- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is PEST Analysis?
- How It Works
- Applications
The Bottom Line
- Corporate Finance
- Financial Analysis
What Is PEST Analysis? Its Applications and Uses in Business
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/wk_headshot_aug_2018_02__william_kenton-5bfc261446e0fb005118afc9.jpg)
Investopedia / Ellen Lindner
PEST analysis (political, economic, social, and technological) is a management method whereby an organization can assess major external factors that influence its operation in order to become more competitive in the market. As described by the acronym, those four areas are central to this model.
A popular variation on the PEST analysis format, especially in the U.K., is the PESTLE strategic planning approach, which includes the additional aspects of legal and environmental.
Key Takeaways
- PEST analysis stands for political, economic, social, and technological.
- This type of analysis is used to gauge external factors that could impact the profitability of a company.
- Generally, it is more effective with larger organizations that are more likely to experience the effects of macro events.
- PEST analysis is commonly used in conjunction with SWOT analysis, which stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Understanding PEST Analysis
It is believed that PEST analysis was first introduced under the name ETPS by Harvard professor Francis J. Aguilar. In the 1967 publication "Scanning the Business Environment," Aguilar presented the economic, technical, political, and social factors as being major influences on the business environment. Subsequently, the letters were rearranged to create a convenient and quirky acronym used today.
The core of PEST analysis is the belief that a comprehensive assessment of the major areas of influence that affect the sector in which an organization is positioned, as well as the organization itself, can facilitate more effective strategic planning.
This planning can be undertaken to maximize the organization’s ability to capitalize on conditions as they exist and to be forewarned of and better prepared for imminent changes, allowing the organization to stay ahead of competitors.
Components of PEST Analysis
Political: The political aspect of PEST analysis focuses on the areas in which government policy and/or changes in legislation affect the economy, the specific industry, and the organization in question. Areas of policy that may particularly affect an organization include tax and employment laws. The general political climate of a nation or region, as well as international relations , can also greatly influence the organization.
Economic: The economic portion of the analysis targets the key factors of interest and exchange rates , economic growth, supply and demand , inflation , and recession.
Social: The social factors that may be included in a PEST analysis are demographics and age distribution, cultural attitudes, and workplace and lifestyle trends.
Technological: The technological component considers the specific role and development of technologies within the sector and organization, as well as the wider uses, trends, and changes in technology. Government spending on technological research may also be a point of interest in this area.
Applications of PEST Analysis
PEST analysis can assist an organization in recognizing and thereby capitalizing on opportunities offered by existing conditions in the business environment. It can also be used for identifying current or possible future challenges, allowing for effective planning of how to best manage these challenges.
PEST analysis can also be applied in assessing the in-house structure of an organization in order to identify strengths and weaknesses in its internal politics, economic outlook , social climate, and technology base. The results of this analysis can facilitate changes or improvements in areas identified as subpar.
PEST analysis can be used in conjunction with other forms of strategic business analysis, such as the SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) model, for an even more comprehensive result. Conducting a comparison between these completed analyses can provide a very solid basis for informed decision-making.
What Is PEST vs. PESTLE Analysis?
PEST analysis stands for "political, economic, social, and technological" whereas PESTLE stands for the same but adds "legal" and "environmental" factors to the analysis. These areas are considered when assessing the impact of external factors on a company's profitability.
How Do You Do a PEST Analysis?
To do a PEST analysis, you must consider the different factors under each category (political, economic, social, and technological), and how these factors affect your business. For the political component, you would assess laws, regulations, government policies, and tariffs, for example. For the economic component, some of the topics you would assess would include access to financing, cost of living, interest rates, inflation, and labor costs. For the social component, you would consider consumer trends and behaviors, education, division of wealth, population growth rates, and health. For the technological component, you would assess areas such as artificial intelligence growth, innovation, research and development, social networking, and cybersecurity.
How Often Should a PEST Analysis Be Done?
A PEST analysis can be done as often as a business would like. It is good to perform a PEST analysis when there have been significant changes that may impact a business, such as a change in interest rates, new government policies, or the introduction of new technology. It should be done often so as not to become outdated.
By analyzing the political, economic, societal, and technological factors that impact its business, a company can plan, reorganize, and adjust to these external factors in order to become a more successful operation. A business's success is not only predicated on how well it internally manages its operations but also on how it functions in the larger world. PEST analysis helps it to succeed in that aspect.
Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development. “ PESTLE Analysis .”
Rastogi, Nitank and Trivedi, M.K. “ PESTLE Technique—A Tool to Identify External Risks in Construction Projects .” International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology , vol. 3, no 1, 2016, pp. 385-386.
PESTLE Analysis. “ What Is PESTLE Analysis? An Important Business Analysis Tool .”
PESTLE Analysis. “ What Is a SWOT Analysis? 2 Examples of What It’s Used For .”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SWOTAnalysis_final-899758832a37461c819fc13d7c4b98b2.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

- Demo Videos
- Interactive Product Tours
- Request Demo
What is PEST Analysis?
The PEST analysis is a useful tool for understanding market growth or decline, and as such the position, potential and direction for a business. PEST is an acronym for Political, Economic, Social and Technological factors, which are used to assess the market for a business or organizational unit. Sometimes it's expanded to include legal and environmental factors and called a PESTLE analysis.

A PEST analysis guides us to identify effective strategies for setting priority, allocating resources, planning for time and development roadmap and formulating control mechanisms. With this analysis, you can identify potential opportunities and threats associated with your strategy and figure out ways to take advantage of them and avoid them.
Political Factors
These are all about how and to what degree a government intervenes in the economy. This can include - government policy, political stability or instability in overseas markets, foreign trade policy, tax policy, labour law, environmental law, trade restrictions and so on.
It is clear from the list above that political factors often have an impact on organisations and how they do business. Organisations need to be able to respond to the current and anticipated future legislation, and adjust their marketing policy accordingly.
Economic Factors
Economic factors have a significant impact on how an organisation does business and also how profitable they are. Factors include - economic growth, interest rates, exchange rates, inflation, disposable income of consumers and businesses and so on.
These factors can be further broken down into macro-economical and micro-economical factors. Macro-economic factors deal with the management of demand in any given economy. Governments use interest rate control, taxation policy and government expenditure as their main mechanisms for managing macro-economic factors.
Micro-economic factors are all about the way people spend their incomes. This has a large impact on B2C organisations in particular.
Social Factors
Also known as socio-cultural factors, social factors are the areas that involve the shared belief and attitudes of the population. These factors include - population growth, age distribution, health consciousness, career attitudes and so on. These factors are of particular interest as they have a direct effect on how marketers understand customers and what drives them.
Technological Factors
We all know how fast the technological landscape changes and how this impacts the way we market our products. Technological factors affect marketing and the management thereof in three distinct ways:
- New ways of producing goods and services
- New ways of distributing goods and services
- New ways of communicating with target markets
Analyzing these factors will help you and your team gain a comprehensive understanding of the external (macro environmental) factors that may positively or negatively affect your company's strategic planning process. With access to such knowledge, you can quickly come up with strategies that would put the company on the fast track to achieving its goals.
Benefits of PEST Analysis
A company may have all the information it requires about the quality of its infrastructure, the extent of funds, and the employee talent available to it, but it may not be fully aware of the external environment in which it is to operate or launch a new project. It can even predict future prospects of a project or product by studying the PEST factors. Let's list out the some benefits that we can gain from the findings of a PEST Analysis:
- Provides an understanding of the wider business environment.
- Encourages the development of strategic thinking.
- Straightforward and only costs time to do.
- May raise awareness of threats to a project.
- Can help an organisation to anticipate future difficulties and take action to avoid or minimise their effect.
- Can help an organisation to identify and exploit opportunities.
An Example - Impact of Technology Factor
Let's take a moment to consider the impact that technology has had on our country's economy. Most people will agree that technology has made our lives much easier. The Internet, for example, has changed the way we bank, pay our bills, search for goods and services, book holidays, undertake study, and shop.
However, technology has caused serious damage to some businesses. In terms of casualties, the good old fashioned local CD & DVD rental store has taken a monumental hit. Why? Well, let's face it, there's now little need to visit a CD & DVD rental store. Today, most households have access to YouTube, Apple TV and Google Movies on Play Store and etc.
Conducting PEST Analysis
If a PEST analysis involves analyzing forces we have little or no control over, why bother considering them at all? To answer this question, a PEST analysis encourages management to carefully study what is happening in the environments that encapsulate their business.
As business managers we must understand that, although these external forces are largely outside of our control, we still need to carefully consider them. The underlying function of the analysis is not just to review what has already happened, but also predict what is likely to happen in the near future. This ensures we are aware of them and highly perceptive to their possible affects on our business.
The external influences on business vary from country to country. It is very important that those factors are considered. To conducting a PEST Analysis, we can come up a set of brainstorming questions with answers and actions of them related to each of the four factors:
The political arena has a huge influence upon the regulation of businesses, and the spending power of consumers and other businesses. You must consider issues such as:
- How stable is the political environment?
- Will government policy influence laws that regulate or tax your business?
- What is the government's position on marketing ethics?
- What is the government's policy on the economy?
- Does the government have a view on culture and religion?
- Is the government involved in trading agreements such as EU, NAFTA, ASEAN, or others?
The economic environment is a direct influence on all businesses. Obviously if you are studying marketing there is a huge element of economics within the topic itself, and you should be no stranger to the principles of economics. You need to look at:
- Interest rates
- The level of inflation Employment level per capita
- Long-term prospects for the economy Gross Domestic Product (GDP) per capita, and so on
The social and cultural influences on business vary from country to country. It is very important that such factors are considered. Factors to be considered include:
- What is the dominant religion?
- What are attitudes to foreign products and services?
- Does language impact upon the diffusion of products onto markets?
- How much time do consumers have for leisure?
- What are the roles of men and women within society?
- How long are the population living? Are the older generations wealthy?
- Do the population have a strong/weak opinion on green issues?
Technology is vital for competitive advantage, and is a major driver of globalization. Consider the following points:
- Does technology allow for products and services to be made more cheaply and to a better standard of quality?
- Do the technologies offer consumers and businesses more innovative products and services such as Internet banking, new generation mobile telephones, and etc.?
- How is distribution changed by new technologies e.g. books via the Internet, flight tickets, auctions and etc.?
- Does technology offer companies a new way to communicate with consumers e.g. banners, Customer Relationship Management (CRM), and etc.?
Where you have identified significant opportunities, build the actions you'll take to exploit them into your Business Plan. Where you've identified significant risks, take appropriate action to manage or eliminate them.
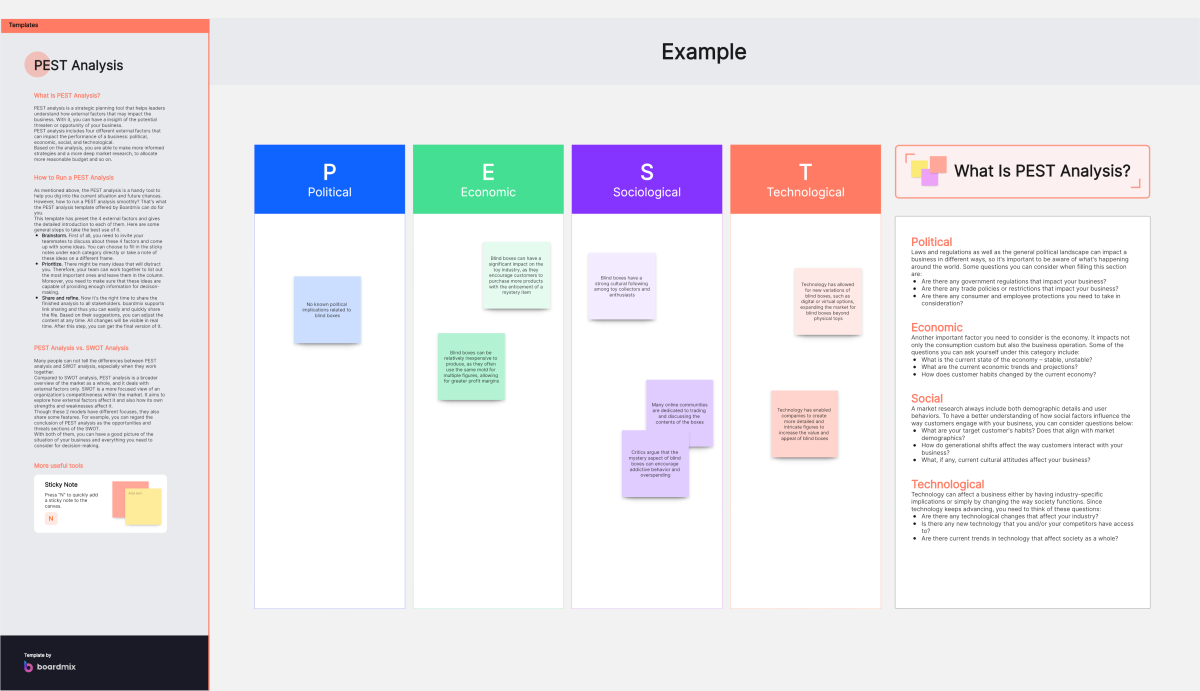
PEST Analysis Template
The table below shows a PEST Analysis Template that consists of some typical kinds of factors people would consider in developing a PEST Analysis model.
PEST Analysis Variants
Traditionally, PEST analysis focuses on political, economic, sociological and technological factors, but increasing awareness of the importance of legal, environmental and cultural factors has led to the evolution of a growing number of variants.
For example:
- PESTLE - Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal and Environmental
- SPECTACLES - Social, Political, Economic, Cultural, Technological, Aesthetic, Customers, Legal, Environmental, Sectoral
- PESTLIED - Political, Economic, Socio-Cultural, Technological, Legal, International, Environmental, Demographic.
- PEST-C , where the C stands for cultural
- SLEEPT-C - Sociological, Legal, Economical, Environmental, Political, Technological and Cultural.
- LONGPESTLE : Local, National, and Global versions of PESTLE. (These are best used for understanding change in multinational organizations.)
Choose the version that best suits your situation.
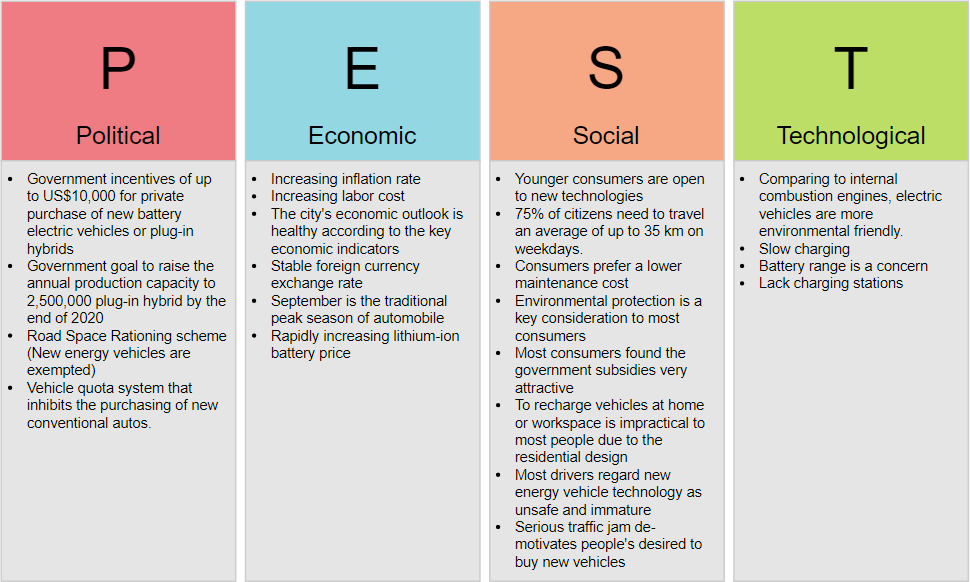
PEST Analysis Example
The figure below shows a PEST Analysis example of the new energy vehicles industry.
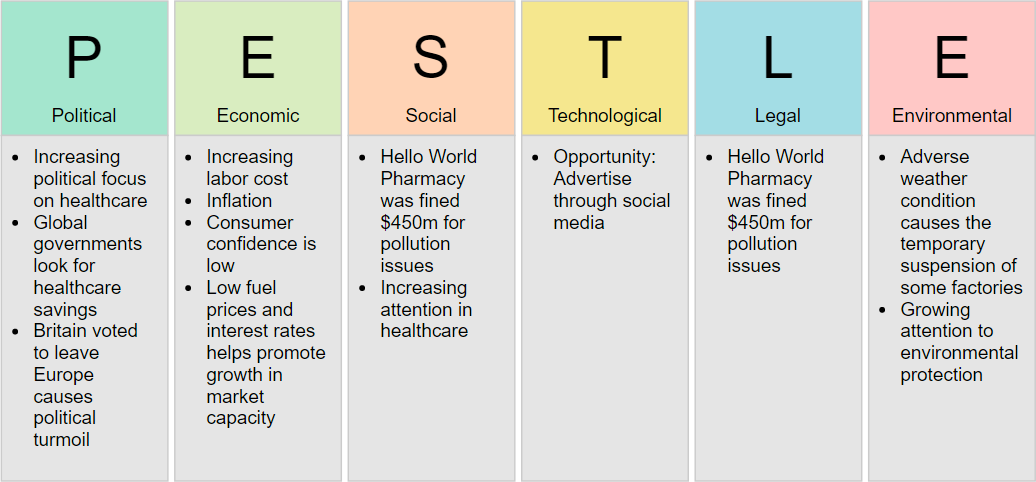
PESTLE Analysis Example
The figure below shows a PESTLE Analysis example of a pharmaceutical company. PESTLE is a varied form of PEST. It has two additional columns L and E for listing the Legal and Environmental factors.
PEST vs SWOT Analysis
PEST is useful before SWOT Analysis - not generally vice-versa - PEST definitely helps to identify SWOT factors. PEST Analysis is often linked with SWOT Analysis, however, the two tools have different areas of focus. There is overlap between PEST and SWOT, in that similar factors would appear in each. That said, PEST and SWOT are certainly two different perspectives:
- PEST Analysis looks at "big picture" factors that might influence a decision, a market, or a potential new business.
- PEST assesses a market, including competitors, from the standpoint of a particular proposition or a business.
- SWOT is an assessment of a business or a proposition, whether your own or a competitor's. at a business, product-line level.
Related Links
- Try PEST Analysis now
- PEST, PESTLE and other strategic analysis tools
* PEST and PESTLE Analysis are powered by Visual Paradigm's web technology. You can create it in both Visual Paradigm Desktop and Visual Paradigm Online .
Turn every software project into a successful one.
We use cookies to offer you a better experience. By visiting our website, you agree to the use of cookies as described in our Cookie Policy .
© 2024 by Visual Paradigm. All rights reserved.
- Privacy statement
Our Recommendations
- Best Small Business Loans for 2024
- Businessloans.com Review
- Biz2Credit Review
- SBG Funding Review
- Rapid Finance Review
- 26 Great Business Ideas for Entrepreneurs
- Startup Costs: How Much Cash Will You Need?
- How to Get a Bank Loan for Your Small Business
- Articles of Incorporation: What New Business Owners Should Know
- How to Choose the Best Legal Structure for Your Business
Small Business Resources
- Business Ideas
- Business Plans
- Startup Basics
- Startup Funding
- Franchising
- Success Stories
- Entrepreneurs
- The Best Credit Card Processors of 2024
- Clover Credit Card Processing Review
- Merchant One Review
- Stax Review
- How to Conduct a Market Analysis for Your Business
- Local Marketing Strategies for Success
- Tips for Hiring a Marketing Company
- Benefits of CRM Systems
- 10 Employee Recruitment Strategies for Success
- Sales & Marketing
- Social Media
- Best Business Phone Systems of 2024
- The Best PEOs of 2024
- RingCentral Review
- Nextiva Review
- Ooma Review
- Guide to Developing a Training Program for New Employees
- How Does 401(k) Matching Work for Employers?
- Why You Need to Create a Fantastic Workplace Culture
- 16 Cool Job Perks That Keep Employees Happy
- 7 Project Management Styles
- Women in Business
- Personal Growth
- Best Accounting Software and Invoice Generators of 2024
- Best Payroll Services for 2024
- Best POS Systems for 2024
- Best CRM Software of 2024
- Best Call Centers and Answering Services for Busineses for 2024
- Salesforce vs. HubSpot: Which CRM Is Right for Your Business?
- Rippling vs Gusto: An In-Depth Comparison
- RingCentral vs. Ooma Comparison
- Choosing a Business Phone System: A Buyer’s Guide
- Equipment Leasing: A Guide for Business Owners
- HR Solutions
- Financial Solutions
- Marketing Solutions
- Security Solutions
- Retail Solutions
- SMB Solutions
What Is a PEST Analysis?

