

What Is Creative Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 20 Examples)
Creative writing begins with a blank page and the courage to fill it with the stories only you can tell.
I face this intimidating blank page daily–and I have for the better part of 20+ years.
In this guide, you’ll learn all the ins and outs of creative writing with tons of examples.
What Is Creative Writing (Long Description)?
Creative Writing is the art of using words to express ideas and emotions in imaginative ways. It encompasses various forms including novels, poetry, and plays, focusing on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes.

Table of Contents
Let’s expand on that definition a bit.
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries.
It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
In essence, creative writing lets you express ideas and emotions uniquely and imaginatively.
It’s about the freedom to invent worlds, characters, and stories. These creations evoke a spectrum of emotions in readers.
Creative writing covers fiction, poetry, and everything in between.
It allows writers to express inner thoughts and feelings. Often, it reflects human experiences through a fabricated lens.
Types of Creative Writing
There are many types of creative writing that we need to explain.
Some of the most common types:
- Short stories
- Screenplays
- Flash fiction
- Creative Nonfiction
Short Stories (The Brief Escape)
Short stories are like narrative treasures.
They are compact but impactful, telling a full story within a limited word count. These tales often focus on a single character or a crucial moment.
Short stories are known for their brevity.
They deliver emotion and insight in a concise yet powerful package. This format is ideal for exploring diverse genres, themes, and characters. It leaves a lasting impression on readers.
Example: Emma discovers an old photo of her smiling grandmother. It’s a rarity. Through flashbacks, Emma learns about her grandmother’s wartime love story. She comes to understand her grandmother’s resilience and the value of joy.
Novels (The Long Journey)
Novels are extensive explorations of character, plot, and setting.
They span thousands of words, giving writers the space to create entire worlds. Novels can weave complex stories across various themes and timelines.
The length of a novel allows for deep narrative and character development.
Readers get an immersive experience.
Example: Across the Divide tells of two siblings separated in childhood. They grow up in different cultures. Their reunion highlights the strength of family bonds, despite distance and differences.
Poetry (The Soul’s Language)
Poetry expresses ideas and emotions through rhythm, sound, and word beauty.
It distills emotions and thoughts into verses. Poetry often uses metaphors, similes, and figurative language to reach the reader’s heart and mind.
Poetry ranges from structured forms, like sonnets, to free verse.
The latter breaks away from traditional formats for more expressive thought.
Example: Whispers of Dawn is a poem collection capturing morning’s quiet moments. “First Light” personifies dawn as a painter. It brings colors of hope and renewal to the world.
Plays (The Dramatic Dialogue)
Plays are meant for performance. They bring characters and conflicts to life through dialogue and action.
This format uniquely explores human relationships and societal issues.
Playwrights face the challenge of conveying setting, emotion, and plot through dialogue and directions.
Example: Echoes of Tomorrow is set in a dystopian future. Memories can be bought and sold. It follows siblings on a quest to retrieve their stolen memories. They learn the cost of living in a world where the past has a price.
Screenplays (Cinema’s Blueprint)
Screenplays outline narratives for films and TV shows.
They require an understanding of visual storytelling, pacing, and dialogue. Screenplays must fit film production constraints.
Example: The Last Light is a screenplay for a sci-fi film. Humanity’s survivors on a dying Earth seek a new planet. The story focuses on spacecraft Argo’s crew as they face mission challenges and internal dynamics.
Memoirs (The Personal Journey)
Memoirs provide insight into an author’s life, focusing on personal experiences and emotional journeys.
They differ from autobiographies by concentrating on specific themes or events.
Memoirs invite readers into the author’s world.
They share lessons learned and hardships overcome.
Example: Under the Mango Tree is a memoir by Maria Gomez. It shares her childhood memories in rural Colombia. The mango tree in their yard symbolizes home, growth, and nostalgia. Maria reflects on her journey to a new life in America.
Flash Fiction (The Quick Twist)
Flash fiction tells stories in under 1,000 words.
It’s about crafting compelling narratives concisely. Each word in flash fiction must count, often leading to a twist.
This format captures life’s vivid moments, delivering quick, impactful insights.
Example: The Last Message features an astronaut’s final Earth message as her spacecraft drifts away. In 500 words, it explores isolation, hope, and the desire to connect against all odds.
Creative Nonfiction (The Factual Tale)
Creative nonfiction combines factual accuracy with creative storytelling.
This genre covers real events, people, and places with a twist. It uses descriptive language and narrative arcs to make true stories engaging.
Creative nonfiction includes biographies, essays, and travelogues.
Example: Echoes of Everest follows the author’s Mount Everest climb. It mixes factual details with personal reflections and the history of past climbers. The narrative captures the climb’s beauty and challenges, offering an immersive experience.
Fantasy (The World Beyond)
Fantasy transports readers to magical and mythical worlds.
It explores themes like good vs. evil and heroism in unreal settings. Fantasy requires careful world-building to create believable yet fantastic realms.
Example: The Crystal of Azmar tells of a young girl destined to save her world from darkness. She learns she’s the last sorceress in a forgotten lineage. Her journey involves mastering powers, forming alliances, and uncovering ancient kingdom myths.
Science Fiction (The Future Imagined)
Science fiction delves into futuristic and scientific themes.
It questions the impact of advancements on society and individuals.
Science fiction ranges from speculative to hard sci-fi, focusing on plausible futures.
Example: When the Stars Whisper is set in a future where humanity communicates with distant galaxies. It centers on a scientist who finds an alien message. This discovery prompts a deep look at humanity’s universe role and interstellar communication.
Watch this great video that explores the question, “What is creative writing?” and “How to get started?”:
What Are the 5 Cs of Creative Writing?
The 5 Cs of creative writing are fundamental pillars.
They guide writers to produce compelling and impactful work. These principles—Clarity, Coherence, Conciseness, Creativity, and Consistency—help craft stories that engage and entertain.
They also resonate deeply with readers. Let’s explore each of these critical components.
Clarity makes your writing understandable and accessible.
It involves choosing the right words and constructing clear sentences. Your narrative should be easy to follow.
In creative writing, clarity means conveying complex ideas in a digestible and enjoyable way.
Coherence ensures your writing flows logically.
It’s crucial for maintaining the reader’s interest. Characters should develop believably, and plots should progress logically. This makes the narrative feel cohesive.
Conciseness
Conciseness is about expressing ideas succinctly.
It’s being economical with words and avoiding redundancy. This principle helps maintain pace and tension, engaging readers throughout the story.
Creativity is the heart of creative writing.
It allows writers to invent new worlds and create memorable characters. Creativity involves originality and imagination. It’s seeing the world in unique ways and sharing that vision.
Consistency
Consistency maintains a uniform tone, style, and voice.
It means being faithful to the world you’ve created. Characters should act true to their development. This builds trust with readers, making your story immersive and believable.
Is Creative Writing Easy?
Creative writing is both rewarding and challenging.
Crafting stories from your imagination involves more than just words on a page. It requires discipline and a deep understanding of language and narrative structure.
Exploring complex characters and themes is also key.
Refining and revising your work is crucial for developing your voice.
The ease of creative writing varies. Some find the freedom of expression liberating.
Others struggle with writer’s block or plot development challenges. However, practice and feedback make creative writing more fulfilling.
What Does a Creative Writer Do?
A creative writer weaves narratives that entertain, enlighten, and inspire.
Writers explore both the world they create and the emotions they wish to evoke. Their tasks are diverse, involving more than just writing.
Creative writers develop ideas, research, and plan their stories.
They create characters and outline plots with attention to detail. Drafting and revising their work is a significant part of their process. They strive for the 5 Cs of compelling writing.
Writers engage with the literary community, seeking feedback and participating in workshops.
They may navigate the publishing world with agents and editors.
Creative writers are storytellers, craftsmen, and artists. They bring narratives to life, enriching our lives and expanding our imaginations.
How to Get Started With Creative Writing?
Embarking on a creative writing journey can feel like standing at the edge of a vast and mysterious forest.
The path is not always clear, but the adventure is calling.
Here’s how to take your first steps into the world of creative writing:
- Find a time of day when your mind is most alert and creative.
- Create a comfortable writing space free from distractions.
- Use prompts to spark your imagination. They can be as simple as a word, a phrase, or an image.
- Try writing for 15-20 minutes on a prompt without editing yourself. Let the ideas flow freely.
- Reading is fuel for your writing. Explore various genres and styles.
- Pay attention to how your favorite authors construct their sentences, develop characters, and build their worlds.
- Don’t pressure yourself to write a novel right away. Begin with short stories or poems.
- Small projects can help you hone your skills and boost your confidence.
- Look for writing groups in your area or online. These communities offer support, feedback, and motivation.
- Participating in workshops or classes can also provide valuable insights into your writing.
- Understand that your first draft is just the beginning. Revising your work is where the real magic happens.
- Be open to feedback and willing to rework your pieces.
- Carry a notebook or digital recorder to jot down ideas, observations, and snippets of conversations.
- These notes can be gold mines for future writing projects.
Final Thoughts: What Is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is an invitation to explore the unknown, to give voice to the silenced, and to celebrate the human spirit in all its forms.
Check out these creative writing tools (that I highly recommend):
Read This Next:
- What Is a Prompt in Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 200 Examples)
- What Is A Personal Account In Writing? (47 Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Short Story (Ultimate Guide + Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Romance Novel [21 Tips + Examples)

What is Creative Writing? A Key Piece of the Writer’s Toolbox
Not all writing is the same and there’s a type of writing that has the ability to transport, teach, and inspire others like no other.
Creative writing stands out due to its unique approach and focus on imagination. Here’s how to get started and grow as you explore the broad and beautiful world of creative writing!
What is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is a form of writing that extends beyond the bounds of regular professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature. It is characterized by its emphasis on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes or poetic techniques to express ideas in an original and imaginative way.
Creative writing can take on various forms such as:
- short stories
- screenplays
It’s a way for writers to express their thoughts, feelings, and ideas in a creative, often symbolic, way . It’s about using the power of words to transport readers into a world created by the writer.
5 Key Characteristics of Creative Writing
Creative writing is marked by several defining characteristics, each working to create a distinct form of expression:
1. Imagination and Creativity: Creative writing is all about harnessing your creativity and imagination to create an engaging and compelling piece of work. It allows writers to explore different scenarios, characters, and worlds that may not exist in reality.
2. Emotional Engagement: Creative writing often evokes strong emotions in the reader. It aims to make the reader feel something — whether it’s happiness, sorrow, excitement, or fear.
3. Originality: Creative writing values originality. It’s about presenting familiar things in new ways or exploring ideas that are less conventional.
4. Use of Literary Devices: Creative writing frequently employs literary devices such as metaphors, similes, personification, and others to enrich the text and convey meanings in a more subtle, layered manner.
5. Focus on Aesthetics: The beauty of language and the way words flow together is important in creative writing. The aim is to create a piece that’s not just interesting to read, but also beautiful to hear when read aloud.
Remember, creative writing is not just about producing a work of art. It’s also a means of self-expression and a way to share your perspective with the world. Whether you’re considering it as a hobby or contemplating a career in it, understanding the nature and characteristics of creative writing can help you hone your skills and create more engaging pieces .
For more insights into creative writing, check out our articles on creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree and is a degree in creative writing worth it .
Styles of Creative Writing
To fully understand creative writing , you must be aware of the various styles involved. Creative writing explores a multitude of genres, each with its own unique characteristics and techniques.
Poetry is a form of creative writing that uses expressive language to evoke emotions and ideas. Poets often employ rhythm, rhyme, and other poetic devices to create pieces that are deeply personal and impactful. Poems can vary greatly in length, style, and subject matter, making this a versatile and dynamic form of creative writing.
Short Stories
Short stories are another common style of creative writing. These are brief narratives that typically revolve around a single event or idea. Despite their length, short stories can provide a powerful punch, using precise language and tight narrative structures to convey a complete story in a limited space.
Novels represent a longer form of narrative creative writing. They usually involve complex plots, multiple characters, and various themes. Writing a novel requires a significant investment of time and effort; however, the result can be a rich and immersive reading experience.
Screenplays
Screenplays are written works intended for the screen, be it television, film, or online platforms. They require a specific format, incorporating dialogue and visual descriptions to guide the production process. Screenwriters must also consider the practical aspects of filmmaking, making this an intricate and specialized form of creative writing.
If you’re interested in this style, understanding creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree can provide useful insights.
Writing for the theater is another specialized form of creative writing. Plays, like screenplays, combine dialogue and action, but they also require an understanding of the unique dynamics of the theatrical stage. Playwrights must think about the live audience and the physical space of the theater when crafting their works.
Each of these styles offers unique opportunities for creativity and expression. Whether you’re drawn to the concise power of poetry, the detailed storytelling of novels, or the visual language of screenplays and plays, there’s a form of creative writing that will suit your artistic voice. The key is to explore, experiment, and find the style that resonates with you.
For those looking to spark their creativity, our article on creative writing prompts offers a wealth of ideas to get you started.
Importance of Creative Writing
Understanding what is creative writing involves recognizing its value and significance. Engaging in creative writing can provide numerous benefits – let’s take a closer look.
Developing Creativity and Imagination
Creative writing serves as a fertile ground for nurturing creativity and imagination. It encourages you to think outside the box, explore different perspectives, and create unique and original content. This leads to improved problem-solving skills and a broader worldview , both of which can be beneficial in various aspects of life.
Through creative writing, one can build entire worlds, create characters, and weave complex narratives, all of which are products of a creative mind and vivid imagination. This can be especially beneficial for those seeking creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
Enhancing Communication Skills
Creative writing can also play a crucial role in honing communication skills. It demands clarity, precision, and a strong command of language. This helps to improve your vocabulary, grammar, and syntax, making it easier to express thoughts and ideas effectively .
Moreover, creative writing encourages empathy as you often need to portray a variety of characters from different backgrounds and perspectives. This leads to a better understanding of people and improved interpersonal communication skills.
Exploring Emotions and Ideas
One of the most profound aspects of creative writing is its ability to provide a safe space for exploring emotions and ideas. It serves as an outlet for thoughts and feelings , allowing you to express yourself in ways that might not be possible in everyday conversation.
Writing can be therapeutic, helping you process complex emotions, navigate difficult life events, and gain insight into your own experiences and perceptions. It can also be a means of self-discovery , helping you to understand yourself and the world around you better.
So, whether you’re a seasoned writer or just starting out, the benefits of creative writing are vast and varied. For those interested in developing their creative writing skills, check out our articles on creative writing prompts and how to teach creative writing . If you’re considering a career in this field, you might find our article on is a degree in creative writing worth it helpful.
4 Steps to Start Creative Writing
Creative writing can seem daunting to beginners, but with the right approach, anyone can start their journey into this creative field. Here are some steps to help you start creative writing .
1. Finding Inspiration
The first step in creative writing is finding inspiration . Inspiration can come from anywhere and anything. Observe the world around you, listen to conversations, explore different cultures, and delve into various topics of interest.
Reading widely can also be a significant source of inspiration. Read different types of books, articles, and blogs. Discover what resonates with you and sparks your imagination.
For structured creative prompts, visit our list of creative writing prompts to get your creative juices flowing.
Editor’s Note : When something excites or interests you, stop and take note – it could be the inspiration for your next creative writing piece.
2. Planning Your Piece
Once you have an idea, the next step is to plan your piece . Start by outlining:
- the main points
Remember, this can serve as a roadmap to guide your writing process. A plan doesn’t have to be rigid. It’s a flexible guideline that can be adjusted as you delve deeper into your writing. The primary purpose is to provide direction and prevent writer’s block.
3. Writing Your First Draft
After planning your piece, you can start writing your first draft . This is where you give life to your ideas and breathe life into your characters.
Don’t worry about making it perfect in the first go. The first draft is about getting your ideas down on paper . You can always refine and polish your work later. And if you don’t have a great place to write that first draft, consider a journal for writing .
4. Editing and Revising Your Work
The final step in the creative writing process is editing and revising your work . This is where you fine-tune your piece, correct grammatical errors, and improve sentence structure and flow.
Editing is also an opportunity to enhance your storytelling . You can add more descriptive details, develop your characters further, and make sure your plot is engaging and coherent.
Remember, writing is a craft that improves with practice . Don’t be discouraged if your first few pieces don’t meet your expectations. Keep writing, keep learning, and most importantly, enjoy the creative process.
For more insights on creative writing, check out our articles on how to teach creative writing or creative writing activities for kids.
Tips to Improve Creative Writing Skills
Understanding what is creative writing is the first step. But how can one improve their creative writing skills? Here are some tips that can help.
Read Widely
Reading is a vital part of becoming a better writer. By immersing oneself in a variety of genres, styles, and authors, one can gain a richer understanding of language and storytelling techniques . Different authors have unique voices and methods of telling stories, which can serve as inspiration for your own work. So, read widely and frequently!
Practice Regularly
Like any skill, creative writing improves with practice. Consistently writing — whether it be daily, weekly, or monthly — helps develop your writing style and voice . Using creative writing prompts can be a fun way to stimulate your imagination and get the words flowing.
Attend Writing Workshops and Courses
Formal education such as workshops and courses can offer structured learning and expert guidance. These can provide invaluable insights into the world of creative writing, from understanding plot development to character creation. If you’re wondering is a degree in creative writing worth it, these classes can also give you a taste of what studying creative writing at a higher level might look like .
Joining Writing Groups and Communities
Being part of a writing community can provide motivation, constructive feedback, and a sense of camaraderie. These groups often hold regular meetings where members share their work and give each other feedback. Plus, it’s a great way to connect with others who share your passion for writing.
Seeking Feedback on Your Work
Feedback is a crucial part of improving as a writer. It offers a fresh perspective on your work, highlighting areas of strength and opportunities for improvement. Whether it’s from a writing group, a mentor, or even friends and family, constructive criticism can help refine your writing .
Start Creative Writing Today!
Remember, becoming a proficient writer takes time and patience. So, don’t be discouraged by initial challenges. Keep writing, keep learning, and most importantly, keep enjoying the process. Who knows, your passion for creative writing might even lead to creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
Happy writing!
Brooks Manley

Creative Primer is a resource on all things journaling, creativity, and productivity. We’ll help you produce better ideas, get more done, and live a more effective life.
My name is Brooks. I do a ton of journaling, like to think I’m a creative (jury’s out), and spend a lot of time thinking about productivity. I hope these resources and product recommendations serve you well. Reach out if you ever want to chat or let me know about a journal I need to check out!
Here’s my favorite journal for 2024:

Gratitude Journal Prompts Mindfulness Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Anxiety Reflective Journal Prompts Healing Journal Prompts Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Journal Prompts Mental Health Journal Prompts ASMR Journal Prompts Manifestation Journal Prompts Self-Care Journal Prompts Morning Journal Prompts Evening Journal Prompts Self-Improvement Journal Prompts Creative Writing Journal Prompts Dream Journal Prompts Relationship Journal Prompts "What If" Journal Prompts New Year Journal Prompts Shadow Work Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Overcoming Fear Journal Prompts for Dealing with Loss Journal Prompts for Discerning and Decision Making Travel Journal Prompts Fun Journal Prompts
Inspiring Ink: Expert Tips on How to Teach Creative Writing
You may also like, a guide to journaling for healing + 50 healing prompts.
What Animal Represents Creativity?
Creative writing jobs – what you can do with a creative writing degree, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Productivity
- Favorite Journals

Writing Nestling

What Is Creative Writing? (Definition & 11 Best Steps)
Creative writing is the celestial dance of words, an art form that transcends the ordinary to forge literary constellations that illuminate the human experience.
At its core, creative writing is a cosmic exploration of imagination, a journey into the uncharted realms where storytelling becomes a vehicle for self-expression, creativity, and connection.
It encompasses a diverse array of genres, from the poetic landscapes of verse to the intricate narratives of fiction and the introspective reflections of creative nonfiction.
Creative writing is both an ancient practice, rooted in the oral traditions of storytelling, and a contemporary force, shaped by the dynamic currents of literary movements and the digital age.
In this cosmic voyage of words, writers become cosmic architects, crafting worlds, characters, and emotions that resonate across the galaxies of human thought and emotion.
This exploration delves into the historical evolution, elements, genres, and the transformative process of creative writing, inviting both novice stargazers and seasoned explorers to embark on a literary odyssey through the cosmos of human imagination.
Table of Contents
What Is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is the process of expressing thoughts, ideas, and emotions through the artful use of language. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
Idea Generation
Start by brainstorming and generating ideas. This could be inspired by personal experiences, observations, or purely imaginative concepts.
Organize your thoughts and structure your writing. This might involve outlining the plot for a story, creating characters, or planning the flow of a poem.
Choosing a Form or Genre
Decide on the type of creative writing you want to pursue – whether it’s fiction, non-fiction, poetry, drama, or any other form.
Setting the Tone and Style
Define the tone and style of your writing. This could range from formal to informal, humorous to serious, depending on the intended effect.
Creating Characters or Themes
Develop characters, themes, or central ideas that will drive your narrative and engage your audience.
Begin writing your first draft. Allow yourself the freedom to explore ideas without worrying too much about perfection at this stage.
Review and revise your work. This involves refining your language, improving clarity, and ensuring your writing effectively communicates your intended message or story.
Pay attention to grammar, spelling, and punctuation. Edit your work to eliminate errors and enhance overall readability.
Seek feedback from peers, writing groups, or mentors. Constructive criticism can help you identify areas for improvement and refine your work.
Make final adjustments based on feedback and your own revisions. Polish your creative writing until you are satisfied with the result.
Publishing or Sharing
Decide whether you want to share your work publicly. This could involve submitting it to literary magazines, self-publishing, or simply sharing it with friends and family.
Creative writing is a dynamic and iterative process, allowing for continuous refinement and exploration of ideas.

