- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Teaching Expertise
- Classroom Ideas
- Teacher’s Life
- Deals & Shopping
- Privacy Policy

51 Creative Writing Activities For The Classroom: Comics, Prompts, Games, And Pretend Play
January 4, 2024 // by Milka Kariuki
Creative writing can be tough for learners of any age. From knowing where to start to establishing the vocabulary to develop their story, there are a bunch of different skills they’ll need to perfect their creative writing pieces. There are so many creative writing activities out there, but which ones are best for your kiddos? Our list of 51 creative writing activities is the perfect place to start looking if you’ve got a creative writing unit coming up! Read on and see which ones might grab your little writers’ attention!
1. Make Your Own Comic Books
We bet your kiddos just love comic books! Let them create their very own in the style of the super popular Diary of a Wimpy Kid books! Encourage your students to come up with their own plot, dialogue, and illustrations to spark their creativity. Even your most reluctant writers will love this fun activity!
Learn More: Puffin Schools
2. Mad Libs
Using Mad Libs is a super popular way to develop your little creative writers! Use these free printables to get their creative juices flowing as they try to come up with words to fill the gaps to create weird and wonderful new stories. The best thing is that you can use these printables as many times as you like as their answers will be different each time!
Learn More: Teacher Vision
3. Flash Fiction
Flash fiction is a fantastic way to get your kiddies writing creatively while keeping things short and sweet! Use the range you prompts included in this resource to challenge them to write a creative story in less than 100 words. Flash fiction is amazing because your students won’t be overwhelmed by a huge writing task and it also means that your more confident writers will need to focus on the quality of their work, not the quantity!
Learn More: TES
4. Write a Story Based on the Ending
Test your students’ creativity by providing them with writing prompts that start at the end! In backward story writing, your budding writers will need to plan and pen a story that eventually leads to the ending you give them. This idea is a fantastic way to turn your traditional creative writing lesson on its head and in many ways take the pressure off your kids, as ending their stories is often the most difficult part for them!
Learn More: Teachers Pay Teachers
5. Found Poetry
Your learners will love this fun and creative found poetry activity. You can encourage them to collect words or a group of words from a favorite story or song then write them on a piece of paper or cut them out of a printed page. The overall goal is to have them rearrange the words differently to make an interesting poem with a unique writing style or genre!
Learn More: Homeschooling Ideas
6. Picture Dictionary
A picture dictionary is a brilliant way to support every member of your younger elementary class in their creative writing. The words paired with pictures give your writers a ‘dictionary’ that they can use pretty independently, so your less confident writers or non-native English-speaking students can still access your writing lessons!
Learn More: Twinkl
7. Creative Journal Writing
Why not start a creative journal with your kiddos? Have them engage in daily journaling activities by giving them a different creative prompt each day. For instance, write a story about what would happen if dogs took over the world or what would you do if you were the security guard at a zoo and someone stole an animal? The fun is never-ending with these prompts!
Learn More: Think Written
8. Roll a Story
Roll-a-Story is one of the best ways to help any of your kids who are suffering from a bout of writer’s block! They’ll roll the dice to discover the character, setting, and problem for their story then set to work weaving their creative tale! It could be a story about a wise doctor being chased by a mysterious creature in a casino, or maybe a rich artist losing their wallet in a library. Then it’s up to your students to fill in the gaps!
Learn More: TPT
9. Pass-it-on Story Writing
There’s no telling quite where this fun writing game will end up! Start by writing the first sentence of a story on a piece of paper then pass it around your class, having your kids come up with a sentence that continues the story. The paper is then passed around the whole class until every student has contributed. Finally, once it makes its way back to you, read out your collaborative story to the whole class!
Learn More: Minds In Bloom
10. Picture Writing Prompts
Creative writing prompts activities test not only your little ones’ imaginations but also their ability to craft a story and dialogue from that. Display an intriguing picture prompt for your class and have a discussion about it, recording their ideas. You could discuss what the person or animal in the picture is doing or what they’re thinking, where they think the picture was taken, and much more. They can use your collective notes to inspire their story!
Learn More: Pandora Post
11. What’s the Question?
What’s the Question is a simple, yet super engaging game that requires your young learners to think creatively. Spark their creativity by writing an answer on the whiteboard such as “the moon would explode,” and task your kiddos with coming up with a question to match it. There’ll be lots of laughs as everyone shares what they came up with!
Learn More: That Afterschool Life
12. Creative Writing Printables
This website is absolutely full of quick and fun graphics for children that’ll encourage their creative writing! The cute graphics and simple directions make it an easy bellringer activity for your writing class. Just print out some of these cool sheets and let your students get creative as they write thank-you notes to helpful heroes or finish little cartoon comics!
Learn More: Jarrett Lerner
13. Paint Chip Poetry
Nothing says creative writing quite like figurative language! Grab some of these free paint swatches from your local home improvement store and have your students create metaphors about their chosen color! We love this low-prep activity as once your kids have finished their poems, they’re a ready-made multi-colored display that’ll brighten the walls of your classroom!
Learn More: Fabulous In Fifth
14. Story Storm Activities
Once again, these Jarrett Lerner activities do not disappoint! Your students will have a blast pretending they are the principal for a day and they’ll get to create their very own rules for the school. Not only will this be an engaging writing exercise that we’re sure they’ll love getting creative with, but it also challenges children to think about why rules in school are important.
Learn More: Tara Lazar
15. Story Bag
Story bags are a fantastic way to destroy any kind of writer’s block! Grab an assortment of random objects from your home or classroom and pop them into the story bag. Next, gather your students around and pull out all the objects in the bag. Can they then write a story connecting all the items? Be sure to leave time to let them share their stories at the end of the lesson!
Learn More: Life Hack
16. Change the Ending
An easy way to ease your kiddos into the writing process is by having them rewrite part of a story. Grab their favorite read-aloud, and challenge them to come up with a new ending! They’ll need to finish the story in a way that makes sense, but aside from that, they can be as creative as they like! Your reluctant readers will like this one as much of the work on setting and characters has already been done!
Learn More: Make Beliefs Comix
17. Plot Twist Writing Prompts
BUT WAIT – there’s a twist…This fun writing practice is perfect for older middle or high school but could also be simplified for younger students. Write these twist prompts on notecards and have your kids draw one each before letting them go off and write a story around their chosen twist! They’ll be eager to share their finished work with classmates at the end. After all, who doesn’t love a good plot twist?
Learn More: Pinterest
18. Craft Box Craft
Every kid loves the book The Day the Crayons Quit for its creative narrative about this familiar box of coloring supplies! This extension activity rolls art and creative writing into one! Your students will have fun coming up with dialogue for each of the different crayons and you could even make it into a fun display for your classroom walls!
Learn More: Buggy And Buddy
19. Dialogue Pictures
Personalizing writing activities always makes it more engaging for kids! Print out a picture of yourself with a blank speech bubble, and model how to add in some dialogue. Then, let your kiddos practice speech bubbling with a photo of themselves, a pet, or a favorite celebrity, and have them come up with some interesting things for each of their subjects to say!
Learn More: SSS Teaching
20. Figurative Language Tasting
Your students will be creative writers in no time after practicing their figurative language with food tasting! Not only do tasty treats make this activity incredibly fun, but it also brings the writing process of metaphors and hyperbole to life. Just give each of your kids a few pieces of candy or snacks, and have them practice writing figures of speech relating to each one! They’ll have the words on the tip of their tongue- literally!
Learn More: It’s Lit Teaching
21. Explode the Moment
One of my favorite writing concepts as a teacher is ‘exploding the moment’. This method is perfect for showing your kiddies that even the smallest moment can be turned into an imaginative, descriptive story! Start by having them brainstorm some ideas and expand on tiny memories like losing a tooth, getting a pet, or making a winning goal in a soccer game!
Learn More: Raise The Bar Reading
22. Round-Robin Storytelling
Round-robin storytelling is the perfect collaborative creative writing activity! This one can be done verbally or in writing, and it challenges your class to build a story using a given set of words. They’ll have a fun and challenging time figuring out how to incorporate each piece into one cohesive story.
Learn More: Random Acts Of Kindness
23. Acrostic Poems
Acrostic poetry is one of the least intimidating creative writing exercises as there are no rules other than starting each line with the letter from a word. Challenge your kiddies to use each letter in their name to write lines of poetry about themselves, or they could choose to write about their favorite food or animal!
Learn More: Surfin’ Through Second
24. Sentence Sticks
This exercise requires minimal prep and can be used in so many different ways. All you’ll need are some craft sticks in which you will write sentences with blanks and word banks. Your young writers can then pull a stick and fill in the blanks to practice creative thinking! Task them with a different goal each time; can they make the sentence silly or sad for example?
Learn More: Liz’s Early Learning Spot
25. Conversation Prompts
These fun prompts require your kids to think creatively and answer a range of interesting questions. They’ll be excited to write stories about waking up with a mermaid tail or describe what is in a mystery package delivered to their doorstep! These creative prompts are perfect for bellringers or transitions throughout the school day!
Learn More: Twitter
26. Pretend Play Writing
Do you remember playing with fake money and fake food when you were younger? This idea takes it a step further by incorporating some writing practice! All you’ll have to do is print the templates for dollars, shopping lists, and recipes then let your little learners have fun with these play-pretend writing ideas!
Learn More: Prekinders
27. Question Cubes
Your class will be on a roll with these amazing question cubes! Whether the cubes are used for responding to a story, brainstorming the plot of a story, or practicing speech and listening, they are an easy, affordable tool for your little readers and writers! You can snag some foam dice at the dollar store and hot glue questions on each side to spark some creative writing ideas for your class.
Learn More: A Love 4 Teaching
28. Balderdash
Not only is Balderdash an addicting board game, but it can even be used in the classroom! Your little learners will have a blast as they create made-up, imaginative definitions for words, important people, and dates. Whoever guesses the real answer out of the mix wins the points!
Learn More: EB Academics
29. Two Sentence Horror Story
This creative writing exercise is best for older students and would be a great one to try out around Halloween! You’ll be challenging your learners to write a story that runs chills up their readers’ spines, but there’s a twist…the story can only be two sentences long! Your kiddos will love writing and sharing their writing to see who can come up with the spookiest short story!
30. Telephone Pictionary
Another game that your kids will be begging to play over and over again is telephone pictionary! The first player will write down a random phrase, and the next person must draw their interpretation of the phrase. The third player will write what they think the picture is and so on!
Learn More: Imagine Forest
31. Consequences
You need at least two players for this fun creative writing game. Each pair or group of kids will start by having one person write a random phrase and conceal it by folding the paper. Then, they pass it to the next student to fill in the blank using the prompt. Once all the blanks are filled in, let them unfold the paper and get ready to reveal some seriously silly stories!
32. Story Wands
Story wands are a fun way to have your kids respond to stories and study what makes something their favorite. Responding to what they’re reading is a super helpful exercise in preparing them for creative writing as it allows your students to connect to their favorite stories. By figuring out what elements make stories great, this is sure to help them in their own creative writing assignments!
Learn More: Little Lifelong Learners
33. The Best Part of Me
Probably my favorite creative writing activity, this one is infused with social-emotional learning and self-esteem building! Let your students get to choose their favorite physical characteristics about themselves; whether it be their eyes, hands, feet, etc. Then, they take a picture to attach to their written reasoning! Make sure to boost the creative element of this writing task by encouraging your learners to use a bunch of adjectives and some figurative language!
Learn More: Sarah Gardner Teaching
34. Me From A-Z
Challenge your kiddos to get creative by coming up with 26 different words to describe themselves! Me From A-Z gives your students the opportunity to explore who they are by coming up with words describing them in some way using each letter of the alphabet. Why not let them decorate their lists and turn them into a display celebrating the uniqueness of each of your class members?
35. How to Make Hot Chocolate
How-to writing is a great way to get the creative writing wheels turning in your kiddies’ brains! They’ll have a fun time coming up with their instructions and ways to explain how to make hot chocolate! Do they have a secret recipe that’ll make the best-ever hot cocoa!? Once they’ve written their instructions, be sure to try them out and do a taste-test of their recipes!
Learn More: Teacher Mama
36. Give Yourself a Hand
Hands up if you love this idea! For this creative writing activity, have your little ones trace their hand on a piece of paper and decorate it with accessories. Then, encourage them to write a list of all the different things they do with their hands all over their tracing! This is a great warm-up to get the creative gears turning.
Learn More: Write Now Troup
37. Word Picture Poem
A word picture poem is a fantastic way to challenge your kids to write descriptive poetry about a common object! Your little poets will learn to find beauty in ordinary things and strengthen their sensory language skills and their vocabulary. For some added fun, you can even task them with writing a short story about the item as well! The results are sure to be fun to read!
Learn More: Teaching With Terhune
38. Shape Poem
Shape poems are some of the most creative poetry as they combine words and art into one! First, your young poets can choose an object to use as their muse and lightly trace an outline onto some paper. Then, they’ll write words along the outlined shape in the form of a poem that describes the object! The result is a bunch of fun and striking poems that’ll look great displayed around your classroom!
39. Crazy Hair Poetry
Here’s another one that combines writing and art! Start by guiding your kiddos in drawing a self-portrait then adding some crazy hair by blowing watercolor paints around! After the paint dries, have your kids come up with a short but creative poem describing their hair art.
Learn More: Grade School Giggles
40. Fingerprint Poetry
Nothing is more creative than getting your kiddies to let down the barriers in their mind and tap into their stream of consciousness! Show them how to pick a topic and then let their words flow straight from mind to paper in a swirling pattern. This fingerprint idea can be used for a get-to-know-you activity as well!
Learn More: Kristen Dembroski
41. Doggie Haiku Poems
Put a fun twist on classic haiku poetry! Your students will have a paw-some time writing three-line poems about dogs which they can then illustrate afterwards! Before starting the activity, you can use Dogku by Andrew Clements as a read-aloud to get your class hooked on this idea!
Learn More: Teaching Fourth
42. Fractured Fairy Tale
Ever wondered if the Big Bad Wolf was framed? Or if Sleeping Beauty was actually a snorer? Your writers in training will have a fun time taking a classic fairytale and putting their own spin on it! Following five simple steps, your kids will be funky fairytale authors in no time!
43. Letter Writing
These creative letter-writing prompts are sure to boost your kiddies’ imaginative writing skills! Whether writing to a pen pal or a favorite celebrity, letter writing is a great way to practice handwriting, word flow, descriptive language, and communicating all rolled into one! Have your writers grab their pencils and let the creativity flow as they write fun response letters to these prompts!
44. Hersey’s Kisses Similes
Teach sensory language and similes by connecting this tasty treat with the sense of taste! Your students will have a lovely time brainstorming how chocolate connects to each of our senses and applying that knowledge by writing some sweet similies! What a fantastic way to teach them how to use these essential creative writing tools!
Learn More: Teacher By The Beach
45. Sensory Poetry
Another great way to teach sensory details is to have your learners write poems about their favorite foods! Task them with writing a line for each sense to describe the food! Everyone will be hungry after this creative writing lesson so it might be a good idea to have some snacks on hand!
Learn More: Mrs. Tice’s Class
46. Season Personification
Each season of weather has an array of characteristics making this the perfect activity to practice personification in creative writing! Allow your little writers to choose a season to write about as if it were a person with human characteristics. Winter is a no-brainer! It’s Elsa!
Learn More: Write Shop
47. Class Book of Character Traits
To be creative writers, your kids need to know how to create realistic characters for their stories. For this class book, you’ll start by giving each student two opposing character traits. Next, have them demonstrate these traits by illustrating two characters and displaying them through dialogue!
Learn More: Crafting Connections
48. Socialgrams
With Instagram being all the rage these days, your kiddos will have a fun time creating a ‘socialgram’ on paper! Challenge them to create a descriptive and engaging caption to go along with their “photo” in the post. Then, classmates can comment on each other’s work!
Learn More: Breezy Special Ed
49. Story Introduction Worksheets
Creative writing worksheets are a simple, minimal-prep tool to use in your creative writing units. Print out a variety of options, and have your kids practice their skills by finishing imaginative story introductions. By giving them a place to start their story, you can really take the pressure off your kids which will help ease them into the creative writing process!
Learn More: Lanternfish ESL
50. Dialogue Worksheets
Here’s another low-prep option for the last-minute planners! Pre-written dialogue can help guide the mood of the story and allow your kiddies to just focus on filling in the characters’ actions. This is also a great way to model how dialogue is spaced out and balanced in a story!
Learn More: ESL Writing Worksheets
51. Character Trait Posters
In this personalized character trait activity, your students will create a poster of themselves and label it with a bunch of different character traits. Descriptive, interesting characters are what make a story captivating, so this is a great introduction to understanding characters and their physical as well as personality traits! This is an activity that’s sure to help them build a strong foundation for their creative writing skills to build from!
Learn More: Life In First Grade
ThinkWritten
300 Fun Writing Prompts for Kids: Story Starters, Journal Prompts & Ideas
Are you a parent or teacher? Here are 300 fun and creative writing prompts for kids to spark the imagination of young writers everywhere. Use these kids writing ideas as journaling prompts, story starters or just for fun!

We may receive a commission when you make a purchase from one of our links for products and services we recommend. As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases. Thank you for support!
Sharing is caring!
It’s never too early to start writing, and so we’ve created this fun list of 300 creative kids writing prompts for teacher and parents to use.
You’ll love these fun ideas for kids writing prompts to use as creative sparks to get young imaginations writing in no time!

These are perfect to use as kids journal writing prompts, as short story writing prompts, or just for exercises to help students and children of all ages tap into their creativity. Maybe your kids will write an essay, maybe a poem, or maybe even a whole book!
Whether you are a teacher or parent looking to inspire your kids to write, or maybe even an adult who would like to practice writing with a more playful and young-hearted approach, I hope you find these creative writing prompts inspiring!
Buy the Printable Cards! We will always have this list of 300 kids writing prompts available for free, but I’m very excited to now also offer an ad-free printable version of these prompts in my online Etsy shop. Thank you for your support!
The Ultimate List of 300 Fun & Creative Writing Prompts for Kids
#1. Imagine a giant box is delivered to your front doorstep with your name on it. What’s inside and what happens when you open it?
#2. Write a short story about what it might be like if you woke up one morning with a mermaid tail.
#3. Which is better, winter or summer? Write about the reasons why you think winter or summer is better.
#4. Write about what would it be like if you had an alligator as a pet.
#5. If you had $1,000, what would you buy and why?
#6. Write a story using these 5 words: apple, train, elephant, paper, banjo
#7. What do you want be when you grow up and why?
#8. Who is your favorite person on the planet? What do you like most about that person?
#9. If you could have any secret super power, what would you want it to be and why?
#10. Write about 3 places you would like to travel someday. What do these three places have in common?
#11. Write about a time you felt really happy. What happened? What made you feel happy?
#12. Imagine what would happen if someone shrunk you down to be only 1″ tall. How would your life change?
#13. If you were in charge of the whole world, what would you do to make the world a happier place?
#14. Write a story about what it would be like to climb to the very top of the highest mountain in the world.
#15. If you were in charge of planning the school lunch menu, what foods would you serve each day?
#16. What are some of your favorite animals? What do you like about them?

#17. Imagine that dogs take over the world. What do they make the humans do?
#18. Write a story about flying to outer space and discovering a new planet.
#19. You are a mad scientist and have invented a new vegetable. What is it called? What does it look like? What does it taste like? Most importantly: Is it safe to eat?
#20. You go to school one morning to discover your best friend has been turned into a frog by an evil witch! How do you help your friend?
#21. Describe what it is like when trees lose all of their leaves in the autumn season.
#22. Write about your favorite sport and why you like it so much.
#23. Imagine what it might be like to live on a boat all the time and write about it.
#24. If you had one wish, what would it be?
#25. Write about what you might do if you have the super power to become invisible.
#26. You are walking through the forest when one of the trees starts talking to you. What does it say? What do you do?
#27. The weather forecast is calling for a blizzard in the middle of the summer. What do you do?
#28. What types of transportation will people have in the future?
#29. What were some of your favorite toys when you very little? Do you still enjoy playing with them?
#30. What would a day in your life be like if you were a movie star?
#31. Imagine you’ve invented a time machine! What year do you travel to?
#32. What are your favorite things to do over summer vacation?
#33. What is your favorite holiday and why?
#34. If you could meet any fictional character from a book, who would it be?
#35. You are writing a travel guide for kids visiting your city. What places do you think they should visit?
#36. What is a food you hate? Write about it!
#37. Imagine what it would be like if there was no electricity. What would be different in your daily routine?
#38. You are building a new city! What types of things do you think your city needs? How will you convince people to move to your new city?
#39. What is your favorite movie? Write your review of the movie and why you think people should watch it.

#40. Imagine you get a magic sweater for your birthday. What happens when you wear the sweater? What do you do with these new found magical powers?
#41. You are the security guard at the zoo and someone has stolen a rhinoceros! How do you track down the thief?
#42. You have been invited to have lunch with the queen. What foods do you eat and what topics do you and the queen discuss?
#43. If you could design a school uniform, what types of clothes would you suggest? What colors would they be?
#44. Imagine you are a reporter interviewing a celebrity about their life. What questions do you ask?
#45. You are running a lemonade stand. Describe the steps for how you make lemonade and the types of customers you see during the day.
#46. Write a story about being the ruler of an underwater world.
#47. Write an acrostic poem for the word “treehouse”.
#48. You decide to grow a sunflower, but the sunflower grows so tall it reaches up to the sky! Write about what happens when you decide to climb to the top. What do you discover?
#49. Imagine you look out the window and it is raining popsicles from the sky! Write a story about the experience.
#50. If you could be any animal, which one would you be and why?
#51. If you were on a spaceship, what would you be most excited about seeing?
#52. Do you have any pets at home? Write an essay about how you take care of your pets. If you do not have a pet, what type of pet might you like?

#53. Imagine you are opening a store that only sells items which are blue. What types of items do you sell?
#54. Have you ever lost something that is important to you? Were you able to find it?
#55. Write a story about a kid who is moving to a new school. How do you think they might feel?
#56. Rewrite the ending of your favorite fairy tale. For example, what would have happened if Cinderella never went to the ball?
#57. Have you ever forgotten to do your homework? What happened?
#58. Do you have a favorite song? Write about the type of music you like to listen to.
#59. Imagine your parents wake you up one morning to tell you they will take you to do anything you want to do for the whole day – you don’t even have to go to school or do your chores. What would you choose to do and why?
#60. Do you like amusement parks? What are some of your favorite rides?
#61. Write a story using these three words: detective, piano, and pizza.
#62. Have you ever been to the beach? Write about your favorite things to do. If you have never been to the beach, what would you like to do the first time you visit?
#63. Is there a favorite tv show you like to watch? Write about your favorite character and why they are your favorite.
#64. Write a poem using onomatopoeia , where the words you use are pronounced similar to the sound they make. For example, buzz, bark, sizzle, slam and pop.
#65. Have you ever had to stand in line to wait a long time for something? What did you do while you waited? How did you feel while waiting? How did you feel once the wait was over?
#66. Is it a good idea to keep ALL secrets a secret? Write about examples of when it is okay to spill a secret – and when it isn’t.
#67. Is there something you are good at doing? Write about your best strengths.
#68. What historical time period and location would you go back to live in if you could? Write about it!
#69. Write about 5 things you can do that are important for you to stay healthy and safe.
#70. Do you think thunderstorms are scary? Why or why not?
#71. What would you most like to learn over the next year? Think about things that interest you or questions you might have about the world and make a list!
#72. You are going on a trip to a jungle safari! What items do you pack in your suitcase?

#73. Imagine you are sitting at home one day and you hear someone shrieking in the living room they see a mouse in the house! Write a story about what might happen next.
#74. You are writing a letter to someone who is having a hard time making new friends at school. What do you write? What advice do you give them?
#75. Imagine you just met a magician – but their beloved rabbit who they pull out of a hat for all the tricks has been kidnapped! How do you help find the rabbit?
#76. Do you hear what I hear? Set a timer for 5 minutes and write about all of the sounds you hear in those 5 minutes.
#77. Imagine you go to get a haircut and they accidentally shave your head! How do you feel about that and what would you do?
#78. Do you find it easy to talk to people you don’t know? What are some ways you can start up a conversation with someone you have never met before?
#79. Are there any chores you have to do at home? What are they? What do you like – and not like – about each one?
#80. Open up a random book to any page. Write for 5 minutes about the first word you read.
#81. Pretend you are a writer for your city’s newspaper. Who would you like to interview for a news story and why?
#82. There are many fictional characters who live in unusual houses, such as the old woman who lived in a shoe. What kind of unusual house would you like to live in? Write about what it would be like to live in an unusual house!
#83. Write a list of 10 things you can do to practice kindness to others.
#84. Is there a homework subject you dread? Why do you not like getting homework in that subject?
#85. What is your favorite month of the year? Write about why you like it and some of your favorite things to do during that month.
#86. Imagine you are planning a surprise birthday party for someone. How do you keep it a surprise?
#87. Pretend you walked outside to find a sleeping dragon in the grass! Why is the dragon there? Is it a friendly dragon? What do you do? Write about it!
#88. What are you grateful for today and why?
#89. You were on your way to a very important event when you fell into a puddle. Now what?
#90. Have you ever watched a movie and didn’t like how it ended? Write what you think should happen instead.
#91. Can you answer this riddle from Alice in Wonderland ? How is a raven like a writing desk?
#92. Imagine you are the captain of a pirate ship. Write a diary entry for what your day was like.
#93. If you could start any type of business, what kind of business would you start? What types of products or services would you provide?
#94. Write a sequel to one of your favorite fairy tales. For example, what was Goldilocks’s next adventure after she left the bears?
#95. What is something you are afraid of? What helps you to feel less afraid of something? What would you say to a friend who feels scared to help them feel less afraid?
#96. Write a letter to your future self in 20 years.

#97. In addition to basic survival needs such as food, water, air and shelter, what are 3 things you would you need to be happy?
#98. If you could invent a robot of any type who could do anything you imagine, what types of things would you would have the robot to do?
#99. Which do like better? Apples or Oranges? How are they alike? How are they different?
#100. Why did the chicken cross the road? You are a detective and are assigned to the case. How do solve the mystery?
#101. Write instructions for how to make your favorite snack. Be sure you add your favorite tips and suggestions for how to select the best ingredients!
#102. Imagine you borrowed a friend’s favorite lucky pencil to help you pass a math test – but then it snapped in half! How will you ever tell the news to your friend?
#103. Look around the current room you are sitting in and choose 3 random objects that are nearby. Now write a story or poem that includes those three items!
#104. Write a letter to the author of a book you recently read and tell them what you liked most about the book.
#105. Ernest Hemingway is famous for writing a six word story. Can you write a story in just 6 words?
#106. What do you think will be the future for cell phones? Will people still use them in 25 years or will something else take its place?
#107. Do you want to go to college? Why or why not?
#108. Write a story or poem about a kitten who wanders off and gets lost. How does the kitten find its way home?
#109. Currently, it is required by law that kids go to school. Do you think this is a good or bad idea?
#110. If you could invent a new board game, what would it be called? How is it played? What are the rules? What makes it fun to play? Write about it!
#111. Imagine you come home to discover your entire bedroom is covered in ketchup! What on earth happened? What is your reaction? How do you clean everything up?
#112. What is something you learned today?
#113. Would you rather have a goldfish or shark as a pet?
#114. From A-Z: make a list of something for every letter of the alphabet.
#115. Have you ever gone fishing? If you have, did you like it? Why or why not? If you haven’t, do you think you might want to?
#116. What is one of the most important things you do each and every day?
#117. Write a story about Gretchen the Grouch, a girl who is always angry! Will she ever be happy? Why is she so grumpy all of the time?
#118. How do you feel when someone takes something of yours without asking? What is a good way to deal with it when that happens?
#119. Write a poem that starts with the word “if”.
#120. Write a story about a family of rabbits who live in the woods. What are some of the challenges they face?
#121. What clothes do you think are the most comfortable? What kind of clothes do you like to wear the most? What clothes do you NOT like to wear?
#122. Imagine there are no grocery stores and you must get your own food. What are some of the ways you find food? What types of things do you eat?
#123. What are 3 things you can do that are good for the environment?
#124. If you could meet any famous person today, who would you want to meet and why? What questions might you ask them?
#125. A tongue twister is a quick poem where many of the words start with the same letter and are similar in sound. For example, “Peter picked a peck of pickled peppers.” Try writing your own with this fun kids writing prompt!
#126. What is the first thing you think of when you hear or see the word green?
#127. A hero is someone who is admired for their courage and achievements. What do you think makes someone a hero? Who are some of your heroes?
#128. What did you do during summer vacation last year? What do you want to do for summer vacation this year?
#129. Write a story about a super hero dog who saves the day! Who does the dog help and why?

#130. Would you rather live somewhere that is always cold, or somewhere that is always hot? Write about which one you would rather choose.
#131. Have you ever volunteered to help a charity? If so, write about the experience! If not, what are some charities you think you might like to volunteer for?
#132. What does the word courage mean to you?
#133. What makes you unique? What are some things about you that make you an individual?
#134. Have you ever been to a museum? What is your favorite thing to look at on display?
#135. What can you do to set a good example for others to be kind?
#136. A Tall Tale is a story that exaggerates something that actually happened. Write a tall tale about something that recently happened to you.
#137. What is one of your favorite toys that you think you might still want to have and play with when you are 22 years old?
#138. Oh no! Everyone around you is sick with a nasty cold! Write a silly poem about how you try to avoid catching their germs!
#139. Personification is when a non-living object takes on human characteristics. Write a story where you personify a common electronic gadget in your house, such as the Television or toaster.
#140. Write a poem using similes, which is when you say an object is like something else. Here is an example of a simile: “Her eyes were as blue as the sky.”
#141. Have you ever read a book written by Dr. Suess? Write your own “Suess-style” story, complete with rhymes and made up words.
#142. Do you have any siblings? Think about what it might mean to be a good brother or sister and write about it!
#143. Make a list of questions to interview your parents or grandparents about what it was like when they were growing up as a kid. Then, ask them the questions and write about their answers!
#144. You are in charge of writing a new radio show just for kids! What topics will you talk about? What music do you play?
#145. What do you usually eat for breakfast every day? What, in your opinion, is the greatest breakfast food ever created? What makes it so great?
#146. Write a 12 line poem where every line is about a different month of the year.
#147. What is something you look forward to doing the most when you are an adult?
Use these prompts in your classroom! Get the ad-free printable version of these prompts to inspire your students to write! Thank you for your support!
#148. Do you like to try new things? What is something new you have tried recently or would like to try?
#149. Imagine what it might be like to be alive in Egypt when the pyramids were built. Write about what it was like.
#150. A credo is a statement of personal beliefs. Try writing your own credo for things that you believe in and feel are important.
#151. The circus has come to town but they have no place to perform! How do you help the ringmaster find a place to put on a show?

#152. Do you like to act? What are some of your favorite actors or actresses? What do you think makes someone a good actor or actress?
#153. “Practice makes perfect” is a popular saying. What is something you like to practice so you can become better at it? A sport? A musical instrument? A special skill? Do you like to practice?
#154. Write about what it might be like to be water drops freezing and turning into ice.
#155. Do you think it is important to keep your room clean? What do you like about having a clean room?
#156. Imagine your parents are sending you away for a two week summer camp trip. Would you be excited? Why or why not?
#157. What are you currently learning about in history class? Write a fictional story about someone from the past you are learning about.
#158. Many wars have been fought in the past. Instead of going to war, what do you think countries could do to resolve their differences peacefully?
#159. Every year over 8 billion plastic bottles and cans are thrown away. What are some things you can do to help encourage your family and friends to recycle?
#160. Imagine if you were the principal of the school. What might you do differently? What things would you do that are the same? Write about it!
#161. Pretend that one day you are at your neighbor’s house and you notice a strange noise coming from the basement. You go downstairs to investigate to see a large machine running with many lights and buttons. Why is it there?
#162. Write an essay that starts with the line, “Tomorrow, I hope…”
#163. If you could give one thing to every child in the world, what would you want to give them?
#164. Do you have a piggy bank at home? How do you earn money to add to your savings?

#165. What qualities make a house a home? What are 3 things you think every house should have?
#166. Would you rather go scuba diving or rock climbing? Write about which one you think you would like to do more and why.
#167. Do you think it is a good idea for kids to write a daily journal? What are some of the benefits of writing every day?
#168. Do you like watching fireworks or are they too noisy? Write about a time when you saw fireworks in the sky.
#169. Oh no! Your friend has turned into a statue! How did this happen? What do you do? Does your friend ever turn back into a person again?
#170. If you could be any movie character, who would you be and why?
#171. A mysterious message appears in code on your computer screen. What could it mean?
#172. If you could go to work with one of your parents for a day, what do you think the day would be like? What types of things do your parents do at work all day long?
#173. Imagine you are the President and you are creating a new national holiday. What is your holiday about? How is it celebrated? What day of the year do you celebrate? Write about it!
#174. You won a never-ending lifetime supply of spaghetti noodles! What will you do with all of these noodles?
#175. Would you rather be a bunny rabbit or a hawk? Why did you choose the one you chose?
#176. Your teacher has been acting mysterious lately. After school one day, you notice a weird green light shining through underneath the door of your classroom. What do you do? What is happening with your teacher?
#177. Write an article about tips for how kids can be more organized and study well for tests.
#178. Look at any product in your house and read the ingredients labels. Research what each ingredient is. Do you think these ingredients are good or bad for people?
#179. If you were a doctor, what do you think would be the most important part of your job every day?
#180. The school librarian needs your help! A truck just arrived with 2,000 books and she can’t fit all the books onto the shelves! What do you do? How do you find a place to put all these books?
#181. Do you think it would be fun to plant a garden? What types of plants would you want to grow? Write about your garden ideas.
#182. What is a sport or activity you would like to try playing for the first time?
#183. Do you think kids should be allowed to do the same things as adults? What things do you think kids should be able to do that only grown-ups can?
#184. Imagine you and your parents switch places for a day. Your parents are the kids and you are now in charge! What would you do?
#185. Write a get-well letter to someone who has been sick. What can you say to make them feel better?
#186. If you could visit any planet in the solar system, which planet would you like to visit the most and why? Write about what it might be like.
#187. Have you ever been to a farm? What did you like about it? If you haven’t been to a farm, do you think you might like to visit one? Why or why not?
#188. The mayor of the city has a big problem and needs your help! What is the problem and how will you solve it?
#189. Pretend your little sister ate carrots for dinner and the next morning woke up with rabbit ears! How did this happen? What do you do? Will she be a rabbit forever?
#190. Imagine you wake up in the morning to find out you get to relive any day of your life again for the whole day. What day would you want to experience again and why?
#191. Do you think you might like to be a firefighter? Why or why not?

#192. You are a lawyer and your client has been accused of stealing a car. How do you convince the jury your client is innocent?
#193. Think of the four elements: fire, air, earth, and water. Which of these four elements do you like the best?
#194. What would you do if you could be invisible for a whole day? Do you think you would enjoy it or be glad to be back to normal the next day? Write about it!
#195. Imagine you are a meteorologist and people are starting to get angry that your weather predictions are always wrong. What do you do?
#196. If you could create any law, what would it be? Why do you think the law is an important one to have?
#197. You are going incognito and need to hide to your identity so you aren’t recognized or discovered while you walk through the city. What type of disguise do you wear?
#198. Write a persuasive letter to your parents explaining why you should get a new pet. Make sure you provide a convincing argument they won’t be able to refuse!
#199. Your friend wants to do something dangerous. What should you do?
#200. How do you think the world would be different if there were no oceans?
#201. What do you do when someone disagrees with your opinions? Is there a better way to handle conflicting opinions?
#202. What do you think you as a kid could do to help encourage more people to read?
#203. Do you have a good luck charm? What makes this item lucky? When do you use it? How do you use it?
#204. What is at the end of a rainbow? Imagine you follow a rainbow to the end. What do you discover? Is it a pot of gold, or something else?
Use these prompts in your classroom! Get the ad-free printable version of these prompts to inspire your students to write! Thank you for your support!
#205. What do you think the consequences should be for someone who is caught cheating on a test at school?
#206. Imagine you are riding your bike one day when you encounter an older kid who wants to steal your bike. What do you do?
#207. You are the lead singer and star of a famous rock and roll band, but there is one problem – your drummer is jealous of your fame! How do you solve this situation?
#208. If you could help a group of kids in any part of the world, what kids would you want to help the most and why? What are some things you think would help these kids?
#209. Everyone knows the house on the end of the street is haunted. What are some of the strange things that happen there? Why is the house haunted?
#210. You notice at school one day there is a door to a secret passage next to the janitor’s closet and decide to explore. Where does it lead? Why is it there? Do you go alone or bring a friend along?
#211. A bucket list is a list of things you want to accomplish in your lifetime. What are 5 things on your bucket list?
#212. Imagine the perfect treehouse or clubhouse for you and all of your friends as a place to hang out. Describe what it is like inside.
#213. Do you get bored easily? Make a list of things you can do whenever you feel like you are bored and there is nothing fun to do!
#214. Now vs. Then: Think about how today is different from one year ago. How have you changed? What things in your life are different?
#215. Write your autobiography about your life.
#216. It’s a heat wave! What do you do when the weather is hot? What are some of your favorite ways to stay cool?
#217. What are three important safety tips every kid should know to stay safe?
#218. What genre of books do you like to read the most? Write about the characteristics of the genre and list some of your favorite books as examples.
#219. Holiday Traditions: How does your family celebrate the different holidays and events? What are some traditions you do each and every year?
#220. Imagine one day in science class a science experiment goes terribly wrong and now you and all of your classmates have superpowers! What are your superpowers and what do you do with them?

#221. Who is favorite teacher? Why are they your favorite?
#222. You are baking a cake, but you accidentally put salt in the cake instead of sugar. Nobody will eat it! How do you feel? What will you do next time?
#223. Do you think it is important to have good table manners? What do you think some good manners to practice might be?
#224. Many schools no longer teach cursive handwriting. Do you think this is a good or bad thing? Do you know how to write cursive handwriting? Would you like to learn if you haven’t?
#225. If you were the owner of a theme park, what types of rides and attractions would have? Describe what they would be like and why people would want to visit your park.
#226. Your parents give you $100 to spend at the grocery store. What do you buy and why?
#227. Some people who are alive today grew up without computers or video games. What would you do if you didn’t have a computer or video games? How would life be different?
#228. You walk into your living room and discover there is a giant elephant standing there. How did the elephant get there? What do you do about it? How do you explain the elephant in the living room to your parents?
#229. Have you ever had a weird dream? What happened in the dream? What do you think it means?
#230. Do you like to draw or paint? Write a story inspired by a painting, doodle, or sketch.
#231. You are being sent on a mission to outer space to live in a space station for 5 years. What supplies do you pack and why?
#232. What is the scariest creature alive on earth? Describe in detail what makes it so horrifying.
#233. What do you think your pet might say if they could talk to you?
#234. Imagine your school is putting on a talent show. What act will you perform? What other acts will be in the show?
#235. If you could breathe under water, what would you do?
#236. What time of day do you think school should start? Write a convincing argument on why or why not the time of day school starts should change.
#237. If you were to start your own YouTube video channel, what would the videos on your channel be about?
#238. Do you like to cook? What are some things you like to make and eat?
#239. Your school is having a field day and you are in charge of planning the activities and games. What types of activities and games would you plan for the event?
#240. If you had a remote control drone that takes video of everything it sees from the sky and you could take it anywhere, what would you film? For example, the inside of a volcano or soar it over the plains of Africa.
#241. The Bermuda Triangle is an area of the ocean where many ships and planes have gone missing. Why do you think this could be? Write a story about what it might be like to travel there.
#242. There are 7 great wonders of the world – which one do you think is the most wonderful?
#243. If you could speak any foreign language fluently, which one would you like to speak and why?
#244. You are inventing a new flavor of ice cream! What is the new flavor called and what ingredients do you need to make it?
#245. Would you rather go to a baseball game or read a good book? What reasons do you have for your choice?
#246. You walk outside to get your mail and your mailbox starts talking to you! What does your mailbox have to say?
#247. Imagine you are a famous person. What are you most famous for? What is it like to be famous?
#248. What do you think would be the most fun job in the world to have? Give examples of why you think it would be a fun job to have.
#249. Write a poem about an object that is shiny and dazzling.
#250. Do you like to watch the Olympics? Why or why not? If yes, what is your favorite Olympic sport?
#251. What kind of car do you want to drive when you are older? Do you think learning to drive will be easy or hard?
#252. What do you think would make for a great gift to give someone on their birthday?
#253. Describe a time when you needed help and someone helped you. What did they help you with and how did it make you feel?
#254. If you could be any type of fruit or vegetable, what would you be and why?
Love these prompts? Get the ad-free printable version of these prompts to use at home or in the classroom!
#255. Do you think it is more important to have a good imagination or have all the facts proven?
#256. Do you have a favorite aunt, uncle, or another relative? Write a story about their life and why you like to be with them.
#257. Think of a time you laughed really, really hard. What was so funny? Why were you laughing? Write about it!
#258. Write a poem about an emotion. For example: happy, sad, angry, embarrassed, guilty.
#259. Do you ever have a hard time falling asleep? What are some things that help you feel sleepy?
#260. If you could drive a car, where would you drive and why?
#261. Imagine you are trading places with your friend for a day. What will it be like to be at their house? What will your friend think while they are at your house? Write about it!
#262. If you could break a world record, what would it be? What do you think would be necessary to be able to break the world record?
#263. Imagine you live in Colonial times. What would it be like to grow up as a kid in Colonial America?
#264. You are building a new city. What is the name of your city? What is the weather like? What buildings will you build?
#265. What do you think it would be like to work as a sailor on big ship in the ocean each day?