Table of Contents
In business, there’s only so much you can control. You can decide which products and services you offer, how much you charge, who supplies you and whom you employ. However, many factors are entirely out of your control, and without detailed knowledge of those variables, it’s a lot harder to run a successful business.
Many companies use a political, economic, social and technological (PEST) analysis to assess their business environment and understand external threats and opportunities.
What is a PEST analysis?
A PEST analysis is an assessment of the political, economic, social and technological factors that could affect a business now and in the future. The purpose of a PEST analysis is to give a company’s management team a better understanding of the market they’re operating in now and how they can prepare for potential shifts, such as regulatory changes.
Elements of a PEST analysis
A PEST analysis covers political, economic, social and technological factors. Here’s more about each:
P (political)
The “P” in the analysis refers to the political factors that help or hinder a business.
“We see this currently in the U.S., particularly in the area of international business,” said grant professional Donna Lubrano. “We look at tariffs, trade deals as they are developed not only by the economics or business side but what political relationships influence those decisions.”
A PEST analysis examines the following political factors:
- Employment regulations: Will it become more expensive to employ staff because of minimum-wage laws , safety-at-work legislation, pension contributions, healthcare contributions and more? Are tax authorities classifying more contractors as employees ?
- Environment: Can profit levels be maintained if authorities demand a less-polluting production process or if they levy a charge on companies in your sector for post-use cleanup of your products?
- Government policy: Are laws that a government passes conducive to businesses and, specifically, to your business?
- Intellectual property protection: Do a country’s laws and court systems recognize the rights of intellectual property holders? In addition, how hard is it to seek redress in instances of copyright infringement and intellectual property theft ?
- Property rights: Do you have sufficient rights to protect and exploit resources and your assets?
- Stability: Unstable political environments, particularly in countries with regular (and often forced) changes of government, make planning difficult. In more stable countries, will a particular party coming to power materially affect your business and its profitability?
- Tariffs: If you expand your business internationally by importing materials for production or exporting finished products to customers, how will tariffs affect your business’s production costs and pricing competitiveness?
- Taxation: How does the current government’s tax policy affect your small business taxes ? For example, does it impact your business’s cash flow , allowable tax deductions and profit margins ?
- Trade restrictions: Are there sanctions (or likely sanctions) against doing business with a country you’re targeting?
E (economic)
The “E” in a PEST analysis refers to outside economic issues that can play a role in a company’s success. Look at interest rates, exchange inflation, unemployment, gross domestic product , credit availability, and the rise and fall of the middle class.
A PEST analysis examines the following economic factors:
- Access to credit: For higher-ticket products and services, can consumers or business customers easily access competitively priced credit to purchase from your company?
- Business investment levels: Do companies in your target market regularly replace their machinery and equipment, or do they try to make these assets last as long as possible?
- Cost of living: How high is the cost of living where you do business? Higher prices affect business competitiveness because they increase housing costs and require staff to be paid more to mitigate those costs.
- Economic growth or decline: What is the current state of the economy? If an economy is improving, consumers and businesses will likely have more cash to purchase products or services. Economic growth triggers higher investment levels by businesses in general.
- Exchange rates and interest rates: What are the economic considerations for other countries that affect your business? Countries with more robust economies suffer fewer currency-value fluctuations; this is important if you import or export products. In addition, these countries are more likely to have higher interest rates that dampen local inflation, although this has not always been the case since the Great Recession of 2008-2009.
- Tariffs and restrictions: How do tariffs and international restrictions affect your business? Globalized countries where tariffs and restrictions have largely been removed enjoy faster economic growth and improved socioeconomic conditions for customers and staff.
- Inflation: What is the current level of inflation? Higher levels of inflation erode the value of money faster. In some cases, businesses may not be keen to pass on higher costs to customers, so profits fall.
- Labor costs and workforce skill levels: What is the state of the labor market? A shortage of workers with in-demand career skills will lead to rising labor costs that will hurt profitability. Sometimes, a shortage may be severe enough to require companies to spend more on employee training .
- Market conditions: How fast is the market growing? How big is the total market? How many competitors are in this market, and how does this affect pricing and costs?
- Spending habits: Are the consumers or businesses you target spending more money on your products and services? Are they spending a different way — for example, moving from in-person to online spending?
- Tax levels: What are the tax rates in the areas where you’d like to do business? If given a choice between two states or countries where almost every other PEST consideration is equal, a company may be more likely to target lower-tax countries first for investment.
The “S” in a PEST analysis relates to the social environment of a given industry’s market — how consumer needs are shaped and what brings consumers to the market for a purchase.
“We look at what changes in culture and society are taking place,” Lubrano said. “The drive to eat healthier, the drive to care for the environment, baby boomers staying in the workforce longer, adults having fewer children later in life. All of these impact how consumers buy houses, cars, etc.”
A PEST analysis examines these social factors:
- Productivity: How productive is your workforce? The more productive a workforce is, the more competitively your business can price products or services or increase profit margins.
- Consumer trends/tastes/fashions: What are the latest consumer trends, and should your business take advantage of them? In the process of turning ideas into products , there is often a substantial time lapse between inception, creation and launch. Therefore, tracking trends, tastes and fashions is crucial to ensuring any new product’s success.
- Corporate responsibility and values: What are your company’s and employees’ values? It’s increasingly important to Gen Z and millennials that their brands of choice support their values. Should you launch a corporate social responsibility program and implement diversity, equity and inclusion training ?
- Division of wealth: Is there a large wealth gap? According to an often-cited 2015 study in the journal Human Relations , economic inequality hurts organizational performance. It also affects growth in consumption rates during periods of economic decline.
- Education: What are the education levels of your staff and candidate pool? Educational quality varies among states and countries. Lower education levels require a more significant investment in staff training and may be matched by lower levels of pay.
- Employment patterns and job market trends: What are the job market and typical work arrangement like in your area? Many states and countries have shifted toward part-time work and self-employment, making it harder to recruit and hire employees . In addition, the type of staff you wish to recruit may be in particular demand, leading to higher employment costs.
- Generational attitude shifts: Does your company employ people of different generations? Workers’ expectations of employers may differ among generations, necessitating a change in how team members are rewarded, targeted and remunerated.
- Population health: Will you invest in your staff’s mental and physical well-being to reduce absenteeism and improve productivity ?
- Population demographics: Does a state or market contain your ideal potential employees and customers?
- Population growth rate: What is the population growth rate in your area? States or countries whose populations are growing primarily through immigration may experience slower pay-rate growth due to increased competition.
- Social mobility: How easy is it for workers to move up the socioeconomic ladder? States or countries with larger middle classes that are easier to enter often have higher economic growth rates and lower income inequality rates.
- Unionization: Is unionization common in your industry? How might this affect the expectations of your workforce? Many employers believe that more highly unionized workforces cost more and are less flexible, although this is disputed.
T (technological)
Technology plays a massive role in business and can have positive and negative effects. Some organizations may have challenges adjusting to tech trends, including new products and services, so it’s essential to assess existing and imminent technology from all angles.
A PEST analysis examines these technological factors:
- Artificial intelligence (AI): How will the growth of AI affect your business? AI is transforming businesses with new ways to optimize efficiency and productivity. What are the potential applications for your sector and business?
- Automation and robotics: How will workplace automation technologies affect your industry and business? Many sectors now automate as many processes as possible to use raw materials more efficiently, offer better service to clients, and manufacture more products at a cheaper cost per unit.
- Cybersecurity and data protection: Does your business have solid cybersecurity and data protection measures in place? Cyberattacks continue to affect businesses, so companies should collect only the data they need for operation and protect that data with robust cybersecurity practices .
- Disruptive technologies: What new technologies might open new markets for your company? Which of these should you invest in to grow your business?
- Innovation: Given the accelerated rate of technological innovation affecting many sectors, should you invest in innovation now to stay ahead of the curve, or react to competitors’ innovations?
- Remote work: Do existing technology and infrastructure allow staff to work remotely? Are you accessing appropriate remote work tools to maximize productivity?
- Research and development (R&D): Should you invest in R&D in jurisdictions with significant R&D tax credits and breaks?
- Social networking: Should your company invest in social media for business to promote its products and services and hire staff via social platforms? Should you invest in apps such as Slack and Asana to enable smoother communication among employees in different locations?
- Tech hubs: Should your company (or part of the company) relocate to tech hubs where technological innovation is more likely because of the availability of staff, investors, suppliers, educational establishments and service providers?
How to conduct a PEST analysis
Now that you know what a PEST analysis is, it’s time to gather the data. Follow these steps to conduct a PEST analysis:
1. Identify the political factors.
Conduct internal research to identify what types of laws or policies affect your company. These factors may include the following:
- Material or product sourcing (e.g., import quotas, tariffs, price supports and subsidies, preferences)
- Human resources (e.g., visas, Equal Employment Opportunity Commission requirements, vaccine requirements)
- Manufacturing/operations (e.g., Occupational Safety and Health Administration requirements)
- Accounting and finance (e.g., IRS requirements; tax hikes, breaks and deductions; Securities and Exchange Commission reporting requirements)
- Marketing and customer demand (e.g., online business law requirements, CAN-SPAM Act)
Consult an attorney or the people in charge of HR compliance , safety, reporting, finance and accounting. Each should be familiar with current and proposed laws.
2. Identify the economic factors.
Determine which economic factors affect your business.
- If you sell consumer goods and services, look at the consumer price index, inflation, employment, consumer confidence, disposable income and wages.
- If you sell high-ticket items that require financing, look at interest rates.
- If you sell business-to-business (B2B) services, such as marketing or consulting, look at unemployment and other recession measures.
- If you sell or buy products as components, consider supply chain issues and tariffs.
- If you employ relatively low-wage workers, examine salaries and employment to determine whether you need to raise wages to attract talent.
3. Identify the social factors.
If you have conducted market research on customer or target market perceptions and demographics, this step is at least partially done. It’s also a good idea to read industry publications, which frequently highlight social factors that affect the industry as a whole.
Talk to your customer service and sales staff to get feedback from customers on why they buy, return or cancel your offerings. If you have a local business, conduct a market analysis periodically to understand your potential customers.
4. Identify the technological factors.
Although identifying technological factors is particularly important in tech industries, these considerations affect every industry in some way.
Read industry publications and conduct a competitive analysis to learn about new technologies and innovative ways to deliver products and services in your field. Look for the following updates:
- New programming languages and methods that will make your product or service faster, more accurate or more detailed
- New apps that deliver your products or services in different ways
- New technology or processes that you can use to make your products stronger, smarter, cheaper, more convenient or more readily available
Benefits of a PEST analysis
A PEST analysis focuses exclusively on external factors, such as current and future regulations, taxes, political issues, environmental legislation and employment laws. Here’s how it can help your business.
- A PEST analysis improves your understanding of your company. No company is an island; each business is intricately connected to its customers and society. By understanding the factors that can boost or reduce your success, you can get a sense of how your business can make a difference in other people’s lives.
- A PEST analysis informs long-term strategic planning. Conducting a PEST analysis every year helps you anticipate changes and plan for the future. You have the opportunity to prepare for shifts in the market and society in general. This will save you money, prevent lost revenue and position you well against competitors.
- A PEST analysis alerts you to potential threats and dangers. When you are aware of potential threats, you can address or prevent them. Be proactive about implementing policies to gain a competitive edge, devote resources to influencing laws that may hurt your business, or make strategic alliances that give you a stronger market position.
- A PEST analysis provides insight into valuable business opportunities. Be the first in your field to take advantage of beneficial government policies or market opportunities. By keeping your finger on the pulse of the market, you can be in the right place with the right message.
A well-executed PEST analysis can help your company successfully navigate changes in the world around it and signal new opportunities to expand into different markets and territories.
PEST analysis disadvantages and limitations
Although there are many potential benefits of a PEST analysis, it can also have limitations. Consider the following drawbacks:
- Ever-changing environments: Because these environments are so dynamic, your analysis could be outdated within days or even hours.
- Guesswork: You must make assumptions about specific factors, so there’s always a chance of miscalculation.
- Data overload: Because a PEST analysis involves such large data sets, it takes careful analysis to parse the data and decide how to use it to your advantage.
- Risk of inaccuracy: Most of the time, you’ll get your information from outside sources, so you can’t be sure it’s 100 percent accurate.
What is a PESTLE analysis?
A PESTLE analysis is similar to a PEST analysis, but it includes two additional factors: legal and environmental.
- Legal: When examining legal factors, a company should evaluate how legal changes and interpretations could affect it, directly or indirectly, according to Daniel Feiman, managing director at consulting and training firm Build It Backwards. Feiman recommended examining law changes, global law conflicts and Supreme Court decisions in this portion of the analysis.
- Environmental: For the environmental portion of the analysis, Feiman recommended examining how environmental regulations, such as laws surrounding endangered species, could affect the business.
Feiman also suggested measuring each PESTLE factor against the following considerations:
- Potential impact: Low, medium or high
- Time frame: Immediate, short-term or long-term
- Type: Positive or negative
- Direction of impact: Increasing or decreasing
- Relative importance: High, medium or low
Other types of business analyses
For a PEST analysis to be truly valuable, it should be used in conjunction with the following analyses:
- SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats): A SWOT analysis allows you to identify your company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. SWOT analyses are best suited for making major business decisions or determining the associated risks.
- MOST (mission, objectives, strategies and tactics): A MOST analysis helps a business align with its missions and objectives by analyzing its internal strategies and tactics. This analysis is especially helpful for making organizational strategy decisions.
- SCRS (strategy, current state, requirements and solution): An SCRS is a solution-based analysis that helps you identify the correct course of action to address a business challenge or issue. By analyzing your business’s current state and requirements, you can develop an effective strategy that will solve the problems your business faces.
Using a PEST analysis for business decision-making
Using a PEST analysis to assess your business’s environment, including any external threats and opportunities, is an excellent way to inform decisions and strategies. It is especially effective for larger businesses that want to understand their place in their industry.
Sammi Caramela contributed to this article. Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.

