Reference management. Clean and simple.

What is a literature review? [with examples]

What is a literature review?
The purpose of a literature review, how to write a literature review, the format of a literature review, general formatting rules, the length of a literature review, literature review examples, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, related articles.
A literature review is an assessment of the sources in a chosen topic of research.
In a literature review, you’re expected to report on the existing scholarly conversation, without adding new contributions.
If you are currently writing one, you've come to the right place. In the following paragraphs, we will explain:
- the objective of a literature review
- how to write a literature review
- the basic format of a literature review
Tip: It’s not always mandatory to add a literature review in a paper. Theses and dissertations often include them, whereas research papers may not. Make sure to consult with your instructor for exact requirements.
The four main objectives of a literature review are:
- Studying the references of your research area
- Summarizing the main arguments
- Identifying current gaps, stances, and issues
- Presenting all of the above in a text
Ultimately, the main goal of a literature review is to provide the researcher with sufficient knowledge about the topic in question so that they can eventually make an intervention.
The format of a literature review is fairly standard. It includes an:
- introduction that briefly introduces the main topic
- body that includes the main discussion of the key arguments
- conclusion that highlights the gaps and issues of the literature
➡️ Take a look at our guide on how to write a literature review to learn more about how to structure a literature review.
First of all, a literature review should have its own labeled section. You should indicate clearly in the table of contents where the literature can be found, and you should label this section as “Literature Review.”
➡️ For more information on writing a thesis, visit our guide on how to structure a thesis .
There is no set amount of words for a literature review, so the length depends on the research. If you are working with a large amount of sources, it will be long. If your paper does not depend entirely on references, it will be short.
Take a look at these three theses featuring great literature reviews:
- School-Based Speech-Language Pathologist's Perceptions of Sensory Food Aversions in Children [ PDF , see page 20]
- Who's Writing What We Read: Authorship in Criminological Research [ PDF , see page 4]
- A Phenomenological Study of the Lived Experience of Online Instructors of Theological Reflection at Christian Institutions Accredited by the Association of Theological Schools [ PDF , see page 56]
Literature reviews are most commonly found in theses and dissertations. However, you find them in research papers as well.
There is no set amount of words for a literature review, so the length depends on the research. If you are working with a large amount of sources, then it will be long. If your paper does not depend entirely on references, then it will be short.
No. A literature review should have its own independent section. You should indicate clearly in the table of contents where the literature review can be found, and label this section as “Literature Review.”
The main goal of a literature review is to provide the researcher with sufficient knowledge about the topic in question so that they can eventually make an intervention.
How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
3 straightforward steps (with examples) + free template.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019
Quality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

38 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very timely.
I appreciate.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

How I fled bombed Aleppo to continue my career in science
Career Feature 08 MAY 24

Illuminating ‘the ugly side of science’: fresh incentives for reporting negative results

Hunger on campus: why US PhD students are fighting over food
Career Feature 03 MAY 24
Japan can embrace open science — but flexible approaches are key
Correspondence 07 MAY 24

US funders to tighten oversight of controversial ‘gain of function’ research
News 07 MAY 24

France’s research mega-campus faces leadership crisis
News 03 MAY 24

Mount Etna’s spectacular smoke rings and more — April’s best science images

Plagiarism in peer-review reports could be the ‘tip of the iceberg’
Nature Index 01 MAY 24
Rowland Fellowship
The Rowland Institute at Harvard seeks outstanding early-career experimentalists in all fields of science and engineering.
Cambridge, Massachusetts
Rowland Institute at Harvard
Postdoctoral Fellowship: Chemical and Cell Biology
The 2-year fellowship within a project that will combine biochemical, cell biological and chemical genetic approaches to elucidate migrasome biology
Umeå, Sweden
Umeå University
Clinician Researcher/Group Leader in Cancer Cell Therapies
An excellent opportunity is available for a Group Leader with expertise in cellular therapies to join the Cancer Research program at QIMR Berghofer.
Herston, Brisbane (AU)
QIMR Berghofer
Faculty Positions at the Center for Machine Learning Research (CMLR), Peking University
CMLR's goal is to advance machine learning-related research across a wide range of disciplines.
Beijing, China
Center for Machine Learning Research (CMLR), Peking University
Faculty Positions at SUSTech Department of Biomedical Engineering
We seek outstanding applicants for full-time tenure-track/tenured faculty positions. Positions are available for both junior and senior-level.
Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Southern University of Science and Technology (Biomedical Engineering)
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Literature Reviews
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain what literature reviews are and offer insights into the form and construction of literature reviews in the humanities, social sciences, and sciences.
Introduction
OK. You’ve got to write a literature review. You dust off a novel and a book of poetry, settle down in your chair, and get ready to issue a “thumbs up” or “thumbs down” as you leaf through the pages. “Literature review” done. Right?
Wrong! The “literature” of a literature review refers to any collection of materials on a topic, not necessarily the great literary texts of the world. “Literature” could be anything from a set of government pamphlets on British colonial methods in Africa to scholarly articles on the treatment of a torn ACL. And a review does not necessarily mean that your reader wants you to give your personal opinion on whether or not you liked these sources.
What is a literature review, then?
A literature review discusses published information in a particular subject area, and sometimes information in a particular subject area within a certain time period.
A literature review can be just a simple summary of the sources, but it usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis. A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information. It might give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations. Or it might trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates. And depending on the situation, the literature review may evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant.
But how is a literature review different from an academic research paper?
The main focus of an academic research paper is to develop a new argument, and a research paper is likely to contain a literature review as one of its parts. In a research paper, you use the literature as a foundation and as support for a new insight that you contribute. The focus of a literature review, however, is to summarize and synthesize the arguments and ideas of others without adding new contributions.
Why do we write literature reviews?
Literature reviews provide you with a handy guide to a particular topic. If you have limited time to conduct research, literature reviews can give you an overview or act as a stepping stone. For professionals, they are useful reports that keep them up to date with what is current in the field. For scholars, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the writer in his or her field. Literature reviews also provide a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. Comprehensive knowledge of the literature of the field is essential to most research papers.
Who writes these things, anyway?
Literature reviews are written occasionally in the humanities, but mostly in the sciences and social sciences; in experiment and lab reports, they constitute a section of the paper. Sometimes a literature review is written as a paper in itself.
Let’s get to it! What should I do before writing the literature review?
If your assignment is not very specific, seek clarification from your instructor:
- Roughly how many sources should you include?
- What types of sources (books, journal articles, websites)?
- Should you summarize, synthesize, or critique your sources by discussing a common theme or issue?
- Should you evaluate your sources?
- Should you provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history?
Find models
Look for other literature reviews in your area of interest or in the discipline and read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or ways to organize your final review. You can simply put the word “review” in your search engine along with your other topic terms to find articles of this type on the Internet or in an electronic database. The bibliography or reference section of sources you’ve already read are also excellent entry points into your own research.
Narrow your topic
There are hundreds or even thousands of articles and books on most areas of study. The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to get a good survey of the material. Your instructor will probably not expect you to read everything that’s out there on the topic, but you’ll make your job easier if you first limit your scope.
Keep in mind that UNC Libraries have research guides and to databases relevant to many fields of study. You can reach out to the subject librarian for a consultation: https://library.unc.edu/support/consultations/ .
And don’t forget to tap into your professor’s (or other professors’) knowledge in the field. Ask your professor questions such as: “If you had to read only one book from the 90’s on topic X, what would it be?” Questions such as this help you to find and determine quickly the most seminal pieces in the field.
Consider whether your sources are current
Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. In the sciences, for instance, treatments for medical problems are constantly changing according to the latest studies. Information even two years old could be obsolete. However, if you are writing a review in the humanities, history, or social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be what is needed, because what is important is how perspectives have changed through the years or within a certain time period. Try sorting through some other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to consider what is currently of interest to scholars in this field and what is not.
Strategies for writing the literature review
Find a focus.
A literature review, like a term paper, is usually organized around ideas, not the sources themselves as an annotated bibliography would be organized. This means that you will not just simply list your sources and go into detail about each one of them, one at a time. No. As you read widely but selectively in your topic area, consider instead what themes or issues connect your sources together. Do they present one or different solutions? Is there an aspect of the field that is missing? How well do they present the material and do they portray it according to an appropriate theory? Do they reveal a trend in the field? A raging debate? Pick one of these themes to focus the organization of your review.
Convey it to your reader
A literature review may not have a traditional thesis statement (one that makes an argument), but you do need to tell readers what to expect. Try writing a simple statement that lets the reader know what is your main organizing principle. Here are a couple of examples:
The current trend in treatment for congestive heart failure combines surgery and medicine. More and more cultural studies scholars are accepting popular media as a subject worthy of academic consideration.
Consider organization
You’ve got a focus, and you’ve stated it clearly and directly. Now what is the most effective way of presenting the information? What are the most important topics, subtopics, etc., that your review needs to include? And in what order should you present them? Develop an organization for your review at both a global and local level:
First, cover the basic categories
Just like most academic papers, literature reviews also must contain at least three basic elements: an introduction or background information section; the body of the review containing the discussion of sources; and, finally, a conclusion and/or recommendations section to end the paper. The following provides a brief description of the content of each:
- Introduction: Gives a quick idea of the topic of the literature review, such as the central theme or organizational pattern.
- Body: Contains your discussion of sources and is organized either chronologically, thematically, or methodologically (see below for more information on each).
- Conclusions/Recommendations: Discuss what you have drawn from reviewing literature so far. Where might the discussion proceed?
Organizing the body
Once you have the basic categories in place, then you must consider how you will present the sources themselves within the body of your paper. Create an organizational method to focus this section even further.
To help you come up with an overall organizational framework for your review, consider the following scenario:
You’ve decided to focus your literature review on materials dealing with sperm whales. This is because you’ve just finished reading Moby Dick, and you wonder if that whale’s portrayal is really real. You start with some articles about the physiology of sperm whales in biology journals written in the 1980’s. But these articles refer to some British biological studies performed on whales in the early 18th century. So you check those out. Then you look up a book written in 1968 with information on how sperm whales have been portrayed in other forms of art, such as in Alaskan poetry, in French painting, or on whale bone, as the whale hunters in the late 19th century used to do. This makes you wonder about American whaling methods during the time portrayed in Moby Dick, so you find some academic articles published in the last five years on how accurately Herman Melville portrayed the whaling scene in his novel.
Now consider some typical ways of organizing the sources into a review:
- Chronological: If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials above according to when they were published. For instance, first you would talk about the British biological studies of the 18th century, then about Moby Dick, published in 1851, then the book on sperm whales in other art (1968), and finally the biology articles (1980s) and the recent articles on American whaling of the 19th century. But there is relatively no continuity among subjects here. And notice that even though the sources on sperm whales in other art and on American whaling are written recently, they are about other subjects/objects that were created much earlier. Thus, the review loses its chronological focus.
- By publication: Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on biological studies of sperm whales if the progression revealed a change in dissection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies.
- By trend: A better way to organize the above sources chronologically is to examine the sources under another trend, such as the history of whaling. Then your review would have subsections according to eras within this period. For instance, the review might examine whaling from pre-1600-1699, 1700-1799, and 1800-1899. Under this method, you would combine the recent studies on American whaling in the 19th century with Moby Dick itself in the 1800-1899 category, even though the authors wrote a century apart.
- Thematic: Thematic reviews of literature are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time. However, progression of time may still be an important factor in a thematic review. For instance, the sperm whale review could focus on the development of the harpoon for whale hunting. While the study focuses on one topic, harpoon technology, it will still be organized chronologically. The only difference here between a “chronological” and a “thematic” approach is what is emphasized the most: the development of the harpoon or the harpoon technology.But more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. For instance, a thematic review of material on sperm whales might examine how they are portrayed as “evil” in cultural documents. The subsections might include how they are personified, how their proportions are exaggerated, and their behaviors misunderstood. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point made.
- Methodological: A methodological approach differs from the two above in that the focusing factor usually does not have to do with the content of the material. Instead, it focuses on the “methods” of the researcher or writer. For the sperm whale project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of whales in American, British, and French art work. Or the review might focus on the economic impact of whaling on a community. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed. Once you’ve decided on the organizational method for the body of the review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out. They should arise out of your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period. A thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue.
Sometimes, though, you might need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. Put in only what is necessary. Here are a few other sections you might want to consider:
- Current Situation: Information necessary to understand the topic or focus of the literature review.
- History: The chronological progression of the field, the literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Methods and/or Standards: The criteria you used to select the sources in your literature review or the way in which you present your information. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed articles and journals.
Questions for Further Research: What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
Begin composing
Once you’ve settled on a general pattern of organization, you’re ready to write each section. There are a few guidelines you should follow during the writing stage as well. Here is a sample paragraph from a literature review about sexism and language to illuminate the following discussion:
However, other studies have shown that even gender-neutral antecedents are more likely to produce masculine images than feminine ones (Gastil, 1990). Hamilton (1988) asked students to complete sentences that required them to fill in pronouns that agreed with gender-neutral antecedents such as “writer,” “pedestrian,” and “persons.” The students were asked to describe any image they had when writing the sentence. Hamilton found that people imagined 3.3 men to each woman in the masculine “generic” condition and 1.5 men per woman in the unbiased condition. Thus, while ambient sexism accounted for some of the masculine bias, sexist language amplified the effect. (Source: Erika Falk and Jordan Mills, “Why Sexist Language Affects Persuasion: The Role of Homophily, Intended Audience, and Offense,” Women and Language19:2).
Use evidence
In the example above, the writers refer to several other sources when making their point. A literature review in this sense is just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence to show that what you are saying is valid.
Be selective
Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the review’s focus, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological.
Use quotes sparingly
Falk and Mills do not use any direct quotes. That is because the survey nature of the literature review does not allow for in-depth discussion or detailed quotes from the text. Some short quotes here and there are okay, though, if you want to emphasize a point, or if what the author said just cannot be rewritten in your own words. Notice that Falk and Mills do quote certain terms that were coined by the author, not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. But if you find yourself wanting to put in more quotes, check with your instructor.
Summarize and synthesize
Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each paragraph as well as throughout the review. The authors here recapitulate important features of Hamilton’s study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study’s significance and relating it to their own work.
Keep your own voice
While the literature review presents others’ ideas, your voice (the writer’s) should remain front and center. Notice that Falk and Mills weave references to other sources into their own text, but they still maintain their own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with their own ideas and their own words. The sources support what Falk and Mills are saying.
Use caution when paraphrasing
When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author’s information or opinions accurately and in your own words. In the preceding example, Falk and Mills either directly refer in the text to the author of their source, such as Hamilton, or they provide ample notation in the text when the ideas they are mentioning are not their own, for example, Gastil’s. For more information, please see our handout on plagiarism .
Revise, revise, revise
Draft in hand? Now you’re ready to revise. Spending a lot of time revising is a wise idea, because your main objective is to present the material, not the argument. So check over your review again to make sure it follows the assignment and/or your outline. Then, just as you would for most other academic forms of writing, rewrite or rework the language of your review so that you’ve presented your information in the most concise manner possible. Be sure to use terminology familiar to your audience; get rid of unnecessary jargon or slang. Finally, double check that you’ve documented your sources and formatted the review appropriately for your discipline. For tips on the revising and editing process, see our handout on revising drafts .
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Jones, Robert, Patrick Bizzaro, and Cynthia Selfe. 1997. The Harcourt Brace Guide to Writing in the Disciplines . New York: Harcourt Brace.
Lamb, Sandra E. 1998. How to Write It: A Complete Guide to Everything You’ll Ever Write . Berkeley: Ten Speed Press.
Rosen, Leonard J., and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
Troyka, Lynn Quittman, and Doug Hesse. 2016. Simon and Schuster Handbook for Writers , 11th ed. London: Pearson.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