#266. Imagine you are the teacher for the day. What types of activities do you make the students in the class do?
#267. How would you feel if your parents told you that you would be getting a new baby brother or sister? Write about it!
#268. Do you know any good jokes? What are some of your favorite jokes? What makes them funny? Do you think you could write your own?
#269. Imagine you are floating down a river on a raft. What types of things can you see from the river that you normally wouldn’t see from the land?
#270. You want to start a new hobby collecting something. What kinds of things would you collect and why?
#271. Your mom announces she is having a yard sale. Would you let her sell any of your things? Why or why not?
#272. Imagine you walk out your front door one morning and it is raining popcorn! What do you do?
#273. You are camping in the woods one night and hear a scary noise. What do you do? What might be the cause?
#274. What do you think might make kids really happy to go to school? What are some things you think schools should do so that it could be more fun?
#275. Today’s lunch at the cafeteria was unusually horrible. You are a detective on the case to investigate. What do you think is the cause?
#276. If you had a tree that grows money, what would you do?
#277. What would you do if you had a unicorn as a pet?
#278. Would you rather go to the zoo or go to the aviary? Which one would you pick and why?
#279. What are some safety tips you should follow when riding a bike?
#280. You are designing the cover of a magazine. What are some of the headlines on the cover?
#281. Are you afraid of the dark? Why or why not?
#282. If you could learn to play any type of musical instrument, which one would you like to learn how to play and why?
#283. Imagine you are playing a sport that involves a ball, such as soccer, baseball or kickball. What would it be like if the ball could talk?
#284. You come home to discover a friendly alien has been living in your closet. What do you do? Why is there an alien in your closet?
#285. Is there something you are afraid of that you wish you weren’t afraid of? Write about it.
#286. Write about the best party you’ve ever been to. What made the day fun and special?
#287. What makes you feel loved and cared about? What are some ways people can show you that they love and care about you?
#288. There is a kite flying competition coming up and you are going to design your own kite. What will your kite look like? What colors will it be? Will it have any certain shape?
#289. You are given the challenge to drop an egg on the floor – without it breaking! What are some things you might try to make sure the egg won’t break?
#290. What are some of the things you can do every day to stay healthy?
#291. Do you think grown-ups are boring? Why do you think they are so boring all of the time? What is something fun that boring grown-ups could do instead of being so boring?
#292. Write a lyrical poem or song about what kids do while they are at school all day long.
#293. What are the first things you like to do when you are done with school each day? What are some of the activities you like when you are not at school?
#294. Imagine dinosaurs were still alive today. How do you think our lives would be different?
#295. Would you rather visit a volcano or a desert? Which one would you choose and why?
#296. Is there a sound you think is annoying? What types of sounds drive you crazy? Write about them!
#297. What do you think it would be like to be the size of an ant for a day? What types of things would you do?

#298. Imagine one of your stuffed animals comes to life and starts talking to you. What types of things will you talk about? What will you do?
#299. What makes you feel happiest? Write about the things in life that make you feel happy!
#300. Imagine there is no gravity. What kind of things would you do you for fun? How would some of the things you already do for fun be different?
Buy the Printable Cards! We will always have this list of 300 kids writing prompts available for free, but I’m very excited to now also offer an ad-free printable version of these prompts in my online Etsy shop. Thank you for your support!
Parents and teachers, I hope you enjoyed these 300 writing prompts for kids and that you will use them to inspire your children’s creative imaginations.
These prompts of course can be used in a number of different ways and can be adapted for a variety of different styles of writing !
What do you think? Do you think these are good conversation and story starters for kids? Do you have any ideas for writing prompts you would like to share?
And of course, if you’d like to make it super fun and easy to use these prompts at home or in your classroom, be sure to get our ad-free printable version of these kids writing prompt cards now available in my Etsy shop.
We’d love to hear your thoughts on different creative writing ideas and topics for kids to write about! Share your thoughts in the comments below!
Chelle Stein wrote her first embarrassingly bad novel at the age of 14 and hasn't stopped writing since. As the founder of ThinkWritten, she enjoys encouraging writers and creatives of all types.
Similar Posts

7 Creative Writing Exercises For Writers

365 Creative Writing Prompts

42 Fantasy Writing Prompts & Plot Ideas

108 Romance Writing Prompts & Love Story Ideas

101 Poetry Prompts & Ideas for Writing Poems
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Get our FREE Classroom Seating Charts 🪑
150 Inspiring Picture Writing Prompts To Spark Creativity (Free Google Slides)
Use a picture to write a thousand words!

Creative writing is a challenge for many students, often because they can’t come up with anything to write about. That’s why we love picture writing prompts. Each one sparks the imagination and helps young writers jump right into crafting a story to match. We rounded up a whole collection of intriguing images to help kids in grades K-12 along. Plus we designed a set of free Google Slides featuring all of the prompts so you can easily share them with students.
Tip: Start by showing students the picture (or let them choose from among several) without making any comment about what they’re seeing. For kids who still struggle to get started, suggest a potential title or opening sentence, like the examples included here.
Don’t miss our free downloadable. Grab your full set of ready-to-go Picture Writing Prompts Google Slides with all of the prompts below.
Elementary Picture Writing Prompts
Middle school picture writing prompts, high school picture writing prompts, art picture writing prompts.
When kids first see these picture writing prompts, they may or may not immediately feel inspired. Try asking general questions like these to get them started:
- What are the names of the people or animals in the picture?
- How do you think the people or animals in the picture are feeling?
- How would you describe the setting, including the weather, sounds, smells, etc.?
- What do you think the people or animals are saying or are about to say?
- What happened right before this picture was taken? What will happen next?
Included below are more questions for each image to boost creativity, along with potential titles and opening lines.
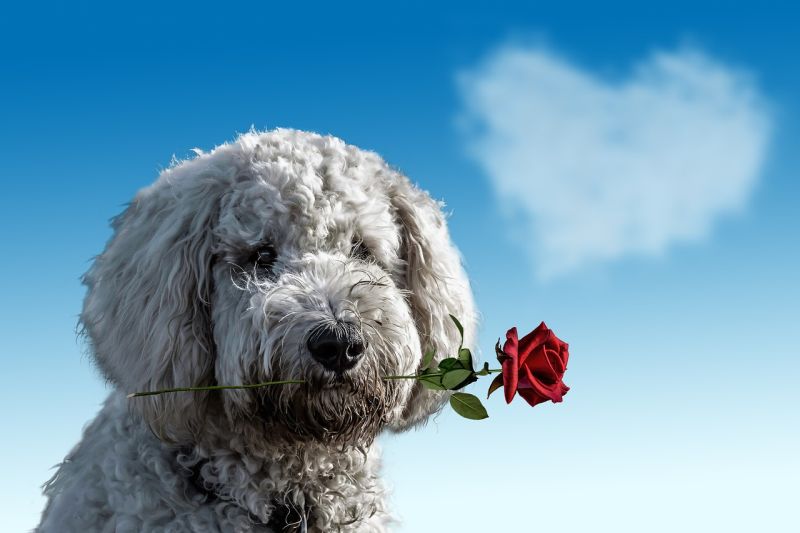

Opening Line Idea: When Larry fell in love, he fell hard.
Jump-Start Questions: Where did the dog get the rose? Who or what is the dog bringing the rose to? Can the dog talk like a human?
Ask for a Sign

Opening Line Idea: When the new sign appeared on Main Street, everyone in town wondered exactly what it meant.
Jump-Start Questions: Does the sign read “ask,” or do the letters A-S-K stand for something else instead? Who put up the sign, and why? Why is the sign lit up during the day when no other lights are on?
Snowy Footprints
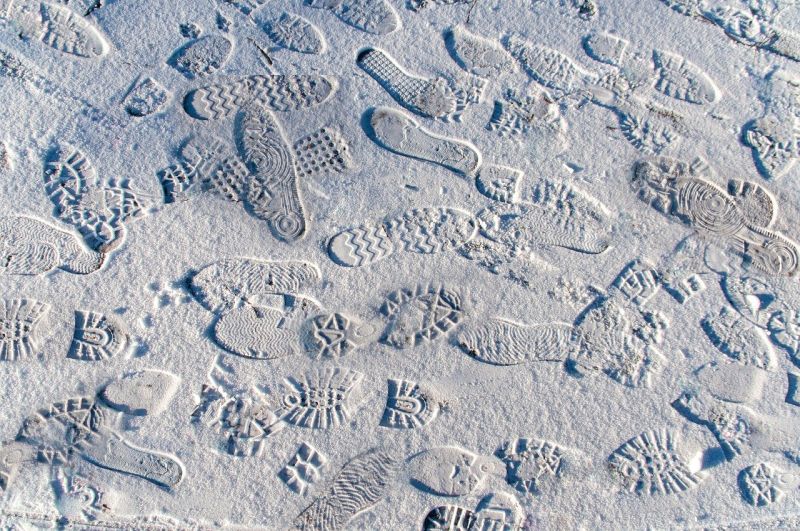

Opening Line Idea: After that crazy day, all that was left to show for it was footprints in the snow.
Jump-Start Questions: How many different people made these prints? Is this snow, or could it be some other white substance? Were the people who made these prints walking or running?
Dinosaur Bones
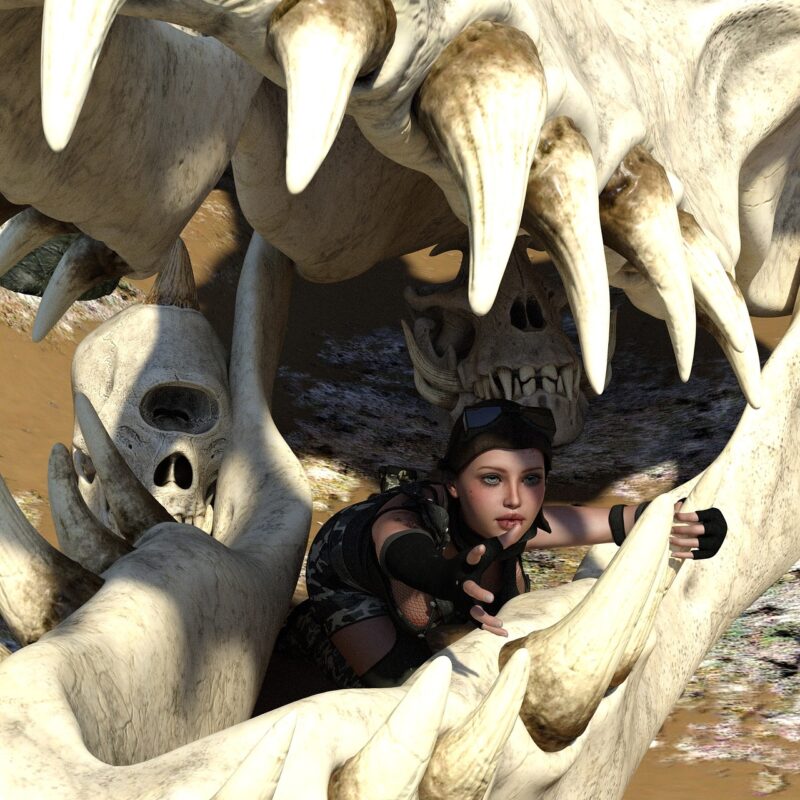

Opening Line Idea: “Come with me if you want to live!” Ash said, reaching out a hand.
Jump-Start Questions: What creature is this the skull of? Why is the person inside the skull in the first place? Is the person in the picture asking for help or inviting someone to join them inside the skull?
Undersea Treasure
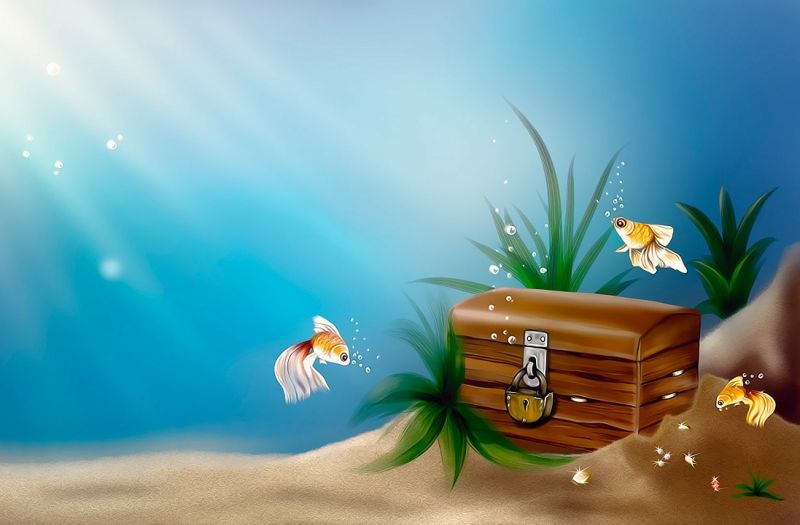

Opening Line Idea: For years, no one saw the locked treasure chest but the local fish, who wondered what it could contain.
Jump-Start Questions: Who left this treasure chest here, and when? What are three different things that could be inside? Do the bubbles mean there’s something alive inside the chest?
A Game of Fetch
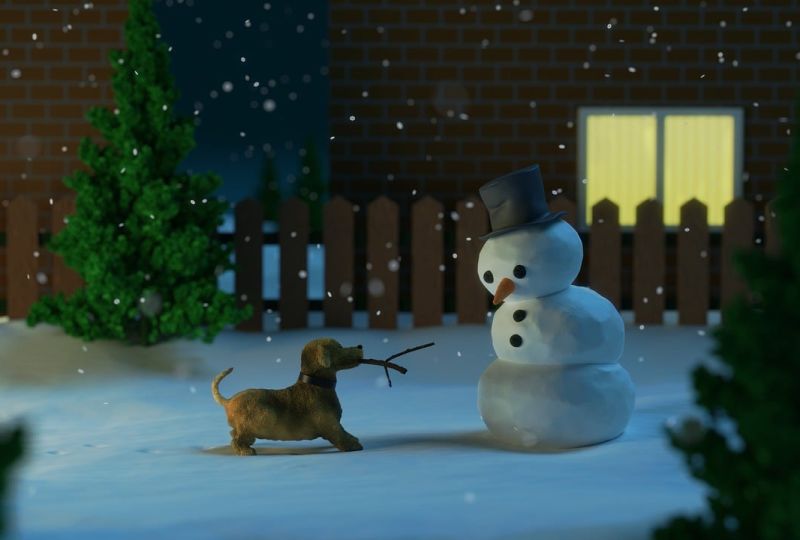

Opening Line Idea: To Scout, it was a game, but to Mr. Freezy, it was much more.
Jump-Start Questions: Are the dog and snowperson friends? Who built the snowperson, and where did they get the hat? Who does the dog belong to?
Ladybug Gossip
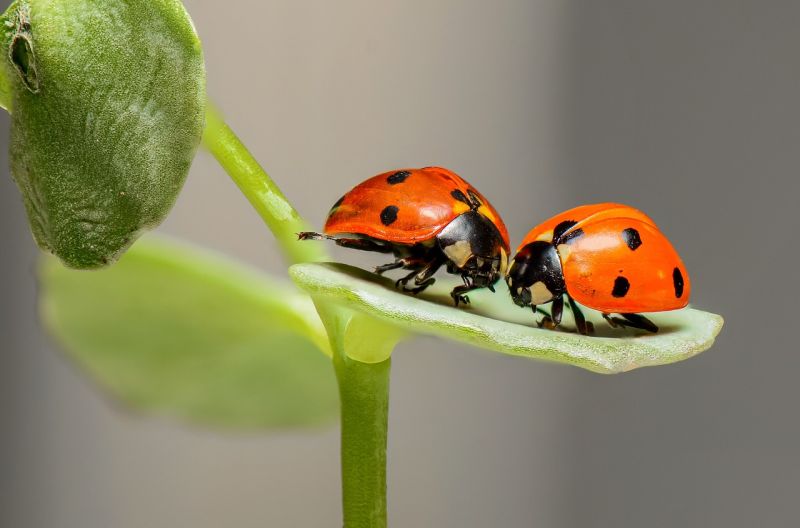

Opening Line Idea: The ladybug’s picnic was an excellent chance to meet up with old friends and hear all the latest gossip.
Jump-Start Questions: Are these ladybugs friends or enemies? Are the leaves very small, or are the ladybugs very big? Was this picture taken in a garden, a wild meadow, or some other place?
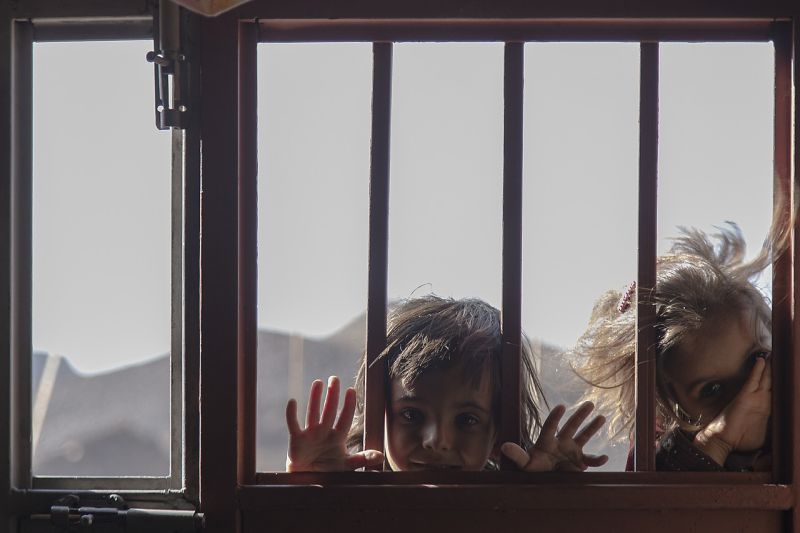

Opening Line Idea: We met them when they peeked into our window, watching us as we watched cartoons.
Jump-Start Questions: Are these children looking into their own house or someone else’s? Do they want to come inside or would they rather stay outside? Who is looking at the children from the other side of the window?
King of the Jungle
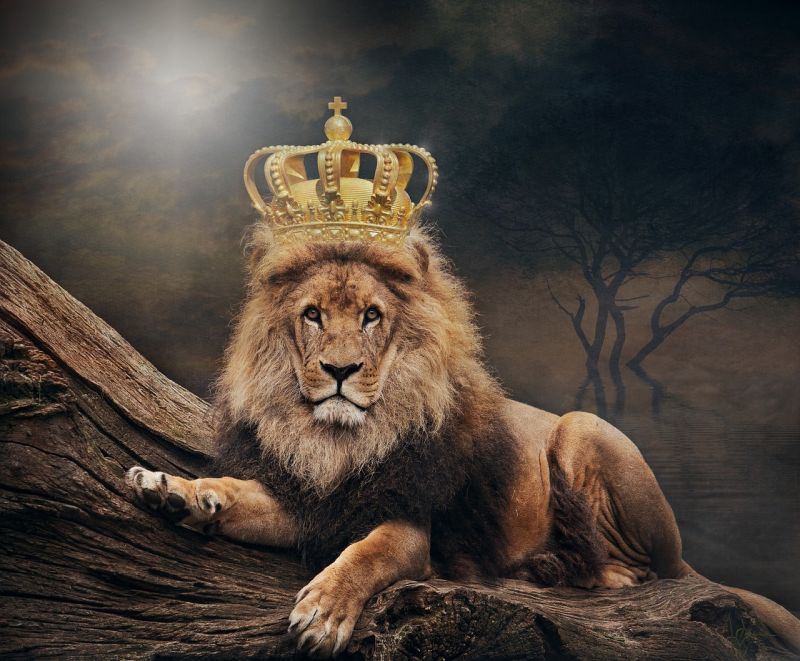

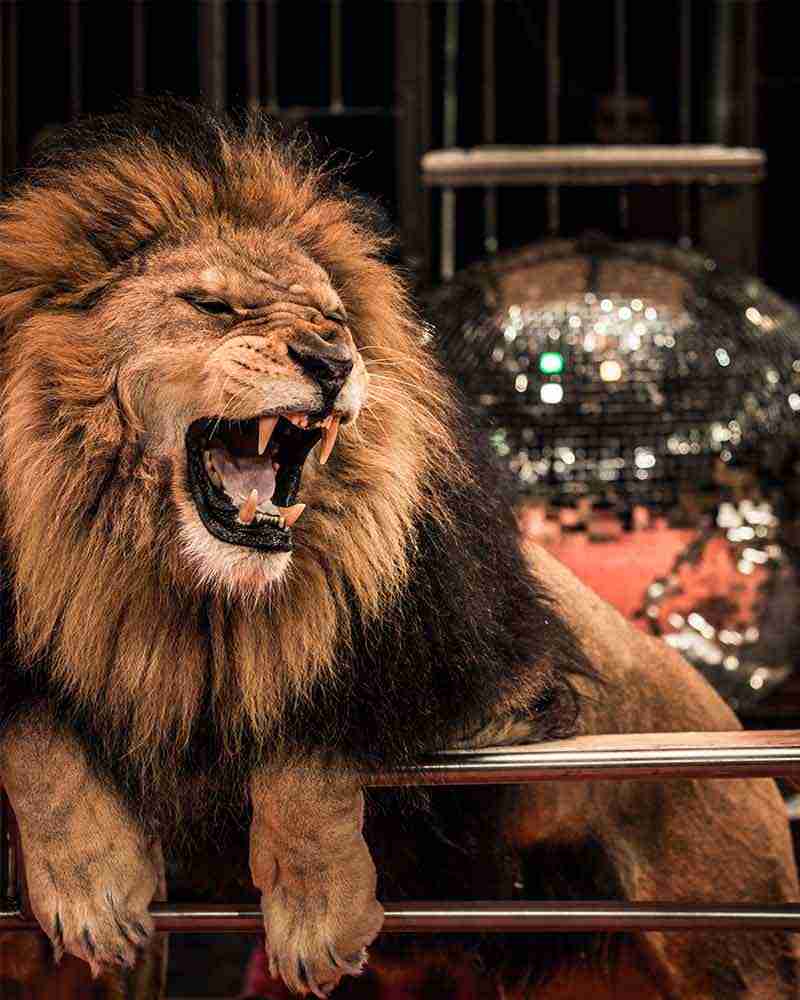
Opening Line Idea: It wasn’t the crown that made Amari the king of all he surveyed.
Jump-Start Questions: Is this lion in the wild or in captivity like a zoo? Is the crown real, or is the lion imagining it? How does the person taking the photo feel about the lion?
The Final Pitch
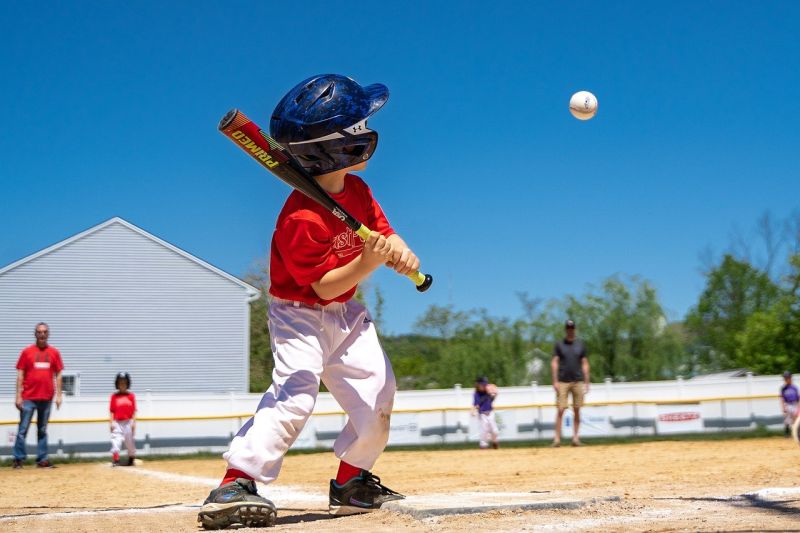

Opening Line Idea: It all came down to this—the final pitch in a game that was tied 2-2.
Jump-Start Questions: Does the player hit the ball, and if so, do they make it to a base? What is the score of the game so far? How did the player get dirt on their knees?
Doggie Massage
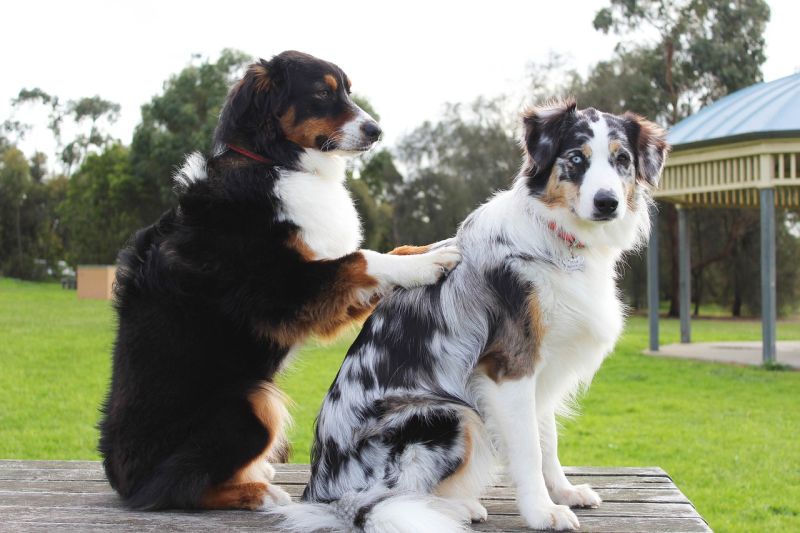

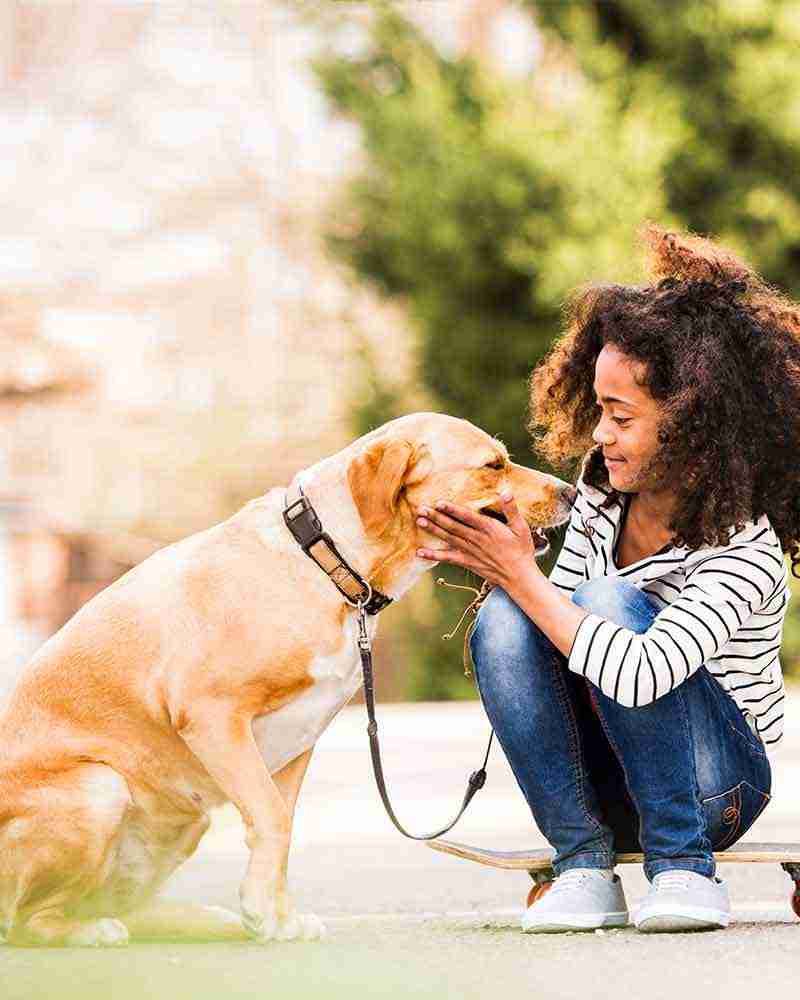
Opening Line Idea: Every dog in the neighborhood knew that Rocky gave the best massages and was always willing to lend an ear too.
Jump-Start Questions: Do these two dogs know each other, or did they just meet? Is the dog on the right feeling happy, annoyed, or something else? Give three different reasons why the dogs are sitting like this.
Skateboard Life
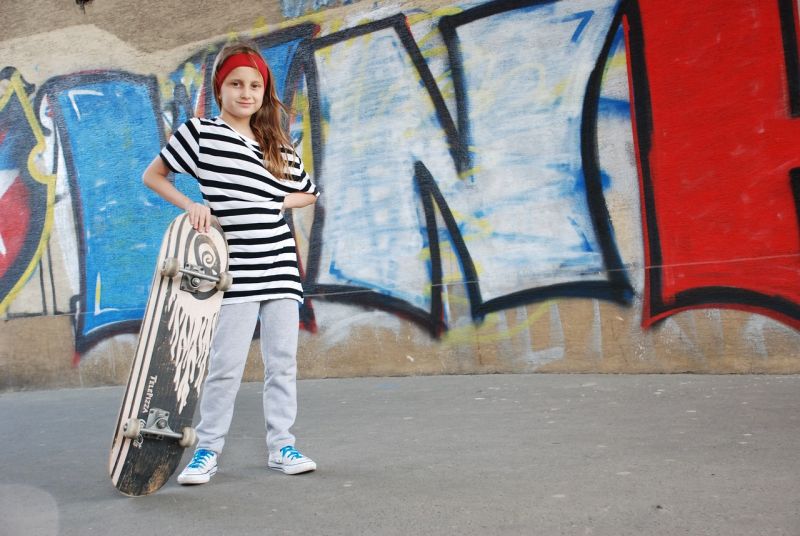

Opening Line Idea: When Charli got her first skateboard, she made herself a promise.
Jump-Start Questions: What does the graffiti on the wall mean, and how did it get there? Where did this girl get her skateboard from? Who taught her how to skateboard?
Garden of the Past
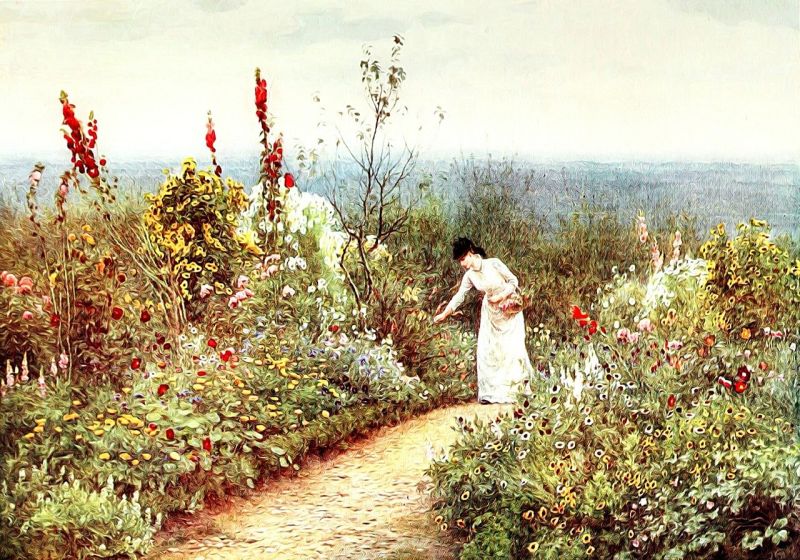

Opening Line Idea: The woman walked in the garden every day, never saying a word.
Jump-Start Questions: Where and when does this garden grow? Who planted this garden and why? What will the woman do with the flowers she is picking?
Sunset Friends
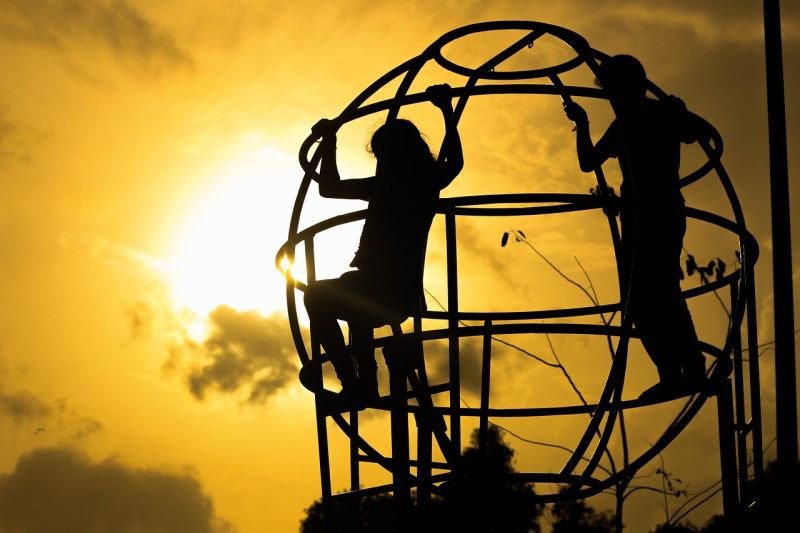

Opening Line Idea: They met on the jungle gym every day at sunset, sharing everything about their days.
Jump-Start Questions: Was this photo taken in the morning or the evening? What time of year is it? Are the children playing on the jungle gym or just hanging out and talking?
Pink Umbrellas
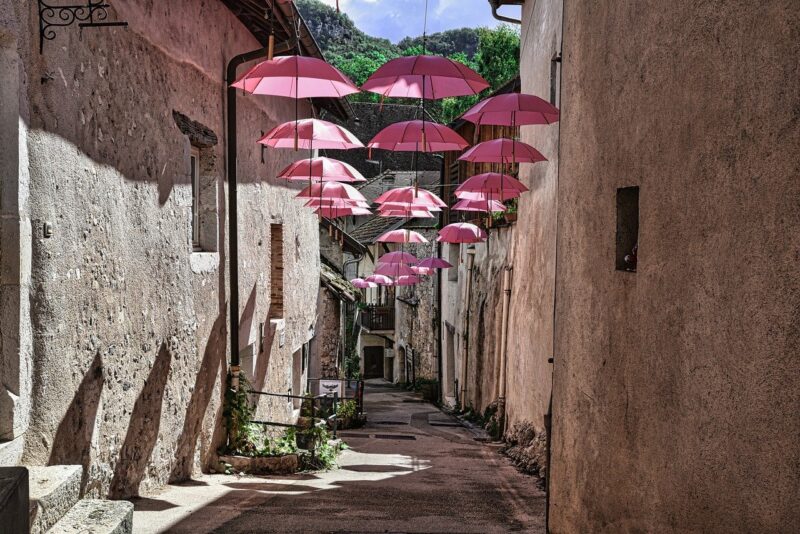

Opening Line Idea: When the pink umbrellas first appeared, Toni thought they might be magic.
Jump-Start Questions: Where and when was this picture taken? Who hung the pink umbrellas? Who lives in the buildings along this alley?
Firefly Forest
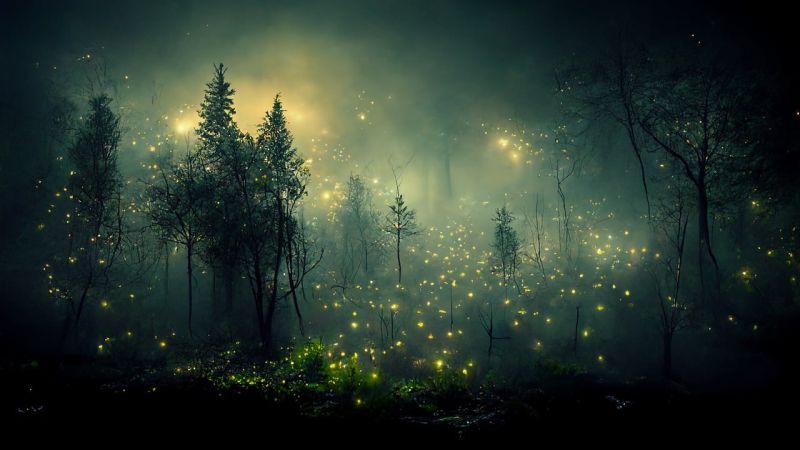

