Year 6 writing at greater depth (GDS): quick wins, guidance and helpful materials
Note: This website works best with Javascript enabled. With Javascript disabled some parts of the website may not work as expected.

This is not an ideal time for a blog about end of KS2 statutory writing assessment. It’s the week after SATs for one thing. So, this blog is deliberately geared towards the immediate weeks ahead. It’s clear from so many conversations, across so many schools, that quick win advice might go down well right now. For some, addressing gaps caused by pandemic disruptions remained a priority up until recently. It’s hardly surprising that talk has been of expected drops in the numbers achieving GDS standard in writing. Still, there have been a number of requests for support in identifying writing opportunities that might be helpful in the final stretch of the assessment window.
This blog aims to provide some guidance along those lines. It does not reflect our wider views and approaches to developing reader-writers. It’s a deliberately short term and strategic look at primary writing with a particular aim in mind. It’s also an attempt to take some of the weight from our year 6 colleagues’ shoulders in what has been another challenging year. Under 'normal' circumstances, this time of year for the Year 6 teacher, especially the new-to-year-6 teacher, is seared into my own teaching memory. It can feel lonelier than it should, no matter how many times you might be told “You’ve got this”, no matter how healthy an outlook we might have on the place and nature of statutory KS2 assessments.
So, without any apologies, I’ll crack on with some targeted advice and helpful links.
The blog has three sections:
- section 1 looks at examples of pupil’s writing from the STA and highlights a broader view of what might constitute GDS writing. I think this might be most useful in relation to nudging possible borderline cases, and for some quick win writing opportunities in the run up to the close of the assessment window
- section 2 offers links to four evergreen, hugely helpful blogs from our Assessment Team (@HertsAssessment) colleagues, offering practical guidance related to writing moderation and the TAFs
- section 3 gathers links to my earlier blogs on the topic of GDS writing for those that have joined Twitter/become familiar with our blogs more recently. These offer further writing opportunities

1. In search of a benchmark: widening writing exemplifications
1a. core exemplifications.
Just briefly, let’s remember Frankie in all this. Frankie the ‘epitome’ of GDS .
Frankie stands as the one-and-only STA exemplification of writing judged to be representative of GDS for writing. My relationship with Frankie’s writing efforts rivals some of my friendships in terms of how often we get to interact. In recent weeks, we’ve become aware of newer teachers/year 6 returners that are not familiar with this bank of work.
For those not familiar, it’s essential reading under the current system. If you haven’t before, read the work and the associated commentaries, focusing on the most useful, perhaps less florid parts. This will give you a common reference point with year 6 teachers across the country. You can find it here:
Gov.UK: Teacher assessment exemplification: English writing - working at greater depth within the expected standard, Frankie .
Keep in mind this statement from the opening of the exemplification files:
"Exemplification materials illustrate only how 'pupil can' statements in the frameworks might be met. They do not dictate a particular method of teaching, or the evidence expected from the classroom, which will vary from school to school. "
The word 'might' is important here – Frankie is one manifestation of the standard, not a definitive model. This is good news. Otherwise, we’d all best enrol our children in ballet classes at the earliest opportunity.
Reading each piece and considering the most useful parts of the commentaries can help us to keep in mind aspects of writing that we might want to draw attention to when working with the most assured writers. Exemplification banks, without the commentaries, can also offer some useful opportunities for focused reading for our children to see the work of others and consider what they like/dislike and how they would have gone about a similar task. This can add further layers to awareness of the limitless networks of choices that writers have at their disposal.
I used the plural ‘exemplification banks’ deliberately. Turning to one of the EXS exemplifications might help Frankie seem a little less lonely.
Meet Leigh , handily remembered as Near-Leigh GDS Leigh. My former colleague Clare Hodgson, our then moderation lead, wrote about Leigh’s work and how it might offer more helpful hints in an earlier blog for the assessment team.
Take a read of this helpful snippet in which Clare flags some learning relating to bullet 3 of the GDS statements. I’d thoroughly recommend reading the whole of this immensely popular blog .
Obviously, writing such as 'Frankies' clearly meets this statement - but how 'assured and conscious' do our Y6 writers need to be? Here it is worth turning to the 'Leigh' exemplification file as a benchmark as Leigh only narrowly misses the greater depth standard. There is one piece - piece B - where Leigh is able to meet the 'assured and conscious control' statement. The annotations on the remaining pieces show where Leigh has been less consistent and hence why the award remains at expected standard.
Reflect too, as you read the collection, on the purpose and audience for each piece in the collection. Are there enough opportunities for Leigh to write formally? Could more opportunities for formal writing have helped? Does the recount provide any evidence for Greater depth? (No!) Additionally, has Leigh been given adequate time to re-draft some sections of his/her work to consider precision of language, or tidy up punctuation? The implications are that greater depth writers may need longer to craft their writing, as well as more exposure to a range of reading material and a range of tasks that have clearly defined purpose and audience.
Leigh’s writing is offered as one of two banks that exemplify writing demonstrating sufficient evidence of the requirements for a judgement of EXS, but was evaluated as stronger than their fellow EXS-achiever Morgan. Towards the end of each bank there is a tick-grid showing which pieces meet which bullet point in each standard. Here’s Leigh’s tally sheet for the EXS statements. If it was a game of bingo, you’d be getting excited:

It's almost a clean sweep. Bullet two and three relate to narrative features and are demonstrated sufficiently well in two pieces to secure an overall nod of approval for those two statements, as shown by the tick in the final column. Piece A did not offer evidence of the EXS spelling list statement, but given that every other piece does, it’s no wonder that that statement is also judged to be fully met.
Nice work Leigh. So let’s give the GDS bullets a quick once-over.

