Filter by Keywords

Project Management
How to write a project report (with steps & templates).
March 21, 2024
Juggling all the different components of a project can be quite a challenge. If that weren’t enough, you also have to write a project status report to update key stakeholders on the project’s progress. The struggle is real.
So where do you start? Fortunately, we have the answer. And that’s precisely why we put together this guide—to walk you through the process so you have a clear path from start to finish.
Learn more about creating project reports and different types of project status reports. Plus, you’ll walk away with five free project report templates, carefully crafted to streamline your project management workflow, save you time, and impress your stakeholders. 🤩
What is a Project Report?
How to write a project report, 1. project status report, 2. project progress report, 3. project cost benefit analysis report, 4. project time tracking report, 5. project resource report, 6. project risk report, 7. project variance report, 8. project performance report, 9. project completion report, why is project reporting important, 1. final project report template, 2. project status report template, 3. digital marketing report template, 4. employee daily activity report template, 5. campaign report template, create professional project reports in less time with clickup.
A project report is a document offering a comprehensive overview of a project’s objectives, progress, team performance, and milestone accomplishments. It also gives an account of the challenges faced during a project’s execution , solutions devised to tackle them, and the lessons learned during the process.
Project managers create these reports to communicate with other project stakeholders—including team members, sponsors, clients, and other interested parties—to ensure everyone’s on the same page. The document also serves as a foundation for further evaluation and analysis to ensure the project says on track and achieves its goals. 🎯

Creating a project report doesn’t have to be a daunting task. Follow these three simple steps to create your first project report with ease.
Understand the purpose of the report
Before you create a project report, you need to understand the purpose of the report (the “why”) and know your target audience (the “who”). This will guide the content, structure, and tone of your project report.
Gather and organize the relevant information
At this point, you need to gather project information relevant to your project report. Make sure your data is accurate, reliable, and up-to-date. Organize the gathered information in a logical and structured manner.
- Executive summary : As its name suggests, this project summary gives readers a quick overview of the whole report. It’s a snapshot that highlights the most important parts of the project. While it’s placed at the start of the report, it’s often written last. It covers the project’s objectives, methodology, major outcomes, and conclusions.
- Introduction: This sets the context and expectations of the entire report. It includes the project’s purpose and scope, project schedule, the problems it aims to address, and the methodologies to get there. It also outlines the structure and organization of the rest of the report.
- Body: Typically, this is the longest part of project management reports because it dives into in-depth details, including project progress, data collection, analysis reports, constraints, and limitations. Remember that whatever you include here should reflect the purpose of your project report and the preferences of your target audience.
- Conclusions & Recommendations: Based on your findings and analysis, identify opportunities for improvement, suggest strategies for addressing them, or propose avenues for future research.
Format and proofread the report
Ensure that your project report follows a consistent formatting style—headings, subheadings, and bullet points will make it easier to read. In addition, scan your report for spelling or grammar errors and typos.
Types of Project Reports
Project reports come in diverse formats, with each serving different use cases. Here are nine of the most commonly used types of project reports.
A project status report is a document that gives a snapshot of where your project stands at any given moment. It’s like answering the question, “How’s the project doing?”
But instead of just saying “The project is fine,” you actually dive into the project goals, tasks completed, milestones achieved, challenges faced, lessons learned, potential roadblocks, and next steps.
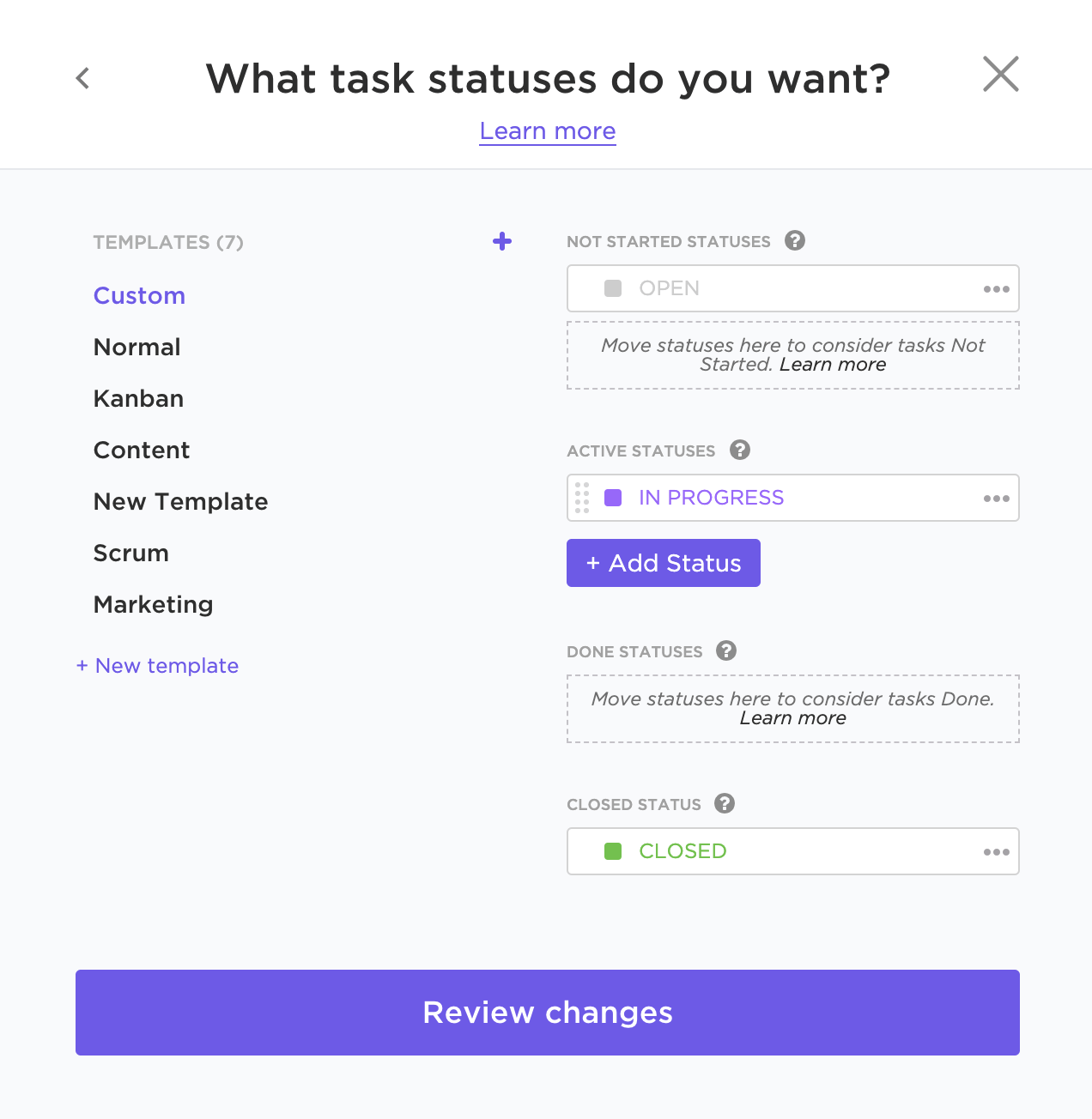
Whether it’s a weekly project status report or a monthly status report, this documentation eliminates the need for status meetings while giving stakeholders the most recent status of the project.
A project progress report is slightly similar to a status update report, as they both discuss task progress. However, the progress report is more quantitative and zooms in on individual tasks and project milestones .
It’s like taking a magnifying glass and examining the progress of each task, one by one. For example, it could include in-depth information on the percentage of completion and current status of each task (completed, on track, delayed, etc.).
The cost-benefit analysis report is usually prepared before a project is put into motion. Of the various project reports, this one aims to answer a simple question: “Is it worth pursuing this project?”
To answer this question, the report first assesses all project costs like operational expenses, materials, salaries, equipment, and potential risks.
It then considers the projected benefits, such as increased profit margins, cost savings, improved efficiency, or happier customers. Finally, the report compares the costs to the benefits to determine if it’s time to move forward or explore other options.
A project time-tracking report is a document that records and summarizes time spent on project activities. Each project team member contributes to writing this report—they track and record the amount of time they’ve spent on tasks and submit it to the project manager. ⏰
Thankfully, the rise of project management tools has eliminated the need for paper-based time-tracking submissions. They make it easy for team members to submit accurate and detailed time reports to the project manager—while reducing the administrative burden of manual report compilation.
Project managers can see how time is spent and the overall productivity of team members. As a result, they’re able to make informed decisions, such as redistributing workload (aka workload management ), reassigning tasks, and providing feedback and support to team members.
A project resource dashboard offers a bird’s-eye view of how resources (e.g., labor, equipment, materials, budget, etc.) are allocated in a project. Think of it as a comprehensive resource inventory, listing every project task, the responsible party, and the resources being used.
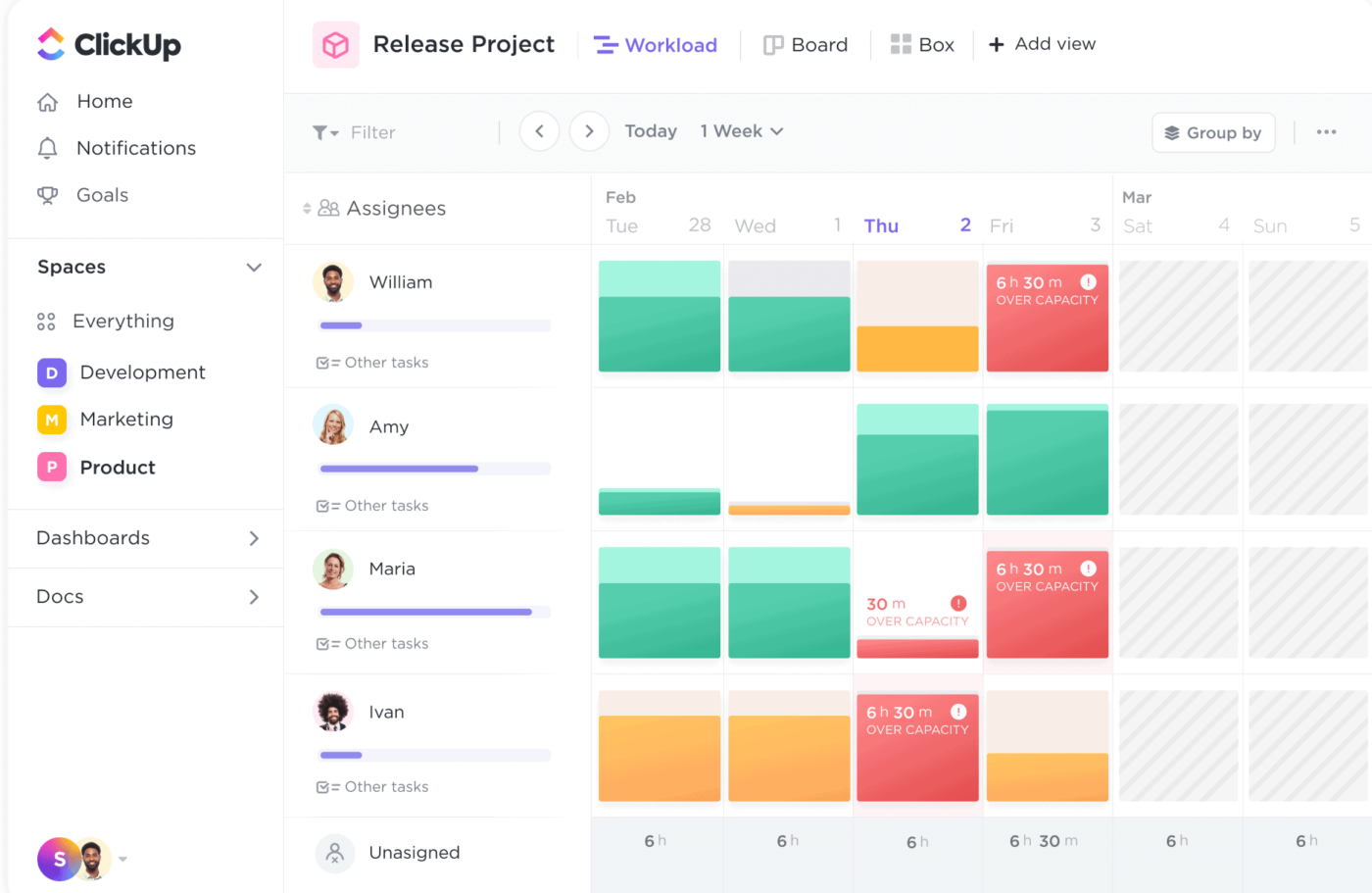
Project reports like this help project managers keep track of resource availability, identify potential resource constraints or shortages, and make informed decisions about resource allocation and optimization.
A project risk report offers a comprehensive analysis of potential risks, their likelihood of occurrence, their potential impact on the project, and recommended mitigation strategies.
Rather than waiting for future events to derail the project, project reports like this one allow project managers to take a more proactive approach to risk management—thereby boosting the chances of overall project success.
A project variance report reveals the gaps or deviations between project plans and the actual performance or results achieved. It compares various factors—like budget, time, resources, and scope—and their planned values with their actual values, then computes the differences (or variances).
By analyzing these variances, project managers and stakeholders can discuss the possible reasons behind them, identify areas that need attention, and take corrective actions where necessary.
A project performance report evaluates the overall performance and achievements of a project against predetermined metrics and objectives. It includes information on project deliverables, key performance indicators (KPIs) , and stakeholder satisfaction.
This report helps project managers assess project success, identify areas for improvement, and communicate the project’s performance to stakeholders.
A project completion report marks the end of a project journey. It summarizes the entire project lifecycle, from initiation to closure. This report contains an overview of the project’s objectives, deliverables, milestones, challenges, and recommendations for future projects.
Writing project reports may initially seem redundant and time-consuming. However, it plays a crucial role in achieving project success. While a few benefits were hinted at earlier, let’s get a better picture of why project reports should not be overlooked.
More clarity
Creating a project report allows you to step back and reflect on the project’s progress. As you record the milestones, successes, and challenges, a wealth of insights begin to unfold—strengths, weaknesses, and areas that need attention.
This holistic view of the project’s health helps you steer it toward the desired outcomes and ensure it stays on track.
Encourages evaluation and analysis
Project reports allow you to evaluate and analyze the different aspects of a project in a systematic way—gathering relevant data, analyzing them, and evaluating their significance. By giving your project a critical analysis, you can uncover valuable insights, identify patterns, draw meaningful conclusions, and take strategic action. 🛠️
Enhances communication and collaboration
Creating a project report challenges you to present the project’s progress and results to stakeholders in a clear and coherent manner. A well-written report promotes project transparency and ensures everyone is on the same page.
It also facilitates collaboration by providing a common reference point for discussions, feedback, and decision-making.
Boosts professionalism and credibility
When you present a comprehensive and well-structured report, it shows that you have conducted thorough research, followed a methodical approach, and can effectively communicate complex information. This, in turn, boosts your reputation, enhances your credibility, and showcases your expertise among peers, colleagues, and potential employers.
Knowledge preservation
A project report serves as a valuable reference for future research or projects. By documenting your process, methodologies, challenges, lessons, and results, you create a resource that can be consulted and built upon by others.
This contributes to the cumulative knowledge in your field and fosters a culture of collaboration and innovation.
Improves Team Alignment
Project reports are instrumental in enhancing team alignment. They provide a clear, concise snapshot of progress, identifying accomplishments, challenges, and next steps. This enables all team members to understand the project’s current status and their respective roles in achieving the overall objectives.
Check out these project report templates for teams:
- Nonprofit Organizations Project Report
- Operations Teams Project Report
- Finance Teams Project Report
- DevOps Teams Project Report
- Agile Teams Project Report
- Sales Teams Project Report
5 Project Report Examples & Templates
Sure, you could write project reports from scratch and spend countless hours formatting and structuring them. But why would you when you can use free project report templates? They provide a structure and format for your report so you can simply plug in your data and customize the design to fit your needs. Not only do project report templates speed up the report creation process, but they also enhance the overall quality of your reports.
Let’s jump right in to explore our top five project report templates. 📈
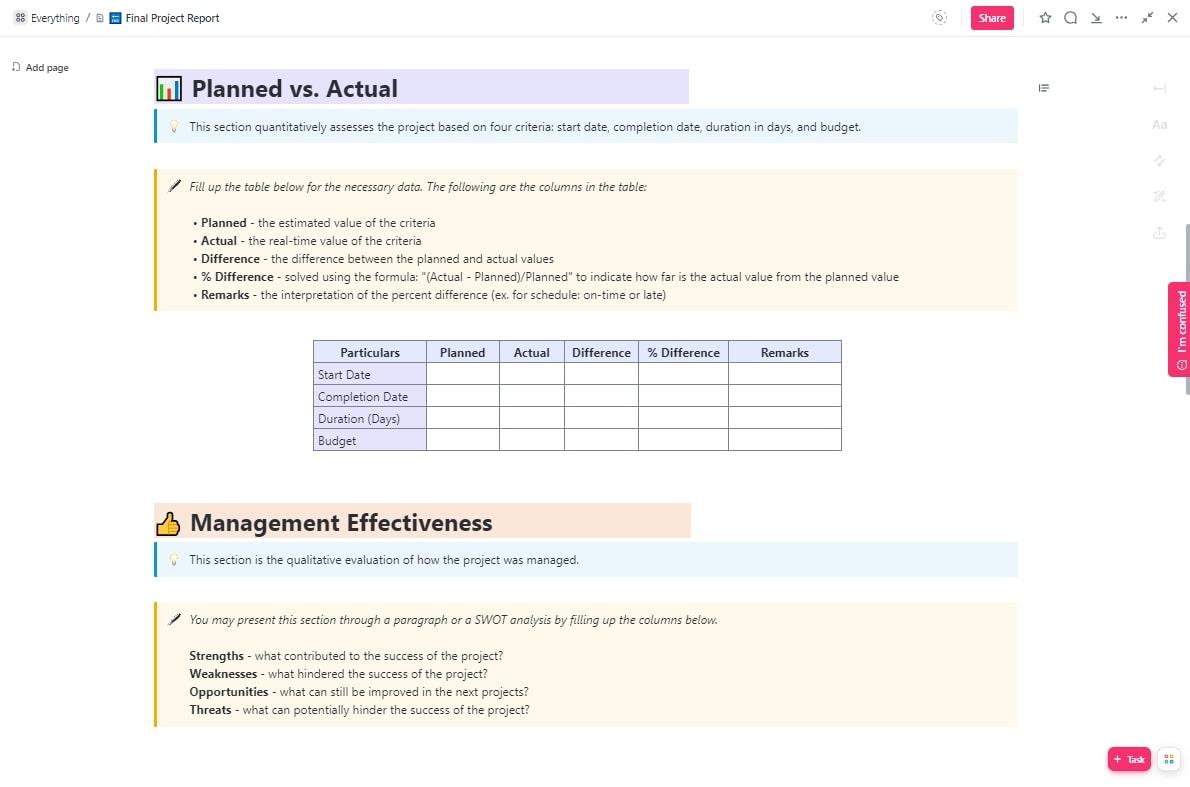
A final project report is the perfect finishing touch to conclude a project and highlight its achievements. ClickUp’s Final Project Report Template provides a solid structure to help you put it together with the following key sections:
- Planned vs. Actual: A quantitative breakdown of how the project deviated from the original plan with regard to its start date, completion date, duration, and budget
- Management Effectiveness: A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis evaluating how the project was managed
- Project Learnings : Share the important project lessons learned by the team throughout the lifespan of the project
- Contract Terms Checklist : A simple table listing the various contract terms, whether they were completed, and any remarks you have
- Overall Performance rating: A 1 out of 5 rating of the different aspects of the project, from planning and execution to leadership and communication
This template is built in ClickUp Docs , which means you have unlimited flexibility for customization—add extra sections and tweak the appearance to suit your taste. And guess what? The table of content updates in real-time as you add, edit, or delete multiple headers.
If you want to wow your team and clients, this project status report template will help you get the job done.
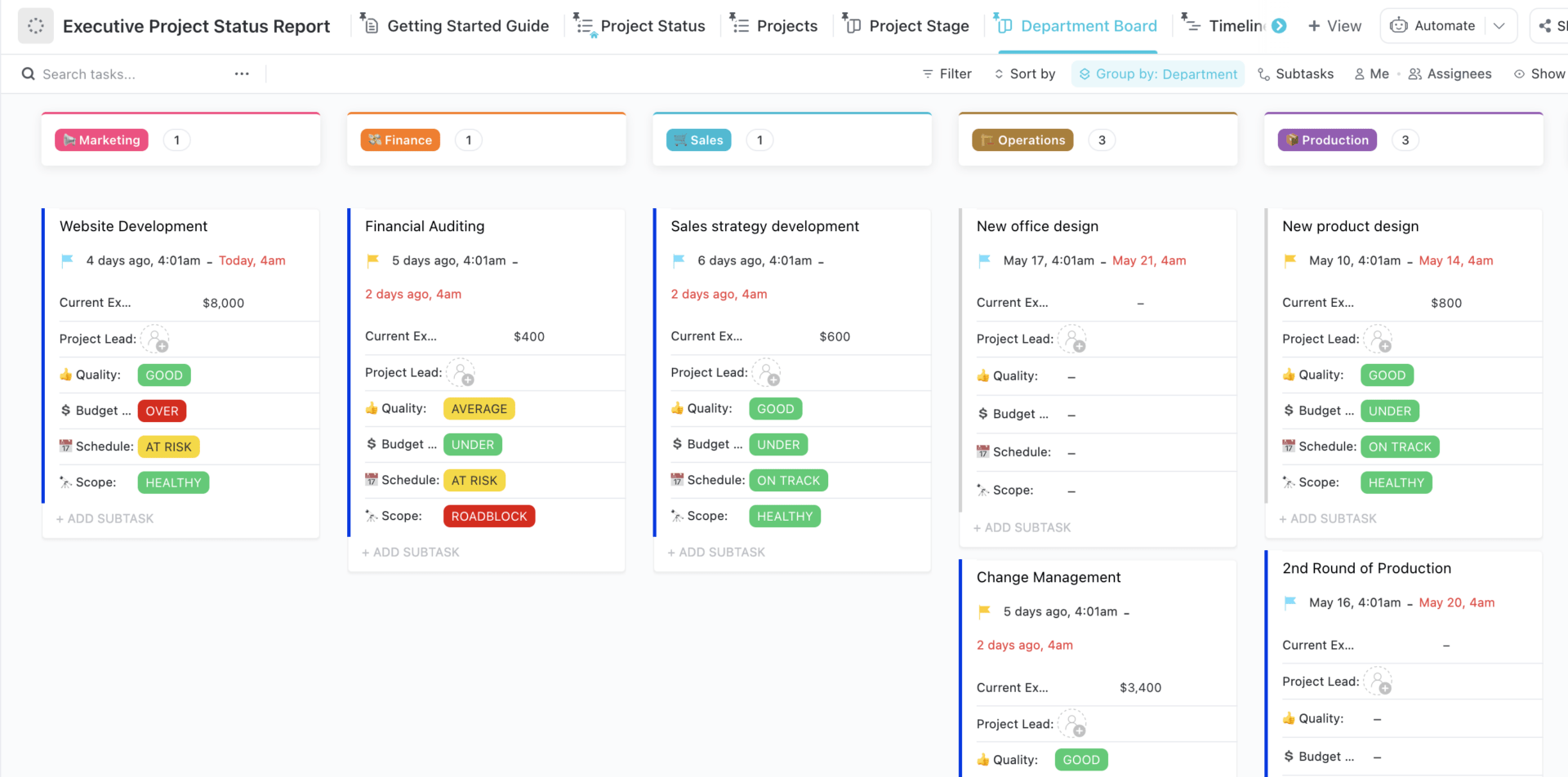
Writing a project status report is fairly straightforward. But staring at a blank document and worrying about crafting perfectly manicured sentences can make this process last a lot longer than it should.
Thankfully, ClickUp’s Project Status Report Template is here to save the day! Built inside ClickUp Whiteboards, this template provides a hassle-free method to quickly capture key project details in a visually engaging way.
- General information: Cover general project details (e.g., project name, objectives, project timeline , reporting period, etc.) which you’ll need to fill in only once
- Progress details: Use color-coding to share in-progress, at-risk, delayed, and completed tasks
- Support and resources: List out assets (e.g., labor, money, etc.) needed for a smooth operation
- Highlights and takeaways: Share key lessons learned and other noteworthy highlights
- What went well/What needs improvement: Use this opportunity to reflect on the project’s progress and share the areas that performed well and what needs attention
- Next steps: Highlight the key action items that need to get done to keep the project on track
Enter the details under each of these sections onto sticky notes, which’ll help you quickly pour down your thoughts without worrying about writing perfect sentences. It’s also very helpful for stakeholders as the information on sticky notes is short and straight to the point.
This template removes the pressure of creating a status report and saves valuable time—all while keeping key stakeholders informed and up to date.
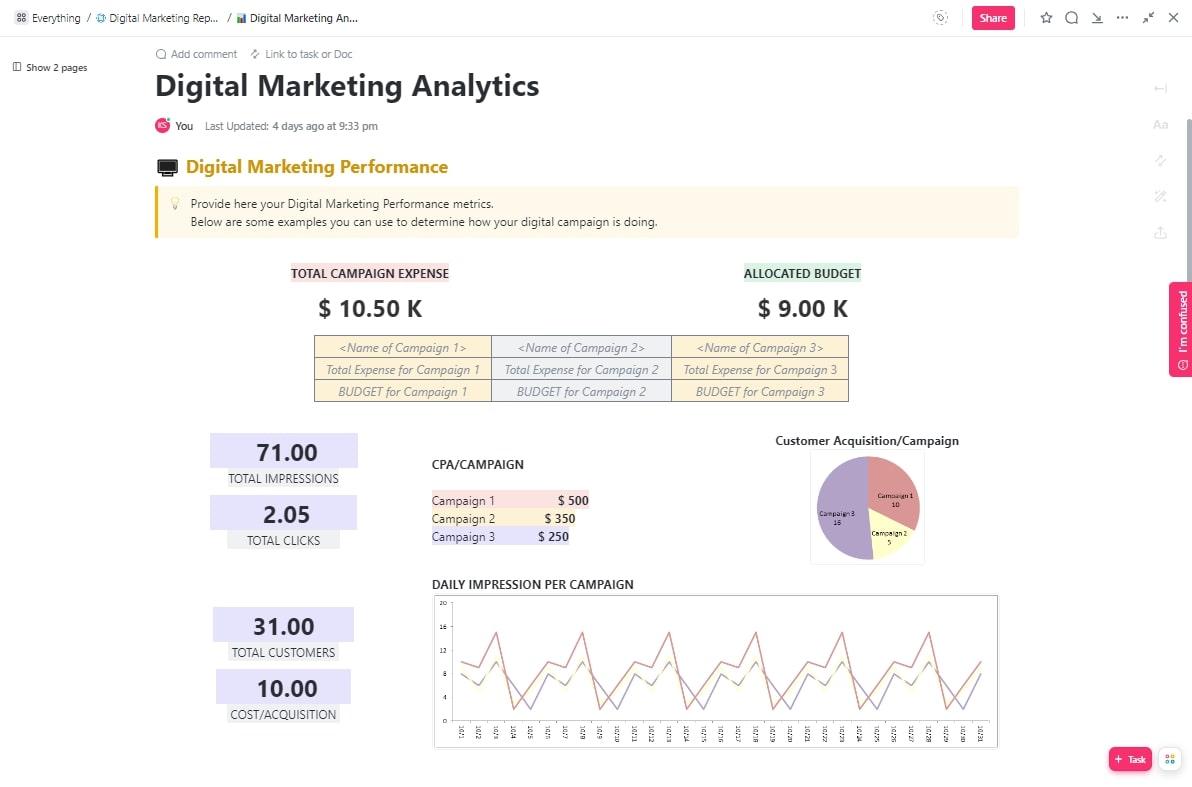
After running a digital marketing campaign project, you need to gather key metrics from the campaign and present it to key stakeholders for evaluation, performance analysis, and notes for future improvements.
Sharing this info across multiple digital channels can get overwhelming but there’s no need to worry. ClickUp’s Digital Marketing Report Template has you covered with everything you need. Plus, it’s neatly broken down into the following sections:
- Digital Marketing Performance: This section lets you summarize the overall performance of your campaign by capturing key details like project budget allocations, actual expenses, cost per acquisition, total impressions, and total clicks across multiple campaigns
- Web Analytics Report: This section analyzes website performance during and after the project’s completion. It captures metrics like page views, bounce rate, traffic sources, and overall conversion rate
- Social Media Campaign Performance: This section analyzes social media performance by measuring metrics like impressions, followers, and engagement rate—all in a simple table for each social media platform
Use this template to present the performance of your digital marketing project in a simple and visually engaging way. This makes it easy to identify trends, analyze the impact of your campaign, and make informed decisions regarding future marketing initiatives.
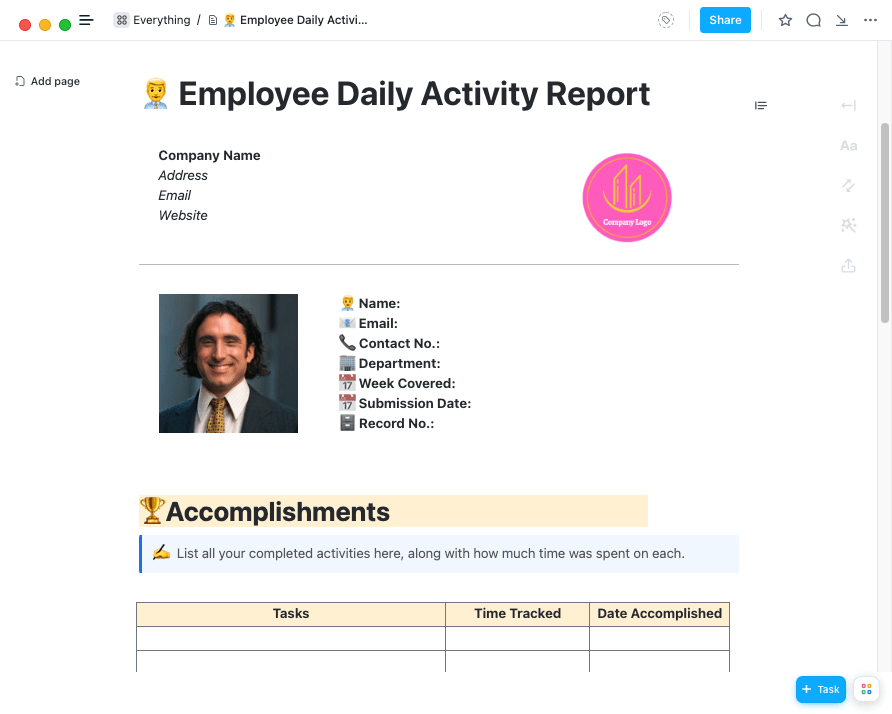
A key way to stay on track and guarantee overall project success is to engage team members in the process.
The Employee Daily Activity Report Template by ClickUp has a simple tabular layout that makes it easy for team members to record and keep track of:
- Completed tasks and the time spent on each
- Ongoing tasks and their due dates
- Upcoming tasks and any support they’ll need
This template encourages each team member to get work done and ask for support when needed—while allowing you to keep the project on track by providing support and maximizing team performance.

Remember the Digital Marketing Report Template we looked at earlier? You can choose to further analyze the marketing performance section, with elements from this Campaign Report Template by ClickUp .
Dive deeper into how each marketing channel contributed to overall ad cost, ad revenue, and ad conversion rate. You can further break down each channel’s performance by analyzing the metrics from each individual campaign on that channel.
There you have it—your secret sauce for creating an effective project report in a fraction of the time. And that’s only scratching the surface … working inside ClickUp unlocks a lot more perks.
Not only does ClickUp make project reporting easy and quick, but it also gives you access to free project management templates to enhance your workflow. Quickly assign tasks to your team, keep track of progress, discuss updates, and collaborate on documents and whiteboards—all in one place. ✨
Did we mention the integrations? ClickUp plays nicely with other apps, allowing you to seamlessly connect your favorite tools to supercharge your team’s productivity. And let’s not forget about the time you’ll save using ClickUp’s automations—a feature that lets you breeze through repetitive tasks that used to eat up valuable time across project management reports.
Just imagine what you can do with those extra hours—maybe enjoy a cup of coffee or catch up with your team about how best you can support them. Make project reporting a blast with ClickUp and boost your chances of a successful project.
Get started by signing up for free on ClickUp today … Ready? Set? Report!
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
How to Write a Project Report (with Best Practices Templates for Microsoft 365)
Key Take Aways
What you’ll learn:
- How AI can enhance project reports with predictive analysis and actionable insights
- A 7-step checklist for making sure that your project reports are easily accessible and consumable by stakeholder
- The importance of using project management software for streamlining project reporting, especially in the age of remote working
- Why you should use the Microsoft 365 platform for project reporting and some out of the box examples from BrightWork 365
By: Shubhangi Pandey | Published on: Mar 14, 2024 | Categories: BrightWork 365 , Microsoft 365 , Project Reporting | 0 comments

In an age where remote work is becoming the new every day and data-driven decision-making is more crucial than ever, project reporting has become more than a managerial obligation. It’s an art and a science that combines traditional project tracking with modern metrics and advanced data visualization.
This guide will walk you through seven essential steps to craft a project report that informs and engages your stakeholders. We’ll explore the role of AI in project management, delve into the importance of remote work metrics, and discuss cutting-edge data visualization tools that can make your reports more insightful.
Whether you’re a seasoned project manager or just getting started with project management basics , these steps will help you write a project report that adds value to your organization’s knowledge base for future projects.
Why are Project Management Tools Vital for Report Writing?
The importance of robust project management tools for effective report writing cannot be overstated. Here’s why:
- Centralization : Project management tools are a central hub for all your project data, streamlining project management and reporting processes.
- Efficient Tracking : These tools make it easier to monitor work progress during the monitoring phase of project management , helping you stay on top of tasks and milestones.
- Risk Identification : Advanced features enable you to spot potential risks early, allowing for proactive management.
- Stakeholder Communication : Keep all stakeholders in the loop with real-time updates and comprehensive reports.
- Data Visualization : Utilize features like Power BI to transform raw data into insightful visuals, aiding in better decision-making.
- Custom Reports : Depending on organizational needs, create specialized reports that offer in-depth analysis and recommendations upon project completion.
The Evolution of AI in Project Management Tools for Report Writing
When crafting an impactful project report, your tools can be a game-changer. And let’s talk about the elephant in the room: Artificial Intelligence. AI is no longer just a buzzword – it’s a reality transforming project management and reporting.
According to a systematic literature review published in MDPI , AI’s role in project management is increasingly significant, offering advanced capabilities like predictive analytics and risk assessment.
The Power of Predictive Analytics
These advanced AI tools centralize your project data and offer predictive analytics, risk assessment, and automated insights that can be invaluable for your report. Like Power BI revolutionized data visualization, AI algorithms can sift through massive amounts of data to highlight trends, predict risks, and recommend actions.
Making AI Accessible for Every Project Manager
Imagine reporting on what has happened and providing stakeholders with insights into what could happen. It’s like giving your project report a crystal ball. And don’t worry – embracing AI doesn’t mean you have to be a tech wizard. Many modern project management tools benefit from built-in AI features.
A thesis from DiVA portal explores the implementation of AI in project management and its impact on working personnel, indicating that AI is becoming more accessible and user-friendly.
The Future of Data-Driven Decision Making
AI’s capabilities equip stakeholders with data-driven insights for strategic decisions. It’s not just about tracking work and identifying risks anymore – it’s about forecasting them and offering actionable solutions. Welcome to the future of project reporting.
Types of Project Reports and Their Formats
Understanding the types of project reports you need to create is crucial. Whether it’s a project summary report, a project health report, or a project completion report, each serves a unique purpose and audience.
Knowing the format, whether a pie chart, bar chart, or complete chart, can also help present the data effectively. Writing a report is a valuable opportunity to evaluate the project, document lessons learned, and add to your organization’s knowledge base for future projects.
Data Visualization: Modern Tools and Techniques
Data visualization has come a long way from simple pie charts and bar graphs. With the advent of AI, we now have tools that can display and interpret data. Think of AI-powered heat maps that can show project bottlenecks or predictive line graphs that forecast project completion based on current trends.
Techniques for Effective Data Presentation
Modern data visualization techniques like interactive dashboards, real-time data streams, and even augmented reality (AR) representations are making it easier than ever to understand complex project metrics. These aren’t just for show; they offer actionable insights that can significantly impact project outcomes.
Making Data Visualization Accessible
The best part? These advanced visualization tools are becoming increasingly user-friendly. You don’t need to be a data scientist to use them. Most project management software now integrates seamlessly with these tools, making it easier than ever to incorporate advanced data visualization into your regular reporting.
The New Normal of Remote Work
In today’s digital age, remote work is becoming the new normal. As project managers, adapting our reporting techniques to this changing landscape is crucial.
Critical Metrics for Remote Teams
When it comes to remote teams, some metrics become even more critical. Think along the lines of ‘Remote Engagement Rate,’ ‘Digital Communication Effectiveness,’ and ‘Virtual Team Collaboration.’ These KPIs offer a more nuanced understanding of how remote teams are performing.
Tools for Tracking Remote Work Metrics
Fortunately, modern project management tools have features specifically designed to track these remote work metrics. From time-tracking software to virtual “water cooler” moments captured for team morale, these tools make remote work measurable in ways we couldn’t have imagined a few years ago.
Project Timeline and Milestones
A well-defined project timeline and key milestones are essential for any project. They not only help in keeping the project on track but also provide a basis for decision-making.
Project management software can automate this process, ensuring that reports are always up-to-date. Try the steps outlined below for writing better project reports.
Manage Projects with Microsoft 365, Power Platform, and Teams
Collaborate seamlessly from anywhere, with brightwork 365 and microsoft teams..