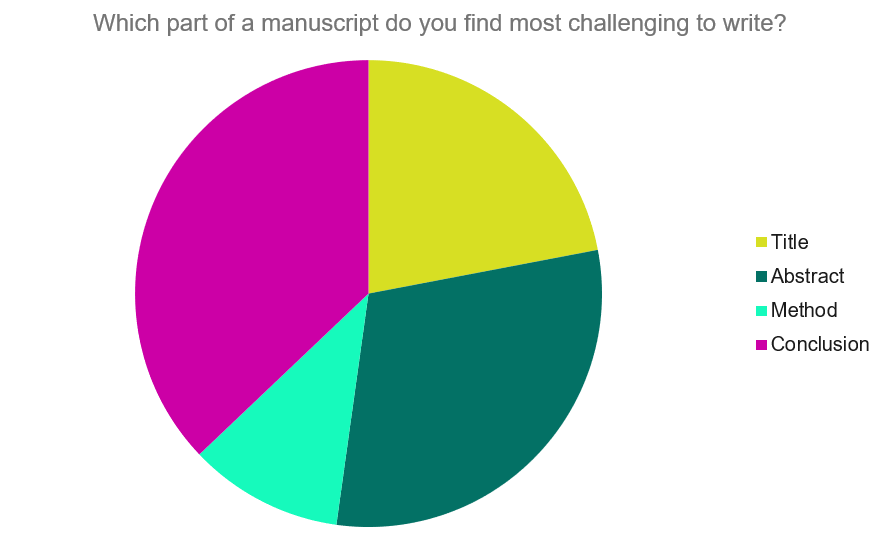
The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
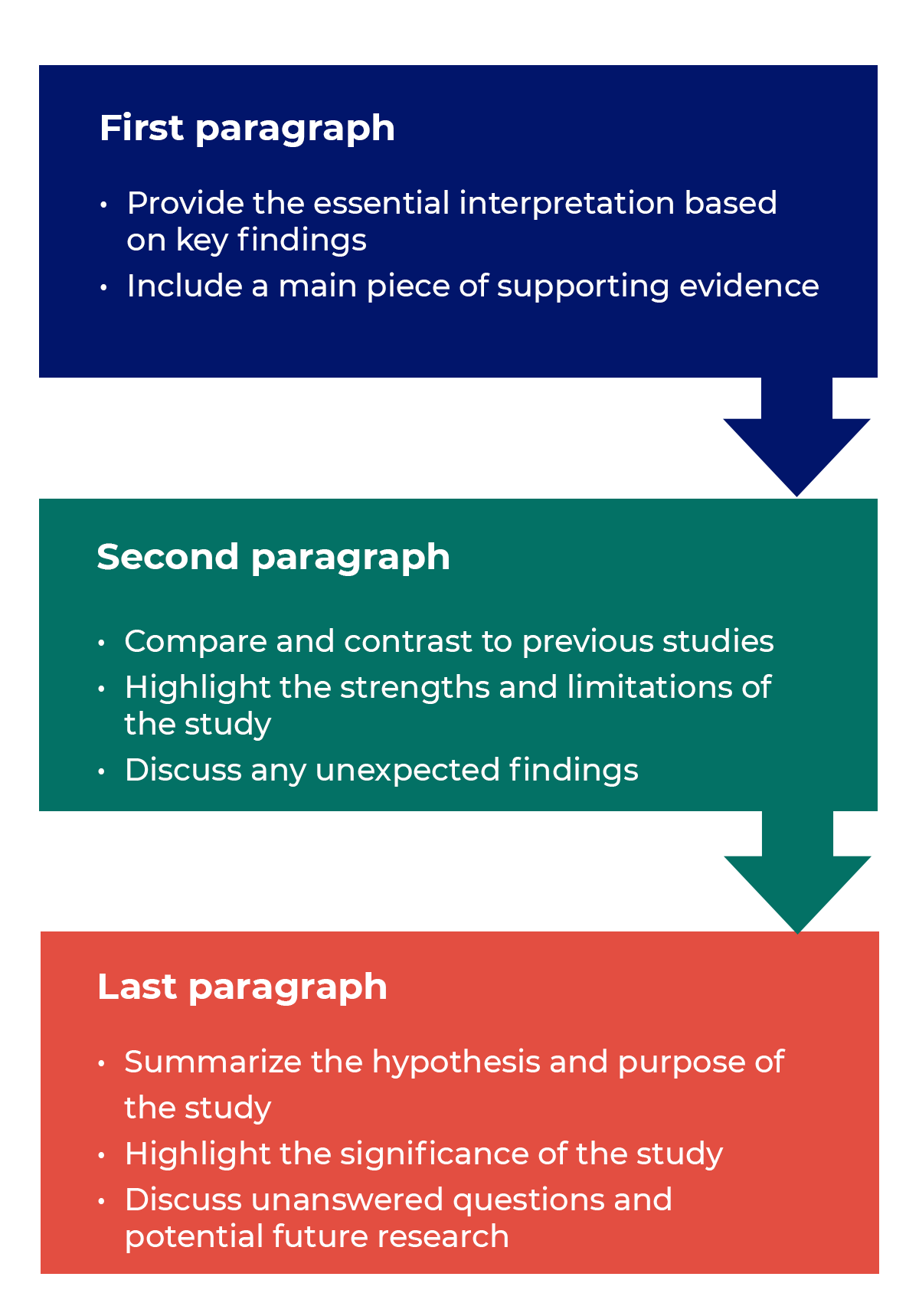
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Sample Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts
Have an exemplary literature review.
- Literature Review Sample 1
- Literature Review Sample 2
- Literature Review Sample 3
Have you written a stellar literature review you care to share for teaching purposes?
Are you an instructor who has received an exemplary literature review and have permission from the student to post?
Please contact Britt McGowan at [email protected] for inclusion in this guide. All disciplines welcome and encouraged.
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Mar 22, 2024 9:37 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
How to Write the Discussion Section of a Research Paper
The discussion section of a research paper analyzes and interprets the findings, provides context, compares them with previous studies, identifies limitations, and suggests future research directions.
Updated on September 15, 2023

Structure your discussion section right, and you’ll be cited more often while doing a greater service to the scientific community. So, what actually goes into the discussion section? And how do you write it?
The discussion section of your research paper is where you let the reader know how your study is positioned in the literature, what to take away from your paper, and how your work helps them. It can also include your conclusions and suggestions for future studies.
First, we’ll define all the parts of your discussion paper, and then look into how to write a strong, effective discussion section for your paper or manuscript.
Discussion section: what is it, what it does
The discussion section comes later in your paper, following the introduction, methods, and results. The discussion sets up your study’s conclusions. Its main goals are to present, interpret, and provide a context for your results.
What is it?
The discussion section provides an analysis and interpretation of the findings, compares them with previous studies, identifies limitations, and suggests future directions for research.
This section combines information from the preceding parts of your paper into a coherent story. By this point, the reader already knows why you did your study (introduction), how you did it (methods), and what happened (results). In the discussion, you’ll help the reader connect the ideas from these sections.
Why is it necessary?
The discussion provides context and interpretations for the results. It also answers the questions posed in the introduction. While the results section describes your findings, the discussion explains what they say. This is also where you can describe the impact or implications of your research.
Adds context for your results
Most research studies aim to answer a question, replicate a finding, or address limitations in the literature. These goals are first described in the introduction. However, in the discussion section, the author can refer back to them to explain how the study's objective was achieved.
Shows what your results actually mean and real-world implications
The discussion can also describe the effect of your findings on research or practice. How are your results significant for readers, other researchers, or policymakers?
What to include in your discussion (in the correct order)
A complete and effective discussion section should at least touch on the points described below.
Summary of key findings
The discussion should begin with a brief factual summary of the results. Concisely overview the main results you obtained.
Begin with key findings with supporting evidence
Your results section described a list of findings, but what message do they send when you look at them all together?
Your findings were detailed in the results section, so there’s no need to repeat them here, but do provide at least a few highlights. This will help refresh the reader’s memory and help them focus on the big picture.
Read the first paragraph of the discussion section in this article (PDF) for an example of how to start this part of your paper. Notice how the authors break down their results and follow each description sentence with an explanation of why each finding is relevant.
State clearly and concisely
Following a clear and direct writing style is especially important in the discussion section. After all, this is where you will make some of the most impactful points in your paper. While the results section often contains technical vocabulary, such as statistical terms, the discussion section lets you describe your findings more clearly.
Interpretation of results
Once you’ve given your reader an overview of your results, you need to interpret those results. In other words, what do your results mean? Discuss the findings’ implications and significance in relation to your research question or hypothesis.
Analyze and interpret your findings
Look into your findings and explore what’s behind them or what may have caused them. If your introduction cited theories or studies that could explain your findings, use these sources as a basis to discuss your results.
For example, look at the second paragraph in the discussion section of this article on waggling honey bees. Here, the authors explore their results based on information from the literature.
Unexpected or contradictory results
Sometimes, your findings are not what you expect. Here’s where you describe this and try to find a reason for it. Could it be because of the method you used? Does it have something to do with the variables analyzed? Comparing your methods with those of other similar studies can help with this task.
Context and comparison with previous work
Refer to related studies to place your research in a larger context and the literature. Compare and contrast your findings with existing literature, highlighting similarities, differences, and/or contradictions.
How your work compares or contrasts with previous work
Studies with similar findings to yours can be cited to show the strength of your findings. Information from these studies can also be used to help explain your results. Differences between your findings and others in the literature can also be discussed here.
How to divide this section into subsections
If you have more than one objective in your study or many key findings, you can dedicate a separate section to each of these. Here’s an example of this approach. You can see that the discussion section is divided into topics and even has a separate heading for each of them.
Limitations
Many journals require you to include the limitations of your study in the discussion. Even if they don’t, there are good reasons to mention these in your paper.
Why limitations don’t have a negative connotation
A study’s limitations are points to be improved upon in future research. While some of these may be flaws in your method, many may be due to factors you couldn’t predict.
Examples include time constraints or small sample sizes. Pointing this out will help future researchers avoid or address these issues. This part of the discussion can also include any attempts you have made to reduce the impact of these limitations, as in this study .
How limitations add to a researcher's credibility
Pointing out the limitations of your study demonstrates transparency. It also shows that you know your methods well and can conduct a critical assessment of them.
Implications and significance
The final paragraph of the discussion section should contain the take-home messages for your study. It can also cite the “strong points” of your study, to contrast with the limitations section.
Restate your hypothesis
Remind the reader what your hypothesis was before you conducted the study.
How was it proven or disproven?
Identify your main findings and describe how they relate to your hypothesis.
How your results contribute to the literature
Were you able to answer your research question? Or address a gap in the literature?
Future implications of your research
Describe the impact that your results may have on the topic of study. Your results may show, for instance, that there are still limitations in the literature for future studies to address. There may be a need for studies that extend your findings in a specific way. You also may need additional research to corroborate your findings.
Sample discussion section
This fictitious example covers all the aspects discussed above. Your actual discussion section will probably be much longer, but you can read this to get an idea of everything your discussion should cover.
Our results showed that the presence of cats in a household is associated with higher levels of perceived happiness by its human occupants. These findings support our hypothesis and demonstrate the association between pet ownership and well-being.
The present findings align with those of Bao and Schreer (2016) and Hardie et al. (2023), who observed greater life satisfaction in pet owners relative to non-owners. Although the present study did not directly evaluate life satisfaction, this factor may explain the association between happiness and cat ownership observed in our sample.
Our findings must be interpreted in light of some limitations, such as the focus on cat ownership only rather than pets as a whole. This may limit the generalizability of our results.
Nevertheless, this study had several strengths. These include its strict exclusion criteria and use of a standardized assessment instrument to investigate the relationships between pets and owners. These attributes bolster the accuracy of our results and reduce the influence of confounding factors, increasing the strength of our conclusions. Future studies may examine the factors that mediate the association between pet ownership and happiness to better comprehend this phenomenon.
This brief discussion begins with a quick summary of the results and hypothesis. The next paragraph cites previous research and compares its findings to those of this study. Information from previous studies is also used to help interpret the findings. After discussing the results of the study, some limitations are pointed out. The paper also explains why these limitations may influence the interpretation of results. Then, final conclusions are drawn based on the study, and directions for future research are suggested.
How to make your discussion flow naturally
If you find writing in scientific English challenging, the discussion and conclusions are often the hardest parts of the paper to write. That’s because you’re not just listing up studies, methods, and outcomes. You’re actually expressing your thoughts and interpretations in words.
- How formal should it be?
- What words should you use, or not use?
- How do you meet strict word limits, or make it longer and more informative?
Always give it your best, but sometimes a helping hand can, well, help. Getting a professional edit can help clarify your work’s importance while improving the English used to explain it. When readers know the value of your work, they’ll cite it. We’ll assign your study to an expert editor knowledgeable in your area of research. Their work will clarify your discussion, helping it to tell your story. Find out more about AJE Editing.

Adam Goulston, PsyD, MS, MBA, MISD, ELS
Science Marketing Consultant
See our "Privacy Policy"

Ensure your structure and ideas are consistent and clearly communicated
Pair your Premium Editing with our add-on service Presubmission Review for an overall assessment of your manuscript.
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., how to write a successful book chapter for..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, what is academic writing: tips for students, why traditional editorial process needs an upgrade.

Systematic Review Discussion Example

Automate every stage of your literature review to produce evidence-based research faster and more accurately.
What should be included in the discussion section of a systematic review.
There are a number of key elements that are included in a discussion section of a systematic review. Remember to use all these elements to ensure the quality of your review remains high, that your review is deemed useful to your peers, and that the validity of your systematic review cannot be questioned.
The first thing to do in your discussion is to summarize your most important findings. This can simply be identifying your key results. Be careful not to just repeat all the results you have outlined in your previous sections. Instead, once you have briefly mentioned them, go on to interpret them. The results from included studies are presented in a summary. The results are then compared among different studies, and the consistent themes, agreements, and contradictions among studies are identified. The consistencies are reported and reasons for contradictions are given. The themes and agreement among the studies are used to answer the research question. Your interpretations need to be backed up by evidence so that they make the intended impact. Interpretations can be based on your critical thinking. Your interpretations of study findings can be compared to the interpretation of another review on the same topic.
Another way to ensure that your review is as persuasive as possible is to discuss any strengths and weaknesses at this point, in your discussion. It is advisable to first talk about the most notable strengths and limitations of included studies. Afterward, you can show how the characteristics of individual included studies have affected the strengths and limitations of the review. Identifying weaknesses may not be immediately obvious for some writers of reviews. However, they are essential to include, especially in the discussion section, as it means you can explain them and examine why your findings are still valid, despite such weaknesses. Discussing strengths will support your view even further. By highlighting both strengths and weaknesses together, you can dismiss any negative criticism before it even begins.
Learn More About DistillerSR
(Article continues below)
How Long Should A Discussion Be In A Systematic Review?
When it comes to the length of a discussion section, there is never really a right or wrong answer. The length of the discussion section is a systematic review is usually determined by the number of included studies, the scope of the research question, and the ability of the author to analyze and synthesize data from the included studies. That being said, given the breadth and number of areas to be covered as mentioned above, it will never be just one paragraph. Examining the strengths and weaknesses of your review alone will often call for a couple of paragraphs of discussion. Then you assert your findings that will answer your research question and support your initial hypothesis. This will likely demand another paragraph or two at least.
The Importance of Systematic Review Discussion
Remember that the discussion section of your review is, arguably, the most important part of your work. It is where you can put your label on all previous studies conducted, and highlight why your research into the area has been a worthwhile process. It is an opportunity for you to set yourself apart, and have your paper be seen as evidence for the subject matter in question. Therefore, the importance of a systematic review discussion cannot be overstated. The discussion section of a review is your chance to present the results of your analysis, which takes into account all previous studies or research in the area.
3 Reasons to Connect

- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: May 9, 2024 11:05 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
Published on 21 August 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 25 October 2022.