Back to our imagined game of bingo. It’s far from a full house but Leigh does manage to get a complete line of ticks for Piece B (third column) and a close-to-complete line for piece E (sixth column).
It’s by looking at these pieces that we can begin to broaden our view of the nature of writing that might support a judgement of GDS. Frankie is a very particular, ballet-obsessed writer who may well skew judgements towards a very secure bank of evidence demonstrating the standard. Leigh is a very particular, different kind of writer, offering pieces that might draw closer parallels with the writing produced by your children. In piece B, we have something that we might fairly characterise as 'very recognisably primary school writing'. It’s writing that with the right inputs, we might see from confident Year 4 writers. Here its labelled as procedural; for our purposes I am going to call it Very Fancy Instructions. Take a look, read the piece, read the commentaries, and consider how you might apply some of those pointers to writing from your own curriculum. It’s a style of writing that is likely very familiar to your young writers. Might Piece B offer some inspiration for some instructional writing based on rich, well-known content?
Piece E, a retelling of Jack and the Beanstalk in something like the Star Wars universe, meets all but bullet 3 (as discussed by Clare above). Once again the commentaries are instructive and acknowledge some strengths in the manipulation of grammar, and some indications of why it doesn’t quite hit the spot. Might this be useful in revisiting earlier narrative writing with a view to some targeted editing with that bullet point in mind? Further developing the literary language used in a piece, moving beyond structures more typical of day-to-day speech will likely pay dividends. Giving children the chance to revisit earlier writing with a more mature eye can make all the difference and is a perfectly legitimate writing activity. Writers revisit old work; writers put down a project and pick it up later, with fresh, or older, wiser eyes. Your writers shouldn’t be any different – and that really can be a very quick win. It’s also immensely gratifying for children to appreciate for themselves their own progress and growth as writers in their time with you. Revising earlier pieces will provide an opportunity for this, as well as a further lesson that writing is something to be crafted over time, not just within the context of a single lesson or unit.
1b. Lessons from moderation materials

Besides Leigh’s writing, there are further samples to draw from in the collections used in Lead moderator/moderator standardisation exercises. These can be found in various locations, but our friends at Babcock offer up a beautifully well-organised webpage gathering them all together for very easy access. Thank you Babcock – this has been so useful in terms of its clear layout.
Please do me a quick favour, to help with orientation, if this is new to you:
- follow this link - Devon County Council: KS2 Pupil Writing Collections (previously Babcock)
- scroll down slowly enough to count the number of collections judged at GDS
I make it nine. Nine is better than one. Include Leigh here and we have nine-and-a-bit. Frankie is no longer the singular star in a GDS solar system. We’ve got a galaxy of pointers, all with commentaries and some really nice pieces to broaden the horizons of all three standards.
Let me direct you to 2019 KS2 standardisation exercise 2 and take a look at Pupil C’s work, judged as meeting GDS. This one gave a number of moderators pause for thought. It has many nice touches, but it has its shaky moments. Here’s a top tip: if you are ever unsure whether a bank represents achievement at EXS or GDS, read it out loud. It really helps. Try reading some of Pupil C out loud. You’ll pick up on some less confident stretches, minor lapses, and moments where they seem to become somewhat locked into a groove, unsure of where to go next.
This writing is officially judged to have indicated a higher achievement than Leigh’s but I also think it offers a less intimidating vision of what GDS might look like. Some evidence banks scream GDS almost instantly. They are just plainly, obviously GDS through and through. That's arguably less useful in terms of mapping out the standard, and certainly not so useful in helping us make a call on borderline cases.
From this bank, and again like Leigh, take a look at the pieces that stand out as fairly common primary writing tasks, for example Piece B, the science investigation . Familiarity is helpful. What do they do there that makes that piece contribute to the overall judgement? Might your children do better? For instance, I think the investigation loses sight of its purpose once it gets to the second page, and there are real lapses in clarity. A sharper, scaled down version of the evaluations would have helped me maintain a better understanding of the learning from this investigation. Might this present an opportunity to revisit some similar work from across the year?
Then there’s Piece C, an information text on a ‘newly discovered, genetically engineered hybrid animal’ drawing upon research of two distinct species:

For our purposes here, let’s just note some especially helpful aspects of this piece:
- it legitimately offers scope to make use of more formal language structures (bullet 3) and as such achieves a suitably authoritative and expert register (bullet 2)
- each section is very short – generally around the 50-60 word mark. Writing in chunks or bursts on distinct aspects of the topic should generally be less demanding than a task that builds in additional challenges from text level conventions or requirements. I can picture my children taking a section in turn (perhaps on differently coloured paper to reinforce their distinctness - don't ask me why, it just seems to help keep things in their rightful place) and working in a very focused, deliberate way for each domain
- the range of conjunctive language is relatively limited but is used effectively to link ideas (and when, where, despite, because, before, also)
- perhaps most importantly, the familiarity and friendliness of the form – this type of text is a a staple in non-fiction reading across the primary phase, and will have likely had a place in writing lessons in multiple year groups, across the phases
- finally, keep in mind the availability of books that provide a rich bank of language/language features as helpful incidental models of this kind of writing, for example Norman Messenger’s The Land of Neverbelieve as well as online entries describing the features of real animals just waiting to try a new kind of coupling
In terms of quick wins, you might want to think about those tasks that are most obviously aligned to generic primary writing: Leigh’s procedural/instructions writing based on a taught topic; the science write up; the information text; the narrative sequences/episodes (as opposed to full short stories). They may well prove useful as targeted reading, close to the act of writing. Discuss with children what they like and what sort of friendly critique they might offer the authors. Try and divorce these pieces from their statutory assessment context and any sense of 'teaching to the test' and instead foster a notion that we are simply looking at, and evaluating, some work from peers in a wider community of writers. Take note of features that they find especially effective and begin to consider how this might influence their own writing, whether in fresh composition or in revisiting and revising older work.
2. Guidance related to writing moderation/TAFs
This section provides a series of links to blogs from our colleagues in the Assessment Team ( @HertsAssessment ). Each provides helpful and accessible insights from previous rounds of moderation based on the current TAF.
'Write away!' and other lessons derived from the 2018 KS2 Writing Moderations
Clare Hodgson, my former co-presenter of our Y6 GDS writing course, wrote this extremely helpful blog drawing upon her experiences as a lead moderator, and those of the moderation team she worked with. This blog was written in October of that year, so keep in mind that much of the advice is geared towards the rest of that academic year. That said, it contains an extremely helpful checklist for downloading that should prove helpful at this late stage of the year. Clare offers five, easily-digested ‘lessons’, that will also serve as a very helpful primer for next year – especially for those new to year 6, or new to the Year 6 writing framework.
Declaration of Independence
As the title suggests, this blog looks at the notion of independence and independent writing. If any questions remain in relation to this aspect of the statutory requirements, here’s a good place to head.
With sincere thanks to our colleagues on the Assessment Team.
3. Earlier blogs on GDS
I’d just like to bring this blog to a close by flagging some further pieces that I put together between 2017 and 2021. Between them they offer a range of guidance and suggestions designed to support the achievement of GDS but situated within the context of whole class teaching. Please note that the earliest blogs reflect the Interim Teacher Assessment Frameworks (2016 and 2017). Expectations have changed – and if you didn’t teach under those, well, that’s something to be thankful for. Three of those blogs, the In Search of…series, explicitly address the challenges around expectations for formal and informal writing. Please note, the infamous requirement to shift between levels of formality, like some kind of language-based Hokey Cokey, no longer applies. And that is a very good thing indeed. Nonetheless, the wider points about voice, register and levels of formality should still be useful. Each link has a summary so that you can target your reading according to your needs.
The long and the short of GDS in Year 6 writing
An introduction to the current framework, with a brief exploration of each of the four bullets.
GDS and writing in year 6: keeping things focused now time is short
This blog built on the one directly above it. It looks at the role that reading might play in developing writing and offers some suggestions around particular approaches to instruction that might prove especially helpful when time is running short. As such, it offers further quick win suggestions, in addition to those given in Section 1.
Martin Galway