How to Write a Project Report
Writing an effective project report is crucial for evaluating the project’s health, keeping stakeholders informed, and setting the stage for future projects. Here are seven steps to guide you through the process.
1. Decide the Objective
Take some time during the project management initiation phase to think about the purpose of the report. Do you need to describe, explain, recommend, or persuade? Having a clear goal from the outset ensures that you stay focused, making engaging your reader easier.
Understanding the objective is the cornerstone of effective project reporting. Whether crafting a project summary report or a detailed project performance report, aligning your content with the aim will make your report more coherent and actionable.
This is also the stage where you decide the key milestones and metrics to highlight in the report.
2. Understand Your Audience
Understanding your audience is crucial for crafting a report that resonates. Whether you’re writing for stakeholders or team members, the language, data, and visuals should be tailored to their preferences and needs.
- Language & Tone : Consider the communication style of your audience. Is a formal or informal tone more appropriate? Tailoring your language can build rapport and make your message more impactful.
- Data & Graphics : Choose the types of data and visual aids that will most effectively convey your message to your specific audience.
- Personal Preferences : Pay attention to how your audience typically communicates, whether in emails or other documents and try to mirror that style.
- Report Format : Different stakeholders may require different levels of detail. A project manager may want an in-depth analysis, while a sponsor only needs an executive summary.
- Audience Personas : Utilize audience personas to guide the tone, style, and content, ensuring your report caters to the diverse needs of all project stakeholders.
3. Report Format and Type
Before you start, check the report format and type. Do you need to submit a written report or deliver a presentation? Do you need to craft a formal, informal, financial, annual, technical, fact-finding, or problem-solving report?
You should also confirm if any project management templates are available within the organization.
Checking these details can save time later on!
Different types of project reports serve other purposes. A project status report provides a snapshot of where the project is, while a project health report dives deeper into metrics.
Make sure to consider the medium – will this report be a PDF, a slideshow, or an interactive dashboard? The format can significantly impact how the information is received.
4. Gather the Facts and Data
Including engaging facts and data will solidify your argument. Start with your collaborative project site and work out as needed. Remember to cite sources such as articles, case studies, and interviews.
To build a compelling case in your report, start mining your collaborative project site for crucial metrics like project milestones, resource utilization, and project health. Supplement this with additional data from external sources like articles and case studies.
Utilize data visualization tools like pie charts or bar graphs to make complex information easily digestible. Ensure the data is current to maintain the report’s credibility and remember to cite your sources for added reliability.
5. Structure the Report
How you arrange your report is pivotal in how well your audience can digest the material. A logically organized report improves readability and amplifies its impact in delivering the core message.
Your report should have a natural progression, leading the reader from one point to the next until a decisive conclusion is reached. Generally, a report is segmented into four key components:
- Opening Overview: This is the first thing your reader will see, and it’s usually crafted after the rest of the report is complete. Make this section compelling, as it often influences whether the reader will delve deeper into the report.
- Introduction: This section sets the stage by offering background information and outlining the report’s cover. Make sure to specify the report’s scope and any methodologies employed.
- Body: Here’s where your writing prowess comes into play. This is the meat of the report, filled with background, analyses, discussions, and actionable recommendations. Utilize data and visual aids to bolster your arguments.
- Final Thoughts: This is where you tie all the report’s elements together in a neat bow. Clearly state the following steps and any actions the reader should consider.
6. Readability
Spend some time making the report accessible and enjoyable to read. If working in Word, the Navigation pane is a great way to help your reader work through the document. Use formatting, visuals, and lists to break up long text sections.
Readability is not just about the text but also about the visual elements like pie charts, bar colors, and even the background color of the report. Use these elements to break the monotony and make the report more engaging. Also, consider adding a table of contents for longer reports to improve navigation.
The first draft of the report is rarely perfect, so you will need to edit and revise the content. If possible, set the document aside for a few days before reviewing it or ask a colleague to review it.
Editing is not just about correcting grammatical errors – it’s also about ensuring that the report aligns with its initial objectives and is tailored to its audience. Use this stage to refine the report’s structure, clarify its key points, and eliminate any unnecessary jargon or technical terms to the reader’s understanding.
Automate and Streamline Project Reporting with Microsoft 365
Project reporting can often be a laborious and time-consuming task. Especially on a project where there are so many moving parts and different people involved, getting a clear picture of what’s going on can be pretty tricky.
That is why we recommend moving to a cloud-based solution for project management and reporting – and you might have guessed it: we recommend Microsoft 365! If you’re considering SharePoint, check out our build vs buy guide.
Why use Microsoft 365 for project reporting?
There are many benefits to using Microsoft 365 as the platform for your project management reporting, including:
- Centralizing your project management and reporting on Microsoft 365 brings your project information into one place, so you can automate reporting and save time. If you’re still using excel for project management , here’s why you should consider switching.
- You can access configurable and filterable reports based on the audience by leveraging the available reporting mechanisms in Power Apps, Power BI, and Excel. Everyone can see the information in the way they need.
- Linked into the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, reports can appear in Power Apps, Power BI, exported to Excel, emailed in Outlook, or seen in MS Teams, so reports are available wherever the audience is working.
- Having project data maintained in a single platform means that project reports are always up to date. No more chasing up PMs or team members for the latest document version!
5 Ways you can use BrightWork 365 for Project and Portfolio Reporting
BrightWork 365 is a project and portfolio management solution for Microsoft 365 and the Power Platform. Here are five ways you can leverage BrightWork 365 and Microsoft 365 for more efficient project reporting:
1. Capture Project Status Reports in a few minutes
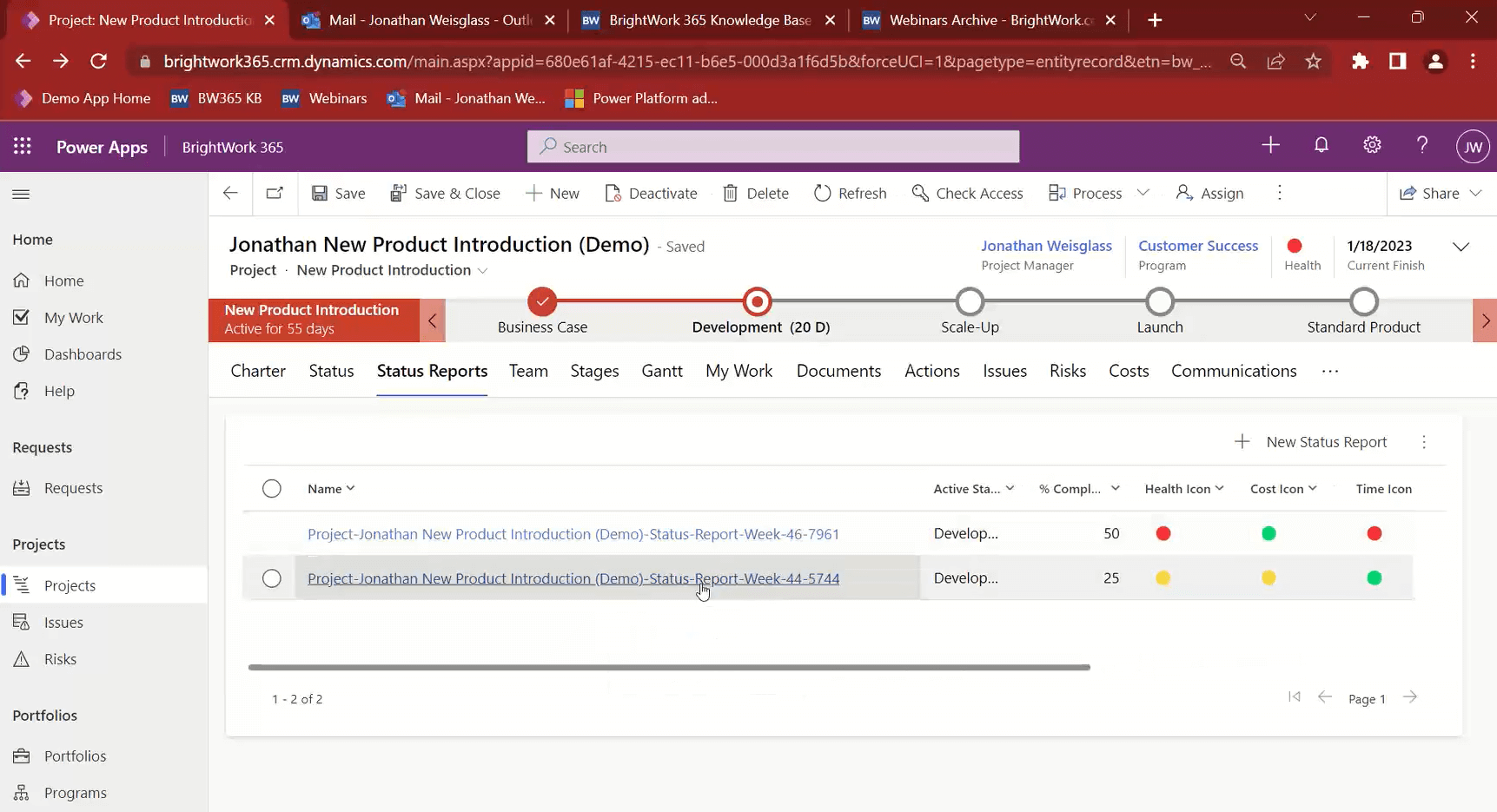
BrightWork project sites have a “Status” tab where the project manager can capture what is happening. This is not a status report but a place for the PM to log the current status.
It is not a snapshot, as it will change regularly, but the info here will become part of the status report once the PM creates one. once the PM chooses to create one.
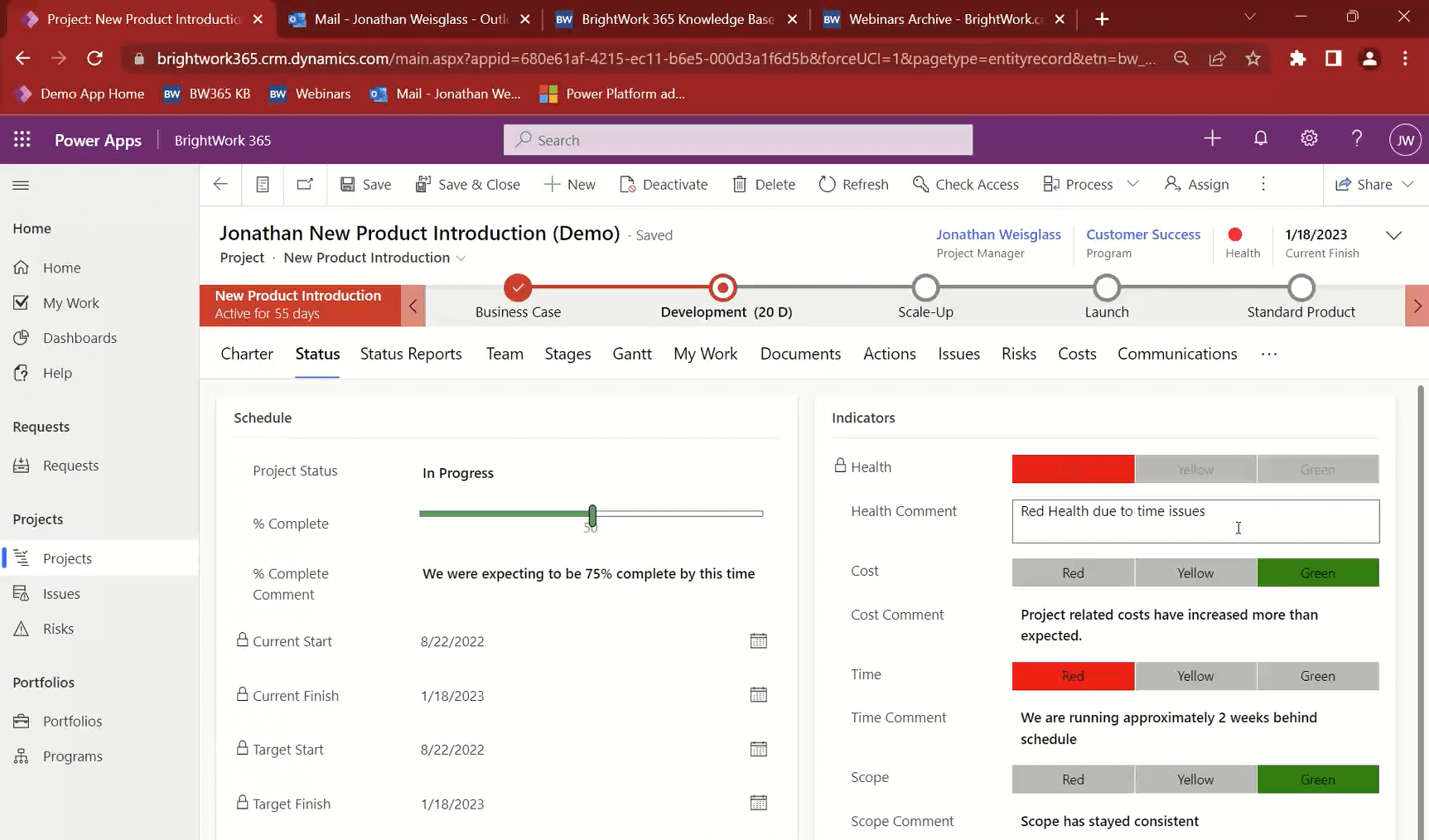
The Status Reports tab is where you can capture a snapshot of the project status at a point in time. It will bring in all the info from the “Status” tab, but you have the ability to add comments.
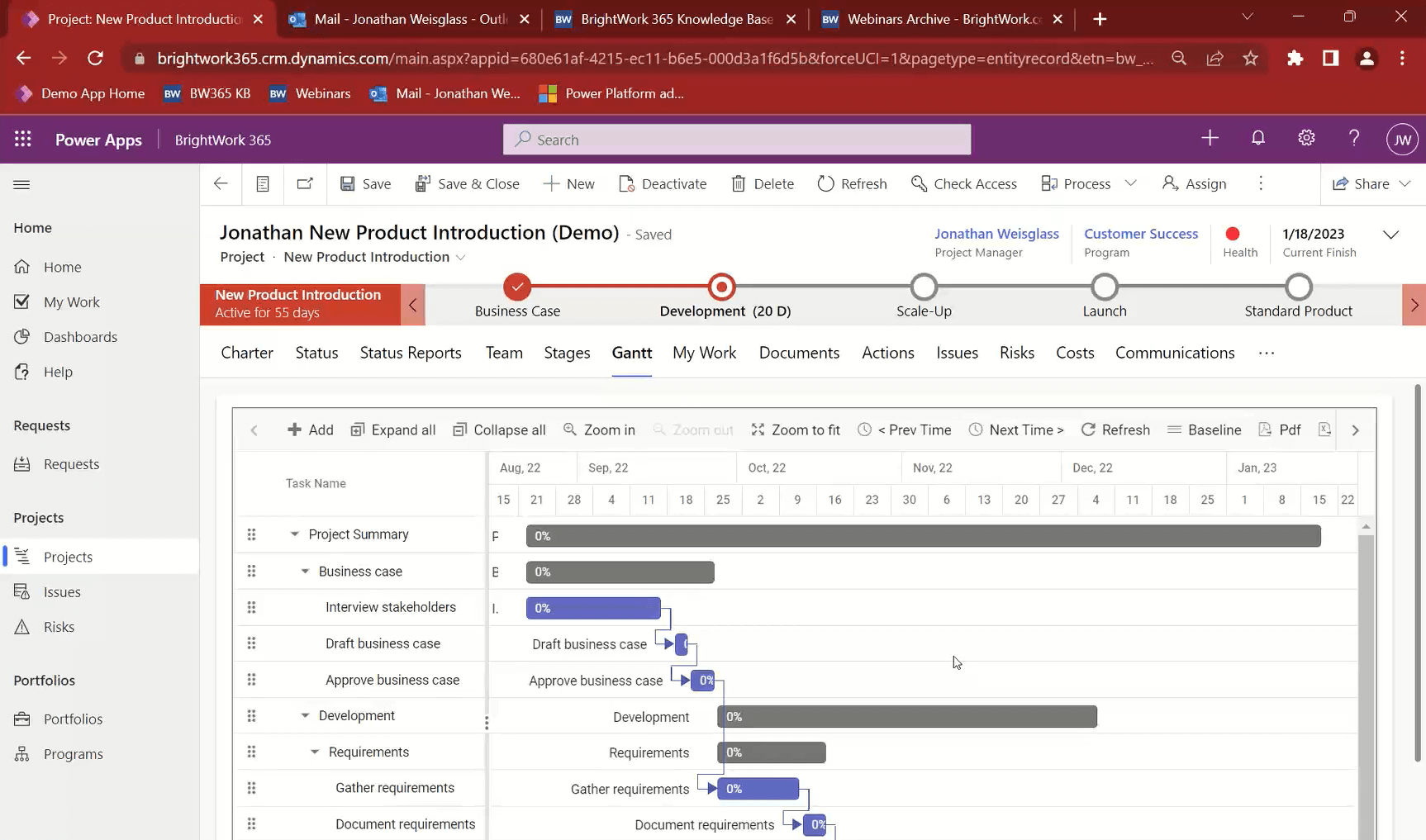
2. Track the project schedule with Gantt
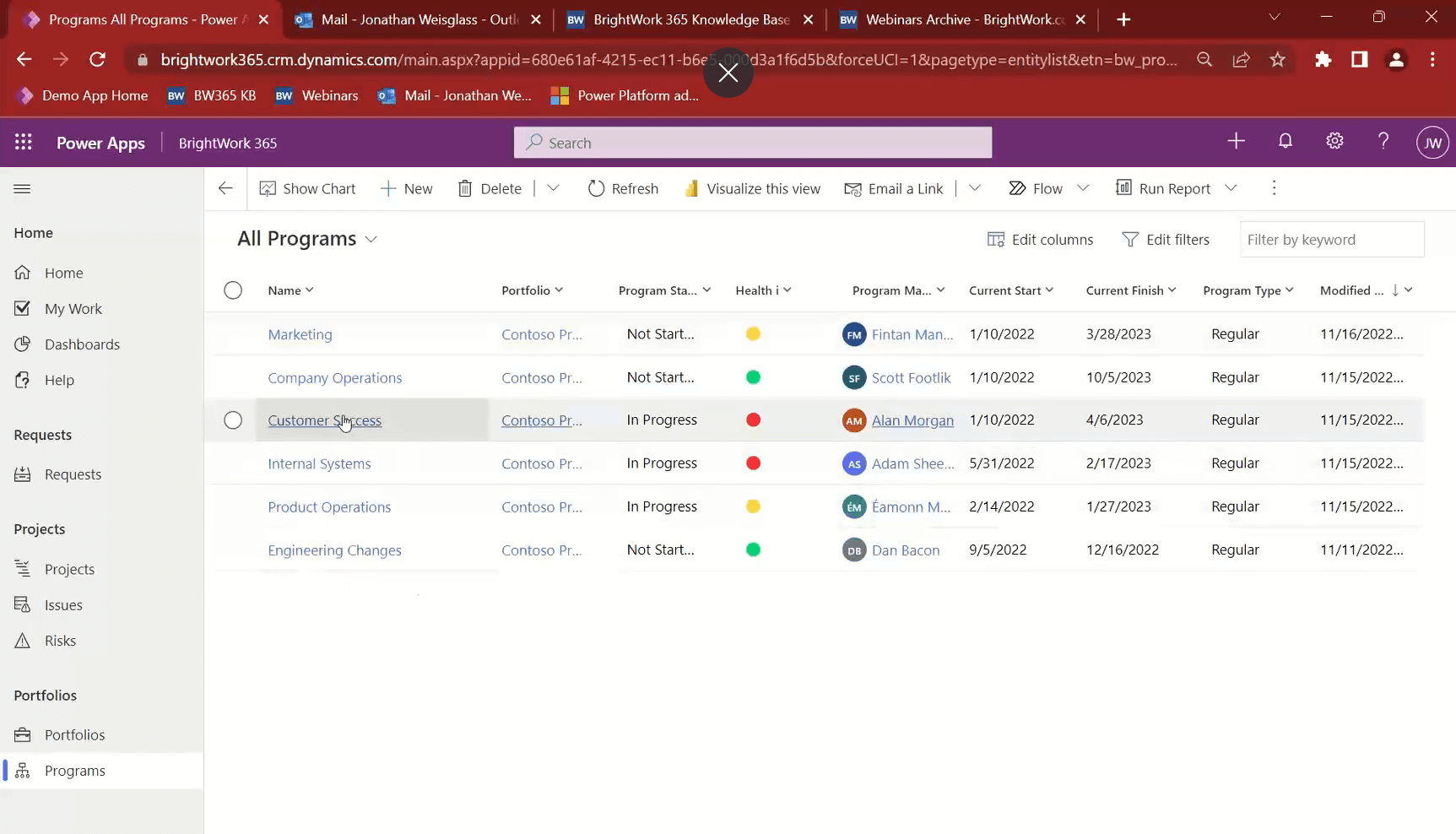
3. Get High-Level Visibility into Programs and Portfolios
BrightWork 365 enables a hierarchy for your project management – with Portfolios being the highest level. For example, a portfolio may house all the projects in a company.
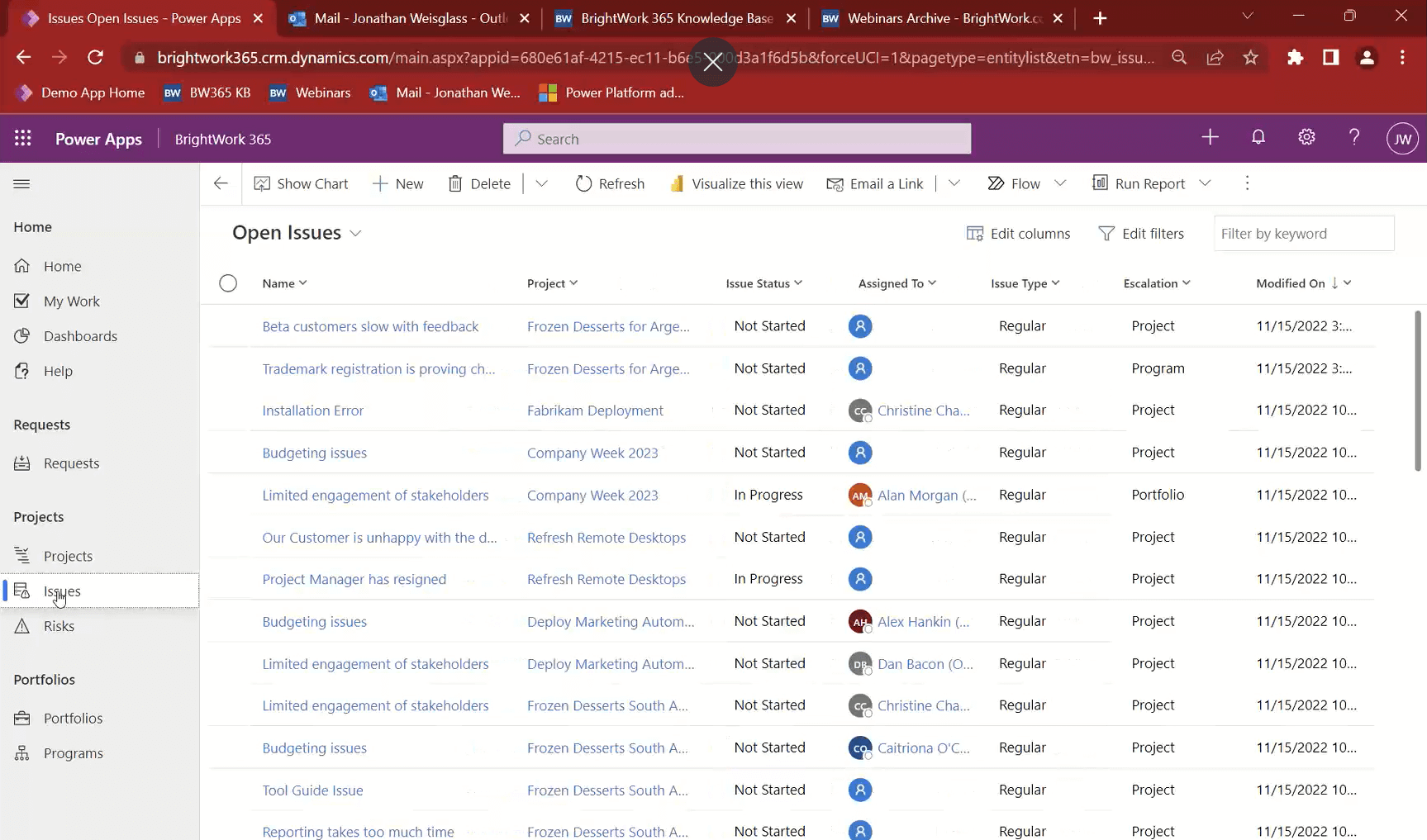
4. Surface Risks and Issues across all projects
One of the most critical elements for senior executives and project stakeholders is being aware of the project risks, especially understanding any issues that arise quickly.
5. Leverage Visual and Interactive Reports
The type and format of a report often depends on the audience. For example, senior executives often want the high-level details of a project. That’s where BrightWork 365 Power BI Dashboards come in.
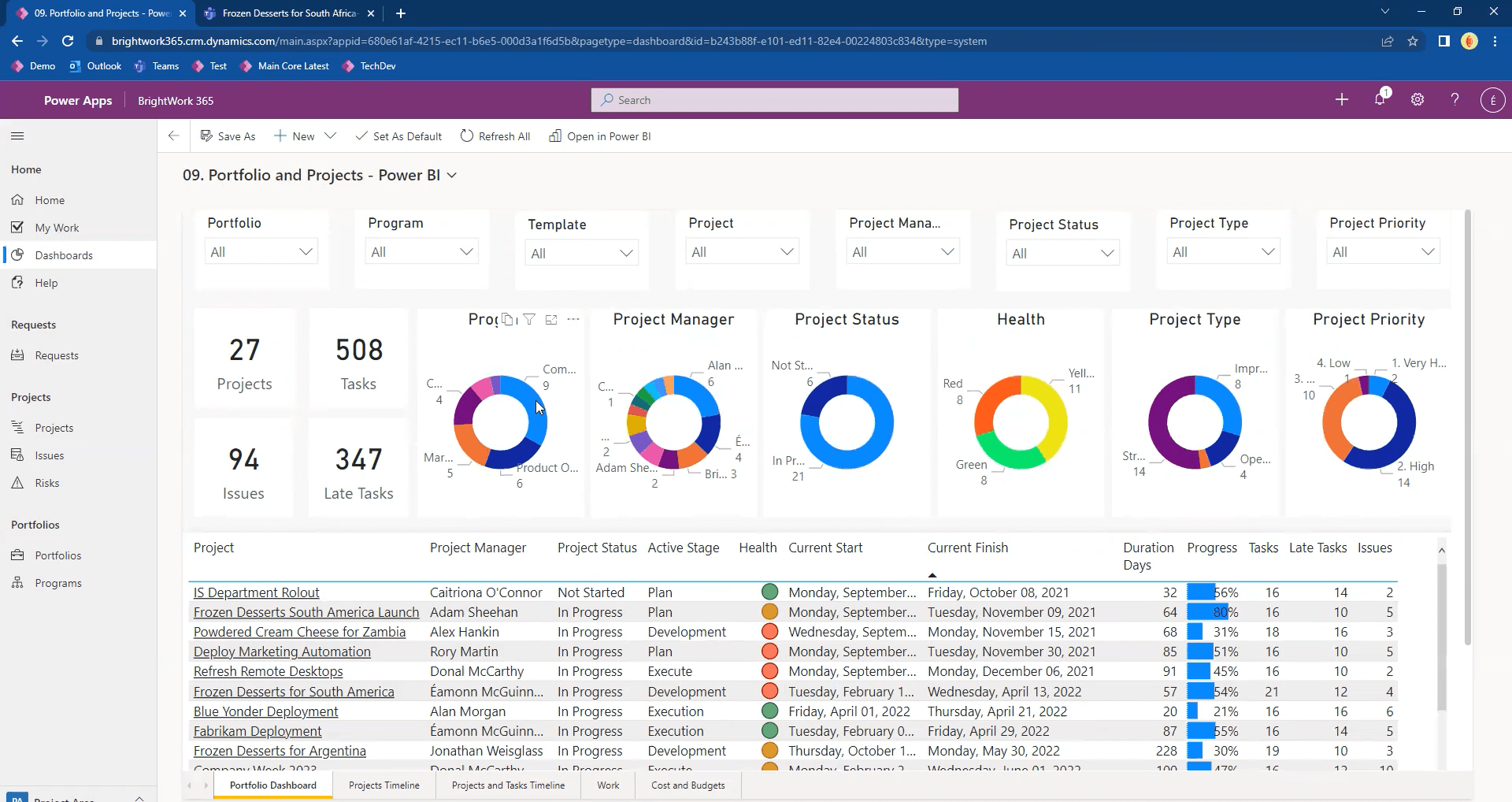
Spend less time on your project reports with BrightWork 365
Streamline your project reporting process with BrightWork 365, a tool to centralize and automate your project data. Whether you prefer real-time dashboards or scheduled email reports, BrightWork 365 adapts to your needs, eliminating the tedious aspects of project reporting. Consider the following:
- Centralization : BrightWork 365 consolidates all project information into a single platform, making it easier to manage and report.
- Real-Time Reporting : As data is updated, reports are generated in real-time, ensuring you always have the most current information.
- Flexible Access : Reports can be accessed through various methods, including logging in to view customizable dashboards or receiving scheduled email summaries.
- Efficiency : The tool automates the reporting process, freeing time and reducing manual effort.
Conclusion: The Future of Project Reporting
Project reporting has undergone a significant transformation, thanks partly to technological advancements like Microsoft 365 and BrightWork 365 . As we’ve discussed, it’s not just about tracking tasks and milestones anymore.
Today’s project reports are data-rich, AI-enhanced documents that offer predictive analytics and actionable insights. They also cater to the unique challenges and KPIs relevant to remote teams.
As we look to the future, we can expect even more advancements in project reporting technology. However, the core principles of clear objectives, a deep understanding of your audience, and a well-structured format will remain constant.
By adhering to the steps outlined in this guide, you’ll be well-equipped to adapt to new tools and technologies, ensuring that your project reports remain valuable for decision-making and strategic planning.
Editor’s Note: This post was originally published in September 2016 and has been updated for freshness, accuracy, and comprehensiveness
Image credit
Shubhangi Pandey
Shubhangi is a product marketing enthusiast, who enjoys testing and sharing the BrightWork 365 project portfolio management solution capabilities with Microsoft 365 users. You can see her take on the experience of the template-driven BrightWork 365 solution, its unique project management success approach, and other personalized services across the site and social channels. Beyond BrightWork, Shubhangi loves to hunt for the newest Chai Latte-serving café, where she can read and write for hours.
Don't forget to share this post!
Privacy overview.
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. It is mandatory to procure user consent prior to running these cookies on your website.

How to Write a Project Report In 5 Easy Steps (Template Included)
Written by samantha ferguson.
Last updated on 9th May 2024
The reasons why projects fail are plentiful but it typically comes back to poor planning or a lack of organisation.
A solid project report can eliminate these issues and ensure you stay on track to complete your goals.
So, let’s take a look at how to write a project report in 5 easy steps…
What is a project report?
A project report is a document that contains helpful information so that teams can ensure their project stays on track, runs successfully, and completes on time.
There are different types of project reports that are used at different periods throughout a project’s lifespan, but they all contain similar data that covers things like progress, tasks, roadblocks, stakeholders, and financial information.
Why is a project report important?
Project reports are important for many reasons. A project report gives your project a sense of direction that can help you maintain consistency throughout the project, even as it passes between different people and teams. Your project report will also be a great document to refer back to if things get difficult, so you can stay on track.
Even in the first instance, before your project kicks off, a project report can help you to manage your budget, workload, and any foreseen risks. It can also give stakeholders insight into the specifics of the project to help manage expectations from the start.
Types of project report
There are many different types of project reports that will help you manage different aspects of your project. For example, a resource report will help you to understand the resources you’ll need for the project, how much resource you have at your disposal, and will also help you to predict when your resources will need to be replenished. Other examples include:
Now, let’s dive into 3 of the biggest, most important types of project reports.
1. General project report
This is your first project report. It should cover predictions and plans for how you expect the project to go, and give you a clear sense of direction when it comes to things like budget , timelines, and everything else you need to keep track of in order for your project to be considered a success.
2. Progress report
A progress report – as you may have guessed – comes in the middle and helps you document your progress. It’s important to keep reassessing your project to see if you are where you expect to be and to help you make adjustments along the way.
3. Project completion report
As you wrap up your project, a project completion report can be a great way to reflect on what went well and what went wrong. This can not only help you wrap up the current project neatly, it can also inform future projects and ensure you don’t make the same mistakes twice.
How to write a project report in only 5 steps
There are many different types of project reports. So, of course, the writing of each one will differ slightly depending on who they are aimed at and what the content of the project report is.
However, there are still some core steps to follow for each. Let’s take a look at how to write a project report in 5 steps.
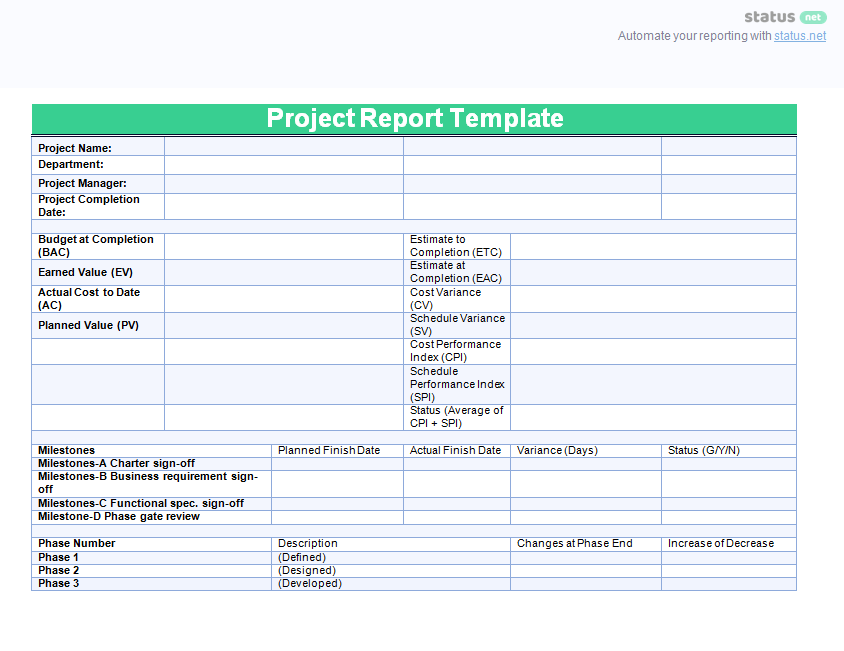
1. Start with the basics
At the very top of your project report should be a simple table that includes all of the core information for the project. Here’s an example:
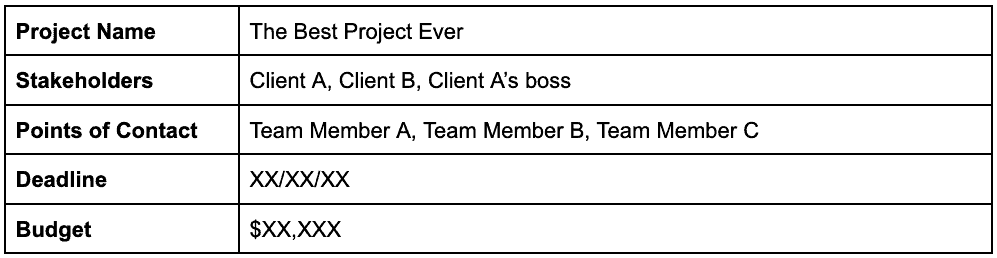
The table for your project will probably vary slightly to this, but hopefully this gives you an idea of the most important top-level information to include.
Underneath this table you should have a short summary of the project. This can be just a couple of sentences that sum up the objectives and goals. Think of this kind of like an elevator pitch for the project.
2. Cover your objectives
Now it’s time to go into more detail. List out each objective for the project, including what you need to do to achieve each one.
For example, let’s pretend our project is to create a brand video. There are many objectives, such as:
Each objective will need to be completed in order to go on to the next. And each objective requires different resources and skill sets. All of this should be recorded, in detail, in your project report.
3. List your obstacles
Next, list any predicted obstacles or risks. This may feel like a waste of time because of course you’re going to be avoiding risks and obstacles as often as you can. However, it’s important to be aware of the potential roadblocks that might appear so that you are prepared to handle them without slowing down.
Some example obstacles for the brand video project could be:
Next to each obstacle, jot down a quick plan for how you would solve this issue if it happened. For example, for “weather ruins a shoot” your potential solution could be to “choose a backup location”.
4. Create a project timeline
With any project, it’s important to know how long everything’s going to take. This is the best way to estimate how much time, money, and resource is required.
A project timeline will help plot a path forward. To create a project timeline all you need to do is break down each objective into tasks and add a deadline for each task. It also helps to add an owner to each task, so you know who the point of contact is for each section of the timeline.
This can be tricky to manage but becomes so much easier with a project management tool, like Project.co . When you create a project on Project.co, all of your clients and team members can see everything that goes on with the project in one centralised place. This includes tasks that can be allocated to team members, assigned a date, and a status – so everyone involved in the project can see how it’s progressing:
You can also add comments, attachments, priority tags, and more.
Plus, it’s easy to keep track of several tasks at once by using the calendar view:
Other views available are kanban, list, and scheduler.
5. Cover project communication
Somewhere on your project report you should include a link to your communication guidelines . This will help everyone involved on the project to understand what’s expected of them when it comes to communication, for example what tools to use and how to communicate.
This can help your project run more smoothly and create a better result for everyone. According to our Communication Statistics 2022 , 94% of people feel that the businesses they deal with could improve when it comes to communication and project management .
Writing a project report: 7 top tips
1. be clear.
The perfect project report is clear and concise. Try your best to leave no room for errors or misunderstandings, and write in short definitive sentences.
Being clear is especially important when it comes to timelines and targets. It can be helpful to plot out your tasks in a visual way, like a kanban view . This will make your project timeline easy to scan and understand.
2. Be thorough
While it’s important to be clear and concise, it’s equally important to be thorough. Try to include as much relevant information in your project reports as possible.
One of the main functions of project reports, particularly project status reports, is to inform stakeholders on the progress of the project. So the more thorough you can be, the better.
3. Be appropriate
A project report is an internal document that’s likely going to be shared between many different departments or teams in your business, so it’s important to make sure your language is appropriate.
Keep the culture of the business in mind when writing your report. Use the same kind of tone and language that you would in other internal communication documents. This is especially important when you consider more than a third (35%) of businesses have lost an employee because of poor internal communication .
4. Be honest
Your project report is not the place to sugarcoat anything. You should be honest, and brutally so. This means giving accurate and realistic figures, deliverables and deadlines.
A project report should be a factual account so that everyone has a clear understanding of the data and knows exactly what to expect from the project.
5. Be quick
It may seem contradictory to tell you to be thorough and quick with your project reports, but this just means don’t overload people with unnecessary information. Be succinct and to-the-point with every aspect of the report, from points of contact to resources and any potential roadblocks.
The idea is for your project reports to be as easy to digest as possible, especially if you’re supplying busy stakeholders with a steady stream of ongoing status reports.
6. Be prepared
No project runs perfectly, so it can be helpful to be prepared for bumps in the road. You might want to leave an ‘other’ or ‘notes’ section at the bottom of your report where you can jot down anything that’s changed along the way.
It can also help to leave room for slight adjustments in your timeline. Just a couple of buffer days here and there can really reduce stress for your teams, and also help ensure your deadlines are more realistic.
7. Be proud
When you’re carefully documenting things like risks and problems, your project report can become pretty gloomy. So it’s important to even it out by also celebrating your team’s achievements.
Every project has ups and downs, and by giving as much attention to the ‘ups’ as you do the ‘downs’ you can boost team morale and this can be reflected back on your project.
Free project report template
As promised, here is your free project report template !
Final thoughts
A solid project report can act almost like a map that clearly directs you towards your end goal, helping you to avoid risks along the way and take the best route to success.
In addition to a project report, a project management platform can also help you to maintain your focus and manage your project with ease, thanks to centralised communication and complete visibility of all your work. Click here to get started for free .

⭐️ All your work in one place
🗓 Never miss a deadline
🗂 Never lose a file
🏅 Simple for your clients
⚡️ Powerful for your team
Create your FREE account

How to Write a Project Report: Step-By-Step Guide [+ 4 Free Templates]
By archtc on December 26, 2017 — 21 minutes to read
- How to Write a Project Report: Step-By-Step Guide Part 1
- Project Report Templates: Free Download Part 2
- Additional Resources Part 3
- How to Dramatically Reduce Time You Spend Creating Reports Part 4
At some point during the implementation of a project, a project report has to be generated in order to paint a mental image of the whole project. Ultimately, a project report must maximize the insight gained with minimal effort from the reader. Apart from describing its results, it must also explain the implications of those results to the organization and its business operations.
How to Write a Project Status Report:
The most common type of project report, a project status report provides a general state of the project to its stakeholders. It quantifies work performed and completed in measurable terms. It compares this with an established baseline to see if the project is on track or; if adjustments have to be made if the project is behind its schedule. It keeps everyone on the same page and manages each other’s expectations.
Project status reports are accomplished to serve the following purposes;
- to keep an updated flow of information in relation to the project’s progress
- to immediately address issues and concerns that may come up at any point of the project’s implementation or duration
- to document reasons for changes and adjustments made to the original plan for the project
- to monitor fund utilization and to ensure that the project expenses are still within the budget
- to serve as a basis for decision-making and addressing problems
- to keep track of the team’s performance and individual contributions
- to act as a uniform procedure for communicating project development to the stakeholders.
Status reports are most effective when they follow a standard form with predefined fields that need to be regularly updated. Doing so will save time and provide consistency and predictability of the information the stakeholders will receive about the status of the project.
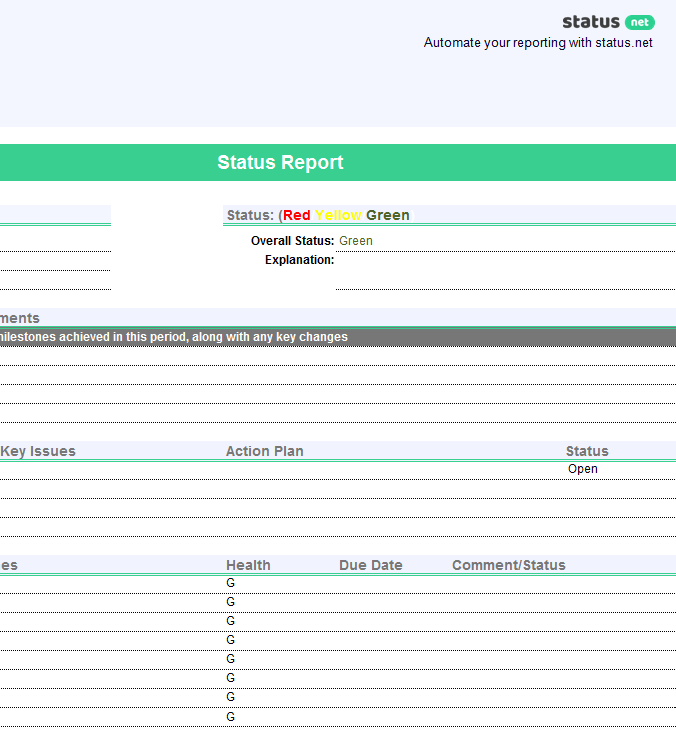
WHAT TO INCLUDE
For a status report to be comprehensive, it must include the following elements:
Summary/overall health of the project, facts on the project progress, target vs. actual accomplishments, action(s) taken, risks and issues, keys to an effective project status report.
- Submit the report on time . A status report is time sensitive and sending it late defeats the purpose of such a report.
- Giving complete but inaccurate information is just as bad as giving accurate but incomplete information . Since stakeholders rely on the status report for a heads-up on the project, and its content is used as the basis for decision-making, it is critical that the report provides both complete and accurate information.
- Do not cover up bad news or adverse reports as these are all part of the transparency of the status report . Keep in mind that being open with the stakeholders, whether the project is sailing smoothly or not, will benefit both the team and the client, since any problems there are will be immediately given attention and solved.
- Be proud of the team’s accomplishments, after all, this is what the clients and the stakeholders will want to know about .
- Anticipate questions from the clients or stakeholders and be prepared to answer them .
- Be familiar with the culture of the organization and respect the information hierarchy they observe . There are instances when the CEO wants to be the first to know about the contents of these reports before cascading it to his downlines. On the other hand, middle managers will want a head start on these reports so they can also anticipate and prepare for any reaction from the top executives.
- Craft the status report in such a way that there will be no information overload . It should contain necessary information that the stakeholders need to know. Lengthy reports will consume not only the writer’s time but also that of the reader. Too many details also give an impression of micro management.
Risk Registers
All projects, or any activities of business, face risks. It is just a matter of how an organization identifies, assesses, analyzes, and monitors these risks. With a Risk Register, an organization is equipped with a tool to better respond to problems that may arise because of these risks. It helps in the decision-making process and enables the stakeholders to take care of the threats in the best way possible.
A Risk Register, also called an Issue Log, is iterative because it will be updated periodically depending on how often the team identifies a potential risk. It may also be updated if the characteristics of the existing potential risks change as the project progresses.
The Risk Register document contains information about the following:
Risk Identification
- Risk Category: Grouping these risks under different categories is helpful. Doing so will provide a way to make a plan of action that will address most, if not all of the risks falling under the same category, saving time, effort, and resources.
- Risk Description: Provide a brief explanation of the identified potential risk. The description can be done in a variety of ways depending on the level of detail. A general description can be difficult to address while giving too much detail about the risk may entail a significant amount of work. Three factors to consider when making a risk description are: the way these risks are going to be managed, who will handle them, and the reporting requirements of the person receiving the risk register.
- Risk ID: Assign a unique identification code to each risk identified to track it in the risk register easily. Create a system of coding in such a way that the category to which the said risk belongs is easily identifiable.
Risk Analysis
- Project Impact: Indicate the potential effect of the assumed risk on different aspects of the project such as budget, timelines, quality, and performance.
- Likelihood: Referring to the possibility of the risk occurring, the likelihood can be expressed qualitatively—high, medium, low—or quantitatively, if there is enough information available. Whatever criteria are to be used, assign a number—with the highest value corresponding to that which is most likely to occur.
Risk Evaluation
Using the table above, the identified risk can be ranked this way:
- Risk Trigger: These are the potential risk events that will trigger the implementation of a contingency plan based on the risk management plan. This plan should have been prepared prior to the development of a risk register.
Risk Treatment
- Prevention Plan: This enumerates the steps or action to be taken to prevent the risks from occurring.
- Contingency Plan: On the other hand, the contingency plan determines the steps or action to be taken once the risk events have occurred. This program also contains the measures to be taken to reduce the impact of such risks to the project.
- Risk Owner: The person responsible for managing risk, and the implementation of the prevention and contingency plans, it can be anyone among the stakeholders—members of the team, a project manager, or project sponsors.
- Residual Risk: Sometimes, a risk cannot be entirely eliminated after treatment. Part of it may linger throughout the duration of the project, but once it has been treated, it can be considered as a low-level risk.
Keys to an Effective Risk Register
- The first risk register must be created as soon as the project plan and the risk management plan has been approved . This initial risk register must be integrated into the project plan.
- Active risks during a particular period must also be included in the project status report .
- Risk management is an iterative process which is why the risk register must also be updated from time to time . Updates can be made when new risks are identified or there have been changes in the risks already in the register.
- The numerical value assigned to the likelihood and severity levels must remain constant throughout the duration of the whole project .
- Likewise, any terms used must be defined, and this definition must be utilized consistently .
Project Closure Report
As the end of a project, a Project Closure Report signals its culmination. Its submission officially concludes a project and implies that funds and resources will no longer be needed, and everything will go back to its status prior to the implementation of the project.
This process is critical as it will officially tie up all loose ends and prevent confusion among stakeholders.
This particular type of project report summarizes information on the project results, the criteria used to measure the effectiveness of the project delivery process, and the feedback from the stakeholders. Each performance metric includes an assessment and a narration of how the team performed on such metrics.
This performance metric describes how the team utilized the budget in carrying out the project effectively. Under this performance metric, the following aspects are measured:
Component Breakdown
Budget variance, explanations for key variances.
Describe how the team implemented the project within the expected time frame and schedule.
Overall Project Duration
Schedule variance, the explanations for key variances, change management.
This metric refers to the team’s ability to handle and manage changes throughout the project’s implementation effectively. It is measured through the following:
Total Number of Changes
The impact of the changes, the highlight of changes, quality management.
This particular metric refers to the team’s ability to observe and comply with quality standards during the project’s implementation.
Total Number of Defects Identified
The explanation for resolved defects, risk and issue management.
This metric deals with how risks and matters that occurred during project implementation were handled and resolved by the team. Key points to include are the following:
The impact of the Risks and Issues to the Project
Human resource management.
This refers to the team’s ability to carry out the project effectively.
Project Organization Structure
This metric looks at how the stakeholders participated in the project.
Decision-makers
Communication management.
Under this metric, communication throughout the duration of the project is assessed.
Communication Management Plan
- Summarize essential feedback collected . Describe the method by which these comments were gathered and who was solicited for feedback. Also include how they responded to each question and briefly discuss which items received great responses from the participants and which ones got few answers.
- Take note of common themes or trends of feedback gathered .
- From the feedback gathered, also take note of any opportunities from this feedback and discuss how these opportunities can be applied to future projects, or in the organization itself .
Lesson Learned
- Give a brief discussion of what the team learned when carrying out the project . Among these learnings, discuss which ones can be applied to future projects and how it will impact not only those future projects but also the whole organization.
Other Metrics
Other points of interest may not have been captured in the Project Status Report and may be included in the Project Closeout Report. Some of these factors include:
Duration and Effort by Project Phase
Benefits realized, benchmark comparisons, keys to an effective project closure report.
- The closure report is mostly a summary of all efforts related to the project . It is important to ensure that all highlights of the project have been properly documented so that retrieval of these reports is easier and all efforts will be acknowledged.
- Emphasize the high points the project delivered, how efficiently it was done, and what has been learned from the process.
- If there are notable variances during the project implementation, make sure to provide a fact-based explanation on it . In addition, the impact of this difference must also be described.
- A critical point in a project closure report is establishing the link between the project performance, the lessons learned, and the steps that will be taken by the organization for its continuous improvement . Aside from the project deliverables, another valuable output of a project is the learnings derived from the process and how it will be translated into concrete concepts applicable to the business processes of the organization.
Executive Summary
A little bit different from the types of project reports previously mentioned, an Executive Summary is a distinct kind of report which uses different language. It is a high-level report which aims to provide a bigger and deeper understanding of the project—how it will benefit the organization and how it will fit into future business strategies. It is written with a busy executive in mind, someone who has a lot of important things to do and may find reading a lengthy piece of prose a waste of precious time. Factual and objective, this particular type of project report must be able to provide a realistic status of the project, as business executives understand that everything may not go according to the plan.
Some may confuse an executive summary with an abstract but, in reality, they are clearly distinct from one another and serve a different purpose.
An abstract is usually written for academic or scientific papers. It is written with a topic sentence which, generally, gives an overview of what the article is about. It is, then, supported by two or three supporting sentences which support the main idea of the topic sentence.
An executive summary, on the other hand, is composed of different sections discussing almost every significant aspect of an undertaking. It consists of sequentially arranged key points supported by conclusions and recommendations. Check our in-depth article on how to write an effective executive summary .
Things to Remember in Writing Project Reports
Here are some of the principles that need to be observed in writing an effective project report;
Write for the reader
The report should have a structure, ensure that the report is evidence-based and is supported by data, make it as objective as possible.
There is a clear distinction between facts and opinions . These should never be used together, especially if the report is dwelling on a failed project. The report becomes subjective if it reflects personal opinions of the writer. Make it objective by eliminating all parts which are not based on facts and real events. If it is really necessary to include a personal view or opinion, make sure to explicitly identify it as such. A separate section of the project report may be devoted to the writer’s personal opinion to keep the rest of the report unbiased.
There are a number of ways project reporting helps an organization, a team, and even the project itself and here are some of them:
It tracks the progress of the project
It helps identify risks, it helps manage project cost, it gives stakeholders an insight on how the project is performing, project report template: free download.
Click Here to Download Project Status Report XLSX