Historical Evolution of Creative Writing
Embarking on a literary time-travel, the historical evolution of creative writing unfolds like an intricately woven tapestry, blending the whispers of ancient oral traditions with the bold strokes of individual expression that emerged during the Renaissance.
Picture storytellers captivating audiences with folk tales around ancient campfires, only to witness the metamorphosis into written words that took place during humanity’s transition from the spoken to the written word.
As the winds of change blew through literary landscapes, the Renaissance breathed life into personal narratives, and Romanticism embraced the turbulent storms of emotion.
Modernism then shattered conventional boundaries, paving the way for experimental forms that mirrored the tumultuous twentieth century.
Today, creative writing stands at the intersection of tradition and innovation, a dynamic force shaped by the echoes of the past and the untamed creativity of the present.
Origins in oral traditions
The origins of creative writing can be traced back to the rich tapestry of human storytelling woven through the fabric of oral traditions.
In the dim glow of ancient campfires, our ancestors spun tales that danced between reality and imagination, passing down knowledge, wisdom, and cultural identity from one generation to the next.
These oral narratives, often rooted in folklore and myths, were the heartbeat of communities, connecting individuals through shared stories.
From the captivating epics of Homer to the enchanting fairy tales whispered in the corners of the world, the oral tradition laid the foundation for the written word, embodying the essence of human creativity, imagination, and the innate desire to communicate through the power of narrative.
Development through literary movements
The historical journey of creative writing unfolds through the dynamic currents of literary movements, each a vibrant chapter in the evolution of human expression.
The Renaissance, a cultural rebirth, marked a pivotal shift as writers embraced the power of individual expression and departed from medieval constraints.
Romanticism followed, a tempest of emotion that stormed the structured landscapes of literature, championing nature, passion, and the sublime.
Modernism emerged as a bold departure from traditional forms, ushering in experimental narratives and fragmented perspectives that mirrored the complexities of the 20th century.
Today’s creative writing landscape, shaped by these movements, is a kaleidoscope of diverse voices and styles, a testament to the enduring influence of literary evolution on the human experience.
Elements of Creative Writing
Dive into the alchemy of creative writing, where the elements of storytelling blend and dance like cosmic particles in a celestial ballet.
Picture the plot and structure as the architectural skeleton, a blueprint for worlds yet to be born. Characters, like sentient constellations, come to life, breathing the very essence of authenticity into the narrative cosmos.
Amidst the vast expanse of setting and atmosphere, landscapes materialize like dreams, painting scenes that are both vivid and haunting.
Style and voice emerge as the enchanting melodies, each writer composing a unique symphony that resonates in the reader’s soul.
In this literary crucible, the elements fuse, giving birth to tales that are not just written but are crafted, where words become spells, and the act of creation is nothing short of magical.
Genres in Creative Writing
Step into the kaleidoscope of creative expression, where genres in creative writing are the vibrant hues that paint the literary canvas with boundless imagination.
Fiction, a realm where novel universes unfurl with every turn of the page, beckons explorers to traverse landscapes of intrigue and emotion.
Poetry, the language of the soul, weaves verses that resonate in the heart’s chambers, from the traditional sonnets to the avant-garde free forms that defy gravity.
Creative nonfiction becomes a literary mirror, reflecting the kaleidoscope of reality through memoirs and essays, blurring the lines between experience and artistry.
These genres are not mere labels; they are portals into worlds where storytelling transcends boundaries, and writers become architects of realms that captivate the mind, stir the emotions, and linger in the echoes of the reader’s imagination.
Fiction, the enchanting realm where the alchemy of words transforms imagination into reality, beckons readers into worlds unknown.
It is the literary tapestry where storytellers weave tales that dance on the precipice between reality and fantasy. Novels, the architects of this fantastical landscape, sculpt characters with palpable depth, crafting intricate plotlines that unfold like secrets waiting to be revealed.
From the classic works of timeless masters to the contemporary symphonies of emerging voices, fiction transcends time and space, inviting readers to escape the ordinary and venture into the extraordinary.
In this boundless expanse, emotions become tangible, and the echoes of imaginary footsteps resonate long after the last page is turned. Fiction is not merely a genre; it is a passport to alternate realities, a magic carpet that carries readers to places uncharted and emotions unexplored.
Poetry, the language of the heart and the echo of the soul, is an art form that transcends the boundaries of ordinary expression.
In the symphony of words, poets become maestros, conducting emotions and experiences into verses that sing with rhythm and grace.
From the structured elegance of traditional forms to the unbridled freedom of free verse, poetry captures the ineffable and distills it into the purest essence.
Every line is a brushstroke painting vivid imagery, and each stanza is a melody that resonates in the chambers of the reader’s spirit. Poets wield words like alchemists, transforming mundane moments into profound revelations.
In the delicate dance between language and emotion, poetry stands as a testament to the human capacity to turn the ordinary into the extraordinary, inviting readers to immerse themselves in the beauty of finely crafted language and the endless possibilities of the poetic imagination.
Creative Nonfiction
Creative nonfiction, a captivating blend of factual precision and artistic expression, serves as a literary bridge between the realms of truth and imagination.
In this genre, writers embark on a compelling journey of storytelling that mines the depths of reality to craft narratives as rich and engaging as any fiction.
From memoirs that illuminate the intricacies of personal experiences to thought-provoking essays that dissect the tapestry of the human condition, creative nonfiction is a mosaic of authenticity painted with the brushstrokes of literary finesse.
The genre encourages writers to artfully blur the lines between fact and narrative, weaving a tapestry that captures the essence of life in all its complexities.
It is a genre where truth is not merely recounted but elevated to the status of art, inviting readers to explore the profound and the ordinary with fresh eyes and a heightened appreciation for the power of storytelling.

The Creative Writing Process
Embark on the enigmatic odyssey of the creative writing process, where inspiration is a clandestine muse that whispers in the stillness of creativity.
The inception, a cosmic spark, ignites the imagination, unleashing a torrent of ideas that cascade like shooting stars across the writer’s mind. The drafting phase is a dance with chaos, a raw manifestation of thoughts and emotions onto the blank canvas of the page.
Yet, the revision process emerges as the phoenix rising from the literary ashes, where words transform and refine, revealing the alchemical magic of refining ideas into a harmonious narrative.
Seeking feedback becomes a cosmic conversation, where the writer navigates the cosmos of criticism to unveil hidden constellations in their work.
The creative writing process is not a linear trajectory but a celestial dance , where writers traverse the nebulae of creativity, forging galaxies of prose and poetry that linger in the reader’s universe long after the final punctuation mark.
Idea generation, the pulsating heartbeat of the creative process, invites writers into the boundless cosmos of imagination.
It is an ethereal dance with inspiration, where sparks of creativity ignite the mind like constellations in the night sky. Whether drawn from personal experiences, fleeting observations, or the whispers of dreams, ideas are the raw stardust that writers mold into narrative galaxies.
The process is as unpredictable as a meteor shower, with writers navigating the celestial expanse to capture elusive fragments of brilliance.
From the quiet corners of introspection to the cacophony of the world, the art of idea generation transforms the mundane into the extraordinary, inviting writers to embark on a cosmic odyssey where every fleeting notion has the potential to blossom into a literary supernova.
Drafting and Revising
Drafting and revising, the twin constellations of the writing process, encapsulate the transformative journey of turning nebulous ideas into polished prose.
In the initial act of drafting, writers plunge into the creative abyss, weaving words into a tapestry of raw emotions and vivid imagery.
It is an untamed exploration, where the exhilarating rush of creation takes precedence over perfection. Yet, the true alchemy occurs in the refining crucible of revision. Like a sculptor chiseling away excess stone to reveal a masterpiece, writers meticulously carve and reshape their narratives.
It is a dance with words, a delicate balancing act of preserving the authenticity of the initial draft while enhancing clarity, coherence, and resonance.
Revision is not merely correction; it is the conscious evolution of a narrative, where every nuanced change breathes new life into the prose.
The tandem of drafting and revising, akin to the ebb and flow of cosmic forces, is the dynamic heartbeat that propels a piece of writing from its embryonic stages to the polished brilliance that captivates the reader’s soul.
Publishing and Sharing
Publishing and sharing mark the culmination of a writer’s odyssey, where the crafted words are prepared to venture beyond the solitary realm of creation.
It is a moment of revelation, where the manuscript, once a private universe, prepares to meet the wider cosmos of readership.
The publishing process, be it through traditional avenues or the burgeoning world of self-publishing, involves the meticulous preparation of the work for public consumption.
The act of sharing becomes a cosmic ripple, as the writer’s voice resonates across the literary landscape, forging connections with readers who may find solace, inspiration, or sheer enjoyment in the words.
It is a dance of vulnerability and courage, as writers release their creations into the literary cosmos, hoping their narrative constellations will find a home in the hearts and minds of others.
The symbiotic relationship between writer and reader transforms the act of publishing into a shared cosmic experience, where words transcend the individual and become part of a collective literary universe.
Challenges and Rewards of Creative Writing
Navigating the cosmos of creative writing reveals a celestial dance of challenges and rewards, where each word penned is a step into the cosmic unknown.
The challenges emerge like elusive comets, from the gravitational pull of writer’s block threatening to derail creativity, to the constant cosmic quest for a harmonious balance between originality and marketability.
Yet, these challenges are the cosmic forge that tempers the writer’s mettle, honing resilience and creativity in the crucible of adversity.
The rewards, akin to dazzling supernovae, illuminate the journey. The cathartic joy of crafting a sentence that resonates, the cosmic connections formed with readers who find solace or delight in the prose – these are the celestial jewels that make the struggles worthwhile.
In the vast expanse of creative writing, challenges and rewards orbit each other like binary stars, their gravitational pull shaping the unique trajectory of every writer’s cosmic odyssey.
Overcoming writer’s block
Writer’s block, that elusive shadow cast over the creative landscape, can feel like navigating a cosmic void where inspiration is but a distant star.
It is the gravitational force that stymies the flow of words and leaves the writer stranded in a sea of blank pages. Yet, overcoming writer’s block is an act of cosmic resilience.
Writers embark on a journey through the nebulae of creativity, employing various strategies to break free from the entangled cosmic web.
Whether it’s the cosmic power of free writing to unravel mental knots or the meteoric inspiration found in changing the writing environment, overcoming writer’s block becomes a transformative process.
It is the writer’s spacecraft pushing through the cosmic fog, a testament to the indomitable spirit that seeks to create even in the face of cosmic resistance.
In this dance with the muse, writers rediscover the cosmic symphony of their imagination and emerge from the creative void with newfound brilliance.
Balancing originality and marketability
In the cosmic dance of creative writing, striking the delicate balance between originality and marketability is akin to navigating the gravitational forces of two celestial bodies.
Originality, the pulsating core of creativity, propels writers into uncharted literary realms, forging unique constellations of thought and expression.
Yet, the cosmic reality of marketability orbits nearby, where commercial considerations seek gravitational stability.
It’s an intricate interplay; too much originality may risk veering into the obscure, while an excessive focus on marketability might compromise the authenticity of the creative vision.
Writers become cosmic architects, constructing narratives that not only resonate with their individual voice but also align with the gravitational pull of audience preferences.
Balancing these cosmic forces is a perpetual challenge, requiring writers to dance on the edge of innovation while staying tethered to the gravitational pull of a wider readership.
In this cosmic balancing act, writers discover the celestial equilibrium where originality and marketability harmonize, creating literary galaxies that captivate both the cosmos of creativity and the earthly realms of audience engagement.
Impact of Creative Writing on Society
Creative writing is the cosmic echo of the human soul, resonating through the annals of time and leaving an indelible imprint on the fabric of society.
It serves as a literary constellation, illuminating the collective consciousness with narratives that mirror, challenge, and redefine societal values.
From ancient epics that shaped cultural identities to contemporary works that spark revolutions of thought, creative writing is a cosmic force that fosters empathy, dismantles prejudices, and holds a mirror to the complexities of the human experience.
It is the catalyst for societal metamorphosis, a cosmic dance that encourages dialogue, fuels revolutions, and shapes the very contours of cultural evolution.
In the vast cosmos of creative expression, the impact of writing is not merely confined to the pages; it permeates the collective psyche, becoming a celestial force that guides, questions, and ultimately shapes the destiny of societies on this cosmic voyage through time.
Educational and Professional Opportunities in Creative Writing
Embarking on the cosmic odyssey of creative writing isn’t just a journey into the realms of imagination; it’s a launchpad to educational and professional constellations that illuminate diverse career trajectories.
Creative writing programs become celestial academies, nurturing literary supernovae through workshops, mentorship, and the exploration of narrative galaxies.
The academic pursuit of the craft transforms writers into cosmic architects, honing not only their creativity but also the analytical skills essential for dissecting the intricacies of language.
Beyond the academic cosmos, the professional opportunities in creative writing are as vast as the universe itself.
Writers may navigate the celestial waters of journalism, become starry-eyed screenwriters crafting cinematic adventures, or soar as literary explorers, publishing novels that leave an indelible mark on the literary cosmos.
In the intersection of education and profession, creative writing unfolds as a cosmic tapestry where words aren’t just written but become portals to boundless opportunities in the vast expanse of the literary universe.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about What Is Creative Writing?
What exactly is creative writing, and how does it differ from other forms of writing.
Creative writing is the vibrant, expressive art of using words to craft narratives that go beyond mere conveyance of information. It stands apart by prioritizing imagination, self-expression, and often blurs the lines between reality and fiction.
How does the historical evolution of creative writing influence contemporary practices?
The historical journey of creative writing, from ancient oral traditions to the digital age, has shaped the very DNA of the craft. It influences contemporary practices by offering a rich tapestry of literary movements, styles, and themes that writers can draw inspiration from or subvert.
Can anyone become a creative writer, or is it a skill reserved for a select few?
Absolutely anyone can become a creative writer! While innate talent can be an asset, the essence of creative writing lies in practice, exploration, and the willingness to cultivate one’s unique voice and perspective.
What are the key elements that make up creative writing, and how do they contribute to the overall narrative?
The elements of creative writing, such as plot, characterization, setting, style, and voice, are the building blocks that construct the literary cosmos. They contribute by creating immersive worlds, memorable characters, and distinctive narratives that resonate with readers.
How can one overcome writer’s block, a common challenge in creative writing?
Overcoming writer’s block is like navigating through a cosmic fog. Strategies include engaging in free writing, changing the writing environment, seeking inspiration from different mediums, or simply taking a cosmic break to recharge creative energies.
Is creative writing limited to novels and poetry, or are there other genres to explore?
Creative writing spans a diverse universe of genres. While novels and poetry are prominent, there’s also creative nonfiction, flash fiction, screenplays, and more. The cosmos of creative writing is vast and welcomes exploration.
How does one balance the fine line between originality and marketability in creative writing?
Balancing originality and marketability requires navigating a cosmic dance. It involves maintaining authenticity while considering the audience’s preferences, creating a celestial equilibrium where the writer’s unique voice resonates within a broader readership.
What educational and professional opportunities are available in the field of creative writing?
The educational galaxy offers creative writing programs and degrees, nurturing writers with both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Professionally, opportunities range from traditional publishing avenues to scriptwriting, journalism, and the expansive realm of digital content creation.
In conclusion, creative writing is a cosmic odyssey, an ever-expanding universe of imagination, expression, and connection.
From its ancient roots in oral traditions to the dynamic currents of contemporary literary movements, creative writing has evolved into a diverse and influential art form.
It is a transformative process that involves the careful balance of elements, the exploration of various genres, and the persistent journey through the challenges and rewards of crafting narratives.
Creative writing is not confined to the realms of novels and poetry; it encompasses a vast cosmos of possibilities, from memoirs to screenplays, flash fiction to creative nonfiction.
As writers embark on this celestial exploration, they become architects of worlds, sculptors of characters, and composers of narratives that resonate across the collective human experience.
The educational and professional opportunities within this realm further amplify its significance, turning creative writing into both a personal pursuit and a communal force shaping the literary landscape.
In the grand celestial tapestry of human expression, creative writing emerges as a luminous constellation, inviting writers and readers alike to traverse the cosmic expanse of imagination and storytelling.
Related Posts:
- What Is Medium Used For? Ultimate Guide For Beginners
- What Is A Personal Account In Writing? (Explained)
- What Is A Universal Statement In Writing? (Explained)
- What Does Freeform Mean In Fanfiction?
- How To Describe A Spaceship In A Story (10 Best Tips)
- Body Swap Writing (9 Best Tips & Ultimate Guide)
Similar Posts

How Do Websites Make Money With Ads? (12 Best Ways)
In the bustling digital landscape, the question of how websites make money with ads unveils a fascinating tapestry of strategies, innovations, and symbiotic relationships. As the heartbeat of the online ecosystem, websites navigate the intricate dance between user experience and revenue generation. From the bold strokes of display ads to the nimble precision of programmatic…

Do You Italicize Titles? (Easy Guide & Explained)
Welcome to the intriguing realm of typographical finesse – the nuanced practice of italicizing titles. In the vast landscape of written expression, the question of whether to italicize titles can be a labyrinthine endeavor, navigating the subtle nuances that distinguish literary works. As we embark on this linguistic odyssey, we’ll unravel the conventions, explore the…

12 Best Ways To Connect With Other Bloggers
In the vast and dynamic landscape of the blogosphere, establishing connections with fellow bloggers is not just a networking strategy but a key to unlocking a wealth of opportunities, collaborations, and shared growth. The digital realm offers a multitude of avenues for forging meaningful connections, from social media platforms that serve as virtual meeting grounds…

Is Content Writing A Stressful Job? (Yes, 12 Big Stressors)
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, where words wield the power to shape perceptions and drive engagement, content writing stands at the forefront of communication. However, behind the artful prose and strategic narratives, a question looms: Is content writing a stressful job? This inquiry delves into the dynamic interplay between creativity and pressure, exploring the multifaceted…

12 Best Ways To Write Essays When You Are Stuck
Navigating the labyrinth of essay writing can be a thrilling intellectual adventure, but occasionally, even the most seasoned writers find themselves at a crossroads, grappling with the notorious writer’s block. It’s during these challenging moments that the quest for creative solutions becomes paramount. In this exploration, we delve into a myriad of strategies, akin to…

Why Writing By Hand Is Better For Memory And Learning (10 Best Tips)
In an era characterized by the proliferation of digital devices and the ever-expanding realm of virtual communication, the timeless art of writing by hand retains a profound significance in memory formation and learning processes. Beyond its aesthetic appeal, handwriting embodies a rich tapestry of cognitive engagement, tactile experience, and psychological resonance. This introductory exploration delves…

Elements of Creative Writing
J.D. Schraffenberger, University of Northern Iowa
Rachel Morgan, University of Northern Iowa
Grant Tracey, University of Northern Iowa
Copyright Year: 2023
ISBN 13: 9780915996179
Publisher: University of Northern Iowa
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Robert Moreira, Lecturer III, University of Texas Rio Grande Valley on 3/21/24
Unlike Starkey's CREATIVE WRITING: FOUR GENRES IN BRIEF, this textbook does not include a section on drama. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
Unlike Starkey's CREATIVE WRITING: FOUR GENRES IN BRIEF, this textbook does not include a section on drama.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
As far as I can tell, content is accurate, error free and unbiased.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The book is relevant and up-to-date.
Clarity rating: 5
The text is clear and easy to understand.
Consistency rating: 5
I would agree that the text is consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Modularity rating: 5
Text is modular, yes, but I would like to see the addition of a section on dramatic writing.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
Topics are presented in logical, clear fashion.
Interface rating: 5
Navigation is good.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No grammatical issues that I could see.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
I'd like to see more diverse creative writing examples.
As I stated above, textbook is good except that it does not include a section on dramatic writing.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Chapter One: One Great Way to Write a Short Story
- Chapter Two: Plotting
- Chapter Three: Counterpointed Plotting
- Chapter Four: Show and Tell
- Chapter Five: Characterization and Method Writing
- Chapter Six: Character and Dialouge
- Chapter Seven: Setting, Stillness, and Voice
- Chapter Eight: Point of View
- Chapter Nine: Learning the Unwritten Rules
- Chapter One: A Poetry State of Mind
- Chapter Two: The Architecture of a Poem
- Chapter Three: Sound
- Chapter Four: Inspiration and Risk
- Chapter Five: Endings and Beginnings
- Chapter Six: Figurative Language
- Chapter Seven: Forms, Forms, Forms
- Chapter Eight: Go to the Image
- Chapter Nine: The Difficult Simplicity of Short Poems and Killing Darlings
Creative Nonfiction
- Chapter One: Creative Nonfiction and the Essay
- Chapter Two: Truth and Memory, Truth in Memory
- Chapter Three: Research and History
- Chapter Four: Writing Environments
- Chapter Five: Notes on Style
- Chapter Seven: Imagery and the Senses
- Chapter Eight: Writing the Body
- Chapter Nine: Forms
Back Matter
- Contributors
- North American Review Staff
Ancillary Material
- University of Northern Iowa
About the Book
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing in the genres of fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States. They’ve selected nearly all of the readings and examples (more than 60) from writing that has appeared in NAR pages over the years. Because they had a hand in publishing these pieces originally, their perspective as editors permeates this book. As such, they hope that even seasoned writers might gain insight into the aesthetics of the magazine as they analyze and discuss some reasons this work is so remarkable—and therefore teachable. This project was supported by NAR staff and funded via the UNI Textbook Equity Mini-Grant Program.
About the Contributors
J.D. Schraffenberger is a professor of English at the University of Northern Iowa. He is the author of two books of poems, Saint Joe's Passion and The Waxen Poor , and co-author with Martín Espada and Lauren Schmidt of The Necessary Poetics of Atheism . His other work has appeared in Best of Brevity , Best Creative Nonfiction , Notre Dame Review , Poetry East , Prairie Schooner , and elsewhere.
Rachel Morgan is an instructor of English at the University of Northern Iowa. She is the author of the chapbook Honey & Blood , Blood & Honey . Her work is included in the anthology Fracture: Essays, Poems, and Stories on Fracking in American and has appeared in the Journal of American Medical Association , Boulevard , Prairie Schooner , and elsewhere.
Grant Tracey author of three novels in the Hayden Fuller Mysteries ; the chapbook Winsome featuring cab driver Eddie Sands; and the story collection Final Stanzas , is fiction editor of the North American Review and an English professor at the University of Northern Iowa, where he teaches film, modern drama, and creative writing. Nominated four times for a Pushcart Prize, he has published nearly fifty short stories and three previous collections. He has acted in over forty community theater productions and has published critical work on Samuel Fuller and James Cagney. He lives in Cedar Falls, Iowa.
Contribute to this Page

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What is Creative Writing?
Discover What Is Creative Writing as we unravel the art of self-expression through words. In this blog, learn the meaning and techniques of creative writing, igniting your imagination and honing your storytelling skills. Unlock the world of literary creativity and learn how to craft compelling narratives that captivate readers.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Report Writing Course
- Effective Communication Skills
- Speed Writing Course
- E-mail Etiquette Training
- Interpersonal Skills Training Course

Creative Writing is a form of art that allows people to express their thoughts, ideas, and emotions through the written word. It is a mode of self-expression that combines imagination with linguistic skills to create compelling narratives, poems, and other forms of literature. A Statista survey found that 76,300 Authors, Writers and Translators work in the United Kingdom alone in 2023. This shows Creative Writing is a demanding career worldwide.To know more about it, read this blog, to learn What is Creative Writing, how to write captivating narratives, and discover the essence of expressive writing.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Creative Writing
2) Key elements of Creative Writing
3) Types of Creative Writing
4) Importance of Creative Writing
5) The Creative Writing process
6) Tips for effective Content Writing
7) Conclusion
Understanding What is Creative Writing
Creative Writing is the art of crafting original content that elicits readers' emotions, thoughts, and imagination. Unlike Academic or Technical Writing, Creative Writing allows for more personal expression and imaginative exploration. It encompasses various forms such as fiction, poetry, non-fiction, and drama, all of which share the common thread of artistic storytelling.