Building Better Businesses
Insights on business strategy and culture, right to your inbox. Part of the business.com network.
More Like this
What is a pestle analysis a complete pestle analysis guide, what is a pestle analysis.
A PESTLE analysis examines external market factors – including Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental – and market trends that might impact your organization’s direction, performance, and position in the marketplace. Used in tandem with a SWOT analysis, it helps your organization examine external factors that could influence your organization’s opportunities and threats . In this article, we’ll dig into what is a PESTLE analysis, what each factor covers, and how to use it in tandem with your SWOT.
DOWNLOAD THE FREE GUIDE

So why do I need to conduct a PESTLE Analysis?
The last few years have been a whirlwind of change and uncertainty – a global pandemic, natural disasters, looming recession, war, inflation, and more. Organizations have faced a great deal related to external market factors directly impacting their organizations. Current events have been stressful enough for any organization to worry about, whether you’re well-established or new in your market.
While the global situation is intimidating for many current and future leaders, this helpful analysis can help you assess and plan for what might impact your organization – and either seize those forces as opportunities or work to mitigate them as threats. Using a PESTLE allows you to look ahead at challenges your organization may encounter and create strategies to address them.
Pro Tip: We covered using this tool a few years back during the start of the COVID pandemic. This article has some helpful tips on using this analysis to examine market megatrends.
The PESTLE Analysis Framework Explained
As we mentioned earlier, this analysis looks at the external Political, Environmental, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors that would influence your organization’s strengths and weaknesses. A PESTLE analysis is best used in tandem with your SWOT analysis . As demonstrated below, this framework looks at the macro-trends in your operating environment.
As you complete your planning process, this looks at the external analysis portion of your environmental scan – also known as what is happening in your market.

Pro Tip: A PESTLE analysis looks at external market forces, so they will not influence your organization’s internal strengths or weaknesses . Strengths and weaknesses come from traits or characteristics your organization already processes.
What are Political factors?

Political factors are those brought on by the government or politics. These are the external political forces affecting your organization, including governmental policies, government leadership, foreign trade and foreign relations, political issues and trends, tax policy, regulations, and de-regulation trends.
A few examples might include the influx of capital from the Paycheck Protection Plan, the change in tariffs on imports from China, and the war and conflict from Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
Questions to ask:
- What shifts have occurred in the political climate?
- How might those shifts impact our organization? Are they headwinds, or tailwinds?
- Are they short- or long-term plays?
- What are the political threats you should monitor?
What are Economic factors?

The economic factors look at the external forces that can impact the economy your organization operates in. Examples include rising inflation rates, changes and shifts in consumer spending, changes in the supply chain, demand curves, and the health of the global economy.
These economic factors can look at the local economy, national economy, and global economy.
- What is the current health of the economy? How might that impact our organization?
- Are there headwinds or tailwinds in our supply chain?
- What local economic factor might impact our business?
What are Sociological factors?

Sociological factors consider the changes in the greater social environment, such as social justice movements or other social trends like changing opinions on your product or shifting populations and demographics. It’s essential to consider sociological trends that are at play¬— not just in your organization’s immediate environment—but also in the broader environment that your customers are coming from.
- Are there changing trends in our market’s demographics or population? How best do we serve them?
- How are changing social factors going to impact our organization?
- What shifts can be observed in consumer behavior, sentiment, or opinion?
What are Technological factors?

Changes in technology affect a business’s positioning. Some recent examples are the rise of cryptocurrency (which can also fall into the economic category), the emergence of popular work-from-home technology, AI developments, and even concerns over cyber security or other technological issues. It is important to consider how technology can prove to be both an opportunity for your organization, or a threat to it.
- How has the technology in our market changed? Is that an opportunity or threat?
- Are you using available technology to its full advantage?
- How much does emerging technology impact your organization?
What are Legal factors?

While similar to the political aspects, the legal elements look at the practical application of the political factors into rules and regulations that may affect your business or customers. These are the laws and regulations that impact your organization.
This could include updated laws, new regulations, or abolishing laws. Depending on your business, local, state, and federal laws and regulations are worth scrutinizing.
- What changes in our international, national, and local legislation impact our organization?
- How are these legal changes going to impact our organization positively or negatively?
- What legal forces may be on the horizon?
What are Environmental factors?

Environmental factors are affected by weather, geography, climate change, and health crises. In addition to the public health crisis caused by the COVID pandemic, the world has also been impacted by wildfires across the globe.
Organizations should consider the short-term and long-term impacts of these accelerating changes, e.g., rising ocean levels, drier and warmer seasons, and yearly weather conditions such as hurricanes and typhoons.
- What environmental factors are impacting us right now?
- What environmental factors might impact us in the future?
- What environmental factors do we need to monitor?
Bonus – What are Ethical factors?
Over the last few years, business and marketing strategy experts have added a third ‘E’ to the PESTLE- the ethical factor. This can include things such as fair-trade practices, child labor issues, even society’s increasing demand for conscious business models, and corporate social responsibility.
- What external ethics forces are impacting the market?
- What changes to your business or suppliers might you consider?
- What kind of impact or example do you hope your company may set?
Advantages and Disadvantages of a PESTLE Analysis
What are the advantages of using a pestle analysis.
There are several advantages to conducting a this analysis for your business. Here’s a breakdown:
- It is a simple and straightforward framework that is easy to implement into your strategic plan.
- It also allows you and your team to facilitate a great understanding of the wider business environment and how current events can potentially affect your business.
- Additionally, it helps organizations anticipate business threats and figure out how to mitigate the risks and it helps organizations spot business opportunities on which they can capitalize.
What are the disadvantages of using a PESTLE analysis?
While it’s a great tool, here are a few of the disadvantages to using this:
- One of the disadvantages of doing this type of assessment is that it can be as light or as heavy as one wants to make it.
- It is easy to oversimplify the data or collect insufficient data.
- It is also easy to make it too heavy by collecting too much data and becoming so overwhelmed that you don’t know where to start. This is a phenomenon called ‘analysis paralysis.’
- It’s a great tool, but it doesn’t analyze your organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses. That’s why we recommend using it in conjunction with your SWOT analysis.
Best Practices- When and How to Use this Assessment:
You should conduct your PESTLE analysis in the pre-planning stages of your business or strategic plan with a SWOT analysis. A SWOT analysis looks at your organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses and the external opportunities and threats the market presents. This will be an excellent companion piece to your SWOT as it informs your SWOT by looking at all aspects of the external market environment.
So, when conducting your analysis, break down each factor and look at both the positive aspects you can leverage (the opportunities) and the pitfalls to avoid (the threats) within the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental spheres. If you want to see some real world examples, check out our PESTLE Analysis Examples .
While this exercise is typically conducted in the beginning stages of a strategic plan, it is best to set a regular cycle to check in and revisit it. With the speed at which things are constantly shifting and changing, the analysis you conducted five years ago may need to be revised today. It is best to update it at a minimum every three years. Or, when you update your SWOT. It can be helpful to look at these trends annually, too. Make it a habit to keep a pulse on current events and market changes, so you always know what is going on in your market and how it will affect your organization.
Conclusion: Where does PESTLE Analysis fit into strategic planning?
Leveraging your PESTLE analysis as the first step to your business and strategic planning process is the ultimate way to ensure that you know all the areas your business can capitalize on and which pitfalls you can work on to mitigate. This will help you get the complete picture of where your organization is playing and just what you need to ensure that you will win.
PESTLE Analysis FAQs
A PESTLE analysis examines external market factors – including Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental – and market trends that might impact your organization’s direction, performance, and position in the marketplace. Used in tandem with a SWOT analysis, it helps your organization examine external factors that could influence your organization’s opportunities and threats .
It also allows you and your team to facilitate a great understanding of the wider business environment and how current events can potentially affect your business. Additionally, it helps organizations anticipate business threats and figure out how to mitigate the risks and it helps organizations spot business opportunities on which they can capitalize.
One of the disadvantages of a PESTLE analysis is that it can be as light or as heavy as one wants to make it. It is easy to oversimplify the data or collect insufficient data. While it’s a great tool, but it doesn’t analyze your organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses. That’s why we recommend using it in conjunction with your SWOT analysis.
This helpful analysis can help you assess and plan for what might impact your organization – and either seize those forces as opportunities or work to mitigate them as threats. Using a PESTLE allows you to look ahead at challenges your organization may encounter and create strategies to address them.
While a PESTLE analysis is typically conducted in the beginning stages your strategic planning process to help evaluate your organization’s macro-market. It is best when used in tandem with your SWOT analysis to analayze the current state of your organization.
Comments Cancel
Join 60,000 other leaders engaged in transforming their organizations., subscribe to get the latest agile strategy best practices, free guides, case studies, and videos in your inbox every week..

Leading strategy? Join our FREE community.
Become a member of the chief strategy officer collaborative..
Free monthly sessions and exclusive content.
Do you want to 2x your impact.

What is a PEST analysis? How to do a PEST analysis and examples
A PEST Analysis is a study that helps an organization identify opportunities and threats of the external macro environment. The macro environment refers to uncontrollable external factors that affect a company. PEST is an acronym for P olitical, E conomic, S ocial and T echnological. They are four factors that can affect a company’s current and future performance.
A PEST Analysis can help an organization create a long-term strategy by keeping track of the external factors. It may also help determine how these factors may affect a business’ performance and growth.
According to PESTLE Analysis :
“A PEST Analysis helps you determine how these factors will affect the performance and activities of your business in the long-term.”
“It is often used in collaboration with other analytical business tools.”
Useful for many types of companies
This tool is extremely useful for global businesses and those that want to expand overseas. It is useful because it shows us what changes are occurring in the business environment.
Additionally, it can help you decide whether to initiate or abandon a new project. Specifically, projects that are vulnerable to factors over which you have no control.

The PEST analysis can help you make a decision on how profitable a country, region, and area can be for your business. All data gathered through this tool focuses on what the business needs to do to get ahead.
When making commercial and strategic decisions, we need objective analyses, forecasts, and data. The Pest Analysis is completely objective.
How to do a PEST Analysis
Before using the PEST tool, it is important to understand all the factors. You can then brainstorm each one.
Some factors are opportunities for the companies. Others, on the other hand, are potential threats . All of them are relevant. However, you should focus on the ones that affect your business the most.
You should then attribute either opportunities or threats in detail to each factor.
The factors that we attribute threats and opportunities to are:
Political factors
Political factors help determine to what extent government regulations and laws are influencing the business environment or marketplace.
Trade regulations, political stability, and employment laws are also important.
Economic factors
Economic factors let senior management know which economic issues are affecting the business. They also tell them which ones are likely to have a long-term impact.
GDP growth, inflation, interest rates, and unemployment, for example, are important factors. GDP stands for G ross D omestic P roduct . Foreign exchange rates and businesses cycles also affect business performance.
Social factors
With the PEST Analysis, a company can analyze socio-cultural factors and determine what’s best for its target market. It also helps the company determine what is best for consumer needs.
Demographics, cultural trends, and education are some factors. So are lifestyle, age distribution, and population.
Demography is the study of human populations and which factors make them change, such as migration, births, and deaths. Demographics are statistical data relating to human populations and groups within those populations.
Technological factors
With these factors, senior management can assess how technological advances may affect the company. They can also help determine a whole industry’s prospects.
New technologies, the technology cycle, and spending are important factors to consider. So are technology awareness and the Internet.
PEST Analysis – different types
There are several different types of PEST Analyses. Choose which is most relevant to your company.
- PESTLE or PESTEL : Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental.
- SLEPT : Social, Legal, Economic, Political, and Technological.
- STEPE : Social, Technological, Economic, Political, and Ecological.
- STEEPLE : Social, Technological, Economic, Environmental, Political, Legal, and Ethical.
- PESTLIED : Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, International, Environmental, and Demographic.
Performing analyses simultaneously
Business professionals often carry out different types of analyses simultaneously. They may perform a SWOT Analysis alongside a PEST Analysis.
A SWOT Analysis is a diagram that helps organizations identify key weaknesses, strengths, opportunities, and threats.
With SWOT Analyses, companies can create new strategies to position themselves better in the marketplace. We also refer to it as a SWOT Matrix .
Video – PEST Analysis
In this video, Shad Morris explains how to conduct a PEST Analysis. He says it can help a company decide whether to, for example, break into a foreign market.
Share this:
- Renewable Energy
- Artificial Intelligence
- 3D Printing
- Financial Glossary