- HFL Education Board of Directors
- HFL members information
- Corporate social responsibility
- HFL Education Executive
- Education Services team
- Business Services team
- Anti-racism statement
- Gender, ethnicity and disability pay gap
- Latest news
- HFL Education podcast
- Press and media
- Contract services - academies
- Contract services - maintained schools
- Key Stage 1 (KS1) Reading Fluency Project
- Key Stage 2 (KS2) Reading Fluency Project
- Key Stage 3 (KS3) Reading Fluency Project
- Key Stage 4 (KS4) Reading Fluency Project
- Collaboration with the Education Endowment Foundation (EEF)
- KS2 Reading Fluency Project: Education Endowment Foundation (EEF) funded trial
- Early Years advisory and consultancy support for schools
- Early Years expert keynote speakers and trainers
- Early Years PVI services
- Early Years PVI and schools training
- Early Years Quality Standards (EYQS)
- Evaluate the Effectiveness of your Early Years Provision (EEEYP)
- Safeguarding Audit for the Early Years
- Supporting Smooth Transitions
- Foundation subjects and curriculum design
- Secondary school effectiveness
- GCSE English, maths and science and maths 'A'-level remote revision support
- Anti-bullying
- Behaviour and attitudes to learning
- Herts Voices
- HFL Education Wellbeing Quality Mark
- Online safety
- Race equity and anti-racism
- Relationships Education, including RSE, RSHE and PSHE
- SEND support for mainstream schools
- Eastern Partnership UK (SEND)
- Special Schools and Educational Support Centres
- Leadership and management support
- Small Schools' Programme
- The Great School Framework
- Curriculum Modelling and Timetable Service
- Business management services
- Financial services for academies
- Financial services for maintained schools
- Supporting governing boards
- Clerking services
- Governance consultancy services
- Governor training
- Modern Governor
- Governors in Hertfordshire
- GDPR Data Protection Officer and Toolkit Service
- GDPR Health Check
- Leadership recruitment
- Teach in Herts
- HFL Supply Framework
- HR Advisory Service
- HR Business Partner Service
- HR Consultancy
- Mediation Service
- Investigation Service
- Restructure and Organisation Design Service
- TUPE Support Service
- 360-Degree Feedback Service
- Insights Discovery
- HR Training and L&D
- Staff Absence Insurance
- Financial Planning and Support for Staff
- Managed Payroll Service
- Occupational Health Service and Employee Assistance Programme
- Create and implement a digital strategy
- EdTech in schools
- HFL Broadband
- HFL MIS Framework
- Making the most of your MIS
- Technology in Schools Service Desk
- HFL Education Hub
- HFL Education Annual Mathematics Challenge
- All resources
- Early Years
- Mathematics
- Religious education
- Equality and diversity
- HR and recruitment
- School business management
- Technology and MIS
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Education, training and skills
- School curriculum
- Primary curriculum, key stage 2
- Tests and assessments (key stage 2)
Teacher assessment exemplification: KS2 English writing
Examples of pupils' work to support teachers' assessment of English writing at the end of key stage 2.
Teacher assessment exemplification: English writing - working towards the expected standard, Dani
Ref: ISBN 978-1-78644-852-1, STA/18/8104/e
PDF , 2.13 MB , 30 pages
Teacher assessment exemplification: English writing - working at the expected standard
Ref: ISBN 978-1-78644-850-7, STA/18/8102/e
PDF , 1.97 MB , 44 pages
Teacher assessment exemplification: English writing - working at the expected standard, Leigh
Ref: ISBN 978-1-78644-849-1, STA/18/8101/e
PDF , 3.14 MB , 44 pages
Teacher assessment exemplification: English writing - working at greater depth within the expected standard, Frankie
Ref: ISBN 978-1-78644-851-4, STA/18/8103/e
PDF , 2.01 MB , 36 pages
These exemplification materials provide examples of pupils’ work to support teachers in making judgements against the new statutory teacher assessment frameworks for English writing at the end of key stage 2. They are for use from the 2018/2019 academic year onwards.
They illustrate how the ‘pupil can’ statements in the frameworks might be met. They do not dictate a particular method of teaching, or the evidence expected from the classroom, which will vary from school to school.
If teachers are confident in their judgements they may choose not to refer to these materials. These exemplification materials are provided to help teachers make their judgements where they want additional guidance.
Local authorities may also find the materials useful to support external moderation visits.
Related content
Is this page useful.
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey .
Having trouble logging in? Some users have reported difficulties following a site update. If this includes you, please email [email protected] so we can get you up and running.
Making great literacy lessons easy. Why join Plazoom?
Year 6 SATS Writing Evidence: Non-chronological report, bridges – Teacher Assessment Framework KS2
Resource Collection KS2 SATs Support
This is a free resource
Or subscribe today and you'll also get access to....
- Unlimited access to 1,500+ resources
- Over 80 expert CPD guides
- Free subscription to Teach Reading & Writing magazine, and digital access to all back issues
- New resources every week
- Exclusive, member-only resource collections
- Plus lots more...
Do you have enough independent writing to assess your year 6 pupils against the writing Teacher Assessment Framework for the end of Key Stage 2?
Plazoom has created a selection of writing activities, linked to the foundation subjects where possible, to provide opportunities for independent writing. These could be used to assess pupils against the TAF statements for writing, providing vital evidence of the standard that pupils are working which could be used for internal or external moderation.
‘Pupils’ writing, on which teachers base their judgements, must be produced independently by the pupil.’ (Key stage 2 teacher assessment guidance, October 2019). This writing activity provides success criteria to help pupils understand what they have learnt and a stimulus for writing but teachers should ‘avoid modelling or over scaffolding the expected outcome.’ (Key Stage 2 teacher assessment guidance, October 2019)
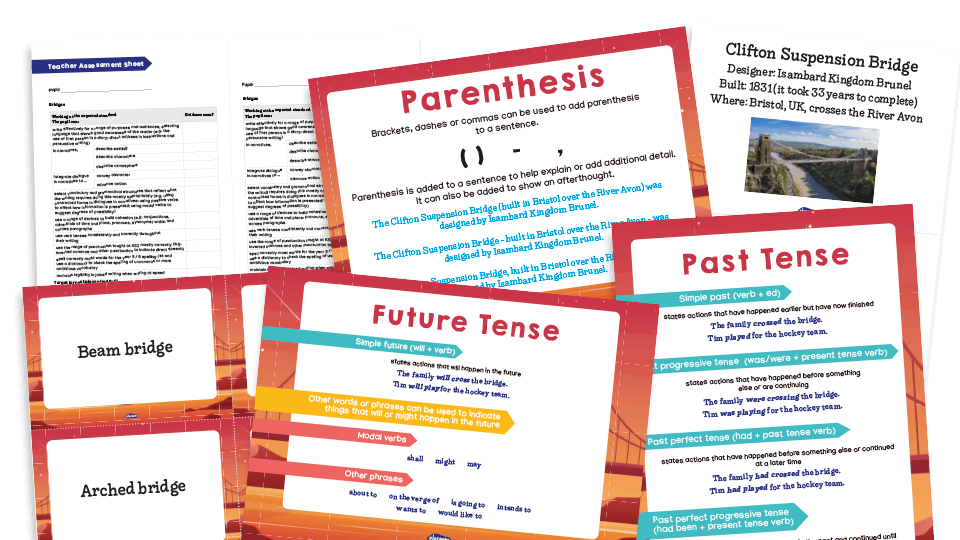
In this writing task, pupils will write a non-chronological report about bridges. This could be used within a DT topic focusing on bridge designs, learning how complex structures can be strengthened, stiffened and reinforced. Pupils will explore different bridge types and their design and match examples of these types of bridges using the cards provided. Pupils will need some knowledge of bridge types or have access to resources to complete research.
The activity can be used to provide an opportunity for cross-curricular writing, allowing pupils to complete independent research, demonstrating their subject knowledge of bridge design.
What is included in this Year SATs writing resource?
- Personal writing skills checklist
For pupils to write their own writing checklists to encourage independent editing.
- Bridges writing skills checklist
A list of features, without modelled examples, for pupils to use as a checklist for editing writing.
- Parenthesis poster
A poster for display with examples of how parenthesis should be punctuated
- Tenses poster
A poster with examples of tenses to revisit this grammar with the class
- Non-chronological report writing poster
A poster to display listing features found in persuasive writing
- Famous bridges image cards
A set of PDF cards showing famous bridges from around the world.
- Types of bridge cards
A set of PDF cards with images of different bridge structures
- Bridges planning sheet
To support pupils when planning and organising their ideas. Two versions are available, one to create a fact file on a famous bridge and the second for a report about a particular bridge type (e.g. beam, arch etc)
- Themed writing paper
A PDF writing sheet for pupils to use when writing the final draft of their writing.
- Teacher assessment sheets
For teachers to use to assess pupils against the year 6 writing TAF statements which could be placed in pupil’s books as a record of evidence seen.
TAF Statements the writing could provide evidence for
