking with OR broadens a search (increases the number of results) by searching for any of the alternative keywords
Example: perspective OR attitude
- Link different concepts with AND
- Linking with AND narrows a search (reduces the number of results) by retrieving only those records that include all of your specified keywords
Example: inclusive education AND student perspective
- using NOT narrows a search by excluding certain search terms
- Most searches do not require the use of the NOT operator
Example: education NOT higher education will retrieve all results that include the word education but don’t contain the phrase higher education .
See the website for venn diagrams demonstrating the function of AND/OR/NOT:
Combine the search terms using Boolean
Advanced search operators - truncation and wildcards
Use symbols to retrieve word variations:
The truncation symbol is commonly an asterisk * and is added at the end of a word.
- The asterisk applied to the root of a word captures other endings to that root word making it useful for retrieving singular, plural and other variations of a keyword.
Example: educat * will retrieve educat ion, educat ors, educat ional , etc
Note: If you don't want to retrieve all possible variations, an easy alternative is to utilise the OR operator instead e.g. education OR educational.
The wildcard symbols include the question mark ? and hash #. They replace zero, one or more characters in the middle of a word.
Example: wom # n finds woman or women, behavio ? r finds behaviour or behavior.
The symbols may vary in different databases - See the Database search tips guide for details or check the Help link in any database.

Phrase searching
Use quotes to keep word order when searching for phrases.
For phrase searching, place two or more words in "inverted commas" or "quote marks".
Example: “inclusive education”
In some databases, words may be searched separately if the quote marks are not used. In other databases, word order may be maintained without the need for quote marks.
See the Database search tips for details on phrase searching in key databases, or check the Help link in any database.
Subject headings (index terms)
Identify appropriate subject headings (index terms).
Many databases use subject headings to index content. These are selected from a controlled list and describe what the article is about.
A comprehensive search strategy is often best achieved by using a combination of keywords and subject headings where possible.
In-depth knowledge of subject headings is not required for users to benefit from improved search performance using them in their searches.
Advantages of subject searching:
- Helps locate articles that use synonyms, variant spellings, plurals
- Search terms don’t have to appear in the title or abstract
Note: Subject headings are often unique to a particular database, so you will need to look for appropriate subject headings in each database you intend to use.
Subject headings are not available for every topic, and it is best to only select them if they relate closely to your area of interest.
Create a gold set
It is useful to build a ‘sample set’ or ‘gold set’ of relevant references before you develop your search strategy. .
Sources for a 'gold set' may include:
- key papers recommended by subject experts or supervisors
- citation searching - looking at a reference list to see who has been cited, or using a citation database (eg. Scopus, Web of Science) to see who has cited a known relevant article
- results of preliminary scoping searches.
The papers in your 'gold set' can then be used to help you identify relevant search terms
- Look up your 'sample set' articles in a database that you will use for your literature review. For the articles indexed in the database, look at the records to see what keywords and/or subject headings are listed.
The 'gold set' will also provide a means of testing your search strategy
- When an indexed article is not retrieved, your search strategy can be revised in order to include it (see what concepts or keywords can be incorporated into your search strategy so that the article is retrieved).
- If your search strategy is retrieving a lot of irrelevant results, look at the irrelevant records to determine why they are being retrieved. What keywords or subject headings are causing them to appear? Can you change these without losing any relevant articles from your results?
Example search strategy
An example of a search strategy incorporating all three concepts that could be applied to different databases is shown below:.

The above search strategy in a nested format (for use in a single search box) would look like:
(student* OR pupil* OR "young people" OR learner*) AND (perception* OR experience OR voice OR perspective*) AND (inclusi* OR "special education" OR belonging OR disabilit*)
- << Previous: Search strategies - Education/Social sciences topic example
- Next: Keyword search activity >>
Conducting a Literature Review
- Getting Started
- Developing a Question
- Searching the Literature
- Identifying Peer-Reviewed Resources
- Managing Results
- Analyzing the Literature
- Writing the Review
Need Help? Ask Your librarian!

Search Strategies
- Boolean Operators
Once you have identified the key concepts of your research question (see "Developing a Question"), you can use those concepts to develop keywords for your search strategy. The following tips and techniques will help you design a precise and relevant search strategy.
Keywords are any words you might use to search the record of an article, book, or other material in library databases. The database searches through the metadata (such as title, authors, publication, abstract, etc.) to find resources that contain the word you searched, and may also search through the full text of the material.
Keywords are most successful when you're searching for the words that the authors use to describe the research topic, as most databases will search for those specific words within the record of the article. To increase your chance of returning relevant results, consider all of the words that might be used to describe the research you're trying to find, and try some of these out in sample searches to determine which words return the best results.
Search Tips - Keywords
- Search for singular and plural terms together: (physician OR physicians)
- Search for both the American and British spelling of words: (behavior OR behaviour)
- Search for synonyms of terms together: (teenager OR adolescent)
- Search for phrases inside of quotation marks: ("young adult")
Use Boolean operators to combine keywords for more precise search results.
AND - If the term must be included in your search:
influenza AND vaccine
OR - If terms are interchangeable, i.e. synonyms. Place OR'd terms within parentheses:
(influenza OR flu) AND vaccine
NOT - If a term should not be included in your search. This Boolean operator is rarely necessary for literature reviews.
(influenza OR flu) AND vaccine NOT H1N1
Note how we've used parentheses in the examples above. Search strings like these are similar to mathematical equations, where you perform the actions within the parentheses before proceeding from left to right to run the search. For example, using the search [(influenza OR flu) AND vaccine] will find results that have a term relating to influenza/flu, as well as the term vaccine.
If we moved the parentheses, it would be a very different search. [influenza OR (flu AND vaccine)] will provide results that use the term influenza, as well as results that use both the terms flu and vaccine. This means you would get results having to do with influenza but perhaps nothing to do with vaccination.
Here are a few examples of how this search would be different depending on the arrangement of booleans and keywords. The area highlighted in pink represents the search results that would be returned with this search.