The discussion section is where you delve into the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results .
It should focus on explaining and evaluating what you found, showing how it relates to your literature review , and making an argument in support of your overall conclusion . It should not be a second results section .
There are different ways to write this section, but you can focus your writing around these key elements:
- Summary: A brief recap of your key results
- Interpretations: What do your results mean?
- Implications: Why do your results matter?
- Limitations: What can’t your results tell us?
- Recommendations: Avenues for further studies or analyses
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What not to include in your discussion section, step 1: summarise your key findings, step 2: give your interpretations, step 3: discuss the implications, step 4: acknowledge the limitations, step 5: share your recommendations, discussion section example.
There are a few common mistakes to avoid when writing the discussion section of your paper.
- Don’t introduce new results: You should only discuss the data that you have already reported in your results section .
- Don’t make inflated claims: Avoid overinterpretation and speculation that isn’t directly supported by your data.
- Don’t undermine your research: The discussion of limitations should aim to strengthen your credibility, not emphasise weaknesses or failures.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Start this section by reiterating your research problem and concisely summarising your major findings. Don’t just repeat all the data you have already reported – aim for a clear statement of the overall result that directly answers your main research question . This should be no more than one paragraph.
Many students struggle with the differences between a discussion section and a results section . The crux of the matter is that your results sections should present your results, and your discussion section should subjectively evaluate them. Try not to blend elements of these two sections, in order to keep your paper sharp.
- The results indicate that …
- The study demonstrates a correlation between …
- This analysis supports the theory that …
- The data suggest that …
The meaning of your results may seem obvious to you, but it’s important to spell out their significance for your reader, showing exactly how they answer your research question.
The form of your interpretations will depend on the type of research, but some typical approaches to interpreting the data include:
- Identifying correlations , patterns, and relationships among the data
- Discussing whether the results met your expectations or supported your hypotheses
- Contextualising your findings within previous research and theory
- Explaining unexpected results and evaluating their significance
- Considering possible alternative explanations and making an argument for your position
You can organise your discussion around key themes, hypotheses, or research questions, following the same structure as your results section. Alternatively, you can also begin by highlighting the most significant or unexpected results.
- In line with the hypothesis …
- Contrary to the hypothesised association …
- The results contradict the claims of Smith (2007) that …
- The results might suggest that x . However, based on the findings of similar studies, a more plausible explanation is x .
As well as giving your own interpretations, make sure to relate your results back to the scholarly work that you surveyed in the literature review . The discussion should show how your findings fit with existing knowledge, what new insights they contribute, and what consequences they have for theory or practice.
Ask yourself these questions:
- Do your results support or challenge existing theories? If they support existing theories, what new information do they contribute? If they challenge existing theories, why do you think that is?
- Are there any practical implications?
Your overall aim is to show the reader exactly what your research has contributed, and why they should care.
- These results build on existing evidence of …
- The results do not fit with the theory that …
- The experiment provides a new insight into the relationship between …
- These results should be taken into account when considering how to …
- The data contribute a clearer understanding of …
- While previous research has focused on x , these results demonstrate that y .
Even the best research has its limitations. Acknowledging these is important to demonstrate your credibility. Limitations aren’t about listing your errors, but about providing an accurate picture of what can and cannot be concluded from your study.
Limitations might be due to your overall research design, specific methodological choices , or unanticipated obstacles that emerged during your research process.
Here are a few common possibilities:
- If your sample size was small or limited to a specific group of people, explain how generalisability is limited.
- If you encountered problems when gathering or analysing data, explain how these influenced the results.
- If there are potential confounding variables that you were unable to control, acknowledge the effect these may have had.
After noting the limitations, you can reiterate why the results are nonetheless valid for the purpose of answering your research question.
- The generalisability of the results is limited by …
- The reliability of these data is impacted by …
- Due to the lack of data on x , the results cannot confirm …
- The methodological choices were constrained by …
- It is beyond the scope of this study to …
Based on the discussion of your results, you can make recommendations for practical implementation or further research. Sometimes, the recommendations are saved for the conclusion .
Suggestions for further research can lead directly from the limitations. Don’t just state that more studies should be done – give concrete ideas for how future work can build on areas that your own research was unable to address.
- Further research is needed to establish …
- Future studies should take into account …
- Avenues for future research include …

Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 25). How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 13 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/discussion/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a results section | tips & examples, research paper appendix | example & templates, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction.
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
How to write a literature review introduction (+ examples)
The introduction to a literature review serves as your reader’s guide through your academic work and thought process. Explore the significance of literature review introductions in review papers, academic papers, essays, theses, and dissertations. We delve into the purpose and necessity of these introductions, explore the essential components of literature review introductions, and provide step-by-step guidance on how to craft your own, along with examples.
Why you need an introduction for a literature review
When you need an introduction for a literature review, what to include in a literature review introduction, examples of literature review introductions, steps to write your own literature review introduction.
A literature review is a comprehensive examination of the international academic literature concerning a particular topic. It involves summarizing published works, theories, and concepts while also highlighting gaps and offering critical reflections.
In academic writing , the introduction for a literature review is an indispensable component. Effective academic writing requires proper paragraph structuring to guide your reader through your argumentation. This includes providing an introduction to your literature review.
It is imperative to remember that you should never start sharing your findings abruptly. Even if there isn’t a dedicated introduction section .
Instead, you should always offer some form of introduction to orient the reader and clarify what they can expect.
There are three main scenarios in which you need an introduction for a literature review:
- Academic literature review papers: When your literature review constitutes the entirety of an academic review paper, a more substantial introduction is necessary. This introduction should resemble the standard introduction found in regular academic papers.
- Literature review section in an academic paper or essay: While this section tends to be brief, it’s important to precede the detailed literature review with a few introductory sentences. This helps orient the reader before delving into the literature itself.
- Literature review chapter or section in your thesis/dissertation: Every thesis and dissertation includes a literature review component, which also requires a concise introduction to set the stage for the subsequent review.
You may also like: How to write a fantastic thesis introduction (+15 examples)
It is crucial to customize the content and depth of your literature review introduction according to the specific format of your academic work.
In practical terms, this implies, for instance, that the introduction in an academic literature review paper, especially one derived from a systematic literature review , is quite comprehensive. Particularly compared to the rather brief one or two introductory sentences that are often found at the beginning of a literature review section in a standard academic paper. The introduction to the literature review chapter in a thesis or dissertation again adheres to different standards.
Here’s a structured breakdown based on length and the necessary information:
Academic literature review paper
The introduction of an academic literature review paper, which does not rely on empirical data, often necessitates a more extensive introduction than the brief literature review introductions typically found in empirical papers. It should encompass:
- The research problem: Clearly articulate the problem or question that your literature review aims to address.
- The research gap: Highlight the existing gaps, limitations, or unresolved aspects within the current body of literature related to the research problem.
- The research relevance: Explain why the chosen research problem and its subsequent investigation through a literature review are significant and relevant in your academic field.
- The literature review method: If applicable, describe the methodology employed in your literature review, especially if it is a systematic review or follows a specific research framework.
- The main findings or insights of the literature review: Summarize the key discoveries, insights, or trends that have emerged from your comprehensive review of the literature.
- The main argument of the literature review: Conclude the introduction by outlining the primary argument or statement that your literature review will substantiate, linking it to the research problem and relevance you’ve established.
- Preview of the literature review’s structure: Offer a glimpse into the organization of the literature review paper, acting as a guide for the reader. This overview outlines the subsequent sections of the paper and provides an understanding of what to anticipate.
By addressing these elements, your introduction will provide a clear and structured overview of what readers can expect in your literature review paper.
Regular literature review section in an academic article or essay
Most academic articles or essays incorporate regular literature review sections, often placed after the introduction. These sections serve to establish a scholarly basis for the research or discussion within the paper.
In a standard 8000-word journal article, the literature review section typically spans between 750 and 1250 words. The first few sentences or the first paragraph within this section often serve as an introduction. It should encompass:
- An introduction to the topic: When delving into the academic literature on a specific topic, it’s important to provide a smooth transition that aids the reader in comprehending why certain aspects will be discussed within your literature review.
- The core argument: While literature review sections primarily synthesize the work of other scholars, they should consistently connect to your central argument. This central argument serves as the crux of your message or the key takeaway you want your readers to retain. By positioning it at the outset of the literature review section and systematically substantiating it with evidence, you not only enhance reader comprehension but also elevate overall readability. This primary argument can typically be distilled into 1-2 succinct sentences.
In some cases, you might include:
- Methodology: Details about the methodology used, but only if your literature review employed a specialized method. If your approach involved a broader overview without a systematic methodology, you can omit this section, thereby conserving word count.
By addressing these elements, your introduction will effectively integrate your literature review into the broader context of your academic paper or essay. This will, in turn, assist your reader in seamlessly following your overarching line of argumentation.
Introduction to a literature review chapter in thesis or dissertation
The literature review typically constitutes a distinct chapter within a thesis or dissertation. Often, it is Chapter 2 of a thesis or dissertation.
Some students choose to incorporate a brief introductory section at the beginning of each chapter, including the literature review chapter. Alternatively, others opt to seamlessly integrate the introduction into the initial sentences of the literature review itself. Both approaches are acceptable, provided that you incorporate the following elements:
- Purpose of the literature review and its relevance to the thesis/dissertation research: Explain the broader objectives of the literature review within the context of your research and how it contributes to your thesis or dissertation. Essentially, you’re telling the reader why this literature review is important and how it fits into the larger scope of your academic work.
- Primary argument: Succinctly communicate what you aim to prove, explain, or explore through the review of existing literature. This statement helps guide the reader’s understanding of the review’s purpose and what to expect from it.
- Preview of the literature review’s content: Provide a brief overview of the topics or themes that your literature review will cover. It’s like a roadmap for the reader, outlining the main areas of focus within the review. This preview can help the reader anticipate the structure and organization of your literature review.
- Methodology: If your literature review involved a specific research method, such as a systematic review or meta-analysis, you should briefly describe that methodology. However, this is not always necessary, especially if your literature review is more of a narrative synthesis without a distinct research method.
By addressing these elements, your introduction will empower your literature review to play a pivotal role in your thesis or dissertation research. It will accomplish this by integrating your research into the broader academic literature and providing a solid theoretical foundation for your work.
Comprehending the art of crafting your own literature review introduction becomes significantly more accessible when you have concrete examples to examine. Here, you will find several examples that meet, or in most cases, adhere to the criteria described earlier.
Example 1: An effective introduction for an academic literature review paper
To begin, let’s delve into the introduction of an academic literature review paper. We will examine the paper “How does culture influence innovation? A systematic literature review”, which was published in 2018 in the journal Management Decision.

The entire introduction spans 611 words and is divided into five paragraphs. In this introduction, the authors accomplish the following:
- In the first paragraph, the authors introduce the broader topic of the literature review, which focuses on innovation and its significance in the context of economic competition. They underscore the importance of this topic, highlighting its relevance for both researchers and policymakers.
- In the second paragraph, the authors narrow down their focus to emphasize the specific role of culture in relation to innovation.
- In the third paragraph, the authors identify research gaps, noting that existing studies are often fragmented and disconnected. They then emphasize the value of conducting a systematic literature review to enhance our understanding of the topic.
- In the fourth paragraph, the authors introduce their specific objectives and explain how their insights can benefit other researchers and business practitioners.
- In the fifth and final paragraph, the authors provide an overview of the paper’s organization and structure.
In summary, this introduction stands as a solid example. While the authors deviate from previewing their key findings (which is a common practice at least in the social sciences), they do effectively cover all the other previously mentioned points.
Example 2: An effective introduction to a literature review section in an academic paper
The second example represents a typical academic paper, encompassing not only a literature review section but also empirical data, a case study, and other elements. We will closely examine the introduction to the literature review section in the paper “The environmentalism of the subalterns: a case study of environmental activism in Eastern Kurdistan/Rojhelat”, which was published in 2021 in the journal Local Environment.
The paper begins with a general introduction and then proceeds to the literature review, designated by the authors as their conceptual framework. Of particular interest is the first paragraph of this conceptual framework, comprising 142 words across five sentences:
“ A peripheral and marginalised nationality within a multinational though-Persian dominated Iranian society, the Kurdish people of Iranian Kurdistan (a region referred by the Kurds as Rojhelat/Eastern Kurdi-stan) have since the early twentieth century been subject to multifaceted and systematic discriminatory and exclusionary state policy in Iran. This condition has left a population of 12–15 million Kurds in Iran suffering from structural inequalities, disenfranchisement and deprivation. Mismanagement of Kurdistan’s natural resources and the degradation of its natural environmental are among examples of this disenfranchisement. As asserted by Julian Agyeman (2005), structural inequalities that sustain the domination of political and economic elites often simultaneously result in environmental degradation, injustice and discrimination against subaltern communities. This study argues that the environmental struggle in Eastern Kurdistan can be asserted as a (sub)element of the Kurdish liberation movement in Iran. Conceptually this research is inspired by and has been conducted through the lens of ‘subalternity’ ” ( Hassaniyan, 2021, p. 931 ).
In this first paragraph, the author is doing the following:
- The author contextualises the research
- The author links the research focus to the international literature on structural inequalities
- The author clearly presents the argument of the research
- The author clarifies how the research is inspired by and uses the concept of ‘subalternity’.
Thus, the author successfully introduces the literature review, from which point onward it dives into the main concept (‘subalternity’) of the research, and reviews the literature on socio-economic justice and environmental degradation.
While introductions to a literature review section aren’t always required to offer the same level of study context detail as demonstrated here, this introduction serves as a commendable model for orienting the reader within the literature review. It effectively underscores the literature review’s significance within the context of the study being conducted.
Examples 3-5: Effective introductions to literature review chapters
The introduction to a literature review chapter can vary in length, depending largely on the overall length of the literature review chapter itself. For example, a master’s thesis typically features a more concise literature review, thus necessitating a shorter introduction. In contrast, a Ph.D. thesis, with its more extensive literature review, often includes a more detailed introduction.
Numerous universities offer online repositories where you can access theses and dissertations from previous years, serving as valuable sources of reference. Many of these repositories, however, may require you to log in through your university account. Nevertheless, a few open-access repositories are accessible to anyone, such as the one by the University of Manchester . It’s important to note though that copyright restrictions apply to these resources, just as they would with published papers.
Master’s thesis literature review introduction
The first example is “Benchmarking Asymmetrical Heating Models of Spider Pulsar Companions” by P. Sun, a master’s thesis completed at the University of Manchester on January 9, 2024. The author, P. Sun, introduces the literature review chapter very briefly but effectively:

PhD thesis literature review chapter introduction
The second example is Deep Learning on Semi-Structured Data and its Applications to Video-Game AI, Woof, W. (Author). 31 Dec 2020, a PhD thesis completed at the University of Manchester . In Chapter 2, the author offers a comprehensive introduction to the topic in four paragraphs, with the final paragraph serving as an overview of the chapter’s structure:
PhD thesis literature review introduction
The last example is the doctoral thesis Metacognitive strategies and beliefs: Child correlates and early experiences Chan, K. Y. M. (Author). 31 Dec 2020 . The author clearly conducted a systematic literature review, commencing the review section with a discussion of the methodology and approach employed in locating and analyzing the selected records.

Having absorbed all of this information, let’s recap the essential steps and offer a succinct guide on how to proceed with creating your literature review introduction:
- Contextualize your review : Begin by clearly identifying the academic context in which your literature review resides and determining the necessary information to include.
- Outline your structure : Develop a structured outline for your literature review, highlighting the essential information you plan to incorporate in your introduction.
- Literature review process : Conduct a rigorous literature review, reviewing and analyzing relevant sources.
- Summarize and abstract : After completing the review, synthesize the findings and abstract key insights, trends, and knowledge gaps from the literature.
- Craft the introduction : Write your literature review introduction with meticulous attention to the seamless integration of your review into the larger context of your work. Ensure that your introduction effectively elucidates your rationale for the chosen review topics and the underlying reasons guiding your selection.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox.
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
The best answers to "What are your plans for the future?"
10 tips for engaging your audience in academic writing, related articles.