Click Here to Download Project Update Report DOC

Click Here to Download Project Update Report 2 DOCX
Click Here to Download General Project Report DOCX
—————————————————————————-
Templates on ProsperForms:
Edit and use this template
Additional Sources
- How to Write an Outstanding Weekly Report + Free Template Download
- Project Status Dashboard and Project Tracking
- How to Create a Project Meeting Template + Free Download
The Ultimate Guide to Creating a Project Report: How to write a Project Report with Templates
Writing an effective project report is a crucial skill for any project manager. A well-written report clearly communicates the status and progress of a project to key stakeholders and outlines key next steps. This comprehensive guide will teach you how to write a professional project report in 7 steps using free report templates.
A project report is a document that summarizes project data based on economic and financial analysis, progress status, risks, and results to date. It provides stakeholders with information about your project including goals, timeline, budget, resources, risks, and performance.
This guide covers different types of project reports, key components to include, and tips for writing reports efficiently. With sample project report templates, you’ll learn how to create a polished report to keep your project on track.
Why Are Project Reports Important?
Project reports are a critical part of project management. A well-written report helps project managers in the following ways:
Communicates the current status of the project to stakeholders
Highlights project risks, issues, scope changes
Tracks project progress against schedule and budget
Identifies areas that need improvement
Keeps the project team and stakeholders aligned
Creates documentation for the entire project
Demonstrates the value of the project
In short, project reports keep everyone informed about the health of a project. Reports provide the data and insights needed to make good decisions and keep the project on schedule.
What are the Different Types of Project Reports?
There are several different types of project reports, each serving a different purpose. The type of report you’re creating depends on the needs of stakeholders and phase of the project.
Here are some common types of project management reports:
Project Status Report
A project status report communicates where the project stands at a specific point in time. It compares project progress and performance to the original plan. Status reports help identify issues, risks, or changes early. Include sections like progress since last report, upcoming milestones, risk management, and issue log.
Progress/Performance Report
Similar to a status report, a progress or performance report summarizes project progress. It describes work completed in the given timeframe as well as metrics related to budget, schedule, quality, resources, and risks. Use key performance indicators to evaluate progress.
Project Summary Report
A project summary report is an overview of the entire project from inception to completion. It recaps key objectives, milestones, outputs, budget, and lessons learned. Project sponsors often request a summary report as part of project closure.
Analysis Reports
Analysis reports take a deep dive into a specific aspect of the project, like costs, risks, quality, or procurement. Examples include cost-benefit analysis, earned value, forecasting, and gap analysis. Analysis reports identify problems and recommend actions.
Project Management Reports
Project management reports focus on the performance of the project team. They track resource usage, capacity, budgets, timesheets, and project management metrics. Task tracking and burn down reports fall into this category.
Key Components of a Project Report
While the exact format changes based on report type, certain elements are common to all project reports:
Project Overview
The overview provides background on project goals, scope, timeline, deliverables, resources, and sponsors. It summarizes the purpose and objectives of the project.
Status Summary
The status summary analyzes where the project stands at the time of the report. It highlights milestones achieved, upcoming milestones, percentage of work completed, plus budget and schedule status. Charts are helpful to display status visually.
Work Completed
This section describes the activities, deliverables, and work products finished during the reporting period. Reference the project plan, timeline, and work breakdown structure.
Work Pending
Work pending lists the activities and milestones still remaining. Are any critical path items behind schedule? How will you get back on track? Explain upcoming work and priorities.
Issues and Risks
The issues and risks section calls out problems, changes, action items, and risks impacting the project. It identifies who is responsible for resolving each item and next steps. New risks should be added to the risk register.
Budget Status
Budget status compares planned budget vs. actuals spent to date. Track spending by cost center, work package, or resource. Explain any budget deficits or overruns.
Schedule Status
Compare original schedule vs. actual progress. Are milestones on track? Report schedule variance and identify activities that are ahead or behind schedule. Explain delays.
Recommendations and Next Steps
Finish the report with next steps and recommendations to get the project back on track or improve performance going forward. Present options and actions for consideration.
Attach relevant facts, figures, and documents that support the project report as appendices. Examples include the risk register, issue log, schedule, budgets, charts, and graphics.
7 Steps to Writing a Polished Project Report
Follow these steps to produce a professional project report your stakeholders will actually want to read:
Step 1 - Determine Report Requirements
Start by defining the purpose, audience, and required contents based on the report type. Identify the questions that need answering and data that must be included. Connect with stakeholders to understand their needs.
Step 2 - Select Report Format and Structure
The format and structure can vary based on the project and organization. Follow company templates if available. Common structural elements include an executive summary, introduction, body, conclusion/recommendations, and appendices.
Step 3 - Gather Data and Content
Compile the data inputs needed for each section of the report. Sources include the project plan, schedule, risk register, budget, quality records, timesheets, and performance metrics. Leverage project management systems to pull data.
Step 4 - Analyze Data
Analyze the project data and turn it into meaningful insights. Calculate metrics like schedule and cost variance. Evaluate project risks, issues, and changes. Assess progress relative to KPIs. Identify trends.
Step 5 - Write First Draft
Following your selected outline, start writing the first draft incorporating the analysis done in step four. Use clear, concise language. Keep sentences short. Include charts and graphs to visualize data.
Step 6 - Formatting and Style
Apply formatting like colors, fonts, page layouts, headings, and white space for visual appeal. Create an organized, scannable report. Maintain consistency in style and tone. Follow company templates and best practices.
Step 7 - Review and Finalize
Allow subject matter experts to review the draft report. Incorporate feedback and edits. Verify facts and figures. Complete final formatting and touch-ups before sharing the polished version with stakeholders.
Project Report Templates and Examples
Reinventing the wheel for each report wastes time. Start with pre-built templates then customize with your specifics. Here are free templates and samples:
Project status report template
Project management report templates
Status report PowerPoint
Progress report template
Summary report samples
Project closure report
Leverage templates to create well-formatted reports with pre-built sections, content examples, and design elements. Add colors, charts, and branding to match company guidelines.
Tips for Writing Better Project Reports
Follow these best practices for clear, targeted project reports:
Focus on stakeholders - Understand stakeholders’ needs and tailor content accordingly. Include relevant facts and data points they care about.
Be visual - Charts, graphs, images allow readers to grasp status, trends, and insights quickly.
Use executive summaries - Condense findings into a 1-2 page executive summary with top takeaways, recommendations, and action items.
Keep reports brief - Avoid long, dense reports. Use an appendix for supplemental data.
Mind formatting - Well-formatted reports with ample white space, headings, and visual hierarchy are easier to digest.
Simplify language - Write in clear, simple business language. Define acronyms. Avoid jargon that requires insider knowledge.
Proofread thoroughly - Fix grammar and spelling mistakes that undermine credibility.
Update templates frequently - Tweak report templates regularly to improve flow, formatting, and effectiveness.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Writing compelling project reports is a learned skill. This guide outlined a step-by-step methodology to produce polished project reports that impress stakeholders using data, templates, and best practices.
Here are some final recommendations on creating excellent project reports:
Follow the 7 step process
Start with templates then customize
Focus on visual appeal and easy scanning
Analyze data to gain meaningful insights
Keep sentences and sections short
Make critical information obvious
Project reporting helps managers maintain control, alignment, and visibility. With practice and feedback, you can level up your report writing skills over time. Now it's your turn - go create some outstanding project reports!
Get started
- Project management
- CRM and Sales
- Work management
- Product development life cycle
- Comparisons
- Construction management
- monday.com updates
How to write a project report: [templates + guide]
Writing a project report is an essential but often overlooked contributor to your project’s health. However, without the use of automation and templates, it can be a little time-consuming to collect and organize the relevant data that the project generates.
In this post, we’ll explore the basics of project reporting. We’ve included some useful templates and tips to create clear and helpful project reports in less time.
If you want to start creating better project reports using monday.com, sign up today.
What is a project report?
A project report is a document where you share details about different areas of your project. Depending on the report type , your audience, and your intention, the details you showcase might differ.
Project reports can be broken down by time— daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly— or a number of other factors like risk, budget, and project management style. Bottom line? They simplify the process of gathering and disseminating information about key information on the project. For instance, a typical report might include:
- Resources you’ve used so far
- How project time is being spent
- How you’re doing against key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Workload and team availability
What is the purpose of project reporting?
Reporting gives you, your team, and your stakeholders the ability to track project progress against the original plan. The main goal of a project report is to improve decision-making, to help you make sense of your project data, and decide what your next steps should be. This in turn can impact your budget, timeliness, and project success.
It also plays a vital role in your stakeholder engagement strategy, as it keeps everyone informed on the progress of projects they’re interested in. Those are just a few of the reasons why project reporting has become the most common activity among PMOs (Project Management Offices).

( Image Source )
5 steps to create a useful project report
Project reports can be useful – or they can end up as a 20-page PDF that lives in a drawer somewhere. To put together a report that your project stakeholders can use to gain insights, make decisions and optimize processes, take the following systematic approach to writing your project reports:
1. Define the purpose and scope: Clearly establish the goals, objectives, target audience, and information needs of your project report. 2. Gather and organize data: Collect and organize all relevant data, ensuring its accuracy and reliability. 3. Structure and outline: Create a clear and logical structure for your report and outline the key points you want to cover. 4. Present information effectively: Use clear and concise language and visual aids like graphs or charts to present the information in an easily understandable, visually appealing manner. 5. Review and revise: Proofread your report for any errors or inconsistencies, ensure that it addresses the defined purpose and scope, and revise as necessary to improve clarity.
The different types of project management reports [with templates]
You can split project reports into different types and categories. Here are five different types of project mangement reports, with monday.com templates you can customize for your unique project and team set-up.
1. Project status report
Probably the most frequently used, a project status report offers a general overview of the current status of your projects. A project status report answers the question: “How likely is it that we’ll complete this project on time without overrunning costs?”
These reports analyze whether you’re meeting project goals and key performance indicators. With our single project template , creating a status report is easier than ever.
![the report of project How to write a project report: [templates + guide]](https://dapulse-res.cloudinary.com/image/upload/template_center/project_management/single_project/screenshots%20/single_project_first.png)
2. Resource workload report
Resource workload reports help you visualize what your team’s working on, when they’re working on it, and how much work is left. These also reports help you understand how your assets are being used and make sure your actions are aligned with the overall objective.
Our resource management template helps you organize all your assets, locations, and people into one place and track every action with accuracy. You can also manage your resource allocation initiatives and make sure you don’t assign the same resource twice in multiple tasks.

3. Portfolio report
Portfolio reports take a look at all your projects and consolidate all the data into a single document. These reports capture high-level milestones, status, progress, and highlights of your portfolio strategy.
With our portfolio management template , you can track unlimited projects on a single board and get a quick snapshot of their health and profitability.

4. Task list/Time-tracking report
Time-tracking reports, also known as timesheets, help you measure how your team is spending their time and spot potential bottlenecks.
With our team task list template , you can bring in your entire organization, assign tasks to peers, track time and measure the project progress at a glance.
5. Expense report
A project might seem healthy – until everyone starts reporting expenses at the end of the time period. With our expense tracking template , you can proactively manage your cash flow regardless of your accounting skills (or lack thereof!)

Want to try out these templates – and much more? Check out monday.com today.
FAQs about Project Reports
What are the benefits of a project report.
A project report provides a comprehensive overview of a project’s objectives, progress, and outcomes, serving as a valuable documentation and communication tool. It allows stakeholders to assess your project’s effectiveness, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions based on reliable data.
What are the main types of project reports?
The most commonly used types of project reports include:
- Progress reports
- Resource management reports
- Project portfolio reports
- Time-tracking reports
- Evaluation reports
- Final reports
What are the main components of a project report?
This will depend on the project and the type of report you’re using, but project reports might include:
- Project objective
- Project scope
- Project milestones
- Project expenses or budget
- Project schedule and timeline
- Project progress
- Resource management
- Risk assessment
- Stakeholder communication
- Financial summary
How to create insightful project reports with monday.com
monday.com makes it easy to create effective project reports. Try it for yourself and see:
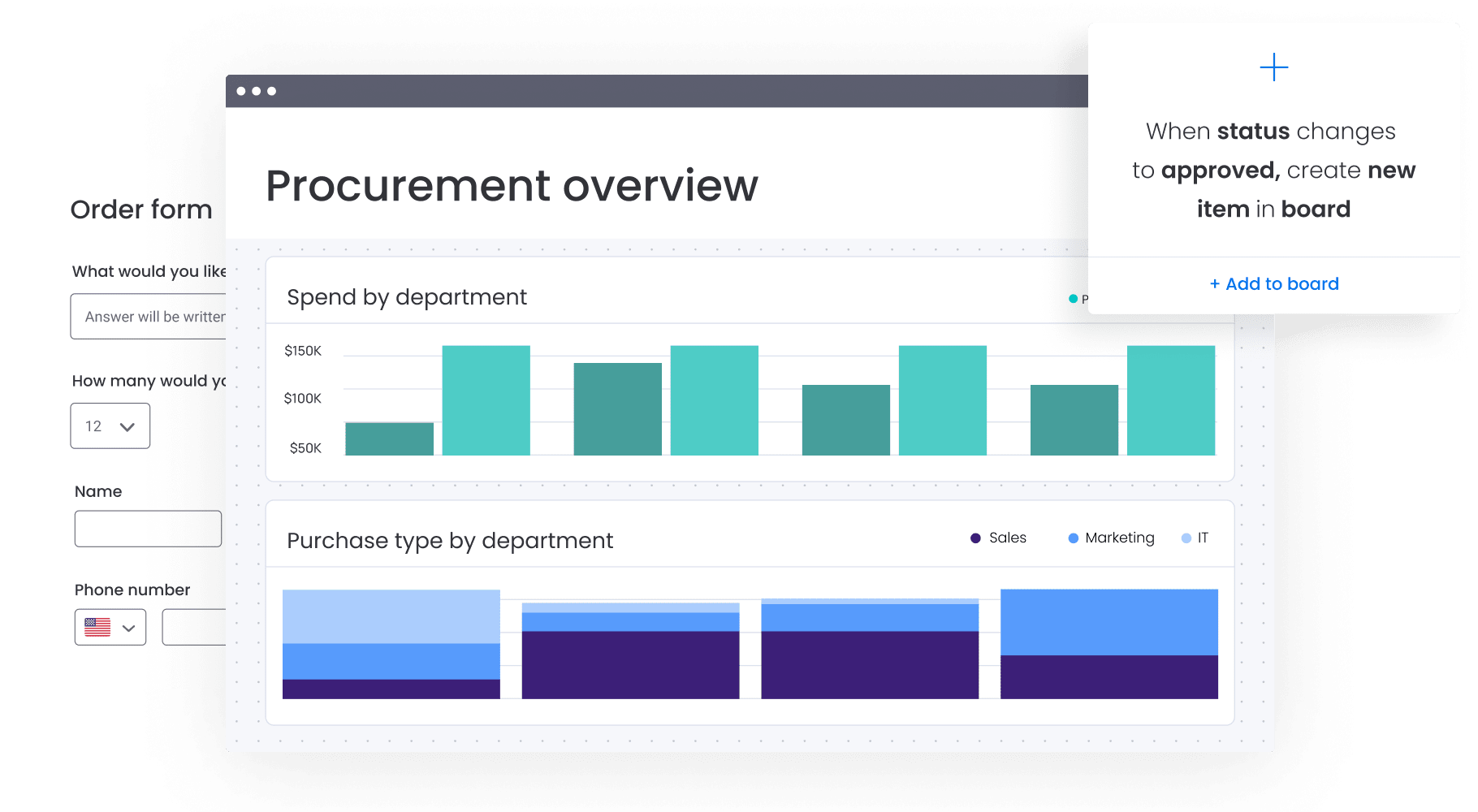
Here’s why monday.com can make your project reporting better:
- Track project data in a centralized location, so you have all the information you need to make useful reports.
- Use monday.com’s customized visualization tools to visualize and summarize project data the way you want to see it.
- Set up dashboards to see all of your projects at a glance.
- Take advantage of monday.com’s reporting functionality . You can choose between built-in report templates or customized reports if you have more specific requirements.
- Share your reports with project stakeholders , team members, or even clients directly from monday.com.
- Our embedded communication tools let you collaborate on your reports in real-time, gather feedback, and address any questions or concerns.
Send this article to someone who’d like it.
Popular Insights:
Best Project Management Software
Mind Mapping Software
How to Write a Project Report
Share this Article:
Our content and product recommendations are editorially independent. We may make money when you click links to our partners. Learn more in our Editorial & Advertising Policy .
What Is a Project Report?
Why are project reports important.
Read more: What is Project Management? Definition, Types & Examples
Examples of Project Reports
Tips for creating useful project reports.
- Pinpoint the purpose: Understand the purpose of the project report and what you are being asked to convey.
- Know the audience: Who are you creating the report for, and what they want to know about the project?
- Choose a report format: Choose whether it will be a presentation, a link to a file, or a printed document.
- Draft the report: Create a rough draft of what you are preparing and review it carefully. Make sure you are including all of the details you want to share with the team, and reach out to team leads to fill in any gaps before finalizing.
- Consider layout: Give the report a good structure and effective layout. Make it easy to spot the most important information first at a scan, and list other details as secondary.
- Highlight key content: If a report is more than a few pages in length, create a table of contents and subheadings for easy review. Readers should be able to quickly find key information.
- Proofread: Use simple and easy-to-read language that is free of grammatical, spelling, and punctuation errors.
Featured Partners: Project Management Software
{{ title }}.
Sign up for our emails and be the first to see helpful how-tos, insider tips & tricks, and a collection of templates & tools. Subscribe Now
Featured Partners
You should also read
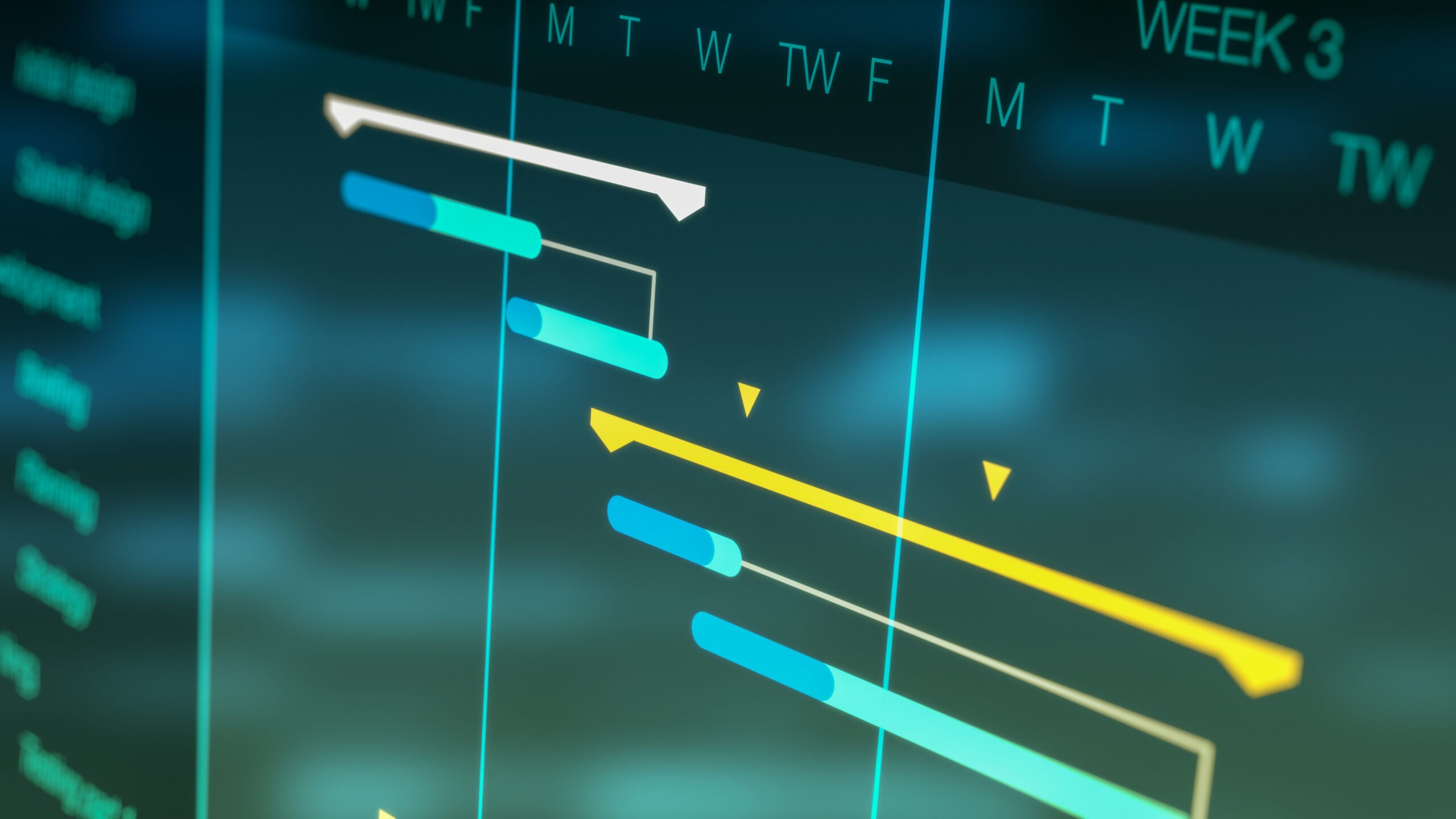

Creating Gantt Charts in Microsoft Project: Ultimate Guide

Project Executive: Roles, Responsibilities, and How to Become One

What Is Cost-Benefit Analysis: A Practical Guide
Join our newsletter.
Subscribe to Project Management Insider for best practices, reviews and resources.
By clicking the button you agree of the privacy policy

Get the Newsletter
You might also like.

83 Project Management Terms & Concepts to Know
What Is a Problem Statement & How to Effectively Create One
How to Hire the Best Project Manager
Want to create project reports with just a few clicks?
Project Reporting: In-Depth Guide to Project Reports
Project reports and reporting are a fundamental part of project management and a project’s success. Documents such as the project summary report serve as practical tools that provide a detailed account of the project’s progress, challenges, and strategies.
Documenting every aspect of a project includes following certain steps and making sure that information is available to managers, stakeholders, and team members.
Whether you’re a seasoned project manager wanting to refine your own project management skills and create better project reports or want to create a project report for the first time, this article will guide you through the entire reporting process.
Want to create comprehensive project reports with just a few clicks?
Choose a simple, fast and secure time tracking solution that ensures timely timesheets, keeps your project budgets in check and automatically calculates billable hours.
What is project reporting?
Project reporting is the process of collecting, analyzing, and disseminating information about a project’s progress and project team performance.
This kind of reporting involves gathering project data like key metrics and insights related to various aspects of the project, including timelines, project budget , resources, the status of operations, risks, and project milestones .
Project reporting exists to keep stakeholders and team members informed about the project’s development, being an essential tool when making decisions regarding any related situation.
The bottom line is that effective project reporting provides transparency on every action for everyone involved. Project reporting serves as a communication tool, fostering collaboration and accountability among team members and stakeholders .

What is a project report?
A project report is a detailed document that provides a detailed overview of a project’s planning, execution, and outcomes.
It serves as a formal record, communicating essential information about the project’s progress, performance, and status to the various project stakeholders involved. This document plays a crucial role in fostering communication, transparency, and accountability within a project, assisting decision-makers when making decisions.
Typically, project management reports include these key points:
- The current status of the project and the project’s current direction
- Information about the timeline and project schedule
- Details about the project budget and resources used and/or needed
- Cost-benefit analysis report
- An outline of the upcoming tasks, realistic project objectives, and key milestones
- Strategies to address challenges, ensuring stakeholders clearly understand the project’s trajectory.
It’s important to also include an assessment of potential risks and challenges , and the solutions that may be the appropriate response if those ever arise.
It must also include the list of the pre-determined key performance indicators (KPIs) , measures that assess the project’s performance against predefined project goals and objectives.

Who prepares a project report?
Usually, the project report is the responsibility of the project manager , unless another member of the team is designated to do it. It’s important to add that the responsibility for creating the project report may vary depending on the size and structure of the organization , as well as the nature of the project.
The project manager is usually the most well-acquainted team member with the project’s details, progress, and challenges, making them the best person to provide a complete and detailed project overview report .
In larger organizations, there might be dedicated project coordinators, analysts, or reporting specialists who collaborate with the project manager to gather relevant information and create the report.
Benefits of a project report in project management
A project report is a vital part of a project management operation not only for its purpose as a reference document but also as a communication tool.
Beyond being a formality, a well-crafted project report is essential in communicating information to stakeholders, guiding decision-making, and ensuring transparency throughout the project lifecycle .
Let’s explore the benefits of building a project report.
1. Improving communication and transparency
It serves as a communication bridge, offering stakeholders, team members, and decision-makers a clear and transparent view of the project’s status, progress, successes, and challenges.
2. Informing decision-making
Because it provides detailed insights into various aspects of the project, the project report empowers decision-makers to make informed choices. It facilitates the identification of potential issues and allows for timely adjustments to keep the project on track.
- Read also: Why quick decision-making is so important?
3. Informing resource allocation
Project reports include information on budget use, resource allocation , and financial aspects, among others. This data enables organizations to optimize resource allocation for current and future projects.
4. Enabling risk management
The identification and assessment of risks are integral components of a project report. This information helps teams develop strategies to mitigate risks, enhancing overall project resilience.
5. Evaluating performance
Having key performance indicators (KPIs) and progress updates in a project report enables stakeholders to evaluate the project’s performance against predefined benchmarks, ensuring alignment with organizational objectives.
6. Engaging stakeholders
A well-prepared project report keeps stakeholders informed about the project’s purpose, goals, and accomplishments. This involvement fosters a sense of collaboration and accountability.
7. Documentation purposes
Project reports serve as crucial documentation for auditing purposes and compliance with organizational standards, industry regulations, or contractual obligations. It also creates a historical record of the project, providing a reference point for future projects.
8. Evaluating the project
When the project is complete, the report serves as a comprehensive record for evaluating the project’s overall success, documenting lessons learned, and facilitating the closure process.
9. Continuous improvement
Through the analysis of past projects documented in reports, organizations can get valuable insights and use this information for continuous improvement. Lessons learned from one project can inform the approach to future initiatives.

12 Common project report types
Various types of project reports cater to different needs and objectives throughout the project lifecycle. There is often a need for more than one effective project report, and it’s essential to understand the different types of reports and when to use them.
Understanding the nuances of these project report types allows project managers and teams to tailor their communication to specific needs and issues.
1. Progress report (aka project status report)
This type of report provides an overview of the project’s status, highlighting completed tasks, milestones achieved, and work in progress. It keeps stakeholders informed about the project’s development.
For basic progress reporting, use the task tracker template .
2. Risk report
This one focuses on identifying, assessing, and managing potential risks associated with the project. It also helps to outline strategies to manage projects, mitigate risks, and ensure proactive risk management.
- Read also: How to create a project risk management plan
3. Financial report
Another type of project management report is a financial report. It documents the details of the project’s financial aspects, including budget allocation, expenses, resource utilization, etc. It helps in tracking financial health and adherence to budget requirements.
- TIP: Read our guide about cost tracking in project management
4. Quality assurance report
It focuses on the quality of project deliverables, processes, and outcomes. It outlines measures taken to secure the overall quality of the project.
5. Status report
The project status report provides a concise summary of the project’s current state, including accomplishments, challenges, and upcoming milestones.
Project status reports are also known as project health reports.
6. Milestone report
This type of project completion report highlights the specific milestones achieved during the project, indicating progress and how the project timeline is being handled.
7. Issues log
The issues log document issues or challenges encountered during the project. It includes details about the nature of the issue, its impact, and proposed or implemented solutions.
8. Implementation report or project summary report
Created after the completion of the project, this report evaluates all project data, including the project plan, results, outcomes, what was learned during the project, and its overall project success. It provides insights for future projects.
9. Resource allocation report
The resource reports summarize the distribution of resources, including staff, equipment, materials, and budget. It helps optimize resource utilization when managing projects and ensures that resources meet the project requirements.
10. Communication plan
Those are project reports that outline the communication strategy and explain how information is shared among team members, stakeholders, and other relevant parties.
11. Forecast report
Forecast project reports created by project managers include projections for future project activities and potential challenges, supporting planning and decision-making for the upcoming phases of the project.
12. Closure report
This type of report summarizes the project’s overall performance, achievements, and challenges, and it should also include recommendations for future work.
How to write a project report
Making sure that effective project reporting is in place is incredibly helpful for the project’s lifecycle. By structuring the report for maximum impact, each step plays a crucial role in delivering clear and useful information to stakeholders.
To create effective project reports, follow these tips:
Define the main goal of the project report
Consider what information you want to convey, whether you need to address project risks, and who the intended audience is.
Research your audience well
Tailor your language and wording based on your audience. Before building and sending a report, understand who will receive it and adjust your communication style accordingly.
Choose the type or types of report you’ll be using
Evaluate the team’s needs, the stakeholders’ expectations, and the project type to determine the most suitable report type. Align it with the project itself.
Use templates
Templates can save you precious time. Find or create templates tailored to the specific focus of your report to expedite the formatting process and provide a standardized structure for conveying the same data more effectively.
- TIP: Save time by downloading these time management templates that you can use for reporting.
Make sure you’re including all the relevant information
A comprehensive report should include the most important details from your project, focusing on the most recent and critical information. Keep the report concise by including essential elements such as original deadlines, project tasks completed, potential issues, and individual team member responsibilities.
Keep the information well-organized
The report needs to be fairly easy to consult for clarity and impact. Prioritize information based on importance, arranging it in a logical order.
Choose the report format
Choosing the right report format is crucial as it ensures that the information is presented in a clear, accessible, and engaging manner.
This usually means using familiar formats like PowerPoint slides, PDFs, interactive dashboards, or Word docs to fit what different project stakeholders prefer.
Use a structure
A well-defined structure typically includes an executive summary, an introduction, a body of information presenting essential information (issues, team needs, project analysis, etc), and a conclusion.
Revise it and proofread it thoroughly
Do meticulously proofread for spelling errors, formatting issues, and accuracy in calculations and numbers . Ask for input from team members to catch any errors you might have missed. Another pair of eyes can be a big help.
Depending on the project needs or the company’s policy itself, it’s advised to maintain a regular reporting routine to provide project stakeholders with a consistent view of the project’s progress.

Create automated project reports with Timeular
As we’ve been explaining through this article, accurate project reporting is essential for successful project management. The key element of your project reports are time reports .
This is where a time reporting system like Timeular comes in , providing automated time tracking.
They not only enhance the accuracy and efficiency of your project reports but also offer comprehensive insights. They help in minimizing errors in tracking work hours and project progress, making the reporting process more streamlined and reliable.
Effortless, smart, and secure project time tracking
Timeular is a user-friendly and secure app that helps you create time reports with just a few clicks:
- Create detailed project reports
- Manage project expenses and project budgets
- Generate availability reports and reports on resource allocation
- Monitor the time dedicated to specific tasks
- Evaluate the productivity of your project team
Its simplicity and smart features make time tracking an integral and effortless part of your project management routine.
Choose your favorite time tracking method
In Timeular, you can pick the time tracking method that best adapts to your workstyle: use a physical time Tracker , automatic time tracking , or keyboard shortcuts , all ensuring a smooth and fast tracking experience.
Effects? Time tracking takes less than 1 minute a day!
Don’t chase timesheets ever again
All team members track work time, time off, and overtime in a single place. Thanks to effortless time capturing , which can be either automated or enhanced by smart time tracking methods and automated tracking reminders , you make sure that timesheets are always complete and ready whenever you need to write a project report.
Track billable hours automatically
As a project manager, you can effortlessly tag tasks as billable or non-billable, allowing for simple tracking of time invested in various projects and clients. By assigning hourly rates to specific tasks or team members, the system automatically computes costs.
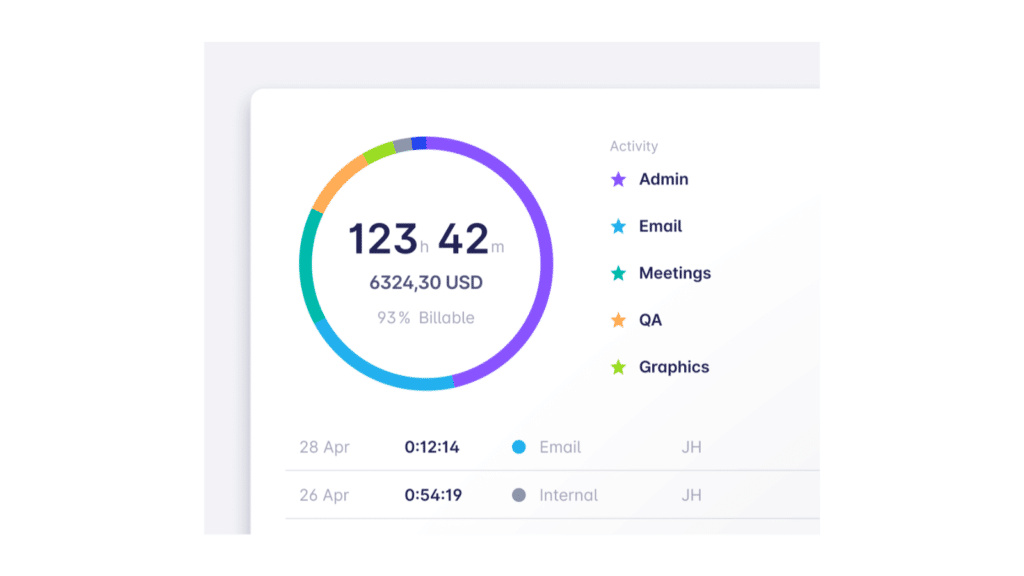
This feature is instrumental in checking up project’s health and creating an insightful project management report. Monitoring project expenses, guaranteeing precise client billing , and offering valuable information regarding your team’s productivity additionally improves your project management skills .
- Discover the benefits of the Timeular billable hours tracker for more details.
You can finally keep project budgets in check
Timeular’s data is particularly valuable for creating precise status reports regarding project budgets. Keep your budgets in check by setting the planned hours for each project and hourly rates for each task or team member.
We will let you know when you are approaching certain limits to keep you away from overspending and overservicing your clients.

Smoothly integrate with your project management tools
You can easily track the time of all the tasks monitored in your project management software thanks to integrations provided by Timeular and Zapier. You can build your own integrations, too, using API.
- Salesforce time tracking
- ClickUp time tracking
- Jira time tracking
- HubSpot time tracking
- Trello time tracking

Project reporting is an integral aspect of project management , a compass that guides projects from inception to completion. Hopefully, this article serves as a guide that has proven the significance of project reports, their types, and the critical role they play in effective communication, decision-making, and accountability.
From understanding the basics of project reporting to exploring various report types , including progress reports, risk reports, and financial reports, this guide can help project managers and teams with the knowledge to tailor their reporting to the project’s specific needs.
As we also explored, the benefits of project reporting are vast , from improving communication and transparency to informing decision-making, optimizing resource allocation, and enabling risk management.
Project reports not only document project details but also contribute to continuous improvement and serve as historical records for future initiatives.
You might be interested in:
- Project management tracking
- What is project monitoring?
- How to measure project profitability
- Timekeeping policy
- What is the first step in project cost management?
Welcome to Timeular 👋
A valid email is required. E.g. [email protected] .
Thank you for your interest in SSO, we’re working on this! Meanwhile, you can sign up with an email address and password.
Reset password
Check your email to reset your password.
Please use a password with at least 8 characters.
How to write a Project Report - Guide & Templates
Table of contents, what is a project outline, what is a project report.
A project report is a document created for a team or company that ensures a project stays on track. The project report should describe progress, milestones, and roadblocks.
Why is a project report important?
Project Reports are a core part of any project management process. There are a few key documents necessary for successful project progress, and a project report is undoubtedly one of them.
Alongside a project plan, a project report holds significant weight in justifying budgets, team members, tools, and other resources. In this article, we'll explore one of the two types of project reports any project manager needs to be able to write.Report number one is an ongoing project status report ; this report will be needed on more than one occasion throughout a project's life span and explores the overall progress of the project.
Report number two is a project completion report ; this report comes at the end of the project and wraps everything up.
We've also provided a project report template that you can adapt to your project and project report type that you need.

A Complete Guide to Project Reports
Why write a project report in the first place.
This report is so crucial in keeping key players up to date - we'll explore who exactly you need to be writing for in the next point. A project status report is needed to give a summary of a project , significant changes, and to keep a record of the project's progress.
A project status report adds milestones and target reminders to the process. Without the report, many project teams will struggle to keep up the momentum on long term projects.
Who prepares project reports?
A project status report is typically prepared by insiders who are involved in its day-to-day workings. Usually this is the project management team, a body of project managers and department executives with general or specific knowledge of the project.
Who is a project status report for?
A project report will need to be written for different people; each stakeholder will require different information that's important to them - remember this when putting together the progress of the project. It's not a one size fits all situation.
You may be dealing with sensitive information that could damage relationships or even severe them if put in front of the wrong eyes. At the same time, you could be releasing information that isn't relevant to certain people; in receiving an onslaught of information someone may miss the data or info that is specifically important for their eyes.
Different people that need to see an ongoing project status report:
- Project Stakeholders need the status report to stay in the loop and aligned with other team members
- Project Team need to know the project's progress across all departments and divisions
- Project Sponsors use the project status report to provide necessary guidance and resources to the teams and managers
- Leadership uses project status reports to stay apprised of the project's progress
- Finance Team use the project status report to determine areas that need funding allocation and to avoid potential cost overruns
- Contractors can see the project's priorities and timelines and allocate time and resources accordingly
- Project Management uses the status report to produce project manager reports on their department's progress
When to write a project status report?
This largely depends on the timeline (or predicted timeline for that matter) outlined in your project manager reports . If your project is expected to run over a few years, it may be best to create quarterly project status reports. However, if your project is set to run around six months to a year, monthly is recommended.
For all of the help that project status reports provide, it's important to remember that they can be pretty time consuming to make. We've provided a sample project report in this article to make your job easier; however, it's still a process. This is why we recommend incorporating a project proposal template as well.
For all the time a project manager is putting into a status report, they're not putting the work into managing their team. Pick a regular period to deliver the report in and put it in the Gantt calendar. Be conscious of the time it consumes, and try to stick to the real-time delivery dates.
In doing this, you'll save a lot of time with unnecessary communication from different players. Questions like "What’s the status of XYZ?" "How's the budget looking for XYZ for the project?" can all wait for the regular report- leaving the team to focus on their job.
How to write a Project Report in 7 Steps
Step 1: define your objectives.
Clearly state the purpose of the report and explain why it is necessary. Defining your objectives and providing smart goal examples can help you stay focused while writing and keep those reading the report engaged and informed.
Step 2: Have Your Audience in Mind
When writing project reports, tailor the content and your tone of voice to the audience as much as possible. Use impactful graphics and important data to connect with the people who will be reading this report.
Step 3: Write the Outline
Before you start writing, first create a list of all the sections in your report. For more details, check "What to Include in a Project Status" below, or take a look at our status report templates .
Step 4: First Draft
After your outline and analysis, you can start a rough draft. As the name suggests, it doesn't need to be perfect. If you are looking for a tool to help you put together project reports, try our document editor .
Step 5: Fine Tune Your Analysis
As time permits and new information comes in, fill in any data gaps or highlight any current or potential issues you find. Use the 'Findings' section to focus on the values, and make clear any limitations of the analysis.
Step 6: Recommend Next Steps
Once you have completed your data analysis, you will be able to propose actionable ideas towards the project's mutually desired outcome. The more solid your analysis and findings are, the more credible your project reports will be.
Step 7: Polish for Distribution
Before you send your report, proofread for grammar, spelling, and typos so that your final document looks as professional as possible. If you're sending the report in a group email, keep an eye on the file size.
What to include in a project status report?
Depending on who you're writing the report for, this will change. However, there are a few core elements to include for the project progress , despite who is reading the project report.
Executive Summary
If you are wondering how to write a report about a project, start with an executive summary. Short overviews provide the reader with the essential takeaways from the report without having to read all the project details. Executive summaries are very helpful for those who need a quick glance at the project's general direction without wading through a lot of data.
Project Progress
In the project status report, the project's progress is tracked with real metrics. This provides an overview of the project's status and budget and also identifies potential risks and issues. This data-driven approach provides project management with feedback and enables them to make adjustments.
It's important to document all of the resources you had mapped out in your project plan . What do you have left still available? What have you used and found insufficient? Of what resources do you need more? This can include project management tools and physical resources like software or a PDF, but also human resources.
Timelines and targets
It's essential to give everyone an overview of your project timelines in these status reports, especially those that are outside of your project team and not using the project management software you're using.
At this point, be realistic with your timelines, not optimistic . Refer back to your Gantt calendar to help with this. Save your optimism for team meetings to spur your project team on in working more efficiently and hitting deadlines. In the reporting part, you need to be honest with your timelines and deliverables, both with the goals you have or have not hit and those you expect to be on time with or not.
Many players further down the line will be working on the information you provided in this section of the project reports, it therefore needs to be accurate so they can manage their workload and be available on the predicted date.
Notable changes
This can radically vary but needs to be anything notable that's happened and is no longer abiding by the initial project plan. If you're using editable report samples for projects rather than a PDF, you can go back and edit your project plan to accommodate changes.
However, it's not recommended. You can't guarantee that your team will continuously be referencing the initial project plan once they've got a clear scope of what they need to do for the entire project.
Funding & budgets
The project manager should use the time dedicated to a project status report to reflect his or her budget. Accounting skills are vital for a project manager's success, and being able to handle a large budget will come in handy when it comes to managing the overall funding of a project.
In this part of the report, give a clear overview of expenses, predicted expenses, and visually highlights where you were over or under budget in real-time. The team can learn from this, not only for future projects but even for next month's project management status report.
Team performance
Use goals and targets to quantitatively identify if the team is performing well. While doing this, it's essential to consider the hurdles they've had to jump along the way. Have they faced exceptional circumstances that were not planned? If so, how did they cope and react to these challenges?
Risk management
This is the final part of the Project Status report and one of the most important skill sets for a successful project manager: Risk Management . A project manager needs to have a certain amount of hindsight at play in their everyday work and be able to give an executive summary of all risks.
In the project status report, give an overview of any predicted risks and try to display them tiered so that any reader has a clear overview of what the greatest risks are right through to very low-level risks, and what can be done to prevent them. Always have a Plan B and adapt it every time a project status report is created.
The risk management report is often best accompanied by a risk analysis meeting. Come out of your meeting with detailed meeting minutes and use your team's knowledge and perspective to give a comprehensive overview of all the risks at play.

Project Report Examples
There are several different types of project reports. Here are some project reporting examples of the most widely used types.
Project Status Report
A project status report is used to communicate the project’s progress and to ensure that all parties involved are kept in the loop. Project status report examples include updates to all stakeholders as the project progresses, amended project plans, and notifications of any issues or risks that have arisen.
Project Tracking Report
Project tracking reports provide real numbers, metrics, and other key indicators of the project's progress. Tracking project report examples include data concerning project status, tasks, team performance, completion rate and other metrics in a comprehensive report.
Project Performance Report
Project performance reports are a more specialized project status report. Examples include overviews of progress, resource allocation, and costs. Project performance reports help monitor the project's current direction and forecast its success. Using performance reports, the team can address issues that are holding the project back.
Project Health Report
Project health reports are an example of project management reports that help identify potential issues before they occur, saving the firm money, time, and resources. When project sponsors and supervisors are notified of risks, they can adjust strategy accordingly before problems manifest.
Project Summary Report
You are writing for busy people when you prepare a project management report. Examples of tasks completed and financials let them see important data quickly, then allocate their time to sections that directly concern them. A project summary report should highlight key milestones and point out upcoming tasks.
Project Time Tracking Report
Project time tracking reports can help project managers gauge their teams' efficiency and identify areas for improvement. For example, project reports can show which parts of the project are requiring more time to complete and reallocate resources from issues that are requiring less hours than expected.
Best practices when writing a project report
Wondering how to write a report on a project effectively? Look no further, we've got you covered!There are a few things you need to remember when putting together a project report to help ensure it's efficient and supports the project's success.
Knowing how to write project reports successfully is largely dependent on honesty.
There is no use in hiding deliverables or viewing the truth through rose-tinted glasses. You're not creating a presentation to win someone over here; you're creating a factual report to make sure everyone has as clear an overview as possible.
Stay honest throughout your reporting, give accurate numbers (don't round up or down), and don't make excuses. Remain critical.
Give as much information as possible
This comes at your judgment, but the more relevant information, the better. A project manager will have a fantastic overview of a project and the current status. For that reason, they're the best person to put together a project status report.
However, a project manager shouldn't be afraid to let team members fill in parts of the report if they have a better overview of a particular task within the project. Assign different areas of the project report to different team members and then review everything before the report is submitted.
Write clearly
Clear and concise writing skills are so crucial in making sure your project report is understood. Don't view the project status report as something you just need to get done and delivered.
Review it, make sure there are no spelling mistakes or grammatical errors. You'll be surprised at what the power of a comma can, do. See? Make sure the read of your report is as smooth as your project management skills.
Celebrate success
For all of the faults, risks, and problems you report in your project status report, it's essential to document your successes. A project is a rollercoaster. There will be ups and downs and spirals and flips. Identify which of these are wins and celebrate them.
By celebrating success, you will lift the morale of the project team and remind the project manager of what has been achieved so far.
Write for aliens
A proper project manager report example will be accessible for a wide audience.You'll be writing a project plan for many people, many of whom will not have had direct exposure to your team, your company, or the task/s at hand. When we say write for aliens, we mean writing for someone who has no clue what's happening.
Even the simplest of abbreviations or presumptions can be interpreted as something entirely different by someone else. Leave no room for error or misunderstanding.
Don't be afraid to use visuals
Visual support is fantastic for getting your point across or displaying information more clearly in a project status report. Visual aids can break up the monotony of the report if there's a lot of copy, which will be a welcomed relief on the eyes of any reader.
They say a picture is worth a thousand words and for a good reason, if you're struggling to get your point across, then look for an example of it online. Use visuals as a supporting example of what you're saying.
Automate processes where you can
Despite each project having its own landscape, you can surprise yourself with the amount that you can automate in your reporting process. Learn how to make the most of excel spreadsheets and tool integrations to see how you can backfill or auto-populate data into your project report.
It's these small time-saving hacks that will make your project report more efficient and better looking in the future.