Truncation allows you to quickly include all variations of a word in your search. Use the root of the keyword and add an asterisk (*). For example:
nurs* = nurse, nurses, nursing, nursery
IMPORTANT: Notice that "nursery" is also retrieved in the above search. Truncation will save you from having to include a large number of synonyms, but it will also add a certain number of irrelevant results. You can limit this effect by using the NOT Boolean operator, i.e. NOT nursery.
Wild cards allow you to replace a letter in a keyword to retrieve all variations of the spelling. For example:
p?ediatric = pediatric, paediatric
Free-Text vs. Thesaurus Searching
While you can search any word as a keyword, databases also contain an official list of the terms they use to describe the subject of each article, called Subject Headings. You can look up Subject Headings in the thesaurus of the database, using the thesaurus's search box to pull up the recommended Subject Heading for a given keyword. When searching specifically for Subject Headings, the database will only search the Subject Headings field within the record of each article (ie, not the title, abstract, etc.). This is a much more targeted method of searching, and is an excellent addition to your search strategy.
A strong search strategy will use both free-text (keyword) searching and thesaurus searching, to ensure that all relevant articles have been retrieved by the search. The lists below outline the strengths and weaknesses of both types of search strategies.
Free-Text Searching
- Natural language words describing your topic
- More flexible search strategy - can use any term in any combination
- Database looks for keywords anywhere in the record - not necessarily connected together
- May yield too many or too few results
- May yield many irrelevant results
Thesaurus Searching
- Pre-defined "controlled vocabulary" words used to describe the content of each item in a database
- Less flexible search strategy - need to know the exact controlled vocabulary term
- Database looks for subjects only in the subject heading or descriptor field, where the most relevant words appear
- If too many results, you can use subheadings to focus on one aspect of a broader topic
- Results are usually very relevant to the topic
MIT Libraries. Database Search Tips: Keywords vs. Subjects. https://libguides.mit.edu/c.php?g=175963&p=1160804
Each database has their own thesaurus. You will need to adapt your search strategy for each database to take advantage of their unique thesaurus.
PubMed uses MeSH terms (Medical Subject Headings). You can learn more about finding and using MeSH terms here:
- The Basics of Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) in MEDLINE/PubMed: A Tutorial
CINAHL uses CINAHL Headings. You can learn more about finding and use these terms here:
- Using CINAHL/MeSH Headings
In other databases, look for a link with the terms "headings", "subject headings", or "thesaurus" to find the appropriate thesaurus terms for your search.
Citation Searching
Citation searching is a search strategy that allows you to search either forward or backwards time through the literature based on an identified relevant article:
You can search forward in time by using databases that allow you to search for other articles that have cited the identified relevant article. (Web of Science and Google Scholar can do this automatically.)
- Web of Science (Clarivate Analytics)
- Google Scholar
You can search backward in time by reviewing the reference list of the identified relevant article for additional article citations.
For more information about how to perform citation searches, check out this guide from the University of Toledo Libraries:
- How To: Cited Reference Searches in Web of Science Guide from the University of Toledo
Retrieving Materials
Select a database.
When searching for articles, it is best to use an appropriate subject database rather than the SearchIT catalog. Be sure to select your database from the Spokane Academic Library homepage to ensure that you will have access to full-text articles.

"Find It @ WSU" Button in PubMed
When you have found an article that you would like to read in its entirety, look for the "Find It @ WSU" Button. This button will take you to the article entry in the SearchIT catalog.
Here's what that looks like in PubMed.

"Find It @ WSU" Button in CINAHL

"Find It @ WSU" Button in PsycINFO

Accessing the Full-Text Article
After selecting the "Find It @ WSU" Button, you will be taken to the article entry in SearchIT. Select the link under the Access Options box to be directed to the full-text article.

If an article is not available in the WSU Libraries collection, you can request the article through interlibrary loan by selecting the link under "Access Options".
See the Using Interlibrary Loan section for more information.

- << Previous: Developing a Question
- Next: Identifying Peer-Reviewed Resources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 16, 2024 3:40 PM
- URL: https://libguides.libraries.wsu.edu/litreview
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
How To Structure Your Literature Review
3 options to help structure your chapter.
By: Amy Rommelspacher (PhD) | Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | November 2020 (Updated May 2023)
Writing the literature review chapter can seem pretty daunting when you’re piecing together your dissertation or thesis. As we’ve discussed before , a good literature review needs to achieve a few very important objectives – it should:
- Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic
- Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these
- Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one)
- Inform your own methodology and research design
To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure . Get the structure of your literature review chapter wrong and you’ll struggle to achieve these objectives. Don’t worry though – in this post, we’ll look at how to structure your literature review for maximum impact (and marks!).