10 key skills of successful master’s students

How to write effective cover letters for a paper submission

Dealing with failure as a PhD student

Reject decisions: Sample peer review comments and examples
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 12 May 2024
Association between problematic social networking use and anxiety symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Mingxuan Du 1 ,
- Chengjia Zhao 2 ,
- Haiyan Hu 1 ,
- Ningning Ding 1 ,
- Jiankang He 1 ,
- Wenwen Tian 1 ,
- Wenqian Zhao 1 ,
- Xiujian Lin 1 ,
- Gaoyang Liu 1 ,
- Wendan Chen 1 ,
- ShuangLiu Wang 1 ,
- Pengcheng Wang 3 ,
- Dongwu Xu 1 ,
- Xinhua Shen 4 &
- Guohua Zhang 1
BMC Psychology volume 12 , Article number: 263 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
A growing number of studies have reported that problematic social networking use (PSNU) is strongly associated with anxiety symptoms. However, due to the presence of multiple anxiety subtypes, existing research findings on the extent of this association vary widely, leading to a lack of consensus. The current meta-analysis aimed to summarize studies exploring the relationship between PSNU levels and anxiety symptoms, including generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, and fear of missing out. 209 studies with a total of 172 articles were included in the meta-analysis, involving 252,337 participants from 28 countries. The results showed a moderately positive association between PSNU and generalized anxiety (GA), social anxiety (SA), attachment anxiety (AA), and fear of missing out (FoMO) respectively (GA: r = 0.388, 95% CI [0.362, 0.413]; SA: r = 0.437, 95% CI [0.395, 0.478]; AA: r = 0.345, 95% CI [0.286, 0.402]; FoMO: r = 0.496, 95% CI [0.461, 0.529]), and there were different regulatory factors between PSNU and different anxiety subtypes. This study provides the first comprehensive estimate of the association of PSNU with multiple anxiety subtypes, which vary by time of measurement, region, gender, and measurement tool.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Social network refers to online platforms that allow users to create, share, and exchange information, encompassing text, images, audio, and video [ 1 ]. The use of social network, a term encompassing various activities on these platforms, has been measured from angles such as frequency, duration, intensity, and addictive behavior, all indicative of the extent of social networking usage [ 2 ]. As of April 2023, there are 4.8 billion social network users globally, representing 59.9% of the world’s population [ 3 ]. The usage of social network is considered a normal behavior and a part of everyday life [ 4 , 5 ]. Although social network offers convenience in daily life, excessive use can lead to PSNU [ 6 , 7 ], posing potential threats to mental health, particularly anxiety symptoms (Rasmussen et al., 2020). Empirical research has shown that anxiety symptoms, including generalized anxiety (GA), social anxiety (SA), attachment anxiety (AA), and fear of missing out (FoMO), are closely related to PSNU [ 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 ]. While some empirical studies have explored the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms, their conclusions are not consistent. Some studies have found a significant positive correlation [ 13 , 14 , 15 ], while others have found no significant correlation [ 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 ]. Furthermore, the degree of correlation varies widely in existing research, with reported r-values ranging from 0.12 to 0.80 [ 20 , 21 ]. Therefore, a systematic meta-analysis is necessary to clarify the impact of PSNU on individual anxiety symptoms.
Previous research lacks a unified concept of PSNU, primarily due to differing theoretical interpretations by various authors, and the use of varied standards and diagnostic tools. Currently, this phenomenon is referred to by several terms, including compulsive social networking use, problematic social networking use, excessive social networking use, social networking dependency, and social networking addiction [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 ]. These conceptual differences hinder the development of a cohesive and systematic research framework, as it remains unclear whether these definitions and tools capture the same underlying construct [ 27 ]. To address this lack of uniformity, this paper will use the term “problematic use” to encompass all the aforementioned nomenclatures (i.e., compulsive, excessive, dependent, and addictive use).
Regarding the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms, two main perspectives exist: the first suggests a positive correlation, while the second proposes a U-shaped relationship. The former perspective, advocating a positive correlation, aligns with the social cognitive theory of mass communication. It posits that PSNU can reinforce certain cognitions, emotions, attitudes, and behaviors [ 28 , 29 ], potentially elevating individuals’ anxiety levels [ 30 ]. Additionally, the cognitive-behavioral model of pathological use, a primary framework for explaining factors related to internet-based addictions, indicates that psychiatric symptoms like depression or anxiety may precede internet addiction, implying that individuals experiencing anxiety may turn to social networking platforms as a coping mechanism [ 31 ]. Empirical research also suggests that highly anxious individuals prefer computer-mediated communication due to the control and social liberation it offers and are more likely to have maladaptive emotional regulation, potentially leading to problematic social network service use [ 32 ]. Turning to the alternate perspective, it proposes a U-shaped relationship as per the digital Goldilocks hypothesis. In this view, moderate social networking usage is considered beneficial for psychosocial adaptation, providing individuals with opportunities for social connection and support. Conversely, both excessive use and abstinence can negatively impact psychosocial adaptation [ 33 ]. In summary, both perspectives offer plausible explanations.
Incorporating findings from previous meta-analyses, we identified seven systematic reviews and two meta-analyses that investigated the association between PSNU and anxiety. The results of these meta-analyses indicated a significant positive correlation between PSNU and anxiety (ranging from 0.33 to 0.38). However, it is evident that these previous meta-analyses had certain limitations. Firstly, they focused only on specific subtypes of anxiety; secondly, they were limited to adolescents and emerging adults in terms of age. In summary, this systematic review aims to ascertain which theoretical perspective more effectively explains the relationship between PSNU and anxiety, addressing the gaps in previous meta-analyses. Additionally, the association between PSNU and anxiety could be moderated by various factors. Drawing from a broad research perspective, any individual study is influenced by researcher-specific designs and associated sample estimates. These may lead to bias compared to the broader population. Considering the selection criteria for moderating variables in empirical studies and meta-analyses [ 34 , 35 ], the heterogeneity of findings on problematic social network usage and anxiety symptoms could be driven by divergence in sample characteristics (e.g., gender, age, region) and research characteristics (measurement instrument of study variables). Since the 2019 coronavirus pandemic, heightened public anxiety may be attributed to the fear of the virus or heightened real life stress. The increased use of electronic devices, particularly smartphones during the pandemic, also instigates the prevalence of problematic social networking. Thus, our analysis focuses on three moderators: sample characteristics (participants’ gender, age, region), measurement tools (for PSNU and anxiety symptoms) and the time of measurement (before COVID-19 vs. during COVID-19).
The present study was conducted in accordance with the 2020 statement on Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) [ 36 ]. To facilitate transparency and to avoid unnecessary duplication of research, this study was registered on PROSPERO, and the number is CRD42022350902.
Literature search
Studies on the relationship between the PSNU and anxiety symptoms from 2000 to 2023 were retrieved from seven databases. These databases included China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang Data, Chongqing VIP Information Co. Ltd. (VIP), Web of Science, ScienceDirect, PubMed, and PsycARTICLES. The search strings consisted of (a) anxiety symptoms, (b) social network, and (c) Problematic use. As shown in Table 1 , the keywords for anxiety are as follows: anxiety, generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, fear of missing out, and FoMO. The keywords for social network are as follows: social network, social media, social networking site, Instagram, and Facebook. The keywords for addiction are as follows: addiction, dependence, problem/problematic use, excessive use. The search deadline was March 19, 2023. A total of 2078 studies were initially retrieved and all were identified ultimately.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Retrieved studies were eligible for the present meta-analysis if they met the following inclusion criteria: (a) the study provided Pearson correlation coefficients used to measure the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms; (b) the study reported the sample size and the measurement instruments for the variables; (c) the study was written in English and Chinese; (d) the study provided sufficient statistics to calculate the effect sizes; (e) effect sizes were extracted from independent samples. If multiple independent samples were investigated in the same study, they were coded separately; if the study was a longitudinal study, they were coded by the first measurement. In addition, studies were excluded if they: (a) examined non-problematic social network use; (b) had an abnormal sample population; (c) the results of the same sample were included in another study and (d) were case reports or review articles. Two evaluators with master’s degrees independently assessed the eligibility of the articles. A third evaluator with a PhD examined the results and resolved dissenting views.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Two evaluators independently coded the selected articles according to the following characteristics: literature information, time of measurement (before the COVID-19 vs. during the COVID-19), sample source (developed country vs. developing country), sample size, proportion of males, mean age, type of anxiety, and measurement instruments for PSNU and anxiety symptoms. The following principles needed to be adhered to in the coding process: (a) effect sizes were extracted from independent samples. If multiple independent samples were investigated in the same study, they were coded separately; if the study was a longitudinal study, it was coded by the first measurement; (b) if multiple studies used the same data, the one with the most complete information was selected; (c) If studies reported t or F values rather than r , the following formula \( r=\sqrt{\frac{{t}^{2}}{{t}^{2}+df}}\) ; \( r=\sqrt{\frac{F}{F+d{f}_{e}}}\) was used to convert them into r values [ 37 , 38 ]. Additionally, if some studies only reported the correlation matrix between each dimension of PSNU and anxiety symptoms, the following formula \( {r}_{xy}=\frac{\sum {r}_{xi}{r}_{yj}}{\sqrt{n+n(n-1){r}_{xixj}}\sqrt{m+m(m-1){r}_{yiyj}}}\) was used to synthesize the r values [ 39 ], where n or m is the number of dimensions of variable x or variable y, respectively, and \( {r}_{xixj} \) or \( {r}_{yiyj}\) represents the mean of the correlation coefficients between the dimensions of variable x or variable y, respectively.
Literature quality was determined according to the meta-analysis quality evaluation scale developed [ 40 ]. The quality of the post-screening studies was assessed by five dimensions: sampling method, efficiency of sample collection, level of publication, and reliability of PSNU and anxiety symptom measurement instruments. The total score of the scale ranged from 0 to 10; higher scores indicated better quality of the literature.
Data analysis
All data were performed using Comprehensive Meta Analysis 3.3 (CMA 3.3). Pearson’s product-moment coefficient r was selected as the effect size index in this meta-analysis. Firstly, \( {\text{F}\text{i}\text{s}\text{h}\text{e}\text{r}}^{{\prime }}\text{s} Z=\frac{1}{2}\times \text{ln}\left(\frac{1+r}{1-r}\right)\) was used to convert the correlation coefficient to Fisher Z . Then the formula \( SE=\sqrt{\frac{1}{n-3}}\) was used to calculate the standard error ( SE ). Finally, the summary of r was obtained from the formula \( r=\frac{{e}^{2z}-1}{{e}^{2z}+1}\) for a comprehensive measure of the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms [ 37 , 41 ].
Although the effect sizes estimated by the included studies may be similar, considering the actual differences between studies (e.g., region and gender), the random effects model was a better choice for data analysis for the current meta-analysis. The heterogeneity of the included study effect sizes was measured for significance by Cochran’s Q test and estimated quantitatively by the I 2 statistic [ 42 ]. If the results indicate there is a significant heterogeneity (the Q test: p -value < 0.05, I 2 > 75) and the results of different studies are significantly different from the overall effect size. Conversely, it indicates there are no differences between the studies and the overall effect size. And significant heterogeneity tends to indicate the possible presence of potential moderating variables. Subgroup analysis and meta-regression analysis were used to examine the moderating effect of categorical and continuous variables, respectively.
Funnel plots, fail-safe number (Nfs) and Egger linear regression were utilized to evaluate the publication bias [ 43 , 44 , 45 ]. The likelihood of publication bias was considered low if the intercept obtained from Egger linear regression was not significant. A larger Nfs indicated a lower risk of publication bias, and if Nfs < 5k + 10 (k representing the original number of studies), publication bias should be a concern [ 46 ]. When Egger’s linear regression was significant, the Duval and Tweedie’s trim-and-fill was performed to correct the effect size. If there was no significant change in the effect size, it was assumed that there was no serious publication bias [ 47 ].
A significance level of P < 0.05 was deemed applicable in this study.
Sample characteristics
The PRISMA search process is depicted in Fig. 1 . The database search yielded 2078 records. After removing duplicate records and screening the title and abstract, the full text was subject to further evaluation. Ultimately, 172 records fit the inclusion criteria, including 209 independent effect sizes. The present meta-analysis included 68 studies on generalized anxiety, 44 on social anxiety, 22 on attachment anxiety, and 75 on fear of missing out. The characteristics of the selected studies are summarized in Table 2 . The majority of the sample group were adults. Quality scores for selected studies ranged from 0 to 10, with only 34 effect sizes below the theoretical mean, indicating high quality for the included studies. The literature included utilized BSMAS as the primary tool to measure PSNU, DASS-21-A to measure GA, IAS to measure SA, ECR to measure AA, and FoMOS to measure FoMO.
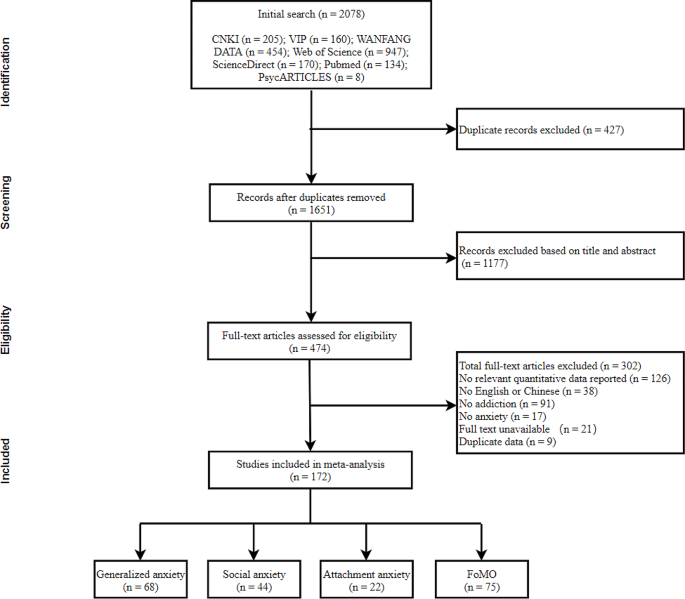
Flow chart of the search and selection strategy
Overall analysis, homogeneity tests and publication bias
As shown in Table 3 , there was significant heterogeneity between PSNU and all four anxiety symptoms (GA: Q = 1623.090, I 2 = 95.872%; SA: Q = 1396.828, I 2 = 96.922%; AA: Q = 264.899, I 2 = 92.072%; FoMO: Q = 1847.110, I 2 = 95.994%), so a random effects model was chosen. The results of the random effects model indicate a moderate positive correlation between PSNU and anxiety symptoms (GA: r = 0.350, 95% CI [0.323, 0.378]; SA: r = 0.390, 95% CI [0.347, 0.431]; AA: r = 0.345, 95% CI [0.286, 0.402]; FoMO: r = 0.496, 95% CI [0.461, 0.529]).
Figure 2 shows the funnel plot of the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms. No significant symmetry was seen in the funnel plot of the relationship between PSNU and GA and between PSNU and SA. And the Egger’s regression results also indicated that there might be publication bias ( t = 3.775, p < 0.001; t = 2.309, p < 0.05). Therefore, it was necessary to use fail-safe number (Nfs) and the trim and fill method for further examination and correction. The Nfs for PSNU and GA as well as PSNU and SA are 4591 and 7568, respectively. Both Nfs were much larger than the standard 5 k + 10. After performing the trim and fill method, 14 effect sizes were added to the right side of the funnel plat (Fig. 2 .a), the correlation coefficient between PSNU and GA changed to ( r = 0.388, 95% CI [0.362, 0.413]); 10 effect sizes were added to the right side of the funnel plat (Fig. 2 .b), the correlation coefficient between PSNU and SA changed to ( r = 0.437, 95% CI [0.395, 0.478]). The correlation coefficients did not change significantly, indicating that there was no significant publication bias associated with the relationship between PSNU and these two anxiety symptoms (GA and SA).
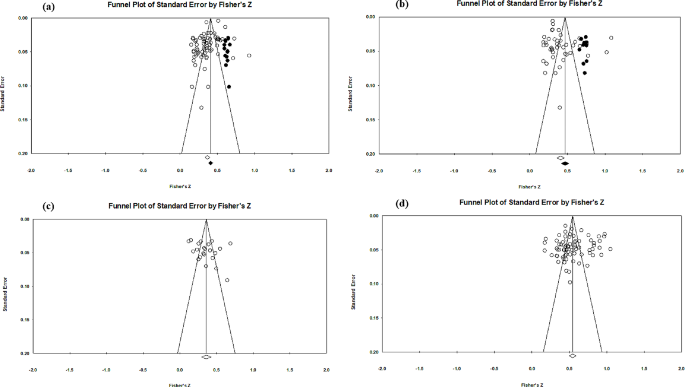
Funnel plot of the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms. Note: Black dots indicated additional studies after using trim and fill method; ( a ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and GA; ( b ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and SA; ( c ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and AA; ( d ) = Funnel plot of the PSNU and FoMO
Sensitivity analyses