Key elements of Creative Writing
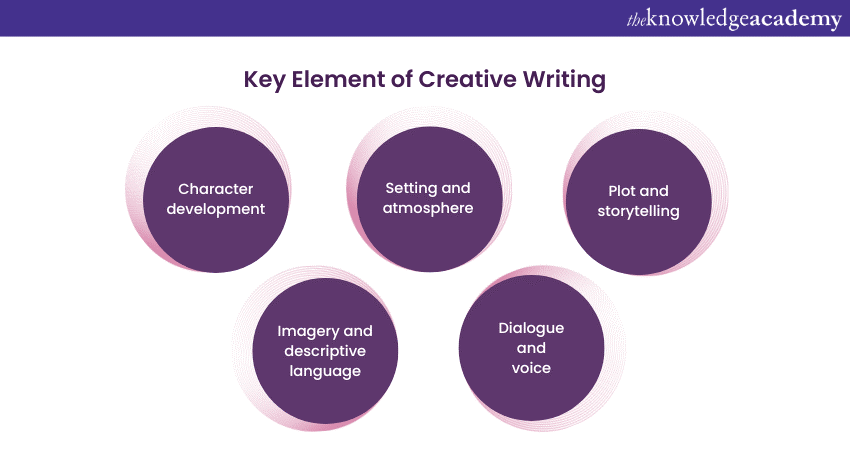
2) Character development: Compelling characters are the heart of any great story. Through careful development, characters become relatable, complex, and capable of driving the plot forward.
3) Setting and atmosphere: The setting and atmosphere create the backdrop for the story. By skilfully crafting these elements, Writers can enhance the overall mood and tone, allowing readers to feel like they're living within the story's world.
4) Plot and storytelling: A well-crafted story keeps readers engaged and invested in the narrative's progression. This includes introducing conflicts, building tension, and crafting satisfying resolutions .
5) Dialogue and voice: Dialogue adds authenticity to characters and provides insight into their personalities. A distinctive narrative voice also contributes to the story's uniqueness and captivates readers.
Types of Creative Writing
Creative Writing encompasses various genres and forms, each offering a unique platform for expressing creativity, storytelling, and emotion. As you delve into the world of Creative Writing, it's essential to explore the various types and discover which resonates with you the most. Here are some of the prominent types of Creative Writing:
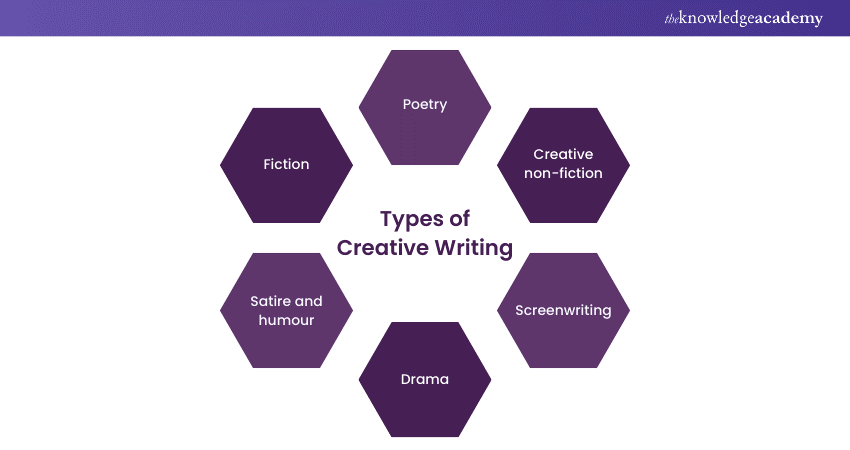
1) Fiction
Fiction is perhaps the most well-known type of Creative Writing. It involves inventing characters, settings, and plotlines from scratch. Writers have the freedom to create entire worlds and realities, whether they're set in the past, present, future, or even in alternate dimensions.
Novels, short stories, novellas, and flash fiction are all forms of fiction that engage readers through compelling characters, intriguing conflicts, and imaginative settings. From fantasy realms to gritty crime dramas, fiction transports readers to new and exciting places.
2) Poetry
Poetry is the art of condensing language to evoke emotions, provoke thoughts, and communicate complex ideas using rhythm, rhyme, and vivid imagery. Poems' conciseness requires Writers to choose their words carefully, often crafting multiple layers of meaning within a few lines.
Poetry can take various forms, including sonnets, haikus, free verse, and slam poetry. Each form carries its own rules and conventions, allowing Poets to experiment with structure and sound to create impactful compositions. Moreover, poetry delves into the depth of emotions, exploring themes ranging from love and nature to social issues and personal reflections.
3) Creative non-fiction
Non-fiction writing draws from real-life experiences, observations, and research to convey information, insights, and personal perspectives. This form includes genres such as essays, memoirs, biographies, autobiographies, and journalistic pieces.
Non-fiction Writers blend storytelling with factual accuracy, presenting their ideas in a compelling and informative manner. Personal essays offer a glimpse into the writer's thoughts and experiences. At the same time, memoirs and autobiographies share personal journeys and reflections, connecting readers with the author's life story.
4) Drama and playwriting
Playwriting is the creation of scripts for theatrical performances. The challenge lies in crafting engaging dialogue and constructing scenes that captivate both the audience and the performers.
Dramatic Writing requires an understanding of pacing, character motivations, and the visual aspects of storytelling. While Theatrical Writing requires a keen sense of the following:
a) Character dynamics: Building relationships between characters and exploring their motivations and conflicts.
b) Stage directions: Providing clear instructions for actors, directors, and stage designers to bring the play to life.
c) Dramatic structure: Crafting acts and scenes that build tension and engage the audience.
5) Satire and humour
Satire and humour utilise wit, sarcasm, and clever wordplay to critique and mock societal norms, institutions, and human behaviour. This form of Creative Writing often challenges readers to view the world from a different perspective.
Moreover, it encourages them to question established conventions. Satirical works, whether in literature, essays, or satirical news articles, aim to entertain while also prompting reflection on serious topics.
Master Copywriting skills with our Copywriting Course – join today and become an expert Copywriter!
Importance of Creative Writing
Creative Writing holds a profound significance beyond its role as a literary pursuit. It bridges imagination and reality, fostering personal growth, communication skills, and cultural preservation. Here's a closer look at why Creative Writing is of paramount importance:
1) Personal expression and catharsis
Creative Writing is a sanctuary for self-expression. Individuals can voice their innermost thoughts, emotions, and experiences through poetry, stories, and essays. This act of sharing vulnerabilities and joy brings about a cathartic release, offering a therapeutic outlet for emotional expression. Moreover, it cultivates a deeper understanding of oneself, promoting self-awareness and self-acceptance.
2) Cultivation of communication skills
The art of Creative Writing cultivates effective Communication Skills that transcend the written word. Writers learn to convey ideas, concepts, and feelings coherently and captivatingly.
This proficiency extends to verbal communication, enabling Writers to articulate their thoughts with clarity and eloquence. As a result, it enriches interpersonal relationships and professional endeavours.
3) Nurturing empathy and perspective
Writers develop a heightened sense of empathy as they craft diverse characters and explore multifaceted narratives. Immersing oneself in the shoes of different characters fosters understanding and tolerance for various viewpoints and backgrounds. Readers, in turn, experience this empathy, gaining insight into the complexities of human nature and the diverse tapestry of human experience.
4) Exploration of social issues
Writers wield the power to effect change through their words. They can shed light on societal issues, challenge norms, and provoke critical conversations. By addressing topics such as social justice, equality, and environmental concerns, Creative Writing becomes a catalyst for positive transformation and advocacy.
5) Connection and impact
Creative Writing builds bridges between individuals by establishing connections on emotional and intellectual levels. Stories resonate across cultures, transcending geographical and temporal boundaries. The impact of a well-crafted story can be enduring, leaving a mark on readers' hearts and minds.
Unlock your creative potential with our Creative Writing Training - register now!
The Creative Writing process
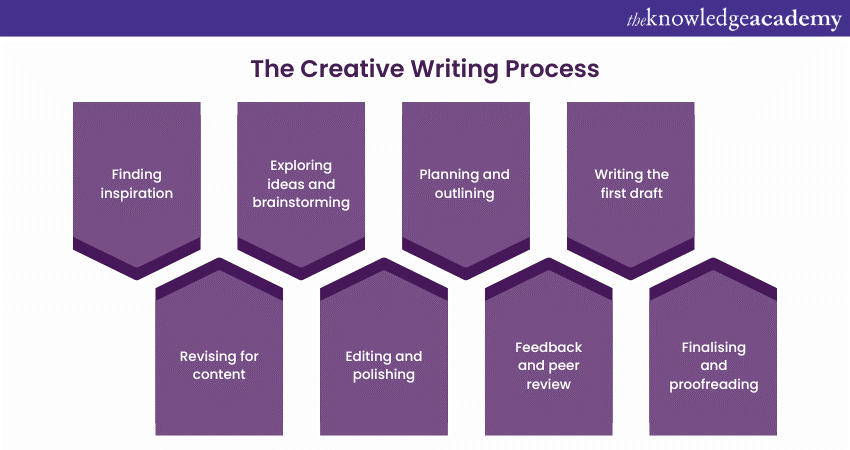
Creating a compelling piece of Creative Writing is a journey that involves a series of steps, each contributing to the evolution of your story. Whether you're crafting a short story, a novel, or a poem, here's a breakdown of the Creative Writing process in eight essential steps:
1) Finding inspiration
The process begins with a moment of inspiration—a fleeting thought, an intriguing image, or a powerful emotion. Inspiration can strike anywhere—nature, experiences, dreams, or simple observation.
Keep a journal or digital note-taking app to capture these sparks of inspiration as they occur. Explore your interests, passions, and emotions to identify themes and ideas that resonate with you.
2) Exploring ideas and brainstorming
Once you've identified an inspiring concept, delve deeper. Brainstorm ideas related to characters, settings, conflicts, and themes. Jot down all possibilities, allowing your imagination to roam freely. This stage is about generating a wealth of creative options that will serve as building blocks for your story.
3) Planning and outlining
Organise your thoughts by creating an outline. Outline your story's major plot points, character arcs, and pivotal moments. This outline acts as a roadmap, guiding you through the narrative's progression while providing flexibility for creative surprises.
4) Writing the first draft
Once you are done with your outline, start writing your first draft. Don't worry about perfection—focus on getting your ideas onto paper. Let your creativity flow and allow your characters to surprise you. The goal is to have a complete manuscript, even if it's messy and imperfect.
5) Revising for content
Once the first draft is complete, take a step back before revisiting your work. During this stage, focus on revising for content. Analyse the structure of your plot, the development of your characters, and the coherence of your themes. Make necessary changes, add details, and refine dialogue. Ensure that your story's foundation is solid before moving on.
6) Editing and polishing
Edit your Manuscript for grammar, punctuation, sentence structure, and style. Pay attention to clarity and consistency. Also, focus on enhancing the flow of your writing and creating a polished narrative that engages readers.
7) Feedback and peer review
Share your revised work with others—friends, writing groups, or beta readers—to gather feedback. Constructive criticism can highlight blind spots and offer perspectives you might have missed. Use this feedback to refine your work further.
8) Finalising and proofreading
Incorporate the feedback you've received and make final revisions. Proofread meticulously for any remaining errors. Ensure that your work is formatted correctly and adheres to any submission guidelines if you plan to publish or share it.
Tips for effective Creative Writing
Here are some of the useful tips you should consider incorporating in your process of writing :
1) Show, don't tell: Instead of directly stating emotions or details, "showing" involves using actions, thoughts, and dialogue to convey information. This technique allows readers to draw their own conclusions and become more immersed in the story.
2) Use of metaphors and similes: Metaphors and similes offer creative ways to describe complex concepts by comparing them to something familiar. These literary devices add depth and creativity to your writing.
3) Building suspense and tension: By strategically withholding information and creating unanswered questions, Writers can build suspense and keep readers eagerly turning pages.
4) Crafting memorable beginnings and endings: A strong opening captures readers' attention, while a satisfying conclusion leaves a lasting impact. These elements bookend your story and influence readers' overall impression.
5) Experimenting with point of view: The choice of point of view (first person, third person, etc.) shapes how readers experience the story. Experimenting with different perspectives can lead to unique narrative opportunities.
Conclusion
We hope this blog gave you a clear idea of What is Creative Writing, along with its process and useful tips. The Creative Writing process is not linear; you might find yourself revisiting earlier steps as your story evolves. Embrace the journey, allowing your writing to develop and transform through each phase.
Enhance your Academic Writing prowess with our comprehensive Academic Writing Masterclass . - sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
a) Literary Agent
b) Screenwriter
c) Video Game Story Writer
d) Copywriter
e) Website Editor
f) Creative Director
There are several resources or recommended readings which can help you to hone your Creative Writing skills. Here we have discussed some of such resources:
a) “On Writing: A Memoir of the Craft" by Stephen King
b) "Bird by Bird: Some Instructions on Writing and Life" by Anne Lamott
c) "Writing Down the Bones: Freeing the Writer Within" by Natalie Goldberg
d) Joining book clubs
e) Reading a variety of authors and genre
f) Practicing writing regular prompts and exercises.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide. Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Personal Development courses , including Organisational skills training, Emotional Intelligence Training, and Report Writing Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Journalism . Our Business Skills blogs covers a range of topics related to Sports Journalism, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Creative Writing skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 14th Jun 2024
Fri 30th Aug 2024
Fri 11th Oct 2024
Fri 13th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
VIDEO COURSE
Finish your draft in our 3-month master class. Sign up now to watch a free lesson!
Learn How to Write a Novel
Finish your draft in our 3-month master class. Enroll now for daily lessons, weekly critique, and live events. Your first lesson is free!

Guides • Perfecting your Craft
Last updated on Feb 14, 2023
10 Types of Creative Writing (with Examples You’ll Love)
A lot falls under the term ‘creative writing’: poetry, short fiction, plays, novels, personal essays, and songs, to name just a few. By virtue of the creativity that characterizes it, creative writing is an extremely versatile art. So instead of defining what creative writing is , it may be easier to understand what it does by looking at examples that demonstrate the sheer range of styles and genres under its vast umbrella.
To that end, we’ve collected a non-exhaustive list of works across multiple formats that have inspired the writers here at Reedsy. With 20 different works to explore, we hope they will inspire you, too.
People have been writing creatively for almost as long as we have been able to hold pens. Just think of long-form epic poems like The Odyssey or, later, the Cantar de Mio Cid — some of the earliest recorded writings of their kind.
Poetry is also a great place to start if you want to dip your own pen into the inkwell of creative writing. It can be as short or long as you want (you don’t have to write an epic of Homeric proportions), encourages you to build your observation skills, and often speaks from a single point of view .
Here are a few examples:
“Ozymandias” by Percy Bysshe Shelley
Nothing beside remains. Round the decay Of that colossal Wreck, boundless and bare The lone and level sands stretch far away.

This classic poem by Romantic poet Percy Shelley (also known as Mary Shelley’s husband) is all about legacy. What do we leave behind? How will we be remembered? The great king Ozymandias built himself a massive statue, proclaiming his might, but the irony is that his statue doesn’t survive the ravages of time. By framing this poem as told to him by a “traveller from an antique land,” Shelley effectively turns this into a story. Along with the careful use of juxtaposition to create irony, this poem accomplishes a lot in just a few lines.
“Trying to Raise the Dead” by Dorianne Laux
A direction. An object. My love, it needs a place to rest. Say anything. I’m listening. I’m ready to believe. Even lies, I don’t care.
Poetry is cherished for its ability to evoke strong emotions from the reader using very few words which is exactly what Dorianne Laux does in “ Trying to Raise the Dead .” With vivid imagery that underscores the painful yearning of the narrator, she transports us to a private nighttime scene as the narrator sneaks away from a party to pray to someone they’ve lost. We ache for their loss and how badly they want their lost loved one to acknowledge them in some way. It’s truly a masterclass on how writing can be used to portray emotions.
If you find yourself inspired to try out some poetry — and maybe even get it published — check out these poetry layouts that can elevate your verse!
Song Lyrics
Poetry’s closely related cousin, song lyrics are another great way to flex your creative writing muscles. You not only have to find the perfect rhyme scheme but also match it to the rhythm of the music. This can be a great challenge for an experienced poet or the musically inclined.
To see how music can add something extra to your poetry, check out these two examples:
“Hallelujah” by Leonard Cohen
You say I took the name in vain I don't even know the name But if I did, well, really, what's it to ya? There's a blaze of light in every word It doesn't matter which you heard The holy or the broken Hallelujah
Metaphors are commonplace in almost every kind of creative writing, but will often take center stage in shorter works like poetry and songs. At the slightest mention, they invite the listener to bring their emotional or cultural experience to the piece, allowing the writer to express more with fewer words while also giving it a deeper meaning. If a whole song is couched in metaphor, you might even be able to find multiple meanings to it, like in Leonard Cohen’s “ Hallelujah .” While Cohen’s Biblical references create a song that, on the surface, seems like it’s about a struggle with religion, the ambiguity of the lyrics has allowed it to be seen as a song about a complicated romantic relationship.
“I Will Follow You into the Dark” by Death Cab for Cutie
If Heaven and Hell decide that they both are satisfied Illuminate the no's on their vacancy signs If there's no one beside you when your soul embarks Then I'll follow you into the dark

You can think of song lyrics as poetry set to music. They manage to do many of the same things their literary counterparts do — including tugging on your heartstrings. Death Cab for Cutie’s incredibly popular indie rock ballad is about the singer’s deep devotion to his lover. While some might find the song a bit too dark and macabre, its melancholy tune and poignant lyrics remind us that love can endure beyond death.
Plays and Screenplays
From the short form of poetry, we move into the world of drama — also known as the play. This form is as old as the poem, stretching back to the works of ancient Greek playwrights like Sophocles, who adapted the myths of their day into dramatic form. The stage play (and the more modern screenplay) gives the words on the page a literal human voice, bringing life to a story and its characters entirely through dialogue.
Interested to see what that looks like? Take a look at these examples:
All My Sons by Arthur Miller
“I know you're no worse than most men but I thought you were better. I never saw you as a man. I saw you as my father.”

Arthur Miller acts as a bridge between the classic and the new, creating 20th century tragedies that take place in living rooms and backyard instead of royal courts, so we had to include his breakout hit on this list. Set in the backyard of an all-American family in the summer of 1946, this tragedy manages to communicate family tensions in an unimaginable scale, building up to an intense climax reminiscent of classical drama.
💡 Read more about Arthur Miller and classical influences in our breakdown of Freytag’s pyramid .
“Everything is Fine” by Michael Schur ( The Good Place )
“Well, then this system sucks. What...one in a million gets to live in paradise and everyone else is tortured for eternity? Come on! I mean, I wasn't freaking Gandhi, but I was okay. I was a medium person. I should get to spend eternity in a medium place! Like Cincinnati. Everyone who wasn't perfect but wasn't terrible should get to spend eternity in Cincinnati.”
A screenplay, especially a TV pilot, is like a mini-play, but with the extra job of convincing an audience that they want to watch a hundred more episodes of the show. Blending moral philosophy with comedy, The Good Place is a fun hang-out show set in the afterlife that asks some big questions about what it means to be good.
It follows Eleanor Shellstrop, an incredibly imperfect woman from Arizona who wakes up in ‘The Good Place’ and realizes that there’s been a cosmic mixup. Determined not to lose her place in paradise, she recruits her “soulmate,” a former ethics professor, to teach her philosophy with the hope that she can learn to be a good person and keep up her charade of being an upstanding citizen. The pilot does a superb job of setting up the stakes, the story, and the characters, while smuggling in deep philosophical ideas.
Personal essays
Our first foray into nonfiction on this list is the personal essay. As its name suggests, these stories are in some way autobiographical — concerned with the author’s life and experiences. But don’t be fooled by the realistic component. These essays can take any shape or form, from comics to diary entries to recipes and anything else you can imagine. Typically zeroing in on a single issue, they allow you to explore your life and prove that the personal can be universal.
Here are a couple of fantastic examples:
“On Selling Your First Novel After 11 Years” by Min Jin Lee (Literary Hub)
There was so much to learn and practice, but I began to see the prose in verse and the verse in prose. Patterns surfaced in poems, stories, and plays. There was music in sentences and paragraphs. I could hear the silences in a sentence. All this schooling was like getting x-ray vision and animal-like hearing.

This deeply honest personal essay by Pachinko author Min Jin Lee is an account of her eleven-year struggle to publish her first novel . Like all good writing, it is intensely focused on personal emotional details. While grounded in the specifics of the author's personal journey, it embodies an experience that is absolutely universal: that of difficulty and adversity met by eventual success.
“A Cyclist on the English Landscape” by Roff Smith (New York Times)
These images, though, aren’t meant to be about me. They’re meant to represent a cyclist on the landscape, anybody — you, perhaps.
Roff Smith’s gorgeous photo essay for the NYT is a testament to the power of creatively combining visuals with text. Here, photographs of Smith atop a bike are far from simply ornamental. They’re integral to the ruminative mood of the essay, as essential as the writing. Though Smith places his work at the crosscurrents of various aesthetic influences (such as the painter Edward Hopper), what stands out the most in this taciturn, thoughtful piece of writing is his use of the second person to address the reader directly. Suddenly, the writer steps out of the body of the essay and makes eye contact with the reader. The reader is now part of the story as a second character, finally entering the picture.
Short Fiction
The short story is the happy medium of fiction writing. These bite-sized narratives can be devoured in a single sitting and still leave you reeling. Sometimes viewed as a stepping stone to novel writing, that couldn’t be further from the truth. Short story writing is an art all its own. The limited length means every word counts and there’s no better way to see that than with these two examples:

“An MFA Story” by Paul Dalla Rosa (Electric Literature)
At Starbucks, I remembered a reading Zhen had given, a reading organized by the program’s faculty. I had not wanted to go but did. In the bar, he read, "I wrote this in a Starbucks in Shanghai. On the bank of the Huangpu." It wasn’t an aside or introduction. It was two lines of the poem. I was in a Starbucks and I wasn’t writing any poems. I wasn’t writing anything.