But wait – is this the right time?
Deciding on the structure of your literature review should come towards the end of the literature review process – after you have collected and digested the literature, but before you start writing the chapter.
In other words, you need to first develop a rich understanding of the literature before you even attempt to map out a structure. There’s no use trying to develop a structure before you’ve fully wrapped your head around the existing research.
Equally importantly, you need to have a structure in place before you start writing , or your literature review will most likely end up a rambling, disjointed mess.
Importantly, don’t feel that once you’ve defined a structure you can’t iterate on it. It’s perfectly natural to adjust as you engage in the writing process. As we’ve discussed before , writing is a way of developing your thinking, so it’s quite common for your thinking to change – and therefore, for your chapter structure to change – as you write.
Need a helping hand?
Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components – an introduction , a body and a conclusion .
Let’s take a closer look at each of these.
1: The Introduction Section
Just like any good introduction, the introduction section of your literature review should introduce the purpose and layout (organisation) of the chapter. In other words, your introduction needs to give the reader a taste of what’s to come, and how you’re going to lay that out. Essentially, you should provide the reader with a high-level roadmap of your chapter to give them a taste of the journey that lies ahead.
Here’s an example of the layout visualised in a literature review introduction:
Your introduction should also outline your topic (including any tricky terminology or jargon) and provide an explanation of the scope of your literature review – in other words, what you will and won’t be covering (the delimitations ). This helps ringfence your review and achieve a clear focus . The clearer and narrower your focus, the deeper you can dive into the topic (which is typically where the magic lies).
Depending on the nature of your project, you could also present your stance or point of view at this stage. In other words, after grappling with the literature you’ll have an opinion about what the trends and concerns are in the field as well as what’s lacking. The introduction section can then present these ideas so that it is clear to examiners that you’re aware of how your research connects with existing knowledge .

2: The Body Section
The body of your literature review is the centre of your work. This is where you’ll present, analyse, evaluate and synthesise the existing research. In other words, this is where you’re going to earn (or lose) the most marks. Therefore, it’s important to carefully think about how you will organise your discussion to present it in a clear way.
The body of your literature review should do just as the description of this chapter suggests. It should “review” the literature – in other words, identify, analyse, and synthesise it. So, when thinking about structuring your literature review, you need to think about which structural approach will provide the best “review” for your specific type of research and objectives (we’ll get to this shortly).
There are (broadly speaking) three options for organising your literature review.

Option 1: Chronological (according to date)
Organising the literature chronologically is one of the simplest ways to structure your literature review. You start with what was published first and work your way through the literature until you reach the work published most recently. Pretty straightforward.
The benefit of this option is that it makes it easy to discuss the developments and debates in the field as they emerged over time. Organising your literature chronologically also allows you to highlight how specific articles or pieces of work might have changed the course of the field – in other words, which research has had the most impact . Therefore, this approach is very useful when your research is aimed at understanding how the topic has unfolded over time and is often used by scholars in the field of history. That said, this approach can be utilised by anyone that wants to explore change over time .

For example , if a student of politics is investigating how the understanding of democracy has evolved over time, they could use the chronological approach to provide a narrative that demonstrates how this understanding has changed through the ages.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself to help you structure your literature review chronologically.
- What is the earliest literature published relating to this topic?
- How has the field changed over time? Why?
- What are the most recent discoveries/theories?
In some ways, chronology plays a part whichever way you decide to structure your literature review, because you will always, to a certain extent, be analysing how the literature has developed. However, with the chronological approach, the emphasis is very firmly on how the discussion has evolved over time , as opposed to how all the literature links together (which we’ll discuss next ).
Option 2: Thematic (grouped by theme)
The thematic approach to structuring a literature review means organising your literature by theme or category – for example, by independent variables (i.e. factors that have an impact on a specific outcome).
As you’ve been collecting and synthesising literature , you’ll likely have started seeing some themes or patterns emerging. You can then use these themes or patterns as a structure for your body discussion. The thematic approach is the most common approach and is useful for structuring literature reviews in most fields.
For example, if you were researching which factors contributed towards people trusting an organisation, you might find themes such as consumers’ perceptions of an organisation’s competence, benevolence and integrity. Structuring your literature review thematically would mean structuring your literature review’s body section to discuss each of these themes, one section at a time.

Here are some questions to ask yourself when structuring your literature review by themes:
- Are there any patterns that have come to light in the literature?
- What are the central themes and categories used by the researchers?
- Do I have enough evidence of these themes?
PS – you can see an example of a thematically structured literature review in our literature review sample walkthrough video here.
Option 3: Methodological
The methodological option is a way of structuring your literature review by the research methodologies used . In other words, organising your discussion based on the angle from which each piece of research was approached – for example, qualitative , quantitative or mixed methodologies.
Structuring your literature review by methodology can be useful if you are drawing research from a variety of disciplines and are critiquing different methodologies. The point of this approach is to question how existing research has been conducted, as opposed to what the conclusions and/or findings the research were.

For example, a sociologist might centre their research around critiquing specific fieldwork practices. Their literature review will then be a summary of the fieldwork methodologies used by different studies.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself when structuring your literature review according to methodology:
- Which methodologies have been utilised in this field?
- Which methodology is the most popular (and why)?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the various methodologies?
- How can the existing methodologies inform my own methodology?
3: The Conclusion Section
Once you’ve completed the body section of your literature review using one of the structural approaches we discussed above, you’ll need to “wrap up” your literature review and pull all the pieces together to set the direction for the rest of your dissertation or thesis.
The conclusion is where you’ll present the key findings of your literature review. In this section, you should emphasise the research that is especially important to your research questions and highlight the gaps that exist in the literature. Based on this, you need to make it clear what you will add to the literature – in other words, justify your own research by showing how it will help fill one or more of the gaps you just identified.
Last but not least, if it’s your intention to develop a conceptual framework for your dissertation or thesis, the conclusion section is a good place to present this.