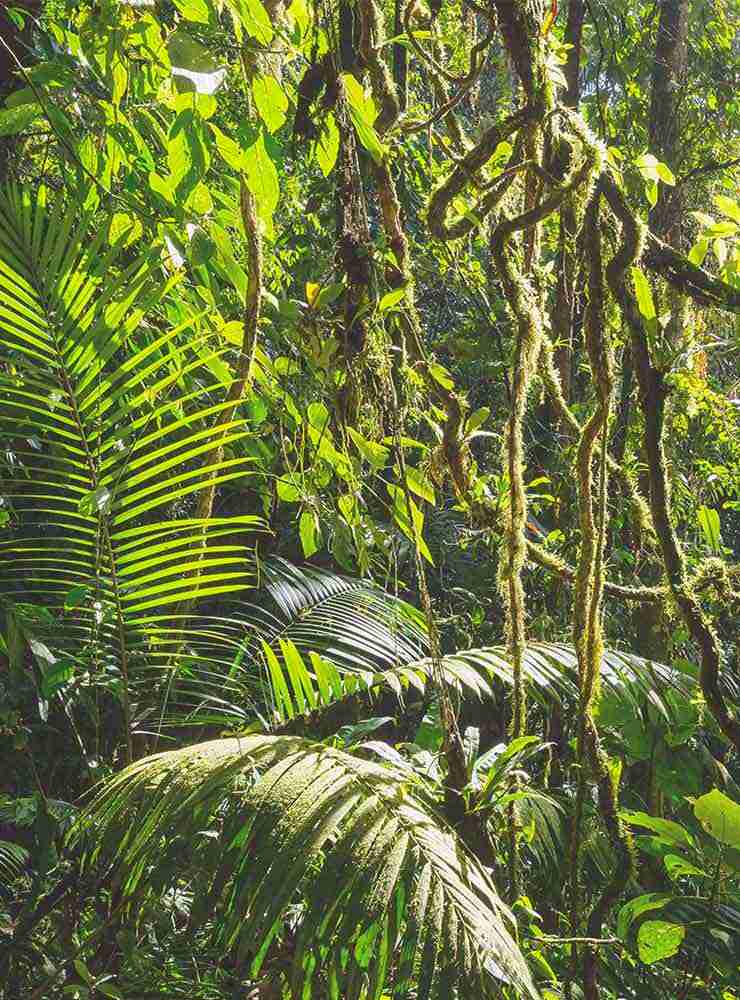
Opening Line Idea: Olivia was surprised to discover that the fireflies didn’t just glow, they also sang.
Jump-Start Questions: Are all the lights in this picture fireflies, or is something else glowing? What does this forest sound and smell like? Would you want to be in this forest alone in the middle of the night?
Robot Spider
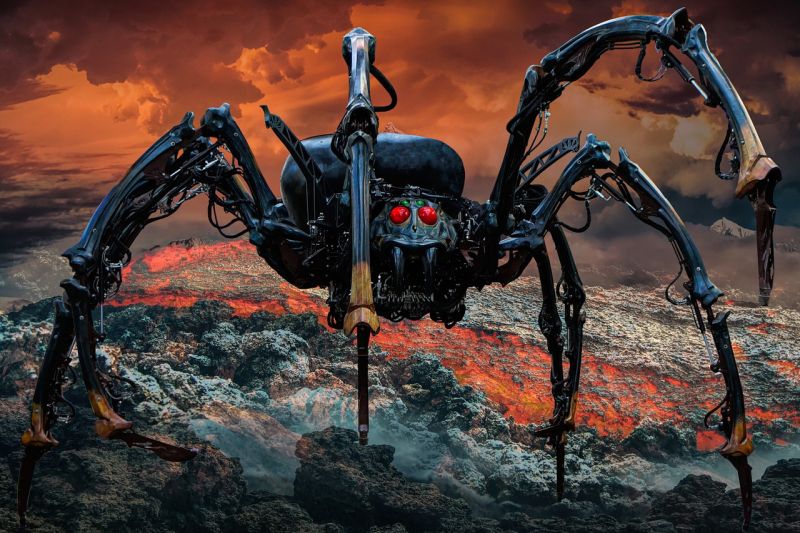

Opening Line Idea: When it first crawled ashore, the mechanical spider moved slowly.
Jump-Start Questions: Was this robot spider built by humans, or does it come from another planet? Does the spider run on its own, or is there a person or creature inside it? Where is the spider now, and where is it going?
Fallen House
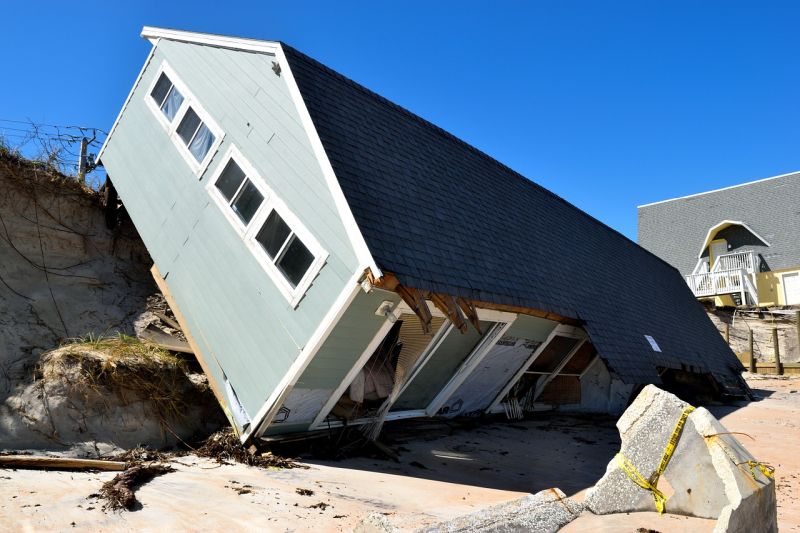

Opening Line Idea: Staring at their house, which was now on its side, the whole family was in shock.
Jump-Start Questions: Who used to live in this house? Was anyone inside the house when it fell, and are they OK? What caused the house to fall but not be completely destroyed?
Red Riding Hood
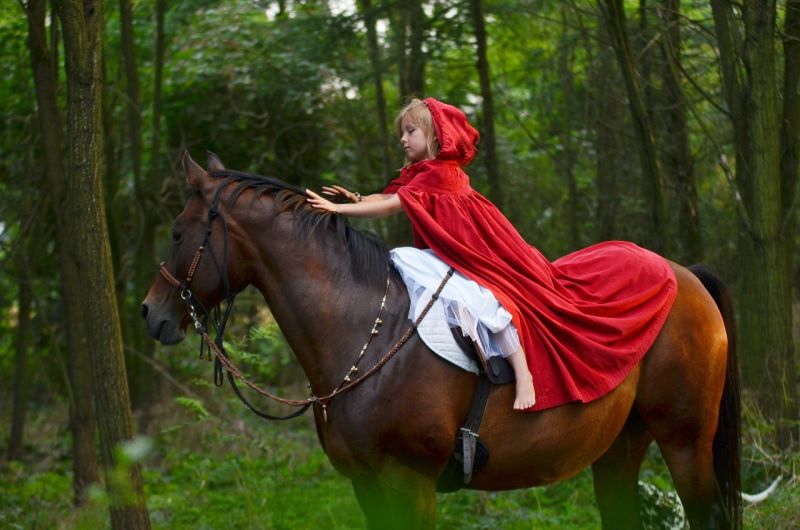

Opening Line Idea: If only she’d been riding her faithful steed the day she’d met the Big Bad Wolf, things might have been very different.
Jump-Start Questions: Why is the girl barefoot? Why is the horse wearing a necklace? Who gave the girl her red hood and cape?
Kangaroo Fall
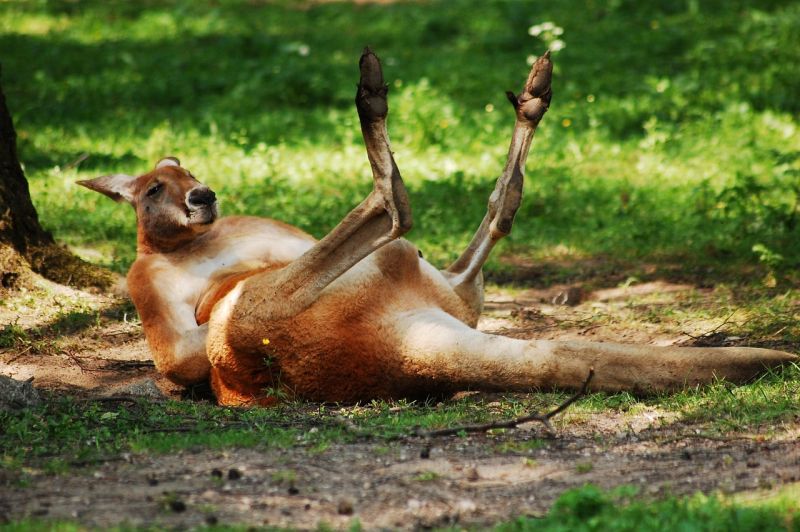

Opening Line Idea: “Well, this is embarrassing,” thought Bouncer, as laughter filled the air around him.
Jump-Start Questions: Did this kangaroo fall over, or is it just lying down? Where does the kangaroo live? Is there anything in the picture to explain what the kangaroo is doing?
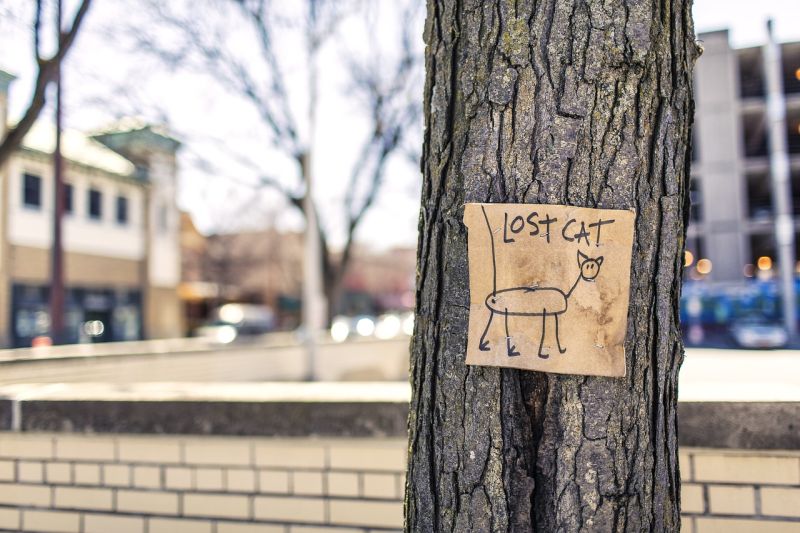

Opening Line Idea: Daci’s big brother said her signs wouldn’t help them find their runaway cat, but he was wrong.
Jump-Start Questions: Is this sign about a real lost cat? Who drew the picture? Does anyone ever find the lost cat?
Penguin Bookshop
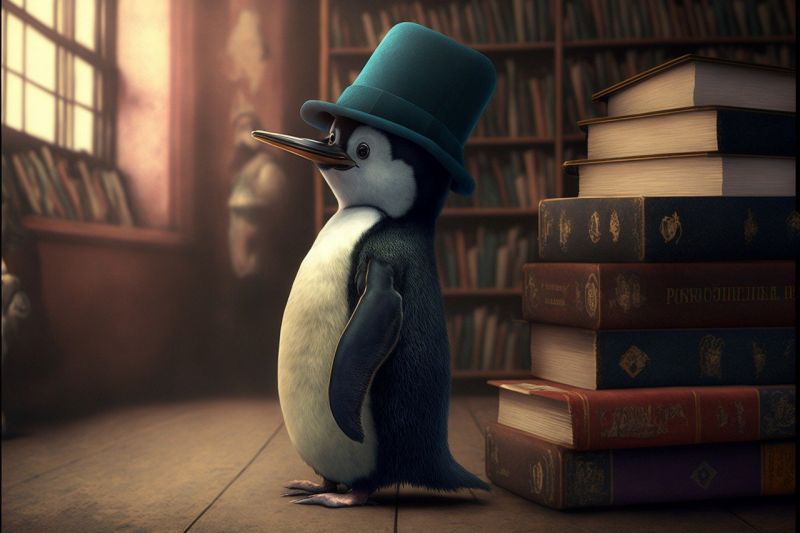

Opening Line Idea: A visit to Sir Pickerel’s Penguin Bookshop is always an adventure.
Jump-Start Questions: Does the penguin own the bookstore, or is he only shopping there? Where did the penguin get his hat? What kind of books does the penguin like best?
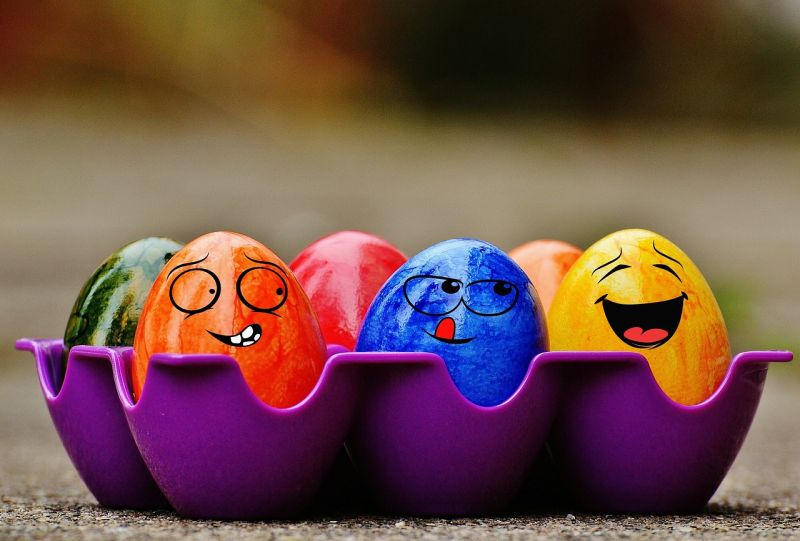

Opening Line Idea: Of all the eggs in the carton, Ella was the one who could always crack you up.
Jump-Start Questions: Who colored these eggs? Are these real bird eggs or are they made of something else? Where are these eggs, and why are they there?
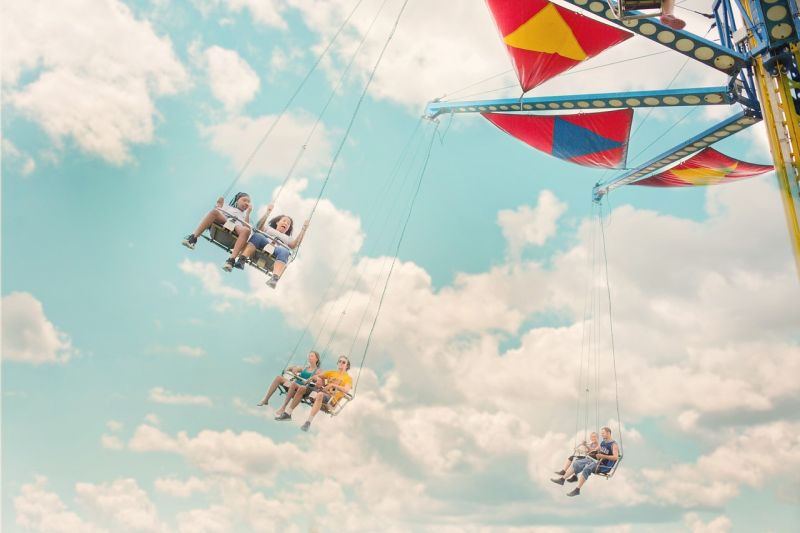

Opening Line Idea: That was the year Min was finally tall enough to ride the Sky Swings, but now she wasn’t so sure.
Jump-Start Questions: How high are these swings? Would you want to ride the swings? How would you feel if you were soaring through the air?
Rubber Duck Parade
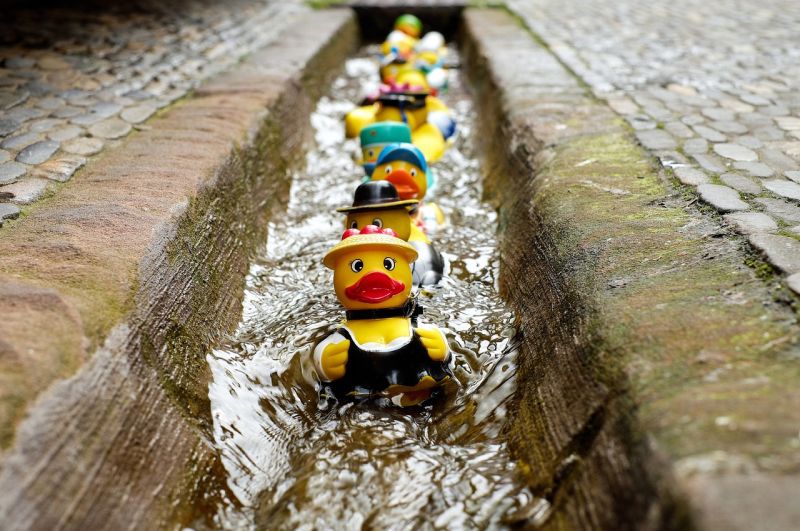

Opening Line Idea: It was truly an honor to be asked to lead the Spring Duck Parade.
Jump-Start Questions: Who put these ducks in the gutter? Are the ducks having fun, or are they being forced to be there? What would you do if you were walking along and saw these ducks?
Teddy Story Time
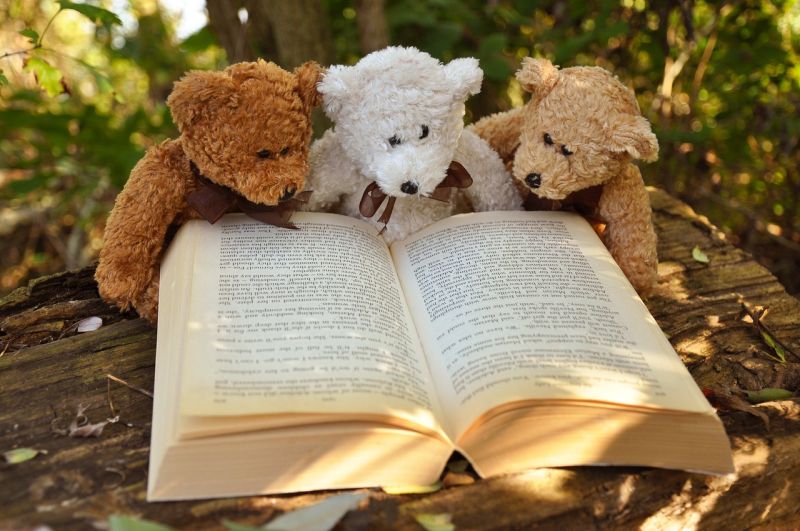

Opening Line Idea: Every afternoon, the three friends gathered for story time in their favorite spot in the woods.
Jump-Start Questions: What book are the bears reading? Where did the bears get the book? Are the bears all the same age?
Underwater School
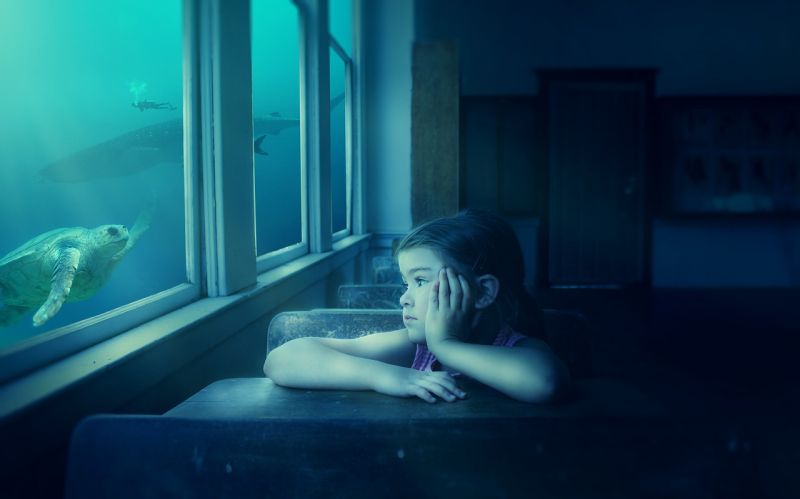

Opening Line Idea: Nia thought going to school underwater would be exciting, but some days she really missed going outside for recess.
Jump-Start Questions: How does the child in the picture feel as she looks out the window? Where is the child? Why does the room look so dark?
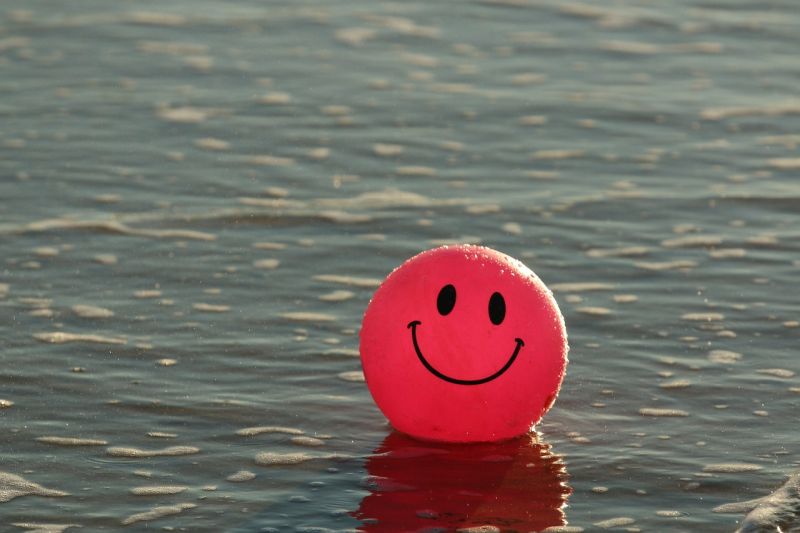

Opening Line Idea: The day Amos started his journey down the river, the sun was shining brightly.
Jump-Start Questions: What body of water is the ball floating in? How did it get there? Who does the ball belong to?
Turtle Trouble
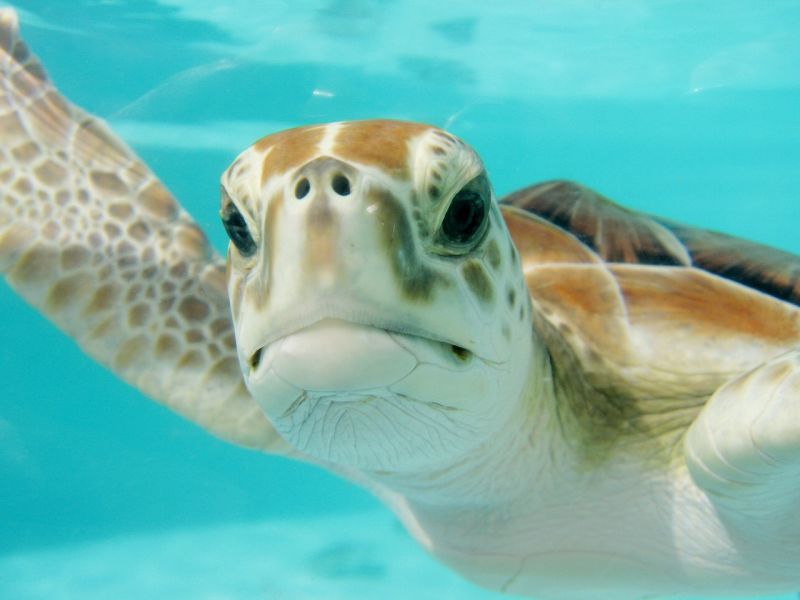

Opening Line Idea: “None shall pass,” growled the old sea turtle, blocking the way.
Jump-Start Questions: What body of water is the turtle swimming in? How old is the turtle? How did the person who took the picture get so close to the turtle?
Dinosaur Race
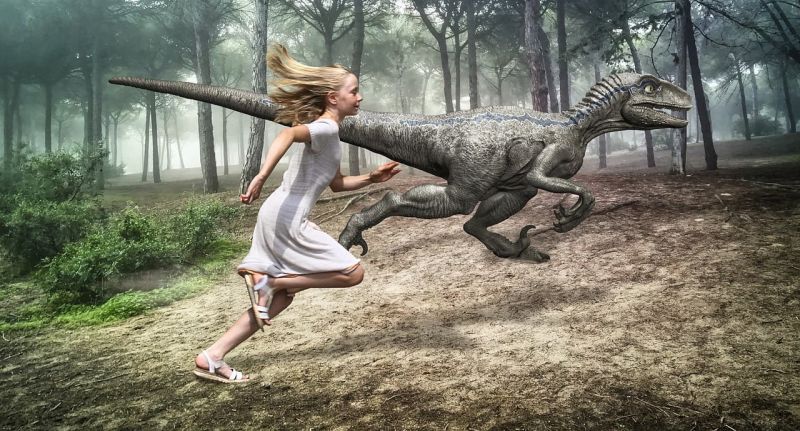

Opening Line Idea: Pia was supposed to keep Balthazar on a leash, but once they reached the forest, she set him free and they both began to run.
Jump-Start Questions: What kind of dinosaur is this? Where are the girl and the dinosaur running to (or running from)? Is the dinosaur wild or the girl’s pet?
Finally Seeing Eye to Eye
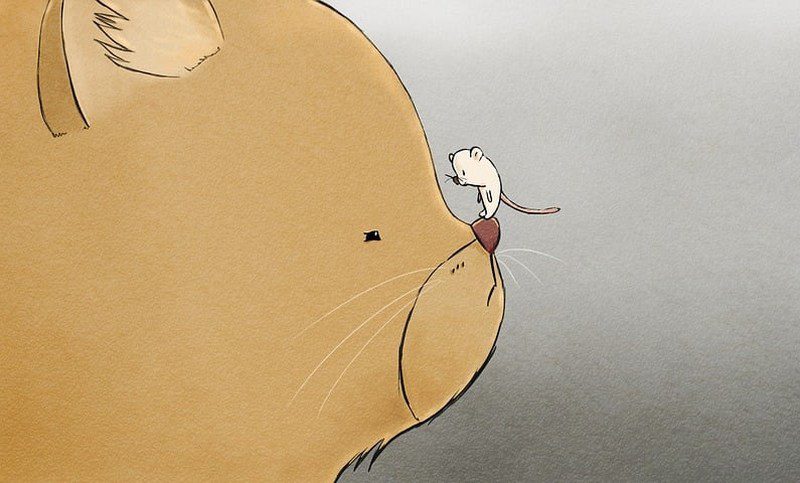

Opening Line Idea: “So, we meet at last, face-to-face,” Lord Squeakerton said to his enemy, the Count of Catnip.
Jump-Start Questions: How did the mouse get onto the cat’s nose? How does the cat feel about the mouse being there? Are the cat and mouse friends or enemies?
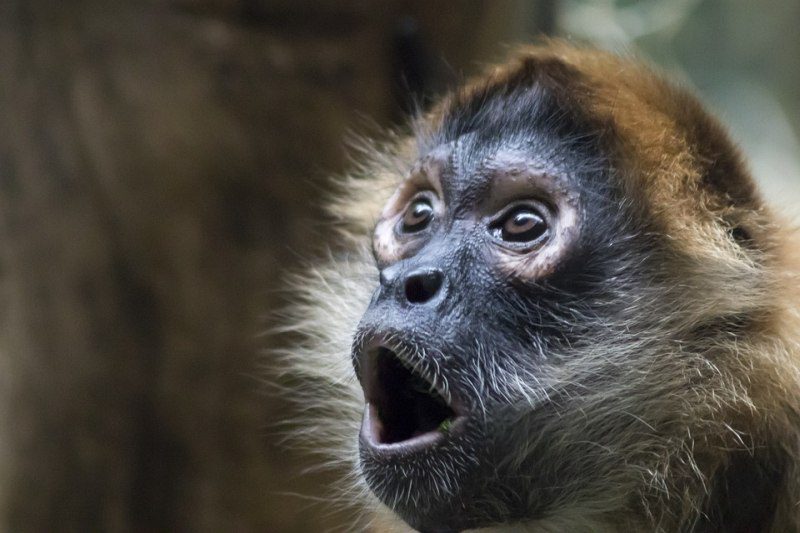

Opening Line Idea: It takes a lot to surprise a monkey, but you don’t see something like this every day.
Jump-Start Questions: What is the monkey looking at? How was the monkey feeling at that moment? If there was a speech bubble coming out of the monkey’s mouth, what would it say?
Not Coming Out
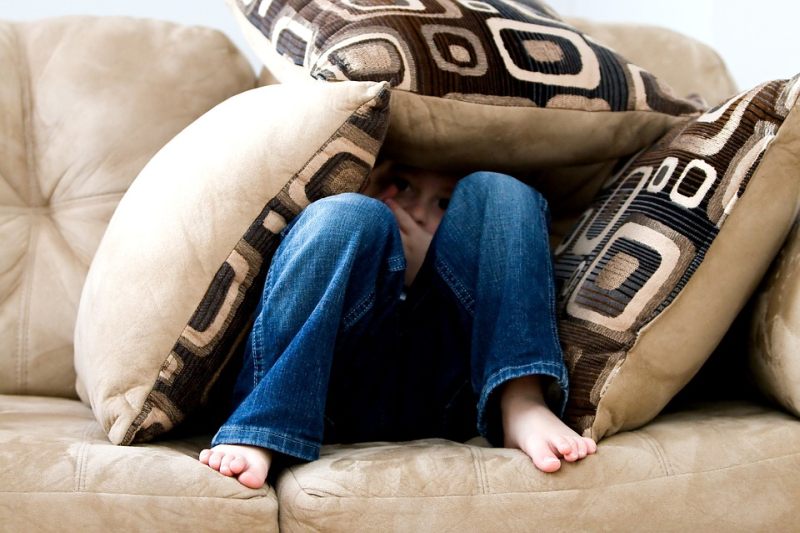

Opening Line Idea: The day started out normally enough, but by the end, Chris knew he was in over his head.
Jump-Start Questions: Is the child hiding, playing, or doing something else? Is the child at home or at someone else’s house? Are the child’s feet cold without socks?
Life on Other Planets
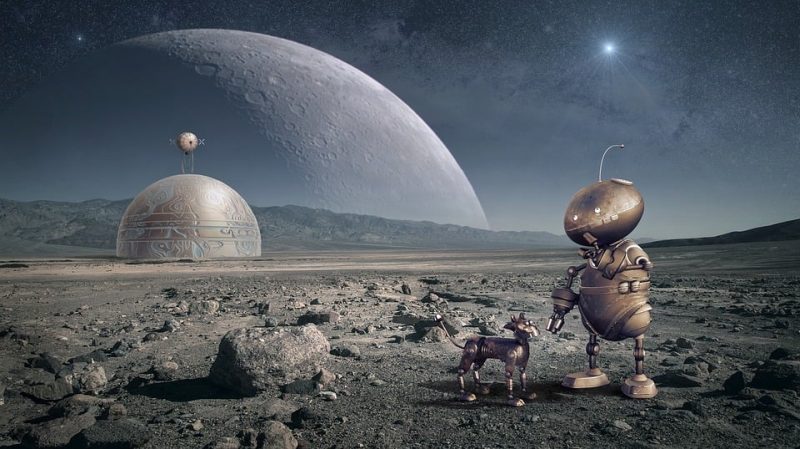

Opening Line Idea: “Hurry up,” Grnklor told his robopup. “We have to get back inside before nightfall.”
Jump-Start Questions: What planet is this? Are the creatures robots, aliens, or something else? Could you breathe the air if you were standing on this planet?
Reindeer Games
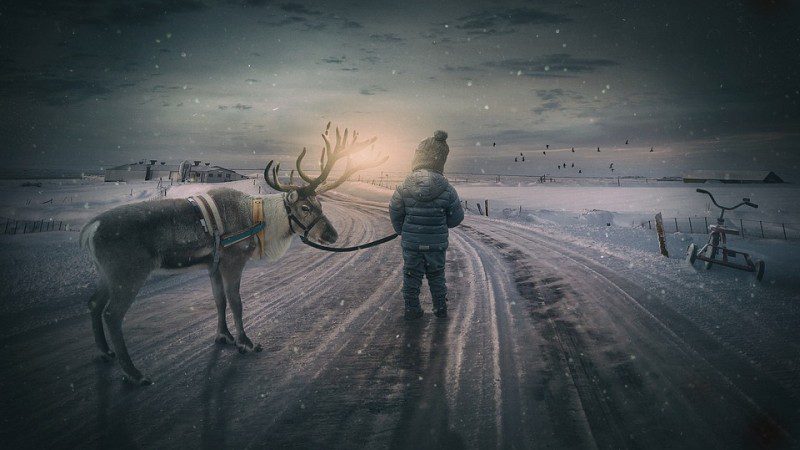

Opening Line Idea: The wind had died down, but the setting sun seemed to take all the warmth of the day with it.
Jump-Start Questions: Is the sun rising or setting? Who does the tricycle on the right belong to? Where are the child and the reindeer going, and why is the deer wearing a harness?
Something To Celebrate
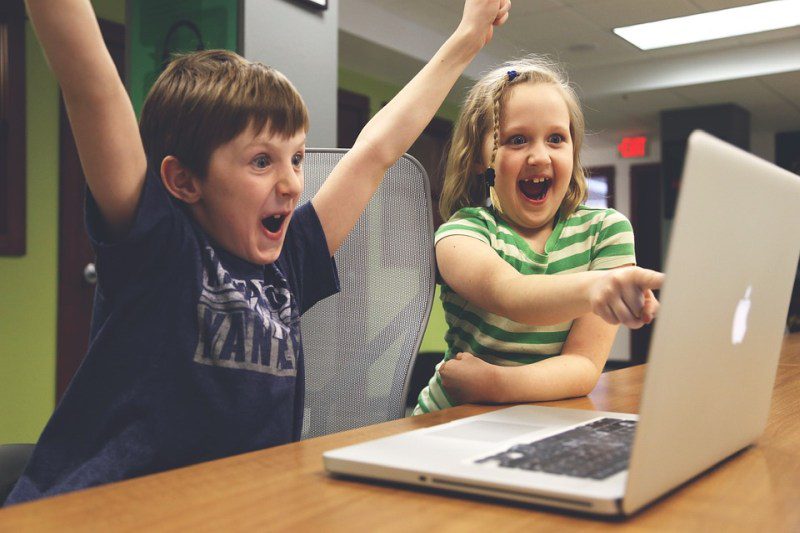

Opening Line Idea: Their classmates could hear their shouts of joy from all the way down the hall.
Jump-Start Questions: What is showing on the computer screen? How do these kids know each other? Where are these kids?
Home Sweet Mushroom
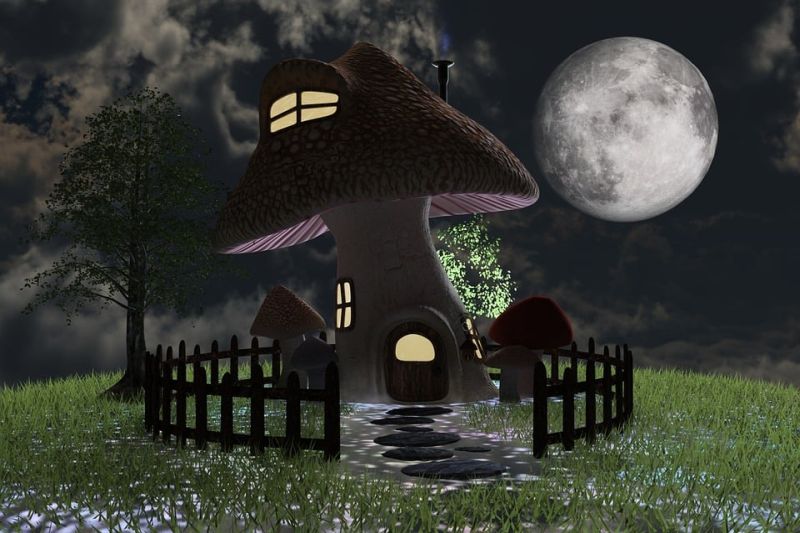

Opening Line Idea: When the fairies that lived in the garden invited her to stay with them for awhile, Maria wasn’t sure what to expect.
Jump-Start Questions: Who lives in the mushroom? Is this mushroom very big, or are the creatures who live in it very small? Did the mushroom grow this way, or did someone turn it into a house?
Loch Ness Mystery
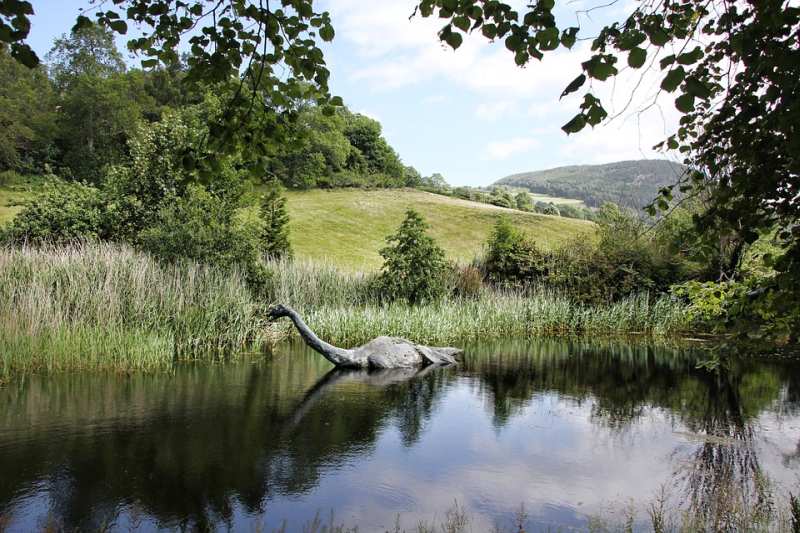

Opening Line Idea: “There it is! I told you Nessie is real!” Angus whispered to Lee.
Jump-Start Questions: Is the creature in the picture real or a statue of some kind? If it’s a statue, who put it there and why? How was the person who took this picture feeling at this moment?
Lonely Bear
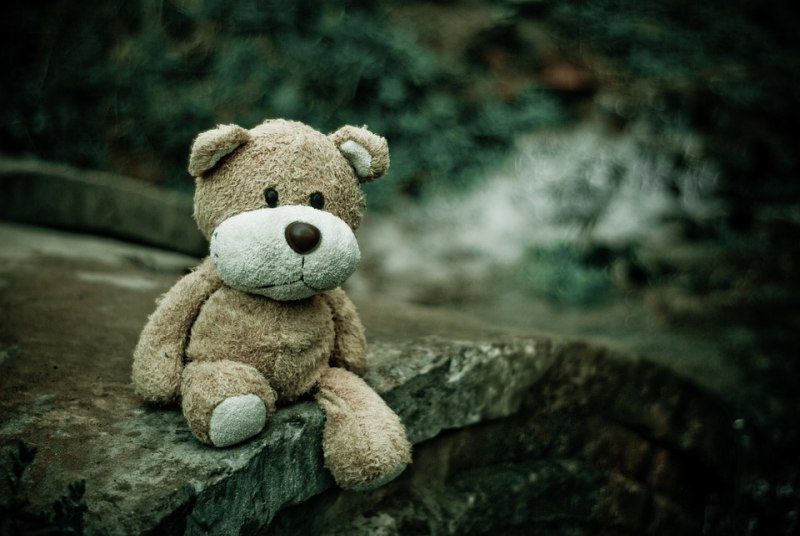

Opening Line Idea: It was hard to say who was lonelier that night, Amil or his lost stuffed bear, Jasper.
Jump-Start Questions: Who does the bear belong to? Is its owner nearby, or is the bear lost? How old is the bear?
Sometimes You Lose
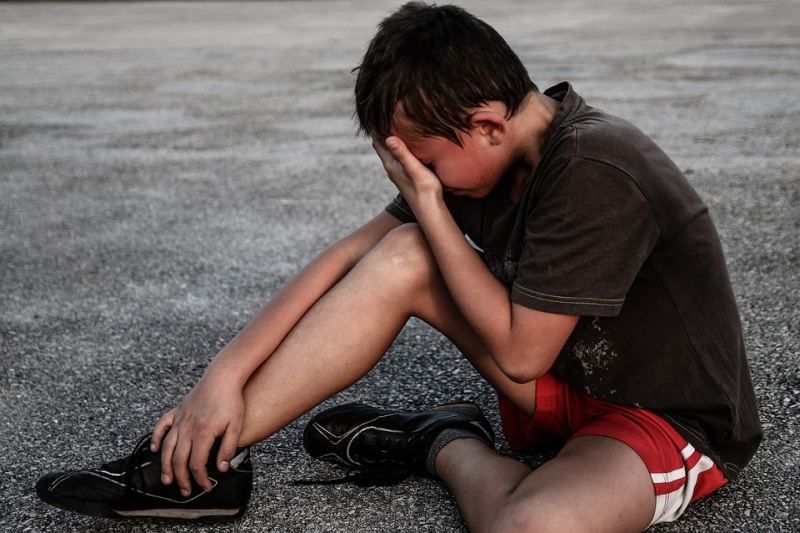

Opening Line Idea: When his team lost the championship, Miguel was crushed, but it turned out to be the best thing that ever happened to him.
Jump-Start Questions: Why is the boy upset? What would the boy’s friends say to him? What would his parents say to him?
Middle school writing prompts can be a little more complex, with pictures that have a lot of potential interpretations. You can use the same questions to kick-start creative thinking as you would with elementary students (see above), plus deeper questions like these:
- How does the picture make you feel?
- Who took the picture and why?
- What incidents led up to the moment of the image?
- What are three different things that could happen next?
- Does this picture take place in the past, present, or future?
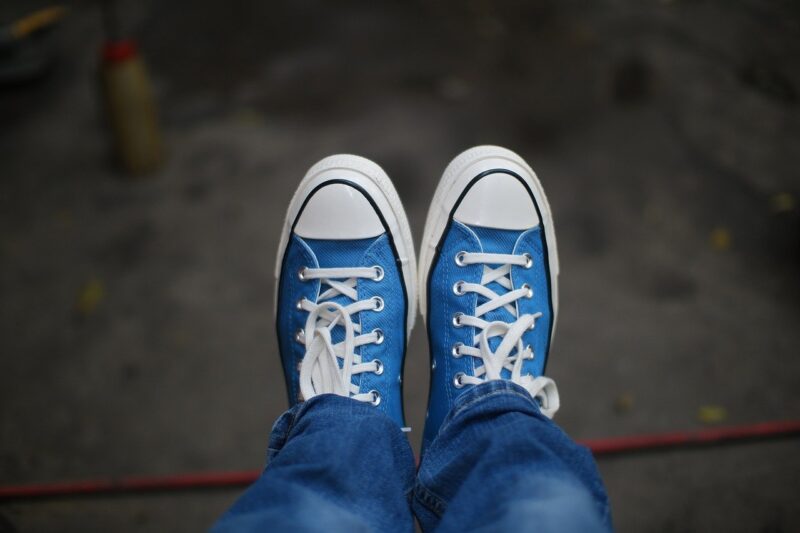

Opening Line Idea: Morgan was incredibly proud of those shoes, paid for entirely with money from after-school jobs.
Jump-Start Questions: Who is wearing the shoes? Would you like to have shoes like this? Imagine the shoes a year from now, dirty and worn; how did they get that way?
Never Lose Hope

Opening Line Idea: With his last bit of energy, Kai scrawled his message in the wet paint.
Jump-Start Questions: Who wrote this message and why? Where is this message written? Who might see and be inspired by the message?