A Project Report Template
Use this project report sample as a starting point for your project reports. Adapt it to your company and project needs and share it with the right people to ensure your project stays on track.

Clément Rog is working in our Marketing team from Lyon, France. He loves geography, playing legos with his son, and sharing convictions about marketing or design.
Working remotely? So are we since 2016. Slite may be the right communication tool for you!
Managing projects remotely discover our list of the best softwares to use in 2022..

Create a Project report
With Project, you can create and customize striking graphical reports of whatever project data you want, without having to rely on any other software. As you work on the project, the reports change to reflect the latest info — no manual updates required. See a list of all reports and how you can use them.
Select the Report tab.
In the View Reports group, select the type of report you want and then pick a specific report.
For example, to open the Project Overview report, select Report > Dashboards > Project Overview .
The Project Overview report combines graphs and tables to show where each phase of the project stands, upcoming milestones, and tasks that are past their due dates.

Project provides dozens of reports you can use right away, but you don’t have to let that limit your choices. You can customize the content and the look of any of the reports, or build a new one from scratch.
Work with your report
Change the data in a report, change how a report looks, make your own report, share a report, make a new report available for future projects, more ways to report project info.
You can choose the data that Project shows in any part of a report.
Select the table or chart you want to change.
Use the Field list pane on the right of the screen to pick fields to show and filter information.

In the Project Overview report, you could change the % Complete chart to show critical subtasks instead of top-level summary tasks:
Select anywhere in the % Complete chart.
In the Field List pane, go to the Filter box and pick Critical .
In the Outline Level box, pick Level 2 . For this example, this is the first level of the outline that has subtasks instead of summary tasks.
The chart changes as you make your selections.
With Project, you control the look of your reports, from no-nonsense black and white to explosions of colors and effects.
Tip: You can make a report part of a split view so you can see the report change in real time as you work on project data. To learn more, see Split a view .
Select anywhere in the report and then select Report Tools Design to see the options for changing the look of the whole report. From this tab, you can change the font, color, or theme of the whole report. You can also add new images (including photos), shapes, charts, or tables here.
When you select individual elements (charts, tables, and so on) of a report, new tabs appear at the top of the screen with options for formatting that part.

Drawing Tools Format tab. Format shapes and text boxes .
Picture Tools Format tab. Add effects to pictures .
Table Tools Design and Table Tools Layout tabs. Configure and tweak tables, like you would in other Office programs .
Chart Tools Design and Chart Tools Format tabs. Configure and tweak charts.
Say you decide that the % Complete chart in the Project Overview report needs a facelift.

Select anywhere in the % Complete chart, and then select Chart Tools Design .
Pick a new style from the Chart Styles group. This style removes the lines and adds shadows to the columns.
Give the chart some depth. Select Chart Tools Design > Change Chart Type .

Select Column > 3-D Stacked Column .
Add a background color. Select Chart Tools Format > Shape Fill , and then pick a new color.
Change the bar colors. Select the bars to select them, then select Chart Tools Format > Shape Fill , and pick a new color.
Move the numbers off the bars. Select the numbers to choose them, and then drag them upward.
Just a few clicks make a big difference. And we only scratched the surface of the formatting options.

Select Report > New Report .
Pick one of the four options, and then choose Select .
Give your report a name and start adding information to it.
Blank Creates a blank canvas. Use the Report Tools Design tab to add charts, tables, text, and images.
Chart Project creates a chart comparing Actual Work, Remaining Work, and Work by default. Use the Field List pane to pick different fields to compare, and then use the controls to change the color and format of the chart.
Table Use the Field List pane to choose what fields to display in the table (Name, Start, Finish, and % Complete appear by default). The Outline level box lets you select how many levels in the project outline the table should show. You can change the look of the table on the Table Tools Design and Table Tools Layout tabs.
Comparison Sets two charts side-by-side. The charts have the same data at first. Select one chart and pick the data you want in the Field List pane to begin differentiating them.
Any of the charts you create from scratch are fully customizable. You can add and delete elements and change the data to meet your needs.
Click anywhere in the report.
Select Report Tools Design > Copy Report .
Paste the report into any program that displays graphics.
Tip: You might need to resize and line up the report when you paste it into its new home.
You can also print the report to share it the old-fashioned way.
Use the Organizer to copy a new report into the global template for use in future projects.
See a list of all reports and how you can use them.
Compare actual work against your estimates with burndown reports .
Create a timeline of key tasks and milestones.
Set the status date for project reporting.
Project for the web offers two main options for reporting: Excel and Power BI Desktop. Excel reporting comes with Microsoft 365, while Power BI Desktop is licensed separately.
When managing a project in Project for the web, export your project to Excel allows you to:
Create reports and visuals
Send a file containing project details to external stakeholders
Archive copies of your project data for audit and compliance
Print copies of your project
Here's how to export your project:
Go to project.microsoft.com and open the project you want to export to Excel.
In the top right corner, select the three dots ( ... ), then select Export to Excel .
When you see the message " All done! We've exported [your project name]. " at the bottom of the screen, you can look for your new Excel file where you store your downloads.
When you open the Excel file containing your project, you'll see a worksheet named "Project tasks" that contains a summary of project-wide information at the top, including its name, project manager, and the start and finish dates, duration, and percent complete for the whole project. You'll also see what date it was exported. Under that, you'll see a table of all the information for your project.
More about Excel Report options
Import and analyze data
Create a PivotTable to analyze worksheet data
Ideas in Excel
Power BI Desktop
To get started, connect to Project for the web data through Power BI Desktop , then open the Project Power BI template and explore the reports it includes.
Important: You'll need a Power BI subscription (and a Project subscription in many cases) to use this reporting tool. See the following section for details.
To use Power BI reports on Project for the web data, you need to be a licensed user of Power BI Desktop or Power BI Pro. See Power BI Pricing for more information.
To build or customize Power BI reports on Project for the web data, you'll also need Project Plan 3 (formerly Project Online Professional) or Project Plan 5 (formerly Project Online Premium).

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project management |
- 8 steps to write an effective project s ...
8 steps to write an effective project status report

Effective project status reports are the best way to keep your stakeholders aligned and in the loop during your project progress. These high-level updates proactively let your team know if a project is on track, at risk, or off track—so you can course correct if necessary to hit your deadlines every time. Learn how to create project status reports in a few easy steps, plus check out a template you can use right away.
It’s the end of the week and here you are again: having to dig through a variety of spreadsheets, emails, and tools to patch together an update of how your project is doing.
Instead of manually assembling this information, use a project status report template to streamline this process for you. That way, you spend less time on unnecessary data gathering and more time on work that matters.
Whether you’re gearing up for your first ever project status report or you’re looking for a better system than the one you currently use, this article will walk you through what a progress report is, how you can build one, and how to use project status reports to hit your project deadlines on time, every time. Here’s how.
What is a project status report?
Project status reports are timely updates on the progress of your projects. Written concisely, project reports offer high-level information about project progress, so team members get at-a-glance insight into what’s happening within the project. With a timely status report, you can ensure your entire project team and cross-functional stakeholders understand what’s on track, what’s blocked, and what’s coming next.
Regularly sharing project status reports is important because they help you keep all project stakeholders in the loop and aligned on how your project is progressing. They answer the questions everyone has before team members even have a chance to ask them. They show and tell your team that you’re on track, making you (and everyone else) feel confident.
How often you share project status reports depends on your project’s timeline. Some projects benefit from weekly reporting, while others only need to be updated once a month. Schedule your project reports as frequently as is helpful for your stakeholders. These shouldn’t be reactive reports on things going poorly—rather, effective reports keep your team updated on the project’s progress, whether the project is on track, at risk, or off track.
The benefits of effective project reporting
Reporting isn’t just something you should do for the sake of doing it. Effective reporting has a variety of benefits. When you correctly report on project status, you effectively:
Keep track of project health
The worst thing for a project is when you arrive at the end of the timeline and realize you were off track the whole time. No one likes being blindsided—and as the project manager, you’re empowered to make sure your team is aware of your project health at all times.
Progress reports are a way to do that without too much manual work. Because these reports mix high-level summaries with some important metrics, everyone has a sense of the project's health. And if the project is off track? You can quickly and proactively fix it—so you still hit your project deadline on time and on budget.
Summarize project progress
Project status reports are not real-time reports. These reports are summaries of what happened during the past week, two weeks, or month of project work. They’re an opportunity for your stakeholders to stay informed on how well you’re sticking to the project plan .
If you’re looking for tips on how to report on projects in real time, check out our article on universal reporting tools for every team .
Reduce manual work
As the project manager, you already have enough on your plate. You don’t need to also spend hours every week or month grabbing data from different places. Project reporting tools make it easy to find all of this information in one place, and create a project status report with the click of a button.
Share next steps and action items
Project status reports should go out to your project team, project sponsor, important stakeholders, and cross-functional team members. Because these are high-level reports, they’re appropriate for anyone who wants to stay informed about project progress.
This is the optimal way to let everyone know what’s happening without getting into the details. If there are important project next steps or action items, share them here so everyone knows what to expect.
Proactively identify blockers
If your project isn’t on track, your status report lets others know what the delay is and what you’re doing to resolve any blockers, allowing you to show off your proactive approach to getting things back to where they should be. Similar to the project risk management process , proactive status reporting helps you identify and overcome issues before they impact your project timeline.
Say goodbye to status meetings
The day of the status meeting is over. We now know these aren’t effective ways to spend your time. Unlike face-to-face meetings, project status reports are shared in a central tool that team members can check asynchronously when they want to. They can refer back to the information, or dig deeper into the project if necessary. Save your face-to-face meeting time for valuable meetings like brainstormings or all hands.
Before you report: Combine reporting with effective project management
The biggest benefit of project status reporting is that it reduces your manual work, centralizes information, and makes it easy to keep everyone up to date. If your information is scattered across multiple tools, you can’t effectively use project reporting templates—you still need to manually open this Excel spreadsheet and that team email to gather your information.
Instead, make sure you’re using project management software as your central source of truth. With project management software you:
Have a central source of truth so team members can see who’s doing what by when.
Can easily visualize project information in a Gantt chart , Kanban board , calendar, or spreadsheet-style list view.
Create status reports with the click of a button.
Offer a place for team members who read the status report and want more details to look and find the information they need.
Have access to additional project information, like your project plan, communication plan , project goals, milestones, deliverables , and more.
Naturally, we think Asana is a great option. Asana is a work management tool your entire team can use. Your cross-functional collaborators need a way to view past status reports. Your key stakeholders need a bird’s eye view of the entire program or project portfolio management progress. And your team members need a way to track individual work throughout the project lifecycle.
8 steps to write a great project status report
So, how do you go about doing project status reports? Be sure to create a clear structure you can use consistently for all future status reports. You should also make sure it matches with your project brief to keep your report on topic.
Follow this guide to understand what to include in your project status report, and watch as we put each step into practice with an example of an Employee Satisfaction project.
1. Build your report where work lives
Before you build your report, make sure you’re already tracking your work information in a project management tool. That way, you don’t have to manually grab information from a host of sources—instead, you can reduce manual work and create a report with a few clicks.
Starting off with a project management tool makes it easy to capture dependencies and note upcoming tasks so you’re never blindsided about your project health.
2. Name your report
A great option is to simply use the project name for clarity. If you’re reporting on this project regularly, you should also include a date or timestamp.
Example project report title: February 2020 - Employee satisfaction initiative
3. Indicate project health
The project health is the current status of the project. Project health may change from report to report, especially if you run into blockers or unblock big project risks. Look for a project management tool that allows you to communicate the project’s status and whether or not it’s on track. One way to do this is to use a color coding system (green = on track, yellow = at risk, red = off track).
Example project health update: Project status is on track.
4. Quickly summarize the status report
Your project status report summary should be brief—about 2-3 sentences. The goal here is to give readers who may not have time to read the entire report a quick TL;DR of the most important facts.
This is the first section of your report, so it’s the best place to:
Include highlights
Flag major blockers
Note unexpected project risks
Example status report summary: Our survey results are in and being reviewed. At first glance, we’re seeing 80% employee satisfaction, up 3 points from the last survey. The Engagement Committee is working with the Executive team on what new engagement initiatives to implement in our key target areas, which include career growth and transparency.
5. Add a high-level overview of each key area
Depending on your project, your key areas may vary from report to report, or they may stay consistent. For example, in an Agile project that’s continuously improving, you’d likely use dynamic key areas that cover the things your team worked on during the last sprint. Alternatively, for an event planning project, there are a set number of key areas that you always want to touch on, like promotion, signups, and speakers.
For each key area in the status report, add a few bullet points that give an update on progress, accomplishments, and upcoming work.
Example high-level overview of a key area: Survey results
70% of employees took the satisfaction survey.
Our overall satisfaction rating is 80%.
Only 57% of employees report having a clear path towards career advancement, down 5% since the last survey.
41% of employees listed transparency as the number one improvement they’d like to see.
6. Add links to other documents or resources
While you shouldn’t include every little detail about how your project is going, some people will want to know more. For stakeholders who are looking for more in-depth information, provide links to documents or resources. This can include more specific project information, like links to specific project milestones , or the broader impacts of the project, like a reference to the business goals the project is contributing to.
Example: Include a link to the employee satisfaction survey , as well as to the larger company OKR around increasing employee engagement over the course of the fiscal year.

7. Flag any blockers the project has run into
All projects run into roadblocks. These can come in the form of project risks , unexpected increases to the budget , or delays that impact the project timeline . Keeping stakeholders in the loop when issues arise will help everyone adjust accordingly to stay on track.
Example roadblock: The executive team wants to look at results before the engagement committee meets again, but won’t be able to do so for another three weeks. This will delay our overall project timeline.
8. Highlight next steps
These could include a list of next steps, kudos you want to give someone, or anything else you want to highlight.
Example: Thank you Sarah A. for sending out multiple communications to employees encouraging them to participate in the survey!
Template for creating your project status report
To quickly put everything you learned in the previous section to use, write your next project status report using this easy-to-fill-out template:
Report name:
Name your report. This can be as simple as the project name and the date of the report.
Project health:
Is the project on track, at risk, or delayed?
Include a short description of the most important takeaways from your project status report here. Keep in mind that busy stakeholders may only look at this section, so include any highlights or blockers the entire team needs to know about
Key area 1: High-level overview
Specific details about progress, accomplishments, and upcoming work.
Key area 2: High-level overview
Key area 3: High-level overview
Additional information and links:
Link to relevant project details or higher-level project information that stakeholders might be curious about. This section is a chance for team members to dig deeper on specifics, or understand how the project initiative fits into your larger strategic goals .
Are there any challenges you’re facing? How will you resolve them?
Additional notes or highlights:
Are there any additional things your team needs to know? What are the main next steps?
Example project status report
While a how-to guide on writing project status reports is helpful, sometimes seeing a real-life example allows you to really see what your own update could look like, right? We thought you might agree, so here’s an example you may find useful:
Report name: Ebook launch
Project status: On track
Great progress this week! We are still in the concept phase, but Avery Lomax will be choosing a topic this week. Content and Design teams are standing by and ready to get started once we give the go ahead.
Planning team met to discuss an overall topic
We have three final ideas and will choose one on Friday
A brief is due to the Content team the following Thursday
The Content team is ready to start writing copy as soon as our idea is finalized
They are gathering pertinent company information that should be included
Design reviewed five ebook examples to determine the style they liked
They will be choosing a template by next Tuesday
Jen is out of the office all next week so please direct any content questions to Joy
Thank you to Henry for curating a huge list of topics for us to choose from!
Issues/challenges:
The e-book’s deadline is tight, as we all know. It’s critical that we’re all working in our project management tool to keep everyone organized and on track. Thanks!
Streamline reporting with a work management tool
The above report is clear and easy to follow. By building this report in a work management tool like Asana, you can automatically fill each section but the summary. Here’s what the above report looks like in Asana:
![the report of project [Product UI] Example Asana project status report for an ebook launch meeting (Status Updates)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/f4db2f8c-dc13-47b9-86ae-b8835fccb5ac/inline-how-project-status-reports-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Project status reporting best practices
Now you know what to include in your project status report, but you may still have a few additional questions. As you’re creating status reports for your project, these best practices will help you formulate a winning update.
How often should you report out?
The frequency with which you send project updates depends on the type of project you’re running. If your project has a short timeframe, or if things are moving quickly, aim to send weekly project status reports. Alternatively, if the initiative you’re reporting on is a long-term project, you probably only need to send biweekly or even monthly reports. The most important thing is making sure your project stakeholders are up to date.
When you use a project reporting tool, you can set a task for yourself to always send status reports on a certain day each week. These recurring reminders make it easy to keep stakeholders informed, whether you're sending weekly status updates or monthly progress reports. Either way, stakeholders will begin to expect your updates, which means less frequent check-ins from them (plus they’ll appreciate always being in the loop).
By sending regular reports, you can avoid multiple meetings related to a project (we all know unnecessary meetings have their own reputation ). Skip the check-in meetings and save your time for more important work.
Who should you include?
It depends on the project and who is involved, but typically plan to send an update to any stakeholders working on your project. You should have created a stakeholder analysis—outlining all stakeholders, sponsors, and team members—during the project planning process, but refer to your project plan if you aren’t sure.
Even if that week’s status report doesn’t affect a particular team member, you should still share it with everyone. It’s important for everyone to have a high-level overview. Team members who don’t need to review the report in depth can quickly skim your summary section, while others who are more involved can dive into the details you’ve provided.
How detailed should you get?
A project status report shouldn’t offer every little detail. Let the work tell the story—you’re simply curating information and adding a little color. Think of a project status report as a top line message—just the most important pieces of your project that affect most of stakeholders should be included.
You should always indicate whether the project is on track, at risk, or off track, give a quick summary of what’s complete and what’s upcoming, then link out to other resources for people who want more details.
Where should you write your project status report?
The best way to draft and share status updates is with a work management tool . Look for a tool that offers an overview of your project, so your team has a central source of truth for all project-related work. That way, instead of managing projects in spreadsheets , you can keep it all—status updates, project briefs, key deliverables, and important project milestones—in one place. Your reports will be easily shareable, and stakeholders can look back on previous reports at any time, avoiding email overload on your end.
![the report of project [Product UI] Example Asana Project Overview for a product marketing launch project (Project Overview)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/b98ec6f2-2167-42f3-8bb5-4c7964970294/inline-how-project-status-reports-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Wrapping your project up: summarizing your work
The status reports we’ve been talking about are always sent during a project to keep everyone in the loop. However, once the project is finished, it’s smart to send out a final summary report. Think of this as the executive summary for your project. This is your chance to offer stakeholders a wrap-up to the project. Use it to officially close it out.
Again, it’s a high-level overview, but instead of including updates and statuses, you’ll provide a summary of how the overall project went. Here are a few questions to answer in a project summary report:
What were the goals of this project and were they met?
Was the project completed on time and on budget (if applicable)?
What successes should be highlighted?
What challenges did we run into?
What can we learn from this project to help us on future projects?
Keep every stakeholder on track with status reports that write themselves
If you’re looking to over-deliver on your next project, try sending project status updates. They keep you productive, efficient, and accountable, while giving everyone else a quick (and engaging) look into what’s been happening.
Use the resources we’ve provided to create reports that give just enough information without diving into too much detail. Find a project management solution like Asana that has features designed specifically to help with status reports. You’ll save time and be as organized as possible.
Related resources
What are story points? Six easy steps to estimate work in Agile
What is a flowchart? Symbols and types explained

How to choose project management software for your team

7 steps to complete a social media audit (with template)
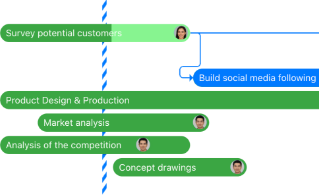
Finally see how to stop getting stuck in a project management tool
20 min. personalized consultation with a project management expert
How to Write a Great Project Report
Project reports assist in monitoring current progress and comparing it to the original schedule.
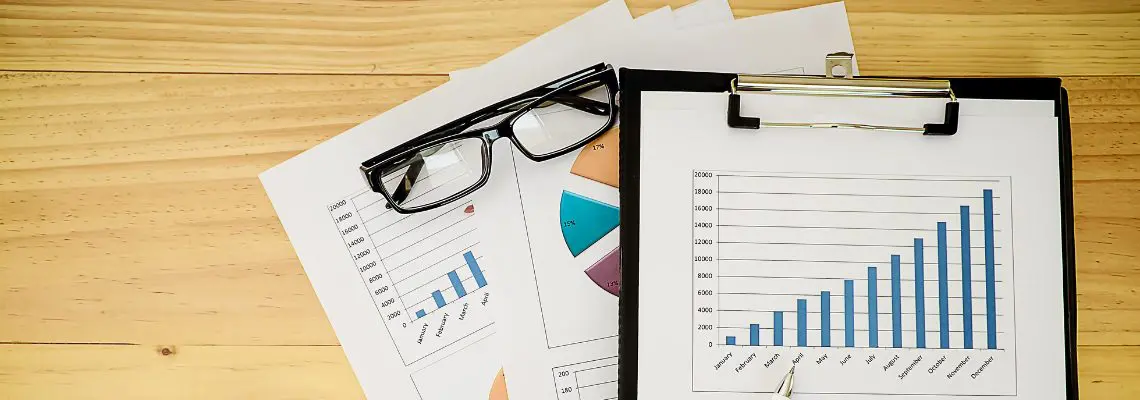

A project report is a handy tool for project managers as it helps them stay focused on tasks and keeps team members on track to achieving a successful project outcome. It also provides status updates at each key step of the project, so that project stakeholders, the management, and other relevant personnel can follow the progression of the entire project until completion.
Key components of project management reports include an executive summary, the project’s progress, potential risks and risk management steps, the project budget, and project timelines . It may also be necessary to include the project team’s performance, resources allocated to the project, and a conclusion.
Here are the steps you should take to write a project report:
1. Determine the Project Report’s Purpose
Before you can write a project report, you need to determine its goals and objectives. Knowing these helps you set the path the entire report will follow.

To identify the report’s purpose and goals, first, figure out why you’re writing the project report and what it hopes to achieve. For instance, does the project report aim to describe something to your upper management team, or does it aim to persuade the project sponsor to take action on something?
Here are some typical business report objectives:
- Selecting the best investment proposal
- Approval of project
- Risk identification
- Cost management
- Financial assistance
- Test business soundness
- Reevaluating project cost values and budgets
- Performance evaluation to keep the project on track
- Providing status updates to verify the project’s progress
How well you understand your objectives determines how clear and descriptive the report will be and how easy it will be for readers to quickly grasp your points. The report objectives help to provide context for the project and ensure you touch on the essential aspects of the project that are necessary to achieve your project goals.
2. Know Your Audience
Good knowledge of your audience—who you’re writing for—helps you better understand how to write a project report excellently. Knowing your audience helps you determine the communication style for your report. It also helps you understand the type of information to include, whether you should write using plain language or in industry jargon, and whether you should use graphics, among other things.
For instance, when writing a technical report for team members in a software development project, you may feel comfortable using your industry’s terms. If the report will also be shared with clients who are not in the tech field, you may consider writing plainly, in lay terms.
Note, though, that there are instances your project report audience is a mix of different categories of individuals. Check out the diagram below:
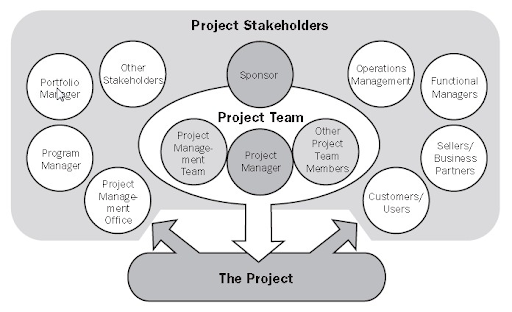
In a scenario where your audience consists of key stakeholders who don’t know the industry jargon and your team who is familiar with the technical language, ensure that you use a universal or widely recognized style of report writing. For instance, if you really need to include technical concepts since there’s no other way to describe a concept, include a definition of the concept.
3. Specify the Report Type and Format
Before you write a project report, check to see which type of report will be the most suitable for the report. Again, you want every part of your project report to be clearly understood. You won’t be able to achieve that if your report is the wrong type.
Ultimately, your report type will depend on your report objective. Here are some examples of project reports you can have depending on your project report goal:
- Annual reports
- Project status updates
- Project health reports
- Project summary reports
- Weekly status reports
- Project risk reports
- Time-tracking reports
- Technical reports
- Financial reports, etc.
So, if you have to provide an overview of the results of your recently-concluded marketing campaign to upper management, project summary reports might be your best bet. If you need to provide weekly updates on the status of the company’s website redesign, then weekly status reports will do.

Once you’ve determined your project report type, you can easily determine its format. You can access report templates, like the one below, online. They come pre-structured for your use, so all you need to do is follow the flow when drafting your report.
If your organization uses a tool for project management , you can also check if the platform has a project report template you can use.
Your company’s preferred project management software can give your team real-time access to the report. Creating a QR code for a PDF document, meanwhile, may be a good way to distribute the report to those who have no access to the software. All they need to do is take a picture of the QR code, click on the link, and they’ll have access to the document.
4. Write the Report
Even if you already know your project report flow thanks to your project report template, it can still be difficult to determine what to write in each report’s section.

What you need to remember is that report sections will vary depending on the project report type. However, all reports have four primary parts:
Executive Summary
This is the leading part of the report, but it can only be put together when you’ve finished writing the entire report.
It should briefly summarize what your report is about. It may include the following critical elements enumerated above.
Introduction
When putting your project report together, the introduction comes beneath the summary. In your introduction, you provide the context within which the report was written. Unlike the executive summary which usually already incorporates some report conclusions, your introduction doesn’t include any of those.
This part of the report should be written in non-technical language, again for clarity for every audience category.
Usually the lengthiest part of your project report, the body requires you to go into full, technical details, if necessary. To structure this section of the report, you must fully discuss the work and efforts exerted to complete the project up until the time of writing. It should contain your analysis, data, background info, and other relevant discussions.
Here, you bring together all the elements of your report to a close. If there are any actions you want your audience to take after reading your report, this is a good place to state them.
Back up the content of your report with quality facts and data. Engaging and useful data helps readers believe your deductions and serves as evidence or proof that what you have said is true. They eliminate assumptions or guesses and help key stakeholders make informed decisions.
In some cases, facts and data also help to measure the progress on the journey to achieving set project milestones. They highlight specific areas that require more attention, resources, organization, or research to ensure the success of the project.

Contrary to popular belief, data is not entirely the same as fact. Data is a recording of a fact or figure that is gathered for analysis or reference. A fact, on the other hand, is a piece of information that can be proven to be true by the use of evidence.
For documents like customer service reports that analyze a lot of numerical data, it’s best to present such data visually for the sake of clarity.
You may present the numerical data in a pie graph or a bar chart , like in the customer service team report above, for instance.
As you include visuals in your report, ensure that the key elements in the graphic representation are clear and readable. Individual elements of visuals should be distinct, regardless of the background color of the report document.
Lastly, it’s crucial to cite any sources you use in your report to make it credible and authoritative.
5. Edit and Proofread
Like every piece of writing, there are bound to be errors and miscommunication in the report after the first draft. So, you must read and review your report a couple of times to ensure you spot and eliminate these.
Break up long paragraphs of text with whitespace or visuals to improve readability. Correct spelling mistakes or grammatical issues. Also, make sure your language tone is consistent throughout the report.
You can ask a colleague to help you review the report for errors or employ editing services if you want a professional alternative. You can also use a grammar or spell-checker tool to help you identify mistakes.
Editing and proofreading the report are critical to ensuring you come up with a final document that achieves its purpose. So, don’t skip this critical step.
Final Thoughts
As a project manager , you will have to learn how to draft project reports for your team members, the management, and relevant project stakeholders.
The good news is, writing a project report isn’t as hard as it sounds.
Begin by gaining a good understanding of the purpose of the report. Then determine the audience you’re writing for and the type of report you want to write. Write the content of your report under the four main report elements. Incorporate facts and data to solidify your report. Lastly, edit and review your work for any errors you may have missed.
Follow these tips and you’ll create an excellent project report that achieves its purpose. Good luck!
About the Author: James Westfield is the Marketing Manager for Writer , an AI writing platform designed for teams. He has over 10 years of experience in the industry. When James isn’t in the office, you can find him on the golf course.

FREE 20 MIN. CONSULTATION WITH A PROJECT MANAGEMENT EXPERT
Wanna see how to simplify your workflow with Zenkit in less than a day?
More from Daryl Bush
4 Metrics You Should Track for Better Hybrid Work Productivity
More from Asmo
5 Tips for Managing Multiple Projects at Once
10 Project Planning Best Practices
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Zenkit Comment Policy
At Zenkit, we strive to post helpful, informative, and timely content. We want you to feel welcome to comment with your own thoughts, feedback, and critiques, however we do not welcome inappropriate or rude comments. We reserve the right to delete comments or ban users from commenting as needed to keep our comments section relevant and respectful.
What we encourage:
- Smart, informed, and helpful comments that contribute to the topic. Funny commentary is also thoroughly encouraged.
- Constructive criticism, either of the article itself or the ideas contained in it.
- Found technical issues with the site? Send an email to [email protected] and specify the issue and what kind of device, operating system, and OS version you are using.
- Noticed spam or inappropriate behaviour that we haven’t yet sorted out? Flag the comment or report the offending post to [email protected] .
What we’d rather you avoid:
Rude or inappropriate comments.
We welcome heated discourse, and we’re aware that some topics cover things people feel passionately about. We encourage you to voice your opinions, however in order for discussions to remain constructive, we ask that you remember to criticize ideas, not people.
Please avoid:
- name-calling
- ad hominem attacks
- responding to a post’s tone instead of its actual content
- knee-jerk contradiction
Comments that we find to be hateful, inflammatory, threatening, or harassing may be removed. This includes racist, gendered, ableist, ageist, homophobic, and transphobic slurs and language of any sort. If you don’t have something nice to say about another user, don't say it. Treat others the way you’d like to be treated.
Trolling or generally unkind behaviour
If you’re just here to wreak havoc and have some fun, and you’re not contributing meaningfully to the discussions, we will take actions to remove you from the conversation. Please also avoid flagging or downvoting other users’ comments just because you disagree with them.
Every interpretation of spamming is prohibited. This means no unauthorized promotion of your own brand, product, or blog, unauthorized advertisements, links to any kind of online gambling, malicious sites, or otherwise inappropriate material.
Comments that are irrelevant or that show you haven’t read the article
We know that some comments can veer into different topics at times, but remain related to the original topic. Be polite, and please avoid promoting off-topic commentary. Ditto avoid complaining we failed to mention certain topics when they were clearly covered in the piece. Make sure you read through the whole piece before saying your piece!
Breaches of privacy
This should really go without saying, but please do not post personal information that may be used by others for malicious purposes. Please also do not impersonate authors of this blog, or other commenters (that’s just weird).
Table of Contents
What is a project report, 5 steps to create a project report from scratch, project report objectives, project report components, common project report types, project report use cases, project report examples, opening and viewing reports with microsoft , change data in your report , change the report format , make your report , share your report , choose the right program, train to become a project leader today, how to create a project report: objectives, components, and more.
Managing a project is by no means an easy feat. Many moving parts can make it complicated to stay focused on the tasks and keep stakeholders up to date on the project status. This is why project reports are a useful tool for project managers .
These project reports can be used to provide direction for team members, offer status updates for partners or management teams, and successfully manage risk mitigation – to name just a few!
Learn from experts who help you pass the examination post enrolling in Simplilearn's PMP training course. Sign-up today for PMP® Certification Training Course !
Let’s take a closer look at how to create a project report including its many objectives, components, and examples of project reports.
A project report is a comprehensive document that provides detailed information about a specific project. It typically outlines the project's objectives, scope, methodology, progress, findings, and outcomes. A project report often includes details about the project's goals, activities, timelines, resources used, challenges faced, and the results achieved. It serves as a formal record of the project's lifecycle, serving both as a documentation of the work done and as a communication tool to convey the project's status and outcomes to stakeholders, sponsors, or interested parties. Project reports are commonly used in various fields such as business, engineering, research, and academia to assess the effectiveness and success of a project.
Creating project reports is an integral part of evaluating project success. Documenting the lessons learned and sharing them with a larger team in an organized way can help with future projects. You can use different tools to put together your project report. Here are 7 basic steps involved in creating a project report -
1. Know Your Objective
Sit down, evaluate your objectives, and understand what you want to describe, explain, recommend, and prove with your report. Having set goals will not only help you proceed with your project report but also help readers understand your point of view.
2. Recognize Your Audience
Your audience plays an essential role in making your project report a success. A formal annual report differs from a financial report: the language, representation of data, and analysis changes per your target audience .
3. Data Collection
The chances of you having a solid report is when data supports it. Data plays an essential role in making people believe in your derivations. Also, support your claims by citing sources such as case studies, surveys, interviews, etc.
4. Structure the Report
A project report is further divided into certain sections. These 4 are the most common divisions of a project report:
- Summary: The summary gives the reader a download of all covered in the project report. Even though a summary is placed at the beginning of a project report, you can only write it once your entire report is complete.
- Introduction: Mention the outline of the report, give context and mention the scope and methodologies used in the report.
- Body: This is the lengthy section of the report as it contains background details, analysis, data, and graphics.
- Conclusion: This section brings the entire project report together.
5. Edit and Proofread
Once your project report is ready, read it multiple times with some time gap. You can ask your co-workers to review it.
Become a Project Management Professional
- 6% Growth In Jobs Of Project Management Profiles By 2024
- 22 Million Jobs Estimated For Project Management Professionals By 2027
PMP® Certification Training
- Access to Digital Materials from PMI
- 12 Full-Length Simulation Test Papers (180 Questions Each)
Post Graduate Program in Project Management
- Receive Post Graduate Program Certificate and Alumni Association Membership from UMass Amherst
- 8X higher live interaction in live online classes by industry experts
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Katrina Tanchoco
Shell - manila ,.
The interactive sessions make a huge difference as I'm able to ask for further clarifications. The training sessions are more engaging than the self-paced modules, it's easier now that i first decided to take up the online classroom training, and then followed it up with the self-paced learning (online and readings).
PHC Business Manager , Midlands and Lancashire Commissioning Support Unit
I wanted to transition into the Project Management field and wanted the right opportunity to do so. Thus, I took that leap forward and enrolled in this course. My learning experience was fantastic. It suited my learning style.
Every project report starts with a solid project report objective. Your objective should provide precise direction for the rest of the report. Consider what purpose you want your project report to serve. Are you describing new risks or explaining project delays? Or will your report focus on persuading management teams or stockholders to invest additional funds into the project?
A thorough understanding of your objective will help guide you in writing the report and make the purpose of the report clear to all stakeholders.
Here are a few examples of project report objectives:
- Requesting approval for a new project
- Tracking the progress of the project
- Identifying and managing risks
- Managing costs and budgets
- Requesting financial assistance
Your project report will be bursting with essential information about your project. Although the content of your report will differ depending on the type of report you’re creating, keeping your report organized will make it easy for the reader to follow along without missing any critical points. Organize your data and content into sections that allow all stakeholders to quickly reference.
Consider including some of the following project report components:
Executive Summary
The first section of your report will likely include an executive summary. The brief overview should provide all the essential takeaways from the report, allowing the reader to understand the report's contents without having to read through all of the project details.
Project Progress
This component includes real metrics that track your project’s progress. It offers an overview of the project's status and budget while identifying risks or issues that may have emerged. Helping project management and other stakeholders reflect on the project schedule and make amendments as needed.
Risks and Risk Management
What risks have developed that may affect the quality, timeline, or budget of your project? How will you control these emerging elements? It’s inevitable that all projects will face risks, so it’s how you intend to manage those risks that’s important to the project team and stakeholders. Include a detailed analysis of the risk, your proposed solutions, and how these new elements will affect the project as a whole.
Are your financials where they need to be for the current status of your project? Will more capital be required to reach your goals effectively? Provide a detailed overview of the allocation of your budget including materials, labor, and operating costs.
Reflect on your project goals. Is the project behind, ahead, or on schedule? How will any changes to your timelines affect your budget or resources? Include an overview of tasks that have already been completed and a comprehensive schedule of remaining tasks.
Resources may include materials, machinery, or even funding required to complete your project. Provide a detailed summary of your current resource allocation. What are detrimental resources for your project running low? Are there any excess amounts?
Team Performance
Is your team completing tasks efficiently? Are there any skill or knowledge gaps that need to be addressed? Compare your team’s performance to your initial goals to identify the group’s progress.
A project report is a simple and detailed description of the essence of the project and its aims and aspirations. The business management team and stakeholders are kept updated on every development regarding the project; based on that, they prepare their strategy. This vital information keeps the communication line open between the management team and the stakeholders, providing them with a complete picture of every action concerning the project.
A project report includes the necessary recommendations for all types of businesses, established and start-ups. Moreover, organizations use project reports to procure financial help from institutions. Project reports can be of various types that help everyone complete a project successfully. Based on the report, your team can take up any activity that benefits the project.
Status Reports
It talks about the progress going on with a project. It also states various significant activities associated with the project. This status report organizes the communication medium between the team and the stakeholders. It summarizes the finished tasks on the project at hand. It includes the budgetary details and the timeline of the project. It also helps identify the risks related to the project and measures to tackle them beforehand. The status report also keeps track of the events or actions or any activity taken in the past. Status reports are carried out weekly, daily, monthly, or quarterly. They help collect and distribute information about crucial activities in a project in a smooth manner.
Progress Report
While executing a project, a progress report is inevitably carried out to update everything about the project. It usually includes things like if the project baseline is fulfilled. It indicates the initial plan you prepared along with your stakeholders about a project regarding the expectations, schedules, cost, deliverables , and scope of it. A progress report informs your stakeholders how much progress has been made in the above directions.
You should prepare this status report in a specific manner by stating the project title, contact information, a summary of the status, and providing all the information about the budget, timeline, and expected completion date of the project. You can take the help of several such free templates available online to make the status report.
Risk Reports
This type of report explains the risks associated with the project in a documented form. It covers details about risks that are managed already and the emerging ones. It includes the overall risk profile of the project. Risk reports identify and state potential risks that could alter the duration of the project and tips to manage them.
Board Executive Reports
An executive report is a summary of the business plan of an organization for lending partners. It enables the team members to collect and combine the results of numerous research studies to help them decide on the project. It is the starting point of arranging a dialogue with the investors. It should be written in such a way that it creates the best impression in the minds of the lenders. It should be short and precise and comprehensively analyze the project.
Cost Benefit Analysis Report
This kind of report helps organizations know if a particular project is possible or not. It will show you how much the project will benefit your organization against the investment. It will help you decide if a project is worth taking on for your organization and how much business profit it will get you at the end of the day. Alternatively, it will also help your organization better utilize its resources while progressing with the project. You can monitor your project expenses and spending to manage your funds better.
Resource Reports
This report highlights the distribution of resources according to the project tasks. The team members and the investors get the necessary information by reading this report on how well the resources are distributed in the project. It will give detailed narration about which team is assigned to which task according to the date wise. This type of report is beneficial for an organization to know if there is over allocation of resources as this could harm the project. Overall allocation happens when there are insufficient resources to complete all the crucial activities of the project.
Variance Reports
This report helps you compare your overall project plan with the project's end result. It uses metrics to inform you if your project is running according to the timeline, ahead of time, or running late. Moreover, it will streamline the data based on the comparisons you have made on the project. With the availability of various project management tools , preparing this kind of report has become easier now. It cuts down your hard work by creating the project activity report and conveying it to the stakeholders.
Gap Analysis Report
This report will examine the project's current status in the context of schedule, cost, and labor and, subsequently, compare the targeted status. It discovers and examines the gap between these two aspects and prepares a strategy or action plan on how to do the needful to reach the targeted objectives. Every business, whether a budding one or an established one, will need this kind of gap analysis report to perform better in terms of projects. This report will tell you how to take the successful step to graduate to the next level of your business. This will tell you whether you are fulfilling your business objectives and using your resources carefully.
There are several common use cases for project reports in project management. These include:
Project Status Report
A project status report is used regularly throughout a project to communicate the project’s progress in conjunction with the original project plan. The status report of a project provides all stakeholders with updates on the project’s development and performance. Your status report may cover issues or risks that have emerged and include your amended project plan.
Project Tracking Report
A project tracking report offers real numbers, metrics, and other key indicators that measure the project’s overarching progress. This comprehensive report covers all aspects of the project, including project status, tasks, project team performance, and how much of the project has been completed.
Project Performance Report
Performance reports provide an overview of the project’s progress, a breakdown of resource allocation, and costs to date. Your performance report will help monitor the project’s current direction and forecast how well it will perform.
Project Health Report
A health report offers an analysis of any problem areas or risks within your project. Completing a project health report can help identify any potential issues before they occur, saving you time, money, and resources.
Project Summary Report
A project summary report provides a quick snapshot of the project’s status. Along with tasks completed and a summary of financials, the brief report should include any key highlights or milestones and a glance at upcoming scheduled tasks.
Project Time Tracking Report
Project time tracking reports help the team and all stakeholders better understand the time allocation for each task. It’s a useful tool for project managers to gauge their teams' efficiency and identify what areas need improvement.
Not sure where to start with your next project report? Consulting the right project report example can help you gain the direction you need.
Click here for a status report example.
Using Project, one can easily create new reports or customize them for various types of project data without relying on any other application or software. MS Project offers dozens that you can use right away. You can also customize any report’s content and look or build a new one from scratch.
- Click the Report tab and then click the View Reports group.
- Select the type of report you need.
For instance, if you have to open the Project Overview report, navigate Report > Dashboards > Project Overview.
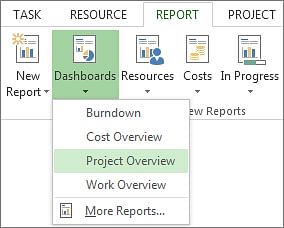
Reports Dashboard Option
Reports are customizable. So, you choose the data that MS Project will show in any part of a report. Follow the steps below to change the data in your report:
- Click the chart or table you would like to alter.
- Use the Field list pane present on the right side to select fields to filter and show data.
- Also, clicking a chart displays three pop-up buttons on the right-hand side of the chart. You can opt for the Chart Elements or Chart Filters button to select elements and filter chart data.
For instance, take the previous Project Overview report as an example. You can change the % Complete chart and display critical subtasks rather than top-level summary tasks using the below-mentioned steps:
- Click anywhere in the % Complete chart.
- Now, in the Field List pane, navigate to the Filter box.
- Select the Critical option.
- Next, pick level 2 in the Outline Level box. Let’s suppose that this is the first level of the outline with subtasks rather than summary tasks.
- The chart will reflect the change as you make your selections.
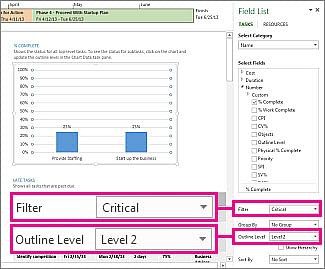
Changes in the % Complete Chart
Using Project, you can go from monotonous black-white to vivid effects and colors. With the Split view, you will be able to view the real-time report changes while you make the changes. To change the report format, take the following steps:
- Click the report (you can click anywhere).
- Now click Report Tools and click the Design tab. It will display options for changing the look of the entire report.
- Using this tab, you can alter the color, font, or theme of the entire report. You can also include images, charts, shapes, or tables here.
Report Tools Options
- Clicking on individual elements such as tables, charts, and others of a report will display new tabs at the top of the screen for formatting that part.
Table Styles
- Use the Drawing Tools Format tab to change shapes.
- The Picture Tools Format tab will help you add picture effects.
- You can configure and tweak tables using the Table Tools Design and Table Tools Layout tabs.
- The Chart Tools Format and Chart Tools Design tabs help tweak charts. Also, clicking on a chart displays three buttons on the right side of the chart. You can use the Chart Styles button to modify the chart color or style.
Suppose you plan to change the % Complete chart in the Project Overview report. Click anywhere in the chart and tap on the Chart Tools Design.
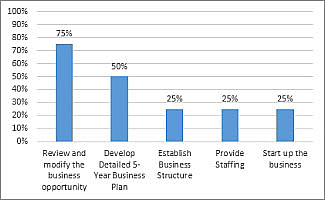
% Complete Chart
- From the Chart Styles, pick a new style for your chart. The option selected in the following image adds shadows to the columns and removes the lines.
Chart Styles in Chart Tools Design
- Next, you can click Chart Tools Design > Change Chart Type to add some depth.