Example: Thematically Structured Review
In the video below, we unpack a literature review chapter so that you can see an example of a thematically structure review in practice.
Let’s Recap
In this article, we’ve discussed how to structure your literature review for maximum impact. Here’s a quick recap of what you need to keep in mind when deciding on your literature review structure:
- Just like other chapters, your literature review needs a clear introduction , body and conclusion .
- The introduction section should provide an overview of what you will discuss in your literature review.
- The body section of your literature review can be organised by chronology , theme or methodology . The right structural approach depends on what you’re trying to achieve with your research.
- The conclusion section should draw together the key findings of your literature review and link them to your research questions.
If you’re ready to get started, be sure to download our free literature review template to fast-track your chapter outline.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

27 Comments
Great work. This is exactly what I was looking for and helps a lot together with your previous post on literature review. One last thing is missing: a link to a great literature chapter of an journal article (maybe with comments of the different sections in this review chapter). Do you know any great literature review chapters?
I agree with you Marin… A great piece
I agree with Marin. This would be quite helpful if you annotate a nicely structured literature from previously published research articles.
Awesome article for my research.
I thank you immensely for this wonderful guide
It is indeed thought and supportive work for the futurist researcher and students
Very educative and good time to get guide. Thank you
Great work, very insightful. Thank you.
Thanks for this wonderful presentation. My question is that do I put all the variables into a single conceptual framework or each hypothesis will have it own conceptual framework?
Thank you very much, very helpful
This is very educative and precise . Thank you very much for dropping this kind of write up .
Pheeww, so damn helpful, thank you for this informative piece.
I’m doing a research project topic ; stool analysis for parasitic worm (enteric) worm, how do I structure it, thanks.
comprehensive explanation. Help us by pasting the URL of some good “literature review” for better understanding.
great piece. thanks for the awesome explanation. it is really worth sharing. I have a little question, if anyone can help me out, which of the options in the body of literature can be best fit if you are writing an architectural thesis that deals with design?
I am doing a research on nanofluids how can l structure it?
Beautifully clear.nThank you!
Lucid! Thankyou!
Brilliant work, well understood, many thanks
I like how this was so clear with simple language 😊😊 thank you so much 😊 for these information 😊
Insightful. I was struggling to come up with a sensible literature review but this has been really helpful. Thank you!
You have given thought-provoking information about the review of the literature.
Thank you. It has made my own research better and to impart your work to students I teach
I learnt a lot from this teaching. It’s a great piece.
I am doing research on EFL teacher motivation for his/her job. How Can I structure it? Is there any detailed template, additional to this?
You are so cool! I do not think I’ve read through something like this before. So nice to find somebody with some genuine thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. thank you for starting this up. This site is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with a little originality!
I’m asked to do conceptual, theoretical and empirical literature, and i just don’t know how to structure it
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Literature Reviews & Search Strategies
- Defining the Literature Review
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Choosing Databases
Overview of Search Strategies
Search strategies, subject searching, example: iteratively developing + using keywords, demonstration: developing keywords from a question, demonstration: an advanced search.
- Organizing Your Literature
- Books: Research Design & Scholarly Writing
- Recommended Tutorials
There are many ways to find literature for your review, and we recommend that you use a combination of strategies - keeping in mind that you're going to be searching multiple times in a variety of ways, using different databases and resources. Searching the literature is not a straightforward, linear process - it's iterative (translation: you'll search multiple times, modifying your strategies as you go, and sometimes it'll be frustrating).
- Known Item Searching
- Citation Jumping
Some form of a keyword search is the way most of us get at scholarly articles in database - it's a great approach! Make sure you're familiar with these librarian strategies to get the most out of your searches.
Figuring out the best keywords for your research topic/question is a process - you'll start with one or a few words and then shift, adapt, and expand them as you start finding source that describe the topic using other words. Your search terms are the bridge between known topics and the unknowns of your research question - so sometimes one specific word will be enough, sometimes you'll need several different words to describe a concept AND you'll need to connect that concept to a second (and/or third) concept.
The number and specificity of your search terms depend on your topic and the scope of your literature review.
Connect Keywords Using Boolean
Make the database work more.
...uses the asterisk (*) to end a word at its core, allowing you to retrieve many more documents containing variations of the search term. Example: educat* will find educate, educates, education, educators, educating and more.
Phrase Searching
...is when you put quotations marks around two or more words, so that the database looks for those words in that exact order. Examples: "higher education," "public health" and "pharmaceutical industry."
Controlled Vocabulary
... is when you use the terms the database uses to describe what each article is about as search terms. Searching using controlled vocabularies is a great way to get at everything on a topic in a database.
Databases and search engines are probably going to bring back a lot of results - more than a human can realistically go through. Instead of trying to manually read and sort them all, use the filters in each database to remove the stuff you wouldn't use anyway (ie it's outside the scope of your project).
To make sure you're consistent between searches and databases, write down the filters you're using.
A Few Filters to Try
Once you know you have a good article , there are a lot of useful parts to it - far beyond the content.
Not sure where to start? Try course readings and other required materials.
Useful Parts of a Good Article
Ways to use citations.
- Interactive Tutorial: Searching Cited and Citing Practice starting your search at an article and using the references to gather additional sources.