WTS Use paragraphs to organise ideas. In non-narrative writing, use simple devices to structure the writing and support the reader (e.g. headings, subheadings, bullet points) EXS To write effectively for a range of purposes and audiences, selecting language that shows good awareness of the reader To select vocabulary and grammatical structures that reflect what the writing requires, doing this mostly appropriately – parenthesis To use the range of punctuation taught at key stage 2 mostly correctly GDS To select the appropriate form for writing and drawing independently on what they have read as models for their own writing. To use the range of punctuation taught at key stage 2 correctly and, where necessary, use such punctuation precisely to enhance meaning and avoid ambiguity
This resource is part of the KS2 SATs Support collection. View more from this collection
- Teacher notes
Trending Today
Ks2 comprehension – classic literature…, ks1 and ks2 writing templates for…, year 1 home learning pack (1), year 6 spelling revision – ks2…, look inside.
Click through to see what this resource has to offer
More from this collection
Ks2 sats spag revision blaster - colons, semi-colons, dashes (clauses and bullet points), year 6 sats writing evidence: time traveller leaflet, ancient civilisations (history) –..., word classes - ks2 sats spag revision blaster, year 6 sats practice - spag questions - word families, year 6 sats practice - spag questions - formal language, including the subjunctive, year 6 sats practice - spag questions - tenses, year 6 sats writing evidence: keeping safe online – teacher assessment framework ks2, year 6 sats writing evidence: a diary recount – teacher assessment framework ks2, browse by year group, upgrade now.
Click 'Upgrade now' to activate your subscription. An invoice will appear on your accounts page and be sent by email. Once paid, the benefits of your full account will be unlocked within five days.
Find out why teachers and school leaders love PlanBee
- 📚 Cross-Curricular Topics
- ✂️ Design & Technology
- ♻️ Education for Social Responsibility
- 🌍 Geography
- ⛪️ Religious Education
- 🎉 Special Days
- 🦸♀️ Special People
- 🏫 Whole School CURRICULUM PACKS
- Vision and Principles
- Our Curriculum Offer
- Whole School Curriculum Packs
- Become a Whole School Member
- FREE Schemes of Work
- Sample Packs
- Learn at Home
- Objective Checker
- How does it work?
- Special Offers
- BECOME A MEMBER 🧡
Non-chronological reports
What is a non-chronological report.
A non-chronological report is a non-fiction text that is not written in time order. They are written to give information on a particular subject or event, without actually referring to the order in which things happen. Non-chronological reports are often referred to as information texts as they give factual information about the topic or event.
Instructions are not an example of a non-chronological report since it would be impossible to follow them correctly were they not in the correct order. Similarly, explanation texts are also presented in time order so are not non-chronological reports.
Below is an example of a non-chronological report taking from our Lost in the Rainforest Non-Chronological Reports scheme for Year 3.
What are the features of a non-chronological report?
Here are the key features of non-chronologicl reports. Not all non-chronological reports will contain every single feature listed below but they will include some of them.
1. A heading - The heading should be nice and big so it catches the readers eye. It should make it very clear to the reader what the non-chronological report is about. Sometimes, the heading can take the form of a question which then the non-chronological report answers.
2. An introductory paragraph - This paragraph gives an overview of the topic the non-chronological report is about. It is found just below the heading and before the main body of the report.
3. Subheadings - Non-chronological reports are laid out in pargraphs. Each paragraph focusses on a different aspect of the topic of the report. So that the reader knows what each paragraph is about, subheadings are used as signposts. They enable the reader to quickly find the part of the non-chronological report they are interested in finding out about. These subheadings can, like the heading, also take the form of questions.
4. Paragraphs - Non-chronological reports are organised into paragraphs. Each paragraph focusses on a different aspect of the subject being discussed.
5. Technical vocabulary - Non-chronological reports often contain topic specific vocabulary. These may not be known to the reader and are thus either explained within the report itself or are sometimes listed in the glossary found at the back of the information book. Children need to be taught this topic-specific vocabulary explicitly so that they can use it with confidence in their non-chronological report writing.
6. Images with captions - These could be photographs, illustrations or diagrams with labels. The images have captions. The captions help the reader to understand what the image is showing.
7. Written in the third person - Non-chronological reports are written in the third person and have a formal tone.
8. Formal language - The purpose of this type of writing is to give facts rather than opinions. Therefore, non-chronological reports use formal language.
9. Present tense - Non-chronological reports are normally written in the present tense unless they are writing about an event that has happened in the past.
Here at PlanBee, we have created this FREE Features of Non-Chronological Reports Poster for you to download and use in your classroom:
How are children taught about non-chronological reports?
Here are the stages children will typically go through when learning to write a non-chronological report:
Stage 1 - Reading and Analysing
The beginning of a unit on non-chronological reports will usually involve reading a range of high quality examples of the text type. Children will identify features that are common to non-chronological reports (see above) and will draw up a list of success criteria for good non-chronological reports. At this stage of the teaching sequence, children will often be required to compare non-chronological reports. Using a bad example (often written by the teacher); children can then see why the key features of non-chronological reports are needed.
Teachers will often share a WAGOLL (What A Good One Looks Like) with the children at this stage in order to identify the key features of the text type. We have a teaching Wiki on WAGOLL to help:
Stage 2 - Research
The next stage children will often be involved with is researching using information texts. For children to be able to write a quality non-chronological report on a topic, they will obviously need to know lots about that topic. Therefore, children will need to use a range of texts on the topic to become experts in it. Note taking, bullet pointing and answering comprhension questions using non-chronological reports could all happen at this stage. The topic precific vocabulary needed will also need to be understood by the children.
Stage 3 - Sentence level work
By this point, the children will have a good understanding of the key features of non-chronological reports and will have researched the topic so that they can write with confidence about it. In this next stage, children will normally focus on a sentence level objective that the class is working on. For example, in Year 4 children might practice using fronted adverbials in their factual sentences while in year 2, work on using conjunctions might take place. They will then apply this sentence level work to their writing at length later in the unit.
Stage 4 - Planning and drafting
Children will then typically use a planner of some description to plan out the paragraphs they will be writing in their non-chronological report. They will think about what the heading, subeadings and content of each paragraph will be. Once this has taken place, children will use their plan to draft their non-chronological report. They will have access to word banks, sentence starters and their research undertaken previosuly to help them.
Stage 5 - Editing
Once children have drafted their non-chronological report, they will then typically be involved with editing and impoving their writing. A really useful way of doing this is through the use of editing stations. There is a very useful teaching Wiki and a FREE pack full of word banks, posters and other resources that you can download. The links to these are here:
Stage 6 - Presentation and evaluation
The final stage of the writing process will be children writing up their non-chronological report. They may do this on special paper and have more creative freedom over the layout and presentation. Children will then evaluate their own and each others' writing in relation to the success criteria drawn up in the first stage of the unit (see stage 1 - research). This writing will often be mounted and displayed as a celebration of children's achievements.