- You can change the columns by clicking Column > 3-D Stacked Column.
- To add a background color, click Chart Tools Format > Shape Fill. Now pick a new color. You can explore more color options by clicking on more fill colors.
Color Options for Chart
- Alter bar colors by selecting the bars and then click the Chart Tools Format > Shape Fill option. Pick the color you want.
- You can drag the numbers upwards to get them off the chart.
The above-stated changes will be reflected as follows.
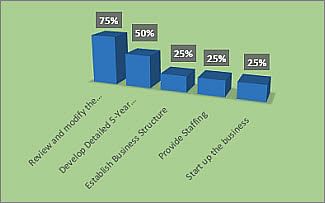
% Complete Chart on Making the Changes
Take the following steps to create a new report.
- Click the Report tab and then click New Report.
- Pick from the four options:
- Blank: Provides a blank canvas that you can use to add charts, text, tables, and images using the Report Tools Design tab.
- Chart: It is suitable for comparing Actual Work, Work by default, and Remaining Work. Using the Field List pane, you can pick different fields for comparison or use the controls to alter the format and color of the chart.
- Table: It displays tabular information. Using the Field List pane, you can select what fields are to be displayed in the table.
- Comparison: It gives you two charts side-by-side. Initially, they will have the same data. You can click on the chart and choose the information of your choice in the Field List pane.
Types of New Report Styles
- Name your report and start adding information to it. All charts are fully customizable. You can easily add or delete elements to meet your needs.
- You can make your new report available for future projects by using the Organizer to copy this new report into the global template.
- Click anywhere in the report.
- Navigate Report Tools Design > Copy Report.
Copy Report Option
- Now paste the report into any program of your choice. You might have to resize or align the report when you paste it elsewhere. You can also opt for the printing option for sharing hard copies.
Are you looking to take your project management skills to the next level? Look no further than Simplilearn's comprehensive project management courses!
Our courses are designed to help professionals at every level of experience to develop and enhance their project management skills, whether you're just starting out in the field or looking to advance your career. With our courses, you'll gain practical, hands-on experience in managing projects from start to finish, and learn best practices and industry standards that will set you apart from the competition.
Program Name PMP® Certification Training Course PMP Plus Post Graduate Program In Project Management glyph Icons All Geos All Geos All Geos University PMI Simplilearn University of Massachusetts Amherst Course Duration 90 Days of Flexible Access to Online Classes 36 Months 6 Months Coding experience reqd No No No Skills you wll learn 8+ PM skills including Work Breakdown Structure, Gantt Charts, Resource Allocation, Leadership and more. 6 courses including Project Management, Agile Scrum Master, Implementing a PMO, and More 9+ skills including Project Management, Quality Management, Agile Management, Design Thinking and More. Additional Benefits -Experiential learning through case studies -Global Teaching Assistance -35PDUs -Learn by working on real-world problems -24x7 Learning support from mentors -Earn 60+ PDU’s -3 year course access Cost $$ $$$$ $$$$ Explore Program Explore Program Explore Program
Become a digital-age project leader with Simplilearn’s PMP® Certification Training . Created to align with the Project Management Professional (PMP®) certification, you’ll learn the frameworks, tools, and skills to drive successful projects.
In this course, you will learn how to manage quality and risk, create effective strategies, implement best practices, and ultimately, deliver results.
1. What is a project report and its significance?
A project report summarizes a project's key aspects, including its goals, timeline, budget, progress, and outcomes. It provides project managers with critical information to monitor and evaluate the project's performance, identify potential risks and challenges, and communicate progress to stakeholders.
2. What is the format of a project report?
A project report format is completely customizable depending on the project requirements and your choices. However, it should focus on the specific objectives of the project, its methodology, major findings, and progress.
3. How do you prepare a project report?
Preparing a project report is simple. Click Report > New Report and choose from the four options. Now, give a suitable name to the report and start adding information.
4. What is a project report with an example?
A project report is a document providing detail on the project’s overall status or specific aspects of its performance. Irrespective of the report type, it contains project data based on economic, financial, technical, managerial or production aspects. For example, a Cost Overview report tells the current cost status of the project. It also reveals planned costs, remaining costs, cumulative costs, actual costs, and percentage of completion to help understand if the project is within budget.
5. How do you write a complete project report?
Writing a complete project report entails a proper start and closure, including
- Labeling the document and writing the project overview
- Including a section for the project’s scope
- A well-formulated project performance analysis.
- Highlighting the project’s accomplishments, results, and outcomes.
Our Project Management Courses Duration And Fees
Project Management Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
Get Free Certifications with free video courses
Project Management
Learn from industry experts with free masterclasses.
Career Masterclass: How to Successfully Ace the PMP Exam on Your First Attempt in 2024
How to Successfully Ace the PMP Exam on Your First Attempt in 2024
Career Fast-track
Panel Discussion: The Startup Career Strategy - The Highs and Lows
Recommended Reads
Project Management Interview Guide
How to Create a Google Analytics Report?
What is Google Data Studio and How to Create Report On It?
Report: The Future of IT Jobs in India
Communicating Project Status to an Executive
How to Create a Maven Project in Eclipse
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
The Top 17 Free Project Report Templates For Effective Project Management
By Kate Eby | August 5, 2019 (updated August 7, 2023)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, you’ll find a comprehensive list of project report templates to support your project management efforts. These pre-built templates are free to download in a variety of formats, including Excel, Word, PowerPoint, PDF, and Google Docs.
Included on this page, you'll find many free, downloadable templates for your next project, including a project status report template , a daily project progress report template , a business project report template , and many more.
Project Status Report Template
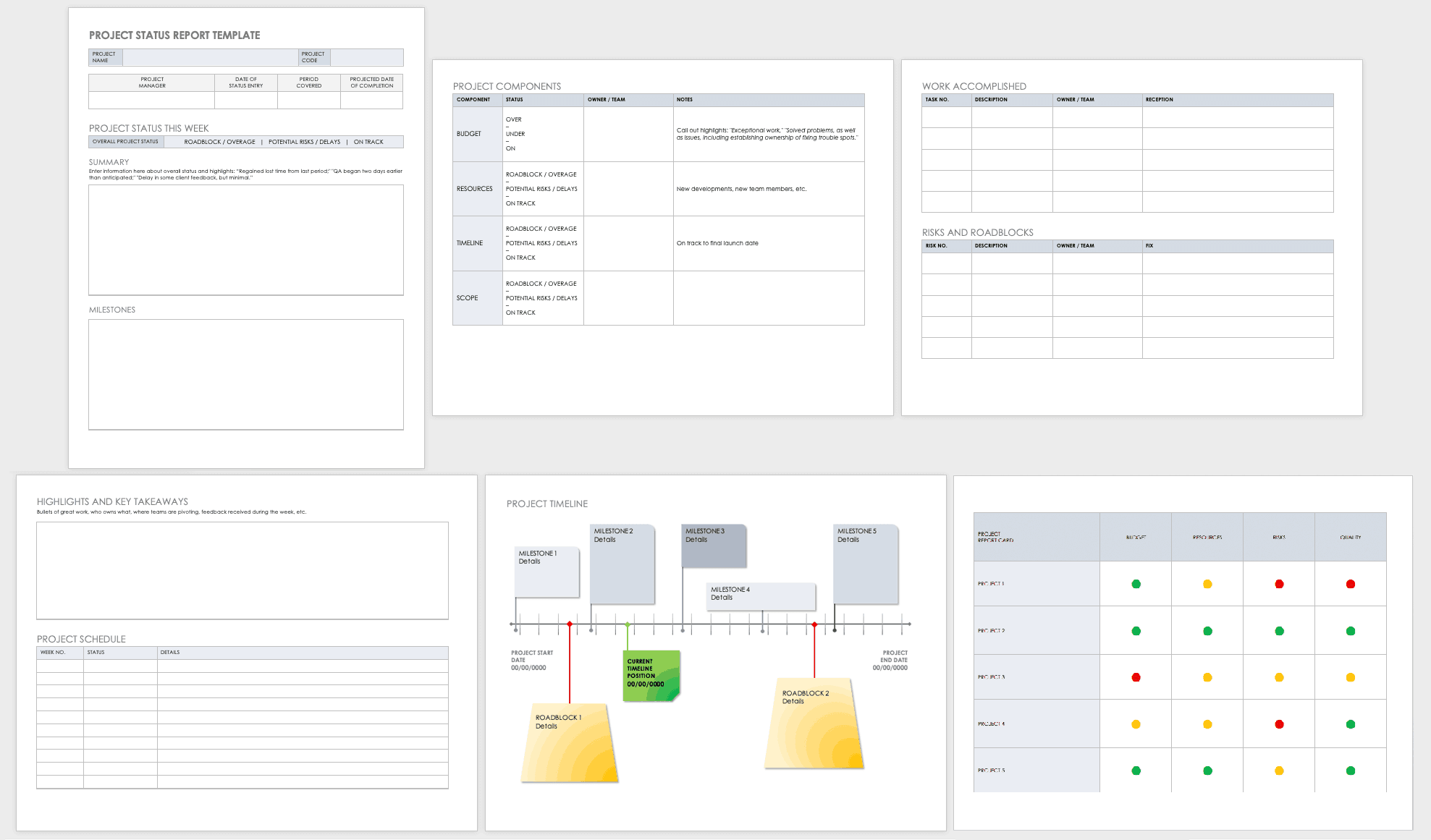
Download Project Status Report Template
Word | PowerPoint | Smartsheet
Consistent and thorough status reporting is an essential component of effective project management. Ensure you meet project objectives by utilizing this customizable project status report template. This template provides space to summarize the project and track risks, roadblocks, milestones, accomplishments, and key takeaways. It also includes a visual project timeline to give you easy visibility into major project events.
One-Page Project Status Report Template
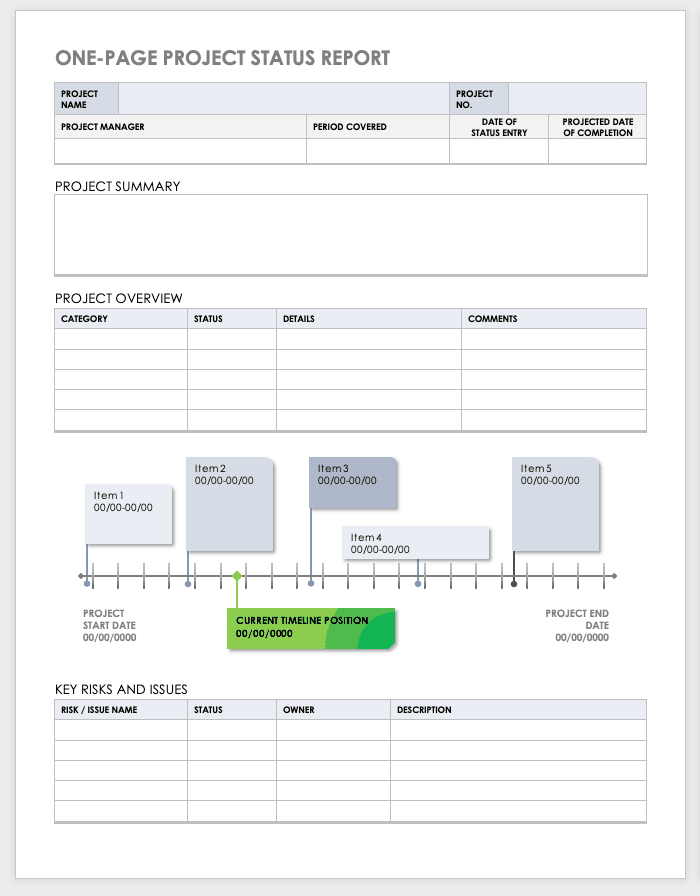
Download One-Page Project Status Report Template
Word | PDF | Smartsheet
This template covers all the primary elements of the project status report in a convenient one-page format. The pre-built status report provides an overview of project status by category (i.e., budget, scope, etc.), project timeline, key risks and issues, as well as issue ownership to ensure that you account for and complete all project action items on schedule. Learn how to create an effective project status report in this article .
Project Report Dashboard Template
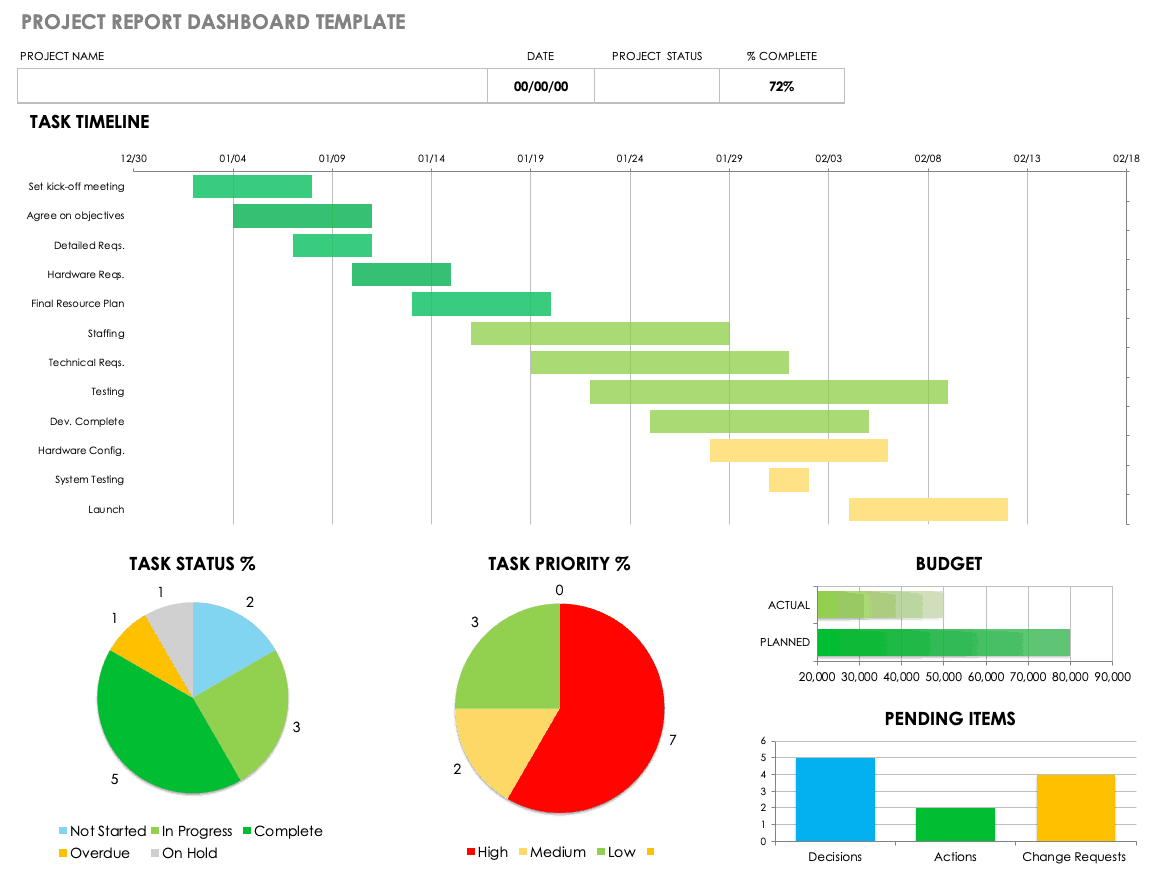
Download Project Report Dashboard Template - Excel
Having a clear visual of a project’s high-level metrics and overall performance enables a project manager to identify and home in on problem areas that need further attention. Download this project report dashboard template to track the status of key components of a project, including tasks, costs, and pending action items. This template also helps you support the decisions you make for future project initiatives. Check out this article to find more free Excel dashboard templates for all of your business needs .
Daily Project Progress Report Template
Download Daily Project Progress Report Template
Excel | Word | PDF
Provide stakeholders with insight into a project’s daily development using this progress report template. This template provides space to outline progression details, work completed, equipment used, workers on site, task locations, delays, incidents, and more. This report allows you to compare activity progress with the project plan to effectively maintain governance.
Performance Project Report Template
Download Performance Project Report Template
Communicate the performance of key project elements using this customizable project performance report template. Detail key activities, deadlines, work quality, risks, budgeting performance, and more to ensure you carry out major project deliverables on schedule and according to plan.
Project Summary Report Template
Download Project Summary Report Template
Effective project management requires that you keep lines of communication open (between the team and client) and ensure that the information you present is accurate and up to date. Provide all stakeholders with the current status of key projects, milestones, steering committee escalations, progress, and upcoming events using this pre-built project summary report template.
Weekly Project Status Report Template

Download Weekly Project Status Report Template
Excel | Word | Smartsheet
This customizable project status report template provides a snapshot of a project’s health on any given week. Track overall project performance and the status of each project component, including budget, resources, scope, milestones, work accomplished, roadblocks, highlights, and more. This template also comes with a pre-built visual timeline to display major project details at a glance.
Monthly Project Status Report Template
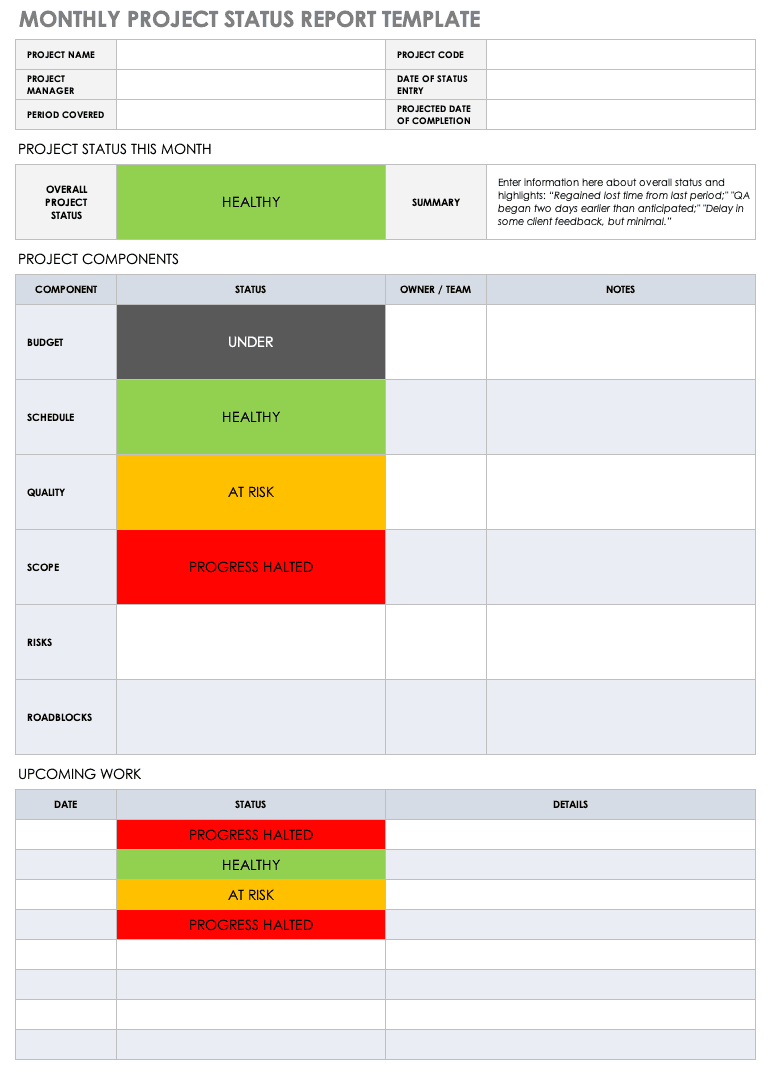
Download Monthly Project Status Report Template
Excel | Word
This project status report template captures the status of key project elements at a monthly view. Use this downloadable template to track notable project components that are complete, in progress, on hold, or at risk and outline deadlines and details for upcoming work.
Stoplight Project Status Report Template
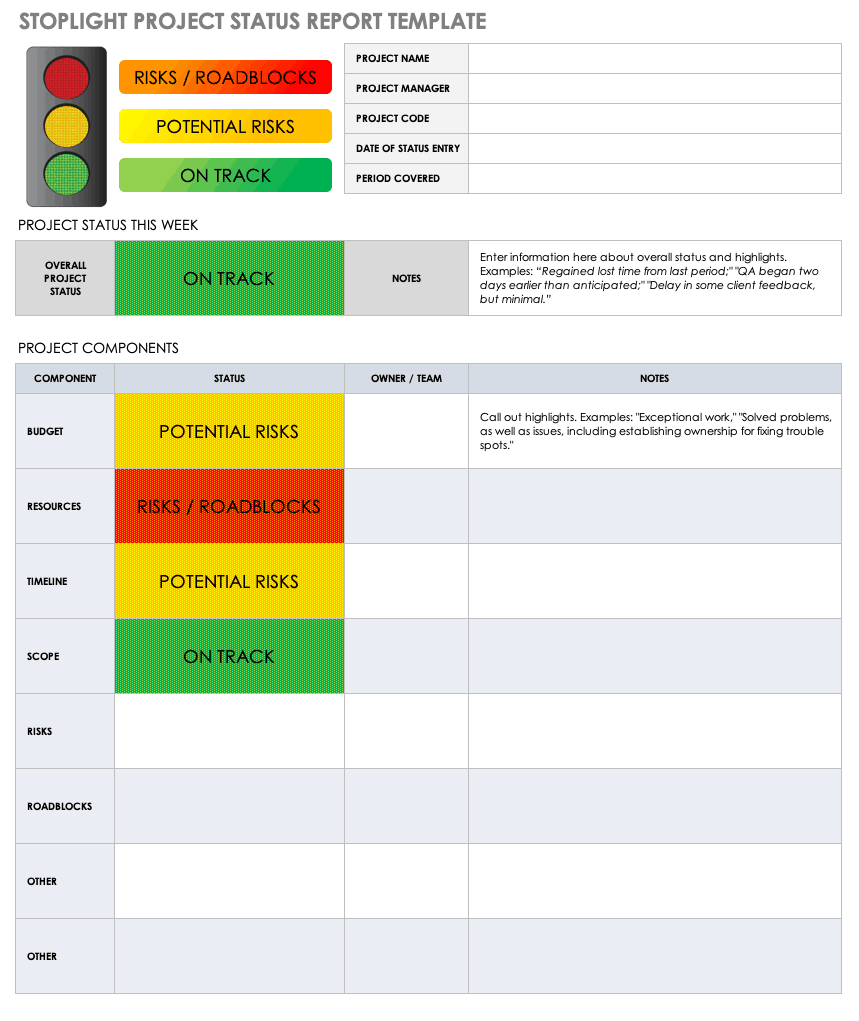
Download Stoplight Project Status Report Template
Stoplight project status reports are an effective way to visualize project items that require immediate attention and additional planning. Use the stoplight key to define the parameters of what constitutes a red, yellow, or green status and ensure that the client and team members are on the same page regarding these conditions. This template will help keep the process streamlined.
Business Project Report Template
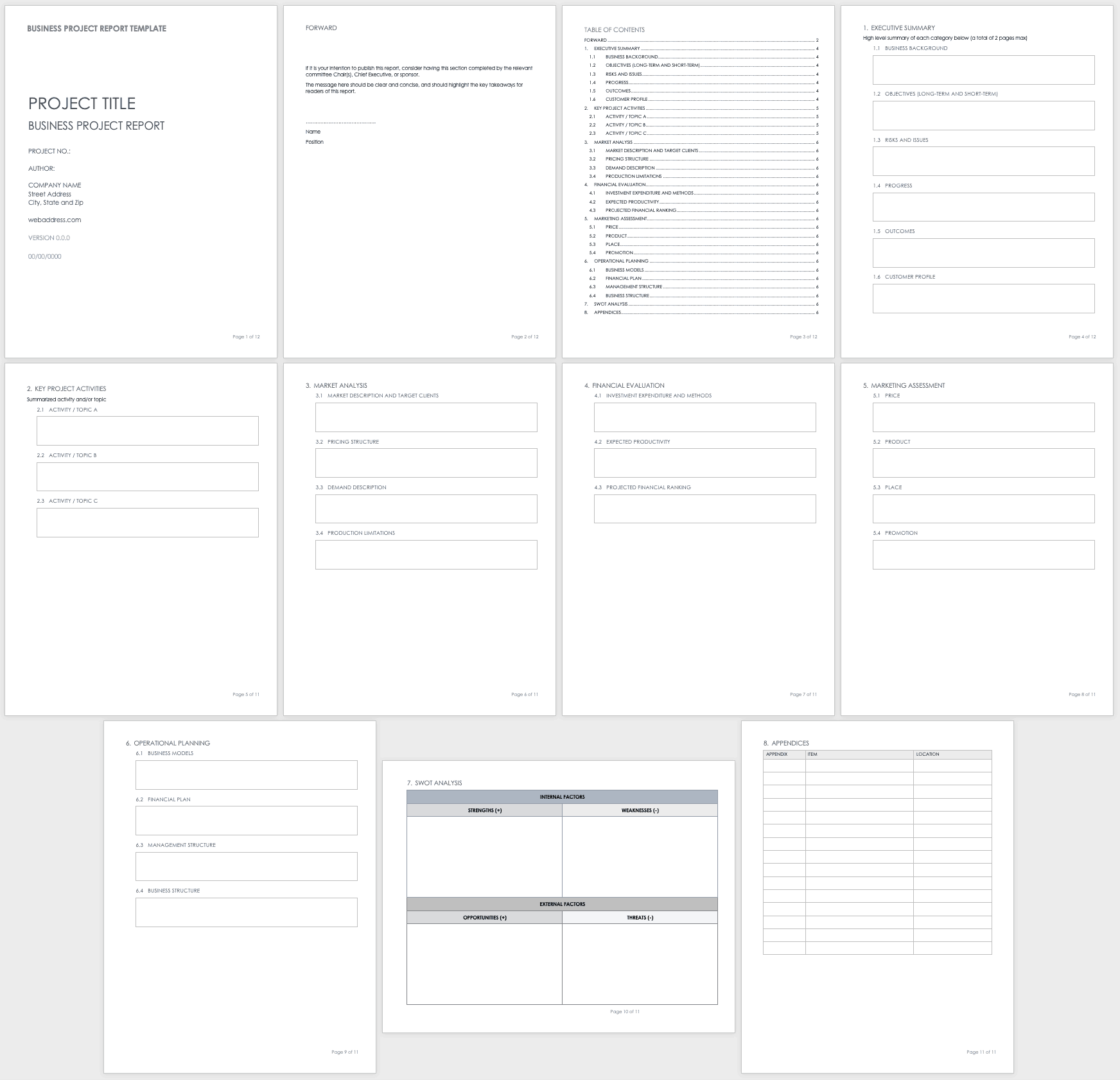
Download Business Project Report Template
Word | Google Docs
A business project report is a detailed document that serves as a roadmap for a proposed project or business venture. This business project report template provides a solid basis to expand upon according to your needs. It includes space for a table of contents, an executive summary, key project activities, a marketing analysis, a SWOT analysis, recommendations, appendices, and more.
IT Project Status Report Template
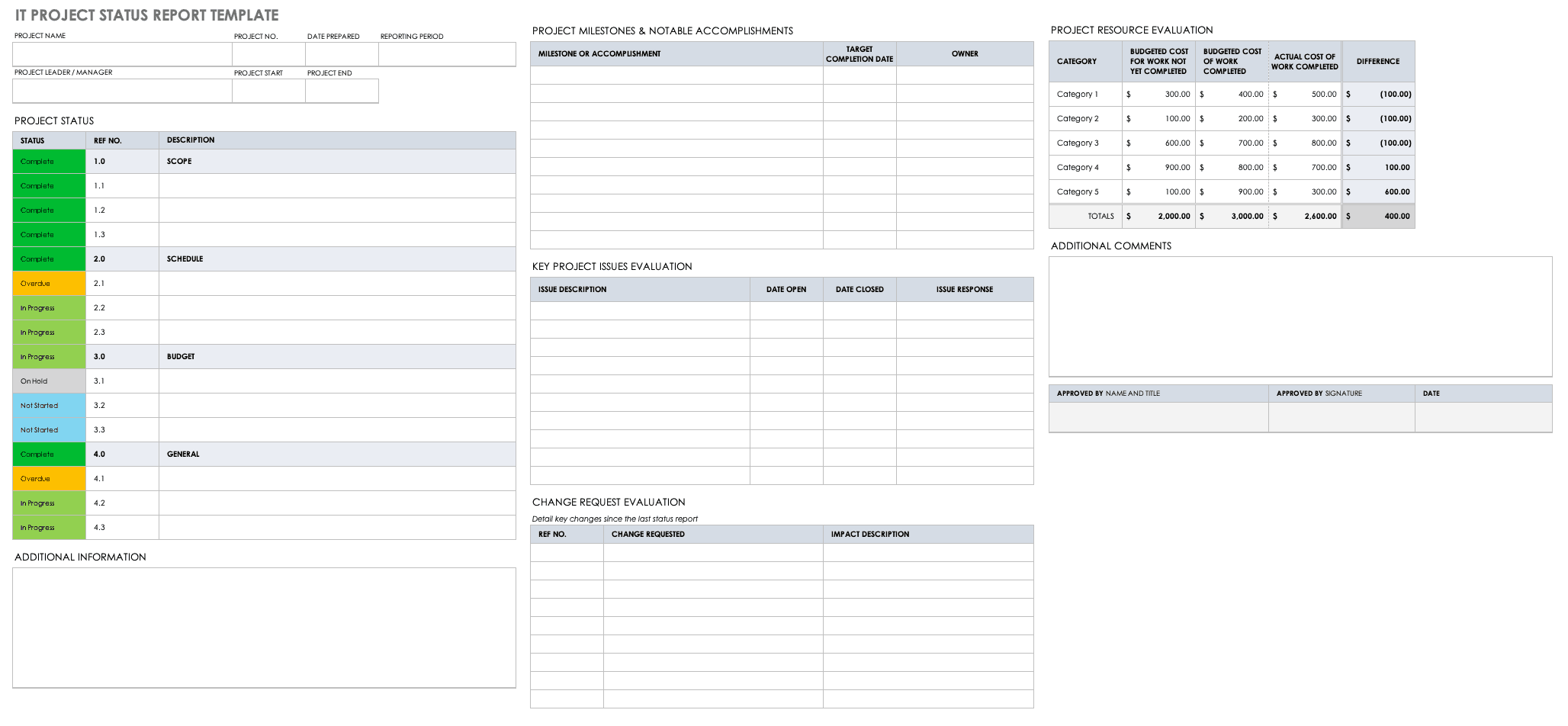
Download IT Project Status Report Template
Information technology project management and operations can be complex and involve many moving parts. Between balancing the budget, making adjustments mid-project, and meeting the needs of project stakeholders, this pre-built IT project status report template will help ensure that you track and account for all the key components of your project. This template provides room for project milestones, open and closed issues, change requests, resource evaluation, and the current status of all major project categories. Learn the essential tips for successful IT project management by checking out this article .
Construction Project Report Template

Download Construction Project Report Template
Excel | Word | PDF | Google Docs
Effective reporting is a key factor in the overall success of a construction project. This pre-built construction project report template includes all major day-to-day project details, like daily progress, materials and equipment used, number of workers and work hours performed on site, progress obstructions, and official visitors. Additionally, the template includes space for the inspector to sign off on the report in order to ensure overall project compliance. For a wide variety of free construction management templates to download, visit this page .
Executive Project Report Template

Download Executive Project Report Template
An executive project report is a high-level view of the project that highlights progress, without getting into the granular details of the project. Use this customizable executive project report template to communicate the essential elements of the project, including key milestones, accomplishments, risks, issues, financial overview, and project requirements.
Final Project Report Template
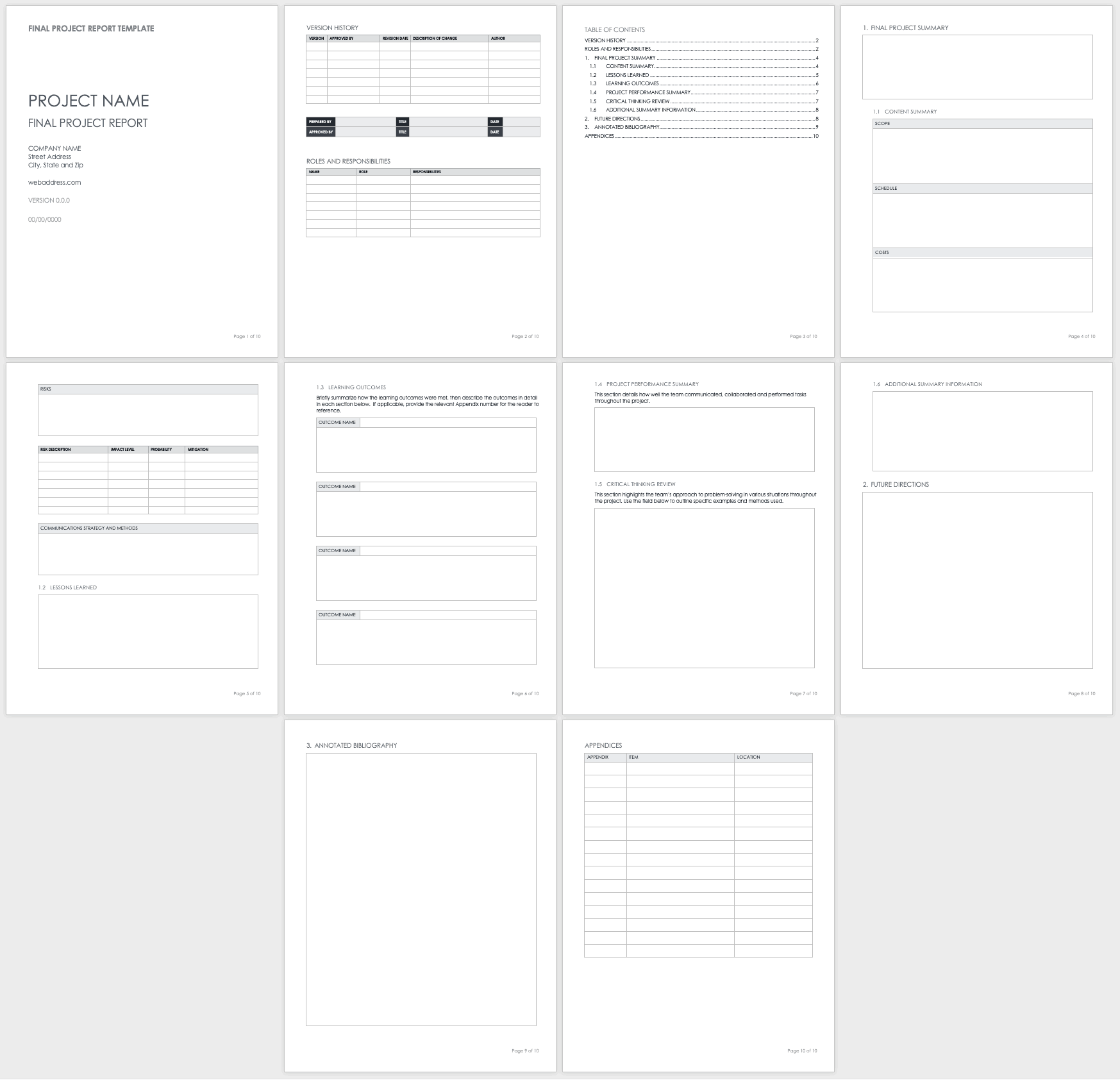
Download Final Project Report Template
The purpose of the final project report is to briefly and clearly summarize the outcomes of a completed project. This final project report template contains a table of contents, as well as space for names and roles of team members, project summary, scope, costs, risks, communication strategies, learning outcomes, top-level project performance details, and more.
Project Report Template for Teams or Departments
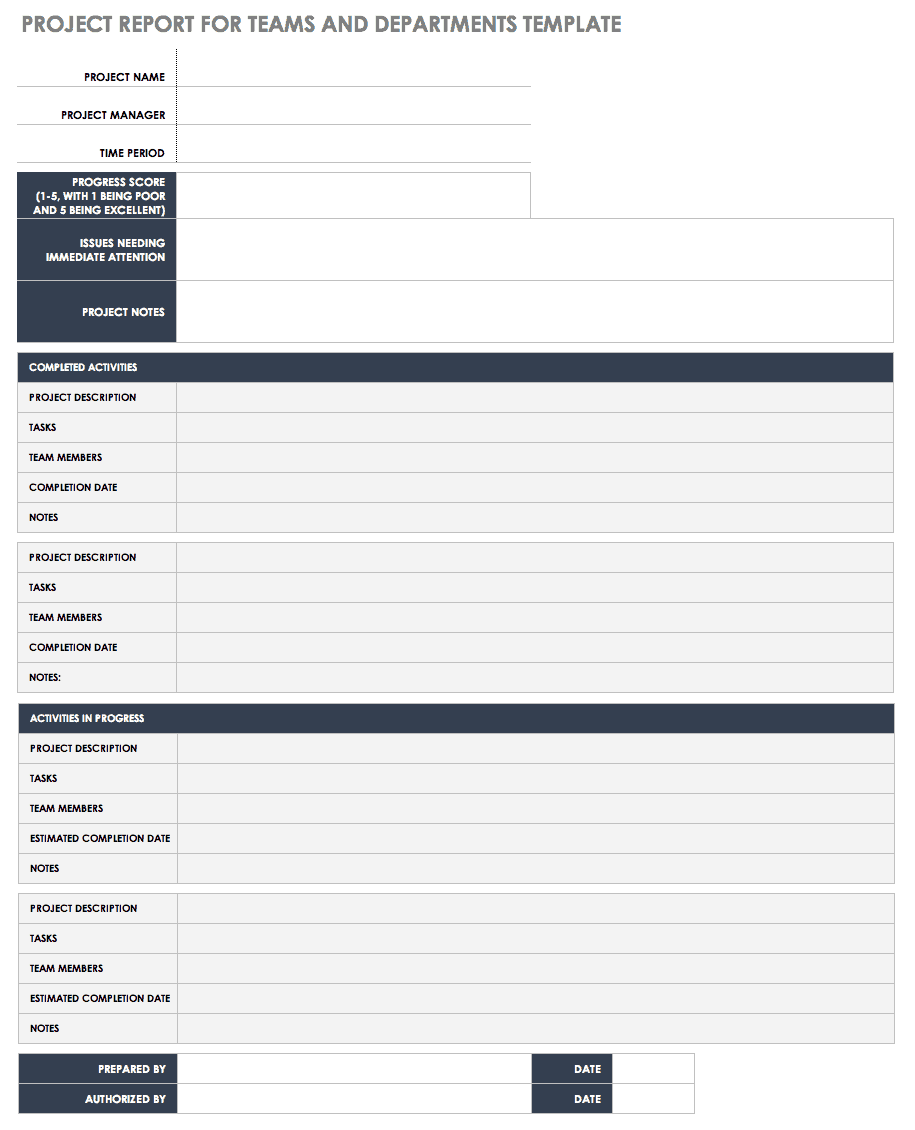
Download Project Report Template for Teams or Departments
Teams or departments can use this project report to communicate the status of project activities: That is, they can indicate whether they have completed an activity or whether an activity is still in progress. Use this template to track key tasks, team members involved, deadlines, progress scores, issues needing attention, and other project developments to ensure teams or departments account for and complete assignments on schedule.
Project Report for Stakeholders and Partners
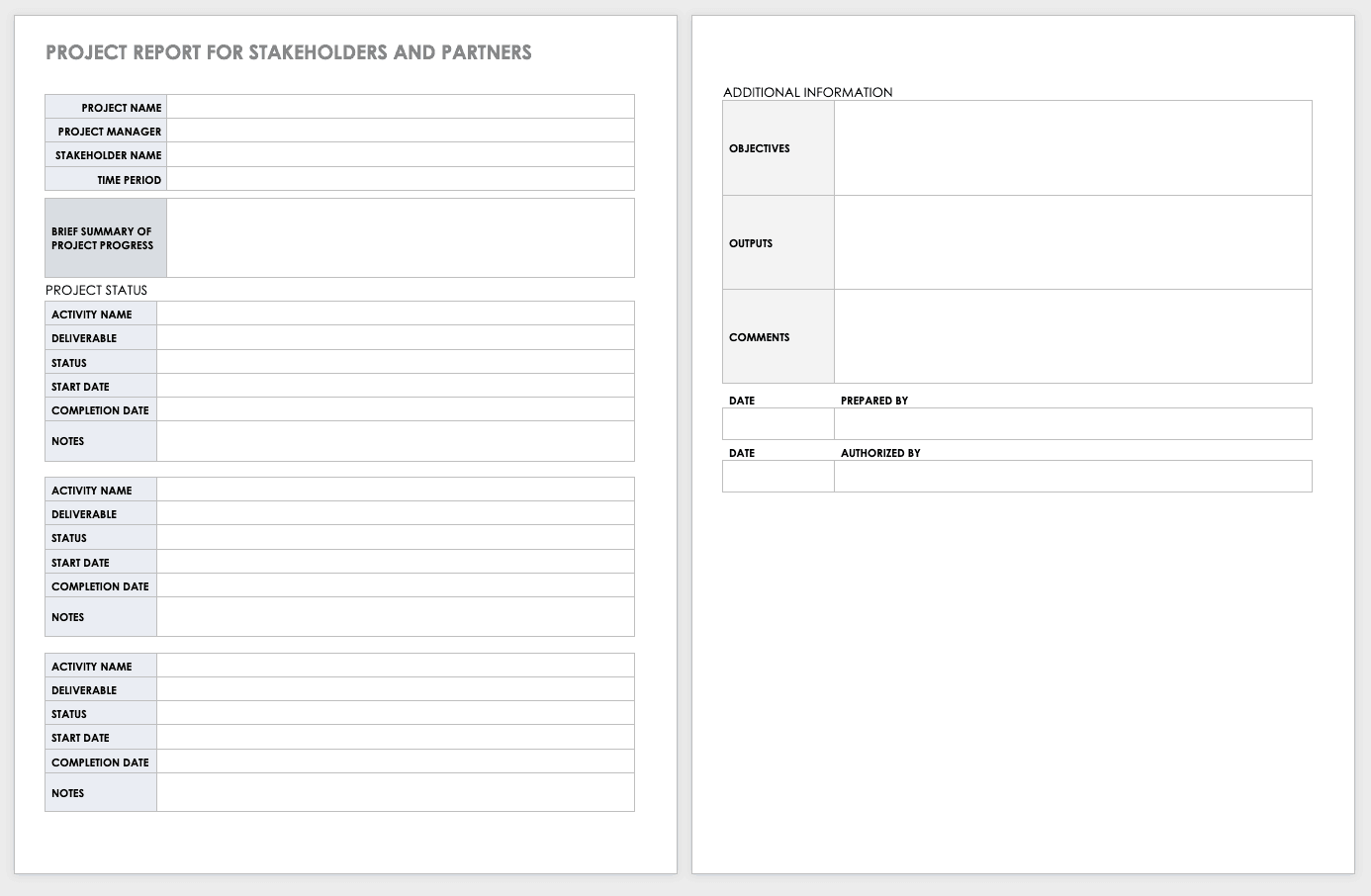
Download Project Report for Stakeholders and Partners
Use this project report is to provide key stakeholders and partners with high-level visibility into a project’s overall performance. Briefly summarize progress, project deliverables, start and end dates, outputs, and other major project details to keep stakeholders up to date on current project happenings.
Project Postmortem Report Template
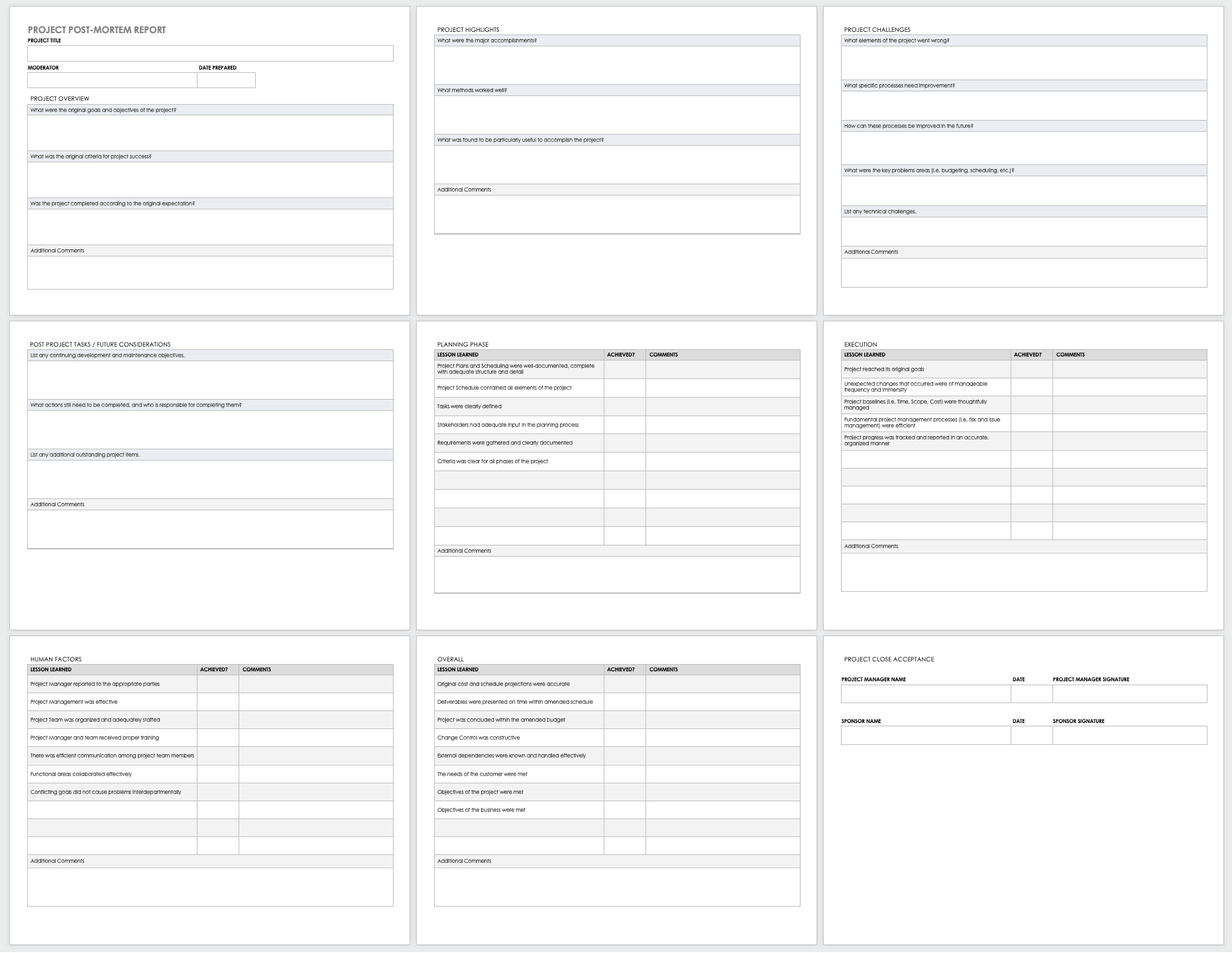
Download Project Post-Mortem Report Template
This customizable project postmortem report template should be completed as a workshop comprised of key team members within a week of concluding the project work. This report highlights project details, such as accomplishments, problem areas, lessons learned, and more to facilitate the process of analyzing the performance of all the project’s elements. Once you’ve completed this template, the project sponsor should sign off on it to formally close out the project.
Tips on Writing a Project Report
When writing a project report, stick to the facts and back up your claims with data. Consider using a template to give structure to your report, and tailor the report to your audience. We’ve outlined top report-writing tips below:
- Know Your Audience: The type and depth of information you communicate in a report will depend on the nature of your audience. For instance, managers and clients may have a better understanding of the concepts and terminology involved in a project than do stakeholders and other personnel. Effective project reporting, therefore, requires using the appropriate tone and phraseology and knowing when to share high-level versus granular project details. Your audience may also care about different details when viewing a year-end report versus a project status report .
- Give Structure to Your Report: Once you’ve identified your audience and which components of the project to communicate, organize the segments of the report so the information makes sense and is helpful to the reader. For example, you should place project identification and background details near the beginning of the report; place summarizing details near the end.
- Only Provide Facts: The report should remain objective and free from personal bias, regardless of whether the project is failing or performing successfully. If an opinion is needed, it should be labeled clearly and placed in a separate segment of the report. Additionally, the charts, metrics, and other performance data you present in the report should be accurate and up to date so that such information is credible and meaningful to the reader.
- Use a Template: Save time building out your report by using a customizable template to get you started. Templates are beneficial for standardizing processes, and you can easily adapt them to fit your needs. Use the free templates provided above for your reporting needs, and then check out this article for more project management templates .
- Use an Online Reporting Tool: Keeping a project’s development aligned with business goals is the basis of project management, and the success or failure of a project can greatly depend on the tools you use. Employ an online tool that displays data in different ways (e.g., Kanban boards, Gantt views, and dashboards), shows the real-time status of multiple projects, provides various permission levels, and allows you to set up recurring reports (such tools can automatically email these recurring reports at a set frequency to designated stakeholders, which allows project managers to shift their focus to other critical project matters). These online tools provide increased visibility into project processes and status.
Improve Project Reporting with Smartsheet for Project Management
From simple task management and project planning to complex resource and portfolio management, Smartsheet helps you improve collaboration and increase work velocity -- empowering you to get more done.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Our Privacy Notice describes how we process your personal data.
Looking for more
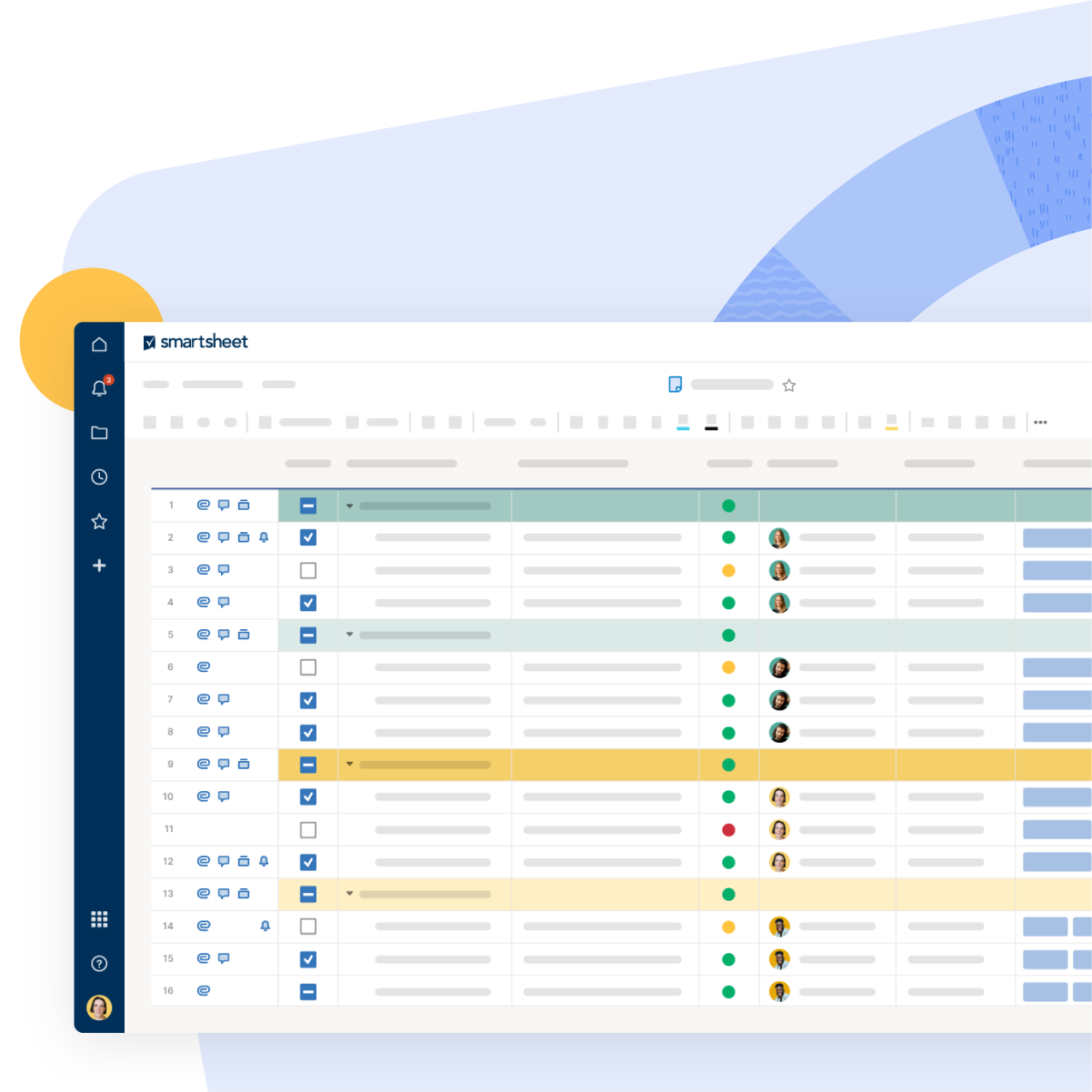
Free 30-day trial
Enable everyone to work better, at scale, with Smartsheet.
Get started for free