Your search results don't have to be frozen in the moment you search! There are a few things you can set up to keep your search going automatically.
Searching using subject headings is a comprehensive search strategy that requires some planning and topic knowledge. Work through this PubMed tutorial for an introduction to this important approach to searching.

Through these videos and the accompanying PDF, you'll see an example of starting with a potential research question and developing search terms through brainstorming and keyword searching.
- Slidedeck: Keywords and Advanced Search PowerPoint slides to accompany the two demonstration videos on developing keywords from a question, and doing an advanced search.
- << Previous: Choosing Databases
- Next: Organizing Your Literature >>
- Last Updated: Jun 14, 2023 11:18 AM
- URL: https://mcphs.libguides.com/litreviews
- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Sample Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts
Have an exemplary literature review.
- Literature Review Sample 1
- Literature Review Sample 2
- Literature Review Sample 3
Have you written a stellar literature review you care to share for teaching purposes?
Are you an instructor who has received an exemplary literature review and have permission from the student to post?
Please contact Britt McGowan at [email protected] for inclusion in this guide. All disciplines welcome and encouraged.
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Mar 22, 2024 9:37 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview

Literature Review - Finding the Resources
- The Literature
- Search Tools
- Formulating your search statement
Keyword search
More search tips - 1, more search tips - 2.
- Buliding on what you have found
- Keeping Track
- Academic Reading
- Citing Sources
- The Learning Lounge
During your literature search, especially when you search for articles in databases, you will rely very much on keyword searching. To conduct a keyword search , you need to formulate a search statement .
Below are the basic steps to develop a search statement. After going through these steps, try to build up your own search statement using this worksheet [pdf]
Here is a diagram to help you understand:
1. Identify the keywords or the main concepts of your research topic.
- For example, for the topic Globalization of Chinese companies , the keywords are Globalization , Chinese and Companies .
2. Think of similar terms (synonyms) or phrases that might also be used to describe these concepts, to ensure that you do not miss out any relevant information. You can use a thesaurus to help you find synonyms. For example, you can first arrange the main concepts in columns. Then under each column write down similar terms or phrases that may also be used to represent that concept:
3. Combine your search terms in a way that a database can understand. To do this, you need to use the words AND , OR , NOT (Boolean operators).
- AND combines different concepts (e.g. Globalization and Chinese listed in different columns of the table above are different concepts).
- OR combines similar concepts (e.g. Chinese and China listed in the same column above are similar concepts).
- NOT excludes the undesirable concepts
4. Make use of truncation, wildcards, parentheses and phrase searching for more productive searching. Symbols commonly used in many search tools including catalogues and databases are:
5. A search statement can then be developed
e.g. Globali?ation AND (Chinese OR China) AND (Compan* OR Corporat* OR Firm*)
Use a form (sometimes called "Quick Search", "Advanced Search" or "Form Search") to search if possible.
For example, this is more user-friendly
When necessary, in order to make the search more focused, limit the search by
- Specific search fields (e.g. journal titles, abstracts, subjects)
- Document types (e.g. scholarly articles, conferences)
- Year of publication, etc.
- << Previous: Search Techniques
- Next: Buliding on what you have found >>
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 4:25 PM
- URL: https://libguides.library.cityu.edu.hk/litreview
© City University of Hong Kong | Copyright | Disclaimer

How to do a Literature Search: Choosing keywords
- Introduction
- Choosing a database
- Choosing keywords
- Using keywords
- Author searching
- Managing your search/results
Choosing keywords: things to think about
It may be tempting to simply type the title of your project into the database search box, but this will not give you the best results! You need to carefully put together a search strategy taking into account the following:
- Endings of words
Abbreviations
American vs english spellings.
On this page we will look at these in turn. The following page will look at how to construct a search strategy.
A synonym is another word with the same meaning. The main problem with topic searching is that there are many words which different authors can use to describe the same topic. For example, if you are looking for articles about drug addiction an author could have used any of the following words or phrases: drug addiction, drug abuse, substance abuse, street drugs, narcotics, heroin use/abuse etc.
Ideally, you should use as many synonyms as possible in your search strategy, particularly if you're having difficulty finding enough information.
If you have difficulty thinking of synonyms, start with one article that is relevant to your topic and view the full record in the library database. It may provide added keywords that will help.
Word endings
Many Library databases, and Google, will automatically find a simple plural for you. For example if you type in drug many databases will search for drug or drugs . Some will attempt to find other word endings too, but with varying levels of success. For example if you type in drug addiction will the database also find articles with the phrase drug addict ? We recommend that you take account of different word endings in your search strategy.
Most databases use a special character to represent zero or any number of letters, called a truncation symbol. It is normally an asterisk *.
addict* will find addic t
addic ts
addic ted
addic tion
addic tions
Phrase searching
A phrase is two or more words linked together in a particular order, for example football match , social work . Most databases will allow you to search for a phrase, in other words to insist that your keywords appear next to each other in a specific order. Entering the phrase in double quotes " " will normally work, but check your specific database help guide to be certain. For example:
"General practitioner" will help you to find articles about GP practices. If you do not use quotes you could find articles on any type of practitioner, that just happen to have the commonly used word word 'general' in the title or abstract.
Is there a common abbreviation for your search topic? The author of an article may have used the abbreviation instead of the full term, so you need to look for both:
- GP or General Practitioner
- ADHD or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
- UFO or Unidentified Flying Object
Journals published in Europe will normally use UK English spellings but journals published in North America will use US English spellings. If you want to find all the articles, you need to take different spellings into account. Here are some common differences in spellings:
US English generally uses fewer vowels:
- Color / colour
- Fetus / foetus
- Archeology / archaeology
US English often uses 'z' where UK English uses 's' near the end of a word:
- Analyze / analyse
- Marketize / marketise
US English sometimes uses 'er' where UK English uses 're':
- Meter / metre
- Fiber / fibre
US English sometimes uses one L near the end of a word where UK English uses two:
- Labeled / labelled
- Canceled / cancelled