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 9 min read
PEST Analysis
Identifying "big picture" opportunities and threats.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
(Also known as PESTLE, PESTEL, PESTLIED, STEEPLE, SLEPT and LONGPESTLE)
Changes in your business environment can create great opportunities for your organization – and cause significant threats.
Opportunities might come from new technologies that help you reach new customers, from new funding streams that allow you to invest in better equipment, and from changes to government policy that opens up new markets.
Threats might include deregulation that exposes you to intensified competition, a shrinking market, or increases to interest rates, which can cause problems if your company is burdened by debt.
PEST Analysis is a simple and widely used tool that helps you to analyze the Political, Economic, Socio-Cultural, and Technological changes in your business environment. So you can gain a better understanding of the "big picture" forces of change that you're exposed to, and, from this, take advantage of the opportunities that they present.
In this article and in the video, below, we'll look at how you can use PEST Analysis to understand and adapt to your current and future business environment.
What Is PEST Analysis?
Harvard professor Francis Aguilar is thought to be the creator of PEST Analysis. He included a scanning tool called ETPS in his 1967 book, "Scanning the Business Environment," which was later amended to PEST. [1]
PEST Analysis is useful for four main reasons:
- It enables you to spot business or personal opportunities, and gives you advanced warning of any significant threats.
- It reveals the direction of change within your business environment, so you can adapt what you're doing to work with the change, rather than against it.
- You can use to analyze risks in your environment as well, so you can avoid starting projects that are likely to fail.
- It gives you an objective view of new and different markets, so you can base business decisions on facts rather than unconscious assumptions when you enter a new country, region, or market.
PEST Analysis is often linked with SWOT Analysis , however, the two tools have different areas of focus.
PEST Analysis looks at "big picture" factors that might influence a decision, a market, or a potential new business. SWOT Analysis explores these factors at a business, product-line or product level.
These tools complement one another and are often used in combination.
How to Use PEST Analysis
Work through the following four steps to analyze your business environment using PEST.
You may like to use our worksheet to guide you through these steps.
Step 1: Brainstorm Factors
First, brainstorm the changes happening in your business environment that will likely impact your organization, focusing on the four key areas of PEST – politics, the economy, socio-cultural changes, and technology.
We've included some common questions to help you do this, but you can tailor these to suit your specific business needs.
Political Factors to Consider
- When is the country's next local, state, or national election? How could this change government or regional policy?
- Who are the most likely contenders for power? What are their views on business policy, and on other policies that affect your organization?
- Depending on the country, how well developed are property rights and the rule of law, and how widespread are corruption and organized crime? How are these situations likely to change, and how is this likely to affect you?
- Could any pending legislation or taxation changes affect your business, either positively or negatively?
- How will business regulation, along with any planned changes to it, affect your business? And is there a trend towards regulation or deregulation?
- How does government approach corporate policy, corporate social responsibility, environmental issues, and customer protection legislation? What impact does this have, and is it likely to change?
- What is the likely timescale of proposed legislative changes?
- Are there any other political factors that are likely to change?
Economic Factors to Consider
- How stable is the current economy? Is it growing, stagnating, or declining?
- Are key exchange rates stable, or do they tend to vary significantly?
- Are customers' levels of disposable income rising or falling? How is this likely to change in the next few years?
- What is the unemployment rate? Will it be easy to build a skilled workforce? Or will it be expensive to hire skilled labor?
- Do consumers and businesses have easy access to credit? If not, how will this affect your organization?
- How is globalization affecting the economic environment?
- Are there any other economic factors that you should consider?
Use Porter's Diamond to align your strategy with your country's business conditions.
Socio-Cultural Factors to Consider
- What is the population's growth rate and age profile? How is this likely to change?
- Are generational shifts in attitude likely to affect what you're doing?
- What are your society's levels of health, education, and social mobility? How are these changing, and what impact does this have?
- What employment patterns, job market trends, and attitudes toward work can you observe? Are these different for different age groups?
- What social attitudes and social taboos could affect your business? Have there been recent socio-cultural changes that might affect this?
- How do religious beliefs and lifestyle choices affect the population?
- Are any other socio-cultural factors likely to drive change for your business?
Values take a central role in any society. Use the Competing Values Framework to identify your organization's values, and Hofstede's Cultural Dimensions to explore the values of your customers.
Technological Factors to Consider
- Are there any new technologies that you could be using?
- Are there any new technologies on the horizon that could radically affect your work or your industry?
- Do any of your competitors have access to new technologies that could redefine their products?
- In which areas do governments and educational institutions focus their research? Is there anything you can do to take advantage of this?
- How have infrastructure changes affected work patterns (for example, levels of remote working)?
- Are there existing technological hubs that you could work with or learn from?
- Are there any other technological factors that you should consider?
There are variations of PEST Analysis that bring other factors into consideration. These include:
- PESTLE/PESTEL: Political, Economic, Socio-Cultural, Technological, Legal, Environmental.
- PESTLIED: Political, Economic, Socio-Cultural, Technological, Legal, International, Environmental, Demographic.
- STEEPLE: Social/Demographic, Technological, Economic, Environmental, Political, Legal, Ethical.
- SLEPT: Socio-Cultural, Legal, Economic, Political, Technological.
- LONGPESTLE: Local, National, and Global versions of PESTLE. (These are best used for understanding change in multinational organizations.)
Choose the version that best suits your situation.
Step 2: Brainstorm Opportunities
Once you've identified the changes that are taking place in your business environment for each area of PEST, it's time to look at each one in detail, and brainstorm the opportunities that they could open up for you. For example, could it help you develop new products, open up new markets, or help you make processes more efficient?
Step 3: Brainstorm Threats
It's also important to clarify and factors that might undermine your business, now and in the future. If you understand this early enough, you may be able to avoid these problems, or minimize their impact.
For example, if a core part of your market is in demographic decline, could you target other areas of the market? Or if technology is threatening a key product, can you adapt to it?
Risk Analysis can help you to assess these threats and devise strategies to manage them.
Step 4: Take Action
Where you have identified significant opportunities, build the actions you'll take to exploit them into your Business Plan . And if you've identified any significant risks, take appropriate action to manage or eliminate them.
PEST Analysis is a great tool you can use to brainstorm threats and opportunities that might be impacting you, as a result of your wider business environment.
PEST stands for:
- P olitical. How government policy and legislation are impacting your business.
- E conomic. How economic factors like growth, inflation and interest rates are affecting your business.
- S ocio-cultural. How trends and lifestyle changes might impact your business.
- T echnological. How new technologies, automation, and the pace of technological change are impacting your business.
You can use these headings to brainstorm the "big picture" characteristics of a business environment (this could be a country, a region, or a new or existing market), and, from this, draw conclusions about the significant forces of change operating within it.
This provides a context for more detailed planning, within which you will be able to minimize risks and take full advantage of the opportunities that present themselves.
Download Worksheet
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Introduction to commercial awareness.
Understanding the space your business operates within
Infographic
All You Need To Know About Commercial Awareness Infographic
Infographic Transcript
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 30% off your first year of Mind Tools
Great teams begin with empowered leaders. Our tools and resources offer the support to let you flourish into leadership. Join today!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Tips for Dealing with Customers Effectively

Pain Points Podcast - Procrastination
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Pain points podcast - starting a new job.
How to Hit the Ground Running!
Ten Dos and Don'ts of Career Conversations
How to talk to team members about their career aspirations.
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
What is emotional intelligence.
Understanding emotions
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
PEST Analysis: Definition, Examples, and Templates
10 minutes read
Introduction
PEST Analysis is a strategic tool used by businesses and marketers to evaluate the macro-environmental factors that can impact their operations, growth, and strategy. It stands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors, which are the primary elements considered in this analysis. By understanding the PEST factors, organizations can better position themselves in the market, anticipate changes, and develop strategies to mitigate risks or capitalize on opportunities. In this article, we will define PEST Analysis , provide examples of its application, and offer templates to help you conduct your own analysis.
What is PEST Analysis
PEST analysis is a strategic management tool used to analyze and evaluate the external factors affecting an organization or a specific project. The acronym "PEST" stands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors. These factors are assessed to understand the potential opportunities and threats they present to the organization's operations or objectives. PEST analysis helps businesses and decision-makers anticipate changes in their external environment and adapt their strategies accordingly.
What is PEST Analysis used for
PEST Analysis is a macro-environmental analysis that helps businesses understand the external factors that can influence their business environment. It is a component of the broader PESTEL or PESTLE analysis, which also includes Environmental and Legal factors. The PEST framework is particularly useful for:
Strategic Planning: PEST Analysis aids in identifying long-term opportunities and threats that could shape the future direction of a business. By analyzing Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors, businesses can anticipate changes in the business environment and strategically plan their growth trajectory.
Market Research: Understanding the broader context in which a market operates is crucial for effective market research. PEST Analysis provides this context by offering insights into the external factors that can impact market trends, consumer behavior, and overall market potential.
Risk Management: In terms of risk management, PEST Analysis helps businesses assess potential risks associated with external factors. For instance, changes in government policies (Political), economic downturns (Economic), shifts in consumer attitudes (Social), or rapid technological advancements (Technological) could pose risks. By anticipating these risks, businesses can develop contingency plans to mitigate their impact.
Competitive Analysis: Lastly, PEST Analysis is useful for evaluating how competitors might be affected by the same external factors. This understanding can help businesses identify competitive advantages or vulnerabilities and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Overall, PEST Analysis provides valuable insights that enable businesses to navigate their macro-environment more effectively for strategic planning, market research, risk management, and competitive analysis.
What are the Components of PEST Analysis?
PEST Analysis serves as a powerful tool for businesses to understand the macro-environmental factors that can influence their operations. Each component of PEST Analysis represents a different aspect of the macro-environment. Let's delve deep into its role in strategic planning, market research, risk management, and competitive analysis.
Risk Management: I n terms of risk management, PEST Analysis helps businesses assess potential risks associated with external factors. For instance, changes in government policies (Political), economic downturns (Economic), shifts in consumer attitudes (Social), or rapid technological advancements (Technological) could pose risks. By anticipating these risks, businesses can develop contingency plans to mitigate their impact.
Whether it's for strategic planning, market research, risk management, or competitive analysis, PEST Analysis provides valuable insights that enable businesses to navigate their macro-environment more effectively.
PEST Analysis Examples for Application
PEST Analysis can provide valuable insights across various industries. Let's look at some examples of how PEST Analysis can be applied in different industries:
PEST Analysis for the Retail Industry
In the retail sector, political factors such as import tariffs and trade policies could significantly impact the cost of goods and ultimately the pricing strategy. Economic factors like consumer spending habits, disposable income levels, and economic stability would directly influence demand patterns. Social trends, including the increasing preference for online shopping or sustainable products, shape consumer behavior. Technological advancements like AI-powered recommendation systems or secure payment technologies also play a crucial role in shaping the retail landscape.
PEST Analysis for the Automotive Industry
For automakers, political factors such as emission regulations or safety standards can dictate design and production decisions. Economic factors like fuel prices or economic downturns can influence consumer buying power and preferences. The shift in social attitudes towards environmentally friendly vehicles has seen a surge in demand for electric vehicles. Technological advancements like autonomous driving technology, electric drivetrains, and connected car technology are reshaping the industry.
PEST Analysis for the Healthcare Industry
In healthcare, political factors like healthcare reforms or policy changes can have a profound impact on how healthcare services are delivered. Economic factors such as public health funding or insurance coverage determine accessibility to healthcare services. Social factors like an aging population or lifestyle trends influence healthcare demand patterns. Technological breakthroughs in areas like telemedicine, AI diagnostics, genomics, and personalized medicine are revolutionizing patient care.

These examples illustrate how PEST Analysis can help businesses in different industries understand their macro-environment better and make strategic decisions accordingly.
How to Conduct a PEST Analysis
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to conduct a PEST analysis.
1. Start by identifying the four key factors that make up a PEST analysis: Political, Economic, Social, and Technological.
2. Political Factors: Analyze the political environment and how it may impact your business. This includes factors such as government stability, regulations, trade policies, and taxation. Look for any political changes or events that may affect your industry or market.
3. Economic Factors: Evaluate the economic factors that can influence your business. Consider factors such as economic growth, inflation rates, interest rates, and exchange rates. Look for any economic trends or patterns that may impact your industry or market.
4. Social Factors: Examine the social factors that can impact your business. This includes factors such as demographic trends, cultural norms, consumer attitudes, and lifestyle changes. Look for any social shifts or movements that may affect your industry or market.
5. Technological Factors: Assess the technological factors that can affect your business. Consider factors such as technological advancements, innovation, automation, and digitalization. Look for any technological developments or disruptions that may impact your industry or market.
6. Gather relevant data and information for each factor. This can be done through market research, industry reports, surveys, and interviews. Ensure that the information collected is accurate and up-to-date.
7. Analyze the data and identify the key opportunities and threats that arise from each factor. This will help you understand the external factors that can impact your business positively or negatively.
8. Prioritize the opportunities and threats based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence. This will allow you to focus on the most significant factors and develop strategies to mitigate risks or capitalize on opportunities.
9. Develop an action plan based on the findings of the PEST analysis. This plan should outline specific steps and initiatives to address the identified opportunities and threats. Assign responsibilities and set deadlines to ensure effective implementation.
10. Regularly review and update the PEST analysis to reflect any changes in the external environment. Keep track of new political, economic, social, and technological developments that may impact your business.
By conducting a PEST analysis, you can gain a better understanding of the external factors that can influence your business. This analysis will help you make informed decisions, develop effective strategies, and stay ahead of the competition in a rapidly changing business environment.
Boardmix: Online Whiteboard for PEST analysis
Boardmix Online Whiteboard is a tool that can help users create PEST analysis charts and diagrams. This online whiteboard platform allows users to collaborate and brainstorm ideas in real time. With the PEST analysis in Boardmix, users can easily identify and analyze the political, economic, social, and technological factors that may impact their business or industry.
Steps of Creating PEST analysis in Boardmix
Creating a PEST analysis in Boardmix is a straightforward process. Here are the steps to follow:
1. Sign in or create an account: Visit the Boardmix website and sign in with your existing account or create a new one if you don't have an account yet.
2. Create a new whiteboard: Once you're signed in, click on the "New board" button to start creating a new whiteboard for your PEST analysis.
3. Add PEST analysis template: In the whiteboard, click on the "Templates" option in the toolbar and search for "PEST analysis." Select the template that suits your needs and click on it to add it to your whiteboard.
4. Customize the template: Customize the PEST analysis template by adding your own content and data. You can edit the text, add or remove sections, and rearrange elements according to your analysis requirements.
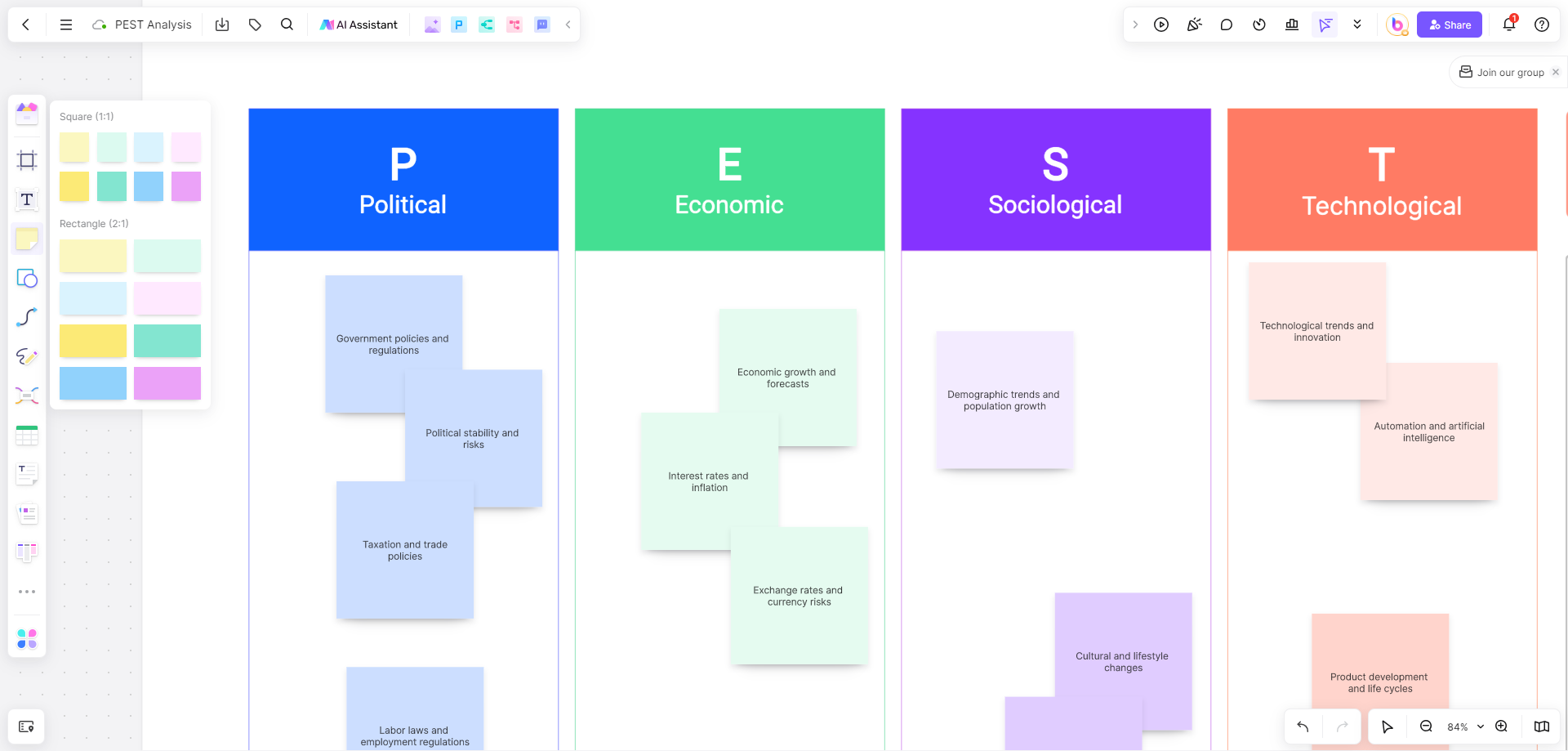
5. Collaborate and gather input: If you're working with a team or stakeholders, use the collaboration features of Boardmix to gather input and insights from others. You can invite team members to join your whiteboard and collaborate in real time.
6. Add notes, comments, and images: Enhance your analysis by adding notes, comments, and images to provide further context and explanations for your findings. This will make your analysis more comprehensive and informative.
7. Export and share: Once your PEST analysis is complete, you can export it in various formats such as PDF or PNG. This allows you to easily share your analysis with colleagues, clients, or other stakeholders.
That's it! You have successfully created a PEST analysis in Boardmix. Enjoy exploring and analyzing the external factors that may impact your business or industry.
Why Use Boardmix to Make PEST Analysis?
When it comes to using Boardmix for PEST analysis, several key features make it a valuable tool.
1. Firstly, Boardmix offers a user-friendly interface that makes it easy for users to navigate and create their PEST analysis charts. The platform is designed to be intuitive and user-friendly, ensuring that even those without technical expertise can easily utilize the tool.
2. Secondly, Boardmix provides a wide range of customization options. Users have the ability to choose from various templates and layouts, allowing them to tailor their analysis to their specific needs. Whether you're analyzing the political, economic, social, or technological factors, Boardmix has the flexibility to accommodate your requirements.
3. Furthermore, Boardmix supports real-time collaboration. This means that multiple users can work on the same analysis simultaneously, enabling teams to brainstorm ideas, share insights, and gather input from different perspectives. This collaborative feature enhances the overall effectiveness of the PEST analysis and ensures that all relevant stakeholders have a voice in the process.
4. Additionally, Boardmix allows users to add notes, comments, and images to their analysis. This functionality enables users to provide further context and explanations for their findings, enhancing the clarity and depth of the analysis. The ability to include images also allows for visual representations of data or examples, making the analysis more engaging and informative.
5. Lastly, Boardmix offers a seamless exporting and sharing process. Once the PEST analysis is complete, users can easily export their charts in various formats such as PDF or PNG. This enables them to share their analysis with colleagues, clients, or other stakeholders.
Overall, the features offered by Boardmix make it an ideal choice for conducting a PEST analysis. Its user-friendly interface, customization options, real-time collaboration capabilities, note-taking functionality, and exporting capabilities ensure a comprehensive and efficient analysis process.