This short story is a delightfully metafictional tale about the struggles of being a writer in New York. From paying the bills to facing criticism in a writing workshop and envying more productive writers, Paul Dalla Rosa’s story is a clever satire of the tribulations involved in the writing profession, and all the contradictions embodied by systemic creativity (as famously laid out in Mark McGurl’s The Program Era ). What’s more, this story is an excellent example of something that often happens in creative writing: a writer casting light on the private thoughts or moments of doubt we don’t admit to or openly talk about.
“Flowering Walrus” by Scott Skinner (Reedsy)
I tell him they’d been there a month at least, and he looks concerned. He has my tongue on a tissue paper and is gripping its sides with his pointer and thumb. My tongue has never spent much time outside of my mouth, and I imagine it as a walrus basking in the rays of the dental light. My walrus is not well.
A winner of Reedsy’s weekly Prompts writing contest, ‘ Flowering Walrus ’ is a story that balances the trivial and the serious well. In the pauses between its excellent, natural dialogue , the story manages to scatter the fear and sadness of bad medical news, as the protagonist hides his worries from his wife and daughter. Rich in subtext, these silences grow and resonate with the readers.
Want to give short story writing a go? Give our free course a go!

FREE COURSE
How to Craft a Killer Short Story
From pacing to character development, master the elements of short fiction.
Perhaps the thing that first comes to mind when talking about creative writing, novels are a form of fiction that many people know and love but writers sometimes find intimidating. The good news is that novels are nothing but one word put after another, like any other piece of writing, but expanded and put into a flowing narrative. Piece of cake, right?
To get an idea of the format’s breadth of scope, take a look at these two (very different) satirical novels:
Convenience Store Woman by Sayaka Murata
I wished I was back in the convenience store where I was valued as a working member of staff and things weren’t as complicated as this. Once we donned our uniforms, we were all equals regardless of gender, age, or nationality — all simply store workers.

Keiko, a thirty-six-year-old convenience store employee, finds comfort and happiness in the strict, uneventful routine of the shop’s daily operations. A funny, satirical, but simultaneously unnerving examination of the social structures we take for granted, Sayaka Murata’s Convenience Store Woman is deeply original and lingers with the reader long after they’ve put it down.
Erasure by Percival Everett
The hard, gritty truth of the matter is that I hardly ever think about race. Those times when I did think about it a lot I did so because of my guilt for not thinking about it.
Erasure is a truly accomplished satire of the publishing industry’s tendency to essentialize African American authors and their writing. Everett’s protagonist is a writer whose work doesn’t fit with what publishers expect from him — work that describes the “African American experience” — so he writes a parody novel about life in the ghetto. The publishers go crazy for it and, to the protagonist’s horror, it becomes the next big thing. This sophisticated novel is both ironic and tender, leaving its readers with much food for thought.
Creative Nonfiction
Creative nonfiction is pretty broad: it applies to anything that does not claim to be fictional (although the rise of autofiction has definitely blurred the boundaries between fiction and nonfiction). It encompasses everything from personal essays and memoirs to humor writing, and they range in length from blog posts to full-length books. The defining characteristic of this massive genre is that it takes the world or the author’s experience and turns it into a narrative that a reader can follow along with.
Here, we want to focus on novel-length works that dig deep into their respective topics. While very different, these two examples truly show the breadth and depth of possibility of creative nonfiction:
Men We Reaped by Jesmyn Ward
Men’s bodies litter my family history. The pain of the women they left behind pulls them from the beyond, makes them appear as ghosts. In death, they transcend the circumstances of this place that I love and hate all at once and become supernatural.
Writer Jesmyn Ward recounts the deaths of five men from her rural Mississippi community in as many years. In her award-winning memoir , she delves into the lives of the friends and family she lost and tries to find some sense among the tragedy. Working backwards across five years, she questions why this had to happen over and over again, and slowly unveils the long history of racism and poverty that rules rural Black communities. Moving and emotionally raw, Men We Reaped is an indictment of a cruel system and the story of a woman's grief and rage as she tries to navigate it.
Cork Dork by Bianca Bosker
He believed that wine could reshape someone’s life. That’s why he preferred buying bottles to splurging on sweaters. Sweaters were things. Bottles of wine, said Morgan, “are ways that my humanity will be changed.”
In this work of immersive journalism , Bianca Bosker leaves behind her life as a tech journalist to explore the world of wine. Becoming a “cork dork” takes her everywhere from New York’s most refined restaurants to science labs while she learns what it takes to be a sommelier and a true wine obsessive. This funny and entertaining trip through the past and present of wine-making and tasting is sure to leave you better informed and wishing you, too, could leave your life behind for one devoted to wine.
Illustrated Narratives (Comics, graphic novels)
Once relegated to the “funny pages”, the past forty years of comics history have proven it to be a serious medium. Comics have transformed from the early days of Jack Kirby’s superheroes into a medium where almost every genre is represented. Humorous one-shots in the Sunday papers stand alongside illustrated memoirs, horror, fantasy, and just about anything else you can imagine. This type of visual storytelling lets the writer and artist get creative with perspective, tone, and so much more. For two very different, though equally entertaining, examples, check these out:
Calvin & Hobbes by Bill Watterson
"Life is like topography, Hobbes. There are summits of happiness and success, flat stretches of boring routine and valleys of frustration and failure."

This beloved comic strip follows Calvin, a rambunctious six-year-old boy, and his stuffed tiger/imaginary friend, Hobbes. They get into all kinds of hijinks at school and at home, and muse on the world in the way only a six-year-old and an anthropomorphic tiger can. As laugh-out-loud funny as it is, Calvin & Hobbes ’ popularity persists as much for its whimsy as its use of humor to comment on life, childhood, adulthood, and everything in between.
From Hell by Alan Moore and Eddie Campbell
"I shall tell you where we are. We're in the most extreme and utter region of the human mind. A dim, subconscious underworld. A radiant abyss where men meet themselves. Hell, Netley. We're in Hell."
Comics aren't just the realm of superheroes and one-joke strips, as Alan Moore proves in this serialized graphic novel released between 1989 and 1998. A meticulously researched alternative history of Victorian London’s Ripper killings, this macabre story pulls no punches. Fact and fiction blend into a world where the Royal Family is involved in a dark conspiracy and Freemasons lurk on the sidelines. It’s a surreal mad-cap adventure that’s unsettling in the best way possible.
Video Games and RPGs
Probably the least expected entry on this list, we thought that video games and RPGs also deserved a mention — and some well-earned recognition for the intricate storytelling that goes into creating them.
Essentially gamified adventure stories, without attention to plot, characters, and a narrative arc, these games would lose a lot of their charm, so let’s look at two examples where the creative writing really shines through:
80 Days by inkle studios
"It was a triumph of invention over nature, and will almost certainly disappear into the dust once more in the next fifty years."

Named Time Magazine ’s game of the year in 2014, this narrative adventure is based on Around the World in 80 Days by Jules Verne. The player is cast as the novel’s narrator, Passpartout, and tasked with circumnavigating the globe in service of their employer, Phileas Fogg. Set in an alternate steampunk Victorian era, the game uses its globe-trotting to comment on the colonialist fantasies inherent in the original novel and its time period. On a storytelling level, the choose-your-own-adventure style means no two players’ journeys will be the same. This innovative approach to a classic novel shows the potential of video games as a storytelling medium, truly making the player part of the story.
What Remains of Edith Finch by Giant Sparrow
"If we lived forever, maybe we'd have time to understand things. But as it is, I think the best we can do is try to open our eyes, and appreciate how strange and brief all of this is."
This video game casts the player as 17-year-old Edith Finch. Returning to her family’s home on an island in the Pacific northwest, Edith explores the vast house and tries to figure out why she’s the only one of her family left alive. The story of each family member is revealed as you make your way through the house, slowly unpacking the tragic fate of the Finches. Eerie and immersive, this first-person exploration game uses the medium to tell a series of truly unique tales.
Fun and breezy on the surface, humor is often recognized as one of the trickiest forms of creative writing. After all, while you can see the artistic value in a piece of prose that you don’t necessarily enjoy, if a joke isn’t funny, you could say that it’s objectively failed.
With that said, it’s far from an impossible task, and many have succeeded in bringing smiles to their readers’ faces through their writing. Here are two examples:
‘How You Hope Your Extended Family Will React When You Explain Your Job to Them’ by Mike Lacher (McSweeney’s Internet Tendency)
“Is it true you don’t have desks?” your grandmother will ask. You will nod again and crack open a can of Country Time Lemonade. “My stars,” she will say, “it must be so wonderful to not have a traditional office and instead share a bistro-esque coworking space.”

Satire and parody make up a whole subgenre of creative writing, and websites like McSweeney’s Internet Tendency and The Onion consistently hit the mark with their parodies of magazine publishing and news media. This particular example finds humor in the divide between traditional family expectations and contemporary, ‘trendy’ work cultures. Playing on the inherent silliness of today’s tech-forward middle-class jobs, this witty piece imagines a scenario where the writer’s family fully understands what they do — and are enthralled to hear more. “‘Now is it true,’ your uncle will whisper, ‘that you’ve got a potential investment from one of the founders of I Can Haz Cheezburger?’”
‘Not a Foodie’ by Hilary Fitzgerald Campbell (Electric Literature)
I’m not a foodie, I never have been, and I know, in my heart, I never will be.
Highlighting what she sees as an unbearable social obsession with food , in this comic Hilary Fitzgerald Campbell takes a hilarious stand against the importance of food. From the writer’s courageous thesis (“I think there are more exciting things to talk about, and focus on in life, than what’s for dinner”) to the amusing appearance of family members and the narrator’s partner, ‘Not a Foodie’ demonstrates that even a seemingly mundane pet peeve can be approached creatively — and even reveal something profound about life.
We hope this list inspires you with your own writing. If there’s one thing you take away from this post, let it be that there is no limit to what you can write about or how you can write about it.
In the next part of this guide, we'll drill down into the fascinating world of creative nonfiction.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
We have an app for that
Build a writing routine with our free writing app.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:

What is Creative Writing?

Written by Scott Wilson

Creative writing is any kind of writing that employs creative literary or poetic techniques in the service of either fiction or non-fiction writing. It involves original composition and expressiveness of the individual author.
Ask ten creative writing professors what creative writing is, and you’ll get eleven different answers. Turn to the dictionary and the definition invokes invention and incorporation of imagination. But what are the limits of imagination? Where does invention begin?
Every sentence in every work ever written began as an act of creation in the mind of the writer.
Creative writing may be most easily defined by what it is not…
- Technical writing
- Professional or business writing
- Scholarly or academic writing
Creative writing is the entire body of the writer’s craft that falls outside the boundaries of the ordinary.
Yet you will find many entries in the canon of those fields that might also be considered creative writing. No one would consign Truman Capote’s groundbreaking In Cold Blood to the sterile cells of mere journalism. But that haunting novel is unquestionably also an important work of investigative reporting.
So, what is creative writing, if a non-fiction novel of a horrific quadruple murder falls into the same scope as a classic of American literature like To Kill a Mockingbird ?
It has to do with style and art. Creative writing goes to the heart of the individual expressiveness of the writer. It breaks the boundaries of the typical. That’s an exercise of artistic skill that can happen in any topic, toward almost any goal. And it’s the heart of what it is to be a writer, no matter what you write about.
Defining creative writing isn’t easy. Rooms full of the best authorities routinely disagree. But what is creative writing , isn’t the most interesting question to ask here. Instead, we would be best served by asking another:
Why Is Creative Writing Important?

Storytellers were plying their craft thousands of years before the written word was invented. The creative spark doesn’t belong to words. It may not even depend on language. It draws instead on a deep part of what it is to be human. Invention, imagination, the urge to create… these are all deep and vital parts of the human experience.
Creative writing is important because it is evocative.
That well of creativity flows forth in many arts and forms of expression. But in creative writing it has found a medium where it can be both preserved and shared. It’s a method of human connection that has no expiration date, no geographical or even cultural limit.
Writers touch the souls of their contemporaries first. But like Shakespeare, Wordsworth, and Lady Murasaki, their reach may also span generations.
Creative Writing Fuels Communication in All Forms of Writing
Although fiction is the first refuge of creative writing, that expressiveness serves the purposes of just about any kind of author.
The goals of most other forms of writing are focused on various kinds of literal communication. A journalist seeks to convey the facts and the context of important news stories. Technical writers need to communicate the details of operating programs and machinery, clearly describing all kinds of minute details with zero ambiguity. Business communications are created with a view toward clarity and concision—helping readers get the main points of the piece quickly and without confusion.
Creative writing can also help to serve these purposes.
Creative writing taps into a different level of communication. While it may, and often does, aspire to other goals like offering clarity and detail, it also goes toward developing emotional connection. The reader will take away more than mere words from a piece of creative writing.
Creative Writing is Important For Making Other Kinds of Writing Compelling
Just as importantly, creative writing entertains. In a story about the importance of algorithmic and high-frequency trading, all kinds of technical details must be absorbed to make sense of the issues. Both technological and economic concepts have to be introduced. In a comprehensive article about the subject, readers from outside the field could be expected to nod off about two pages in.
But put the story in the hands of Michael Lewis, and you get Flash Boys , a New York Times Best Seller.
It’s not important that Flash Boys did well because it was entertaining, however. It’s important because the market trends and activities it described have real impacts on many of the readers. Retirement funds, college savings, family investments… all are affected by the story Flash Boys tells. Today, millions of readers who would never otherwise have understood how their investments were being handled can make an informed assessment… thanks to creative writing.
How To Separate Creative Writing From Less Creative Forms of Writing

In general, it’s safe to say that a piece of writing is creative when it makes use of literary devices such as:
- Narrative development
- Imagination and invention
In Cold Blood passes this test due to Capote’s use of characterization, plot development, and world-building. It’s considered today to be a pioneering example of the non-fiction novel, a paragon of the creative writing world.
The original crime reports, local newspaper articles, and subsequent court documents detail the same events with the same participants. Yet they are not works of creative writing. The incident is described in dry, straightforward, technical language. The timeline is linear and offered without consideration of pace or drama.
Both Capote and the authors of those other articles and documents set out to inform. But Capote’s goal was also to captivate.
New Journalism Tells the Story of How Creative Writing Has an Important Role in Non-Fiction

Books like Wolfe’s The Right Stuff mixed truth and dramatization, documentation and invention, to tell larger stories about serious events. In dramatizing those stories, New Journalism writers also drew more readers and achieved broader awareness of the stories.
At the same time, long-form New Journalism pieces, deeply researched and documented, were able to report stories in depth in a way that traditional journalism often did not. By invoking plot, characterization, and narrative structures, the New Journalists could keep readers involved in long and complex issues ranging from crime to politics to culture.
New Journalism is important in defining what is creative writing because it is clearly an example of both creative and journalistic writing. It demonstrates the ways that creative writing can serve other forms of writing and other kinds of writers.
Of course, it’s also possible to come at the divide from the other shore. Categories of writing that are clearly creative in nature include:
- Novels and novellas
- Flash fiction and short stories
- Plays and film scripts
These works incorporate elements of storytelling that may not always be present in other forms of writing. A newspaper article will often have a setting, action, and characters; creative writing will offer plot, pacing, and drama in describing the same story.
What is Creative Writing Coursework Like in College Degree Programs?

All university students are exposed to basic coursework in English language and communication skills. These all go to the elementary aspects of writing—the ability to construct a sentence, a paragraph, a paper. They teach grammatical rules and other elements that make a work readable to any reader of the English language.
Even the general education requirements in college programs touch on creative writing, however. Students may be assigned to write essays that explore creative styles and imagination. They’ll be assigned to read novels and stories that are time-tested examples of the finest kinds of creative writing. And they’ll be asked to explore their impressions and feelings, and to exercise their imaginations and analyze the intent of the author.
Creative writing programs go beyond the basics to touch the imagination of the writer.
Creative writing exists just on the other side of those general English and literature courses. Students in creative writing classes will be asked to take the extra step of creating their own stories using the techniques they have learned.
In fact, they may be encouraged to break the same rules that were so laboriously learned in their regular English writing classes. Creative writing works to allow writers to tap into their own imagination and emotion to forge a deeper connection with readers.
Student Workshops Offer an Interactive Way of Learning What Creative Writing Is All About
Creative writing degrees will go much further into developing a sense of what creative writing is. they continue to include many reading assignments. but instructors also introduce concepts such as:.
Genre is the method used to categorize written works. Creative writing programs explore the tropes and expectations that exist for different genres and deconstruct them for better understanding.
Story structure and form
The structure and form of a novel and a short story are very different. Creative writing programs explore different formats and how they impact creative storytelling.
Plot is not a universal feature of creative writing, but a good plot can make or break a creative work. Classes look at the features and composition of plot, and also teach plotting.
Voice, tone, and creative expression all come out of the narration of a piece of creative writing. Creative writing courses explore both the textbook forms of narrative and show how to use it to serve plot and story.
Style and rhythm
One clear feature of creative writing in all genres is that it rests on a sense of rhythm and of styling that other types of writing ignore. Many courses found in creative writing degree programs explore the ways in which writing style serves story and hooks the reader.
In addition to formal classes, students will better learn why creative writing is important and the purposes it serves through workshops. These informal gatherings are designed to foster discussion, to present examples of different types of writing, and to critique and hone individual creative writing skills .
Through that process, creative writing degrees help students better identify what creative writing is and how to use it effectively.
Creativity is Important No Matter What Your Career Goals in Writing May Be

Creative writing training allows writers in any genre to develop more complete, more meaningful, and more memorable ways to get a point across. Using the skills and techniques learned in creative writing courses can inject humor, gravity, and other sensations into any piece of writing. And those very techniques can improve concision and clarity.
Figuring out what creative writing is and what it is not, is the first thing you should leave behind in a writing career. The dry definitions of the dictionary or droning English professors are the last place you should look.
Creative writing is the process of engaging your imagination and talent to serve the purpose of whatever piece of writing you are working on. And that’s why creative writing is important.
Creative Writing Research: What, How and Why
- First Online: 23 July 2023
Cite this chapter