Resources to support the teaching of non-chronological reports
Here at PlanBee, we have a huge range of materials that you can use to support your teaching of non-chronological reports:
Non-chronological reports Year 2
Children in Year 2 will write simple information texts related to a topic they are learning about with headings and factual sentences. They may be provided with a frame to support them writing in paragraphs with subheadings.
Non-chronological reports KS2
As children progress through KS2, their non chronological reports will become more sophisticated and show a greater use of the key features of this text type. In Year 3, the use of the key features may still need to be heavily scaffolded by the teacher but as children progress, their use of these will become more independent.
LESSON PACK Castles - Non-chronological reports (Year 2)
LESSON PACK Lost in the Rainforest - Non-chronological reports (Year 3)
FREE Features of a Non-Chronological Report Poster
FREE Editing Station Poster Pack
Added to your cart:
What's Your Email?
Let customers speak for us
Very resourceful
Thanks, Menna!
Thank you so much- I saved hours searching for things and making my own resources. The plans were very easy to use and the resources are excellent (and easy to match up to the activities as they are all labelled in a way that works well). Ill definitely use again!
Thank you for your review - we are so pleased to hear that you have found our resources useful, and that they have saved you time!
Blank Jigsaws
Thanks, Chris!
South America
Thanks, Charlotte!
Thank you - we have found this very useful when introducing show not tell and using it in our writing.
That's great to hear, Jenni! Thank you for taking the time to leave us a review :-)
Hi! Sign in or Register
Help & Contact
- Grammarsaurus Font
- Careers Page