PEST Analysis Templates
To help you get started with your own PEST Analysis, here are simplified templates for each component:
1. Political Factors
- Government policies and regulations
- Political stability and risks
- Taxation and trade policies
- Labor laws and employment regulations
2. Economic Factors
- Economic growth and forecasts
- Interest rates and inflation
- Exchange rates and currency risks
- Consumer spending trends and disposable income
3. Social Factors
- Demographic trends and population growth
- Cultural and lifestyle changes
- Education levels and workforce skills
- Health and environmental concerns
4. Technological Factors
- Technological trends and innovation
- Automation and artificial intelligence
- Product development and life cycles
- Infrastructure and connectivity
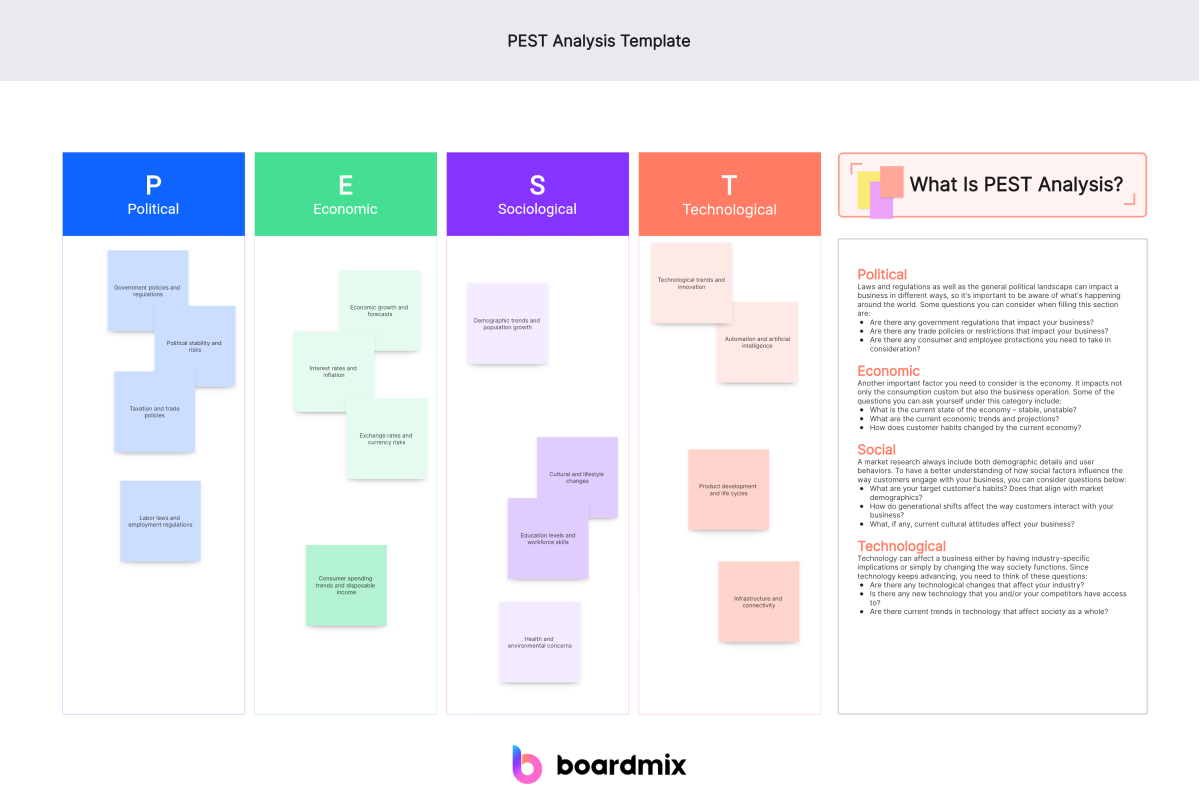
PEST Analysis is a valuable tool for businesses looking to understand and navigate the complex macro-environmental factors that can influence their success. By conducting a thorough PEST Analysis, organizations can gain insights into potential opportunities and threats, allowing them to make informed strategic decisions. The templates provided serve as a starting point, but businesses should tailor their analysis to their specific industry and market context. Boardmix provides a user-friendly interface with various templates and customization options to create visually appealing PEST analysis charts. Users can also add notes, comments, and images to further enhance their analysis. Discover the Boardmix Online Whiteboard for PEST Analysis and conduct a thorough analysis of external environment.
Join Boardmix to collaborate with your team.
Understanding Human Experiences: A Guide to Empathy Maps

Understanding the Importance of Identifying and Connecting with Your Target Audience
![meaning of pest analysis [Guide] Creative Brief: What is It & How to Write](https://cms.boardmix.com/images/articles/creative-brief.png)

[Guide] Creative Brief: What is It & How to Write

How to do a PEST analysis
Lucid Content
Reading time: about 7 min
As a business leader, you understand the importance of staying ahead of the curve, but changes outside your control are constantly influencing your business. If you don’t take the time to identify and understand these external factors, you could be leaving money on the table—or worse, endangering the business itself.
The PEST analysis helps entrepreneurs discover what factors could impact their business and develop strategies to handle those changes. In this article, you will learn the of a PEST analysis and how to complete one.

What is a PEST analysis?
Originally developed in 1967 by Harvard professor Francis Aguilar, PEST analysis is a strategic planning tool that helps organizations identify and evaluate threats and opportunities for the business.
PEST is an acronym describing four primary external factors that influence the business environment: political, economic, socio-cultural, and technological.
Goals of a PEST analysis
The main purpose of PEST analysis is to understand what external forces may affect your organization and how those factors could create opportunities or threats to your business.
PEST analysis helps you:
- Understand current external influences on the business so you can work on facts rather than assumptions.
- Identify what factors could change in the future.
- Mitigate risks and take advantage of opportunities to remain competitive.
- Develop a better long-term strategy.
PEST is particularly useful for understanding the overall market environment. The more threats or risk factors in the market, the more difficult it is to do business. By analyzing the market forces at play, the more strategic you can be in your planning and decision-making.
Additionally, PEST analysis helps organizations strategically plan projects and initiatives so that you only focus on projects that have the greatest chance of success. It also gives you the tools to forecast changes so you can grow your organization with those changes instead of working against them.
PEST vs. SWOT analysis
PEST and SWOT analysis are often used together to better understand the business environment. However, the two frameworks are distinct and apply to different levels of business analysis.
PEST analysis focuses on the big picture and impacts on the overall business, market, and important decisions. PEST is best used for market research and broader analysis of the business environment.
On the other hand, SWOT analysis hones in more narrowly on the organization itself to identify its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. A SWOT analysis is often conducted at the beginning of a new project or to evaluate a product line.

Combining these macro- and micro-level analyses of your business will help you understand a complete picture of your market and your business’s unique opportunities so you can mitigate risks and effectively plan for the future.
When to do a PEST analysis
A PEST analysis is best used when you need a big-picture understanding of your business. Some of the best times to do a PEST analysis include:
- When you’re starting a new business
- When you uncover a major problem
- When/if your business is pivoting
- When you recognize impending changes in one area (e.g., politics) and want to re-evaluate the market
Keep in mind that PEST analyses are macro-level evaluations.
Conducting a PEST analysis is fairly straightforward, but it can be time-consuming. Use the following steps to help you conduct your next PEST analysis—just be sure to give yourself plenty of time to do a thorough evaluation.
1. Consider PEST factors that could impact your business
The first step is to research and gather as much information about your organization’s external influences as possible. Enlist the help of other leaders or managers in the business to ensure you have a comprehensive data set.
As you start brainstorming and gathering data, consider the following list of PEST examples to guide your research:
P: Political factors
Political factors look at how legal and governmental regulations, as well as the political climate, might affect your organization’s freedom to operate and its ultimate profitability.
These factors might include:
- Upcoming local, state, or national elections
- Main political candidates and their views on different policies
- Government regulation of industry or competition
- Trade policies (e.g., tariffs, current or prospective trade deals, etc.)
- Level of corruption or organized crime in your region or country
- Import restrictions
- E-commerce policies
- Consumer and employee protections
E: Economic factors
The economy has a significant impact on any business. Consider the following economic factors that could influence your business operations:
- Current economic stability
- Projected growth and inflation rates
- Interest rates
- Fiscal policies
- Consumer habits and financial stability
- Unemployment rate and competition for jobs
- Access to credit (personal and business)
S: Socio-cultural factors
Socio-cultural factors consider the makeup of the population and your target demographics to understand how well your business can compete in the market. These factors might include age distribution, cultural attitudes, and workplace or lifestyle trends.
As you analyze the market, consider how the following factors could impact your organization:
- Population growth and demographics
- Generational shifts
- Consumer habits and values (e.g., focus on product quality or eco-friendliness)
- Family size and structure
- Consumer lifestyles
- Immigration rates
- Attitudes toward work
T: Technological factors
This step considers technology’s specific role and development in an organization and the industry, as well as broader technological trends and uses that affect society as a whole.
For example, one way technological changes have affected the workforce is by increasing access and availability of remote working opportunities. These changes have far-reaching consequences for the future of work and will impact how organizations structure their businesses and employees.
Other technological factors to consider include:
- The organization’s access to new technology
- The competition’s access to technology
- Rate of technological change
- Evolution of infrastructure
- Government or institutional research
2. Identify opportunities
Once you’ve researched the various ways your organization is influenced and affected by external conditions, start identifying opportunities these changes could provide.
For instance, is there a technological development of which you could take advantage to increase efficiency? Or are there shifts in consumer demographics that could open new markets for your products?
Seek out as many opportunities as possible so you can develop the best strategic response for your business.
3. Identify threats
Unfortunately, change also comes with risks. Whether an economic downturn threatens your bottom line or a competitor’s access to new technology gives them a competitive edge, you need to identify potential threats to your organization so you can mitigate the risks and adapt your strategy accordingly.
The sooner you recognize threats, the more likely you are to avoid them or reduce their impact.
4. Act on your findings
With all your data collected and your opportunities and threats outlined, it’s time to take action. Incorporate these findings into your business plan to take advantage of opportunities and manage threats as soon as possible.

Use Lucidchart for your next PEST analysis
When it comes to PEST analysis, there are a lot of things to consider. Make the process easier with Lucidchart.
Lucidchart is an intelligent diagramming solution that helps businesses visualize their processes, people, and systems. Use Lucidchart’s ready-made business analysis and strategy templates to get started on your analysis today. Because Lucidchart is a cloud-based platform, you can work from multiple devices and easily share your documents with other contributors.
When you’re finished, start a new diagram in Lucidchart to map out your strategy so you can begin taking action on your findings ASAP.

Browse Lucidchart's business analysis and strategy templates. Go now
Browse Lucidchart’s business analysis and strategy templates.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles

A great business analyst is armed with a toolbox of visual modeling techniques to help them drive successful project outcomes. In this article, you'll find nine of the best techniques, including process flows and SWOT analysis diagrams.

What’s the best approach to analyzing your business? Learn the differences between SWOT analysis and gap analysis, and see how either method can help you identify your business's strengths and areas to improve.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with