- Graeme Harper 2
119 Accesses
Creative writing research is actively moving us further toward knowing what creative writing actually is—in terms of our human actions and our responses when doing it. It is approaching such things as completed literary works and author recognition within the activities of creative writing, not mostly as representatives of that practice, and it is paying close attention to the modes, methods and functions of the writerly imagination, the contemporary influence of individual writer environments on writers, to writerly senses of structure and form and our formation and re-formation of writing themes and subjects. We certainly understand creative writing and creative writing research best when we remain true to why creative writing happens, when and where it happens, and how it happens—and creative writing research is doing that, focusing on the actions and the material results as evidence of our actions. Creative writing research has also opened up better communication between our knowledge of creative writing and our teaching of creative writing, with the result that we are improving that teaching, not only in our universities and colleges but also in our schools.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Tesla, Nikola. 1915. The wonder world to be created by electricity. Manufacturers Record 38–39
Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The Honors College, Oakland University, Rochester Hills, USA
Graeme Harper
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Graeme Harper .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Hong Kong Metropolitan University, Ho Man Tin, Hong Kong
Mo-Ling Rebecca Leung
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Harper, G. (2023). Creative Writing Research: What, How and Why. In: Rebecca Leung, ML. (eds) Chinese Creative Writing Studies. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-0931-5_12
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-0931-5_12
Published : 23 July 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-99-0930-8
Online ISBN : 978-981-99-0931-5
eBook Packages : Literature, Cultural and Media Studies Literature, Cultural and Media Studies (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
the nature of creativity in writing
That which is creative results from originality of thought or expression; it's imaginative or original.
From a literary perspective, creative writing is any writing that is the product of original composition, where composition is the art of putting words and sentences together in accordance with the rules of grammar and rhetoric. Creative writing is the act or process of producing a literary work.
Creative writing includes any writing that goes outside the bounds of normal professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature. Writing is usually recognized as creative when its emphasis is placed on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes.
Examples of the kinds of works that can be creatively written include literary forms such as novels, biographies, short stories, and poems.
Creative writing is not restricted to fictional writing, however, as many readers believe. For example, autobiographical and biographical writing can be very creative even though a biography is a written account of a person's life, an organization, a society, a theater, and animal, etc. Subjects like these are drawn from real life, so they must be treated authentically, in a nonfictional vein.
Thus both fictional and nonfictional works can be creatively written.
As with many other literary terms, the definition for what it means to say that a written composition is creative is rather loose. For example, consider feature stories. A feature story is a newspaper or magazine article or report of a person, event, or an aspect of a major event. Feature stories often have a personal slant and are written in an individual style. Personal slants and individual styles are aspects of composition usually associated with creative writing. Technically, then, it's possible to considerer feature stories a form of creative literature, even though strictly speaking they fall under the literary category of journalism.
Academics and other teachers have their own classifications for creative writing. Typically they separate creative writing classes and topics into fictional prose and poetry on one hand and nonfictional writing on the other hand. In fiction and poetry classes their focus is on teaching students how to write in an original style as opposed to imitating preexisting genres. Academics also tend to separate the teaching of writing for the screen and stage (screenwriting and playwriting) from each other, as well as from other kinds of creative writing, even though they both definitely fall under the category of creative writing.
In a general sense, the term creative writing is a contemporary process-oriented name for what has been traditionally been called literature, an activity and a field of authorship that includes a variety of genres.
- For The Muse Of Literature's definition of literature , visit the section called "Literature" versus "l iterature:" tap or click here .
the nature of literary creativity
What's literary creativity?
At first, creativity, creative writers, and creative literature may seem to be entities that are hard to put one's arms around. If you write, exactly what does it mean to say that you demonstrate creativity or write creatively? Why are you creative? What makes you so?
If you're an author who's produced a body of creative literature, exactly what does it mean to say that your works are creative as a whole? Why is one body of work more creative than another that you've produced that is not as creative? Or why is your work less creative than another author's body of work?
In large measure, creative writing is difficult to define because an author's creativity and that of his work exhibit numerous abstractions, vague concepts, and inexplicit qualities that are hard to pin down clarify, or judge. There's no one clear cut formula that defines the nature of creative writing generally, and there's no special way to write that guarantee's that creative work will result. In other words, the properties that make any literary work creative are amorphous: they evince no definite form or specific shape, and they show no particular character, pattern, structure, or composition.
In fact, the world's body of creative writers and the great literary works they have generated possess greatly divergent literary properties, in some cases opposing properties; yet they all seem to fit the bill one way or another. Ironically, one of the properties that characterizes this mass of creative authors and their works is divergence itself; that is, the more unique and original an author or his works, the more creative they are considered to be.
Despite all this intangibility, let's take a swipe at defining creative writing anyway. Instead of procrastinating, if we do this now perhaps later we'll be in a better position to refine what we come up with.
Here are a few preliminary albeit rough ideas for what it means for an author to be creative or to write creatively. They're not all specific or unique to writing, but as a group they all apply to one extent or another:
- To create anything is to to cause it to come into being, as something unique that would not naturally evolve or that is not made by ordinary processes. It's to evolve a thing from one's own thought or imagination, as a work of art, an invention, or as the contents of a creative work of writing.
- Creativity is the state or quality of being creative. It's the capacity to transcend traditional ideas, rules, patterns, relationships, or the like, and to originate meaningful new ideas, forms, methods, interpretations, etc.; it's to express originality, progressiveness, or imagination.
- As a process, creativity is a systematic series of actions directed toward some new or different end or objective; it's a continuous action or set of actions, operation, or series of changes designed to take place in a definite manner that produces a novel result.
- From a writer's point of view, creativity is the process by which he utilizes his innate creative ability to produce written works that exhibit creativity. The process itself may be new and creative.
- Creative writing is writing that expresses an author's creative imagination and originality of thought or expression.
- Writing creatively is the process or act of setting down text that results in literary works that exhibit creativity.
The Muse Of Language Arts attempts to elaborate and to narrow these definitions in sections that follow.
what is creative writing —really?
For example, to keep their discussions simple, many literati — those who specialize in literary subjects like these— equate creative writing with nonfiction writing . According to them, if it's creative writing, it's fiction, and if it's nonfiction, it's not creative writing. They exclude nonfiction writing from creative literature .
They take the inverse position as well. If its fictional writing, it's creative; if it's nonfictional writing, it's not creative.
But actually, among themselves they acknowledge that creative writing is not exclusively fictional, and that not all fictional writing is creative. When pressed to explain, they usually don't hesitate to point out that there's more to the subject than appears on the surface.
As The Muse will soon make clear, it may not at first be apparent that the creative writing definitions cited in the preceding section actually span virtually any kind of writing, even nonfiction writing, so long as nonfictional writing ventures outside the bounds of normal disquisition. Thus creativity may even be exhibited by professional, journalistic, scholarly, or technical forms of writing, depending on how they are done.
In actuality, whether or not it's fictional, a piece of writing is creative if it emphasizes narrative craft, character development (when character and personality are legitimately involved by subject or purpose), and by extensive use of literary tropes.
In the sense of the word creative cited above, creative writing includes virtually any kind of writing, even nonfiction, so long as it ventures outside the bounds of normal disquisition. Thus it may include professional, journalistic, scholarly, or technical forms of writing. Whether or not it's fictional, a piece of writing is creative if it emphasizes narrative craft, character development (when character and personality are legitimately involved), and extensive use of literary tropes.
Notice that virtually all literary and other kinds of fictional works contain significant passages that are nonfictional. For example, even novels, which by definition are works of fictional narrative prose, frequently employ nonfictional passages to introduce relevant facts that describe and establish credibility, background, situation, back stories, and for many other purposes. The fact that novels include nonfiction doesn't automatically mean that they are uncreative. As another example, historical novels are fictional works based on real people or on actual people, locations, or events drawn from history.
Poetry provides yet another example of why neither fiction nor nonfiction can legitimately be equated either with creativity or with non-creativity. A poem is a literary work in metrical form; it sings; it's rhythmical; it's spiritual and aesthetic; it's a highly creative construct. Further, poetry is a literary form that is musical, elevated, and beautiful. Many poems, especially those dubbed lyrical, are outpourings of a poet's personal thoughts and feelings; they seem to express a poet's spontaneous and direct emotions and reactions.
What other form of literature is more artful, more intensely imaginative, more of an outpouring of an author's own thoughts and feelings than is a great poem? Yet many epic and dramatic poems tell tales that are written at least partly to set forth, explain, and interpret nonfictional information such as historical events, real people and places, and actual things. Some convey facts and figures, describe inventions, explain cause-effect relationships, and much more that is not fiction.
Yet the subjects of many poems like these are based on historic fact, real persons, places, or events. Some such poems even seem to gain greater power because the poet is reacting creatively to real rather than to imaginary happenings. Witness poet Henry Wadsworth Longfellow's Paul Revere's Ride , affectionately known as the Midnight Ride of Paul Revere ; witness also ancient Greek tragedy, much of which is a religious outpouring about mythical events believed at the time to be literal, historic truth.
Is all creative writing literary? Is all literature creative?
Most literary works are structured in accordance with the rules of one or another specific literary form —for example, works of art such as poetry, novels, history, biography, and essays each have their own purposes, forms, styles, and ways to be written. Further (and very important), to be called literature in this higher sense of the word a work must express ideas of permanent and universal interest.
Any kind of printed material also can be called literature if it can be written down or printed, has a purpose, and makes sense. This kind of literature includes such forms and writing styles as circulars, leaflets, technical manuals, advertising billboards, or handbills. Although literary forms like these tend to have specific writing structures and writing styles, they don't necessarily have to be structured or written in any particular way; their purpose defines what they are. And very important, they aren't intended to express ideas of permanent and universal interest.
In order to distinguish these two different kinds of literature from each other, The Muse Of Literature reserves two ways to refer to them. The Muse refers to the first kind, the one that expresses ideas of permanent and universal interest, as Literature spelled with a capitol "L;" and The Muse refers to the other kind, the one that does not express ideas of permanent and universal interest, as literature spelled with a lower case "l."
- Explore further the numerous definitions and meanings of the word literature. Visit The Muse Of Literature's feature titled What' s Literature With A Capital "L" : tap or click here.
Cognoscenti who look up their noses at literature regard Literature as offering authors the opportunity to write creatively, and regard literature as not offering authors this opportunity; and the public tends to follow them in their wake. Nothing could be farther from the truth. Ingenuity and imagination are pervasive talents that follow us into almost all corners of human endeavor. Thus, an author who writes creatively does not necessarily have to produce writing that's Literature in the formal sense of the word; literature will do.
It's vital to realize that almost all kinds of writing offer authors the potential to be creative in one way or another, whether they write Literature or literature. T he literature of a science like ornithology, for example, can be creative despite it's factual, unemotive, and unaesthetic character. Literature that deals with a particular scientific subject like ornithology can be creative, as can tourism and travel guides, magazine articles about Hollywood, or news articles about politics, people, and space travel, and many other forms of authorship.
- For some ideas of how and why writing literature can be a creative author's act, see the section titled creative writing and expository writing below on this page.
- Expository writing is a form of nonfiction that encompasses some of the most unimaginative writing there is. Yet it also can be creative. Visit The Muse Of Language Arts feature titled The Expository Prose Writing Creative Domain to find out how and why: tap or click here.
In summary, what most people mean by creative writing depends on their definition of the word creative . Definitions like these can be misleading. In its broadest sense, the act of writing creatively actually demands (and results from) a certain kind of approach to writing and an attitude toward writing rather than from the definition they apply or on adherence to standard or conventional artistic formulas such as predefined literary forms, choice of writing mode, or style of expression.
Indeed, at core creative writing is anti-formulaic; it's the opposite of writing that conforms to rules, regulations, and conventions. In is in this broad sense that The Muse Of Language Arts applies the term creative.
creative writing and non-creative writing compared
The distinction between creative writing and noncreative writing is stark. Hopefully, this comparison between the two forms of writing will help shed light on the nature of of creative writing.
Is there any truth to the notion that, taken as a whole, the world's entire body of fictional literature is more creative than the entire body of nonfictional literature?
However, that doesn't mean that fictional literature is always creative, or that nonfictional literature is never creative, as many people seem to believe. They base this view on the fact that fictional authors invent the things they write but nonfiction authors don't invent because they stick to facts, plain and simple. This view is misguided.
There's no objective way to measure creativity; there are no such things as creativity units and there are no creativity meters for measuring it. But there are good reasons to believe that, taken as a whole, the entire body of fictional literary works is more creative than the entire body of nonfictional literature.
Why? In part, this posture is credible because the process of writing fiction is itself inherently more creative than the process of writing nonfiction. Authors who write fiction must invent the sham facts, people, events, objects, and other components that make up their works, a task that's more challenging than simply referring to, conveying, or writing about actual facts that come from other sources. The act of writing fiction pressures authors to drum up the accounts, characters, stories, subjects, themes, and other literary elements they write about. Just being able to to set words on paper forces fiction writers to think things through, imagine, and innovate.
Also, many kinds of fictional works tend to express symbols and kinds of abstract concepts that don't arise in connection with descriptions of objective facts. Fiction writers like to write about personal and original observations and reactions to their inner lives and outer surroundings. These kinds of topics demand more creative forms and styles of expression.
Although fictional writing contains significant amounts of invented (fictional) information, it's critical to realize that it also contains nonfictional information. If it didn't contain actual (nonfictional) information, there would be nothing for a writer to base his fictional creations on. How could he develop fanciful characterizations of fictional people or places that readers could recognize and understand if there were no real people or places in the world on which to base them? If a writer's fictional inventions were totally his own, they would be unfounded; readers wouldn't recognize them or understand what they mean.
The same sort of premise holds true for nonfictional writing, but in an inverse way. For the most part, non-fiction writers describe real-world facts given to them by others or information they dig up for themselves by doing research; to the best of their ability, they do not present facts unless they are actually present and correct. Nonfiction writers do not manufacture information out of whole cloth with their own imaginations.
Nevertheless, although nonfictional writing primarily contains real factual information, it's critical to realize that it also may contain fictional information. For example, it should come as no surprise that many "how to" illustrations in user manuals are examples made up by their authors. Examples like these should accurately represent reality but they're not meant to be literally correct.
- Explore creative fiction versus creative nonfiction at The Muse Of Language Arts feature of the same name: tap or click here .
Who and What decides whether a literary work is creative?
As just noted, a creative literary work is any kind of writing that evolves from an author's thought or imagination, original ideas or insights, kinds of subjects, modes of expression, points of view, or other literary features or techniques that are significantly new, different, and important; it's a departure from the commonplace and mundane. The creative writing that's exhibited by a literary work is its originality of thought or expression. A work that's creative results from and displays its author's originality of thought, expression, and imagination.
As a result of mistakenly equating creativity with fictional literature, people often tend to misjudge a work's creativity solely by its genre, literary form, and other similar literary characteristics rather than by its actual creative merit. They tend to strongly associate creativity with fictional prose narratives such as novels and short stories; and they strongly associate non-creativity with factual prose such as biographies, histories, essays, etc. But that's a mistake. Novels and short stories are always fictional but they're not always creative; biographies, histories, and essays are always nonfictional, but they're often creative.
What caused these misconceptions about literary creativity to become conventional wisdom? High school and college teachers commonly teach them to students. Teachers illustrate their points about literature with samples that reinforce their conventional preconceptions or biases. Then students carry these false notions with them out of school and into their everyday lives.
These practices gradually became reinforced in schools by convention. Students became accustomed to thinking that fictional works are creative by virtue of their fictional nature, and to thinking that nonfictional works are not creative by virtue of their factual nature.
Why did teachers and schools assume these conventions? How did they become conventional?
Historically, university professors. educators, scholars, literary critics, writing instructors , book reviewers, and book sellers eventually came to apply the term creative writing to fictional works like novels, which they especially prized for their author's imaginary and exciting creations; and to apply the term expository writing to comparatively dull, nonfictional works like newspapers, manuals, or trade journals, which they prized for accurately and economically exposing facts of an objective, factual, and unimaginative character.
This practice of using literary genres and forms to distinguish between creative and non-creative writing rather than to use a work's aesthetic qualities gave teachers a straightforward way to describe and refer to a work's creativity. It was simpler and handier to use a work's genre and form to identify writing that's creative than to use a work's aesthetic qualities, which are less tangible and more difficult to objectively qualify.
creative writing and expository prose writing
By its very nature, expository prose writing is principally a nonfictional medium. Nevertheless, as explained above, that doesn't mean that a given piece of expository prose writing is automatically uncreative.
So when is a piece of expository writing creative?
To answer this questions, first it's necessary to explain what is meant by expository prose.
Exposition is the act of expounding, setting forth, or explaining. To expose is to present, view, exhibit, or display; it's to make known, disclose, or reveal facts, concepts, or ideas. A piece of prose writing is expository when it serves to expound, set forth, or explain.
A literary exposition is a type or class of literary work that's written with this express objective in mind, and no other; its a detailed statement, explanation, or explanatory treatise written in nonfictional narrative prose. Written expositions employ a specific type, class, and style of writing called expository writing.
varieties of expository documents Good expository writing displays literary characteristics that enhance a work's ability to convey facts and general information and to explain them. One of the most important of these characteristics—nay, a requisite characteristic— is that expository works are made up exclusively of nonfictional narrative prose. Consequently, they are only written in nonfictional writing styles. There are many, many varieties of expository prose documents. Some of the most ubiquitous ones are: Reference works (dictionaries, encyclopedias, etc.) Technical works (biological reports, engineering reports, etc.) The impersonal and objective essay High school chemistry or physics lab reports Informational newspaper articles Trip reports Certain kinds of television news Annual corporate reports Certain kinds of nonfictional books (histories, geographies, catalogs, text books, etc.) Scholarly research papers in academic subjects such as history and biography Treatises University syllabuses PhD and Masters theses Corporate policies and procedures manuals Term papers User manuals Dissertations Journals The conjectural or personal essay Course outlines Each of these writing styles is actually a class or group of writing styles. For example, the majority of different annual reports adhere to the same overall language characteristics for annual report writing styles, but one corporation may define a specific writing style for its annual report that differs in details from the style of another corporation. In many cases, not all, the names for many of these expository prose writing styles are also the names for the literary forms that use them. For example, a dictionary is a book containing a selection of the words of a language, usually arranged alphabetically, giving information about their meanings, pronunciations, etymologies, inflected forms, etc.; they are expressed in either the same or another language. The majority of dictionaries use the same or a similar literary format and the same or a similar expository writing style. Consequently, these two aspects of dictionaries —writing style and literary format— have come to be identified with one another. So, most often when you pick up a Webster's dictionary you're not surprised if you see an expositional writing style which is almost the same as the one you see when you pick up a Random House dictionary. Further complicating the expository name calling problem is the fact that two organizations may employ different literary formats or expository writing styles for an expository document they call by the same name. For example, a computer thesaurus is radically different from a paper-bound thesaurus such as The International Roget's Thesaurus . Not only are the names of many expository writing styles the same as their literary forms, many expository literary forms and their writing styles are virtually identical with each other, even though they're called by different names. For example, a dissertation, treatise, and a thesis are essentially the same kind of exposition; they're different designations for the same thing. One source (a dictionary) defines them as: Dissertation: different designations for a written essay, treatise, or thesis, especially (but not always) one written by a candidate for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Treatise: a formal and systematic exposition in writing of the principles of a subject, generally longer and more detailed than an essay Thesis: a proposition stated or put forward for consideration, especially one to be discussed and proved or to be maintained against objections. Some sources might employ these terms interchangeably, as though they all designate the same kind of document; others might not, depending on the situation. That's literary terminology ambiguousness for you! If you're new to exposition, all this may seem a bit confusing at first, but at base it's really a very simple kind of writing. What's vital to remember concerning exposition —what all the expositional forms and writing styles have in common— is that they are all nonfictional. expository grammar and literary characteristics Authors who write expositions often adopt a particular set of grammatical and literary guidelines, especially when they have strong reasons to objectify the material they write, to be impersonal. and to suspend emotional involvement. In order to appear more neutral and objective, they strive to remain anonymous. For example, reference works like dictionaries and encyclopedias normally restrict names of linguists who compile their contents to a cover or title page; they often omit them completely. Corporate policies and procedures manuals and annual reports seldom identify their writing staff because they want to impress readers with a corporate image that appears larger than the individuals who work for it. This anonymity also helps insulate writers from possible public or third-party criticism. Here are the grammatical and literary guidelines that help expository authors write in a neutral manner: Sentence wording should avoid directing a reader's attention to the fact that an author is implicit in the prose he writes. Write with third grammatical person or verb forms, pronouns, etc. Use singular or plural pronouns (he, she, it, they, etc.) in the nominative case. Do not write in the first person or refer to yourself with pronouns. Do not take authorship credit unless appropriate. Do not identify yourself by name in the body of text. Use third person singular verb forms not accompanied by an expressed subject, as in it is raining . Regularly accompany third person verbs with an empty subject word, as in It is raining . Employ only indefinite pronouns and pronominal references. Most annual corporate reports, scholarly research papers on academic subjects, and user manuals possess these literary characteristics, to name a few. The essay An essay is a short literary composition on a particular theme or subject, usually in prose and generally analytic, speculative, or interpretative. It's a kind of expository prose writing because its primary purpose is to expose information and facts. However, it differs from other kinds of expository prose writing in that its purpose also includes analyzing, speculating about, and interpreting the information and facts it presents. Because of this more extensive purpose, the essay is a special variety of expository prose writing. It comes in two forms: The Muse Of Language Arts refers to these forms as: 1) the impersonal and objective essay , and 2) the conjectural or personal essay . Most essays are one or the other of these two kinds of essay; some combine elements from each of them. The impersonal and objective essay Impersonal and objective essays display most of the literary characteristics of other kinds of expository narrative prose writing except that: 1) they follow a free-form prose literary structure that's at the discretion of the author, and 2) they objectively and impersonally explore, explain, analyze, speculate about, and interpret; they introduce conjectures and opinions; and they draw conclusions about relevant subjects, people, events, ideas, issues, etc. These kinds of essays are free-form in the sense that authors are free to adopt any prose writing style they believe to be consistent with their purpose and appropriate for their audience, their publishing medium, or occasional circumstances. Usually that writing style is simple narrative prose that adheres to the grammar and literary characteristics of expository prose noted above. But authors are free to modify these characteristics if they see fit. Impersonal and objective essays are a type literature that The Muse Of Literature spells with a lower case "l," as in literature ; they do not belong to the type of literature that The Muse spells with a capital "L," as in Literature. Because authors of these kinds of essays normally seek to remain anonymous, personal and objective essays are normally penned in the third person. Because it's unemotional and impersonal, this kind of essay is not writing in which expression and form, in connection with ideas of permanent and universal interest, are characteristic or essential features. It's literature spelled with a lowercase "l." Unfamiliar with lower case "l" literature and capital "L" Literature? Visit The Muse Of Literature's page titled "Literature" versus "l iterature" to find out what they are: tap or click here. the conjectural or personal essay Not all essays are completely impersonal, objective, and cool; some are very conjectural and very personal. For these reasons, The Muse calls essays like these conjectural or personal essays . Impersonal and objective essays and conjectural or personal essays both follow a free-form prose literary structure that's at the discretion of the author. Because personally-felt reflections or causes are involved, these kinds of essays are normally penned in the first person. However, unlike impersonal and objective essays, conjectural or personal essays are anything but objective and impersonal. Their primary purpose is to subjectively explore, explain, analyze, speculate about, and interpret; they introduce subjective conjectures and opinions; and they draw subjective, sometimes emotional conclusions about relevant subjects, people, events, ideas, issues, etc. Authors choose to write these types of essays for a variety of reasons. Their purpose might be to: Claim or publicize credit for something they've accomplished Convince or arouse readers to take action Prove a thesis Declare a personal victory Win an argument Make a point Speculate about a proposition or theory Achieve some a controversial, problematical, or personal objective Interpret or analyze something Convey anger or other emotions Convince readers to believe in, reject, or accept of an idea Publicly express gratitude, admiration, or disgust Win readers over to a cause Explain a heartfelt idea Expositions like these usually belong to the type literature that The Muse Of Literature spells with a capital "L" —Literature. Expositions like these tend NOT to belong to the type of literature that The Muse spells with a lowercase "l"—literature. Because it's emotional and personal, this kind of essay is writing in which expression and form, in connection with ideas of permanent and universal interest, are characteristic or essential features. It's Literature It's literature spelled with a capital "L."
creative writing and nonfiction
As already noted many readers and writers accept the notion that nonfiction writing is uncreative just because it's not fictional. True, not all nonfiction writing is creative; much of it is even dull, drab, or commercial. But there's nothing that prevents nonfiction writers from exercising their imaginations and skills, from writing creatively, if they choose to do so. All they have to do is assume the right mind set and sit up straight, to remain fresh, bright, and alive.
Take expository writing for an example. Expository writing is writing or speech primarily intended to convey information or to explain; it's a detailed statement or explanation; it's an explanatory treatise:
No kind of nonfictional writing is more nonfictional than expository prose. Yet, if you examine The Muse's description of the nature of creative writing that you'll find near the top of this page and compare it with the varieties of expository prose outlined in the preceding sections, you'll probably conclude that expository prose writing can be very creative.
After all, nothing can grab your attention like the news of the day when war is immanent and bombs are dropping, or when a government official has been assassinated. A high school or college valedictorian speech will wake you up after a long hard night of partying, especially if it's delivered skillfully by someone you admire. And announcing record breaking profits to your investors is likely to wake them out of a sound sleep, especially if it's clear to the audience why it's getting rich.
It's relatively easy for an author to think up original things to say about situations like these. It's harder but still possible to conceive of interesting and new ways to express facts about dry nonfiction subjects, if only you invest the time and energy.
Conjectural or personal essays are another example of nonfictional writing that can be among some of the most creative writing ever penned. They take many forms and styles, including:
An essay is a short literary composition on a particular theme or subject, usually in prose and generally analytic, speculative, or interpretative.
Essays are among the greatest compositions ever penned. Some of their authors are among our greatest writers. They include Francis bacon, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Robert Burns, Lord Byron, Samuel Taylor Coleridge, Charles Baudelaire, Thomas De Quincy, Alexander Dumas, Johann Goethe, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Heinrich Heine, John Keats, Edgar Allen Poe, Alexander Pushkin, Sir Walter Scott, Mary Shelley, Germaine De Staël, Stendhal, and William Wordsworth. The list goes on and on.
Most essays are an expression of their authors' heartfelt opinions and ideas about subjects such as religion, politics, equal rights, torture, health, social issues, hunger, and other serious, profound, and important subjects. If you write an essay about something you believe in and feel deeply, it's easy to set down your thoughts in a way that projects your emotions to your readers, even while you bring forth facts and data to substantiate your case.
There's also room for creativity for writers who produce impersonal and objective essays, as well as for writers of expository writing generally. There are imaginative ways to skirt boredom despite the severe grammatical and literary restrictions these literary forms impose.
Nonfiction doesn't stop with expository prose and essays. General nonfiction is the branch of literature comprising works of narrative prose dealing with or offering opinions or conjectures upon facts and reality. This branch includes biography and history, as well as other literary fields. What could pose more creative and challenging opportunities for creativity than writing a biography about yourself or about someone else who has lived an exciting or deplorable life, or about an important period in history? There's plenty of room for creativity when writing about people and events like these.
creative writing and fiction
As just noted, some pieces of nonfictional writing are creatively written, others not. By the same token, some pieces of fictional writing may not be creative because they are dull, boring, and unimaginative.
One of the most important kinds of creative writing is the kind of writing that goes on whenever a competent novelist pens a book. Understanding how and why novel writing is a creative art form is a great way to explore the nature of creative writing of all kinds.
The modern novel is defined as a fictitious prose narrative of considerable length and complexity portraying characters and usually presenting a sequential organization of action and scenes. Its characters, events, actions, scenes, and situations are usually all created up by its author (i.e., they're fictional); but other elements such as places and times may be actual or may be invented depending on the author's preferences.
Even fictional elements such as places, actions, and situations may be based on actual characters, events, actions, and situations, but if so the details of their description, conversation, etc. are the result of the author's imagination. They're fictional because they're not historically and factually displayed.
The practice of telling stories like these actually began in antiquity, thousands of years ago, when people used speech to tell stories because writing didn't exist. Today's novels are distinctly different written works that only distantly resemble their forefathers.
Written works that tell fictional stories —literary works that people once called novels or gave other names to— preceded today's modern novels over a time span lasting many centuries, or even millennia. During this evolution individual authors randomly invented and perfected their own writing styles. Theirs was mostly a trial and error process.
The modern novel —that is, the kind of novel being written now—represents the culmination of this long process; it's a comparatively new development, one far more recent than the first kinds of novels that were written. The literary form of today's modern novels represents the summit of hundreds and even thousands of years of creative experimentation that preceded it.
As a result of all this trial and error experimentation with prose narrative stories, today's modern novels are literature that is technically and aesthetically far superior and much more sophisticated vehicles for recounting prose narrative stories. They're more aesthetic, effective, artistic, and creative literary works differing from their predecessors in major technical and linguistic ways.
Hundreds of thousands (even millions) of written fictional works have been created by authors over the millennia, only a small fraction of which are stored in libraries or on computers. Despite this vast production, the original sources for fictional writing are unknown or can only be surmised.
Much that happened long ago to bring about this first ancient advancement in telling stories is unknown. We can't be sure precisely how literary story-telling came about; we can only presume that somehow the human brain changed. It changed both in the way mankind understood stories and in the way it told them.
However, where the modern novel is concerned, history does permit us to pick up threads of the story of how the novel was invented because it's a story that began much later, after printing began, and these records still exist. From these records, it's easy to conclude that the modern novel and it's immediate predecessors were invented by a collection of writers working mostly independently of one another in England in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries.
Not only did these writers invent the modern novel, which is a fictional literary structure; they also devised many of the various literary styles and techniques it employs. Thus, this group of writers gave birth both to the novel and to the way to write it.
Why did they go through this effort? They invented both the modern novel's structure and its writing styles and techniques because they needed both a new literary form and a new writing style in order to achieve the literary results they wanted.
A great number of other kinds of fictional and nonfictional prose narrative works have appeared since the creation of the modern novel in England; they have adopted literary forms and writing styles that are similar to those of the modern novel in great numbers. Thus, the modern novel has played a key role in defining the entire field of modern fictional and nonfictional writing, not just writing for the novel form alone.
This deduction is confirmed by tracing the evolutionary development of fictional and nonfictional narrative writing which occurred in England before, during, and after the modern novel's nascency. Whether in England, France, or other Western countries, no other kind of new narrative prose fiction or nonfiction writing that appeared on the scene so closely resembled those of the modern novel.
And further, after those original creative literary periods fell away into history, other new fictional literary forms, genres, and writing styles evolved from those used by the first modern novel writers. They evolved apace with each other and in parallel with each other throughout Europe, and eventually even in Asia.
Thus the modern novel has played a decisive role in deciding the nature of creative writing in the modern world, not only in fictional genres at large but in nonfictional genres as well. Today the modern novel is a pervasive medium; it's written, sold, bought, and read in vast quantities in almost every corner of the globe.
- Explore the subject of how the modern novel began in greater depth. Visit The Muse Of Language Arts treatment of the birth of the modern novel at the feature called Birth of the Modern Novel: tap or click here .
nonfictional Literature vs. fictional Li terature
How do fictional and nonfictional literature compare with one another?
The traditional definition for nonfictional literature, the one favored by the preponderance of literati, book stores, publishers, and many readers, is that nonfiction is the branch of literature comprising works of narrative prose dealing with or offering opinions or conjectures upon facts and reality, including biography, history, and the essay.
The traditional definition for fictional literature, the one favored by the preponderance of literati, book stores, publishers, and many readers, is that fiction is the class of literature comprising works of imaginative narration, especially in prose form.
But these definitions come to us from literary purists. In reality, biography, history, conjectural or personal essays, and other kinds of literature usually consist of a mixture of both nonfiction and fiction.
Yes, nonfictional biography, history, conjectural or personal essays, and other nonfictional works usually are based on objective facts and contain lots of nonfictional writing.
But consider English historian Edward Gibbon's six-volume book first published in 1776, The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire , was intended by its author to be a definitive nonfictional history that traces the trajectory of Western civilization, including the Islamic and Mongolian conquests, from the height of the Roman Empire to the fall of Byzantium.
At first glance one might expect a history like this to be totally and completely nonfictional, but it isn't. It's filled with Gibbon's personal reflections that he writes subjectively in the first person; it contains controversial and error-filled chapters; and it's missing relevant facts and information, some of which Gibbon he manufactures from his own imagination, guesses at, speculates about, or virtually invents out of whole cloth.
Despite it's defects, all things considered this nonfictional history is a skillfully and cleverly written, highly creative literary work. It's the kind of writing The Muse refers to as literature with a capital "L."
Is this history book nonfiction or fiction? Is it highly creative or plebeian? Is it literature with a capital "L" or literature with a lowercase "l"?
You decide.
Yes, fiction is the class of literature comprising works of imaginative narration, especially in prose form.
But consider Irving Stone's fictional historical novel The Agony and the Ecstasy. Stone intended his book to be a biographical novel of the great Italian Renaissance painter Michelangelo Buonarroti, one that depicts the Italian history and culture in which the painter had been immersed. It explores the character's interaction between himself and his surroundings.
To make it authentic, Stone based his book on 495 letters of Michelangelo's personal correspondence, sculptures, paintings, and other historic materials, which he used to piece together a realistic picture of the painter's life. So accurate was Stone's fictional writing, the Italian government lauded him with several awards for his achievements in highlighting Italian history. Yet so imaginative and creative was his writing, his book remained on bestseller lists for weeks and months.
At first glance one might expect an historic novel like this one to be be highly inventive, and it is; it was filled with made-up dialogue, fabricated situations, subplots that didn't really happen, concocted characters, and other inventions, some based loosely on factual information he'd gathered, others totally his own.
Many of Stone's readership felt that his book was essentially a lie that had little to do with the real Michelangelo or his historical surroundings; they believed that the book was rife with intellectual shortfalls, errors, and misunderstandings, and they resented their belief that the book misinformed and cheated them. Other readers felt that the book was well worth reading because it revealed the spiritual essence of Michelangelo's life and career, his artistic significance, and his many contributions to their cultural inheritance, and did so in an entertaining and enjoyable manner. They were delighted to learn more about the painter's works, what they stood for, and what he had contributed to our culture. Never mind the inaccuracies; if there really were error or omissions, they were only details.
Is this history book in novel form fiction or nonfiction? Did Stone stretch the truth too much to be trusted? Or are the book's fabrications legitimate because they allowed him to get to the heart of what mattered? Given that it's skillfully and cleverly written, is it a highly creative literary work or merely a chest thumper? Is it the kind of writing The Muse refers to as literature with a capital "L" or is it an aesthetic, clumsy, insulting bust?
Conclusion Whatever you decide about these two books, the notion that there's a clear line between fictional and nonfictional writing is a itself a fiction. Although there are sharp differences between the two kinds of writing, in reality the line between them is a blurry one. Fiction and nonfiction are more similar means of communication than many readers and writers realize. Writers often produce a mixture of both kinds of writing. Conventional wisdom asserts that fiction and nonfiction are opposites. That's not the case; actually they're consistent with one another. It's more accurate to say that fiction and nonfiction are complementary and supplementary to one another. This truism applies both to literature with a capital "L" and literature with a lowercase "l." Both fiction and nonfiction offer authors significant opportunities for creativity. The different writing techniques they choose to use for a specific work at hand depend on its literary format, purpose, audience, and circumstantial factors. These techniques are universal; they're available to every writer who possesses the skill, knowhow, and creativity to apply them.
about accurate creative writing terminology
As mentioned above, people often misuse literary terms when they talk about subjects such as creative writing. The words fiction and nonfiction are two of the most abused terms. Which of these two words ar the right ones to use to describe a given piece of literature?
Conventional usage holds that nonfiction is the branch of literature comprising works of narrative prose dealing with or offering opinions or conjectures upon facts and reality; it includes biography (of the non-conjectural kind), history, and the essay.
By contrast, fiction is the class of literature comprising works of imaginative narration, especially in prose form, including narrative prose works such as a novels and short stories, as well as in poetry and drama. Some written works composed with these literary forms may be based on fact, but if so they are primarily the imaginative creations of their authors and hence they are at base fictional.
For these reasons, most literati consider fiction and nonfiction to be opposites, and they distinguish nonfiction from poetry and drama. When speaking of bodies of literature as a whole, they regard fiction to be writing that is creative and nonfiction to be writing that is not creative. This conventional wisdom is accepted by the public at large.
This usage is quite appropriate when made unambiguous by its context. The Muse Of Language Arts and The Muse of Literature recommend that you feel free to employ these terms in this conventional manner whenever you see fit.
However, The Muse recommends that creative writing terminology be employed more accurately when the genuine differences between fiction and nonfiction are under discussion. Fictional and nonfictional writing are not actually contrary or opposing forms of writing, and this distinction should be observed.
Yes, reality is the direct opposite of unreality where objective facts about the natural world are under consideration; but contrary to literary convention, fiction is not the direct opposite of nonfiction where writing is concerned. In actuality, fiction and nonfiction are alike in the sense that both deal real objects and events that behave in realistic ways.
Notice that a given nonfictional work may contain fictional passages or references to fictional entities; and a given fictional work may contain nonfictional information. A given fictional work often will expound, set forth, explain, or present facts and other nonfictional information; it may contain characters, events, settings, actions that describe real people or historic events. Thus the distinction between fictional and nonfictional literature is a blurred one.
Then what's the operative, effective, most basic distinction between fiction and nonfiction, the one that makes the most difference? It's simply this: authors treat facts differently when they write fiction. Authors who write fiction blend and bend facts to suit their imaginations, whereas authors who write nonfiction adhere to facts as closely as possible.
- For a clearer idea of the essential nature of literary fiction and nonfiction, explore The Muse Of Literature's definition of literature. Visit the feature titled What' s Literature With A Capital "L" : tap or click here.
Fiction and nonfiction are alike in two other key ways: Copious quantities of both fictional and nonfictional writing are subjected to abuse by authors who write dully; and relatively limited quantities of both fiction and nonfiction are treated with respect by authors who write with originality of thought and expression.
As a consequence, the terms creative writing and uncreative writing bear an apples-and-oranges relationship to each other, as well as to the terms fiction and nonfiction. Uncreative writing is not a synonym for nonfictional writing , nor is it an antonym for fictional writing.
Because of this apples-oranges relationship, The Muse Of Language Arts prefers to refer to dull, cheerless and inspired fictional writing as uncreative writing ; and The Muse prefers to refer to to dull, cheerless and uninspired nonfictional writing by the same term, as uncreative writing .
Consequently, there's nothing inherently wrong with describing a fictional (so-called creative) work such as a novel, short story, or a detective story as uncreative writing , so long as you genuinely believe that it's unimaginative and unoriginal in the true sense of the term not creative . Many fictional works are examples of uncreative writing in this sense of the term.
Nor is there a problem with describing a nonfictional work as creative, if you genuinely believe that it demonstrates intellectual creativity.
novel novels
Birth of the modern novel.
A modern novel is a fictitious prose narrative (i.e., a concocted story or imaginary account) of considerable length and complexity portraying characters and usually presenting a sequential organization of actions and scenes.
The current body of modern novels is an amazing collection that includes brilliant authors and masterpieces, works exhibiting striking beauty and significance that sparkle with artistic excellence. Compared with other kinds of important literary works that tell stories — and there are many of them—modern novels account for an amazing number of the greatest books ever written.
The modern novel literary form has just experienced its two hundredth birthday . Two hundred years may seem like too long a time to call the modern novel modern , but modern is a relative term. Considering how long mankind has been telling stories that are not novels, even at two centuries the modern novel is a relatively recent development.
What, then, are the literary and linguistic traits that make modern novels truly different from all these other ways to tell stories, and special? What are their technical specs: their literary forms, genres, language characteristics, and other properties? What is it about modern novels that makes them especially effective and meritorious? When, where, how, why, and by whom were they originally conceived?
- Visit this new feature: tap or click here.
What is Nature Writing?
Definition and Examples
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Nature writing is a form of creative nonfiction in which the natural environment (or a narrator 's encounter with the natural environment) serves as the dominant subject.
"In critical practice," says Michael P. Branch, "the term 'nature writing' has usually been reserved for a brand of nature representation that is deemed literary, written in the speculative personal voice , and presented in the form of the nonfiction essay . Such nature writing is frequently pastoral or romantic in its philosophical assumptions, tends to be modern or even ecological in its sensibility, and is often in service to an explicit or implicit preservationist agenda" ("Before Nature Writing," in Beyond Nature Writing: Expanding the Boundaries of Ecocriticism , ed. by K. Armbruster and K.R. Wallace, 2001).
Examples of Nature Writing:
- At the Turn of the Year, by William Sharp
- The Battle of the Ants, by Henry David Thoreau
- Hours of Spring, by Richard Jefferies
- The House-Martin, by Gilbert White
- In Mammoth Cave, by John Burroughs
- An Island Garden, by Celia Thaxter
- January in the Sussex Woods, by Richard Jefferies
- The Land of Little Rain, by Mary Austin
- Migration, by Barry Lopez
- The Passenger Pigeon, by John James Audubon
- Rural Hours, by Susan Fenimore Cooper
- Where I Lived, and What I Lived For, by Henry David Thoreau
Observations:
- "Gilbert White established the pastoral dimension of nature writing in the late 18th century and remains the patron saint of English nature writing. Henry David Thoreau was an equally crucial figure in mid-19th century America . . .. "The second half of the 19th century saw the origins of what we today call the environmental movement. Two of its most influential American voices were John Muir and John Burroughs , literary sons of Thoreau, though hardly twins. . . . "In the early 20th century the activist voice and prophetic anger of nature writers who saw, in Muir's words, that 'the money changers were in the temple' continued to grow. Building upon the principles of scientific ecology that were being developed in the 1930s and 1940s, Rachel Carson and Aldo Leopold sought to create a literature in which appreciation of nature's wholeness would lead to ethical principles and social programs. "Today, nature writing in America flourishes as never before. Nonfiction may well be the most vital form of current American literature, and a notable proportion of the best writers of nonfiction practice nature writing." (J. Elder and R. Finch, Introduction, The Norton Book of Nature Writing . Norton, 2002)
"Human Writing . . . in Nature"
- "By cordoning nature off as something separate from ourselves and by writing about it that way, we kill both the genre and a part of ourselves. The best writing in this genre is not really 'nature writing' anyway but human writing that just happens to take place in nature. And the reason we are still talking about [Thoreau's] Walden 150 years later is as much for the personal story as the pastoral one: a single human being, wrestling mightily with himself, trying to figure out how best to live during his brief time on earth, and, not least of all, a human being who has the nerve, talent, and raw ambition to put that wrestling match on display on the printed page. The human spilling over into the wild, the wild informing the human; the two always intermingling. There's something to celebrate." (David Gessner, "Sick of Nature." The Boston Globe , Aug. 1, 2004)
Confessions of a Nature Writer
- "I do not believe that the solution to the world's ills is a return to some previous age of mankind. But I do doubt that any solution is possible unless we think of ourselves in the context of living nature "Perhaps that suggests an answer to the question what a 'nature writer' is. He is not a sentimentalist who says that 'nature never did betray the heart that loved her.' Neither is he simply a scientist classifying animals or reporting on the behavior of birds just because certain facts can be ascertained. He is a writer whose subject is the natural context of human life, a man who tries to communicate his observations and his thoughts in the presence of nature as part of his attempt to make himself more aware of that context. 'Nature writing' is nothing really new. It has always existed in literature. But it has tended in the course of the last century to become specialized partly because so much writing that is not specifically 'nature writing' does not present the natural context at all; because so many novels and so many treatises describe man as an economic unit, a political unit, or as a member of some social class but not as a living creature surrounded by other living things." (Joseph Wood Krutch, "Some Unsentimental Confessions of a Nature Writer." New York Herald Tribune Book Review , 1952)
- Creative Nonfiction
- What Is Literary Journalism?
- The Conservation Movement in America
- Defining Nonfiction Writing
- A Guide to All Types of Narration, With Examples
- What You Should Know About Travel Writing
- The Essay: History and Definition
- An Introduction to Literary Nonfiction
- Biography of Henry David Thoreau, American Essayist
- Notable Authors of the 19th Century
- Thoreau's 'Walden': 'The Battle of the Ants'
- Genres in Literature
- Must Reads If You Like 'Walden'
- Top 5 Books about Social Protest
- Tips on Great Writing: Setting the Scene