Initially, the findings obtained through the one-study-removed approach indicated that the heterogeneities in the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms were not attributed to any individual study. Nevertheless, it is important to note that sensitivity analysis should be performed based on literature quality [ 223 ] since low-quality literature could potentially impact result stability. In the relationship between PSNU and GA, the 10 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.402, 95% CI [0.375, 0.428]); In the relationship between PSNU and SA, the 8 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.431, 95% CI [0.387, 0.472]); In the relationship between PSNU and AA, the 5 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.367, 95% CI [0.298, 0.433]); In the relationship between PSNU and FoMO, the 11 effect sizes below the theoretical mean scores were excluded from analysis, and the sensitivity analysis results were recalculated ( r = 0.508, 95% CI [0.470, 0.544]). The revised estimates indicate that meta-analysis results were stable.
Moderator analysis
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between psnu and ga.
The results of subgroup analysis and meta-regression are shown in Table 4 , the time of measurement significantly moderated the correlation between PSNU and GA ( Q between = 19.268, df = 2, p < 0.001). The relation between the two variables was significantly higher during the COVID-19 ( r = 0.392, 95% CI [0.357, 0.425]) than before the COVID-19 ( r = 0.270, 95% CI [0.227, 0.313]) or measurement time uncertain ( r = 0.352, 95% CI [0.285, 0.415]).
The moderating effect of the PSNU measurement was significant ( Q between = 6.852, df = 1, p = 0.009). The relation was significantly higher when PSNU was measured with the BSMAS ( r = 0.373, 95% CI [0.341, 0.404]) compared to others ( r = 0.301, 95% CI [0.256, 0.344]).
The moderating effect of the GA measurement was significant ( Q between = 60.061, df = 5, p < 0.001). Specifically, when GA measured by the GAD ( r = 0.398, 95% CI [0.356, 0.438]) and the DASS-21-A ( r = 0.433, 95% CI [0.389, 0.475]), a moderate positive correlation was observed. However, the correlation was less significant when measured using the STAI ( r = 0.232, 95% CI [0.187, 0.276]).
For the relation between PSNU and GA, the moderating effect of region, gender and age were not significant.
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between PSNU and SA
The effects of the moderating variables in the relation between PSNU and SA were shown in Table 5 . The results revealed a gender-moderated variances between the two variables (b = 0.601, 95% CI [ 0.041, 1.161], Q model (1, k = 41) = 4.705, p = 0.036).
For the relation between PSNU and SA, the moderating effects of time of measurement, region, measurement of PSNU and SA, and age were not significant.
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between PSNU and AA
The effects of the moderating variables in the relation between PSNU and AA were shown in Table 6 , region significantly moderated the correlation between PSNU and AA ( Q between = 6.410, df = 2, p = 0.041). The correlation between the two variables was significantly higher in developing country ( r = 0.378, 95% CI [0.304, 0.448]) than in developed country ( r = 0.242, 95% CI [0.162, 0.319]).
The moderating effect of the PSNU measurement was significant ( Q between = 6.852, df = 1, p = 0.009). Specifically, when AA was measured by the GPIUS-2 ( r = 0.484, 95% CI [0.200, 0.692]) and the PMSMUAQ ( r = 0.443, 95% CI [0.381, 0.501]), a moderate positive correlation was observed. However, the correlation was less significant when measured using the BSMAS ( r = 0.248, 95% CI [0.161, 0.331]) and others ( r = 0.313, 95% CI [0.250, 0.372]).
The moderating effect of the AA measurement was significant ( Q between = 17.283, df = 2, p < 0.001). The correlation was significantly higher when measured using the ECR ( r = 0.386, 95% CI [0.338, 0.432]) compared to the RQ ( r = 0.200, 95% CI [0.123, 0.275]).
For the relation between PSNU and AA, the moderating effects of time of measurement, region, gender, and age were not significant.
The impact of moderator variables on the relation between PSNU and FoMO
The effects of the moderating variables in the relation between PSNU and FoMO were shown in Table 7 , the moderating effect of the PSNU measurement was significant ( Q between = 8.170, df = 2, p = 0.017). Among the sub-dimensions, the others was excluded because there was only one sample. Specifically, when measured using the FoMOS-MSME ( r = 0.630, 95% CI [0.513, 0.725]), a moderate positive correlation was observed. However, the correlation was less significant when measured using the FoMOS ( r = 0.472, 95% CI [0.432, 0.509]) and the T-S FoMOS ( r = 0.557, 95% CI [0.463, 0.639]).
For the relationship between PSNU and FoMO, the moderating effects of time of measurement, region, measurement of PSNU, gender and age were not significant.
Through systematic review and meta-analysis, this study established a positive correlation between PSNU and anxiety symptoms (i.e., generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, and fear of missing out), confirming a linear relationship and partially supporting the Social Cognitive Theory of Mass Communication [ 28 ] and the Cognitive Behavioral Model of Pathological Use [ 31 ]. Specifically, a significant positive correlation between PSNU and GA was observed, implying that GA sufferers might resort to social network for validation or as an escape from reality, potentially alleviating their anxiety. Similarly, the meta-analysis demonstrated a strong positive correlation between PSNU and SA, suggesting a preference for computer-mediated communication among those with high social anxiety due to perceived control and liberation offered by social network. This preference is often accompanied by maladaptive emotional regulation, predisposing them to problematic use. In AA, a robust positive correlation was found with PSNU, indicating a higher propensity for such use among individuals with attachment anxiety. Notably, the study identified the strongest correlation in the context of FoMO. FoMO’s significant association with PSNU is multifaceted, stemming from the real-time nature of social networks that engenders a continuous concern about missing crucial updates or events. This drives frequent engagement with social network, thereby establishing a direct link to problematic usage patterns. Additionally, social network’s feedback loops amplify this effect, intensifying FoMO. The culture of social comparison on these platforms further exacerbates FoMO, as users frequently compare their lives with others’ selectively curated portrayals, enhancing both their social networking usage frequency and the pursuit for social validation. Furthermore, the integral role of social network in modern life broadens FoMO’s scope, encompassing anxieties about staying informed and connected.
The notable correlation between FoMO and PSNU can be comprehensively understood through various perspectives. FoMO is inherently linked to the real-time nature of social networks, which cultivates an ongoing concern about missing significant updates or events in one’s social circle [ 221 ]. This anxiety prompts frequent engagement with social network, leading to patterns of problematic use. Moreover, the feedback loops in social network algorithms, designed to enhance user engagement, further intensify this fear [ 224 ]. Additionally, social comparison, a common phenomenon on these platforms, exacerbates FoMO as users continuously compare their lives with the idealized representations of others, amplifying feelings of missing out on key social experiences [ 225 ]. This behavior not only increases social networking usage but also is closely linked to the quest for social validation and identity construction on these platforms. The extensive role of social network in modern life further amplifies FoMO, as these platforms are crucial for information exchange and maintaining social ties. FoMO thus encompasses more than social concerns, extending to anxieties about staying informed with trends and dynamics within social networks [ 226 ]. The multifaceted nature of FoMO in relation to social network underscores its pronounced correlation with problematic social networking usage. In essence, the combination of social network’s intrinsic characteristics, psychological drivers of user behavior, the culture of social comparison, and the pervasiveness of social network in everyday life collectively make FoMO the most pronouncedly correlated anxiety type with PSNU.
Additionally, we conducted subgroup analyses on the timing of measurement (before COVID-19 vs. during COVID-19), measurement tools (for PSNU and anxiety symptoms), sample characteristics (participants’ region), and performed a meta-regression analysis on gender and age in the context of PSNU and anxiety symptoms. It was found that the timing of measurement, tools used for assessing PSNU and anxiety, region, and gender had a moderating effect, whereas age did not show a significant moderating impact.
Firstly, the relationship between PSNU and anxiety symptoms was significantly higher during the COVID-19 period than before, especially between PSNU and GA. However, the moderating effect of measurement timing was not significant in the relationship between PSNU and other types of anxiety. This could be attributed to the increased uncertainty and stress during the pandemic, leading to heightened levels of general anxiety [ 227 ]. The overuse of social network for information seeking and anxiety alleviation might have paradoxically exacerbated anxiety symptoms, particularly among individuals with broad future-related worries [ 228 ]. While the COVID-19 pandemic altered the relationship between PSNU and GA, its impact on other types of anxiety (such as SA and AA) may not have been significant, likely due to these anxiety types being more influenced by other factors like social skills and attachment styles, which were minimally impacted by the epidemic.
Secondly, the observed variance in the relationship between PSNU and AA across different economic contexts, notably between developing and developed countries, underscores the multifaceted influence of socio-economic, cultural, and technological factors on this dynamic. The amplified connection in developing countries may be attributed to greater socio-economic challenges, distinct cultural norms regarding social support and interaction, rising social network penetration, especially among younger demographics, and technological disparities influencing accessibility and user experience [ 229 , 230 ]. Moreover, the role of social network as a coping mechanism for emotional distress, potentially fostering insecure attachment patterns, is more pronounced in these settings [ 231 ]. These findings highlight the necessity of considering contextual variations in assessing the psychological impacts of social network, advocating for a nuanced understanding of how socio-economic and cultural backgrounds mediate the relationship between PSNU and mental health outcomes [ 232 ]. Additionally, the relationship between PSNU and other types of anxiety (such as GA and SA) presents uniform characteristics across different economic contexts.
Thirdly, the significant moderating effects of measurement tools in the context of PSNU and its correlation with various forms of anxiety, including GA, and AA, are crucial in interpreting the research findings. Specifically, the study reveals that the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale (BSMAS) demonstrates a stronger correlation between PSNU and GA, compared to other tools. Similarly, for AA, the Griffiths’ Problematic Internet Use Scale 2 (GPIUS2) and the Problematic Media Social Media Use Assessment Questionnaire (PMSMUAQ) show a more pronounced correlation with AA than the BSMAS or other instruments, but for SA and FoMO, the PSNU instrument doesn’t significantly moderate the correlation. The PSNU measurement tool typically contains an emotional change dimension. SA and FoMO, due to their specific conditional stimuli triggers and correlation with social networks [ 233 , 234 ], are likely to yield more consistent scores in this dimension, while GA and AA may be less reliable due to their lesser sensitivity to specific conditional stimuli. Consequently, the adjustment effects of PSNU measurements vary across anxiety symptoms. Regarding the measurement tools for anxiety, different scales exhibit varying degrees of sensitivity in detecting the relationship with PSNU. The Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale (GAD) and the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales 21 (DASS-21) are more effective in illustrating a strong relationship between GA and PSNU than the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI). In the case of AA, the Experiences in Close Relationships-21 (ECR-21) provides a more substantial correlation than the Relationship Questionnaire (RQ). Furthermore, for FoMO, the Fear of Missing Out Scale - Multi-Social Media Environment (FoMOS-MSME) is more indicative of a strong relationship with PSNU compared to the standard FoMOS or the T-S FoMOS. These findings underscore the importance of the selection of appropriate measurement tools in research. Different tools, due to their unique design, focus, and sensitivity, can reveal varying degrees of correlation between PSNU and anxiety disorders. This highlights the need for careful consideration of tool characteristics and their potential impact on research outcomes. It also cautions against drawing direct comparisons between studies without acknowledging the possible variances introduced by the use of different measurement instruments.
Fourthly, the significant moderating role of gender in the relationship between PSNU and SA, particularly pronounced in samples with a higher proportion of females. Women tend to engage more actively and emotionally with social network, potentially leading to an increased dependency on these platforms when confronting social anxiety [ 235 ]. This intensified use might amplify the association between PSNU and SA. Societal and cultural pressures, especially those related to appearance and social status, are known to disproportionately affect women, possibly exacerbating their experience of social anxiety and prompting a greater reliance on social network for validation and support [ 236 ]. Furthermore, women’s propensity to seek emotional support and express themselves on social network platforms [ 237 ] could strengthen this link, particularly in the context of managing social anxiety. Consequently, the observed gender differences in the relationship between PSNU and SA underscore the importance of considering gender-specific dynamics and cultural influences in psychological research related to social network use. In addition, gender consistency was observed in the association between PSNU and other types of anxiety, indicating no significant gender disparities.
Fifthly, the absence of a significant moderating effect of age on the relationship between PSNU and various forms of anxiety suggests a pervasive influence of social network across different age groups. This finding indicates that the impact of PSNU on anxiety is relatively consistent, irrespective of age, highlighting the universal nature of social network’s psychological implications [ 238 ]. Furthermore, this uniformity suggests that other factors, such as individual psychological traits or socio-cultural influences, might play a more crucial role in the development of anxiety related to social networking usage than age [ 239 ]. The non-significant role of age also points towards a potential generational overlap in social networking usage patterns and their psychological effects, challenging the notion that younger individuals are uniquely susceptible to the adverse effects of social network on mental health [ 240 ]. Therefore, this insight necessitates a broader perspective in understanding the dynamics of social network and mental health, one that transcends age-based assumptions.
Limitations
There are some limitations in this research. First, most of the studies were cross-sectional surveys, resulting in difficulties in inferring causality of variables, longitudinal study data will be needed to evaluate causal interactions in the future. Second, considerable heterogeneity was found in the estimated results, although heterogeneity can be partially explained by differences in study design (e.g., Time of measurement, region, gender, and measurement tools), but this can introduce some uncertainty in the aggregation and generalization of the estimated results. Third, most studies were based on Asian samples, which limits the generality of the results. Fourth, to minimize potential sources of heterogeneity, some less frequently used measurement tools were not included in the classification of measurement tools, which may have some impact on the results of heterogeneity interpretation. Finally, since most of the included studies used self-reported scales, it is possible to get results that deviate from the actual situation to some extent.
This meta-analysis aims to quantifies the correlations between PSNU and four specific types of anxiety symptoms (i.e., generalized anxiety, social anxiety, attachment anxiety, and fear of missing out). The results revealed a significant moderate positive association between PSNU and each of these anxiety symptoms. Furthermore, Subgroup analysis and meta-regression analysis indicated that gender, region, time of measurement, and instrument of measurement significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and specific anxiety symptoms. Specifically, the measurement time and GA measurement tools significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and GA. Gender significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and SA. Region, PSNU measurement tools, and AA measurement tools all significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and AA. The FoMO measurement tool significantly influenced the relationship between PSNU and FoMO. Regarding these findings, prevention interventions for PSNU and anxiety symptoms are important.
Data availability
The datasets are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Problematic social networking use
- Generalized anxiety
- Social anxiety
- Attachment anxiety
Fear of miss out
Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale
Facebook Addiction Scale
Facebook Intrusion Questionnaire
Generalized Problematic Internet Use Scale 2
Problematic Mobile Social Media Usage Assessment Questionnaire
Social Network Addiction Tendency Scale
Brief Symptom Inventory
The anxiety subscale of the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
The anxiety subscale of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale
State-Trait Anxiety Inventory
Interaction Anxiousness Scale
Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale
Social Anxiety Scale for Social Media Users
Social Anxiety for Adolescents
Social Anxiety Subscale of the Self-Consciousness Scale
Social Interaction Anxiety Scale
Experiences in Close Relationship Scale
Relationship questionnaire
Fear of Missing Out Scale
FoMO Measurement Scale in the Mobile Social Media Environment
Trait-State Fear of missing Out Scale
Rozgonjuk D, Sindermann C, Elhai JD, Montag C. Fear of missing out (FoMO) and social media’s impact on daily-life and productivity at work: do WhatsApp, Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat Use disorders mediate that association? Addict Behav. 2020;110:106487.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Mieczkowski H, Lee AY, Hancock JT. Priming effects of social media use scales on well-being outcomes: the influence of intensity and addiction scales on self-reported depression. Social Media + Soc. 2020;6(4):2056305120961784.
Article Google Scholar
Global digital population as of April. 2023 [ https://www.statista.com/statistics/617136/digital-population-worldwide/ ].
Marengo D, Settanni M, Fabris MA, Longobardi C. Alone, together: fear of missing out mediates the link between peer exclusion in WhatsApp classmate groups and psychological adjustment in early-adolescent teens. J Social Personal Relationships. 2021;38(4):1371–9.
Marengo D, Fabris MA, Longobardi C, Settanni M. Smartphone and social media use contributed to individual tendencies towards social media addiction in Italian adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic. Addict Behav. 2022;126:107204.
Müller SM, Wegmann E, Stolze D, Brand M. Maximizing social outcomes? Social zapping and fear of missing out mediate the effects of maximization and procrastination on problematic social networks use. Comput Hum Behav. 2020;107:106296.
Sun Y, Zhang Y. A review of theories and models applied in studies of social media addiction and implications for future research. Addict Behav. 2021;114:106699.
Boustead R, Flack M. Moderated-mediation analysis of problematic social networking use: the role of anxious attachment orientation, fear of missing out and satisfaction with life. Addict Behav 2021, 119.
Hussain Z, Griffiths MD. The associations between problematic social networking Site Use and Sleep Quality, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, Depression, anxiety and stress. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2021;19(3):686–700.
Gori A, Topino E, Griffiths MD. The associations between attachment, self-esteem, fear of missing out, daily time expenditure, and problematic social media use: a path analysis model. Addict Behav. 2023;141:107633.
Marino C, Manari T, Vieno A, Imperato C, Spada MM, Franceschini C, Musetti A. Problematic social networking sites use and online social anxiety: the role of attachment, emotion dysregulation and motives. Addict Behav. 2023;138:107572.
Tobin SJ, Graham S. Feedback sensitivity as a mediator of the relationship between attachment anxiety and problematic Facebook Use. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2020;23(8):562–6.
Brailovskaia J, Rohmann E, Bierhoff H-W, Margraf J. The anxious addictive narcissist: the relationship between grandiose and vulnerable narcissism, anxiety symptoms and Facebook Addiction. PLoS ONE 2020, 15(11).
Kim S-S, Bae S-M. Social Anxiety and Social Networking Service Addiction Proneness in University students: the Mediating effects of Experiential Avoidance and interpersonal problems. Psychiatry Invest. 2022;19(8):702–702.
Zhao J, Ye B, Yu L, Xia F. Effects of Stressors of COVID-19 on Chinese College Students’ Problematic Social Media Use: A Mediated Moderation Model. Front Psychiatry 2022, 13.
Astolfi Cury GS, Takannune DM, Prates Herrerias GS, Rivera-Sequeiros A, de Barros JR, Baima JP, Saad-Hossne R, Sassaki LY. Clinical and Psychological Factors Associated with Addiction and Compensatory Use of Facebook among patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a cross-sectional study. Int J Gen Med. 2022;15:1447–57.
Balta S, Emirtekin E, Kircaburun K, Griffiths MD. Neuroticism, trait fear of missing out, and Phubbing: the mediating role of state fear of missing out and problematic Instagram Use. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2020;18(3):628–39.
Boursier V, Gioia F, Griffiths MD. Do selfie-expectancies and social appearance anxiety predict adolescents’ problematic social media use? Comput Hum Behav. 2020;110:106395.
Worsley JD, McIntyre JC, Bentall RP, Corcoran R. Childhood maltreatment and problematic social media use: the role of attachment and depression. Psychiatry Res. 2018;267:88–93.
de Bérail P, Guillon M, Bungener C. The relations between YouTube addiction, social anxiety and parasocial relationships with YouTubers: a moderated-mediation model based on a cognitive-behavioral framework. Comput Hum Behav. 2019;99:190–204.
Naidu S, Chand A, Pandaram A, Patel A. Problematic internet and social network site use in young adults: the role of emotional intelligence and fear of negative evaluation. Pers Indiv Differ. 2023;200:111915.
Apaolaza V, Hartmann P, D’Souza C, Gilsanz A. Mindfulness, compulsive Mobile Social Media Use, and derived stress: the mediating roles of self-esteem and social anxiety. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2019;22(6):388–96.
Demircioglu ZI, Goncu-Kose A. Antecedents of problematic social media use and cyberbullying among adolescents: attachment, the dark triad and rejection sensitivity. Curr Psychol (New Brunsw NJ) 2022:1–19.
Gao Q, Li Y, Zhu Z, Fu E, Bu X, Peng S, Xiang Y. What links to psychological needs satisfaction and excessive WeChat use? The mediating role of anxiety, depression and WeChat use intensity. BMC Psychol. 2021;9(1):105–105.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Malak MZ, Shuhaiber AH, Al-amer RM, Abuadas MH, Aburoomi RJ. Correlation between psychological factors, academic performance and social media addiction: model-based testing. Behav Inform Technol. 2022;41(8):1583–95.
Song C. The effect of the need to belong on mobile phone social media dependence of middle school students: Chain mediating roles of fear of missing out and maladaptive cognition. Sichuan Normal University; 2022.
Tokunaga RS, Rains SA. A review and meta-analysis examining conceptual and operational definitions of problematic internet use. Hum Commun Res. 2016;42(2):165–99.
Bandura A. Social cognitive theory of mass communication. Media effects. edn.: Routledge; 2009. pp. 110–40.
Valkenburg PM, Peter J, Walther JB. Media effects: theory and research. Ann Rev Psychol. 2016;67:315–38.
Slater MD. Reinforcing spirals: the mutual influence of media selectivity and media effects and their impact on individual behavior and social identity. Communication Theory. 2007;17(3):281–303.
Ahmed E, Vaghefi I. Social media addiction: A systematic review through cognitive-behavior model of pathological use. 2021.
She R, han Mo PK, Li J, Liu X, Jiang H, Chen Y, Ma L, fai Lau JT. The double-edged sword effect of social networking use intensity on problematic social networking use among college students: the role of social skills and social anxiety. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;140:107555.
Przybylski AK, Weinstein N. A large-scale test of the goldilocks hypothesis: quantifying the relations between digital-screen use and the mental well-being of adolescents. Psychol Sci. 2017;28(2):204–15.
Ran G, Li J, Zhang Q, Niu X. The association between social anxiety and mobile phone addiction: a three-level meta-analysis. Comput Hum Behav. 2022;130:107198.
Fioravanti G, Casale S, Benucci SB, Prostamo A, Falone A, Ricca V, Rotella F. Fear of missing out and social networking sites use and abuse: a meta-analysis. Comput Hum Behav. 2021;122:106839.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group* P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):264–9.
Card NA. Applied meta-analysis for social science research. Guilford; 2015.
Peterson RA, Brown SP. On the use of beta coefficients in meta-analysis. J Appl Psychol. 2005;90(1):175.
Hunter JE, Schmidt FL. Methods of meta-analysis: correcting error and bias in research findings. Sage; 2004.
Zhang Y, Li S, Yu G. The relationship between self-esteem and social anxiety: a meta-analysis with Chinese students. Adv Psychol Sci. 2019;27(6):1005–18.
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JP, Rothstein HR. Introduction to meta-analysis. Wiley; 2021.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2002;21(11):1539–58.
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997;315(7109):629–34.
Light RJ, Pillemer DB. Summing up: the science of reviewing research. Harvard University Press; 1984.
Rosenthal R. Meta-Analytic Procedures for Social Science Research Sage Publications: Beverly Hills, 1984, 148 pp. Educational Researcher 1986;15(8):18–20.
Rothstein HR, Sutton AJ, Borenstein M. Publication bias in meta-analysis. Publication bias meta‐analysis: Prev Assess Adjustments 2005:1–7.
Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot–based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta‐analysis. Biometrics. 2000;56(2):455–63.
Al-Mamun F, Hosen I, Griffiths MD, Mamun MA. Facebook use and its predictive factors among students: evidence from a lower- and middle-income country, Bangladesh. Front Psychiatry 2022, 13.
Schou Andreassen C, Billieux J, Griffiths MD, Kuss DJ, Demetrovics Z, Mazzoni E, Pallesen S. The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: a large-scale cross-sectional study. Psychol Addict Behaviors: J Soc Psychologists Addict Behav. 2016;30(2):252–62.
Arikan G, Acar IH, Ustundag-Budak AM. A two-generation study: The transmission of attachment and young adults’ depression, anxiety, and social media addiction. Addict Behav 2022, 124.
Arpaci I, Karatas K, Kiran F, Kusci I, Topcu A. Mediating role of positivity in the relationship between state anxiety and problematic social media use during the COVID-19 pandemic. Death Stud. 2022;46(10):2287–97.
Brailovskaia J, Margraf J. Facebook Addiction Disorder (FAD) among German students-A longitudinal approach. PLoS ONE 2017, 12(12).
Brailovskaia J, Margraf J. The relationship between burden caused by coronavirus (Covid-19), addictive social media use, sense of control and anxiety. Comput Hum Behav. 2021;119:106720–106720.
Brailovskaia J, Margraf J. Addictive social media use during Covid-19 outbreak: validation of the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale (BSMAS) and investigation of protective factors in nine countries. Curr Psychol (New Brunsw NJ) 2022:1–19.
Brailovskaia J, Krasavtseva Y, Kochetkov Y, Tour P, Margraf J. Social media use, mental health, and suicide-related outcomes in Russian women: a cross-sectional comparison between two age groups. Women’s Health (London England). 2022;18:17455057221141292–17455057221141292.
PubMed Google Scholar
Chang C-W, Huang R-Y, Strong C, Lin Y-C, Tsai M-C, Chen IH, Lin C-Y, Pakpour AHH, Griffiths MDD. Reciprocal relationships between Problematic Social Media Use, problematic gaming, and psychological distress among University students: a 9-Month Longitudinal Study. Front Public Health 2022, 10.
Charzynska E, Sussman S, Atroszko PA. Profiles of potential behavioral addictions’ severity and their associations with gender, personality, and well-being: A person-centered approach. Addict Behav 2021, 119.
Chen C-Y, Chen IH, Pakpour AH, Lin C-Y, Griffiths MD. Internet-related behaviors and psychological distress among Schoolchildren during the COVID-19 School Hiatus. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2021;24(10):654–63.
Da Veiga GF, Sotero L, Pontes HM, Cunha D, Portugal A, Relvas AP. Emerging adults and Facebook Use: the validation of the Bergen Facebook Addiction Scale (BFAS). Int J Mental Health Addict. 2019;17(2):279–94.
Dadiotis A, Bacopoulou F, Kokka I, Vlachakis D, Chrousos GP, Darviri C, Roussos P. Validation of the Greek version of the Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale in Undergraduate Students. EMBnetjournal 2021, 26.
Fekih-Romdhane F, Jahrami H, Away R, Trabelsi K, Pandi-Perumal SR, Seeman MV, Hallit S, Cheour M. The relationship between technology addictions and schizotypal traits: mediating roles of depression, anxiety, and stress. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23(1).
Flynn S, Noone C, Sarma KM. An exploration of the link between adult attachment and problematic Facebook use. BMC Psychol. 2018;6(1):34–34.
Fung XCC, Siu AMH, Potenza MN, O’Brien KS, Latner JD, Chen C-Y, Chen IH, Lin C-Y. Problematic use of internet-related activities and Perceived Weight Stigma in Schoolchildren: a longitudinal study across different epidemic periods of COVID-19 in China. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Gonzalez-Nuevo C, Cuesta M, Muniz J, Postigo A, Menendez-Aller A, Kuss DJ. Problematic Use of Social Networks during the First Lockdown: User Profiles and the Protective Effect of Resilience and Optimism. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2022, 11(24).
Hou X-L, Wang H-Z, Hu T-Q, Gentile DA, Gaskin J, Wang J-L. The relationship between perceived stress and problematic social networking site use among Chinese college students. J Behav Addictions. 2019;8(2):306–17.
Hussain Z, Wegmann E. Problematic social networking site use and associations with anxiety, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and resilience. Computers Hum Behav Rep. 2021;4:100125.
Imani V, Ahorsu DK, Taghizadeh N, Parsapour Z, Nejati B, Chen H-P, Pakpour AH. The mediating roles of anxiety, Depression, Sleepiness, Insomnia, and Sleep Quality in the Association between Problematic Social Media Use and Quality of Life among patients with Cancer. Healthcare 2022, 10(9).
Islam MS, Sujan MSH, Tasnim R, Mohona RA, Ferdous MZ, Kamruzzaman S, Toma TY, Sakib MN, Pinky KN, Islam MR et al. Problematic smartphone and Social Media Use among Bangladeshi College and University students amid COVID-19: the role of Psychological Well-Being and Pandemic related factors. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Islam MS, Jahan I, Dewan MAA, Pontes HM, Koly KN, Sikder MT, Rahman M. Psychometric properties of three online-related addictive behavior instruments among Bangladeshi school-going adolescents. PLoS ONE 2022, 17(12).
Jahan I, Hosen I, Al Mamun F, Kaggwa MM, Griffiths MD, Mamun MA. How has the COVID-19 pandemic impacted Internet Use behaviors and facilitated problematic internet use? A Bangladeshi study. Psychol Res Behav Manage. 2021;14:1127–38.
Jiang Y. Problematic social media usage and anxiety among University Students during the COVID-19 pandemic: the mediating role of Psychological Capital and the moderating role of academic burnout. Front Psychol. 2021;12:612007–612007.
Kim M-R, Oh J-W, Huh B-Y. Analysis of factors related to Social Network Service Addiction among Korean High School Students. J Addictions Nurs. 2020;31(3):203–12.
Koc M, Gulyagci S. Facebook addiction among Turkish college students: the role of psychological health, demographic, and usage characteristics. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2013;16(4):279–84.
Lin C-Y, Namdar P, Griffiths MD, Pakpour AH. Mediated roles of generalized trust and perceived social support in the effects of problematic social media use on mental health: a cross-sectional study. Health Expect. 2021;24(1):165–73.
Lin C-Y, Imani V, Griffiths MD, Brostrom A, Nygardh A, Demetrovics Z, Pakpour AH. Temporal associations between morningness/eveningness, problematic social media use, psychological distress and daytime sleepiness: mediated roles of sleep quality and insomnia among young adults. J Sleep Res 2021, 30(1).
Lozano Blasco R, Latorre Cosculluela C, Quilez Robres A. Social Network Addiction and its impact on anxiety level among University students. Sustainability 2020, 12(13).
Marino C, Musetti A, Vieno A, Manari T, Franceschini C. Is psychological distress the key factor in the association between problematic social networking sites and poor sleep quality? Addict Behav 2022, 133.
Meshi D, Ellithorpe ME. Problematic social media use and social support received in real-life versus on social media: associations with depression, anxiety and social isolation. Addict Behav 2021, 119.
Mitropoulou EM, Karagianni M, Thomadakis C. Social Media Addiction, Self-Compassion, and Psychological Well-Being: a structural equation Model. Alpha Psychiatry. 2022;23(6):298–304.
Ozimek P, Brailovskaia J, Bierhoff H-W. Active and passive behavior in social media: validating the Social Media Activity Questionnaire (SMAQ). Telematics Inf Rep. 2023;10:100048.
Phillips WJ, Wisniewski AT. Self-compassion moderates the predictive effects of social media use profiles on depression and anxiety. Computers Hum Behav Rep. 2021;4:100128.
Reer F, Festl R, Quandt T. Investigating problematic social media and game use in a nationally representative sample of adolescents and younger adults. Behav Inform Technol. 2021;40(8):776–89.
Satici B, Kayis AR, Griffiths MD. Exploring the Association between Social Media Addiction and relationship satisfaction: psychological distress as a Mediator. Int J Mental Health Addict 2021.
Sediri S, Zgueb Y, Ouanes S, Ouali U, Bourgou S, Jomli R, Nacef F. Women’s mental health: acute impact of COVID-19 pandemic on domestic violence. Archives Womens Mental Health. 2020;23(6):749–56.
Shabahang R, Shim H, Aruguete MS, Zsila A. Oversharing on Social Media: anxiety, Attention-Seeking, and Social Media Addiction Predict the breadth and depth of sharing. Psychol Rep 2022:332941221122861–332941221122861.
Sotero L, Ferreira Da Veiga G, Carreira D, Portugal A, Relvas AP. Facebook Addiction and emerging adults: the influence of sociodemographic variables, family communication, and differentiation of self. Escritos De Psicología - Psychol Writings. 2019;12(2):81–92.