Free Smartsheet templates
Get free templates

Free ebook: Project & Portfolio Management 101
Get the most out of your PPM efforts with our secrets for success.
Get the free ebook
Recommended Articles

Future of Work Management Report 2023
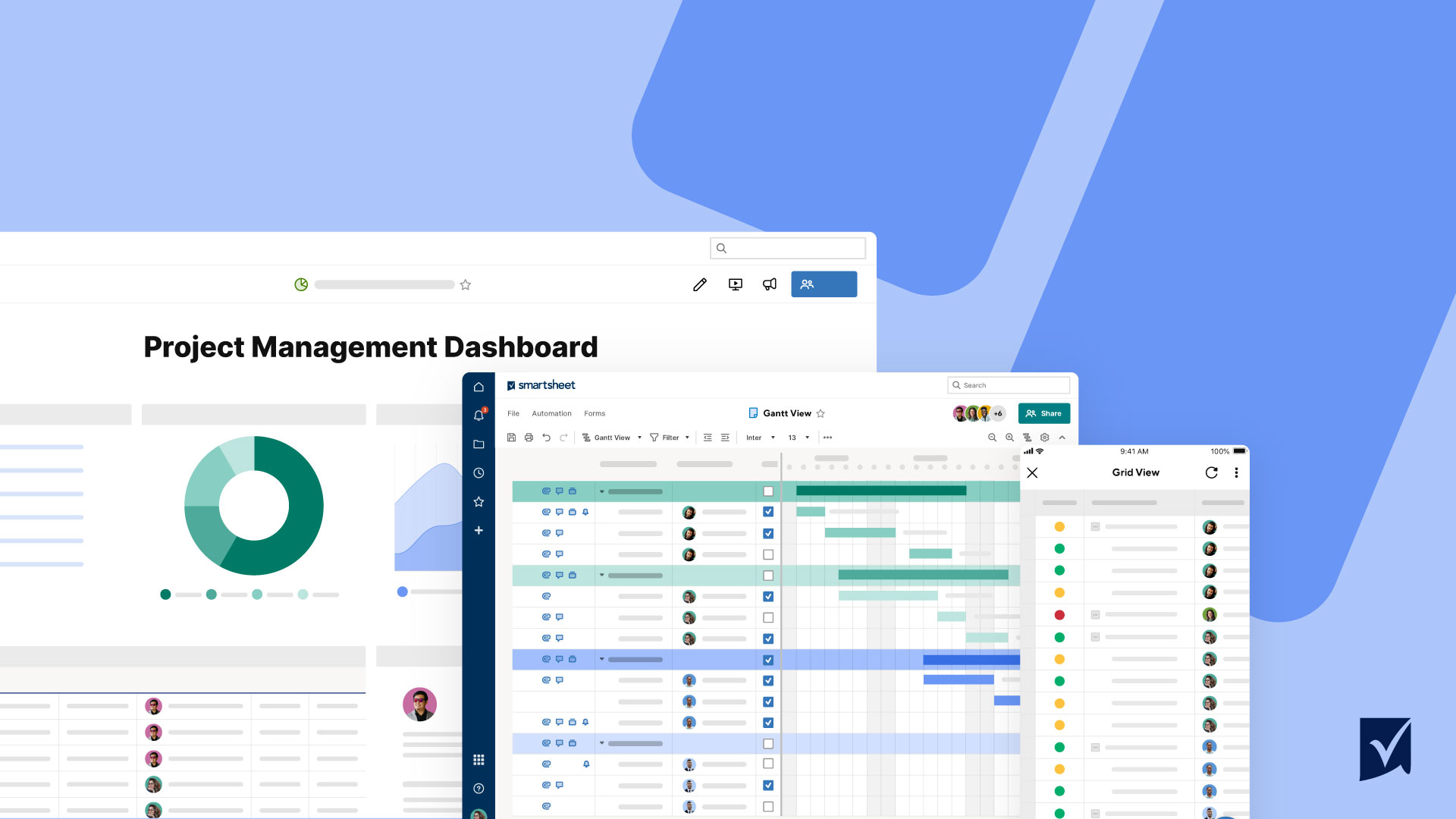
Project Management Guide

Free Project Management Plan Templates
Improve project reporting with instant visibility and real-time collaboration in smartsheet..
- Agile project management
- Status report
How to Create a Project Status Report
Browse topics.
The end of the week is here, so it’s time to sift through spreadsheets, emails, and tools to compile an update on your project's progress. Reporting on your work's status helps maintain team alignment, identify risks early, and ensure the project remains on schedule and within budget.
Switching to a project status report template will streamline this process. Creating a project status report will minimize your time on redundant data collection, freeing more time for meaningful work. Whether preparing your first project status report or seeking a more efficient method, this article will guide you through creating an effective report, helping you consistently meet your project deadlines.
What is a status report?
A project status report is a concise, timely update on your project's progress. It provides essential high-level information, allowing team members and key stakeholders to grasp the project's current state quickly. These reports maintain alignment among all involved parties, highlighting what's on schedule, identifying obstacles, and outlining the next steps.
The frequency of your status reports should align with your project's timeline, varying from weekly to monthly updates depending on the project's nature and stakeholder needs. Far from mere reactions to setbacks, these reports proactively keep your team apprised of the project's health, whether on track, facing risks, or behind schedule. These reports are integral throughout all project phases , ensuring schedule adherence and consistent communication.
Types of project status reports
When you create status reports, the frequency and level of detail depend on your project management requirements. Here's a rundown of different types of status reports and the times they're most effective:
- Daily status report : This status report outlines the daily activities of each team member. It focuses on their current tasks and any issues hindering progress. Typically, it includes a summary of the day's work and achievements from the previous day. These reports are essential for projects that require close monitoring and real-time updates.
- Weekly status report : This report details the project's progress, including the name of the project, the report date, and a summary of the week's work. It also outlines the upcoming week's action plan, challenges, risks, and mitigation strategies. Weekly reports are crucial for tracking short-term project milestones within the broader project plan .
- Monthly status report : The monthly status report provides monthly updates, offering a broader view. It's beneficial for leadership to gauge progress and make informed decisions about the project budget and future activities. The report includes accomplishments, a recap of the month, and plans for the next month.
- Quarterly status report : This report is valuable for a high-level overview, providing a snapshot over four months. It covers the same areas as other reports but often includes graphs and visuals for clearer understanding. Quarterly reports align long-term project milestones with the overall project plan.
Each report type serves a distinct purpose, from detailed, granular updates to comprehensive summaries. The choice depends on the project's complexity, stakeholder information needs, and specific project management software capabilities.
Benefits of project reporting
Project reporting is more than a procedural task. It's also an integral part of effective project management . An accurate project status report offers several key benefits:
- Increased transparency : Project status reports ensure that every team member and stakeholder has a clear view of the project's current status, upcoming tasks, and potential issues. The level of transparency is essential for trust and clarity within the project.
- Track project health : Discovering at the end of the project timeline that things were off course is something you should avoid. Regular progress reports offer high-level summaries and critical metrics, informing everyone about the project's health. If the project is off track, these insights allow quick, proactive adjustments to meet deadlines and stay within budget.
- Effective communication : Status reports enhance communication efficiency. They compile essential details into an easily digestible format, ensuring that everyone involved is on the same page.
- Risk management : Regular reporting is vital in early identification and mitigation of potential risks, preventing them from escalating into major issues.
- Accountability : Team members can access information asynchronously by replacing status meetings with a project status report you share via a central tool. This approach saves valuable time and allows for more focused, productive discussions during meetings.
Project reporting is vital for project managers, as it ensures effective project tracking , clear communication, and a consistent path toward project objectives.
Key elements of a status report
An effective project status report involves several key elements that enhance readability and usefulness. Here's what a robust status report template should include:
- Executive summary : This is where you provide a concise, high-level overview of the project. Aim for no more than six sentences, offering just enough detail to intrigue readers to read the rest of the content.
- Visual progress of the project : A status report should visually represent the project's progress. Use Gantt charts or graphics to showcase completed project milestones and deliverables.
- Overall project schedule : The project schedule is vital, as it outlines deadlines and progress. Opt for visual tools such as dashboards and calendars for clarity and ease of understanding.
- Insights into the project budget : Budget analysis is a core responsibility in project management. The status report should visually represent the budget. For example, you could include pie charts showing expenditures.
- Common challenges and blockers : Be transparent about current obstacles. It allows you to address any issues affecting project execution , from client communication to resource availability.
- Well-communicated next steps : Clearly outline the upcoming tasks and milestones, assigning responsibilities and due dates to specific team members. This approach fosters accountability and sets a clear path for project continuation.
- All project KPIs and metrics : Incorporate a dedicated section for metrics, possibly using graphical elements to make data more engaging. Track and compare KPIs such as cost performance, logged time, customer satisfaction, and productivity to past reports for a comprehensive view of the project's health.
A weekly status report template or any other frequency-specific template should integrate these elements to streamline the reporting process, ensuring that each report is informative and engaging for the entire project team.
Recommended templates
The correct project management template is vital when creating a vision for your project status report. Here are some top recommendations:
- Project status template : Atlassian, in partnership with ASU, has developed a comprehensive project status template. It's adaptable to suit any company's needs. Customize it in Jira by creating issue types or fields relevant to your status report and save it as a new template for ongoing use.
- Weekly status report template : Ideal for encapsulating weekly progress, this template focuses on results rather than hours spent. It's concise, fostering consistent communication with team members and managers.
- Project plan : Handling projects with multiple teams can be challenging. The project plan template simplifies the management of projects of varying sizes and complexities, ensuring stakeholders are always informed.
Steps to writing an effective project status report
Here are some simple steps to follow to write an effective project status report:
Identify the objective
Start by determining the primary goal of your status report. Is it to inform stakeholders of progress, address potential issues, or provide an overview of project health? Clarifying this sets the tone for your report.
Define your target audience
Tailor the content and depth of your report based on who will read it. Different stakeholders might have varying interests, such as project timelines for team members and budget details for financial stakeholders.
Gather the necessary data
Essential for a well-rounded report, this step involves compiling information from multiple sources, including the budget, project timeline details, recent events, and upcoming deadlines. Your project timeline should list key events or actions with dates to provide a chronological view, aiding in creating your status report.
Organize the report
Logically structure your report. Use a status report template to ensure consistency and cover all vital areas, such as progress, budget, and upcoming milestones.
Ensure clarity
Strive for clear, concise language. Avoid jargon unless necessary and explain any complex terms. Clarity ensures that all key stakeholders understand the report’s contents regardless of their familiarity with the project's specifics.
Edit and send
Ensuring your project status report is clear and proofread is essential for maintaining its integrity and effectiveness. The report must be rigorously reviewed for errors and ensure the language conveys the intended message. This aligns with the best practices for creating impactful project status reports and provides the audience with an understanding of the information.
Status report best practices
With an understanding of what a project status report entails and how to craft one, here are some best practices to ensure its effectiveness:
- Accommodate different learning styles : Not everyone absorbs information from text alone. Enhance your status report with visuals such as Gantt charts and graphs, and include external links to emphasize key points. Additionally, consider having synchronous discussions with clients during the review process, as real-time conversations can be more impactful.
- Stay accountable with recurring meetings : Establishing a routine is crucial post- project kickoff . Schedule effective team meetings regularly from the start, making report preparation and sharing a habitual part of your process.
- Keep an ongoing draft : Avoid last-minute rushes by maintaining a draft of your status report. Update it as events unfold, as it will prepare you for unexpected inquiries. This approach ensures you’re ready to present a well-informed status report, especially when juggling multiple projects.
Create effective status reports with Jira
Jira redefines project management efficiency by offering a dynamic suite of features for simple and complex projects. Jira's about more than just planning and tracking, it sets teams up for rapid progress and enables them to stay aligned with broader objectives, critical deadlines, and essential outcomes.
Teams can plan and visualize workflows seamlessly with its intuitive boards. Managing dependencies and aligning with overarching goals is easier with timelines.
Moreover, Jira provides actionable reports that help you make informed decisions, giving you a holistic view of projects. Together, these tools ensure every phase of your project is transparent, coherent, and on schedule. Ready to elevate your status-reporting process? Get Jira for free and experience a seamless transition from planning to execution.
Status report: Frequently asked questions
How often should you create a status report.
The frequency of status reports depends on the project's complexity and stakeholders' needs. Whether weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly, choose a cadence that keeps everyone adequately informed without causing information fatigue. A weekly status report might be a good starting point.
What makes an effective status report?
An effective status report is clear, concise, and focused. It provides valuable insights into the project scope , progress, challenges, and future steps, facilitating informed decision-making .
What’s the difference between a status report and a progress report?
A status report provides a comprehensive overview of a project's current state, including data on progress and other aspects. In contrast, a progress report focuses on the completed tasks and project milestones, aligning with the schedule to demonstrate advancement. Both keep project managers and key stakeholders informed.
Gantt Charts
A Gantt chart is a project management tool that illustrates a project plan. Learn how they can help and see an example of Gantt charts
Creating Project Schedules: Steps & Techniques
Discover the essential steps and techniques for creating an efficient project schedule. Learn how to define tasks, sequence activities, and use tools.

How to Create a Project Report? Know Steps, Components and More

Overview of What Is a Project Report?
A project report is a comprehensive document that outlines a project's details, progress, and outcomes. It provides stakeholders a clear understanding of the project's purpose, scope, and deliverables. A project report serves as a record of the entire project lifecycle, from initiation to completion. A project report enables better decision-making , evaluation, and communication by effectively documenting project-related information.
How to Make a Project Report From Scratch?
Creating a project report from scratch may seem overwhelming, but by following these key steps, you can produce a well-structured and informative report:
- Understand the Purpose : Clearly define the objective and purpose of the project report. Determine the target audience and the specific information they need to gather from the report.
- Gather Relevant Data : Collect all pertinent data related to the project, such as project plans, schedules, budget details, and progress reports. Organise this information to ensure easy reference and accessibility.
- Define the Structure : Establish a logical structure for your project report. Break it into sections, including an executive summary, introduction, methodology, findings, analysis, recommendations, and conclusion. Each section should address specific aspects of the project.
- Write the Content : Start writing each project report section, providing detailed and concise information. Use a conversational writing style while maintaining professionalism. Incorporate relevant technical terms to demonstrate expertise but ensure clarity.
- Include Visuals : Enhance your project report by incorporating relevant visuals, such as charts, graphs, and diagrams. Visual representations can significantly improve understanding and engagement for readers.
- Review and Revise : Once the initial draft of your project report is complete, thoroughly review and revise it. Check for grammatical errors, factual accuracy, and overall coherence. Seek feedback from colleagues or stakeholders to ensure the report effectively conveys its intended message.
- Finalise and Distribute : Make the necessary amendments based on the feedback received and finalise the project report. Consider the appropriate format for distribution, such as printing physical copies or sharing electronically. Ensure the report reaches the intended audience promptly.
You can also check out multiple project report samples available online to see how others have worked and take inspiration from those or you can explore Project Management courses to enhance your skills.
Project Report Objectives
The objectives of a project report are manifold. Some primary goals include:
- Sub-objective: To ensure future reference and accountability.
- Sub-objective: To enable effective decision-making and collaboration.
- Sub-objective: To extract lessons learned and identify areas for improvement in future projects.
Project Report Components
A well-structured project report should typically include the following components:
- Executive Summary : A concise overview of the project report, capturing key highlights, objectives, and outcomes. It provides a comprehensive snapshot for decision-makers.
- Introduction : An introduction sets the context and purpose of the project, explaining why it was undertaken and its importance. It outlines the scope, objectives, and expected deliverables.
- Methodology : This section details the approach, techniques, and tools employed during the project's execution. It explains how various activities were planned, executed, and monitored.
- Findings : Findings describe the project's results, highlighting achievements, challenges, and unexpected outcomes. This section provides a factual account of the project's progress and identifies variances from the initial plan.
- Analysis : The analysis section interprets the project's findings, identifying trends, correlations, and patterns. It critically evaluates the project's performance and presents insights from the data and observations.
- Recommendations : Recommendations suggest potential improvements, actions, or adjustments based on the project's analysis. These suggestions aim to enhance future project planning and implementation.
- Conclusion : The conclusion summarises the key points discussed in the report, reiterating the project's objectives, achievements, and lessons learned. It reinforces the report's main takeaways.
Common Project Report Types
Project reports can vary in purpose and scope, depending on the type of project being documented. Some common types of project reports include:
- Status Reports : These reports provide ongoing updates on the project's progress, including milestones achieved, challenges faced, and next steps. They help stakeholders stay informed about the project's status.
- Feasibility Reports : Feasibility reports assess the practicality and viability of a proposed project. They evaluate resources, costs, risks, and benefits to determine whether the project is worth pursuing.
- Evaluation Reports : Evaluation reports focus on assessing the success and effectiveness of a completed project. They analyse the project's outcomes against predetermined criteria and measure its impact.
Project Report Use Cases
The application of project reports extends across various industries and sectors. Some common use cases include:
- Businesses : Project reports enable businesses to analyse the success of their initiatives, evaluate return on investment (ROI), and make informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
- Government Organisations : Government organisations utilise project reports to monitor public initiatives, assess policy effectiveness, and ensure transparency and accountability in public spending.
- Research Institutions : Project reports play a vital role in research institutions, documenting research methodologies, findings, and recommendations. They support scientific discourse and help advance knowledge in specific domains.
- Academic Institutions : In the academic realm, project reports are essential for students, enabling them to showcase their research, methodologies, and conclusions. They contribute to the learning process and evaluation of student performance.
A well-structured project report empowers project managers and stakeholders with essential information to assess project performance, inform decision-making, and ensure effective communication . By following the outlined steps and considering the components and objectives of a project report, you can produce a comprehensive and insightful document that adds value to your projects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why is a project report important.
A project report is important as it is a detailed record of progress, outcomes, and lessons learned. It facilitates effective communication, evaluation, and decision-making for all stakeholders involved in the project.
How long should a project report be?
Can i use templates for creating project reports, about the author.

TimesPro strives to embody the values of Education 4.0: Learner-centric, industry-relevant, role-specific, and technology-enabled, to make learning accessible for anyone who seeks to grow. We are a learning platform that traverses an individual’s journey through life, making them confident and equipped to rise in this competitive world.
IIM Kozhikode Professional Certificate Programme in Advanced Product Management - Batch 04
IIM Kozhikode
This programme offers practical experience in product development and modification, empowering individuals to navigate the complexities of the market with confidence and proficiency.

IIT Delhi Executive Programme for Advanced Product Management - Batch 2
IIT Delhi's Executive Programme for Advanced Product Management helps you to hone your product management skills by providing you hands-on experience on customer delivery, equipping you with state-of-the-art prototype development processes and tools for both physical and digital products.

Follow us on social media for regular updates, tips, and insights that can help you achieve your career goals!
- Banking & Finance
- Supply Chain Management
- Marketing & Sales
- Technology & Analytics
- Hospitality
- General Management
- Leadership & Strategy
- Operations & Supply Chain
- Human Resources
- Product Management
- Innovation & Transformation
- Executive Education @ Work
- Technology Solutions
- Signature Programmes
- Bespoke Learning
- OD Solutions
- Content Solutions
- Hire-Train-Deploy
- Learning Experience Platform
- Career @ TimesPro
- Media Presence
- Scholarship
- Government Business
- CSR solutions
- Refund Policy
- Grievance Redressal
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Hire From Us
- Institute Alliance
Blog: Healthcare | General Management | MBA | Web 3.0 | Banking & Finance | Leadership & Strategy | Law | Product Management | Innovation & Transformation | Hospitality | Marketing & Sales | Operations & Supply Chain | Human Resources | Technology & Analytics
Academic Partners: IIM Kozhikode | IIM Calcutta | IIM Lucknow | IIM Indore | XLRI Jamshedpur | IIM Raipur | IIT Roorkee | IIM Kashipur | SPJIMR | IIM Tiruchirappalli | IIM Visakhapatnam | MICA | IIM Jammu | IIM Nagpur | KJSIM | BIMTECH | IIM Bodh Gaya | IMI Bhubaneswar | Manipal University | IMT Hyderabad | Jain University | IIM Sirmaur | IIT Jammu | IIT Guwahati | IIT Ropar | University of Hyderabad | IIT Mandi | IHUB Divyasampark
Trending Early Career courses: TimesPro Banking Programme Relationship Managemen t | Post Graduate Programme in Logistics & Supply Chain Management Course | Full Stack Web Development Course | PGDBM-XL - Banking Management | Certificate in Occupational English for Nurses
Trending Executive Education course categories: General Management | Leadership & Strategy | Technology & Analytics | Marketing & Sales
Trending Enterprise Solutions: Technology Solutions | Signature Programmes | Bespoke Learning | OD Solutions | Content Solutions
Trending Web 3.0 courses: Solidity and Ethereum Smart Contracts | Getting Started with Web 3.0 | Blockchain Fundamentals Programme
Copyright ©️ 2024 Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd. All rights reserved.
- Contact sales
- Start free trial
Project Status Reports
This guide to status reports is presented by projectmanager, the project management software trusted by 35,000+ users. make a status report in minutes.
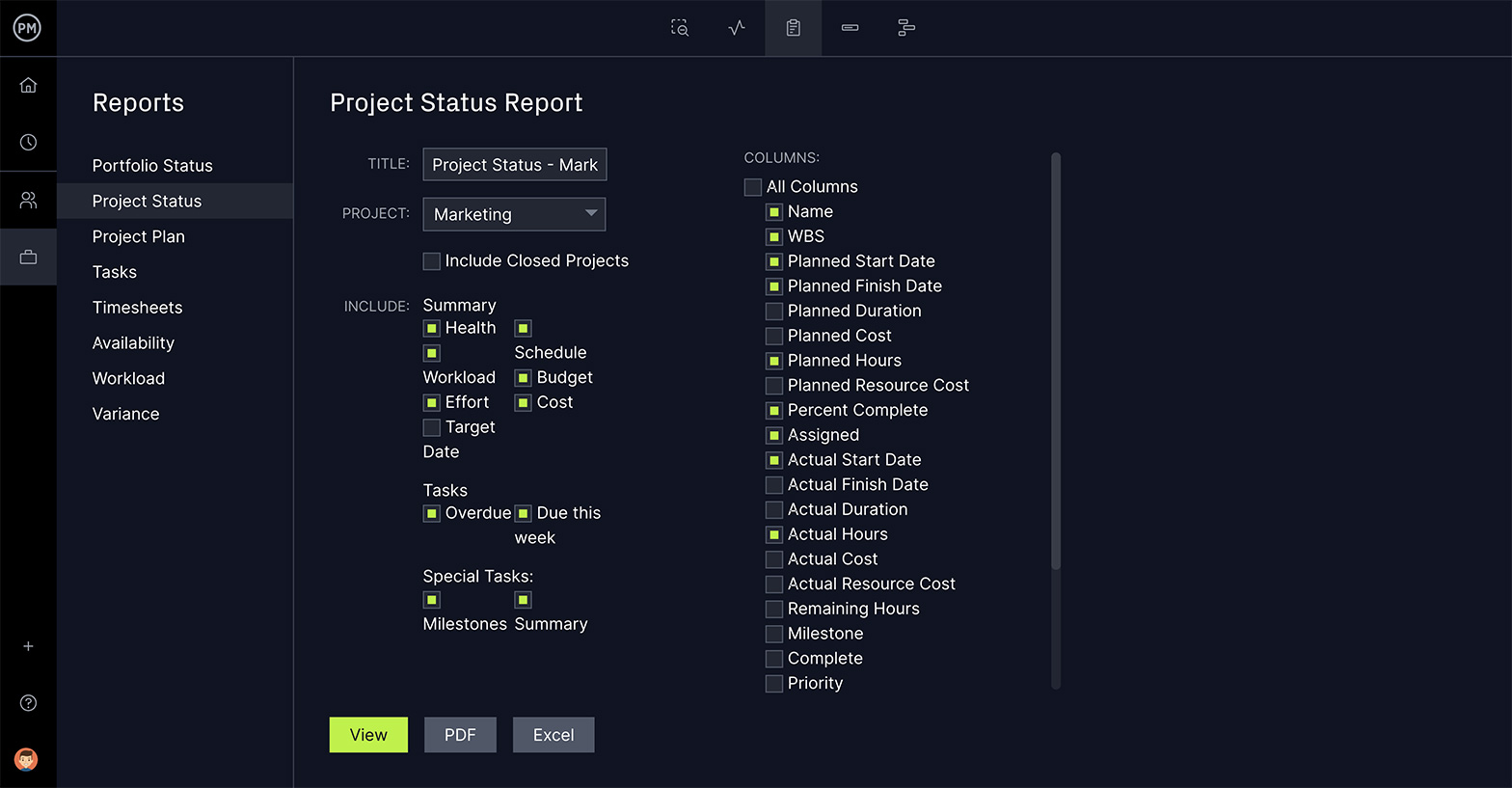
What Is a Project Status Report?
What is the purpose of a project status report, types of project status reports, status report vs. progress report, how to write a project status report, project status report template, project status report example, what should be included in a project status report, what is project reporting software, benefits of project reporting software, must-have features of project reporting software, how to make project status reports in projectmanager, best practices for presenting project status reports, other types of project management reports, try our project reporting software for 30 days.
A project status report is a document that describes the progress of a project within a specific time period and compares it against the project plan. Project managers use status reports to keep stakeholders informed of progress and monitor costs, risks, time and work. Project status reports allow project managers and stakeholders to visualize project data through charts and graphs.
Project status reports are taken repeatedly throughout every phase of the project’s execution as a means to maintain your schedule and keep everyone on the same page. The status report for a project generally includes the following:
- The work that’s been completed
- The plan for what will follow
- The summary of the project budget and schedule
- A list of action items
- Any issues and risks, and what’s being done about them
Related: 12 Essential Project Reports
The true value of a project status report lies beyond its use as a communication channel. It also provides a documented history of the project. This gives you historical data, so the next time you’re planning a similar project, you can avoid any missteps or bottlenecks.
Because project status reports cover so many topics, they were historically time-consuming to create. Fortunately, modern project management software like ProjectManager expedites the all-important status reporting process. Try our automated project reports and simplify your project reporting.
Create a project status report with just a few clicks with ProjectManager— Learn more.
There are several reasons why project managers create status reports. Here are some of the most important.
- Help the project management team keep track of costs, tasks and timelines
- Compare the budget and time forecasts with the actual costs and task duration
- Improve communications across the organization
- Simplify the communication process
- Keep stakeholders informed
- Deliver key messages to the intended target audience
- Improve organizational support for your projects or your team
If you’re reporting to stakeholders, you don’t want to bog them down with unnecessary details. Keep your status reporting presentation light and to the point.
Get your free
- Status Report Template
Use this free Status Report Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
You might create daily, weekly, monthly or quarterly status reports depending on your project management requirements. Here’s a quick overview of when it’s best to use each of them.
Daily Status Report
A daily status report captures what each member of the project team has worked on over the course of that day. It not only highlights what they’re working on currently but addresses any issues that are preventing them from completing their tasks. It includes a summary of today’s work and what was accomplished the day before.
Weekly Status Report
A weekly status report is like the daily status report except it covers a full work week rather than just one day. It includes the name of the project, the date of the status report, a summary outlining what work was done over that time period and the action plan for what to work on for the next week. There will also be a section to list any challenges, risk and mitigation plans to respond to them.
Monthly Status Report
A monthly status report provides a similar update on a project or projects but over a period of a month. It provides leadership with relevant information to better manage the project or projects. As with other frequencies, the team reports on what they’ve accomplished, the month is recapped and the next month’s activities are outlined.
Quarterly Status Report
A quarterly status report is a short and easily digestible snapshot of the project over a period of time, in this case, four months or a quarter of the year. It covers the same territory as the other status reports and is likely to include graphs and other visuals to make all the data easier to grasp.
There are many different types of reports you can generate when managing a project. Some of them are more for the project manager and others for the stakeholders, owners or clients to keep them updated.
We’ve been talking about a status report, but it shouldn’t be confused with a progress report. While a status report has data on the progress over the period of time which is being reported, there’s a wealth of other information beyond the mere progress of the project.
A progress report , on the other hand, details the specific tasks and milestones that have been completed to show that the project is making progress in sync with the project schedule. Like a status report, it’s used to keep managers and stakeholders updated.
Writing a project status report is an essential project management task. Whether you generate one weekly, monthly or quarterly, the steps are essentially the same. Here’s how to write a project status report:
- Determine the objective
- Target your audience (Clients, team members, sponsors, etc)
- Choose the format and type
- Collect your data
- Structure the report
- Make sure it’s clear
Because a project status report follows a basic outline, it can be helpful to use a project status report template. However, a project status report template is only a static document. Using project status reporting software integrates with all your project management tools for greater efficiency.
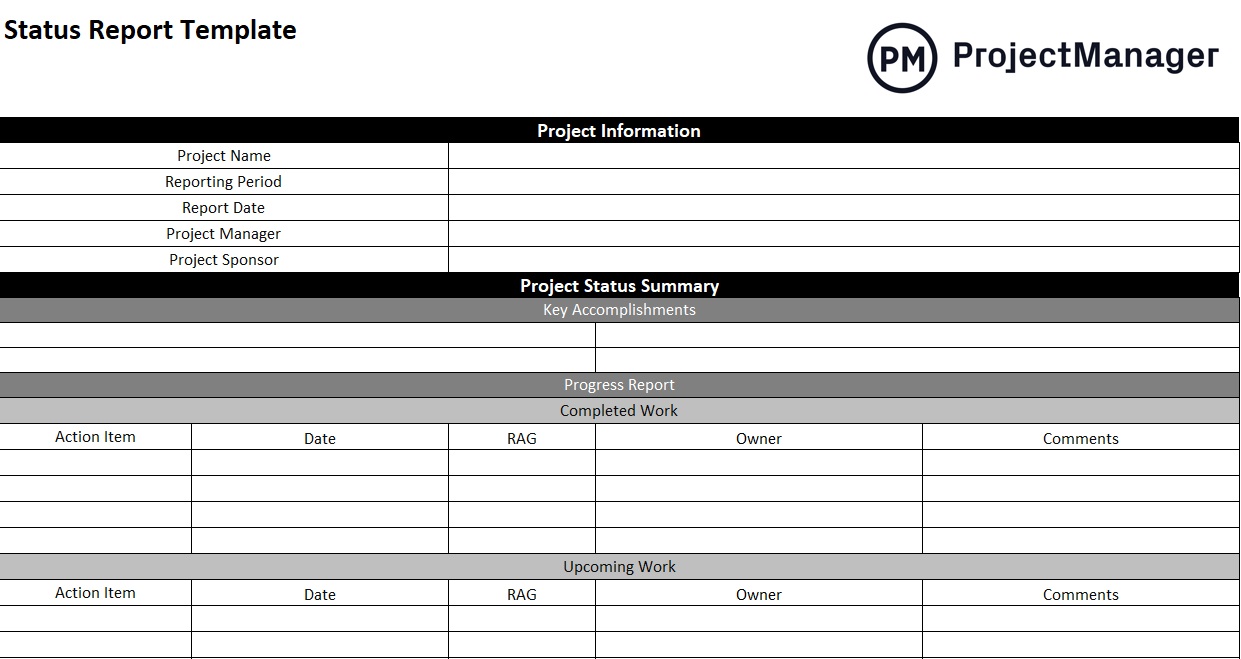
ProjectManager’s free status report template for Excel— Download now.
To better understand the process described above, let’s take a look at a project status report example. For this simple example, we’ll create a weekly status report for a home construction project using our free project status report template.
Imagine a construction contractor who is in charge of building wall frames, installing the insulation, electrical wiring, drywall and interior painting of a brand-new house. A status report example, following our free status report template, would begin with basic project planning information, such as the project name, new house, reporting period would be between Jan. 1-7, the report dated Jan. 9, project manager Joe Johnson and project sponsor Jack Dell.
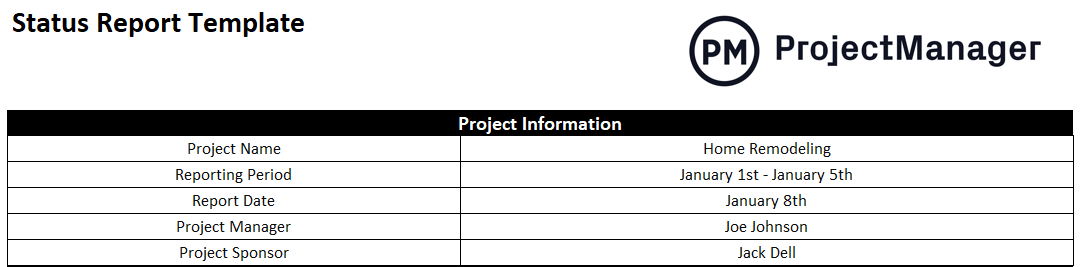
Next is the summary, which highlights the key accomplishments. In this case, it would be the installation of wall frames. The section after zooms into the progress of the project. It starts with smaller action items that are needed to build the wall frames.
These action steps also include the date when they were done and a RAG status. That is a red, amber and green indication of the level of confidence and control over that part of the project. The owner, or team member who did the work is named and any comments not already addressed can be added.
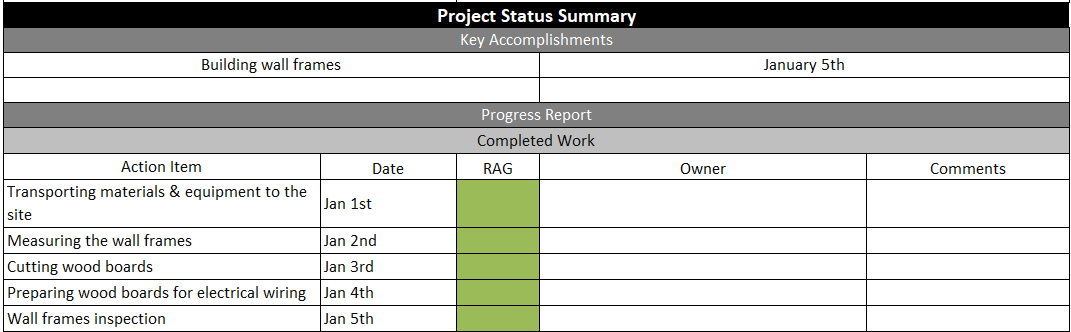
Following that is a section on upcoming work. Here you can add the action items related to electrical wiring, such as marking locations for cable boxes, electrical outputs and threading cables through the wall frames. The section following that will list project deliverables , which in this case will be the wall frames, which are the tangible output that’s been completed during the reporting period.
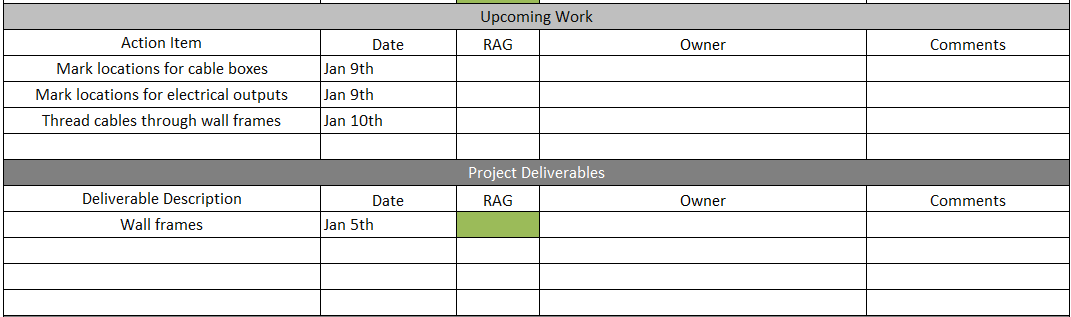
The next section is on the project’s health. It notes the budget spent over the period and what percentage that is in terms of the overall budget. There’s also an overview of the project schedule , scope and quality control and assurance.
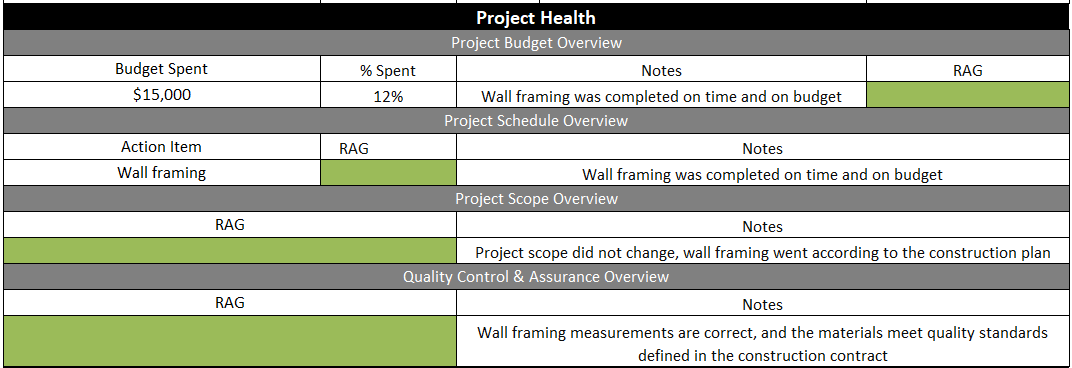
The section after that lists the risk management issues. It lists the risk, its severity, response and owner. Maybe there’s a possibility that the materials or equipment required for electric wiring won’t be delivered on time. This risk would likely be high in terms of severity as it’ll impact the project schedule. To mitigate this, another company may be contacted to see if they’ll deliver on time. You’ll also note who on the team is watching over this risk.
You’ll conclude and add any recommendations if needed. This will provide stakeholders with a clear picture of the status of the project.
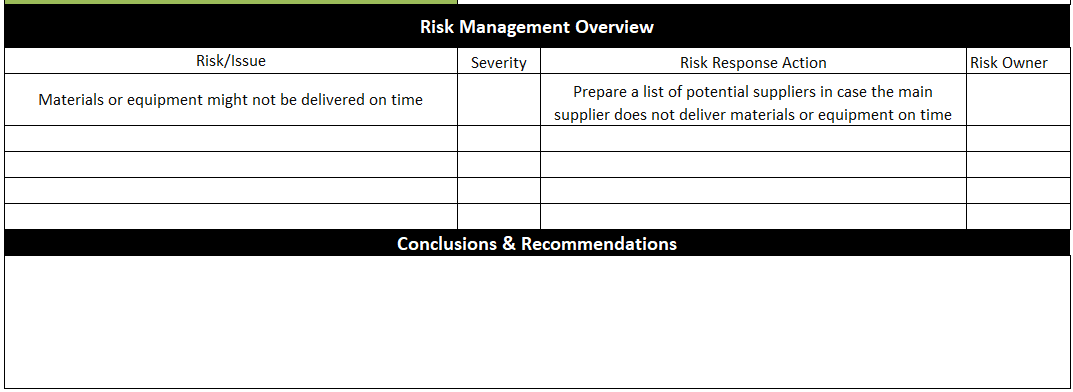
How Do You Ask for a Project Status Report?
A project status update is usually distributed on a regular schedule, but sometimes people want to see a status report immediately. You can ask for a project status update via email, but you don’t want to come across as rude. To request a project status report, you should ask in a professional manner and place your request through the proper channels.
A friendly reminder is never a bad idea, as it maintains a connection, especially if you can offer something of value in return. If you’re using project management software , then you can always get an instant status report by checking the project dashboard that tracks various metrics.
The ProjectManager dashboard delivers your project status instantly. Pull from schedules, budgets, resources and more without the possibility of human error. Then, customize your display and filter information to show only what you want to see, such as remaining resources, project health, tasks and costs. A dashboard can be an excellent alternative to the traditional project status report.
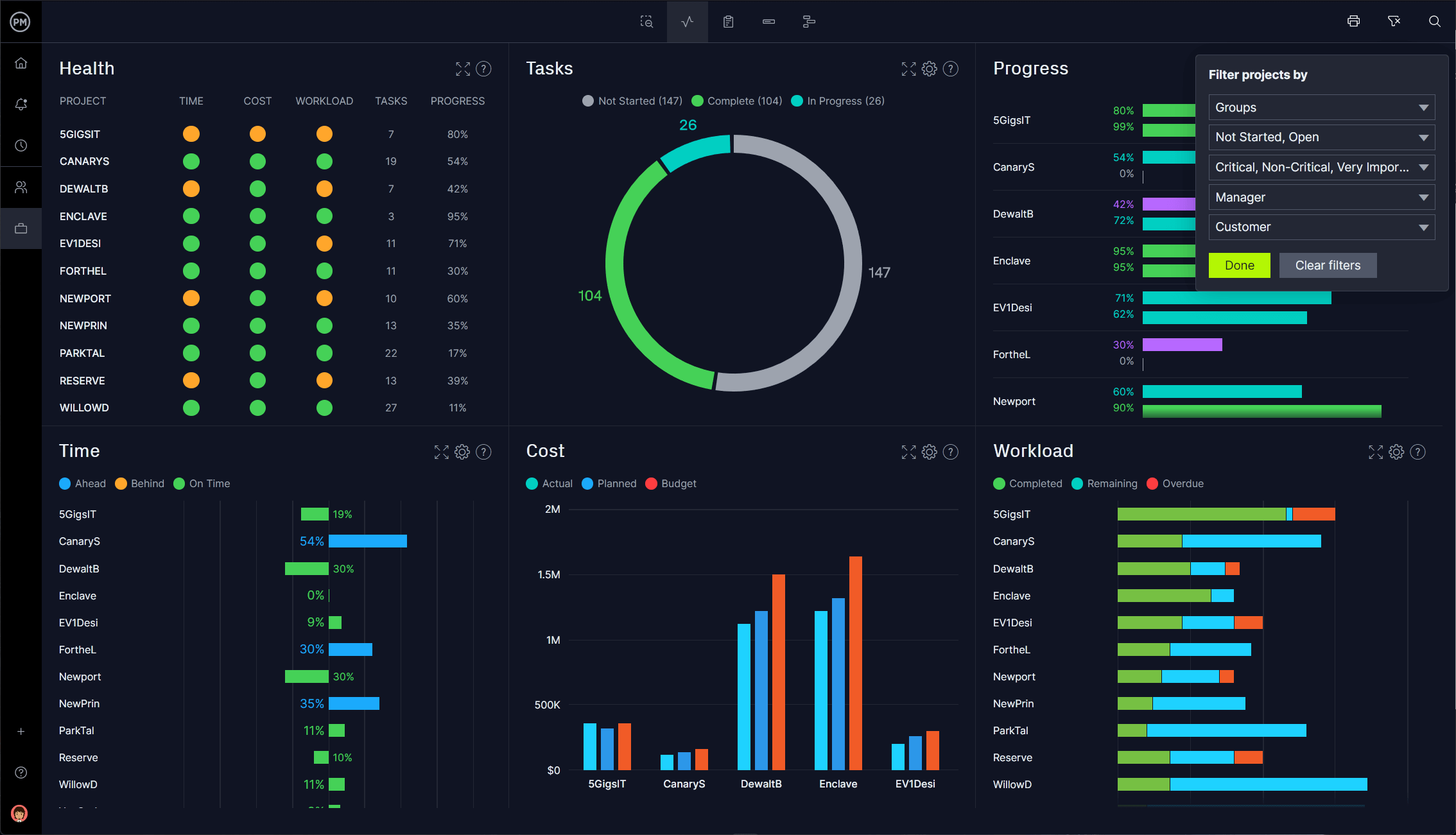
Get real-time project dashboards that you can easily share with stakeholders— Learn more.
The different elements of a project status report organize the different parts into a cohesive whole. The objective of a status report, of course, is to keep stakeholders informed and expose areas of the project that need greater organizational support.
To better communicate these things, be sure to touch on all the following when you compose your project status report.
General Project Info
To start with, you’re going to need to just put down the basics. What is the project name? Who is the project manager? What is the number of resources? All this information is essential, if obvious, to track the paperwork. Don’t assume your stakeholder is familiar with all this information. It’s especially useful when you’re doing historical research for future projects. Roll it into your status report template , if you have one.
General Status Info
Again, you’re going to want to stamp the report with data that will distinguish it from the other project management reports . So, here you want to include what date the report was generated, who the author is and so on.
Milestone Review
Milestones are the major phases of your project. They’re a good way to break up the larger project into smaller, more digestible parts. The milestone review lets you note where you are in terms of meeting those milestones (against where you planned to be at this point) in the project’s life cycle.
Project Summary
One of the main purposes of the status report is to compare the project’s progress with the project plan estimates. To do this, include a short summary of the forecasted completion date and costs of the project . This allows project managers to control the project’s execution and measure success. Be sure to include the activities that are facing issues and how those problems might impact the project’s quality, resources, timeline and costs. Explain what you’re planning to do to resolve these issues and what the results will be once you have fixed the problem.
Issues and Risks
Risks are all the internal and external factors that are a threat to your project. They become issues once they affect your project budget , timeline or scope. List the issues that have arisen over the course of the project to date. What are they? How are you resolving them? What impact they’ll have on the overall project? Apply the same questions to the risks that you’re aware of. Have they shown up? If they have, what are you doing to get the project back on track?
Project Metrics
It’s important to back your report up with hard numbers to prove the statements you’re making. You should have established the metrics for status reporting during the project planning phase .
It’s impossible to know if your project is succeeding without measuring its effectiveness. These metrics are a way to show you’re on track and evaluate what, if anything, needs attention.
Project reporting software is used to automatically collect project data, analyze it, and display the results to help project managers make better decisions when managing a project. The software gathers information from different sources within the project and converts them in spreadsheets, graphs and charts.
Depending on the software, reporting data can be filtered to highlight areas of the project that you need to see at that time. Reports can be generated on various aspects of the project’s progress and performance, such as time, cost, workload, etc.
Reports are also used to keep key stakeholders, such as sponsors and clients, updated on how the project is doing, and therefore, should be shareable.
Having a quick and easy to use tool that instantly pulls up important project data, organizes and displays it simply and clearly helps you keep stakeholders updated. With all the information at your fingertips, you can also make better decisions.
Not all reporting software is the same. To get more bang for your buck, make sure that whatever tool you choose has the following features:
- Converts complicated data into useful reports
- Filters to show only what information you want
- Allows you to create reports on specific time periods
- Share reports and keep stakeholders updated
- Update instantly for greater accuracy
- Monitor actual progress against your plan
- Report on program or portfolio of projects
Project status reports are just one of many reports that are offered by project reporting software, but you’ll also want to make sure the product you choose has the following features as well.
Get Instant Status Reports
As important as reporting software is, you also need to regularly check on the progress of your project as it occurs. A dashboard will provide that high-level view, collecting data and displaying it in graphs and charts to show a variety of project metrics.
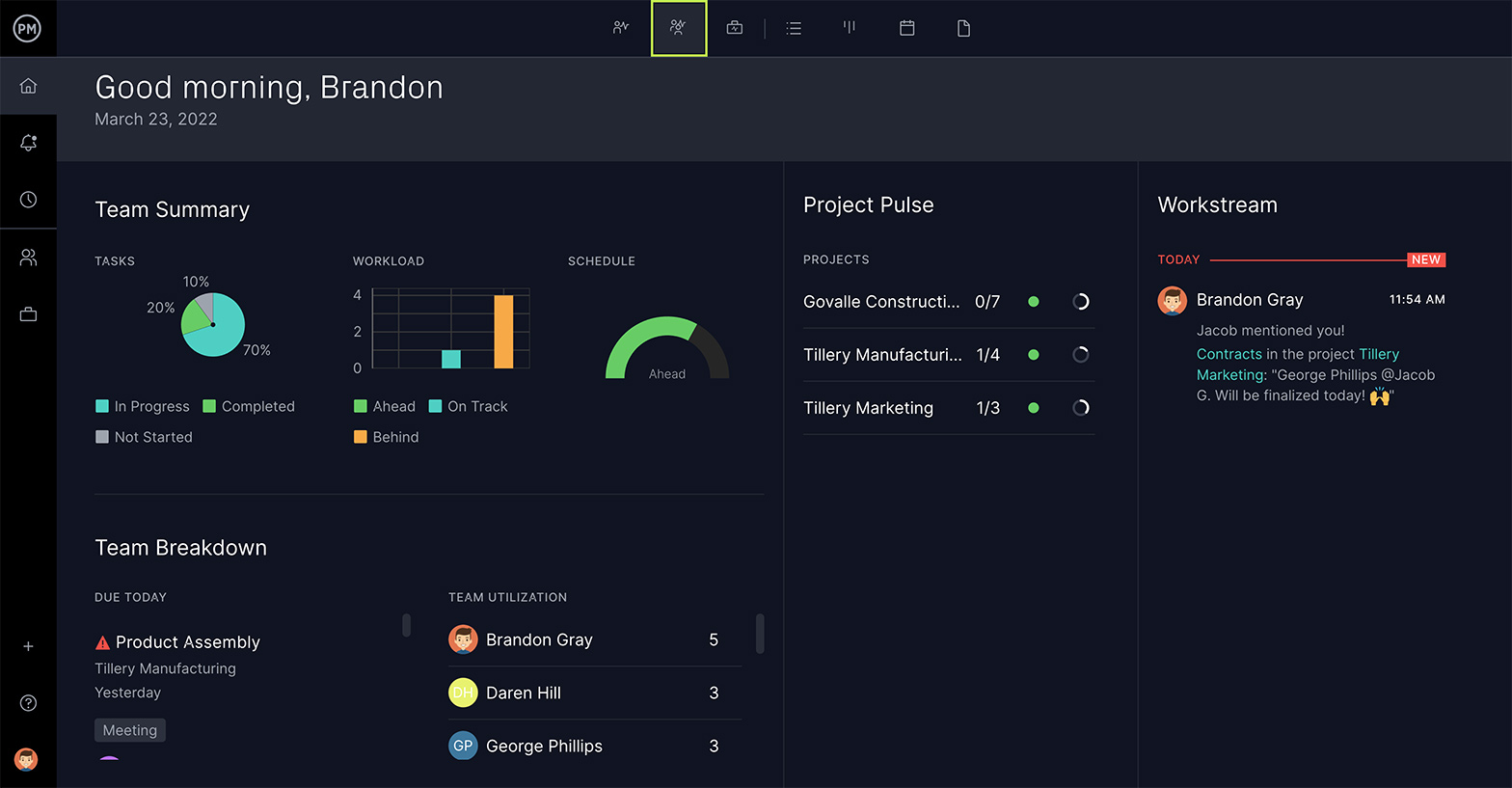
See the Most Current Info
Dashboards and reports capture the project at a particular time, and like a snapshot, capture a past point in time. However, if you’re working with an online reporting tool, the data it collects is displayed in real-time—and the decisions you make will be more informed.