Opening Line Idea: The keyboard button could only be used once, and no one knew exactly what happened when you pressed it.
Jump-Start Questions: Who created this keyboard? Would you press the button? How would you keep from pressing this button accidentally?
Piano Lessons
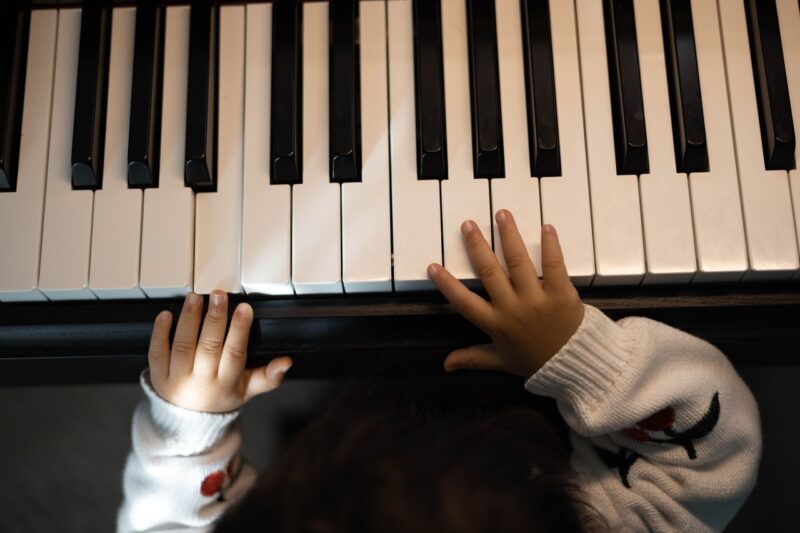

Opening Line Idea: Before she could even speak, Arya was drawn to the black and white keys.
Jump-Start Questions: Where is this piano, and who does it belong to? Will the child touch the keys gently or bang on them loudly? What song would you play on this piano?
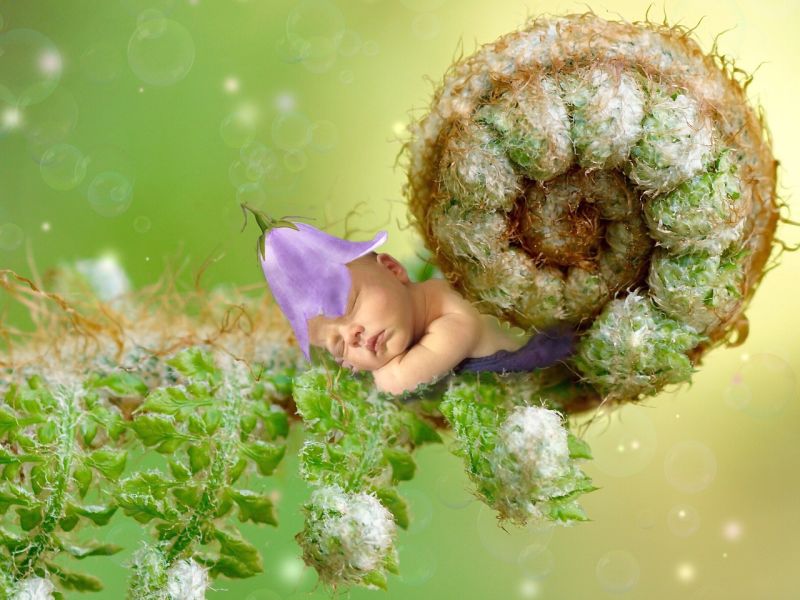

Opening Line Idea: There was no doubt about it, this was was indeed a very special kind of garden.
Jump-Start Questions: Is this a very tiny baby or a very large fern? Who does the baby belong to? Would you like to sleep rolled up in a plant?
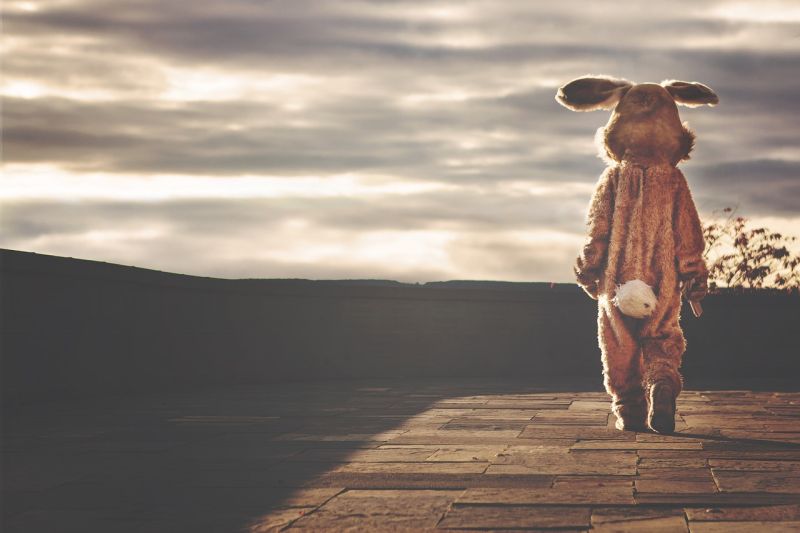

Opening Line Idea: No matter how you looked at it, it had been a very rough day to be the Easter Bunny.
Jump-Start Questions: How did the bunny get so dirty? Is this a large bunny, or a person wearing a bunny suit? Where has the bunny been, and where is it going?
Empty Chairs
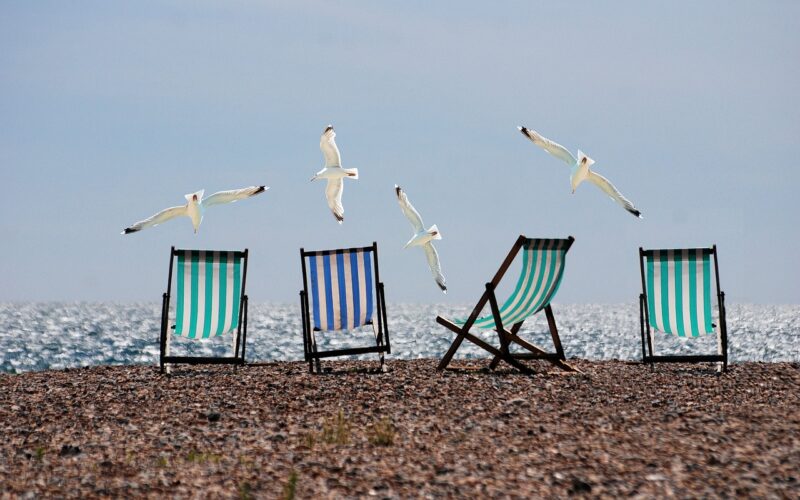

Opening Line Idea: By sunset, all four chairs were empty, and the only signs of life were the gulls swooping down from above.
Jump-Start Questions: Why is one chair a different color from the others? Are these chairs abandoned or just empty temporarily? Why are the seagulls so interested in the chairs?
Floating Treasure
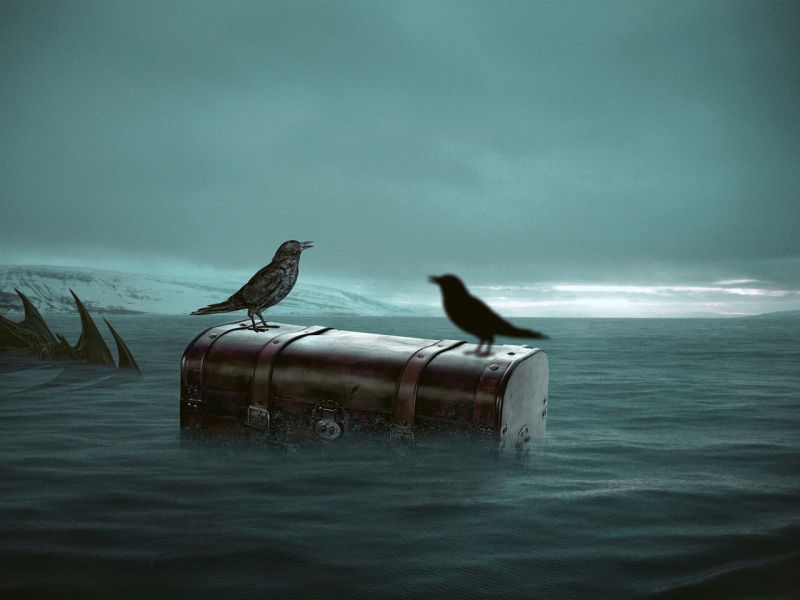

Opening Line Idea: To the birds, it was simply a convenient place to land, but Ali and I knew it was much more than that.
Jump-Start Questions: Would you open this chest if you found it, without knowing what’s inside? What are the spiky shapes on the left side of the picture? Is the bird on the right really there, or is it just a shadow?
Shadow Question
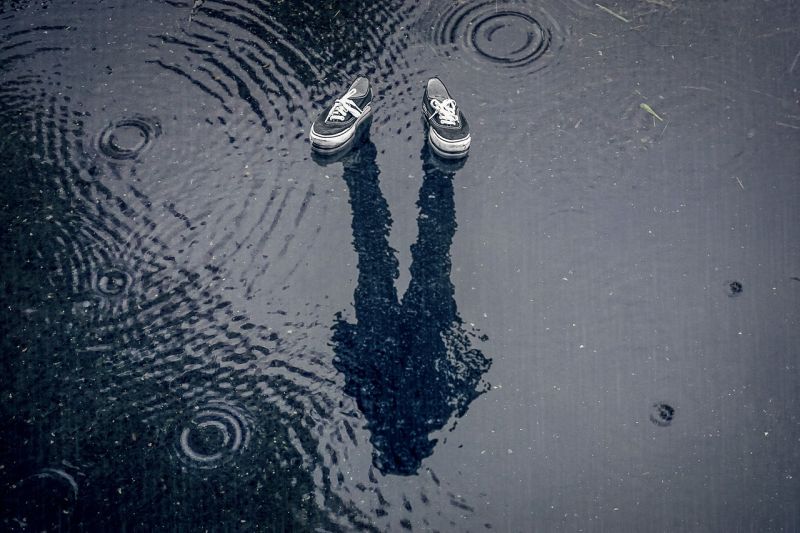

Opening Line Idea: That was the day they discovered that just because you were invisible didn’t mean your shadow was.
Jump-Start Questions: How was this image created, and why? Who do the shoes belong to? How do optical illusions make you feel?
Letter and Key

Opening Line Idea: The day she turned 12, Vivi’s aunt handed her an envelope containing a key … and the family secret.
Jump-Start Questions: What would you hope to find in an old letter like this? How old is the key? Where has this letter been before now?
Space Target

Opening Line Idea: Onyx paused, knowing that once their arrow hit the target, there was no knowing what would happen.
Jump-Start Questions: Is this planet in our galaxy? Is the person pictured a human, a robot, or an alien? What will happen if the person hits the target or misses it?
Mermaid Mystery

Opening Line Idea: It was a mermaid—or was it?
Jump-Start Questions: Is this creature floating in water or in the air? What would you do if you woke up like this one day? How is the creature feeling at this moment?
World on a String

Opening Line Idea: Her dad had promised to give her the world, but she wasn’t expecting three more planets as well.
Jump-Start Questions: Why is the girl holding a suitcase? Who gave the girl the balloons? What does it mean to “have the world on a string”?
Bee Standoff

Opening Line Idea: “This flower ain’t big enough for the both of us!” said Bianca.
Jump-Start Questions: Are the bees from the same colony or rival colonies? Why is this flower so special to the bees? Do you think the bees are cute or scary?
Solitary Seat

Opening Line Idea: For as long as anyone could remember, Angus McGee spent his evenings in the same chair next to the woodstove.
Jump-Start Questions: How long has it been since anyone sat in this chair? What are the books on the floor? What do you think is in the bag on the left?
Best Friends

Opening Line Idea: When you decide to run away from home forever, you can’t possibly leave your best friend behind.
Jump-Start Questions: How is the girl feeling? How far do you think she has already walked? If you were running away from home, what would you take with you?
Dinosaur Demise
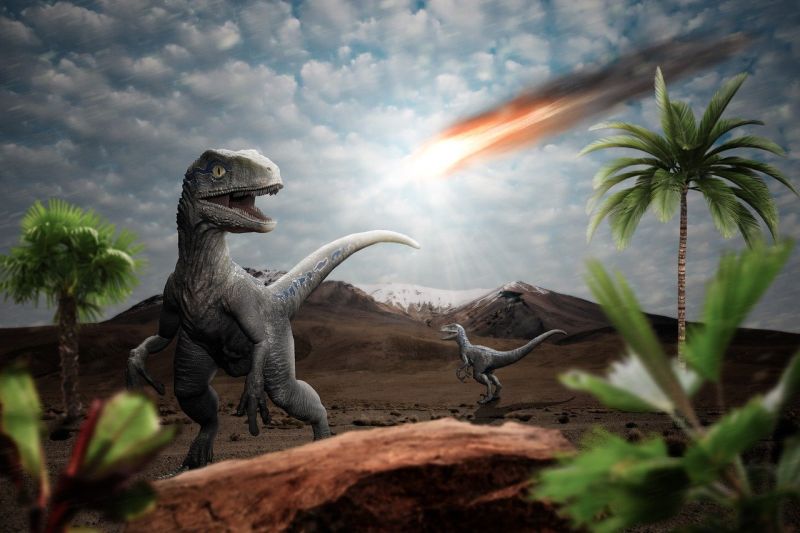

Opening Line Idea: In retrospect, setting the time machine to randomly choose any day and time in the past might not have been such a good idea.
Jump-Start Questions: If you were standing here watching this scene, what would you do? Do these dinosaurs survive whatever happens next? Would you stop the asteroid from killing off the dinosaurs if you could?
Magic Lamps

Opening Line Idea: “Choose wisely,” said the old shopkeeper, “for only one of these lamps is truly magic.”
Jump-Start Questions: Are these lamps brand-new or very old and well cared for? Do you think a magic genie living in a lamp would be good or evil? What wishes would you make, and what would happen if they came true?
Message in a Bottle

Opening Line Idea: The message floated at sea for more than 50 years before the day we found it on the beach.
Jump-Start Questions: If you found a bottle like this, would you open it on your own or invite others to join you? What would you do with the letter inside? How far do you think this bottle has traveled?
Barrel Boat

Opening Line Idea: Of all the ways to impress someone, Jonah thought to himself, this had to be one of the most ridiculous.
Jump-Start Questions: Why is this person in a barrel instead of a boat? Do you think this looks like fun, or would it be scary? Why is the person wearing a life jacket?
Dragon Guardian

Opening Line Idea: When your parents give you your own dragon guardian, your childhood is bound to be enchanted.
Jump-Start Questions: Is this dragon real or the child’s imaginary friend? Is the dragon young or old? How does the child feel about the dragon?
Octopus’s Garden

Opening Line Idea: Wouldn’t you like to be under the sea, in an octopus’s garden in the shade?
Jump-Start Questions: Where was this picture taken? Is the octopus attacking the person or just swimming nearby? How much oxygen does the person have left in their tank?
Around the Corner

Opening Line Idea: After finally pressing “send,” she couldn’t resist peeking around the corner to watch him read the text.
Jump-Start Questions: Do these kids know each other? Does the person in front know the other person is watching them? Who does the car in the distance belong to?
Beam Me Up!

Opening Line Idea: Milo’s earliest memory was of watching his beloved tricycle float into the sky above him, caught in a beam of light.
Jump-Start Questions: Is the tricycle going up or coming down? Where is the light coming from? How does the child in the picture feel right now?
Poison Apple

Opening Line Idea: To join the club, all Aaron had to do was creep up and snatch the apple from the skeleton’s hand without being seen.
Jump-Start Questions: Whose skeleton is this? Is the apple safe to eat? Would you eat this apple?
Giraffe Council

Opening Line Idea: “It is now 3 p.m., and I call this meeting of the Mighty Council of Giraffes to order,” announced Imari.
Jump-Start Questions: Why are these giraffes gathered together? What do giraffes like to talk about? Would you like to be a giraffe?
Mystery Creature

Opening Line Idea: At first glance, it was hard to tell whether the little creature was friend or foe.
Jump-Start Questions: Is this creature big or small? Is it alone, or are there others like it? Would you keep this creature as a pet?

Opening Line Idea: As the sky turned orange, Keisha ran faster than ever and used the last of her energy to push off and soar over the water below.
Jump-Start Questions: Why is this person running? Do they make the jump or fall into the water? Is this person jumping or floating?
The End of Days

Opening Line Idea: Despite their best efforts, they arrived too late—the battle had already begun.
Jump-Start Questions: Is the person going to the city or away from it? Who is attacking and why? What would you do if you saw this scene taking place?
Out of the Book

Opening Line Idea: “Happily ever after” was about to take on a whole new meaning.
Jump-Start Questions: Where is the light coming from in the book? Does the woman know she’s a book character? What will the mouse do when it sees the woman?
Stopped Clock

Opening Line Idea: I was sure that the time on the broken clock was the clue to solving the mystery.
Jump-Start Questions: How long has this clock been stopped at 11:17? Does the clock still work? Who does the clock belong to?
Dueling Webs

Opening Line Idea: It’s never a good idea to build your web too close to another spider’s, but this time she had no choice.
Jump-Start Questions: How do spiderwebs and spiders make you feel? Were these webs made by one spider or two? Would you knock down these webs or leave them alone?
Do Shoes Grow on Trees?

Opening Line Idea: The day I threw my own shoes into the tree was the day I really started to grow up.
Jump-Start Questions: Who threw the first pair of shoes into the tree and why? If you saw a nice pair of shoes, would you try to get them down? Would you throw your own shoes into the tree?
Abstract Art

Opening Line Idea: “So,” asked their art teacher, “what do you think this painting means?”
Jump-Start Questions: Is the paint wet or dry? Is this the whole painting or a small part of a larger one? Who chose these colors and why?
Wandering Robots

Opening Line Idea: Everything about NB-317 was made of cardboard except his heart—that was made of flesh and blood and very capable of being broken.
Jump-Start Questions: Who built this robot? Can the robot smell the flowers? Does the robot belong to someone, or is it an independent being?
Dream Come True

Opening Line Idea: It all started when Quinn watched her favorite movie the night before they assigned partners for the eighth grade science fair project.
Jump-Start Questions: What is in the balloons to allow them to lift and carry a house? Is the house coming up or going down? Would you want to be inside the house right now?
Mysterious Cave
Opening Line Idea: The cave was unlike anything we’d ever seen before, and what was more, it almost seemed like the rock was alive.
Jump-Start Questions: What made these shapes? What do the shapes look like to you? If this were a rock formation, would you want to explore it?
Storm at Sea

Opening Line Idea: As the rain lashed his face and lightning tore apart the sky, Kiran had to admit he’d always thought it would be a lot more fun being a pirate.
Jump-Start Questions: Is anyone on the ship, or is it abandoned? If you were the captain, what would you be thinking right now? What would happen if the ship capsized or was struck by lightning?
Grasshopper Close-Up

Opening Line Idea: That’s when Javed realized it wasn’t that the grasshopper was too big—it was that he was suddenly very, very small.
Jump-Start Questions: Is this grasshopper cute or scary? What is the grasshopper looking at? Would you pick up this grasshopper or shoo it away?
UFO Parking

Opening Line Idea: “Well, that’s convenient,” Javdok remarked to Qabow when they saw the sign.
Jump-Start Questions: Where is this sign located, and who hung it? Would spaceships need parking lots on land, or could you just leave them in the sky and beam down? Do you think this parking lot is free, and if not, how much does it cost to park a spaceship?
High school writers are ready to dig deep, exploring character development and detailed plots. These pictures offer a jumping-off point to set their imaginations free. Try questions like these:
- What mood does the picture evoke?
- If your friend texted you this picture with no explanation, what would you think?
- What would you say to the person in the picture?
- Write five words for each of the five senses (sight, sound, smell, touch, taste) related to the picture.
- Is this picture the beginning, the middle, or the end of the story?
Cyborg Girl

Opening Line Idea: When she was 14, Tasha’s parents finally told her the truth about what she really was.
Jump-Start Questions: Is the cyborg crying or malfunctioning? Who chose the cyborg’s clothes? Has the girl always known she is a cyborg?
BBQ Cookout

Opening Line Idea: “So, I’m guessing no one told you I’m a vegetarian?” asked Sadie with a smile.
Jump-Start Questions: What would you do if you were invited to a meal where there was nothing you could eat? Does this meal look delicious or disgusting? Would you rather be the one grilling or the one cleaning up afterward?

Opening Line Idea: The latest app was like a time machine, allowing people to look back in time, but it also had a dark side.
Jump-Start Questions: What is the man thinking about? Why is the baby picture the only part of the image that’s in color? Would you like to be able to see a picture of what you’ll look like when you’re 80 years old?

Opening Line Idea: She was surrounded by people but never felt more alone.
Jump-Start Questions: What does the woman’s sign say? Is this person homeless, or is she sitting on the street for another reason? Where will this person sleep tonight?
Hippo Troubles

Opening Line Idea: Like all parents, hippos sometimes really need a break from their kids.
Jump-Start Questions: Where do these hippos live? Does the mother hippo feel love for her baby? What would happen if a bee flew into the baby hippo’s mouth?
iPad Farmer

Opening Line Idea: Grandpa Jack never failed to surprise us.
Jump-Start Questions: What will the man do with the vegetables on his lap? Is this man a farmer or just someone who likes to garden on the weekend? Does it surprise you to see this man using technology in this setting?
Marching Band Blues

Opening Line Idea: Kaleel sat sadly on the bench, watching the rest of the band march away in jaunty time to the music.
Jump-Start Questions: Where is the rest of the marching band, and why isn’t this man with them? How long has the man owned the instrument, and who taught him to play? What kinds of music does this man like to listen to?
Never-Ending Tunnel

Opening Line Idea: The tunnel seemed to stretch to infinity, but Jayma knew what was at the end, and it terrified her.
Jump-Start Questions: Does this tunnel scare you or intrigue you? Would you rather walk, run, Rollerblade, or ride a skateboard from one end to the other? If the lights suddenly went out, what would you do?
Carving Out Love
Opening Line Idea: For years, we wondered who “WP” was, and who it was who loved them so much they carved it into a tree for all to see.
Jump-Start Questions: Would you ever carve someone’s initials in a tree? Is carving initials in a tree the same as spray-painting graffiti? Would you feel bad if you had to cut this tree down and burn it for firewood?
Glowing Globe

Opening Line Idea: Just then, the globe began to glow, and Jaxson knew he was about to leap through space and time once again—destination unknown.
Jump-Start Questions: What causes the globe to glow? Is the globe of Earth or another celestial body? What is the man pointing to?
See No Evil

Opening Line Idea: It seemed like a funny joke to pose the skeletons in front of old Mrs. Petoski’s house, but then she turned up dead, and the police said it was murder.
Jump-Start Questions: Who put these skeletons here and why? Which is worse: seeing evil, hearing evil, or speaking evil? How would you feel if you knew these were actual human skeletons, not props?
Upside Down
Opening Line Idea: It’s an odd feeling to wake up one morning and find yourself able to walk on the ceiling.
Jump-Start Questions: What would the advantages and disadvantages of defying gravity be? Can this person go outside without floating away? Why is the microwave on top of the tall refrigerator?
Face at the Fence
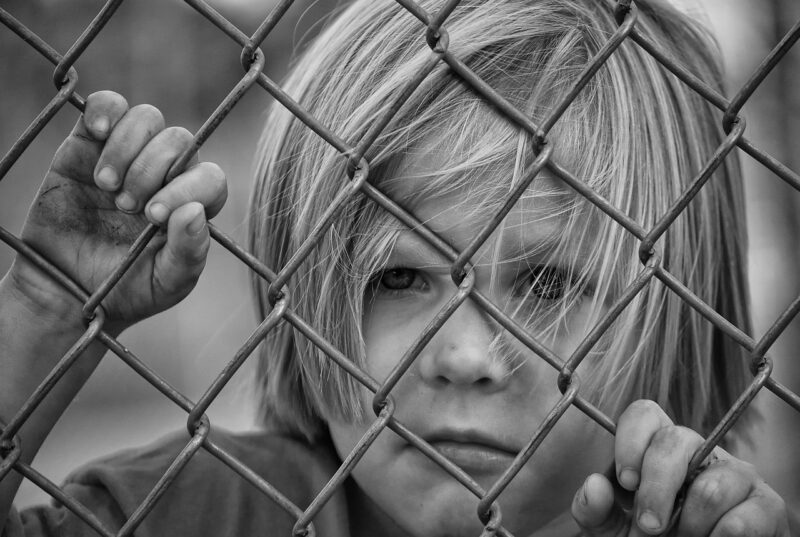

Opening Line Idea: So much depended on which side of the fence you were on.
Jump-Start Questions: Is this child on the outside looking in or the inside looking out? What might the fence be separating the child from? What would happen if the child tried to climb the fence?
Bicycle Race

Opening Line Idea: Finley had trained too hard for this race to come in third—it just wasn’t good enough.
Jump-Start Questions: Are these bikers competing, working as a team, or just biking for fun? What does the front biker’s arm tattoo symbolize? Is coming in second or third the same as losing?
Family Travels

Opening Line Idea: In the picture, my grandmother’s expression is hard to interpret, but she’s told me the story many times.
Jump-Start Questions: What’s in the bags? If you saw this family pulled over on the side of the road, would you stop and ask if they needed help? Who gave the girl the ring she’s wearing on her finger?
Laundromat Antics

Opening Line Idea: Dani never expected to meet her first love feet first.
Jump-Start Questions: Is it safe for this person to be inside the washing machine? What would happen if someone closed the door and walked away? Would you ever crawl inside a washing machine or dryer?

Opening Line Idea: Molly’s mom probably didn’t mean for her to be the one to find the note, but that’s how things turned out.
Jump-Start Questions: What would you do if you found this note and ring? What is the writer sorry for? Would you ever leave a note like this?
Through the Storm
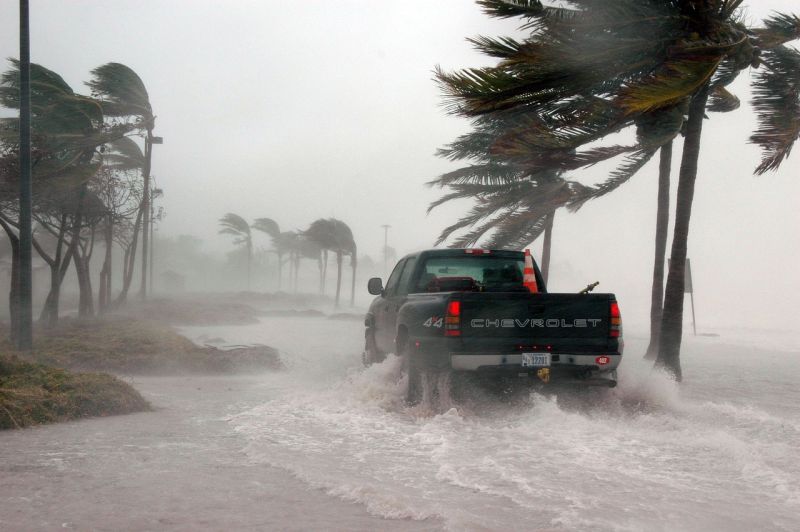

Opening Line Idea: Javier knew it would have been smarter to stay put, but he had to make sure his mom was safe before the worst of the storm arrived.
Jump-Start Questions: Do you think it would be fun to be driving this truck or too dangerous? What would make you drive around in a storm like this? What will the scene look like after the storm has passed?
Lifetime Friends
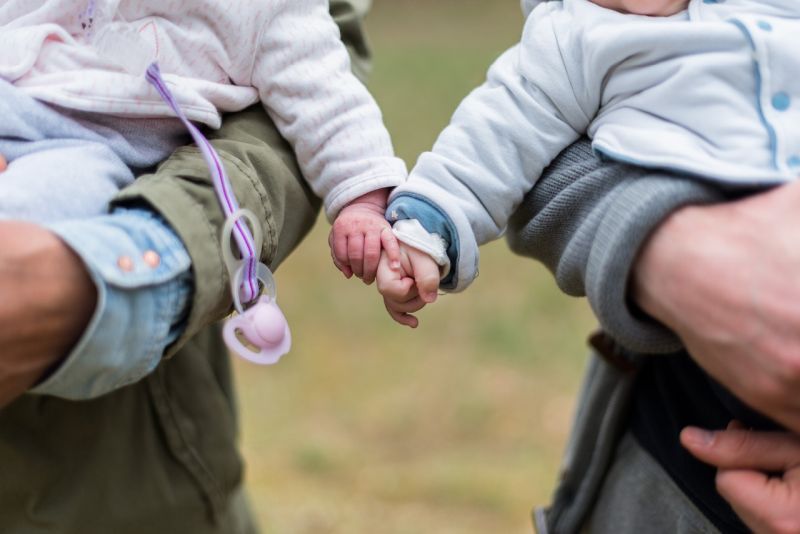

Opening Line Idea: They’d been friends for as long as they could remember—even longer, in fact.
Jump-Start Questions: Who is holding the babies, and how do they know each other? What are the expressions on the babies’ faces right now? Is the baby on the right reaching for the other baby’s pacifier?
Stray Kitten
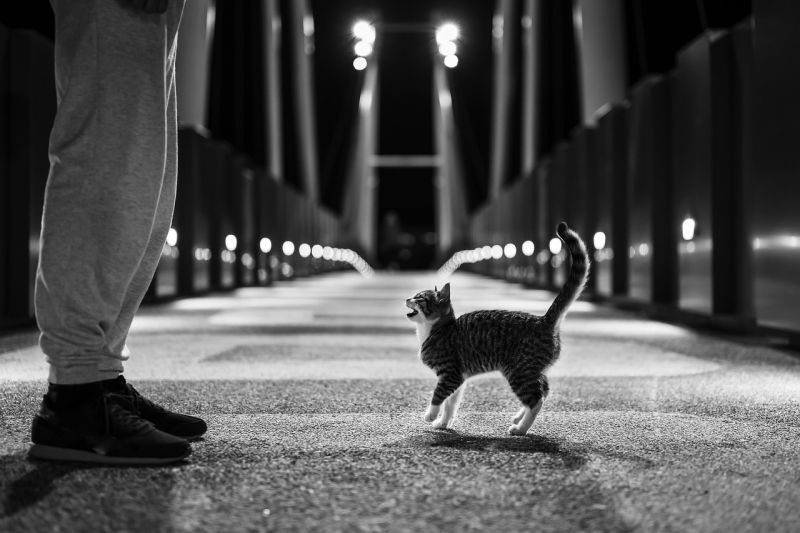

Opening Line Idea: “I am NOT taking you home with me,” Kai told the tiny mewling kitten firmly.
Jump-Start Questions: Would you pick this kitten up and take it home? Is the kitten’s mother nearby? Why is the kitten meowing at the person?
Abandoned Greenhouse
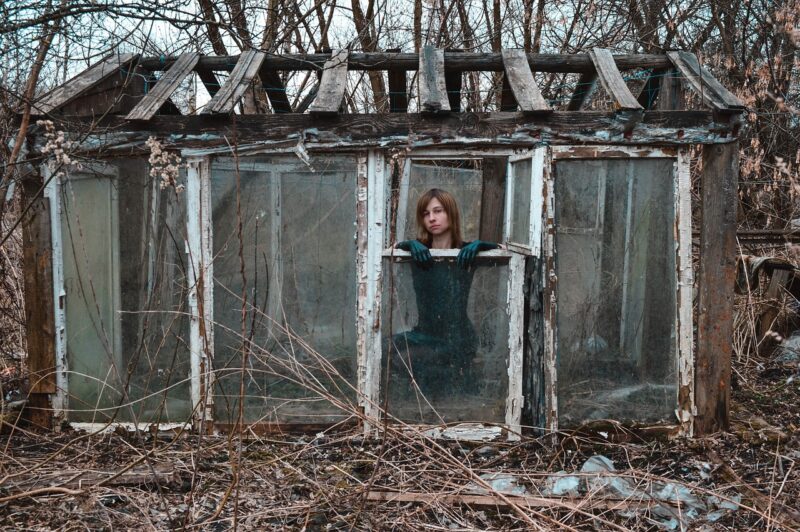

Opening Line Idea: Willow was free to leave at any time, but she couldn’t make herself go.
Jump-Start Questions: Who built this structure and when? How did the woman get inside? Would you rather knock this structure down or renovate it?

Opening Line Idea: Amani’s earliest memory was razor wire—miles and miles of it.
Jump-Start Questions: Does this fence make you feel safe or anxious? What does this fence separate? If you had to get past this fence, what would you do?
Church Graveyard

Opening Line Idea: Everyone feels differently in a graveyard, but for me, they’re very peaceful places.
Jump-Start Questions: Who wrote the epitaphs on the front two graves? Do you find this cemetery peaceful or creepy, and would you feel differently at night? Does anyone ever bring flowers to these graves?
Orb of Death

Opening Line Idea: “Do you really want to know?” Death asked. “Because once you know, you won’t be able to forget.”
Jump-Start Questions: Is the globe showing a reflection or a vision? If Death offered to reveal your future, would you accept? Who did the skull on the left belong to in life?
Missed Shot

Opening Line Idea: Steve was sure his shot would make it, but it bounced off the rim just as the buzzer rang to end the game.
Jump-Start Questions: Is the player in front happy, sad, or something else? Would you rather be playing in the game or watching the game? What is the referee thinking about?
First Contact

Opening Line Idea: This was it—the moment that would change what it meant to be human forever.
Jump-Start Questions: What is reflected in the astronaut’s mask? Will the alien and the human be able to communicate with each other? How would you feel if you were the first human to meet an alien?
One Life To Live

Opening Line Idea: His face said his life had been a hard one, but his eyes told a different tale.
Jump-Start Questions: Where and when did this man get his hat? If you could ask this man one question, what would it be? Why did this man decide to grow a mustache?
Winter Walk
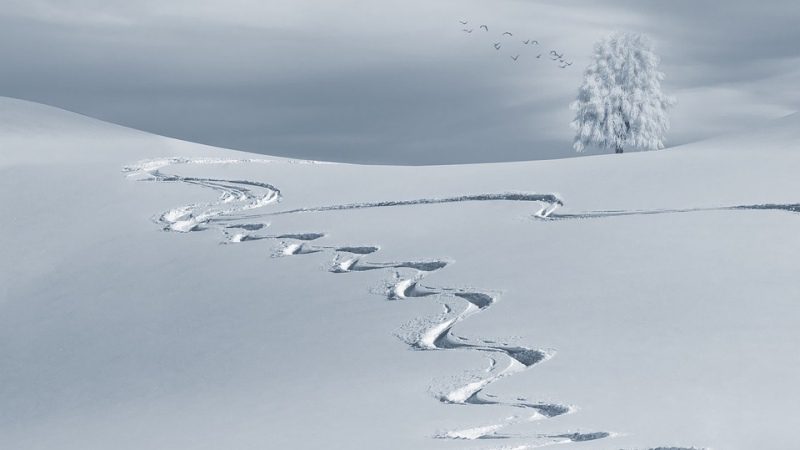

Opening Line Idea: Snow fell, creating a blank canvas to record the story of that fateful walk.
Jump-Start Questions: How would you feel if you were walking in the snow in this scene? How would you find out what made the tracks? How far from civilization was this picture taken?
Train to Nowhere

Opening Line Idea: It certainly wasn’t the most luxurious way to travel, but then again, no one really wanted to make this trip in the first place.
Jump-Start Questions: What would it feel like to sleep here? Why has this place been abandoned? If you looked through the windows, what would you see outside?
Modern Mary Poppins
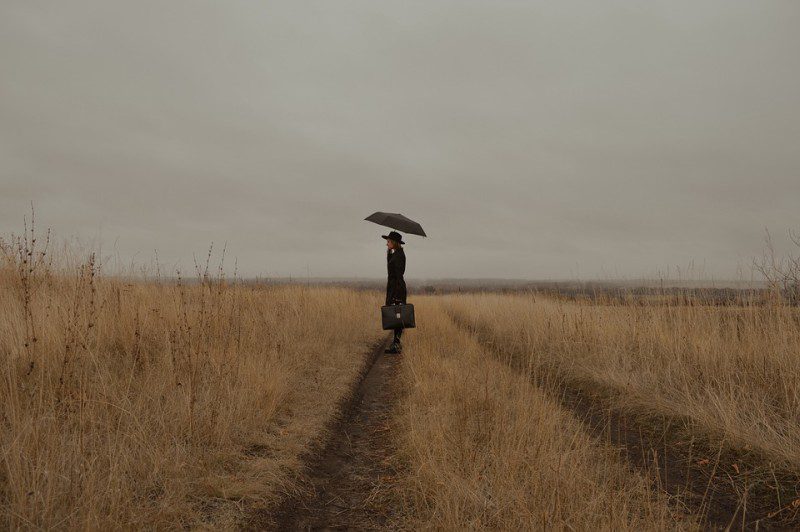

Opening Line Idea: She dropped into our lives on a gray day in midwinter, a hint of the spring that was to come.
Jump-Start Questions: What is in the person’s bag? What are they waiting for? Who made the tracks in this field?
All That Remains
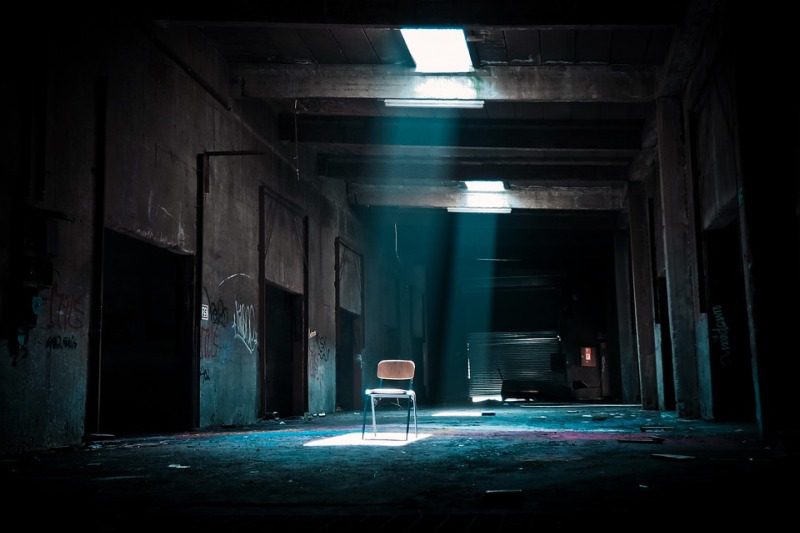

Opening Line Idea: Dust motes filled the air of the abandoned hallway, replacing the voices once heard there.
Jump-Start Questions: Where is the light coming from? What is written on the walls? What would you hear if you were standing here?
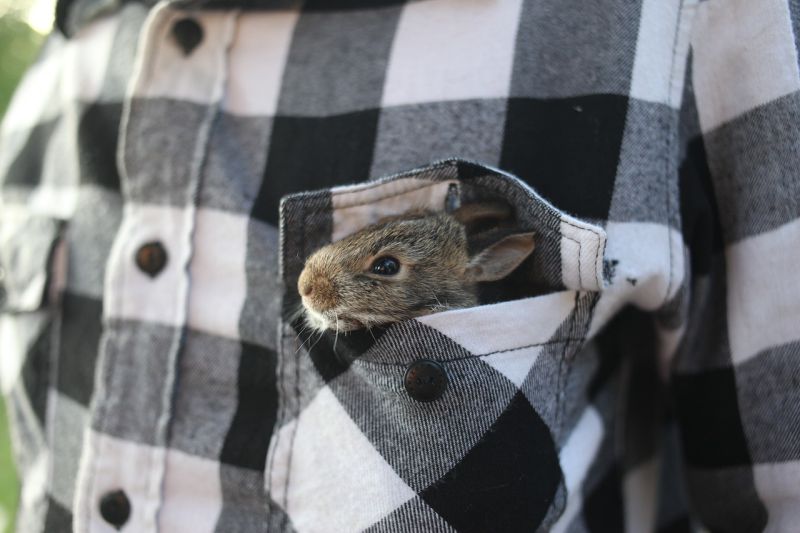

Opening Line Idea: From the day he found the little creature, Luis refused to go anywhere without him.
Jump-Start Questions: How would you feel if you were talking to this person and the animal suddenly poked its head out? What will happen when the creature is too big to fit in the pocket? Would you like a pocket-size pet?
The Question

Opening Line Idea: Their happily ever after began quietly, with a bouquet of wildflowers.
Jump-Start Questions: What is the person in front about to say to the other person? Did they pick the flowers themselves, and do they have any special meaning? Where do the railroad tracks come from and go to?
Night Lights
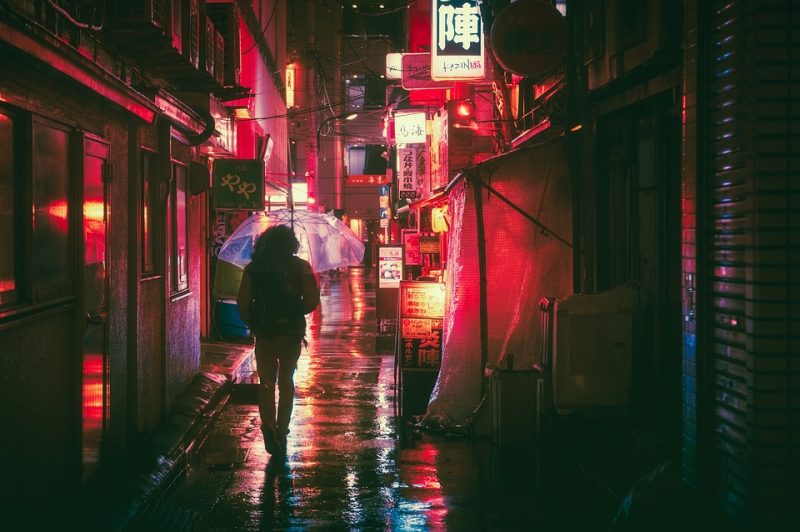

Opening Line Idea: Misty rain both blurred and emphasized the lights that lit Suri’s way home that evening.
Jump-Start Questions: What is this person thinking about as they walk along? If this were you, would feel safe walking alone at night? What do you think the various signs say?
Forest of Fear
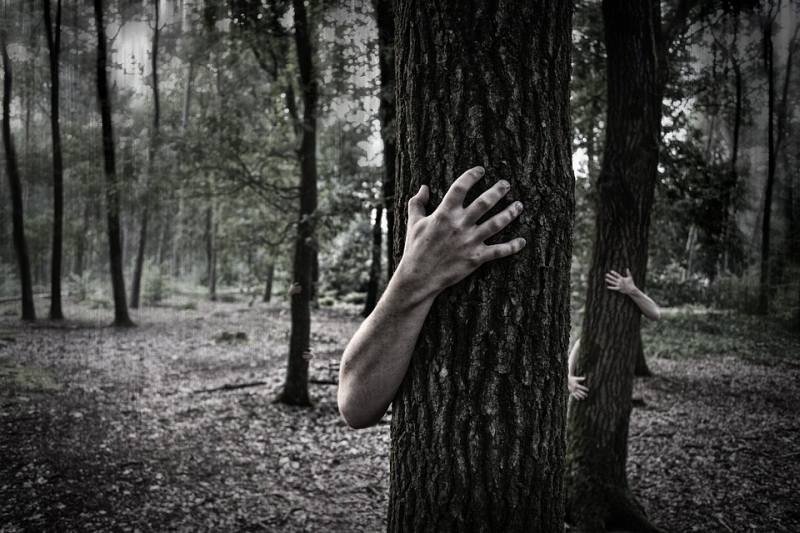

Opening Line Idea: At first, Mateo thought it was a joke, but the screams that followed told him there was nothing remotely funny about it.
Jump-Start Questions: Are there people behind the trees, or are the arms coming out of the trees themselves? Would you investigate or run away? What would you say to these people?