The reason is that the first image has been catalogued with the UK English word ' boot ' and the second one with the American English word ' trunk '. The only way to find both images is to search for both words.
Video: tips for keyword searching (04:38)
- << Previous: Choosing a database
- Next: Using keywords >>
- Last Updated: Nov 22, 2022 9:56 AM
- URL: https://library.bath.ac.uk/literaturesearch
15 Literature Review Examples
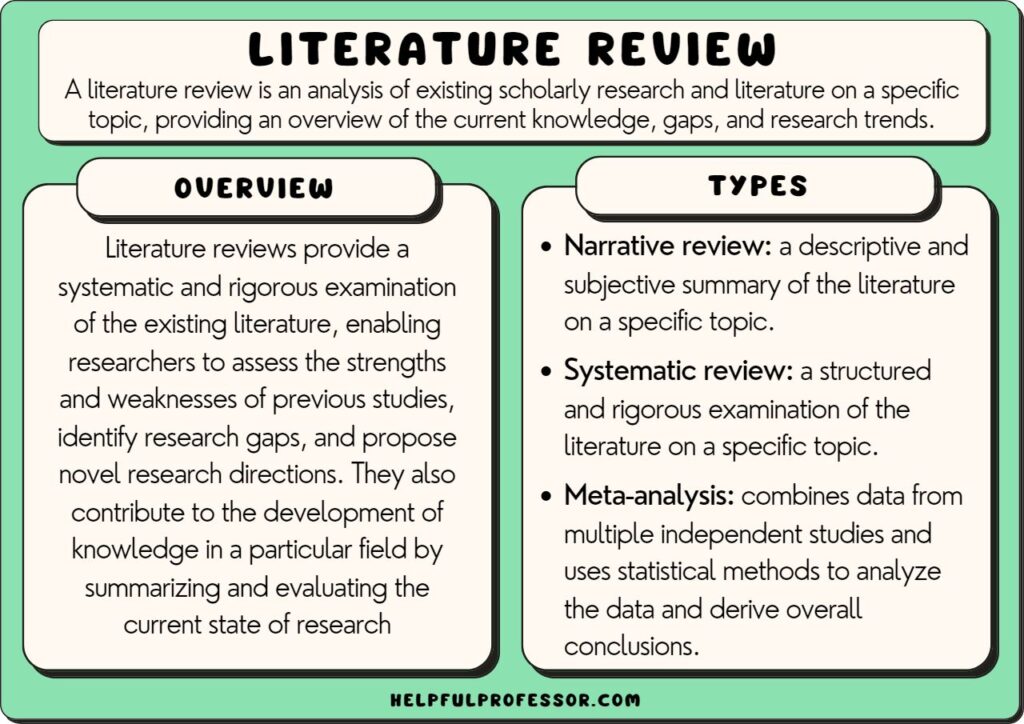
Literature reviews are a necessary step in a research process and often required when writing your research proposal . They involve gathering, analyzing, and evaluating existing knowledge about a topic in order to find gaps in the literature where future studies will be needed.
Ideally, once you have completed your literature review, you will be able to identify how your research project can build upon and extend existing knowledge in your area of study.
Generally, for my undergraduate research students, I recommend a narrative review, where themes can be generated in order for the students to develop sufficient understanding of the topic so they can build upon the themes using unique methods or novel research questions.
If you’re in the process of writing a literature review, I have developed a literature review template for you to use – it’s a huge time-saver and walks you through how to write a literature review step-by-step:
Get your time-saving templates here to write your own literature review.
Literature Review Examples
For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics.
1. Narrative Review Examples
Also known as a traditional literature review, the narrative review provides a broad overview of the studies done on a particular topic.
It often includes both qualitative and quantitative studies and may cover a wide range of years.
The narrative review’s purpose is to identify commonalities, gaps, and contradictions in the literature .
I recommend to my students that they should gather their studies together, take notes on each study, then try to group them by themes that form the basis for the review (see my step-by-step instructions at the end of the article).
Example Study
Title: Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations
Citation: Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/ijcp.12686
Overview: This narrative review analyzed themes emerging from 69 articles about communication in healthcare contexts. Five key themes were found in the literature: poor communication can lead to various negative outcomes, discontinuity of care, compromise of patient safety, patient dissatisfaction, and inefficient use of resources. After presenting the key themes, the authors recommend that practitioners need to approach healthcare communication in a more structured way, such as by ensuring there is a clear understanding of who is in charge of ensuring effective communication in clinical settings.
Other Examples
- Burnout in United States Healthcare Professionals: A Narrative Review (Reith, 2018) – read here
- Examining the Presence, Consequences, and Reduction of Implicit Bias in Health Care: A Narrative Review (Zestcott, Blair & Stone, 2016) – read here
- A Narrative Review of School-Based Physical Activity for Enhancing Cognition and Learning (Mavilidi et al., 2018) – read here
- A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents (Dyrbye & Shanafelt, 2015) – read here
2. Systematic Review Examples
This type of literature review is more structured and rigorous than a narrative review. It involves a detailed and comprehensive plan and search strategy derived from a set of specified research questions.
The key way you’d know a systematic review compared to a narrative review is in the methodology: the systematic review will likely have a very clear criteria for how the studies were collected, and clear explanations of exclusion/inclusion criteria.
The goal is to gather the maximum amount of valid literature on the topic, filter out invalid or low-quality reviews, and minimize bias. Ideally, this will provide more reliable findings, leading to higher-quality conclusions and recommendations for further research.
You may note from the examples below that the ‘method’ sections in systematic reviews tend to be much more explicit, often noting rigid inclusion/exclusion criteria and exact keywords used in searches.
Title: The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review
Citation: Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092422441730122X
Overview: This systematic review included 72 studies of food naturalness to explore trends in the literature about its importance for consumers. Keywords used in the data search included: food, naturalness, natural content, and natural ingredients. Studies were included if they examined consumers’ preference for food naturalness and contained empirical data. The authors found that the literature lacks clarity about how naturalness is defined and measured, but also found that food consumption is significantly influenced by perceived naturalness of goods.
- A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018 (Martin, Sun & Westine, 2020) – read here
- Where Is Current Research on Blockchain Technology? (Yli-Huumo et al., 2016) – read here
- Universities—industry collaboration: A systematic review (Ankrah & Al-Tabbaa, 2015) – read here
- Internet of Things Applications: A Systematic Review (Asghari, Rahmani & Javadi, 2019) – read here
3. Meta-analysis
This is a type of systematic review that uses statistical methods to combine and summarize the results of several studies.
Due to its robust methodology, a meta-analysis is often considered the ‘gold standard’ of secondary research , as it provides a more precise estimate of a treatment effect than any individual study contributing to the pooled analysis.
Furthermore, by aggregating data from a range of studies, a meta-analysis can identify patterns, disagreements, or other interesting relationships that may have been hidden in individual studies.
This helps to enhance the generalizability of findings, making the conclusions drawn from a meta-analysis particularly powerful and informative for policy and practice.
Title: Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s Disease Risk: A Meta-Meta-Analysis
Citation: Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Source: https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060386