Year 6 Model Text – Persuasive advert – Introducing… Puffins! (🏴 P6 , 🇦🇺🇺🇸Grade 5 & 🇮🇪 5th Class)

Year 6 Model Text – Persuasive advert – Punishments 4 you! (🏴 P6 , 🇦🇺🇺🇸Grade 5 & 🇮🇪 5th Class)

Year 6 Model Text – Narrative – Mystique: Route to evil (a rags to riches story) (🏴 P6 , 🇦🇺🇺🇸Grade 5 & 🇮🇪 5th Class)
Year 6 Model Text – Discussion – Should the current Y6 SATs system continue? (🏴 P6 , 🇦🇺🇺🇸Grade 5 & 🇮🇪 5th Class)
Year 6 Model Text – Play Script – Macbeth (🏴 P6 , 🇦🇺🇺🇸Grade 5 & 🇮🇪 5th Class)

Year 6 Model Text – Narrative – Alice in Wonderland (a character flaw story) (🏴 P6 , 🇦🇺🇺🇸Grade 5 & 🇮🇪 5th Class)

Year 6 Model Text – Recount Letter – The throne is mine! (🏴 P6 , 🇦🇺🇺🇸Grade 5 & 🇮🇪 5th Class)
Year 6 Model Text – Newspaper report – Royal Murder (🏴 P6 , 🇦🇺🇺🇸Grade 5 & 🇮🇪 5th Class)

Year 6 Model Text – Instructions – How to survive an air raid (🏴 P6 , 🇦🇺🇺🇸Grade 5 & 🇮🇪 5th Class)

Year 6 Model Text – Persuasive leaflet– Visit Heston Hills (🏴 P6 , 🇦🇺🇺🇸Grade 5 & 🇮🇪 5th Class)

Year 6 Model Text – Play Script – Hamlet (🏴 P6 , 🇦🇺🇺🇸Grade 5 & 🇮🇪 5th Class)