12 Nature-Inspired Creative Writing Prompts
by Melissa Donovan | Feb 20, 2018 | Creative Writing Prompts | 14 comments

Nature inspires, and so do these creative writing prompts.
Today’s post includes a selection of prompts from my book, 1200 Creative Writing Prompts . Enjoy!
Creative writing prompts are excellent tools for writers who are feeling uninspired or who simply want to tackle a new writing challenge. Today’s creative writing prompts focus on nature.
For centuries, writers have been composing poems that celebrate nature, stories that explore it, and essays that analyze it.
Nature is a huge source of inspiration for all creative people. You can find it heavily featured in film, television, art, and music.
Creative Writing Prompts
You can use these creative writing prompts in any way you choose. Sketch a scene, write a poem, draft a story, or compose an essay. The purpose of these prompts is to inspire you, so take the images they bring to your mind and run with them. And have fun!
- A young girl and her mother walk to the edge of a field, kneel down in the grass, and plant a tree.
- The protagonist wakes up in a seemingly endless field of wildflowers in full bloom with no idea how he or she got there.
- Write a piece using the following image: a smashed flower on the sidewalk.
- A family of five from a large, urban city decides to spend their one-week vacation camping.
- An elderly couple traveling through the desert spend an evening stargazing and sharing memories of their lives.
- A woman is working in her garden when she discovers an unusual egg.
- Write a piece using the following image: a clearing deep in the woods where sunlight filters through the overhead lattice of tree leaves.
- Some people are hiking in the woods when they are suddenly surrounded by hundreds of butterflies.
- A person who lives in a metropolitan apartment connects with nature through the birds that come to the window.
- Write a piece using the following image: an owl soaring through the night sky.
- A well-to-do family from the city that has lost all their wealth except an old, run-down farmhouse in the country. They are forced to move into it and learn to live humbly.
- Two adolescents, a sister and brother, are visiting their relatives’ farm and witness a sow giving birth.
Again, you can use these creative writing prompts to write anything at — poems, stories, songs, essays, blog posts, or just sit down and start freewriting.

14 Comments
lovely prompts… really simple line or two that just strikes up imagery and let you freestyle all over it. Nice one
Thanks, Rory!
thanks for the good ideas good short story for someone in grade 8
Thanks. I just read through your list of prompts and got flashes of either beginnings or endings for stories from every one. I’ve not seen prmopts like these much on the web, so well done. Such a simple idea with so much power and potential. If only I had the day off to get cracking!
I love to create and use writing prompts, and I’m glad you found these to be useful. Thanks!
Hello. Supernatural or magic realism is pretty much all I write. I’ve got a prompt. ‘A young teenager is walking home during a storm and ends up getting struck by lightning. The next day they wake up to find that the accident turned them into an inhuman being.’ I’ve heard of this type of scenario before and I thought it would make for a great story. I love creating my own ideas of course but writing prompts are just fun challenge myself with and see what I can create out of already given ideas. I really like the prompts you give. As I said they are enjoyable to mess around with.
Thanks for sharing your prompt, Kristen. I agree that prompts are fun and can be challenging. I’m glad you like these. Keep writing!
#7 Woodland Clearing
Winter trees screen blue and sunny skies, Intense but icy light the heat belies. Spikey, naked, dormant maids and men Wait for the earth to turn around again.
And bring the warmth that touches every thread Of bark and twigs and all that acted dead Until the full-blown leaves create a wall Shortening the view until late fall
When sun and clouds break through the limbs again And show clear-cut those lacey maids and men Black for a time against the coldest air While waiting for the Spring to deck them fair
With leaves that seem to turn the world to green Creating hidden meadows only seen By animals and birds and mist and rains. For ages before calendars and trains.
Humanity intrudes in such a place And fools themselves that they have found a space Where they belong beneath the patchy light To rip and tear and exercise their might.
For meadow edges have no need to stand Between the woods and grassy, open land Where bugs and bears and buntings feel the sun. ‘Till people think they do what must be done.
April 27, 2019
Hi Jennifa. Thanks for sharing your lovely poem here.
That is a stunningly good poem, Jennifa. Far more worthy than just an obscure comment thread here. I hope you found a home for it where more eyes will see it. If you are published anywhere, I’d love to find out.
Wow. These are truly amazing prompts! Just a few lines of inspiration and now my mind is filled with creativity. Please come up with more! <3
You’ll find plenty more in the Writing Prompts Writing Prompts section of the Blog menu.
these are really helpful
Thanks, Flo! I’m glad you found them helpful.
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- Readers & Writers United (wk 46 2010 overview) « Elsie Stills - [...] 12 Nature-Inspired Creative Writing Prompts (Stories – Tuesday 16 Nov.) [...]
- Writing Prompts: 37 Places to Find Them When You Need Inspiration - […] 12. 12 Nature-Inspired Creative Writing Prompts […]
- Here are three inspirational activities to elevate a writer's creativity - Judy Kundert - […] get an idea of how nature can inspire your creativity, try these Nature-Inspired Creative Writing Prompts from these 12…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Subscribe and get The Writer’s Creed graphic e-booklet, plus a weekly digest with the latest articles on writing, as well as special offers and exclusive content.