Generate Reports on Every Aspect
A status report is a key gauge of how your project is performing, but it’s only one perspective. For the full picture, you need to measure progress and more for many angles. Seek out reporting software that also measures task progress, workload, timesheets and more.
Easy Export With Stakeholders
Creating reports is only the beginning. You need to share them with stakeholders, who need to have a broad strokes picture of where the project currently is. During presentations, you want to be able to easily print out a copy or export a PDF to email them.
Fast and Easy Reports
Making reports shouldn’t be time-consuming. It often means complex equations to figure out progress, variance, workload, etc. The best reporting software automates these functions, so you don’t need a math degree or even a calculator to manage your project.
Gain Details for Actionable Insights
Dashboards are great for high-level views of the project, but reports must provide a deeper dive into that data in order for managers to make the critical decisions to steer the project towards a successful end. You want reports that are in depth and cover the entire project.

Project reporting software is a tool to monitor and track project metrics in real time and then collect that data in a report that’s easily shared with project members.
ProjectManager is an award-winning tool that organizes projects and teams by monitoring and reporting on progress and performance. Watch this video to get a better idea of how to create project status and other types of project management reports with ProjectManager.
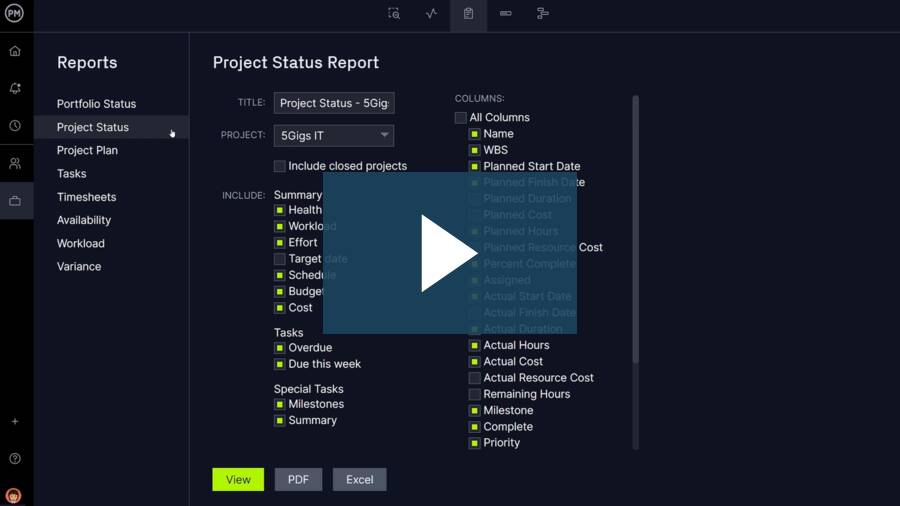
Using the reporting feature of ProjectManager allows you to see the status of project milestones and summary tasks if you filter the report to include them. Reports can be previewed before being exported to a PDF, Excel, CSV or printed. Every report can be customized by selecting the data and columns you want to include.
Here are some of the reports you can create once you have the project management software.
Project Status Report
As mentioned above, the project status gives an overview of where your project currently is, and lets you determine if the project is on time and under budget . It shows the tasks that are due on the week it has been generated, and which are overdue.
Here’s a quick rundown of the options when generating a status report in ProjectManager.
Get the key elements of your project condensed in short to capture the high points in your schedule, budget and costs for stakeholders. You can provide project updates at any time for your team, clients and sponsors.
See which tasks are overdue and when their deadline is to never lose track of your progress and stay on schedule. ProjectManager allows you to assign activities to your team members and communicate with them in real time.
Milestones & Summary Tasks
Note which milestones have been completed to better track the project’s progress. View where you are in terms of completing summary tasks or subtasks on your schedule.
Planned vs. Actual
Know your project variance by tracking the actual progress on the status report, which is compared to where you planned to be at that point in your schedule.
Portfolio Status Report
A portfolio is a collection of projects that one manages. They must work together in alignment with the overall strategy of the organization.
See the health of your full portfolio, and if they’re meeting their schedules and budgets. Get lists of your project managers, team and tasks to better determine your portfolio’s overall health.
Project Plan Report
The project plan is the map that guides your activity when managing a project. This report lets you know whether that plan is being met by your actual progress.
Keep your project on track, within budget and know how far you are from completion. Get an overview of your schedule and a list of all the tasks and when they should be done.
Project Dashboard
Different from the previous reports, which are static documents that are exported as a snapshot of a project, a dashboard can serve as a contemporaneous look into the project.
Get real-time status reports using our project dashboard . Every facet found in a status report is automatically updated across the six metrics of the dashboard for a high view of your project’s performance.

Portfolio Dashboard
Much like the project dashboard, the portfolio dashboard serves as a real-time view, except for a collection of projects rather than a single one.
Set up a portfolio dashboard by creating a folder in the overview projects section. Add projects you want to measure and your portfolio dashboard will track their costs, workload and more.
Whether you’re presenting your weekly status report in a meeting, or sending a weekly email update, it’s a good idea to know the best practices when reporting on a project’s progress before jumping into a presentation of your report.
Communicate
Project status reports are only a single facet of your communication plan . Don’t rely on it fully to communicate everything, but use it to deliver the right data to the right party at the right time.
Know Your Audience
Project status reports are vehicles for communication, but if you’re unsure of the destination, then you’re not going to deliver the goods. Stakeholders such as clients and sponsors want to know the big picture, while team members will be more interested in specifics.
Consistency
Use the same format, distribution cycle and method. Don’t mix things up. That only disrupts the effectiveness of the communication aspect of the report.
Establish Metrics
When planning for the project, figure out how you’re going to measure its progress, and then stick to this method as you report on the project throughout its life cycle.
You want the report to be effective, so don’t obscure it with unnecessary details. Stay to the point, and just report on what needs reporting.
Your audience doesn’t want opinions or unsubstantiated facts. Do the due diligence, and make sure that you’re giving only what your audience wants.
Like consistency, keeping standards of a process and a template for reporting makes sure your report is clear.
There are project management tools that incorporate these best practices, streamlining the reporting process thanks to dashboards and automated reporting features.
Status reports are just one of the many reports project managers use to keep updated on the progress of their projects. Status is more general, while others focus on specific aspects of the project. Some of the more common status-reporting alternatives follow.
Tasks Report
Every project is made up of tasks, often lots of them. You need a report to keep track of them all.
Get all your project tasks collected in one place. Filter the report to show the status of each task to see if there are any roadblocks or bottlenecks holding up progress. You need to take care of issues before they affect your project’s timeline.
Timesheets Report
Teams log their hours on timesheets to submit to managers for payroll. Timesheets are also another way to track progress on a project by monitoring the hours logged on tasks.
View the timesheet of selected team members and know the hours they worked over a range of time using online project management software.
Availability Report
Keeping track of when your team can work when they have paid time off or there’s a holiday is critical to scheduling and workload management.
Know instantly who has too much work on your team and if they’re available to work. Team members are listed in this report with utilization rates. This data helps you reallocate tasks.
Workload Report
The workload is the number of tasks your team has been assigned. Keeping their workload balanced, so no one has too much on their plate, is how you increase productivity and morale.
See your entire team with the number of tasks they’ve been assigned. Know if someone has too many or too few tasks and balance their workload to get more done and not burn people out.
Variance Report
The variance is the difference between what you planned for the project and where you actually are in its execution. This is how you know if your project’s on track or not.
Set the baseline on the Gantt chart tool when planning and get data on your current schedule. Then, compare it against where you planned to be at this point in the schedule.
ProjectManager is a cloud-based software with one-click reporting that seamlessly integrates with planning, scheduling and tracking features. Get real-time data that can be filtered and shared across eight different project reports. With us, you can use one software for all your project management needs.
Companies such as the Bank of America, and organizations such as NASA and the US Postal Service, have used us to manage big and small projects. Over 10,000 teams worldwide get more control over their work and become more productive using our software.
If you want to simplify the reporting process and are looking for a tool that with online Gantt charts , kanban boards to visualize workflow and a dashboard for a high-level view of project metrics, then try our tool free with this 30-day trial .
Start Your Free Trial
Status Report Resources
- Project Reporting Software
- Project Dashboard Software
- Free Project Report Templates
- Communications Plan Template
- Project Dashboard Template
- 5 Lifesaving Project Reports
- How to Track and Report on Projects
- What Are Project Deliverables?
Start your free 30-day trial
Deliver faster, collaborate better, innovate more effectively — without the high prices and months-long implementation and extensive training required by other products.
For enquiries call:
+1-469-442-0620

- Project Management
Project Report: Objectives, Types, Use Cases, Templates
Home Blog Project Management Project Report: Objectives, Types, Use Cases, Templates
Managing a project and creating a project report is not a cakewalk. A project consists of a lot of parameters, and if not analyzed properly, it can result in an unsuccessful end of project report. Project reports are extremely useful for project managers as they allow managers to send regular updates about the projects to the company's stakeholders.
A detailed project report is very insightful since it allows the team members to track the project's status, offer suggestions to improve the project and mitigate risks. Project reports effectively transform the entire journey as they offer clarity regarding every project step.
While management professionals can enrich their knowledge with Project Management certifications by KnowledgeHut to explore project management in-depth, this article will walk you through the basic objectives of a project report, how to create one, and its practical applicability in today's world.
What is a Project Report?
A project report is a document that specifies the status of a project and other related information. In other words, it is a report that includes all the details about a project, navigating each step with great insight. This document helps to ascertain the feasibility of the activities or plans taken to fulfill a particular project's objectives.
The project progress report is a written document that includes all the information about the objectives, challenges, and milestones of the project. It is regularly updated as it tracks the project status and plays a crucial role in planning and managing any project.
A project manager prepares the project status report to update the stakeholders about the progress of the project regularly. The role of a project manager requires them to collaborate with other departments to draft an effective project report.
Why Project Report is Important?
Many believe that a project report is used to raise funds for a specific project or get sponsors. True, it is. But that's not all the purpose of a project plan. It is more than just about the funding. Writing a project report is a valuable process. Here are all the reasons why project reports are important.
- Writing a project report helps you understand and discover what it takes to make your project a success.
- Project reports offer clarity on your ideas. You should also be able to explain the concept to others before sharing your strategies and ideas with investors or friends.
- Planning and creating is worth it if a report helps you avoid making costly mistakes, wasting time, and losing money.
- A project report can increase your chances of a successful project by ensuring that the project manager can record, review and report progress against the baselines and add underlying data as required.
- Numerous studies over the years have shown that companies who plan are more likely to get funding, be successful, and reach their goals than those who don't.

Objectives of a Project Report
Project reports are of immense importance as it is an important tool for analyzing the progress of various projects. If you want to learn why a project manager should create a project report, sign up for the PMP certification to upskill yourself!
The main objectives of a project report are as follows:
1. Requesting permission for an investment plan
A final project report is an insightful document that helps to make new investment plans. It allows the project manager to see and evaluate the expected profits and associated risks in a new project. Project reports are also important for the purpose of registration and approval.
If the stakeholders are satisfied with the project status report, they may allow project managers to take up new projects and make investments in new areas.
2. Tracking the progress of the project
A project report is a summary of the entire process and steps that have been taken to complete the project. It is an effective means of keeping track of the progress of the project. This document helps to point out the steps that have proven beneficial for a project and what has gone wrong.
Tracking a project is important as it helps to find any deviations from the original plan. The stakeholders also feel content as they are updated about the project regularly.
3. Locating and mitigating risks
As a project report provides detailed information about the project, identifying risks is easier. It helps to locate any risks or confusion that are in contrast with the original plan. Additionally, a project report eliminates the risks by taking connective action so as to avoid any downfall regarding the project.
4. Deciding on a budget and managing costs
Since a project report shows the details of all the activities, it very well pinpoints the expenses. So before starting a project, this report helps predict the cost in certain areas so that a proper budget can be drafted. It also takes into account certain considerations that can cause variations in the predicted costs. Following a data-driven approach to budgeting, expenditures can be kept under vigilance leading to profitable project curation.
Hence, a project report establishes the financial stability and viability of a project. It states the income possibility, degree of risk, list of expenses, and various other relevant factors.
5. Asking for financial assistance
Whenever an organization needs financial assistance, providing previous project reports is a great way of attracting funds. When a financial institution will be content that the concerned company is capable of running successful projects, the financial institution will not hesitate to provide financial assistance to such companies.
Characteristics of Project Report
A clear definition is essential for any project to be effective, useful, and achieve its full potential. Clearly defined projects project reports have the following five characteristics:
The project report provides a clear overview of the tasks and goals. The report describes the project's goals and the activities that will be done to achieve them. Only a feasible project can be considered meaningful. It is not a good idea to be too ambitious when planning a project. This could lead to the project not being possible. This could also affect the team morale. These unhealthy situations can lead to high project costs and delayed delivery dates.
2. Resource
It identifies the resources and means required to achieve the desired scope. The project report is the blueprint that outlines the direction the business should take to achieve its goals. Project reports should theoretically be objective 100 percent. They are created by humans tasked with analyzing other people's work, which is bound to produce some subjectivity and opinions. It is crucial to back up your assessment and perspective with hard facts.
It should also be time-bound to make sure that everything is clearly defined. This means that the project must have a defined timeframe for completion. It should include planning, development, execution, and fine-tuning. The project shouldn't take forever to complete. All parties should justify any changes to this timetable, considering the cost of the project's execution, potential costs, and finance costs.
A well-structured report on a project allows for quick access to pertinent information regardless of whether it is relevant to the reader. The hierarchy organizes information in a way that makes it easy to find the most important and useful facts first, and then the technical details are placed in the subordinate sections.
Executives can gain an instant yet comprehensive understanding of the work done. Managers closer to the project have a logical method of finding and reviewing relevant information for themselves and their departments.
Even projects that seem to be moving along smoothly can still have some problems that could cause trouble later on. Every business face risk and must be monitored. The project report will include information about all possible risks that could affect the project's completion and the best ways to recover from the invested money.

Types of Project Report
Here's a brief overview of eight of the most commonly used types of reports; however, they are still vital to the smooth running of the project:
1. Status Reports
One of the most popular report types, Status Report, refers to a type of document that comprises a detailed analysis of the timely progress or status of any project with regard to the planned steps and the decided timeline. The status report enables team members and stakeholders to keep track of the project's progressions.
Instead of narrating lengthy project time and again, project managers rely on this report to briefly offer an insight into the project outline, keeping the process entirely transparent for everyone on the team. A status report will require you to keep track of significant changes, compile them briefly and present them comprehensively.
2. Progress Reports
The most crucial report you'll produce during the course of running an undertaking includes the status report. It's a report that changes the information regarding your project, especially to determine if it's meeting the standards established by the schedule and budget. Another way to update your stakeholders on what the project's status is at the present moment. It is important to be precise in your progress report.
Take note of the information, and create a concise introduction that contains the name of the undertaking, your contact information as well as a short summary of the progress of the project as well as general information regarding the timeframe as well as estimated cost, and completion.
3. Risk Reports
This type of report assists in presenting the steps taken by the risk management team for the teams working on the project or the people who are involved. It records the effective management of emerging and current risks associated with the project. The risk report must include an outline of the overall risk assessment for the project. It should also include details about the risks that could have the possibility of cutting the project as well as the ways you intend to deal with them.
4. Board/Executive Reports
Reports on projects must be tailored to the individuals who will be reading them. Therefore, the report you write for your project board will have a different amount of detail when compared to those who receive the monthly status report that you send the project group as well as the key stakeholders of the business for reports on the project board focus on high-level.
They will want to know about the things that matter to them, such as issues they could help solve, a synopsis of your budget's position, and whether you're on the right track to meet crucial milestones. It is important that your report to the board is presented in a manner that they are able to understand easily.
5. Cost Benefit Analysis Report
In determining if a venture is feasible, one of the reports you'll need to conduct is a cost-benefit analysis report. It's a means of comparing the magnitude of advantage or benefit the project can bring to your company in relation to the cost of investment. It's the most important step when deliberating if the idea is a good one from a business point of view. It is crucial to determine if the project you are considering has value.
This will allow your company to make the most of its resources when it moves ahead with the project and provide the documents to help move forward in the initiative's direction. Using cost analysis to monitor your expenditure and spending is possible to ensure that funds are appropriately allocated. The cost-benefit analysis will show what you're expected to pay for a particular project and then compare it to the advantages or opportunities you'll receive after completing it.
6. Resource Reports
This kind of report on the project permits the project team, as well as the participants, to see how resources are distributed throughout the various tasks that are part of the plan. The report on project resources will detail the members of the project team who are assigned to which job on what day. The report on resource allocation can help to highlight the problem of the under-allocation of resources for projects.
7. Variance Reports
The variance report is helpful for comparing the plans against the actual outcomes of the undertaking. It can be used to determine whether the project is in front of its schedule or over schedule. Additionally, the variance report can analyze and arrange the details of what you're measuring in a project. It can be a budget or a scope.
8. Gap Analysis Report
When you're managing a task or elevating your company to the next level, you'll need an analysis report that will guide you From Point A to Point B. This is known as the gap analysis report. It will let you know whether you're meeting your goals and if you're making use of resources efficiently. A gap analysis report evaluates the present state of your project or business in terms of money, time as well as labor and examines it in relation to the goal condition it hopes to reach. After defining and analyzing the gap between these two points, an action plan can be created to plan the tasks needed to reach the goal.
6 Steps to Write a Project Report
Creating a project report is crucial for determining any project's success. Documenting all the steps in a project and sharing it with other departments helps to learn the basic do's and don'ts whenever taking up any project.
Project report writing involves the following major steps:
Step 1. Set the Objective
When initiating a new project, the first step is to set the objective or goals. Once a company has identified its objectives, the process of measuring its progress and success simplifies. Take a moment and list the reasons for creating a project report. Having clear project objectives will help reduce work redundancy and be on track for everyday tasks.
Step 2. Recognize Your Audience
Not the entire world is the target audience for any project. A project manager has to recognize the perfect audience to which the project caters. It is extremely important to know the taste and preferences of the target audience. What they like and dislike helps to draft a project report that is easily understandable for the audience.
Step 3. Know The Format
A corporate document mainly consists of a particular format. A project progress report is also a formal document, and hence it needs to be drafted in a format that has some labels and templates. However, it is upon the project managers whether they choose a new report template or select any existing ones. It is always better to select a comprehensive template that effectively conveys the agenda behind the project report.
Step 4. Data Collection
A project report is supposed to have sufficient data that can act as proof of what activities have taken place. Data collection is a significant aspect of creating a project report, as everything depends upon data. Accurate data constitutes a major part of the project report, which estimates the successful and lagging segments of a project through relevant data-driven insights. Data can be extracted from various sources such as surveys, international agencies, case studies, interviews, etc.
Step 5. Structure of the Report
The structure of the report basically talks about the presentation of the report. A project status report should be prepared in a manner that is comprehensive, consumable, visually approachable, and easy to understand. The project report structure consists of the following points:
- Summary: Summer is written as a part of the project completion report. It gives readers a brief idea of what the project is all about. The summary is provided at the start of a project report but can only be written once the entire project is completed.
- Introduction: The introduction provides an outline of the report. It gives a clear idea about the topic of the project but does not consist of intricate details. Introduction talks about the scope and the common methodologies used in the project.
- Body: The body constitutes the main section of the report. It consists of all the details and is the longest part of the document. The body includes all the research, analysis, background information, graphics, and so on.
- Conclusion: Being the last section of a report, this marks the end of a project where a clear and concise version of the entire project is presented. It brings the report together.
Step 6. Edit & Review
After the completion of the entire project report, project managers read it to find any gaps to fill. Once the required edits are made, and the review is done, the report gets a check to move forward.
Use Cases of Project Reports
There are a lot of use cases for project reports in the sphere of project management. The best PRINCE2 online course by KnowledgeHut can help you learn the usage of project reports in project management in a more definite way. However, the most common use cases of project reports are enumerated as follows:
1. Preliminary Project Report
A preliminary project report is a document that states the activities and the course of action that will be taken in fulfilling the objectives of the project. This report is prepared in the identification stage and before the start of the project. It mainly includes the following heads:
- The reason for initiating the project (why).
- The activities that are to be done (what).
- The list of associated members of the project (who).
- Timeline of starting and completing the project (when).
- the course of action to be taken for completing the project (how).
2. Project Progress Report
A project progress report is a document that mainly focuses on and lists the everyday progress made by the development team. It tracks the everyday activities of the team members, which is essential for determining the progress of the project. It navigates all the tasks that are completed, ongoing tasks, and yet to be accomplished. That means the amount of work pending and work completed both are present in a project progress report.
3. Project Status Report
A project status report is a document that evaluates the current status of a project. It is inclusive of the project performance and project health. A project status report example can be the communication of the current position of the project to other concerned members and stakeholders.
It also compares the current project status with the original project plan simultaneously to align requirements with the timeline. If a project manager wants to make any amended plan in due course of the project, that is also included in the project status report.
4. Project Time Tracking Report
A project time tracking report is a document that deals with allocating a time period for each task. With this report, the stakeholders can easily understand how much time a particular task has taken to be accomplished. It is a document that can help to locate the areas that are efficient and the areas that need improvement, leading to better productivity among team members.
It is a comprehensive document with a vast scope and includes aspects like tasks, project status, the performance of the team members, and the completion status of the same.
5. Project Performance Report
A project performance report is a document that presents an outline of the status and progress of the project. Additionally, it lists the allocation of resources and the value obtained under them. The report also comprises a breakdown of expenses through the project curation timeline.
The performance report matches the expected budget and the actual costs to analyze the performance of the project. This report is also an important tool for predicting the outcome.
6. Project Health Report
A project health report is a document that states the possible risks that are associated with the project. Preparing a project health report can help ditch risks that may occur in the future. It also lists possible ways of mitigating those risks if the team members are faced with any when the project is ongoing.
7. Project Completion Report
A project completion report is a document that is prepared when the project comes to an end. This report evaluates the overall success of a project and matches the outcomes with the objectives. It is the last document that is submitted in a project report. As a project manager records every detail of the tasks and activities of a project, this report should be detailed, intricate, and compiled with utmost vigilance.
A project completion report makes it easier to conduct an evaluation of the same. The final evaluation is carried out when the project ends to determine the degree of success.
Benefits of Project Report
Project managers and executives use reporting because it is useful in many areas of running a company. The following are some of the most popular benefits of project management reports:
- Budgeting Can be More Precise: Businesses can accurately predict the cost of each project by understanding the costs involved in different aspects. Companies can do this to ensure that they have enough funds in order to finish a project. This helps companies determine if a project is worthwhile.
- Create Realistic Schedules: Project reports can help companies decide which projects they will undertake. A detailed schedule can also aid companies to create realistic budgets and determine when and where they may encounter problems.
- Enhance Project Visibility: Project management reports help keep communication open between project managers, managers, and other stakeholders throughout the project. The reports increase visibility and allow more people with experience to share their thoughts and suggestions on increasing project productivity, reducing costs, or any other advice that could help to make the project a success.
- Minimize Risks in a Project: Managers can prepare for or even eliminate risks in project management reports. Potential risks can be reduced, and projects will be completed faster and more efficiently if you prepare for them.
- Better Management: Project managers and executives can improve their ability to manage projects accurately by using all the information in project management reports. They enable project managers and executives to understand every aspect of a project so they can make adjustments, add tasks or remove them if necessary, and communicate new expectations to their team.
- Improvement Made for the Future: Managers can benefit from project management reports to increase the quality of their future projects. Each report can help you learn what works well in projects and where there are improvements.
If you want to learn more about project report benefits, we suggest PRINCE2 training to boost your project management learning.
Download Printable PDF of Project Report
While project report can simplify work process by adding transparency to your project, they can be lengthy and monotonous tasks. Creating a project report right from scratch might take you hours, taking up the precious time you could have applied on your project. Therefore, we bring your a project report template to reduce your hassle. Check the Project Report PDF or project report on project management for reference.
Transform your management approach with agile methodologies course . Discover how to adjust, cooperate, and create like never before.
Wrapping Up
A project report is an extremely valuable instrument for carrying out a successful project. It states various aspects of a project, such as its overall performance, allocation of resources, everyday progress, and ultimately the whole timeline till completion. The major benefit of a detailed project report is that it has the potential to convince the stakeholders and investors to invest more funds in the project.
A project report is the most important instrument that lets the stakeholders and end users know the present status of any project. If you want to implement your best in project management while learning how to draft an impressive project report, check out KnowledgeHut's Training in Project Management . This training will take you through a detailed curriculum of how to become a successful project manager in the long run!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A project report is important because it summarizes the objectives, budget, resources, timeline, and every other important aspect related to a project. It also enables the project managers to track the outcome and progress of the project. Additionally, it conveys the status of the project to the stakeholders.
An ideal project report should be 1 or 2 pages long. It is a concise document that lets the concerned people know what is on schedule and what is lagging.
A project report includes the progress report, budget, timeline, risks and risk management, resources, and the nature and scope of the project.
The need for managers of projects is extremely high. The PMIProject Management Institute Project Management Institute expects 22 million new jobs to be created by 2027.