Year 6 Model Text – Non-chronological report – Geography of Cornwall (🏴 P6 , 🇦🇺🇺🇸Grade 5 & 🇮🇪 5th Class)
- English Subject Leader Area
- Y1 Explanation
- Y1 Information report
- Y1 Instructions
- Y1 Narrative – Stories
- Y1 Narrative – Character description
- Y1 Narrative – Object description
- Y1 Narrative – Setting description
- Y1 Non-chronological report
- Y1 Persuasive – Advert/leaflet
- Y1 PVPG Texts
- Y1 Recount – Letter/Postcard
- Y1 Recount – Diary
- Y1 Recount – Biography
- Y1 Recount – Science Experiment
- Y2 Explanation
- Y2 Instructions
- Y2 Information report
- Y2 Narrative – Character description
- Y2 Narrative – Characterising speech
- Y2 Narrative – Object description
- Y2 Narrative – Setting description
- Y2 Narrative – Stories
- Y2 Narrative – Playscript
- Y2 Non-chronological report
- Y2 Persuasive – Advert/leaflet
- Y2 Persuasive – Letter
- Y2 PVPG Texts
- Y2 Recount – Biography
- Y2 Recount – Diary
- Y2 Recount – Letter/postcard
- Y2 Recount – Newspaper
- Y2 Recount – Science Experiment
- Y3 Discussion
- Y3 Explanation
- Y3 Instructions
- Y3 Narrative – Character description
- Y3 Narrative – Characterising speech
- Y3 Narrative – Setting description
- Y3 Narrative – Stories
- Y3 Non-chronological report
- Y3 Information report
- Y3 Persuasive – Advert/leaflet/letter
- Y3 Play scripts
- Y3 PVPG Texts
- Y3 Recount – Biography
- Y3 Recount – Diary
- Y3 Recount – Letter/postcard
- Y3 Recount – Newspaper
- Y3 Recount – Science Experiment
- Y4 Recount – Biography
- Y4 Recount – Diary
- Y4 Recount – Letter/postcard
- Y4 Recount – Newspaper/Magazine article
- Y4 Recount – Science Experiment
- Y4 Discussion
- Y4 Instructions
- Y4 Explanation
- Y4 Information report
- Y4 Narrative – Character description
- Y4 Narrative – Characterising speech
- Y4 Narrative – Setting description
- Y4 Narrative – Stories
- Y4 Non-chronological report
- Y4 Persuasive – Advert/leaflet/letter
- Y4 Play scripts
- Y4 PVPG Texts
- Y5 Discussion
- Y5 Explanation
- Y5 Information report
- Y5 Instructions
- Y5 Narrative – Character description
- Y5 Narrative – Characterising speech
- Y5 Narrative – Setting description
- Y5 Narrative – Stories
- Y5 Non-chronological report
- Y5 Persuasive – Advert/leaflet/letter
- Y5 Play scripts
- Y5 PVPG Texts
- Y5 Recount – Biography
- Y5 Recount – Diary
- Y5 Recount – Letter/postcard
- Y5 Recount – Newspaper/Magazine
- Y5 Recount – Science Experiment
- Y6 Discussion
- Y6 Explanation
- Y6 Information report
- Y6 Instructions
- Y6 Narrative – Character description
- Y6 Narrative – Characterising speech
- Y6 Narrative – Setting description
- Y6 Narrative – Stories
- Y6 Non-chronological report
- Y6 Persuasive – Advert/leaflet/letter
- Y6 Play scripts
- Y6 PVPG Texts
- Y6 Recount – Biography
- Y6 Recount – Diary
- Y6 Recount – Letter/postcard
- Y6 Recount – Newspaper/Magazine
- Y6 Recount – Science Experiment
- PVPG Overviews & Literature
- Y6 PVPG Unit
- Y5 PVPG Unit
- Y4 PVPG Unit
- Y3 PVPG Unit
- Y2 PVPG Unit
- Y1 PVPG Unit
- PVPG Display Resources
- Fluency and Reasoning
- SATs Smashers
- SPaG Practice Tests
- Weekly SPaG Checks
- Punctuation
- SPaG Display Resources
- Assessments
- Text-type breakdowns
- Year 1 Unit Guides
- Year 2 Unit Guides
- Year 3/4 Unit Guides
- Year 5/6 Unit Guides
- Descriptologues
- Model Text Feature Spotters
- Y2 Assessments
- Y2 Teaching resources
- Y3 Assessments
- Y3 Teaching resources
- Y4 Assessments
- Y4 Teaching resources
- Y5 Assessments
- Y5 Teaching resources
- Y6 Assessments
- Y6 Teaching resources
- Year 1 Packs
- Year 2 Packs
- Year 3 Packs
- Year 4 Packs
- Year 5 Packs
- Year 6 Packs
- Practice tests
- Shakespeare
- Reading Display Resources
- Y1 Starters/Morning Maths
- Within 10 (A&S)
- Within 20 (A&S)
- Multiplication and Division
- Length and Height
- Weight and Volume
- Position and Direction
- Display resources
- Y2 Starters/Morning Maths
- Y2 Quick 10
- Number and Place Value
- Addition and Subtraction
- Length and Height Y2
- Mass, Capacity and Temperature
- Properties of Shape
- Position and Direction Y2
- Y3 Starters/Morning Maths
- Y3 Quick 10
- Multiplication and Division Part 1 Y3
- Multiplication and Division Part 2 Y3
- Length and Perimeter Y3
- Mass and Capacity Y3
- Y4 Starters/Morning Maths
- Y4 Quick 10
- Multiplication and Division Part 1 Y4
- Multiplication and Division Part 2 Y4
- Fractions Y4
- Decimals Part 1 Y4
- Decimals Part 2 Y4
- Length and Perimeter Y4
- Properties of shape Y4
- Position and direction Y4
- Y5 Starters/Morning Maths
- Y5 Quick 10
- Multiplication and Division Part 1 Y5
- Multiplication and Division Part 2 Y5
- Division Y5
- Long Division Y5/6
- Fractions Y5
- Decimals Part 1 Y5
- Decimals Part 2 Y5
- Perimeter and Area Y5
- Converting units Y5
- Properties of shape Y5
- Position and direction Y5
- Y6 Starters/Morning Maths
- Y6 Quick 10
- Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division
- Fractions Y6
- Decimals Y6
- Percentages Y6
- Ratio and proportion
- Converting Units Y6
- Area Perimeter and Volume Y6
- Position and Direction Y6
- Properties of Shape Y6
- Maths Checklists
- Maths Practice Tests
- SATs Smashers (Maths)
- Science Subject Leader Area
- Animals including humans
- Seasonal Changes
- Living Things and their Habitats
- Forces and Magnets
- Changing states
- Electricity
- Earth and Space
- Science Display Resources
- History Subject Leader Area
- Ancient Egypt
- Anglo-Saxons and Vikings
- Changing Power of Monarchy
- Changes in Toys
- Changes in Technology
- Famous Explorers
- Hospitals and Healthcare
- Kings, Queens and Castles
- Harriet Tubman
- Amelia Earhart
- Katherine Johnson
- William Shakespeare
- Florence Nightingale
- Mary Seacole
- Nelson Mandela
- Captain Tom Moore
- Walt Disney
- Tutankhamun
- Mary Anning
- Martin Luther King
- Malorie Blackman
- John Wesley
- Lilian Bader
- Sir Robert Peel
- Maya Civilisation
- Stone Age to Iron Age
- Black History
- Ancient Greece
- The Great Fire of London
- World War One
- World War Two
- Crime and Punishment
- Shang Dynasty
- History Display Resources
- Geography Display Resources
- Geography Subject Leader Area
- Year 1 – Our Local Park (Fieldwork Unit)
- Year 1 – The World and My School
- Year 1 – Our School Grounds (Fieldwork Unit)
- Year 2 Geography – My Local Area and Tromso, Norway
- Year 2 – My Local Area and Tulum, Mexico
- Year 2 – Weather and Climate (Fieldwork Unit)
- Year 3 – Conservation of Bees (Fieldwork Unit)
- Year 3 – Land Use (Fieldwork Unit)
- Year 3 – The United Kingdom
- Year 4 – My Region and Campania, Italy
- Year 4 – My Region and the South Aegean, Greece
- Year 4 – Locality Units
- Year 4 – Weather and Climate (fieldwork unit)
- Year 5 Geography – My Region and the North Region of Brazil
- Year 5 – My Region and the Western United States
- Year 5 – Biomes (Fieldwork Unit)
- Year 5 – Rivers (Fieldwork Unit)
- Year 6 – The Economic Activity of the UK
- Year 6 – Sustainability (Fieldwork Unit)
- KS1 Christianity
- Art Subject Leader Area
- Y6 – Monochromatic
- Y6 – Chromatic
- Y6 – Sculpture
- Y5 – Monochromatic
- Y5 – Chromatic
- Y5 – Sculpture
- Y4 – Monochromatic
- Y4 – Chromatic
- Y4 – Sculpture
- Y3 – Monochromatic
- Y3 – Chromatic
- Y3 – Sculpture
- Y2 – Monochromatic
- Y2 – Chromatic
- Y2 – Sculpture
- Y1 – Monochromatic
- Y1 – Chromatic
- Y1 – Sculpture
- Famous Artists
- KS2 Projects
- Write with Grammarsaurus
- Sing with Grammarsaurus
- Science with Grammarsaurus
- French Subject Leader Area
- Y4/Y5/Y6 Beginners and Topics
- Y3 (French)
- Y4 (French)
- Y5 (French)
- Y6 (French)
- East of England
- East Midlands
- Greater London
- West Midlands
- Yorkshire & The Humber
- Continuous Provision
- Free resources
- Career Page

Non-Chronological Reports: Pandora
by admins | Jan 27, 2021 | 6D

In English, we have been learning how to write non-chronological reports and this week the children have finally pulled all of their skills together to create a report on Pandora (the alien planet from Avatar). Have a look at the pictures below to see how well they’ve done.