O verview: This study examines the relationship between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Researchers conducted a systematic search of meta-analyses and reviewed several databases, collecting 100 primary studies and five meta-analyses to analyze the connection between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease. They find that the literature compellingly demonstrates that low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels significantly influence the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
- The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research (Wisniewski, Zierer & Hattie, 2020) – read here
- How Much Does Education Improve Intelligence? A Meta-Analysis (Ritchie & Tucker-Drob, 2018) – read here
- A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling (Geiger et al., 2019) – read here
- Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits (Patterson, Chung & Swan, 2014) – read here
Other Types of Reviews
- Scoping Review: This type of review is used to map the key concepts underpinning a research area and the main sources and types of evidence available. It can be undertaken as stand-alone projects in their own right, or as a precursor to a systematic review.
- Rapid Review: This type of review accelerates the systematic review process in order to produce information in a timely manner. This is achieved by simplifying or omitting stages of the systematic review process.
- Integrative Review: This review method is more inclusive than others, allowing for the simultaneous inclusion of experimental and non-experimental research. The goal is to more comprehensively understand a particular phenomenon.
- Critical Review: This is similar to a narrative review but requires a robust understanding of both the subject and the existing literature. In a critical review, the reviewer not only summarizes the existing literature, but also evaluates its strengths and weaknesses. This is common in the social sciences and humanities .
- State-of-the-Art Review: This considers the current level of advancement in a field or topic and makes recommendations for future research directions. This type of review is common in technological and scientific fields but can be applied to any discipline.
How to Write a Narrative Review (Tips for Undergrad Students)
Most undergraduate students conducting a capstone research project will be writing narrative reviews. Below is a five-step process for conducting a simple review of the literature for your project.
- Search for Relevant Literature: Use scholarly databases related to your field of study, provided by your university library, along with appropriate search terms to identify key scholarly articles that have been published on your topic.
- Evaluate and Select Sources: Filter the source list by selecting studies that are directly relevant and of sufficient quality, considering factors like credibility , objectivity, accuracy, and validity.
- Analyze and Synthesize: Review each source and summarize the main arguments in one paragraph (or more, for postgrad). Keep these summaries in a table.
- Identify Themes: With all studies summarized, group studies that share common themes, such as studies that have similar findings or methodologies.
- Write the Review: Write your review based upon the themes or subtopics you have identified. Give a thorough overview of each theme, integrating source data, and conclude with a summary of the current state of knowledge then suggestions for future research based upon your evaluation of what is lacking in the literature.
Literature reviews don’t have to be as scary as they seem. Yes, they are difficult and require a strong degree of comprehension of academic studies. But it can be feasibly done through following a structured approach to data collection and analysis. With my undergraduate research students (who tend to conduct small-scale qualitative studies ), I encourage them to conduct a narrative literature review whereby they can identify key themes in the literature. Within each theme, students can critique key studies and their strengths and limitations , in order to get a lay of the land and come to a point where they can identify ways to contribute new insights to the existing academic conversation on their topic.
Ankrah, S., & Omar, A. T. (2015). Universities–industry collaboration: A systematic review. Scandinavian Journal of Management, 31(3), 387-408.
Asghari, P., Rahmani, A. M., & Javadi, H. H. S. (2019). Internet of Things applications: A systematic review. Computer Networks , 148 , 241-261.
Dyrbye, L., & Shanafelt, T. (2016). A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents. Medical education , 50 (1), 132-149.
Geiger, J. L., Steg, L., Van Der Werff, E., & Ünal, A. B. (2019). A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling. Journal of environmental psychology , 64 , 78-97.
Martin, F., Sun, T., & Westine, C. D. (2020). A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018. Computers & education , 159 , 104009.
Mavilidi, M. F., Ruiter, M., Schmidt, M., Okely, A. D., Loyens, S., Chandler, P., & Paas, F. (2018). A narrative review of school-based physical activity for enhancing cognition and learning: The importance of relevancy and integration. Frontiers in psychology , 2079.
Patterson, G. T., Chung, I. W., & Swan, P. W. (2014). Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits: A meta-analysis. Journal of experimental criminology , 10 , 487-513.
Reith, T. P. (2018). Burnout in United States healthcare professionals: a narrative review. Cureus , 10 (12).
Ritchie, S. J., & Tucker-Drob, E. M. (2018). How much does education improve intelligence? A meta-analysis. Psychological science , 29 (8), 1358-1369.
Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Wisniewski, B., Zierer, K., & Hattie, J. (2020). The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research. Frontiers in Psychology , 10 , 3087.
Yli-Huumo, J., Ko, D., Choi, S., Park, S., & Smolander, K. (2016). Where is current research on blockchain technology?—a systematic review. PloS one , 11 (10), e0163477.
Zestcott, C. A., Blair, I. V., & Stone, J. (2016). Examining the presence, consequences, and reduction of implicit bias in health care: a narrative review. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations , 19 (4), 528-542