Recent Posts
- Grammar Rules: Lay or Lie
- Writing While Inspired
- Thoughts on Becoming a Writer
- How to Write a Book
- Writing Resources: No Plot? No Problem!
Write on, shine on!
Pin It on Pinterest

- Course search
Institute of Continuing Education (ICE)
Please go to students and applicants to login
- Course search overview
Creative writing: an introduction to non-fiction nature writing
- Courses by subject overview
- Archaeology, Landscape History and Classics
- Biological Sciences
- Business and Entrepreneurship
- Creative Writing and English Literature
- Education Studies and Teaching
- Engineering and Technology
- History overview
- Holocaust Studies
- International Relations and Global Studies
- Leadership and Coaching overview
- Coaching FAQs
- Medicine and Health Sciences
- Philosophy, Ethics and Religion
- History of Art and Visual Culture
- Undergraduate Certificates & Diplomas overview
- Postgraduate Certificates & Diplomas overview
- Applying for a Postgraduate Award
- Part-time Master's Degrees overview
- What is a Master's Degree (MSt)?
- How to apply for a Master's Degree (MSt)
- Apprenticeships
- Online Courses
- Career Accelerators overview
- Career Accelerators
- Weekend Courses overview
- Student stories
- Booking terms and conditions
- International Summer Programme overview
- Accommodation overview
- Newnham College
- Queens' College
- Selwyn College
- St Catharine's College
- Tuition and accommodation fees
- Evaluation and academic credit
- Language requirements
- Visa guidance
- Make a Donation
- Register your interest
- Creative Writing Retreats
- Gift vouchers for courses overview
- Terms and conditions
- Financial Support overview
- Concessions
- External Funding
- Ways to Pay
- Information for Students overview
- Student login and resources
- Events overview
- Open Days/Weeks overview
- Master's Open Week 2023
- Postgraduate Open Day 2024
- STEM Open Week 2024
- MSt in English Language Assessment Open Session
- Undergraduate Open Day 2024
- Lectures and Talks
- Cultural events
- In Conversation with...
- International Events
- About Us overview
- Our Mission
- Our anniversary
- Academic staff
- Administrative staff
- Student stories overview
- Advanced Diploma
- Archaeology and Landscape History
- Architecture
- Classical Studies
- Creative Writing
- English Literature
- Leadership and Coaching
- Online courses
- Politics and International Studies
- Visual Culture
- Tell us your student story!
- News overview
- Madingley Hall overview
- Make a donation
- Centre for Creative Writing overview
- Creative Writing Mentoring
- BBC Short Story Awards
- Latest News
- How to find us
- The Director's Welcome
The deadline for booking a place on this course has passed. Please use the 'Ask a Question' button to register your interest in future or similar courses.

One great way for you to really appreciate nature can be to put your experience down in words. It doesn't matter if you're not a wildlife expert - describing wildlife by writing about it means you can learn to see more, hear more, smell more, feel more. This course will introduce a range of techniques to help those who are keen to explore their back yard and beyond to make sense of nature. All you need to bring along is a love of wildlife and a willingness to explore.
Given the nature of creative writing, it is important that students' use of English is sufficiently fluent to be able to understand in English nuances of meaning and have a familiarity with the structure and grammar of English.
Aims of the course:
- To explore a range of styles and techniques in writing about nature.
- To develop participants’ skills in observing and capturing nature in words.
- To increase participants’ awareness and appreciation of nature.
Course content overview:
- This course offers students fresh perspectives on producing creative nature writing.
- Students will learn how to sharpen their senses and heighten awareness and understanding of wildlife.
- The course will show how nature writing can be ‘enlivened’, making it real to the reader
Schedule (this course is completed entirely online):
Orientation Week: 25-31 May 2020
Teaching Weeks: 1 June-5 July 2020
Feedback Week: 6-12 July 2020
Each week of an online course is roughly equivalent to 2-3 hours of classroom time. On top of this, participants should expect to spend roughly 2-3 hours reading material, etc., although this will vary from person to person.
While they have a specific start and end date and will follow a weekly schedule (for example, week 1 will cover topic A, week 2 will cover topic B), our tutor-led online courses are designed to be flexible and as such would normally not require participants to be online for a specific day of the week or time of the day (although some tutors may try to schedule times where participants can be online together for web seminars, which will be recorded so that those who are unable to be online at certain times are able to access material).
Unless otherwise stated, all course material will be posted on the Virtual Learning Environment (VLE) so that they can be accessed at any time throughout the duration of the course and interaction with your tutor and fellow participants will take place through a variety of different ways which will allow for both synchronous and asynchronous learning (discussion boards,etc).
A Certificate of Participation will be awarded to participants who contribute constructively to weekly discussions and exercises/assignments for the duration of the course.
Course textbook/required sources
- No textbook is required reading but students would be advised to use the great outdoors as a source of inspiration, ideas and as a writing laboratory.
- Students should read widely from nature writing – both historic and contemporary. A suggested reading list will be provided.
What our students say - October 2018
“I enjoyed this course much more than I anticipated. I felt the progression over the weeks was well structured and gave us something concrete to practise and build on.”
“Derek’s very fast feedback on our exercises was much-appreciated (and spot-on). His personality also came across in his comments and the respect and care he showed for the students and their work was evident.”
This course is open to everyone, and you don’t need any previous knowledge or experience of the subject to attend.
Our online courses are designed especially for adult learners who want to advance their personal or professional development. They are taught by tutors who are expert in both their subjects and in teaching students of all ages and experiences.
Given the nature of creative writing, it is important that students' use of English is sufficiently fluent to be able to understand in English nuances of meaning and have a familiarity with the structure and grammar of English. Please note that all teaching is in English. You should have near-native command of the English language in order to get the maximum benefit from the course.
For information on bursaries for this course, please see http://www.ice.cam.ac.uk/info/bursaries
General enquiries
Admissions enquiries, course dates, course duration.
Academic Directors, Course Directors and Tutors are subject to change, when necessary.
Qualifications / Credits
Course code.
Institute of Continuing Education Madingley Hall Madingley Cambridge CB23 8AQ
Find us Contact us
Useful information
- Jobs and other opportunities
- Gift vouchers
- Student policies
- Privacy policy
- Data protection policy
- General terms and conditions
Connect with us
© 2024 University of Cambridge
- University A-Z
- Contact the University
- Accessibility
- Freedom of information
Study at Cambridge
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- International students
- Continuing education
- Executive and professional education
- Courses in education
About the University
- How the University and Colleges work
- Visiting the University
- Giving to Cambridge
Research at Cambridge
- Spotlight on...
- About research at Cambridge
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

Creativity and the Brain: How to Be a Creative Thinker
What do we know from research on brain activity involved in creative thought.
Posted April 30, 2024 | Reviewed by Michelle Quirk
- The book "The Creative Act" argues that creativity is a skill we can all use daily.
- Creativity is complex and involves multiple brain regions.
- Research shows that there are several ways to improve our creative thinking.
This post is part 2 of a series.
In my previous post, I wrote that, after being inspired by Rick Rubin’s book, The Creative Act: A Way of Being, I decided to find out what is going on in the human brain that results in creativity. It turned out to be a very complex and complicated subject. That is mainly because it is difficult to clearly define creativity, and there are many different kinds of creative processes, such as visual art, music, creative thinking , etc.
Coming from the field of cognitive processes, I decided that I would concentrate on research related to brain activity involved in creative thought processes. Most of the time, cognitive creativity involves testing the person’s divergent thinking (generating possible solutions to the problem) or convergent thinking (finding a single, correct solution to the problem).
The review of research papers indicated that creative thinking (convergent and divergent thinking) requires the coordination of multiple brain regions, mainly the executive control network (simply speaking involves planning, organizing, problem-solving, and decision-making ), default mode network (areas of the brain that are activated when we are letting our minds wander at rest), and salience network (a network that is involved in the awareness of the feelings associated with rewards). But, obviously, other parts of the brain are also involved, and this depends on the specific goal/outcome that we want to achieve.
I also promised my readers that I would try to find answers to the question of how to be a creative thinker. There are many suggestions on the internet, but let’s see what the research says.
_4.jpg?itok=56gQnN6I)
You can learn how to meditate and practice it daily.
It may come as a surprise to many people, but the majority of the research papers in that area point to the daily practice of meditation as a way to improve creative thinking. It is not a surprise to me because I am a believer in meditation and do it daily. I also encourage all my patients to try to do it daily.
In a Chinese study (Ding, X. et al. 2014), 40 Chinese undergraduate students were assigned to three groups, a meditation group (30 minutes daily for 7 days), a relaxation training group, and a control group. Creativity performance was assessed by the Torrance Test of Creative Thinking (TTCT). The results indicated that the subjects in the meditation group improved their creativity performance on the divergent thinking tasks.
Research studies on meditation also indicate that it helps improve attention/ concentration skills and emotional regulation and reduces stress and anxiety , so it looks like a good daily habit to start.
You can read aloud and do arithmetic calculations.
In a Taiwan study (Lin, WL. et al. 2018), 50 junior high students were divided into a training group or a control group. The training group was reading aloud and performing arithmetic calculations for 20 sessions. The control group played the game Tetris (a puzzle video game). The results indicated that the participants in the training group outperformed the control group in thinking and creative abilities.
You can do neurofeedback.
Neurofeedback is a computer-guided, noninvasive brain-function training based on electroencephalography (EEG) feedback. Neurofeedback is also called neurotherapy, neurobiofeedback, or EEG biofeedback, and it helps control involuntary processes such as muscle tension and heart rate. Usually, the person is responding to a computer display of her/his own electrical activity of the brain, but it may also simply be a sound stimulation. The most important factor is that neurofeedback focuses on helping a person train himself/herself to regulate brain functions.
In an Italian study (Agnoli, S. et al. 2018), 80 female students from the University of Bologna got three neurofeedback training sessions. The researchers also measured the participants’ lifetime creative achievement by using the Creative Activity and Accomplishment Checklist. The results were measured with the divergent thinking tasks (producing original and effective ideas). The results indicated an increase in both originality and fluency. The increase was particularly evident in participants with an initial low creative achievement level.
This is good news for people who believe that they are not that creative. You may get better with neurofeedback training sessions. Artists and athletes do this nowadays to enhance their performance.
You can do overinclusive thinking training.
Overinclusive thinking can be described as increased generalization and/or considering concepts that most people consider unrelated to certain categories, which provides an increased number of options. In a Taiwan study (Chiu, F.C. 2015), the researcher examined the effect of overinclusive thinking on creativity. Four experiments were designed, and the subjects were undergraduate students who were randomly assigned to an overinclusive thinking training group or a control group. The training group did better on the overinclusive thinking that is related to creativity. The fluency and originality performance were higher than in the control group and the insight problem-solving was also better than in the control group.

So, if you would like to be a creative thinker, you can try some of the ideas described above. Good luck on the road to creativity!
Rick Rubin. The Creative Act: A Way of Being . Penguin Press, NY 2023.
Ding, X. et al. “Improving creativity performance by short-term meditation” Behavioral and Brain Functions. Vol. 10, 2014.
Lin, WL. et al. “ Improving junior high students’ thinking and creative abilities with an executive function training program” Thinking Skills and Creativity . Vol. 29, Sept. 2018.
Agnoli, S. et al. “Enhancing creative cognition with a rapid right-parietal neurofeedback procedure.” Neuropsychologia, Vol. 118, Part A Sept. 2018.
Chiu, F.C. “ Improving your creative potential without awareness: Overinclusive thinking training.” Thinking Skills and Creativity . Vol 15. March 2015.

Barbara Koltuska-Haskin, Ph.D., is a neuropsychologist in Albuquerque, New Mexico and the author of How My Brain Works.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Would Limitlessness Make Us Better Writers?
AI embodies hypotheticals I can only imagine for myself. But I believe human impediments are what lead us to create meaningful art.

Updated at 11:45 a.m. ET on April 25, 2024.
The scrolls lay inside glass cases. On one, the writing was jagged; on others, swirling or steady. I was at the National Palace Museum in Taiwan, admiring centuries-old Chinese calligraphy that, the wall text told me, was meant to contain the life force— qi— of the calligrapher expressed through each brushstroke. Though I couldn’t read the language, I was moved to see the work of writers who lived hundreds of years ago, whose marks still seemed to say something about the creators long after they’d passed.
I’m using my fingers to type this now, but every letter is perfectly legible and well spaced. Today, the human body behind the written word is less apparent. When I’m composing an email, Gmail makes suggestions I can deploy in one click: “Awesome!” “Sounds great!” “Yes, I can do that.” Artificial intelligence can produce instantaneous sentences. That a person is responsible for text is no longer a given.
Last year, Alex Reisner reported in The Atlantic that more than 191,000 books had been absorbed into a data set called Books3, which was then used to train generative-AI large language models that may someday threaten to take the place of human writers. Among the books in question was my debut novel, Goodbye, Vitamin , which took me five years to complete. My new novel, Real Americans , took even longer: I began working on it in December 2016, and it’s being released at the end of April, seven years and four months later. Those numbers don’t even account for the years of reading, practice, and education (both formal and self-directed) that preceded the writing itself. Now ChatGPT and other LLMs, trained on a wide store of human-generated literature, stand on the cusp of writing novels in no time at all.
Read: What ChatGPT can’t teach my writing students
This seems, initially, discouraging. Here is an entity that can seemingly do what I do, but faster. At present, it “hallucinates” and gets basic facts wrong, but it may soon be able to generate text that can seamlessly imitate people. Unlike me, it won’t need sleep, or bathroom breaks, or patience, or life experience; it won’t get the flu. In fact, AI embodies hypotheticals I can just imagine for myself: If only I could write all day and night. If only I were smarter and more talented. If only I had endless knowledge. If only I could read whole libraries. What could I create if I had no needs? What might this development mean for writing?
Considering limitlessness has led me to believe that the impediments of human writers are what lead us to create meaningful art. And they are various: limits of our body, limits of our perspectives, limits of our skills. But the constraints of an artist’s process are, in the language of software, a feature, not a bug.
Writing is “a blood-and-guts business,” as the musician Nick Cave has said , literally as well as figuratively. As I type with my hands, my lungs oxygenate the blood that my heart pumps; my brain sends and receives signals. Each of these functions results in the words on this page. In the Middle Ages, monks in the scriptoria wrote: “Two fingers hold the pen, but the whole body toils.” Typing this now, my upper back hurts. I am governed by pesky physical needs: I have to drink water and eat; my mind can’t focus indefinitely. My hands are too cold, and because I haven’t moved it, one foot is going numb. On other occasions, illnesses or injuries have affected my ability to write.
The sensitivities of our fragile human bodies require that our labor takes time. Nothing is more discouraging when I am trying to complete a draft. But this exchange—my finite hours for this creative endeavor—imports meaning: It benefits the work, and makes it richer. Over weeks, months, and years, characters emerge and plots take surprising turns. A thought can be considered day after day and deepened.
While revising my forthcoming book, one of my thighs erupted into a mysterious rash. Sparing gruesome details, let’s just say it disturbed and distracted me. But it also led me to a realization: I’d been approaching the creation of my novel as though it could be perfectible. In reducing my entire self to my cognition alone, akin to a computer, I’d forgotten the truth that I am inseparable from my imperfect body, with its afflictions and ailments. My books emerge from this body.
In his book How to Write One Song , the musician Jeff Tweedy writes: “I aspire to make trees instead of tables.” He was talking about songs, but the concept was revelatory to me as a novelist. Unlike a table, the point of a novel isn’t to be useful or stable or uniform. Instead, it is as singular and particular as its creator, shaped by numerous forces and conditions. In spite of its limits and because of them, a tree is an exuberant organic expression. Though costumed in typeset words, a novel is an exuberant organic expression too.
Read: My books were used to train meta’s generative AI. Good.
AI is creating tables out of our trees. Its infinite iterations are pure veneer: bloodless and gutless, serviceable furniture made of the deforested expanse of human experience. A large language model doesn’t require experience, because it has consumed ours. It appears limitless in its perspective because it writes from an extensive data set of our own. Though writing comes out of these experiences and perspectives, it does not follow that unlimited quantities of each beget maximally substantial work. I believe that the opposite is true.
Compared with AI, we might seem like pitiful creatures. Our lives will end; our memory is faulty; we can’t absorb 191,000 books; our frames of reference are circumscribed. One day, I will die. I foreclose on certain opportunities by pursuing others. Typing this now means I cannot fold my laundry or have lunch with a friend. Yet I believe writing is worth doing, and this sacrifice of time makes it consequential. When we write, we are picking and choosing—consciously or otherwise—what is most substantial to us. Behind human writing is a human being calling for attention and saying, Here is what is important to me . I’m able to move through only my one life, from my narrow point of view; this outlook creates and yet constrains my work. Good writing is born of mortality: the limits of our body and perspectives—the limits of our very lives.
I can imagine a future in which ChatGPT works more convincingly than it does now. Would I exchange the hours that I spent working on each of my two books for finished documents spat out by ChatGPT? That would have saved me years of attempts and failures. But all of that frustration, difficult as it was in the moment, changed me. It wasn’t a job I clocked in and out of, contained within a tidy sum of hours. I carried the story with me while I showered, drove—even dreamed. My mind was changed by the writing, and the writing changed by my mind.
Read: Prepare for the textpocalypse
Working on a novel, I strain against my limits as a bounded, single body by imagining characters outside of myself. I test the limits of my skill when I wonder, Can I pull this off? And though it feels grandiose to say, writing is an attempt to use my short supply of hours to create a work that outlasts me. These exertions in the face of my constraints strike me as moving, and worthy, and beautiful.
Writing itself is a technology, and it will shift with the introduction of new tools, as it always has. I’m not worried that AI novelists will replace human novelists. But I am afraid that we’ll lose sight of what makes human writing worthwhile: its efforts, its inquiries, its bids for connection—all bounded and shaped by its imperfections—and its attempts to say, This is what it’s like for me. Is it like this for you? If we forget what makes our human work valuable, we might forget what makes our human lives valuable too. Novels are one of the best means we have for really seeing one another, because behind each effort is a mortal person, expressing and transmuting their realities to the best of their ability. Reading and writing are vital means by which we bridge our separate consciousnesses. In understanding these limits, we can understand one another’s lives. At least, we can try.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Book News & Features
Ai is contentious among authors. so why are some feeding it their own writing.

Chloe Veltman

The vast majority of authors don't use artificial intelligence as part of their creative process — or at least won't admit to it.
Yet according to a recent poll from the writers' advocacy nonprofit The Authors Guild, 13% said they do use AI, for activities like brainstorming character ideas and creating outlines.
The technology is a vexed topic in the literary world. Many authors are concerned about the use of their copyrighted material in generative AI models. At the same time, some are actively using these technologies — even attempting to train AI models on their own works.
These experiments, though limited, are teaching their authors new things about creativity.
Best known as the author of technology and business-oriented non-fiction books like The Long Tail, lately Chris Anderson has been trying his hand at fiction. Anderson is working on his second novel, about drone warfare.
He says he wants to put generative AI technology to the test.
"I wanted to see whether in fact AI can do more than just help me organize my thoughts, but actually start injecting new thoughts," Anderson says.
Anderson says he fed parts of his first novel into an AI writing platform to help him write this new one. The system surprised him by moving his opening scene from a corporate meeting room to a karaoke bar.
Authors push back on the growing number of AI 'scam' books on Amazon
"And I was like, you know? That could work!" Anderson says. "I ended up writing the scene myself. But the idea was the AI's."
Anderson says he didn't use a single actual word the AI platform generated. The sentences were grammatically correct, he says, but fell way short in terms of replicating his writing style. Although he admits to being disappointed, Anderson says ultimately he's OK with having to do some of the heavy lifting himself: "Maybe that's just the universe telling me that writing actually involves the act of writing."
Training an AI model to imitate style
It's very hard for off-the-shelf AI models like GPT and Claude to emulate contemporary literary authors' styles.
The authors NPR talked with say that's because these models are predominantly trained on content scraped from the Internet like news articles, Wikipedia entries and how-to manuals — standard, non-literary prose.
But some authors, like Sasha Stiles , say they have been able to make these systems suit their stylistic needs.
"There are moments where I do ask my machine collaborator to write something and then I use what's come out verbatim," Stiles says.
The poet and AI researcher says she wanted to make the off-the-shelf AI models she'd been experimenting with for years more responsive to her own poetic voice.
So she started customizing them by inputting her finished poems, drafts, and research notes.
"All with the intention to sort of mentor a bespoke poetic alter ego," Stiles says.
She has collaborated with this bespoke poetic alter ego on a variety of projects, including Technelegy (2021), a volume of poetry published by Black Spring Press; and " Repetae: Again, Again ," a multimedia poem created last year for luxury fashion brand Gucci.
Stiles says working with her AI persona has led her to ask questions about whether what she's doing is in fact poetic, and where the line falls between the human and the machine.
read it again… pic.twitter.com/sAs2xhdufD — Sasha Stiles | AI alter ego Technelegy ✍️🤖 (@sashastiles) November 28, 2023
"It's been really a provocative thing to be able to use these tools to create poetry," she says.
Potential issues come with these experiments
These types of experiments are also provocative in another way. Authors Guild CEO Mary Rasenberger says she's not opposed to authors training AI models on their own writing.
"If you're using AI to create derivative works of your own work, that is completely acceptable," Rasenberger says.