PEST & PESTEL Analysis

PEST analysis is an analysis of the political, economic, social and technological factors in the external environment of an organization, which can affect its activities and performance. [1]
PESTEL model (or PESTLE model) involves the collection and portrayal of information about external factors which have, or may have, an impact on business. [2]
What is a PEST or a PESTEL Analysis
PEST or PESTEL analysis is a simple and effective tool used in situation analysis to identify the key external (macro environment level) forces that might affect an organization. These forces can create both opportunities and threats for an organization. Therefore, the aim of doing PEST is to:
- find out the current external factors affecting an organization;
- identify the external factors that may change in the future;
- to exploit the changes (opportunities) or defend against them (threats) better than competitors would do.
The outcome of PEST is an understanding of the overall picture surrounding the company.
PEST analysis is also done to assess the potential of a new market. The general rule is that the more negative forces are affecting that market, the harder it is to do business in it. The difficulties that will have to be dealt with significantly reduce profit potential and the firm can simply decide not to engage in any activity in that market.
PEST variations
PEST analysis is the most general version of all PEST variations created. It is a very dynamic tool as new components can be easily added to it in order to focus on one or another critical force affecting an organization.
Although the following variations are more detailed analyses than simple PEST, the additional components are just extensions of the same PEST factors. The analysis probably has more variations than any other strategy tool:
STEP = PEST in a more positive approach. PESTEL = PEST + Environmental + Legal PESTELI = PESTEL + Industry analysis STEEP = PEST + Ethical SLEPT = PEST + Legal STEEPLE = PEST + Environmental + Legal + Ethical STEEPLED = STEEPLE + Demographic PESTLIED = PEST + Legal + International + Environmental + Demographic LONGPEST = Local + National + Global factors + PEST
Using the tool
The process of carrying out PEST analysis should involve as many managers as possible to get the best results. It includes the following steps:
- Step 1. Gathering information about political, economic, social and technological changes + any other factor(s).
- Step 2. Identifying which of the PEST factors represent opportunities or threats.
Gathering PEST, PESTEL and STEEPLED information
In order to perform PEST (or any other variation of it), managers have to gather as much relevant information as possible about the firm’s external environment. Nowadays, most information can be found on the internet relatively easily, quickly and with little cost.
When the analysis is done for the first time, the process may take a little longer and as a beginner you may find yourself asking “What changes do I exactly look for in politics, economics, society and technology?” The following templates might be useful when gathering information for PEST, PESTEL and STEEPLED analysis.
NOTE: PEST covers all macro environment forces affecting an organization. Therefore, when doing PESTEL or STEEPLED analysis, legal, environmental, ethical and demographic factors may overlap with PEST factors.
Identifying opportunities and threats
Gathering information is just the first important step in doing a PEST analysis. Once it is done, the information has to be evaluated. There are many factors changing in the external environment but not all of them are affecting or might affect an organization. Therefore, it is essential to identify which PEST factors represent the opportunities or threats for an organization and list only those factors in PEST analysis. This allows focusing on the most important changes that might have an impact on the company.
PEST analysis example
The following table shows a PEST analysis example. It lists opportunities and threats that are affecting a firm in its macro environment.
- Thompson, J. and Martin, F. (2010). Strategic Management: Awareness & Change. 6th ed. Cengage Learning EMEA, p. 86-88, 816
- Rothaermel, F. T. (2012). Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases. McGraw-Hill/Irwin, p. 56-61
- David, F.R. (2009). Strategic Management: Concepts and Cases. 12th ed. FT Prentice Hall, p. 104-114
- Johnson, G, Scholes, K. Whittington, R. (2008). Exploring Corporate Strategy. 8th ed. FT Prentice Hall, p. 55-57
- Wikipedia (2013). PEST analysis. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PEST_analysis
- SWOT Analysis of Walt Disney 2023
- SWOT Analysis of Blackberry 2023
- SWOT analysis of BMW 2023
- SWOT Analysis of eBay 2023
- SWOT Analysis of Dell 2023
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Filter by Keywords
What is PEST Analysis? Templates, Definition, and Examples
January 15, 2024
Seasoned business strategists use ‘PEST (‘political, economic, social, and technological) analysis’ to identify whether a new country, market, or city is the right fit for business expansion.
Plus, as a part of ongoing strategic planning, PEST analysis involves identifying and discovering external forces with significant risks to your business and developing strategies to handle those changes.
Breaking down the causes and potential effects of unexpected changes likely to affect your business helps your team understand what’s happening and build an action plan to fit the technological landscape.
Traditionally, PEST analysis involved writing down the analysis of each economic, social, and technological factor and making assumptions about their changing patterns.
However, whether planning a new product launch or assessing a market for potential threats, new-age affinity diagram tools and a PEST analysis template help make the process easier.
These tools help you constantly monitor and prepare for losses, identify threats, and understand your capabilities in the broader business environment.
This article shares how to perform PEST analysis and the tools to effectively conduct and organize your analysis.
What is PEST Analysis?
PEST analysis is a project forecasting methodology for business professionals and strategists. PEST looks at external factors like political, economic, socio-cultural, and technological changes likely to impact your business performance and revenue.
Professor Francis Aguilar from Harvard University developed this framework in 1967 to assess how these factors affect a business environment. Analyzing PEST factors helps you identify the potential challenges in the current economic environment and leverage the findings as a competitive advantage.
The different PEST factors include:
Political factors
- The current economy and political climate of the country
- Closer look at tax policies, labor regulations, IP protections, and environmental regulations
- Investment scenario, foreign partnership opportunities, and the foreign trade policy
- Government regulations on raw materials, trade regulations, and the approach to tax policy
Economic factors
- Yearly trends in economic factors like Interest rates and inflation rates
- Cost of living, purchasing power, and lifestyle trends
- Economic growth, GDP, disposable income, and employment trends
- Trade restrictions and government policy for international business
- The overall economic health and political stability of the country
Social factors
- The talent pool, labor costs, age distribution, and educational requirements
- Population growth rate, employment patterns, and job market trends
- Current popular brands, consumer trends, health consciousness, and cultural attitudes
Technological factors
- Availability of modern infrastructure to support production and marketing activities
- Adaptiveness toward the latest technologies like automation and artificial intelligence
- Level of disruption and shift in new technology incentives
By the end of a successful PEST analysis, you will be able to answer the following questions:
- Is the political environment of the country stable?
- Is the country witnessing economic growth, and can the target markets afford your product?
- If I start a subsidiary, will I get skilled labor whose social values will match my brand’s value?
- Can the country provide me with the necessary technological factors and infrastructure, or do I need to outsource?
What is PESTLE Analysis?
PESTLE analysis is an extension of PEST analysis. PESTLE considers all the factors of PEST analysis along with two additional factors—legal and environmental conditions, that might impact your business operations.
Legal factors that could affect your business
- Data protection laws
- Discrimination laws
- Consumer protection laws
- Employment laws
Environmental factors to focus on
- Weather and climate conditions
- Waste management initiatives
- Environmental pollution awareness
Importance of a PEST Analysis
What is that one common goal for all businesses, irrespective of the industry they belong to or the product they sell? Usually, it is being profitable, leading the competition, or goals along similar lines.
Now, these goals vary from business to business. However, businesses require a definitive idea about their target market and its preferences before setting the right goals. PEST analysis helps focus on developing an end-to-end marketing plan by analyzing the critical external elements.
Marketing strategists and business professionals require PEST analysis for four main reasons:
- Getting the first mover advantage by spotting excellent business opportunities that competitors have not encountered yet
- Identifying a critical threat and taking necessary precautions before starting operations officially
- Making decisions on quantifiable aspects and not relying solely on assumptions
- Conducting a future assessment to identify how likely or frequently these factors will change in the future to assess the sustainability of your business strategy
Let’s dive deeper into the different scenarios when you should use PEST analysis as a strategic business tool.
When should you use PEST analysis?
PEST analysis is used to understand unexpected changes and proactively evaluate whether a business decision is right for your organization. Some specific use cases where PEST analysis is beneficial are:
Drastic change in external factors
Evaluating the change is overwhelming when a business landscape changes drastically without warning and without the right tools.
A PEST analysis breaks down the external economic and political factors and technological, legal, and environmental changes to understand how they will impact your organization and pivot accordingly.
Let’s take a PEST analysis example. During the Covid-19 lockdowns in China, shipping delays impacted most global companies. With PEST analysis, you could extrapolate and predict the impact of the shipment delay on your future strategy.
Expansion to a new market
As PEST analysis focuses on cultural and economic factors when expanding to new geographies, use this framework to gauge cultural differences. In addition, having a person familiar with the new market helps to develop the go-to-market strategy while considering the cultural factors.
For example, Pepsi’s ‘Come Alive with the Pepsi Generation’ campaign was well-received by English-speaking audiences. However, the Chinese version promised that ‘Pepsi brings your relatives back from the dead,’ but it was not a hit. This is a good example of how PEST analysis would’ve helped prevent this cultural error.
Developing a new product
Developing a new product involves considerable research ranging from consumer trends to spending patterns and identifying the ideal customer profile (ICP).
A PEST analysis helps you consider the external factors your ICP would consider during their decision-making process.
Analyze the long-term vision
PEST analysis is useful when you want to analyze the long-term picture of your business from the lens of strategic thinking:
- When you start a new business or open a subsidiary of your existing business in a new location. Alternatively, you want to re-evaluate the existing market
- Whether the interest rates in the target market are feasible or the business will face a considerable loss
- When you encounter a critical issue (like the Russia-Ukraine war) related to the host country, you want to assess how much it will affect your operations
- You are starting a new product line or pivoting from a service-based business to a product-based business
What is SWOT Analysis, and How is it Different from PEST Analysis?
SWOT analysis, another famous market research technique, is often used with PEST analysis to assess the business environment and other technological factors impacting the change. SWOT analysis stands for—Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
Unlike PEST analysis, where your focus is solely on analyzing the external environment of a business, SWOT analysis assesses both internal and external environments.
Strategists use PEST analysis as a mind-mapping tool to analyze a business environment and identify possible threats and opportunities. You need this framework in the ideation phase of a business.
On the other hand, SWOT analysis software is a more project-specific tool that comes into the picture after you have successfully created a business plan. At this stage, you want to identify your internal strengths to address the external threats and weaknesses so you don’t miss out on the external opportunities.
SWOT and PEST analysis work best when implemented together.
How to Perform a PEST Analysis
Performing a PEST or PESTLE analysis from scratch is time-consuming and resource-intensive. Instead, ClickUp’s PESTLE Analysis Template provides frameworks to understand and analyze the external factors impacting your business environment.
At the same time, using this template, you have identified significant opportunities for revenue growth.
The benefits of using the PESTLE Analysis Template to meet your project objectives are:
- A structured approach to gathering, organizing, and interpreting data
- Helps create strategies tailored to specific political, economic, social, legal, and environmental factors
- Use customized task statuses like ‘WIP,’ ‘Hold,’ ‘Re-open’ to track the progress of a particular external factor till you complete the research
- Opt for different attributes (qualitative and quantitative) to score each factor. For example, notes, risk aspects, and grades for each country
- This template allows you to add up to six attributes to simplify the data analysis
- Like any other problem management software , ClickUp offers three views for this PEST analysis template. The available views are a board view, a list view, and a simple getting-started guide
- The PESTLE analysis template provides regular project management features like adding timelines and custom fields and sending reminders, tags, and labels to ensure everyone’s visibility.
Now, let’s discuss how to use this template to perform your first PEST(LE) analysis.
Identify which aspects of the potential factors to consider
Each environmental factor is associated with multiple elements. If you analyze all these aspects individually, the PEST analysis may take months, even years, to complete. So, the more intelligent strategy is identifying the key aspects highly relevant to your business for each factor.
Suppose you perform a PEST analysis of the macroeconomic factors to understand if you should expand to a new country. Create a project Doc to list all the critical areas for each factor you want to target and factors that might impact your business.

Political factors include the possibility of conflict with other countries, an upcoming election, or special political legislation for international businesses that you should know before starting the project.
The following economic factors to consider are the growth or decline of interest rates and GDP, if there is a significant exchange rate difference, and government policy related to international trade restrictions.
Common socio-cultural factors are consumer buying patterns or preferences and generational value differences that might affect the target market.
Categorize Docs based on tags such as PEST external factors for easy access and searchability. Add necessary resources, guidelines, and company wikis to your Workspace.
Write down the opportunities and threats associated with each factor
Once you collect the data, brainstorm and identify the relevant opportunities and threats. Pairing your PEST analysis with SWOT analysis at this stage will help you.
For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, brands like Slack noticed the following opportunities and threats:
At this stage, use ClickUp Whiteboard for collaborative brainstorming. Here’s how Whiteboard is a creative canvas for your team:
- Collaborate with your team members in real time to add notes, brainstorm in detail, and introduce new ideas
- Convert concepts into action faster by creating specific ClickUp tasks and assigning team members to each task
- Adding images and links at the relevant places helps add context to each task
- Break away from document-based processes and think creatively with visually engaging ideation techniques such as mind maps
- ClickUp’s embedding capabilities allow you to add web, Docs, and task cards to your Whiteboard
At this stage, ClickUp AI streamlines your workflow, whether managing a product release or creating a PEST analysis document for your stakeholders. With ClickUp AI, pull action items from meeting notes and share them with the team, summarize comment threads, and generate project updates for internal and external collaborators.
Time to plan and take actions
Based on all the collated data related to all the macroeconomic factors, set your business goals and the specific actions for each goal.
For example, in the above use case of Slack, some of the relevant business goals could be:
- Increasing Slack’s user base by 80% during the pandemic
- Pivoting from a remote-first tool to a hybrid tool to stay relevant post-pandemic
To fulfill the above goals, the relevant actions will be:
- Adding more remote-working features to Slack, like video calling, built-in project management, and screen recording.
- Adding innovative features and new integrations so that workplaces operating in the hybrid mode will also use this tool.
Also, keep after-action report templates handy to track the actions occasionally and make relevant business decisions.
Document Your Next PEST Analysis with ClickUp
A great way to make the most of a PEST analysis is to use project management tool s to make the information visible to all internal and external stakeholders, collaborate with your team members in real time, and organize this analysis for future reference.
Project managers and business analysts use ClickUp’s project management tool to help everyone stay on the same page regarding external factors that can impact your business.
ClickUp’s PESTLE Analysis Template helps business professionals understand the current and external environment of the business and avoid scope creep .
Start by listing all the external factors on ClickUp Docs, including social factors, and convert text into trackable tasks to stay on top of your ideas.
After this, use ClickUp’s value proposition templates to communicate your offerings, conduct competitive analysis, and develop customer-centric unique value propositions (UVP).
Create tasks for each factor and use ClickUp Goals to stay on track to hit your objectives with clear deadlines.
Convert these plans into actions, break down each action item into multiple tasks, and organize all your tasks in a central ClickUp Dashboard for everyone’s visibility. Get rich insights into the progress of your PEST analysis with line, pie, and bar graphs. Plus, assess the team’s capacity to manage workloads.
Sign up on ClickUp for free .
Create your first PEST analysis and master the art of gathering data effortlessly.
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
- Setting and Tracking Objectives and Key Results: A Comprehensive Guide
- Measuring Progress and Making Adjustments: A Guide to Strategic Planning
- Assessing the Current State: A Comprehensive Look at the Strategic Planning Process
- Applying Principles to Your Own Strategy: A Case Study in Success
- SWOT analysis
- What is SWOT analysis?
- Using SWOT analysis to inform strategy
- How to conduct a SWOT analysis
- Porter's Five Forces
- What is Porter's Five Forces?
- How to apply Porter's Five Forces model
- Using Porter's Five Forces in strategic planning
- PEST analysis
- How to conduct a PEST analysis
- What is PEST analysis?
- Using PEST analysis to identify external factors
- Implementing and monitoring the plan
- Assigning responsibilities
- Creating an action plan
- Measuring progress and making adjustments
- Introduction to strategic planning
- Key components of a strategic plan
- Benefits of strategic planning
- What is strategic planning?
- Steps in the strategic planning process
- Developing strategies and tactics
- Assessing the current state
- Setting goals and objectives
- Market research and analysis
- Using data to inform strategy
- Conducting market research
- Analyzing market trends
- Scenario planning
- What is scenario planning?
- Creating and evaluating scenarios
- Incorporating scenarios into strategic planning
- Financial analysis
- Using financial data in strategic planning
- Forecasting financials
- Assessing financial performance
- Strategy development and implementation
- Expert guidance in strategy implementation
- Ensuring alignment with business goals
- Customized strategic planning services
- Change management consulting
- Managing organizational change
- Implementing new strategies and processes
- Maximizing employee buy-in and adoption
- Performance improvement consulting
- Developing strategies for performance enhancement
- Measuring and monitoring progress
- Identifying areas for improvement
- Success stories
- Real-world examples of successful strategic planning
- Key takeaways and lessons learned
- Applying principles to your own strategy
- Challenges and failures
- Identifying common pitfalls and how to avoid them
- Applying insights to your own strategy
- Learning from failed strategic planning efforts
- Industry-specific case studies
- Examples of strategic planning in specific industries
- Best practices and lessons learned for your industry
- Applying strategies to your own business
- OKR (Objectives and Key Results)
- Understanding the OKR framework
- Integrating OKRs into strategic planning
- Setting and tracking objectives and key results
- Blue Ocean Strategy
- What is Blue Ocean Strategy?
- Case studies and success stories
- Applying Blue Ocean Strategy to your business
- Balanced Scorecard
- What is the Balanced Scorecard?
- Benefits and limitations of the model
- Using the Balanced Scorecard in strategic planning
- Strategic planning frameworks
- Understanding PEST Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn about PEST analysis and its significance in strategic planning

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on PEST analysis, one of the most widely used strategic planning frameworks in the business world. Whether you are a business owner, a marketer, or a student studying business management, understanding PEST analysis is crucial for success. In this article, we will delve into the nitty-gritty of PEST analysis, from its definition and purpose to its application in real-world scenarios. So, what exactly is PEST analysis? PEST stands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors, and it is a framework used to analyze the external environment in which a business operates. By examining these four key areas, businesses can gain a better understanding of the opportunities and threats that may impact their operations.
It is an essential tool for strategic planning and decision-making, as it allows businesses to adapt and stay ahead of the competition. Throughout this article, we will explore each element of PEST analysis in detail and provide real-life examples to help you grasp the concept better. We will also discuss the benefits of using PEST analysis and how it can be applied to various industries. Whether you are new to PEST analysis or looking to refresh your knowledge, this guide has got you covered. So, let's dive into the world of PEST analysis and discover how it can help your business thrive in today's ever-changing landscape. In today's fast-paced and ever-changing business landscape, it is crucial for organizations to have a strong understanding of the external factors that may impact their operations. This is where PEST analysis comes into play.
PEST analysis is a strategic planning framework that helps businesses assess the Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors that may affect their industry and operations. In this article, we will delve into each of these four components in detail to provide a comprehensive understanding of PEST analysis and how it can be used to inform decision-making. Political factors refer to the laws, regulations, and policies set by the government that can have a significant impact on businesses. This can include tax policies, trade regulations, labor laws, and political stability. For example, changes in tax policies can greatly affect a company's profitability, while political instability in a country can disrupt supply chains and business operations.
It is important for businesses to stay up-to-date on political developments and understand how they may impact their operations. Economic factors refer to the overall economic conditions of a country or region and how they may impact businesses. This can include inflation rates, interest rates, consumer spending habits, and GDP growth. Economic factors can greatly influence consumer behavior and purchasing power, which in turn affects businesses. For instance, a recession may lead to a decrease in consumer spending, resulting in lower sales for businesses.
It is crucial for businesses to carefully monitor economic trends and adjust their strategies accordingly. Social factors encompass the cultural norms, values, beliefs, and demographics of a society. These factors can greatly influence consumer behavior and preferences. For example, a company selling halal meat products would need to consider the cultural norms and beliefs of their target market before entering a new market. Social factors also include lifestyle trends, education levels, and population demographics.
Understanding these factors can help businesses tailor their products and services to better meet the needs of their target market. Technological factors refer to the advancements and innovations in technology that can impact businesses. In today's digital age, technology plays a crucial role in shaping industries and disrupting traditional business models. Technological factors can include new software, hardware, automation, and artificial intelligence. Businesses must be aware of technological developments in their industry and adapt accordingly to stay competitive. It is important to note that these four components of PEST analysis may vary depending on the industry and location of the business.
For instance, a company operating in the healthcare industry may face different political and social factors compared to a company in the retail industry. Similarly, a business operating in a developing country may face different economic factors compared to a business in a developed country. In conclusion, PEST analysis is an essential tool for businesses of all sizes and industries. By analyzing the external environment through the lens of political, economic, social, and technological factors, businesses can identify potential opportunities and threats and make informed decisions to stay ahead of the competition. It is crucial for businesses to regularly conduct PEST analysis to stay updated on external factors that may impact their operations and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Political Factors
Technological factors, advancements in technology:, impact on industry:, opportunities and threats:, social factors, demographics:, cultural norms and values:, social trends:, consumer attitudes and behaviors:, ethical considerations:, economic factors, macroeconomic conditions, economic policies, inflation rates and interest rates, consumer spending habits.
By considering these factors, organizations can better understand their external environment and make strategic decisions that will help them thrive in the long run. In conclusion, PEST analysis is an essential tool for businesses to understand their external environment and make informed decisions. By analyzing the political , economic , social , and technological factors, organizations can identify potential opportunities and threats and develop strategies to adapt and thrive in a constantly changing market. It is important for businesses to regularly review and update their PEST analysis to stay ahead of the competition and maintain a competitive advantage.
Related Articles

- Understanding Porter's Five Forces for Strategic Planning
A comprehensive article on how to effectively utilize Porter's Five Forces in strategic planning
- Conducting Market Research: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn everything you need to know about conducting market research and how it can benefit your business.