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
Methods. 1. Mining for terms. Use these tools to find alternate search terms that are related by identifying how often keywords appear and which other terms appear with them by number of occurrences. Ovid Reminer Tool. Upload a file of Medline results saved as a csv or excel file to analyse for term occurrence.
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
A literature review differs from a systematic review, which addresses a specific clinical question by combining the results of multiple clinical trials (an article on this topic will follow as part of this series of publications). ... Example; Select review topic/title: Biomarkers for prostate cancer: Identify keywords and search terms ...
Identify Keywords. To identify keywords, first start by writing out your research statement or question. Then follow these steps: Start by writing your research question, or thesis statement. Underline or circle the two or three most important terms that represent your topic. Example: Are social media users concerned about their personal ...
As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter. Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter.
When writing a literature review it is important to start with a brief introduction, followed by the text broken up into subsections and conclude with a summary to bring everything together. A summary table including title, author, publication date and key findings is a useful feature to present in your review (see Table 1 for an example).
That means once you get started with your keyword search, you can follow the trail of cited and citing papers to efficiently find all the relevant literature. This is a great way to ensure you're not missing anything important when you write a narrative literature review. ... Literature Review examples: Aggregation-induced emission ...
key aspects of the literature review • problem under investigation or research question(s) • clearly stated hypothesis or hypotheses • methods used (including brief descriptions of the study design, sample, and sample size) • study results • • implications (i.e., why this study is important, applications of the results or findings ...
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
A literature search is distinguished from, but integral to, a literature review. Literature reviews are conducted for the purpose of (a) locating information on a topic or identifying gaps in the literature for areas of future study, (b) synthesising conclusions in an area of ambiguity and (c) helping clinicians and researchers inform decision-making and practice guidelines.
For example: How do st udents view inclusive educational practices in schools? Treat each component as a separate concept (there are usually between 2-4 concepts). For each concept list the key words derived from your research question, as well as any other relevant terms or synonyms that you have found in your preliminary searches.
Searching keywords alone is fine to do when you are sure you have included most of the key terms associated with that particular concept. Some search terms will generate large numbers of results.
When searching specifically for Subject Headings, the database will only search the Subject Headings field within the record of each article (ie, not the title, abstract, etc.). This is a much more targeted method of searching, and is an excellent addition to your search strategy. A strong search strategy will use both free-text (keyword ...
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you. ... Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic. Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these. Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one) Inform your own methodology and research design. To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure.
Overview of Search Strategies. There are many ways to find literature for your review, and we recommend that you use a combination of strategies - keeping in mind that you're going to be searching multiple times in a variety of ways, using different databases and resources. Searching the literature is not a straightforward, linear process - it ...
Steps for Conducting a Lit Review; Finding "The Literature" Organizing/Writing; APA Style This link opens in a new window; Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window; MLA Style This link opens in a new window; Sample Literature Reviews. Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts; Have an exemplary literature review? Get Help!
1. Identify the keywords or the main concepts of your research topic. For example, for the topic Globalization of Chinese companies, the keywords are Globalization, Chinese and Companies. 2. Think of similar terms (synonyms) or phrases that might also be used to describe these concepts, to ensure that you do not miss out any relevant ...
Phrase searching. A phrase is two or more words linked together in a particular order, for example football match, social work . Most databases will allow you to search for a phrase, in other words to insist that your keywords appear next to each other in a specific order. Entering the phrase in double quotes " " will normally work, but check ...
Literature Review Examples. For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics. 1. Narrative Review Examples ... Keywords used in the data search included: food, naturalness, natural content, and natural ingredients. ...