Kevin D.Davis
Kevin D. Davis is a seasoned and results-driven Program/Project Management Professional with a Master's Certificate in Advanced Project Management. With expertise in leading multi-million dollar projects, strategic planning, and sales operations, Kevin excels in maximizing solutions and building business cases. He possesses a deep understanding of methodologies such as PMBOK, Lean Six Sigma, and TQM to achieve business/technology alignment. With over 100 instructional training sessions and extensive experience as a PMP Exam Prep Instructor at KnowledgeHut, Kevin has a proven track record in project management training and consulting. His expertise has helped in driving successful project outcomes and fostering organizational growth.
Avail your free 1:1 mentorship session.
Something went wrong
Upcoming Project Management Batches & Dates
- Project Evaluation
- Project Management Methodologies
- Project Management Metrics
- Project Portfolio Management
- Proof of Concept Templates
- Punch List Templates
- Requirement Gathering Process
- Requirements Traceability Matrix
- Resource Scheduling
- Roles and Responsibilities Template
- Stakeholder Engagement Model
- Stakeholder Identification
- Stakeholder Mapping
- Team Alignment Map
- Team Charter
- Templates for Managers
- What is Project Baseline
- Work Log Templates
- Workback Schedule
- Workload Management
- Work Breakdown Structures
- Agile Team Structure
- Avoding Scope Creep
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts
- Precision VS Accuracy
- Scrum-Spike
- User Story Guide
- Creating Project Charters
- Guide to Team Communication
- How to Prioritize Tasks
- Mastering RAID Logs
- Overcoming Analysis Paralysis
- Understanding RACI Model
- Critical Success Factors
- Deadline Management
- Eisenhower Matrix Guide
- Guide to Multi Project Management
- Procure-to-Pay Best Practices
- Procurement Management Plan Template to Boost Project Success
- Project Execution and Change Management
- Project Plan and Schedule Templates
- Resource Planning Templates for Smooth Project Execution
- Risk Management and Quality Management Plan Templates
- Risk Management in Software Engineering
- Stage Gate Process
- Stakeholder Management Planning
- Understanding the S-Curve
- Visualizing Your To-Do List
- 30-60-90 Day Plan
- Work Plan Template
- Weekly Planner Template
- Task Analysis Examples
- Cross-Functional Flowcharts for Planning
- Inventory Management Tecniques
- Inventory Templates
- Six Sigma DMAIC Method
- Visual Process Improvement
- Value Stream Mapping
- Creating a Workflow
- Fibonacci Scale Template
- Supply Chain Diagram
- Kaizen Method
- Procurement Process Flow Chart
- Guide to State Diagrams
- UML Activity Diagrams
- Class Diagrams & their Relationships
- Visualize flowcharts for software
- Wire-Frame Benefits
- Applications of UML
- Selecting UML Diagrams
- Create Sequence Diagrams Online
- Activity Diagram Tool
- Archimate Tool
- Class Diagram Tool
- Graphic Organizers
- Social Work Assessment Tools
- Using KWL Charts to Boost Learning
- Editable Timeline Templates
- Kinship Diagram Guide
- Power of Visual Documentation
- Graphic Organizers for Teachers & Students
- Visual Documentation Techniques
- Visual Tool for Visual Documentation
- Conducting a Thematic Analysis
- Visualizing a Dichotomous Key
- 5 W's Chart
- Circular Flow Diagram Maker
- Cladogram Maker
- Comic Strip Maker
- Course Design Template
- AI Buyer Persona
- AI Data Visualization
- AI Diagrams
- AI Project Management
- AI SWOT Analysis
- Best AI Templates
- Brainstorming AI
- Pros & Cons of AI
- AI for Business Strategy
- Using AI for Business Plan
- AI for HR Teams
- BPMN Symbols
- BPMN vs UML
- Business Process Analysis
- Business Process Modeling
- Capacity Planning Guide
- Case Management Process
- How to Avoid Bottlenecks in Processes
- Innovation Management Process
- Project vs Process
- Solve Customer Problems
- Spaghetti Diagram
- Startup Templates
- Streamline Purchase Order Process
- What is BPMN
- Approval Process
- Employee Exit Process
- Iterative Process
- Process Documentation
- Process Improvement Ideas
- Risk Assessment Process
- Tiger Teams
- Work Instruction Templates
- Workflow Vs. Process
- Process Mapping
- Business Process Reengineering
- Meddic Sales Process
- SIPOC Diagram
- What is Business Process Management
- Process Mapping Software
- Business Analysis Tool
- Business Capability Map
- Decision Making Tools and Techniques
- Operating Model Canvas
- Mobile App Planning
- Product Development Guide
- Product Roadmap
- Timeline Diagrams
- Visualize User Flow
- Sequence Diagrams
- Flowchart Maker
- Online Class Diagram Tool
- Organizational Chart Maker
- Mind Map Maker
- Retro Software
- Agile Project Charter
- Critical Path Software
- Brainstorming Guide
- Brainstorming Tools
- Visual Tools for Brainstorming
- Brainstorming Content Ideas
- Brainstorming in Business
- Brainstorming Questions
- Brainstorming Rules
- Brainstorming Techniques
- Brainstorming Workshop
- Design Thinking and Brainstorming
- Divergent vs Convergent Thinking
- Group Brainstorming Strategies
- Group Creativity
- How to Make Virtual Brainstorming Fun and Effective
- Ideation Techniques
- Improving Brainstorming
- Marketing Brainstorming
- Rapid Brainstorming
- Reverse Brainstorming Challenges
- Reverse vs. Traditional Brainstorming
- What Comes After Brainstorming
- Flowchart Guide
- Spider Diagram Guide
- 5 Whys Template
- Assumption Grid Template
- Brainstorming Templates
- Brainwriting Template
- Innovation Techniques
- 50 Business Diagrams
- Business Model Canvas
- Change Control Process
- Change Management Process
- Macro Environmental Analysis
- NOISE Analysis
- Profit & Loss Templates
- Scenario Planning
- What are Tree Diagrams
- Winning Brand Strategy
- Work Management Systems
- Balanced Scorecard
- Developing Action Plans
- Guide to setting OKRS
- How to Write a Memo
- Improve Productivity & Efficiency
- Mastering Task Analysis
- Mastering Task Batching
- Monthly Budget Templates
- Program Planning
- Top Down Vs. Bottom Up
- Weekly Schedule Templates
- Kaizen Principles
- Opportunity Mapping
- Strategic-Goals
- Strategy Mapping
- T Chart Guide
- Business Continuity Plan
- Developing Your MVP
- Incident Management
- Needs Assessment Process
- Product Development From Ideation to Launch
- Value-Proposition-Canvas
- Visualizing Competitive Landscape
- Communication Plan
- Graphic Organizer Creator
- Fault Tree Software
- Bowman's Strategy Clock Template
- Decision Matrix Template
- Communities of Practice
- Goal Setting for 2024
- Meeting Templates
- Meetings Participation
- Microsoft Teams Brainstorming
- Retrospective Guide
- Skip Level Meetings
- Visual Documentation Guide
- Weekly Meetings
- Affinity Diagrams
- Business Plan Presentation
- Post-Mortem Meetings
- Team Building Activities
- WBS Templates
- Online Whiteboard Tool
- Communications Plan Template
- Idea Board Online
- Meeting Minutes Template
- Genograms in Social Work Practice
- Conceptual Framework
- How to Conduct a Genogram Interview
- How to Make a Genogram
- Genogram Questions
- Genograms in Client Counseling
- Understanding Ecomaps
- Visual Research Data Analysis Methods
- House of Quality Template
- Customer Problem Statement Template
- Competitive Analysis Template
- Creating Operations Manual
- Knowledge Base
- Folder Structure Diagram
- Online Checklist Maker
- Lean Canvas Template
- Instructional Design Examples
- Genogram Maker
- Work From Home Guide
- Strategic Planning
- Employee Engagement Action Plan
- Huddle Board
- One-on-One Meeting Template
- Story Map Graphic Organizers
- Introduction to Your Workspace
- Managing Workspaces and Folders
- Adding Text
- Collaborative Content Management
- Creating and Editing Tables
- Adding Notes
- Introduction to Diagramming
- Using Shapes
- Using Freehand Tool
- Adding Images to the Canvas
- Accessing the Contextual Toolbar
- Using Connectors
- Working with Tables
- Working with Templates
- Working with Frames
- Using Notes
- Access Controls
- Exporting a Workspace
- Real-Time Collaboration
- Notifications
- Meet Creately VIZ
- Unleashing the Power of Collaborative Brainstorming
- Uncovering the potential of Retros for all teams
- Collaborative Apps in Microsoft Teams
- Hiring a Great Fit for Your Team
- Project Management Made Easy
- Cross-Corporate Information Radiators
- Creately 4.0 - Product Walkthrough
- What's New
How to Write a Solid Progress Report for Project Success

Progress reports are like project status updates that help everyone involved understand how things are going. Writing a solid progress report is crucial for keeping your project on track and ensuring its success. In this guide, we’ll break down the process of creating a great progress report, making it easy for you to communicate your project’s progress effectively. We have also included progress report templates for you to get started right away.
Progress Report Template
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

What is a Progress Report
A progress report is a document that provides an overview of the status, advancements, and achievements of a project or task. It typically outlines what has been accomplished, what is currently in progress, and any challenges or obstacles encountered. Progress reports are commonly used in various settings, such as work, education, or personal projects, to keep stakeholders informed about the project’s developments and to ensure everyone is on the same page regarding the current state of affairs.
Progress Report Templates to Keep Track of Project Progress
Daily Progress Report Template
Project Status Report Template
Project Status Summary
Project Dashboard Template
Project Status Summary Template
Why You Need to Use a Progress Report
A progress report promotes a culture of collaboration, accountability, and continuous improvement in project management. Here are several reasons why a progress report is important.
Clear communication: Keeps everyone on the same page by sharing what’s happening in a project.
Tracking achievements: Highlights what has been successfully completed, boosting team morale.
Problem-solving: Identifies and addresses challenges, helping to find solutions and stay on track.
Decision-making: Provides real-time information for informed decision-making during the project.
Accountability: Holds team members responsible for their tasks and deadlines.
Learning and improvement: Creates a record of progress, facilitating learning for future projects.
Efficiency: Keeps the team working efficiently by preventing confusion and misunderstandings.
Collaboration: Encourages collaboration and coordination among team members.
Key Components of a Progress Report
The following components of a progress report collectively provide a comprehensive view of the project’s progress, challenges, and future plans, enabling effective communication and decision-making.
- Introduction : Brief overview of the project, including its purpose and objectives.
- Work completed : Summary of tasks or milestones achieved since the last report.
- Work in progress : Description of current activities, tasks underway, and their status.
- Challenges and issues : Identification and discussion of any problems, roadblocks, or challenges faced.
- Achievements : Recognition and celebration of significant accomplishments and milestones.
- Upcoming tasks : Outline of the next steps, tasks, or milestones planned for the future.
- Timeline and schedule : Review or adjustment of the project timeline or schedule, if necessary.
- Budget overview : Overview of the project’s financial status, including spendings and any budget changes.
- Recommendations : Suggestions for improvements or changes to improve project efficiency.
- Conclusion : A brief summary and conclusion, often including an overall project status assessment.
Challenges of Creating and Using a Progress Report
While project reports are handy for keeping track of project progress, they can pose some challenges.
Time-consuming: Writing a progress report can take time away from actual project work.
Communication issues: Making sure that everyone understands the report may be challenging.
Data accuracy: Getting accurate information for the report can sometimes be difficult.
Overlooking details: Important details may be unintentionally left out.
Balancing detail and brevity: Finding the right level of detail without making the report too lengthy can be tricky.
Tracking complex projects: Managing and reporting progress for complex projects may pose a challenge.
Ensuring regular updates: Getting everyone to consistently update progress can be a hurdle, especially in dynamic work environments.
Best Practices for Creating an Effective Progress Report
Creating an effective progress report involves following some best practices:
- Keep your report clear and straightforward, avoiding jargon or overly complex language.
- Highlight the most important information, emphasizing achievements and addressing challenges.
- Use a consistent format and structure for easy comprehension.
- Submit reports on time to make sure that the information is relevant and up-to-date.
- Provide enough detail to convey the message, but avoid unnecessary information that may overwhelm.
- Use charts or diagrams to visually represent data and trends for better understanding.
- Include potential solutions when discussing challenges, promoting a proactive approach.
Create Your Next Progress Report with Creately
Simplify the process of creating progress reports and streamline project management, communication, and improve overall project success with Creately ’s visual collaboration platform.
Task tracking and assignment
Use the built-in project management tools to create, assign, and track tasks right on the canvas. Assign responsibilities, set due dates, and monitor progress with Agile Kanban boards, Gantt charts, timelines and more. Create task cards containing detailed information, descriptions, due dates, and assigned responsibilities.
Notes and attachments
Record additional details and attach documents, files, and screenshots related to your tasks and projects with per item integrated notes panel and custom data fields. Or easily embed files and attachments right on the workspace to centralize project information. Work together on project documentation with teammates with full multiplayer text and visual collaboration.
Real-time collaboration
Get any number of participants on the same workspace and track their additions to the progress report in real-time. Collaborate with others in the project seamlessly with true multi-user collaboration features including synced previews and comments and discussion threads. Use Creately’s Microsoft Teams integration to brainstorm, plan, run projects during meetings.
Pre-made templates
Get a head start with ready-to-use progress report templates and other project documentation templates available right inside the app. Explore 1000s more templates and examples for various scenarios in the community.
Comprehensive shape libraries
Create any visual aid from flowcharts to timelines with comprehensive shape libraries for over 70 types of diagrams including icons. Illustrate or make annotations easily with freehand drawing and format text without leaving the keyboard with markdown shortcuts.
Progress reports are indispensable in project management. They foster communication, accountability, and a culture of continuous improvement. Make use of the progress report templates we have provided to track your progress and stay organized.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
More Related Articles
Amanda Athuraliya is the communication specialist/content writer at Creately, online diagramming and collaboration tool. She is an avid reader, a budding writer and a passionate researcher who loves to write about all kinds of topics.
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.
Stanford University Public Art Committee announces two major art installations to be unveiled on campus in the next academic year. Sculptor and filmmaker Alia Farid has been chosen to create a temporary work as part of the Stanford Plinth Project, and interactive installation artist and Stanford faculty member Camille Utterback has been commissioned to develop a permanent work for Stanford’s new Data Science and Computation Complex (DSCC). Farid’s work is expected to be installed on Meyer Green’s plinth in the fall of 2024 and will remain on view for three years. Utterback’s work is scheduled to be installed in the winter of 2025. Both works will be viewable by the public.
“Public art is so meaningful for how it brings creative vitality to the Stanford campus in a way that is tangible and open to everyone,” said Deborah Cullinan, vice president for the arts and co-chair of the Public Art Committee with David Lenox, university architect and executive director of campus planning. “It’s thrilling to welcome Alia and her thoughtful work to the university environment and to celebrate Camille as an extraordinary artist already in our midst.”
These publicly accessible projects promise rich engagement opportunities with students and the Stanford community.
Plinth Project: Amulets
“Amulets brings into view an inconspicuous yet significant object of Mesopotamian material culture,” writes Farid about the proposal of two large-scale amulets held up by one another, made of polyester resin, a modern material, and blue faience, the earliest form of ceramic glaze, invented more than 6000 years ago in ancient Mesopotamia, in what is today Iraq.
Working with a group of alum curators to collect and review artist nominations, the Public Art Committee selected Farid’s proposal for the Plinth Project based on its formal beauty, the resonance of significantly important themes to Stanford and the Bay Area, such as the social and environmental impact of extractive industries, and its direct engagement with the collections of Stanford’s Cantor Arts Center and Hoover Institution. Her work will replace the inaugural Plinth Project commission Hello by the Shanghai-based conceptual artist Xu Zhen.
Related story

Stanford’s Public Art Committee set to expand contemporary art offerings across campus
Blue faience is used on tiles, vessels, amulets, beads, and other small objects – examples of which are in the Stanford Family Collections in the Cantor Arts Center – and is often associated with water and used to symbolize this natural element and its faculties: fertility, growth, abundance, and renewal.
In connection with work Farid has been developing on the social and environmental impact of extractive industries in southern Iraq and Kuwait, Amulets also comments obliquely on the environmental degradation and cultural erasure resulting from coalition wars in Iraq. The work’s focus on material history is a contemplation of plastics as a byproduct of oil and the oil reserves that lay beneath the subsoil of the Iraqi marshes, the global pursuit of which has led to the degradation of the water supply and the earth’s resources from which faience is derived.
Amulets at Stanford is Farid’s first North American public art commission. Recent and upcoming solo exhibitions include Chisenhale Gallery, London; Henie Onstad Kunstsenter outside Oslo, Norway; and Contemporary Art Museum Houston in partnership with Rivers Institute and Detroit Institute of Arts, Michigan. In 2023, Farid received The Lise Wilhelmsen Art Award, one of the world’s largest art prizes, and she was shortlisted for the most recent Artes Mundi, the U.K.’s leading biennial exhibition and international contemporary art prize. In 2023-2024, she was the David and Roberta Logie Fellow at Harvard Radcliffe Institute.

A new sculpture on the edge of Meyer Green greets passersby
Data science, computation, art.
“Writing my own software and designing my own interfaces, I develop physical-digital systems that engage people’s bodies instead of just their fingers and eyes,” writes Utterback, associate professor in the Department of Art and Art History in the School of Humanities and Sciences and, by courtesy, in the Department of Computer Science in the School of Engineering .
For the DSCC commission, an ad-hoc committee of Stanford faculty and senior staff sought dynamic artwork that employed the kinds of data-based and computational techniques that will be researched and taught in the building. The committee determined that Utterback’s interactive installation, which links computational systems to human movement and gesture, was an ideal fit for the new complex – and are excited to increase faculty representation in Stanford’s ambitious public art commissions.
Utterback’s permanent installation of hand-painted glass panels layered with live, responsive, computer-generated projections will span a four-story stairwell connecting two buildings in the Data Science and Computation Complex. Imagery will reference themes in the human history of encoding and storytelling linked to these processes, such as ancient record keeping, topographical maps, early bar graphs, and dark matter simulation. Responding to the presence and movement of people in the building, the installation raises questions regarding the connections between physical bodies, data, and how humans seek to understand and depict themselves in the world. Representing many cultural and technical histories, the work will provide an evolving platform to share the story of Stanford’s research and community at the intersection of data science, computer science, and symbolic systems.
Utterback has been a faculty member at Stanford since 2013. She is the recipient of numerous awards and honors, including a Media Arts Grant from the Creative Work Fund (2015) and a MacArthur Foundation Fellowship (2009). She has created site-specific installations for exhibitions and venues, including the American Museum of Natural History, New York, New York; National Portrait Gallery, Washington, D.C.; Pittsburgh Children’s Museum, Pennsylvania; Sacramento International Airport, California; San Jose International Airport, California; and Whitney Museum of American Art, New York, New York.

Secrets of the Papua New Guinea Sculpture Garden
How 10 artists-in-residence from the Sepik River region worked with architects to create an iconic public art environment.
Robin Wander, University Communications: (415) 286-3689, [email protected]
Project Roomkey was meant to ‘protect human life.’ A new report tracks its performance

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
Good morning. It’s Wednesday, May 15 . Here’s what you need to know to start your day.
Evaluating California’s pandemic program to shelter unhoused people
- Wildfire season approaches . Is California ready?
- Need a couch? These are made in L.A.
- And here’s today’s e-newspaper
You're reading the Essential California newsletter
Our reporters guide you through our biggest news, features and recommendations every morning
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.
When the COVID-19 pandemic upended daily life a little over four years ago, state and local health officials were particularly concerned about the coronavirus spreading rapidly among unhoused Californians.
In response, state agencies mobilized quickly to create and launch Project Roomkey , repurposing hotel and motels to provide rooms to unhoused people. The goal of the emergency project was “to protect human life, and to minimize strain on health care system capacity.”
So, how much did Project Roomkey (which I’ll just call PRK moving forward) actually help? A newly released study from research and consulting firm Abt Global attempted to answer that question.
While the study highlights some success in the context of a global health emergency, it also notes shortfalls in later goals aimed at providing its clients with permanent housing.
The study was funded by the California Health Care Foundation and the Conrad N. Hilton Foundation. Researchers collected online survey data from providers in 45 counties, conducted phone interviews with providers in 15 counties and visited sites in five counties, where they interviewed 67 current and former clients of the program.
Their conclusion: PRK achieved its original goals of saving lives and easing pressure on an already overstrained healthcare system. The authors also said the project “enhanced how interim housing is designed and operated in some communities across California.”
But the study comes with a major asterisk, L.A. Times reporter Doug Smith noted in his recent coverage : the “inability to connect information collected at the hotel and motel sites with statewide data from health, housing and other public services agencies left the researchers with only anecdotal evidence to substantiate that conclusion.”
That echoes an ongoing challenge in California’s extensive response to the homelessness crisis: the state does a poor job of tracking how billions of dollars in funding is being spent or how well it’s working .
In total, PRK provided hotel rooms to about 62,000 people in 50 counties and four tribal jurisdictions across the state. The study authors note that the program peaked in October 2020 with more than 16,000 committed rooms, but began to fall off after that.
In L.A. for instance, the program ended in early 2021 after falling well short of its goals. When Mayor Karen Bass took office in late 2022, she launched Safe Inside, which followed a similar strategy of providing temporary rooms with the hopes of permanent housing down the line. Progress has been slow .
Lackluster progress on housing
While PRK was initially launched to boost emergency shelter options across the state, it later evolved to include a rehousing strategy to “ensure no Project Roomkey occupant is forced to exit into unsheltered homelessness,” according to state officials .
But most of PRK’s clients did not trade their temporary room for a permanent home. The authors note that of the 62,000 people who received a California hotel or motel room through the program:
- 25% moved into other emergency shelter sites
- 23% were unaccounted for
- 22% moved in to permanent housing (subsidized or unsubsidized)
- 11% moved in temporarily with friends or family or to transitional housing or motels
- 15% returned to the street
- 4% transferred to institutions such as hospitals, nursing homes or substance abuse treatment facilities
The report also states that longer stays in PRK-funded hotels or motels led to a higher likelihood of permanent housing for people, but other temporary shelters often outperformed PRK sites.
“In the three counties for which they had data on individuals, the researchers found that residents in traditional shelters were more likely to obtain permanent housing,” Doug reported. “In Los Angeles only 19% of Project Roomkey clients moved on to permanent homes, compared with 25% of those leaving shelters.”
It’s also worth noting that while study authors highlight the program’s success at reducing the number of unhoused people getting sick and dying due to the coronavirus, deaths in the unhoused community have increased dramatically in the past several years — even before the pandemic .
Drug overdoses play a major role in those deaths, which have been rising each year in many counties, including Los Angeles and San Diego . But people experiencing homelessness are also dying at higher rates due to heat and cold exposure , traffic collisions and complications from cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Adding to the problem is the fact that the available mortality data are incomplete, meaning the numbers that do get reported are almost certainly an undercount.
The achievements and challenges of Project Roomkey mirror much of what I’ve heard from homelessness experts and advocates for the unhoused:
The systems meant to respond to and reduce homelessness are mostly failing to get people on paths to secure housing. Part of the problem is that homeless service providers don’t control how much housing is getting built in communities — or how many of those homes are affordable to the extremely poor.
And that’s the real solution to our homelessness crisis that temporary rooms don’t achieve on their own, but can help forge a path to: permanent, affordable housing for the more than 180,000 unhoused people (and counting) who need it in the Golden State.
You can read more of Doug Smith’s reporting on the Project Roomkey study here .
Today’s top stories

- Wildfire weather is increasing in California and much of the U.S., a report finds.
- L.A.’s water supplies are in good shape. But is the city ready for the next drought?
Violence on the metro
- Three people were stabbed in two separate incidents on Los Angeles County’s Metro system.
- Column: They want to ride buses and trains, but they’re afraid . For riders old and young, Metro must be safer.
Hepatitis A outbreak
- Hepatitis A is spreading among Los Angeles homeless population , health officials say.
- Hepatitis A scare at the Men’s Central Jail led to more than 1,500 vaccinations.
- Opinion: A deadly but curable disease is thriving in L.A.’s jails . That’s unacceptable.
Crime and courts
- It took a month to ID a law school student’s body. Her fiancé has now been convicted of murder.
- Gunshots fired at an Oakland teen rowing team don’t stop it from finishing the race.
- The shooter of two Jewish men in L.A. agrees to plead guilty to hate crimes .
More big stories
- What you need to know about the bird flu outbreak, concerns about raw milk, and more .
- Climate change is central to both Pope Francis and Newsom . But do Catholic voters care?
- Alice Munro, acclaimed short-story writer and Nobel Prize winner, dies at 92 .
- Summer of 2023 was hottest in 2,000 years , a study finds.
- SpaceX plans to launch 90 rockets from Vandenberg Space Force Base by 2026 . Could that harm the coast?
- East West Players appoints Lily Tung Crystal as its new artistic director .
- Red Lobster offered all-you-can-eat shrimp. That was a mistake.
- Harry and Meghan’s Archewell Foundation was ‘delinquent’ in California . What does that mean?
- Drownings rose among young children after decades of decline . It’s ‘highly concerning,’ CDC says.
- Pro-Palestinian activists protest at Google developer conference amid Israel-Hamas war.
- New York is on a studio building spree to grab a bigger slice of L.A.’s Hollywood pie.
- Buying a home in Southern California? There are now more options.
- Gov. Kristi Noem, who wrote of shooting her dog , to speak at California GOP convention.
Get unlimited access to the Los Angeles Times. Subscribe here .
Commentary and opinions
- Robin Abcarian: ‘Diaper Don’? Trump’s supporters turn the tables on his puerile critics .
- Mariel Garza: Dislike Tesla? OK, but here’s why you should love its Superchargers .
- Sammy Roth: California farmers are low on water. Why not help them go solar?
- Michael Hiltzik: Exxon Mobil is suing its shareholders to silence them about global warming.
Today’s great reads

A lonely desert fire station, the only lifeline for millions of Vegas travelers. Expect to wait for help if you crash in the desert Interstate 15 from Los Angeles to Vegas. There’s only one fire station dedicated to the stretch. Last year, the five-person crew answered nearly 1,000 calls.
Other great reads
- Renting used to be a source of shame to this apartment manager’s daughter. Now it’s a knowing comfort.
- ChatGPT’s new voice mode is giving ‘Her’ vibes .
- Want to live to 100? That may depend on your sex .
How can we make this newsletter more useful? Send comments to [email protected] .
For your downtime

- 🛋️ The best shops for couches made in Los Angeles .
- 🍴 Where every cent of $1 goes at one L.A. restaurant, explained .
- 🎭 Las Vegas’ new must-see show plays with animation, dance and what it means to be human.
- 📖 Miranda July is widening and expanding women’s lives with her new novel: ‘Fiction is my superpower.’
- 🧑🍳 Here’s a recipe for grilled swordfish with quick crushed potatoes and parsley-caper relish .
- ✏️ Get our free daily crossword puzzle, sudoku, word search and arcade games .
And finally ... a great photo
Show us your favorite place in California! We’re running low on submissions. Send us photos that scream California and we may feature them in an edition of Essential California.

Today’s great photo is from Times photographer Christina House. House snapped this photo of actor Jonathan Bailey in downtown L.A.
Have a great day, from the Essential California team
Ryan Fonseca, reporter Kevinisha Walker, multiplatform editor and Saturday reporter Christian Orozco, assistant editor Karim Doumar, head of newsletters
Check our top stories , topics and the latest articles on latimes.com .
Start your day right
Sign up for Essential California for news, features and recommendations from the L.A. Times and beyond in your inbox six days a week.

Ryan Fonseca writes the Los Angeles Times’ Essential California newsletter. A lifelong SoCal native, he has worked in a diverse mix of newsrooms across L.A. County, including radio, documentary, print and television outlets. Most recently, he was an associate editor for LAist.com and KPCC-FM (89.3) public radio, covering transportation and mobility. He returns to The Times after previously working as an assistant web editor for Times Community News, where he helped manage the websites and social media presence of the Burbank Leader, Glendale News-Press and La Cañada Valley Sun. Fonseca studied journalism at Cal State Northridge, where he now teaches the next generation of journalists to develop their voice and digital skills.
More From the Los Angeles Times

Former San Diego sheriff’s deputy faces federal charges in killing of unarmed man

Namaste away: Rangers bar yoga classes at cliffside San Diego park
May 18, 2024

Peril intensifies for Sean ‘Diddy’ Combs after video shows him attacking Cassie Ventura

Supporters say ‘warmhearted’ Mexican Mafia member deserves bail. Wiretaps reveal murder threats
Utah’s higher ed boss was accused of sexual misconduct. Officials sued The Tribune to keep investigation secret.
The state records committee ruled that a draft investigative report sought by the salt lake tribune should be public — but the utah board of higher education is appealing to court..
(Francisco Kjolseth | The Salt Lake Tribune) Former Commissioner of Higher Education Dave Woolstenhulme is seen in this photo from August 23, 2017. He resigned amid a 2023 examination into his conduct, which ended the investigation.
Trying to keep an investigative report secret, the Utah Board of Higher Education has filed a lawsuit arguing it should not have to release the draft account of how it addressed sexual harassment complaints made against the commissioner who was then overseeing the state’s colleges and universities.
The board sued Tribune reporter Courtney Tanner and Utah’s State Records Committee earlier this month, arguing that it should not have to disclose the report because it was the “product of an incomplete grievance process.” Tanner requested the report and other records of any investigation into Dave Woolstenhulme after the former commissioner abruptly resigned last September.
The state records committee ruled the draft report should be released, a decision that the board is asking a district court judge to reverse.
When Woolstenhulme left the job, he said he planned “to pursue other opportunities that have become available.” The Utah Board of Higher Education repeated the same reason after members hastily met to approve his departure.
But the board’s lawsuit says Woolstenhulme resigned two weeks after he received a draft investigative report concerning “complaints” made about him — and his decision to leave ultimately ended the investigation against him, while it was still in the middle of the processes the board follows after receiving complaints.
A record which was released to The Salt Lake Tribune said the investigation into Woolstenhulme began in March 2023 after a Utah State University employee accused the commissioner of sexual misconduct. It appears at least one additional employee came forward after that to also report a sexual harassment allegation against Woolstenhulme.
The document refers to “employees,” in the plural, and a state attorney representing Utah State University also confirmed during a public hearing that the public school received multiple “complaints filed by university employees.” The school has declined to say exactly how many.
Tanner sought the draft investigative report, among other records, in a public records request. The State Records Committee earlier this year ruled that the public interest in releasing the draft outweighed privacy concerns — and ordered its release. However, it also ruled that the original complaints made against Woolstenhulme would not be made public.
The Board of Higher Education’s lawsuit appeals the records committee’s decision about the draft investigative report. The board said in the lawsuit that if it were forced to disclose the draft it would undermine the steps in place for due process, and could disincentivize others from coming forward with similar complaints if they fear they cannot rely on the confidentiality the board offered them.
In his role, Woolstenhulme held the highest ranking position in higher education in the state. He oversaw hundreds of thousands of students and employees across eight public colleges and universities and eight technical colleges. He held the position for four years, starting in 2019 as the interim commissioner before formally taking the post a year later.
Mike Judd, an attorney with Parsons Behle & Latimer who is working in The Tribune’s defense, said the Utah Board of Education’s business is the public’s business — and the law says the board should provide Utahns with easy and reasonable access to records related to that business.
“The public has a significant interest in how our colleges and universities are run,” he said. “And when the system’s commissioner resigns suddenly, the public has a right to understand why.”
“After hearing the board’s arguments against disclosure, the State Records Committee — Utah’s record-access specialists — found that the board is improperly withholding the Woolstenhulme investigation,” he continued. “The Tribune agrees, and it will continue to press for the release of records like these, whether that’s before the committee or in court.”
A spokesperson for the Utah Board of Education declined to comment for this story, saying it does not speak publicly about issues under judicial review.
In the lawsuit, the board detailed the process it follows when complaints like those made against Woolstenhulme are filed: It hires an outside investigator to examine those complaints, who then makes a draft investigative report.
But before a final report can be issued, the lawsuit says that everyone involved must be given the draft investigative report, and be given the opportunity to submit any additional evidence. And after the final investigative report is issued, there’s supposed to be a closed-door hearing where a committee will make a final decision on whether any policies were violated, and whether to order any sanctions.
In Woolstenhulme’s case, the outside investigator did draft the investigative report, according to the lawsuit, and the commissioner was given until Sept. 14 to provide any additional evidence. He resigned on Sept. 11.
“The Board accepted Mr. Woolstenhulme’s resignation,” the lawsuit reads. “At that time, the complaints were dismissed and the investigation process was terminated as per the [Utah Board of Education] policies.”
Woolstenhulme never responded to the draft investigative report, according to the lawsuit. He told a Tribune reporter last week that, “I deny any wrongdoing whatsoever.”
The board noted in its lawsuit that because Woolstenhulme resigned, there was never a final investigative report, there was no hearing, and no determination made into whether Woolstenhulme violated any policies. Therefore, they argued, releasing the report would be releasing a product of a process that was never completed.
Along with undermining the trust of those who file complaints, the board argued in its lawsuit that releasing the draft report would also disincentivize those who are accused of wrongdoing from participating in an investigation if they know that any information “could be disclosed to the public at any point in the process regardless of whether the process has reached its conclusion or a final finding is made.”
If the report were released, the board argued to a district court judge, it would hinder its ability to “effectively uncover and appropriately address misconduct” if those who have information don’t trust and participate in the process.

Donate to the newsroom now. The Salt Lake Tribune, Inc. is a 501(c)(3) public charity and contributions are tax deductible
RELATED STORIES
Former utah higher ed commissioner was under investigation for alleged sexual misconduct when he resigned, student protesters disrupt university of utah graduation while faculty call for school to address police violence, university of utah researcher faked data for years, according to investigators, new president of salt lake community college faces ‘an anti-dei political landscape’ and declining enrollment, opinion: i’ve seen the rise in colon cancer cases. as doctors, we must take young people more seriously., lone peak avalanche: for accomplished adventurer, utah backcountry outing was ‘just a thursday’, opinion: utah inland port wants 9k acres in weber co. you should weigh in., gordon monson: real salt lake is giving utah what it craves — a winner, remembering a latter-day saint feminist, lifelong democrat and social justice warrior, featured local savings.
Apple set to release slimmer iPhone in 2025, the Information reports
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Jaspreet Singh in Bengaluru; Editing by Vijay Kishore
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Technology Chevron

Britain's M&S apologises after website and app hit by 'technical issue'
Visitors saw the message: "PLEASE BEAR WITH US. Sorry you can't shop with us right now."

Advertisement
Supported by
Apple Will Revamp Siri to Catch Up to Its Chatbot Competitors
Apple plans to announce that it will bring generative A.I. to iPhones after the company’s most significant reorganization in a decade.
- Share full article

By Tripp Mickle , Brian X. Chen and Cade Metz
Tripp Mickle, Brian X. Chen and Cade Metz have been reporting on Apple’s plans for generative A.I. for this article since the fall of 2023.
Apple’s top software executives decided early last year that Siri, the company’s virtual assistant, needed a brain transplant.
The decision came after the executives Craig Federighi and John Giannandrea spent weeks testing OpenAI’s new chatbot, ChatGPT . The product’s use of generative artificial intelligence , which can write poetry, create computer code and answer complex questions, made Siri look antiquated, said two people familiar with the company’s work, who didn’t have permission to speak publicly.
Introduced in 2011 as the original virtual assistant in every iPhone, Siri had been limited for years to individual requests and had never been able to follow a conversation. It often misunderstood questions. ChatGPT, on the other hand, knew that if someone asked for the weather in San Francisco and then said, “What about New York?” that user wanted another forecast.
The realization that new technology had leapfrogged Siri set in motion the tech giant’s most significant reorganization in more than a decade. Determined to catch up in the tech industry’s A.I. race, Apple has made generative A.I. a tent pole project — the company’s special, internal label that it uses to organize employees around once-in-a-decade initiatives.
Apple is expected to show off its A.I. work at its annual developers conference on June 10 when it releases an improved Siri that is more conversational and versatile, according to three people familiar with the company’s work, who didn’t have permission to speak publicly. Siri’s underlying technology will include a new generative A.I. system that will allow it to chat rather than respond to questions one at a time.
The update to Siri is at the forefront of a broader effort to embrace generative A.I. across Apple’s business. The company is also increasing the memory in this year’s iPhones to support its new Siri capabilities. And it has discussed licensing complementary A.I. models that power chatbots from several companies, including Google, Cohere and OpenAI.
An Apple spokeswoman declined to comment.
Apple executives worry that new A.I. technology threatens the company’s dominance of the global smartphone market because it has the potential to become the primary operating system, displacing the iPhone’s iOS software, said two people familiar with the thinking of Apple’s leadership, who didn’t have permission to speak publicly. This new technology could also create an ecosystem of A.I. apps, known as agents, that can order Ubers or make calendar appointments, undermining Apple’s App Store, which generates about $24 billion in annual sales.
Apple also fears that if it fails to develop its own A.I. system, the iPhone could become a “dumb brick” compared with other technology. While it is unclear how many people regularly use Siri, the iPhone currently takes 85 percent of global smartphone profits and generates more than $200 billion in sales.
That sense of urgency contributed to Apple’s decision to cancel its other big bet — a $10 billion project to develop a self-driving car — and reassign hundreds of engineers to work on A.I.
Apple has also explored creating servers that are powered by its iPhone and Mac processors, two of these people said. Doing so could help Apple save money and create consistency between the tools used for processes in the cloud and on its devices.
Rather than compete directly with ChatGPT by releasing a chatbot that does things like write poetry, the three people familiar with its work said, Apple has focused on making Siri better at handling tasks that it already does, including setting timers, creating calendar appointments and adding items to a grocery list. It also would be able to summarize text messages.
Apple plans to bill the improved Siri as more private than rival A.I. services because it will process requests on iPhones rather than remotely in data centers. The strategy will also save money. OpenAI spends about 12 cents for about 1,000 words that ChatGPT generates because of cloud computing costs.
(The New York Times sued OpenAI and its partner, Microsoft, in December for copyright infringement of news content related to A.I. systems.)
But Apple faces risks by relying on a smaller A.I. system housed on iPhones rather than a larger one stored in a data center. Research has found that smaller A.I. systems could be more likely to make errors, known as hallucinations, than larger ones.
“It’s always been the Siri vision to have a conversational interface that understands language and context, but it’s a hard problem,” said Tom Gruber, a co-founder of Siri who worked at Apple until 2018. “Now that the technology has changed, it should be possible to do a much better job of that. So long as it’s not a one-size-fits-all effort to answer anything, then they should be able to avoid trouble.”
Apple has several advantages in the A.I. race, including more than two billion devices in use around the world where it can distribute A.I. products. It also has a leading semiconductor team that has been making sophisticated chips capable of powering A.I. tasks like facial recognition.
But for the past decade, Apple has struggled to develop a comprehensive A.I. strategy, and Siri has not had major improvements since its introduction. The assistant’s struggles blunted the appeal of the company’s HomePod smart speaker because it couldn’t consistently perform simple tasks like fulfilling a song request.
The Siri team has failed to get the kind of attention and resources that went to other groups inside Apple, said John Burkey, who worked on Siri for two years before founding a generative A.I. platform, Brighten.ai. The company’s divisions, such as software and hardware, operate independently of one another and share limited information. But A.I. needs to be threaded through products to succeed.
“It’s not in Apple’s DNA,” Mr. Burkey said. “It’s a blind spot.”
Apple has also struggled to recruit and retain leading A.I. researchers. Over the years, it has acquired A.I. companies led by leaders in the field, but they all left after a few years.
The reasons for their departures vary, but one factor is Apple’s secrecy. The company publishes fewer papers on its A.I. work than Google, Meta and Microsoft, and it doesn’t participate in conferences in the same way that its rivals do.
“Research scientists say: ‘What are my other options? Can I go back into academia? Can I go to a research institute, some place where I can work a bit more in the open?’” said Ruslan Salakhutdinov, a leading A.I. researcher, who left Apple in 2020 to return to Carnegie Mellon University.
In recent months, Apple has increased the number of A.I. papers it has published. But prominent A.I. researchers have questioned the value of the papers, saying they are more about creating the impression of meaningful work than providing examples of what Apple may bring to market.
Tsu-Jui Fu, an Apple intern and A.I. doctoral student at the University of California, Santa Barbara, wrote one of Apple’s recent A.I. papers . He spent last summer developing a system for editing photos with written commands rather than Photoshop tools. He said that Apple supported the project by providing him with the necessary G.P.U.s to train the system, but that he had no interaction with the A.I. team working on Apple products.
Though he said he had interviewed for full-time jobs at Adobe and Nvidia, he plans to return to Apple after he graduates because he thinks he can make a bigger difference there.
“A.I. product and research is emerging in Apple, but most companies are very mature,” Mr. Fu said in an interview with The Times. “At Apple, I can have more room to lead a project instead of just being a member of a team doing something.”
Tell us how your law firm is using A.I.
We’d like to hear from lawyers working with generative A.I., including contract lawyers who have been brought on for assignments related to A.I. We won’t publish your name or any part of your submission without contacting you first.
Tripp Mickle reports on Apple and Silicon Valley for The Times and is based in San Francisco. His focus on Apple includes product launches, manufacturing issues and political challenges. He also writes about trends across the tech industry, including layoffs, generative A.I. and robot taxis. More about Tripp Mickle
Brian X. Chen is the lead consumer technology writer for The Times. He reviews products and writes Tech Fix , a column about the social implications of the tech we use. More about Brian X. Chen
Cade Metz writes about artificial intelligence, driverless cars, robotics, virtual reality and other emerging areas of technology. More about Cade Metz
Explore Our Coverage of Artificial Intelligence
News and Analysis
Ilya Sutskever, the OpenAI co-founder and chief scientist who in November joined three other board members to force out Sam Altman before saying he regretted the move, is leaving the company .
OpenAI has unveiled a new version of its ChatGPT chatbot that can receive and respond to voice commands, images and videos.
A bipartisan group of senators released a long-awaited legislative plan for A.I. , calling for billions in funding to propel U.S. leadership in the technology while offering few details on regulations.
The Age of A.I.
D’Youville University in Buffalo had an A.I. robot speak at its commencement . Not everyone was happy about it.
A new program, backed by Cornell Tech, M.I.T. and U.C.L.A., helps prepare lower-income, Latina and Black female computing majors for A.I. careers.
Publishers have long worried that A.I.-generated answers on Google would drive readers away from their sites. They’re about to find out if those fears are warranted, our tech columnist writes .
A new category of apps promises to relieve parents of drudgery, with an assist from A.I. But a family’s grunt work is more human, and valuable, than it seems.
Nebraska AD makes modifications to Memorial Stadium renovation timeline and project plans
LINCOLN, Neb. (KOLN) - Nebraska AD Troy Dannen announced the Memorial Stadium renovation timeline and project plans are undergoing some major changes.
Dannen met with the Board of Regents committees Thursday and ultimately decided the South Stadium will not be torn down following the 2024 season. Instead, Nebraska plans to turn their immediate focus to designing and planning improvements for the East and West Stadiums, with a target to begin work on the East and West no earlier than after the 2025 season.
“South Stadium renovations will remain within the scope of the overall project, but there is no timeline for when that work would begin,” Dannen said in his statement.
Dannen said the decision was made due to three reasons: “First, it needs to help us win. Second, it needs to advance our goals for acquisition and retention of talent. Third, and equally importantly, it must preserve our financial stability – one of the greatest assets of Husker Athletics.”
During the meeting Dannen also communicated that they will not be seeking Board approval at this time for additional work beyond the Phase I upgrades that were approved last October.
“No further construction work will occur until we bring detailed plans and funding back to the Board,” he said. “Our financial stability is a great credit to the work of previous leaders who operated with great fiscal integrity, as well as the generosity and loyalty of Husker fans who have invested in our programs and student-athletes for decades. In this rapidly changing world of college athletics, it’s more important than ever that we maintain that distinct competitive advantage.”
Click here to subscribe to our 10/11 NOW daily digest and breaking news alerts delivered straight to your email inbox.
Copyright 2024 KOLN. All rights reserved.

Man arrested for alleged assault after they barricade themselves inside north Lincoln home

Lincoln woman dies after motorcycle crash near Waverly

Six vehicles involved in crash in northwest Lincoln

Lincoln woman turns herself in days after fatal hit-and-run crash
Latest news.

Omaha Police investigating pair of overnight homicides

Iowans struggle to find homeowners insurance as companies pullout of the state

Large police presence seen in north Lincoln after person barricades themselves inside home

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4. Project Time Tracking Report. A project time-tracking report is a document that records and summarizes time spent on project activities. Each project team member contributes to writing this report—they track and record the amount of time they've spent on tasks and submit it to the project manager. ⏰.
Understanding the objective is the cornerstone of effective project reporting. Whether crafting a project summary report or a detailed project performance report, aligning your content with the aim will make your report more coherent and actionable. This is also the stage where you decide the key milestones and metrics to highlight in the ...
Be succinct and to-the-point with every aspect of the report, from points of contact to resources and any potential roadblocks. The idea is for your project reports to be as easy to digest as possible, especially if you're supplying busy stakeholders with a steady stream of ongoing status reports. 6. Be prepared.
How to Write a Project Report: Step-By-Step GuidePart 1. Project Report Templates: Free DownloadPart 2. Additional ResourcesPart 3. How to Dramatically Reduce Time You Spend Creating ReportsPart 4. At some point during the implementation of a project, a project report has to be generated in order to paint a mental image of the whole project.
A project report is a document that summarizes project data based on economic and financial analysis, progress status, risks, and results to date. It provides stakeholders with information about your project including goals, timeline, budget, resources, risks, and performance.
To put together a report that your project stakeholders can use to gain insights, make decisions and optimize processes, take the following systematic approach to writing your project reports: 1. Define the purpose and scope: Clearly establish the goals, objectives, target audience, and information needs of your project report. 2.
This template covers everything you need to effectively report your project's progress. It features an executive summary and summary of compelling figures, timelines, comparison of targets and outcomes, budget and expenditures. Notice how this report uses charts, graphs, icons and images to visualize key project data.
Examples of Project Reports Project status report: The project status report is a very common and important report that gives a general update on how a project is moving along towards its goals. This report hits on general updates, emerging issues, and milestones. Time tracking report: A project time tracking report pulls data from tracked time or time manually entered via desktop or an app ...
A project report is a detailed document that provides a detailed overview of a project's planning, execution, and outcomes. It serves as a formal record, communicating essential information about the project's progress, performance, and status to the various project stakeholders involved. This document plays a crucial role in fostering ...
Project status report examples include updates to all stakeholders as the project progresses, amended project plans, and notifications of any issues or risks that have arisen. Project Tracking Report Project tracking reports provide real numbers, metrics, and other key indicators of the project's progress.
Give your report a name and start adding information to it. Blank Creates a blank canvas.Use the Report Tools Design tab to add charts, tables, text, and images.. Chart Project creates a chart comparing Actual Work, Remaining Work, and Work by default.Use the Field List pane to pick different fields to compare, and then use the controls to change the color and format of the chart.
1. Build your report where work lives. Before you build your report, make sure you're already tracking your work information in a project management tool. That way, you don't have to manually grab information from a host of sources—instead, you can reduce manual work and create a report with a few clicks.
A project report is a handy tool for project managers as it helps them stay focused on tasks and keeps team members on track to achieving a successful project outcome. It also provides status updates at each key step of the project, so that project stakeholders, the management, and other relevant personnel can follow the progression of the ...
A project report is further divided into certain sections. These 4 are the most common divisions of a project report: Summary: The summary gives the reader a download of all covered in the project report. Even though a summary is placed at the beginning of a project report, you can only write it once your entire report is complete.
Download this project report dashboard template to track the status of key components of a project, including tasks, costs, and pending action items. This template also helps you support the decisions you make for future project initiatives. Check out this article to find more free Excel dashboard templates for all of your business needs.
A project status report is a concise, timely update on your project's progress. It provides essential high-level information, allowing team members and key stakeholders to grasp the project's current state quickly. These reports maintain alignment among all involved parties, highlighting what's on schedule, identifying obstacles, and outlining ...
Project Report Objectives. The objectives of a project report are manifold. Some primary goals include: Documentation: To provide a comprehensive record of all project-related information, including project goals, planning, implementation, and outcomes. Sub-objective: To ensure future reference and accountability.
A project report is a document that provides detail on the overall status of the project or specific aspects of the project's progress or performance. Regardless of the type of report, it is made up of project data based on economic, technical, financial, managerial or production aspects.
A project report is a document that allows a company or team to have an overview of a assignment's requirements and progress. It contains data that relates to the development and completion of an assignment. Typically, project managers create reports that are easy to understand, so that stakeholders, clients and members of various departments ...
A project status report is a document that describes the progress of a project within a specific time period and compares it against the project plan. Project managers use status reports to keep stakeholders informed of progress and monitor costs, risks, time and work. Project status reports allow project managers and stakeholders to visualize ...
The main objectives of a project report are as follows: 1. Requesting permission for an investment plan. A final project report is an insightful document that helps to make new investment plans. It allows the project manager to see and evaluate the expected profits and associated risks in a new project.
A project report is a document that consists of crucial information about a project. It includes information that can be used to evaluate the progress of a project, understand its objective, trace its journey, provide direction to team members, mitigate risks, and communicate a project's success or failure to stakeholders and other business ...
Challenges of Creating and Using a Progress Report. While project reports are handy for keeping track of project progress, they can pose some challenges. Time-consuming: Writing a progress report can take time away from actual project work. Communication issues: Making sure that everyone understands the report may be challenging.
Farid's work is expected to be installed on Meyer Green's plinth in the fall of 2024 and will remain on view for three years. Utterback's work is scheduled to be installed in the winter of ...
The authors note that of the 62,000 people who received a California hotel or motel room through the program: 25% moved into other emergency shelter sites. 23% were unaccounted for. 22% moved in ...
The Utah Board of Higher Education has sued a Salt Lake Tribune reporter and the state records committee, arguing it should not have to release a draft investigative report into sexual misconduct ...
The Smart NAV pilot was designed to explore an extension of a DTCC service, Mutual Fund Profile Service I (MFPS I), the industry standard for transmitting "'Price and Rate" data (referred to as "NAV data"). DTCC, along with 10 market participants and Chainlink, worked together to evaluate the feasibility and industry value of ...
Apple is developing a slimmer version of the iPhone that is likely to be launched by 2025, the Information reported on Friday, citing three people with knowledge of the project.
Apple plans to bill the improved Siri as more private than rival A.I. services because it will process requests on iPhones rather than remotely in data centers. The strategy will also save money ...
Published: May. 17, 2024 at 11:01 AM PDT. LINCOLN, Neb. (KOLN) - Nebraska AD Troy Dannen announced the Memorial Stadium renovation timeline and project plans are undergoing some major changes ...