Opening Line Idea: At the elite level, being a spy meant serious commitments.
Jump-Start Questions: Would you like a cybernetic eye? What would you do if you woke up and found yourself with one against your will? Is this a human with an artificial eye or a very human-like cyborg?
The Yellow Door

Opening Line Idea: On their 14th birthday, every resident of Fresnia was required to stand before the Wall of Doors and make a choice.
Jump-Start Questions: Would you have painted this door yellow or chosen a different color? Do all the doors lead to the same place? Would you open the yellow door first, last, or not at all?
Graffiti Palace
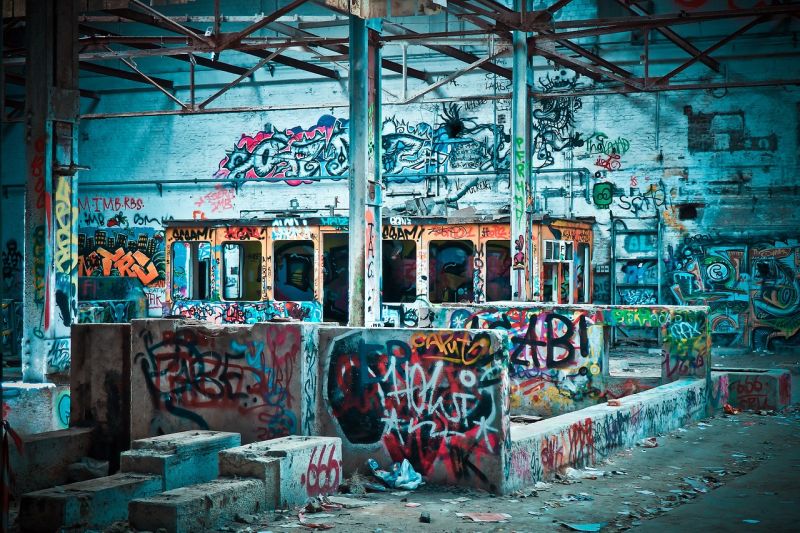

Opening Line Idea: To strangers, it seemed random, but every mark on those walls had deep meaning for us.
Jump-Start Questions: Do you see this graffiti as vandalism or art? If you found a can of spray paint here, would you add your own contribution? What did this building used to be?
Fossil Fish
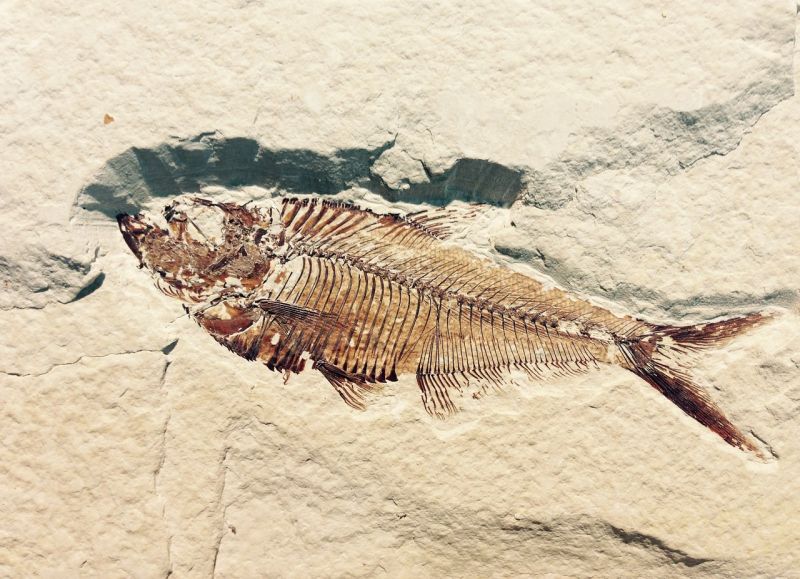

Opening Line Idea: Millions of years ago, the fish gave one final flop before lying still in the deep mud.
Jump-Start Questions: How did this fish die? How was it different from modern fish? What other fossils do you think might be found nearby?
On the Rails

Opening Line Idea: Aliyah stood on the tracks, uncertain of where to go next.
Jump-Start Questions: Is it safe for this person to be walking along these railroad tracks? What kind of music does the person like to play on their guitar? Is the person alone by choice?
These picture prompts are all works of art, some more well known than others. Try providing them to students without sharing the titles first, then offer up the titles if they need some help getting started. We’ve also provided some opening line ideas.
The Dance Class (Edgar Degas)

Opening Line Idea: The studio was dusty, noisy, and crowded, but it was also home.
Greek Funerary Plaque (520-510 BCE)

Opening Line Idea: With one final tap and last dab of paint, the tablet was complete at last.
Washington Crossing the Delaware (Emanuel Leutze)

Opening Line Idea: Was it bravery or sheer foolish bravado?
Kyōsai’s Pictures of One Hundred Demons

Opening Line Idea: “So this is where the wild things are,” she thought.
First Steps, After Millet (Vincent van Gogh)

Opening Line Idea: After so many years of hope and disappointment, this child made it all worthwhile.
Lady Lilith (Dante Gabriel Rossetti)

Opening Line Idea: Every night, without fail, 100 slow and steady strokes, just like her mother taught her.
A Sunday on La Grande Jatte (Georges Seurat)
Opening Line Idea: At what point does afternoon become evening?
After the Hurricane, Bahamas (Winslow Homer)

Opening Line Idea: The skies were clearing, but the seas raged on.
Drawing Lots for Prizes (Kitagawa Utamaro)

Opening Line Idea: It was fun at first, but I soon grew tired of the never-ending parties, dancing, music, and false laughter.
Portions of Field Armor (Jacob Halder)

Opening Line Idea: The armor shone in the morning sun; by evening it would be scratched, worn, and covered in blood.
Sadie Pfeifer, a Cotton Mill Spinner (Lewis Wickes Hine)

Opening Line Idea: She’d never realized the factory would be so incredibly loud, the noise unrelenting and cruel.
Still Life With Monkey, Fruits, and Flowers (Jean Baptiste Oudry)

Opening Line Idea: “This is why we can’t have nice things,” she complained.
Man Leading a Giraffe, 5th Century Byzantine

Opening Line Idea: At this point, he couldn’t help but wonder: Was he leading the giraffe or was the giraffe leading him?
The Three Skulls (Paul Cézanne)

Opening Line Idea: Nothing bothered her more than the empty, vacant eyes.
The Madame B Album (Marie-Blanche Hennelle Fournier)

Opening Line Idea: “Definitely a new species,” confirmed the curator.
Coiled Trumpet in the Form of a Snarling Feline Face (c. 100 BCE to 500 CE)

Opening Line Idea: The trumpet called them all to attention, and the audience fell silent in an instant.
Crazy Quilt With Animals (Florence Elizabeth Marvin)

Opening Line Idea: Every stitch and scrap spun a story.
Storytime (Eugenio Zampighi)

Opening Line Idea: They could spend hours there, and they often did.
Cubist Village (Georges Gaudion)

Opening Line Idea: The Land of Oz looked very different from how Dorothy had described it.
Zig-Zag Passenger and Freight Train (Unknown)
Opening Line Idea: Frankly, I didn’t care where the train was going, or how long it would take to get there.
The Power of Music (William Sidney Mount)

Opening Line Idea: Sammy wanted to join in and lift his voice, but he knew they’d never welcome him in.
The Large Tree (Paul Gauguin)
Opening Line Idea: Outsiders saw it as paradise, and they weren’t far off.
After the Bath (Mary Cassatt)

Opening Line Idea: Motherhood was exhausting, but she found the rewards very sweet indeed.
Wedding Gown (Korea, Late 1800s)

Opening Line Idea: It was the most important gown she’d ever wear, and she begrudged every single stitch it took to make it.
The Contemplator (Eugène Carrière)

Opening Line Idea: Looking back, she seemed to see everything through a strange, dusty haze.
The Girl I Left Behind Me (Eastman Johnson)

Opening Line Idea: She was an old woman now, but when I thought of her, it was always as a brave, stoic child, standing tall atop the hillside as we trudged into the distance.
24c Curtiss Jenny Invert Single

Opening Line Idea: “Do you think anyone will notice?” asked Mr. Semple nervously.
Creeping Baby Doll Patent Model

Opening Line Idea: “Well, that’s mighty unsettling,” Pa said.
Wrecked Zeppelin (British Library)
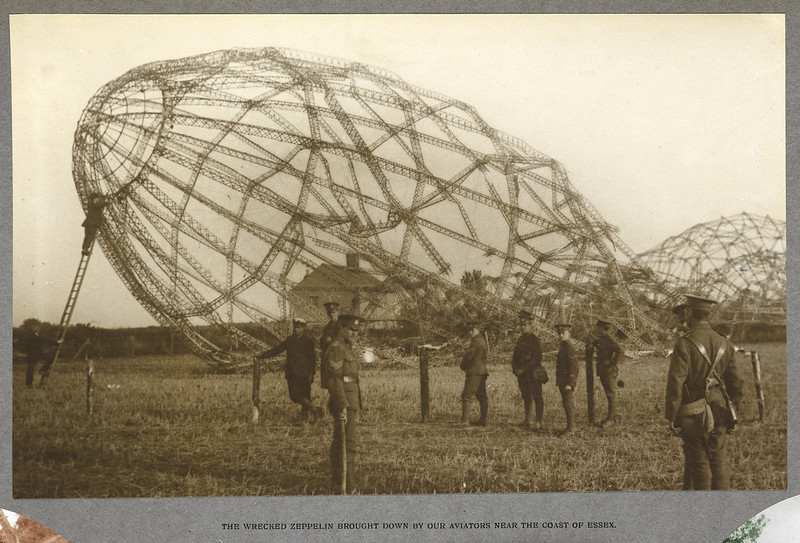

Opening Line Idea: The wreckage drew crowds for weeks, but the great balloon’s demise made little difference in the end.
Skeleton (Tales of Terror Frontispiece)

Opening Line Idea: “Here we go again,” Cedric moaned, as the skeletons pulled him from the grave once more.
Get Your Free Picture Writing Prompt Google Slides
Just click the button below to fill out the form and get instant access to free downloadable Picture Writing Prompts Google Slides with all the prompts included above.
How do you use picture writing prompts in your classroom? Come share ideas and ask for advice in the We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .

You Might Also Like

125 Winning Debate Topics for Middle School Students
Teach students to make effective arguments. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

Writing Prompts for Elementary School Students
Tim Platt/Getty Images
- M.S., Education, Buffalo State College
- B.S., Education, Buffalo State College
Writing is an essential skill and an important part of elementary school studies. However, writing inspiration does not come easily to every student. Like adults, many children experience writer's block , particularly when an assignment is extremely open-ended.
Good writing prompts get students' creative juices flowing , help them write more freely, and ease any anxiety they may feel about the writing process. To integrate writing prompts into your lessons, ask students to choose one writing prompt each day or week. To make the activity more challenging, encourage them to write without stopping for at least five minutes, increasing the number of minutes that they devote to writing over time.
Remind your students that there is no wrong way to respond to the prompts and that they should simply have fun and let their creative minds wander. After all, just as athletes need to warm up their muscles, writers need to warm up their minds.
Elementary School Writing Prompts
- My biggest goal in life is...
- The best book I ever read was...
- The happiest moment in my life was when...
- When I grow up, I want to...
- The most interesting place I have ever been to was...
- Name three things you don't like about school and why.
- The strangest dream I ever had was...
- The person I admire most is...
- When I turn 16, I will...
- Who is the funniest member of your family and why?
- I get scared when...
- Five things I would do if I had more money are...
- What is your favorite sport and why?
- What would you do if you could change the world?
- Dear teacher, I would like to know...
- Dear President Washington, what was it like to be the first president?
- My happiest day was...
- My saddest day was...
- If I had three wishes, I would wish for...
- Describe your best friend, how you met, and why you are friends.
- Describe your favorite animal and why.
- Three things I like to do with my pet elephant are...
- The time a bat was in my house...
- When I become an adult, the first thing I want to do is...
- My best vacation was when I went to...
- The top three reasons that people argue are...
- Describe five reasons that going to school is important.
- What is your favorite television show and why?
- The time I found a dinosaur in my backyard...
- Describe the best present you ever received.
- Describe your most unusual talent.
- My most embarrassing moment was when...
- Describe your favorite food and why.
- Describe your least favorite food and why.
- The top three qualities of a best friend are...
- Write about what you would cook for an enemy.
- Use these words in a story: scared, angry, Sunday, bugs.
- What's your idea of a perfect vacation?
- Write about why someone might be afraid of snakes.
- List five rules that you have broken and why you broke them.
- What is your favorite video game and why?
- I wish someone had told me that...
- Describe the hottest day you can remember.
- Write about the best decision you've ever made.
- I opened the door, saw a clown, and then...
- The last time the power went out, I...
- Write about five things you can do if the power goes out.
- If I were president, I would...
- Create a poem using the words: l o ve, happy, smart, sunny.
- The time my teacher forgot to wear shoes...
- For prompts that ask students to write about a person, encourage them to write two responses—one response about a friend or family member, and another about someone they don't know personally. This exercise encourages children to think outside the box.
- Remind students that their responses can be fantastical. When the confines of realism are eliminated, students are free to think more creatively, which often inspires greater engagement in the project.
If you're looking for more writing ideas, try our lists of journal prompts or ideas for writing about important people in history like Martin Luther King Jr .
- 8 First Day of High School Activities to Get to Know Your Students
- 61 General Expository Essay Topic to Practice Academic Writing
- Discussion Questions to Use in English Conversation
- Writing Prompts for 5th Grade
- Writing Prompts for 7th Grade
- Second Grade Writing Prompts
- 24 Journal Prompts for Creative Writing in the Elementary Classroom
- 40 "Back From Christmas Break" Writing Prompts
- November Writing and Journal Prompts
- First Grade Writing Prompts
- Christmas Journal Writing Prompts
- 4th Grade Writing Prompts
- September Writing Prompts
- Engaging Writing Prompts for 3rd Graders
- December Writing Prompts
- October Writing Prompts
20 Creative Writing Activities for Elementary Students
By andy minshew.
- November 23, 2021
Did you know that November is National Novel Writing Month? While your young learners are probably not ready to write an entire book, this month is a great time to practice creative writing skills with your students. Not only can creative writing be helpful for teaching vocabulary and sentence structure, but it can also encourage students to use imaginative thinkin g —and even find a genuine love of writing!
All of these 20 creative writing activities can be used with elementary school students to practice reading and writing skills. We’ve included options for both early elementary students, who may still be learning to write, and elementary students in upper grades who are ready to work on projects of their choosing.

1. Join the NaNoWriMo organization’s Young Writers Program (YWP) ! Together, your students can work on all sorts of age-appropriate writing challenges and activities throughout the year—including a project of their choice in November!
2. To practice pre-writing skills and collaborating on a project, try these shared writing project activities .
3. If you have any budding cartoonists in your class, this Finish the Comic activity from author Jarrett Lerner can be a great way for younger students to practice writing dialogue.
4. Teach your students about adjectives and writing descriptions with this Popcorn Adjectives activity .
5. Students can learn about creative writing by studying imagery and poetry by established authors. Using this writing worksheet , kids can write out their thoughts about a poem and draw images that stand out to them.
6. To teach creative thinking skills with kindergarteners and early elementary students, try this Mystery Seed writing activity .
7. Get families involved, too! Share these fun home writing activities with your student’s families to help them practice at home.
8. Print out and put together a Writing Jar with tons of creative writing prompts to inspire your students.
9. Check out this resource for even more writing prompts focused on imaginative thinking.

10. Try blackout poetry , an activity that encourages students to make their own beautiful art from a work that already exists.
11. Creative writing isn’t limited to fiction. This narrative writing activity can teach students to write events clearly and in sequence from their real life.
12. For a creative writing project that’s just plain fun, try this Roll a Story activity.
13. This nonfiction project helps children learn to write a letter as they write to a loved one of their choice.
14. If you want to give your students some freedom in choosing a writing assignment, hang up this Writing Prompt Choice Board in your classroom and let them answer whichever prompt they’d like!
15. Encourage students to keep their own journal throughout the year. You could even give them time each morning to respond to a journal prompt .
16. Use this journal page template to help students structure and compile journal entries.
17. These printable Mad Libs can teach children different parts of a sentence while they use their imaginations to create a story.
18. Use this What? So What? Now What? exercise (#6 at the link) to help students structure their creative writing projects.
19. To teach children how to create descriptive sentences, play this Show, Don’t Tell writing activity .
20. If you’d like to hold a month-long creative writing activity, try this 30-Day Writing Challenge for kids .
More education articles

Celebrating Juneteenth 2024: Children’s Books and Activities for Families and Educators

MacKenzie Scott’s Yield Giving Awards Waterford.org a $10 Million Grant
- Primary Hub
- Art & Design
- Design & Technology
- Health & Wellbeing
- Secondary Hub
- Citizenship
- Primary CPD
- Secondary CPD
- Book Awards
- All Products
- Primary Products
- Secondary Products
- School Trips
- Trip Directory
- Trips by Subject
- Trips by Type
- Trips by Region
- Submit a Trip Venue
Trending stories
Top results.

- Creative Writing Prompts Activities And Resources For Ks1 And Ks2 English
Creative writing prompts – Best activities and resources for KS1 and KS2 English

Fed up of reading 'and then…', 'and then…' in your children's writing? Try these story starters, structures, worksheets and other fun writing prompt resources for primary pupils…

What is creative writing?
How to develop opportunities for writing with choice and freedom, creative writing resources for the classroom, creative writing prompts.
According to the Cambridge English Dictionary, ‘creative’ is ‘producing or using original and unusual ideas’, yet I would argue that in writing there’s no such thing as an original idea – all stories are reincarnations of ones that have gone before.
As writers we learn to be expert magpies – selecting the shiny words, phrases and ideas from other stories and taking them for our own.
Interestingly, the primary national curriculum does not mention creative writing or writing for pleasure at all and is focused on the skill of writing.
Therefore, if writing creatively and for pleasure is important in your school, it must be woven into your vision for English.
“Interestingly, the Primary National Curriculum does not mention creative writing or writing for pleasure at all”
Creative writing in primary schools can be broken into two parts:
- writing with choice and freedom
- developing story writing
Writing with choice and freedom allows children to write about what interests and inspires them.
Developing story writing provides children with the skills they need to write creatively. In primary schools this is often taught in a very structured way and, particularly in the formative years, can lack opportunities for children to be creative.
Children are often told to retell a story in their own words or tweak a detail such as the setting or the main character.
Below you’ll find plenty of creative writing prompts, suggestions and resources to help develop both writing for choice and freedom and developing story writing in your classroom.
Here’s an interesting question to consider: if the curriculum disappeared but children still had the skills to write, would they?
I believe so – they’d still have ideas they wanted to convey and stories they wanted to share.
One of my children enjoys writing and the other is more reluctant to mark make when asked to, but both choose to write. They write notes for friends, song lyrics, stories and even business plans.
So how can we develop opportunities to write with choice and freedom in our classrooms?
Early Years classrooms are full of opportunities for children to write about what interests them, but it’s a rarer sight in KS1 and 2.
Ask children what they want to write about
Reading for pleasure has quite rightly been prioritised in schools and the impact is clear. Many of the wonderful ideas from The Open University’s Reading For Pleasure site can be used and adapted for writing too.
For example, ask children to create a ‘writing river’ where they record the writing they choose to do across a week.
If pupils like writing about a specific thing, consider creating a short burst writing activity linked to this. The below Harry Potter creative writing activity , where children create a new character and write a paragraph about them, is an example of this approach.

If you have a spare 20 minutes, listen to the below conversation with Lucy and Jonathan from HeadteacherChat and Alex from LinkyThinks . They discuss the importance of knowing about children’s interests but also about being a writer yourself.
'The confidence Crisis in Creative Writing.' Lucy and Jonathan chat with Alex from @LinkyThinks https://t.co/VClYxiQhcf — HeadteacherChat (@Headteacherchat) August 9, 2022
Plan in time to pursue personal writing projects
There are lots of fantastic ideas for developing writing for pleasure in your classrooms on The Writing For Pleasure Centre’s website .
One suggestion is assigning time to pursue personal writing projects. The Meadows Primary School in Madeley Heath, Staffordshire, does this termly and provides scaffolds for children who may find the choice daunting.
Give children a choice about writing implements and paper
Sometimes the fun is in the novelty. Are there opportunities within your week to give pupils some choices about the materials they use? Ideas could include:
- little notebooks
- a roll of paper
- felt tip pens
- gel pens
Write for real audiences
This is a great way to develop children’s motivation to write and is easy to do.
It could be a blog, a class newsletter or pen pals. Look around in your community for opportunities to write – the local supermarket, a nearby nursing home or the library are often all good starting points.
Have a go yourself
The most successful teachers of story writing write fiction themselves.
Many adults do not write creatively and trying to teach something you have not done yourself in a long time can be difficult. By having a go you can identify the areas of difficulty alongside the thought processes required.
Treat every child as an author
Time is always a premium in the classroom but equally, we’re all fully aware of the impact of verbal feedback.
One-to-one writing conferences have gained in popularity in primary classrooms and it’s well-worth giving these a go if you haven’t already.
Set aside time to speak to each child about the writing they’re currently constructing. Discuss what’s going well and what they could develop.
If possible, timetable these one-to-one discussions with the whole class throughout the year (ideally more often, if possible).
Free KS2 virtual visit and resources

Bring best-selling children’s authors directly into your classroom with Author In Your Classroom. It’s a brilliant free podcast series made especially for schools, and there’s loads of free resources to download too.
More than 20 authors have recorded episodes so far, including:
- Sir Michael Morpurgo
- Dame Jacqueline Wilson
- Michael Rosen
- Joseph Coelho
- Lauren Child
- Frank Cottrell-Boyce
- Benjamin Zephaniah
- Cressida Cowell
- Robin Stevens
Creative writing exercises
Use these inspiring writing templates from Rachel Clarke to inspire pupils who find it difficult to get their thoughts down on the page. The structured creative writing prompts and activities, which range from writing a ‘ through the portal story ‘ to a character creation activity that involves making your own Top Trumps style cards, will help inexperienced writers to get started.
Prompts for creative writing

This free PDF features a range of classroom games, ideas and prompts for creative writing from The National Literacy Trust. The activities can be completed independently, in pairs or in small groups. They’re perfect for National Writing Day.
Create confident writers

Use this inspiring KS2 lesson plan to help children write creatively with confidence. It focuses on eliminating the pressure of writing and turning writing tasks into fun games.
Storyboard templates and story structures

Whether it’s short stories, comic strips or filmmaking, every tale needs the right structure to be told well. This storyboard template resource will help your children develop the skills required to add that foundation to their creative writing.
Ten-minute activities
The idea of fitting another thing into the school day can feel overwhelming, so start with small creative writing activities once a fortnight. Below are a few ideas that have endless possibilities.
Character capers
You need a 1-6 dice for this activity. Roll it three to find out who your character is, what their personality is and what job they do, then think about the following:
- Can you draw them?
- What questions would you ask them if you met them?
- What might their answers be?
- If they were the main character in a story, what might happen?
Download our character capers worksheet .
Setting soup
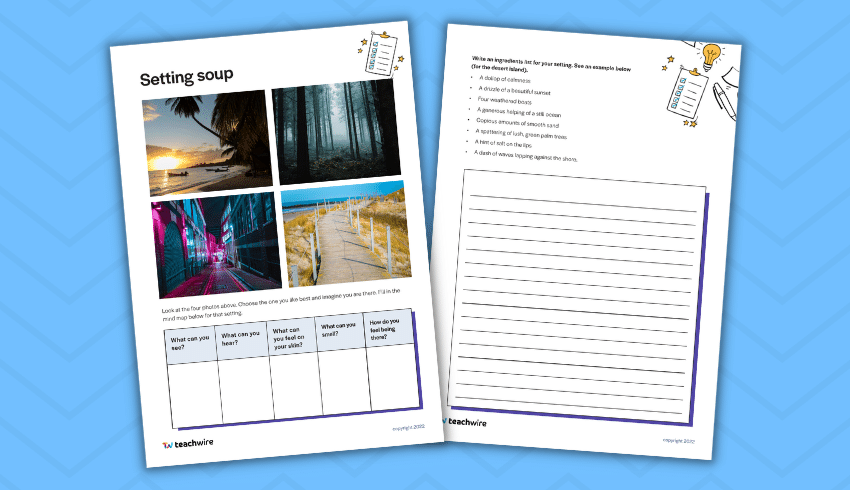
In this activity pupils Look at the four photos and fill in a mind map for one of the settings, focusing on what they’d see, hear, feel, smell and feel in that location. They then write an ingredients list for their setting, such as:
- A dollop of calmness
- A drizzle of a beautiful sunset
- A generous helping of a still ocean
- Copious amounts of smooth sand
- A spattering of lush, green palm trees
Download our setting soup worksheet .
Use consequences to generate story ideas
Start with a game of drawing consequences – this is a great way of building a new character.
Next, play a similar game but write a story. Here’s an example . Download our free writing consequences template to get started.

Roll and write a story
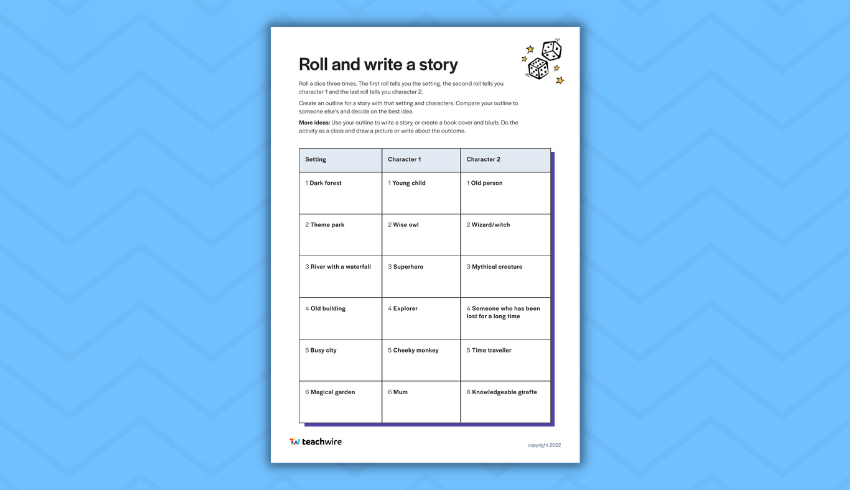
For this quick activity, children roll a dice three times to choose a setting and two characters – for example, a theme park, an explorer and a mythical creature. They then use the results to create an outline for a story.
Got more than ten minutes? Use the outline to write a complete story. Alternatively, use the results to create a book cover and blurb or, with a younger group of children, do the activity as a class then draw or write about the outcome.
Download our roll and write a story worksheet .
Scavenger hunt
Give children something to hide and tell them they have to write five clues in pairs, taking another pair from one clue to the next until the 5th clue leads them to the hidden item.
For a challenge, the clues could be riddles.
Set up pen pals. This might be with children in another country or school, or it could simply be with another class.
What do pupils want to say or share? It might be a letter, but it could be a comic strip, poem or pop-up book.
You need a log-in to access Authorfy’s content but it’s free. The website is crammed with every children’s author imaginable, talking about their books and inspirations and setting writing challenges. It’s a great tool to inspire and enthuse.
There are lots of great resources and videos on Oxford Owl which are free to access and will provide children with quick bursts of creativity.
Creative writing ideas for KS2

This free Pie Corbett Ultimate KS2 fiction collection is packed with original short stories from the man himself, and a selection of teaching resources he’s created to accompany each one.
Each creative writing activity will help every young writer get their creative juices flowing and overcome writer’s block.
WAGOLL text types

Support pupils when writing across a whole range of text types and genres with these engaging writing packs from Plazoom , differentiated for KS1, LKS2 and UKS2.
They feature:
- model texts (demonstrating WAGOLL for learners)
- planning guides
- writing templates
- themed paper
Each one focuses on a particular kind of text, encouraging children to make appropriate vocabulary, register and layout choices, and produce the very best writing of which they are capable, which can be used for evidence of progress.
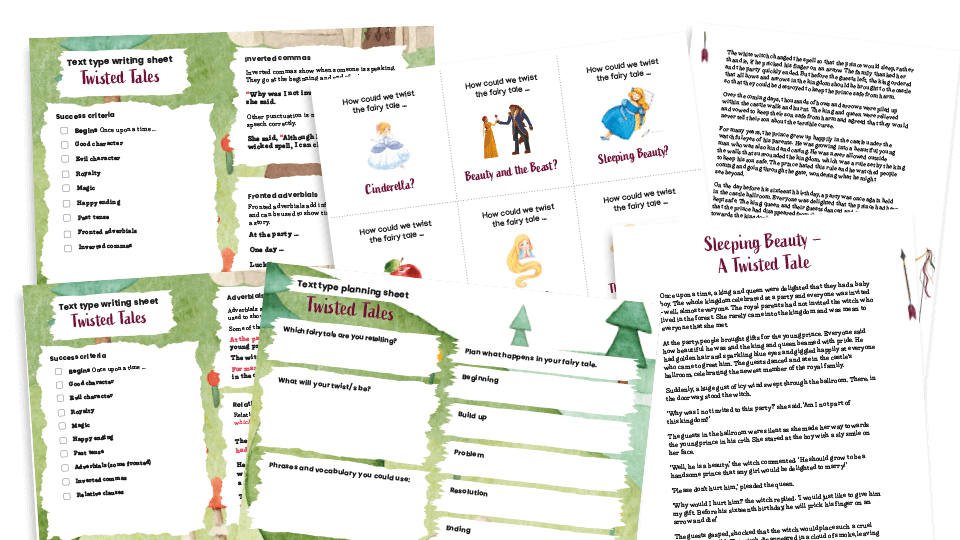
If you teach KS2, start off by exploring fairy tales with a twist , or choose from 50+ other options .
Scaffolds and plot types

A great way to support children with planning stories with structures, this creative writing scaffolds and plot types resource pack contains five story summaries, each covering a different plot type, which they can use as a story idea.
It has often been suggested that there are only seven basic plots a story can use, and here you’ll find text summaries for five of these:
- Overcoming the monster
- Rags to riches
- Voyage and return
After familiarising themselves with these texts, children can adapt and change these stories to create tales of their own.
Use story starters
If some children still need a bit of a push in the right direction, check out our 6 superb story starters to develop creative writing skills . This list features a range of free story starter resources, including animations (like the one above) and even the odd iguana…
Use word mats to inspire

Help pupils to write independently by providing them with helpful vocabulary sheets that they can pick and choose from when doing their own creative writing.
Download our free creative writing word mats here , including:
- Create a spooky atmosphere
- Write an adventure story
- Describe a character’s appearance
- Describe a character’s personality
- Describe how a character moves
- Describe how a character speaks
- Describe a mythical beast
Websites to inspire reluctant writers
I use this Breaking News picture generator in class to stimulate writing of news scripts, then film the pupils reading their script as newscasters.
Classtools also has this amazingly realistic Facebook page creator . Use it to create profile pages for historical figures. You’ll be amazed how much effort pupils put in to creating a ‘Fakebook’ page compared to what they would have done if they’d have been writing a plain biography.
Fotojet has an excellent magazine generator that allows your photo to be placed on actual magazine titles, such as Time and Rolling Stone . Big Huge Labs will convert a photograph into a printable magazine cover.
P ulp-O-Mizer is especially useful when teaching the science fiction genre. You can generate a series of fabulous 1950s pulp-inspired book covers which look the part and are highly customisable, allowing you to change the title, text, colour and illustrations to produce a very professional-looking cover.
Instead of creating boring drawer labels in Word, why not use a Star Wars or Harry Potter font instead? Let children generate their own personalised name tags using some of the typefaces from famous films, bands or brands.
Julian Wood is a deputy headteacher in a Sheffield primary school, a CAS Master Computer Teacher and a Microsoft Innovative Educator.
Creative writing pictures

Using images as writing prompts is nothing new, but it’s fun and effective.
Pobble 365 has an inspiring photo for every day of the year. These are great inspiration for ten-minute free writing activities. You need to log in to Pobble but access to Pobble 365 (the pictures) is free.
Choose two pictures as prompts (you can access every picture for the year in the calendar) or provide children with a range of starter prompts.
For example, with the photo above you might ask children to complete one of the following activities:
- Continue the story using the story starters on Pobble.
- Write down what your dream day would include.
- Create a superhero called Dolphin Dude.
- If you didn’t need to breath when swimming underwater, what would you do? Write about your dream day. It might include rivers, lakes, swimming pools, the seas or oceans.
- If you had a super power, what would it be and why?
The Literacy Shed

Website The Literacy Shed has a page dedicated to interesting pictures for creative writing . There are winter scenes, abandoned places, landscapes, woodlands, pathways, statues and even flying houses.
The Literacy Shed also hosts video clips for inspiring writing and is choc-full of ways to use them. The Night Zookeeper Shed is well worth a visit. There are short videos, activities and resources to inspire creative writing.
Once Upon a Picture

Once Upon a Picture is another site packed with creative writing picture prompts , but its focus is more on illustrations than photography, so its offering is great for letting little imaginations soar.
Each one comes with questions for kids to consider, or activities to carry out.
How to improve creating writing
Developing story writing .
If you decided to climb a mountain, in order to be successful you’d need to be well-equipped and you’d need to have practised with smaller climbs first.
The same is true of creative writing: to be successful you need to be well-equipped with the skills of writing and have had plenty of opportunities to practise.
As a teachers you need to plan with this in mind – develop a writing journey which allows children to learn the art of story writing by studying stories of a similar style, focusing on how effects are created and scaffolding children’s writing activities so they achieve success.
- Choose a focus When planning, consider what skill you want to embed for children and have that as your focus throughout the sequence of learning. For example, if you teach Y4 you might decide to focus on integrating speech into stories. When your class looks at a similar story, draw their attention to how the author uses speech and discuss how it advances the action and shows you more about the characters. During the sequence, your class can practise the technical side of writing speech (new line/new speaker, end punctuation, etc). When they come to write their own story, your success criteria will be focused on using speech effectively. By doing this, the skill of using speech is embedded. If you chose to focus on ALL the elements of story writing that a Y4 child should be using (fronted adverbials, conjunctions, expanded noun phrases, etc), this might lead to cognitive overload.
- Plan in chances to be creative Often teachers plan three writing opportunities: one where children retell the story, one with a slight difference (eg a different main character) and a final one where children invent their own story. However, in my experience, the third piece of writing often never happens because children have lost interest or time has run out. If we equip children with the skills, we must allow them time to use them.
- Utilise paired writing Children love to collaborate and by working in pairs it actually helps develop independence. Give it a go!
- Find opportunities for real audiences Nothing is more motivating than knowing you will get to share your story with another class, a parent or the local nursing home.
- Use high-quality stimuli If your focus is speech, find a great novel for kids that uses speech effectively. There are so many excellent children’s stories available that there’s no need to write your own.
- Use magpie books This is somewhere where children can note down any great words or phrases they find from their reading. It will get them reading as a writer.
Below is a rough outline of a planning format that leads to successful writing opportunities.
This sequence of learning takes around three weeks but may be longer or shorter, depending on the writing type.
Before planning out the learning, decide on up to three key focuses for the sequence. Think about the potential learning opportunities that the stimuli supports (eg don’t focus on direct speech if you’re writing non-chronological reports ).
| – | – | – |
|---|---|---|
| Engage with the stimuli through drama, reading comprehension, character work and short writing exercises. | Practise the writing focuses for the sequence. | Share writing genres and discuss the specific elements contained within, always referring back to your writing focuses. |
| Draw attention to the sequence focuses and how they are employed in the stimuli. | Do further short writing activities. These might be writing in a genre previously taught. | Write with modelling. Put scaffolds in place if needed. Hold one-to-one conferences if possible. |
Ways to overcome fear of creative writing
Many children are inhibited in their writing for a variety of reasons. These include the all-too-familiar ‘fear of the blank page’ (“I can’t think of anything to write about!” is a common lament), trying to get all the technical aspects right as they compose their work (a sense of being ‘overwhelmed’), and the fact that much of children’s success in school is underpinned by an ethos of competitiveness and comparison, which can lead to a fear of failure and a lack of desire to try.
Any steps we can take to diminish these anxieties means that children will feel increasingly motivated to write, and so enjoy their writing more. This in turn will lead to the development of skills in all areas of writing, with the broader benefits this brings more generally in children’s education.
Here are some easily applied and simple ideas from author and school workshop provider Steve Bowkett for boosting self-confidence in writing.
- Keep it creative Make creative writing a regular activity. High priority is given to spelling, punctuation and grammar, but these need a context to be properly understood. Teaching the technicalities of language without giving children meaningful opportunities to apply them is like telling people the names of a car engine’s parts without helping them learn to drive.
- Model the behaviour In other words, when you want your class to write a story or poem, have a go yourself and be upfront about the difficulties you encounter in trying to translate your thoughts into words.
- Go easy on the grammar Encourage children to write without them necessarily trying to remember and apply a raft of grammatical rules. An old saying has it that we should ‘learn the rules well and then forget them’. Learning how to use punctuation, for instance, is necessary and valuable, but when children try and apply the rules consciously and laboriously as they go along, the creative flow can be stifled. Consideration of rules should, however, be an important element of the editing process.
- Keep assessment focused Where you do require children to focus on rules during composition, pick just one or two they can bear in mind as they write. Explain that you will mark for these without necessarily correcting other areas of GaPS. Not only will this save you time, but also children will be spared the demotivating sight of their writing covered in corrections (which many are unlikely to read).
- Value effort If a child tries hard but produces work that is technically poor, celebrate his achievement in making an effort and apply the old ‘three stars and a wish’ technique to the work by finding three points you can praise followed by noting one area where improvements can be made.
- Leave room for improvement Make clear that it’s fine for children to change their minds, and that there is no expectation for them to ‘get it all right’ first time. Show the class before and after drafts from the work of well-known poets and extracts from stories. Where these have been hand written, they are often untidy and peppered with crossings out and other annotations as the writers tried to clarify their thoughts. If you have the facilities, invite children to word process their stories using the ‘track changes’ facility. Encourage children to show their workings out, as you would do in maths.
- Don’t strive for perfection Slay the ‘practice makes perfect’ dragon. It’s a glib phrase and also an inaccurate one. Telling children that practice makes better is a sound piece of advice. But how could we ever say that a story or poem is perfect? Even highly experienced authors strive to improve.
- Come back later Leave some time – a couple of days will do – between children writing a piece and editing or redrafting it. This is often known as the ‘cooling off’ period. Many children will find that they come back to their work with fresh eyes that enable them to pick out more errors, and with new ideas for improving the piece structurally.
- Try diamond 9 Use the diamond ranking tool to help children assess their own work. Give each child some scraps of paper or card and have them write on each an aspect of their writing, such as creating strong characters, controlling pace and tension, describing places and things, using ‘punchy’ verbs etc. Supply these elements as necessary, but allow children some leeway to think of examples of their own. Now ask each child to physically arrange these scraps according to how effectively they were used in the latest piece of work. So two writing elements that a child thinks are equally strong will be placed side by side, while an aspect of the work a child is pleased with will be placed above one that he / she is not so happy with.
- Keep it varied Vary the writing tasks. By this I mean it’s not necessary to ask children always to write a complete story. Get them to create just an opening scene for example, or a vivid character description, or an exciting story climax. If more-reluctant writers think they haven’t got to write much they might be more motivated to have a go. Varying the tasks also helps to keep the process of writing fresh, while the results can form resource banks (of characters, scenes, etc) for future use.
- Help each other Highlight the idea that everyone in the class, including yourself, forms a community of writers. Here, difficulties can be aired, advice can be shared and successes can be celebrated as we all strive to ‘dare to do it and do our best’.
Browse more ideas for National Writing Day .
Sign up to our newsletter
You'll also receive regular updates from Teachwire with free lesson plans, great new teaching ideas, offers and more. (You can unsubscribe at any time.)
Which sectors are you interested in?
Early Years
Thank you for signing up to our emails!
You might also be interested in...