Stockdale LA, Coyne SM. Bored and online: reasons for using social media, problematic social networking site use, and behavioral outcomes across the transition from adolescence to emerging adulthood. J Adolesc. 2020;79:173–83.
Wang Z, Yang H, Elhai JD. Are there gender differences in comorbidity symptoms networks of problematic social media use, anxiety and depression symptoms? Evidence from network analysis. Pers Indiv Differ. 2022;195:111705.
White-Gosselin C-E, Poulin F. Associations Between Young Adults’ Social Media Addiction, Relationship Quality With Parents, and Internalizing Problems: A Path Analysis Model. 2022.
Wong HY, Mo HY, Potenza MN, Chan MNM, Lau WM, Chui TK, Pakpour AH, Lin C-Y. Relationships between Severity of Internet Gaming Disorder, Severity of Problematic Social Media Use, Sleep Quality and Psychological Distress. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17(6).
Yam C-W, Pakpour AH, Griffiths MD, Yau W-Y, Lo C-LM, Ng JMT, Lin C-Y, Leung H. Psychometric testing of three Chinese online-related addictive Behavior instruments among Hong Kong University students. Psychiatr Q. 2019;90(1):117–28.
Yuan Y, Zhong Y. A survey on the use of social networks and mental health of college students during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Campus Life Mental Health\. 2021;19(3):209–12.
Google Scholar
Yurdagul C, Kircaburun K, Emirtekin E, Wang P, Griffiths MD. Psychopathological consequences related to problematic Instagram Use among adolescents: the mediating role of body image dissatisfaction and moderating role of gender. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2021;19(5):1385–97.
Zhang W, Pu J, He R, Yu M, Xu L, He X, Chen Z, Gan Z, Liu K, Tan Y, et al. Demographic characteristics, family environment and psychosocial factors affecting internet addiction in Chinese adolescents. J Affect Disord. 2022;315:130–8.
Zhang L, Wu Y, Jin T, Jia Y. Revision and validation of the Chinese short version of social media disorder. Mod Prev Med. 2021;48(8):1350–3.
Zhang X, Fan L. The influence of anxiety on colleges’ life satisfaction. Chin J Health Educ. 2021;37(5):469–72.
Zhao M, Wang H, Dong Y, Niu Y, Fang Y. The relationship between self-esteem and wechat addiction among undergraduate students: the multiple mediating roles of state anxiety and online interpersonal trust. J Psychol Sci. 2021;44(1):104–10.
Zhao J, Zhou Z, Sun B, Zhang X, Zhang L, Fu S. Attentional Bias is Associated with negative emotions in problematic users of Social Media as measured by a dot-probe Task. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(24).
Atroszko PA, Balcerowska JM, Bereznowski P, Biernatowska A, Pallesen S, Schou Andreassen C. Facebook addiction among Polish undergraduate students: validity of measurement and relationship with personality and well-being. Comput Hum Behav. 2018;85:329–38.
Chen Y, Li R, Zhang P, Liu X. The moderating role of state attachment anxiety and avoidance between social anxiety and social networking sites Addiction. Psychol Rep. 2020;123(3):633–47.
Chen B, Zheng X, Sun X. The relationship between problematic social media use and online social anxiety: the roles of social media cognitive overload and dispositional mindfulness. Psychol Dev Educ. 2023;39(5):743–51.
Chentsova VO, Bravo AJ, Mezquita L, Pilatti A, Hogarth L, Cross-Cultural AS. Internalizing symptoms, rumination, and problematic social networking site use: a cross national examination among young adults in seven countries. Addict Behav 2023, 136.
Chu X, Ji S, Wang X, Yu J, Chen Y, Lei L. Peer phubbing and social networking site addiction: the mediating role of social anxiety and the moderating role of Family Financial Difficulty. Front Psychol. 2021;12:670065–670065.
Dempsey AE, O’Brien KD, Tiamiyu MF, Elhai JD. Fear of missing out (FoMO) and rumination mediate relations between social anxiety and problematic Facebook use. Addict Behav Rep. 2019;9:100150–100150.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yildiz Durak H, Seferoglu SS. Modeling of variables related to problematic social media usage: Social desirability tendency example. Scand J Psychol. 2019;60(3):277–88.
Ekinci N, Akat M. The relationship between anxious-ambivalent attachment and social appearance anxiety in adolescents: the serial mediation of positive Youth Development and Instagram Addiction. Psychol Rep 2023:332941231159600–332941231159600.
Foroughi B, Griffiths MD, Iranmanesh M, Salamzadeh Y. Associations between Instagram Addiction, academic performance, social anxiety, Depression, and life satisfaction among University students. Int J Mental Health Addict. 2022;20(4):2221–42.
He L. Influence mechanism and intervention suggestions on addiction of social network addiction. Gannan Normal University; 2021.
Hu Y. The influencing mechanism of type D personality on problematic social networking sites use among adolescents and intervention research. Central China Normal University; 2020.
Jia L. A study of the relationship between neuroticism, perceived social support, social anxiety and problematic social network use in high school students. Harbin Normal University; 2022.
Lee-Won RJ, Herzog L, Park SG. Hooked on Facebook: the role of social anxiety and need for Social Assurance in Problematic Use of Facebook. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2015;18(10):567–74.
Li H. Social anxiety and internet interpersonal addiction in adolescents and countermeasures. Central China Normal University; 2022.
Lin W-S, Chen H-R, Lee TS-H, Feng JY. Role of social anxiety on high engagement and addictive behavior in the context of social networking sites. Data Technol Appl. 2019;53(2):156–70.
Liu Y. The influence of family function on social media addiction in adolescents: the chain mediation effect of social anxiety and resilience. Hunan Normal University; 2021.
Lyvers M, Salviani A, Costan S, Thorberg FA. Alexithymia, narcissism and social anxiety in relation to social media and internet addiction symptoms. Int J Psychology: J Int De Psychologie. 2022;57(5):606–12.
Majid A, Yasir M, Javed A, Ali P. From envy to social anxiety and rumination: how social media site addiction triggers task distraction amongst nurses. J Nurs Adm Manag. 2020;28(3):504–13.
Mou Q, Zhuang J, Gao Y, Zhong Y, Lu Q, Gao F, Zhao M. The relationship between social anxiety and academic engagement among Chinese college students: a serial mediation model. J Affect Disord. 2022;311:247–53.
Ruggieri S, Santoro G, Pace U, Passanisi A, Schimmenti A. Problematic Facebook use and anxiety concerning use of social media in mothers and their offspring: an actor-partner interdependence model. Addict Behav Rep. 2020;11:100256–100256.
Ruiz MJ, Saez G, Villanueva-Moya L, Exposito F. Adolescent sexting: the role of body shame, Social Physique anxiety, and social networking site addiction. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2021;24(12):799–805.
She R, Kit Han Mo P, Li J, Liu X, Jiang H, Chen Y, Ma L, Tak Fai Lau J. The double-edged sword effect of social networking use intensity on problematic social networking use among college students: the role of social skills and social anxiety. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;140:107555.
Stănculescu E. The Bergen Social Media Addiction Scale Validity in a Romanian sample using item response theory and network analysis. Int J Mental Health Addict 2022.
Teng X, Lei H, Li J, Wen Z. The influence of social anxiety on social network site addiction of college students: the moderator of intentional self-regulation. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2021;29(3):514–7.
Tong W. Influence of boredom on the problematic mobile social networks usage in adolescents: multiple chain mediator. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2019;27(5):932–6.
Tu W, Jiang H, Liu Q. Peer victimization and adolescent Mobile Social Addiction: mediation of social anxiety and gender differences. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(17).
Wang S. The influence of college students self-esteem, social anxiety and fear of missing out on the problematic mobile social networks usage. Huaibei Normal University; 2021.
Wang X. The impact of peer relationship and social anxiety on secondary vocational school students’ problematic social network use and intervention study. Huaibei Normal University; 2022.
Wegmann E, Stodt B, Brand M. Addictive use of social networking sites can be explained by the interaction of internet use expectancies, internet literacy, and psychopathological symptoms. J Behav Addictions. 2015;4(3):155–62.
Yang W. The relationship between the type of internet addiction and the personality traits in college students. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2004.
Yang Z. The relationship between social variables and social networking usage among shanghai working population. East China Normal University; 2013.
Zhang C. The relationship between perceived social support and problematic social network use among junior high school students: a chain mediation model and an intervention study. Hebei University; 2022.
Zhang J, Chang F, Huang D, Wen X. The relationship between neuroticism and the problematic mobile social networks use in adolescents: the mediating role of anxiety and positive self-presentation. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2021;29(3):598–602.
Zhang Z. College students’ loneliness and problematic social networking use: Chain mediation of social self-efficacy and social anxiety. Shanghai Normal University; 2019.
Zhu B. Discussion on mechanism of social networking addiction——Social anxiety, craving and excitability. Liaoning Normal University; 2017.
Blackwell D, Leaman C, Tramposch R, Osborne C, Liss M. Extraversion, neuroticism, attachment style and fear of missing out as predictors of social media use and addiction. Pers Indiv Differ. 2017;116:69–72.
Chen A. From attachment to addiction: the mediating role of need satisfaction on social networking sites. Comput Hum Behav. 2019;98:80–92.
Chen Y, Zhong S, Dai L, Deng Y, Liu X. Attachment anxiety and social networking sites addiction in college students: a moderated mediating model. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2019;27(3):497–500.
Li J. The relations among problematic social networks usage behavior, Childhood Trauma and adult attachment in University students. Hunan Agricultural University; 2020.
Liu C, Ma J-L. Adult attachment orientations and social networking site addiction: the Mediating effects of Online Social Support and the fear of missing out. Front Psychol. 2019;10:2629–2629.
Mo S, Huang W, Xu Y, Tang Z, Nie G. The impact of medical students’ attachment anxiety on the use of problematic social networking sites during the epidemic. Psychol Monthly. 2022;17(9):1–4.
Teng X. The effect of attachment anxiety on problematic mobile social network use: the role of loneliness and self-control. Harbin Normal University; 2021.
Worsley JD, Mansfield R, Corcoran R. Attachment anxiety and problematic social media use: the Mediating Role of Well-Being. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2018;21(9):563–8.
Wu Z. The effect of adult attachment on problematic social network use: the chain mediating effect of loneliness and fear of missing out. Jilin University; 2022.
Xia N. The impact of attachment anxiety on adolescent problem social networking site use: a moderated mediation model. Shihezi University; 2022.
Young L, Kolubinski DC, Frings D. Attachment style moderates the relationship between social media use and user mental health and wellbeing. Heliyon 2020, 6(6).
Bakioglu F, Deniz M, Griffiths MD, Pakpour AH. Adaptation and validation of the online-fear of missing out inventory into Turkish and the association with social media addiction, smartphone addiction, and life satisfaction. BMC Psychol. 2022;10(1):154–154.
Bendayan R, Blanca MJ. Spanish version of the Facebook Intrusion Questionnaire (FIQ-S). Psicothema. 2019;31(2):204–9.
Blachnio A, Przepiorka A. Facebook intrusion, fear of missing out, narcissism, and life satisfaction: a cross-sectional study. Psychiatry Res. 2018;259:514–9.
Casale S, Rugai L, Fioravanti G. Exploring the role of positive metacognitions in explaining the association between the fear of missing out and social media addiction. Addict Behav. 2018;85:83–7.
Chen Y, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Wang K. Effect of fear of’ missing out on college students negative social adaptation: Chain¬ - mediating effect of rumination and problematic social media use. China J Health Psychol. 2022;30(4):581–6.
Cheng S, Zhang X, Han Y. Relationship between fear of missing out and phubbing on college students: the chain intermediary effect of intolerance of uncertainty and problematic social media use. China J Health Psychol. 2022;30(9):1296–300.
Cui Q, Wang J, Zhang J, Li W, Li Q. The relationship between loneliness and negative emotion in college students: the chain-mediating role of fear of missing out and social network sites addiction. J Jining Med Univ. 2022;45(4):248–51.
Ding Q, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Zhou Z. The more gossip, the more addicted: the relationship between interpersonal curiosity and social networking sites addiction tendencies in college students. Psychol Dev Educ. 2022;38(1):118–25.
Fabris MA, Marengo D, Longobardi C, Settanni M. Investigating the links between fear of missing out, social media addiction, and emotional symptoms in adolescence: the role of stress associated with neglect and negative reactions on social media. Addict Behav. 2020;106:106364.
Fang J, Wang X, Wen Z, Zhou J. Fear of missing out and problematic social media use as mediators between emotional support from social media and phubbing behavior. Addict Behav. 2020;107:106430.
Gao Z. The study on the relationship and intervention among fear of missing out self-differentiation and problematic social media use of college students. Yunnan Normal University; 2021.
Gioia F, Fioravanti G, Casale S, Boursier V. The Effects of the Fear of Missing Out on People’s Social Networking Sites Use During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Mediating Role of Online Relational Closeness and Individuals’ Online Communication Attitude. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Gu X. Study on the Inhibitory Effect of Mindfulness Training on Social Media Addiction of College Students. Wuhan University; 2020.
Gugushvili N, Taht K, Schruff-Lim EM, Ruiter RA, Verduyn P. The Association between Neuroticism and problematic social networking sites Use: the role of fear of missing out and Self-Control. Psychol Rep 2022:332941221142003–332941221142003.
Hou J. The study on FoMO and content social media addiction among young people. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2021.
Hu R, Zhang B, Yang Y, Mao H, Peng Y, Xiong S. Relationship between college students’ fear of missing and wechat addiction: a cross-lagged analysis. J Bio-education. 2022;10(5):369–73.
Hu G. The relationship between basic psychological needs satisfaction and the use of problematic social networks by college students: a moderated mediation model and online intervention studies. Jiangxi Normal University; 2020.
Jiang Y, Jin T. The relationship between adolescents’ narcissistic personality and their use of problematic mobile social networks: the effects of fear of missing out and positive self-presentation. Chin J Special Educ 2018(11):64–70.
Li J. The effect of positive self-presentation on social networking sites on problematic use of social networking sites: a moderated mediation model. Henan University; 2020.
Li J, Zhang Y, Zhang X. The impact of Freshmen Social Exclusion on problematic Social Network Use: a Moderated Mediation Model. J Heilongjiang Vocat Inst Ecol Eng. 2023;36(1):118–22.
Li M. The relationship between fear of missing out and social media addiction among middle school students——The moderating role of self-control. Kashi University; 2022.
Li R, Dong X, Wang M, Wang R. A study on the relationship between fear of missing out and social network addiction. New Educ Era 2021(52):122–3.
Li Y. Fear of missing out or social avoidance? The influence of peer exclusion on problematic social media use among adolescents in Guangdong Province and Macao. Guangzhou University; 2020.
Ma J, Liu C. The effect of fear of missing out on social networking sites addiction among college students: the mediating roles of social networking site integration use and social support. Psychol Dev Educ. 2019;35(5):605–14.
Mao H. A follow-up study on the mechanism of the influence of university students’ Qi deficiency quality on WeChat addiction. Hunan University of Chinese Medicine; 2021.
Mao Y. The effect of dual filial piety to the college students ’internet social dependence: the mediation of maladaptive cognition and fear of missing out. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2021.
Moore K, Craciun G. Fear of missing out and personality as predictors of Social networking sites usage: the Instagram Case. Psychol Rep. 2021;124(4):1761–87.
Niu J. The relationship of college students’ basic psychological needs and social media dependence: the mediating role of fear of missing out. Huazhong University of Science and Technology; 2021.
Pi L, Li X. Research on the relationship between loneliness and problematic mobile social media usage: evidence from variable-oriented and person-oriented analyses. China J Health Psychol. 2023;31(6):936–42.
Pontes HM, Taylor M, Stavropoulos V. Beyond Facebook Addiction: the role of cognitive-related factors and Psychiatric Distress in Social networking site addiction. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2018;21(4):240–7.
Quaglieri A, Biondi S, Roma P, Varchetta M, Fraschetti A, Burrai J, Lausi G, Marti-Vilar M, Gonzalez-Sala F, Di Domenico A et al. From Emotional (Dys) Regulation to Internet Addiction: A Mediation Model of Problematic Social Media Use among Italian Young Adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine 2022, 11(1).
Servidio R, Koronczai B, Griffiths MD, Demetrovics Z. Problematic smartphone Use and Problematic Social Media Use: the predictive role of Self-Construal and the Mediating Effect of Fear Missing Out. Front Public Health 2022, 10.