Share this:
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Non-chronological report marking ladder
Subject: English
Age range: 7-11
Resource type: Assessment and revision
Last updated
20 September 2014
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Tes classic free licence
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This I used to guide and assess my students!
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
david.harries
Jeansteele1.
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
GDS and writing in year 6: keeping things focused now time is short. This blog built on the one directly above it. It looks at the role that reading might play in developing writing and offers some suggestions around particular approaches to instruction that might prove especially helpful when time is running short.
Teacher assessment exemplification: English writing - working at greater depth within the expected standard, Frankie Ref: ISBN 978-1-78644-851-4, STA/18/8103/e PDF , 2.01 MB , 36 pages
Year 6 Planning Exemplification 2002-2003: Report Writing Unit Text 13.to secure understanding of the features of non-chronological reports: • introductions to orientate reader; • use of generalisations to categorise; • language to describe and differentiate; • impersonal language; • mostly present tense;
This model text is a non-chronological report about a fictional dinosaur. It has been written to meet the Year 6 expected standard and comes with a handy annotated version detailing the text-type specific features (red), grammar (green), punctuation (purple) and spelling (blue) teaching opportunities should you wish to use this text with your learners.
In this lesson, we will introduce what a non-chronological report is, we will look at the features of a non-chronological report and we will find examples of features in a non-chronological report. Licence. This content is made available by Oak National Academy Limited and its partners and licensed under Oak's terms & conditions ...
Learn how to plan and write a formal report with this English article from BBC Bitesize. Find out the features, structure and language of a non-chronological report.
These Year 6 children were moderated in the 2017/2018 cycle and assessed at a greater depth standard. This document includes 5 examples of a newspaper report on the disappearance of Jesus from his tomb. The document starts with a context for the writing as well as evidence of how a formality shift is shown.
• This document contains a collection of work from a real year 6 pupil, Frankie (whose name has been changed), that meets the requirements for 'pupil can' statements within the statutory teacher assessment framework for 'working at greater depth'. It shows teachers how they might judge whether a pupil has met the relevant standard.
docx, 16.46 KB. Literacy Teaching Resource: Achieving Greater Depth Standard in Year 6 Writing (Word Document) This teaching resource explains how to achieve greater depth standard by using shifts in formality through punctuation, vocabulary and sentence structure. This extends this area of writing assessment not only shifts through dialogue.
Writing non-chronological reports can often be a daunting prospect for KS2 pupils, but our wonderful Non-Chronological Report Examples KS2 resource pack is here to help with fantastic examples that make teaching reports to your Year 3, 4, 5 or 6 students a breeze. It contains a varied selection of non-chronological report examples and ...
A non-chronological report is information, usually a non-fiction text, that is written about a topic or event, which is presented in a way that is not in sequential order. For example, events can be written in any order and not necessarily the order in which they happened. Teach Year 6 children the features of non-chronological reports with ...
UKS2 Writing: Non-Chronological Reports Knowledge Organiser . 18 reviews . Last downloaded on. KS2 Story Writing Competition ... Explore more than 103 "Year 6 Greater Depth Writing Example" resources for teachers, parents and pupils as well as related resources on "Year 6 Greater Depth Writing Example Recount"
This writing activity provides success criteria to help pupils understand what they have learnt and a stimulus for writing but teachers should 'avoid modelling or over scaffolding the expected outcome.' (Key Stage 2 teacher assessment guidance, October 2019) In this writing task, pupils will write a non-chronological report about bridges.
Year 6 Writing Targets Write effectively for a range of purposes and audiences ... persuasive, Recounts, Non chronological reports. Poetry: The Power of Imagery, Narrative poetry, Finding a voice - Reading Poetry W1 I can generate ideas, draft, redraft with a focus and edit written work to ... =getting there = achieved = greater depth .
2. An introductory paragraph - This paragraph gives an overview of the topic the non-chronological report is about. It is found just below the heading and before the main body of the report. 3. Subheadings - Non-chronological reports are laid out in pargraphs. Each paragraph focusses on a different aspect of the topic of the report.
If you are looking for a year 6 WAGOLL, then you have found the right page. We have hundreds of model texts / WAGOLLS written by qualified writing moderators, meaning that our texts meet the expected standard for year 6. Our model texts come with both a blank and an annotated version to support subscribers in recognising the year-group specific grammar, spelling and punctuation teaching ...
Said to originate from the library of eminent Victorian dragonologist Ernest Drake, this book imparts to readers the secrets of the ancient science of dragonology. It includes a host of novelties such as old letters, magic dust, dragon scales, gems, spells in envelopes and booklets of riddles. This book include non-chronological reports on ...
Shifts of formality - Y6 Greater Depth writing lesson. I made a lesson for my observation with top set year 6 - I have roughly 9 children I'll be expecting to reach the Greater Depth standard for writing by June. The lesson plan is basically the smart notebook - it walks you through the lesson step by step. The children start by watching a BBC ...
Non-Chronological Report Success Criteria Topic title covers the whole subject. Brief introduction paragraph gives who/what/when/where overview. Use formal language and present tense verbs. Make the information is organised into paragraphs. Make use of headings and sub-headings. Write in third person Some information may be in fact boxes or bullet-
Non-chronological reports can be taught within the non-fiction genre of texts that children are required to read as part of the KS2 national curriculum. The six non-chronological resource examples in this pack could be read with your class to gauge their knowledge of the features of a non-chronological report at the beginning of their learning and at the end. This pack of non-chronological ...
by admins | Jan 27, 2021 | 6D. In English, we have been learning how to write non-chronological reports and this week the children have finally pulled all of their skills together to create a report on Pandora (the alien planet from Avatar). Have a look at the pictures below to see how well they've done. EM - Pandora.
Year 5/6. Home Learning Platform. 1st -12th June. Antarctica Non Chronological Report. Writing a non-chronological report. Features of a non chronological report.pdf. Non Chron example Guy Fawkes.pdf. Non Chron example.
Non-chronological report marking ladder. Subject: English. Age range: 7-11. Resource type: Assessment and revision. samdaunt77. 4.29 679 reviews. Last updated. 20 September 2014 ... used in best writing (end of unit). Tes classic free licence. Reviews. 4 Something went wrong, please try again later. deslouw. 6 years ago. report. 5. This I used ...