Why join Teachwire?
Get what you need to become a better teacher with unlimited access to exclusive free classroom resources and expert CPD downloads.
Exclusive classroom resource downloads
Free worksheets and lesson plans
CPD downloads, written by experts
Resource packs to supercharge your planning
Special web-only magazine editions
Educational podcasts & resources
Access to free literacy webinars
Newsletters and offers
Create free account
By signing up you agree to our terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Already have an account? Log in here
Thanks, you're almost there
To help us show you teaching resources, downloads and more you’ll love, complete your profile below.
Welcome to Teachwire!
Set up your account.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Commodi nulla quos inventore beatae tenetur.
I would like to receive regular updates from Teachwire with free lesson plans, great new teaching ideas, offers and more. (You can unsubscribe at any time.)
Log in to Teachwire
Not registered with Teachwire? Sign up for free
Reset Password
Remembered your password? Login here

22 Writing Activities To Help Kids Hone Their Writing Skills

Written by Maria Kampen
Prodigy English is here! Get your students playing — and learning — today.
- Prodigy English
Fun writing activities
Creative writing activities, academic writing activities, at-home writing activities, daily writing activities, simple writing prompts for kids.
- How writing activities can bring reluctant writers out of their shells
Try some other educational activities
When kids start writing, they’re unlocking a whole new world of imagination to explore. It’s a great way for them to be creative, express themselves and practice key reading and writing skills.
But as most kids — and adults — will tell you, writing is hard! It can be intimidating to put pen to paper for the first time, and sometimes the challenge of a blank page seems like too much to overcome.
Writing shouldn’t be scary for kids. These 22 fun writing activities can help them:
- Use their imagination
- Think up new stories and ideas
- Share their writing with friends and family
Use them in your classroom or at home to get kids excited about writing!

Writing is supposed to be fun! Use these activities to help kids stretch their imagination and record their thoughts on paper in a fun, low-stress environment.
1. Try online ELA games like Prodigy English
Great for: Grades 1 to 6
Online games are a great way to engage students in the learning process — and Prodigy English is bringing the power of game-based learning to language and reading skill practice!
As students build and create, they’re always practicing key reading and language skills that help them write clearly and effectively. Every correct answer gives players more energy to gather resources, complete daily tasks and earn Wishcoins.
Plus, you can send questions about the topics you want them to practice and collect insights about their learning.
2. Poetry scavenger hunt
Great for: Middle and high school students
Words are all around us, so encourage your students to take inspiration from the real-life writing they see every day. Have students collect printed words and phrases from the world around them, including:
- Magazine ads
- Graphic novels
- Newspaper headlines
- Social media captions
Students can collect and arrange their words on a piece of paper to make a unique piece of poetry. Encourage them to find a key idea and expand on it in creative ways, then have students share their work with the class.
3. Create your own comic strip
Great for: Grades 4 to 10
Students learn in all sorts of ways. For visual learners, creating a comic strip to accompany their story can help them express themselves in a visual medium.
Give students a set number of panels and challenge them to come up with a quick story — just a few sentences. Then, they can illustrate their scene in the style of comic books.
Remind students the point isn’t to be the best artist — it’s to write a story that’s short and exciting.
4. Create your own Madlib
Great for: Elementary and middle school students
Give students vocabulary practice and help them write a silly story at the same time!
Fill a sheet with the outline of the story, then remove key words like:
For younger students, add a word bank to get them started. As students fill in words, they’ll craft a unique story filled with unexpected twists and turns.

Once students start getting in the habit of writing, these creative writing activities can pull new ideas out of their heads and encourage them to experiment with different genres.
5. Acrostics
Great for: Grades 3 to 8
Acrostic poems are a great way to introduce your students to poetry! Start with a meaningful word or name and use it as a theme for the poem.
Writing the word vertically, students can go down the letters and write a short word or phrase that starts with each letter. Acrostic poems help students write within a structure and theme, so it’s easier for them to get started.
6. A letter to your future self
Great for: Middle school and high school
Where do your students see themselves in a year? Five years? Ten years?
A letter to their future selves is a great way for students to explore their own story, and brainstorm what they want to achieve. Not only can students practice their letter-writing skills, they can use their imaginations to develop a growth mindset .
For extra nostalgia, store the letters for students and mail them out once the right amount of time has passed.
7. Write a “Choose your own adventure” story
Great for: Grades 5 and up
Whether it’s a fairy tale, detective story or drama, chances are you’ve had a student tell you they don’t know how their story is supposed to end.
A “Choose-your-own-adventure” story lets students brainstorm different storylines and endings. Once they’re done, encourage them to share their stories with the class so their peers can go on the adventure too.
8. Write a fake advertisement
Great for: Grades 6 and up
Good writing doesn’t just happen in books — it’s all around us!
Whether students are writing advertisements on their own or as part of a project-based learning assignment , this activity helps them build key media literacy skills and practice their snappy storytelling.
Have students make up a new product and advertisement, or encourage them to re-imagine an ad for something they love. It’s also a great way to bring media literacy and interdisciplinary learning to your classroom.
9. Make a story map
Great for: Grades 2 to 8
Not every student is going to be comfortable putting pen to paper right away. Story maps can help students brainstorm details like plot, characters and setting in a way that makes sense for visual learners.
Have students use charts to set out the beginning, middle and end of their stories. Mind maps can also help them plot out details about their characters or setting.
Encourage students to present their story map as a finished product or use it to start writing!

Writing isn’t all fairy tales and short stories — it’s also an important part of learning in middle school, high school and college. Use these academic writing activities to help students understand proper essay structure, grammar and more.
10. Story chains
Great for: Grades 4 to 8
Stories are better when they’re enjoyed with friends and classmates. And story chains encourage every student to get involved!
Put students in small groups of three to six. Give each student a blank piece of paper and have them write the beginning of a story. Then, pass it to the next student in the group so they can write what happens next.
For extra educational value, have students work together to summarize a story from your lesson or an important historical event.
11. Persuasive essays
Sometimes writing is about more than just telling a story. It’s about convincing your readers of your point of view.
Have older students practice their debate skills with persuasive essays. Start with a prompt, then let students make their case. Some of our favorite prompts for this writing assignment include:
- Is it more important to be right or to not hurt someone else’s feelings?
- What important historical figure do you think belongs on the ten-dollar bill and why?
- Do you think you’re born with your personality traits, or do you gain them as you grow up?
Most importantly, make sure students back up their opinions with solid facts and arguments that convince readers to care.
12. Solve a real-world problem
Great for: Grade 6 and up
Climate change, litter, bullying, bad cafeteria food — no matter what students pick, there are lots of real-world problems for them to solve.
Challenge students with a writing assignment that addresses a problem they see in their world. How would they fix it? Whether it’s a short paragraph or a longer essay, encourage them to find something they’re passionate about. After all, that’s where good writing comes from!
13. Vocabulary challenge
Great for: Elementary school students
Vocabulary challenges combine vocabulary strategies with student writing to make your next language arts lesson plan even more engaging.
Give students a new word (or two or three). Once you’re done practicing it and they know what it means, challenge them to use it in a story as creatively as possible.
14. Teach citations
Great for: Grades 1 to 12
Footnotes, endnotes and bibliographies are the least exciting part of writing, but they’re essential skills. As students write more complex research papers, they need to know how to give credit where credit is due. Thankfully, there are lots of online resources to help!
The Purdue Online Writing Lab offers teachers and students resources for all stages of the writing process, including citations. To practice, students can write an annotated bibliography as part of a project-based learning assignment or the first step in writing a longer research paper.

Writing isn’t just something happening in the classroom. These at-home writing ideas can help you support your child as they experiment with prose and poetry.
15. Write letters to a pen pal
Great for: Grades 3 and up
Everyone likes getting mail! Got a friend with kids in a different part of the country, or far-away family members? A pen pal can be a great way for kids to build friendships and practice their writing skills at the same time.
16. Bring a home object to life
“It’s as big as a mountain!”
“That’s the fluffiest thing I’ve ever felt!”
The ways kids describe things can crack us up sometimes. Full of wonder and hyperbole, it’s the perfect spark for creative writing, too.
Encourage kids to practice their figurative language skills with a description of something in your home. Let them pack as much alliteration and exaggeration into the description as they can, then do a dramatic reading out loud.
17. Write reading reactions
If you want to boost reading comprehension and writing skills at the same time, this is the perfect activity. After your child is done reading, encourage them to write a few sentences about what they just read.
Did they like it? What do they think happens next? Which character was their favorite and why? Learning how to express opinions in writing is a valuable skill.
18. Document family stories
Great for: Grades 4 and up
Every family has a unique story, including yours. Make memories with your child when you share stories about important family events or your childhood.
Kids can even interview grandparents, aunts and uncles to record their memories. When you’re done, store them in a shared space so everyone can go back and reminisce.

Writing is a muscle, and you have to flex it every day to get stronger. Use these daily writing activities to make writing part of your everyday routine.
19. Journaling
Great for: Everyone
Sometimes, you’ve just gotta write it out.
Whether you’re trying to make sense of life or just need a place to organize your thoughts, journaling is a great way to unwind, practice mindfulness and build social emotional skills .
All kids need to get started is a notebook and a pen. Let them know you’re not going to read it, but they’re welcome to come to you if there’s something they want to talk about.
20. Blog about your interests
Great for: High school and up
Everyone’s passionate about something. Whatever your students love, encourage them to share it with the world! Blogging is an accessible and fun way to express themselves, nerd out about the things that bring them joy and share their opinions with the world.
Sites like WordPress and Wix offer free website builders to help students get started. This is a great way for kids to build computer skills and digital literacy .
21. Free writing
Write, write, write and don’t stop. That’s the premise behind free writing, a writing practice that can help unlock creativity, discover new ideas and take the pressure out of a blank page.
Give students a five-minute timer and challenge them to write continuously, without worrying about formatting, spelling or grammar. They can write about whatever they want, but there’s only one rule: don’t stop.
22. Answer daily writing prompts
Make time to exercise your brain with daily writing prompts! At the start of the day or as a quick brain break , set aside time for students to respond to a quick daily writing prompt.
Students should have a dedicated journal or binder to make it a seamless part of your lessons. Whether or not you choose to read their writing is up to you, but it’s important to build good daily habits.

A blank page can be a scary sight for a student who doesn’t know what to write about.
Use writing prompts to:
- Kickstart a student’s imagination
- Start your lesson with a fun writing activity
- Give students a topic to debate in writing
Some of our favorite simple writing prompts include:
- Write a story about a wooden door, a can of soda and a blue shoe.
- If you met a monster looking for new friends, what would you do?
- What’s your favorite season? What makes it the best?
- If you could live anywhere in the world, where would it be and why?
- Describe your dream birthday cake.
- Write a story about being cold without using the word “cold.”
- If you could decorate your bedroom any way you wanted, what would it look like?
- Is it better to have lots of friends or just a few really good friends?
- Write a story in 10 words or less.
- Write a story about the best surprise you’ve ever received.
For more writing prompts you can use in and out of the classroom, check out our full list of 225 writing prompts for kids .
Writing activities can bring reluctant writers out of their shells
Writing is hard and can be intimidating for a lot of students.
But even the quietest and most reluctant students have lots of stories to tell! You just have to encourage them to get their words out.
Writing activities help remove some of the pressure and give students:
- A fun way to approach writing
- A starting point for their stories
- Chances to share their writing with students
No two stories are the same, just like your students. Every story can start in a different way, and that’s the beauty of writing prompts.
Whether it’s writing activities or math problems, there are lots of ways to get reluctant learners excited about your lessons with educational activities.
Here are some of our favorites:
- 37 Quick & Easy Brain Breaks for Kids
- 30 Virtual School Activities Students & Educators Love
- 27 Best Educational Games for Kids to Play Sorted by Subject
- 15 Geometry Activities to Engage Students Across Grade Levels
- 36 Fun Word Games for Kids To Help with Vocabulary & Literacy
- 15 Fun, Free & Effective Multiplication Games For Your Classroom
- 20 Exciting Math Games for Kids to Skyrocket New Math Skills On-The-Go
- 21 Classroom Games to Boost Teacher Effectiveness and Student Learning
- 25 Social Emotional Learning Activities & How They Promote Student Well-Being
Which ones can you use in your next lesson?
Prodigy English is a brand-new game-based learning platform helping students build key math skills. As students explore and build a world of their very own, they’ll answer curriculum-aligned reading and language questions that help build essential skills and encourage a love of learning.
Sign up for your free teacher account and get access to teacher tools that help you differentiate learning and track student progress as they play.

Explore issues at the heart of literacy in education with our Bedrock Talks podcast. New episodes now available.

Literacy | Primary schools
9 strategies for improving writing skills in primary school
By Michelle Casey
06 Jan 2023

In this article:
The importance of building writing skills in primary years
Understanding 5 basic writing skills, spelling and punctuation, handwriting, reading comprehension, sentence structure, how to improve learners’ writing in primary school, 1. teach the different writing styles, 2. encourage regular reading in the classroom and at home, 3. give learners a real-life situation to write about, 4. encourage students to keep a diary, 5. give learners opportunities to read aloud, 6. use sentence starters and prompts, 7. engage in cooperative writing, 8. get creative with the teaching, 9. encourage parents to help at home, how bedrock helps primary pupils develop strong writing skills.
Learners use writing as a vehicle through which to express themselves and their ideas, both in and out of the classroom, in every subject across the curriculum. By improving learners’ writing skills, you prepare them for success in wider life.
In this guide, you will find practical advice for teachers on developing fundamental writing skills within the primary classroom.
The ability to express ideas in writing is one of the most important of all skills. Good writing is a mark of an educated person and, perhaps for that reason, it is one of the most important skills sought by employers and higher education institutions (Conley, 2003; Schmoker, 2018).
Developing our learners as writers is more than just asking them to remember tricky spellings, handwriting joins or grammatical constructs. It is a process which is intricate and complicated, but if done consistently and thoroughly, gives learners a tool which is vital for their school years, across all subjects and in life after education.
Writing makes learners’ thinking and learning visible. It provides them with the opportunity to clarify and refine their ideas for others and to themselves.
For learners to progress in their writing, they must have a solid understanding of the 5 basic writing skills and plenty of opportunity to practise and develop these skills.
Grammar is the system and structure of a language and comes with certain rules . It underpins how words are put together meaningfully and sentences are constructed. When writers use good grammar, they can effectively communicate what they want the reader to know. Through learning about nouns , punctuation , tense and aspect , brackets , semicolons , and connectors , learners can make their writing clearer and control its impact on their readers.
Spelling instruction helps learners to develop a connection between letters and their sounds. It also helps learners to recognise high-frequency common exception words. Teaching students strategies for spelling supports them in communicating effectively through writing.
While sentences can be written without punctuation, writing becomes a lot more effective if punctuated correctly. Good punctuation allows writers to convey what they mean and enables readers to understand the intended message or meaning. Every piece of punctuation has a particular role; they all work to give clarity and meaning to our written words.
Read more about the rules behind punctuation.
Handwriting is an important skill for learners to develop. Poor handwriting can harm school performance.
If a learner views handwriting as something arduous, this can reduce their motivation to write. This lack of motivation may lead to a reduction in practice which can further compound handwriting difficulties.
When learners can write comfortably, legibly and at a good pace, it gives them more ‘mental space’ to think about the content and creativity of their writing, as opposed to the logistics.
Learn more about handwriting in primary school.
Reading comprehension is the capacity to read a piece of text and understand the meaning or intent. It is important in the development of writing skills. Before learners can write with meaning, they need to be able to read.
The skills developed in reading and reading comprehension activities feed into many skills required for effective writing. It helps them to:
- Sound out and blend words for meaning
- Extend their vocabulary and learn how to use it contextually
- See how words in a paragraph or in a sentence relate to each other
When the concept of reading at a base level has been achieved, learners can then start to think about a text critically ; they can infer meaning and intent and transfer this to their own writing. As well as this, reading comprehension relies on a strong understanding of vocabulary and grammar ; writing skills work together and strengthen one another.
For writing to progress, learners should have a good grasp of sentence structure. They should know the basic types of sentences : simple, compound and complex.
Learners should also be able to modify sentence structure for effect - for example, by using fronted adverbials or passive voice. Learning different ways they can structure a sentence helps learners convey their intended meaning in their writing.
Improve primary learners' writing skills
Explicit vocabulary and grammar instruction through a deep-learning algorithm to support learners of all abilities.
Teaching learners to recognise the different genres of writing and their characteristics and purpose will help them to implement these techniques in their own writing.
Throughout their schooling, learners should be exposed to a wide variety of nonfiction, narrative and poetry texts.
Within nonfiction , they will be exposed to explanation texts to inform; non-chronological reports to explain and persuasive texts to persuade and entertain, to name a few.
Within narrative texts , learners will examine stories with dilemmas, traditional tales and stories in a historical setting, among others.
Learners will also have the opportunity to explore poetry including structured poetry, visual poetry and free verse .
Learners should be given the opportunity to become familiar with a text type and its features. They should examine the language used, sentence structure, grammatical features and layout. They could highlight and annotate features of the text as they identify them - in this way, they form a kind of checklist for their own writing.
Well-chosen texts provide learners with good-quality models for their writing. In this way, they are exposed to rich language structures which lets them see how writing works and the effect it can have on the reader. Students draw on their reading experiences when producing their own writing.
Learners should be exposed to these high-quality texts across a range of genres, demonstrating a variety of writing styles. It is important that the texts chosen reflect the social and cultural diversity of the class while introducing them to a world outside the familiar.
This exposure can involve Independent Reading, Guided Reading, Shared Reading and just good old Reading for Pleasure, where the teacher or the learners take the lead.
According to the Centre for Literacy in Primary Education (CLPE), ‘Reading texts to children that they are not ready to access independently exposes them to language they can own.’ This gives those struggling readers an opportunity to be enriched by high-quality vocabulary with the right scaffolding .
Learners should be given plenty of opportunities for regular reading in the classroom. Some schools implement a whole-school policy whereby one session per week or fortnight is blocked out for Reading for Pleasure.
Reading is often not only encouraged but required as part of homework tasks. It is normal for there to be certain expectations for reading sessions to be carried out at home. This is often a book from a specific level that the teacher has matched to the learner’s reading ability. However, whatever age-appropriate texts students are reading at home is beneficial: magazines, catalogues, leaflets, websites, and books from home.
Parents/guardians should be encouraged to read with students at home too; this gives learners another perspective on the text from their parent/guardian and (hopefully!) helps foster a love, or at least a like, for reading.
When learners are writing, they should be clear on who their intended audience will be. Will it be their peers? Younger students? The headteacher? The King? The MD of a company?
In being clear on their intended audience, learners can further develop their understanding that writing is a tool for communication and expression. And of course, writing is not limited to literacy lessons - writing is used across all subjects, which gives learners even more opportunity to write for an intended audience and purpose.
The teaching of writing is more effective when learners see the purpose of it, and with an audience in mind, they can adapt their tone accordingly.
Some examples of writing students could produce inspired by text or real life:
- A letter to the headteacher persuading him/her to allow a longer break time.
- A newspaper report on a school/ local event.
- Instructions on how to play Minecraft (or another game that is relevant and appropriate to them).
- Within a topic (e.g., superheroes), learners create their own superhero, then write an explanation text to explain the superhero’s powers, special gadgets, crimes/issues targeted and how they became a superhero.
- After reading a story or part of a story, learners write about an event from a character’s point of view not presented in the text.
Children could have access to free writing journals and, if possible (in the jam-packed curriculum we are all navigating!), time to develop their own personal writing projects, allowing their personal writing style to emerge.
With the popularity of diary-style series like Wimpy Kid and Tom Gates, the idea of keeping a diary may be very attractive to some learners. It is a good way to get children writing outside the classroom environment. Learners who keep a diary are twice as likely to exceed age expectations in writing .
According to the National Literacy Trust , the vast majority of children state that they enjoy writing more when they can choose what to write about. If learners can begin to derive pleasure from writing in this way, then hopefully this can be transferred to writing in a more formal setting.
Giving learners the opportunity to read aloud enables them to hear how punctuation and sentence structure combine in the sentences they read. It may even help them to think more deeply about perspective as they read from the point of view of new characters.
Reading aloud also provides the teacher with chances to correct misconceptions, such as mispronunciations and new vocabulary. These are all skills that can be channelled into their own writing composition.
As well as this, reading aloud is a good way to celebrate a student’s written work - they can present their achievements to their classmates.
Providing students with sentence starters can help with writing flow. It provides reassurance that they are on the right track in their writing. With all the different writing genres our learners are exposed to and then expected to write, it can be beneficial for some learners to have this scaffold .
Sentence starters could be in the form of a ‘word bank’ on the board or on a piece of paper, generated by the teacher. To give learners a little more ownership, this ‘word bank’ of sentence starters could be generated as a class and left on display.
More independent learners may enjoy coming up with their own word banks as they read texts; they can ‘magpie’ sentence starters they’d like to use for their writing.
Cooperative writing is a useful tool in helping learners on their writing journey.
One aspect of this is shared writing. It involves the teacher crafting a piece of writing on a whiteboard. The learners are encouraged to give input, often aided by teacher questioning and prompts. The result is a collaborative passage which learners can use to help with their independent writing.
Another type of cooperative writing is modelled writing. This requires less student input, but the students get to watch the act of writing. The teacher might write a sentence, and then articulate their thought process as to how the vocabulary in the sentence can be improved or what form of punctuation would work best here. In this way, learners can see the strategies the teacher draws on as he or she writes.
A third method of cooperative writing is guided writing. This involves the teacher working with a smaller group of children within the lesson (when the others are ‘on task’). This usually focuses on a specific objective that this group in particular needs support with, e.g., adding more detail to writing by using fronted adverbials. In this approach, the children usually produce their own writing in their English books with the teacher prompting and questioning.
Where possible, try to connect what the children are interested in with their writing. For example, if you have learners interested in Minecraft, they could write a letter of persuasion to the Prime Minister to persuade him to allow Minecraft lessons in school .
Another way of getting the children interested and excited about writing is to use humour. Show learners two emails to compare - both could be complaining about something. One could be written using formal language and the other could be written informally, bordering on being rude.

This lets learners see the effect of both pieces of writing.
Another way to use humour is in writing an explanation text. It could be about something perceived as mundane such as ‘How a Dishwasher Works’ but could be made humourous in the following way:

Children can then use this to write their own explanations in a similar way.
Another idea is to set something up to happen, e.g., to use the superhero topic again - have an adult in school dress up as a ‘thief’ and another adult as a superhero. They could burst into your classroom at an agreed time and have a very dramatic ‘chase’ around the room and the superhero could catch the ‘thief’. Of course, you would have to consider the children in your class and if this would be appropriate for them. This dramatic action could be a good springboard to inspire children to write.
It is important to encourage parental support with writing at home . Parents may need guidance in how they can help their children with writing at home. It might be a good idea to put together a list of ways they can help, for example:
- Allow children to help with everyday writing such as emails, shopping lists, writing birthday cards.
- Try to make sure your child has an area (no matter how big or small) where they can write, as well as the tools for writing.
- Let children write about what interests them: a recipe they have helped make, a film review, a similar story to one they have read, similar lyrics to a song they have heard.
Talking homework tasks are a good way to involve parents. Talking homework is used as part of Ros Wilson’s Big Write approach. Big Writing is when learners produce an extended piece of writing independently.
The night before the Big Write, learners are given a homework task to discuss their ideas with someone at home, for what they could write the next day. This means children are getting lots of input and parents are sharing in the learning.
To learn to write, students need a blend of different skills such as vocabulary knowledge, grammar knowledge, an understanding of sentence structure, fine motor skills and more. While some of these skills come down to dedicated instruction in the classroom, such as when transcribing and practising handwriting, some of the fundamental skills of writing can be boosted by a digital literacy curriculum such as Bedrock Learning.
Bedrock’s vocabulary curriculum teaches learners aged 6-16 the Tier 2 vocabulary they need to thrive, from Year 3 level all the way to advanced reading and vocabulary. Tier 2 vocabulary is taught through an intelligent Block system, ensuring each learner is placed into the right Block for their reading level - this ensures the texts are challenging, yet accessible. The smart Block system differentiates teaching for learners of different abilities, stretching confident readers and supporting struggling readers.
In addition to this, Bedrock’s core curriculum teaches vocabulary alongside a complete grammar curriculum, differentiated for primary and secondary learners . Grammar is taught through bespoke fiction and nonfiction texts , engaging teaching videos and mastery tasks , ensuring long-term retention.
Informed by the National Curriculum, Bedrock’s core curriculum not only teaches learners the grammar they need for their KS2 SATs , but also combines grammar and vocabulary instruction to boost reading comprehension and writing skills overall.
Discover how Bedrock’s curricula can support your learners throughout primary school - and beyond!
Related Articles
Primary schools
How literacy prepares primary pupils for SATs
News | Primary schools
The Key Stage 2 Attainment Report 2022: 4 things you need to know
Explicit literacy instruction, the uk's #1 literacy solution.
Explicit vocabulary, grammar and GCSE English instruction to support learners across the curriculum and beyond the school gates.
Don't forget to share:
You might also discover…

08 Nov 2022

01 Nov 2022
Model Composition for Primary School
Good english composition examples for primary school.
The model compositions compiled here are written by our students. These are good English composition examples and they give you an idea of what primary school students are capable of writing.
We take in a wide range of students in our weekly writing classes and online courses . Some of them are excellent writers but they join us to receive constructive feedback and regular writing practice to continue honing their writing skills. Others are weaker in their writing and need professional guidance from an experienced writing teacher. As long as the child is willing to learn and has a positive attitude, we welcome him/her!
Some of these model compositions featured here are written by our online Writing Academy and Junior Writing Academy students. Others are written by students attending our weekly writing classes conducted by our Writing Coaches. All our Writing Coaches are either former MOE primary school teachers or tutors who are experienced in teaching English and creative writing.
Click here to take a look at how our Writing Coaches mark our student’s compositions based on Content and Language.
The model compositions are grouped according to level. This compilation will be updated as and when we have good English composition examples written by our students. Enjoy reading the stories written by our young writers!
Model Compositions Written By Our Students
A Kind Deed
Lost and Found
A Celebration Gone Wrong
An Adventure
An Embarrassing Incident
A Dangerous Act
A Fortunate Escape
Overcoming A Problem

DOWNLOAD OUR FREE PSLE MODEL COMPOSITION EBOOK TODAY!
*Includes application and analysis of writing techniques
Click on the icon below to chat on WhatsApp or email us at [email protected] or self-help with our FAQs .
Prompt response during working hours on weekdays/Saturdays.

- Services for education institutions
- Academic subject areas
- Peer connection
- Evidence of Studiosity impact
- Case studies from our partners
- Research Hub
- The Tracey Bretag Integrity Prize
- The Studiosity Symposium
- Studiosity for English learners
- Video case studies
- Meet the online team
Academic Advisory Board
Meet the board.
- Social responsibility
- Meet the team
- Join the team

Practice Writing Prompts
Writing prompts for students from Year 3-6, including creating writing, poetry, opinion pieces and newspaper articles.
To become a good writer, you'll need to practise, practise, practise. If you're short on ideas, use our prompts to get started.
- Write an Ode to your favourite food.
- Write a poem from the point of view of an item in your home.
- Write a Haiku that describes your feelings today. What's a haiku? A three-line poem with seventeen syllables, written in a 5/7/5 syllable count.
- Choose your favourite book or film and write a review convincing other people why it’s great.
- Think of one of your least favourite books or films and write a review explaining why it is not so great.
Opinion Piece
- What would be the best Superpower to have? Explain your answer.
- Should schools have uniforms? Why or why not?
- Which are better? Dogs or cats? Explain why.
Newspaper Article
- Your house was robbed! Write an article describing what happened including a headline and a statement from the Police.
- You won an award! Write an article describing what the award was for and what happened at the award ceremony. Include a headline and a quote from yourself.
Creative Writing
- What would be your best holiday ever? Where would you go and what would you do?
- Write a story starting with: “No one ever visited the big house at the end of the street. I should not have done it either.”
- Start a story with: “It was the most beautiful thing I’d ever seen.”
- Choose one of the pictures below and write a story about the scene:

Want to print this out?
Download the writing prompts pdf here.

ABN 41 114 279 668
Student zone, assignment calculator, calendars and organisers, study survival guides, free practice tests, student faqs, download our mobile app, student sign in, success stories.
Student Reviews & Testimonials
Specialist Sign In
Meet our specialists
Meet the team, media and research, student reviews.
Read more on Google

Studiosity acknowledges the Traditional Indigenous Custodians of country throughout Australia, and all lands where we work, and recognises their continuing connection to land, waters, and culture. We pay our respects to Elders past and present.
Contact • FAQ • Privacy • Accessibility • Acceptable Use • Terms of Use AI-for-Learning Polic y • Academic Integrity Policy
- International
- Topical and themed
- Early years
- Special needs
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search
Primary creative writing resources
- Grammar and punctuation
- Guided reading
- Phonics and spelling
- Whole School Literacy
All Creative writing subjects
- Creative writing
- Handwriting
- Language and linguistics
- Non-fiction
- Research and essay skills
- Speaking and listening
Tes primary English resources has an unrivalled range of teaching ideas for creative writing activities. Breathe new life into your lesson plans for KS1 and KS2 with our resources and materials, including: - Creative writing worksheets and activities - Writing activities - Storytelling projects And that's just the beginning! All Tes primary teaching resources are created by teachers, for teachers and have been successfully tried and tested in KS1 and KS2 classrooms.
- Resources Home

NEW: England Reaches Euro 2024 Final! Reading of LATEST Event from the Euros

The Twits Chapter 29 Ending a story

The Twits Chapter 28 Dilemma in story writing

The Twits Chapter 27 Story build up writing

The Twits Chapter 26 Beginning a Story

The Twits Chapter 25 Planning a Story

The Twits Chapter 24 planning a story

The Twits Chapter 23 Tenses

The Twits Chapter 22 Features of instructions

The Twits Chapter 21 Up level sentences

The Twits Chapter 20 Acrostic poems
- Create new account
- Reset your password
Register and get FREE resources and activities
Ready to unlock all our resources?
What is creative writing?

Narrative or creative writing will be developed throughout a child's time at primary school. This table gives a rough idea of how story structure, sentence structure, description and punctuation are developed through story-writing lessons at school. (Please note: expectations will vary from school to school. This table is intended as an approximate guide.)

Download a FREE Creative Writing toolkit!
- KS1 & KS2 workbooks
- Bursting with fill-in prompt sheets and inspiring ideas
- Story structure tips, style guides and editing suggestions
Creative writing in primary school
Story structure Events in a story in an order that makes sense.
Sentence structure Joining two clauses in a sentence with the word 'and.'
Description Simple adjectives to describe people and places.
Punctuation Use of capitals, full stops, exclamation marks and question marks.
Year 2 Story structure Stories sequenced with time-related words such as: then, later, afterwards, next.
Sentence structure Starting to use sentences with two clauses connected by 'and,' 'but,' 'so,' 'when,' 'if' and 'then.' Keeping the tense of the writing consistent.
Description Using a broader range of adjectives.
Punctuation Using capital letters, full stops , question marks , exclamation marks , commas for lists and apostrophes for contracted forms (e.g. they're) and the possessive (e.g. 'Sarah's pen').
Year 3 Story structure Stories structured with a clear beginning, middle and end. Starting to write in paragraphs.
Sentence structure Continuing to use sentences with two parts, linked with connectives such as 'because', 'but' and 'so'.
Description Broad range of adjectives plus some powerful verbs .
Punctuation Using all of the punctuation above. Starting to use some speech punctuation .
Story structure Gaining confidence with structuring a story and with organising paragraphs .
Sentence structure Using sentences connected with more sophisticated connectives such as because,' 'however,' 'meanwhile' and 'although.'
Description Using a range of adjectives, powerful verbs and adverbs. Some use of similes . Using fronted adverbials (placing the adverb at the start of the sentence, e.g. 'Quickly, the children stood up').
Punctuation Increasingly accurate use of speech punctuation. Using commas after fronted adverbials .
Story structure Good structure of description of settings , characters and atmosphere. Integrating dialogue to advance the action. Using time connectives to help the piece of writing to come together.
Sentence structure Using a range of connectives to connect parts of sentences.
Description Using adjectives, powerful verbs and adverbs. Possibly some use of figurative language such as metaphors , similes and personification .
Punctuation Using brackets , dashes or commas to indicate parenthesis .
Story structure Continuing to structure stories confidently. Using adverbials such as: in contrast, on the other hand, as a consequence.
Sentence structure Using more sophisticated connectives like 'although,' 'meanwhile' and 'therefore.' Using the passive form. Using the subjunctive .
Description Continuing to use a range of descriptive language (see above) confidently.
Punctuation Using all of the previously mentioned punctuation correctly. Using semi-colons , colons and dashes to mark the boundary between clauses.
How creative writing is taught in primary schools
When teachers teach creative writing, they usually follow the units suggested by the literacy framework, including the following:
- stories with familiar settings
- stories from other cultures
- fairy tales (also known as traditional tales )
- fantasy stories
- myths and legends
- adventure and mystery
- stories with historical settings.
Teachers will start with a text that they are confident will engage the interest of the class. It is often a good idea to find a well-illustrated text to bring the story alive further. They will spend a week or two 'loitering on the text', which will involve tasks where characters and scenarios from the text are explored in-depth. These tasks may include:
- Drawing a story map or mountain to get an idea of the structure of the story
- Writing a letter from one character to another
- In pairs, improvising a conversation between two characters in the story
- Making notes on a spider diagram about a particular character
- Writing the thoughts of a character at a particular point in the story
- Writing a diary entry as one character in the story
Once teachers feel that the text has been thoroughly explored, they will guide the children in writing their own version of the story . This involves planning the story, brainstorming characters and setting and then writing a draft of the story. Children will then be encouraged to edit and re-write their draft. Teachers may mark the draft and write their own suggestions on it, or they may ask children to swap their writing with their partner and encourage them to make suggestions on each other's work. Throughout this process, teachers are aiming to encourage children to develop skills in the above four sections of the table: story structure, sentence structure, description and punctuation.
Finally, children will write up a 'neat' finished version of their writing. Teachers often give children a format for doing this, such as bordered paper on which they can add illustrations, or a booklet for which they can design a front cover.