Thousands of authors urge AI companies to stop using work without permission
But building an AI system that responds fluently to user prompts requires vast amounts of training data. So the foundational AI models that underpin most of these investigations in literary style may contain copyrighted works.
Rasenberger pointed to the recent wave of lawsuits brought by authors alleging AI companies trained their models on unauthorized copies of articles and books.
"If the output does in fact contain other people's works, that creates real ethical concerns," she says. "Because that you should be getting permission for."
Circumventing ethical problems while being creative
Award-winning speculative fiction writer Ken Liu says he wanted to circumvent these ethical problems, while at the same time creating new aesthetic possibilities using AI.
So the former software engineer and lawyer attempted to train an AI model solely on his own output. He says he fed all of his short stories and novels into the system — and nothing else.
Liu says he knew this approach was doomed to fail.
That's because the entire life's work of any single writer simply doesn't contain enough words to produce a viable so-called large language model.
"I don't care how prolific you are," Liu says. "It's just not going to work."
Liu's AI system built only on his own writing produced predictable results.
"It barely generated any phrases, even," Liu says. "A lot of it was just gibberish."
Yet for Liu, that was the point. He put this gibberish to work in a short story. 50 Things Every AI Working With Humans Should Know , published in Uncanny Magazine in 2020, is a meditation on what it means to be human from the perspective of a machine.
"Dinoted concentration crusch the dead gods," is an example of one line in Liu's story generated by his custom-built AI model. "A man reached the torch for something darker perified it seemed the billboding," is another.
Liu continues to experiment with AI. He says the technology shows promise, but is still very limited. If anything, he says, his experiments have reaffirmed why human art matters.
"So what is the point of experimenting with AIs?" Liu says. "The point for me really is about pushing the boundaries of what is art."
Audio and digital stories edited by Meghan Collins Sullivan .
- large language model
- mary rasenberger
- chris anderson
- sasha stiles
- authors guild
Bachelor of Science in Creative Writing – Journalism Captivate Your Readers

Credit Hours
View Courses
100% online, 8-week courses
Transfer in up to 75% of the degree total
Expand Your Reporting and Writing Skills with an Online Journalism Degree from Liberty University
Have you ever wanted to write for a magazine, news journal, or website? If so, then this program might be for you! At Liberty, you can learn how to compose original text with your own creative flair. Our journalism degree can help you gain the research and writing skills needed to craft compelling pieces that captivate your reader and move them emotionally.
Liberty University’s Bachelor of Science (BS) in Creative Writing – Journalism is an exciting and dynamic degree program that can help prepare you for a career in the media industry. With a focus on writing for social media, news and print, and multimedia storytelling, this journalism major can help equip you with the skills and knowledge you need to excel in a variety of fields.

Ranked in the Top 10% of Niche.com’s Best Online Schools in America
- What Sets Us Apart?
- Private Nonprofit University
- 600+ Online Degrees
- No Standardized Testing for Admission
- Transfer in up to 75% of an Undergrad Degree
- Transfer in up to 50% of a Grad/Doctoral Degree
Why Choose Liberty’s BS in Creative Writing – Journalism Degree?
There are many reasons why you might choose to pursue a Bachelor of Science in Creative Writing – Journalism. One of the main benefits of this degree is that it is 100% online, making it convenient and accessible for students with busy schedules. Additionally, this program is designed to be completed in just 120 credit hours, allowing you to earn your degree quickly and start your career sooner.
Furthermore, the Bachelor of Science in Creative Writing – Journalism program is unique in its focus on both creative writing and journalism. This means you’ll gain a well-rounded education that can provide a great foundation to begin a career in news media and content writing. Whether you want to be a journalist or branch out into other areas of writing, this degree can provide a pathway to accomplishing your goals.
Liberty’s online journalism degree is taught by experienced writers and journalists who have a wealth of knowledge to share. They’ll provide you with guidance and feedback as you develop your skills and work on your writing.
What Will You Study in Our Online Bachelor’s Degree in Journalism?
In the Bachelor of Science in Creative Writing – Journalism program, you can learn competencies that are essential for success in a variety of journalism and creative writing industries. From writing novellas to writing for theater and film, you have the opportunity to develop many abilities that can help boost your marketability. Some of the skills you can develop include:
- Writing and Storytelling : You can learn how to craft compelling stories that engage and inform your audience, whether writing news articles, feature stories, or multimedia content.
- Journalism Fundamentals : You will explore the basics of journalism, including how to conduct interviews, fact-check information, and write in a style that is appropriate for different types of media.
- Print and Digital Publishing : In today’s media landscape, digital skills are essential. You can learn how to use a variety of digital tools and build platforms that focus on maturing your writing skill and brand.
- Professional Skills : In addition to creative and technical skills, you can also develop the professional skills you need to succeed in the workplace – including teamwork, communication, and project management.
Additionally, you can learn how to write for cultural engagement and convey nuanced meaning in your work. Your studies will culminate in a senior capstone that will synthesize the knowledge and training you have gained over the course of this journalism degree.
Potential Career Opportunities
- Professional blogger
- Social media coordinator
Featured Courses
- WRIT 201 – Introduction to Creative Writing
- WRIT 400 – Editing for Publishing
- WRIT 404 – Print and Digital Publishing*
- WRIT 417 – Writing for Cultural Engagement*
*Course guide coming soon
Degree Information
- This program falls under the College of Arts and Sciences .
- View our Undergraduate Arts and Sciences Course Guides (login required).
Degree Completion Plan (PDF)

Not sure what to choose?
Speak to one of our admissions specialists to help you choose the program that best fits your needs.
- Tuition & Aid
Your success is our success, which is why we are committed to providing quality academics at an affordable tuition rate. While other colleges are increasing their tuition, we have frozen tuition rates for the majority of our undergraduate, graduate, and doctoral programs for the past 9 years – and counting.
To continue our mission of providing affordable education, electronic textbooks are provided for all undergraduate courses at no cost to you. As a full-time student, this could save you an estimated $800-2,000 per year on textbooks!
All Tuition & Fees
Financial Aid & Scholarships
Financial Aid Forms & Eligibility
Scholarship Opportunities
Admission Information for Undergraduate Online Degrees
Admission requirements.
- A non-refundable, non-transferable $50 application fee will be posted on the current application upon enrollment (waived for qualifying service members, veterans, and military spouses – documentation verifying military status is required) .
- Students may be allowed to enroll in up to 12 credit hours with Liberty with the submission of an unofficial high school transcript and our High School Self-Certification Form .
- Unofficial transcripts can be used for acceptance purposes with the submission of a Transcript Request Form .
Applicants whose native language is other than English must submit official scores for the Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) or an approved alternative assessment. For information on alternative assessments or TOEFL waivers, please call Admissions or view the official International Admissions policy .
*Official high school transcript requirement may be waived with college transcripts from an accredited college/university showing at least 12 earned credit hours with an acceptable GPA.
Note: A 2.0 or above cumulative GPA is required for admission in good standing.
Transcript Policies
High school transcript policy.
Applicants may submit an unofficial high school transcript with a High School Self-Certification Form in lieu of a final official high school transcript in order to enroll in up to 12 credit hours at Liberty University.
- Applicants may submit a college transcript showing 12 or more credits from an accredited institution and a High School Self-Certification Form in lieu of high school transcripts.
Students must submit official high school transcripts, or official college transcripts showing at least 12 credit hours earned with an acceptable grade point average (GPA) from an accredited institution, in order to register for additional courses.
The official high school transcript, GED requirement, and unofficial high school transcript with a High School Self-Certification Form can be waived if the applicant has earned an associate degree or higher.
Final transcripts must reflect all coursework and final grades received for grades 9-12, a graduation date, and an overall GPA. (Mailed transcripts must be in a sealed and unopened envelope.)
Unofficial College Transcript Policy
Unofficial transcripts combined with a Transcript Request Form can be used for admission. Official transcripts are required within 60 days of the admissions decision or before non-attendance drops for the first set of matriculated classes, whichever comes first, and will prevent enrollment into future terms until all official transcripts have been received.
Before sending unofficial college transcripts, please make sure they include the following:
- Your previous school’s name or logo printed on the document
- Cumulative GPA
- A list of completed courses and earned credit broken down by semester
- Degree and date conferred (if applicable)
Official College Transcript Policy
An acceptable official college transcript is one that has been issued directly from the institution and is in a sealed envelope. If you have one in your possession, it must meet the same requirements. If your previous institution offers electronic official transcript processing, they can send the document directly to [email protected] .
If the student uses unofficial transcripts with a Transcript Request Form to gain acceptance, all official transcripts must be received within 60 days of the admissions decision or before non-attendance drops for the first set of matriculated classes, whichever comes first. Failure to send all official transcripts within the 60-day period will prevent enrollment into future terms until all official transcripts have been received.
Military Transfers
If you have military-only transfer credits (completed basic training and enlistment), you must request an official military transcript. Please go to the Military Transfer Credit webpage to request your military transcript.
International Applicants
If you are an international applicant, you may be required to have your international transcripts reviewed. Information regarding the transcript evaluation process for international students can be found by visiting NACES .
Admissions Office Contact Information
(800) 424-9595 Fax
(888) 301-3577
Email for Questions
[email protected] Email for Documents
Liberty University Online Admissions Verification
1971 University Blvd.
Lynchburg, VA 24515

Ready to Apply?
Submit your application online or over the phone.
Apply by phone: (800) 424-9595
Liberty University is dedicated to providing world-class educational experiences to military students across the globe.
Who May Qualify?
- Active Duty
- Reserve/National Guard
- Veterans/Retirees
- Spouses of Service Members and Veterans/Retirees
- Current Department of Defense Employees
Available Benefits:
- Tuition discounts – $250 per credit hour for undergraduate courses
- Additional discount for veterans who service in a civilian capacity as a First Responder (less than $565 per course) *
- 8-week courses, 8 different start dates each year, and no set login times (may exclude certain courses such as practicums, internships, or field experiences)
- Potential college credit for military training
*Not applicable to certificates.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does liberty partner with and bestselling authors.
Liberty University has partnered with New York Times bestselling author and Christian novelist, Karen Kingsbury, to create the Karen Kingsbury Center for Creative Writing. Your curriculum includes content developed by Karen Kingsbury herself.
Is Liberty University accredited by anyone?
Liberty University holds institutional accreditation through the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools Commission on Colleges ( SACSCOC ).
Who teaches the classes in this degree program?
This online journalism bachelor’s degree is taught by experienced professionals who are experts in the fields of journalism and creative writing.
Inner Navigation
- Why Choose Liberty?
- What Will You Study?
- Admission Information
Have questions?

Are you ready to change your future?
Apply FREE This Week*
Request Information
*Some restrictions may occur for this promotion to apply. This promotion also excludes active faculty and staff, military, non-degree-seeking, DGIA, Continuing Education, WSB, and certificate students.
Request Information About a Program
Request info about liberty university online, what program are you interested in, choose a program level.
Choose a program level
Bachelor’s
Master’s
Certificate
Select a Field of Study
Select a field of study
Select a Program
Select a program
Next: Contact Info
Legal full name.
Enter legal full name
Legal Last Name
Enter legal last name
Enter an email address
Enter a phone number
Full Address
Enter an address
Apt., P.O. Box, or can’t find your address? Enter it manually instead .
Select a Country
Street Address
Enter Street Address
Enter State
ZIP/Postal Code
Enter Zip Code
Back to automated address search
Start my application now for FREE
Celebrating the Spring 2024 MFA Graduates
Read more news.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 08 May 2024
Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3
- Josh Abramson ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0000-3496-6952 1 na1 ,
- Jonas Adler ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9928-3407 1 na1 ,
- Jack Dunger 1 na1 ,
- Richard Evans ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4675-8469 1 na1 ,
- Tim Green ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3227-1505 1 na1 ,
- Alexander Pritzel ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4233-9040 1 na1 ,
- Olaf Ronneberger ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4266-1515 1 na1 ,
- Lindsay Willmore ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4314-0778 1 na1 ,
- Andrew J. Ballard ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4956-5304 1 ,
- Joshua Bambrick ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0003-3908-0722 2 ,
- Sebastian W. Bodenstein 1 ,
- David A. Evans 1 ,
- Chia-Chun Hung ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5264-9165 2 ,
- Michael O’Neill 1 ,
- David Reiman ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1605-7197 1 ,
- Kathryn Tunyasuvunakool ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8594-1074 1 ,
- Zachary Wu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2429-9812 1 ,
- Akvilė Žemgulytė 1 ,
- Eirini Arvaniti 3 ,
- Charles Beattie ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1840-054X 3 ,
- Ottavia Bertolli ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8578-3216 3 ,
- Alex Bridgland 3 ,
- Alexey Cherepanov ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5227-0622 4 ,
- Miles Congreve 4 ,
- Alexander I. Cowen-Rivers 3 ,
- Andrew Cowie ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4491-1434 3 ,
- Michael Figurnov ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1386-8741 3 ,
- Fabian B. Fuchs 3 ,
- Hannah Gladman 3 ,
- Rishub Jain 3 ,
- Yousuf A. Khan ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0201-2796 3 ,
- Caroline M. R. Low 4 ,
- Kuba Perlin 3 ,
- Anna Potapenko 3 ,
- Pascal Savy 4 ,
- Sukhdeep Singh 3 ,
- Adrian Stecula ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6914-6743 4 ,
- Ashok Thillaisundaram 3 ,
- Catherine Tong ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7570-4801 4 ,
- Sergei Yakneen ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7827-9839 4 ,
- Ellen D. Zhong ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6345-1907 3 ,
- Michal Zielinski 3 ,
- Augustin Žídek ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0748-9684 3 ,
- Victor Bapst 1 na2 ,
- Pushmeet Kohli ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7466-7997 1 na2 ,
- Max Jaderberg ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9033-2695 2 na2 ,
- Demis Hassabis ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2812-9917 1 , 2 na2 &
- John M. Jumper ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6169-6580 1 na2
Nature ( 2024 ) Cite this article
172k Accesses
1 Citations
1112 Altmetric
Metrics details
We are providing an unedited version of this manuscript to give early access to its findings. Before final publication, the manuscript will undergo further editing. Please note there may be errors present which affect the content, and all legal disclaimers apply.
- Drug discovery
- Machine learning
- Protein structure predictions
- Structural biology
The introduction of AlphaFold 2 1 has spurred a revolution in modelling the structure of proteins and their interactions, enabling a huge range of applications in protein modelling and design 2–6 . In this paper, we describe our AlphaFold 3 model with a substantially updated diffusion-based architecture, which is capable of joint structure prediction of complexes including proteins, nucleic acids, small molecules, ions, and modified residues. The new AlphaFold model demonstrates significantly improved accuracy over many previous specialised tools: far greater accuracy on protein-ligand interactions than state of the art docking tools, much higher accuracy on protein-nucleic acid interactions than nucleic-acid-specific predictors, and significantly higher antibody-antigen prediction accuracy than AlphaFold-Multimer v2.3 7,8 . Together these results show that high accuracy modelling across biomolecular space is possible within a single unified deep learning framework.
You have full access to this article via your institution.
Similar content being viewed by others

Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold
Targeted protein degradation: from mechanisms to clinic
De novo generation of multi-target compounds using deep generative chemistry
Author information.
These authors contributed equally: Josh Abramson, Jonas Adler, Jack Dunger, Richard Evans, Tim Green, Alexander Pritzel, Olaf Ronneberger, Lindsay Willmore
These authors jointly supervised this work: Victor Bapst, Pushmeet Kohli, Max Jaderberg, Demis Hassabis, John M. Jumper
Authors and Affiliations
Core Contributor, Google DeepMind, London, UK
Josh Abramson, Jonas Adler, Jack Dunger, Richard Evans, Tim Green, Alexander Pritzel, Olaf Ronneberger, Lindsay Willmore, Andrew J. Ballard, Sebastian W. Bodenstein, David A. Evans, Michael O’Neill, David Reiman, Kathryn Tunyasuvunakool, Zachary Wu, Akvilė Žemgulytė, Victor Bapst, Pushmeet Kohli, Demis Hassabis & John M. Jumper
Core Contributor, Isomorphic Labs, London, UK
Joshua Bambrick, Chia-Chun Hung, Max Jaderberg & Demis Hassabis
Google DeepMind, London, UK
Eirini Arvaniti, Charles Beattie, Ottavia Bertolli, Alex Bridgland, Alexander I. Cowen-Rivers, Andrew Cowie, Michael Figurnov, Fabian B. Fuchs, Hannah Gladman, Rishub Jain, Yousuf A. Khan, Kuba Perlin, Anna Potapenko, Sukhdeep Singh, Ashok Thillaisundaram, Ellen D. Zhong, Michal Zielinski & Augustin Žídek
Isomorphic Labs, London, UK
Alexey Cherepanov, Miles Congreve, Caroline M. R. Low, Pascal Savy, Adrian Stecula, Catherine Tong & Sergei Yakneen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Max Jaderberg , Demis Hassabis or John M. Jumper .
Supplementary information
Supplementary information.
This Supplementary Information file contains the following 9 sections: (1) Notation; (2) Data pipeline; (3) Model architecture; (4) Auxiliary heads; (5) Training and inference; (6) Evaluation; (7) Differences to AlphaFold2 and AlphaFold-Multimer; (8) Supplemental Results; and (9) Appendix: CCD Code and PDB ID tables.
Reporting Summary
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Abramson, J., Adler, J., Dunger, J. et al. Accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07487-w
Download citation
Received : 19 December 2023
Accepted : 29 April 2024
Published : 08 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07487-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Major alphafold upgrade offers boost for drug discovery.
- Ewen Callaway
Nature (2024)
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Translational Research newsletter — top stories in biotechnology, drug discovery and pharma.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries. It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
5 Key Characteristics of Creative Writing. Creative writing is marked by several defining characteristics, each working to create a distinct form of expression: 1. Imagination and Creativity:Creative writing is all about harnessing your creativity and imagination to create an engaging and compelling piece of work.
Types of Creative Writing. Examples of creative writing can be found pretty much everywhere. Some forms that you're probably familiar with and already enjoy include: • Fiction (of every genre, from sci-fi to historical dramas to romances) • Film and television scripts. • Songs. • Poetry.
Creative writing is any writing that goes outside the bounds of normal professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature, typically identified by an emphasis on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes or with various traditions of poetry and poetics.Due to the looseness of the definition, it is possible for writing such as feature stories to ...
Creative writing is the celestial dance of words, an art form that transcends the ordinary to forge literary constellations that illuminate the human experience. At its core, creative writing is a cosmic exploration of imagination, a journey into the uncharted realms where storytelling becomes a vehicle for self-expression, creativity, and ...
This free and open access textbook introduces new writers to some basic elements of the craft of creative writing in the genres of fiction, poetry, and creative nonfiction. The authors—Rachel Morgan, Jeremy Schraffenberger, and Grant Tracey—are editors of the North American Review, the oldest and one of the most well-regarded literary magazines in the United States.
Creative Writing is a form of art that allows people to express their thoughts, ideas, and emotions through the written word. It is a mode of self-expression that combines imagination with linguistic skills to create compelling narratives, poems, and other forms of literature. A Statista survey found that 76,300 Authors, Writers and Translators ...
A lot falls under the term 'creative writing': poetry, short fiction, plays, novels, personal essays, and songs, to name just a few. By virtue of the creativity that characterizes it, creative writing is an extremely versatile art. So instead of defining what creative writing is, it may be easier to understand what it does by looking at ...
Creative writing is the process of engaging your imagination and talent to serve the purpose of whatever piece of writing you are working on. And that's why creative writing is important. Many experts have wrecked on the shoals of trying to define creative writing.
What is creative writing? The answer can be simple, but breaking it down is far more useful. Learn more and gain some insightful tips for yourself, as well!
The creative process of writing science-inspired fiction can be rewarding — and the untapped niche is rich in opportunities for originality. Nature - The creative process of writing science ...
Determining the nature of creative writing knowledge therefore offers researchers a considerable array of potential projects. We can also consider what messages we send through our creative writing teaching—messages concerning what we value and who we value (and that last note is consequential because if our teaching suggests only some voices ...
Here The Muse Of Language Arts explores the nature of creative writing. That which is creative results from originality of thought or expression; it's imaginative or original. From a literary perspective, creative writing is any writing that is the product of original composition, where composition is the art of putting words and sentences ...
4. Go outside: Spending time in nature and wide-open spaces can expand your attention, enhance beneficial mind-wandering, and boost creativity. 5. Revisit your creative ideas: Aha moments can give you a high—but that rush might make you overestimate the merit of a creative idea.
Nature writing is a form of creative nonfiction in which the natural environment (or a narrator 's encounter with the natural environment) serves as the dominant subject. "In critical practice," says Michael P. Branch, "the term 'nature writing' has usually been reserved for a brand of nature representation that is deemed literary, written in ...
Language is intrinsically generative in nature (Chomsky, 1965), and perhaps the best example of 'everyday' creativity (Runco, 2014) because of the immense repertoire of possibilities it affords. ... Creative writing task responding to an image and initial sentence (rated on a 1-7 'very impoverished'/'very creative' scale) ...
Nature writing can be about cliffs, lakes, rivers, deserts, gardens, meadows, oceans, remote islands, and underwater worlds. It can be a study of the slices of nature within cities and urban spaces, whether focusing on parks or plants that we find cropping up in pavements. Nature writing can focus on developments in agriculture, new farming ...
Nature inspires, and so do these creative writing prompts. Today's post includes a selection of prompts from my book, 1200 Creative Writing Prompts. Enjoy! Creative writing prompts are excellent tools for writers who are feeling uninspired or who simply want to tackle a new writing challenge. Today's creative writing prompts focus on nature.
Creative Nonfiction: Nature Writing. By Melissa Nunez, written June 2021. from the creative nonfiction summer 2021 series. Nature writing is fertile ground for a writer, especially a female writer, to examine through vivid imagery and powerful metaphor the beauty, vulnerability, and strength within and without us. Mother Earth.
Given the nature of creative writing, it is important that students' use of English is sufficiently fluent to be able to understand in English nuances of meaning and have a familiarity with the structure and grammar of English. Please note that all teaching is in English. You should have near-native command of the English language in order to ...
Nature writing has grown in popularity as a genre in recent years, but writing about nature in general can also be a great creative exercise, as it encourages you to observe details and put those observations into words. You can use these tips to practice nature writing: 1. Always keep a notebook handy. The first thing you want to do is ensure ...
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects.
The MFA in Creative Writing program is designed to help you become an excellent creative writer across the genres of creative fiction, nonfiction, screenwriting, and poetry.
Key points. Nature excites our creative impulses. Natural settings are essential for creativity to prosper. Imagination is fostered via regular contacts with the natural world. The Remote ...
The review of research papers indicated that creative thinking (convergent and divergent thinking) requires the coordination of multiple brain regions, mainly the executive control network (simply ...
Writing is "a blood-and-guts business," as the musician Nick Cave has said, literally as well as figuratively. As I type with my hands, my lungs oxygenate the blood that my heart pumps; my ...
The vast majority of authors don't use artificial intelligence as part of their creative process — or at least won't admit to it. Yet according to a recent poll from the writers' advocacy ...
Liberty University's Bachelor of Science (BS) in Creative Writing - Journalism is an exciting and dynamic degree program that can help prepare you for a career in the media industry. With a ...
One of the most rewarding times of the year in the Creative Writing program at WVU is the end of the spring semester, when graduating MFA students get to read from their theses to a crowd of family, colleagues, and English department faculty. On Thursday, April 25, at 7:30 p.m. in the Milano Reading Room of the Downtown University Library, the ...
The introduction of AlphaFold 21 has spurred a revolution in modelling the structure of proteins and their interactions, enabling a huge range of applications in protein modelling and design2-6.