Sheldon P, Antony MG, Sykes B. Predictors of problematic social media use: personality and life-position indicators. Psychol Rep. 2021;124(3):1110–33.
Sun C, Li Y, Kwok SYCL, Mu W. The relationship between intolerance of uncertainty and problematic Social Media Use during the COVID-19 pandemic: a serial mediation model. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2022, 19(22).
Tang Z. The relationship between loneliness and problematic social networks use among college students: the mediation of fear of missing out and the moderation of social support. Jilin University; 2022.
Tomczyk Ł, Selmanagic-Lizde E. Fear of missing out (FOMO) among youth in Bosnia and Herzegovina — Scale and selected mechanisms. Child Youth Serv Rev. 2018;88:541–9.
Unal-Aydin P, Ozkan Y, Ozturk M, Aydin O, Spada MM. The role of metacognitions in cyberbullying and cybervictimization among adolescents diagnosed with major depressive disorder and anxiety disorders: a case-control study. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy; 2023.
Uram P, Skalski S. Still logged in? The Link between Facebook Addiction, FoMO, Self-Esteem, Life satisfaction and loneliness in social media users. Psychol Rep. 2022;125(1):218–31.
Varchetta M, Fraschetti A, Mari E, Giannini AM. Social Media Addiction, fear of missing out (FoMO) and online vulnerability in university students. Revista Digit De Investigación en Docencia Universitaria. 2020;14(1):e1187.
Wang H. Study on the relationship and intervention between fear of missing and social network addiction in college students. Yunnan Normal University; 2021.
Wang M, Yin Z, Xu Q, Niu G. The relationship between shyness and adolescents’ social network sites addiction: Moderated mediation model. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2020;28(5):906–9.
Wegmann E, Oberst U, Stodt B, Brand M. Online-specific fear of missing out and internet-use expectancies contribute to symptoms of internet-communication disorder. Addict Behav Rep. 2017;5:33–42.
Wegmann E, Brandtner A, Brand M. Perceived strain due to COVID-19-Related restrictions mediates the Effect of Social needs and fear of missing out on the risk of a problematic use of Social Networks. Front Psychiatry 2021, 12.
Wei Q. Negative emotions and problematic social network sites usage: the mediating role of fear of missing out and the moderating role of gender. Central China Normal University; 2018.
Xiong L. Effect of social network site use on college students’ social network site addiction: A moderated mediation model and attention bias training intervention study. Jiangxi Normal University; 2022.
Yan H. The influence of college students’ basic psychological needs on social network addiction: The intermediary role of fear of missing out. Wuhan University; 2020.
Yan H. The status and factors associated with social media addiction among young people——Evidence from WeChat. Chongqing University; 2021.
Yang L. Research on the relationship of fear of missing out, excessive use of Wechat and life satisfaction. Beijing Forestry University; 2020.
Yin Y, Cai X, Ouyang M, Li S, Li X, Wang P. FoMO and the brain: loneliness and problematic social networking site use mediate the association between the topology of the resting-state EEG brain network and fear of missing out. Comput Hum Behav. 2023;141:107624.
Zhang C. The parental rejection and problematic social network sites with adolescents: the chain mediating effect of basic psychological needs and fear of missing out. Central China Normal University; 2022.
Zhang J. The influence of basic psychological needs on problematic mobile social networks usage of adolescent: a moderated mediation model. Liaocheng University; 2020.
Zhang Y, Chen Y, Jin J, Yu G. The relationship between fear of missing out and social media addiction: a cross-lagged analysis. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2021;29(5):1082–5.
Zhang Y, Jiang W, Ding Q, Hong M. Social comparison orientation and social network sites addiction in college students: the mediating role of fear of missing out. Chin J Clin Psychol. 2019;27(5):928–31.
Zhou J, Fang J. Social network sites support and addiction among college students: a moderated mediation model. Psychology: Techniques Appl. 2021;9(5):293–9.
Andreassen CS, Torsheim T, Brunborg GS, Pallesen S. Development of a Facebook addiction scale. Psychol Rep. 2012;110(2):501–17.
Andreassen CS, Billieux J, Griffiths MD, Kuss DJ, Demetrovics Z, Mazzoni E, Pallesen S. The relationship between addictive use of social media and video games and symptoms of psychiatric disorders: a large-scale cross-sectional study. Psychol Addict Behav. 2016;30(2):252.
Elphinston RA, Noller P. Time to face it! Facebook intrusion and the implications for romantic jealousy and relationship satisfaction. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2011;14(11):631–5.
Caplan SE. Theory and measurement of generalized problematic internet use: a two-step approach. Comput Hum Behav. 2010;26(5):1089–97.
Jiang Y. Development of problematic mobile social media usage assessment questionnaire for adolescents. Psychology: Techniques Appl. 2018;6(10):613–21.
Wang X. College students’ social network addiction tendency: Questionnaire construction and correlation research. Master’s thesis Southwest University; 2016.
Derogatis LR. Brief symptom inventory 18. Johns Hopkins University Baltimore; 2001.
Lovibond PF, Lovibond SH. The structure of negative emotional states: comparison of the Depression anxiety stress scales (DASS) with the Beck Depression and anxiety inventories. Behav Res Ther. 1995;33(3):335–43.
Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB, Löwe B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(10):1092–7.
Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica. 1983;67(6):361–70.
Spielberger CD, Gonzalez-Reigosa F, Martinez-Urrutia A, Natalicio LF, Natalicio DS. The state-trait anxiety inventory. Revista Interamericana de Psicologia/Interamerican Journal of Psychology 1971, 5(3&4).
Marteau TM, Bekker H. The development of a six-item short‐form of the state scale of the Spielberger State—trait anxiety inventory (STAI). Br J Clin Psychol. 1992;31(3):301–6.
Leary MR. Social anxiousness: the construct and its measurement. J Pers Assess. 1983;47(1):66–75.
Liebowitz MR. Social phobia. Modern problems of pharmacopsychiatry 1987.
Alkis Y, Kadirhan Z, Sat M. Development and validation of social anxiety scale for social media users. Comput Hum Behav. 2017;72:296–303.
La Greca AM, Stone WL. Social anxiety scale for children-revised: factor structure and concurrent validity. J Clin Child Psychol. 1993;22(1):17–27.
Fenigstein A, Scheier MF, Buss AH. Public and private self-consciousness: Assessment and theory. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1975;43(4):522.
Mattick RP, Clarke JC. Development and validation of measures of social phobia scrutiny fear and social interaction anxiety. Behav Res Ther. 1998;36(4):455–70.
Peters L, Sunderland M, Andrews G, Rapee RM, Mattick RP. Development of a short form Social Interaction anxiety (SIAS) and Social Phobia Scale (SPS) using nonparametric item response theory: the SIAS-6 and the SPS-6. Psychol Assess. 2012;24(1):66.
Brennan KA, Clark CL, Shaver PR. Self-report measurement of adult attachment: an integrative overview. Attachment Theory Close Relationships. 1998;46:76.
Wei M, Russell DW, Mallinckrodt B, Vogel DL. The experiences in Close Relationship Scale (ECR)-short form: reliability, validity, and factor structure. J Pers Assess. 2007;88(2):187–204.
Bartholomew K, Horowitz LM. Attachment styles among young adults: a test of a four-category model. J Personal Soc Psychol. 1991;61(2):226.
Przybylski AK, Murayama K, DeHaan CR, Gladwell V. Motivational, emotional, and behavioral correlates of fear of missing out. Comput Hum Behav. 2013;29(4):1841–8.
Xiaokang S, Yuxiang Z, Xuanhui Z. Developing a fear of missing out (FoMO) measurement scale in the mobile social media environment. Libr Inform Service. 2017;61(11):96.
Bown M, Sutton A. Quality control in systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2010;40(5):669–77.
Turel O, Qahri-Saremi H. Problematic use of social networking sites: antecedents and consequence from a dual-system theory perspective. J Manage Inform Syst. 2016;33(4):1087–116.
Chou H-TG, Edge N. They are happier and having better lives than I am: the impact of using Facebook on perceptions of others’ lives. Cyberpsychology Behav Social Netw. 2012;15(2):117–21.
Beyens I, Frison E, Eggermont S. I don’t want to miss a thing: adolescents’ fear of missing out and its relationship to adolescents’ social needs, Facebook use, and Facebook related stress. Comput Hum Behav. 2016;64:1–8.
Di Blasi M, Gullo S, Mancinelli E, Freda MF, Esposito G, Gelo OCG, Lagetto G, Giordano C, Mazzeschi C, Pazzagli C. Psychological distress associated with the COVID-19 lockdown: a two-wave network analysis. J Affect Disord. 2021;284:18–26.
Yang X, Hu H, Zhao C, Xu H, Tu X, Zhang G. A longitudinal study of changes in smart phone addiction and depressive symptoms and potential risk factors among Chinese college students. BMC Psychiatry. 2021;21(1):252.
Kuss DJ, Griffiths MD. Social networking sites and addiction: ten lessons learned. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017;14(3):311.
Ryan T, Chester A, Reece J, Xenos S. The uses and abuses of Facebook: a review of Facebook addiction. J Behav Addictions. 2014;3(3):133–48.
Elhai JD, Levine JC, Dvorak RD, Hall BJ. Non-social features of smartphone use are most related to depression, anxiety and problematic smartphone use. Comput Hum Behav. 2017;69:75–82.
Jackson LA, Wang J-L. Cultural differences in social networking site use: a comparative study of China and the United States. Comput Hum Behav. 2013;29(3):910–21.
Ahrens LM, Mühlberger A, Pauli P, Wieser MJ. Impaired visuocortical discrimination learning of socially conditioned stimuli in social anxiety. Soc Cognit Affect Neurosci. 2014;10(7):929–37.
Elhai JD, Yang H, Montag C. Fear of missing out (FOMO): overview, theoretical underpinnings, and literature review on relations with severity of negative affectivity and problematic technology use. Brazilian J Psychiatry. 2020;43:203–9.
Barker V. Older adolescents’ motivations for social network site use: the influence of gender, group identity, and collective self-esteem. Cyberpsychology Behav. 2009;12(2):209–13.
Krasnova H, Veltri NF, Eling N, Buxmann P. Why men and women continue to use social networking sites: the role of gender differences. J Strateg Inf Syst. 2017;26(4):261–84.
Palmer J. The role of gender on social network websites. Stylus Knights Write Showc 2012:35–46.
Vannucci A, Flannery KM, Ohannessian CM. Social media use and anxiety in emerging adults. J Affect Disord. 2017;207:163–6.
Primack BA, Shensa A, Sidani JE, Whaite EO, yi Lin L, Rosen D, Colditz JB, Radovic A, Miller E. Social media use and perceived social isolation among young adults in the US. Am J Prev Med. 2017;53(1):1–8.
Twenge JM, Campbell WK. Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: evidence from a population-based study. Prev Med Rep. 2018;12:271–83.
Download references
This research was supported by the Social Science Foundation of China (Grant Number: 23BSH135).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Mental Health, Wenzhou Medical University, 325035, Wenzhou, China
Mingxuan Du, Haiyan Hu, Ningning Ding, Jiankang He, Wenwen Tian, Wenqian Zhao, Xiujian Lin, Gaoyang Liu, Wendan Chen, ShuangLiu Wang, Dongwu Xu & Guohua Zhang
School of Education, Renmin University of China, 100872, Beijing, China
Chengjia Zhao
School of Media and Communication, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Dongchuan Road 800, 200240, Shanghai, China
Pengcheng Wang
Department of Neurosis and Psychosomatic Diseases, Huzhou Third Municipal Hospital, 313002, Huzhou, China
Xinhua Shen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
GZ, XS, XL and MD prepared the study design, writing - review and editing. MD and CZ wrote the main manuscript text. MD and HH analyzed data and edited the draft. ND, JH, WT, WZ, GL, WC, SW, PW and DX conducted resources and data curation. All authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Xinhua Shen or Guohua Zhang .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Du, M., Zhao, C., Hu, H. et al. Association between problematic social networking use and anxiety symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Psychol 12 , 263 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01705-w
Download citation
Received : 25 January 2024
Accepted : 03 April 2024
Published : 12 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01705-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Fear of missing out
- Meta-analysis
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The discussion section is where you delve into the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results.. It should focus on explaining and evaluating what you found, showing how it relates to your literature review and paper or dissertation topic, and making an argument in support of your overall conclusion.It should not be a second results section.. There are different ways to write this ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
The discussion section is one of the final parts of a research paper, in which an author describes, analyzes, and interprets their findings. They explain the significance of those results and tie everything back to the research question(s). In this handout, you will find a description of what a discussion section does, explanations of how to ...
Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic. Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these. Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one) Inform your own methodology and research design. To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
Definition. A literature review is an assessment of the sources in a chosen topic of research. In a literature review, you're expected to report on the existing scholarly conversation, without adding new contributions. If you are currently writing one, you've come to the right place. In the following paragraphs, we will explain: the objective ...
Okay - with the why out the way, let's move on to the how. As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter.
The literature reviewed in the introduction should: Introduce the topic. Establish the significance of the study. Provide an overview of the relevant literature. Establish a context for the study using the literature. Identify knowledge gaps. Illustrate how the study will advance knowledge on the topic. As you can see, literature review plays a ...
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
Here is a sample paragraph from a literature review about sexism and language to illuminate the following discussion: However, other studies have shown that even gender-neutral antecedents are more likely to produce masculine images than feminine ones (Gastil, 1990).
Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and ...
Steps for Conducting a Lit Review; Finding "The Literature" Organizing/Writing; APA Style This link opens in a new window; Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window; MLA Style This link opens in a new window; Sample Literature Reviews. Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts; Have an exemplary literature review? Get Help!
The discussion section can be written in 3 parts: an introductory paragraph, intermediate paragraphs and a conclusion paragraph. For intermediate paragraphs, a "divide and conquer" approach, meaning a full paragraph describing each of the study endpoints, can be used. In conclusion, academic writing is similar to other skills, and practice ...
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels ...
The discussion section of your research paper is where you let the reader know how your study is positioned in the literature, what to take away from your paper, and how your work helps them. It can also include your conclusions and suggestions for future studies. First, we'll define all the parts of your discussion paper, and then look into ...
2. MOTIVATE YOUR RESEARCH in addition to providing useful information about your topic, your literature review must tell a story about how your project relates to existing literature. popular literature review narratives include: ¡ plugging a gap / filling a hole within an incomplete literature ¡ building a bridge between two "siloed" literatures, putting literatures "in conversation"
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
If you are new to the world of systematic literature reviews, or even if you have completed several of them, it can be helpful to have a review discussion example to refer to.Referring to an example gives you the best stance to start with, and helps you produce a review that is reliable, reputable, and trustworthy. In this article, we will work through how to write a discussion for a ...
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
The discussion section is where you delve into the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results.. It should focus on explaining and evaluating what you found, showing how it relates to your literature review, and making an argument in support of your overall conclusion.It should not be a second results section.. There are different ways to write this section, but you can focus your ...
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
These sections serve to establish a scholarly basis for the research or discussion within the paper. In a standard 8000-word journal article, the literature review section typically spans between 750 and 1250 words. The first few sentences or the first paragraph within this section often serve as an introduction.
A growing number of studies have reported that problematic social networking use (PSNU) is strongly associated with anxiety symptoms. However, due to the presence of multiple anxiety subtypes, existing research findings on the extent of this association vary widely, leading to a lack of consensus. The current meta-analysis aimed to summarize studies exploring the relationship between PSNU ...