- The Importance of Measuring and Monitoring Progress in Performance Improvement Consulting
Learn why measuring and monitoring progress is essential in performance improvement consulting and how it can help businesses achieve their goals.

Learn the best practices for setting and tracking objectives and key results in your strategic planning process.
Leave Message
All fileds with * are required
Save my data for future comments
- The Power of Strategic Planning
- A Comprehensive Guide to Implementing New Strategies and Processes
- The Importance of Analyzing Market Trends
- Assessing Financial Performance: A Comprehensive Guide
- Applying Insights to Your Own Strategy: How to Succeed in the Face of Challenges and Failures
- Forecasting Financials: A Comprehensive Overview for Strategic Planning
- Creating and Evaluating Scenarios for Strategic Planning
- How to Conduct a PEST Analysis: Uncovering Key Factors for Strategic Planning
- How to Use the Balanced Scorecard in Strategic Planning
- A Comprehensive Look at Managing Organizational Change
- Learning from Failed Strategic Planning Efforts: Understanding the Importance of Reflection and Adaptation
- Best Practices and Lessons Learned for Your Industry: Capturing Readers' Attention
- Integrating OKRs into Strategic Planning: A Comprehensive Overview
- Real-World Examples of Successful Strategic Planning
- Maximizing Employee Buy-In and Adoption: Strategies for Successful Change Management
- Creating an Action Plan: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Planning
- The Importance of Assigning Responsibilities in the Strategic Planning Process
- Understanding PEST Analysis: Identifying External Factors for Strategic Planning
- Understanding the OKR Framework for Strategic Planning
Understanding SWOT Analysis: A Comprehensive Overview
- A Beginner's Guide to Conducting a SWOT Analysis
- How Customized Strategic Planning Services Can Boost Your Business
- What is Blue Ocean Strategy and How Can it Transform Your Business?
- Using SWOT Analysis to Inform Strategy: A Comprehensive Overview
- Understanding the Balanced Scorecard: A Strategic Planning Model
- Using Financial Data in Strategic Planning: A Comprehensive Guide
- Identifying Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them: A Guide for Success
- How Case Studies and Success Stories Can Revolutionize Your Strategic Planning Models
- Setting goals and objectives: A Strategic Planning Process
- Applying Blue Ocean Strategy to Your Business
- Incorporating Scenarios into Strategic Planning: A Comprehensive Guide
- Expert Guidance in Strategy Implementation: A Comprehensive Overview
- How to Craft a Successful Case Study: Key Takeaways and Lessons Learned
- An Overview of Porter's Five Forces Model
- How to Ensure Alignment with Business Goals for Successful Strategy Implementation
- Key Components of a Strategic Plan: A Comprehensive Overview
Improving Performance: Identifying Areas for Success
- Applying Strategies to Boost Your Business
- Strategies for Enhancing Performance: Unlocking Your Potential
- How to Master Scenario Planning: A Comprehensive Guide
- Examples of Strategic Planning in Specific Industries
- A Complete Guide to Strategic Planning
- Understanding Porter's Five Forces: A Comprehensive Overview
- Using Data to Inform Strategy: How to Use Market Research and Analysis for Strategic Planning
Benefits and Limitations of the Model
- Developing Strategies and Tactics: A Comprehensive Guide to the Strategic Planning Process
Recent Articles

Which cookies do you want to accept?
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} AI that works. Coming June 5, Asana redefines work management—again. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Get early access .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project planning |
4 steps of the PEST analysis process

A PEST analysis is a research tool that helps you analyze the surrounding political, economic, socio-cultural, and technological environment that can affect your business. Learn how this tool can help prevent risk and inform your team’s future business decisions.
Change can be scary. Oftentimes, the best way to deal with change is to understand it. Breaking down the causes for—and potential effects of—any unexpected changes can help your team digest what's happening and come up with an action plan that fits your needs.
That's where a PEST analysis comes in. Use this tool to better understand how external changes are impacting your business—and what you should do about it.
What is a PEST analysis?
A PEST analysis is a research tool that helps you analyze the external political, economic, socio-cultural, and technological changes that can affect your business. This is a shortened version, as sometimes the acronym is lengthened to PESTEL to include legal and environmental factors in addition to the first four.
What does PEST stand for?
PEST is an acronym that stands for political, economic, socio-cultural, and technological. These are all external factors your team should consider when making business decisions. You may also see PESTEL which includes environmental and legal, in addition to the four mentioned previously.
The PEST analysis tool is useful for four main reasons:
Helps spot business opportunities and provides a warning in advance of any dangers or threats to your business.
Analyzes risks in your current environment so your business can avoid any projects that are likely to fail.
Creates an objective view of new or different markets based on quantifiable facts, instead of pre-existing assumptions on a specific region or market.
PEST analysis vs. SWOT analysis
A PEST analysis is often associated with a SWOT analysis , but these two tools focus on different parts of your strategy.
A PEST analysis is a tool to help analyze the external environment so your team can create more accurate decisions for big picture financial decisions. This is the tool you would use when you are considering any economic factors or potential changes to your business strategy .
A SWOT analysis narrows in on a more project-specific level. SWOT analysis helps to find strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for a specific project or business plan. You can use information from a PEST analysis to inform a SWOT analysis.
When to use a PEST analysis
A PEST analysis can help you break down and understand external conditions and changes that are impacting your business. You can use a PEST analysis reactively to understand unexpected changes or proactively to evaluate whether a market or decision is right for your company. Take a look at some specific instances where a PEST analysis can be beneficial.
When external forces drastically change
Sometimes external forces can change the business landscape drastically with no warning. This type of change happens quickly and, without the right tools to evaluate what's happening, they can feel really overwhelming.
A PEST analysis can help you break down the external political, economic, socio-cultural, and technological (plus environmental and legal) changes to quickly understand how they will influence your team. Use this tool to evaluate the impact these external factors will have on your team and pivot accordingly.
For example, in April of 2022, COVID-19 lockdowns in China led to worldwide shipping delays . This type of delay impacts a huge swath of companies, and it’s hard to understand how—or when—your company will be impacted. A PEST analysis can help you extrapolate and predict how current external changes will impact your future strategy, so you can adjust accordingly.
Expanding into a new market
You can use a PEST analysis to look at topics you may not typically consider, such as economic and cultural factors, when you’re expanding into a new demographic or market. It’s helpful to have someone on your team who’s familiar with the new market to assist with developing strategy. If you don’t have someone who’s familiar with the new market, you may run into some cultural roadblocks you may not have considered as an outsider of that culture.
For example, in the 1960s, General Mills expanded their cake mix market into Japan after a successful run in America. They advertised being able to cook a cake in a rice cooker, since many Japanese households at the time did not have an oven. In Japan, rice is considered a sacred food, so the rice cooker was often solely used for that purpose—cooking rice. The thought was that mixing other ingredients into the rice cooker would change the taste of the rice itself. This oversight was one of the biggest reasons why cake mix sales did not meet expectations. This is a good example of how a PEST analysis could have prevented this cultural misstep.
Developing a new product
When you’re developing a new product, there’s a lot of research involved, including figuring out the ideal customer profile (ICP). A PEST analysis can help you think more about the external factors that affect your ICP and how that would influence their decision making process .
On the business side, a PEST analysis can also help you understand how external factors affect the development of a new product. For example, an independent coffee company may be interested in finding a new source for their coffee beans. The sourcer would want to consider the political, economic, socio-cultural, and technological factors to ensure that their business practices are ethical and a good match for their business model.
4 steps of PEST analysis
While a PEST analysis covers large, overarching topics, the format for creating one is quite simple. Here are the four steps you take to complete a PEST analysis.
Step 1: Brainstorm potential factors
In this first step, you’ll want to think about all of the environmental factors that affect your business as a whole. This is where the acronym PEST comes in. PEST stands for:
Political: Are there any elections coming up that may affect your business? Any initiatives on this ballot that may affect how your business performs? Are there any government regulations you need to consider before moving forward with your project?
Economic: What does the current economy look like—is it growing, plateauing, or declining? If you conduct business internationally, are exchange rates affected at all? Is the economy affecting your target market’s purchasing habits? Are there any tariffs or trade restrictions you should be aware of? What does the unemployment rate look like right now—will this affect your hiring plans?
Socio-cultural: Are there any societal attitudes that may affect your business? Are there employment trends in the areas you’re looking to hire? Are there any generational differences that may affect a customer's decision making process? Are there any social movements that are affecting potential career attitudes?
Technological : Are there any new technological innovations that can affect the way you conduct business? Do your competitors have access to a new technology that you may not have access to? Are you looking to add a new type of technology to your business that may affect how you conduct business?
Environmental : What impact will your new business venture have on the environment? What impact will the environment have on your business? Will weather greatly affect how your business operates?
Legal: Are there any current laws or regulations that are affecting how your business operates? Should your team get into legal trouble, do you have a strategy in place for how to handle it?
Step 2: Brainstorm opportunities
After you analyze the four different factors within the PEST acronym, consider any potential opportunities that your business can branch into. This is where a SWOT analysis comes in handy—after you brainstorm these four factors, you can use this analysis to inform how you can create a SWOT analysis as you expand your business.
Consider the COVID-19 pandemic as an example. There were many different political, economic, socio-cultural, and technological changes that came with the lockdown. As a result, companies like Zoom experienced huge growth as teams turned to remote solutions that focused on collaboration and real-time connection.
Step 3: Brainstorm threats
Similar to how you would analyze threats for a SWOT analysis, this is where you consider any potential threats based on the information you gathered in step one. While you are assessing potential business threats, consider creating contingency plans in the event that a potential risk does happen.
A common example of this scenario is an election year—how will you conduct business depending on the outcome of the election? Since election cycles happen consistently, your business has enough time to craft potential plans if an election can greatly disrupt your business.
Step 4: Take action
Based on all of the information you’ve gathered, now is the time to start the strategic planning process and establish your business goals . Understanding these potential threats, factors, and opportunities will help your team through the decision-making process and will inform your future strategy.
Tip : Highlight key areas of your business plan and explain which external factor is affecting this decision. For example, you could highlight the fact that your business is located in a college town to explain why you’re looking to hire more entry-level employees to your team.
Document your PEST analysis with a work management tool
A PEST analysis is best used when your entire team has access to the information. Consider housing your PEST analysis in a project management tool like Asana . Asana helps your team organize tasks and mark dependencies, all while allowing your team to access important information asynchronously.
Related resources
How to track utilization rate and drive team profitability

How to accomplish big things with long-term goals
Smooth product launches are simpler than you think