Give your child a headstart
- FREE articles & expert information
- FREE resources & activities
- FREE homework help
More like this

Teaching creative writing in primary schools: a systematic review of the literature through the lens of reflexivity
- Open access
- Published: 17 June 2023
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Georgina Barton ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2703-238X 1 ,
- Maryam Khosronejad 2 ,
- Mary Ryan 2 ,
- Lisa Kervin 3 &
- Debra Myhill 4
6527 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Teaching writing is complex and research related to approaches that support students’ understanding and outcomes in written assessment is prolific. Written aspects including text structure, purpose, and language conventions appear to be explicit elements teachers know how to teach. However, more qualitative and nuanced elements of writing such as authorial voice and creativity have received less attention. We conducted a systematic literature review on creativity and creative aspects of writing in primary classrooms by exploring research between 2011 and 2020. The review yielded 172 articles with 25 satisfying established criteria. Using Archer’s critical realist theory of reflexivity we report on personal, structural, and cultural emergent properties that surround the practice of creative writing. Implications and recommendations for improved practice are shared for school leaders, teachers, preservice teachers, students, and policy makers.
Similar content being viewed by others

Re-imagining narrative writing and assessment: a post-NAPLAN craft-based rubric for creative writing

Radical rubrics: implementing the critical and creative thinking general capability through an ecological approach

Autofictionalizing Reflective Writing Pedagogies: Risks and Possibilities
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Creative writing in schools is an important part of learning, assessment, and reporting, however, there is evidence globally to suggest that such writing is often stifled in preference to quick on-demand writing, usually featured in high-stakes testing (Au & Gourd, 2013 ; Gibson & Ewing, 2020 ). Research points to this negatively impacting particularly on students from diverse backgrounds (Mahmood et al., 2020 ). When teachers teach on-demand writing typical pedagogical traits are revealed, those that are often referred to as formulaic (Ryan & Barton, 2014 ). When thinking about creative writing, however, Wyse et al. ( 2013 ) noted that it involves the absence of structure and teaching creative writing requires an ‘open’ pedagogical approach for students to be given imaginative choice. By this, they mean that teachers need to consider less formulaic ways to teach writing so that students can experience different opportunities and ways to write creatively. They argued that if students are not given the flexibility to experiment through writing then their creativity might be stifled. Similarly, Barbot et al. ( 2012 ), who carried out a study with a panel of 15 experts of creative writing, posited that creative writing is when students draw on their imagination and other creative processes to create fictional narratives or writing that is ‘unusually original’. They also noted that creative writing is important for the development of students’ critical and creative thinking skills and ways in which they can approach life in creative ways.
Creative writing is defined in various ways in literature. Wang ( 2019 ) defined creative writing as a form of original expression involving an author’s imagination to engage a reader. Other definitions of creative writing involve the notion of children’s imagination, choice, and originality and much research has explored the concept of creativity within and through the writing process.
While creative writing is defined in various ways, and the many ways that it is treated in literacy education, this article is not concerned with the nature of the term per se. Rather, it focusses on research about creative writing and creativity in writing to understand how research unpacks the personal and contextual characteristics that surround creative writing practices. To this aim, we adopt a broad definition of creative writing as a form of original writing involving an author’s imagination and self-expression to engage a reader (Wang, 2019 ). Creative writing is important for children’s development (Grainger et al., 2005 ), allowing them to use their imagination and broaden their ability to problem-solve and think deeply. Creativity in writing refers to specific aspects within a writing product that can be deemed creative. Some examples include the use of senses and how a writer might engage a reader (Deutsch, 2014 ; Smith, 2020 ).
International research on teaching writing has indicated a loss in innovative or creative pedagogical practices due to the pressure on teachers to teach prescribed writing skills that are assessed in high-stakes tests (Göçen, 2019 ; Stock & Molloy, 2020 ), often resulting in specific trends including teaching a genre approach to writing (Polesel et al., 2012 ; Ryan & Barton, 2014 ). A comprehensive meta-analysis by Graham et al ( 2012 ), designed to identify writing practices with evidence of effectiveness in primary classrooms, found that explicitly teaching imagery and creativity was an effective teaching practice in writing. In addition, a review of methods related to teaching writing conducted by Slavin et al. ( 2019 ) included studies that statistically reported causal relationships between teacher practice and student outcomes. Common themes in Slavin et al’s ( 2019 ) quest for improving writing included comprehensive teacher professional development, student engagement and enjoyment, and explicit teaching of grammar, punctuation, and usage. While they did not specifically cite creativity, motivating environments and cooperative learning were important characteristics of writing programs.
This systematic literature review aims to share empirical international research in the context of elementary/primary schools by exploring creativity in writing and the conditions that influence its emergence. It specifically aims to answer the question: What influences the teaching of creative writing in primary education? And how can reflexivity theorise these influences? The review shares scholarly work that attempts to define personal aspects of creative writing including imagination, and creative thinking; discusses creative approaches to teaching writing, and shows how these methods might support students’ creative writing or creative aspects of writing.
Writing is a complex process that involves students making decisions about word choice, sentence, and text structure, and ways in which to engage readers. Such decisions require a certain amount of reflection or at times deeper reflexive judgments by both teachers and students. Consequently, we draw on Archer’s ( 2012 ) critical realist theory of reflexivity to guide our review as research shows that reflexive thinking in practice can improve writing outcomes (Ryan et al., 2021 ). Archer ( 2007 ) highlights how reflexivity is an everyday activity involving mental processes whereby we think about ourselves in relation to our immediate personal, social, and cultural contexts. She suggests we make decisions through negotiating the connected emergences of personal properties (PEPs) related to the individual, structural properties (SEPs) related to the contextual happenings and cultural properties (CEPs) related to ideologies, each of which is influenced by the other developments. These decisions influence, and are influenced by, our subsequent actions. In applying reflexivity theory to writing (see Ryan, 2014 ), we cannot simply focus on the writing product, but should also interrogate the process of writing, that is, the influences on decision-making and design which are enabled or constrained through pedagogical practices in the classroom. Writing practices and outputs are formed through the interplay of personal, structural, and cultural conditions. Student decisions and actions about writing ensue through the mediation of personal (e.g. beliefs, motivations, interests, experiences), structural (e.g. curriculum, programs, testing regimes, teaching strategies, resources), and cultural (e.g. norms, expectations, ideologies, values) conditions. Therefore, teachers play an important role in facilitating the interplay of these conditions for their students and recontextualising curricula and policy (Ryan et al., 2021 ). For example, by enabling students’ agency and creating an authentic purpose for writing, teachers can balance the personal conditions of students (such as their motivation and interest) against the structural effects of the curriculum requirements. Using a reflexive approach to investigating the literature on creative writing we aim to reveal the personal, structural, and cultural conditions surrounding the study and the practice of creative writing. We argue that it is through the understanding of these conditions that we can theorise how a. students might make their writing more creative and b. how teachers might establish classroom conditions conducive to creativity.
The approach taken for this paper was guided by the PRISMA method (Moher et al., 2009 ) for conducting systematic literature reviews (see Table 1 ).
Our electronic search involved several databases: researchers’ library online catalogue, EBSCO host ultimate, ProQuest, Eric, Web of Science, Informit, and ScienceDirect. Using the following search terms: creativ* AND (‘teaching methods’ OR pedagog*) AND writing AND (elementary OR primary) to search titles and abstracts as well as limiting the search to peer-reviewed articles written in English within a 10-year timeframe (2011–2020), we initially retrieved 172 articles. Information about all 172 articles was input into a data spreadsheet including author, article title, journal title, volume and issue number, and abstract. Once completed, these articles were divided into two equal groups and two researchers were assigned to review the articles for relevancy against the following inclusion criteria:
Studies were peer-reviewed empirical research published in English;
Participants were primary students and/or teachers;
Students were not specifically English as a Second or Additional Language/Dialect learners (samples of culturally and linguistically diverse students in primary classrooms were included);
Studies were not carried out in curriculum areas other than English; and
Studies did not have a specific focus on digital technologies in the classroom.
For this systematic review, we were interested in the ways in which teachers thought about, understood, and taught the ‘creative’ aspect of writing.
The 25 studies that met the inclusion criteria were synthesised to review what influences the improvement of creative writing in primary education. We analysed the papers for how creative writing and/or creative aspects in writing were viewed as well as how teachers might best support students to develop reflexive capacities to improve the creative aspects of writing. We also identified any personal, structural, and/or cultural emergences that might impact on the effectiveness of students’ creative writing. Two of the authors read the entire articles and identified four main categories of research which were (1) understanding creative writing; (2) creative thinking and its contribution to writing; (3) creative pedagogy; and (4) what students can do to be more creative in their writing. These were cross-checked by the entire research team. Some of the papers fit more than one of these themes. In the next section, each theme is introduced and defined and then the articles that fall within the theme are reviewed.
Overall a total number of 25 articles had overlapping themes that included various personal and contextual aspects. Figure 1 shows what we have identified as the key themes under each category. In the next sections, we represent papers based on their main theme.
The personal, structural, and cultural conditions surrounding creative writing
Personal emergent properties
A total number of 13 articles were about what students can do to be more creative in their writing (Mendelowitz, 2014 ; Steele, 2016 ) and how teachers’ and students’ personal characteristics relate to the development of creative writing. These articles were mainly focussed on the personal emergent aspects of writing (Alhusaini & Maker, 2015 ; Barbot et al., 2012 ; Cremin et al., 2020 ; DeFauw, 2018 ; Dobson, 2015 ; Dobson & Stephenson, 2017 , 2020 ; Edwards-Groves, 2011 ; Healey, 2019 ; Lee & Enciso, 2017 ; Macken-Horarik, 2012 ; Ryan, 2014 ). The personal aspects identified in our review were (1) personal views about creative writing, (2) creative thinking, (3) writer identity, (4) learner motivation and engagement, and (5) knowledge and capabilities.
Personal views about creative writing
From our systematic review, we identified three articles exploring views about what creative writing is, and more specifically the role that it plays and the elements that make creative writing, in primary classrooms. One of these studies was focussed on the views and experiences of experts in writing (Barbot et al., 2012 ), whereas the other two investigated students’ perspectives and experiences (Alhusaini & Maker, 2015 ; Healey, 2019 ). Barbot et al’s ( 2012 ) work, for example, recognised that creative writing involves both cognitive and metacognitive abilities. This was determined by the expert panel of people whose work related to writing including teachers, linguists, psychologists, professional writers, and art educators. The panel were asked to complete an online survey that rated the relative importance of 28 identified skills needed to creatively write. Six broad categories were identified as a result of the responses and the rank given to each factor by the expert groups (See Table 2 ). They acknowledged that these features cross over various age groups from children to professional writers.
Findings suggested that each independent rater weighted different key components of creative writing as being more or less important for children. Overall, the findings showed.
a global ‘consensus’ across the expert groups indicated that creative writing skills are primarily supported by factors such as observation, generation of description, imagination, intrinsic motivation and perseverance, while the contributions of all of the other relevant factors seemed negligible (e.g. intelligence, working memory, extrinsic motivation and penmanship). (p. 218)
One factor that was ranked as critical by most respondents, but underemphasised by teachers, was imagination. Teachers’ work in classrooms around creative writing is complex due to the difficulty in defining imagination (Brill, 2004 ). Teachers also under-rated other aspects related to creative cognition.
Another study that explored students’ creativity in writing was conducted by Alhusaini and Maker ( 2015 ) in the south-west of the United States. Participants included 139 students with mixed ethnicities including White, Mexican American, and Navajo. This study involved six elementary/primary school teachers judging students’ writing samples of open-ended stories. To assess the work a Written Linguistic Assessment tool, which was based on the Consensual Assessment Technique [CAT] (Amabile, 1982 ) was implemented. According to Baer and McKool ( 2009 ), The CAT involves experts rating written artefacts or artistic objects by using their ‘sense of what is creative in the domain in question to rate the creativity of the products in relation to one another’ (p. 4). Interestingly, Alhusaini and Maker ( 2015 ) found the CAT to be effective in relation to interrater reliability. The authors do not share what the Judge’s Guidelines to Assess Students’ Stories entail. They mention the difference between technical quality and creativity and note that assessors were able to distinguish the differences between the two, but the reader is not made aware of the aspects of each quality. Overall, the study revealed that one of the most challenging problems in the field of creativity and writing is trying to measure creativity across cultures by using standardised tests. Such studies could have implications for other students from culturally and linguistically diverse backgrounds as teachers become more aware of cultural nuances in constituting ‘creative’ in creative writing.
The final study we identified in this category was by Healey ( 2019 ). Healey employed an Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis (IPA) and explored how eight children (11–12 Years of age) experienced creative writing in the classroom. He shared how children’s writing experiences were based on ‘the affect, embodiment, and materiality of their immediate engagement with activities in the classroom’ (p. 184). Results from student interviews showed three themes related to the experience of writing: the writing world (watching, ideas from elsewhere, flowing); the self (concealing and revealing, agency, adequacy); and schooled writing (standards, satisfying task requirements, rules of good writing). The author stated that children’s consciousness shifts between their imagination (The Writing World) and set assessment tasks (Schooled Writing). Both of these worlds affect the way children experience themselves as writers. Further findings from this work argued that originality of ideas and use of richer vocabulary improved students’ creative writing. Vocabulary improvement included diversity of word meanings, appropriate usage of words, words being in line with the purpose of the text; while originality of ideas featured creative and unusual (original) ideas—which in many ways is difficult to define.
Overall, when concerned with personal views and attitudes in creative writing, the two studies by Healey ( 2019 ) and Barbot et al. ( 2012 ) show contrasting findings about ‘imagination’ captured through the view of students and teachers, respectively. While Healey’s ( 2019 ) study suggests that children shift between their imagination and set assessment tasks in creative writing, Barbot et al. ( 2012 ) highlight the lack of attention to imagination among their participated teachers. Although these results cannot be generalised, they highlight the significance of understanding personal emergent properties that both students and teachers bring to the classroom and the way that they interact to affect the experience of creative writing for learners. From this theme, we suggest the importance of educators acknowledging students’ imagination through their definition of creative writing as well as providing quality time for students to choose what they write through imaginative thought. We now turn to creative thinking and related pedagogical approaches to teaching creative writing from the research literature.
Creative thinking
We identified two articles that were focussed on creative thinking and its contribution to writing (Copping, 2018 ; Cress & Holm, 2016 ). Copping ( 2018 ) explored writing pedagogy and the connections between children’s creative thinking, or a ‘new way of looking at something’ (p. 309), and their writing achievement. The study involved two primary schools in Lancashire, one in an affluent area and one in an underprivileged area. Approximately 28 children from each school were involved in two, 2-day writing workshops based on a murder mystery the children had to solve. Findings from this study revealed that to improve students’ writing achievement (1) a thinking environment needs to be created and maintained, (2) production processes should have value, (3) motivation and achievement increase when there is a tangible purpose, and (4) high expectations lead to higher attainment.
Cress and Holm’s ( 2016 ) study described a curricular approach implemented by a first-grade teacher and their class comprised 13 girls and 11 boys. The project known as the Creative Endeavours project aimed to develop creative thinking by (1) creating an environment of respect with a positive classroom climate. (2) offering new and challenging experiences, and (3) encouraging new ideas rather than praise. The authors argued that through peer collaboration and the flexibility to choose their own projects, children can become more authentically engaged in the writing process. The children wrote about their experiences and their choices, and reflected upon the projects undertaken. In this study, it was revealed that the children showed diversity in their writing assignments including presentation through sewing, photography, and drama. While there were only two papers in this particular theme, their findings are supported by systematic reviews (Graham et al., 2012 ; Slavin et al., 2019 ) that emphasise not only new ways of exploring a range of concepts for learning but also the creation of motivating environments for improving writing (Copping, 2018 ). In addition to the significance of positive and encouraging learning environments, these two studies suggest that setting ‘high expectations’ or ‘challenging experiences’ are conducive to creative thinking however, teachers would need to set appropriate, reflexive conditions for this to occur.
Writer identity
Studies in this category revolve around choice and learner writer identity. The study carried out by Dobson and Stephenson ( 2017 ) focussed on developing a community of writers involving 25 primary school pupils from low socio-economic backgrounds. The project was offered over 2 weeks and featured a number of creative writing workshops. The authors applied the theoretical frameworks of practitioner enquiry and discourse analysis to explore the children’s creative writing outputs. They argued that the workshops, which promoted intertextuality and freedom for the children as writers, enabled a shifting of their ‘writer’ identities (Holland et al., 1998). Dobson and Stephenson ( 2017 ) showed that allowing students to make decisions and choices in regard to authentic writing purposes supported a more flexible approach. They recommend stronger partnerships between schools and universities in relation to research on creative writing, however, it would be important for these relationships to be sustainable.
The second paper on this theme is by Ryan ( 2014 ) who noted that writing is a complex activity that requires appropriate thinking in relation to the purpose, audience, and medium of a variety of texts. Writers always make decisions about how they will present subject matter and/or feelings through all of the modes. Ryan ( 2014 ) suggested that writing is like a performance ‘whereby writers shape and represent their identities as they mediate social structures and personal considerations’ (p. 130). The study analysed writing samples of culturally and linguistically diverse Australian primary students to uncover the types of identities students shared. It found that three different types of writers existed—the school writers who followed teacher instructions or formulas to produce a product; the constrained writers who also followed instructions and formulas but were able to add in some authorical voice; and the reflexive writers who could show a definite command of writing and showed creative potential. Ryan ( 2014 ) argued that teachers’ practices in the classroom directly influence the ways in which students express these identities. She stated that when students are provided choices in writing, they are more able to shape and develop their voices. Such choices would need to include quality time and support to be reflexive in the decisions being made by the students.
The Teachers as Writers project (2015–2017) was conducted by Cremin, Myhill, Eyres, Nash, Wilson, and Oliver. In a recent paper ( 2020 ), the team reported on a collaborative partnership between two universities and a creative writing foundation. Professional writers were invited to engage with teachers in the writing process and the impact of these interactions on classroom teaching practices was determined. Data sets included observations, interviews, audio-capture (of workshops, tutorials and co-mentoring reflections), and audio-diaries from 16 teachers; and a randomised controlled trial (RCT) involving 32 primary and secondary classes. An intervention was carried out involving teachers writing in a week long residence with professional writers, one-on-one tutorials, and extra time and space to write. They also continued learning through two Continuing Professional Development (CPD) days. Results showed that teachers’ identities as writers shifted greatly due to their engagement with professional authors. The students responded positively in terms of their motivation, confidence, sense of ownership, and skills as writers. The professional authors also commented on positive impacts including their own contributions to schools. Conversely, these changes in practice did not improve the students’ final assessment results in any significant way. The authors noted that assuming a causal relationship between teachers’ engagement with writing workshops and students’ writing outcomes was spurious. They, therefore, developed further research building on this learning.
Knowledge and capabilities
The role of knowledge and capability is central to the articles in this category. In Australia, Macken-Horarik ( 2012 ) reported on the introduction of a national curriculum for English. This article drew on Systemic Functional Linguistics (SFL) by investigating the potential of Halliday’s notion of grammatics for understanding students’ writing as acts of creative meaning in context. Macken-Horarik ( 2012 ) argued that students needed to know deeply about language so that they could make creative decisions with their writing. She outlined that a ‘good enough’ grammatics would assist teachers in becoming comfortable with ‘playful developments in students’ texts and to foster their control of literate discourse’ (p. 179).
A project carried out by Edwards-Groves in 2011 highlights the role of knowledge about digital technologies in writing practices. 17 teachers in primary classrooms in Australia were asked to use particular digital technologies with their students when constructing classroom texts. Findings showed that an extended perspective on what counts as writing including the writing process was needed. Results revealed that collaborative methods when constructing diverse texts required teachers to rethink pedagogies towards writing instruction and what they consider as writing. It was argued that technology can be used to enhance creative possibilities for students in the form of new and dynamic texts. In particular, it was noted that teachers and students should be aware that digital technologies can both constrain and/or enable text creation in the classroom depending on a number of variables including knowledge and understanding, locating resources and logistical issues such as connectivity and reliability.
In addition, Mendelowitz’s ( 2014 ) study argued that nurturing teachers’ own creativity assisted their ability to teach writing more generally. She noted several ‘interrelated variables and relationships that still need to be given attention in order to gain a more holistic understanding of the challenges of teaching creative writing’ (p. 164). According to Mendelowitz ( 2014 ), elements that impacted on these challenges include teachers’ school writing histories, conceptualisations of imagination, classroom discourses, and pedagogy. Documenting teachers’ work through interviews and classroom observations by the researcher, the study found that teachers need to be able to define imagination and imaginative writing and know what strategies work best with their students. She noted that the teacher’s approaches to teaching writing ‘powerfully shaped by the interactions between their conceptualisations and enactments of imaginative writing pedagogy’ (p. 181) and that these may either limit or create a space for students to be more creative with their writing.
Such Personal Emergent Properties show that individual attributes of both teachers and students are important in learning creative writing. The next section of the paper explores the articles that shared various structural and cultural properties.
Structural emergent properties
In the subset of structural emergent properties, we mainly identified pedagogical approaches for creative writing that explored primary school learning and teaching (Christianakis, 2011a ; Christianakis, 2011b ; Coles, 2017 ; DeFauw, 2018 ; Hall & Grisham-Brown, 2011 ; Portier et al., 2019 ; Rumney et al., 2016 ; Sears, 2012 ; Steele, 2016 ; Southern et al., 2020 ; Yoo & Carter, 2017 ). These pedagogical approaches were aimed at addressing issues related to personal emergent properties such as motivation and engagement, and confidence in writing. The two categories of writing pedagogies were those that engaged professional authors and artists in teaching about creative writing, and the approaches that involved play(ful) activities, and use of visual arts, and drama.
Engaging professional authors and artists
Interestingly, many of the studies used literary forms and/or professional creative authors to spike interest and motivation in the students. Coles’ ( 2017 ) study, for example, used a garden-themed poetry writing project to support 9–10-year-old children’s creative writing in a London primary school. The 5-week project partnered with a professional creative writing organisation that facilitated the Ministry for Stories (MoS) writing centres across the USA. The study found that the social relationships created through this partnership allowed for a more inclusive and socially generative model of creativity. This meant that teachers should not just include creative aspects in assessment rubrics but rather recognise that creativity is encouraged through imagination and working with others. The researchers found improvements in the children’s participation in classroom writing activities as well as diversity in the ways they expressed their writing. The approach valued ‘rich means of expression rather than a set of rules to be learnt’ (p. 396). They also acknowledged issues associated with school–community partnerships including the sustainability of the practice.
Similarly, Rumney et al. ( 2016 ) found that using creative multimodal activities increased students’ confidence and motivation for writing. The study implemented the Write Here project with over 900 children in 12 primary and secondary schools. The study involved the children visiting local art galleries to work with professional authors and artists. Case studies were presented about pre-writing activities, the actual gallery work and post-gallery follow-up sessions. It aimed to improve students’ social development and literacy outcomes through diverse learning activities such as visual art and play in different contexts such as art galleries and classrooms. Like Coles’ ( 2017 ) study, this project showed that creative activities (e.g. talking about and acting out pictures; using story maps; backwards writing and planning) engaged students more than just teaching skills.
In addition, DeFauw’s ( 2018 ) study had student-centred learning and leadership at the core when working with a children’s book author for one year. The collaboration involved three face-to-face sessions with the author as well as online communication through blog posts. Data included recorded interactions, readings and pre and post interviews with teachers ( n = 9), students ( n = 36), and the author. The partnership showed that students’ interest was activated and sustained due to the situational context as well as the extended time given to students to interact with the author. The project improved students’ interest in and motivation to write as a result of engaging with authors and hearing about their own experience and writing strategies. It also found that teachers gained more confidence to support students’ exploration of writing in more creative ways. The creative pedagogies were also used in addressing issues related to creative writing outcomes for students, including teachers’ lack of confidence about pedagogies (Southern et al., 2020 ). Through a creative social enterprise approach, the authors facilitated professional development and learning involving artist-led activities for students. The program called Zip Zap had been implemented in schools in Wales and England, and data were collected through focus groups with teachers, students, and parents/carers. Observations of some of the professional development workshops were also video recorded. Third space theory was used to describe the collaborative practice between educators and artists that supported students’ creative writing outcomes. It was noteworthy that involving ‘creative’ practitioners largely focussed on the specific strategies that could be used in classrooms, to which our next section now turns.
Play(ful) activities, visual arts, and drama
Much research explores how to best support students who find writing difficult. Sears’ research ( 2012 ) is a case in point. The author shared how visual arts may be an effective way to improve struggling students with writing. They argued that the visual arts can provide ways of ‘accessing and expressing [student] ideas and ultimately opening a world of creative possibilities’ (p. 17). In the study, six third-grade students engaged with drawing and painting as pre-writing strategies, leading to the creation of poems based on the artworks. The students’ final poems were assessed and showed improved knowledge of all 6 technical categories in writing: ideas, organisation, fluency, voice, word choice, and conventions. The author also argued that students’ motivation to write increased as a result of the visual art activities.
A study by Portier et al. ( 2019 ) investigated approaches to teaching writing that were motiving and engaging for students. Involving 10 northern rural communities in Canada, the project implemented collaborative, play(ful) learning activities alongside sixteen teachers and their students. Interestingly, the study, like many others in our review, found a disconnect ‘between the achievement of curricular objectives and the implementation of play(ful) learning activities’ (p. 20); an approach valued in early childhood education. The students were supported through action research projects in creating texts with different purposes. Students’ motivation as well as samples of work were analysed and showed that student interest areas and collaborative approaches benefited both teachers and students. Further research on how reflexive thinking might have influenced these benefits is recommended.
Similarly, Lee and Enciso ( 2017 ) highlighted the importance of motivation and engagement in their study. In a collaboration with Austin Theatre Alliance, Lee and Enciso ( 2017 ) investigated how dramatic approaches to teaching, such as through expanded imagination and improvisation, can improve students’ story writing. They argued that the students’ motivation to write was also increased. The study was carried out through a controlled quasi-experimental study over 8 weeks of story-writing and drama-based programs. 29 third-grade classrooms in various schools, located in an urban district of Texas, were involved. The study also pre- and post-tested the students’ writing self-efficacy through story building. The study found that students were more able to use their cultural knowledge such as ‘culturally formed repertoires of language and experience to explore and express new understandings of the world and themselves…’ (p. 160) for creative writing purposes but needed more quality resources to support opportunities such as the Literacy for Life program. A most important finding was that for children who experience poverty, drama-based activities developed and led by teaching artists were extremely powerful and allowed the students to express themselves in entertaining ways. We do note that ‘entertainment’ and or engagement might mean different things for different students so reflexive approaches to deciding what these are would be necessary.
Steele’s ( 2016 ) study also looked at supporting teachers’ work in the classroom. Involving 6 out of 20 teacher workshop participants in Hawaii, this exploratory case study utilised observations, interview, and portfolio analyses of teacher and student work. Findings from the study showed that some teachers relished moving away from everyday ‘typical’ practice and increased student voice and choice. Other teachers, however, found it difficult to take risks and hence respond to student needs and ideas.
Dobson and Stephenson’s ( 2020 ) study focussed on the professional development of primary school teachers using drama to develop creative writing across the curriculum. The project was sponsored by the United Kingdom Literacy Association and ran for two terms in a school year. Researchers based the research on a collaborative approach involving academics and four teachers working with theatre educators to use process drama. Data sets included lesson observations, notes taken during learning conversations, and interviews with the teachers. The findings showed that three of the four teachers resisted some of the methods used such as performance; resulting in a lack of child-centred learning. The remaining teacher could take on board innovative practice, which the researchers attributed to his disposition. The study argued that these teachers, while a small participant group, needed more support in feeling confident in implementing new and creative approaches to teaching writing.
The final study, identified as addressing creative pedagogies for creative writing, was carried out by Yoo and Carter ( 2017 ) as professional development for teachers. Data included teacher survey responses and field notes taken by the researchers at each workshop (note: number of workshops and participants is unknown). The program aimed to investigate how emotions play a role in teachers’ work when teaching creative writing. The researchers found that intuitive joint construction of meaning was important to meet the needs of both primary and secondary teachers. A community of practice was established to support teachers’ identities as writers (see also Cremin et al., 2020 ). Findings showed that teachers who already identified as writers engaged more positively in the workshop.
These studies presented some approaches for teachers to consider how to teach creative writing. For example, the need to value unique spaces for students to write, including authentic connections with people and places outside of school environments was shared. Further, the need for quality stimuli and time for writing was acknowledged. Several other studies identified that blended teaching approaches to support student learning outcomes in the area of creative writing is important for schools and teachers to consider. We do acknowledge there may be other methods available to support students in creative writing, however, understanding what types of SEPs are impacting on teaching creative writing is an important step in determining improvements in schools.
Cultural emergent properties
Christianakis ( 2011a , 2011b ) wrote two papers about children’s creative text development with an emphasis on the cultural aspects. The first was an ethnographic study across 8 months with a year five class in East San Francisco Bay. The study included audio recording the students’ conversations and analysing over 900 samples of work. In the classroom, students were involved in a range of meaning-making practices including those that were arts-based and multimodal. The conversations with the students involved the researcher asking questions such: tell me more about this drawing, how did you come up with the idea? or why did you make this choice? The study found that there was a need for schools to reconceptualise the teaching of writing ‘to include not only orthographic symbols, but also the wide array of communicative tools that children bring to writing’ (p. 22). The author argued that unless corresponding institutional practices and ideologies were interrogated then improved practice was unlikely.
Christianakis’ ( 2011b ) second article, from the same project, explored more specifically the creation of hybrid rap poems by the children. She explicated how educators needed to negotiate and challenge dominant practices in primary classroom literacy learning. Like many studies before, a strong recommendation was to be more inclusive of youth popular cultures and culturally relevant literacies for students to be more engaged in creative writing practices. For Christianakis, culturally relevant literacies meant practices that embraced diversity in class and race and accounted for, and challenged, the dominant hegemonic curriculum that ‘privileges a traditional canon’ (p. 1140).
In summary, we found several themes under PEPs that could be considered for further research including those outlined in Table 3 below.
Discussion and implications for classroom practice
From this systematic literature review, several positions were exposed about the personal, structural, and cultural influences (Archer, 2012 ; Ryan, 2014 ) on teaching creative writing. These include limited teacher and student knowledge of what constitutes creative writing (Personal Emergent Properties [PEPs]), and no shared understanding or expectation in relation to creative writing pedagogy in their context (Cultural Emergent Properties [CEPs]). The negative impact of standardised testing and trending approaches on how teachers teach writing (CEP; Structural Emergent Properties [SEPs]) could also be considered (see AUTHORS 1 and 3, 2014 for example). In addition, teachers’ poor self-efficacy in terms of teaching creative writing (PEP); a paucity of quality professional development about teaching and assessing creative writing (SEP); and issues related to the sustainability of creative approaches to teach writing (SEP; CEP) need to be considered by leaders and teachers in schools. Our literature review advances knowledge about creative writing by revealing two interconnected areas that affect creative writing practices. Findings suggest that a parallel focus on personal conditions and contextual conditions—including structural and cultural—has the potential to improve creative writing in general. Below, we share some implications and recommendations for improved practice by focussing on both (1) personal views about creative writing and (2) the structural and cultural aspects that affect creative writing practices at schools.
Focussing on personal views about creative writing
School leaders and teachers must clearly define what creative writing is, what key skills constitute creative writing.
From our search it was apparent that schools and their educators often do not have a clear idea or indeed a shared idea as to what constitutes creative writing in relation to their own context. Without a well-defined focus for creative writing students may find it difficult to know what is required in classroom tasks and assessment. In addition, when planning for creative writing in school programs, teachers should consider flexible learning opportunities and choice for their students when developing their creative writing skills. Such flexibility should also involve choice of topic, ways of working (e.g. peer collaboration, individual activities etc.), and open discussions led by students in the classroom as shown throughout this paper. It would also be important for leaders and teachers to interrogate current approaches to teaching writing which we argued in the introduction to be formulaic and genre based.
Improve teacher self-efficacy, confidence, and content knowledge in teaching writing
Many of our studies showed that teachers who lacked confidence about writing themselves had less knowledge and skills to teach writing than those that may have participated in projects encouraging ‘teachers as writers’. Further, improved knowledge of grammar (as highlighted in Macken-Horarik’s, 2012 work); talk about writing in the classroom and other spaces (Cremin et al., 2020 ) and the writing process (see Ryan, 2014 ) could assist teachers in becoming more confident to take risks in the classroom with their students. Above all being playful about writing through extended conversations and practices is required.
Focussing on the structural and cultural resources
Improve training and further professional development and learning about teaching and assessing creative writing.
In order for the above personal attributes to be improved, further professional development and learning are required. Many of the papers presented throughout this review demonstrated the powerful impact of immersive professional learning for teachers. Working alongside professional authors, researchers, drama practitioners, visual artists, poets, for example, provided positive opportunities for teachers to learn about writing but also to feel more confident to teach it without imposing strict boundaries on students. We argue for professional development to be both formal and informal including such approaches as coaching and mentoring in the classroom. Demonstrated practice alongside the teacher is also recommended. This, in turn, would address the ongoing issue of creative writing being stifled for students in the classroom context.
Consider sustainability of creative pedagogic approaches and spaces for creative writing in curriculum planning
Many of the studies throughout this paper shared creative approaches to teaching writing but there were concerns that some of these methods may not be sustainable. It is important for school leaders to support the work of teachers in relation to teaching creative writing. We acknowledge that there is increasing uncertainty and scrutiny surrounding teachers’ everyday work (Knight, 2020 ), however, continued engagement in learning about and participating in creative pedagogy for writing is highly recommended. In addition, the studies suggested the provision of appropriate and authentic spaces in which students could creatively write and these often included spaces outside of the normal classroom environment and arts-based approaches implemented in such spaces. Teachers should be encouraged to collaborate and take risks rather than follow predetermined strategies for every lesson. A whole of school practice can be developed with important conversations about the ideologies that inform the school’s approach to writing.
Schools should not stifle creativity in the classroom due to the infiltration of standardised and/or trending approaches to teaching and assessing writing
It is evident that pedagogical approaches to teaching writing have been stifled by more formulaic methods aiming to meet expectations of standardised tests despite other evidence showing the benefits of more productive, engaging, and creative approaches to teaching writing as highlighted above. This can be particularly the case for students from non-dominant backgrounds where writing about cultural and life experiences through innovative practices has been proven to empower their voices (Johnson, 2021 ). The research shows that when students are offered rigid structures of texts, no choice of genres, and indeed word lists, their own decisions about writing are diminished (Ryan & Barton, 2013 ). It has been proven that students’ engagement and motivation to write can increase when they are able to write directly from their own experience or in social groups. It is therefore recommended that school leaders and teachers reconsider their ideologies about writing and explicitly indicate the importance of real-world purposes for writing—not just formulised, quick writing as usually included in external tests—but also those that encourage students’ growth in imagination, creativity, and innovative thought.
This systematic review used a lens of reflexivity to situate writing as a process of active and creative design whereby students make conscious decisions about their writing, with guidance from their teachers. As explained, we see creative writing as writing that engages a reader and, therefore, requires knowledge of authorial voice and appropriate word choice. This involves reflexive decisions relating to personal, structural, and cultural emergent properties. Predominant in the literature was the striking influence of CEPs or the values and expectations ascribed to writing, which in turn influence the strategies and resources (SEPs) and the experiences and motivations of students and teachers in the classroom (PEPs). Writing is about more than a series of perfectly formed sentences in a recognisable structure, which dominates conceptions of writing through high-stakes testing globally. It is about engagement with the expressive self, emergent identities, and relationships to places and people and above all communicating to and/or entertaining a reader. Without quality education in creative writing, society is at risk of losing an art form that is important for cultural practice and expression (Watson, 2016 ).
We do foresee several limitations with such a review, largely related to the positive nature of the studies in relation to creative approaches to teaching writing as well as the relatively small numbers of participants in some of the studies. Most of the studies reported favourably on the approaches taken by teachers to influence student motivation towards writing with limited comments about adverse effects. In terms of contributions, the notion that students need to draw on creative thought and ideas when writing means that teachers and leaders must think about diverse ways to teach writing. We argue, on the basis of the findings, that inquiry-based and reflexive professional learning projects about creativity are crucial for primary classrooms: what creativity means in different contexts and for different writers; how it is enabled; and the decisions and actions that emerge when creative and reflexive design guide our approach to classroom writing. Without quality knowledge and understanding of what creative writing is and how it is taught, we would be at risk of diminishing students’ self-expression and ability to communicate meaning to others in literary forms.
Alhusaini, A. A., & Maker, C. J. (2015). Creativity in students’ writing of open-ended stories across ethnic, gender, and grade groups: An extension study from third to fifth grades. Gifted and Talented International, 30 (1–2), 25–38.
Article Google Scholar
Amabile, T. M. (1982). Children's artistic creativity: Detrimental effects of competition in a field setting. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin , 8 (3), 573–578.
Archer, M. (2007). Making our way through the world: Human reflexivity and social mobility . Cambridge University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Archer, M. (2012). The reflexive imperative in late modernity . Cambridge University Press.
Au, W., & Gourd, K. (2013). Asinine assessment: Why high-stakes testing is bad for everyone, including English teachers. English Journal , 14–19.
Baer, J., & McKool, S. (2009). Assessing creativity using the consensual assessment technique . IGI Global.
Barbot, B., Tan, M., Randi, J., Santa-Donato, G., & Grigorenko, E. L. (2012). Essential skills for creative writing: Integrating multiple domain-specific perspectives. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 7 (3), 209–223.
Brill, F. (2004). Thinking outside the box: Imagination and empathy beyond story writing. Literacy, 38 (2), 83–89.
Christianakis, M. (2011a). Children’s text development: Drawing, pictures, and writing. Research in the Teaching of English, 46 (1), 22–54.
Google Scholar
Christianakis, M. (2011b). Hybrid texts: Fifth graders, rap music, and writing. Urban Education, 46 (5), 1131–1168.
Coles, J. (2017). Planting poetry: Sowing seeds of creativity in a year 5 class changing english. Studies in Culture and Education, 24 (4), 386–398.
Copping, A. (2018). Exploring connections between creative thinking and higher attaining writing. Education, 46 (3), 307–316.
Cremin, T., Myhill, D., Eyres, I., Nash, T., Wilson, A., & Oliver, L. (2020). Teachers as writers: Learning together with others. Literacy, 54 (2), 49–59.
Cress, S. W., & Holm, D. T. (2016). Creative endeavors: Inspiring creativity in a first-grade classroom. Early Childhood Education Journal, 44 (3), 235–243.
DeFauw, D. L. (2018). One school’s yearlong collaboration with a children’s book author. Reading Teacher., 72 (30), 355–367.
Deutsch, L. (2014). Writing from the senses: 59 exercises to ignite creativity and revitalize your writing . Shambhala Publications.
Dobson, T. (2015). Developing a theoretical framework for response: Creative writing as response in the Year 6 primary classroom. English in Education, 49 (3), 252–265.
Dobson, T., & Stephenson, L. (2017). Primary pupils’ creative writing: Enacting identities in a Community of Writers. Literacy, 51 (3), 162–168.
Dobson, T., & Stephenson, L. (2020). Challenging boundaries to cross: Primary teachers exploring drama pedagogy for creative writing with theatre educators in the landscape of performativity. Professional Development in Education, 46 (2), 245–255.
Edwards-Groves, C. (2011). The multimodal writing process: Changing practices in contemporary classrooms. Language and Education, 25 (1), 49–64.
Gibson, R., & Ewing, R. (2020). Transforming the curriculum through the arts . Springer.
Göçen, G. (2019). The effect of creative writing activities on elementary school students’ creative writing achievement, writing attitude and motivation. Journal of Language and Linguistic Studies, 15 (3), 1032–1044.
Graham, S., McKeown, D., Kiuhara, S., & Harris, K. R. (2012). A meta-analysis of writing instruction for students in the elementary grades. Journal of Educational Psychology, 104 (4), 879.
Grainger, T., Goouch, K., & Lambirth, A. (2005). Creativity and writing: Developing voice and verve in the classroom . Routledge.
Hall, A. H., & Grisham-Brown, J. (2011). Writing development over time: Examining preservice teachers' attitudes and beliefs about writing. Journal of Early Childhood Teacher Education, 32 (2), 148–158.
Healey, B. (2019). How children experience creative writing in the classroom. The Australian Journal of Language and Literacy, 42 (3), 184–194.
Johnson, T. (2021). Identity placement in social justice issues through a creative writing curriculum . Unpublished Masters thesis. Hamline University.
Knight, R. (2020). The tensions of innovation: Experiences of teachers during a whole school pedagogical shift. Research Papers in Education, 35 (2), 205–227.
Lee, B. K., & Enciso, P. (2017). The big glamorous monster (or Lady Gaga’s adventures at sea): Improving student writing through dramatic approaches in schools. Journal of Literacy Research, 49 (2), 157–180.
Macken-Horarik, M. (2012). Why school English needs a ‘good enough’ grammatics (and not more grammar). Changing English: Studies in Culture and Education, 19 (2), 179–194.
Mahmood, M. I., Mobeen, M., & Abbas, S. (2020). Effect of high-stakes exams on creative writing skills of ESL learners in Pakistan. Research Journal of Social Sciences and Economics Review, 1 (3), 169–179.
Mendelowitz, B. (2014). Permission to fly: Creating classroom environments of imaginative (im)possibilities. English in Education, 48 (2), 164–183.
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., The PRISMA Group. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Medicine, 6 (7), e1000097.
Polesel, J., Dulfer, N., & Turnbull, M. (2012). The experience of education: The impacts of high stakes testing on school students and their families . The Whitlam Institute.
Portier, C., Friedrich, N., & Stagg Peterson, S. (2019). Play(ful) pedagogical practices for creative collaborative literacy. Reading Teacher, 73 (1), 17–27.
Rumney, P., Buttress, J., & Kuksa, I. (2016). Seeing, doing, writing: The write here project. SAGE Open, 6 (1).
Ryan, M. (2014). Writers as performers: Developing reflexive and creative writing identities. English Teaching: Practice & Critique, 13 (3), 130–148.
Ryan, M., & Barton, G. M. (2013). Working towards a ’’thirdspace' in the teaching of writing to middle years students. Literacy Learning: The Middle Years , 21 (3), 71–81.
Ryan, M., & Barton, G. (2014). The spatialized practices of teaching writing in Australian elementary schools: Diverse students shaping discoursal selves. Research in the Teaching of English , 303–329.
Ryan, M., & Daffern, T. (2020). Assessing writing: Teacher-led approaches. Teaching Writing: Effective approaches for the middle years.
Ryan, M., Khosronejad, M., Barton, G., Kervin, L. & Myhill, D. (2021). A reflexive approach to teaching writing: Enablements and constraints in primary school classrooms. Written Communication.
Sears, E. (2012). Painting and poetry: Third graders’ free-form poems inspired by their paintings. Journal of Inquiry and Action in Education, 5 (1), 17–40.
Slavin, E. R., Lake, C., Inns, A., Baye, A., Dachet, D., & Haslam, J. (2019). A quantitative synthesis of research on writing approaches in years 3 to 13 . Education Endowment Foundation.
Smith, H. (2020). The writing experiment: Strategies for innovative creative writing . Routledge.
Southern, A., Elliott, J., & Morley, C. (2020). Third space creative pedagogies: Developing a model of shared CPDL for teachers and artists to support reading and writing in the primary curricula of England and Wales. International Journal of Education and Literacy Studies, 8 (1), 24–31.
Steele, J. (2016). Becoming creative practitioners: Elementary teachers tackle artful approaches to writing instruction. Teaching Education, 27 (1), 1037829. https://doi.org/10.1080/10476210.2015.1037829
Stock, C., & Molloy, K. (2020). Where are the students?: Creative writing in a high-stakes world. Idiom, 56 (3), 19.
Wang, L. (2019). Rethinking the significance of creative writing: A neglected art form behind the language learning curriculum. Cambridge Open-Review Educational Research, 6 , 110–122.
Watson, V. M. (2016). Literacy is a civil write: The art, science, and soul of transformative classrooms. Social Justice Instruction: Empowerment on the Chalkboard , 307–323.
Wyse, D., Jones, R., Bradford, H., & Wolpert, M. A. (2013). Teaching English, language and literacy . Routledge.
Yoo, J., & Carter, D. (2017). Teacher emotion and learning as praxis: Professional development that matters. Australian Journal of Teacher Education, 42 (3), 38–52.
Download references
Open Access funding enabled and organized by CAUL and its Member Institutions. The project that informed this systematic review was on the teaching of writing and funded by the Australian Research Council. The views expressed here are in no way reflective of the ARC.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Education, University of Southern Queensland, Springfield, QLD, Australia
Georgina Barton
Australian Catholic University, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Maryam Khosronejad & Mary Ryan
Faculty of Social Sciences, University of Wollongong, Wollongong, NSW, Australia
Lisa Kervin
Centre for Research in Writing, The University of Exeter, Exeter, UK
Debra Myhill
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Georgina Barton .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest regarding this paper.
Etical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Barton, G., Khosronejad, M., Ryan, M. et al. Teaching creative writing in primary schools: a systematic review of the literature through the lens of reflexivity. Aust. Educ. Res. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13384-023-00641-9
Download citation
Received : 19 July 2022
Accepted : 26 May 2023
Published : 17 June 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13384-023-00641-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Creative writing
- Primary classrooms
- Teaching writing
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