What is stakeholder analysis and why is it important?
What is a PEST analysis?
Last updated
1 April 2024
Reviewed by
PEST analysis is an evaluation of political, economic, social, and technological factors that can affect your business operations, growth, and development. Analyzing these four factors regularly can help you make better business decisions.
Used in combination with other analyses, PEST factor evaluation can help a business stay ahead of the competition by taking a proactive approach in preparing for future threats and opportunities.
Market analysis template
Save time, highlight crucial insights, and drive strategic decision-making
- PEST analysis: definition
PEST analysis is a framework for evaluating the external factors (political, economic, social, and technological) that may affect business operations. By performing this analysis, business owners can determine what may await their company in the future and which changes they should make to ensure successful adaptation to new developments.
- The four elements of PEST analysis
PEST is an acronym that stands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological. Here is a breakdown of the essential PEST analysis elements:
Political factors
Political factors demonstrate how political issues such as elections, new regulations, and policy changes can affect your business. Examples include:
Upcoming elections
Government industry regulations
New trade policies
Import restrictions
Tax policies
Employment laws
Property rights
Political stability
This information can help you plan for compliance tactics, allocate budgets for adjusting to new policies, change product development approaches, and more.
For example, when employment regulation changes (e.g., minimum wage increase), you may need to raise salaries or provide extra benefits to remain compliant. Or if you are importing or exporting products, the imposition of restrictions or new regulations could mean changes in business operations and logistics.
Economic factors
Economic factors allow business owners to study and consider macroeconomic influences, including:
Economic growth and stability
Interest rates
Exchange rates
Inflation rates
Fiscal policies
Unemployment rates
Consumer buying habits
This data can help you evaluate consumer demand, product costs, expansion possibilities, and competition levels.
For example, if costs of living are increasing, you might need to raise salaries to mitigate the situation. If the economy is improving (or declining), your customers and clients are likely to have more (or less) money to invest in your products and services. Meanwhile, high inflation means lower purchasing power.
Social factors
There are many social factors that may affect your business growth and development. These involve demographic elements, age distribution, lifestyle trends, and more. Examples are:
Consumer lifestyles
Family structures
Consumer habits
Ecological trends
Generational shifts
Educational trends
Work trends
Health of the population
Social factors can help you identify and segment your target audience as well as gather insight regarding approaches to challenges or pain points.
For example, a major shift toward remote work could help you adjust your approach in attracting top talent. Alternatively, a shift in fashion trends could dictate your upcoming product development tactics.
Technological factors
Technological factors involve studying how technology affects consumer behavior and demands in addition to changing the way work is done, products are produced, or services are delivered.
These factors include:
Individual access to new tech solutions
Tech infrastructure evolution
Rise of artificial intelligence implementation
Industry innovations
Cybersecurity
With this information in mind, you can make predictions about your company's success in the industry if it takes full advantage of the available technologies.
For example, new chatbot technologies can help you improve your customer support efforts and make changes to the way your team works. Or maybe you need to move your company's headquarters to a tech hub in order to gain a competitive edge.
- Benefits of PEST analysis
The benefits of conducting PEST analysis regularly are:
Gaining valuable insight into a company's present and future
Leveraging access to long-term strategic planning
Discovering new business opportunities
Preparing for external environmental threats
When used together with the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) analysis, PEST analysis can yield more productive results.
- How to conduct a PEST analysis
Taking a structured approach to PEST analysis can help you minimize unnecessary action and start taking advantage of results in real-time.
Step 1: Identify PEST factors
The analysis begins with using reliable resources to gather political, economic, social, and technological data relevant to your industry and niche.
Political – study the relevant laws pertaining to your business and potential changes in the near future. Find out what the consequences of not following these laws are, or whether you are eligible for exceptions.
Economic – evaluate market trends, tax changes, inflation rates, and other elements that may affect your business.
Social - study your consumers, buying trends, fashion trends, and other information that may affect consumer buying behavior.
Technological – evaluate the technology you are using, learn about innovations in your industry, and find out what the costs of implementing new tech may be.
Once you know which factors can affect your business, proceed to step 2.
Step 2: Discover opportunities
Factors that you evaluate during the first step can help you find opportunities for change. At this moment, you may need to identify the budget for the analysis-related changes.
Step 3: Identify threats
PEST analysis doesn't just give you an overview of opportunities. The information you gather can help you identify threats to your business operations. Taking a proactive approach to threat mitigation can help you get ahead of the competition.
- Making PEST analysis part of your business strategy
Analyzing PEST factors doesn't just help you prepare for the future; it provides valuable insight into current business operation and management. Data gathered when identifying PEST factors for your niche can help you grow and develop your company in a highly competitive environment.
Combined with other analyses, including SWOT, MOST (Mission, Objective, Strategies, Tactics), and SCRS (Strategy, Current State, Requirements, Solutions), PEST can help you stay on top of your game, no matter how quickly the world changes.
What are the economic factors in PEST analysis?
Economic factors in PEST analysis are financial / economic elements that may impact your business operations. They can include exchange, inflation, and unemployment rates, fiscal policies, and the like.
What is a SWOT and PEST analysis?
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) analysis and Political, Economic, Social, and Technological (PEST) analysis are two approaches to evaluating the integrity of your business and learning about which outside factors may influence it.
Who created the PEST analysis?
Harvard Business School professor Francis Aguilar created the foundation for the PEST analysis in 1967. It first appeared in his book called Scanning the Business Environment.
What is a PEST analysis diagram?
A PEST analysis diagram is a framework for identifying political, economic, social, and technological changes that may impact your business in the future. This analysis allows you to take proactive measures to stay on top of your business strategies in the ever-changing external environment.
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 3 April 2024
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 26 May 2023
Last updated: 11 April 2023
Last updated: 22 July 2023
Last updated: 1 June 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
Suggest a new Definition
Proposed definitions will be considered for inclusion in the Economictimes.com
- PREV DEFINITION Personal Selling Read More
- NEXT DEFINITION Place Place in the marketing mix refers to the channel, or the route, through which goods move from the source to the final user. Read More
What is 'PEST Analysis'
Read More News on
- MARKETING SWOT ANALYSIS PEST ANALYSIS
The five forces model of analysis was developed by Michael Porter to analyze the competitive environment in which a product or company works. Description: There are five forces that act on any product/ brand/ company: 1. The threat of entry: competitors can enter from any industry, channel, function, form or marketing activity. How best can the company take care of the threat of new entrants? 2
Advertising is a means of communication with the users of a product or service. Advertisements are messages paid for by those who send them and are intended to inform or influence people who receive them, as defined by the Advertising Association of the UK. Description: Advertising is always present, though people may not be aware of it. In today's world, advertising uses every possible media to
An advertorial is a form of advertisement in a newspaper, magazine or a website which involves giving information about the product in the form of an article. Usually, a brand pays the publisher for such an article. Description: Advertorials are advertisements that appear in the media, be it magazines, newspapers or websites. Advertorials are paid content. They are used by marketers to educa
erved the tags 'affiliate links' or 'sponsored posts' on websites before? Or have you wondered if it might be possible to earn money anytime, from anywhere? Well, that is the concept behind affiliate marketing. Affiliate marketing is a concept where an affiliate who enjoys a product and promotes the products on their social platforms receives a profit whenever a sale is made. Did you know that aff
Ambient Advertising is about placing ads on unusual objects or in unusual places where you wouldn’t usually expect to have an advertisement. Description: Ambient advertising evolved as a concept because it has a lasting impact on the minds of consumers which makes it more effective. Ambient advertising is all about creativity, and how effectively the advertiser is able to communicate the message
Ambush marketing, a term first coined by marketing guru Jerry Welsh, has not really been rigorously defined. However, it broadly refers to a situation in which a company or product seeks to ride on the publicity value of a major event without having contributed to the financing of the event through sponsorship. It is typically targeted at major sporting events - like the Olympic Games or the world
Behavioral segmentation is a more focused form of market segmentation that groups different consumers based on specific behavioral patterns they display when making buying a product. Description: Behavioral segmentation classifies organizations and individuals into different categories based on how they act or behave towards products. It involves classifying consumers or grouping them based on
'Blue Ocean Strategy is referred to a market for a product where there is no competition or very less competition. This strategy revolves around searching for a business in which very few firms operate and where there is no pricing pressure. Description: Blue Ocean Strategy can be applied across sectors or businesses. It is not limited to just one business. But, let's first understand what is B
A brand tribe could be regarded as a group of people who collectively identify themselves with the product and share similar views and notions about the brand. They are not just consumers of the product, but play a major role in its promotion. Description: A product is successful when it becomes a cult. Companies are not just selling consumers their products nowadays, but an idea, a vision as h
Brand valuation is the process used to calculate the value of a brand or the amount of money another party is prepared to pay for it. Description: A brand comprises tangible as well as intangible elements relating to the company's style, culture, positioning, messages, promises and value proposition. Brand Valuation, subsequently, is an estimate of the financial value of a brand. There is no un
Related News

Mail this Definition
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
PESTLE Analysis
Insights and resources on business analysis tools
PESTLE Analysis Examples to Better Explain the Framework
Last Updated: Apr 4, 2024 by Jim Makos Filed Under: PEST Analysis , PEST Examples
Before discussing some PESTLE analysis examples in the next 6 minutes, let’s remind ourselves that PESTLE analysis is an incredibly popular business analysis tool. Not only is it extremely easy to use , but it’s also very effective . PESTLE analysis helps you analyze a chosen organization from six different perspectives: Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental . By doing so, you unlock a powerful understanding of how a given business is performing from every angle. Despite its apparent simplicity, many beginners struggle with conducting their own PESTLE analyses. In this article, we want to eliminate any confusion surrounding this unique business analysis tool. Today’s PESTLE analysis examples will demonstrate how you, too, can use it.
What is PESTLE Analysis
As touched on above, PESTLE analysis is a business framework that looks at things from six crucial viewpoints. To conduct a PESTLE analysis, you find as much information as you can about the business, and separate it between the six categories. The key to getting the PESTLE analysis template right is understanding what each category of PESTLE analysis factors stands for. Remember, these are external factors that an organization has no control over. Find more about external factors here , as PESTLE is not the only type of analysis that relies on them ( STEEP is another)!
Now, let’s examine some external forces examples for better comprehension.
Political factors examples
Every organization operates within some kind of political environment. The question is: how does that political environment affect the business itself? In this category, you’ll find information about everything from international relations (which can affect an organization’s ability to do business across borders) to political instability (which can severely thwart an organization). For a complete list of political factors affecting a business or organization, we have a complete guide here .
Economic factors examples
Similarly, every organization is exposed to the economies of the markets in which it operates. The beauty of PESTLE analysis is that you can consider factors as broad or as specific as you like. For the economic factors affecting a business, you can discuss the international economy, national economies, or even regional economies. For a complete list of economic factors affecting a business or organization, click here .
Social factors examples
An important part of any business is the consumer. The sociocultural column of PESTLE analysis allows you to explore how trends in society and culture — which are ultimately trends in the consumer — affect a business. For example, if a business sells just one specific product, how is the consumer approach to that product changing? For a complete list of social factors affecting a business or organization, check out this article .
Technological factors examples
Businesses are becoming increasingly technological, hence the importance of the T in the PESTLE analysis template. This is your chance to explore any of the technological factors affecting a business, including both technological constraints and advancements. This may refer to access to technology within a given region or the development of new technologies within an industry. But there are a lot more in technological factors, as we have seen here .
Legal factors examples
If you’re familiar with PEST analysis , you might have noticed that PESTLE analysis is the same thing — just with an added L and E. Of course, the L in PESTLE analysis refers to legal factors. Often, these legal factors have some overlap with political factors — but not always. Examples of topics that might be discussed in this category include trade laws, labor laws, and intellectual property laws, and how each affects a business. Here is a complete list of legal factors.
Environmental factors examples
A category of growing importance is the environmental one. Many businesses, especially those in primary industry , have some kind of impact on the environment. This part of PESTLE analysis is about knowing what that impact is, what effects that might have, and how businesses can improve in this department. Here is a more detailed explanation and a breakdown of environmental factors.
Simply put, PESTLE analysis is about filling out a brief profile about an organization for each of these categories. As long as you know what to put in each category (which we hope we explained well enough above), then it’s just a question of sourcing your data. For more information about that, we highly recommend our step-by-step guide on how to do a PESTLE analysis .
PESTLE Analysis Examples
If you’re new to PESTLE analysis, some examples are probably what you want to see most. In this section, we’ll introduce you to some PESTLE analysis examples of both countries and businesses.
PESTLE Analysis Examples of a Country
Unlike other business analysis tools, PESTLE analysis works just as well for countries as it does businesses. That’s right: you can analyze the standings of an entire country with the PESTLE model!
When referring to countries, here’s what PESTLE analysis often looks like:
- Political: What are the country’s political relations like with others?
- Economic: How is the country’s economy doing?
- Sociocultural: What impactful societal and cultural customs does the country have?
- Technological: How is the country with regard to adoption and development of tech?
- Legal: What is the legal landscape like in the country?
- Environmental: What is the country’s impact on the environment?
Here are four PESTLE Analysis examples of countries that you can find on our blog. We purposefully picked three completely different countries to give you an idea of how the results differ:
- PEST analysis of Germany
- PEST analysis of China
- PEST analysis of Canada
- PESTLE Analysis of Japan
Between those three PESTLE Analysis examples, you should get a pretty clear idea of what PESTLE analysis of a country should include exactly.
PESTLE Analysis Examples of a Business
Aside from analyzing countries, you can, of course, analyze businesses with the PESTLE analysis framework. Earlier in this post, we detailed how you can interpret each of the six categories of the acronym. If you follow the advice given up there, you shouldn’t have any trouble with knowing what to include!
Here are three PESTLE analysis examples of businesses which you can find on our blog:
- PESTLE analysis of Nike
- PESTLE analysis of Apple
- PESTLE analysis of Tesla
If you read through those three PESTLE analysis examples, we guarantee you’ll be ready to create your own!
PESTLE Analysis Examples of an Industry
Apart from businesses, organizations and countries, PESTLE analysis and other business frameworks can be used on whole industries. We can do a PEST or a STEEPLE analysis for example, on industries to assess the external factors that influence all the companies that are doing business in that niche.
Here are some PESTLE analysis examples on individual industries:
- PESTLE analysis of the Food industry
- PESTLE Analysis of the Real Estate Industry
- PESTLE Analysis of the Logistics Industry
- PESTLE Analysis of the Agriculture Industry
- PEST analysis of the Healthcare industry
- PEST analysis of the Airline industry
More PESTLE Analysis Examples
If you’re looking for more great examples of PESTLE analysis, we highly recommend you take a look around our website here at PESTLEanalysis.com. You can try searching for “PESTLE”, a specific company, or “industry” on the top right, and look around the blog yourself for a complete selection of business analysis information, including PESTLE and many other techniques.
As you can see, PESTLE analysis is a pretty simple business analysis tool. You simply gather up as much information as you can about a business or country, and then spread it across the six PESTLE categories: Political, Economic, Sociocultural, Technological, Legal, and Environmental. You now know how to to a PESTLE Analysis by yourself.
We hope you found our PESTLE analysis examples helpful, and wish you the best of luck with conducting your own analysis!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
PEST Analysis (Political, Economic, Social, and Technological) is a method whereby an organization can assess major external factors that influence its operation in order to become more ...
A combination of PEST and SWOT analysis usually gives a clearer understanding of a situation with related internal and external factors; PESTLE analysis is an extension of PEST analysis that covers legal and environmental factors; I'm going to explain the PEST analysis as simply as possible with examples and a template for better understanding.
The PEST analysis is a useful tool for understanding market growth or decline, and as such the position, potential and direction for a business. PEST is an acronym for Political, Economic, Social and Technological factors, which are used to assess the market for a business or organizational unit. Sometimes it's expanded to include legal and ...
A PEST analysis is an assessment of the political, economic, social and technological factors that could affect a business now and in the future. The purpose of a PEST analysis is to give a ...
In business analysis, PEST analysis ("political, economic, socio-cultural and technological") describes a framework of macro-environmental factors used in the environmental scanning component of strategic management.It is part of an external environment analysis when conducting a strategic analysis or doing market research, and gives an overview of the different macro-environmental factors to ...
A PESTLE analysis is best used in tandem with your SWOT analysis. As demonstrated below, this framework looks at the macro-trends in your operating environment. As you complete your planning process, this looks at the external analysis portion of your environmental scan - also known as what is happening in your market. Pro Tip:
PESTLE Analysis (also known as PEST Analysis) is a popular tool used by companies to analyze the external factors that may impact their operations. It is a comprehensive framework that examines six key areas: Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental.By conducting a PESTLE Analysis, businesses can better understand their current and potential markets, identify ...
A PEST Analysis is a study that helps an organization identify opportunities and threats of the external macro environment. The macro environment refers to uncontrollable external factors that affect a company. PEST is an acronym for Political, Economic, Social and Technological.They are four factors that can affect a company's current and future performance.
PEST Analysis is a great tool you can use to brainstorm threats and opportunities that might be impacting you, as a result of your wider business environment. PEST stands for: Political. How government policy and legislation are impacting your business. Economic. How economic factors like growth, inflation and interest rates are affecting your ...
PEST Analysis is a strategic tool used by businesses and marketers to evaluate the macro-environmental factors that can impact their operations, growth, and strategy. It stands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors, which are the primary elements considered in this analysis. By understanding the PEST factors, organizations ...
PEST analysis focuses on the big picture and impacts on the overall business, market, and important decisions. PEST is best used for market research and broader analysis of the business environment. On the other hand, SWOT analysis hones in more narrowly on the organization itself to identify its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
PEST stands for political, economical, sociocultural, and technological. A PEST analysis examines these four factors and their potential effects in relation to the subject of your analysis. It is used for businesses, organizations, products, ideas, and general concepts. But as a tool for business analysts, it's primarily used within business ...
Definition. PEST analysis is an analysis of the political, economic, social and technological factors in the external environment of an organization, which can affect its activities and performance. [1] PESTEL model (or PESTLE model) involves the collection and portrayal of information about external factors which have, or may have, an impact on business.
Templates, Definition, and Examples. Seasoned business strategists use 'PEST ('political, economic, social, and technological) analysis' to identify whether a new country, market, or city is the right fit for business expansion. Plus, as a part of ongoing strategic planning, PEST analysis involves identifying and discovering external ...
PEST analysis is a strategic planning framework that helps businesses assess the Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors that may affect their industry and operations. In this article, we will delve into each of these four components in detail to provide a comprehensive understanding of PEST analysis and how it can be used to ...
The PEST analysis tool is useful for four main reasons: Helps spot business opportunities and provides a warning in advance of any dangers or threats to your business. Reveals how the external business environment is changing so your team can practice workplace adaptability. Analyzes risks in your current environment so your business can avoid ...
PEST analysis: definition PEST analysis is a framework for evaluating the external factors (political, economic, social, and technological) that may affect business operations. By performing this analysis, business owners can determine what may await their company in the future and which changes they should make to ensure successful adaptation ...
PESTEL Analysis Framework. The PESTEL analysis framework is a strategic tool used by businesses and organizations to assess and analyze the macro-environmental factors that can impact their operations and decision-making. PESTEL represents the acronym for Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal elements.
Explaining PESTLE analysis is easy since it is a simple, straightforward analysis used in strategic planning. Below, we'll go through everything you need to know about the PESTLE tool with examples for easier comprehension. Let's start by briefly explaining the PESTLE model of analysis with a clear PESTLE definition.
A PESTLE analysis, sometimes called PEST or PESTEL analysis, is a tool businesses use to assess macroeconomic factors that impact their operations. Macroeconomics is the study of large-scale economic elements, often relating to countries as a whole.The factors this analysis represents are political, economic, social, technological, legal and ...
PEST Analysis is a measurement tool which is used to assess markets for a particular product or a business at a given time frame. PEST stands for Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors. Once these factors are analysed organisations can take better business decisions. Description: PEST Analysis helps organizations take better ...
Here are four PESTLE Analysis examples of countries that you can find on our blog. We purposefully picked three completely different countries to give you an idea of how the results differ: PEST analysis of Germany. PEST analysis of China. PEST analysis of Canada. PESTLE Analysis of Japan.
PESTEL Analysis. A framework to assess political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors. Over 1.8 million professionals use CFI to learn accounting, financial analysis, modeling and more. Start with a free account to explore 20+ always-free courses and hundreds of finance templates and cheat sheets.