11+ creative writing guide with 50 example topics and prompts
by Hayley | Nov 17, 2022 | Exams , Writing | 0 comments
The 11+ exam is a school entrance exam taken in the academic year that a child in the UK turns eleven.
These exams are highly competitive, with multiple students battling for each school place awarded.
The 11 plus exam isn’t ‘one thing’, it varies in its structure and composition across the country. A creative writing task is included in nearly all of the 11 plus exams, and parents are often confused about what’s being tested.
Don’t be fooled into thinking that the plot of your child’s writing task is important. It is not.
The real aim of the 11+ creative writing task is to showcase your child’s writing skills and techniques.
And that’s why preparation is so important.
This guide begins by answering all the FAQs that parents have about the 11+ creative writing task.
At the end of the article I give my best tips & strategies for preparing your child for the 11+ creative writing task , along with 50 fiction and non-fiction creative writing prompts from past papers you can use to help your child prepare. You’ll also want to check out my 11+ reading list , because great readers turn into great writers.
Do all 11+ exams include a writing task?
Not every 11+ exam includes a short story component, but many do. Usually 3 to 5 different prompts are given for the child to choose between and they are not always ‘creative’ (fiction) pieces. One or more non-fiction options might be given for children who prefer writing non-fiction to fiction.
Timings and marking vary from test to test. For example, the Kent 11+ Test gives students 10 minutes for planning followed by 30 minutes for writing. The Medway 11+ Test gives 60 minutes for writing with ‘space allowed’ on the answer booklet for planning.
Tasks vary too. In the Kent Test a handful of stimuli are given, whereas 11+ students in Essex are asked to produce two individually set paragraphs. The Consortium of Selective Schools in Essex (CCSE) includes 2 creative writing paragraphs inside a 60-minute English exam.
Throughout the UK each 11+ exam has a different set of timings and papers based around the same themes. Before launching into any exam preparation it is essential to know the content and timing of your child’s particular writing task.
However varied and different these writing tasks might seem, there is one key element that binds them.
The mark scheme.
Although we can lean on previous examples to assess how likely a short story or a non-fiction tasks will be set, it would be naïve to rely completely on the content of past papers. Contemporary 11+ exams are designed to be ‘tutor-proof’ – meaning that the exam boards like to be unpredictable.
In my online writing club for kids , we teach a different task each week (following a spiral learning structure based on 10 set tasks). One task per week is perfected as the student moves through the programme of content, and one-to-one expert feedback ensures progression. This equips our writing club members to ‘write effectively for a range of purposes’ as stated in the English schools’ teacher assessment framework.
This approach ensures that students approaching a highly competitive entrance exam will be confident of the mark scheme (and able to meet its demands) for any task set.
Will my child have a choice of prompts to write from or do they have to respond to a single prompt, without a choice?
This varies. In the Kent Test there are usually 5 options given. The purpose is to gather a writing sample from each child in case of a headteacher appeal. A range of options should allow every child to showcase what they can do.
In Essex, two prescriptive paragraphs are set as part of an hour-long English paper that includes comprehension and vocabulary work. In Essex, there is no option to choose the subject matter.
The Medway Test just offers a single prompt for a whole hour of writing. Sometimes it is a creative piece. Recently it was a marketing leaflet.
The framework for teaching writing in English schools demands that in order to ‘exceed expectations’ or better, achieve ‘greater depth’, students need to be confident writing for a multitude of different purposes.
In what circumstances is a child’s creative writing task assessed?
In Essex (east of the UK) the two prescriptive writing tasks are found inside the English exam paper. They are integral to the exam and are assessed as part of this.
In Medway (east Kent in the South East) the writing task is marked and given a raw score. This is then adjusted for age and double counted. Thus, the paper is crucial to a pass.
In the west of the county of Kent there is a different system. The Kent Test has a writing task that is only marked in appeal cases. If a child dips below the passmark their school is allowed to put together a ‘headteacher’s appeal’. At this point – before the score is communicated to the parent (and probably under cover of darkness) the writing sample is pulled out of a drawer and assessed.
I’ve been running 11+ tutor clubs for years. Usually about 1% of my students passed at headteacher’s appeal.
Since starting the writing club, however, the number of students passing at appeal has gone up considerably. In recent years it’s been more like 5% of students passing on the strength of their writing sample.
What are the examiners looking for when they’re marking a student’s creative writing?
In England, the government has set out a framework for marking creative writing. There are specific ‘pupil can’ statements to assess whether a student is ‘working towards the expected standard,’ ‘working at the expected standard’ or ‘working at greater depth’.
Members of the headteacher panel assessing the writing task are given a considerable number of samples to assess at one time. These expert teachers have a clear understanding of the framework for marking, but will not be considering or discussing every detail of the writing sample as you might expect.
Schools are provided with a report after the samples have been assessed. This is very brief indeed. Often it will simply say ‘lack of precise vocabulary’ or ‘confused paragraphing.’
So there is no mark scheme as such. They won’t be totting up your child’s score to see if they have reached a given target. They are on the panel because of their experience, and they have a short time to make an instant judgement.
Does handwriting matter?
Handwriting is assessed in primary schools. Thus it is an element of the assessment framework the panel uses as a basis for their decision.
If the exam is very soon, then don’t worry if your child is not producing immaculate, cursive handwriting. The focus should simply be on making it well-formed and legible. Every element of the assessment framework does not need to be met and legible writing will allow the panel to read the content with ease.
Improve presentation quickly by offering a smooth rollerball pen instead of a pencil. Focus on fixing individual letters and praising your child for any hint of effort. The two samples below are from the same boy a few months apart. Small changes have transformed the look and feel:

Sample 1: First piece of work when joining the writing club

Sample 2: This is the same boy’s improved presentation and content
How long should the short story be.
First, it is not a short story as such—it is a writing sample. Your child needs to showcase their skills but there are no extra marks for finishing (or marks deducted for a half-finished piece).
For a half hour task, you should prepare your child to produce up to 4 paragraphs of beautifully crafted work. Correct spelling and proper English grammar is just the beginning. Each paragraph should have a different purpose to showcase the breadth and depth of their ability. A longer – 60 minute – task might have 5 paragraphs but rushing is to be discouraged. Considered and interesting paragraphs are so valuable, a shorter piece would be scored more highly than a rushed and dull longer piece.
I speak from experience. A while ago now I was a marker for Key Stage 2 English SATs Papers (taken in Year 6 at 11 years old). Hundreds of scripts were deposited on my doorstep each morning by DHL. There was so much work for me to get through that I came to dread long, rambling creative pieces. Some children can write pages and pages of repetitive nothingness. Ever since then, I have looked for crafted quality and am wary of children judging their own success by the number of lines competed.
Take a look at the piece of writing below. It’s an excellent example of a well-crafted piece.
Each paragraph is short, but the writer is skilful.
He used rich and precisely chosen vocabulary, he’s broken the text into natural paragraphs, and in the second paragraph he is beginning to vary his sentence openings. There is a sense of control to the sentences – the sentence structure varies with shorter and longer examples to manage tension. It is exciting to read, with a clear awareness of his audience. Punctuation is accurate and appropriate.

11+ creative writing example story
How important is it to revise for a creative writing task.
It is important.
Every student should go into their 11+ writing task with a clear paragraph plan secured. As each paragraph has a separate purpose – to showcase a specific skill – the plan should reflect this. Built into the plan is a means of flexing it, to alter the order of the paragraphs if the task demands it. There’s no point having a Beginning – Middle – End approach, as there’s nothing useful there to guide the student to the mark scheme.
Beyond this, my own students have created 3 – 5 stories that fit the same tight plan. However, the setting, mood and action are all completely different. This way a bank of rich vocabulary has already been explored and a technique or two of their own that fits the piece beautifully. These can be drawn upon on the day to boost confidence and give a greater sense of depth and consideration to their timed sample.
Preparation, rather than revision in its classic form, is the best approach. Over time, even weeks or months before the exam itself, contrasting stories are written, improved upon, typed up and then tweaked further as better ideas come to mind. Each of these meets the demands of the mark scheme (paragraphing, varied sentence openings, rich vocabulary choices, considered imagery, punctuation to enhance meaning, development of mood etc).
To ensure your child can write confidently at and above the level expected of them, drop them into my weekly weekly online writing club for the 11+ age group . The club marking will transform their writing, and quickly.
What is the relationship between the English paper and the creative writing task?
Writing is usually marked separately from any comprehension or grammar exercises in your child’s particular 11+ exam. Each exam board (by area/school) adapts the arrangement to suit their needs. Some have a separate writing test, others build it in as an element of their English paper (usually alongside a comprehension, punctuation and spelling exercise).
Although there is no creative writing task in the ISEB Common Pre-test, those who are not offered an immediate place at their chosen English public school are often invited back to complete a writing task at a later date. Our ISEB Common Pre-test students join the writing club in the months before the exam, first to tidy up the detail and second to extend the content.
What if my child has a specific learning difficulty (dyslexia, ADD/ADHD, ASD)?
Most exam boards pride themselves on their inclusivity. They will expect you to have a formal report from a qualified professional at the point of registration for the test. This needs to be in place and the recommendations will be considered by a panel. If your child needs extra arrangements on the day they may be offered (it isn’t always the case). More importantly, if they drop below a pass on one or more papers you will have a strong case for appeal.
Children with a specific learning difficulty often struggle with low confidence in their work and low self-esteem. The preparations set out above, and a kids writing club membership will allow them to go into the exam feeling positive and empowered. If they don’t achieve a pass at first, the writing sample will add weight to their appeal.
Tips and strategies for writing a high-scoring creative writing paper
- Read widely for pleasure. Read aloud to your child if they are reluctant.
- Create a strong paragraph plan where each paragraph has a distinct purpose.
- Using the list of example questions below, discuss how each could be written in the form of your paragraph plan.
- Write 3-5 stories with contrasting settings and action – each one must follow your paragraph plan. Try to include examples of literary devices and figurative language (metaphor, simile) but avoid clichés.
- Tidy up your presentation. Write with a good rollerball pen on A4 lined paper with a printed margin. Cross out with a single horizontal line and banish doodling or scribbles.
- Join the writing club for a 20-minute Zoom task per week with no finishing off or homework. An expert English teacher will mark the work personally on video every Friday and your child’s writing will be quickly transformed.
Pressed for time? Here’s a paragraph plan to follow.
At Griffin Teaching we have an online writing club for students preparing for the 11 plus creative writing task . We’ve seen first-hand what a difference just one or two months of weekly practice can make.
That said, we know that a lot of people reading this page are up against a hard deadline with an 11+ exam date fast approaching.
If that’s you (or your child), what you need is a paragraph plan.
Here’s one tried-and-true paragraph plan that we teach in our clubs. Use this as you work your way through some of the example prompts below.
11+ creative writing paragraph plan
Paragraph 1—description.
Imagine standing in the location and describe what is above the main character, what is below their feet, what is to their left and right, and what is in the distance. Try to integrate frontend adverbials into this paragraph (frontend adverbials are words or phrases used at the beginning of a sentence to describe what follows—e.g. When the fog lifted, he saw… )
Paragraph 2—Conversation
Create two characters who have different roles (e.g. site manager and student, dog walker and lost man) and write a short dialogue between them. Use what we call the “sandwich layout,” where the first person says something and you describe what they are doing while they are saying it. Add in further descriptions (perhaps of the person’s clothing or expression) before starting a new line where the second character gives a simple answer and you provide details about what the second character is doing as they speak.
Paragraph 3—Change the mood
Write three to four sentences that change the mood of the writing sample from light to gloomy or foreboding. You could write about a change in the weather or a change in the lighting of the scene. Another approach is to mention how a character reacts to the change in mood, for example by pulling their coat collar up to their ears.
Paragraph 4—Shock your reader
A classic approach is to have your character die unexpectedly in the final sentence. Or maybe the ceiling falls?
11+ creative writing questions from real papers—fictional prompts
- The day the storm came
- The day the weather changed
- The snowstorm
- The rainy day
- A sunny day out
- A foggy (or misty) day
- A day trip to remember
- The first day
- The day everything changed
- The mountain
- The hillside
- The old house
- The balloon
- The old man
- The accident
- The unfamiliar sound
- A weekend away
- Moving house
- A family celebration
- An event you remember from when you were young
- An animal attack
- The school playground at night
- The lift pinged and the door opened. I could not believe what was inside…
- “Run!” he shouted as he thundered across the sand…
- It was getting late as I dug in my pocket for the key to the door. “Hurry up!” she shouted from inside.
- I know our back garden very well, but I was surprised how different it looked at midnight…
- The red button on the wall has a sign on it saying, ‘DO NOT TOUCH.’ My little sister leant forward and hit it hard with her hand. What happened next?
- Digging down into the soft earth, the spade hit something metal…
- Write a story which features the stopping of time.
- Write a story which features an unusual method of transport.
- The cry in the woods
- Write a story which features an escape
11+ creative writing questions from real papers—non-fiction prompts
- Write a thank you letter for a present you didn’t want.
- You are about to interview someone for a job. Write a list of questions you would like to ask the applicant.
- Write a letter to complain about the uniform at your school.
- Write a leaflet to advertise your home town.
- Write a thank you letter for a holiday you didn’t enjoy.
- Write a letter of complaint to the vet after an unfortunate incident in the waiting room.
- Write a set of instructions explaining how to make toast.
- Describe the room you are in.
- Describe a person who is important to you.
- Describe your pet or an animal you know well.
Activity: Story Mountain
Complete the story mountain to plan your sotry with a beginning, middle, and end.
Activity: Character profile
Come up with lots of interesting details about the lead character in your story.
Video: How to develop storytelling skills
Suzy Ditchburn offers practical tips for improving storytelling confidence.
5. Find story inspiration
You can find fun story ideas anywhere! Why not raid your kitchen cupboards or hunt through the attic to find lost treasures? Anything from an old hat to a telescope will do the trick. What could the object be used for? Who might be looking for it? What secrets could it hold? Suggest different genres such as mystery or science fiction and discuss how the item might be used in this kind of story.
Real-world facts can also be a great source of inspiration. For example, did you know a jumping flea can accelerate faster than a space rocket taking off into orbit? What crazy story can your child make out of this fact? Newspapers and news websites can be great for finding these sorts of ideas.
If your child prefers non-fiction, use the facts you find to create a fact sheet, a poster or a mini-book.
6. Get drawing
If your child isn’t sure where to start, it can sometimes be helpful to sketch out their ideas first. For instance, can they draw a picture of a dastardly villain or a brave hero? How about a scary woodland or an enchanted castle? Can they draw the shark or spider they want to write an information book about?
Your child might also find it useful to draw maps or diagrams. What are all the different areas of their fantasy landscape called? How is the baddie’s base organised? Or for non-fiction, where does their shark or spider live?
Some children might enjoy taking this idea a step further and drawing their own comics. This is great practice – it stretches your child’s creativity, gets them thinking about plot, character, and dialogue, and is a big confidence boost once they’ve finished and have an amazing story to look back on.
For more ideas on writing stories, look at our Creative Writing page or check out our Creative writing books .
What your child will learn at school
Click on the links below to find out about the writing skills children practise year by year.
Writing Composition in Year 1 (age 5–6)
In Year 1, your child will learn:
- to write simple sentences
- to say a sentence out loud before writing it down
- to put sentences into the right order to tell a short story
- to re-read what they have written to check that it makes sense
- to talk about their writing with their teacher or classmates
- to read their writing out loud to their teacher or the class.
Writing Composition in Year 2 (age 6–7)
In Year 2, your child will learn:
- to write about things that have happened to them
- to make up simple stories
- to write about real events
- to write simple poems
- to write non-fiction for different purposes
- to plan their writing by either talking about what they want to write or by writing down key words
- to read their own writing and make changes to it
- to read their writing out loud.
Writing Composition in Year 3 (age 7–8)
In Year 3, your child will learn:
- to talk about similar pieces of writing, and using these to help them plan their own
- to plan their writing by talking about it or writing down key words
- to use a rich vocabulary and a range of sentence structures to make their writing interesting
- to create settings, characters, and plots for stories
- to use simple organisational devices (for example, headings and sub-headings) when writing non-fiction
- to proof-reading their writing for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors
Writing Composition in Year 4 (age 8–9)
In Year 4, your child will continue to practise the skills they learnt in Year 3. They will:
- talk about similar pieces of writing, and using these to help them plan their own
- plan their writing by talking about it or writing down key words
- use a rich vocabulary and a range of sentence structures to make their writing interesting
- create settings, characters, and plots for stories
- use simple organisational devices (for example, headings and sub-headings) when writing non-fiction
- proof-reading their writing for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors
- read their writing out loud.
Writing Composition in Year 5 (age 9–10)
In Year 5, your child will learn to:
- decide who they are writing for and what this means for their writing
- plan their writing before they start
- choose the right style and structure to match the type of text they are writing
- choose the right vocabulary and grammar for their writing
- write a story with interesting vocabulary and dialogue
- write non-fiction with features such as headings, captions, bullet points, subheadings and diagrams
- use a consistent tense throughout their piece
- check their own writing and the writing of their classmates, making useful comments.
Writing Composition in Year 6 (age 10–11)
In Year 6, your child will learn to:
- write non-fiction with features such as headings, captions, bullet points, subheadings, diagrams
Creative writing through the arts in primary schools
- Original Research
- Published on: September 12, 2019

- Art and Design |
- Creativity |
- Cross-Curricular |
- Language and literacy |
- Professional learning
Can more arts and creativity in primary schools improve children’s writing? Our research to address this question began at a time when primary schools were facing continuous pressure to raise writing standards and, simultaneously, struggling to maintain a broad and creative curriculum.
Integrating arts with writing…
Our strategy to integrate arts with writing coincided with publication of a new National Curriculum ( DfE Department for Education - a ministerial department responsi , 2014). Designed to raise standards in core subjects, the programme of study for English is detailed and prescriptive, with more than 60 pages of precise specifications for Key Stages 1 and 2. In contrast, there is little emphasis upon art, design or music, with guidance for these subjects slim at just two pages each. This goes against many educators’ better judgement, as it risks forcing a narrowing of the curriculum, including restricting approaches to the teaching of writing, in order to meet required levels of performance on standardised tests (Beard, 2019).
This is a rather different policy landscape from two decades ago when, inspired by the ‘All our futures’ report (NACCCE, 1999), there was strong interest in the importance of arts and creativity in all types of education. The government-funded Creative Partnerships programme saw artists partnering with schools, with many positive outcomes, including benefits for children’s language and literacy learning (Safford and Barrs, 2005).
The importance of learning through the arts and valuing a range of modes of representation, including physical and emotional expression, remains vital. Opportunities to explore ideas through art, drama, music and movement foster children’s imagination and can help develop their thoughts into extended writing (CLPE, 2018).
In the absence of artists in schools, due to diminishing budgets, it is a challenge to provide worthwhile arts experiences. Teachers, who may not have received any in-depth arts training, need to acquire knowledge and skills in arts subjects. To enable teachers to elicit children’s ideas effectively, we consider that specific artist-led professional development is needed.
The project
In response to this, two successful arts and creative writing pilot projects (one with early career teachers and another focused upon promotion of student voice) were initiated by Royal Opera House Bridge (ROHB) and Essex schools in collaboration with Anglia Ruskin University. Our current three-year ‘Creative Writing through the Arts’ (2016–2019) project continues these partnerships and is funded by the Paul Hamlyn Foundation ‘More and Better’ scheme, with investment from ROHB and 45 primary schools in South Essex (to support the costs of this valuable professional learning opportunity for teachers). The project aim is to promote children’s creative writing skills through integration of writing with art, dance, drama, film and music activities in primary school classrooms (from Foundation Stage to Year 6).
Teachers undertake professional development in each of the five arts subjects, through ‘Inspiration Day’ workshops with creative practitioners. These are immersive days, one held near the beginning of each school term, where teachers participate in activities and reflect upon ways to utilise new arts techniques in their lesson planning. Teachers then implement ideas in their classrooms, supported by mentoring visits from the creative practitioners.
For example, on an Inspiration Day for music, teachers listened to ‘Ritual Fire Dance’ by Manuel de Falla, identifying and describing elements of the music in lay-person’s terms (e.g. loud, quiet, fast, slow, smooth, quivery, stabbing). On second listening, they jotted down a story that the music could be portraying and then created compositions, using percussion instruments, based on the sounds and story of the piece, and performed these to one another. Taking this inspiration back into school, one Year 4 class were reading the book FArTHER by Grahame Baker-Smith, about a father who goes off to war. To evoke the emotions in the story, students listened to Puccini’s ‘Sono Andati?’ (from La Boheme ) and created a large ‘emotions cloud’, before writing heartfelt diary entries from the perspective of the son.
This model is repeated for all art forms, with different ‘Inspiration Day’ activities and varied approaches to follow-up mentoring by the artists, including half-day school visits for discussions, observations, team teaching and co-planning of lessons, and small group follow-up where teachers share what is working well in their teaching through the art form and where they are facing challenges, and are supported by the artist and their peers to envisage new possibilities (see Luff et al., 2018; Luff et al., forthcoming).
The research and evaluation
An integral element of the project is collaborative action research between academics and the 45 project teachers, taking into account student voice. In each of the three years of the project, 15 teachers carry out action research to explore the effectiveness of the approach for students in their class, assess potential to incorporate arts across the curriculum, and reflect upon the outcomes. Their findings are shared verbally (at termly action research meetings), through narrative reports and on a final summary poster for the Celebration Event at the end of each year, where posters are shared along with exciting displays of supporting evidence.
At the action research meetings, the teacher-researchers share and analyse findings from across their classrooms, identifying common themes and recognising benefits of working through the arts. These findings from the teacher action research are cross-validated through independent assessment of writing samples collected from children in each of the participating classes. Teachers also complete questionnaires at the beginning and end of the school year, researchers visit schools to attend to student voice, and interviews are carried out with headteachers (for details see Davis et al., 2017; Luff et al., 2018; Luff et al., forthcoming).
Key findings
The findings reported here summarise benefits for students, teachers and schools found from the first two years of the Creative Writing through the Arts project (Davis et al., 2017; Luff et al., 2018), with illustrative examples. The project is currently concluding, and findings from the third year of the project and across the three years of the project will be reported this year (Luff et al., forthcoming).
Students’ writing
Students gain ideas and meaningful reasons for writing, write more and produce work of higher quality. With arts input that fires their imagination, children display originality in their work and incorporate an expanded range of all tiers of vocabulary. Increased use of literary devices is shown in their arts-inspired writing: detail and description through expanded noun phrases, similes and metaphors; emphasis (alliteration, onomatopoeia); development of character and setting; use of rhetorical devices; foreshadowing; symbolism; and use of viewpoint and voice. Some of these characteristics are well illustrated in this extract of writing from a Year 4 student, inspired by dance activities linked to Gulliver’s Travels :
Why I thougt? Why must I sufer? What crime have I commited? Who have I sinned against?… I wonder, are these walls solid. For whenever I leaned against a wall I felt my mind, body and soul fall into an endless abis of misery, doubt, fear and all things negative. Shrouded by darkness, I lost everything my life force, my strength, my life…
Students’ learning
The children’s enthusiasm for the arts activities results in high motivation to write, including for boys. They engage with arts and writing processes, showing involvement and sustained attention. As expressed by one teacher:
The children have been so engaged with all the activities and are so much more eager to want to write. Children who previously shied away from more creative activities now love it when we incorporate arts activities into lessons… The class are so eager to share their work with their peers and their confidence as writers has blossomed… Even previously reluctant writers are those who are coming up to me, asking if they can share their work with the class. Children have also mentioned that they are regularly writing stories and poems at home. There has definitely been a shift in terms of enthusiasm to write and what is being produced has been to a better standard than before.
Teachers are inspired by their participation in the project and often surprised and excited by outcomes for all students. They report gains in enthusiasm and confidence in arts-based teaching, and claim that their teaching of writing has been (re)invigorated.
Teachers used student voice tasks and techniques to encourage critical reflection, self-assessment and extension of learning. There is often a sense of mutual learning between children and teacher. For example, from a Year 2 teacher:
I’ve become aware since doing the project that I can be too structured in some of my teaching, so this session I left the children to it and watched their ideas pan out. I now feel more confident to try out some of my own ideas and be more inventive.
Teachers have also appreciated the professional learning opportunity and community, and establishing a network of other teachers to discuss issues with, as well as the development of skills, knowledge and techniques for teaching using creative art forms.
The schools in the project value the increase in creative and cultural learning. There is immediate sharing of tools, techniques and strategies, and some specific activities have been disseminated through and across schools. There is growing wider implementation of the creative ideas, for example within teaching school alliances and academy chains. One headteacher expressed a desire for the approach to become embedded:
For us, it’s been a lovely project to be part of and I think… in years to come, we will see the benefits of it, when it becomes a natural part of our daily practice… My hope is that, like most things, it becomes part of the school’s ethos and actually you don’t even think about it, it’s just a natural thing to do.
Implications for practice
Overall, the project explores and celebrates the value of educators working in partnership with the cultural sector to develop curriculum and pedagogy for successful writing through the arts. The project offers insights for curriculum design in primary schools as the wheel turns towards more broad and balanced approaches. The project is timely in the light of a realisation, backed by Ofsted The Office for Standards in Education, Children’s Services (2019), that the curriculum has narrowed too much and that teaching an integrated creative curriculum does not preclude excellence in writing. We advocate a cross-curricular approach that values rich learning for the whole child, whatever their talents and interests. For this to happen, it is essential that teachers and schools feel confident in their creative knowledge and skills, and so we recommend the involvement of artists and creative practitioners in future initial teacher training Abbreviated to ITT, the period of academic study and time in and worthwhile, cost-effective continued professional development.
Beard R (2019) Reading and writing in primary schools: Processes, practices and priorities. ASPE Bulletin , Issue 3. Available at: www.aspe-uk.eu/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/ASPE_Bulletin_Issue3_March2019.pdf (accessed 22 July 2019).
Centre for Primary Literacy Education (CLPE) (2018) Writing in primary schools: What we know works. Available at: https://clpe.org.uk/library-and-resources/what-we-know-works-booklets/writing-primary-schools-what-we-know-works (accessed 2 June 2019).
Davis G, Luff P, Kanyal M et al. (2017) Creative Writing through the Arts 2016–2019. End of year report, Autumn 2017. Available at: http://arro.anglia.ac.uk/702478/ (accessed 2 June 2019).
Department for Education The ministerial department responsible for children’s serv (DfE) (2014) National Curriculum in England: Framework for key stages 1 to 4. Available at: www.gov.uk/government/publications/national-curriculum-in-england-framework-for-key-stages-1-to-4 (accessed 2 June 2019).
Luff P, Acton F, Feist A et al. (2018) Creative Writing through the Arts 2016–2019. End of year report, Autumn 2018. Available at: https://arro.anglia.ac.uk/703659/ (accessed 2 June 2019).
Luff P, Kanyal M, Quayle D et al. (forthcoming) Creative Writing through the Arts 2016–2019. Final research report.
National Advisory Committee on Creative and Cultural Education (NACCCE) (1999) All Our Futures: Creativity, Culture and Education . London: DfEE. Available at: http://sirkenrobinson.com/pdf/allourfutures.pdf (accessed 2 June 2019).
Ofsted (2019) The education inspection framework. Available at: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/801429/Education_inspection_framework.pdf (accessed 2 June 2019).
Safford K and Barrs M (2005) Creativity and literacy: Many routes to meaning. Available at: https://clpe.org.uk/library-and-resources/research/research (accessed 2 June 2019).
From this issue

Issue 7: Arts, Creativity and Cultural Education
Autumn 2019
Impact Articles on the same themes

From the editor

Transforming assessment principles and practices through collaboration: A case study from a primary school and university

- Perspective Article
The currency of assessment for learners with SEND

Rethinking assessment: How learner profiles can shift the debate towards equitable and meaningful holistic assessment

Assessing progress in special schools: Reviews and recommendations

Classroom assessment in flux: Unpicking empirical evidence of assessment practices

The role of frequent assessment in science education at an international school in Singapore
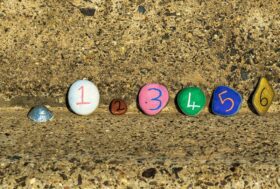
- Teacher Reflection
Teaching creativity: An international perspective on studying art in the UK

Improving academic resilience and self-efficacy through feedback: Moving from ‘what’ to ‘how’

Mind the gap: What are national assessments really telling us about vocabulary and disadvantaged students?
Pears Pavillion Corum Campus 41 Brunswick Square London WC1N 1AZ
[email protected] 020 3433 7624


COMMENTS
High school students can either be tasked with more complex writing prompts or breathe nuance into simple story ideas. Students can drive these prompts in a million different ways. So while not necessarily more complicated than middle school, these prompts can be tweaked, either by the student or teacher, to encourage thought-provoking output.
By figuring out what elements make stories great, this is sure to help them in their own creative writing assignments! Learn More: Little Lifelong Learners. 33. The Best Part of Me. Probably my favorite creative writing activity, this one is infused with social-emotional learning and self-esteem building!
Which is better, winter or summer? Write about the reasons why you think winter or summer is better. #4. Write about what would it be like if you had an alligator as a pet. #5. If you had $1,000, what would you buy and why? #6. Write a story using these 5 words: apple, train, elephant, paper, banjo. #7.
150 Inspiring Picture Writing Prompts To Spark Creativity (Free Google Slides) Use a picture to write a thousand words! By Jill Staake, B.S., Secondary ELA Education. Jan 18, 2024. Creative writing is a challenge for many students, often because they can't come up with anything to write about. That's why we love picture writing prompts.
Good writing prompts get students' creative juices flowing, help them write more freely, and ease any anxiety they may feel about the writing process.To integrate writing prompts into your lessons, ask students to choose one writing prompt each day or week. To make the activity more challenging, encourage them to write without stopping for at least five minutes, increasing the number of ...
Story language. Ask your child to think of some fabulous words to use in their story writing. They might be long words or simple ones, or they might be great descriptive words or words that help create pace and tension. Encourage them to jot these down and refer to the list as they write their story.
This narrative writing activity can teach students to write events clearly and in sequence from their real life. 12. For a creative writing project that's just plain fun, try this Roll a Story activity. 13. This nonfiction project helps children learn to write a letter as they write to a loved one of their choice. 14.
Try these story starters, structures, worksheets and other fun writing prompt resources for primary pupils…. by Laura Dobson. DOWNLOAD A FREE RESOURCE! Creative writing prompts - 5 worksheets plus word mats for KS1 and KS2 pupils. Download Now.
Once students start getting in the habit of writing, these creative writing activities can pull new ideas out of their heads and encourage them to experiment with different genres. 5. Acrostics. Great for: Grades 3 to 8. Acrostic poems are a great way to introduce your students to poetry!
8. Get creative with the teaching. Where possible, try to connect what the children are interested in with their writing. For example, if you have learners interested in Minecraft, they could write a letter of persuasion to the Prime Minister to persuade him to allow Minecraft lessons in school.
11. Hard Work Pays Off. Write about a character who wanted something very much, and how he or she worked hard to get it. Purpose: Creative writing for primary 3 students should draw from the child's imagination to construct an inspiring story. Read more: How to Make Creative Writing for Primary 3 Easy for Children. 12.
4 x fun and flexible creative writing lessons which will excite even the most reluctant writers; fun activities which guide your pupils through the key elements of narrative writing (descriptive settings, developing characters and structuring a story); creative writing competition linked to the less...
Good English Composition Examples for Primary School. The model compositions compiled here are written by our students. These are good English composition examples and they give you an idea of what primary school students are capable of writing. We take in a wide range of students in our weekly writing classes and online courses. Some of them ...
Writing prompts for students from Year 3-6, including creating writing, poetry, opinion pieces and newspaper articles. To become a good writer, you'll need to practise, practise, practise. If you're short on ideas, use our prompts to get started. Write an Ode to your favourite food. Write a poem from the point of view of an item in your home.
Phonics and spelling. Whole School Literacy. More. Tes primary English resources has an unrivalled range of teaching ideas for creative writing activities. Breathe new life into your lesson plans for KS1 and KS2 with our resources and materials, including: - Creative writing worksheets and activities. - Writing activities. - Storytelling projects.
What is creative writing? Children are encouraged to read and write a range of genres in their time at primary school. Each year they will focus on various narrative, non-fiction and poetry units; we explain how story-writing lessons help develop their story structure, grammar and punctuation skills.
Narration - the voice that tells the story, either first person (I/me) or third person (he/him/she/her). This needs to have the effect of interesting your reader in the story with a warm and ...
Creative-Writing Prompts Templates. Shipwrecked If you're drowning trying to find creative-writing topics for the classroom, then pictures are a great way to stimulate ideas. Download our Creative-Writing Prompts Templates and choose the pirate-themed image to ask children to write about being shipwrecked on an island and finding hidden ...
Creative writing plays an important role in a child's literacy development. This article makes suggestions for the instruction and evaluation of children's stories. Most children enter school with a natural interest in writing, an inherent need to express themselves in words (Graves, 1983). Couple this with a child's love of stories and ...
Due to the significance of creative writing instruction, there has been significant focus on creative writing practices in primary schools (Graham et al., 2012(Graham et al., , revised 2018Göçen ...
Interestingly, many of the studies used literary forms and/or professional creative authors to spike interest and motivation in the students. Coles' study, for example, used a garden-themed poetry writing project to support 9-10-year-old children's creative writing in a London primary school. The 5-week project partnered with a ...
11+ creative writing questions from real papers—non-fiction prompts. Write a thank you letter for a present you didn't want. You are about to interview someone for a job. Write a list of questions you would like to ask the applicant. Write a letter to complain about the uniform at your school.
3. Try some real-world writing. Writing for a real purpose can be a great way to fit in some practice. Writing cards, shopping lists, or letters or messages to relatives can be motivating real-life reasons for writing, and can show children how useful it is to be able to write well. They will also learn that we use different writing styles in ...
The project aim is to promote children's creative writing skills through integration of writing with art, dance, drama, film and music activities in primary school classrooms (from Foundation Stage to Year 6). Teachers undertake professional development in each of the five arts subjects, through 'Inspiration Day' workshops with creative ...